Maps (791)
1784 Anderson Antique Map Capt Cook Exploration of the Society Islands in French Polynesia
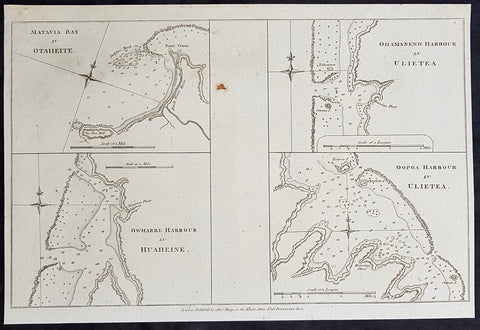
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea; Owharre Harbourin Huaheine; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Date : 1784
- Ref # : 32153
- Size : 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map with surveys and depth soundings of four bays and harbours, of various bays & harbours of the Society Islands, French Polynesia made by explorers during the 17th & 18th centuries.
The first map is Matavia Bay, on the island of Tahiti (Otaheite), the second is Fare (Owharre) Harbour on the island of Huahine & the last two are Ohamaneno & Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) harbours on the island of Raiatea (Ulietea) was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A description of the four Bays & Harbours and their relevance to Capt Cook and other South Seas explorers are;
1.Matavia Bay in Otaheite (Tahiti) - first European to visit Tahiti Capt. Samuel Wallis anchored in Matavai Bay in 1767 as did Louis-Antoine de Bougainville in 1768 & Capt James Cook landed in Matavai Bay in 1769 and returned in his next two voyages.
2. Owharre (Fare) Harbour in Huaheine (Huahine) Captain Cook arrived in fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour
3. Ohamaneno Harbour (Port) in Ulietea (Raiatea)
4. Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) Harbour in Ulietea (Raiatea)
Raiatea - The first European to record sighting Raiātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva. The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Raiātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, travelled with European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
Tahiti.
1784 Anderson Antique Map Capt Cook Exploration of the Society Islands in French Polynesia
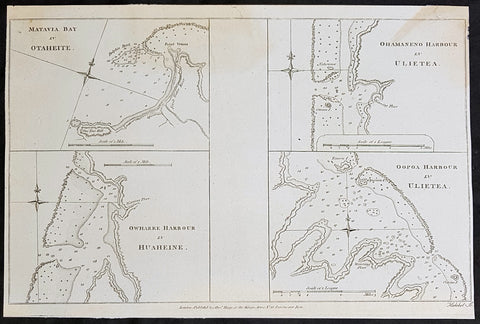
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea; Owharre Harbourin Huaheine; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Date : 1784
- Ref # : 32154
- Size : 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map with surveys and depth soundings of four bays and harbours, of various bays & harbours of the Society Islands, French Polynesia made by explorers during the 17th & 18th centuries.
The first map is Matavia Bay, on the island of Tahiti (Otaheite), the second is Fare (Owharre) Harbour on the island of Huahine & the last two are Ohamaneno & Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) harbours on the island of Raiatea (Ulietea) was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A description of the four Bays & Harbours and their relevance to Capt Cook and other South Seas explorers are;
1.Matavia Bay in Otaheite (Tahiti) - first European to visit Tahiti Capt. Samuel Wallis anchored in Matavai Bay in 1767 as did Louis-Antoine de Bougainville in 1768 & Capt James Cook landed in Matavai Bay in 1769 and returned in his next two voyages.
2. Owharre (Fare) Harbour in Huaheine (Huahine) Captain Cook arrived in fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour
3. Ohamaneno Harbour (Port) in Ulietea (Raiatea)
4. Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) Harbour in Ulietea (Raiatea)
Raiatea - The first European to record sighting Raiātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva. The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Raiātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, travelled with European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
Tahiti.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Map 3 x Cook Islands & 1 x Society Island - Cook in 1777
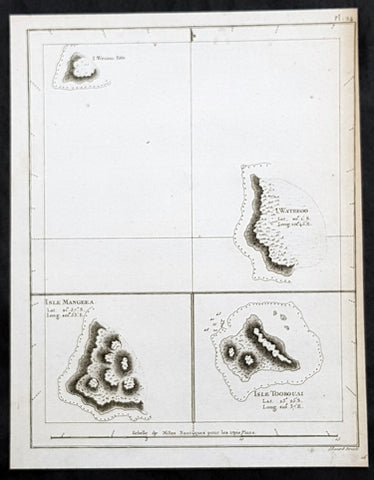
- Title : I. Wenooa Ette; I. Wateeoo; Isle Mangeea; Isle Toobouai
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 32164
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of three of the Cook Islands, Takutea (Wanooaette) Atiu (Wateeoo) and Mangaia (Mangeea) and a 4th map of the Island of Tubuai (Toobouai) in French Polynesia near Tahiti, visited by Captain Cook in HMS Resolution & Discovery in September 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\\\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom margin cropped into title
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Cook Islands is a self-governing island country in the South Pacific Ocean in free association with New Zealand. It comprises 15 islands whose total land area is 240 square kilometres.
Spanish ships visited the islands in the 16th century; the first written record of contact with the islands came in 1595 with the sighting of Pukapuka by Spanish sailor Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, who called it San Bernardo (Saint Bernard). Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, a Portuguese captain working for the Spanish crown, made the first recorded European landing in the islands when he set foot on Rakahanga in 1606, calling it Gente Hermosa.
British navigator Captain James Cook arrived in 1773 and 1777 and named the island of Manuae Hervey Island. Later, the name Hervey Islands came to be applied to the entire southern group; the name Cook Islands, in honour of Cook, first appeared on a Russian naval chart published in the 1820s
Takutea, in the Cook Islands, is a small uninhabited island 21 kilometres northwest of Atiu in the southern Cook Islands.
Takutea is the only island in the Cook Islands that never had a permanent population. When Captain James Cook sighted the island on 4 April 1777, and some crew members went ashore, they found some huts, but no evidence of a permanent settlement.
Atiu, also known as Enuamanu (meaning land of the birds), is an island 187 km northeast of Rarotonga, in the Southern Islands group of the Cook Islands Archipelago.
The first recorded European to arrive at Atiu was Captain Cook. He sighted the island on March 31, 1777 and made tentative contact with some of the people over the next few days.
Mangaia (traditionally known as A ua u Enua, which means terraced) is the most southerly of the Cook Islands and the second largest, after Rarotonga.
The first recorded European to arrive at Mangaia was Captain James Cook on 29 March 1777.
Tubuai part of the Society Islands is located 640 km south of Tahiti. Tubuai was first viewed by Europeans when it was mapped by Captain James Cook in 1777, although his party did not disembark. Cook discovered the islands name, Toobouai, from the natives who surrounded his ship in their canoes (a Tahitian named Omai, who was part of Cooks group, translated)
The next Europeans to arrive were the mutineers of the HMS Bounty in 1789. Mutineer Fletcher Christian, in looking for an island on which to permanently hide, had scoured Blighs maps and nautical charts and decided on Tubuai.
Upon arrival at Tubuai, a conflict arose while the mutineers were still on their ship and several islanders were killed in their canoes. The site of this event in the lagoon on the north side of the island is called Baie Sanglant (Bloody Bay)
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Thomas Bowen (1767-1790) was an engraver and son of Emanuel Bowen, map and print seller, engraver to George II and to Louis XV of France who worked in London from 1714 producing some the best and most attractive maps of the 18th century. He had plans for completing a major County Atlas but, finding the task beyond his means, joined with Thomas Kitchin to publish “The Large English Atlas”. Many of the maps were issued individually from 1749 onwards and the whole atlas was not finally completed until 1760. With one or two exceptions they were the largest maps of the counties to appear up to that time (27” x 20”) and were unusual in that blank areas around each map are filled with historical and topographical detail which makes fascinating and amusing reading. The atlas was reissued later in reduced size. Apart from his county maps and atlases of different parts of the world he also issued (with John Owen) a book of road maps based, as was usual at that time, on Ogilby but again incorporating his own style of historical and heraldic detail. Thomas helped his father during his lifetime and produced many fine maps in his own right after his fathers death.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Map of Kerguelen Island, South Indian Ocean Cook in 1776
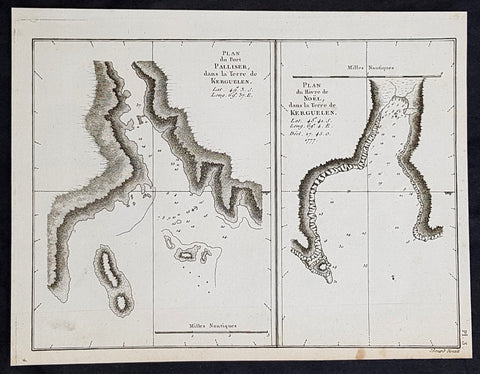
- Title : Plan du Port Palliser dans la Terre de Kerguelen; Plan du du Havre de Noel dans la Terre de Kerguelen....1777
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 32194
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of two maps on one sheet, the first of Port Palliser on the Island of Kerguelen and the second of Christmas Bay also located on the Island of Kerguelen in the very Southern Indian Ocean - midway between Africa, Antarctica and Australia - visited by Captain Cook in HMS Resolution & Discovery in December 25-30th 1776, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\\\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Kerguelen Islands, sometimes called the Desolation Islands, are located in the southern Indian Ocean and were discovered by the French navigator Yves de Kerguelen-Trémarec in 1772. On Christmas Day, 1776 Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored in Oiseau Bay, which he named Christmas Harbour. Cooks men discovered a bottle containing a message in Latin left by Kerguelens men. Cook wrote in his log: I could have very properly called the island Desolation Island to signalise its sterility, but in order not to deprive M. de Kerguelen of the glory of having discovered it, I have called it Kerguelen Land.
The Kerguelen Islands or the Kerguelen Archipelago are located in the southern Indian Ocean. The main island, Grande Terre, is 6,675 km² and it is surrounded by another 300 smaller islands and islets, forming an archipelago of 7,215 km². The climate is cold and very windy and the seas are usually rough. The islands are part of a submarine large igneous province called the Kerguelen Plateau.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Thomas Bowen (1767-1790) was an engraver and son of Emanuel Bowen, map and print seller, engraver to George II and to Louis XV of France who worked in London from 1714 producing some the best and most attractive maps of the 18th century. He had plans for completing a major County Atlas but, finding the task beyond his means, joined with Thomas Kitchin to publish “The Large English Atlas”. Many of the maps were issued individually from 1749 onwards and the whole atlas was not finally completed until 1760. With one or two exceptions they were the largest maps of the counties to appear up to that time (27” x 20”) and were unusual in that blank areas around each map are filled with historical and topographical detail which makes fascinating and amusing reading. The atlas was reissued later in reduced size. Apart from his county maps and atlases of different parts of the world he also issued (with John Owen) a book of road maps based, as was usual at that time, on Ogilby but again incorporating his own style of historical and heraldic detail. Thomas helped his father during his lifetime and produced many fine maps in his own right after his fathers death.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
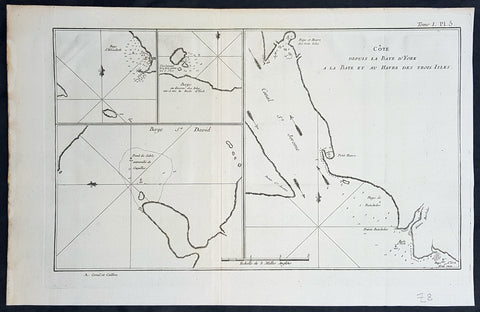
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map of Magellan Straits, Bachelor River, Punta Arenas, Chile, Byron 1766
- Title : Baye d Elizabeth; Baye au dessons des Isles vis a vis la Rade d York; Côte depuis la Baye d York a la Baye et au Havre des Trois Isles; Baye St. David
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16027
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map, four maps on the one sheet, of;
1. Elizabeth Bay.
2. York Bay.
3. York Bay-Three Island Bay
4.St. Davids Bay.
all located north of Carlos III island, on Punta Arenas in the Chilean Arctic - from Bachelor River north to York Bay - in the Straits of Magellan, Chile. This chart was compiled by Commodore John Byron, who visited the region in HMS Dolphin on his circumnavigation of the globe, between 1764-66, and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Strait of Magellan
(Estrecho de Magallanes) is a navigable sea route separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Ferdinand Magellan a Portuguese explorer and navigator in the service of Charles I of Spain, became the first European to navigate the strait in 1520 during his circumnavigation of the globe.
Other early explorers included Francis Drake (1578). In February 1696 the first French expedition, under the command of M. de Gennes reached the Strait of Magellan. The expedition is described by the young French explorer, engineer and hydrographer François Froger in his A Relation of a Voyage (1699).
The strait was first carefully explored and thoroughly charted by Phillip Parker King, who commanded the British survey vessel HMS Adventure, and in consort with HMS Beagle spent five years surveying the complex coasts around the strait (1826–1830). A report on the survey was presented at two meetings of the Geographical Society of London in 1831.
Vice-Admiral The Hon. John Byron was a British Royal Navy officer and politician. He was known as Foul-weather Jack because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sailed in the squadron under George Anson on his voyage around the world, though Byron made it to southern Chile, and returned to England with the captain of HMS Wager. He was governor of Newfoundland following Hugh Palliser, who left in 1768. He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764-1766. He fought in battles in The Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral of the White before his death in 1786.
In early 1764 the British Admiralty determined that it would require a permanent naval settlement off the South American coast, in order to resupply naval vessels seeking to enter the Pacific via Cape Horn. Captain Byron was selected to explore the South Atlantic for a suitable island upon which to establish such a settlement. The South American mainland was controlled by Spain, which was hostile to local expansion of British interests; to disguise Byrons mission it was announced that he had been appointed the new commander of the Navys East Indies Station. Byron set sail in June 1764, ostensibly to take up the East Indies post. For the voyage he was granted command of the 24-gun frigate HMS Dolphin and the 20-gun sloop HMS Tamar.
Byron\'s two-vessel flotilla crossed the Atlantic over the winter of 1764 and made its way slowly down the South American coast. The Admiralty had ordered Byron to first seek Pepys Island, reputedly discovered off the Patagonian coast by the corsair Ambrose Cowley in 1683. Byron reached the co-ordinates given by Cowley in January 1765, but there was no sign of the island and the search was swiftly abandoned. On 5 February Byron reached the Patagonian settlement of Port Desire where he resupplied his vessels from the storeship HMS Florida.
Between June 1764 and May 1766, Byron completed his own circumnavigation of the globe as captain of HMS Dolphin. This was the first such circumnavigation that was accomplished in less than 2 years. His actions nearly caused a war between Great Britain and Spain, as both countries had armed fleets ready to contest the sovereignty of the Falkland Islands. Later Byron encountered islands and extant residents of the Tuamotus and Tokelau Islands, and Nikunau in the southern Gilbert Islands; he also visited Tinian in the Northern Marianas Islands.
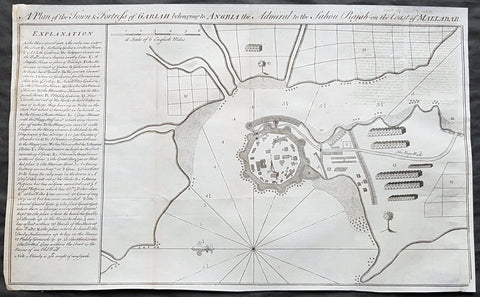
1760 Bowen Antique Map, Plan Fort & Town of Vijaydurg, Maharashtra State, India
- Title : A plan of the town and fortress of Gariah belonging to Angriah the admiral to the Sahou Rajah
- Size: 18 1/4in x 12in (465mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1760
- Ref #: 40986-2
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a plan of the fort and town of Gheriah, Girye or Gheriya, today called Vijaydurg in Maharashtra state in NW India (485 kms from Mumbai) was published by Emmanual Bowen in 1760.
The map contains many numbered & lettered references to particular areas of interest within the fort, town and surrounds.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/4in x 12in (465mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/4in x 12in (465mm x 305mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Vijaydurg is said to be the oldest fort in Sindhudurg coast. In the Pre-Independence era it was also known as Eastern Gibraltar. This is because the fort was almost unconquerable. Under the leadership of Kanhoji Angre, it withstood many naval attacks by the British and the Dutch. Kanhoji Angre died on 4 July 1729 and the Angres control of the fort ended in 1756 after the Peshwa-British Alliance defeated the Angres clan. In 1818 Vijaydurg was completely in the hand of the British Empire.
Kanhoji Angre 1669 – 1729 was a chief of the Maratha Navy in 18th century India. In historical records, he is also known as Conajee Angria or Sarkhel Angré (Sarkhel is a title equal to Admiral of a fleet).
Kanhoji fought against the British, Dutch and Portuguese naval interests on the coasts of India during the 18th century. As a result, his European enemies labeled him a pirate. Despite the attempts of the British and Portuguese to subdue Angre, he remained undefeated until his death.
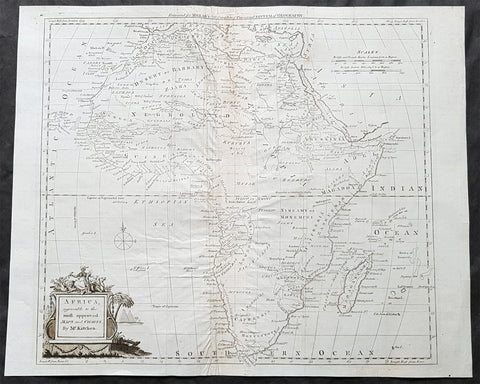
1782 Thomas Kitchin Large Original Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africa agreeable to the most approved Maps and Charts by Mr Kitchin
- Size: 17in x 14in (435mm x 355mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1782
- Ref #: 24047
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved map of Africa by the famous English cartographer Thomas Kitchin was published for the 1782 edition of George Henry Millars New Complete & Universal System of Geography
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 14in (435mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13 1/2in (380mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Centerfold re-enforced on verso
Plate area: - Creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Centerfold re-enforced on verso
Background:
Millar, George Henry
Was responsible for the publication of The new and universal system of geography : being a complete history and description of the whole world, containing a particular, full, accurate, circumstantial and entertaining account, including the antient and present state of all the various countries of Europe, Asia, Africa, and America, as divided into empires, kingdoms, states, republics, and colonies.. Printed by Alexander Hogg ..., 1782.
This comprehensive world geography and history was liberally illustrated with decorative plates and maps covering Europe, Asia, Africa, and America with information about the history, geography, climate, people, flora and fauna etc. It also includes important eighteenth century voyages and discoveries including Captain Cook\\\\\\\'s second voyage. Although his third voyage is not included, there is a plate illustrating his death in Hawaii. Other illustrations include city views from around the world, native costumes and occupations, and indigenous flora and fauna. The foldout maps were engraved by Kitchin, Bowen, Conder and Lodge with plates by several renowned English engravers. There is a fine map of the American colonies and city plans for the harbors of New York, Charleston, Havana, and Boston. Complete with upwards of 120 capital engravings with 25 maps. Published by Alexander Hogg, London.
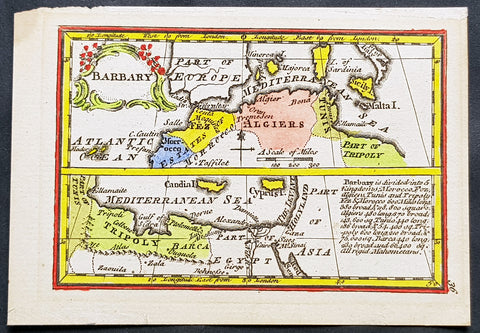
1758 John Gibson Antique Miniature Map Barbary or Berber Coast Nth Africa - Rare
- Title : Barbary
- Size: 4 1/2in x 3 1/4in (115mm x 83mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1758
- Ref #: 31422
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Barbary Coast, North Africa from Morocco to Egypt - a beautiful example of the art of miniature map making - was published by John Gibson in his 1758 edition of Atlas Minimus.
(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 4 1/2in x 3 1/4in (115mm x 83mm)
Plate size: - 4in x 2 3/4in (100mm x 70mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The term Barbary Coast or Berbery or Berber Coast, was the term Europeans used from the 16th to early 19th century to refer to much of the collective land of the Berber people.
The term Barbary Coast emphasizes the Berber coastal regions and cities throughout the middle and western coastal regions of North Africa – what is now modern nations of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya. The English term Barbary (and its European varieties: Barbaria, Berbérie, etc.) referred mainly to the entire Berber lands including non-coastal regions, deep into the African continent, as seen in European geographical and political maps published during the 17th–20th centuries.
The name derives from the Berber people of North Africa. In the West, the name commonly evoked the Barbary pirates and Barbary slave traders based on that coast—who attacked ships and coastal settlements in the Mediterranean Sea and eastern North Atlantic Ocean, and captured and traded slaves or goods from Europe, America and sub-Saharan Africa. These actions finally provoked the Barbary Wars of the early 19th century. The slaves and goods were being traded and sold throughout the Ottoman Empire or to the Europeans themselves.
Barbary was not always a unified political entity. From the 16th century onwards, it was divided into the political entities of the Regency of Algiers, Tunis, and Tripolitania (Tripoli). Major rulers petty monarchs during the times of the Barbary states\' plundering parties included the Pasha or Dey of Algiers, the Bey of Tunis and the Bey of Tripoli.
Before then, the territory was usually divided between Ifriqiya, Morocco, and a west-central Algerian state centered on Tlemcen or Tiaret. Powerful Berber dynasties such as the Almohads (12th century) and briefly thereafter the Hafsids, occasionally unified it for short periods. From a European perspective, Tripoli in modern-day Libya, was considered its capital or chief city—though Marrakesh in Morocco was the largest and most important Berber city at the time. Some saw Algiers in Algeria, or Tangiers in Morocco as the capital.
Purchase of Christian captives in the Barbary States.
The first United States military land action overseas, executed by the U.S. Marines and Navy, was the Battle of Derna, Tripoli, (a coastal town in modern eastern Libya) in April 1805. It formed part of an effort to destroy all of the Barbary pirates, to free American slaves in captivity, and to put an end to piracy acts between these warring tribes on the part of the Barbary states, which were themselves member states of the Ottoman Empire. The opening line of the Marines\' Hymn refers to this action: From the halls of Montezuma to the shores of Tripoli.... This was the first time the United States Marine Corps took part in offensive actions outside of the United States.
The word razzia is, via Italian and French, from Algerian Arabic ghaziya (غزية \"raiding\"), originally referring to slave raids conducted by Barbary pirates.
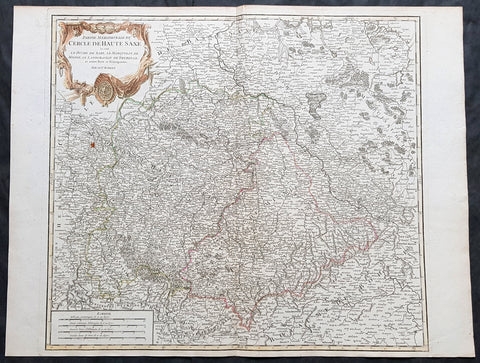
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of Saxony, Meissen, Thuringia, Leipzig
- Title : Partie Meridionale Du Cercle De Haute Saxe...Par Le Sr. Robert
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41573
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of part of the Saxony region of Germany, centering on the district of Meissen & Thuringia and the city of Leipzig, by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (560mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Saxony is a landlocked federal state of Germany, bordering the federal states of Brandenburg, Saxony Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig.
Saxony is the 10th-largest of Germany\'s 16 states, with an area of 18,413 square kilometres (7,109 sq mi), and the sixth-most populous, with 4 million people.
The history of the state of Saxony spans more than a millennium. It has been a medieval duchy, an electorate of the Holy Roman Empire, a kingdom, and twice a republic.
The area of the modern state of Saxony should not be confused with Old Saxony, the area inhabited by Saxons. Old Saxony corresponds roughly to the modern German states of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and the Westphalian part of North Rhine-Westphalia.
The territory of the Free State of Saxony became part of the Holy Roman Empire by the 10th century, when the dukes of Saxony were also kings (or emperors) of the Holy Roman Empire, comprising the Ottonian, or Saxon, Dynasty. Around this time, the Billungs, a Saxon noble family, received extensive fields in Saxony. The emperor eventually gave them the title of dukes of Saxony. After Duke Magnus died in 1106, causing the extinction of the male line of Billungs, oversight of the duchy was given to Lothar of Supplinburg, who also became emperor for a short time.
In 1137, control of Saxony passed to the Guelph dynasty, descendants of Wulfhild Billung, eldest daughter of the last Billung duke, and the daughter of Lothar of Supplinburg. In 1180 large portions west of the Weser were ceded to the Bishops of Cologne, while some central parts between the Weser and the Elbe remained with the Guelphs, becoming later the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg. The remaining eastern lands, together with the title of Duke of Saxony, passed to an Ascanian dynasty (descended from Eilika Billung, Wulfhild\'s younger sister) and were divided in 1260 into the two small states of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg. The former state was also named Lower Saxony, the latter Upper Saxony, thence the later names of the two Imperial Circles Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg. Both claimed the Saxon electoral privilege for themselves, but the Golden Bull of 1356 accepted only Wittenberg\'s claim, with Lauenburg nevertheless continuing to maintain its claim. In 1422, when the Saxon electoral line of the Ascanians became extinct, the Ascanian Eric V of Saxe-Lauenburg tried to reunite the Saxon duchies.
However, Sigismund, King of the Romans, had already granted Margrave Frederick IV the Warlike of Meissen (House of Wettin) an expectancy of the Saxon electorate in order to remunerate his military support. On 1 August 1425 Sigismund enfeoffed the Wettinian Frederick as Prince-Elector of Saxony, despite the protests of Eric V. Thus the Saxon territories remained permanently separated. The Electorate of Saxony was then merged with the much bigger Wettinian Margraviate of Meissen, however using the higher-ranking name Electorate of Saxony and even the Ascanian coat-of-arms for the entire monarchy. Thus Saxony came to include Dresden and Meissen. In the 18th and 19th centuries Saxe-Lauenburg was colloquially called the Duchy of Lauenburg, which in 1876 merged with Prussia as the Duchy of Lauenburg district.
Saxony-Wittenberg, in modern Saxony-Anhalt, became subject to the margravate of Meissen, ruled by the Wettin dynasty in 1423. This established a new and powerful state, occupying large portions of the present Free State of Saxony, Thuringia, Saxony-Anhalt and Bavaria (Coburg and its environs). Although the centre of this state was far to the southeast of the former Saxony, it came to be referred to as Upper Saxony and then simply Saxony, while the former Saxon territories were now known as Lower Saxony.
In 1485, Saxony was split. A collateral line of the Wettin princes received what later became Thuringia and founded several small states there (see Ernestine duchies). The remaining Saxon state became still more powerful and was known in the 18th century for its cultural achievements, although it was politically weaker than Prussia and Austria, states which oppressed Saxony from the north and south, respectively.
Between 1697 and 1763, the Electors of Saxony were also elected Kings of Poland in personal union.
In 1756, Saxony joined a coalition of Austria, France and Russia against Prussia. Frederick II of Prussia chose to attack preemptively and invaded Saxony in August 1756, precipitating the Third Silesian War (part of the Seven Years\' War). The Prussians quickly defeated Saxony and incorporated the Saxon army into the Prussian army. At the end of the Seven Years\' War, Saxony recovered its independence in the 1763 Treaty of Hubertusburg.
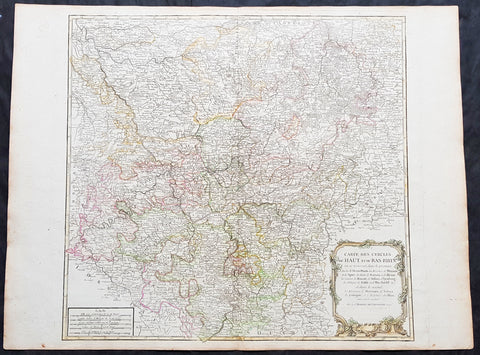
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of North Rhine-Westphalia Bonn Cologne
- Title : Carte Des Cercles Du Haut et du Bas Rhin.....Par Le Sr. Robert
- Size: 26 1/2in x 19 3/4in (670mm x 505mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41574
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of part of Western Germany centering on the Rhine River and the cities of Bonn & Cologne, today the North Rhine-Westphalia by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 19 3/4in (670mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 19in (550mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
North Rhine-Westphalia is located in western Germany covering an area of 34,084 square kilometres and a population of 17.6 million, the most populous and the most densely populated German state apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, and the fourth-largest by area. Düsseldorf is the state capital and Cologne is the largest city. North Rhine-Westphalia features four of Germany\'s 10 largest cities: Düsseldorf, Cologne, Dortmund, and Essen, and the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan area, the largest in Germany and the third-largest on the European continent.
Around AD 1, numerous incursions occurred through Westphalia and perhaps even some permanent Roman or Romanized settlements. The Battle of Teutoburg Forest took place near Osnabrück (as mentioned, whether this is in Westphalia is disputed) and some of the Germanic tribes who fought at this battle came from the area of Westphalia. Charlemagne is thought to have spent considerable time in Paderborn and nearby parts. His Saxon Wars also partly took place in what is thought of as Westphalia today. Popular legends link his adversary Widukind to places near Detmold, Bielefeld, Lemgo, Osnabrück, and other places in Westphalia. Widukind was buried in Enger, which is also a subject of a legend.
Along with Eastphalia and Engern, Westphalia (Westfalahi) was originally a district of the Duchy of Saxony. In 1180, Westphalia was elevated to the rank of a duchy by Emperor Barbarossa. The Duchy of Westphalia comprised only a small area south of the Lippe River.
Parts of Westphalia came under Brandenburg-Prussian control during the 17th and 18th centuries, but most of it remained divided duchies and other feudal areas of power. The Peace of Westphalia of 1648, signed in Münster and Osnabrück, ended the Thirty Years\' War. The concept of nation-state sovereignty resulting from the treaty became known as Westphalian sovereignty.
As a result of the Protestant Reformation, there is no dominant religion in Westphalia. Roman Catholicism and Lutheranism are on relatively equal footing. Lutheranism is strong in the eastern and northern parts with numerous free churches. Münster and especially Paderborn are thought of as Catholic. Osnabrück is divided almost equally between Catholicism and Protestantism.
After the defeat of the Prussian Army at the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, the Treaty of Tilsit in 1807 made the Westphalian territories part of the Kingdom of Westphalia from 1807 to 1813. It was founded by Napoleon and was a French vassal state. This state only shared the name with the historical region; it contained only a relatively small part of Westphalia, consisting instead mostly of Hessian and Eastphalian regions.
After the Congress of Vienna, the Kingdom of Prussia received a large amount of territory in the Westphalian region and created the province of Westphalia in 1815. The northernmost portions of the former kingdom, including the town of Osnabrück, had become part of the states of Hanover and Oldenburg.
The state of North Rhine-Westphalia was established by the British military administration\'s \"Operation Marriage\" on 23 August 1946, by merging the province of Westphalia and the northern parts of the Rhine Province, both being political divisions of the former state of Prussia within the German Reich. On 21 January 1947, the former state of Lippe was merged with North Rhine-Westphalia. The constitution of North Rhine-Westphalia was then ratified through a referendum.
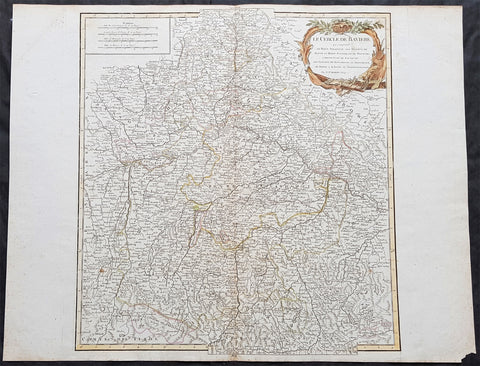
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of Bavaria & River Danube, Germany
- Title : Le Cercle De Baviere.......Par Le Sr. Robert
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41577
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Bavaria, Germany - centering on the River Danube - by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 19 1/2in (510mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Bavaria officially the Free State of Bavaria is a landlocked federal state of Germany, occupying its southeastern corner. With an area of 70,550.19 square kilometres, Bavaria is the largest German state by land area. Its territory comprises roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With 12.9 million inhabitants, it is Germany\'s second-most-populous state after North Rhine-Westphalia. Bavaria\'s capital and largest city, Munich, is the third-largest city in Germany.
The history of Bavaria stretches from its earliest settlement and formation as a duchy in the 6th century CE through the Holy Roman Empire to becoming an independent kingdom and a state of the Federal Republic of Germany.
The Duchy of Bavaria dates back to the year 555. In the 17th century CE, the Duke of Bavaria became a Prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire. The Kingdom of Bavaria existed from 1806 to 1918, when Bavaria became a republic. In 1946, the Free State of Bavaria re-organised itself on democratic lines after the Second World War.
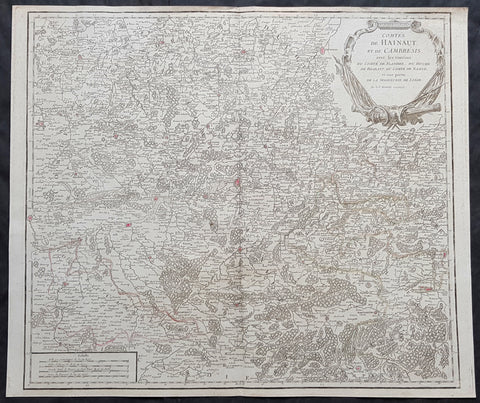
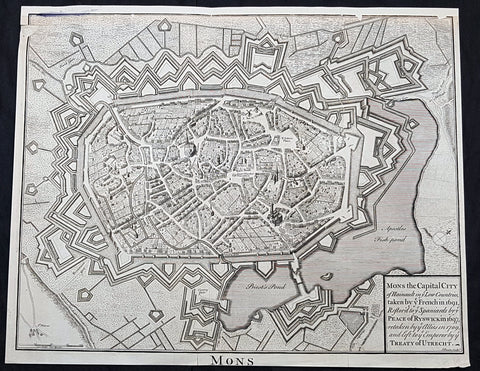
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map The County of Hainaut Belgium & France
- Title : Comte De Hainaut et de Cambres.......Par Le Sr. Robert
- Size: 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41564
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Hainaut region of Belgium - centering on the city of Mons - by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The County of Hainaut sometimes given the spelling Hainault, was a historical lordship within the medieval Holy Roman Empire with its capital eventually established at Mons (Dutch: Bergen), and named after the river Haine, both now in Belgium. Besides Mons, it included the city of Valenciennes, now in France. It consisted of what is now the Belgian province of Hainaut and the eastern part of the French département of Nord.
Originally a gau of Lotharingia, Hainaut was briefly a part of West Francia (911–25) before becoming definitively attached to Germany. The county was divided in 958 and only emerged in its more or less final form in 1071. Hainaut was culturally and linguistically French. In 1432, Hainaut was acquired by the House of Valois-Burgundy and in 1477 passed to the Habsburgs with the rest of the Burgundian Netherlands and became part of the Burgundian Circle in 1512. It was ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1555 to 1714. In 1659 and 1678 southern Hainaut was acquired by France, and in 1797 the rest of the county was ceded to France by the Emperor Francis II, who was also count of Hainaut.
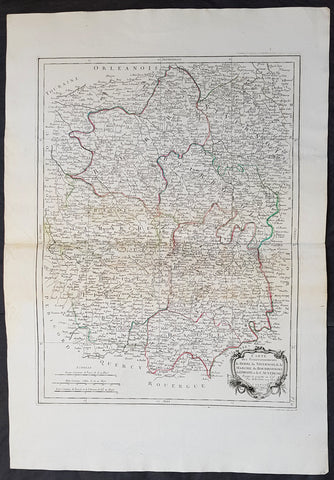
1777 Santini Antique Map French Provinces, Bourges Nevers Guéret Moulins Limoges
- Title : Carte Des Gouvernements du Berri, du Nivernois, de la Marche, du Bourbonnois, du Limosim et de L Auvergne...Par M Bonne 1771....A Venise...P Santini...1777
- Date : 1777
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50197
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique map of French Provinces of Berry (Bourges) Nivernais (Nevers) Marche (Guéret) Bourbonnais (Moulins) Limousin (Limoges) & Auvergne (Clermont-Ferrand) was engraved in 1777 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - after Robert Bonne and was published by Francois Santini (active 1776-84) in his 2 volume edition of Atlas Universal 1776-84. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 17in (595mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
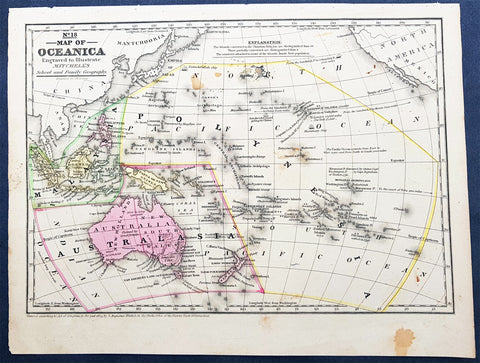
1839 Samuel Augustus Mitchell Antique Map of New Holland, New Zealand & Oceania
- Title : No 18 Map of Oceania...Entered according to Act of Congress in the year 1839 by S Augustus Mitchell
- Date : 1839
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 32148
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Description:
This detailed original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of New Holland - Australia, New Zealand, Polynesia & Micronesia, Oceania by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in 1839 - dated - was published in Mitchells School and Family Geography
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Early map of Australia and Oceania, the east coast is still referred to as NSW, with no sign of development of Melbourne or Victoria with New Zealand listing early Cook & Maori place names.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Caribbean Islands of Guadeloupe & Martinique
- Title : L Isle De La Martinique; Isles De La Guadeloupe...Par M Bonne
- Date : 1780
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40556
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Caribbean Islands of Guadeloupe & Martinique by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Two small worm holes
Plate area: - Two small worm holes
Verso: - Two small worm holes
Background:
Martinique is an insular region of France located in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea.
Guadeloupe is an insular region of France located in the Leeward Islands, part of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean.
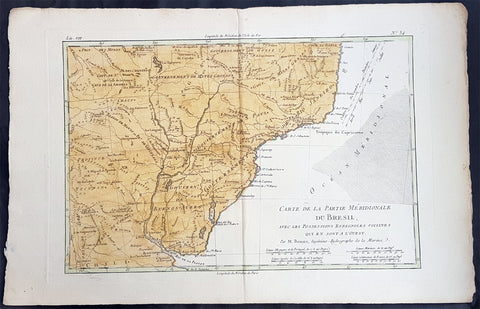
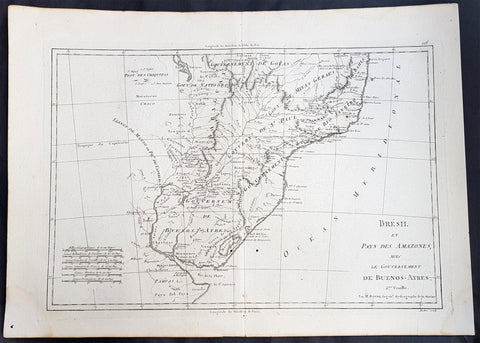
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 40851
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
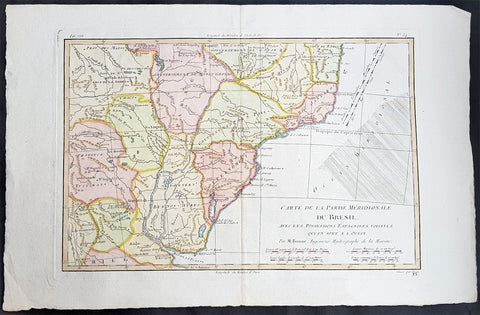
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 16042-1
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 40552
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
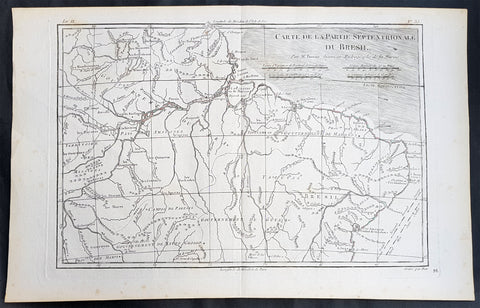
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31685
- Size: 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
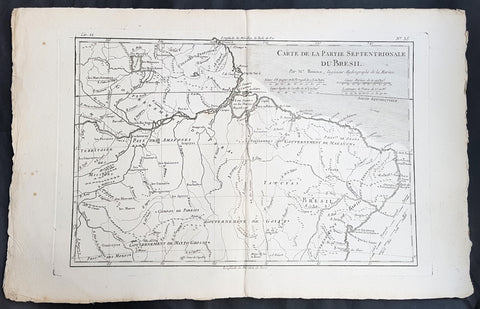
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40850
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
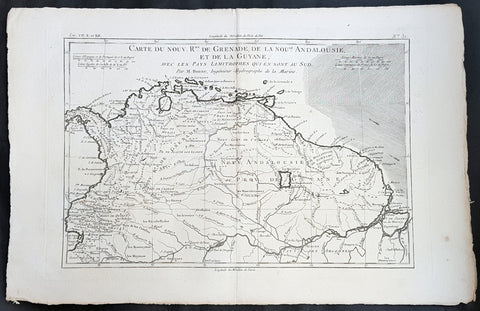
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
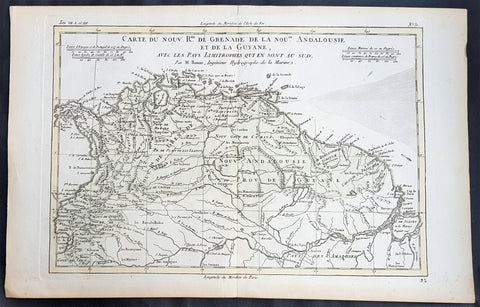
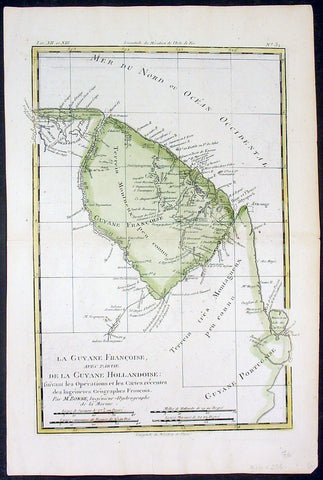
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40848
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31681
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Peru, The Amazon River, South America
- Title : Carte Du Perou avec une partie des pays quien sont al est... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 60565
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of West South America Peru & The Amazon River
- Title : Perou et Pays Circonvoisins... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40551
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of South America Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 16059
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of South America French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 16059
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of the Cape Verde Islands & Plan of Praia
- Title : Isles Du Cap-Verd; Plan de la Rade de la Praya...Par M Bonne
- Ref : 40546
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of the Cape Verde Islands, West Africa with an inset map of the harbour & city of Praia, by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Cape Verde officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country spanning an archipelago of 10 volcanic islands in the central Atlantic Ocean. It forms part of the Macaronesia ecoregion, along with the Azores, Canary Islands, Madeira, and the Savage Isles.
The Cape Verde archipelago was uninhabited until the 15th century, when Portuguese explorers discovered and colonized the islands, establishing the first European settlement in the tropics. Ideally located for the Atlantic slave trade, the islands grew prosperous throughout the 16th and 17th centuries, attracting merchants, privateers, and pirates. The end of slavery in the 19th century led to economic decline and emigration. Cape Verde gradually recovered as an important commercial center and stopover for shipping routes. Incorporated as an overseas department of Portugal in 1951, the islands continued to campaign for independence, which was peacefully achieved in 1975.
Praia is the capital and largest city of Cape Verde, an island nation in the Atlantic Ocean west of Senegal. It lies on the southern coast of Santiago island in the Sotavento Islands group.
1574 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the City of Lubeck, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Lubeck
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 22708
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Lubeck, in the northern German state Schleswig-Holstein was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1574 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Lübeck is a city in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany, on the river Trave.
In the 14th century Lübeck became the Queen of the Hanseatic League, being by far the largest and most powerful member of that medieval trade organization. In 1375 Emperor Charles IV named Lübeck one of the five Glories of the Empire, a title shared with Venice, Rome, Pisa and Florence. Several conflicts about trading privileges resulted in fighting between Lübeck (with the Hanseatic League) and Denmark and Norway – with varying outcome. While Lübeck and the Hanseatic League prevailed in conflicts in 1435 and 1512, Lübeck lost when it became involved in the Count\'s Feud, a civil war that raged in Denmark from 1534 to 1536. Lübeck also joined the pro-Lutheran Schmalkaldic League of the mid-16th century.
After its defeat in the Count\'s Feud, Lübeck\'s power slowly declined. The city remained neutral in the Thirty Years\' War of 1618–1648, but the combination of the devastation from the decades-long war and the new transatlantic orientation of European trade caused the Hanseatic League – and thus Lübeck with it – to decline in importance. However, even after the de facto disbanding of the Hanseatic League in 1669, Lübeck still remained an important trading town on the Baltic Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Weissenburg Bavaria Germany
- Title : Die Statt Wyssenburg
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 30351
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Weißenburg (Weissenburg) in Bavaria in Middle Franconia - identified by the cities Coate of Arms with double headed eagle atop of a castle - was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Weißenburg in Bayern (formerly also Weißenburg im Nordgau) is a town in Middle Franconia, Germany. It is the capital of the district Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen. Weissenburg is located in central Bavaria, in the south of the administrative region Mittelfranken.
The history of Weißenburg is generally traced back to the Roman fort that was built in the area towards the end of the first century. The settlement, which included Thermae, lay on the border of the Roman Empire and on the Tabula Peutingeriana from the 4th century it had the name Biriciana. Germanic tribes destroyed the fort and settled in what is still the city centre. The first mention of the name Weißenburg is in a deed dating from 867. The city became the seat of a royal residence during the reign of the Franks and according to legend, Charlemagne stayed there to supervise the construction of Fossa Carolina.
The city became a Free Imperial City in 1296 and continued to grow until the Reformation. Following the example of Nuremberg the city joined the Protestant side but it suffered heavily in the ensuing wars. However, the rights of the city as a Free Imperial City and an Imperial Estate were restored in the final peace treaty and some growth resumed. Despite its insignificant size and economic importance, the city, like the other 50-odd free imperial cities, was virtually independent.
Weissenburg lost its independence in 1802 and became part of the Bavarian kingdom in 1806. It was however saved from insignificance with the construction of a railway between Nuremberg and Augsburg which goes through the city and which supported industrialisation. Following World War II over 6,000 refugees and people expelled from the territories which Germany lost settled in the city and have since played an important role in its industry and culture.
The many stages in the history of Weissenburg can still be seen today. There are many ruins from the Roman times. One of the finest is the remains of a Roman bath which was excavated in 1977 and has been turned into a museum. The city wall from the Middle Ages has survived almost intact with its towers and in the Gothic Town Hall the city\'s elected members have held their meetings from 1476.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to bottom margin, no loss
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the city of Poitiers in Poitou France
- Title : Die Statt Puttiers
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 30381
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the French city of Poitiers on the Clain River in the Vienne Dept of central western France, was published in the French Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Poitiers is a city on the Clain river in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and also of the Poitou.
The type of political organisation existing in Poitiers during the late medieval or early modern period can be glimpsed through a speech given on 14 July 1595 by Maurice Roatin, the town\'s mayor. He compared it to the Roman state, which combined three types of government: monarchy (rule by one person), aristocracy (rule by a few), and democracy (rule by the many). He said the Roman consulate corresponded to Poitiers\' mayor, the Roman senate to the town\'s peers and échevins, and the democratic element in Rome corresponded to the fact that most important matters can not be decided except by the advice of the Mois et Cent (broad council).1 The mayor appears to have been an advocate of a mixed constitution; not all Frenchmen in 1595 would have agreed with him, at least in public; many spoke in favour of absolute monarchy. The democratic element was not as strong as the mayor\'s words may seem to imply: in fact, Poitiers was similar to other French cities, Paris, Nantes, Marseille, Limoges, La Rochelle, Dijon, in that the town\'s governing body (corps de ville) was highly exclusive and oligarchical: a small number of professional and family groups controlled most of the city offices. In Poitiers many of these positions were granted for the lifetime of the office holder.
The city government in Poitiers based its claims to legitimacy on the theory of government where the mayor and échevins held jurisdiction of the citys affairs in fief from the king: that is, they swore allegiance and promised support for him, and in return he granted them local authority. This gave them the advantage of being able to claim that any townsperson who challenged their authority was being disloyal to the king. Every year the mayor and the 24 échevins would swear an oath of allegiance between the hands of the king or his representative, usually the lieutenant général or the sénéchaussée. For example, in 1567, when Maixent Poitevin was mayor, king Henry III came for a visit, and, although some townspeople grumbled about the licentious behaviour of his entourage, Henry smoothed things over with a warm speech acknowledging their allegiance and thanking them for it.
In this era, the mayor of Poitiers was preceded by sergeants wherever he went, consulted deliberative bodies, carried out their decisions, heard civil and criminal suits in first instance, tried to ensure that the food supply would be adequate, visited markets.
In the 16th century, Poitiers impressed visitors because of its large size, and important features, including royal courts, university, prolific printing shops, wealthy religious institutions, cathedral, numerous parishes, markets, impressive domestic architecture, extensive fortifications, and castle.
16th-century Poitiers is closely associated with the life of François Rabelais and with the community of Bitards.
The town saw less activity during the Renaissance. Few changes were made in the urban landscape, except for laying way for the rue de la Tranchée. Bridges were built where the inhabitants had used gués. A few hôtels particuliers were built at that time, such as the hôtels Jean Baucé, Fumé and Berthelot. Poets Joachim du Bellay and Pierre Ronsard met at the University of Poitiers, before leaving for Paris.
During the 17th century, many people emigrated from Poitiers and the Poitou to the French settlements in the new world and thus many Acadians or Cajuns living in North America today can trace ancestry back to this region.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins cropped into border
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light toning along centerfold
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 32163
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31975
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31988
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40973
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Huge 4 Sheet Antique Map of Spain, Portugal, Balearic Is
- Title : 1854 Handtke & Flemming Huge 4 Sheet Antique Map of Spain, Portugal, Balearic Is
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 32087
- Size: 32in x 26 1/2in (815mm x 675mm) joined
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique very large 4 x sheet map of Spain & Portugal by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 32in x 26 1/2in (815mm x 675mm) joined
Plate size: - 32in x 26 1/2in (815mm x 675mm) joined
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Many of the original charts and maps drawn by the first Portuguese and Spanish navigators have survived for the very good reason that, on completion of their voyages, pilots were obliged to hand over their manuscript notes to the Casa da India (founded 1504) in Lisbon or to the equivalent Casa de Contrataci6n de las Indias (founded 1504) in Seville. The clear intention was to maintain secrecy over new discoveries and control over the distribution of cartographic material, not always successfully, as it happened; pilots and navigators seem to have changed allegiance with impunity and, in consequence, many of the earliest and most informative charts were compiled as far away as Genoa, Venice, Florence and Ancona, presumably from sources outside the Portuguese and Spanish Casas.It is apparent that few manuscripts reached the printing stage and, indeed, are so rare that any study of them must be regarded as a specialist subject. (Ref Tooley M&B)
1824 Louis Vivien Large Antique Map of the Confederation of German States
- Title : Carte Generale de Etats compesantL Confederation Germanique...1824
- Size: 27 1/2in x 23in (700mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1824
- Ref #: 40713
Description:
This finely engraved original large antique map of the confederation of German states and central Europe, by Louis Vivien in his Elephant Folio atlas, Atlas Universal
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 23in (700mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The German Confederation was an association of 39 German-speaking states in Central Europe (adding the mainly non-German speaking Kingdom of Bohemia and Duchy of Carniola), created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to coordinate the economies of separate German-speaking countries and to replace the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved in 1806. The German Confederation excluded German-speaking lands in the eastern portion of the Kingdom of Prussia (East Prussia, West Prussia and Posen), the German cantons of Switzerland, and Alsace within France which was majority German speaking.
The Confederation was weakened by rivalry between the Kingdom of Prussia and the Austrian Empire, revolution, and the inability of the multiple members to compromise. In 1848, revolutions by liberals and nationalists attempted to establish a unified German state with a progressive liberal constitution under the Frankfurt Convention. The ruling body, the Confederate Diet, was dissolved on 12 July 1848, but was re-established in 1850 after failed efforts to replace it.
The Confederation was finally dissolved after the Prussian victory in the Seven Weeks War over Austria in 1866. The dispute over which had the inherent right to rule German lands ended in favour of Prussia, leading to the creation of the North German Confederation under Prussian leadership in 1867, to which the eastern portions of the Kingdom of Prussia were added. A number of South German states remained independent until they joined the North German Confederation, which was renamed and proclaimed as the German Empire in 1871 for the now unified Germany with the Prussian king as emperor (Kaiser) after the victory over French Emperor Napoleon III in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870.
Most historians have judged the Confederation to have been weak and ineffective, as well as an obstacle to the creation of a German nation-state. However, the Confederation was designed to be weak, as it served the interests of the European Great Powers, especially member states Austria and Prussia.
Vivien, Louis 1802 - 1896
Louis Vivien , or Vivien de Saint-Martin was a French geographer who was born in Saint-Martin-de-Fontenay and died in Versailles, France in 1896.
He settled in Paris under the Restoration, and became known with his publication of the Electoral and Administrative Map in 1823 and his comprehensive Universal Atlas in 1825, collaborating with Jacques Bibliomappe -Charles Bailleul from 1828. Vivien was foremost a geographer but was also a publisher of works in other fields, including historical books on the General History of the French Revolution and the History of Napoleon. He also translated various English works, such as the novels of Walter Scott .
He also wrote the New Annals of Travels between 1845 and 1854 and briefly the French Athenaeum between 1847 & 1848. He contributed to numerous periodicals such as Le Constitutionnel, Revue contemporaine, Revue germanique & La Presse. He also wrote L Année géographique between 1863 and 1875 before passing the baton to G. Maunoir and Henri Duveyrier.
He is mainly known though, for his three cartographical works, A History of Geographical Discoveries, A New Dictionary of Universal Geography and the Universal Atlas of Geography. The first of these publications he completed after the 1848 Revolution with the latter two completed by Louis Rousselet and Franz Schrader.
Vivien was Honorary President of the Geographical Society, of which he was one of the founder members. He also laureate of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles-Lettres as well as a member of the Asian Society , the Society of Ethnology along with a large number of learned societies and European academies.
Main works of Vivien de Saint-Martin
- General History of the French Revolution, the Empire, the Restoration, the Monarchy of 1830, up to and including 1841 (4 volumes in 2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat Brothers, 1841-1842.
- History of Napoleon and the Empire (2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat brothers, 1844.
- History of geographical discoveries of European nations in various parts of the world (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1845-1846.
- Research on primitive populations and the oldest traditions of the Caucasus , Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1847.
- Studies of Ancient Geography and Asian Ethnography (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1850-1852.
- Historical and geographical description of Asia Minor (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1852.
- Study on the Greek and Latin Geography of India , Paris, Imperial Printing, 1858.
- Study on the geography and the primitive populations of north-west India, according to the Vedic hymns , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1860.
- North Africa in Greek and Roman antiquity, historical and geographical study , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1863.
- History of geography and geographical discoveries from the earliest times to the present day , Paris, Hachette, 1873.
- With Franz Schrader : Universal Atlas of Geography built from the original sources and the most recent documents , Paris, Hachette, 1876-1915.
- With Louis Rousselet : New dictionary of universal geography (9 volumes), Paris, Hachette, 1879-1900.
1855 US Coast Survey & A D Bache Antique Map Lower Colorado River Valley & San Diego, California
- Title : US Coast Survey A D Bache Superintendant Map of the Vicinity of Monterey Bay California...By W P Blake esq. 1855
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 93018
This original antique lithograph map of the lower Colorado River Valley and San Diego, by Alexander Dallas Bache (great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin) in 1855 - dated - was published by the official chart-maker of the United States, the office of The US Coast Survey.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Colorado River is a major river of the western United States and northwest Mexico in North America. Its headwaters are in the Rocky Mountains where La Poudre Pass Lake is its source. Located in north central Colorado it flows southwest through the Colorado Plateau country of western Colorado, southeastern Utah and northwestern Arizona where it flows through the Grand Canyon. It turns south near Las Vegas, Nevada, forming the Arizona–Nevada border in Lake Mead and the Arizona–California border a few miles below Davis Dam between Laughlin, Nevada and Needles, California California before entering Mexico in the Colorado Desert. Most of its waters are diverted into the Imperial Valley of Southern California. In Mexico its course forms the boundary between Sonora and Baja California before entering the Gulf of California.
The Colorado forms the border of California to the west and Arizona to the east for most of its course through the desert Lower Colorado River Valley (LCRV), where its character changes significantly from fast-flowing whitewater to a low gradient braided stream with a wide floodplain. Here, the Colorado River ranges in width from 700 to 2,500 ft (200 to 800 m) and from 8 to 100 ft (2 to 30 m) in depth. It becomes a losing stream, with a gradual reduction in volume both due to evaporation in the hot desert climate and massive diversions for irrigation, urban areas, industry and thermo-electric power generation. The average flow rate of 14,180 cubic feet per second (402 m3/s) at Davis Dam diminishes to just 2,060 cubic feet per second (58 m3/s) at the Mexican border.
At Needles, California the Colorado is crossed by Interstate 40; shortly downstream it passes the Topock Marsh in Topock Gorge and widens into Lake Havasu, formed by Parker Dam. Lake Havasu provides recreation as well as the home of the retired U.K. London Bridge in Lake Havasu City, Arizona, now the New London Bridge. Near Parker Dam are the first two major diversions of the lower Colorado: the Colorado River Aqueduct, which travels 240 miles (390 km) west to Los Angeles and San Diego, California; and the Central Arizona Project, which sends water 340 miles (550 km) east towards Phoenix and Tucson, Arizona. The intermittent Bill Williams River joins the Colorado from the east in Lake Havasu, just above Parker Dam.
U.S. Coast Survey (Office of Coast Survey)
The Office of Coast Survey is the official chart-maker of the United States. Set up in 1807, it is one of the U.S. governments oldest scientific organizations. In 1878 it was given the name of Coast and Geodetic Survey (C&GS). In 1970 it became part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The agency was established in 1807 when President Thomas Jefferson signed the document entitled An act to provide for surveying the coasts of the United States. While the bills objective was specific—to produce nautical charts—it reflected larger issues of concern to the new nation: national boundaries, commerce, and defence.
The early years were difficult. Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, who was eventually to become the agencys first superintendent, went to England to collect scientific instruments but was unable to return through the duration of the War of 1812. After his return, he worked on a survey of the New York Harbor in 1817, but Congress stepped in to suspend the work because of tensions between civilian and military control of the agency. After several years under the control of the U.S. Army, the Survey of the Coast was reestablished in 1832, and President Andrew Jackson appointed Hassler as superintendent.
The U.S. Coast Survey was a civilian agency but, from the beginning, members of the Navy and Army were detailed to service with the Survey, and Navy ships were also detailed to its use. In general, army officers worked on topographic surveys on the land and maps based on the surveys, while navy officers worked on hydrographic surveys in coastal waters.
Alexander Dallas Bache, great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, was the second Coast Survey superintendent. Bache was a physicist, scientist, and surveyor who established the first magnetic observatory and served as the first president of the National Academy of Sciences. Under Bache, Coast Survey quickly applied its resources to the Union cause during the Civil War. In addition to setting up additional lithographic presses to produce the thousands of charts required by the Navy and other vessels, Bache made a critical decision to send Coast Survey parties to work with blockading squadrons and armies in the field, producing hundreds of maps and charts. Bache detailed these activities in his annual reports to Congress.
Coast Survey cartographer Edwin Hergesheimer created the map showing the density of the slave population in the Southern states.
Bache was also one of four members of the governments Blockade Strategy Board, planning strategy to essentially strangle the South, economically and militarily. On April 16, 1861, President Lincoln issued a proclamation declaring the blockade of ports from South Carolina to Texas. Baches Notes on the Coast provided valuable information for Union naval forces.
Maps were of paramount importance in wartime:
It is certain that accurate maps must form the basis of well-conducted military operations, and that the best time to procure them is not when an attack is impending, or when the army waits, but when there is no hindrance to, or pressure upon, the surveyors. That no coast can be effectively attacked, defended, or blockaded without accurate maps and charts, has been fully proved by the events of the last two years, if, indeed, such a proposition required practical proof.
— Alexander Dallas Bache, 1862 report.
Coast Survey attracted some of the best and brightest scientists and naturalists. It commissioned the naturalist Louis Agassiz to conduct the first scientific study of the Florida reef system. James McNeill Whistler, who went on to paint the iconic Whistlers Mother, was a Coast Survey engraver. The naturalist John Muir was a guide and artist on Survey of the 39th Parallel across the Great Basin of Nevada and Utah.
The agencys men and women (women professionals were hired as early as 1845) led scientific and engineering activities through the decades. In 1926, they started production of aeronautical charts. During the height of the Great Depression, Coast and Geodetic Survey organized surveying parties and field offices that employed over 10,000 people, including many out-of-work engineers.
In World War II, C&GS sent over 1,000 civilian members and more than half of its commissioned officers to serve as hydrographers, artillery surveyors, cartographers, army engineers, intelligence officers, and geophysicists in all theaters of the war. Civilians on the home front produced over 100 million maps and charts for the Allied Forces. Eleven members of the C&GS gave their lives during the war.
Alexander Dallas Bache 1806 – 1867 was an American physicist, scientist, and surveyor who erected coastal fortifications and conducted a detailed survey to map the mid-eastern United States coastline. Originally an army engineer, he later became Superintendent of the U.S. Coast Survey, and built it into the foremost scientific institution in the country before the Civil War.
Alexander Bache was born in Philadelphia, the son of Richard Bache, Jr., and Sophia Burrell Dallas Bache. He came from a prominent family as he was the nephew of Vice-President George M. Dallas and naval hero Alexander J. Dallas. He was the grandson of Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Dallas and was the great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin.
Bache was a professor of natural philosophy and chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania from 1828 to 1841 and again from 1842 to 1843. He spent 1836–1838 in Europe on behalf of the trustees of what became Girard College; he was named president of the college after his return. Abroad, he examined European education systems, and on his return he published a valuable report. From 1839 to 1842, he served as the first president of Central High School of Philadelphia, one of the oldest public high schools in the United States.
In 1843, on the death of Professor Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, Bache was appointed superintendent of the United States Coast Survey. He convinced the United States Congress of the value of this work and, by means of the liberal aid it granted, he completed the mapping of the whole coast by a skillful division of labor and the erection of numerous observing stations. In addition, magnetic and meteorological data were collected. Bache served as head of the Coast Survey for 24 years (until his death).
1855 George Philip Large Antique Lithograph Map of Queensland & South Pacific
- Title : Islands in the Pacific Ocean...Liverpool, Published by George Philip & Son...Printed by G Gellatley, Edin.
- Size: 25in x 20 1/2in (630mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 70066
Description:
This original lithograph antique map of Australia & The South Pacific Ocean by George Philip & Son in 1855 and was print by J. Gellatley.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (630mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (630mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin corner ripped
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map is easily dated as Queensland is still named NSW, with statehood achieved in 1859.
Philip, George 1800–1882
George Philip was a cartographer and map publisher. He had one son, also George (1823–1902), who was admitted to the business in 1848. The eventual company, George Philip & Son Ltd, continued to operate successfully until in 1987 when it was sold to Reed International .
George senior was born in Huntly, Aberdeenshire to a staunchly Calvinist family. In 1819 he became assistant to the Liverpool bookseller, William Grapel and in 1834 started his own business in Liverpool producing maps and educational books.
The business expanded rapidly. He used cartographers (such as John Bartholomew the elder, August Petermann, and William Hughes) to produce maps on copper plates. Philip then had these printed and hand-coloured by his women tinters. By the time he produced his county maps of 1862 he was using machine coloured maps produced on power-driven lithographic presses.
The firm also supplied atlases and textbooks overseas starting with an atlas for Australian schools in 1865 and for New Zealand in 1869. The demand from board schools, established after 1870, enabled further expansion in the market for general textbooks, school stationery, atlases and wall maps
1814 John Thomson Large Antique Map of The Russian Empire
- Title : Russian Empire ...John Thomson....1814
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (720mm x 530mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1814
- Ref #: 31910
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of The Russian Empire by John Thomson in 1814 - dated at the foot of the map - was published in the large 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Light
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (720mm x 530mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West.
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of the Welsh County of Monmouth
- Title : The county of Monmouth by Robt. Morden...Sold by Abel Swale Awsham & John Churchill
- Size: 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 70317
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Welsh county of Monmouth by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of Huntington in County of Cambridgeshire England
- Title : Huntington Shire by Robt. Morden...Sold by Abel Swale Awsham & John Churchill
- Size: 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 92680
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the English region of Huntingdonshire, in the county of Cambridgeshire by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map Birds Eye View City of Mons, Walloon, Belgium
- Title : Mons the capital city of Hainault in ye French in 1691,restor.d to ye Spaniards by ye Peace of Ryswick in 1697,retaken by ye Allies in 1709 and left to ye Emperor by ye Treaty of Utrecht
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 91299
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map a Bird Eye View of the city of Mons, Belgium - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin restored, smudge along top left border
Plate area: - Small loss to left of image
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Mons is a Walloon city and municipality, and the capital of the Belgian province of Hainaut. The Mons municipality includes the former communes of Cuesmes, Flénu, Ghlin, Hyon, Nimy, Obourg, Jemappes, Ciply, Harmignies, Harveng, Havré, Maisières, Mesvin, Nouvelles, Saint-Denis, Saint-Symphorien, Spiennes and Villers-Saint-Ghislain.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. The population grew quickly, trade flourished, and several commercial buildings were erected near the GrandPlace. In 1814, King William I of the Netherlands increased the fortifications, following the fall of the First French Empire. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry. In 1830, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle the fortifications, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects.
In 1515, Charles V took an oath in Mons as Count of Hainaut. In this period of its history, the city became the target of various occupations, starting in May 1572 with the Protestant takeover by Louis of Nassau, who had hoped to clear the way for the French Protestant leader Gaspard de Coligny to oppose Spanish rule. After the murder of de Coligny during the St. Bartholomews Day massacre, the Duke of Alba took control of Mons in September 1572 in the name of the Catholic King of Spain. This spelled the ruin of the city and the arrest of many of its inhabitants; from 1580 to 1584, Mons became the capital of the Southern Netherlands.
On 8 April 1691, after a nine-month siege, Louis XIVs army stormed the city, which again suffered heavy casualties. From 1697 to 1701, Mons was alternately French or Austrian. After being under French control from 1701 to 1709, the Dutch army gained the upper hand in the Battle of Malplaquet. In 1715, Mons returned to Austria under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht (1713). But the French did not give up easily; Louis XV besieged the city again in 1746. After the Battle of Jemappes (1792), the Hainaut area was annexed to France and Mons became the capital of the Jemappes district.
Following the fall of the First French Empire in 1814, King William I of the Netherlands fortified the city heavily. In 1830, however, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle fortified cities such as Mons, Charleroi, and Namur. The actual removal of fortifications only happened in the 1860s, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry, which strongly influenced the culture and image of the Borinage region as a whole. It was to become an integral part of the sillon industriel, the industrial backbone of Wallonia.
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map Birds Eye View City of Namur, Walloon, Belgium
- Title : The City of Namur with the Castle and other Fortifications
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 15970
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map a Bird Eye View of the city of Namur, Belgium - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin restored
Plate area: - Small loss to left of image
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Mons is a Walloon city and municipality, and the capital of the Belgian province of Hainaut. The Mons municipality includes the former communes of Cuesmes, Flénu, Ghlin, Hyon, Nimy, Obourg, Jemappes, Ciply, Harmignies, Harveng, Havré, Maisières, Mesvin, Nouvelles, Saint-Denis, Saint-Symphorien, Spiennes and Villers-Saint-Ghislain.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. The population grew quickly, trade flourished, and several commercial buildings were erected near the GrandPlace. In 1814, King William I of the Netherlands increased the fortifications, following the fall of the First French Empire. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry. In 1830, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle the fortifications, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects.
In 1515, Charles V took an oath in Mons as Count of Hainaut. In this period of its history, the city became the target of various occupations, starting in May 1572 with the Protestant takeover by Louis of Nassau, who had hoped to clear the way for the French Protestant leader Gaspard de Coligny to oppose Spanish rule. After the murder of de Coligny during the St. Bartholomews Day massacre, the Duke of Alba took control of Mons in September 1572 in the name of the Catholic King of Spain. This spelled the ruin of the city and the arrest of many of its inhabitants; from 1580 to 1584, Mons became the capital of the Southern Netherlands.
On 8 April 1691, after a nine-month siege, Louis XIVs army stormed the city, which again suffered heavy casualties. From 1697 to 1701, Mons was alternately French or Austrian. After being under French control from 1701 to 1709, the Dutch army gained the upper hand in the Battle of Malplaquet. In 1715, Mons returned to Austria under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht (1713). But the French did not give up easily; Louis XV besieged the city again in 1746. After the Battle of Jemappes (1792), the Hainaut area was annexed to France and Mons became the capital of the Jemappes district.
Following the fall of the First French Empire in 1814, King William I of the Netherlands fortified the city heavily. In 1830, however, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle fortified cities such as Mons, Charleroi, and Namur. The actual removal of fortifications only happened in the 1860s, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a center of heavy industry, which strongly influenced the culture and image of the Borinage region as a whole. It was to become an integral part of the sillon industriel, the industrial backbone of Wallonia.
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of Huntington in County of Cambridgeshire England
- Title : Huntington Shire by Robt. Morden...Sold by Abel Swale Awsham & John Churchill
- Size: 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 50149
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the English region of Huntingdonshire, in the county of Cambridgeshire by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
1765 Homann Large Antique Map of The Zurich Canton, Switzerland - Tigurini
Antique Map
- Title : Canton Zurich sive Illustratis Helvetiorum Respublica Tigurina...1765
- Ref #: 50175
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Zurich Canton of Switzerland, the hoome of the Tigurini Tribe of Helvetii, by the Homann firm was engraved in 1765 - dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair to top and left margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Soiling and re-enforced to the left of the verso
Background:
The Tigurini were a clan or tribe forming one out of four pagi (provinces) of the Helvetii.[1][2] The Tigurini were the most important group of the Helvetii, mentioned by both Caesar and Poseidonius, settling in the area of what is now the Swiss canton of Vaud, corresponding to the bearers of the late La Tène culture in western Switzerland. Their name has a meaning of lords, rulers (cognate with Irish tigern lord). The other Helvetian tribes included the Verbigeni and the Tougeni (sometimes identified with the Teutones), besides one tribe that has remained unnamed.
1747 Tobias Lotter Antique Miniature Map of Asia, Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Asia
- Size: 5 1/2in x 4 1/2in (140mm x 115mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1747
- Ref #: 93110
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique miniature map of Asia by Tobias Lotter was published in the 1747 edition of Atlas Geographicus Portatilis XXIX mappis orbis habitabilis regna exhibens.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 5 1/2in x 4 1/2in (140mm x 115mm)
Plate size: - 5 1/2in x 4 1/2in (140mm x 115mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1814 Dr Playfairs Large Antique Map of France in Departments
Antique Map
- Title : France in Departments Drawn and Engraved for Dr Playfairs Geography.
- Size: 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1814
- Ref #: 31154
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved map of France was published in the 1814 edition of A System of Geography Ancient and Modern (1810–14) (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
Playfair, Rev James Octavius 1738 - 1819
Rev Playfair was a Scottish minister and author and an eminent figure in the Scottish Enlightenment. He was born at West Bendochy in Perthshire the son of George Playfair (d. 1786), a farmer, and his wife, Jean Roger (d. 1804).[1]
He studied at St Andrews University and then became minister of Newtyle (1770–77) and Meigle (1777–1800). He was then appointed Principal of St Andrews University in 1800. During this period he was also minister of St Leonard\\\'s Church in St Andrews.
In 1779 St Andrews awarded him an honorary doctorate (DD). In 1787 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposers were John Playfair (a distant cousin) and Alexander Fraser Tytler.[2]
He was the official histiographer of the then Prince of Wales.
He died at Dalmarnock near Glasgow. He is buried in Glasgow but is also memorialised on the grave of his wife in the churchyard of St Andrews Cathedral.
Publications:
1. A System of Chronology (1782)
2. A System of Geography Ancient and Modern (1810–14)
3. General Atlas Ancient and Modern (1814)
4. A Geographical and Statistical Description of Scotland (1819)
1860 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of The Pacific - Australia to California
Antique Map
- Title : The Pacific Ocean
- Ref #: 70063
- Size: 26 1/2in x 19in (675mm x 490mm)
- Date : 1860
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original steel plate engraved hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was published in the 1860 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 19in (675mm x 490mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 19in (675mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Weller, Edward 1819 – 1884
Weller was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.