City Plans (19)
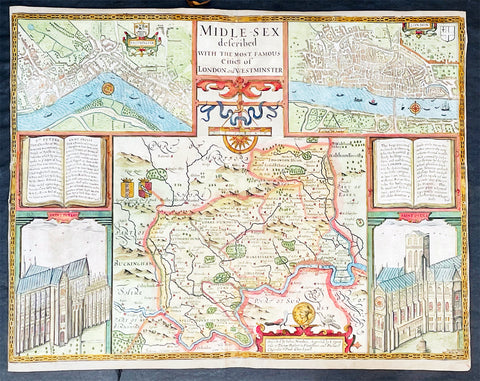
1676 John Speed Antique Map of County of Midlesex Views London & Westminster
- Title : Midle-sex Described with the most Famous Cities of London and Westminster
- Date : 1676
- Size: 20 1/4in x 16 3/4in (515mm x 425mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Ref: 35613
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map & views of London and the English county of Middlesex by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine.
The map is embellished with the famous birds-eye views of London, Westminster and the churches of St Peters (Westminster Abbey) and old St Pauls before the great fire of London in 1666. English descriptive text of London on the verso.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/4in x 16 3/4in (515mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/4in x 15 1/2in (515mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (2mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins cropped to plate-marks
Plate area: - Re-enforced along centerfold very small loss in places, light creasing
Verso: - Re-enforced along centerfold and in several places with transparent archival tape
Background:
This county map of Middlesex, now greater London, illustrates the market towns of Enfield, Pancras, Osterley and Staines. The map is dominated by four large vignettes with the environs of London and the county situated in the central portion of the map. The actual cartography is based on the surveys performed by John Norden, the earlier English antiquary and map maker, who unsuccessfully attempted to publish an updated county atlas of the United Kingdom before Speed. Norden also lived most of his life in Middlesex, thus becoming an obvious source for the map.
The City of London is clearly shown on the lower right of the map with villages such as Hamsted, Pancras, Kensington and Paddington marked around the city. To the lower centre of the map is an acknowledgement to the original survey by Norden, augmented by Speed himself.
Although the cartography is of some note, it is the vignettes for which this map is justly famous. To the two bottom corners are the famous Churchs of St. Peter (Westminster Abbey) Westminster on the left and St. Pauls to the right. This is the medieval Cathedral of St. Pauls, just after it had lost its spire in 1561 and before the Great Fire of 1666, in which it was destroyed then rebuilt in its present form by Sir Christopher Wren. Above these two church vignettes are two text panels in the form of books, the one on the left describing the two churches and the other on the right with a description of London itself.
Finally, two large vignettes on the upper left and right corners depict the two cities of Westminster and London respectively. It is believed that Speed was not responsible for either of these images, more likely drawing from Norden, although there are no surviving evidence of this, to date yet to be found. There are also theories that these two views may have come from either a German sources or other lost birds-eye views of London by unknown persons.
Due to modern growth of London and border changes, the county of Middlesex no longer exists, but there is little doubt this is the most the best map of London and Middlesex published in the 17th century. English text on verso
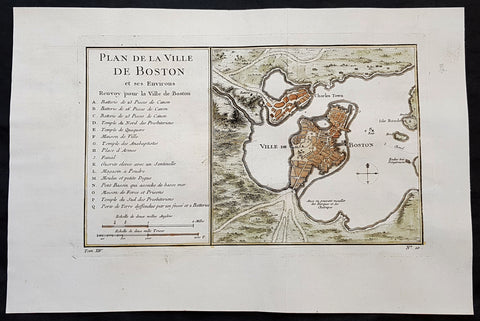
1756 J N Bellin Antique Map of The City of Boston & Charlestown
Antique Map
- Title : Plan de la Ville De Boston et ses Environs
- Ref #: 93417
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (350mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Boston and surrounding areas - one of the earliest obtainable maps of the city - by Jacques Nicholas Bellin in 1756 - was published in the French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Beautiful map with great street and building detail in both Boston and Charlestown, showing parts of Ronde Isle and the mainland. Important buildings and areas identified in an idex at the left of the map. Including three cannon batteries, the Presbyterian Church, the Quaker temple, the Anabaptist Church, the City Hall, the Armory, Faneuil Hall (Spelled Fanal), etc. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (350mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 7 1/2in (285mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Boston is the capital city and most populous municipality of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States.
Boston is one of the oldest cities in the United States, founded on the Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by Puritan settlers from England. It was the scene of several key events of the American Revolution, such as the Boston Massacre, the Boston Tea Party, the Battle of Bunker Hill, and the Siege of Boston. Upon U.S. independence from Great Britain, it continued to be an important port and manufacturing hub as well as a center for education and culture.
In the 1820s, Boston\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s population grew rapidly, and the city\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European immigrants. Irish immigrants dominated the first wave of newcomers during this period, especially following the Irish Potato Famine; by 1850, about 35,000 Irish lived in Boston. In the latter half of the 19th century, the city saw increasing numbers of Irish, Germans, Lebanese, Syrians, French Canadians, and Russian and Polish Jews settling in the city. By the end of the 19th century, Boston\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s core neighborhoods had become enclaves of ethnically distinct immigrants. Italians inhabited the North End, Irish dominated South Boston and Charlestown, and Russian Jews lived in the West End. Irish and Italian immigrants brought with them Roman Catholicism. Currently, Catholics make up Boston\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s largest religious community and the Irish have played a major role in Boston politics since the early 20th century; prominent figures include the Kennedys, Tip O\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'Neill, and John F. Fitzgerald.
Between 1631 and 1890, the city tripled its area through land reclamation by filling in marshes, mud flats, and gaps between wharves along the waterfront. The largest reclamation efforts took place during the 19th century; beginning in 1807, the crown of Beacon Hill was used to fill in a 50-acre mill pond that later became the Haymarket Square area. The present-day State House sits atop this lowered Beacon Hill. Reclamation projects in the middle of the century created significant parts of the South End, the West End, the Financial District, and Chinatown.
After the Great Boston Fire of 1872, workers used building rubble as landfill along the downtown waterfront. During the mid- to-late 19th century, workers filled almost 600 acres of brackish Charles River marshlands west of Boston Common with gravel brought by rail from the hills of Needham Heights. The city annexed the adjacent towns of South Boston (1804), East Boston (1836), Roxbury (1868), Dorchester (including present day Mattapan and a portion of South Boston) (1870), Brighton (including present day Allston) (1874), West Roxbury (including present day Jamaica Plain and Roslindale) (1874), Charlestown (1874), and Hyde Park (1912). Other proposals were unsuccessful for the annexation of Brookline, Cambridge and Chelsea.
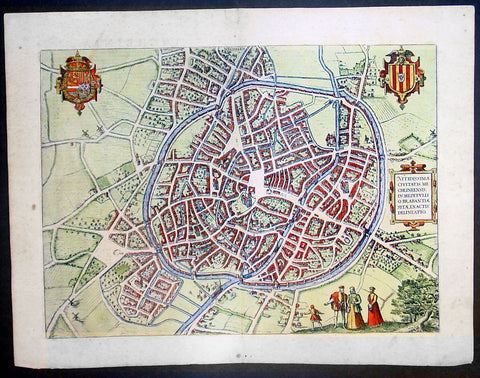
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Large Antique Print a View of Mechelen, Belgium
Antique Map
- Title : Mechelen - Nitidissimae Civitatis Mechlineensis in meditullio Brabantiae sitae, exactis: delineatio
- Ref #: 16247
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map a birds-eye view of the city of Mechelen in the Antwerp province of Flanders, Belgium was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II (1572-1612) intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
Franz Hogenberg's birthplace is illustrated twice. In the view presented in Volume I the cityscape is dominated by the massive tower belonging to the cathedral of Sint-Rombout, which measures almost 100 m in height. Behind the cathedral to the right lies the Onze-Lieve-Vrouwe church built in the Brabantine late Gothic style. In the present plate Mechelen is seen in a bird's-eye view from the northwest. Clearly apparent is the almost circular shape of the inner city, which has already spread beyond the bounds of the canal ringing the old city wall. In the Middle Ages staple rights and the cloth trade brought Mechelen great prosperity. In 1336 the city passed to the Duchy of Brabant, later to Burgundy, and developed into a highly regarded centre of commerce. The collapse of the cloth industry prompted the development of new areas of manufacturing, such as cannon and bell founding. In 1477 Mechelen passed to the Habsburgs and from 1507 to 1530, under the regency of Margaret of Austria, was capital of the Habsburg Netherlands. In 1559 Mechelen became an archbishopric and over the course of the Wars of Religion grew into a centre of the Counter-Reformation. For some time it was also the seat of the highest tribunal of the Habsburg Netherlands. (Taschen)
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13 1/2in (470mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
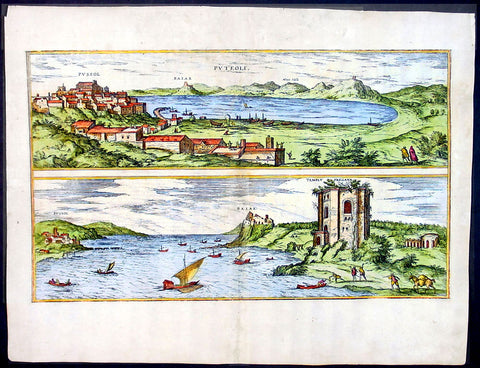
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Map of Pozzuoli Bay Naples Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Puteoli et Baiae
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92687
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique 2 x birds-eye view of the Bay of Pozzuoli -in the Gulf of Naples - with The city of Pozzuoli & the Port Of Baia visible was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The Gulf of Naples is a 10-mile wide gulf located in the south western coast of Italy, (province of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean Sea & is bordered on the north by the cities of Naples and Pozzuoli. To the east is Mount Vesuvius, and on the south by the Sorrentine Peninsula and its main town Sorrento; the Peninsula separates it from the Gulf of Salerno.
Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of Dicaearchia. The Roman colony was established in 194 BC, and took the Latin name Puteoli 'little wells', referring to the many hot springs in the area, most notably Solfatara. This is because Pozzuoli lies in the center of the Campi Flegrei, a caldera.
Puteoli was the great emporium for the Alexandrian grain ships, and other ships from all over the Roman world. It also was the main hub for goods exported from Campania, including blown glass, mosaics, wrought iron, and marble. The Roman naval base at nearby Misenum housed the largest naval fleet in the ancient world. It was also the site of the Roman Dictator Sulla's country villa and the place where he died in 78 BC.
The local volcanic sand, pozzolana formed the basis for the first effective concrete, as it reacted chemically with water. Instead of just evaporating slowly off, the water would turn this sand/lime mix into a mortar strong enough to bind lumps of aggregate into a load-bearing unit. This made possible the cupola of the Pantheon, the first real dome.
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 12in (485mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repair to top centre margin
Plate area: - Small professional repairs & light age toning to centrefold
Verso: - None
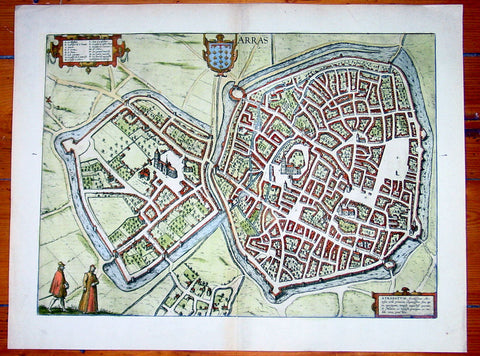
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Large Antique Map of the City of Arras, France
Antique Map
- Title : Arras
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92833
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map a birds-eye view of the French City of Arras - the capital of the Pas de Calais region - was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II (1572-1612) intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14in (485mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1718 Slezer Antique Print View of Kelso Abby & Township, Scotland
- Title : The Abby of Kelso
- Date : 1718
- Ref # : 24953
- Size : 18 ½in x 14 ½in (470mm x 360mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique print a view of Kelso Abby & Kelso Town, Scotland was published in the 1718 edition of John Slezer's 'Theatrum Scotiae'.
Kelso Abbey is a ruined Scottish abbey in Kelso, Scotland. It was founded in the 12th century by a community of Tironensian monks first brought to Scotland in the reign of Alexander I. It occupies ground overlooking the confluence of the Tweed and Teviot waters, the site of what was once the Royal Burgh of Roxburgh and the intended southern centre for the developing Scottish kingdom at that time. Kelso thus became the seat of a pre-eminently powerful abbacy in the heart of the Scottish Borders.
In the 14th century, Roxburgh became a focus for periodic attack and occupation by English forces and Kelso's monastic community survived a number of fluctuations in control over the area, restoring the abbey infrastructure after episodes of destruction and ultimately retaining Scottish identity. From 1460 onwards, life for the abbey probably grew more settled, but came once again under attack in the early sixteenth century. By the mid-century, through a turbulent combination of events, the abbey effectively ceased to function and the building fell into ruin.
Although the site of Kelso Abbey has not been fully excavated in modern times, evidence suggests that it was a major building with two crossings. The only remains standing today are the west tower crossing and part of the infirmary. The massive design and solid romanesque style of the tower indicate a very large building of formidable, semi-military construction and appearance, evidence of the importance with which Roxburgh was regarded when the abbacy was at the height of its power.
This is an important and rare print as Slezer s Theatrum Scotiae is one of the earliest records of early Scottish towns & major buildings. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 ½in x 14 ½in (470mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 16 ½in x 11in (420mm x 275mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections: Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1718 Slezer Antique Print View of Falkland Palace, Fife, Scotland
- Title : Palace of Falkland
- Date : 1718
- Ref # : 24958
- Size : 18 ½in x 14 ½in (470mm x 360mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique print a view of the internal courtyard of Falkland Palace, home of the Scottish Kings - was published in the 1718 edition of John Slezer's 'Theatrum Scotiae'.
Falkland Palace in Falkland, Fife, Scotland, is a former royal palace of the Scottish Kings. The Scottish Crown acquired Falkland Castle from MacDuff of Fife in the 14th century. In 1402 Robert Stewart, 1st Duke of Albany imprisoned his nephew David Stewart, Duke of Rothesay, the eldest son of King Robert III of Scotland, at Falkland. The incarcerated Duke eventually died there from neglect and starvation. Albany was exonerated from blame by Parliament, but suspicions of foul play persisted, suspicions which never left Rothesay's younger brother the future James I of Scotland, and which would eventually lead to the downfall of the Albany Stewarts. John Debrett, writing in 1805, was in no doubt of Duke Robert's motives and guilt. This Robert, Duke of Albany, having obtained the entire government from his brother, King Robert, he caused the Duke of Rothesay to be murdered, thinking to bring the Crown into his own family; but to avoid the like fate, King Robert resolved to send his younger son James, to France, then about nine years old, who being sea-sick, and forced to land on the English coast ... was detained a captive in England eighteen years. At these misfortunes King Robert died of grief in 1406. Between 1501 and 1541 Kings James IV and James V of Scotland transformed the old castle into a beautiful royal palace: with Stirling Castle it was one of only two Renaissance palaces in Scotland. To address the poor state of the garden and park, James V appointed a new Captain and Keeper, William Barclay, Master of Rhynd, in March 1527. Ten years later, James V extended his father's buildings in French renaissance style. He died at Falkland in December 1542 after hearing that his wife had given birth to a daughter—Mary, Queen of Scots. Falkland became a popular retreat with all the Stewart monarchs. They practised falconry there and used the vast surrounding forests for hawking and for hunting deer. Wild boar, imported from France, were kept in the Park, within a fence made by the Laird of Fernie. Nearby Myres Castle is the hereditary home of the Royal Macers and Sergeants at Arms who served Falkland Castle since at least the sixteenth century. John Scrimgeour of Myres supervised building at the Palace from 1532 to 1563. After the Union of the Crowns (1606), James VI and I, Charles I, and Charles II all visited Falkland. A fire partially destroyed the palace during its occupation by Cromwell's troops and it quickly fell into ruin.
This is an important and rare print as Slezer s Theatrum Scotiae is one of the earliest records of early Scottish towns & major buildings. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 ½in x 14 ½in (470mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 16 ½in x 11in (420mm x 275mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections: Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
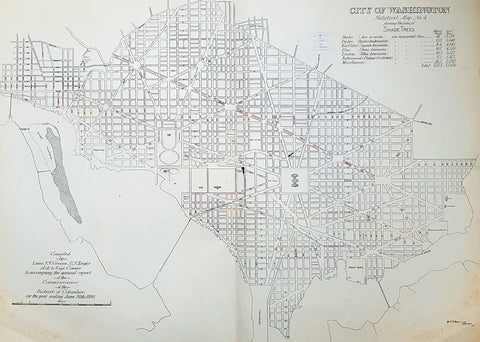
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Lines of Planted Trees in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 4 showing the lines of Shade Trees.....Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16266
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the lines of Trees planted very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
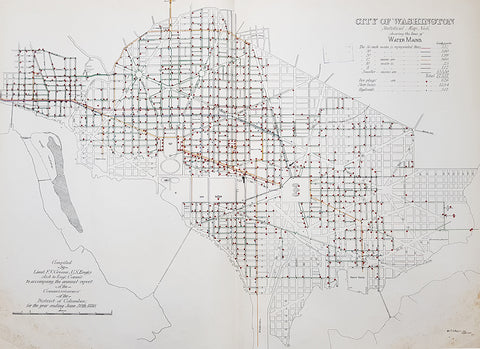
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Location of the Water Mains in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 6 showing the lines of Water Mains...Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16263
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the location of the Water Mains very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
1574 Munster Large Antique Print View of The French City of Tours
- Title : Die Statt Tours
- Ref #: 22614
- Size: 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the French city of Tours was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1574 edition of Cosmographia.
Tours is a city located in the centre-west of France. It is the administrative centre of the Indre-et-Loire department and the largest city in the Centre-Val de Loire region of France (although it is not the capital, which is the region's second-largest city, Orléans). Tours stands on the lower reaches of the River Loire, between Orléans and the Atlantic coast. The surrounding district, the traditional province of Touraine, is known for its wines, for the alleged perfection (as perceived by some speakers) of its local spoken French, and for the Battle of Tours (732).
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle hisCosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographiaappeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications ofCosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: -None
Verso: - None
1574 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the City of Tours, France
- Title : Die Statt Tours
- Ref #: 22614
- Size: 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the French city of Tours, France was published in the French Section of Sebastian Munsters 1574 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Tours is a city in the centre-west of France. It is the administrative centre of the Indre-et-Loire department and the largest city in the Centre-Val de Loire region of France
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
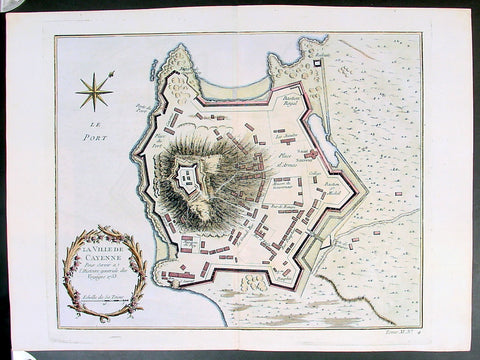
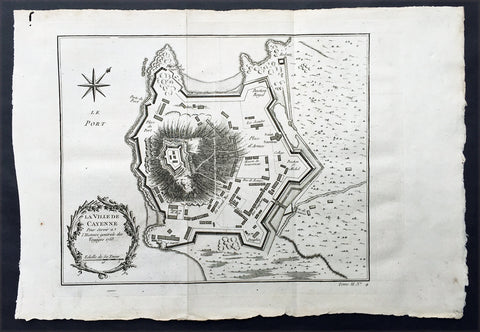
Copy of 1753 Bellin Antique Map Plan of the City of Cayenne French Guyana, South America
- Title: La Ville De Cayenne...1753
- Date: 1753
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25648
- Size: 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved original antique map a plan of the city of Cayenne capital of French Guyana, South America was engraved by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1753 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Jacques Nicolas Bellin for Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague in 1747. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
1753 Bellin Antique Map Plan of the City of Cayenne French Guyana, South America
- Title: La Ville De Cayenne...1753
- Date: 1753
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92016
- Size: 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved original antique map a plan of the city of Cayenne capital of French Guyana, South America was engraved by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1753 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Jacques Nicolas Bellin for Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague in 1747. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
1760 Vue D Optic Antique Print View of Hampton Court Palace, Richmond London
- Title : Vue du Palias Royal de Hampton Court a 15 Milles de Londres
- Date : 1760
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 92704
- Size: 19in x 12 3/4in (480mm x 325mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original antique print, a view of Hampton Court Palace was published as part of the Vues d’Optique in 1760.
Hampton Court Palace: is a royal palace in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, Greater London, in the historic county of Middlesex, and within the postal town East Molesey, Surrey. It has not been inhabited by the British Royal Family since the 18th century. The palace is 11.7 miles (18.8 kilometres) south west of Charing Cross and upstream of central London on the River Thames. It was originally built in 1514 for Cardinal Thomas Wolsey, a favourite of King Henry VIII. In 1529, as Wolsey fell from favour, the King seized the palace for himself and later enlarged it. Along with St. James's Palace, it is one of only two surviving palaces out of the many owned by King Henry VIII.
In the following century, King William III's massive rebuilding and expansion project was intended to rival Versailles. Work ceased in 1694, leaving the palace in two distinct contrasting architectural styles, domestic Tudor and Baroque. While the palace's styles are an accident of fate, a unity exists due to the use of pink bricks and a symmetrical, if vague, balancing of successive low wings.
Vues d' Optique or Perspective Views: Perspective views, or "vues d'optique," are a special type of popular print published in Europe during the 18th century. These prints provided a form of entertainment when viewed through a device called an "optical machine" or an "optique." The most characteristic feature of the perspective views is their emphasized linear perspective, done to further intensify the enhanced appearance of depth and illusionistic space in the prints when viewed through an optique. When displayed in the optique, the prints might transport the viewer into a far away place---an unknown city, or perhaps into the midst of a dramatic bit of contemporary history. Another attribute of these prints is their bright, often heavy hand coloring, applied boldly so as to show the tints when viewed through the lens.
A number of perspective prints depicted American scenes at the time of the Revolution for a European audience hungry for news of the events in the British colonies. As documents of American history and European printmaking, these are unusual and appealing eighteenth-century prints.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic & bright
Paper size: - 19in x 12 3/4in (480mm x 325mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Small smudge & toning to sky
Verso: - Small repair, no loss
1598 Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the city of Poitiers in Poitou France
- Title : Die Statt Puttiers
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 30381
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the French city of Poitiers on the Clain River in the Vienne Dept of central western France, was published in the French Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Poitiers is a city on the Clain river in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and also of the Poitou.
The type of political organisation existing in Poitiers during the late medieval or early modern period can be glimpsed through a speech given on 14 July 1595 by Maurice Roatin, the town\'s mayor. He compared it to the Roman state, which combined three types of government: monarchy (rule by one person), aristocracy (rule by a few), and democracy (rule by the many). He said the Roman consulate corresponded to Poitiers\' mayor, the Roman senate to the town\'s peers and échevins, and the democratic element in Rome corresponded to the fact that most important matters can not be decided except by the advice of the Mois et Cent (broad council).1 The mayor appears to have been an advocate of a mixed constitution; not all Frenchmen in 1595 would have agreed with him, at least in public; many spoke in favour of absolute monarchy. The democratic element was not as strong as the mayor\'s words may seem to imply: in fact, Poitiers was similar to other French cities, Paris, Nantes, Marseille, Limoges, La Rochelle, Dijon, in that the town\'s governing body (corps de ville) was highly exclusive and oligarchical: a small number of professional and family groups controlled most of the city offices. In Poitiers many of these positions were granted for the lifetime of the office holder.
The city government in Poitiers based its claims to legitimacy on the theory of government where the mayor and échevins held jurisdiction of the citys affairs in fief from the king: that is, they swore allegiance and promised support for him, and in return he granted them local authority. This gave them the advantage of being able to claim that any townsperson who challenged their authority was being disloyal to the king. Every year the mayor and the 24 échevins would swear an oath of allegiance between the hands of the king or his representative, usually the lieutenant général or the sénéchaussée. For example, in 1567, when Maixent Poitevin was mayor, king Henry III came for a visit, and, although some townspeople grumbled about the licentious behaviour of his entourage, Henry smoothed things over with a warm speech acknowledging their allegiance and thanking them for it.
In this era, the mayor of Poitiers was preceded by sergeants wherever he went, consulted deliberative bodies, carried out their decisions, heard civil and criminal suits in first instance, tried to ensure that the food supply would be adequate, visited markets.
In the 16th century, Poitiers impressed visitors because of its large size, and important features, including royal courts, university, prolific printing shops, wealthy religious institutions, cathedral, numerous parishes, markets, impressive domestic architecture, extensive fortifications, and castle.
16th-century Poitiers is closely associated with the life of François Rabelais and with the community of Bitards.
The town saw less activity during the Renaissance. Few changes were made in the urban landscape, except for laying way for the rue de la Tranchée. Bridges were built where the inhabitants had used gués. A few hôtels particuliers were built at that time, such as the hôtels Jean Baucé, Fumé and Berthelot. Poets Joachim du Bellay and Pierre Ronsard met at the University of Poitiers, before leaving for Paris.
During the 17th century, many people emigrated from Poitiers and the Poitou to the French settlements in the new world and thus many Acadians or Cajuns living in North America today can trace ancestry back to this region.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins cropped into border
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light toning along centerfold
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Weissenburg Bavaria Germany
- Title : Die Statt Wyssenburg
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 30351
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Weißenburg (Weissenburg) in Bavaria in Middle Franconia - identified by the cities Coate of Arms with double headed eagle atop of a castle - was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Weißenburg in Bayern (formerly also Weißenburg im Nordgau) is a town in Middle Franconia, Germany. It is the capital of the district Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen. Weissenburg is located in central Bavaria, in the south of the administrative region Mittelfranken.
The history of Weißenburg is generally traced back to the Roman fort that was built in the area towards the end of the first century. The settlement, which included Thermae, lay on the border of the Roman Empire and on the Tabula Peutingeriana from the 4th century it had the name Biriciana. Germanic tribes destroyed the fort and settled in what is still the city centre. The first mention of the name Weißenburg is in a deed dating from 867. The city became the seat of a royal residence during the reign of the Franks and according to legend, Charlemagne stayed there to supervise the construction of Fossa Carolina.
The city became a Free Imperial City in 1296 and continued to grow until the Reformation. Following the example of Nuremberg the city joined the Protestant side but it suffered heavily in the ensuing wars. However, the rights of the city as a Free Imperial City and an Imperial Estate were restored in the final peace treaty and some growth resumed. Despite its insignificant size and economic importance, the city, like the other 50-odd free imperial cities, was virtually independent.
Weissenburg lost its independence in 1802 and became part of the Bavarian kingdom in 1806. It was however saved from insignificance with the construction of a railway between Nuremberg and Augsburg which goes through the city and which supported industrialisation. Following World War II over 6,000 refugees and people expelled from the territories which Germany lost settled in the city and have since played an important role in its industry and culture.
The many stages in the history of Weissenburg can still be seen today. There are many ruins from the Roman times. One of the finest is the remains of a Roman bath which was excavated in 1977 and has been turned into a museum. The city wall from the Middle Ages has survived almost intact with its towers and in the Gothic Town Hall the city\'s elected members have held their meetings from 1476.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to bottom margin, no loss
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1574 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the City of Lubeck, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Lubeck
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 22708
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Lubeck, in the northern German state Schleswig-Holstein was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1574 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Lübeck is a city in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany, on the river Trave.
In the 14th century Lübeck became the Queen of the Hanseatic League, being by far the largest and most powerful member of that medieval trade organization. In 1375 Emperor Charles IV named Lübeck one of the five Glories of the Empire, a title shared with Venice, Rome, Pisa and Florence. Several conflicts about trading privileges resulted in fighting between Lübeck (with the Hanseatic League) and Denmark and Norway – with varying outcome. While Lübeck and the Hanseatic League prevailed in conflicts in 1435 and 1512, Lübeck lost when it became involved in the Count\'s Feud, a civil war that raged in Denmark from 1534 to 1536. Lübeck also joined the pro-Lutheran Schmalkaldic League of the mid-16th century.
After its defeat in the Count\'s Feud, Lübeck\'s power slowly declined. The city remained neutral in the Thirty Years\' War of 1618–1648, but the combination of the devastation from the decades-long war and the new transatlantic orientation of European trade caused the Hanseatic League – and thus Lübeck with it – to decline in importance. However, even after the de facto disbanding of the Hanseatic League in 1669, Lübeck still remained an important trading town on the Baltic Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1574 Munster Large Antique Print - View of The German City of Landau, Bavaria
- Title : Die Statt Landaw
- Ref #: 22668
- Size: 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the Bavarian City of Landau NE of Munich was engraved in 1547 - the date is engraved at the foot of the image - and was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1574 edition of Cosmographia.
Landau or Landau in der Pfalz (pop. 41,821) is an autonomous (kreisfrei) city surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long-standing cultural centre, and a market and shopping town, surrounded by vineyards and wine-growing villages of the Palatinate wine region. Landau lies east of the Palatinate forest, Europe's largest contiguous forest, direct on the German Wine Route.
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle hisCosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographiaappeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications ofCosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: -None
Verso: - None
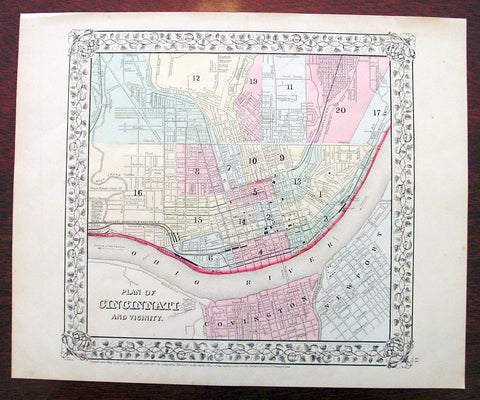
1869 Mitchell Antique Map - Plan of The City of Cincinnati
- Title : Plan of Cincinnati and Vicinity....1869 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35044
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique city plan map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None