Maps (791)
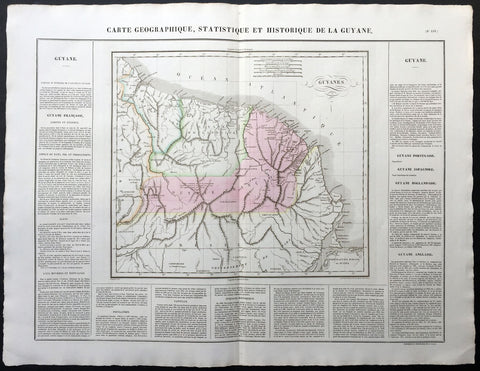
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of Guyana South America
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique De La Guyane
- Ref #: 70036
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
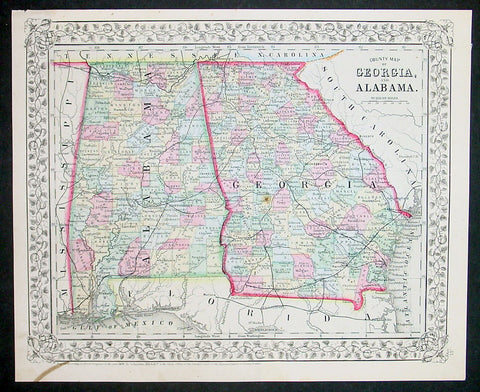
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of Georgia and Alabama
- Title : County Map of Georgia and Alabama....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35038
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
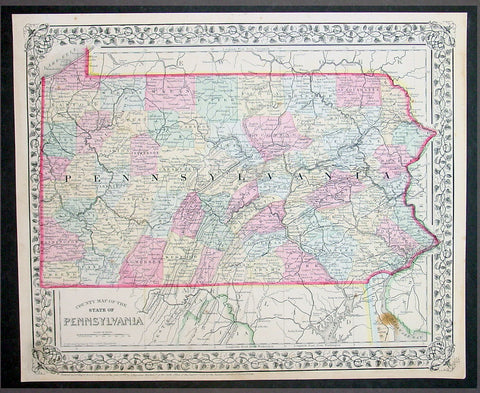
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of the State of Pennsylvania
- Title : County Map of Florida, Mobile....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35051
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
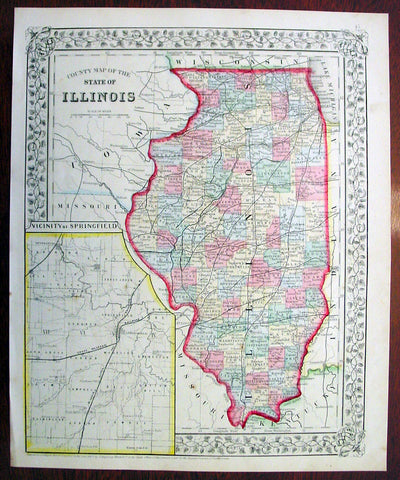
1869 Mitchell Antique Map of The State of Illinois
- Title : County Map of the State of Illinois....1869 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35045
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell Antique County Map of Iowa and Missouri
- Title : County Map of the States of Iowa and Missouri....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35047
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of Virginia & West Virginia
- Title : County Map of Virginia and West Virginia....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35036
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
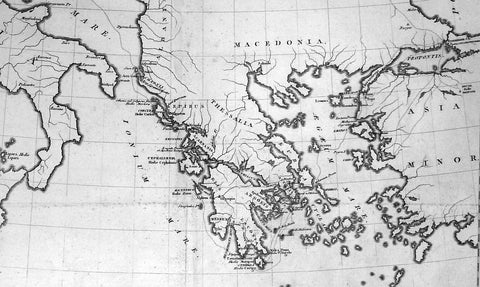
1802 Lechevalier Antique Map of Italy Greece & Turkey Troy
- Title : Carte Du Golphe Adriatique et De L Archipel pour servir ou Voyage de la Troade
- Ref #: 70207
- Size: 20in x 19in (510mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique map of the voyage of Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier from Italy to the Greece and Turkey - specifically the Biga Peninsular home of the ancient city of Troy in NW Turkey - was published in the Atlas of Charts & Views that accompanied the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier's (1752 - 1836) Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786.
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homer's Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His title, "Voyage de la Troade" was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 19in (510mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 18in (485mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning along fold as issued
Verso: - Light age toning
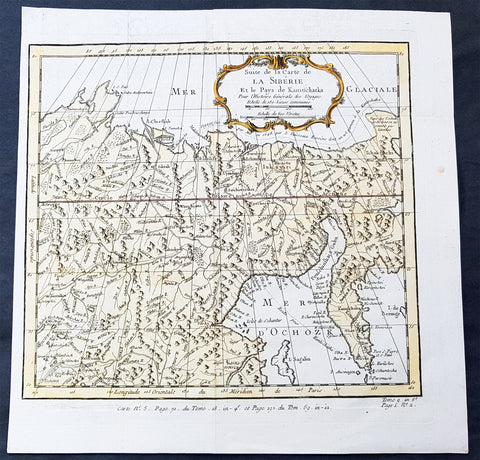
1758 Bellin Old, Antique Map of Eastern Siberia and the Kamchatka Peninsula Russia
- Title : Suite de la Carte de La Siberie et le Pays Kamtschatka
- Ref #: 60929
- Size: 11 3/4in x 11 3/4in (300mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Eastern Russia & Siberia including the Kamchatka Peninsular and south to northern China by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 12in (305mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 9 1/2in (285mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
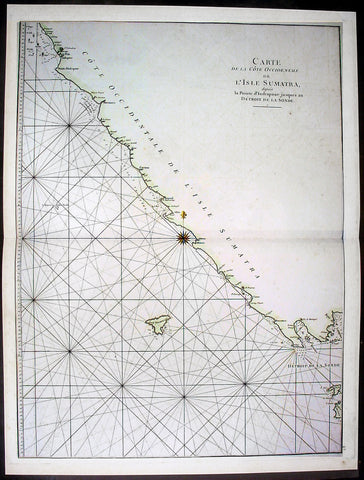
1745 Mannevillette Large Antique Map of Sumatra Coastline of Indonesia
- Title : Carte De La Cote Occidentale De L Isle Sumatra
- Ref #: 33661
- Size: 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large hand coloured original antique map a coastal sea chart of the south west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia - centering on the city of Bengkulu stretching south to Tanjungkarang-Telukbetung and north to Mukomuko - was published in the enlarged version of Le Neptune Oriental by Jean Baptiste De Mannevillette in 1745.
Born in Le Havre of a seafaring family d`Apres de Mannevillette had a long and distinguished career as a navigator and one of the first French hydrographers. After studying mathematics in Paris, he gained early experience of the sea in a voyage at the age of nineteen to the Caribbean. During many subsequent voyages he assembled a collection of material for a projected hydrographical atlas which, with the support of the Academie des Sciences, was published in Paris in 1745 under the title Le Neptune Oriental. In spite of the popularity of the first issue, it failed to satisfy the author and he spent nearly thirty years, often with the assistance of his friend, Alexander Dalrymple, the English hydrographer, in the preparation of a revised and enlarged edition which eventually was issued in 1775.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2n x 20in (675mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min ½in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
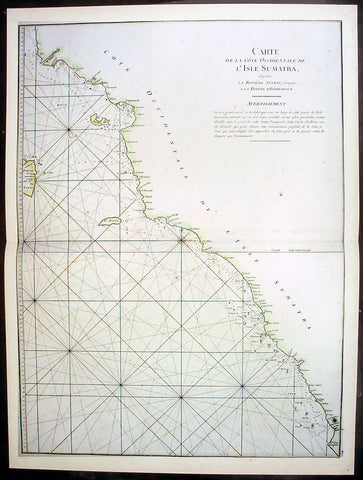
1745 Mannevillette Large Antique Map Sumatra Coastline of Indonesia
- Title : Carte De La Cote Occidentale De L Isle Sumatra
- Ref #: 33662
- Size: 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large hand coloured original antique map a sea chart of the west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia - centering on the city of Padang stretching south to Indrapura and north to Aceh - was published in the enlarged version of Le Neptune Oriental by Jean Baptiste De Mannevillette in 1745. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2n x 20in (675mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min ½in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
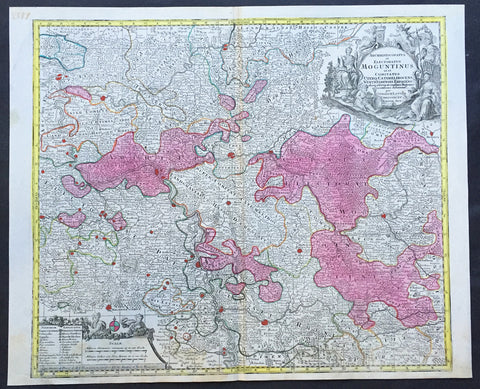
1756 Lotter Large Antique Map of Rhine Koblenz, Germany
- Title : Archiepiscopatus et Electoratus Moguntinus...
- Ref #: 50169
- Size: 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautiful hand coloured original antique map of the Rhine River region of central western Germany was engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotter in 1756.
The map centres on the city of Frankfurt stretches along the Rhine River from Koblenz in the North to Speir in the South. Wertheim in the east to Kern in the west (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22 ½in x 19 ½in (570mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
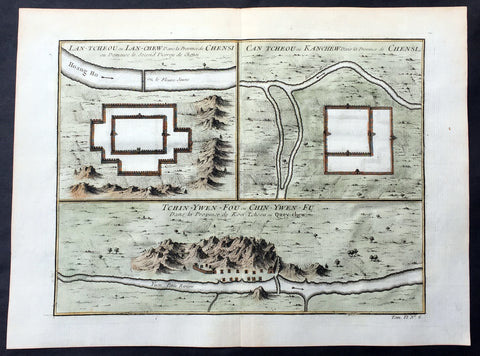
1755 Prevost Antique Map Lanzhou & Zhangye in Gansu - Guiyang in Guizhou, China
- Title: Lan-Tcheou ou Lan-Chew dans la Province Chensi…/Can Tcheou ou Kan-Chew dans la Province de Chensi…/Tchin-Ywen-Fou ou Chin-Ywen-Fu dans la Province de Koei-Tcheou ou Quey-Chew
- Date: 1755
- Size: 13 1/2in x 10in (345mm x 255mm)
- Ref: 25725
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a birds-eye view of the walled cities of Lanzhou & Zhangye in the Gansu province of Northern China and the city of Guiyang in the Guizhou province of Southwest China by Jakob van Schley in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Lanzhou is the capital and largest city of Gansu Province in Northwest China. The prefecture-level city, located on the banks of the Yellow River
Originally in the territory of the Western Qiang peoples, Lanzhou became part of the territory of the State of Qin in the 6th century BC.
In 81 BC, under the Han dynasty (206 BC–220 AD), it was taken from the Huns\' Huandi Chanyu and made the seat of Jincheng commandery (jùn), and later of the Jincheng county (xian), later renamed Yunwu. The city used to be called the Golden City, and since at least the first millennium BC it was a major link on the ancient Northern Silk Road, and also an important historic Yellow River crossing site. To protect the city, the Great Wall of China was extended as far as Yumen. Parts of the Great Wall still exist within the built-up area.
After the fall of the Han dynasty, Lanzhou became the capital of a succession of tribal states. In the 4th century it was briefly the capital of the independent state of Liang. The Northern Wei dynasty (386–534) reestablished Jincheng commandery, renaming the county Zicheng. Mixed with different cultural heritages, the area at present-day Gansu province, from the 5th to the 11th century, became a center for Buddhist study. Under the Sui Dynasty(581–618) the city became the seat of Lanzhou prefecture for the first time, retaining this name under the Tang dynasty (618–907). In 763 the area was overrun by the Tibetan Empire and in 843 was conquered by the Tang. Later it fell into the hands of the Western Xia dynasty (which flourished in Qinghai from the 11th to 13th century) and was subsequently absorbed by the Song dynasty (960–1126) in 1041. The name Lanzhou was reestablished, and the county renamed Lanzhuan.
After 1127 it fell into the hands of the Jin dynasty, and after 1235 it came into the possession of the Mongol Empire.
Under the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) the prefecture was demoted to a county and placed under the administration of Lintao superior prefecture, but in 1477 Lanzhou was reestablished as a political unit.
The city acquired its current name in 1656, during the Qing dynasty. When Gansu was made a separate province in 1666, Lanzhou became its capital.
In 1739 the seat of Lintao was transferred to Lanzhou, which was later made a superior prefecture called Lanzhou.
Lanzhou was badly damaged during the Dungan revolt in 1864–1875. In the 1920s and 1930s it became a center of Sovietinfluence in northwestern China. During the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) Lanzhou, linked with Xi\'an by highway in 1935, became the terminus of the 3,200 km (2,000 mi) Chinese–Soviet highway, used as a route for Soviet supplies destined for the Xi\'an area. This highway remained the primary traffic route of northwestern China until the completion of the railway from Lanzhou to Ürümqi, Xinjiang. During the war Lanzhou was heavily bombed by the Japanese.
During the 1937 Japanese invasion of China, the Guominjun Muslim Generals Ma Hongkui and Ma Bufang protected Lanzhou with their cavalry troops, putting up such resistance that the Japanese never captured Lanzhou. The city is the seat of a currently vacant Roman Catholic diocese and was previously the center of a vicariate apostolic(Vicariate Apostolic of Northern Kan-Su)
Zhangye , formerly romanized as Changyeh or known as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Gansu Province in the People\'s Republic of China. It borders Inner Mongolia on the north and Qinghai on the south. Its central district is Ganzhou, formerly a city of the Western Xia and one of the most important outposts of western China.
Zhangye lies in the center of the Hexi Corridor. The area is on the frontier of China Proper, protecting it from the nomads of the northwest and permitting its armies access to the Tarim Basin. During the Han Dynasty, Chinese armies were often engaged against the Xiongnuin this area. It was also an important outpost on the Silk Road.[citation needed]Before being overrun by the Mongols, it was dominated by the Western Xia, and before by the Uyghurs from at least the early 10th century. Its relation to the larger Uyghur state of Qocho is obscure, but it may have been a vassal.
The Mongol Emperor Kublai Khan is said to have been born in the Dafo Temple, Zhangye, now the site of the longest wooden reclining Buddha in China.[citation needed] Marco Polo\'s journal states that he spent a year in the town during his journey to China.
The pine forests of the Babao Mountains (part of the Qilian range) formerly regulated the flow of the Ruo or Hei Shui, Ganzhou\'s primary river. By ensuring that the meltwaters lasted throughout the summer, they avoided both early flood and later drought for the valley\'s farmers. Despite reports that they should thus be protected in perpetuity, an imperial official in charge of erecting the poles for China\'s telegraph network ordered them cleared in the 1880s. Almost immediately, the region became prone to flooding in the summer and draught in the autumn, arousing local resentment.
Christian missionaries arrived in 1879, after Suzhou was found to be too hostile for their settlement.
Guiyang is the capital of Guizhou province of Southwest China. It is located in the center of the province, situated on the east of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, and on the north bank of the Nanming River, a branch of the Wu River.
Guiyang was a 7th-century military outpost under the Sui and Tang, when the area around it was known as Juzhou. It grew into a city named Shunyuan under the Mongolian Yuandynasty sometime between their 1279 southwestern campaignsand 1283. By the time Guizhoubecame a full province in 1413, its capital at Guiyang was also known as Guizhou. It became a prefectural seat under the Mingand Qing. Guiyang grew rapidly during the development of the southwest that occurred after the Japanese invasion of China during World War II.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 10in (345mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 8 1/2in (295mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
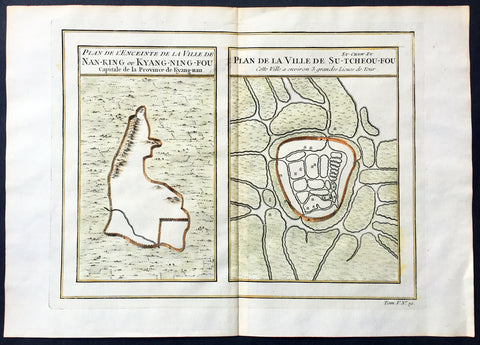
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Map, View of Nanking or Nanjing in Jiangsu, China
- Title: Plan De L Enceinte de la Ville De Nan-King ou Kyang-Ning-Fou Capitale de la Province de Kyang-nan; Plan de la Ville De Su-Tcheou-Fou
- Date: 1755
- Size: 13 1/2in x 10in (345mm x 255mm)
- Ref: 25695
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a birds-eye view of the walled cities of Nanjing & Zhenzhou, in the Jiangsu Province of China by Jakob van Schley in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Nanjing formerly romanized as Nanking and Nankin, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People\'s Republic of China and the second largest city in the East China region, with an administrative area of 6,600 km2 (2,500 sq mi) and a total population of 8,270,500.
Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949, and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to one of the world\'s largest inland ports.
Nanjing, one of the nation\'s most important cities for over a thousand years, is recognized as one of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. It has been one of the world\'s largest cities, enjoying peace and prosperity despite wars and disasters. Nanjing served as the capital of Eastern Wu, one of the three major states in the Three Kingdoms period (211–280); the Eastern Jin and each of the Southern Dynasties (Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang and Chen), which successively ruled southern China from 317–589; the Southern Tang, one of the Ten Kingdoms (937–76); the Ming dynasty when, for the first time, all of China was ruled from the city (1368–1421);[15] and the Republic of China (1927–37, 1945–49) prior to its flight to Taiwan during the Chinese Civil War. The city also served as the seat of the rebel Taiping Heavenly Kingdom (1851–64) and the Japanese puppet regime of Wang Jingwei (1940–45) during the Second Sino-Japanese War. It suffered appalling atrocities in both conflicts, including the Nanjing Massacre.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 10in (345mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (295mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
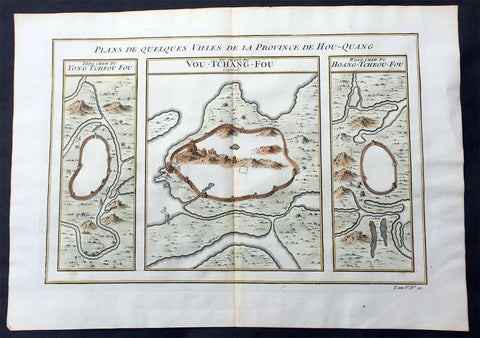
1755 Prevost Antique Map of Wuhan in Hubei, China - Huangzhou & Hoang-Tcheou-Fou
- Title: Plans De Quelques VIlles De La Province de Hou-Quang; Yong Tcheou Fou; Vou-Tchang-Fou; Hoang-Tcheou-Fou
- Date: 1755
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Ref: 25540
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a birds-eye view of three walled cities of the central Chinese province of Hubei, Huangzhou, Wuhan & Hoang-Tcheou-Fou, on the Yangtze River, by Jakob van Schley in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Hubei or Hou-Quang is a province located in central China. Hubei means north of the lake, referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital is Wuhan, a major transportation thoroughfare and the political, cultural, and economic hub of Central China.
Hubei is an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the Qin dynasty, after the powerful State of Chu that existed here during the Eastern Zhou dynasty. It borders Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxito the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province.
Below is a description of each city & excerts from Jean Baptiste Du Haldes Description Geographique, Historique, Chronologique, Politique, et Physique de l\'Empire de la Chine published in 1735 of each city.
1. Yong tcheou fou - Huangzhou District is an urban district of Huanggang, Hubei, China. Huangzhou was previously a separate city which administered a prefecture in its own right.
The Seventh City, Yong tcheou fou.
This city, the most Southern of the Province, is surrounded with Mountains, whose Verdure renders a very agreeable Prospect, and is situate on the Banks of a River, which not far from thence runs into the Siang kiang. The Water of this River is so clear and limpid, that in the deepest Places you may count the Stones and Flints that are at the Bottom : There grows plenty of Bamboos in some part of this District and in others the Lien hoa, with yellow Flowers : There are eight Cities in its Jurisdiction, one of the Second Order, and seven of the Third.
Besides these principal Cities, there are two of the Second Order, which are not subject to any Fou, or City of the First Order, and have each a Jurisdiction over other Cities : The first is called Tsin tcheou, and is on the Frontiers of the Province of Koei tcheou, it has in its District three Cities of the Third Order : The second is called Tching Tcheou, a very large and populous City, built between two Rivers ; five Cities of the Third Order are subject to it, all situated on the Frontiers of the City of Quang Tong : Tho\' this City is full of Mountains, yet they do not hinder its Cultivation.
2. Vou-Tchang-Fou - Wuhan - is the capital of Hubei province, China, and is the most populous city in Central China. It lies in the eastern Jianghan Plain at the intersection of the middle reaches of the Yangtze and Han rivers.
With a 3,500-year-long history, Wuhan is one of the most ancient and civilized metropolitan cities in China. During the Han dynasty, Hanyang became a fairly busy port. In the winter of 208/9, one of the most famous battles in Chinese history and a central event in the Romance of the Three Kingdoms—the Battle of Red Cliffs—took place in the vicinity of the cliffs near Wuhan. Around that time, walls were built to protect Hanyang (AD 206) and Wuchang (AD 223). The latter event marks the foundation of Wuhan. In AD 223, the Yellow Crane Tower was constructed on the Wuchang side of the Yangtze River. Cui Hao, a celebrated poet of the Tang dynasty, visited the building in the early 8th century; his poem made it the most celebrated building in southern China. The city has long been renowned as a center for the arts (especially poetry) and for intellectual studies. Under the Mongol rulers (Yuan dynasty), Wuchang was promoted to the status of provincial capital; by the dawn of the 18th century, Hankou had become one of China\'s top four most important towns of trade.
The First City, and Capital of the Province, Vou chang fou
This is both the Capital of the Province, and the North Part of it, called Hou pe, where resides the Tsong tou of both Parts of this Province , it has under its particular Jurisdiction one City of the Second , Order, and nine of the Third.
Vou chang is almost in the Centre of the Empire, and situate in a Place which may most easily communicate with the rest of the Provinces. This City joined to Han yang, from which it is separated only by the Breadth of the River Yang tse kiang, and the little River Han forms a Place the best Peopled, and of the greatest Resort in China ; one may compare the Extent of this City to Paris, and Han Tang to Lyons, or Rouen: Add to this, an incredible Number of Barks of all Sizes, which lie some in one River, some in the other, for the length of French Leagues, to the number of eight or ten thousand Vessels, among which there are hundreds every way as large as the most part of those that lie at Nantz. Certainly, if one considers nothing else but this Forest of Masts which are upon the fine River Yang tse Kiang, about a League broad in this Place, tho\' it is 150 Leagues from the Sea, and deep enough for the greatest Vessels, it will justly raise our Wonder; but when one gains the Top of any Ascent, and discovers such a vast Extent of Ground covered with Houses, we should scarcely believe our won eyes, or at least must think it the finest Sight in the World.
One may judge, by the Number of Rivers and Lakes with which this Province is watered, how fruitful it is, and how easily the Trading with the rest of the Empire, by means of the great River Yang tse Kiang, must needs inrich it.
What is farther worthy of Observation, is the fine Cristal which is dug out of the Mountains, the plentiful Crops of the best Tea, and the extraordinary Demand for Bamboo Paper, which is manufactured here.
3. Hoang tcheou fou - The Eighth City.
The Situation of this City is on the Banks of the River Yang tse kiang ; its small distance from the Capital, and the Number of Lakes which surround it, render it a most agreeable Place for Habitation ; it is extremely well peopled, and for Trade gives place to few other Cities. There come there daily a surprising Number of Barks, loaded with all forts of Merchandize.
The whole District is admirably well cultivated, I and agreeably diversified by the Rivers and Brooks that Water it, as well as by the Mountains which bound it on the North ; some of these Mountains are covered with Trees, which are of great service to the Inhabitants ; there are also Fountains, which have the Property of giving Tea a delicious Taste.
There are taken in the River near the City great Numbers of Tortoises, some great, some small, which the Nobility keep in their Gardens for Diversion, and also at their Pleasure-Houses. They make excellent Arrack, which is very strong, and takes Fire in an Instant, and hath no bad Smell ; there are also very good Chestnuts, and very large. Its District: contains nine Cities, one of the Second Order, and eight of the Third. The South Part of the Province of Hou quang.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
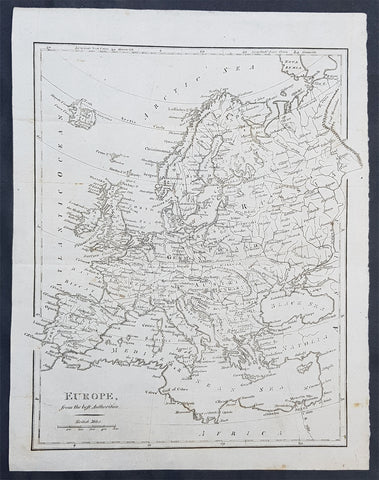
1797 John Cary Original Antique Map of Europe
- Title : Europe from the Best Authorities
- Size: 12 1/2in x 10in (315mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 92766
- Date : 1797
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12 1/2in x 10in (315mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10in (315mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
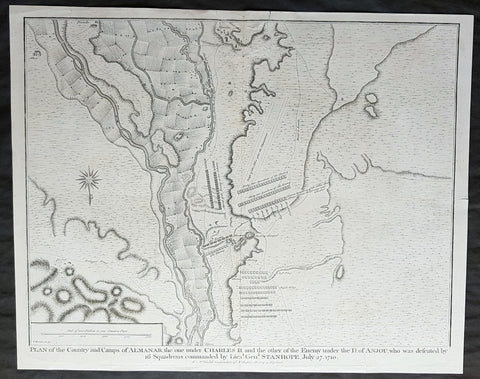
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map Battle of Almenar Balaguer, Catalonia, Spain
- Title : Plan of the Country and Camps of Almanar, the one under Charles II and the other of the Enemy under the D of Anjou who was defeated by 16 Squadrons commanded by Lieut. Gen. Stanhope, July 27 1710
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22174
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Almenar, near Balaguer, Catalonia, Spain in 1710 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - Repair to top of image, no loss
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Almenar took place on 27 July 1710 in the War of the Spanish Succession, between the troops of Phillip V and the Archduke Charles. Philip V\'s army having been defeated was forced to evacuate Catalonia and regroup behind the Ebro.
In spring of 1710, the Borbonic army had entered Catalonia from Aragón crossing the Segre river on March 15. On May 3, Philip V, the Borbon claimant to the throne, joined the army.
The opposing allied army, consisting of Austrian, British, and Dutch troops, was joined by Archduke Charles of Austria, the Habsburg claimant, in June.
In July, General Guido Starhemberg received reinforcements and decided to attack. He crossed the Noguera river taking up positions on the heights of Almenar.
Stanhope then crossed the Segre at Balaguer (north of Lerida) marching to the bridge of Alfarras, crossing it on 27 July.
Villadarias opened the battle with a cavalry attack which was initially successful, but the initiative was wasted by pursuing groups of fleeing enemies.
Then the British infantry attacked the left wing which fled, taking the second line with it. Then the Austrians attacked and destroyed the right wing, where Philip V risked his life fighting and was almost captured by the allies.
The Borbonic troops had to leave Catalonia and withdraw to Aragón, where the Battle of Saragossa took place on August 20.
Villadarias was relieved of his command and replaced by the Marquis de Bay.
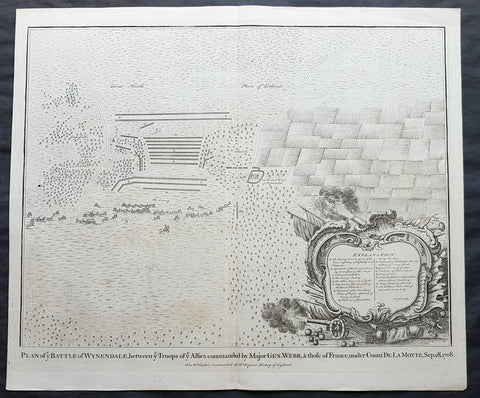
1745 N Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 01-9034
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
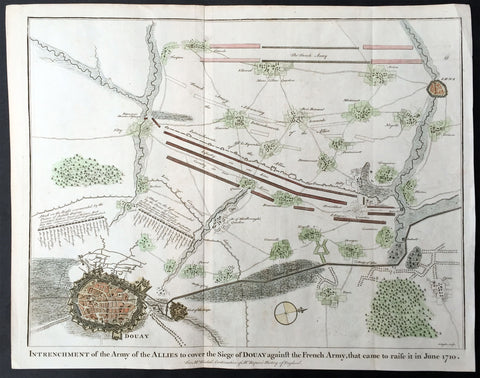
1745 N Tindal Original Antique Map Siege of Douai, Flanders, North France in 1710
- Title : Intrenchment of the Army of the Allies to cover the Siege of Douay against the French Army that came to raise it in June 1710.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22212
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Siege of Douai, Flanders in Northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A large battle plan showing both siege and works against a fortified Douai, Flanders and the detailed dispositions and battle lines of Lord Marlborough\'s army against the French, and thier attempt to lift the siege in June 1710.
Successive sieges from 1710 to 1712 during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13), almost completely destroyed Douai by the British Army. By 1713, the town was fully integrated into France. Douai became the seat of the Parliament of Flanders.
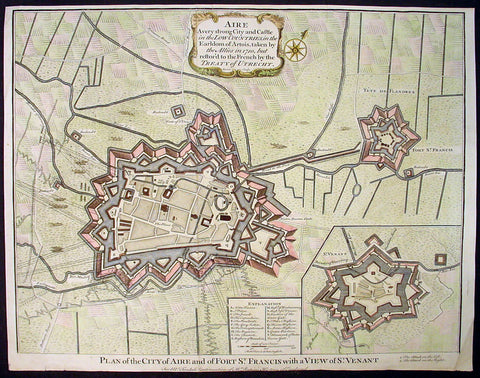
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map of Aire-sur-la-Lys, Fort St Francis & St Venant, France
-
Title : Plan of the City of Aire and Fort of St. Francis with a view of St.Venant
Sep. 28, 1708 - Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22218
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan & birds eye view of the French city of Aire-sur-la-Lys, a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France along with Fort St Francis and Fort St Venant - used by Lord Marlborough during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Aire-sur-la-Lys is located 10 miles (16 km) southeast of Saint-Omer, by the banks of the Leie and the Laquette rivers.
It is mentioned for the first time in 857 and developed around a fort or castrum built by Baldwin II, Count of Flanders in response to the Norman invasions. More growth followed with the establishment of the Collegiate church of Saint-Pierre by Baldwin V, Count of Flanders.
The town was laid siege ten times between 1127 and 1710. It was separated from the County of Flanders and attached to the County of Artois in 1196. Subsequently ruled by the Burgundians then by the Spanish.
The town was besieged in 1676 by Vauban and retaken for France, although it remained a Spanish possession until 14 April 1713, when, by the Treaty of Utrecht, it finally became a part of France.
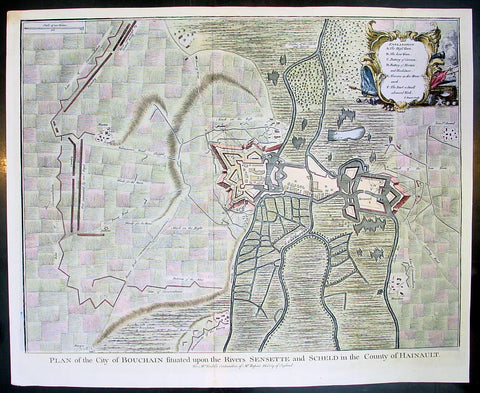
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22198
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
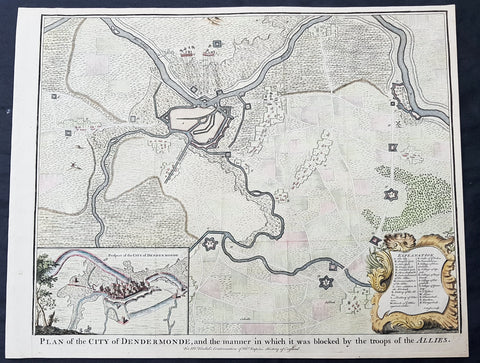
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan & View Siege of Dendermonde, Belgium in 1706
- Title : Plan of the City of Dendermonde, and the manner in which it was blocked by the troops of the Allies
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22157
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the Belgium city of Dendermonde and surrounding regions during the siege of Dendermonde in 1706 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Dendermonde is a Belgian city and municipality located in the Flemish province of East Flanders in the Denderstreek. The municipality comprises the city of Dendermonde proper and the towns of Appels, Baasrode, Grembergen, Mespelare, Oudegem, Schoonaarde, and Sint-Gillis-bij-Dendermonde. Dendermonde is located at the mouth of the river Dender, where it flows into the Scheldt. The town has a long-standing (folkloric) feud with Aalst (situated south along the same river), which dates back from the Middle Ages.
The city is an administrative, commercial, educational, and medical centre for the surrounding region. The current Mayor of Dendermonde is Piet Buyse (Christian Democratic and Flemish).
Some interesting La-Tène artifacts were found in Appels, proof that this region of the Scheldt was inhabited in prehistory. Grave sites from the 2nd and 6th century also attest to dense settlement in Gallo-Roman and Merovingian times. In 843, the Treaty of Verdun placed Dendermonde in Lotharingia. After the Norman invasions of 883, however, Baldwin II took over the region and incorporated it into the German part of the newly founded County of Flanders.
Otto II built a fort here in the 10th century, encouraging further settlements in the area. The town received its city charter in 1233 and grew quickly after that thanks to a thriving cloth industry. Several cloisters, chapels and churches, and a fortified defensive wall were built as well. A cloth hall and belfry were erected on the market square in the mid 14th century. The town’s prosperity, however, gave rise to severe competition with cities such as Ghent and to occasional attacks and plunders by neighbours. In 1384, the whole area came under the control of the Valois dukes of Burgundy.
The 16th century saw a decline in Dendermonde’s fortunes. In 1572 Dendermonde was conquered by William the Silent. The same year however Spanish troops under Duke Alexander Farnese of Parma, took over the city, looted and mostly destroyed it. A decade later, the Spaniards built their own fortress between the Dender and the Scheldt. In 1667, it was France’s turn to advance on the city, but the allied troops of the Netherlands and England, under the Duke of Marlborough, caused the heaviest damage in 1706. The city was then fortified by the Austrians against further French ambitions. After a last siege by Louis XV, the city could finally breathe to the point that the fortifications were dismantled a few decades later.
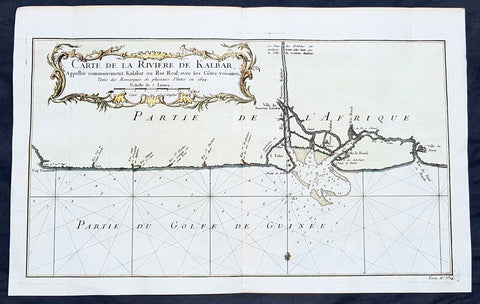
1750 Bellin Antique Map Calabar River, Calabar, Nigeria West Africa - Salve Port
- Title: Carte De la Riviere De Kalbar...Pilotes en 1699
- Date: 1750
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25652
- Size: 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Calabar River Mouth, Calabar City in Nigeria, West Africa - a significant slave port of the 17th & 18th centuries - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Detailed coastal map of Guinea coast of Western Africa, is based upon the 1699 voyage of James Barbot & John Grazilhier to New Calabar, Bandi, and Doni Rivers.
Barbot and Grazilhier each gave famous accounts of their experiences in the slave trade in the second half of the 17th Century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/4in x 7 1/2in (260mm x 195mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
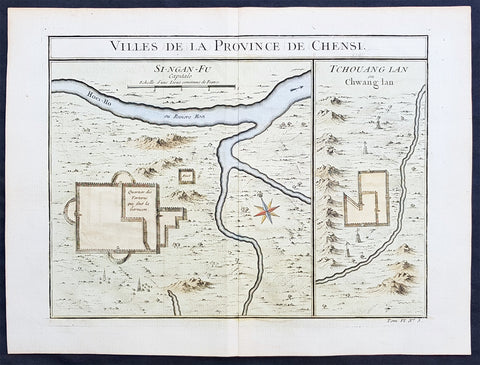
Copy of 1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Map of Xi an & Guanzhong in Shaanxi Province China
- Title: Villes De La Province De Chensi (Si-ngan-fu Capitale / Tchouang Lan ou Chwang lan)
- Date: 1755
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25726
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a birds-eye view of the walled city of Xi an & the historical region of the Guanzhong Plain in the Shaanxi Province of Northern China by Jakob van Schley in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Shaanxi is a province of the People\'s Republic of China. Officially part of the Northwest China region.
Shaanxi is considered one of the cradles of Chinese civilization. Thirteen feudal dynasties established their capitals in the province during a span of more than 1,100 years, from the Zhou Dynasty to the Tang Dynasty.
The province\'s principal city and current capital, Xi\'an, is one of the four great ancient capitals of China and is the eastern terminus of the Silk Road, which leads to Europe, the Arabian Peninsula and Africa.
Under the Han Dynasty, the Northern Silk Road was expanded to advance exploration and military purposes to the west. This Northern Silk Road is the northernmost of the Silk Roads and is about 2,600 kilometres (1,600 mi) in length. It connected the ancient Chinese capital of Xi an to the west over the Wushao Ling Pass to Wuwei and emerging in Kashgar before linking to ancient Parthia.
Under the Ming dynasty, Shaanxi was incorporated into Gansu but was again separated in the Qing dynasty.
One of the most devastating earthquakes in history occurred near Hua Shan, in south-eastern part of Shaanxi Province on January 23, 1556, killing an estimated 830,000 people (see 1556 Shaanxi earthquake).
Xi an is the capital of Shaanxi province in China. It is a sub-provincial city located in the center of the Guanzhong Plain in Northwestern China. One of the oldest cities in China, Xi\'an is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals, having held the position under several of the most important dynasties in Chinese history, including Western Zhou, Qin, Western Han, Sui, and Tang. Xi\'an is the starting point of the Silk Road and home to the Terracotta Army of Emperor Qin Shi Huang.
Guanzhong Plain, is a historical region of China corresponding to the lower valley of the Wei River. It is called Guanzhong or \'within the passes\', as opposed to \'Guandong\' or \'east of the pass\', i.e., the North China Plain. The North China Plain is bordered on the west by mountains. The Yellow River cuts through the mountains at the Hangu Pass or Tongguan separating Guanzhong from Guandong.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
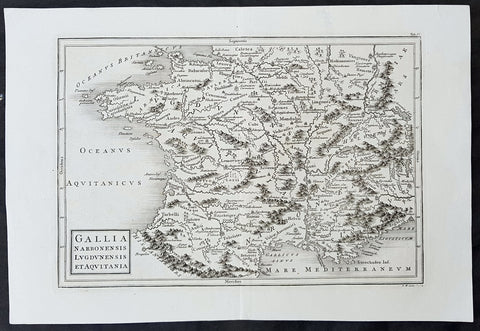
1750 Christop. Cellarius Original Antique Map of France - Gallia
- Title : Gallia Narbonensis Lugdvnensis et Acvitania
- Size: 15in x 10 1/2in (380mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 31353
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map of France by Christoph. Cellarius was published in the 1750 edition of Geographica Antiqua.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10 1/2in (380mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Geographica was one of the most popular geographical publications of the 17th and 18th centuries, lasting well into the 19th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Cellarius, Christopher, 1638-1707
Christopher Cellarius (Keller) was professor of Oriental languages at Halle university and the author of numerous books including his most famous work the atlas Geographica Antiquafirst published in 1686 and being reissued with updated plates until the early 19th century.
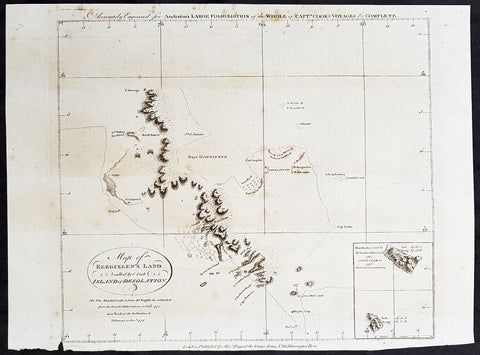
1784 Anderson Antique Map SW Regions of Kerguelen Islands in South Indian Ocean
- Title : Map of Kerguelens Land Called by C Cook Island of Desolation
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 21694
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the the Kerguelen Islands in the very Southern Indian Ocean explored by Capt Cooks during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in December 1776 was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cook\\\'s first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ...published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small tear to bottom margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
The Kerguelen Islands also known as the Desolation Islands are a group of islands in the southern Indian Ocean constituting one of the two exposed parts of the mostly submerged Kerguelen Plateau. They are among the most isolated places on Earth, located 450 km (280 mi) northwest of the uninhabited Heard Island and McDonald Islands and more than 3,300 km (2,051 mi) from Madagascar, the nearest populated location (excluding the Alfred Faure scientific station in Île de la Possession, about 1,340 km (830 mi) from there, and the non-permanent station located in Île Amsterdam, 1,440 km (890 mi) away). The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands, Amsterdam, and Saint Paul Islands, and France\'s Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean are part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands and are administered as a separate district.
The main island, Grande Terre, is 6,675 km2 in area and is surrounded by a further 300 smaller islands and islets, forming an archipelago of 7,215 km2. The climate is raw and chilly with frequent high winds throughout the year. The surrounding seas are generally rough and they remain ice-free year-round. There are no indigenous inhabitants, but France maintains a permanent presence of 45 to 100 scientists, engineers and researchers. There are no airports on the islands, so all travel and transport from the outside world is conducted by ship.
Kerguelen Islands appear as the Ile de Nachtegal on Philippe Buache\'s map from 1754 before the island was officially discovered in 1772. The Buache map has the title Carte des Terres Australes comprises entre le Tropique du Capricorne et le Pôle Antarctique où se voyent les nouvelles découvertes faites en 1739 au Sud du Cap de Bonne Esperance (Map of the Southern Lands contained between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Pole, where the new discoveries made in 1739 to the south of the Cape of Good Hope may be seen). It is possible this early name was after Abel Tasman\'s ship De Zeeuwsche Nachtegaal. On the Buache map, Ile de Nachtega\" is located at 43°S, 72°E, about 6 degrees north and 2 degrees east of the accepted location of Grande Terre.
The islands were officially discovered by the French navigator Yves-Joseph de Kerguelen-Trémarec on 12 February 1772. The next day Charles de Boisguehenneuc landed and claimed the island for the French crown. Yves de Kerguelen organised a second expedition in 1773 and arrived at the \"baie de l\'Oiseau\" by December of the same year. On 6 January 1774 he commanded his lieutenant, Henri Pascal de Rochegude, to leave a message notifying any passers-by of the two passages and of the French claim to the islands. Thereafter, a number of expeditions briefly visited the islands, including that of Captain James Cook in December 1776 during his third voyage, who verified and confirmed the passage of de Kerguelen by discovering and annotating the message left by the French navigator.
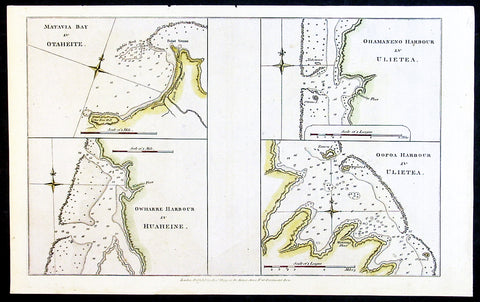
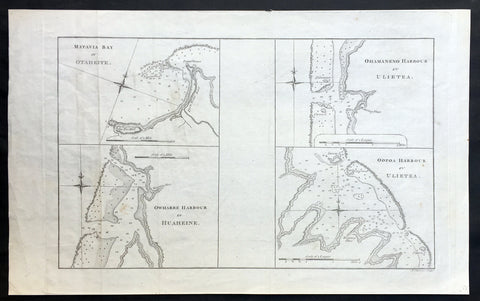
1784 Anderson Antique Map Capt Cook Exploration of the Society Islands in French Polynesia
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea; Owharre Harbourin Huaheine; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Date : 1784
- Ref # : 32197
- Size : 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map with surveys and depth soundings of four bays and harbours, of various bays & harbours of the Society Islands, French Polynesia made by explorers during the 17th & 18th centuries.
The first map is Matavia Bay, on the island of Tahiti (Otaheite), the second is Fare (Owharre) Harbour on the island of Huahine & the last two are Ohamaneno & Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) harbours on the island of Raiatea (Ulietea) was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A description of the four Bays & Harbours and their relevance to Capt Cook and other South Seas explorers are;
1.Matavia Bay in Otaheite (Tahiti) - first European to visit Tahiti Capt. Samuel Wallis anchored in Matavai Bay in 1767 as did Louis-Antoine de Bougainville in 1768 & Capt James Cook landed in Matavai Bay in 1769 and returned in his next two voyages.
2. Owharre (Fare) Harbour in Huaheine (Huahine) Captain Cook arrived in fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour
3. Ohamaneno Harbour (Port) in Ulietea (Raiatea)
4. Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) Harbour in Ulietea (Raiatea)
Raiatea - The first European to record sighting Raiātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva. The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Raiātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, travelled with European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
Tahiti.
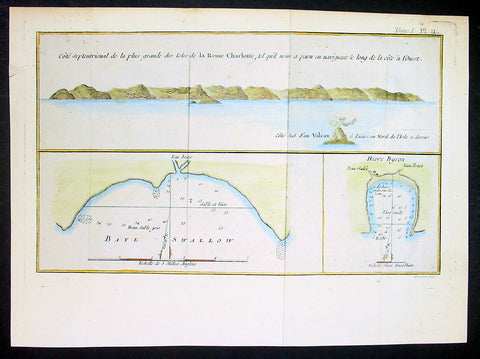
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map Nendo Isle, Nupani, Solomon Islands - Carteret 1767
- Title : Cote septentrional de la plus grande des isles de la Reine Charlotte; Baye Swallow; Havre Byroni
- Ref : 21589-1
- Size: 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique nautical chart & coastal view of the Island of Nendo (then called Lord Egmonts Island or New Guernsey) along with inset maps of Swallow Bay & Byrons Harbour on Nendo and a view of the nearby volcanic island of Nupani was drawn by Captain Phillip Carteret in July-August 1767 aboard his ship Swallow, accompanying Captain Samuel Wallis during his circumnavigation of the world, was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Capt. Philip Carteret (1733-1796)
was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navy\\\\\\\'s circumnavigation expeditions in 1764-66 and 1766-69.
Carteret entered the Navy in 1747, serving aboard the Salisbury, and then under Captain John Byron from 1751 to 1755. Between 1757 and 1758 he was in the Guernsey on the Mediterranean Station. As a lieutenant in the Dolphin he accompanied Byron during his voyage of circumnavigation, from June 1764 to May 1766.
In 1766 he was made a commander and given the command of the Swallow to circumnavigate the world, as consort to the Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis. The two ships were parted shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Carteret discovering Pitcairn Island and the Carteret Islands, which were subsequently named after him. In 1767, he also discovered a new archipelago inside Saint George\\\\\\\'s Channel between New Ireland and New Britain Islands (Papua New Guinea) and named it Duke of York Islands, as well as rediscovered the Solomon Islands first sighted by the Mendana in 1568, and the Juan Fernandez Islands first discovered by Juan Fernandez in 1574. He arrived back in England, at Spithead, on 20 March 1769.
He was promoted to post captain in 1771.
Nendo is the largest of the Santa Cruz Islands, located in the Temotu province of the Solomon Islands. The island is also known as Santa Cruz, Ndeni, Nitendi or Ndende. The name Santa Cruz was given to the island in 1595 by the Spanish navigator Alvaro de Mendaña, who unsuccessfully started a colony there.
The Nupani Atoll is located about 65 km to the West of the main group of the Reef Islands.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Map HMS Resolution & Adventure in the Tonga Islands 1773
- Title : Carte Des Isles Des Amis ( Friendly Islands)
- Ref : 21764
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Tonga Islands with the routes taken by HMS Resolution & Adventure, during Captain James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
Exert From Cooks diary A Voyage Towards the South Pole.........after leaving Raiatea (Society Islands) on 18 September 1773, Cook directed his course towards Amsterdam Island (Tongatapu), discovered by Tasman in 1643, intending to verify Tasmans charting against his own charts. The ships stayed for three days, thoroughly enjoying the reception they had received and called the group the Friendly Islands. On his second visit he headed for the Nomuka, the largest island of the south central group of Tonga.......
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1773 Cook Antique Maps Tahiti, Raiatea & Huaheine Isles French Polynesia in 1769
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite ; Owharre Harbour in Huaheine ; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea ; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Size: 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 31216
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map, four maps on the one sheet;
1. Matavia Bay, Tahiti (Otaheite) - Windward Islands
2. Ohamaneno (Vaiaau) Harbour Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
3. Owharre (Bourayne Bay) Harbour in Huaheine - Leeward Islands
4. Oopoa (Opoa) Harbour, Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
all located in French Polynesia, South Pacific were complied by Capt James Cook during his first voyage of discovery in 1769, was published in the 1773 edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1773
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (365mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Matavai Bay is located on the north coast of Tahiti, the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia.
The first European known to have visited Tahiti was Lieutenant Samuel Wallis, in Dolphin, who landed on 17 June 1767 in Matavai Bay.
Captain James Cook anchored in the bay on 13 April 1769, on a sandy spit on the northeast end of Matavai Bay - named Point Venus by Cook.
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
Captain Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774.
Huahine is an island located among the Society Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Leeward Islands group (Iles sous le Vent).
Captain Cook arrived Fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour. They met with leading chief Ori (Mato). Cook returned on 3 Sept. 1773 and met with Oris son Teri itaria, the new ari i rahi of the island.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
1878 Petermann Antique Map of Northern Territory Australia - William McMinn 1876
- Title : Neue Aufnahmen in Nord-Australien Nach. Ringwood & Mc Minn...Gotha: Justus Perthes 1878
- 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1878
- Ref #: 82058
Description:
This scarce original antique lithograph map of north-west Northern Territory, Australia showing Palmerston at Port Darwin, place names and exploration routes, including that of William McMinn in 1876, by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1878 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William McMinn (1844 – 14 February 1884) was an Australian surveyor and architect, based in Adelaide.
He was born in Newry, County Down, Ireland, a son of Joseph McMinn and his wife Martha McMinn (née Hamill), who with their large family emigrated to Adelaide on the Albatross, arriving in September 1850.
After completing school, he was apprenticed to the architect James Macgeorge, but first practiced as a surveyor. He was involved in Boyle Travers Finniss\'s ill-fated 1865 expedition to Northern Australia surveying the area around the Adelaide River. Following the desertion of a majority of the party to Singapore, McMinn and 5 others purchased a 23-foot open boat which they named the Forlorn Hope and sailed it 2,000 miles (3,200 km) to Champion Bay, Geraldton, Western Australia. He was later involved in the 1872 surveying of the Overland Telegraph from Port Augusta to Darwin.
McMinn began practising as an architect in 1867, briefly in partnership with Daniel Garlick, and later with some others, but usually independently. He designed many grand private residences, but also designed or assisted in the design of many of Adelaide\'s grand public buildings. Whilst in partnership with Edward John Woods, he designed the original Venetian Gothic building of the University of Adelaide, considered his greatest work.
1760 Bowen Antique Map, Plan Fort & Town of Vijaydurg, Maharashtra State, India
- Title : A plan of the town and fortress of Gariah belonging to Angriah the admiral to the Sahou Rajah
- Size: 18 1/4in x 12in (465mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1760
- Ref #: 21950
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, a plan of the fort and town of Gheriah, Girye or Gheriya, today called Vijaydurg in Maharashtra state in NW India (485 kms from Mumbai) was published by Emmanual Bowen in 1760.
The map contains many numbered & lettered references to particular areas of interest within the fort, town and surrounds.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/4in x 12in (465mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/4in x 12in (465mm x 305mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Vijaydurg is said to be the oldest fort in Sindhudurg coast. In the Pre-Independence era it was also known as Eastern Gibraltar. This is because the fort was almost unconquerable. Under the leadership of Kanhoji Angre, it withstood many naval attacks by the British and the Dutch. Kanhoji Angre died on 4 July 1729 and the Angres control of the fort ended in 1756 after the Peshwa-British Alliance defeated the Angres clan. In 1818 Vijaydurg was completely in the hand of the British Empire.
Kanhoji Angre 1669 – 1729 was a chief of the Maratha Navy in 18th century India. In historical records, he is also known as Conajee Angria or Sarkhel Angré (Sarkhel is a title equal to Admiral of a fleet).
Kanhoji fought against the British, Dutch and Portuguese naval interests on the coasts of India during the 18th century. As a result, his European enemies labeled him a pirate. Despite the attempts of the British and Portuguese to subdue Angre, he remained undefeated until his death.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Large Antique Map The Battle of Schellenberg, Germany 1704
- Title : Battle of Donawert fought on the 2nd of June 1704 between a detachment of ye Allies and a body of French and Bavarian Troops
- Size: 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 22160
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved military map of the Battle of Schellenberg, also known as the Battle of Donauwörth in the Donau-Ries district of Swabia, in Bavaria, Germany - during the Spanish War of Succession - was engraved by John Basire and published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
The Battle of Schellenberg, also known as the Battle of Donauwörth, was fought on 2 July 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. The engagement was part of the Duke of Marlboroughs campaign to save the Habsburg capital of Vienna from a threatened advance by King Louis XIVs Franco-Bavarian forces ranged in southern Germany. Marlborough had commenced his 400 km march from Bedburg, near Cologne, on 19 May; within five weeks he had linked his forces with those of the Margrave of Baden, before continuing on to the river Danube. Once in southern Germany, the Allies task was to induce Max Emanuel, the Elector of Bavaria, to abandon his allegiance to Louis XIV and rejoin the Grand Alliance; but to force the issue, the Allies first needed to secure a fortified bridgehead and magazine on the Danube, through which their supplies could cross to the south of the river into the heart of the Electors lands. For this purpose, Marlborough selected the town of Donauwörth.
1794 John Russell Large Antique Map of South America
- Title : A General Map of South America Drawn fro the Best Surveys by J Russell 1794
- Ref #: 92579
- Size: 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1794
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map of South America by John Russell was published by H D Symonds in 1794 - dated. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, small repair to left fold & right side of image no loss
Verso: - Folds as issued, soiling along folds
1830 Sydney Hall Antique Map of Australia, New Holland, Swan River Settlement
- Title : Australia & Islands Adjacent
- Ref #: 35074
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
- Date : 1830
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate original antique map by Sydney Hall was published in the 1830 edition of Halls General Atlas published by Longman & co., London. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1738 J B D Anville Antique Map of North Africa, Spain, Sardinia & Sicily
- Title : Carte de La Partie de L Afrique ou les Carthaginios de L Histoire Ancienne de Mr Rollin..Sr D Anville...1738
- Size: 20in x 12in (510mm x 303mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1738
- Ref #: 70314
Description:
This magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of North Africa, Spain, Sardinia & Sicily - with an inset plan of Carthage by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D Anville in 1738 - dated - was published in Mr Charles Rollins Atlas. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 12in (510mm x 303mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 10 1/2in (495mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\\\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\\\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
1789 John Harrison Large Antique Map of Western Europe - Italy to Germania to UK
- Title : Germanie, France, Italie, Espange, Isles Britanniques Dans un Age intermediare de L Ancienne Geographie et de la Moderne Drawn & engraved from D Anvilles Atlas for John Harrison...1789
- Date : 1789
- Size: 19in x 16 1/2in (480mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 15645
Description:
This large magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique map of Western Europe, after J B D Anville, was engraved in 1789 - dated in the title - and was published for John Harrisons Ancient & Modern Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 16 1/2in (480mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14in (480mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Roman Empire was the post-Roman Republic period of the ancient Roman civilization, with a government headed by emperors and large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. The city of Rome was the largest city in the world c. 100 BC – c. AD 400, with Constantinople (New Rome) becoming the largest around AD 500, and the Empire\\\'s population grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world\\\'s population at the time) The 500-year-old republic which preceded it had been severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflict, during which Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and executions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar\\\'s adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the annexation of Egypt. Octavian\\\'s power was then unassailable and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively marking the end of the Roman Republic.
1765 T. Bowen & M Postlethweyt Antique Map of European Russia, Baltics, Lapland
- Title : Europe Plate II
- Date : 1765
- Size: 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 01-1584
Description:
This wonderful large detailed original copper plate engraved antique map of European Russia, parts of Lapland, Sweden, Latvia & Lithuania by Thomas Bowen was published in the 1765 edition of Malachy Postlethweyts monumental 2 Volume tomes on Universal Dictionary of Trade & Commerce concentrating on various states of trade, including slavery, between England and America published between 1751 & 1774.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, orange, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West.
Postlethweyt, Malachy 1707 – 1767
Malachy Postlethweyts Dictionary of Trade & Commerce:
A monumental dictionary of trade and commerce. It is based in part on the Dictionnaire universel de Commerce (Paris: 1723-30) of Jacques Savary de Bruslon, under whose name it is often catalogued, but has been adapted by Postlethwayt for a British audience, with substantial enlargements and improvements, and entirely new material relating to England and her colonies. Postlethwayt devoted twenty years to the preparation of the dictionary, which was first published in 1751-55 & includes a description of British affairs in North America since the peace of 1763.
As with his other works, the dictionary demonstrates Postlethway’s deep commitment to the expansion and strengthening of English trade. Included are entries for geographical locations (Africa, Antilles, Canada, Japan, Louisiana, &c.), products (brandy, cardamom, codfish, diamonds, sugar, &c.), trading companies (Dutch East India Company, English African Company, &c.), treaties of commerce, and a vast range of other information of value to merchants (bankruptcy, currency, bills of exchange, brokerage, exportation, landed interest, privateering, &c.). The Dictionary is also important for containing almost the whole substance of Richard Cantillon’s Essay on Commerce, its first appearance in print.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of The Straits of Magellan, Chile, South America
- Title : Detroit De Magellan avec les plans des Principaux... Par M. Bonne
- Ref : 40569
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Straits of Magellan, South America - with 14 inset maps of different bays and inlets of the straits - by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - wo small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The Strait of Magellan: (Estrecho de Magallanes) is a navigable sea route separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Ferdinand Magellan a Portuguese explorer and navigator in the service of Charles I of Spain, became the first European to navigate the strait in 1520 during his circumnavigation of the globe.
Other early explorers included Francis Drake (1578). In February 1696 the first French expedition, under the command of M. de Gennes reached the Strait of Magellan. The expedition is described by the young French explorer, engineer and hydrographer François Froger in his A Relation of a Voyage (1699).
The strait was first carefully explored and thoroughly charted by Phillip Parker King, who commanded the British survey vessel HMS Adventure, and in consort with HMS Beagle spent five years surveying the complex coasts around the strait (1826–1830). A report on the survey was presented at two meetings of the Geographical Society of London in 1831.
1824 Louis Vivien Large Antique Map of Spain & Portugal
- Title : Carte De La Peninsule Hispanique...1824
- Size: 29in x 23in (740mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1824
- Ref #: 40717
Description:
This finely engraved original large antique map of Spain & Portugal by Louis Vivien in his Elephant Folio atlas, Atlas Universal
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 23in (740mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19in (635mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Many of the original charts and maps drawn by the first Portuguese and Spanish navigators have survived for the very good reason that, on completion of their voyages, pilots were obliged to hand over their manuscript notes to the Casa da India (founded 1504) in Lisbon or to the equivalent Casa de Contrataci6n de las Indias (founded 1504) in Seville. The clear intention was to maintain secrecy over new discoveries and control over the distribution of cartographic material, not always successfully, as it happened; pilots and navigators seem to have changed allegiance with impunity and, in consequence, many of the earliest and most informative charts were compiled as far away as Genoa, Venice, Florence and Ancona, presumably from sources outside the Portuguese and Spanish Casas. It is apparent that few manuscripts reached the printing stage and, indeed, are so rare that any study of them must be regarded as a specialist subject. (Ref Tooley M&B)
Vivien, Louis 1802 - 1896
Louis Vivien , or Vivien de Saint-Martin was a French geographer who was born in Saint-Martin-de-Fontenay and died in Versailles, France in 1896.
He settled in Paris under the Restoration, and became known with his publication of the Electoral and Administrative Map in 1823 and his comprehensive Universal Atlas in 1825, collaborating with Jacques Bibliomappe -Charles Bailleul from 1828. Vivien was foremost a geographer but was also a publisher of works in other fields, including historical books on the General History of the French Revolution and the History of Napoleon. He also translated various English works, such as the novels of Walter Scott .
He also wrote the New Annals of Travels between 1845 and 1854 and briefly the French Athenaeum between 1847 & 1848. He contributed to numerous periodicals such as Le Constitutionnel, Revue contemporaine, Revue germanique & La Presse. He also wrote L Année géographique between 1863 and 1875 before passing the baton to G. Maunoir and Henri Duveyrier.
He is mainly known though, for his three cartographical works, A History of Geographical Discoveries, A New Dictionary of Universal Geography and the Universal Atlas of Geography. The first of these publications he completed after the 1848 Revolution with the latter two completed by Louis Rousselet and Franz Schrader.
Vivien was Honorary President of the Geographical Society, of which he was one of the founder members. He also laureate of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles-Lettres as well as a member of the Asian Society , the Society of Ethnology along with a large number of learned societies and European academies.
Main works of Vivien de Saint-Martin
- General History of the French Revolution, the Empire, the Restoration, the Monarchy of 1830, up to and including 1841 (4 volumes in 2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat Brothers, 1841-1842.
- History of Napoleon and the Empire (2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat brothers, 1844.
- History of geographical discoveries of European nations in various parts of the world (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1845-1846.
- Research on primitive populations and the oldest traditions of the Caucasus , Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1847.
- Studies of Ancient Geography and Asian Ethnography (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1850-1852.
- Historical and geographical description of Asia Minor (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1852.
- Study on the Greek and Latin Geography of India , Paris, Imperial Printing, 1858.
- Study on the geography and the primitive populations of north-west India, according to the Vedic hymns , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1860.
- North Africa in Greek and Roman antiquity, historical and geographical study , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1863.
- History of geography and geographical discoveries from the earliest times to the present day , Paris, Hachette, 1873.
- With Franz Schrader : Universal Atlas of Geography built from the original sources and the most recent documents , Paris, Hachette, 1876-1915.
- With Louis Rousselet : New dictionary of universal geography (9 volumes), Paris, Hachette, 1879-1900.
1638 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Beauvais Region, France
- Title : Beauvaisis Comitatus Belovacium
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1638
- Ref #: 50178
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the Beauvais region of Northern France - centering on the city of Beauvais & the Oise River running through the cities of Noyon, Compiègne, Creil by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1638 Latin edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Beauvais is a city and commune in northern France. It serves as the capital of the Oise département, in the Hauts-de-France region. Beauvais is located approximately 75 kilometres from Paris.
Beauvais was known to the Romans by the Gallo-Roman name of Caesaromagus (magos is Common Celtic for field). The post-Renaissance Latin rendering is Bellovacum from the Belgic tribe the Bellovaci, whose capital it was. In the ninth century it became a countship, which about 1013 passed to the bishops of Beauvais, who became peers of France from the twelfth century. At the coronations of kings the Bishop of Beauvais wore the royal mantle and went, with the Bishop of Langres, to raise the king from his throne to present him to the people.
De Bello Gallico II 13 reports that as Julius Caesar was approaching a fortified town called Bratuspantium in the land of the Bellovaci, its inhabitants surrendered to him when he was about 5 Roman miles away. Its name is Gaulish for place where judgements are made, from *bratu-spantion. Some say that Bratuspantium is Beauvais. Others theorize that it is Vendeuil-Caply or Bailleul sur Thérain.
From 1004 to 1037, the Count of Beauvais was Odo II, Count of Blois.
In a charter dated 1056/1060, Eudo of Brittany granted land in pago Belvacensi (Beauvais, Picardy) to the Abbey of Angers Saint-Aubin
In 1346 the town had to defend itself against the English, who again besieged it in 1433. The siege which it endured in 1472 at the hands of the Duke of Burgundy, was rendered famous by the heroism of the towns women, under the leadership of Jeanne Hachette, whose memory is still celebrated by a procession on 27 June (the feast of Sainte Angadrême), during which women take precedence over men.
An interesting hoard of coins from the High Middle Ages became known as the Beauvais Hoard, because some of the British and European coins found with the lot were from the French abbey located in Beauvais. The hoard, which contained a variety of rare and extremely rare Anglo-Norman pennies, English and foreign coins, was reputed to have been found in or near Paris.
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of the English County of Cambridgeshire
- Title : Cambridgeshire...Sold by Abel Swal and Awsham& John Churchill Sutton Nicholls sculp.
- Size: 16 1/4in x 15in (460mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 40181
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the English county of Cambridgeshire by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16 1/4in x 15in (460mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 14 1/2in (450mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
1856 James Virtue Antique Map of New Zealand and the Colonies of Australia
- Title : New Zealand and the Australian Colonies of Great Britain James S Virtue
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1856
- Ref #: 93052
Description:
This original lithograph antique map of New Zealand and the Colonies of Australia was published by James Virtue in 1856, just after Victorian statehood in 1851 and just prior to Queensland statehood in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A highly detailed map just prior to the gold and population boom of both Australia and New Zealand, with much of Australia unexplored in the center.
Virtue, George & James
George Virtue (1794 – 1868) was a 19th-century London publisher, well known for printing engravings. His publishing house was located at 26 Ivy Lane, Paternoster Row, London, EC
Virtue selected accomplished artists, employed the best engravers, and produced books that were rarely surpassed in elegance and correctness for the period. Chief among his publications were the following, all illustrated by William Henry Bartlett: Switzerland, by William Beattie, 2 vols. 1836; Scotland, by W. Beattie, 1838; The Waldenses, by W. Beattie, 1838; American Scenery, 2 vols. 1840; Description of the Beauties of the Bosphorus, by Julia Pardoe, 1840; and The Danube, its History and Scenery, by W. Beattie, 1844. Virtue created a prodigious business, issuing upwards of twenty thousand copper and steel engravings through his career.
In 1848, Virtue purchased two magazines. One was an art publication, The Art Union, which had been founded in 1839 by Hodgson & Graves, then purchased in 1847 by Chapman & Hall. The second purchase was controlling interest in Sharpe\\\\\\\'s London Magazine, a literary and cultural magazine, Arthur Hall publisher. In 1849, Virtue renamed the art magazine The Art Journal and, in time, it became known as the premier art publication of Great Britain. Also in 1849, he created a new firm with Arthur Hall called Arthur Hall, Virtue & Co
James Sprent Virtue (1829 – 1892) inherited the publishing business from his father, George, after his retirement in 1855
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1856 Captain Richard Delafield Antique Maps of Genoa & Venice Italy - Art of War
Antique Map
- Title : Harbour Defences plate 19; Defences of Naval Depot and City of Genoa; Defence of Naval Depot and City of Venice
- Ref #: 90119
- Size: 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original lithograph map of Genoa & Venice Italy was engraved by John T Bowen & co. Philadelphia, was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Left fold rejoined, light age toning
Verso: - Left margin rejoined with archival tape
Background:
In the beginning of 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics Forts City of Lyons, France
Antique Map
- Title : Detached Forts about the City of Lyons
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90123
- Size: 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of various forts in and around the French city of Lyons - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The ceintures de Lyon (Belts of Lyon) were a series of fortifications built between 1830 and 1890 around the city of Lyon, France to protect the city from foreign invasion.
The belts comprised two defensive barriers that included forts, lunettes, ramparts, batteries, and other defensive structures. Many of these structures proved to be ineffective in war due to advancement in weapon technology and the evolution of attack strategies at the time. Some of the fortifications of the ceintures de Lyon have been destroyed, though many remain today.
In 1830 the maréchal de camp, Hubert Rohault de Fleury, commenced a project designed by military engineer Baron Haxo. With a budget of 10,000,000 francs (approximately €67,000,000 as of 2015) allocated for Lyon between 1831 and 1839, this first project included the restoration of the fortifications between Croix Rousse and Fourvière; the construction of two forts on the plateau of Caluire (Fort de Montessuy and Fort de Caluire, connected by the Enceinte de Caluire), facing the Dombes; closing access to the Presquîle by the construction of a south-facing building; building two forts – Fort de la Duchère and Fort de Grange Blanche – to protect access routes towards Paris and Auvergne.
The fortification of the city is divided into three sectors: The north was protected by the wall of Croix-Rousse and the structures between the Rhône and the Saône. The command was situated at fort de Montessuy. The west was covered by the hillfort of Fourvière and the associated forts of Vaise at Sainte-Foy. The command was situated at fort Saint-Irénée. The east was defended by the Redoute du Haut-Rhône and Fort de la Vitriolerie on the left bank of the Rhône. The command was situated at Fort Lamothe.
The work required almost 20,000 workers, which were locally sourced in an attempt to avoid insurrection such as the ongoing unrest of the Lyon silk workers (Canuts) over increased capitalism. Work began in 1831 to build seven structures, each structure requiring between 400 and 500 workers. The scope of this project included the construction of Fort de Montessuy and Fort de Caluire to the north; Fort des Brotteaux, Fort Montluc and Fort du Colombier to the east; the Redoute de la Part-Dieu to the west; and Fort Saint-Irénée, to protect the entire area.
In January 1831, an uprising began at a work site in Charpennes, however it was quickly stopped by the army. Other insurrections took place the same year, a series of Canut revolts, which succeeded in rallying soldiers on the side of the Canuts, resulting in the death of captain Viquesnel, aide-de-camp of Fleury, and the temporary withdrawal of the 20,000 soldiers who eventually retook the city in December 1831.
In 1832, three other structures were built to reinforce the defenses to the east: The Redoute de la Tête dor, Fort La Motte, and the Redoute des Hirondelles. A treaty was signed between the city of Lyon and the War Department, which stipulated that the city had to cede the land necessary for the construction of military buildings to the War Department, while the forts themselves would still belong to the city if the military decided to abandon them. It is thanks to this treaty that the forts of Croix Rousse, Fourvière, Loyasse, Vaise, and Saint-Jean would later be returned to the city.
Construction resumed in 1840. First the Fort de la Vitriolerie in 1840, then Fort de Sainte-Foy-lès-Lyon and the Lunette des Charpennes in 1842, Fort de la Duchère in 1844, the Redoute du Petit Sainte-Foy-lès-Lyon in 1852, and finally the Redoute du haut-Rhône in 1854.
A law was voted in on 10 July 1851, which defined the methods of destruction of these buildings or construction on their land. By 1854, 19 structures including 10 forts had been built around Lyon, creating a nearly 14-kilometre (8.7 mi) fortified perimeter.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
Antique Map
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90144
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
Antique Map
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90194
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1744 Georg Mattaus Seutter Antique Map of France
Antique Map
- Title : Gallia....a Matth. Seuttero...T C Lotter, Geogr.
- Ref #: 93393
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of France was engraved by Tobias Lotter and was published in the 1744 edition of GM Seutters Atlas Minor Prae cipua Orbis Terrarum Imperia Regna et Provincias...., Augsburg, Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (265mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - None
Background:
Atlas Minor was a series of beautiful maps of all parts of the world. Georg Matthäus Seutter was one of the most and important of the German cartographers of the 18th century, being appointed as the Geographer to the Imperial Court. His son, Albrecht Carl, joined Matthäus and eventually inherited the business. The maps from Atlas Minor were drawn by the two Seutters and engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotte. These maps are highly detailed and engraved with a bold hand with equally strong original hand color in the body of the map as was the 18th century German style. The cartouches were left uncolored in order to emphasize the elaborately detailed illustrations for which German maps are especially prized. These are some of the most decorative and interesting maps of the eighteenth century.
1851 John Tallis Antique map of the Island of Jamaica
Antique Map
- Title : Jamaica
- Date : 1851
- Size: 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35616
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Jamaica, with decorative vignettes of Kingston, Port Antonio, Port Royal, a sugar mill and a flying fish, was published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light crease left side of image
Verso: - None