World (38)
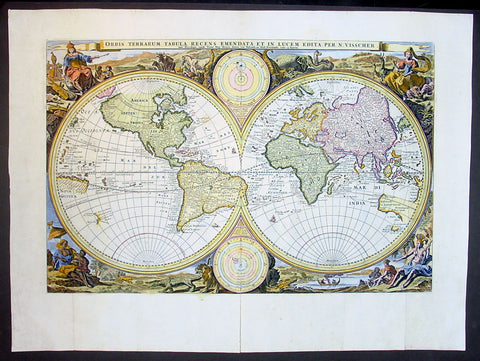
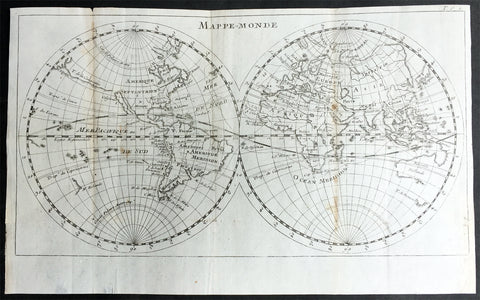
1598 J Moretus & A Ortelius 1st Edition of The Peutinger Tables, Ancient Roman Empire Maps x 4
Antique Map
- Title : Tabula Peutingeriana. Tabula itineraria ex illustri Peutingerorum Bibliotheca quae Augusta Vindel. est. Beneficio Marco Velseri septemviri Augustani in lucem edita.
- Size: 22in x 20in (560mm x 510mm) each
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1598
- Ref #: 50519, 50520, 50521, 50522
Description:
For three decades, locating rare & unusual and maps has been one our main goals and I believe with the following maps we have reach a milestone. The following maps originate from the oldest direct linage of any maps we have offered, going back to the height of the Roman Empire. These are some of the rarest and most fascinating maps it has been my pleasure to offer.
In 1265 a Monk, in the German city of Colmar produced a hand written map, on parchment, of the imperial highways and cities of the ancient Roman world. When joined, the result was a scroll measuring 6.75m long & 34cm wide, covering an area from southeast England to present day Sri-Lanka. That map of 1265 was copied from an earlier 4th or 5th century map, itself copied from a 2nd century map that originated from a 1st century BC map from Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, a Roman General & architect. When Agrippa died in 12BC his map was engraved in marble and displayed in the Porticus Vipsania in the Campus Agrippae area in Rome.
In 1494 the German Scholar, Conrad Celtes, discovered the Colmar scroll in a library, in the city of Worms. After his death in 1508, Celtes bequeathed the scroll to Konrad Peutinger, after whom the map is named. The scroll was kept in the Peutinger family until it was purchased by Prince Eugene of Savoy in 1714 and finally purchased for the Habsburg Imperial Court Library in Vienna, where it resides today.
As early as 1577 Abraham Ortelius, the Flemish cartographer, was aware of the existence of the Peutinger Tables, at that stage owned by Mark Welser. In 1591 Welser had two sections of the scroll printed by Aldus Manutius in Venice. Ortelius thought these inadequate and so commissioned the scroll engraved onto 8 separate plates . Ortelius supervised the engraving of the plates but did not live to see the results. In December 1598 the first edition of the 8 plates were printed individually, in limited numbers, by Johannes Moretus in Antwerp and are today amongst some of the rarest sets of maps available. To save space for printing in the first & second atlases in 1619 & 1624, two plates were printed per page, thus saving space. At that point a change was made to each plate, the engraving of a descriptive title at the bottom of each plate.
These maps we are offering are unique, being printed two per page but without the addition of the titles. So the conclusion we have come to is that these were prototypes printed to see if the printing of two plates per page were possible prior to the changes to the plates, making them unique.
We know that there were a total of 300 sets of these tables published in 1619 & 1624 atlases Theatrum Geographiae Veteris & Parergon , of which very few have survived. As for the 1598 edition, we do not know the number published or how many have survived but there is no doubt the number is very low in the single digits. Also I can find no record of sale for this original 1598 1st Moretus edition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 20in (560mm x 510mm) each
Plate size: - 20 1/4in x 7 1/2in (505mm x 195mm) each
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tabula Peutingerian also referred to as Peutingers Tabul or The Peutinger Table, is an illustrated itinerarium (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the cursus publicus, the road network of the Roman Empire. The map covers Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia, including the Middle East, Persia, and India.
The map was found as a 13th-century parchment copy based on a document from the 4th or 5th century, that contained a copy of the world map, originally prepared by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa a Roman general & architect active during the reign of the emperor Augustus (27 BC – AD 14). After Agrippas death in 12 BC, that map was engraved in marble and put on display in the Porticus Vipsania in the Campus Agrippae area in Rome, close to the Ara Pacis building.
The original Roman map, of which the 13th century parchment copy may be the only surviving copy, was last revised in the 4th or early 5th century. This is illustrated by the inclusion of the city of Constantinople, founded in 328, and the prominence of Ravenna, seat of the Western Roman Empire from 402 to 476, which suggests a fifth-century revision. The presence of certain cities of Germania Inferior that were destroyed in the mid-fifth century also provides proof or 4th or 5th century revision.
The surviving 13th century map itself was created by a monk in Colmar in modern-day eastern France in 1265. It is a parchment scroll, 0.34 metres (1 foot 1 inch) high and 6.75 metres (22.1 feet) long, assembled from eleven sections, a medieval reproduction of the original scroll.
The 13th century parchment map is very schematic, designed to give a practical overview of the road network, as opposed to an accurate representation of geographic features: the land masses shown are distorted, especially in the east–west direction. The map shows many Roman settlements and the roads connecting them, as well as other features such as rivers, mountains, forests and seas. The distances between settlements are also given. In total no fewer than 555 cities and 3,500 other place names are shown on the map. The three most important cities of the Roman Empire at the time – Rome, Constantinople and Antioch – are represented with special iconic decoration.
Besides the totality of the empire, the map also shows areas in the Near East, India and the Ganges, Sri Lanka (Insula Taprobane), and even an indication of China. It even shows a Temple to Augustus at Muziris (present day Kodungallur) on the modern-day Malabar Coast, one of the main ports for trade with the Roman Empire on the southwest coast of India. On the western end of the scroll, the absence of Morocco, the Iberian Peninsula, and the British Isles indicates that a twelfth original section has been lost in the surviving copy; the missing section was reconstructed in 1898 by Konrad Miller.
The map appears to be based on itineraries, lists of destinations along Roman roads, as the distances between points along the routes are indicated. Travellers would not have possessed anything so sophisticated as a modern map, but they needed to know what lay ahead of them on the road and how far. The Peutinger Table represents these roads as a series of stepped lines along which destinations have been marked in order of travel. The shape of the parchment pages accounts for the conventional rectangular layout. However, a rough similarity to the coordinates of Ptolemys earth-mapping gives some writers hope that some terrestrial representation was intended by the unknown original compilers.
The stages and cities are represented by hundreds of functional place symbols, used with discrimination from the simplest icon of a building with two towers to the elaborate individualized portraits of the three great cities. Some conclud that the semi-schematic, semi-pictorial symbols reproduce Roman cartographic conventions of the itineraria picta described by 4th-century writer Vegetius, of which this is the sole known testimony.
The 13th century copy map was discovered in a library in the city of Worms by German scholar Conrad Celtes in 1494, who was unable to publish his find before his death and bequeathed the map in 1508 to Konrad Peutinger, a German humanist and antiquarian in Augsburg, after whom the map is named. The Peutinger family kept possession of the map for more than two hundred years until it was sold in 1714. It then bounced between several royal and elite families until it was purchased by Prince Eugene of Savoy for 100 ducats; upon his death in 1737, it was purchased for the Habsburg Imperial Court Library in Vienna (Hofbibliothek). It is today conserved at the Austrian National Library at the Hofburg palace in Vienna.
The map was copied for Dutch cartographer Abraham Ortelius by Johannes Moretus and published separetly, shortly after his death, in 1598. The maps were not published in an atlas until 1619 by Petrus Bertius and again in the Ortelius Parageon in 1624.
A partial first edition was printed at Antwerp in 1591 (titled Fragmenta tabulæ antiquæ) , Johannes Moretus, printed the full Tabula in December 1598, in Antwerp. Johannes Janssonius published another version in Amsterdam, c. 1652.
In 1753 Franz Christoph von Scheyb published a copy, and in 1872 Konrad Miller, a German professor, was allowed to copy the map. Several publishing houses in Europe then made copies. In 1892 publishers Williams and Norgate published a copy in London, and in 1911 a sheet was added showing the reconstructed sections of the British Isles and the Iberian peninsula missing in the original.
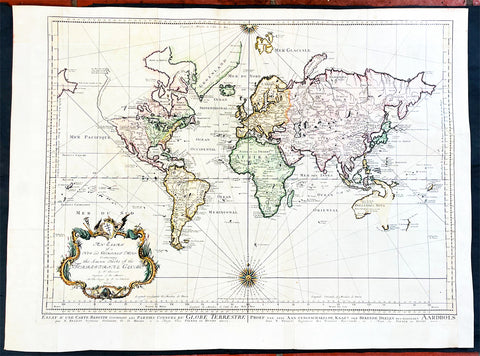
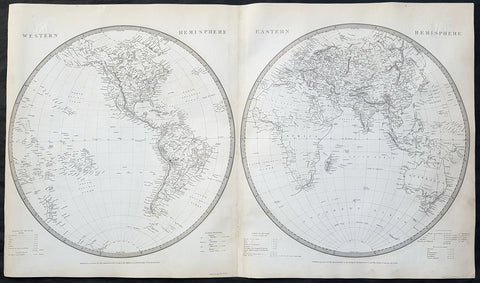
1630-31 Hondius Antique World & Four Continental Maps America Africa Asia & Europe
Antique Map
- Title : Nova Totius Terrarum; America Noviter Delineata; Africae Nova Tabula; Asia recens summa; Europa Exactissime.
- Date : 1630-31
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm) ea
- Condition: (A & A+) Very Good & Fine Condition
- Ref: 43164; 43157; 43158; 43160; 43159
Description:
These 5 original, hand coloured copper plate engraved world and 4 continental maps, engraved by Henricus Hondius between 1630 and 1631 were published in the same 1639 edition of the Hondius/Mercator Atlas.
Henricus Hondius' World and Four Continent Maps are a series of highly detailed and beautifully illustrated and hand coloured maps that represent some of the finest examples of 17th-century cartography & artistry. The world map features ornate illustrations of ships, sea monsters, and mythological creatures, as well as depictions of important cities and landmarks around the globe. The four continent maps - Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas - are similarly detailed and feature intricate illustrations of people, animals, and mythological figures from each region. These maps are notable for their use of the Mercator projection and their accuracy in depicting the size and shape of the continents. Henricus Hondius' maps were highly valued during his lifetime and continue to be prized by collectors and scholars today for their historical significance and artistic beauty.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - Please see background description below
Plate size: - Please see background description below
Margins: - Please see background description below
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see background description below
Plate area: - Please see background description below
Verso: - Please see background description below
Background:
Nova Totius Terrarum: Dated 1630. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margin size. General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15in (545mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Old expert re-enforcement of margins front & verso. 4 small wormholes to margins
Plate area: - Creasing, slight separation of centerfold on bottom section of map
Verso: - Centerfold re-enforced
Overall condition: - VG
America Noviter Delineata: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Bottom margin of centerfold re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Africae Nova Tabula: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Slight separation to bottom of centerfold
Verso: - Bottom margin of centerfold re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Asia recens summa: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Bottom centerfold & left corner margin re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Europa Exactissime: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Bottom margin re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
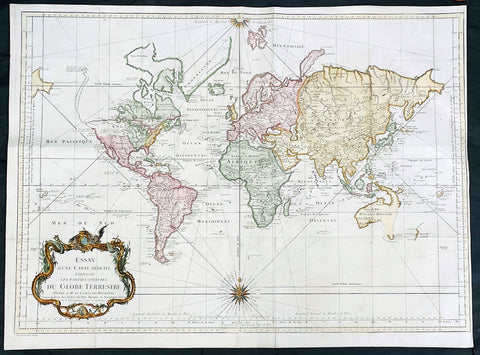
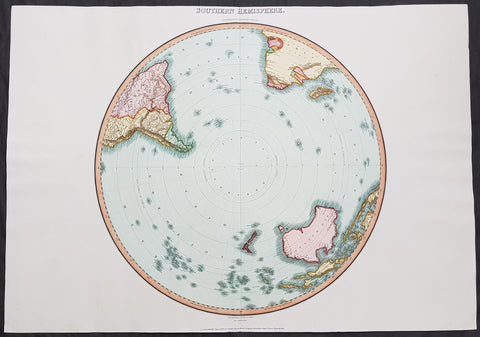
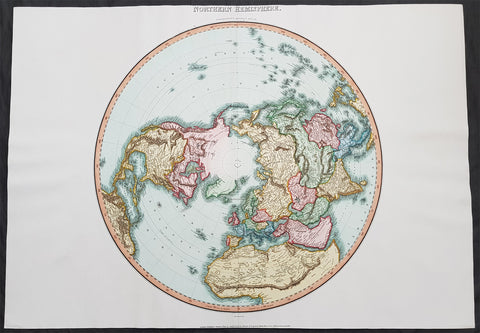
1595 Abraham Ortelius Antique Epitome Atlas with 106 Maps - Rare, Unique & Beautiful
-
Title: Epitome theatri Orteliani...Philippo Gallaeo Arnoldus Cocinx MDXCV
- Ref: 3090
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
-
Size: 8vo
- Date: 1595
Description:
This stunning, original antique pocket Epitome Atlas, Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theatre of the Orb of the World) - with 106 beautifully hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique maps of the entire 16th century world, by Abraham Ortelius, was published in 1595 - dated on the title page, Latin edition - by Philip Galle.
The atlas has been lovingly and professionally restored with fine vellum binding, end papers. Each page has been lovingly cleaned and faithfully re-coloured and tabbed back into the atlas as originally published. Along with the new end papers, the atlas contains the original dated title page, frontispiece, 6 text pages 109 maps, descriptive text and finally three index pages shown to the left.
A unique opportunity to acquire one of the best, if not the best Epitome Atlas, on the market.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later & early coloring
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, pink, blue, black
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Atlas size: - 8vo
Map sizes: - 5 3/4in x 4in (145mm x 100mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: None
Plate area: - Very light ink notations on title and Psalm pages, light age toning on a few pages
Verso: - None
Background: The pocket versions, or Epitome, of Abraham Ortelius folio Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum was published by Philip Galle with text by Pieter Heyns. Between 1577 & 1598 Galle issued 11 editions, of which 10 editions were printed by Christopher Platin , with this lone edition printed by Arnoldus Coninx in 1595,making it an extremely rare & unique item. .
The Dutch edition published by Heyn's son Zacharias in 1596, was a re-issue of of the 1583 edition. In addition to the Dutch, French, Latin & Italian editions an English one was produced. The maps for the English edition, the last from Galles map plates, were printed in Antwerp and shipped to London for publication by John Norton in 1602.
The first two editions, of Epitome, contained sixty-six miniatures and six small folding maps including one of the world dated 1574. They were all rather crudely drawn and engraved by Galle, with narrow decorated borders. From 1583 he gradually introduced a new set of maps, adding quality and quantity replacing the originals until they had grown to 123 by 1598.
Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theatre of the Orb of the World) is considered to be the first true modern atlas. Written by Abraham Ortelius, strongly encouraged by Gillis Hooftman and originally printed on 20 May 1570 in Antwerp, it consisted of a collection of uniform map sheets and supporting text bound to form a book for which copper printing plates were specifically engraved. The Ortelius atlas is sometimes referred to as the summary of sixteenth-century cartography. The publication of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570) is often considered as the official beginning of the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography (approximately 1570s–1670s) (Ref: King; Van Den Broecke; Tooley)
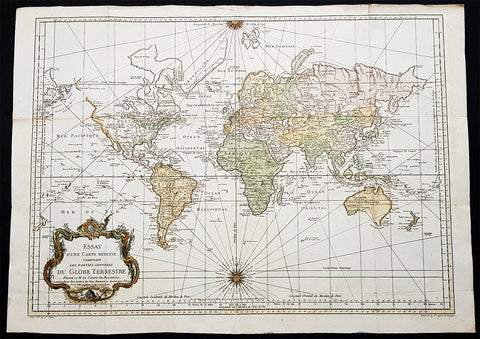
1774, 1777 & 1785 Capt James Cook 3 Atlas Volumes 1st Editions 204 Maps & Prints
- Title : 1. Figure du Banks 2. Premier Voyage De Cook 3. Troisieme Voyage De Cook
- Ref #: 93498, 93499, 93500
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Date : 1774; 1777; 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
A unique and rare opportunity to acquire all three of Captain James Cooks 1st French edition Atlases (4to, Quatro), published to accompany the publication of his 3 voyages of discovery in 1774, 1777 & 1785. The atlases contain a total of 204 large folding, double page and single page maps and prints. It is very rare to find all three atlases complete and available together at the same time.
The contents of all three atlases are in fine condition, with a fresh, heavy impression and clean paper of all maps and prints.
As stated there are 204 maps and prints 51 in the 1st volume, 66 in the second volume and 87 in the second volume. Please view the images above, that include a few images of the 204 maps and prints as well as an itemized list of each volume.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Some scuffing and wear to boards & spines
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Timeline First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Timeline - Second Voyage 1772 - 1775
In July 1772 Resolution, commanded by Captain Cook, and Discovery, commanded by Lieutenant Furneaux, set sail from Britain, via Madiera (Jul-Aug) and Cape Town, South Africa (Oct-Nov), towards the Antarctic in search of the Great Southern Continent.
During January 1773 the ships took on fresh water, charts of the voyage being marked with:
......Here we watered our Ship with Ice the 1st. Time 26S 44W and Here we compleated our Water/26S 20W but became separated in thick fog: Here we parted company…. and The Resolutions Track after we parted Company on the 8 of February 1773......
The ships became the first known to have crossed the Antarctic Circle (17 January 1773). On 9th January Cook wrote:
.......we hoisted out three Boats and took up as much as yielded about 15 Tons of Fresh Water, the Adventure at the same time got about 8 or 9 and all this was done in 5 or 6 hours time; the pieces we took up and which had broke from the Main Island, were very hard and solid, and some of them too large to be handled so that we were obliged to break them with our Ice Azes before they could be taken into the Boats...... Cook, Journals II, 74.)
The ships met again in New Zealand (February-May 1773) and set off to explore the central Pacific, calling at Tahiti (August), where, from the island of Raiatea, they took aboard Omai who returned with the Adventure to England (7 September).
After visiting Amsterdam and Middelburg, two islands that Cook called the Friendly Islands (Tongan group) (October) the ships became separated and never met again. Both ships returned separately to New Zealand. (November) A boats crew from the Adventure were killed by Maori (17 December) and the ship sailed for Britain, arriving July 1774.
Cook on Resolution attempted another search for the Great Southern Continent (November 1773), crossing the Antarctic Circle on 20th December 1773. However, the ice and cold soon forced him to turn north again and he made another search in the central Pacific for the Great Southern Continent. In January 1774 he turned south again, crossing the Antarctic Circle for the second time. Captain Cooks Journal, 2nd January 1774.
Cook sailed north, arriving at Easter Island in March 1774. Cook was too ill to go ashore but a small party explored the southern part of the island. The artist William Hodges painted a group of the large statues of heads (moia) for which the island has become famous.
Cook then sailed to the Marquesas (March); Tahiti (April) and Raiatea (June); past the Cook Islands and Niue, or Savage Islands as Cook called them; Tonga (June); Vatoa, the only Fijian Island visited by Cook (July); New Hebrides (July-August); New Caledonia (September) and Norfolk Island (October); before returning to New Zealand (October 1774).
Not all the peoples of the islands visited by Cook were friendly and when his ship approached Niue the local people would not let his crew ashore. Cook wrote:
.......The Conduct and aspect of these Islanders occasioned my giving it the Name of Savage Island, it lies in the Latitude of 19 degrees 1 Longitude 169 degrees 37 West, is about 11 Leagues in circuit, of a tolerable height and seemingly covered with wood amongst which were some Cocoa-nutt trees......(Cook, Journals II, 435, 22 June 1774.)
En route for New Zealand, Cook sailed west and explored the islands which he called the New Hebrides, now known as Vanuatu, arriving on 17 July 1774. The people were Melanesian, not Polynesian, and spoke different languages and had different customs. Cook recorded:
........The Men go naked, it can hardly be said they cover their Natural parts, the Testicles are quite exposed, but they wrap a piece of cloth or leafe round the yard (nautical slang for the penis) which they tye up to the belly to a cord or bandage which they wear round the waist just under the Short ribs and over the belly and so tight that it was a wonder to us how they could endure it.......(Cook, Journals II, 464, 23 July 1774)
Cook sailed past or visited nearly all the islands in the group, including landfalls at Malekula, Tanna and Erromango. He later moved on to New Caledonia.
Cooks reception by the New Hebrideans was generally hostile. At Erromango during the landing on 4th August 1774 the marines had to open fire when the natives tried to seize the boat and started to fire missiles. Cook wrote:
....…I was very loath to fire upon such a Multitude and resolved to make the chief a lone fall a Victim to his own treachery…happy for many of these poor people not half our Musquets would go of otherwise many more must have fallen.......(Cook, Journals II, 479, 4th August 1774)
Some of Cooks crew were slightly injured but several natives were wounded and their leader killed. Back on the ship Cook had a gun fired to frighten off the islanders and decided to depart.
Cook left New Zealand to return to Britain via the Southern Ocean in November 1774 and arrived in Tierra del Fuego, South America, in December. Cook took on stores and spent the holiday in what he called Christmas Sound. He described the area:......except those little tufts of shrubbery, the whole country was a barren Tack (or Rock) doomed by Nature to everlasting sterility......(Cook, Ms Journal PRO Adm 55/108)
Cook left South America in early January 1775 and set off across the southern Atlantic for Cape Town, South Africa. On the way he tried to confirm the location of a number of islands charted by Alexander Dalrymple on an earlier voyage. On 17 January 1775 Cook arrived at the cold, bleak, glaciated island he called South Georgia and spent 3 days charting it before sailing on.
Cook headed east and in late January came across the South Sandwich Islands that he again charted and then sailed on to Cape Town, arriving in late March 1775. He then headed across the Atlantic via St. Helena and Ascension Island (May), the Azores (July) and landed at Portsmouth on 30th July 1775.
On his return Cook became a national hero. He was presented to the King, made a member of the Royal Society and received its Copley Medal for achievement. Cook was promoted to post-captain of Greenwich Hospital and wrote up his account of the voyage. This did not mean retirement for Cook who went on his third and final voyage the following year.
The second voyage was one of the greatest journeys of all time. During the three years the ships crews had remained healthy and only four of the Resolutions crew had died. Cook disproved the idea of the Great Southern Continent; had become the first recorded explorer to cross the Antarctic Circle; and had charted many Pacific islands for the first time.
Timeline - Third Voyage 1776 - 1780
In 1776 Cook sailed in a repaired Resolution (July) to search for the North West Passage and to return Omai to his home on Huahine in the Society Islands.
He sailed via the Canary Islands and was joined at Cape Town, South Africa, by the Discovery, commanded by Charles Clerke.
The Discovery was the smallest of Cooks ships and was manned by a crew of sixty-nine. The two ships were repaired and restocked with a large number of livestock and set off together for New Zealand ( December).
Cook sailed across the South Indian Ocean and confirmed the location of Desolation Island, later known as Kerguelen Island. Cook wrote of Christmas Harbour where he first anchored on 25th December 1776:
........I found the shore in a manner covered with Penguins and other birds and Seals…so fearless that we killed as ma(n)y as we chose for the sake of their fat or blubber to make Oil for our lamps and other uses… Here I displayd the British flag and named the harbour Christmas harbour as we entered it on that Festival........(Cook, Journals III, i, 29-32)
Cook sailed east, arriving at Van Diemens Land/Tasmania (January 1777) and Queen Charlottes Sound, New Zealand (February). The Maori were wary at first, expecting Cook to take revenge for the killing of members of the Adventures crew in 1773, but instead Cook befriended the leader of the attack.
The ships stayed for nearly two weeks in New Zealand, restocking with wild celery and scurvy grass and trading with the local Maori who set up a small village in Ship Cove. Cook set off around the islands of the south Pacific (February), visiting the Cook Islands (April); Tongan Islands (July); and Tahiti (August-December 1777)
In 1778 Cook visited the Hawaiian islands, or Sandwich Islands as he named them, for the first time. Cook wrote:
........We no sooner landed, that a trade was set on foot for hogs and potatoes, which the people gave us in exchange for nails and pieces of iron formed into some thing like chisels….At sun set I brought every body on board, having got during the day Nine tons of water….about sixty or eighty Pigs, a few Fowls, a quantity of potatoes and a few plantains and Tara roots.......(Cook, Journals III, i. 269 & 272)
In February 1778 Cook sailed from the Hawaiian Islands across the north Pacific to the Oregan coast of North America. He travelled up the coast in bad weather until he found a safe harbour, Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada. There he refitted the ships, explored the area and developed relations with the local people.
Cook described a village there, probably Yoquot:
….their houses or dwellings are situated close to the shore…Some of these buildings are raised on the side of a bank, theses have a flooring consisting of logs supported by post fixed in the ground….before these houses they make a platform about four feet broad…..so allows of a passage along the front of the building: They assend to this passage (along the front of the building) by steps, not unlike some at our landing places in the River Thames........(Cook, Journals III, i, 306)
Cook left Nootka Sound in April 1778 and sailed north along the Alaskan coast looking for inlets that might lead to the Northwest passage but was then forced to turn south. By July he had rounded the Alaskan Peninsula and was able to sail north again, visiting the Chukotskiy Peninsula, Russia, before heading out into the Bering Sea.
Cook described the summer huts, or yarangas, of the Chukchi people as:
.........pretty large, and circular and brought to a point at the top; the framing was of slight poles and bone, covered with the skins of Sea animals…About the habitations were erected several stages ten or twelve feet high, such as we had observed on some part of the American coast, they were built wholly of bones and seemed to be intended to dry skins, fish &ca. upon, out of reach of their dogs........(Cook, Journals III, I, 413)
After entering the Bering Sea on 11th August 1778, Cook crossed the Arctic Circle and went as far north as latitude 70 degrees 41 North before being forced back by the pack ice off Icy Cape, Alaska. On the ice all around the ships were large numbers of walruses. About a dozen of these huge animals were killed to replenish the supplies of fresh meat and to provide oil for the lamps.
Cook had to turn west and worked his way down the Russian coast, eventually heading south and east into Norton Sound, Alaska, in September 1778. He wrote of their very brief encounter with the inhabitants of Norton Sound:
....…a family of the Natives came near to the place where we were taking off wood…I saw no more than a Man, his wife and child…...(Cook, Journals III, I, 438)
After a short period spent searching for the Northwest Passage Cook realised that it was too late in the year to make any progress and so sailed for warmer winter quarters in the Hawaiian Islands, arriving there in December 1778.
After circumnavigating the big island of Hawaii for over a month the ships finally anchored in Kealakekua Bay on 16th January 1779. The Hawaiians in over 1000 canoes came out to welcome them, the arrival of the ships coinciding with celebrations to mark the religious festival of Makahiki to the god Lono. The Hawaiians seem to have treated Cook as a personification of the god and at first relations were good on this second visit. However, relationships became strained and Cook left the island on 4th February 1779.
When Cook left Hawaii his ships ran into gales which broke a mast, forcing him to return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs on 11th February. This time the native people were less friendly and stole the cutter of the Discovery. The next day, the 14th February 1779, Cook went ashore to take the Hawaiian king into custody pending the return of the cutter but a fight developed and Cook, four of his marines and a number of natives were killed. Cooks remains were buried at sea in Kealakekua Bay.
Charles Clerke took over command of the stunned expedition and explored the other Hawaiian islands before sailing north to search for the North-West Passage. The ships called at Kamchatka, Russia, (April-June) where they were welcomed by the governor, Behm, at Bolsheretsk. Behm took news of the expedition and Cooks death overland to St. Petersburg from where it reached Europe and Britain.
Having made another voyage into the Arctic in search of the Northwest Passage (June-July) the ships returned to Kamchatka in August. In November they set off sailing south along the east coast of Japan, between Taiwan and the Phillipines and arrived at Macao, China, in December.
In January 1780 the expeditions left for home, crossing the Indian Ocean, calling at Cape Town (April-May) and arriving back in Stromness, Orkney, in August but not returning to London until October 1780.
News of Cooks death reached Britain in January 1780, ahead of the return of Resolution and Discovery in October 1780. The voyage was written up and published and Cooks life gradually commemorated in articles, books, medals and monuments.
The achievements of the voyage were overshadowed by the deaths of both Cook and his second-in-command, Clerke. The main purpose of the voyage, the discovery of the Northwest Passage, was not realised but large tracts of the Pacific and Arctic coasts of America and Russia were charted.
Early attempts to summarise the life of Cook appeared in the popular press soon after news of his death reached Britain. Articles in journals such as the Westminster Magazine, published in January 1780, included Biographical Anecdotes of Capt. Cook, charting his life from his birth in Marton, North Yorkshire. The first published biography of Cook, Life of Captain James Cook, by Andrew Kippis, appeared a few years later in 1788.
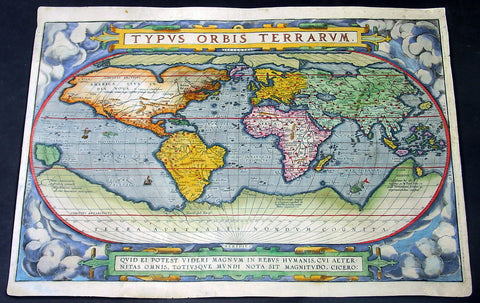
1588 Abraham Ortelius Antique Oval World Map - Rarest Edition, Ort 2:3
- Title : Typus Orbis Terrarum
- Date : 1588
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: Ort1
- Size: 20in x 14 ½in (510mm x 370mm)
This magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved rare antique Oval World map (Ort 2:3) was engraved by Franciscus (Frans) Hogenberg and was published in the 1588 edition of Abraham Ortelius Atlas <i>Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. </i>
To emphasis how rare this map is consider the following. Ortelius published a total of 6950 of these world maps in 3 states (3250 1st state, 500 2nd state & 3200 3rd state) between 1570 and 1612. Today only 411 are known to have survived. Of these surviving 411 only 14 are of the 2nd state (Ort 2) and of these 14 only 4 are Ort 2:3 state, making this one of the rarest Ortelius maps available on the market at any time. Blank verso.
This map is part of my personal collection and has been framed to Museum quality. I will sell the map with the frame, with additional cost TBN if required.
The map was acquired from Marcel P R van den Broecke - author of Ortelius Atlas Maps - in Holland, collector and dealer and is accompanied by Certificate of Authenticity from Marcel van den Broecke.
Ortelius published 3 World maps over the life of his atlas <i>Theatrum Orbis Terrarum</i>, between 1570 & 1612. These 3 maps are referred to as Ort 1, Ort 2 & Ort 3. Over the life of these maps, necessary changes, repairs & updates were made to the plates, these changes are referred to as states. The first map or Ort 1 required 5 changes, Ort 2 required 3 changes and Ort 3 was changed twice.
This map was published in 1588 and is the last state of Ort 2, identified by the changes to the western South American coastline, whilst still retaining the decorative cloud surround as in Ort1. Ort 3 was changed by removing the cloud surrounds replacing them with medallions and strap-work This is a beautiful map with original hand colouring, on sturdy clean paper with original margins.
Below is a concise list of the states of the map <i>Typus Orbis Terrarum</i>
- 1st edition (Ort 1) – States 1.1 through to 1.5.
A total of 3250 maps from this plate were published between 1570 & 1584. Today it is estimated that there are 236 loose copies in circulation of all 5 states.
- 2nd edition (Ort 2) - States 2.1 through to 2.3.
A total of only 500 maps from this plate were published between 1586 & 1588. Today it is estimated that there are 14 loose copies in circulation of all 3 states.
- 3rd edition (Ort 3) – States 3.1 through to 3.2.
A total of 3200 maps from this plate were published between 1589 & 1612. Today it is estimated that there are 161 loose copies in circulation of both states. (Ref: Van Den Broecke; Tooley; Shirley; Rosenthal)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 14 ½in (510mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 19 ½in x 13 1/4in (495mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min ½in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional 11cm restoration to bottom margin, 1cm into image. Light soiling
Plate area: - Small 2cm sq professional restoration below the ST of Australis
Verso: - Map backed on fine archival Japanese paper
Background:
The Ortelius world map is a simplified one-sheet reduction of Mercators large world map which had appeared the year before. Nearly all the legends, textual panels and decorative features of Mercators map have been omitted; between the oval circumference of the map and the outer frame are now clouds and below, a quotation from Cicero. From surviving correspondence, it is known that Mercator generously encouraged Ortelius to make use of his published research; he also provided him with coordinates of places in America and other newly discovered regions of the world. In the first edition South America retains the unusual bulged south-west coast as drawn by Mercator. There is also a prudent comment adjacent to New Guinea querying whether this large island is part of the southern continent or not.
The original plate, like a number of others in the Atlas, were signed by the engraver Franciscus (Frans) Hogenberg and was used for the first sixteen editions of the Theatrum.
In nearly all places there is text on the reverse of the map in the language indicated but a few copies are known which lack reverse text. Between 1575 and 1579 the plate became cracked along the lower left hand corner. The crack was roughly mended and the whole border of the clouds substantially reworked; editions from 1579 to 1584 contain this revised state 2 of plate 1. Ortelius subsequently produced two further world maps, each slightly improved geographically.
Several of these states co-existed; for instance although plate 3 carries the date 1587, it does not seem to have been issued until 1592. Only one example has been sighted of the first state plate 2 of 1586. State 3 of plate 2 is also uncommon but it re-appears in the British Librarys copy of the Dutch 1598 edition of the Theatrum which, as noted by Koeman, was often made up of earlier stock sheets.
Ortelius map was copied widely, and derivatives were later used to illustrate works by Voisin, Broughton, Maffei, Bell-Forest, Petri, Hakluyt and others.
Cartographical sources were Gerard Mercator 1569 & Gastaldi 1561 world maps and Diego Gutierrez portolan map of the Atlantic.
Next to the list at the bottom of the text, Ortelius mentions in his Catalogues Auctorum the world maps by Peter ab Aggere from Mechelen, Sebastian Cabotus from Venice, Laurentius Fries from Antwerp, Jacobus Gastaldi, Gemma Frisius from Antwerp, Guicciardinus from Antwerp, Doco ab Hemminga Frisius, and Orontius Finæus from Paris.
Background of the Atlas <i>Theatrum Orbis Terrarum</i>
For the first time, in 1570, all the elements of the modern Atlas were brought to publication in Abraham Ortelius Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. This substantial undertaking assembled fifty-three of the best available maps of the world by the most renowned and up to date geographers.
Unlike earlier compositions, such as the Italian composite or Lafreri Atlases, each of Ortelius maps was engraved specifically for his Atlas according to uniform format. Through its launching, pre-eminence in map publishing was transferred from Italy to the Netherlands, leading to over a hundred years of Dutch supremacy in all facts of cartographical production.
There were a total of 7300 copies of Theatrum published between 1570 - 1612 from 31 editions.
1774 Malachy Postlethwayt Antique 2 Volume Atlas 7 Large Cont Maps North America
Antique Map
- Title : The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commercewith large Improvements Adapting the Same to the Present State of British Affairs in America since the last Treaty of Peace made in the year 1763....MDCCLXXIV
- Ref #: 93529
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: Large Folio
- Date : 1774
Description:
These very large, heavy leather backed original antique dictionary & atlas volumes of early Global Economic Commerce by Malachy Postlethwayt was published in 1774.
The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce in 2 volumes is the 4th edition published in London by W. Strahan, J and F. Rivington, et al., in 1774. The first edition was published between 1751 & 1755. Titles in red and black with engraved vignettes, engraved allegorical frontispiece to volume 1 (offset onto title) and contain 24 engraved folding maps sheets that when assembled make 7 complete very large maps. Occasional minor spotting, contemporary diced calf, re-backed preserving original contrasting morocco labels, extremities repaired.
The seven maps once assembled, to the left, are as follows with titles, cartographers dates and dimensions;:
1. A Correct Map of Europe by Thomas Kitchin after D Anville, 80cm x 70cm, 1774
2. Africa Performed by the Sr D Anville Samuel Bolton after D Anville, 103cm x 94cm, 1774
3. A New and Correct Map of the Coast of Africa, so called Slave Coast Map, Richard Seale 48cm x 38cm, 1774
4. North America Performed under the Patronage of Louis Duke of Orleans Richard Seale after D Anville, 88cm x 86cm, 1774
5. South America Thomas Kitchin after D Anville, 124cm x 75cm, 1774
6. First Part of Asia RW Seale, after D Anville, 83cm x 77cm, 1755
7. Second Part of Asia R W Seale, after D Anville, 96cm x 70cm, 1755
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - Please see above
Plate size: - Please see above
Margins: - Please see above
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see above
Plate area: - Please see above
Verso: - Please see above
Background:
Postlethwayts most noted work, The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, appeared after he had devoted twenty years to its preparation. The first edition was published in London in instalments between 1751 and 1755, and then in subsequent editions as a two-volume set in 1757, 1766, and 1774. This dictionary was a translation, with large additions and improvements, from Jacques Savary des Bruslons Dictionnaire universal de commerce (1723–1730). Postlethwayts dictionary was a huge storehouse of economic facts, laws and theory and his departures from the French version reflected his greater interest in political problems; his more intense economic nationalism; and his exuberant belief in the economic usefulness of experimental philosophy
In the 1757 edition of the Universal Dictionary, Postlethwayt outlined his vision for the establishment of a British mercantile college to benefit those who intended to work as merchants, or in gathering public revenue, or in merchandizing. He proposed that theoretical training for business should occur in formal academies and involve the study of mercantile computations, foreign exchanges and the intrinsic value of foreign coins, double-entry accounting, languages, geography, and public revenues and related laws. Postlethwayts ideas appear to have been influential in developing the statutes and procedures of the Portuguese School of Commerce, established in Lisbon in 1759.
It is documented that Thomas Jefferson gave a copy of this dictonary to his son in law, Thomas Mann Randolph, and as a prolific reader we must assumed also read by Jefferson.
Postlethwayt, Malachy 1707-1767
Malachy Postlethwayt was a prolific English writer and publicist on matters of mercantilist economics in the 1740s and 1750s. Little is known about his upbringing or formal education, although he is believed to be the brother of James Postlethwayt (d. 1761), a writer on finance and demography. Malachy Postlethwayt was elected a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London in 1734. His writings are claimed by Edgar Johnson to have exerted a good deal of influence on the trend of British economic thought.
Postlethwayt was alleged to be propagandist for the mercantilist endeavours of the Royal Africa Company, whose interests were well served by his publications The African Trade, the Great Pillar and Supporter of the British Plantation Trade in North America (1745) and The National and Private Advantages of the African Trade Considered (1746). These works supported a strategy of British commercial and manufacturing expansion through trade with Africa and the colonies, and promoted the importance of slavery for British commerce and industry.
Postlethwayts most noted work, The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, appeared after he had devoted twenty years to its preparation. The first edition was published in London in instalments between 1751 and 1755, and then in subsequent editions as a two-volume set in 1757, 1766, and 1774. This dictionary was a translation, with large additions and improvements, from Jacques Savary des Bruslons Dictionnaire universal de commerce (1723–1730). Postlethwayts dictionary was a huge storehouse of economic facts, laws and theory and his departures from the French version reflected his greater interest in political problems; his more intense economic nationalism; and his exuberant belief in the economic usefulness of experimental philosophy
In the 1757 edition of the Universal Dictionary, Postlethwayt outlined his vision for the establishment of a British mercantile college to benefit those who intended to work as merchants, or in gathering public revenue, or in merchandizing. He proposed that theoretical training for business should occur in formal academies and involve the study of mercantile computations, foreign exchanges and the intrinsic value of foreign coins, double-entry accounting, languages, geography, and public revenues and related laws. Postlethwayts ideas appear to have been influential in developing the statutes and procedures of the Portuguese School of Commerce, established in Lisbon in 1759.
Postlethwayts most important contribution to economic literature is regarded by many to be Britains Commercial Interest Explained and Improved (1757), in which he outlines his concept of physical commerce and the policies England should follow to attain commercial parity with foreign rivals.
Whether Postlethwayts writings were his original thoughts and words is a matter for conjecture. His Universal Dictionary included ideas taken from fifty other past or contemporary writers and that it had scattered throughout it practically all of Richard Cantillons Essai sur la nature du commerce en général (Essay on the Nature of Commerce in General, 1755). Although Postlethwayt was alleged widely to be a plagiarist, this accusation is believed to be exaggerated.
Postlethwayt died suddenly on September 13, 1767, and was buried in the Old Street Churchyard, Clerkenwell, in London.
Postlethwayt also published:
- The African Trade the great Pillar and Support of the British Plantation Trade in America, &c., 1745.
- The Natural and Private Advantages of the African Trade considered, &c., 1746.
- Britains Commercial Interest Explained, Vol. I of his Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, 1747.[5]
- Considerations on the making of Bar Iron with Pitt or Sea Coal Fire, &c. In a Letter to a Member of the House of Commons, London, 1747.
- Considerations on the Revival of the Royal-British Assiento, between his Catholic Majesty and the … South-Sea Company. With an … attempt to unite the African-Trade to that of the South-Sea Company, by Act of Parliament, London, 1749.
- The Merchants Public Counting House, or New Mercantile Institution, &c., London, 1750.
- A Short State of the Progress of the French Trade and Navigation, &c., London, 1756.
- Great Britains True System. … To which is prefixed an Introduction relative to the Forming a New Plan of British Politicks with respect to our Foreign Affairs, &c., London, 1757.
- Britains Commercial Interest explained and improved, in a Series of Dissertations on several important Branches of her Trade and Police. … Also … the Advantages which would accrue … from an Union with Ireland, 2 vols., London, 1757; 2nd edit., With … a clear View of the State of our Plantations in America, &c., London, 1759.
- In Honour to the Administration. The importance of the African Expedition considered, &c., London, 1758
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
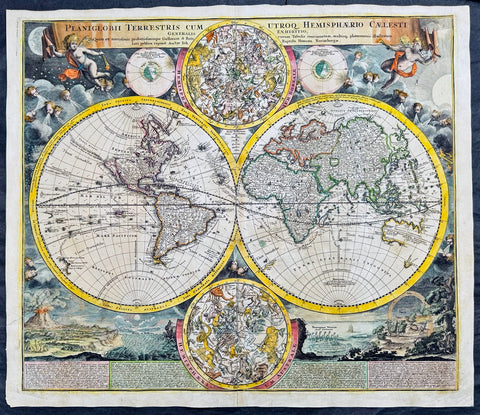
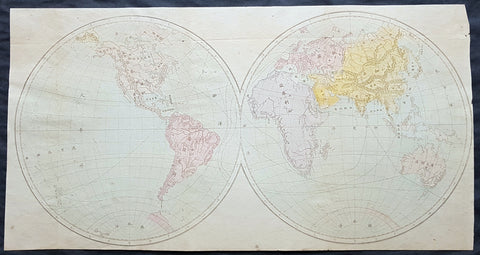
1707 Homann Rare Ist Edition Twin Hemisphere World Antique Map, California Isle.
Antique Map
- Title : Planiglobii Terrestris Cum Utroq. Hemisphaerio Caelesti Generalis Exhibitio.
- Date : 1707
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 61006
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original scarce first edition copper plate engraved antique twin hemisphere world map by Johann Baptist Homann was engraved in 1707 and published in Homanns 1710 edition of Neuer Atlas.
Later editions of the map is commonly misidentified as first editions. In later editions the words Cum Priviligo (Imperial privilege or permission) are engraved in the title, this privilege was later awarded to the Homanns and included in all future maps. In later editions California is shown as a peninsular and not an Island as shown in this map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/4in x 19 1/4in (515mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Professional paper rejoin left margin 2in into image, no loss. Light age toning
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
The map evokes the Dutch maps of the previous century, featuring an insular California and a depiction of Australia and the South Pacific that resembles that of Abel Tasman. Homann nonetheless incorporated a significant detail from the state-of-the-art maps of the Parisian geographer Guillaume De l'Isle, and the English polymath Edmund Halley. The map is a rich compendium of explorers' routes, including Magellan, Tasman, Gaetani, and Chaumont, as well as the extremely current voyages of Dampier (whose discovery of Nova Britannia near New Guinea is shown with a date of 1700). Above and below the cruxes of the main hemispheres are a pair of celestial hemispheres. At the bottom is a beautifully engraved panorama illustrating volcanoes, earthquakes, the tides, marine vortices, rain, and rainbows. These themes are significant in that they are neither mythological nor allegorical: they are plainly discussed natural phenomena. The map, then, is a visual representation of a shift to a more modern, scientific approach to the study of the world that would be typical of the 18th century.
Homann describes his sources as 'the latest and most approved maps of the French and the Dutch'. The bulk of Asia, Africa, and Europe appear to derive from the c. 1700 Peter Schenk Haemisphaeriorum Tabula Carthesiana, while the labeling scheme shows a strong similarity to the c. 1700 Danckerts De Werelt Caart. The primary French source is certainly Guillaume de l'Isle's 1700 Mappe-Monde. The explorers' tracks, the illustration of the Sargasso Sea, and an astonishing (and erroneous) sighting of Antarctica all derive from De l'Isle. Likewise with the treatment of the Pacific Northwest coast and Asiatic northeast, including the channel separating Terra Iesso from the mainland. Otherwise, the general models of Asia, Africa, and South America closely follow the c. 1700 Schenk.
The mapping of North America, here, is very different from either the Schenk or the 1700 De l'Isle. Although Homann retained California as an Island, the map was quite up to date. It presents a largely correct delineation of the Great Lakes and the Mississippi. The northwest part of Canada and the course of the Mississippi reveal the likely source: De l'Isle's 1703 Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France (including the Baron Lahontan's spurious geography) and De l'Isle's Carte du Mexique et de la Floride. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
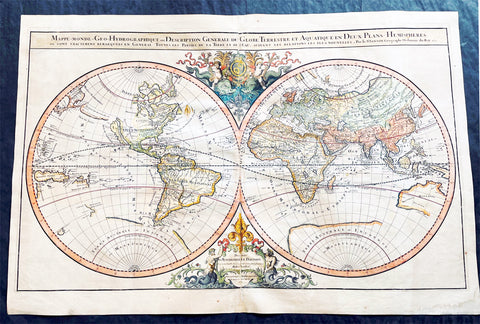
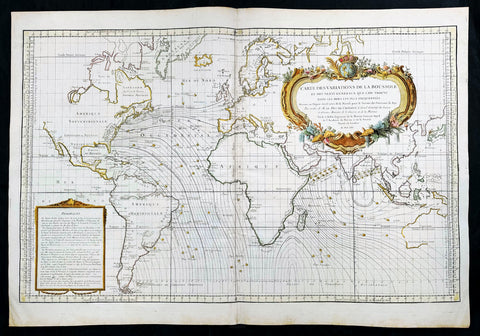
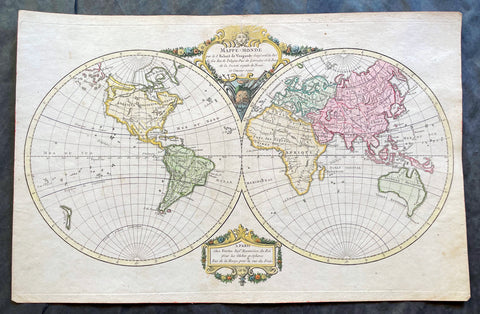
1691 Alexis Hubert Jaillot Large Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map, California Island
Antique Map
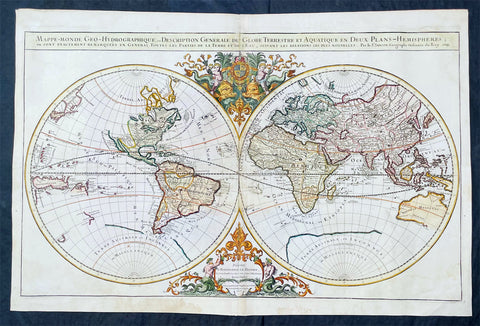
- Title : Mappe-monde Geo-Hydrographique ou Description Generale du Globe Terrestre et Aquatique en Deux-Plans-Hemipsheres ou son Exactement Remarquees en General Toutes les Parties de la Terre et de L Eau, suivant les Relations les plus Nouvelles, par le S. Sanson Geographe Ordinaire du Roy 1691
- Ref #: 93406
- Size: 37in x 24 1/2in (940mm x 620mm)
- Date : 1691
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique Twin Hemisphere World map by Alexis Hubert Jaillot - after Nicolas sanson - was engraved in 1691 - dated - and was published by Jaillot in his large Atlas Nouveau.
There were 4 plates engraved for this map between 1674 & 1705. This map is from the third plate, first engraved in 1691.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 37in x 24 1/2in (940mm x 620mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 23in (887mm x 541mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, light staining in bottom right margin
Plate area: - Age toning, uplift along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning, light staining on verso not affecting the image
Background:
As was common at the time of publication California is depicted as an island. The idea of an insular California first appeared as a work of fiction in Garci Rodriguez de Montalvos c. 1510 romance Las Sergas de Esplandian, where he writes Know, that on the right hand of the Indies there is an island called California very close to the side of the Terrestrial Paradise; and it is peopled by black women, without any man among them, for they live in the manner of Amazons. Baja California was subsequently discovered in 1533 by Fortun Ximenez, who had been sent to the area by Hernan Cortes. When Cortez himself traveled to Baja, he must have had Montalvos novel in mind, for he immediately claimed the Island of California for the King. By the late 16th and early 17th century ample evidence had been amassed, by explorations of the region by Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarcon and others, that California was in fact a Peninsula and not an island. However, by this time other factors were in play. Francis Drake had sailed north and claimed New Albion near modern day Washington or Vancouver for England. The Spanish thus needed to promote Cortes claim on the Island of California to preempt English claims on the western coast of North America. The significant influence of the Spanish crown on European cartographers caused a major resurgence of the Insular California theory, of which Sanson - hence Jaillot - was a primary proponent, in the mid to late 17th century. Shortly after this map was published Eusebio Kino, a Jesuit missionary, traveled overland from Mexico to California, proving conclusively the peninsularity of California. But the myth was upheld in many maps until as late as the mid 18th century.
Traveling northwest, away from the mainland, is the land of Terre de Jesso or Je Co. or Terre de la Compagnie. Though Yesso or Jesso is a name usually associated with Hokkaido (which here is drawn as part of mainland Asia), this land mass is more commonly called Gama or Gamaland. Gama was supposedly discovered in the 17th century by a mysterious figure known as Jean de Gama. Various subsequent navigators claim to have seen this land and it appeared in numerous maps well into the late 18th century. At times it was associated with Hokkaido, in Japan, and at other times with the mainland of North America. On this map it has the resemblance to Gerhard Mullers peninsula which emerged in the late 18th century. Based on numerous sightings but no significant exploration of the Aleutian Islands, Muller postulated that the archipelago was in fact a single land mass. This he mapped extending from the North American mainland towards Asia much as the Terre de Compagnie does on this map. It is not inconceivable that navigators sailing in the northern seas from Asia could have made this same error in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Moving east of California into the North American mainland are the Spanish colony of New Mexico. Santa Fe, its capital, had been founded in 1610 and here it is situated far to the north of its actual location, on the Colorado (Rio Norte) rather than the Rio Grande or Santa Fe River. It also appears near a mysterious lake named Apache. The Apache Lake is drawn as the source of the Rio Norte or Colorado River. Though the origins of this lake are somewhat mysterious, they may be associated with Native American reports of the Great Salt Lake or another lake in the region brought back by the Onate and Coronado expeditions.
In the eastern part of New Mexico territory is the land of Quivira. Quivira, along with Cibola, was one of the Seven Cities of Gold of Spanish folklore. The story beings in 1150 when Merida, Spain, was conquered by the Moors from North Africa. The citys seven bishops fled the city taking with them much of the cities riches. Legend told that they each founded a great city in a far away unknown land. With the discovery of the New World and the fabulous riches plundered by Cortez and Pizarro, the Seven Cities became associated with New World legends. Coronado, hearing tales of the rich Aztec homeland of Azatlan somewhere to the north believed he was hunting for Quivira in what is today the American southwest. It was subsequently mapped and sought, though like most kingdoms of gold never found, for some 300 years before disappearing from maps in the early 19th century.
To the north Sanson maps is a barely recognizable Hudson Bay with several openings to the west. Beyond the waters of Hudson Bay and north of Insular California, Sanson leaves the largely unknown land blank, leaving open the hope of a Northwest Passage. Just to the south of the Hudson Bay we see a very early mapping of the Great Lakes. Ontario, Erie, and Huron are recognizable, but both Lake Michigan and Lake Superior open speculatively to the west, again suggesting the possibility of navigable water route to the Pacific.
On the Eastern coast of North America, Sanson recognizes French Claims to Canada, English claims to the Massachusetts Bay Colony, Dutch claims in New Amsterdam (New York), and Swedish claims in New Jersey.
In Spanish Florida, which extends north to include most of the American Southeast, Lake Apalache or the Great Freshwater Lake of the American Southeast is noted. This lake, first mapped by De Bry and Le Moyne in the mid 16th century, is a mis-mapping of Floridas Lake George. While De Bry correctly mapped the lake as part of the River May or St. Johns River, cartographers in Europe erroneously associated it with the Savannah River, which instead of Flowing south from the Atlantic (Like the May), flowed almost directly from the Northwest. Lake Apalache was subsequently relocated somewhere in Carolina or Georgia, where Sanson maps it and where it would remain for several hundred years.
Southward is the well mapped Caribbean and once again the map is rife with cartographic speculation. While the South American coastlands are well mapped, the interior is largely unknown. Explorers throughout the late 16th and early 17th century, enthralled by Pizarros conquests in Peru and tales of other gold rich empires in the interior, were actively seeking El Dorado.
Most Europeans believe that the most likely site of the El Dorado legend was the mythical city of Manoa located by Sanson on the shores of the Lake Parima, near modern day Guyana, Venezuela, or northern Brazil. Manoa was first identified by Sr. Walter Raleigh in 1595. Raleigh did not visit the city of Manoa (which he also believes is El Dorado) himself due to the onset of the rainy season, however he describes the city, based on indigenous accounts, as resting on a salt lake over 200 leagues wide. This lake, though no longer mapped as such, does have some basis in fact. Parts of the Amazon were, at the time dominated by a large and powerful Indigenous trading nation known as the Manoa. The Manoa traded the length and breadth of the Amazon. The onset of the rainy season inundated the great savannahs of the Rupununi, Takutu, and Rio Branco or Parima rives. This inundation briefly connected the Amazon and Orinoco river systems, opening an annual and well used trade route for the Manoans. The Manoans who traded with the Incans in the western Amazon, had access to gold mines on the western slopes of the Andes, and so, when Raleigh saw gold rich Indian traders arriving in Guyana, he made the natural assumption for a gold hungry European in search of El Dorado. When he asked the Orinocans where the traders were from, they could only answer, Manoa. Thus did Lake Parime or Parima and the city of Manoa begin to appear on maps in the early 17th century. The would continue to be mapped in this area until about 1800.
Further south Sanson maps a large and prominent Laguna de Xarayes as the northern terminus of the Paraguay River. The Xarayes, a corruption of Xaraiés meaning Masters of the River, were an indigenous people occupying what are today parts of Brazils Matte Grosso and the Pantanal. When Spanish and Portuguese explorers first navigated up the Paraguay River, as always in search of El Dorado, they encountered the vast Pantanal flood plain at the height of its annual inundation. Understandably misinterpreting the flood plain as a gigantic inland sea, they named it after the local inhabitants, the Xaraies. The Laguna de los Xarayes almost immediately began to appear on early maps of the region and, at the same time, almost immediately took on a legendary aspect. The Lac or Laguna Xarayes was often considered to be a gateway to the Amazon and the Kingdom of El Dorado.
Across the the Atlantic is the well mapped coast of continental Africa, much is unknown of the interior and like South America much speculation and myth abounds. With the Nile, Sanson followed the Ptolemaic two lakes at the base of the Montes de Lune theory. Though Sanson does map both lakes, naming the western lake Zaire, he does not specifically name the Mountains of the Moon (though they are sketched in).
Just south of Sansons Lake Zaire, is the Kingdom of Monomatapa. This region of Africa held a particular fascination for Europeans since the Portuguese first encountered it in the 16th century. At the time, this area was a vast empire called Mutapa or Monomotapa that maintained an active trading network with faraway partners in India and Asia. As the Portuguese presence in the area increased in the 17th century, the Europeans began to note that Monomatapa was particularly rich in gold. They were also impressed with the numerous well crafted stone structures, including the mysterious nearby ruins of Great Zimbabwe. This combination led many Europeans to believe that King Solomons Mines, a sort of African El Dorado, must be hidden in this region. Monomotapa did in fact have rich gold mines in the 16th and 17th centuries, but most have these had been exhausted by the 1700s.
In Asia, Sanson offers us a fairly accurate mapping of Asia Minor, Persia and India. The Capsian Sea is corrected to a north-south axis though is a bit lumpy in form. He names numerous Silk Route cities through Central Asia including Samarkand, Tashkirgit, Bukhara, and Kashgar. Far to the north he associates Mongolia and Siberia with the Biblical lands of Gog and Magog.
Sanson maps, but does not name, the apocryphal Lake of Chiamay roughly in what is today Assam, India. Early cartographers thought that such a lake must exist as the source of four important Southeast Asian river systems including the Irrawaddy, the Dharla, the Chao Phraya, and the Brahmaputra. This lake began to appear in maps of this region as early as the 16th century and persisted well into the mid 18th century. Its origins are unknown but may originate in a lost 16th century geography prepared by the Portuguese scholar Jao de Barros. It was also heavily discussed in the journals of Sven Hedin, who believed it to be associated with Indian mythology that a sacred lake linked several holy subcontinent river systems. There are even records that the King of Siam led an invasionary force to take control of the lake in the 16th century. Nonetheless, the theory of Lake Chimmay was ultimately disproved and it disappeared from maps entirely by the 1760s.
Further east still the Korean peninsula unnaturally narrow. Just offshore the Japanese Islands emerge only to disappear and reappear on the opposite side of the map. The form of the islands approximates accuracy and Edo or Tokyo Bay is clearly recognizable. Several Japanese cities, including Yendo (Edo or Tokyo) are noted. Hokkaido is attached to the continent and the Japanese Kuril Islands extend eastward to meet up the aforementioned Gama Land or Terre de la Compagnie.
To the south Australia itself appears as New Holland. Much of the northern and western shores, including the Gulf of Carpentaria, have been mapped but the eastern shores remain unexplored and the interior entirely unknown. Tasmania, labeled Terre de Diemens appears according to its discovery and mapping by Able Tazman in 1642. A little further south and east is an extremely embryonic New Zealand. There is no trace of the a two island layout or, for that matter, a eastern shoreline. Also in evidence is the mysterious Terre de Quir a great landmass supposedly discovered by the 16th century Spanish navigator and religious zealot Pedro Fernandez de Quiros. Quiros set sail in search of the speculative southern continent and may in fact have discovered several important South Seas islands, however, he stopped just shy of glory and turned around shortly before sighting New Zealand. Even so, Quiros was a voracious self promoter and descriptions of his findings were circulated throughout Europe. Terre de Quir or Terre de Quiros appears on various maps of the region until put to rest by the 18th century explorations of Captain Cook.
Massing at the base of the map is the speculative southern continent or Terre Australe. Long before the discovery of Antarctica, the southern continent, supposedly capping the South Pole, was speculated upon by European geographers in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was thought that the globe was a place of balances and thus geographers presumed the bulk of Eurasia must be counterbalanced by a similar landmass in the Southern Hemisphere, just as, they argued, the Americas counterbalanced Africa and Europe. Many explorers in the 16th and 17th centuries sought the Great Southern continent, including Quiros, Drake, and Cook, but Antarctica itself was not truly discovered until Edward Bransfield and William Smith sighted the Antarctic Peninsula in 1820. All in all a magnificent and fascinating map of the world. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
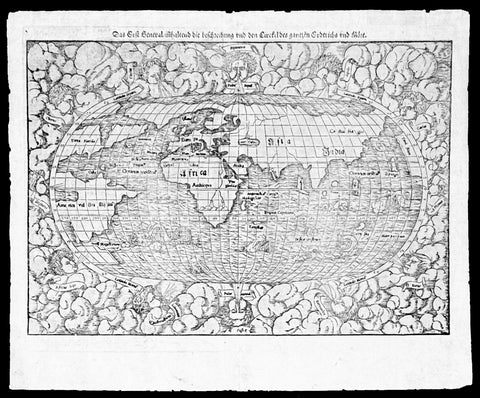
1550 Munster Rare Antique World Map - early depiction of America, Post Columbus
Antique Map
- Title : Das Erst General Inhaltend die Beschreibung und den Cirkel des Gantzen Erdtriche und
- Ref #: 35671
- Size: 16 1/2in x 12 3/4in (415mm x 315mm)
- Date : 1550
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This wood-block engraved original antique oval World Map was engraved by David Kandel, initials engraved bottom left "DK" and was published in the 1550 edition of Cosmographia by Sebastian Munster.
One of the most recognizable maps of the 16th century considered the first map to identify the Pacific Ocean, as here, 'Mare Pacificum.' This is the world of the educated 16th century European, divided into Asia, Europe, India, Africa and America. The southern latitudes are inhabited by a variety of sea monsters and sailing ships.
One of the best examples I have seen of this map for sometime, nice heavy impression on clean sturdy paper with original margins.
The American continent is barely recognizable, only a scant 58 years after European discovery by Christopher Columbus. North America is defined as Terra Florida showing an enormous inlet extending towards the eastern seaboard in the vicinity of modern day North Carolina named Verrazano's Sea. Apparently Verrazano, coasting the Outer Banks, observed the Pamlico Sound and assumed that beyond the narrow coastal banks, an open sea gave direct access to the pacific - wishful thinking at best. Verrazano's Sea appears so dramatically on few maps, but persisted in lesser forms for nearly a century.
South America with tentacle like protrusions in all directions, is largely amorphous, but the Rio de la Plata and the Strait of Magellan are clear. Tierra del Fuego is enormous, with no mention of greater Terra Australias, an interesting omission by Munster.
Europe is vaguely recognizable and connected, via an arctic peninsula, to Greenland and North America.
Asia/Pacific extends eastward far enough to reappear just north of America. Ceylon is not present, but a landmass bearing roughly the shape and position of Sumatra is identified as Tapobrana (a term more commonly associated with Ceylon). Japan appears as Zipangri.
Unlike many other world maps of the time, Munster has left out the concept of a 'Terra Australis Incognita' altogether choosing to show ocean instead.
Africa follows the Ptolemaic model with the Nile finding its source in a mountain range and two associated lakes.
The whole is surrounded by twelve named and prominent wind heads - one for each direction.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 12 1/2in (400mm x 310mm)
Plate size: - 15 3/4in x 12 1/2in (400mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small knicks to margin edges
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: This wood-cut engraved World map was prepared for the 1550 edition of Sebastian Münster's Cosmographia to replace the earlier World map by Sebastian Munster which had appeared in the editions of the Geographia and Cosmographia from 1540 onwards. The publisher, from 1552, was Heinrich Petri, Münster's son-in-law.
This "new world" map is on an oval projection, similar in many respects to the previous Munster world map, but with the woodcutter's initials "DK" added, identified as those of the engraver David Kandel, in the lower left-hand corner.
The titles of the wind-heads are now in banners and the east and west winds, unlike the 1540 version, do not protrude inside the oval circumference. North America still retains its unusual shape almost bisected by water but the earlier note indicating a route to the Moluccas has been omitted...."
The map was first issued in the 1550 edition of Cosmographia, and appeared in all subsequent editions through to 1578, with the title varying according to the language of the edition. On the verso the wood block is the title and text, in Latin.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographia appeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
1719 Alexis Jaillot Large Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map Scarce Final Edition
Antique Map
- Title : Mappe-monde Geo-Hydrographique ou Description Generale du Globe Terrestre et Aquatique en Deux-Plans-Hemipsheres ou son Exactement Remarquees en General Toutes les Parties de la Terre et de L Eau, suivant les Relations les plus Nouvelles, par le S. Sanson Geographe Ordinaire du Roy 1719....(1706)
- Date : 1719
- Size: 36 3/4in x 24 1/2in (930mm x 620mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35648
Description:
This very large original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique Twin Hemisphere World map by Alexis Hubert Jaillot - after Nicolas Sanson - was engraved in 1719 - dated - and was published in the last edition of Alex Jaillot's large Elephant Atlas Nouveau.
This map is from the first plate (of 4) published by Jaillot containing the signature of the engraver Louis Cordier. There were at least 9 states of this first plate in 1674, 1679, 1681, 1684, 1691, 1696, 1700, 1706 & 1719. There was little change in these plate with the exception of the 1706 & 1719 editions which incorporated much of the new information from North America, Asia, Africa and the Pacific.
This last 1719 edition had a limited publication and is therefore scarce.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36 3/4in x 24 1/2in (930mm x 620mm)
Plate size: - 35 1/2in x 22in (887mm x 541mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light wear along centerfold, light staining adjacent to middle of centerfold
Verso: - Staining on verso not affecting the image.
Background:
As was common at the time of publication California is depicted as an island. The idea of an insular California first appeared as a work of fiction in Garci Rodriguez de Montalvos c. 1510 romance Las Sergas de Esplandian, where he writes Know, that on the right hand of the Indies there is an island called California very close to the side of the Terrestrial Paradise; and it is peopled by black women, without any man among them, for they live in the manner of Amazons. Baja California was subsequently discovered in 1533 by Fortun Ximenez, who had been sent to the area by Hernan Cortes. When Cortez himself traveled to Baja, he must have had Montalvos novel in mind, for he immediately claimed the Island of California for the King. By the late 16th and early 17th century ample evidence had been amassed, by explorations of the region by Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarcon and others, that California was in fact a Peninsula and not an island. However, by this time other factors were in play. Francis Drake had sailed north and claimed New Albion near modern day Washington or Vancouver for England. The Spanish thus needed to promote Cortes claim on the Island of California to preempt English claims on the western coast of North America. The significant influence of the Spanish crown on European cartographers caused a major resurgence of the Insular California theory, of which Sanson - hence Jaillot - was a primary proponent, in the mid to late 17th century. Shortly after this map was published Eusebio Kino, a Jesuit missionary, traveled overland from Mexico to California, proving conclusively the peninsularity of California. But the myth was upheld in many maps until as late as the mid 18th century.
Traveling northwest, away from the mainland, is the land of Terre de Jesso or Je Co. or Terre de la Compagnie. Though Yesso or Jesso is a name usually associated with Hokkaido (which here is drawn as part of mainland Asia), this land mass is more commonly called Gama or Gamaland. Gama was supposedly discovered in the 17th century by a mysterious figure known as Jean de Gama. Various subsequent navigators claim to have seen this land and it appeared in numerous maps well into the late 18th century. At times it was associated with Hokkaido, in Japan, and at other times with the mainland of North America. On this map it has the resemblance to Gerhard Mullers peninsula which emerged in the late 18th century. Based on numerous sightings but no significant exploration of the Aleutian Islands, Muller postulated that the archipelago was in fact a single land mass. This he mapped extending from the North American mainland towards Asia much as the Terre de Compagnie does on this map. It is not inconceivable that navigators sailing in the northern seas from Asia could have made this same error in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Moving east of California into the North American mainland are the Spanish colony of New Mexico. Santa Fe, its capital, had been founded in 1610 and here it is situated far to the north of its actual location, on the Colorado (Rio Norte) rather than the Rio Grande or Santa Fe River. It also appears near a mysterious lake named Apache. The Apache Lake is drawn as the source of the Rio Norte or Colorado River. Though the origins of this lake are somewhat mysterious, they may be associated with Native American reports of the Great Salt Lake or another lake in the region brought back by the Onate and Coronado expeditions.
In the eastern part of New Mexico territory is the land of Quivira. Quivira, along with Cibola, was one of the Seven Cities of Gold of Spanish folklore. The story beings in 1150 when Merida, Spain, was conquered by the Moors from North Africa. The citys seven bishops fled the city taking with them much of the cities riches. Legend told that they each founded a great city in a far away unknown land. With the discovery of the New World and the fabulous riches plundered by Cortez and Pizarro, the Seven Cities became associated with New World legends. Coronado, hearing tales of the rich Aztec homeland of Azatlan somewhere to the north believed he was hunting for Quivira in what is today the American southwest. It was subsequently mapped and sought, though like most kingdoms of gold never found, for some 300 years before disappearing from maps in the early 19th century.
To the north Sanson maps is a barely recognizable Hudson Bay with several openings to the west. Beyond the waters of Hudson Bay and north of Insular California, Sanson leaves the largely unknown land blank, leaving open the hope of a Northwest Passage. Just to the south of the Hudson Bay we see a very early mapping of the Great Lakes. Ontario, Erie, and Huron are recognizable, but both Lake Michigan and Lake Superior open speculatively to the west, again suggesting the possibility of navigable water route to the Pacific.
On the Eastern coast of North America, Sanson recognizes French Claims to Canada, English claims to the Massachusetts Bay Colony, Dutch claims in New Amsterdam (New York), and Swedish claims in New Jersey.
In Spanish Florida, which extends north to include most of the American Southeast, Lake Apalache or the Great Freshwater Lake of the American Southeast is noted. This lake, first mapped by De Bry and Le Moyne in the mid 16th century, is a mis-mapping of Floridas Lake George. While De Bry correctly mapped the lake as part of the River May or St. Johns River, cartographers in Europe erroneously associated it with the Savannah River, which instead of Flowing south from the Atlantic (Like the May), flowed almost directly from the Northwest. Lake Apalache was subsequently relocated somewhere in Carolina or Georgia, where Sanson maps it and where it would remain for several hundred years.
Southward is the well mapped Caribbean and once again the map is rife with cartographic speculation. While the South American coastlands are well mapped, the interior is largely unknown. Explorers throughout the late 16th and early 17th century, enthralled by Pizarros conquests in Peru and tales of other gold rich empires in the interior, were actively seeking El Dorado.
Most Europeans believe that the most likely site of the El Dorado legend was the mythical city of Manoa located by Sanson on the shores of the Lake Parima, near modern day Guyana, Venezuela, or northern Brazil. Manoa was first identified by Sr. Walter Raleigh in 1595. Raleigh did not visit the city of Manoa (which he also believes is El Dorado) himself due to the onset of the rainy season, however he describes the city, based on indigenous accounts, as resting on a salt lake over 200 leagues wide. This lake, though no longer mapped as such, does have some basis in fact. Parts of the Amazon were, at the time dominated by a large and powerful Indigenous trading nation known as the Manoa. The Manoa traded the length and breadth of the Amazon. The onset of the rainy season inundated the great savannahs of the Rupununi, Takutu, and Rio Branco or Parima rives. This inundation briefly connected the Amazon and Orinoco river systems, opening an annual and well used trade route for the Manoans. The Manoans who traded with the Incans in the western Amazon, had access to gold mines on the western slopes of the Andes, and so, when Raleigh saw gold rich Indian traders arriving in Guyana, he made the natural assumption for a gold hungry European in search of El Dorado. When he asked the Orinocans where the traders were from, they could only answer, Manoa. Thus did Lake Parime or Parima and the city of Manoa begin to appear on maps in the early 17th century. The would continue to be mapped in this area until about 1800.
Further south Sanson maps a large and prominent Laguna de Xarayes as the northern terminus of the Paraguay River. The Xarayes, a corruption of Xaraiés meaning Masters of the River, were an indigenous people occupying what are today parts of Brazils Matte Grosso and the Pantanal. When Spanish and Portuguese explorers first navigated up the Paraguay River, as always in search of El Dorado, they encountered the vast Pantanal flood plain at the height of its annual inundation. Understandably misinterpreting the flood plain as a gigantic inland sea, they named it after the local inhabitants, the Xaraies. The Laguna de los Xarayes almost immediately began to appear on early maps of the region and, at the same time, almost immediately took on a legendary aspect. The Lac or Laguna Xarayes was often considered to be a gateway to the Amazon and the Kingdom of El Dorado.
Across the the Atlantic is the well mapped coast of continental Africa, much is unknown of the interior and like South America much speculation and myth abounds. With the Nile, Sanson followed the Ptolemaic two lakes at the base of the Montes de Lune theory. Though Sanson does map both lakes, naming the western lake Zaire, he does not specifically name the Mountains of the Moon (though they are sketched in).
Just south of Sansons Lake Zaire, is the Kingdom of Monomatapa. This region of Africa held a particular fascination for Europeans since the Portuguese first encountered it in the 16th century. At the time, this area was a vast empire called Mutapa or Monomotapa that maintained an active trading network with faraway partners in India and Asia. As the Portuguese presence in the area increased in the 17th century, the Europeans began to note that Monomatapa was particularly rich in gold. They were also impressed with the numerous well crafted stone structures, including the mysterious nearby ruins of Great Zimbabwe. This combination led many Europeans to believe that King Solomons Mines, a sort of African El Dorado, must be hidden in this region. Monomotapa did in fact have rich gold mines in the 16th and 17th centuries, but most have these had been exhausted by the 1700s.
In Asia, Sanson offers us a fairly accurate mapping of Asia Minor, Persia and India. The Capsian Sea is corrected to a north-south axis though is a bit lumpy in form. He names numerous Silk Route cities through Central Asia including Samarkand, Tashkirgit, Bukhara, and Kashgar. Far to the north he associates Mongolia and Siberia with the Biblical lands of Gog and Magog.
Sanson maps, but does not name, the apocryphal Lake of Chiamay roughly in what is today Assam, India. Early cartographers thought that such a lake must exist as the source of four important Southeast Asian river systems including the Irrawaddy, the Dharla, the Chao Phraya, and the Brahmaputra. This lake began to appear in maps of this region as early as the 16th century and persisted well into the mid 18th century. Its origins are unknown but may originate in a lost 16th century geography prepared by the Portuguese scholar Jao de Barros. It was also heavily discussed in the journals of Sven Hedin, who believed it to be associated with Indian mythology that a sacred lake linked several holy subcontinent river systems. There are even records that the King of Siam led an invasionary force to take control of the lake in the 16th century. Nonetheless, the theory of Lake Chimmay was ultimately disproved and it disappeared from maps entirely by the 1760s.
Further east still the Korean peninsula unnaturally narrow. Just offshore the Japanese Islands emerge only to disappear and reappear on the opposite side of the map. The form of the islands approximates accuracy and Edo or Tokyo Bay is clearly recognizable. Several Japanese cities, including Yendo (Edo or Tokyo) are noted. Hokkaido is attached to the continent and the Japanese Kuril Islands extend eastward to meet up the aforementioned Gama Land or Terre de la Compagnie.
To the south Australia itself appears as New Holland. Much of the northern and western shores, including the Gulf of Carpentaria, have been mapped but the eastern shores remain unexplored and the interior entirely unknown. Tasmania, labeled Terre de Diemens appears according to its discovery and mapping by Able Tazman in 1642. A little further south and east is an extremely embryonic New Zealand. There is no trace of the a two island layout or, for that matter, a eastern shoreline. Also in evidence is the mysterious Terre de Quir a great landmass supposedly discovered by the 16th century Spanish navigator and religious zealot Pedro Fernandez de Quiros. Quiros set sail in search of the speculative southern continent and may in fact have discovered several important South Seas islands, however, he stopped just shy of glory and turned around shortly before sighting New Zealand. Even so, Quiros was a voracious self promoter and descriptions of his findings were circulated throughout Europe. Terre de Quir or Terre de Quiros appears on various maps of the region until put to rest by the 18th century explorations of Captain Cook.
Massing at the base of the map is the speculative southern continent or Terre Australe. Long before the discovery of Antarctica, the southern continent, supposedly capping the South Pole, was speculated upon by European geographers in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was thought that the globe was a place of balances and thus geographers presumed the bulk of Eurasia must be counterbalanced by a similar landmass in the Southern Hemisphere, just as, they argued, the Americas counterbalanced Africa and Europe. Many explorers in the 16th and 17th centuries sought the Great Southern continent, including Quiros, Drake, and Cook, but Antarctica itself was not truly discovered until Edward Bransfield and William Smith sighted the Antarctic Peninsula in 1820. All in all a magnificent and fascinating map of the world. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
1778 Matthaus Lotter Large Oval World Map showing Capt Cooks 1st Voyage - Rare 1st edition
Antique Map
- Title : Mappe Monde ou carte generale de l`Univers sur une projection nouvelle d`une sphere ovale pour mieux entendre les distances entre l`Europe et Amerique avec le tour du monde du Lieut Cook et Tous Les Decouvertes Nouvelles...MDCCLXXVIII
- Date : 1778 (1st edition)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35629
- Size: 39in x 21in (990mm x 535mm)
Description:
This very large, impressive original copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on an Ortelius Oval Projection, showing the tracks of Captain Cooks 1st Voyage to the South Seas, was engraved and published by Matthäus Albrecht Lotter in 1778, dated in title. The map was re-issued in 1782 & 1787 to include the tracks of Cooks 2nd & 3rd voyages of discovery.
This 1st edition Lotter Oval map is scarce with only a small few available on the open market.
This map was one of the first world maps published to cash in on the publicity over Captain James Cooks Circumnavigation of the world and the first European survey of New Zealand and the East Coast of Australia. Beautifully executed and dominated by New Holland, Australia, for the first time almost complete on a world map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39in x 21in (990mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 37 1/2in x 19 1/4in (955mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
This large world map was one of the first to show the discoveries of the east coast of Australia and New Zealand by James Cook on his first voyage of Discovery. The shadow line from Tasmania west to Western Australia was not filled in until the later discoveries of Bass Strait by Bass and Matthew Flinders in 1797 and the southern coast by Baudin and Flinders in 1803. Also included along the New Holland coastline is the earlier Dutch discoveries of Hartog 1616, the van Leeuwin 1619, Nuyts 1627, de Wit 1628 and Tasman 1642-44. The Trial Islands near present-day Dampier, named after the English ship the Trial, which were incorrectly charted by Gerritsz after the false reports provided by Captain Brookes, are also noted.
Cooks First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cooks command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on HMS Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earths distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research.
Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the HMS Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
The Ortelius Oval Projection is a map projection used for world maps largely in the late 16th and early 17th century. It is neither conformal nor equal-area but instead offers a compromise presentation. It is similar in structure to a pseudocylindrical projection but does not qualify as one because the meridians are not equally spaced along the parallels. The projection\'s first known use was by Battista Agnese (flourished 1535–1564) around 1540, although whether the construction method was truly identical to Ortelius\'s or not is unclear because of crude drafting and printing. The front hemisphere is identical to Petrus Apianus\'s 1524 globular projection.
The projection reached a wide audience via the popular map Typus Orbis Terrarum by Abraham Ortelius beginning in 1570. The projection (and indeed Ortelius maps) were widely copied by other mapmakers such as Giovanni Pietro Maffei, Fernando de Solis, and Matteo Ricci.
1782 Matthaus Lotter Large World Map Tracking of Cooks Voyages 1768, 1772 & 1776
Antique Map
- Title : Mappe Monde ou carte generale de l`Univers sur une projection nouvelle d`une sphere ovale pour mieux entendre les distances entre l`Europe et Amerique avec le tour du monde du Lieut Cook et Tous Les Decouvertes Nouvelles...MDCCLXXXII
- Date : 1782 (2nd edition)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35646
- Size: 38 1/2in x 21in (985mm x 535mm)
Description:
This very large, impressive original copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on an Ortelius Oval Projection, was engraved and published by Matthäus Albrecht Lotter in 1782, dated in title.
The map was first issued in 1778 and re-issued in 1782 & 1787 and included all three of Cooks voyages of discovery.
This map was one of the first world maps published to cash in on the publicity over Captain James Cooks Circumnavigation of the world and the first European survey of New Zealand and the East Coast of Australia. Beautifully executed and dominated by New Holland, Australia, for the first time almost complete on a world map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 38 1/2in x 21in (985mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 37 1/2in x 19 1/4in (955mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issue, light soiling
Plate area: - Folds as issue, light soiling
Verso: - Folds as issue, light soiling
Background:
This large world map was one of the first to show the discoveries of the east coast of Australia and New Zealand by James Cook on his first voyage of Discovery. The shadow line from Tasmania west to Western Australia was not filled in until the later discoveries of Bass Strait by Bass and Matthew Flinders in 1797 and the southern coast by Baudin and Flinders in 1803. Also included along the New Holland coastline is the earlier Dutch discoveries of Hartog 1616, the van Leeuwin 1619, Nuyts 1627, de Wit 1628 and Tasman 1642-44. The Trial Islands near present-day Dampier, named after the English ship the Trial, which were incorrectly charted by Gerritsz after the false reports provided by Captain Brookes, are also noted.
Cooks First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cook\\\\\\\'s command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on the Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earth\\\\\\\'s distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research.
Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
Cooks Second Voyage (1772-1775)
Based on the success of his first voyage, Cook was appointed by the Admiralty to lead a second expedition. Two ships were employed with Cook commanding the Resolution and Captain Tobias Furneaux in charge of the Adventure. The purpose was to circumnavigate the globe as far south as possible to confirm the location of a southern continent. Cook proved that there was no Terra Australis, which supposedly was located between New Zealand and South America. Cook was convinced, however, that there was land beyond the southern ice fields. In his pursuit of this idea, this expedition was the first European voyage to cross the Antarctic Circle. In addition, in two great sweeps through the Southern latitudes, Cook made an incredible number of landfalls including New Zealand, Easter Island, the Marquesas, Tahiti and the Society Islands, the Tonga Islands, the New Hebrides, New Caledonia, and a number of smaller islands.
In addition to these navigational accomplishments and the accompanying expansion of geographical knowledge, the expedition also recorded a vast amount of information regarding the Pacific islands and peoples, proved the value of the chronometer as an instrument for calculating longitude, and improved techniques for preventing scurvy.
Cooks Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cooks third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\\\\\\\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cooks death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cooks death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
The Ortelius Oval Projection is a map projection used for world maps largely in the late 16th and early 17th century. It is neither conformal nor equal-area but instead offers a compromise presentation. It is similar in structure to a pseudocylindrical projection but does not qualify as one because the meridians are not equally spaced along the parallels. The projection\'s first known use was by Battista Agnese (flourished 1535–1564) around 1540, although whether the construction method was truly identical to Ortelius\'s or not is unclear because of crude drafting and printing. The front hemisphere is identical to Petrus Apianus\'s 1524 globular projection.
The projection reached a wide audience via the popular map Typus Orbis Terrarum by Abraham Ortelius beginning in 1570. The projection (and indeed Ortelius maps) were widely copied by other mapmakers such as Giovanni Pietro Maffei, Fernando de Solis, and Matteo Ricci.
1827 Herisson Large Rare Original Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map, Capt J Cook
Antique Map
- Title : La mappe-monde ou le globe terrestre, représenté en deux hemisphères, l'un oriental l'autre occidental, où sont marquées les découvertes les plus récentes, faites par Mackenzie, Vancouver, La Pérouse, Bruce, Renell, Mungo Park, Joub [sic] Barrow, Franklin et Parry. Dressée par Hérisson, élève de Mr. Bonne / Indication des trois voyages de Cook et de celui de La Pérouse … … À Paris : chez Basset, 1827
- Date : 1827
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Ref #: 70815
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This impressive scarce & large scale double hemisphere original antique map, by the French cartographer Eustache Herisson, was published in 1827, dated in text.
The main feature of the map is the illustration of the tracks taken by most recent explorers of the time. From Captain James Cook, to George Vancouver in Canada, Jean-Francois la Perouse in the Pacific, Alexander Humboldt in America, John Franklin and William Parry in Canada.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Several small repairs to margin not affecting the image, age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning, repairs as noted
Background:
With the exception of the Arctic region of North America, which shows a land bridge connecting Greenland with Alaska and an inland polar sea, the landmasses are drawn with contemporary accuracy. Politically the world was a very different place. North America was still divided by the Old World major powers, Britain, France & Spain. As already noted northern Canada was still to be fully mapped, the interior of Africa was still largely unexplored by Europeans. The European settlement of Australia & New Zealand was still in its infancy Australia and the Antarctic region was still only known by the voyage of Cook some 40 years earlier. The explorers noted below were some of the 18th century adventurers responsible for filling in the cartographically unknown
Captain James Cook FRS 1728 – 1779 was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the Royal Navy. Cook made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific Ocean, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand.
Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years\' War, and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the Saint Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec. This helped bring Cook to the attention of the Admiralty and Royal Society. This notice came at a crucial moment in both Cook\'s career and the direction of British overseas exploration, and led to his commission in 1766 as commander of HM Bark Endeavour for the first of three Pacific voyages.
In three voyages Cook sailed thousands of miles across largely uncharted areas of the globe. He mapped lands from New Zealand to Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean in greater detail and on a scale not previously achieved. As he progressed on his voyages of discovery he surveyed and named features, and recorded islands and coastlines on European maps for the first time. He displayed a combination of seamanship, superior surveying and cartographic skills, physical courage and an ability to lead men in adverse conditions.
Cook was attacked and killed while attempting to kidnap Kalaniʻōpuʻu, a Hawaiian chief, during his third exploratory voyage in the Pacific in 1779. He left a legacy of scientific and geographical knowledge which was to influence his successors well into the 20th century, and numerous memorials worldwide have been dedicated to him.
Captain George Vancouver 1757 – 1798 was a British officer of the Royal Navy, best known for his 1791–95 expedition, which explored and charted North America\'s north-western Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of contemporary Alaska, British Columbia, Washington, and Oregon. He also explored the Hawaiian Islands and the southwest coast of Australia.
In Canada, Vancouver Island and the city of Vancouver are named after him, as are Vancouver, Washington, in the United States, Mount Vancouver on the Yukon/Alaska border, and New Zealand\'s sixth highest mountain
Jean François de Galaup, comte de La Perouse 1741 – 1788 was a French Naval officer and explorer whose expedition vanished in Oceania after the French government decided to complete the work of Captain james Cook.
Alexander Humboldt 1769 – 1859 was a Prussian geographer, naturalist, explorer, and influential proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher, and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt (1767–1835). Humboldt\'s quantitative work on botanical geography laid the foundation for the field of biogeography. Humboldt\'s advocacy of long-term systematic geophysical measurement laid the foundation for modern geomagnetic and meteorological monitoring.
Between 1799 and 1804, Humboldt travelled extensively in Latin America, exploring and describing it for the first time from a modern scientific point of view. His description of the journey was written up and published in an enormous set of volumes over 21 years. Humboldt was one of the first people to propose that the lands bordering the Atlantic Ocean were once joined (South America and Africa in particular). Humboldt resurrected the use of the word cosmos from the ancient Greek and assigned it to his multi-volume treatise, Kosmos, in which he sought to unify diverse branches of scientific knowledge and culture. This important work also motivated a holistic perception of the universe as one interacting entity. He was the first person to describe the phenomenon and cause of human-induced climate change, in 1800 and again in 1831, based on observations generated during his travels.
Rear-Admiral Sir John Franklin 1786 –1847 was an English Royal Navy officer and explorer of the Arctic. Franklin also served as Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen\'s Land (now Tasmania) from 1837 to 1843. He disappeared on his last expedition, attempting to chart and navigate a section of the Northwest Passage in the Canadian Arctic. The icebound ships were abandoned and the entire crew perished from starvation, hypothermia, tuberculosis, lead poisoning and scurvy.
Rear Admiral Sir William Edward Parry, RN, FRS 1790 - 1855 was an English rear-admiral and Arctic explorer. His 1819 voyage through the Parry Channel was probably the most successful in the long quest for the Northwest Passage. In 1827 he attempted one of the earliest expeditions to the North Pole. He reached 82°45′ North latitude, setting the record for human exploration farthest North that stood for nearly five decades before being surpassed at 83°20′26″ by Albert Hastings Markham in 1875–1876.
1677 Nicolas Visscher Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map
- Title : Orbis Terrarum Tabula Recens Emendata Et In Lucem Edita Per N. Visscher
- Date : 1677
- Size: 22in x 16in (560mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 30005
This beautiful, original map is the second state of the second world map prepared by Nicolas Visscher in 1677 for insertion in a Dutch Bible. The first state of this second world map was published in 1663.
General Condition:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & sturdy
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, red, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 16in (560mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 18 3/4in x 12 1/4in (475mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Left & right folds as issued, small professional repair along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background: A number of bibles published in the Netherlands contain world maps, those from 1657 onwards contained this map by Visscher. The maps tend to be conservative in form, with certain areas such as California (as a peninsular) being represented more correctly than current theories at the time. On Visschers map parts of Australia and Van Diemens land are marked, but not the north coast of Australia discovered by Tasman's second voyage in 1644.
In the corners the four continents are shown in allegorical form with examples of their animal life and inhabitants. Two circular diagrams depict the heavens.
There were later edition s of the Ravesteyn Bible in at least 1660, 1662, 1667 and 1670. Editions prior to 1657 did not contain maps, although Nicolas Visscher's farther Claes Visscher and another engraver from Amsterdam, Jacob Savry, prepared regional biblical maps in the 1640's. Maps were often added to bibles at a later date. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley)
1750 J N Bellin Large Antique World Map on Mercators Projection - 27091
Antique Map
- Title : An Essay of a New and Complet Map Containing the Known Part of the Terrestial Globe by N Bellin....MDDCL
- Date : 1750
- Size: 30 1/2in x 22 1/2in (825mm x 570mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27091
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on Mercators Projection by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved by Jacobus van der Schley in 1750 - dated in the title - and was published in Dutch/English by Pierre d Hondt, publisher, operated out of the Hague.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30 1/2in x 22 1/2in (825mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin extended from plate -mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
First edition of Bellins large mid-18th century world map, published in Paris. This map pre-dates the major world discoveries of the late 18th century including the North West coast of America, the Sandwich Islands, and the Voyages of Capt Cook soon to map the East Coast of Australia & NZ.
This edition is most noteworthy for its marvelous early projection of Australia and New Zealand, each with largely speculative coastlines. Australia is still attached to New Guinea and has several notes of early exploration shown. New Zealand is barely known and with only a portion of its western coastline.
No sign of Antarctica and the NW Coast of America includes the first notes of Russian exploration.
In North America Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de l’Ouest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the “Archipel de Nord”.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labelled “Nouvelle Holland”, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1748 J N Bellin Large Antique World Map on Mercators Projection - 27007
Antique Map
- Title : Essay d une Carte Reduite Contenant les parties connuees Du Globe Terrestre...1748
- Date : 1748
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27007
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on Mercators Projection was engraved in 1748 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin - dated in the title.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20 1/2in (710mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin extended from plate -mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
First edition of Bellins large mid-18th century world map, published in Paris. This map pre-dates the major world discoveries of the late 18th century including the North West coast of America, the Sandwich Islands, and the Voyages of Capt Cook soon to map the East Coast of Australia & NZ.
This edition is most noteworthy for its marvelous early projection of Australia and New Zealand, each with largely speculative coastlines. Australia is still attached to New Guinea and has several notes of early exploration shown. New Zealand is barely known and with only a portion of its western coastline.
No sign of Antarctica and the NW Coast of America includes the first notes of Russian exploration.
In North America Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de l’Ouest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the “Archipel de Nord”.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labelled “Nouvelle Holland”, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1748 (1770) Nicolas Bellin Large Antique World Map updated by Capt. Cook
Antique Map
- Title : Essay d une Carte Reduite Contenant les parties connuees Du Globe Terrestre...Par N Bellin...1748
- Size: 30 1/2in x 22in (785mm x 560mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1748 (1770)
- Ref #: 93353
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique World Map, on Mercators Projection, is dated 1748 by Nicolas Bellin, updated showing the discoveries of Captain James Cook in his first voyage of Discovery from 1769-1772.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30 1/2in x 22in (785mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2in x 20 1/2in (725mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The map presents the entire world on Mercator Projection based on a Paris (LIsle de Fer) meridian, exhibiting post-Cook geography throughout, but most specifically in the Pacific and along the northwest coast of America.
North America to the west of the Mississippi is vaguely rendered according to 16th century expeditions into the region by Coronado, La Salle, De Soto, and others.
Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de lOuest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the Archipel de Nord.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labeled Nouvelle Holland, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemens Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state.
It is of interest that there is a common misconception regarding this map that suggests the first edition was dated 1748. There are editions with a printed date of 1748, but these are actually later editions. The 1748 date is a printing error in which 8 and 4 are transposed, the actual date of publication being 1784. The first edition of this map is the 1778 example shown here. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1812 Pinkerton Large Antique Stereographic Projection Map of Southern Hemisphere
- Title : Southern Hemisphere....Drawn Under the Direction of Mr Pinkerton by L Herbert Neele Sculp. 352 Starnd.....London Published August 31st 1812 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 60540
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1812
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique stereographic projection style map of the Southern Hemisphere, Australia, New Zealand & Antarctica by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1812 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In geometry, the stereographic projection is a particular mapping (function) that projects a sphere onto a plane. The projection is defined on the entire sphere, except at one point: the projection point. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective. It is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet. It is neither isometric nor area-preserving: that is, it preserves neither distances nor the areas of figures.
Intuitively, then, the stereographic projection is a way of picturing the sphere as the plane, with some inevitable compromises. Because the sphere and the plane appear in many areas of mathematics and its applications, so does the stereographic projection; it finds use in diverse fields including complex analysis, cartography, geology, and photography. In practice, the projection is carried out by computer or by hand using a special kind of graph paper called a stereographic net, shortened to stereonet, or Wulff net.
The stereographic projection was known to Hipparchus, Ptolemy and probably earlier to the Egyptians. It was originally known as the planisphere projection. Planisphaerium by Ptolemy is the oldest surviving document that describes it. One of its most important uses was the representation of celestial charts. The term planisphere is still used to refer to such charts.
In the 16th and 17th century, the equatorial aspect of the stereographic projection was commonly used for maps of the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. It is believed that already the map created in 1507 by Gualterius Lud was in stereographic projection, as were later the maps of Jean Roze (1542), Rumold Mercator (1595), and many others. In star charts, even this equatorial aspect had been utilised already by the ancient astronomers like Ptolemy.
François d\'Aguilon gave the stereographic projection its current name in his 1613 work Opticorum libri sex philosophis juxta ac mathematicis utiles (Six Books of Optics, useful for philosophers and mathematicians alike).
In 1695, Edmond Halley, motivated by his interest in star charts, published the first mathematical proof that this map is conformal. He used the recently established tools of calculus, invented by his friend Isaac Newton.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
1765 Bellin Large Antique World Map of Global Winds & Magnetic Variations
Antique Map
- Title : Carte des Variations de la Boussole et des Vents Generaux que l'on Trouve dans les Mers les Plus Frequentees
- Date : 1765
- Size: 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35665
Description:
This original very large hand coloured copper plate engraved antique world map, illustrating global magnetic and ocean wind variations, was engraved in 1765 - dated- and published by Jacques Nicholas Bellin, Paris.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 23in (875mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
An elegantly designed and precisely drafted sea chart of the oceans sailed by French navigators in the 18th century. Drawn by J. N. Bellin, who during his over fifty years of work in the French Hydrographic Service was appointed the first Ingenieur hydrographe de la Marine. This chart extends from California to Japan and focuses on the Atlantic and Indian oceans. The French sphere of influence in the West Indies, Africa, and India, would have generated this interest in compass and wind variations applied to a Mercator projection covering most of the world.
By 1765, France had lost most of its overseas empire in America following the Seven Years War (French and Indian War in America), so knowledge of the sea routes was important to holding what was left. Besides a wealth of hydrographic information, including little wind heads throughout, this beautiful map features an exquisite title cartouche featuring the French crown surmounting the globe. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, Burden)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1812 Pinkerton Large Antique Stereographic Projection Map of Northern Hemisphere
- Title : Northern Hemisphere....Neele Sculp. 352 Strand.....London Published October 1st 1812 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 60542
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1812
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique stereographic projection style map of the Northern Hemisphere, North America, Canada, Europe, Asia, Africa & The North Pole by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1812 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In geometry, the stereographic projection is a particular mapping (function) that projects a sphere onto a plane. The projection is defined on the entire sphere, except at one point: the projection point. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective. It is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet. It is neither isometric nor area-preserving: that is, it preserves neither distances nor the areas of figures.
Intuitively, then, the stereographic projection is a way of picturing the sphere as the plane, with some inevitable compromises. Because the sphere and the plane appear in many areas of mathematics and its applications, so does the stereographic projection; it finds use in diverse fields including complex analysis, cartography, geology, and photography. In practice, the projection is carried out by computer or by hand using a special kind of graph paper called a stereographic net, shortened to stereonet, or Wulff net.
The stereographic projection was known to Hipparchus, Ptolemy and probably earlier to the Egyptians. It was originally known as the planisphere projection. Planisphaerium by Ptolemy is the oldest surviving document that describes it. One of its most important uses was the representation of celestial charts. The term planisphere is still used to refer to such charts.
In the 16th and 17th century, the equatorial aspect of the stereographic projection was commonly used for maps of the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. It is believed that already the map created in 1507 by Gualterius Lud was in stereographic projection, as were later the maps of Jean Roze (1542), Rumold Mercator (1595), and many others. In star charts, even this equatorial aspect had been utilised already by the ancient astronomers like Ptolemy.
François d\'Aguilon gave the stereographic projection its current name in his 1613 work Opticorum libri sex philosophis juxta ac mathematicis utiles (Six Books of Optics, useful for philosophers and mathematicians alike).
In 1695, Edmond Halley, motivated by his interest in star charts, published the first mathematical proof that this map is conformal. He used the recently established tools of calculus, invented by his friend Isaac Newton.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
1676 John Speed Antique Atlas Title Pages x 2 Empire of Great Britaine & World
Antique Map
- Title : The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine, A Prospect of the most famous Parts of the World by John Speed...London Thomas Bassett and Richard Chiswell 1676; The Achievement of our Soveraigne King Charles the 11D.
- Date : 1676
- Size: 22 1/2in x 17 1/2in (570mm x 445mm)
- Ref #: 42005/42006
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Price: $1250.00US
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured, copper plate engraved antique Title and Dedication Pages was published for the 1676 edition of John Speeds double atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine & Atlas A Prospect of the most Famous Parts of the World printed by Thomas Bassett and Richard Chiswell, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 17 1/2in (570mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/4in x 9 3/4in (385mm x 250mm) each
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
John Speeds The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published in 1610/11 by John Sudbury and George Humble, and contained the first set of individual county maps of England and Wales besides maps of Ireland and a general map of Scotland. Most, but not all, of the county maps have town plans on them; those showing a Scale of Passes being the places he had mapped himself. The county maps were the first consistent attempt to show territorial divisions, such as boundaries of hundreds, but it was Speed’s town plans that were a major innovation and probably his greatest contribution to British cartography. The Theatre was an immediate success: the first print run of around 500 copies must have sold quickly because many editions followed. Sudbury and Humble realized, given the increasing popularity of both county and world atlases and in the light of the success of Abraham Ortelius’s Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, the potential demand for an English world atlas.
In 1627, two years before his death, Speed published Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World with 21 finely engraved maps, which was the first world atlas produced by an Englishman. There is a fascinating text describing the areas shown on the back of the maps in English, although a rare edition of 1616 of the British maps has a Latin text – this is believed to have been produced for the Continental market. Its maps are famous for their bordering panels of national characters in local costume and panoramic views depicting the areas of major towns and cities. Much of the engraving was done in Amsterdam at the workshop of Jodocus Hondius. The maps of the world and America show California as an island and are amongst the earliest ever printed to depict this seventeenth-century cartographic myth.
1716 Doppelmayr Antique Celestial Chart Tycho Brahes Motion of Venus & Mercury
- Title : Motus In Coelo Spirales : Quos Planetae inferiores Venus et Mercurius secundum Tychonicorum Hypothesin exhibent, pro exemplo ad annum Christi praecipue 1712 et 1713 ; Cum Privilegio Sac. Caes. Maiestatis / Geometri`ce descripti a Ioh. Gabriele Doppelmaiero Mathem. Prof. Publ. operâ Ioh. Baptistae Homanni
- Size: 24 1/2in x 21in (625mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1716
- Ref #: 82033
Description:
This fine hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique astronomical chart showing the Geocentric motion of the inner planets of Mercury and Venus according to the Tychonic hypothesis for the years 1712 and 1713 by Johann Doppelmayr, was first published in Homanns Atlas von hundert Charten in 1712 & the Grossen Atlas in 1712. In 1742 Doppelmayr collected most of the Astronomical charts he had prepared over the years for the Homann publishing firm and published The Atlas Coelestis with 30 Astronomical Plates, including this one.
This chart was published according to the famous Tycho Brahes cosmological system that described the complex movements of Venus and Mercury as viewed from earth. The center of the chart is filled with a delightful scene of cherubs swinging through the clouds. Two text panels at lower corners describe the movements of the planets.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 21in (625mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Bottom centerfold re-joined
Verso: - None
Background:
Doppelmayrs best-known astronomical work is his Atlas Coelestis in quo Mundus Spectabilis et in eodem Stellarum omnium Phoenomena notabilia, circa ipsarum Lumen, Figuram, Faciem, Motum, Eclipses, Occultationes, Transitus, Magnitudines, Distantias, aliaque secundum Nic. Copernici et ex parte Tychonis de Brahe Hipothesin. Nostri intuitu, specialiter, respectu vero ad apparentias planetarum indagatu possibiles e planetis primariis, et e luna habito, generaliter e celeberrimorum astronomorum observationibus graphice descripta exhibentur, cum tabulis majoribus XXX, published in 1742 by the heirs of Homann in Nuremberg.
In this atlas, Doppelmayr collected most of the astronomical and cosmographical plates which he had prepared over the years for the Homann publishing firm and which had appeared in several of their atlases. These earlier atlases allow us to infer approximate dates for the design and preparation of many of Doppelmayr’s cosmographical plates.
The earliest ones are plates 2 and 11 as they were already included in Homann’s first atlas, the Neuer Atlas bestehend in auserlesenen und allerneusten Land-Charten ueber die gantze Welt, und zwar erstlich nach Astronomischer Betrachtung der Bewegung des Himmels in dem Systemate Copernico-Hugeniano, dann auch nach der nturlichen Beschaffenheit und geographischen Eintheilung der mit Wasser umgebenen allgemeinen Erd-Kugeln in ihre besondere Monarchien, Koenigreiche, Staaten und Laender (Nuremberg, 1707).
Plates 3 and 7 to 10 were first published in Homann’s Atlas von hundert Charten(Nuremberg, 1712), whereas plates 1, 4 and 15 to 25 can be dated between 1716 and 1724 as they were not included in Homanns Grossen Atlas (Nuremberg, 1716), but are mentioned in Hagers list of plates sold by Homann at his death in 1724.
The plates depicting the constellations (nrs. 16 to 25) were probably prepared and engraved in the early 1720s as the Atlas Portatilis Coelestis, oder compendiose Vorstellung des gantzen Welt-gebudes, in den Anfangs-grunden der wahren Astronomie (1723) of Johann Leonard Rost refers to a set of celestial hemispheres drawn by Doppelmayr. The choice and the style of the constellation figures on these plates is based on the Firmamentum Sobiescianum sive Uranographia (Danzig, 1687) of the Polish astronomer Johannes Hevelius, who also avoided the use of Bayer’s Greek letters for identifying the individual stars, and they were clearly executed before the publication of John Flamsteeds star catalogue (London, 1725) and star atlas (London, 1729).
Doppelmayr, Johann Gabriel 1677 - 1750
Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr (also spelled Doppelmaier or Doppelmair) was the son of the Nuremberg merchant Johann Siegmund Doppelmayr (1641-1686) and was born on 27 September 1677 (many early sources incorrectly give his year of birth as 1671). His father had an interest in applied physics and was one of the first to design a vertical vacuum air pump in Nuremberg.
Doppelmayr enrolled at the Ägidiengymnasium in 1689 and after completing his studies in 1696 enrolled at the nearby university of Altdorf to study law which he completed in 1698 with a dissertation on the Sun. He then attended lectures on mathematics and natural philosophy by Johann Christoph Sturm (1635-1703) which he completed in 1699 with his dissertation De visionis sensu nobilissimo, ex camerae obscurae tenebris illustrato. He continued his studies on physics and mathematics at the university of Halle where he also learned French and Italian.
In September 1700, Doppelmayr traveled to Berlin and from there, through Lower Saxony, to Holland where he visited Franeker and Amsterdam on his way to Utrecht where he stayed for a couple of months to continue his studies on physics and mathematics and to master the English language.
In April 1701, Doppelmayr went to Leiden where he stayed in the house of the astronomy professor Lothar Zumbach von Koesfeld and learned (probably in the Musschenbroek workshop) how to grind and figure telescope lenses. He then traveled to Rotterdam and in May to England where he visited Oxford and London.
After returning to Holland in the end of 1701, Doppelmayr spent another five months in Leiden, where he followed astronomy lessons from Lothar Zumbach von Koesfeld. After visiting Utrecht, Deventer, Osnabrück, Hannover, Kassel, Marburg, Gießen, Wetzlar and Frankfurt, Doppelmayr returned to Nuremberg in August 1702 and was appointed professor of mathematics at the Ägidiengymnasium in 1704, a position that he would hold until his death.
In 1723, he received an invitation to become the professor of mechanics at the Academy of St. Petersburg, but Doppelmayr declined and suggested that they should ask the Swiss mathematician Nikolaus Bernouilli for this position.
Doppelmayr died on 1 December 1750 in Nuremberg, and many believed that this was caused by the fatal effects of a powerful electrical shock which he had received shortly before while experimenting with a battery of electric capacitors. Other sources, however, suggest that Doppelmayr’s electrical experiments were performed several years earlier and were not the cause of his death.
1780 Robert De Vaugondy Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map
Antique Map
- Title : Mappe-Monde par Robert de Vaugondy Geographe ord du Roi
- Size: 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (440mm x 290mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1780
- Ref #: 17060
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique Twin Hemisphere World Map by Robert De Vaugondy was engraved in 1780 - dated in title and published in the same year.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (440mm x 290mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (440mm x 290mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Fine twin hemisphere world map illustrating the known world in the 18th century. Although almost complete there are a few regions of uncertainty. The route taken by Cook on his final voyage is included which reaches from Australia, New Zealand to Hawaii and the very northern reaches of western North America which were surveyed and mapped by Cook extensively. There is some indication of a northern Arctic region there is no mention of the great southern Antarctica regions. A great map showing the world at the beginning of modern era. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1844 Johnston Large Antique World Map Nation of Texas, Wilkes & Ross Antarctica
Antique Map
- Title : Chart of the World on Mercators Projection
- Ref #: 51011
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
- Date: 1844
Description:
This large original 1st edition, uncommon hand coloured antique lithograph world map was published by W & AK Johnston in his General Atlas, 1844.
A Pacific centered map emphasising the contemporary nation of Texas in North America, a few years prior to joining the union, along with the latest discoveries in Antarctica, or Southern Continent (as it was then known) by Charles Wilkes (1840) and James Ross (1841)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1850 Scarce Chinese Twin Hemisphere World Map - 世界
- Title : 世界
- Size: 18in x 9 1/2in (460mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1850
- Ref #: 61129
Description:
This scarce, original antique Chinese Twin Hemisphere World Map - with global trade routes to and from China - was published ca 1850.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 9 1/2in (460mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 9 1/2in (460mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Chinese Cartography
The earliest known maps to have survived in China date to the 4th century BC. In 1986, seven ancient Chinese maps were found in an archeological excavation of a Qin State tomb in what is now Fangmatan, in the vicinity of Tianshui City, Gansu province. Before this find, the earliest extant maps that were known came from the Mawangdui Han tomb excavation in 1973, which found three maps on silk dated to the 2nd century BC in the early Han Dynasty. The 4th century BC maps from the State of Qin were drawn with black ink on wooden blocks. These blocks fortunately survived in soaking conditions due to underground water that had seeped into the tomb; the quality of the wood had much to do with their survival. After two years of slow-drying techniques, the maps were fully restored.
The territory shown in the seven Qin maps overlap each other. The maps display tributary river systems of the Jialing River in Sichuan province, in a total measured area of 107 by 68 km. The maps featured rectangular symbols encasing character names for the locations of administrative counties. Rivers and roads are displayed with similar line symbols; this makes interpreting the map somewhat difficult, although the labels of rivers placed in order of stream flow are helpful to modern day cartographers.–93 These maps also feature locations where different types of timber can be gathered, while two of the maps state the distances in mileage to the timber sites. In light of this, these maps are perhaps the oldest economic maps in the world since they predate Strabo\\\'s economic maps.
In addition to the seven maps on wooden blocks found at Tomb 1 of Fangmatan, a fragment of a paper map was found on the chest of the occupant of Tomb 5 of Fangmatan in 1986. This tomb is dated to the early Western Han, so the map dates to the early 2nd century BC. The map shows topographic features such as mountains, waterways and roads, and is thought to cover the area of the preceding Qin Kingdom.
In China, the earliest known geographical Chinese writing dates back to the 5th century BC, during the beginning of the Warring States (481–221 BC). This was the Yu Gong or Tribute of Yu chapter of the Shu Jing or Book of Documents. The book describes the traditional nine provinces, their kinds of soil, their characteristic products and economic goods, their tributary goods, their trades and vocations, their state revenues and agricultural systems, and the various rivers and lakes listed and placed accordingly. The nine provinces in the time of this geographical work were very small in size compared to their modern Chinese counterparts. The Yu Gong\\\'s descriptions pertain to areas of the Yellow River, the lower valleys of the Yangtze, with the plain between them and the Shandong Peninsula, and to the west the most northern parts of the Wei River and the Han River were known (along with the southern parts of modern-day Shanxi province)
The oldest reference to a map in China comes from the 3rd century BC. This was the event of 227 BC where Crown Prince Dan of Yan had his assassin Jing Ke visit the court of the ruler of the State of Qin, who would become Qin Shi Huang (r. 221–210 BC). Jing Ke was to present the ruler of Qin with a district map painted on a silk scroll, rolled up and held in a case where he hid his assassin\\\'s dagger.Handing to him the map of the designated territory was the first diplomatic act of submitting that district to Qin rule.Instead he attempted to kill Qin, an assassination plot that failed. From then on maps are frequently mentioned in Chinese sources.
The three Han Dynasty maps found at Mawangdui differ from the earlier Qin State maps. While the Qin maps place the cardinal direction of north at the top of the map, the Han maps are orientated with the southern direction at the top. The Han maps are also more complex, since they cover a much larger area, employ a large number of well-designed map symbols, and include additional information on local military sites and the local population. The Han maps also note measured distances between certain places, but a formal graduated scale and rectangular grid system for maps would not be used—or at least described in full—until the 3rd century (see Pei Xiu below). Among the three maps found at Mawangdui was a small map representing the tomb area where it was found, a larger topographical map showing the Han\\\'s borders along the subordinate Kingdom of Changsha and the Nanyue kingdom (of northern Vietnam and parts of modern Guangdong and Guangxi), and a map which marks the positions of Han military garrisons that were employed in an attack against Nanyue in 181 BC.
An early text that mentioned maps was the Rites of Zhou.Although attributed to the era of the Zhou Dynasty, its first recorded appearance was in the libraries of Prince Liu De (c. 130 BC), and was compiled and commented on by Liu Xin in the 1st century AD. It outlined the use of maps that were made for governmental provinces and districts, principalities, frontier boundaries, and even pinpointed locations of ores and minerals for mining facilities.Upon the investiture of three of his sons as feudal princes in 117 BC, Emperor Wu of Han had maps of the entire empire submitted to him.
From the 1st century AD onwards, official Chinese historical texts contained a geographical section (Diliji), which was often an enormous compilation of changes in place-names and local administrative divisions controlled by the ruling dynasty, descriptions of mountain ranges, river systems, taxable products, etc. From the time of the 5th century BC Shu Jing forward, Chinese geographical writing provided more concrete information and less legendary element. This example can be seen in the 4th chapter of the Huainanzi (Book of the Master of Huainan), compiled under the editorship of Prince Liu An in 139 BC during the Han Dynasty (202 BC–202 AD). The chapter gave general descriptions of topography in a systematic fashion, given visual aids by the use of maps (di tu) due to the efforts of Liu An and his associate Zuo Wu. In Chang Chu\\\'s Hua Yang Guo Chi (Historical Geography of Szechuan) of 347, not only rivers, trade routes, and various tribes were described, but it also wrote of a \\\'Ba June Tu Jing\\\' (\\\'Map of Szechuan\\\'), which had been made much earlier in 150.
Local mapmaking such as the one of Szechuan mentioned above, became a widespread tradition of Chinese geographical works by the 6th century, as noted in the bibliography of the Sui Shu. It is during this time of the Southern and Northern Dynasties that the Liang Dynasty (502–557) cartographers also began carving maps into stone steles (alongside the maps already drawn and painted on paper and silk)
In the year 267,Pei Xiu (224–271) was appointed as the Minister of Works by Emperor Wu of Jin, the first emperor of the Jin Dynasty. Pei is best known for his work in cartography. Although map making and use of the grid existed in China before him, he was the first to mention a plotted geometrical grid and graduated scale displayed on the surface of maps to gain greater accuracy in the estimated distance between different locations. Pei outlined six principles that should be observed when creating maps, two of which included the rectangular grid and the graduated scale for measuring distance. Historians compare him to the Greek Ptolemy for his contributions in cartography. However, Howard Nelson states that, although the accounts of earlier cartographic works by the inventor and official Zhang Heng (78–139) are somewhat vague and sketchy, there is ample written evidence that Pei Xiu derived the use of the rectangular grid reference from the maps of Zhang Heng.
Later Chinese ideas about the quality of maps made during the Han Dynasty and before stem from the assessment given by Pei Xiu, which was not a positive one. Pei Xiu noted that the extant Han maps at his disposal were of little use since they featured too many inaccuracies and exaggerations in measured distance between locations. However, the Qin State maps and Mawangdui maps of the Han era were far superior in quality than those examined by Pei Xiu. It was not until the 20th century that Pei Xiu\\\'s 3rd century assessment of earlier maps\\\' dismal quality would be overturned and disproven. The Qin and Han maps did have a degree of accuracy in scale and pinpointed location, but the major improvement in Pei Xiu\\\'s work and that of his contemporaries was expressing topographical elevation on maps.
In the year 605, during the Sui Dynasty (581–618), the Commercial Commissioner Pei Ju (547–627) created a famous geometrically gridded map. In 610 Emperor Yang of Sui ordered government officials from throughout the empire to document in gazetteers the customs, products, and geographical features of their local areas and provinces, providing descriptive writing and drawing them all onto separate maps, which would be sent to the imperial secretariat in the capital city.
The Tang Dynasty (618–907) also had its fair share of cartographers, including the works of Xu Jingzong in 658, Wang Mingyuan in 661, and Wang Zhongsi in 747. Arguably the greatest geographer and cartographer of the Tang period was Jia Dan (730–805), whom Emperor Dezong of Tang entrusted in 785 to complete a map of China with her recently former inland colonies of Central Asia, the massive and detailed work completed in 801, called the Hai Nei Hua Yi Tu (Map of both Chinese and Barbarian Peoples within the (Four) Seas). The map was 30 ft long (9.1 m) and 33 ft high (10 m) in dimension, mapped out on a grid scale of 1-inch (25 mm) equaling 100 li (unit) (the Chinese equivalent of the mile/kilometer). Jia Dan is also known for having described the Persian Gulf region with great detail, along with lighthouses that were erected at the mouth of the Persian Gulf by the medieval Iranians in the Abbasid period (refer to article on Tang Dynasty for more).
During the Song Dynasty (960–1279) Emperor Taizu of Song ordered Lu Duosun in 971 to update and \\\'re-write all the Tu Jing in the world\\\', which would seem to be a daunting task for one individual, who was sent out throughout the provinces to collect texts and as much data as possible. With the aid of Song Zhun, the massive work was completed in 1010, with some 1566 chapters. The later Song Shi historical text stated (Wade-Giles spelling):
........Yuan Hsieh (d. +1220) was Director-General of governmental grain stores. In pursuance of his schemes for the relief of famines he issued orders that each pao (village) should prepare a map which would show the fields and mountains, the rivers and the roads in fullest detail. The maps of all the pao were joined together to make a map of the tu (larger district), and these in turn were joined with others to make a map of the hsiang and the hsien (still larger districts). If there was any trouble about the collection of taxes or the distribution of grain, or if the question of chasing robbers and bandits arose, the provincial officials could readily carry out their duties by the aid of the maps.....
Like the earlier Liang Dynasty stone-stele maps (mentioned above), there were large and intricately carved stone stele maps of the Song period. For example, the 3 ft (0.91 m) squared stone stele map of an anonymous artist in 1137, following the grid scale of 100 li squared for each grid square. :Plate LXXXI What is truly remarkable about this map is the incredibly precise detail of coastal outlines and river systems in China (refer to Needham\\\'s Volume 3, Plate LXXXI for an image). The map shows 500 settlements and a dozen rivers in China, and extends as far as Korea and India. On the reverse, a copy of a more ancient map uses grid coordinates in a scale of 1:1,500,000 and shows the coastline of China with great accuracy.
The famous 11th century scientist and polymath statesman Shen Kuo (1031–1095) was also a geographer and cartographer. His largest atlas included twenty three maps of China and foreign regions that were drawn at a uniform scale of 1:900,000. Shen also created a three-dimensional raised-relief map using sawdust, wood, beeswax, and wheat paste, while representing the topography and specific locations of a frontier region to the imperial court. Shen Kuo\\\'s contemporary, Su Song (1020–1101), was a cartographer who created detailed maps in order to resolve a territorial border dispute between the Song Dynasty and the Liao Dynasty.
The Da Ming hunyi tu map, dating from about 1390, is in multicolour. The horizontal scale is 1:820,000 and the vertical scale is 1:1,060,000.
In 1579, Luo Hongxian published the Guang Yutu atlas, including more than 40 maps, a grid system, and a systematic way of representing major landmarks such as mountains, rivers, roads and borders. The Guang Yutu incorporates the discoveries of naval explorer Zheng He\\\'s 15th century voyages along the coasts of China, Southeast Asia, India and Africa. The Mao Kun map published in 1628 is thought to be based on a strip map dated to the voyages of Zheng He.
From the 16th and 17th centuries, several examples survive of maps focused on cultural information. Gridlines are not used on either Yu Shi\\\'s Gujin xingsheng zhi tu (1555) or Zhang Huang\\\'s Tushu bian (1613); instead, illustrations and annotations show mythical places, exotic foreign peoples, administrative changes and the deeds of historic and legendary heroes. Also in the 17th century, an edition of a possible Tang Dynasty map shows clear topographical contour lines. Although topographic features were part of maps in China for centuries, a Fujian county official Ye Chunji (1532–1595) was the first to base county maps using on-site topographical surveying and observations.
The Korean made Kangnido based on two Chinese maps, which describes the Old World.
After the 1949 revolution, the Institute of Geography under the aegis of the Chinese Academy of Sciences became responsible for official cartography and emulated the Soviet model of geography throughout the 1950s. With its emphasis on fieldwork, sound knowledge of the physical environment and the interrelation between physical and economic geography, the Russian influence counterbalanced the many pre-liberation Western-trained Chinese geography specialists who were more interested in the historical and culture aspects of cartography. As a consequence, China\\\'s main geographical journal, the Dili Xuebao (地理学报) featured many articles by Soviet geographers. As Soviet influence waned in the 1960s, geographic activity continued as part of the process of modernisation until it came to a stop with the 1967 Cultural Revolution.
1796 Barrow Large Antique Map Sea Chart Lord Macartneys Voyage England to China
Antique Map
- Title : A General Chart on Mercators Projection, To Shew The Track of the Lion and Hindostan from England to the Gulph of Pekin in China, and of their return to England, with the daily statement of the Barometer and Thermometer as observed at noon; containing also the limits of the Chinese Empire, as extended by the Conquests of the present Emperor Tchien-Lung
- Ref #: 93409
- Size: 39 1/2in x 26 1/2in (1.00m x 675mm)
- Date : 1796
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This very large original copper plate engraved antique map, a chart, by John Barrow, in 1796, was issued in the atlas volume of the official account by George Staunton of Lord George Macartneys travels to China, An Authentic Account of an Embassy from the King of Great Britain to the Emporer of China in 1796..
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39 1/2in x 26 1/2in (1.00m x 675mm)
Plate size: - 38in x 24 1/2in (960mm x 620mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Light soiling along bottom folds, as issued
Verso: - Bottom folds re-enforced along bottom folds
Background:
Lord George Macartney was Britains first envoy to China, tasked with convincing Emperor Qianlong to ease restrictions on trade between Great Britain and China and to allow the 1st British embassy to be established. He was not successful in either of these endeavours.
The map shows the track of two ships, the Lion and Hindostan, on their routes from England to China and back. Each days progress was recorded along the route, with several notations to the dangers along the way.
The map was drawn by John Barrow, who was the private secretary to Lord Macartney.
The chart extends from Turon Bay (present day Da Nang, Vietnam) up the coast of eastern Asia to the Gulph of Leao-Tung in the Whang-Hai or Yellow Sea (the Gulf of Bohai in the Yellow Sea). The track of the Lion, Hindostan, and Tenders is traced, with soundings, sea bottom classifications, temperature and barometric readings, dates, and assorted notes, such as Lion and Tenders parted from the Hindostan in the fog. China is divided into several provinces, and many towns and cities are named, including Beijing (here referred to as Pekin). A portion of the Great Wall of China is depicted and rivers are accompanied by notes on their courses and sources. Taiwan is depicted with incomplete borders to the east of the ships\' track. Engraved by B. Baker and published by George Nicol.
Barrow, Sir John 1764 - 1848
Barrow, 1st Baronet, was an English civil servant, geographer, linguist and writer. Barrows legacy has been met with mixed analysis. Some historians regard Barrow as an instrument of imperialism who portrayed Africa as a resource rich land devoid of any human or civilized elements. Nonetheless, other historians consider Barrow to have promoted humanitarianism and rights for South Africans.
Barrow was born the only child of Roger Barrow, a tanner in the village of Dragley Beck, in the parish of Ulverston, Lancashire. He was schooled at Town Bank grammar school, Ulverston, but left at age 13 to found a Sunday school for the poor.
Barrow was employed as superintending clerk of an iron foundry at Liverpool. At only 16, he went on a whaling expedition to Greenland. By his twenties, he was teaching mathematics, in which he had always excelled, at a private school in Greenwich.
Barrow taught mathematics to the son of Sir George Leonard Staunton; through Stauntons interest, he was attached on the first British embassy to China from 1792 to 1794 as comptroller of the household to Lord Macartney. He soon acquired a good knowledge of the Chinese language, on which he subsequently contributed articles to the Quarterly Review; and the account of the embassy published by Sir George Staunton records many of Barrows valuable contributions to literature and science connected with China.
Barrow ceased to be officially connected with Chinese affairs after the return of the embassy in 1794, but he always took much interest in them, and on critical occasions was frequently consulted by the British government.
Some historians attribute the stagnation thesis to Barrow; that China was an extremely civilized nation that was in a process of decay by the time of European contact.
In 1797, Barrow accompanied Lord Macartney as private secretary in his important and delicate mission to settle the government of the newly acquired colony of the Cape of Good Hope. Barrow was entrusted with the task of reconciling the Boer settlers and the native Black population and of reporting on the country in the interior. In the course of the trip, he visited all parts of the colony; when he returned, he was appointed auditor-general of public accounts. He then decided to settle in South Africa, married, and bought a house in 1800 in Cape Town. However, the surrender of the colony at the peace of Amiens (1802) upset this plan.
During his travels through South Africa, Barrow compiled copious notes and sketches of the countryside that he was traversing. The outcome of his journeys was a map which, despite its numerous errors, was the first published modern map of the southern parts of the Cape Colony. Barrows descriptions of South Africa greatly influenced Europeans understanding of South Africa and its peoples. William John Burchell (1781–1863) was particularly scathing: As to the miserable thing called a map, which has been prefixed to Mr. Barrows quarto, I perfectly agree with Professor Lichtenstein, that it is so defective that it can seldom be found of any use.
Barrow returned to Britain in 1804 and was appointed Second Secretary to the Admiralty by Viscount Melville, a post which he held for forty years – apart from a short period in 1806–1807 when there was a Whig government in power. Lord Grey took office as Prime Minister in 1830, and Barrow was especially requested to remain in his post, starting the principle that senior civil servants stay in office on change of government and serve in a non-partisan manner. Indeed, it was during his occupancy of the post that it was renamed Permanent Secretary. Barrow enjoyed the esteem and confidence of all the eleven chief lords who successively presided at the Admiralty board during that period, and more especially of King William IV while lord high admiral, who honoured him with tokens of his personal regard.
In his position at the Admiralty, Barrow was a great promoter of Arctic voyages of discovery, including those of John Ross, William Edward Parry, James Clark Ross and John Franklin. The Barrow Strait in the Canadian Arctic as well as Point Barrow and the city of Barrow in Alaska are named after him. He is reputed to have been the initial proposer of Saint Helena as the new place of exile for Napoleon Bonaparte following the Battle of Waterloo in 1815. Barrow was a fellow of the Royal Society and received the degree of LL.D from the University of Edinburgh in 1821. A baronetcy was conferred on him by Sir Robert Peel in 1835. He was also a member of the Raleigh Club, a forerunner of the Royal Geographical Society.
Barrow retired from public life in 1845 and devoted himself to writing a history of the modern Arctic voyages of discovery (1846), as well as his autobiography, published in 1847. He died suddenly on 23 November 1848. The Sir John Barrow monument was built in his honour on Hoad Hill overlooking his home town of Ulverston, though locally it is more commonly called Hoad Monument. Mount Barrow and Barrow Island in Australia are believed to have been named for him.
1856 A H Dufour Very Large Antique World Map on Mercators Projection - Scarce
- Title : Mappe-Monde Planispherique Physique et Hydrographique. CH Dyonnet..1856
- Ref #: 61019
- Size: 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large, magnificent hand coloured original copper plate antique World Map on Mercators Projection -adorned with scientific data - by Adolphe Hippolyte Dufour was engraved by Charles Dyonnet in 1857 - dated in the title - for Dufours 1860 edition of his monumental elephant folio Atlas Physique, Historique et Politique Geographie Modernepublished by Pauline Et La Chevalier, Paris.
The 19th century French cartographer Auguste-Henri Dufour began publishing the dramatic elephant folio Atlas Universel, also occasionally titled Grand Atlas Universal, around 1855. Several editions appeared between its initial publication in the 1850s and a final run c. 1870. The 1863 and 1864 editions in particular are highly desirable among collectors because the United States and North America maps illustrate the proposed, but unrealized, state of Corona (roughly modern day Utah). The atlas contained roughly 40 maps, most of which were engraved by Louis Antoine (the maps) and Deletre (typography) under the supervision of Charles Dyonnet, official engraver of the Depot de la Marine. The Atlas Universal was published in Paris and edited by the firm of Paulin et le Chevalier, 60 Rue Richelieu.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charles Dyonnet 1822 - 1880 was an extremely active Paris based engraver working in the mid to late 19th century. From his offices at 220 Rue St. Jacques, Paris, Dyonnet engraved numerous maps for many of the most prominent 19th French cartographic publishers including Vuillemin, Dufour, Fremin and Duvotenay. From 1850-1861, he held the coveted position of Graveur du Dépot de la Marine, and in this position engraved numerous French naval and military maps. Dyonnet had a detail oriented and aesthetically minded hand and is responsible from some of the most beautiful French maps to emerge during the 19th century. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1715 William Dampier Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map, California Is. Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Mappe-Monde
- Ref #: 61142
- Size: 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1715
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautiful copper-plate engraved scarce, original antique Twin Hemisphere World Map by William Dampier was published in the 1715 French edition of A New Voyage Around the World (Nouveau Voyage autour du Monde)
Fantastic map showing the route taken by Dampier on his first voyage in his ship Roebuck, visiting NW Australia, GOM and Southern Africa whilst circumnavigating the world. California is shown as an island as was the popular belief at the time.
Background: William Dampier (1651 - 1715) was an English explorer and navigator who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australia's first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the Admiralty with his book A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, before being court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crewmate who may have inspired Daniel Defoe's Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Horatio Nelson, Charles Darwin.
In 1679, Dampier joined the crew of the buccaneer Captain Bartholomew Sharp on the Spanish Main of Central America, twice visiting the Bay of Campeche, or "Campeachy" as it was then known, on the north coast of Mexico. This led to his first circumnavigation, during which he accompanied a raid across the Isthmus of Darién in Panama and took part in the capture of Spanish ships on the Pacific coast of that isthmus. The pirates then raided Spanish settlements in Peru before returning to the Caribbean.
Dampier made his way to Virginia, where in 1683 he was engaged by the privateer John Cooke. Cooke entered the Pacific via Cape Horn and spent a year raiding Spanish possessions in Peru, the Galápagos Islands, and Mexico. This expedition collected buccaneers and ships as it went along, at one time having a fleet of ten vessels. Cooke died in Mexico, and a new leader, Edward Davis, was elected captain by the crew.
Dampier transferred to the privateer Charles Swan's ship, Cygnet, and on 31 March 1686 they set out across the Pacific to raid the East Indies, calling at Guam and Mindanao. Spanish witnesses saw the predominantly English crew as not only pirates and heretics but also cannibals. Leaving Swan and 36 others behind on Mindanao, the rest of the privateers sailed on to Manila, Poulo Condor, China, the Spice Islands, and New Holland. Contrary to Dampier's later claim that he had not actively participated in actual piratical attacks during this voyage, he was in fact selected in 1687 to command one of the Spanish ships captured by Cygnet's crew off Manila.
On 5 January 1688, Cygnet "anchored two miles from shore in 29 fathoms" on the northwest coast of Australia, near King Sound. Dampier and his ship remained there until March 12, and while the ship was being careened Dampier made notes on the fauna and flora and the indigenous peoples he found there. Among his fellows were a significant number of Spanish sailors, most notably Alonso Ramírez, a native of San Juan, Puerto Rico Later that year, by agreement, Dampier and two shipmates were marooned on one of the Nicobar Islands. They obtained a small canoe which they modified after first capsizing and then, after surviving a great storm at sea, called at "Acheen" (Aceh) in Sumatra.
Dampier returned to England in 1691 via the Cape of Good Hope, penniless but in possession of his journals. He also had as a source of income a slave known as Prince Jeoly (or Giolo), from Miangas (now Indonesia), who became famous for his tattoos (or "paintings" as they were known at the time). Dampier exhibited Jeoly in London, thereby also generating publicity for a book based on his diaries.
The publication of the book, A New Voyage Round the World, in 1697 was a popular sensation, creating interest at the Admiralty. In 1699, Dampier was given command of the 26-gun warship HMS Roebuck, with a commission from King William III (who had ruled jointly with Queen Mary II until her death in 1694). His mission was to explore the east coast of New Holland, the name given by the Dutch to what is now Australia, and Dampier's intention was to travel there via Cape Horn.
The expedition set out on 14 January 1699, too late in the season to attempt the Horn, so it headed to New Holland via the Cape of Good Hope instead. Following the Dutch route to the Indies, Dampier passed between Dirk Hartog Island and the Western Australian mainland into what he called Shark Bay on 6 August 1699. He landed and began producing the first known detailed record of Australian flora and fauna. The botanical drawings that were made are believed to be by his clerk, James Brand. Dampier then followed the coast north-east, reaching the Dampier Archipelago and Lagrange Bay, just south of what is now called Roebuck Bay, all the while recording and collecting specimens, including many shells. From there he bore northward for Timor. Then he sailed east and on 3 December 1699 rounded New Guinea, which he passed to the north. He traced the south-eastern coasts of New Hanover, New Ireland and New Britain, charting the Dampier Strait between these islands (now the Bismarck Archipelago) and New Guinea. En route, he paused to collect specimens such as giant clams.
By this time, Roebuck was in such bad condition that Dampier was forced to abandon his plan to examine the east coast of New Holland while less than a hundred miles from it. In danger of sinking, he attempted to make the return voyage to England, but the ship foundered at Ascension Island on 21 February 1701. While anchored offshore the ship began to take on more water and the carpenter could do nothing with the worm-eaten planking. As a result, the vessel had to be run aground. Dampier's crew was marooned there for five weeks before being picked up on 3 April by an East Indiaman and returned home in August 1701.
Although many papers were lost with Roebuck, Dampier was able to save some new charts of coastlines, and his record of trade winds and currents in the seas around Australia and New Guinea. He also preserved a few of his specimens. In 2001, the Roebuck wreck was located in Clarence Bay, Ascension Island, by a team from the Western Australian Maritime Museum. Because of his widespread influence, and also because so little exists that can now be linked to him, it has been argued that the remains of his ship and the objects still at the site on Ascension Island – while the property of Britain and subject to the island government's management – are actually the shared maritime heritage of those parts of the world first visited or described by him. His account of the expedition was published as A Voyage to New Holland in 1703.
The War of the Spanish Succession had broken out in 1701, and English privateers were being readied to act against French and Spanish interests. Dampier was appointed commander of the 26-gun ship St George, with a crew of 120 men. They were joined by the 16-gun Cinque Ports with 63 men, and sailed on 11 September 1703 from Kinsale, Ireland. The two ships made a storm-tossed passage round Cape Horn, arriving at the Juan Fernández Islands off the coast of Chile in February 1704. While watering and provisioning there, they sighted a heavily armed French merchantman, which they engaged in a seven-hour battle but were driven off.
Dampier succeeded in capturing a number of small Spanish ships along the coast of Peru, but released them after removing only a fraction of their cargoes because he believed they "would be a hindrance to his greater designs. The greater design he had in mind was a raid on Santa María, a town on the Gulf of Panama rumoured to hold stockpiles of gold from nearby mines. When the force of seamen he led against the town met with unexpectedly strong resistance, however, he withdrew. In May 1704, Cinque Ports separated from St George and, after putting Alexander Selkirk ashore alone on an island for complaining about the vessel's seaworthiness, sank off the coast of what is today Colombia. Some of its crew survived being shipwrecked but were made prisoners of the Spanish.
It was now left to St George to make an attempt on the Manila galleon, the main object of the expedition. The ship was sighted on 6 December 1704, probably Nuestra Señora del Rosario. It was caught unprepared and had not run out its guns. But while Dampier and his officers argued over the best way to mount an attack, the galleon got its guns loaded and the battle was joined. St George soon found itself out-sized by the galleon's 18- and 24-pounders, and, suffering serious damage, they were forced to break off the attack.
The failure to capture the Spanish galleon completed the break-up of the expedition. Dampier, with about thirty men, stayed in St George, while the rest of the crew took a captured barque across the Pacific to Amboyna in the Dutch settlements. The undermanned and worm-damaged St George had to be abandoned on the coast of Peru. He and his remaining men embarked in a Spanish prize for the East Indies, where they were thrown into prison as pirates by their supposed allies the Dutch but later released. Now without a ship, Dampier made his way back to England at the end of 1707.
In 1708, Dampier was engaged to serve on the privateer Duke, not as captain but as sailing master. Duke beat its way into the South Pacific Ocean round Cape Horn in consort with a second ship, Duchess. Commanded by Woodes Rogers, this voyage was more successful: Selkirk was rescued on 2 February 1709, and the expedition amassed £147,975 (equivalent to £19.9 million today) worth of plundered goods. Most of that came from the capture of a Spanish galleon, Nuestra Señora de la Encarnación y Desengaño, along the coast of Mexico in December 1709.
In January 1710, Dampier crossed the Pacific in Duke, accompanied by Duchess and two prizes. They stopped at Guam before arriving in Batavia. Following a refit at Horn Island (near Batavia) and the sale of one of their prize ships, they sailed for the Cape of Good Hope where they remained for more than three months awaiting a convoy. They left the Cape in company with 25 Dutch and English ships, with Dampier now serving as sailing master of Encarnación. After a further delay at the Texel, they dropped anchor at the Thames in London on 14 October 1711.
Dampier may not have lived to receive all of his share of the expedition's gains. He died in the Parish of St Stephen Coleman Street, London. The exact date and circumstances of his death, and his final resting place, are all unknown. His will was proven on 23 March 1715, and it is generally assumed he died earlier that month, but this is not known with any certainty. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light age toning along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued, light age toning along folds
1712 J Senex & W Whiston Large Antique Astronomy Print of Planets & Solar System
Antique Map
- Title : A Scheme of the Solar System with the Orbits of the Planets and Comets belonging thereto, Described from Dr. Halley\'s accurate Table of Comets Philosoph, Transact. No. 297. Founded on Sr. Isaac Newton\'s wonderful discoveries By Wm. Whiston M.A.
- Size: 27in x 21in (585mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1712
- Ref #: 80773
Description:
This large original important copper plate engraved antique map of the Planets & Solar System according to Edmund Halley, Isaac Newton & William Whiston by John Senex in 1712, was published in his Elephant Folio Atlas.
This map is rare and is unfortunately damaged, not unusual for these large maps. Approx 4in strip from the left side of the map & approx 1in from the bottom of the map is missing and has been mounted on contemporary 18th century paper. Still the majority of the map remains and is still a fascinating look into our knowledge of Solar System at the beginning of the 18th century. At the moment there a couple for sale online selling for between $1500 - $5000
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (585mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (585mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Approx 4in strip from the left side of the map is missing
Plate area: - Two repairs to top of image
Verso: - Repairs as noted
Background:
A large and impressive chart of the solar system, paying particular attention to the motions of the planetary bodies and the paths of comets. The chart was originally engraved in 1712 by Senex to accompany the lectures of the controversial theologian, astronomer, and polymath William Whiston. The chart was issued again in 1720 by Senex alone, and finally by Bowles and Sayer in the 1760s. The System is shown as a number of concentric orbits with the Sun at centre, criss-crossed by the broad elliptical paths of a number of comets. At top, the planets are shown pictorially, clumped together in an attempt to demonstrate scale. As the chart was engraved at the beginning of the eighteenth century, the outer planets past Saturn are not included. Earths moon is accorded an honorary spot among the planets, while the moons of the other planets are shown in the grand scheme as Satellites. The alchemical symbols for the zodiac are included along the outside ring of the System, and the chart is absolutely covered by explanatory text.
William Whiston (1667-1752) was an English mathematician, theologian, historian and religious writer. Born in Leicestershire, Whiston was a leading figure in popularising the ideas of Sir Issac Newton, who was his mentor and teacher. Whiston was a professor of mathematics at the University of Cambridge but was expelled from his position in 1710 due to his unorthodox religious beliefs and views. Whiston was a believer of Arianism, the idea that Christ is subordinate to God, the concept of Christ is based on the belief that the Son of God did not always exist but was begotten by God the Father. He also rejected the notion of eternal torment in hellfire. What especially placed him against church authorities, was he viewed the Trinity as a lie after extensive personal research convinced him the origin of the Trinity teaching to be pagan. Whiston wrote A New Theory of the Earth, published in 1696, in which he presented a description of the divine creation of the Earth, postulating that the earth originated from the atmosphere of a comet.
1841 Ferdinando Artaria Early Antique Map of The Lost City of Pompeii, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Plan de Pompei. Pianta della Città di Pompei Cheserve di corredo alla nuovissima Guida d'Italia.
- Ref #: 61202
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 20 1/2in x 12 1/2in (510mm x 320mm)
- Date: 1841
Description
This original copper-plate antique map of the lost city of Pompeii by Ferdinando Artaria in 1841.
The map depicts the famously devastated city from the Villa of Diomede to the amphitheater. Colors differentiate between public buildings, private buildings, buildings in ruins, and areas that had not yet been excavated. Numbers identify over 110 locations throughout the city, including The Forum, Basilica, Amphitheater, and Giulio Felice house which are identified by name.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 12 1/2in (510mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 12 1/2in (510mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Ferdinando Artaria (1781 - June 25, 1843) was an Italian publisher and seller of maps, music, and prints. Artaria opened his first shop around 1805. He soon began collaborating with Giuseppe Werz (1764 - 1827), who introduced lithographic techniques from Bavaria to Italy in 1808. Artaria opened his own lithography works in 1817 and the name changed to Ferdinando Artaria e Figlio in 1837. This business was the first to publish aquatints made from daguerrotypes. After Artaria died, his son Pasquale ran the business. He sold it to his brother-in-law Francesco Scacchi (1807 - 1900) in 1852, who changed the name of the firm to Ditta Artaria di Gerdinando Sacchi e figli' in 1872. After Scacchi's death, his sons Edoardo and Alberto ran the business until 1921, when it was acquired by the 'BOttega di Poesia' publishing house.
1837 SDUK Large Original Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map
- Title : Western Hemisphere; Eastern Hemisphere
- Date : 1837
- Size: 26 1/2in x 15 1/2in (675mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 32528
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique twin hemisphere world map was engraved by J & C Walker and was published by the SDUK in 1837.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 15 1/2in (675mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 15 1/2in (675mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Blind library stamp
Verso: - Centerfold re-joined
Background:
The map depicts the Western and Eastern Hemispheres offering a fascinating snapshot of the world during a period of rapid globalization and discovery. Both maps note towns, rivers, mountains, deserts, islands, and various other important topographical details. Elevation throughout is rendered by hachure.
The map of the Western Hemisphere covers North America, South America, West Indies and most of Polynesia, including New Zealand. The Antarctic continent, first sighted in 1820, but neglected during the first half of the 19th century, does not appear on the map.
The map of the Eastern Hemisphere includes the entirety of Asia, Europe and Africa as well as Australia and much of the Pacific. The interior of Australia is largely blank though the coastal colonies are noted. These include Mediterranean North Africa, Egypt, Abyssinia, the western Niger valley, the Congo, South Africa, and the lands of Mozambique and Zimbabwe.
This map is part of a Series of Maps, Modern and Ancient, issued by subscription. Each folder in the series would contain a set of two maps bound together. These two maps were issued in folder no. XCII. Original folder includes the names of committee members of the ‘Society’, maps already published, the contents and the printer and publication details. These maps were engraved by J. and C. Walker. This folder was printed by William Clowes and Sons for the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge in their September 30, 1841 subscriber’s edition folder. The folder at the time was priced at 1 shilling plain or 1 shilling 6 pence for colored maps.
1821 Brue Large Antique World Map of Mercators Projection - New Holland, Texas
- Title : Mappemonde Physique...par Brue......1821
- Ref #: 32440
- Size: 24in x 18in (610mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1821
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original antique World map on Mercator's projection was engraved in 1821 - the date is engraved in the title - and was published in Adrien Brue's (1786 - 1832) large Atlas Universel de Geographie.
A fantastic World map in a time of great change. The map centres on New Holland or Australia (officially named Australia in 1824 by the British) Mexico still holds sway on the western portion of North America. Much of Capt. Cooks discoveries are recognised on this map in NW America and the south Pacific but not his explorations in Antarctica and beyond. Central Africa still remains relatively unexplored by the Europeans as does the Artic north of Canada. A fantastic map. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24in x 18in (610mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15 1/2in (545mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling in margins, repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - Soiling and spotting to top of map
Verso: - Soiling
1816 John Thomson Large Antique Map of Southern India & Northern Sri Lanka
- Title : Southern Hindostan....Drawn & Engraved for Thomsons New General Atlas, 1816
- Date : 1816
- Size: 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 41004
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of South India & northern Sri Lanka by John Thomson was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1816 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons New General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin soiling and cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The cartography of India begins with early charts for navigation and constructional plans for buildings. Indian traditions influenced Tibetan and Islamic traditions, and in turn, were influenced by the British cartographers who solidified modern concepts into India\'s map making
A prominent foreign geographer and cartographer was Hellenistic geographer Ptolemy (90–168) who researched at the library in Alexandria to produce a detailed eight-volume record of world geography. During the Middle Ages, India sees some exploration by Chinese and Muslim geographers, while European maps of India remain very sketchy. A prominent medieval cartographer was Persian geographer Abu Rayhan Biruni (973–1048) who visited India and studied the country\'s geography extensively.
European maps become more accurate with the Age of Exploration and Portuguese India from the 16th century. The first modern maps were produced by Survey of India, established in 1767 by the British East India Company. Survey of India remains in continued existence as the official mapping authority of the Republic of India.
1740 Guillaume Delisle Original Antique Atlas Title Page of Atlante Novissimo
- Title : Atlante Novissimo Del Sig. r Guglielmo De L Isle
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 70345
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique frontispiece from the Italian version of Guillaume Delisle atlas Atlante Novissimo, was published by Girolamo Albrizzi in 1740.
The architectural columns are flanked by both male & female Roman soldier. At the top of the structure, a pair of putti hold aloft the covering drapes. Within the structure are two internal cartouche, one a vignette view of the city of Venice, where the atlas was published, and above, the symbol for the Society of Jesus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1682 Du Val Original Antique Map of North Pole, North America, Europe, Russia
- Title : Terres Arctiques.. Septemtrional et Boreales.
- Date : 1682
- Size: 6 1/2in x 6in (160mm x 155mm)
- Ref #: 22138
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original 1682 antique map of the North Pole by Pierre Du Val was published in his 1682 miniature atlas, 'Géographie Universelle'.Jacques Nicholas Bellindu
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 6 1/2in x 6in (160mm x 155mm)
Plate size: - 5in x 4in (125mm x 100mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A driving force for the exploration of the Arctic was the desire of European monarchs to find an alternate trading route to China, via either a Northwest Passage along the coast of North America, or a Northeast Passage along the coast of Siberia. A number of expeditions sought such routes in the 1500-1700s, which resulted in the discovery of much of northern North America, but no viable passage.
In 1524, under the direction of the king of France, Giovanni da Verrazano took the entrance to Hudson River (now New York City) to be the entrance for the passage, and ten years later Jacques Cartier likewise discovered the St. Lawrence estuary. The first Englishman to seek the passage was Martin Frobisher in three voyages up to 60°N between 1576 and 1578. On his first voyage, relations with the natives quickly became hostile, and a prisoner was brought back to England. John Davis followed in 1585, 1586, and 1587 charting the strait west of Greenland that now bears his name.
Financed by the Dutch, in 1609 the Englishman Henry Hudson followed Verrazano's course, and explored the river that now bears his name. The following year he discovered the vast inlet (now called Hudson Bay) beyond Davis Strait. Robert Bylot and navigator William Baffin undertook two expeditions in 1615 and 1616, exploring the north coast of Greenland up to 78°N and then along the Canadian archipelago to Lancaster Sound. Convinced it was only a bay, Baffin concluded that no Northwest Passage existed, and interest in searching for one waned for the next 200 years.
Other explorers were drawn to search for a Northeast Passage connecting the White Sea and Bering Sea. The Dutch navigator William Barents led three expeditions east of Novaya Zemlya, and on the third expedition in 1596 claimed Spitsbergen. From the early 16th century, Russian navigators used shallow draft vessels with reinforced bottoms (kochi) to cross the Kara Sea and explore the Ob and Yenisey rivers. Yermak's Cossacks expanded the Russian presence eastward, crossing the Ural Mountains in 1581. In 1601, Mangazeya town was founded at Taz River between the Ob and Yenisey rivers, and dozens of boats from Pomor lands began annual navigations.
Throughout the first quarter of the 17th century, a great number of merchants, trappers and Cossacks moved east and north, settled East Siberia and explored the northern Siberian coast. In 1610, the Yenisey River was navigated to its northern estuary and the coast to the estuary of the Pyasina was explored. Cape Chelyuskin was overtaken from the west in 1617, Yakutian Cossacks Ivan Rebrov and Ilya Perfilyev headed down to the Lena River estuary and made the first sea voyage to the Yana River in 1633, and in 1639, the Pacific shore was reached by Ivan Moskvitin and his detachment of Cossacks. In a 15-year timespan, all Siberian river estuaries from Khatanga to Kolyma had been discovered and a large part of the Northeast Passage from the White Sea to Kolyma estuary had been covered. Semen Dezhnev traversed the final segment in 1648, leading 90 Cossacks on a journey from the Kolyma to Anadyr Rivers, discovering the strait between Asia and America (proving that they were different continents) and passing the cape which now bears his name.
1845 Sydney Hall Large Antique World Map insets Singapore, Hong Kong, Cape, TAS
- Title : 1845 Sydney Hall Large Antique World Map insets Singapore, Hong Kong, Cape, TAS
- Size: 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Date : 1843
- Ref #: 32258-1
Description:
This large original steel-plate antique world map - with 5 inset maps of Hong Kong, Van Diemens Land, Calcutta, Singapore & the Colony Of Good Hope - by Sydney Hall was published by Longman & co. in 1845. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small loss to top centerfold, into border
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape, light soiling
Background:
A highly detailed and attractive map of the world, with seven inset maps of British colonies: Hong Kong, Van Diemens Land, Calcutta, Singapore & the Colony Of Good Hope. A note on the Pitcairn Islands records their colonisation by the mutineers from the Bounty.
Also prominent in North America is an independent Texas along with an extended Mexico into the SW and California regions.
1762 Bonne, Janvier, & Zannoni Original Antique Atlas Title Page to Atlas Modern
- Title : Atlas Moderne ou Collection De Cartes Sur toutes les parties du Globe Terrestre
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 92277
- Date : 1762
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique frontispiece from the atlas Atlas Moderne of a Collection of Maps by Rigobert Bonne, Jean Janvier, & Rizzi Zannoni was published by Jean Lattre in 1762, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1767 Clouet Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map - Misshapen Australia
- Title : De La Terre En General
- Ref #: 16275
- Size: 23in x 16in (585mm x 410mm)
- Date : 1767
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, large beautifully hand coloured original antique Twin Hemisphere World Map - with an unusually depicted southern coast of Australia and French text on the General views of the World at the time - by Jean Baptiste Louis Clouet (1730-87) was published byMondhare et Jean, Paris in the 1767 edition of Clouets Atlas Geographie moderne avec une introduction. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 16in (585mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 13in (575mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None