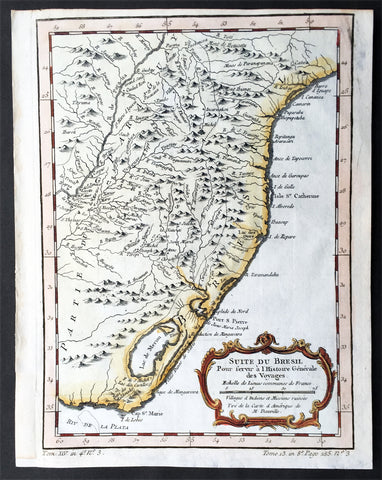
Maps (791)
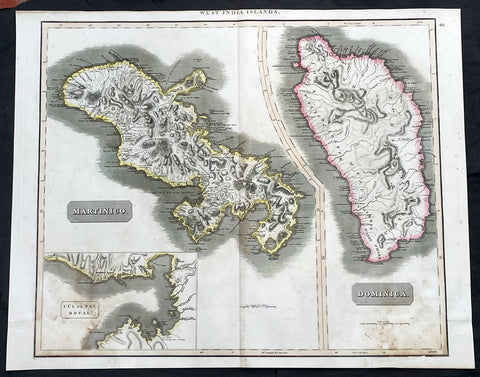
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Islands of Martinique & Dominica
Antique Map
- Title : West India Islands: Martinico (Cul de Sac Royal); Dominica
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35606
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands of Martinique and Dominica was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Age toning
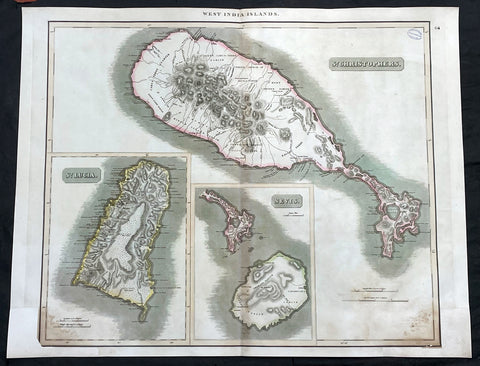
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Is. St Christopher St Lucia Nevis
Antique Map
- Title : West India Islands: St Christopher; St Lucia; Nevis
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35609
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
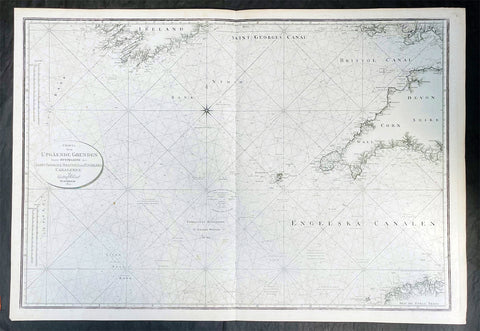
1801 Gustaf Klint Large Map Sea Chart Celtic Sea Ireland to Bristol, Cornwall et
Antique Map
-
Title : Charta ofver Upgaende Grunden Jemte Opningarne Till Saint George, Bristols och Engelska Canalerne Gustaf af Klint Stockholm 1801
- Ref #: 35615
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 39 1/2in x 27in (990mm x 685mm)
- Date : 1801
Description:
This very large original copper plate engraved map a sea chart of The Celtic Sea, from southern Ireland to the Bristol Channel, Cornwall & The Scilly Islands was by the Swedish naval officer and cartographer Gustaf af Klint was engraved and published in 1801, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 39 1/2in x 27in (990mm x 685mm)
Plate size: - 39 1/2in x 27in (990mm x 685mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Celtic Sea is an area of the Atlantic Ocean that stretches from the southern coast of Ireland to the western coast of Brittany in France. It is named after the Celtic culture that was once dominant in the region. The sea is bordered by several countries including Ireland, the United Kingdom, and France. It is a busy shipping route, with commercial vessels transporting goods between ports in Europe and North America. The sea is also important for fishing, with a variety of fish species, such as mackerel, herring, and cod, found in its waters. Additionally, the Celtic Sea is known for its rich marine biodiversity, with numerous species of dolphins, whales, and seabirds inhabiting the area.
Klint, Gustaf af 1774 - 1840
Gustaf af Klint was a Swedish naval officer born on September 14, 1772, in Örebro, Sweden. He began his naval career at the age of 16, joining the Swedish Navy in 1788. Over the years, he served in various positions and rose through the ranks, becoming a captain in 1801.
In addition to his naval career, Gustaf af Klint was also a skilled cartographer. He produced several detailed maps of the Swedish coast and Baltic Sea, which were widely used by sailors and navigators at the time. His maps were known for their accuracy and attention to detail, making them an essential tool for safe navigation in the often treacherous waters of the Baltic Sea.
One of Gustaf af Klint's most significant contributions to cartography was his work on the "Sea Atlas of the Baltic Sea," which he began in 1806. The atlas contained detailed maps of the entire Baltic Sea region, including the coasts of Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. The maps were meticulously drawn, with precise soundings, navigational hazards, and coastal features clearly marked.
Gustaf af Klint retired from the Swedish Navy in 1824, having reached the rank of Rear Admiral. He continued to work on his sea atlas until his death in 1840, leaving behind a lasting legacy as one of Sweden's most accomplished naval officers and cartographers. Today, his maps are considered a valuable historical record of the Baltic Sea region and are sought after by collectors and historians alike.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1808 Jean Henri Cless Antique Print of The Cartographer Guillaume Delisle
Antique Map
- Title : Guillaue De L Isle Geb. zu Paris d. 28 Febr. 1675 gest. ebendas d. 25 Jan 1726
- Date : 1808
- Size: 7in x 4 1/2in (180mm x 115mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 91417
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of the famous cartographer Guillaume Delisle, by Jean Henri Cless was published in 1808 in Allgemeine Geographische Ephemeriden' (Universal Geographical Ephemerides (i.e. encyclopedia) by Friedrich Bertuch
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 7in x 4 1/2in (180mm x 115mm)
Plate size: - 5 1/2in x 3 1/2in (140mm x 90mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Following the long period of Dutch domination, the Homann family became the most important map publishers in Germany in the eighteenth century, the business being founded by J.B. Homann in Nuremberg about the year 1702. Soon after publishing his first atlas in 1707 he became a member of the Berlin academy of Sciences and in 1715 he was appointed Geographer to the Emperor. After the founder's death in 1724, the firm was continued under the direction of his son until 1730 and was then bequeathed to his heirs on the condition that it trades under the name of Homann Heirs. The firm remained in being until the next century and had a wide influence on map publishing in Germany. Apart from the atlases the firm published a very large number of individual maps.
The Homman's produced a Neuer Atlas in 1714, a Grosser Atlas in 1737, and an Atlas Maior with about 300 maps in 1780. They also issued a special Atlas of Germany with full sized plans of principal cities, school atlases and an Atlas of Silesia in 1750 with 20 maps.
Cless, Jean Henri 1774- 1812
A pupil of Jacques-Louis David , he began to be active around 1800 and exhibited in Paris at the Salons from 1804 to 1808.
According to the Thieme-Becker 2 artistic dictionary , he returned to Alsace in 1811 , where many private collections hold his works.
Cless was also a draftsman and miniaturist .
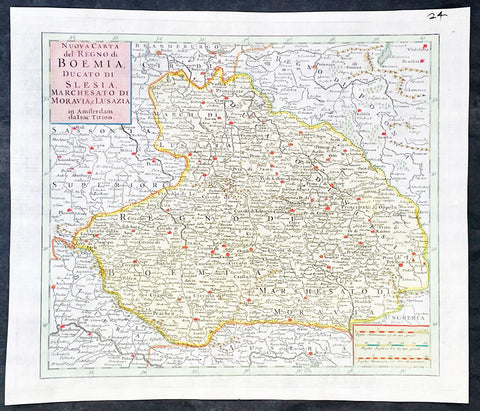
1740 Isaac Tirion Antique Map of Bohemia, Silesia, Moravia - Germany, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Nuova Carta del Regno di Boemia Ducato Di Slesia, Marches Ato Di Moravia e lusazia in Amsterdam da Isac Tirion
- Ref #: 35636
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 14 1/2in x 12 1/2in (365mm x 315mm)
- Date : 1740
- Price: $149US
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the central European countries of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Duchy of Silesia, Marquisate of Moravia, and Lusatia by Isaac Tirion, was published in 1740 in Amsterdam.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 12 1/2in (365mm x 315mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10 1/2in (315mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Bohemia is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia proper as a means of distinction
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
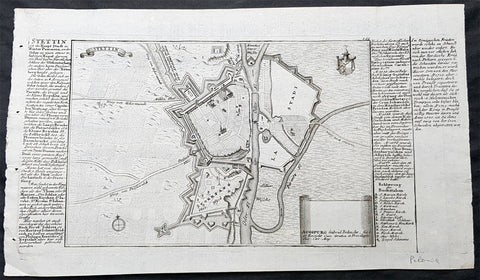
1725 Gabriel Bodenehr Antique Map Birds Eye View of Szczecin or Stettin, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Stettin
- Ref #: 93494
- Size: 13 1/2in x 8in (335mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1725
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map, a birds eye view of the city of Szczecin or Stettin, Poland along with descriptive text was published in Gabriel Bodenehrs Force d Europe in 1725.
Bodenehr a copper engraver and publisher, bought the numerous copper plates of Johann Stridbeck (1640 – 1716) and revised them and along with his own maps, views and plans published them in several works with different titles.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 8in (335mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 6 1/2in (330mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Szczecin/Stettin is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major seaport and Polands seventh-largest city.
Szczecin is located on the river Oder, south of the Szczecin Lagoon and the Bay of Pomerania. The city is situated along the southwestern shore of Dąbie Lake, on both sides of the Oder and on several large islands between the western and eastern branches of the river. Szczecin is adjacent to the town of Police and is the urban centre of the Szczecin agglomeration, an extended metropolitan area that includes communities in the German states of Brandenburg and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
The cities recorded history began in the 8th century as a Lechitic Pomeranian stronghold, built at the site of the Ducal castle. In the 12th century, when Szczecin had become one of Pomeranias main urban centres, it lost its independence to Piast Poland, the Duchy of Saxony, the Holy Roman Empire and Denmark. At the same time, the House of Griffins established themselves as local rulers and the population was Christianized. After the Treaty of Stettin in 1630, the town came under the control of the Swedish Empire and became in 1648 the Capital of Swedish Pomerania until 1720, when it was acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia and then the German Empire. Following World War II Stettin became part of Poland in accordance with the Potsdam Agreement, resulting in the almost complete expulsion of the pre-war German population.
Bodenehr, Gabriel I fl 1673-1765
Engraver and mapmaker of Augsburg, from a family dynasty of engravers and publishers. Son of Johann Georg Bodenehr (1631-1704), father of Gabriel II (whose work is difficult to distinguish) and brother of Georg Conrad. In 1717 the family took over the Augsburg publishing house of Stridbeck. His works include Atlas Curieux (1704), Curioser Staats und Kriegs Theatrum (1715), and Europens Pracht und Macht (c.1720).
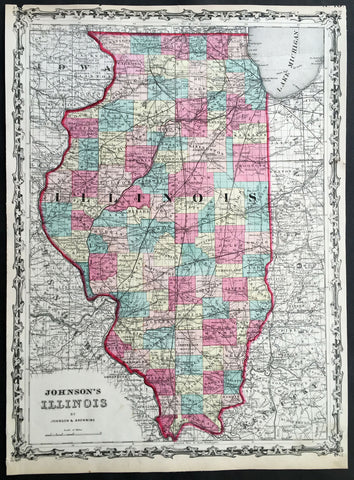
1860 A J Johnson Large Antique 1st edition Map of The State of Illinois, USA
- Title : Johnson's Illinois by Johnson & Browning
- Ref #: 50671
- Size: 17 1/2in x 13in (450mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1860
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original 1st edition map of the State of Illinois was published by A J Johnson in the 1860 edition ofJohnson's New Illustrated Family Atlas.
Background:
1st Edition, 1st issue. Most of the maps in this atlas come from Colton's 1859 edition of the General Atlas, published by Johnson and Browning, indicating the Johnson connection; some do not come from this atlas, and their sources are: the New England maps (scale 1" = 9 miles) come from Colton's map of New England and then the sub-maps of Vermont and New Hampshire, Mass/Conn/R.I.; the Ohio/Indiana is still a mystery; all the 1" = 24 miles maps (Iowa, Kentucky, etc.) come from Colton's Map of the United States and the Canadas, originally published by J. Calvin Smith in 1843 (see W. Heckrotte's copies and his list of editions); and the Colton General Atlas maps used by Johnson come from Colton's Travellers Series of maps - see our copies of Penn., Indiana. Colton mentions "The National Atlas of the United States, constructed from the Public Surveys..large Folio" as in preparation in his 1855 catalogue; this may be the embryonic Johnson Atlas. Colton used his wall maps "cut up" for pocket maps and Atlases. Johnson's maps of S. America, Europe, Africa, and (in the first edition, first issue, only) China, East Indies etc., all come from D. Griffing Johnson's Map of the World, 1847. These atlas maps are updated (esp. Africa). Colton took over the publication of the World Map in 1849, issued editions to 1868 (Ristow p318). Also, Johnson's N. America map is the inset N. America in Smith's Map of the U.S., the Canadas, etc. This first issue of Johnson's Family Atlas differs from the later 1860 edition in a small N.Y. (from the Colton U.S. map), small Texas, and many of the maps have fewer views or no views or different configurations. Clearly, this was a first attempt that was refined later in the year. Another issue of this same edition was published in Richmond, Virginia, the home town of Browning (I.L.). The California map originates with Johnson's New Illustrated and Embellished County
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink green yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 13in (450mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13in (450mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in 312mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning, light chipping to margin edges
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Uniform age toning
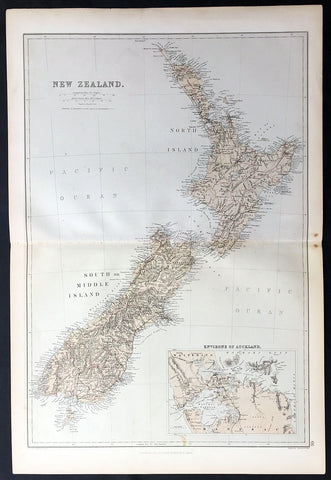
1870 Blackie & Son Large Antique Map of New Zealand w/ inset plan of Auckland
- Title : New Zealand
- Ref: 80571
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original antique map of New Zealand with an inset map of Auckland and its environs by John Bartholomew was published by Blackie & Son of Glasgow & London in the 1870 edition of the Geographical Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
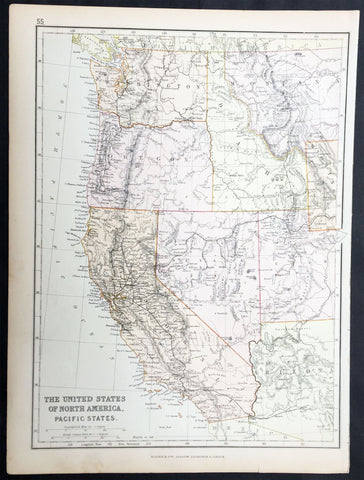
1870 Blackie & Son Antique Map The Western United States of America
- Title : The United States of North America Pacific States
- Ref #: 80560
- Size: 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique lithograph map of the Western United States of America including Washington, Oregon, California, Arizona, Nevada, Idaho, Montana, Utah & part of Wyoming was engraved by Edward Weller andpublished by Blackie & Son of Glasgow in the1870 edition of the Geographical Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
Margins: - min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
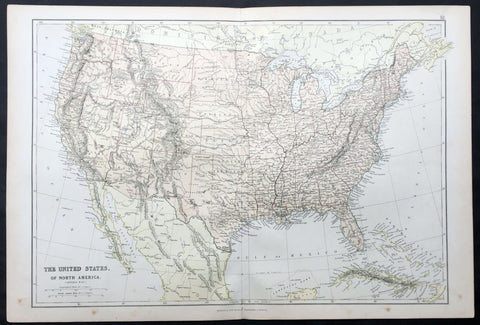
1870 Blackie & Son Large Antique Map of The United States of America
- Title : The United States of North America
- Ref #: 80558
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique lithograph map of The United States of America was engraved by Edward Weller and published by Blackie & Son of Glasgow & London in the 1870 edition of the Geographical Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min 1/4in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
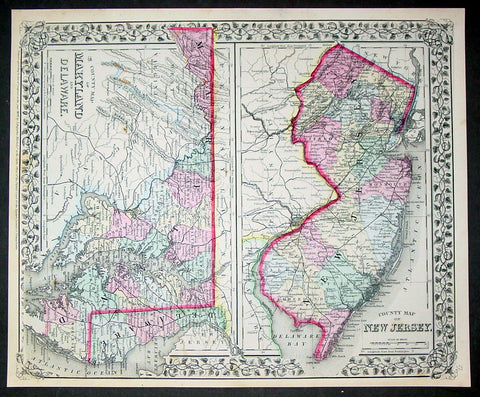
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Maps New Jersey, Maryland, Delaware
- Title : County Map of New Jersey; County Map of Maryland and Delaware....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35033
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
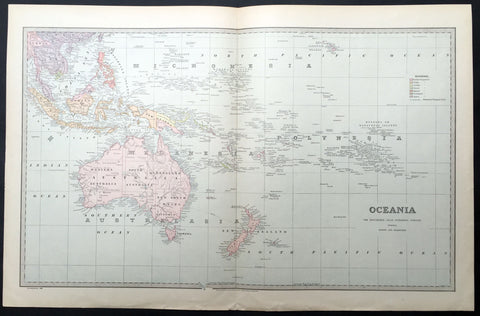
1888 Large Pic Atlas Large Antique Map Oceania Australia, New Zealand
- Title : Oceania
- Ref : 40969
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1574 Munster Large Antique Print - View of The German City of Landau, Bavaria
- Title : Die Statt Landaw
- Ref #: 22668
- Size: 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the Bavarian City of Landau NE of Munich was engraved in 1547 - the date is engraved at the foot of the image - and was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1574 edition of Cosmographia.
Landau or Landau in der Pfalz (pop. 41,821) is an autonomous (kreisfrei) city surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long-standing cultural centre, and a market and shopping town, surrounded by vineyards and wine-growing villages of the Palatinate wine region. Landau lies east of the Palatinate forest, Europe's largest contiguous forest, direct on the German Wine Route.
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle hisCosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographiaappeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications ofCosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: -None
Verso: - None
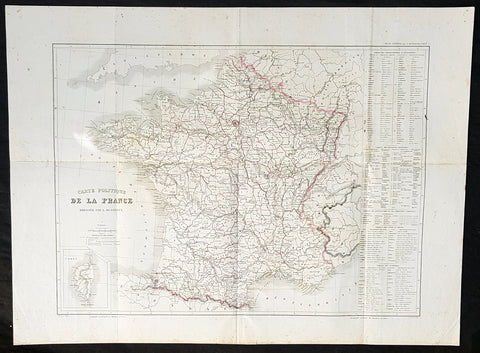
1846 Louis Dussieux Large Antique Map of The Political Boundaries of France
- Title : 1846 Louis Dussieux Large Antique Map of The Political Boundaries of France
- Size: 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1846
- Ref #: 32414
Description:
This large hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map was published by Louis Dussieux in the 1846 edition of Atlas Generale
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Dussieux, Louis 1815 - 1894
Dussieux was a French Geographer, prolific during the mid 19th century. After winning prizes in competitions of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles Letters in 1839 and 1840, he was appointed recorder of military history and geography at the Saint - Cyr Special School in 1842 and became the professor of history in 1850. In 1843 he was appointed correspondent for the Historical Monuments Committee.
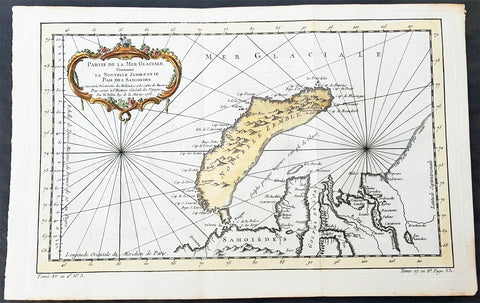
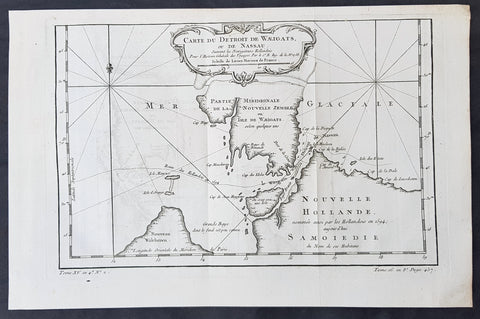
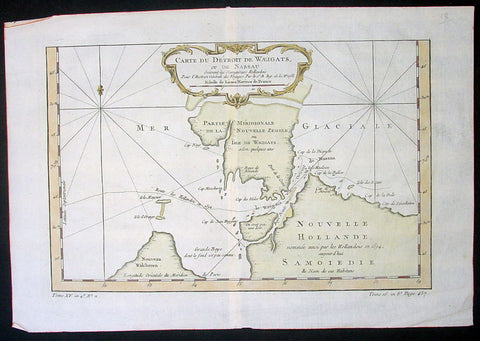
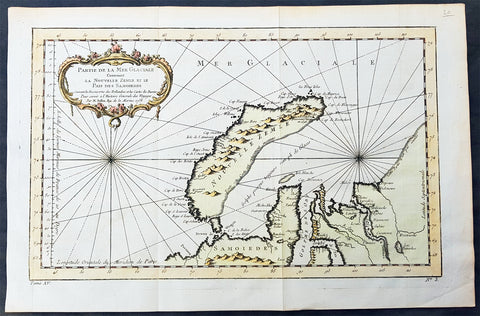
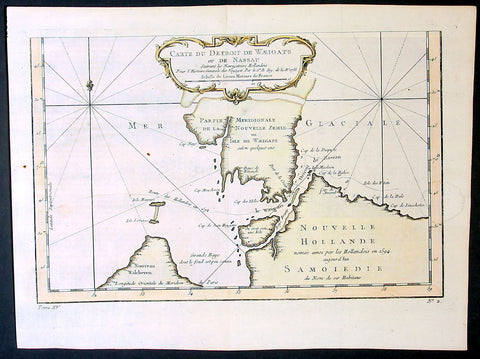
1758 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Russia The Island of Novaya Zemlya
- Title : Partie De La Mer Glaciale Contenant La Nouvelle Zemle...M. Bellin...1758
- Ref #: 60968
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (380mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Novaya Zemlya also known as Nova Zembla (especially in Dutch), is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in northern Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the Northern island. Novaya Zemlya is composed of two islands, the northern Severny Island and the southern Yuzhny Island, which are separated by Matochkin Strait.
The Russians knew of Novaya Zemlya from the 11th century, when hunters from Novgorod visited the area. For western Europeans, the search for the Northern Sea Route in the 16th century led to its exploration. The first visit from a west European was by Hugh Willoughby in 1553, and he met Russian ships from the already established hunting trade. Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya in 1594, and in a subsequent expedition of 1596 rounded the Northern point and wintered on the Northeast coast. (Barentsz died during the expedition, and may have been buried on the Northern island.) During a later voyage by Fyodor Litke in 1821–1824, the west coast was mapped. Henry Hudson was another explorer who passed through Novaya Zemlya while searching for the Northeast Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
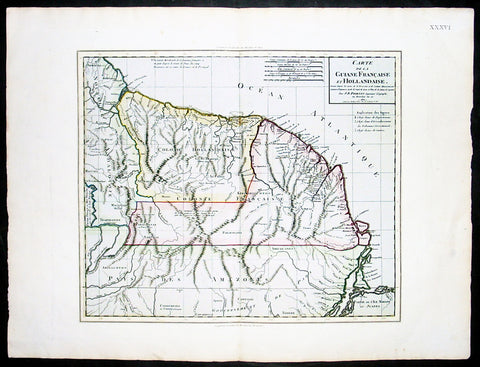
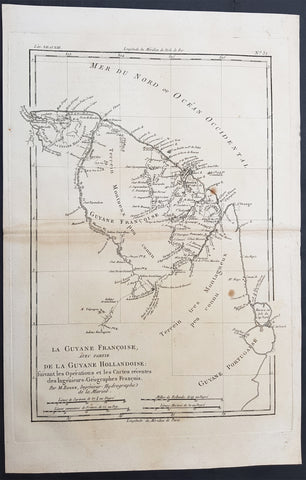
1802 Poirson Large Antique Map of French & Dutch Guyana
- Title : Carte De La Guiane Francaise et Hollandaise...J B Poirson...1802
- Ref #: 92520
- Size: 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America, was engraved by Jean Baptiste Poirson in 1802 - the date is engraved in the Title.
J.B. Poirson (1760-1831) was a French geographer & engineer who published a number of Atlases - including the Malte-Brun Atlas - between 1790 & 1830. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (500mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
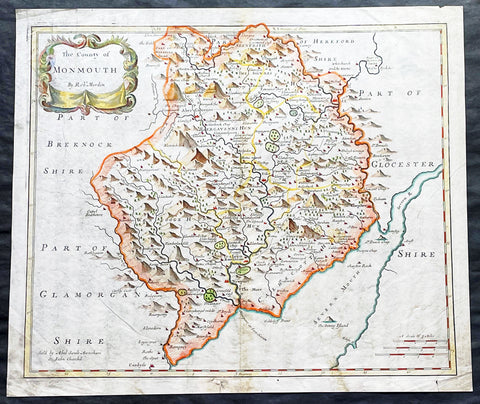
1695 Morden Antique Map The Welsh County of Monmouth
- Title : The County of Monmouth by Robert. Morden
- Ref #: 50155
- Size: 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1695
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Welsh county of Monmouth was engraved by Robert Morden & published by Abel Swale & John Churchil for the 1695 edition of Willam Camden's Britannia.
William Camden was an historian who first published his Britannia, a description and history of Britain, in 1586. Written in Latin, the book contained only a general map of the country but had a wide circulation and eventually in 1607 an edition (the sixth) was published with a series of maps with Latin text on the reverse.
Further editions in English were published in 1610 and 1637 but without text. (Many more editions were published up until 1806 with map contributions from Blaeu in 1617, John Bill 1626, Robert Morden 1695-1772 and John Cary 1789-1806)
In the 1610 & 1617 editions the maps were mostly engraved by William Kip and William Hole and were based on those of Christopher Saxton, but six were copied from John Norden.
The map of Pembroke is by George Owen and the general maps of England/Wales, Scotland and Ireland were probably taken from Mercator. Kip reduced the size of each map for Britannia from the originals published by Christopher Saxton in 1579. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, blue, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 14in (420mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - 4 small repairs to bottom margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
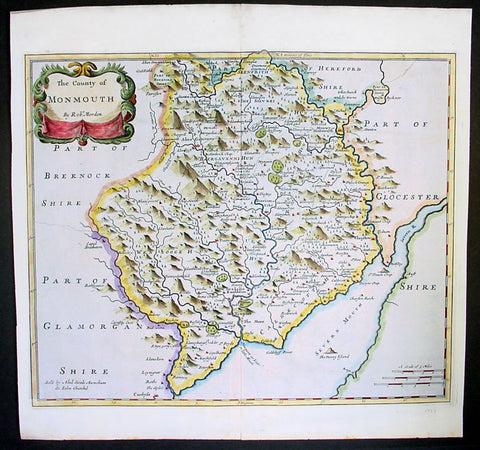
1695 Morden Antique Map The Welsh County of Monmouth
- Title : The County of Monmouth by Robert. Morden
- Ref #: 40869
- Size: 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1695
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Welsh county of Monmouth was engraved by Robert Morden & published by Abel Swale & John Churchil for the 1695 edition of Willam Camden's Britannia.
William Camden was an historian who first published his Britannia, a description and history of Britain, in 1586. Written in Latin, the book contained only a general map of the country but had a wide circulation and eventually in 1607 an edition (the sixth) was published with a series of maps with Latin text on the reverse.
Further editions in English were published in 1610 and 1637 but without text. (Many more editions were published up until 1806 with map contributions from Blaeu in 1617, John Bill 1626, Robert Morden 1695-1772 and John Cary 1789-1806)
In the 1610 & 1617 editions the maps were mostly engraved by William Kip and William Hole and were based on those of Christopher Saxton, but six were copied from John Norden.
The map of Pembroke is by George Owen and the general maps of England/Wales, Scotland and Ireland were probably taken from Mercator. Kip reduced the size of each map for Britannia from the originals published by Christopher Saxton in 1579. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, blue, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 14in (420mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - 4 small repairs to bottom margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
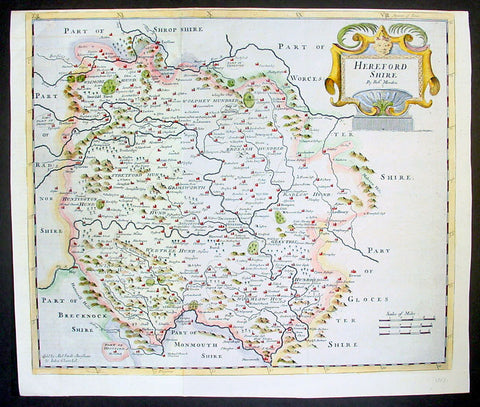
1695 Rob. Morden Antique Map English County of Hereford
- Title : Hereford Shire by Rob. Morden
- Ref #: 40868
- Size: 17in x 15in (430mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1695
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This attractive original antique map of the English county of Hereford, by Robert Morden, was published in the 1695 edition of Camden's Britannia.
William Camden was an historian who first published his Britannia, a description and history of Britain, in 1586. Written in Latin, the book contained only a general map of the country but had a wide circulation and eventually in 1607 an edition (the sixth) was published with a series of maps with Latin text on the reverse.
Further editions in English were published in 1610 and 1637 but without text. (Many more editions were published up until 1806 with map contributions from Blaeu in 1617, John Bill 1626, Robert Morden 1695-1772 and John Cary 1789-1806)
In the 1610 & 1617 editions the maps were mostly engraved by William Kip and William Hole and were based on those of Christopher Saxton, but six were copied from John Norden.
The map of Pembroke is by George Owen and the general maps of England/Wales, Scotland and Ireland were probably taken from Mercator. Kip reduced the size of each map for Britannia from the originals published byChristopher Saxton in 1579. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic, heavy
Paper size: - 17in x 15in (430mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 15in (430mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (4mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped close to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
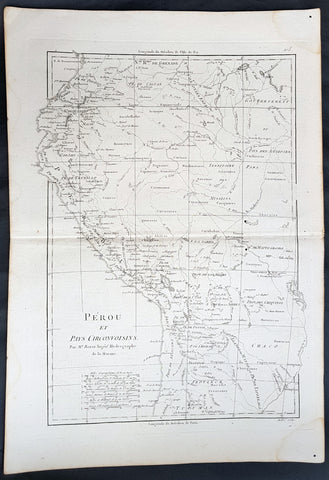
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Peru, South America
- Title : Perou et Pays Circonvoisins... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40551
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
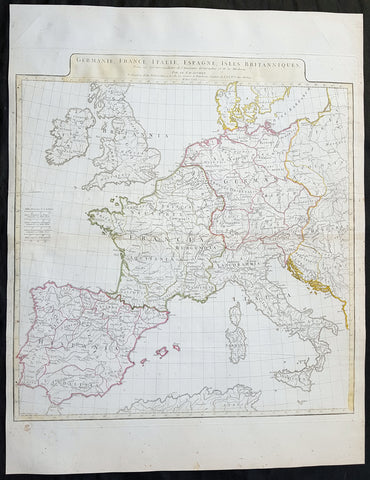
1771 J B D Anville Large Original Antique Map of Western Europe & Britain
- Title : Germanie, France, Italie, Espagne, Isles Britanniques...MDCCLXXI
- Size: 25 1/2in x 20in (650mm x 525mm)
- Ref #: 92305
- Date : 1771
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved and highly detailed original antique map of Western Europe and The British Isles by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville was engraved in 1771 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D\'Anville\'s large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 20in (650mm x 525mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing along centerfold
Plate area: - Creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Creasing along centerfold
1780 Bonne Antique Map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40849
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
In 1498 French Guiana was first visited by Europeans when Christopher Columbus sailed to the region on his third voyage and named it the \"Land of pariahs\".[citation needed] In 1608 the Grand Duchy of Tuscany did an expedition to the area in order to create an Italian colony for the commerce of Amazonian products to Renaissance Italy, but the sudden death of Ferdinando I de\' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany stopped it.
In 1624 France attempted to settle in the area, but was forced to abandon it in the face of hostility from the Portuguese, who viewed it as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas. However French settlers returned in 1630 and in 1643 managed to establish a settlement at Cayenne along with some small-scale plantations. This second attempt would again be abandoned following Amerindian attacks. In 1658 the Dutch West Indies Company seized French territory to establish the Dutch colony of Cayenne. The French returned once more in 1664, and founded a second settlement at Sinnamary (this was attacked by the Dutch in 1665).
In 1667 the English seized the area. Following the Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667 the area was given back to France. The Dutch briefly occupied it for a period in 1676.
After the Treaty of Paris in 1763, which deprived France of almost all her possessions in the Americas other than Guiana and a few islands, Louis XV sent thousands of settlers to Guiana who were lured there with stories of plentiful gold and easy fortunes to be made. Instead they found a land filled with hostile natives and tropical diseases. One and a half years later only a few hundred survived. These fled to three small islands which could be seen off shore and named them the Iles de Salut (or \"Islands of Salvation\"). The largest was called Royal Island, another St. Joseph (after the patron saint of the expedition), and the smallest of the islands, surrounded by strong currents, Île du Diable (the infamous \"Devil\'s Island\"). When the survivors of this ill-fated expedition returned home, the terrible stories they told of the colony left a lasting impression in France.
In 1794, after the death of Robespierre, 193 of his followers were sent to French Guiana. In 1797 the republican general Pichegru and many deputies and journalists were also sent to the colony. When they arrived they found that only 54 of the 193 deportées sent out three years earlier were left; 11 had escaped, and the rest had died of tropical fevers and other diseases. Pichegru managed to escape to the United States and then returned to France where he was eventually executed for plotting against Napoleon.
Later on, slaves were brought out from Africa and plantations were established along the more disease-free rivers. Exports of sugar, hardwood, Cayenne pepper and other spices brought a certain prosperity to the colony for the first time. Cayenne, the capital, was surrounded by plantations, some of which had several thousand slaves.
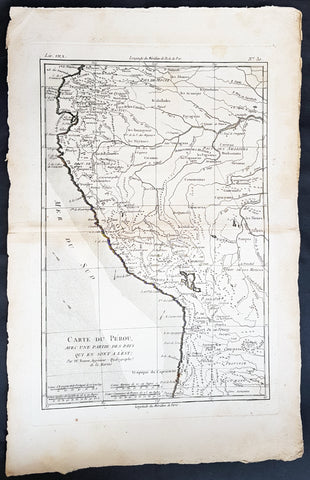
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of West South America Peru & The Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Perou... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40843
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
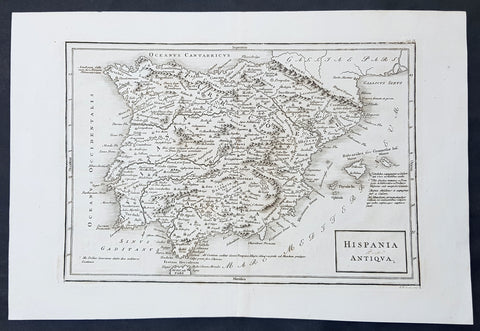
1750 C. Cellarius & RW Seale Original Antique Map of Spain & Balearic Islands
- Title : Hispania Antiqua
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31354
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original copper-plate engraved antique map of Spain by Christopher Cellarius was engraved by RW Seale and published in the 1750 edition of Geographica Antiqua.
Richard William Seale was a prolific engraver of the mid 18th century responsible between 1744-47 for Maps of Continents and Maps for Mr Tindals Continuation of Rapins History of England in 1745. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Geographica was one of the most popular geographical publications of the 17th and 18th centuries, that lasted into the 19th century, a fine map (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
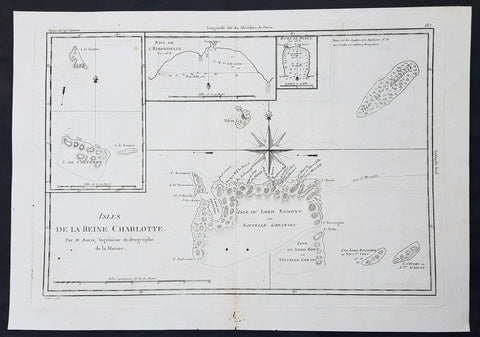
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Santa Cruz Isles, Solomon Islands Sth Pacific Lord Howe, Nendo
- Title : Isles De La Reine Charlotte
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40580
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Santa Cruz Island, of the Temotu Province in the Solomon Islands, Nendo Island & Lord Howe Island was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small worm holes in bottom margin
Plate area: - Two small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Map of four island with compass rose. Santa Cruz Island, of Santa Cruz Island, of the Temotu Province in the Solomon Islands, based on Cook\'s discoveries, was named after Queen Charlotte, wife of King George III.
The Isle du Lord Edgemont (present day Nendo Island) and Isle du Lord Howe islands have been only partially engraved to show the explored portions.
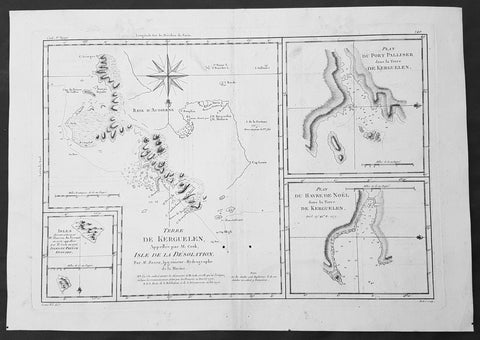
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Kerguelen, Desolation Island South Indian Ocean
- Title : Terre De Kerguelen, Appellee par M. Cook, Isle De La Desolation. Par M. Bonne; Plan Du Port Palliser dans la Terre De Kerguelen: Plan Du Havre De Noel dans la Terre De Kerguelen: Isles decouvertes par Mr. Marion Du Fresne en 1772, appellees par M.Cook en 1776, Isles Du Prince Edouard
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40585
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of parts of the Kerguelen Islands, also known as the Desolation Islands, in the southern Indian Ocean, was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
The map also includes three inset maps, the first two of Port Palliser & Noel Bay on Kerguelen Island, with the third inset map of the Prince Edward Islands - part of South Africa.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Two small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Kerguelen’s land was named for Yves de Kerguelen, a French navigator and explorer who sailed around the islands in 1772 along with Marion Du Fresne another French explorer who was in the vicinity in that same year. Capt. James Cook didn’t sight the islands until his 3rd voyage in 1776, having failed in his first attempts on earlier voyages. On Christmas Eve 1776, Cook’s ships the Resolution and the Discovery anchored in a Bay which he called Christmas Harbor, only staying long enough to replenish his water, and as the islands were so bleak and treeless, he called them Desolation Isles. Bonne’s chart was taken from original surveys by Kerguelen, Du Fresne and Capt. James Cook and was finely engraved by Gaspard Andre.
The Kerguelen Islands also known as the Desolation Islands, are a group of islands in the southern Indian Ocean constituting one of the two exposed parts of the mostly submerged Kerguelen Plateau. They are among the most isolated places on Earth, located 450 km (280 mi) northwest of the uninhabited Heard Island and McDonald Islands and more than 3,300 km (2,051 mi) from Madagascar, the nearest populated location (excluding the Alfred Faure scientific station in Ile de la Possession, about 1,340 km (830 mi) from there, and the non-permanent station located in Île Amsterdam, 1,440 km (890 mi) away). The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands, Amsterdam, and Saint Paul Islands, and France\'s Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean are part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands and are administered as a separate district.
Kerguelen Islands appear as the \"Ile de Nachtegal\" on Philippe Buache\'s map from 1754 before the island was officially discovered in 1772. The Buache map has the title Carte des Terres Australes comprises entre le Tropique du Capricorne et le Pôle Antarctique où se voyent les nouvelles découvertes faites en 1739 au Sud du Cap de Bonne Esperance (\'Map of the Southern Lands contained between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Pole, where the new discoveries made in 1739 to the south of the Cape of Good Hope may be seen\'). It is possible this early name was after Abel Tasman\'s ship \"De Zeeuwsche Nachtegaal.\" On the Buache map, \"Ile de Nachtegal\" is located at 43°S, 72°E, about 6 degrees north and 2 degrees east of the accepted location of Grande Terre.
The islands were officially discovered by the French navigator Yves-Joseph de Kerguelen-Trémarec on 12 February 1772. The next day Charles de Boisguehenneuc landed and claimed the island for the French crown. Yves de Kerguelen organised a second expedition in 1773 and arrived at the \"baie de l\'Oiseau\" by December of the same year. On 6 January 1774 he commanded his lieutenant, Henri Pascal de Rochegude, to leave a message notifying any passers-by of the two passages and of the French claim to the islands. Thereafter, a number of expeditions briefly visited the islands, including that of Captain James Cook in December 1776 during his third voyage, who verified and confirmed the passage of de Kerguelen by discovering and annotating the message left by the French navigator.
Soon after their discovery, the archipelago was regularly visited by whalers and sealers (mostly British, American and Norwegian) who hunted the resident populations of whales and seals to the point of near extinction, including fur seals in the 18th century and elephant seals in the 19th century. Since the end of the whaling and sealing era, most of the islands\' species have been able to increase their population again.
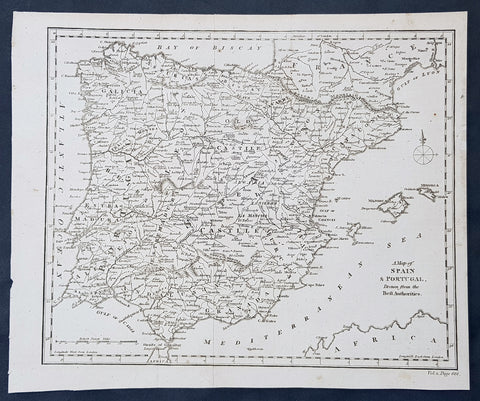
1790 Aaron Arrowsmith Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & Balearic Islands
- Title : A Map of Spain & Portugal Drawn from the Best Authorities
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 30218
- Date : 1790
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Aaron Arrowsmith was published in the 1790 edition of Cruttwells Atlas, to his GazetterJohn Arrowsmithaaron Arrowsmith
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
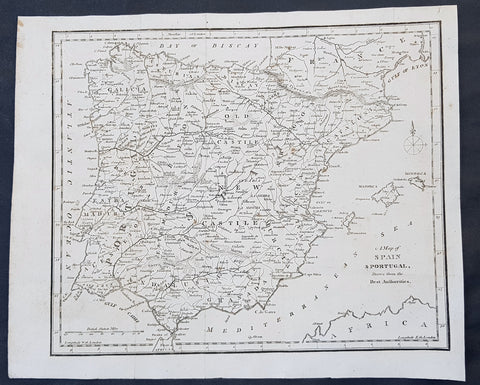
1797 John Cary Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & The Balearic Islands
- Title : A Map of Spain & Portugal Drawn from the Best Authorities
- Size: 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 92755
- Date : 1797
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by John Cary was published in the 1797 edition of Moores Geography
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
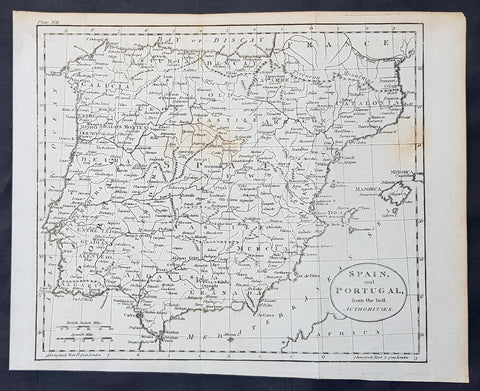
1770 Thomas Kitchin Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & Balearic Islands
- Title : Spain and Portugal from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70189
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthrie\'s Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
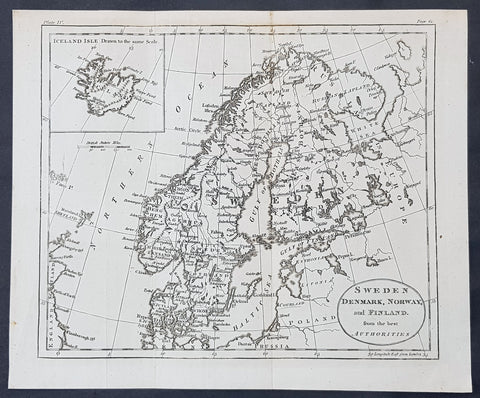
1770 John Cary Original Antique Map Sweden, Denmark, Norway, Finland & Iceland
- Title : Sweden, Denmark, Norway and Finland from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70177
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthrie\'s Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
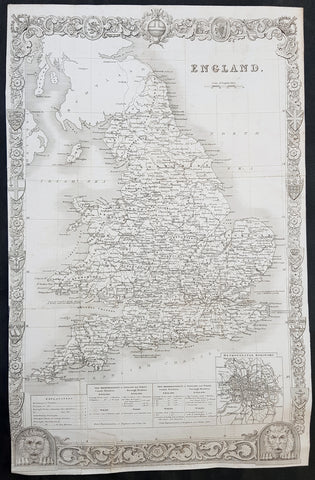
1836 Thomas Moule Large Original Antique Map of England & Wales
- Title : England
- Size: 17in x 11in (430mm x 280mm)
- Ref #: 31112
- Date : 1836
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique map of England was engraved for the 1836 edition of Thomas Moules English Counties Delineatedby W. Schmollinger.
Inset plan of Metorpolitan Boroughs of London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (430mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 11in (430mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - Folds as issued, repair to bottom border & left bottom fold
Verso: - Re-enforced along folds
Background:
When considering the work of English map makers we tend, perhaps, to think too much in terms of county maps, dominated by the names of Saxton and Speed, but we should not underrate the contribution to the sum of geographical knowledge made in other spheres, such as the sea charts of Edward Wright, Robert Dudley and Greenvile Collins, the discoveries of James Cook, the road maps of Ogilby and Cary, the meteorological and magnetic charts compiled by Edmund Halley, to mention only a few.
In 1558 Queen Elizabeth came to the throne in the midst of a fast changing world. In 1563 a nineteen sheet map, copies of which survive only in manuscript form, was completed by Laurence Nowell, and no doubt, the issue of Mercator\'s large-scale map of the British Isles in 1564 had an important influence on the thought of the period. A few years later a national survey was commissioned privately, although probably at the instigation of Lord Burghley, the Lord Treasurer, but subsequently was completed with royal encouragement. The outcome was Christopher Saxton\'s Atlas of EngIand and Wales, started about 1570 and published in 1579 - the first printed set of county maps and the first countrywide atlas on such a splendid scale produced anywhere. A Welsh antiquarian, Humphrey Lhuyd completed a set of surveys that were even more successful than Saxton in which he had produced fine manuscript maps of England and Wales which were used by Ortelius in editions of his Atlas from 1573 onwards.
The earliest maps of the 17th century, attributed to William Smith of the College of Heralds, covered only twelve counties based on Saxton/Norden and were presumably intended to be part of a complete new atlas. They were printed in the Low Countries in 1602-3 and were soon followed by maps for the Latin edition of Camden\'s Britannia dated 1607. In 1610-11 the first edition of John Speed\'s famous county Atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published and immediately replaced Saxton\'s in popular appeal. Although Speed assembled much of his material from the earlier works of Saxton, Norden and others, a considerable part of the up-to-date information, especially relating to the inset town plans depicted on his maps, was obtained first hand. The maps undoubtedly owed much of their popularity to the splendid engravings of high quality made in the workshops in Amsterdam of Jodocus Hondius to whom Speed sent his manuscripts, the plates subsequently being returned to London for printing.
In 1645, Volume IV of the famous Blaeu World Atlas covering the counties of England and Wales was published in Amsterdam. These maps have always been esteemed as superb examples of engraving and design, the calligraphy being particularly splendid, but nevertheless they were nearly all based on Saxton and Speed and added little to geographical knowledge.
Not until the latter part of the century do we find an English map maker of originality with the capacity to put new ideas into practice. John Ogilby, one of the more colourful figures associated with cartography, started life as a dancing master and finished as King\'s Cosmographer and Geographic Printer. After publishing a small number of county maps, somewhat on the lines of John Norden he issued in 1675 the Britannia, the first practical series of detailed maps of the post roads of England and Wales on a standard scale of 1,760 yards to the mile. Up to the end of the century and beyond, reprints and revisions of Saxton\'s and Speed\'s atlases continued to appear and the only other noteworthy county maps were Richard Blome\'s Britannia (1673), John Overton\'s Atlas (c. 1670) and Robert Morden\'s maps for an English translation of Camden\'s Britannia published in 1695.
Another noted cartographer of the day was Captain Greenvile Collins, and of his work in surveying the coasts of Great Britain culminating in the issue in 1693 of the Great Britain\'s Coasting Pilot. Apart from these charts, English cartographers published during the century a number of world atlases. Speed was the first Englishman to produce a world atlas with the issue in 1627 of his A Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World. Other atlases appeared later in the century by Peter Heylin, John Seller, William Berry, Moses Pitt and Richard Blome, whilst Ogilby found time to issue maps of Africa, America and Asia. Far more important, from the purely scientific point of view, was the work of Edmund Halley, Astronomer Royal, who compiled and issued meteorological and magnetic charts in 1688 and 1701 respectively.
At the beginning of the eighteenth century the Dutch map trade was finally in decline, the French in the ascendant and the English to a great extent still dominated by Saxton and Speed except, as we have shown, in the spheres of sea charts and road maps. There were atlases by John Senex, the Bowles family, Emanuel and Thomas Bowen, Thomas Badeslade and the unique bird\'s-eye perspective views of the counties, The British Monarchy by George Bickham. In 1750-60 Bowen and Kitchin\'s The Large English Atlas containing maps on a rather larger scale than hitherto was published.
In 1759 the Society for the encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce offered an award of £100 for the best original surveys on this scale and by the end of the century about thirty counties had been re-surveyed. These maps, many of which formed, in later years, the basis for the first issues of county maps by the Ordnance Survey Office were not only decorative but a tremendous improvement geographically on earlier local maps. As a consequence, the skills and expertise of the new-style cartographers soon enabled them to cover the world as well as the domestic market. Thomas Jefferys was such a man; he was responsible for a number of the new 1 in. to 1 mile county surveys and he issued an edition of Saxton\'s much battered 200-year-old plates of the county maps, but he is better known for many fine maps of North America and the West Indies. His work was continued on the same lines by William Faden, trading as Faden and Jefferys. Other publishers such as Sayer and Bennett and their successors Laurie and Whittle published a prodigious range of maps, charts and atlases in the second half of the century. A major influence at this time was John Cary who, apart from organizing the first re-survey of post roads since Ogilby and subsequently printing the noted Travellers\' Companion, was a prolific publisher of atlases and maps of every kind of all parts of the world. After starting work with Cary, and taking part in the new road survey, Aaron Arrowsmith set up in his own business and went on to issue splendid large-scale maps of many parts of the world. Both Cary\'s and Arrowsmith\'s plates were used by other publishers until far into the next century and, in turn, their work was taken up and developed by James Wyld (Elder and Younger) and Tallis and Co.
Later into the 19th century some of the better known cartographers and publishers were by Henry Teesdale (1829-30), Christopher and John Greenwood, surveyors, Thomas Moule, a writer on heraldry and antiques (1830-36) and John Walker (1837) but by about the middle of the century few small-scale publishers survived and their business passed into the hands of large commercial concerns such as Bartholomews of Edinburgh and Philips of London who continue to this day. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
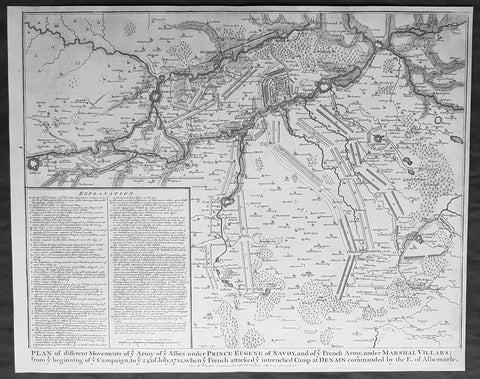
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle Plan of Denain, France in 1712
- Title : Plan of the movements of ye Armies of ye Allies under Prince Eugene of Savoy and of ye French Army under Marshal Villars; from ye beginning of ye campaign to ye 24th July 1712, when ye French attacked ye intrenchement Camp at Denain commanded by the E. of Albemarle
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22155
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan of the Battle of Denain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - centering on the cities of Douai & Bouchain in northern France, was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Denain was fought on 24 July 1712, as part of the War of the Spanish Succession. It resulted in a French victory under Marshal Villars against Dutch and Austrian forces under Prince Eugene of Savoy.
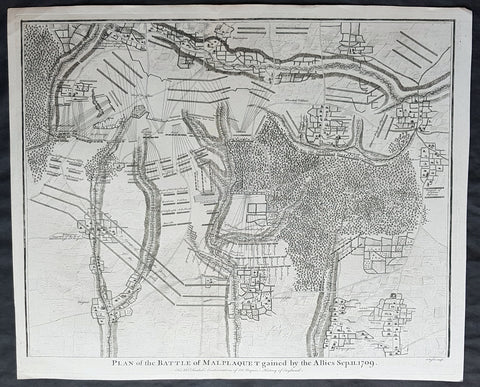
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22173
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
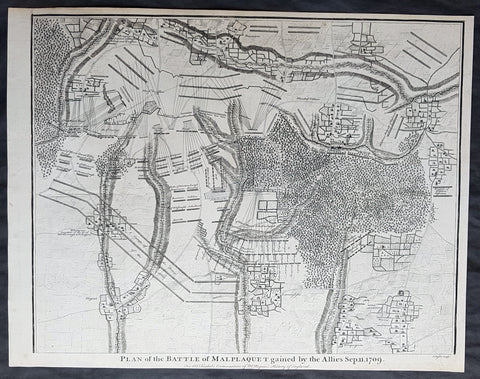
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22154
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
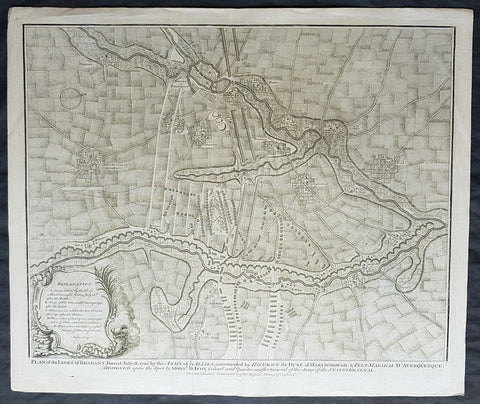
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map Plan of the Battle of Elixheim, Brabant in 1705
- Title : Plan of the Battle lines of Brabant Forced July 18 1705 by the Army of ye Allies commanded by His Grace the Duke of Marlborough & Felt-Marshall D Averquerque Designed upon the spot by Mons D Ivoy Colonel and Quater master General of the Army of the States General
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 01-8714
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Elixheim, in 1705, also known as the Passage of the Lines of Brabant - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Elixheim, 18 July 1705, also known as the Passage of the Lines of Brabant was a battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The Duke of Marlborough successfully broke through the French Lines of Brabant, an arc of defensive fieldworks stretching in a seventy-mile arc from Antwerp to Namur. Although he was unable to bring about a decisive battle, the breaking and subsequent razing of the lines would prove critical to the allied victory at Ramillies the next year.
Early in the campaigning season, Marlborough attempted to launch an invasion of France up the Moselle valley. This effort was halted by a combination of supply shortages and an excellent French defensive position in front of Sierck, and Marlborough and his army were recalled by the Dutch States General when Marshall Villeroi attacked and took the fortress of Huy and threatened Liege. Having rushed back to the Low Countries (and forcing Villeroi to retreat behind his defenses), Marlborough retook Huy, and then planned to break through the lines to bring Villeroi to battle.
On the evening of 17 July Marlborough sent the Dutch troops under Marshal Overkirk in a feint southwards towards Namur, drawing Villeroi and 40,000 men after them. Overnight he marched with his own English and Scottish troops northwards to the small village of Eliksem (Elixheim), and there broke through the lines without resistance. Early the next day, as Overkirk\'s men countermarched northwards to join with Marlborough, a French detachment attacked the small force of allied troops drawn up to the west of the lines, facing south. Following a short but intense cavalry battle, in which Marlborough was often personally engaged, they were driven off, and Villeroi withdrew his army to the west, behind the river Dyle.
Unable to pursue the French with any vigour on the day of the battle due to the exhaustion of his men, who had marched all night and then fought an intense battle, Marlborough nonetheless still hoped to bring Villeroi to battle. He was frustrated in manoeuvering to the west of the lines in the month immediately following the breakthrough. A final effort in early August, using wagons loaded with supplies to remove his dependency on his lines of communication, while successful in forcing Villeroi\'s army to make a stand close to Waterloo, ultimately failed to bring about a battle due to the veto exercised by the Dutch Field Deputies, notably Slangenburg. The Duke was forced to content himself with the capture of the fortress of Leau and the levelling of the Lines of Brabant between Leau and the Meuse.
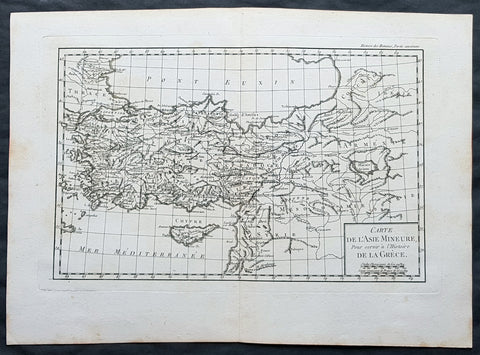
1769 J B D Anville Original Antique Map of Turkey, Cyprus, Asia Minor, Syria
- Title : Carte De L Asie Minerure Pour Servir a L Histoire De La Grece
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 32346
- Date : 1769
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville in the 1769 edition of his atlas Geographie Ancienne et Abregee. or Modern and Ancient Geography (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
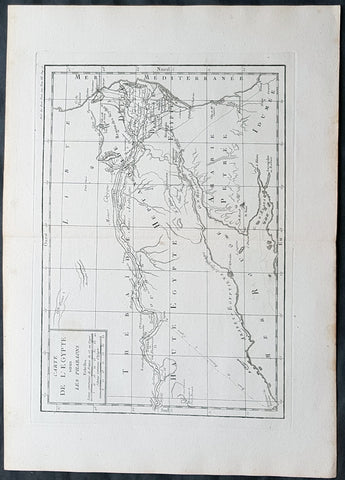
1769 J B D Anville Original Antique Map of Egypt & The Nile in Time of Pharaohs
- Title : Carte De L Egypte sous Les Pharaons
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 32342
- Date : 1769
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D'Anville in the 1769 edition of his atlas Geographie Ancienne et Abregee. or Modern and Ancient Geography (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
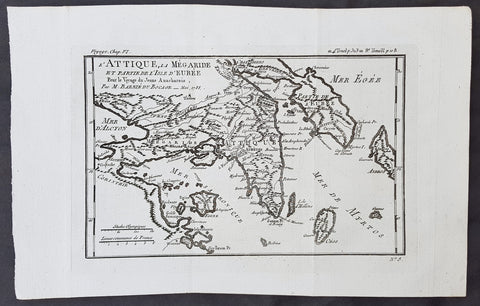
1782 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map of Attica Megaris Thebes Euboea, Greece
- Title : l Attique, la Megaride et partie de l Isle d Eubee, Pour le Voyage du Jeune Anacharsis.....1785
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16463
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1785 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greecein 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8 1/2in x 7 1/2in (215mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Turkey in Europe - Greece to Hungary
- Title : Turquie D Europe...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40526
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of The Russian Empire
- Title : Carte De L Empire de Russie en Europe et en Asie...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31674
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 R. Bonne Original Antique Map of Mogul Empire, India, Tibet, Tibet & Ganges
- Title : Carte de la Partie superieure D L Inde en Daca du Gange...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31661
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1760 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya & Barent Arctic Russia
- Title : Carte des Pais Habites par Les Samojedes et Ostiacs...
- Size: 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 60930
- Date : 1760
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets and the environs of the Arctic Barents & Kara Sea by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in the 1760 edition of Antoine François Prevosts Histoire Generale des Voyages
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1758 Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya Nenets, Russia Willem Barentsz
- Title : Carte Du Détroit De Weigats ou De Nassau, suivant les Navigateurs Hollandois Pour l Histoire Générale des Voyages.1758
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 60965
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, with the Kara Straits and parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets - here named New Holland by the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1758 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The map depicts the Détroit de Waeigats - currently the Kara Straits - that divides the island of Novaya Zemlya from the northern Russian mainland. Novaya Zemlya was also called \"Isle De Waeigats\" & the northern Russian coast was called \"Nouvelle Hollande\", by Willem Barentsz during the Dutch in a 1594 Arctic exploration.
Willem Barentsz 1550 – 1597 was a Dutch navigator, cartographer, and Arctic explorer. He went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northeast passage. During his third expedition, the crew was stranded on Novaya Zemlya for almost a year. Barentsz died on the return voyage in 1597. In the 19th century, the Barents Sea was named after him.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1758 Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya Nenets, Russia Willem Barentsz
- Title : Carte Du Détroit De Weigats ou De Nassau, suivant les Navigateurs Hollandois Pour l Histoire Générale des Voyages.1758
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 23311
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, with the Kara Straits and parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets - here named New Holland by the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1758 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The map depicts the Détroit de Waeigats - currently the Kara Straits - that divides the island of Novaya Zemlya from the northern Russian mainland. Novaya Zemlya was also called \"Isle De Waeigats\" & the northern Russian coast was called \"Nouvelle Hollande\", by Willem Barentsz during the Dutch in a 1594 Arctic exploration.
Willem Barentsz 1550 – 1597 was a Dutch navigator, cartographer, and Arctic explorer. He went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northeast passage. During his third expedition, the crew was stranded on Novaya Zemlya for almost a year. Barentsz died on the return voyage in 1597. In the 19th century, the Barents Sea was named after him.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1758 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Russia The Island of Novaya Zemlya
- Title : Partie De La Mer Glaciale Contenant La Nouvelle Zemle...M. Bellin...1758
- Ref #: 25638
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (380mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Novaya Zemlya also known as Nova Zembla (especially in Dutch), is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in northern Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the Northern island. Novaya Zemlya is composed of two islands, the northern Severny Island and the southern Yuzhny Island, which are separated by Matochkin Strait.
The Russians knew of Novaya Zemlya from the 11th century, when hunters from Novgorod visited the area. For western Europeans, the search for the Northern Sea Route in the 16th century led to its exploration. The first visit from a west European was by Hugh Willoughby in 1553, and he met Russian ships from the already established hunting trade. Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya in 1594, and in a subsequent expedition of 1596 rounded the Northern point and wintered on the Northeast coast. (Barentsz died during the expedition, and may have been buried on the Northern island.) During a later voyage by Fyodor Litke in 1821–1824, the west coast was mapped. Henry Hudson was another explorer who passed through Novaya Zemlya while searching for the Northeast Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1758 Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya Nenets, Russia Willem Barentsz
- Title : Carte Du Détroit De Weigats ou De Nassau, suivant les Navigateurs Hollandois Pour l Histoire Générale des Voyages.1758
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25639
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, with the Kara Straits and parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets - here named New Holland by the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1758 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The map depicts the Détroit de Waeigats - currently the Kara Straits - that divides the island of Novaya Zemlya from the northern Russian mainland. Novaya Zemlya was also called \"Isle De Waeigats\" & the northern Russian coast was called \"Nouvelle Hollande\", by Willem Barentsz during the Dutch in a 1594 Arctic exploration.
Willem Barentsz 1550 – 1597 was a Dutch navigator, cartographer, and Arctic explorer. He went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northeast passage. During his third expedition, the crew was stranded on Novaya Zemlya for almost a year. Barentsz died on the return voyage in 1597. In the 19th century, the Barents Sea was named after him.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1755 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, Camarin to Cape St Marie
- Title : Suite du Bresil.
- Ref #: 61078
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Southern Brazil from from Camarin to Cape St Marie by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7in (240mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1784 Anderson Antique Map Capt Cook Exploration of the Society Islands in French Polynesia
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea; Owharre Harbourin Huaheine; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Date : 1784
- Ref # : 16082
- Size : 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map with surveys and depth soundings of four bays and harbours, of various bays & harbours of the Society Islands, French Polynesia made by explorers during the 17th & 18th centuries.
The first map is Matavia Bay, on the island of Tahiti (Otaheite), the second is Fare (Owharre) Harbour on the island of Huahine & the last two are Ohamaneno & Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) harbours on the island of Raiatea (Ulietea) was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A description of the four Bays & Harbours and their relevance to Capt Cook and other South Seas explorers are;
1.Matavia Bay in Otaheite (Tahiti) - first European to visit Tahiti Capt. Samuel Wallis anchored in Matavai Bay in 1767 as did Louis-Antoine de Bougainville in 1768 & Capt James Cook landed in Matavai Bay in 1769 and returned in his next two voyages.
2. Owharre (Fare) Harbour in Huaheine (Huahine) Captain Cook arrived in fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour
3. Ohamaneno Harbour (Port) in Ulietea (Raiatea)
4. Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) Harbour in Ulietea (Raiatea)
Raiatea - The first European to record sighting Raiātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva. The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Raiātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, travelled with European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
Tahiti.