Maps (930)
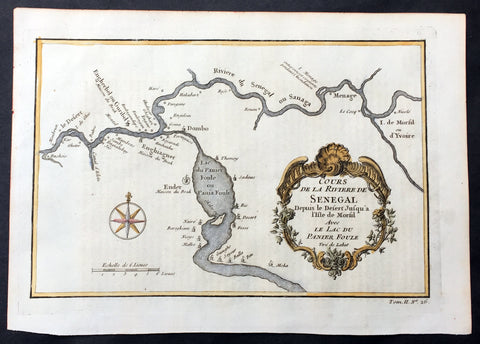
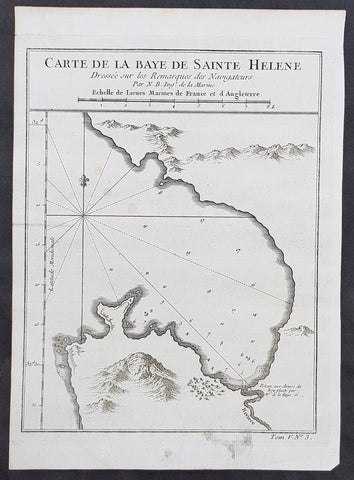
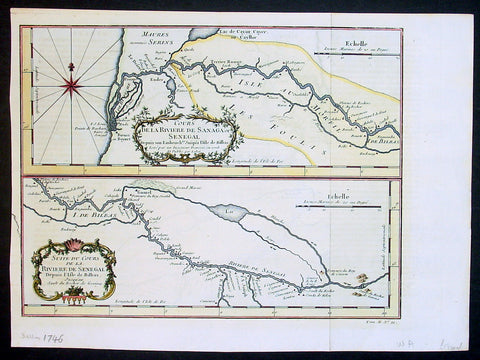
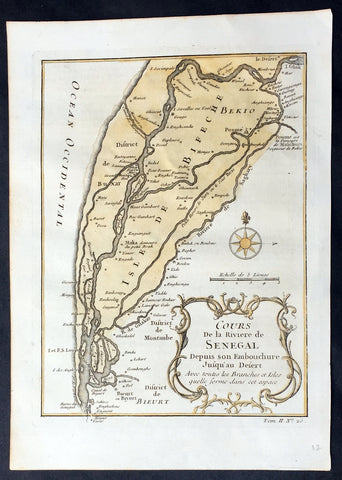
1757 Bellin Antique Map The Senegal River, Bethio & N Dombo, Senegal West Africa
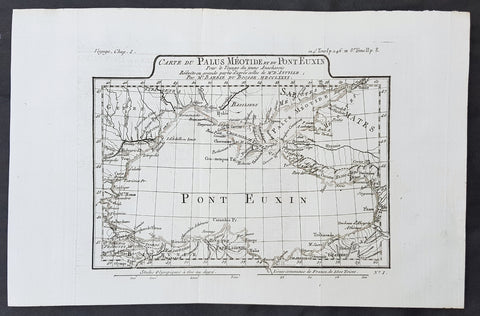
- Title : Cours de la Riviere de Senegal Depuis le Desert Jusqu a Isle de Morsil...
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Ref #: 25785
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Senegal River in the Bethio & N Dombo regions of Northern Senegal and Mauritania in West Africa by Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The Senegal River is a 1,086 km (675 mi) long river in West Africa that forms the border between Senegal and Mauritania.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 6 1/2in (250mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
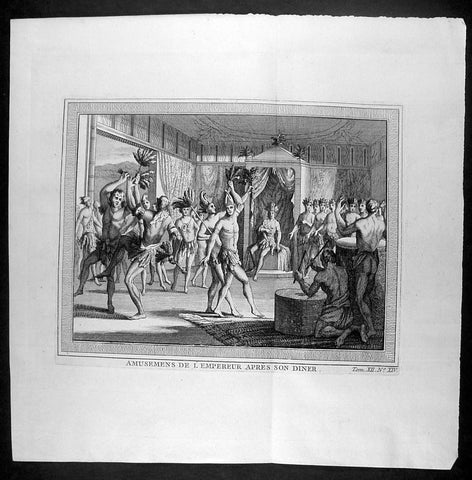
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Print of Aztec Dancers & Musicians Mexico - after De Bry
- Title : Amusemens De L Empereur Apres Son Diner
- Ref #: 25962
- Size: 10in x 10in (255mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique print of Aztec dancers and musicians performing for the Aztec Emperor, in modern day Mexico, by Jakob van Schley - after De Bry - in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 10in (255mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8in x 6in (205mm x 155mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
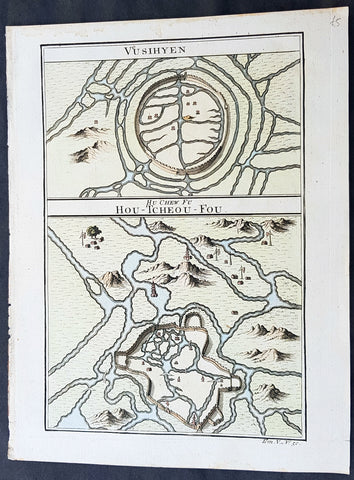
1755 Prevost Antique Plans Cities of Jinhua & Pinghu in Zhejiang Province, China
- Title: Vusihyen; Hou-Tcheou-Fou
- Date: 1755
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Ref: 23400
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map, plans of the cities of Jinhua & Pinghu in the eastern Chinese province of Zhejiang by Jakob van Schley in 1755 - after Jean-Baptiste Du Halde - was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1789.
Jean-Baptiste Du Halde, born in Paris on 1 February 1674 and died 18 August 1743, was a French Jesuit historian specializing in China. He did not travel to China, but collected seventeen Jesuit missionaries\\\' reports and provided an encyclopedic survey of the history, culture and society of China and Chinese Tartary, that is, Manchuria.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Zhejiang formerly romanized as Chekiang, is an eastern coastal province of China. Zhejiang is bordered by the Jiangsu province and the Shanghai municipality to the north, the Anhui province to the northwest, the Jiangxi province to the west, and the Fujian province to the south. To the east is the East China Sea, beyond which lies the Ryukyu Islands of Japan.
Zhejiang was finally conquered by the Mongols in the late 13th century who later established the short lived Yuan Dynasty.
The Ming dynasty, which drove out the Mongols in 1368, finally established the present day province of Zhejiang with its borders having little changes since this establishment.
As in other coastal provinces, number of fortresses were constructed along the Zhejiang coast during the early Ming to defend the land against pirate incursions. Some of them have been preserved or restored, such as Pucheng in the south of the province (Cangnan County).
Under the late Ming dynasty and the Qing dynasty that followed it, Zhejiang\'s ports were important centers of international trade.
In 1727 the to-min or \'idle people\' of Cheh Kiang province (a Ningpo name still existing), the yoh-hu or \'music people\' of Shanxi province, the si-min or \'small people\' of Kiang Su (Jiangsu) province, and the Tanka people or \'egg-people\' of Canton (to this day the boat population there), were all freed from their social disabilities, and allowed to count as free men. Cheh Kiang is another romanization for Zhejiang. The Duomin are a caste of outcasts in this province.
During the First Opium War, the British navy defeated Eight Banners forces at Ningboand Dinghai. Under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking, signed in 1843, Ningbo became one of the five Chinese treaty ports opened to virtually unrestricted foreign trade. Much of Zhejiang came under the control of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom during the Taiping Rebellion, which resulted in a considerable loss of life in the north-western and central parts of the province, sparing the rest of Zhejiang from the disastrous depopulation that occurred. In 1876, Wenzhou became Zhejiang\'s second treaty port. Jianghuai Mandarin speakers later came to settle in these depopulated regions of northern Zhejiang.
Jinhua is a prefecture-level city in central Zhejiang province in eastern China. It borders the provincial capital of Hangzhou to the northwest, Quzhou to the southwest, Lishui to the south, Taizhou to the east, and Shaoxing to the northeast.
The history of Jinhua dates back to the 2nd century BC, when it was a county subordinate to Shaoxing. It was given the name Jinhua under the Sui dynasty in AD 598 and later became the seat of a prefecture. The present city and its walls date to the time of the Mongol emperors in 1352.
The most famous native of Jinhua is Huang Chuping, a Daoist holy man of the 4th century and reputed immortal whose descendants still live in the area. Wuyang Shan (Reclining Sheep Mountain) is said to be a sheep which was turned to stone by Huang, a trick which he learned through his years of diligently studying Daoism.
Economically Jinhua has always prospered from its position as the regional collecting and processing center for agricultural and forestry products (chiefly rice and bamboo). It is currently the second most important grain producing area in Zhejiang. In 1985 Jinhua was promoted to City status, and now is responsible for administering four cities, four counties and a district. Animals raised there include dairy cattle, meat hogs (for the production of Jinhua ham, a famous local product for 900 years) and honeybees. Jinhua\'s industrial sector has developed more recently, producing machinery, metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, building supplies and electrical and electronic equipment.
The Tang dynasty painter Guan Xiu (Kuan-hsiu) was born in Jinhua. He is known for his paintings of Buddhist holy men.
There are numerous scenic and historical sites in the Jinhua region, including many places associated with the Immortal Huang, and a palace of the Dukes of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom.
Pinghu is a county-level city in northeast Zhejiang Province, just outside Shanghai. It sits next to the East China Sea and the north shore of Hangzhou Bay. Prior to the Ming Dynasty, Pinghu was part of Haiyan County. In 1430 Pinghu County was established. In 1991 Pinghu became a county-level city under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Jiaxing.
Zhapu, the site of a deepwater harbor, was the principal site of China\'s foreign trade with Korea and Japan during the 18th and 19th century.
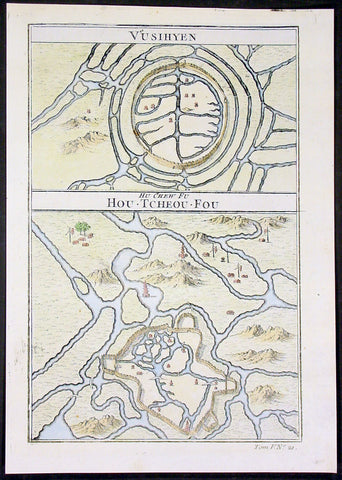
1755 Prevost Antique Plans Cities of Jinhua & Pinghu in Zhejiang Province, China
- Title: Vusihyen; Hou-Tcheou-Fou
- Date: 1755
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Ref: 15831
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map, plans of the cities of Jinhua & Pinghu in the eastern Chinese province of Zhejiang by Jakob van Schley in 1755 - after Jean-Baptiste Du Halde - was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1789.
Jean-Baptiste Du Halde, born in Paris on 1 February 1674 and died 18 August 1743, was a French Jesuit historian specializing in China. He did not travel to China, but collected seventeen Jesuit missionaries\\\' reports and provided an encyclopedic survey of the history, culture and society of China and Chinese Tartary, that is, Manchuria.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Zhejiang formerly romanized as Chekiang, is an eastern coastal province of China. Zhejiang is bordered by the Jiangsu province and the Shanghai municipality to the north, the Anhui province to the northwest, the Jiangxi province to the west, and the Fujian province to the south. To the east is the East China Sea, beyond which lies the Ryukyu Islands of Japan.
Zhejiang was finally conquered by the Mongols in the late 13th century who later established the short lived Yuan Dynasty.
The Ming dynasty, which drove out the Mongols in 1368, finally established the present day province of Zhejiang with its borders having little changes since this establishment.
As in other coastal provinces, number of fortresses were constructed along the Zhejiang coast during the early Ming to defend the land against pirate incursions. Some of them have been preserved or restored, such as Pucheng in the south of the province (Cangnan County).
Under the late Ming dynasty and the Qing dynasty that followed it, Zhejiang\'s ports were important centers of international trade.
In 1727 the to-min or \'idle people\' of Cheh Kiang province (a Ningpo name still existing), the yoh-hu or \'music people\' of Shanxi province, the si-min or \'small people\' of Kiang Su (Jiangsu) province, and the Tanka people or \'egg-people\' of Canton (to this day the boat population there), were all freed from their social disabilities, and allowed to count as free men. Cheh Kiang is another romanization for Zhejiang. The Duomin are a caste of outcasts in this province.
During the First Opium War, the British navy defeated Eight Banners forces at Ningboand Dinghai. Under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking, signed in 1843, Ningbo became one of the five Chinese treaty ports opened to virtually unrestricted foreign trade. Much of Zhejiang came under the control of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom during the Taiping Rebellion, which resulted in a considerable loss of life in the north-western and central parts of the province, sparing the rest of Zhejiang from the disastrous depopulation that occurred. In 1876, Wenzhou became Zhejiang\'s second treaty port. Jianghuai Mandarin speakers later came to settle in these depopulated regions of northern Zhejiang.
Jinhua is a prefecture-level city in central Zhejiang province in eastern China. It borders the provincial capital of Hangzhou to the northwest, Quzhou to the southwest, Lishui to the south, Taizhou to the east, and Shaoxing to the northeast.
The history of Jinhua dates back to the 2nd century BC, when it was a county subordinate to Shaoxing. It was given the name Jinhua under the Sui dynasty in AD 598 and later became the seat of a prefecture. The present city and its walls date to the time of the Mongol emperors in 1352.
The most famous native of Jinhua is Huang Chuping, a Daoist holy man of the 4th century and reputed immortal whose descendants still live in the area. Wuyang Shan (Reclining Sheep Mountain) is said to be a sheep which was turned to stone by Huang, a trick which he learned through his years of diligently studying Daoism.
Economically Jinhua has always prospered from its position as the regional collecting and processing center for agricultural and forestry products (chiefly rice and bamboo). It is currently the second most important grain producing area in Zhejiang. In 1985 Jinhua was promoted to City status, and now is responsible for administering four cities, four counties and a district. Animals raised there include dairy cattle, meat hogs (for the production of Jinhua ham, a famous local product for 900 years) and honeybees. Jinhua\'s industrial sector has developed more recently, producing machinery, metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, building supplies and electrical and electronic equipment.
The Tang dynasty painter Guan Xiu (Kuan-hsiu) was born in Jinhua. He is known for his paintings of Buddhist holy men.
There are numerous scenic and historical sites in the Jinhua region, including many places associated with the Immortal Huang, and a palace of the Dukes of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom.
Pinghu is a county-level city in northeast Zhejiang Province, just outside Shanghai. It sits next to the East China Sea and the north shore of Hangzhou Bay. Prior to the Ming Dynasty, Pinghu was part of Haiyan County. In 1430 Pinghu County was established. In 1991 Pinghu became a county-level city under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Jiaxing.
Zhapu, the site of a deepwater harbor, was the principal site of China\'s foreign trade with Korea and Japan during the 18th and 19th century.
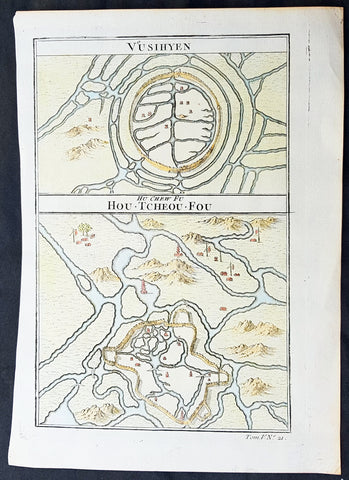
1755 Prevost Antique Plans Cities of Jinhua & Pinghu in Zhejiang Province, China
- Title: Vusihyen; Hou-Tcheou-Fou
- Date: 1755
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Ref: 15830
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map, plans of the cities of Jinhua & Pinghu in the eastern Chinese province of Zhejiang by Jakob van Schley in 1755 - after Jean-Baptiste Du Halde - was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1789.
Jean-Baptiste Du Halde, born in Paris on 1 February 1674 and died 18 August 1743, was a French Jesuit historian specializing in China. He did not travel to China, but collected seventeen Jesuit missionaries\\\' reports and provided an encyclopedic survey of the history, culture and society of China and Chinese Tartary, that is, Manchuria.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Zhejiang formerly romanized as Chekiang, is an eastern coastal province of China. Zhejiang is bordered by the Jiangsu province and the Shanghai municipality to the north, the Anhui province to the northwest, the Jiangxi province to the west, and the Fujian province to the south. To the east is the East China Sea, beyond which lies the Ryukyu Islands of Japan.
Zhejiang was finally conquered by the Mongols in the late 13th century who later established the short lived Yuan Dynasty.
The Ming dynasty, which drove out the Mongols in 1368, finally established the present day province of Zhejiang with its borders having little changes since this establishment.
As in other coastal provinces, number of fortresses were constructed along the Zhejiang coast during the early Ming to defend the land against pirate incursions. Some of them have been preserved or restored, such as Pucheng in the south of the province (Cangnan County).
Under the late Ming dynasty and the Qing dynasty that followed it, Zhejiang\'s ports were important centers of international trade.
In 1727 the to-min or \'idle people\' of Cheh Kiang province (a Ningpo name still existing), the yoh-hu or \'music people\' of Shanxi province, the si-min or \'small people\' of Kiang Su (Jiangsu) province, and the Tanka people or \'egg-people\' of Canton (to this day the boat population there), were all freed from their social disabilities, and allowed to count as free men. Cheh Kiang is another romanization for Zhejiang. The Duomin are a caste of outcasts in this province.
During the First Opium War, the British navy defeated Eight Banners forces at Ningboand Dinghai. Under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking, signed in 1843, Ningbo became one of the five Chinese treaty ports opened to virtually unrestricted foreign trade. Much of Zhejiang came under the control of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom during the Taiping Rebellion, which resulted in a considerable loss of life in the north-western and central parts of the province, sparing the rest of Zhejiang from the disastrous depopulation that occurred. In 1876, Wenzhou became Zhejiang\'s second treaty port. Jianghuai Mandarin speakers later came to settle in these depopulated regions of northern Zhejiang.
Jinhua is a prefecture-level city in central Zhejiang province in eastern China. It borders the provincial capital of Hangzhou to the northwest, Quzhou to the southwest, Lishui to the south, Taizhou to the east, and Shaoxing to the northeast.
The history of Jinhua dates back to the 2nd century BC, when it was a county subordinate to Shaoxing. It was given the name Jinhua under the Sui dynasty in AD 598 and later became the seat of a prefecture. The present city and its walls date to the time of the Mongol emperors in 1352.
The most famous native of Jinhua is Huang Chuping, a Daoist holy man of the 4th century and reputed immortal whose descendants still live in the area. Wuyang Shan (Reclining Sheep Mountain) is said to be a sheep which was turned to stone by Huang, a trick which he learned through his years of diligently studying Daoism.
Economically Jinhua has always prospered from its position as the regional collecting and processing center for agricultural and forestry products (chiefly rice and bamboo). It is currently the second most important grain producing area in Zhejiang. In 1985 Jinhua was promoted to City status, and now is responsible for administering four cities, four counties and a district. Animals raised there include dairy cattle, meat hogs (for the production of Jinhua ham, a famous local product for 900 years) and honeybees. Jinhua\'s industrial sector has developed more recently, producing machinery, metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, building supplies and electrical and electronic equipment.
The Tang dynasty painter Guan Xiu (Kuan-hsiu) was born in Jinhua. He is known for his paintings of Buddhist holy men.
There are numerous scenic and historical sites in the Jinhua region, including many places associated with the Immortal Huang, and a palace of the Dukes of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom.
Pinghu is a county-level city in northeast Zhejiang Province, just outside Shanghai. It sits next to the East China Sea and the north shore of Hangzhou Bay. Prior to the Ming Dynasty, Pinghu was part of Haiyan County. In 1430 Pinghu County was established. In 1991 Pinghu became a county-level city under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Jiaxing.
Zhapu, the site of a deepwater harbor, was the principal site of China\'s foreign trade with Korea and Japan during the 18th and 19th century.
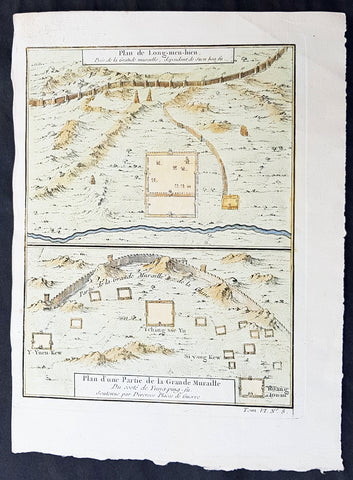
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Map Hebei Province, China, The Great Wall & Forts
- Title: Plan de Long-men-hien Pres de la Grande Muraille, dependant de Duen hoa fu; Plan d une Partie de la Grande Muraille. Du coste de Yung-ping-fu. Soutenue par Diverses Plaees de Guerre
- Date: 1755
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 34140
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plans of parts of the Great Wall of China in what is today the north part of the Hebei Province of China - then called Pecheli - by Jakob van Schley in 1755 - after Jean-Baptiste Du Halde - was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1789.
Jean-Baptiste Du Halde, born in Paris on 1 February 1674 and died 18 August 1743, was a French Jesuit historian specializing in China. He did not travel to China, but collected seventeen Jesuit missionaries\\\' reports and provided an encyclopedic survey of the history, culture and society of China and Chinese Tartary, that is, Manchuria.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Hebei is a province of Northern China. Its one-character abbreviation is Jì, named after Ji Province, a Han Dynasty province (zhou) that included what is now southern Hebei. The name Hebei literally means north of the river referring to its location entirely to the north of the Huang He Yellow River.
During the Tang Dynasty (618–907), the area was formally designated Hebei (north of the Yellow River) for the first time. During the earlier part of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, Hebei was fragmented among several regimes, though it was eventually unified by Li Cunxu, who established the Later Tang (923–936). The next dynasty, the Later Jin under Shi Jingtang, posthumously known as Emperor Gaozu of Later Jin, ceded much of modern-day northern Hebei to the Khitan Liao Dynasty in the north; this territory, called the Sixteen Prefectures of Yanyun, became a major weakness in the Chinese defense against the Khitans for the next century, since it lay within the Great Wall.
During the Northern Song Dynasty (960–1127), the sixteen ceded prefectures continued to be an area of hot contention between Song China and the Liao Dynasty. The Southern Song Dynasty that came after abandoned all of North China, including Hebei, to the Jurchen Jin Dynasty after the Jingkang Incident in 1127 of the Jin–Song wars.
The Mongol Yuan Dynasty divided China into provinces but did not establish Hebei as a province. Rather, the area was directly administrated by the Secretariat at capital Dadu. The Ming Dynasty ruled Hebei as Beizhili meaning Northern Directly Ruled, because the area contained and was directly ruled by the imperial capital, Beijing; the Northern designation was used because there was a southern counterpart covering present-day Jiangsu and Anhui. When the Manchu Qing Dynasty came to power in 1644, they abolished the southern counterpart, and Hebei became known as Zhili, or simply Directly Ruled. During the Qing Dynasty, the northern borders of Zhili extended deep into what is now Inner Mongolia, and overlapped in jurisdiction with the leagues of Inner Mongolia.
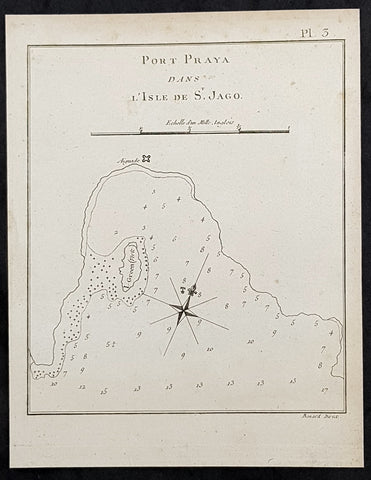
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Map of Port Praia, The Cape Verde Islands - Cook in 1772
- Title : Port Praya Dans L Isle de St Jago
- Size: 9in x 7in (230mm x 180mm)
- Ref #: 32172-1
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Port of Praia, on the Cape Verde Islands visited by Captain James Cook in 1772, in HMS Resolution & Adventure, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
Cooks Journal (1772)......
Jul. 2 Thu. Sandwich and Palliser aboard. Cook reports favourably. Cook receives Admiralty Instructions and scientific instruments.
3 Fri. Arrives Plymouth.
13 Mon. Resolution and Adventure sail from Plymouth. (From hereon Cook’s dates, as in Journal, are used. )
20 Mon. Off Cape Finisterre.
22 Wed. Off Sisargas Islands.
29 Wed. Anchors in Funchal Road, Madeira.
30 Thu. Goes ashore. Provisions ships. Makes observations.
Aug. 2 Sun. Sails from Madeira.
4 Tue. Off Palma, Canary Isles.
5 Wed. Off Ferro (Faro), (Hierro).
9 Sun. Off Bonavista.
10 Mon. Off Mayo.
13 Thu. Anchors at Porto Prayo, Santiago, Cape Verde Islands. Provisions ships and makes observations.
15 Sat. Sails from Porto Prayo and heads south.
20 Thu. Henry Smock, Carpenter’s mate, lost overboard while at work.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9in x 7in (230mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 7in (230mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Praia Harbor or Porto da Praia in the capital and largest city of Cape Verde, is the city\'s harbor located southeast of Praia and south of the island of Santiago, Cape Verde.
In the 16th century, the small settlement was founded and was named Praia de Santa Maria (now Gamboa), later in 1612, another settlement was founded. It became a settlement, later town that would serve as a harbor and around the 19th century, it was the popular alternative to Cidade Velha due to its high harbour fees, in the mid 19th century, Praia became a city.
Praia was raided for the only time in 1585 during the Capture of Santiago, his ships were stationed at the harbor and landed on the beach. Jacques Cassard arrived at Praia Harbour at Praia Negra on May 5, 1712 and brought with it 12 ships, where he led a huge attack on Ribeira Grande (now Cidade Velha) and conquered, sacked and destroyed it. After the Cassard expedition, the island capital was moved to Praia and several cannons were installed in the east of Plateau facing the harbour, one of them at the battery and barracks today where Quartel Jaime Mota is located, Praia became the chief port of Cape Verde and one of the main ports of the western portion of West Africa. The harbour as Porto Praya was mentioned in the 1747 French/Dutch map by Jacques Nicolas Bellin.
The Battle of Porto Praya took place on April 16, 1781, part of the Anglo-French War of 1778-83 took place inside the harbor. Before the battle on 13 March 1781 Johnstone sailed from Spithead, England with a fleet of 37 ships, including five ships of the line, three frigates, and a large number of troop convoy ships. In early April the fleet anchored in the neutral harbour of Porto Praya in the Portuguese-controlled Cape Verde Islands to take on water and supplies. One of Suffren\'s ships, the Artésien, had originally been destined for America, and was in need of water, so the French fleet paused when it approached Santiago on 16 April, and Suffren ordered the Artésien to the harbour. The battle took part with Great Britain and France and began and later, the French won the battle, for a day the waters were either British or French.[4] As more ports were constructed in the west of West Africa, its port was not mainly used.
Thomas Bowen (1767-1790) was an engraver and son of Emanuel Bowen, map and print seller, engraver to George II and to Louis XV of France who worked in London from 1714 producing some the best and most attractive maps of the 18th century. He had plans for completing a major County Atlas but, finding the task beyond his means, joined with Thomas Kitchin to publish The Large English Atlas. Many of the maps were issued individually from 1749 onwards and the whole atlas was not finally completed until 1760. With one or two exceptions they were the largest maps of the counties to appear up to that time (27 x 20) and were unusual in that blank areas around each map are filled with historical and topographical detail which makes fascinating and amusing reading. The atlas was reissued later in reduced size. Apart from his county maps and atlases of different parts of the world he also issued (with John Owen) a book of road maps based, as was usual at that time, on Ogilby but again incorporating his own style of historical and heraldic detail. Thomas helped his father during his lifetime and produced many fine maps in his own right after his fathers death.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
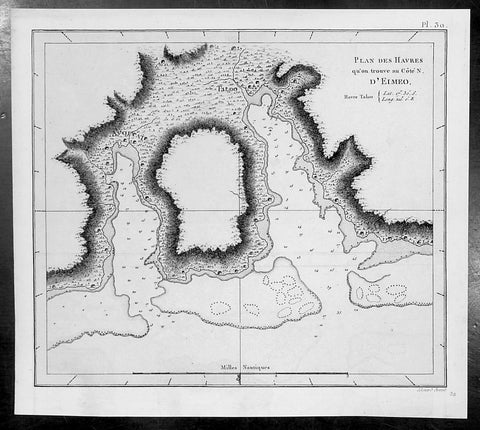
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Map of Moorea Island in French Polynesia - Cook in 1776
- Title : Plan des Havres qu on trouve au Cote N D Eimeo
- Size: 9 1/2in x 8 1/2in (245mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 32167
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
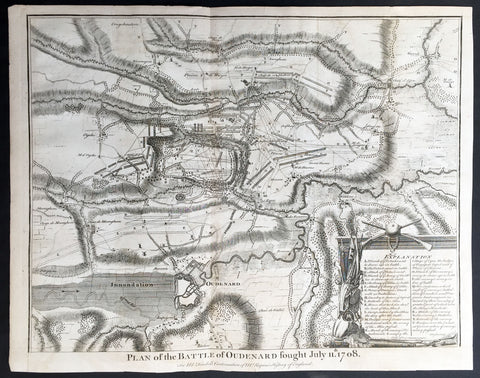
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the harbour of Talough on the north side of the Island of Moorea (Eimeo) in the Winward Islands of French Polynesia, near Tahiti, visited by Captain Cook in HMS Resolution & Discovery in December 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\\\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Cook journal July to Sept. 1777............Arrival at Moorea (Eimeo)
On 30th, Samwell wrote at eleven o\'clock anchored in a very good harbour at Eimeo unknown to us before, tho it is one of the best Harbours we have met with among the South Sea Islands.\" Cook added This harbour is called Talough it is situated on the North side of the island in the district of Oboonohou; it extends in south or SBE between the hills above two miles, for security and the goodness of its bottom it is not inferior to any harbour I have met with in any of the islands, and has this advantage over most of them, that a Ship can sail both in and out with the reigning trade wind, so that the access and recess are equally easy.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 8 1/2in (245mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 8 1/2in (245mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Moorea is a high island in French Polynesia, one of the Windward Islands, part of the Society Islands, 17 kilometres northwest of Tahiti.
The first European that recorded its sight was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606. The first European to arrive on the island were the Englishmen Samuel Wallis and James Cook. Captain James Cook first landed on Tahiti, where he planned the 1769 Transit of Venus observed from Tahiti and Moorea. Cook revisited the island again in 1777 during his 3rd and final voyage.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Thomas Bowen (1767-1790) was an engraver and son of Emanuel Bowen, map and print seller, engraver to George II and to Louis XV of France who worked in London from 1714 producing some the best and most attractive maps of the 18th century. He had plans for completing a major County Atlas but, finding the task beyond his means, joined with Thomas Kitchin to publish “The Large English Atlas”. Many of the maps were issued individually from 1749 onwards and the whole atlas was not finally completed until 1760. With one or two exceptions they were the largest maps of the counties to appear up to that time (27” x 20”) and were unusual in that blank areas around each map are filled with historical and topographical detail which makes fascinating and amusing reading. The atlas was reissued later in reduced size. Apart from his county maps and atlases of different parts of the world he also issued (with John Owen) a book of road maps based, as was usual at that time, on Ogilby but again incorporating his own style of historical and heraldic detail. Thomas helped his father during his lifetime and produced many fine maps in his own right after his fathers death.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
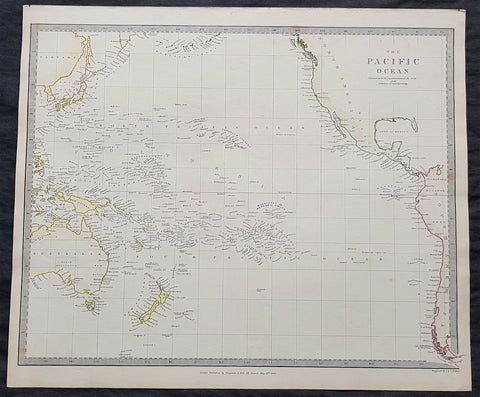
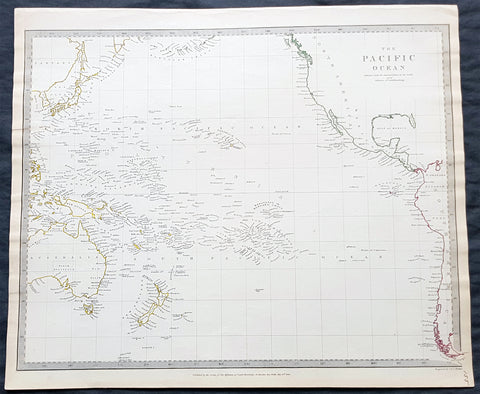
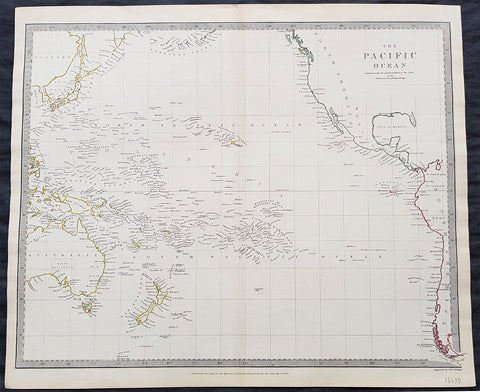
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0944
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
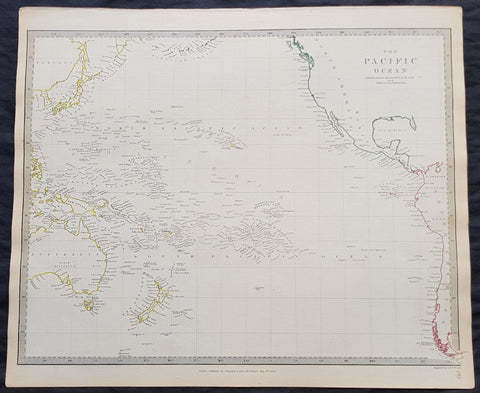
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 24668
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
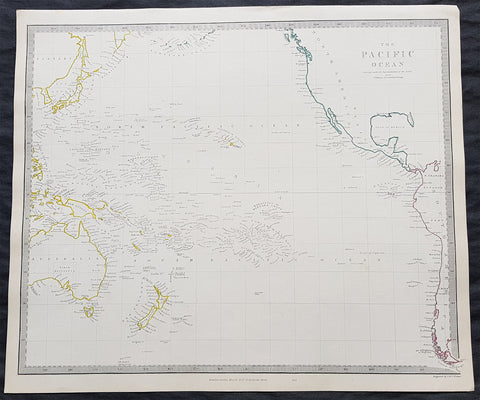
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0954-1
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
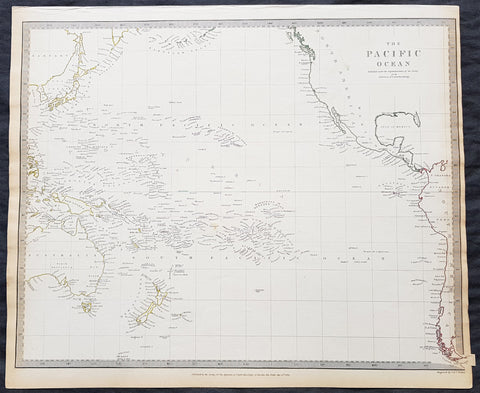
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0964
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 91362
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 31980
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
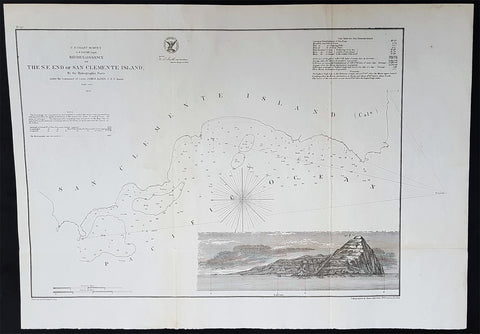
1856 A D Bache Scarce Antique Map of San Clemente Island, San Diego, California
- Title : US Coast Survey A D Bache Supt Reconnaissance of The SE End of San Clemente Island...1856
- Size: 20 1/2in x 14in (520mm x 360mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1856
- Ref #: 93028
Description:
This large rare, original lithograph early antique map of San Clemente Island, off San Diego, California by Alexander Dallas Bache (great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin) in 1856 - dated - was published by the official chart-maker of the United States, the office of The US Coast Survey.
The Office of the Coast Survey, founded in 1807 by President Thomas Jefferson and Secretary of Commerce Albert Gallatin, is the oldest scientific organization in the U.S. Federal Government. Jefferson created the Survey of the Coast, as it was then called, in response to a need for accurate navigational charts of the new nation\\\'s coasts and harbors.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 14in (520mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 14in (520mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Verso: - Some folds re-enforced with archival tape
U.S. Coast Survey (Office of Coast Survey)
The Office of Coast Survey is the official chart-maker of the United States. Set up in 1807, it is one of the U.S. governments oldest scientific organizations. In 1878 it was given the name of Coast and Geodetic Survey (C&GS). In 1970 it became part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The agency was established in 1807 when President Thomas Jefferson signed the document entitled An act to provide for surveying the coasts of the United States. While the bills objective was specific—to produce nautical charts—it reflected larger issues of concern to the new nation: national boundaries, commerce, and defence.
The early years were difficult. Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, who was eventually to become the agencys first superintendent, went to England to collect scientific instruments but was unable to return through the duration of the War of 1812. After his return, he worked on a survey of the New York Harbor in 1817, but Congress stepped in to suspend the work because of tensions between civilian and military control of the agency. After several years under the control of the U.S. Army, the Survey of the Coast was reestablished in 1832, and President Andrew Jackson appointed Hassler as superintendent.
The U.S. Coast Survey was a civilian agency but, from the beginning, members of the Navy and Army were detailed to service with the Survey, and Navy ships were also detailed to its use. In general, army officers worked on topographic surveys on the land and maps based on the surveys, while navy officers worked on hydrographic surveys in coastal waters.
Alexander Dallas Bache, great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, was the second Coast Survey superintendent. Bache was a physicist, scientist, and surveyor who established the first magnetic observatory and served as the first president of the National Academy of Sciences. Under Bache, Coast Survey quickly applied its resources to the Union cause during the Civil War. In addition to setting up additional lithographic presses to produce the thousands of charts required by the Navy and other vessels, Bache made a critical decision to send Coast Survey parties to work with blockading squadrons and armies in the field, producing hundreds of maps and charts. Bache detailed these activities in his annual reports to Congress.
Coast Survey cartographer Edwin Hergesheimer created the map showing the density of the slave population in the Southern states.
Bache was also one of four members of the governments Blockade Strategy Board, planning strategy to essentially strangle the South, economically and militarily. On April 16, 1861, President Lincoln issued a proclamation declaring the blockade of ports from South Carolina to Texas. Baches Notes on the Coast provided valuable information for Union naval forces.
Maps were of paramount importance in wartime:
It is certain that accurate maps must form the basis of well-conducted military operations, and that the best time to procure them is not when an attack is impending, or when the army waits, but when there is no hindrance to, or pressure upon, the surveyors. That no coast can be effectively attacked, defended, or blockaded without accurate maps and charts, has been fully proved by the events of the last two years, if, indeed, such a proposition required practical proof.
— Alexander Dallas Bache, 1862 report.
Coast Survey attracted some of the best and brightest scientists and naturalists. It commissioned the naturalist Louis Agassiz to conduct the first scientific study of the Florida reef system. James McNeill Whistler, who went on to paint the iconic Whistlers Mother, was a Coast Survey engraver. The naturalist John Muir was a guide and artist on Survey of the 39th Parallel across the Great Basin of Nevada and Utah.
The agencys men and women (women professionals were hired as early as 1845) led scientific and engineering activities through the decades. In 1926, they started production of aeronautical charts. During the height of the Great Depression, Coast and Geodetic Survey organized surveying parties and field offices that employed over 10,000 people, including many out-of-work engineers.
In World War II, C&GS sent over 1,000 civilian members and more than half of its commissioned officers to serve as hydrographers, artillery surveyors, cartographers, army engineers, intelligence officers, and geophysicists in all theaters of the war. Civilians on the home front produced over 100 million maps and charts for the Allied Forces. Eleven members of the C&GS gave their lives during the war.
Alexander Dallas Bache 1806 – 1867 was an American physicist, scientist, and surveyor who erected coastal fortifications and conducted a detailed survey to map the mid-eastern United States coastline. Originally an army engineer, he later became Superintendent of the U.S. Coast Survey, and built it into the foremost scientific institution in the country before the Civil War.
Alexander Bache was born in Philadelphia, the son of Richard Bache, Jr., and Sophia Burrell Dallas Bache. He came from a prominent family as he was the nephew of Vice-President George M. Dallas and naval hero Alexander J. Dallas. He was the grandson of Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Dallas and was the great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin.
Bache was a professor of natural philosophy and chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania from 1828 to 1841 and again from 1842 to 1843. He spent 1836–1838 in Europe on behalf of the trustees of what became Girard College; he was named president of the college after his return. Abroad, he examined European education systems, and on his return he published a valuable report. From 1839 to 1842, he served as the first president of Central High School of Philadelphia, one of the oldest public high schools in the United States.
In 1843, on the death of Professor Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, Bache was appointed superintendent of the United States Coast Survey. He convinced the United States Congress of the value of this work and, by means of the liberal aid it granted, he completed the mapping of the whole coast by a skillful division of labor and the erection of numerous observing stations. In addition, magnetic and meteorological data were collected. Bache served as head of the Coast Survey for 24 years (until his death).
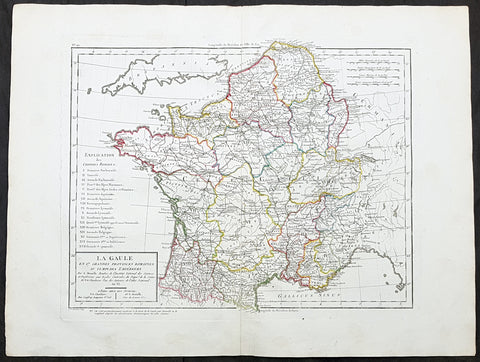
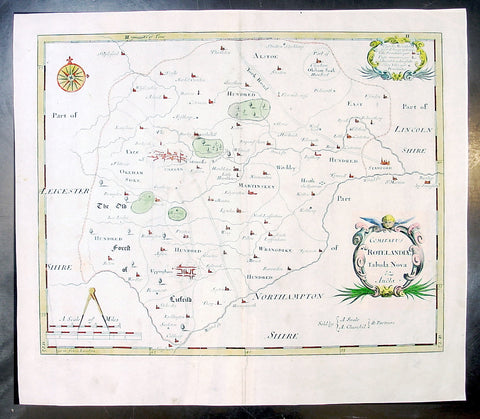
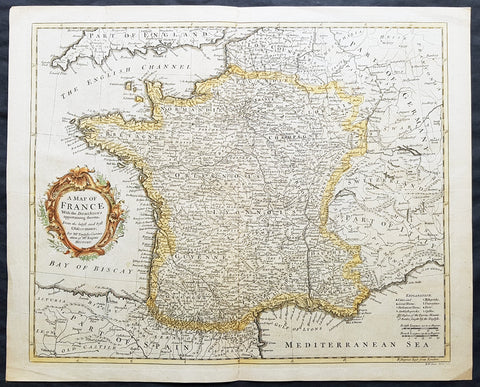
1797 Edme Mentelle & Pierre Tardieu Large Antique Map of France
- Title : La Gaule en 17 Grandes Provinces Romaines au Temps des Empereurs...
- Size: 23in x 17in (590mm x 435mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1797
- Ref #: 26677
Description:
This large original hand coloured antique map of France by Edme Mentelle was engraved by Pierre Tardieu and was published in the 1797 edition of Mentelles Atlas Universal. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 17in (590mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 14in (435mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Mentelle, Edme 1730 - 1816
Mentelle was a French geographer.
Student of Jean-Baptiste Louis Crévier at the Collège de Beauvais (at the time a constituent college of the University of Paris), he found employment with the Ferme générale.
The poems and comedic plays he published early in his career were not successful. He turned to the study of geography and taught geography at the École Militaire during the 1760s. During the 1780s he taught geography to the royal household and in 1786 designed a globe, which is still on display in the Dauphins apartments at the Palace of Versailles.
A supporter of the French Revolution, he taught at the Écoles centrales and at the École Normale Supérieure. He was elected to the Institut de France in 1795.
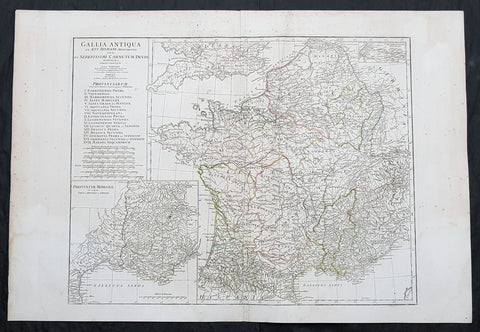
1760 J B D Anville Large Antique Map of Roman France
Antique Map
- Title : Gallia Antiqua ex Aevi Romani......D Anville...MDCCLX
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1760 (dated)
- Ref #: 92296
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique map of Roman France was engraved in 1760 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 18 1/4in (595mm x 465mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing, light age toning
Plate area: - Creasing
Verso: - Creasing, light age toning
Background:
In 600 BC, Ionian Greeks, originating from Phocaea, founded the colony of Massalia (present-day Marseille), on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. This makes it Frances oldest city. At the same time, some Gallic Celtic tribes penetrated parts of the current territory of France, and this occupation spread to the rest of France between the 5th and 3rd century BC.
The concept of Gaul emerged at that time; it corresponds to the territories of Celtic settlement ranging between the Rhine, the Atlantic Ocean, the Pyrenees and the Mediterranean. The borders of modern France are roughly the same as those of ancient Gaul, which was inhabited by Celtic Gauls. Gaul was then a prosperous country, of which the southernmost part was heavily subject to Greek and Roman cultural and economic influences.
Around 390 BC the Gallic chieftain Brennus and his troops made their way to Italy through the Alps, defeated the Romans in the Battle of the Allia, and besieged and ransomed Rome. The Gallic invasion left Rome weakened, and the Gauls continued to harass the region until 345 BC when they entered into a formal peace treaty with Rome. But the Romans and the Gauls would remain adversaries for the next centuries, and the Gauls would continue to be a threat in Italy.
Around 125 BC, the south of Gaul was conquered by the Romans, who called this region Provincia Nostra (Our Province), which over time evolved into the name Provence in French. Julius Caesar conquered the remainder of Gaul and overcame a revolt carried out by the Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix in 52 BC. According to Plutarch and the writings of scholar Brendan Woods, the Gallic Wars resulted in 800 conquered cities, 300 subdued tribes, one million men sold into slavery, and another three million dead in battle.
Gaul was divided by Augustus into Roman provinces. Many cities were founded during the Gallo-Roman period, including Lugdunum (present-day Lyon), which is considered the capital of the Gauls. These cities were built in traditional Roman style, with a forum, a theatre, a circus, an amphitheatre and thermal baths. The Gauls mixed with Roman settlers and eventually adopted Roman culture and Roman speech (Latin, from which the French language evolved). The Roman polytheism merged with the Gallic paganism into the same syncretism.
From the 250s to the 280s AD, Roman Gaul suffered a serious crisis with its fortified borders being attacked on several occasions by barbarians. Nevertheless, the situation improved in the first half of the 4th century, which was a period of revival and prosperity for Roman Gaul. In 312, Emperor Constantin I converted to Christianity. Subsequently, Christians, who had been persecuted until then, increased rapidly across the entire Roman Empire. But, from the beginning of the 5th century, the Barbarian Invasions resumed. Teutonic tribes invaded the region from present-day Germany, the Visigoths settling in the southwest, the Burgundians along the Rhine River Valley, and the Franks (from whom the French take their name) in the north.
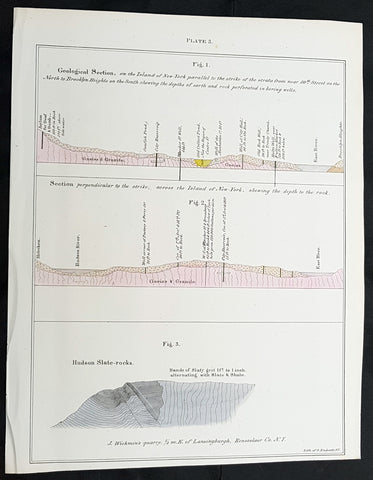
1842 William Mather Antique Cross Section Geology Print The Island of New York
Antique Map
- Title : Geological Section, on the Island of New York.....
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93063
Description:
This original hand coloured antique lithograph of 3 cross sectional geological maps, views on the Island of New York by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
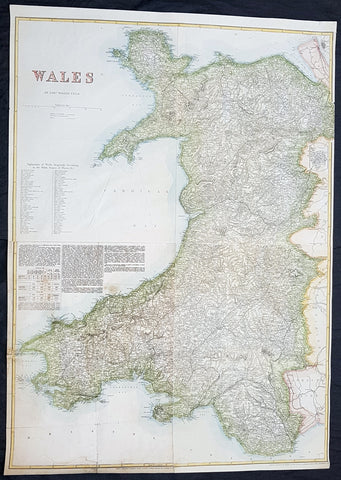
1878 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of Wales
Antique Map
- Title : Wales by Edward Weller FRGS
- Size: 34 1/2in x 24 1/2in (880m x 620mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1878
- Ref #: 70570
Description:
This very large original hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of Wales by Edward Weller was published by Cassell, Petter & Galpin.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 34 1/2in x 24 1/2in (880m x 620mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 24 1/2in (880m x 620mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - 13in repair to bottom left sheet, no loss
Verso: - Repair as noted
Background:
Cassell & Co is a British book publishing house, founded in 1848 by John Cassell (1817–1865), which became in the 1890s an international publishing group company.
John Cassell (1817–1865), who was in turn a carpenter, temperance preacher, tea and coffee merchant, finally turned to publishing. His first publication was on 1 July 1848, a weekly newspaper called The Standard of Freedomadvocating religious, political, and commercial freedom. The Working Man\\\\\\\'s Friend became another popular publication. In 1849 Cassell was dividing his time between his publishing and his grocery business. In 1851 his expanding interests led to his renting part of La Belle Sauvage, a London inn which had been a playhouse in Elizabethan times. The former inn was demolished in 1873 to make way for a railway viaduct, with the company building new premises behind. La Belle Sauvage was destroyed in 1941 by WWII bombing as well as many archives.
Thomas Dixon Galpin who came from Dorchester in Dorset and George William Petter who was born in Barnstaplein Devon were partners in a printing firm and on John Cassell\\\\\\\'s bankruptcy in June 1855 acquired the publishing company and Cassell\\\\\\\'s debts. Between 1855 and 1858 the printing firm operated as Petter and Galpin and their work was published by W. Kent & Co.
John Cassell was relegated to being a junior partner after becoming insolvent in 1858, the firm being known as Cassell, Petter & Galpin. With the arrival of a new partner, Robert Turner, in 1878, it became Cassell, Petter, Galpin & Company. Galpin was the astute business manager. George Lock, the founder of Ward Lock, another publishing house, was Galpin\\\\\\\'s first cousin. Petter resigned in 1883 as a result of disagreement over publishing fiction, and in 1888 the company name was changed to Cassell & Co, Ltd, following Galpin\\\\\\\'s retirement and Petters death.
Weller, Edward 1819 – 1884
Weller was a British engraver and cartographer who was one of the first to produce maps using lithography. He was a London-based working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury.
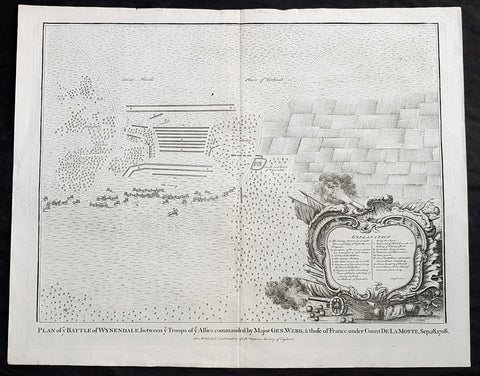
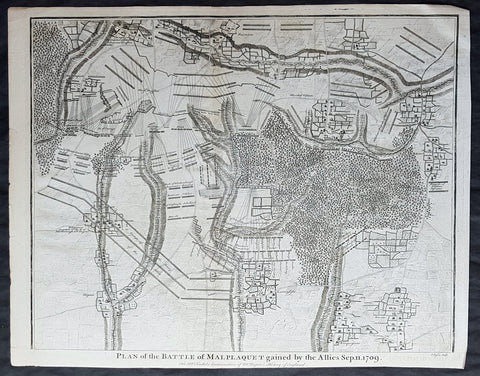
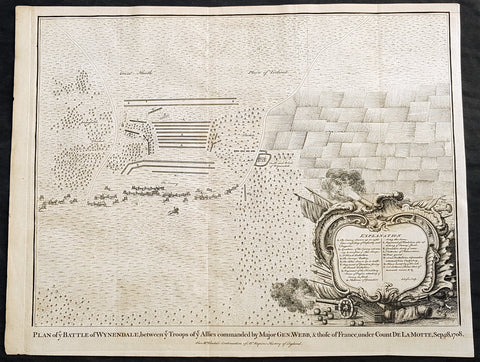
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22165
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
1836 Moule Antique Map The English County of Cheshire
- Title : Cheshire
- Date : 1836
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92439
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Description:
This finely engraved original beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the English county of Cheshire by Thomas Moule was published in the 1836 edition of Barclays Dictionary. Moules maps were some of the the last original decorative maps published in the 19th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1695 Morden Antique Map The English County of Rutland
- Title : Comitatus Rotelandiae Tabula Nova & Aucta
- Ref #: 50145
- Size: 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
- Date : 1695
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the English County of Rutland was engraved by Robert Morden for the 1695 edition of Camden's Britannia.
William Camden was an historian who first published his Britannia, a description and history of Britain, in 1586. Written in Latin, the book contained only a general map of the country but had a wide circulation and eventually in 1607 an edition (the sixth) was published with a series of maps with Latin text on the reverse.
Further editions in English were published in 1610 and 1637 but without text. (Many more editions were published up until 1806 with map contributions from Blaeu in 1617, John Bill 1626, Robert Morden 1695-1772 and John Cary 1789-1806)
In the 1610 & 1617 editions the maps were mostly engraved by William Kip and William Hole and were based on those of Christopher Saxton, but six were copied from John Norden.
The map of Pembroke is by George Owen and the general maps of England/Wales, Scotland and Ireland were probably taken from Mercator. Kip reduced the size of each map for Britannia from the originals published byChristopher Saxton in 1579. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, blue, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 11 1/2in (370mm x 290mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25m)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15659
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
1745 Tindal Antique Battle Map of Oudenaarde, Belgium in 1708 - Britain & France
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Oudenard fought July 11th 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15661
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the Battle of Oudenard or Oudenaarde, in Flemish Belgium, in 1708 between Britain & its allies and France and its allies - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Oudenarde (or Oudenaarde) was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 11 July 1708 between the forces of Great Britain, the Dutch Republic and the Holy Roman Empire on the one side and those of France on the other. It took place at Oudenaarde (now in Belgium) and was a great victory for the allies.
Great Britain, the Netherlands, and the Holy Roman Empire were horrified at the thought of a union between Spain and France which caused them to ally against France, beginning the War of the Spanish Succession. The commander of the allied armies was John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, whose chief deputy was the commander of the Empire\'s army Prince Eugène of Savoy, who was his close friend.
Meanwhile, the two French army commanders were very quarrelsome. Louis Joseph, duc de Vendôme was a seasoned, experienced soldier. The Duke of Burgundy had considerably less experience and owed his position to the fact he was the grandson of the King, Louis XIV of France.
Marlborough\'s army consisted of about 80,000 men (113 infantry battalions and 180 cavalry squadrons) just south of Brussels. Eugène\'s forces were assembled at Coblenz. These two areas were somewhat far apart, while the French army\'s 85,000 soldiers (139 battalions and 204 squadrons) were concentrated near Mons.
At this time, the French commanders began quarrelling. Vendôme wanted to attack the city of Huy, which could draw Marlborough in pursuit. The eventual plan adopted, however, (under orders from Louis XIV) was to attack Flanders. The army moved eastward, until they reached the city of Braine-l\'Alleud, which was about 25 km south of Brussels, and also threatened the nearby city of Leuven. Marlborough placed his forces a few miles south of Leuven, in order to cover both threatened cities.
The French army then remained inactive for more than a month. This apparently allowed the extremely behind schedule Eugène to bring his army from the Rhine River. On 5 July, however, the French unexpectedly moved west, taking the cities of Bruges and Ghent (although about 300 British soldiers held out in Ghent for a few days). This extremely demoralized Marlborough and his army, and he did not recover until Eugène was at his side.
The French army had the entire length of the Scheldt River from the French border to the newly taken city of Ghent. Only one British fortress remained: Oudenaarde. If they took that city, Marlborough\'s army would be cut off from the coast, causing them to lose communications with England.
Marlborough detected this objective, and also correctly guessed the method by which the French troops would attempt to take it. They would march down the east bank of the Scheldt (closer to Marlborough\'s troops), while leaving a large covering force between the two opposing armies. The French army marched on 8 July, toward the city of Lessines. However, Marlborough made one of the most inspired forced marches in history, taking the city on 10 July. This forced the French commanders to attempt simply to march across the Scheldt and thereby take the city of Oudenaarde.
Again Marlborough ordered a forced march. This time, though, he ordered 11,000 troops to hold the main crossing point across the Scheldt, under the command of his Quartermaster General, William Cadogan. Cadogan\'s force built 5 additional pontoon bridges to allow Marlborough to get his 80,000-strong army across the river, until French foragers discovered the allied presence around 09:00 AM.
Cadogan, a superb Irish cavalry commander, ordered some dragoons, under Danish General Jørgen Rantzau, to take prisoners from the French advance guard. Many of those troops escaped and alerted Lieutenant General Charles-Armand de Gontaut, duc de Biron, who commanded the vanguard, of the presence of Allied troops on the west bank.
When de Biron advanced, he was disagreeably surprised by the large number of Allied cavalry already across the river, along with the approaching Allied infantry. Although he was ordered to attack by Vendôme, he hesitated upon seeing the reinforced line of 20 battalions (including the four that had been left to guard the pontoon bridges). Biron\'s own forces comprised only 7 battalions and 20 squadrons. He had been given reliable advice that cavalry could not negotiate the marshy terrain in the area and decided not to attempt a crossing. At this time, Eugène, along with 20 squadrons of Prussian cavalry, moved across the river and occupied crucial positions.
While Biron\'s troops were manoeuvring, the leading British infantry brigade had arrived, under the inexperienced but gifted John Campbell, 2nd Duke of Argyll. Cadogan, with authority from Marlborough, attacked Biron\'s 7 battalions (of Swiss mercenaries) with his soldiers (mainly cavalry). The isolated Swiss mercenaries were immediately pushed back and the Allied force destroyed Biron\'s squadrons, until they reached a large mass of French cavalry, at which point they were forced to retire, outnumbered. The force which performed this action was Rantzau\'s cavalry, with the future King George II of England among them.
Burgundy, making another mistake, decided to attack (over protests by Vendôme). The French right wing began to attack the Allied positions near Eine, while the left wing (for an unknown reason) remained stationary near Huise. A very strong position was held by the Allied left wing. 28 cavalry squadrons protected the right flank of Cadogan\'s infantry, which would receive the attack (which proceeded at about 4:00 p.m.).
Burgundy ordered the assault, which landed on Prussian cavalry squadrons under Dubislav Gneomar von Natzmer. Although hard fighting ensued, the attack was dispersed. Then, Vendôme made a dubious decision and led an attack of twelve regiments, fighting hand-to-hand with a half-pike. This meant that while one commander (Burgundy) was in his headquarters, with no view of the battle, the other was fighting, with no possibility of control.
Most historians agree that the weakened Allied right flank would have been destroyed, had the French left wing attacked. Vendôme realized this, asking Burgundy for permission to attack with the left wing. Burgundy sent a messenger with a refusal but the messenger failed to deliver the message. The situation worsened with Vendôme believing that an attack would support his troops, who were lengthening their line, threatening to envelop the Allied left flank. As Argyll\'s regiments approached, they lengthened the Allied line but too slowly and not great enough in extent, to prevent the French from threatening such an envelopment.
Marlborough moved his headquarters to the left flank, giving Eugène command of the right flank (which still checked the left wing of the French army). While the right was under pressure, Marlborough made a brilliant command decision: he placed 18 newly arrived Hessian and Hanoverian battalions in the left flank, while replacing 20 of Prussian General Carl von Lottum\'s battalions, moving them to Eugène\'s support. This moved fresh troops to the critical left, while reinforcing the right flank (and resting Lottum\'s troops). Marlborough then began formulating a new plan of double encirclement. He had the entire Dutch Army, under Field Marshal Count Hendrik Overkirk, an experienced military officer. His force was unable to cross the collapsed pontoon bridges near Oudenaarde, forcing him to use the stone bridges in the city, delaying him for an hour. Marlborough went ahead with his plan, having Eugène\'s cavalry charge towards Burgundy\'s headquarters. The French Household Cavalry, the Maison du Roi, were able to turn them back and Marlborough, with only the 18 Hessian and Hanoverian battalions, was unable to do much other than keep the French right in check. At about 20:30, Overkirk\'s troops had arrived and flanked the French right wing. This was in conjunction with a dual attack by Marlborough and Eugène. Overkirk\'s manoeuvre was successful, with much of the French army being routed or captured but there was not enough daylight to complete the manoeuvre.
The French army retired to Ghent, with its commanders quarreling; only darkness and a few broken pontoon bridges saved the army from destruction. For unknown reasons, about half of the French army was kept in reserve, without participating at all. There was a great mass of French cavalry and infantry in some raised ground north of the Norken River and many of Burgundy\'s troops remained inactive. There were many bad decisions in the French army. The cavalry had remained in reserve, mainly because of the advice that the ground was impassable. The entire left wing (the troops under Burgundy and the large mass north of the Norken) was kept in reserve. They could easily have destroyed the rather weak right wing of the Allied army. Had a concerted attack been carried out, with Vendôme attacking with his main body to envelop the Allied right, while Burgundy attacked with the left (before Overkirk and the rest of Argyll\'s troops arrived), the French army could have easily won. The French army lost about 14–15,000 soldiers (about 8,000 of whom were prisoners) and 25 guns, while the Allies lost fewer than 3,000.
1745 Tindal Antique Map of France during the Spanish War of Succession 1701-13
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Oudenard fought July 11th 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15661
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the Battle of Oudenard or Oudenaarde, in Flemish Belgium, in 1708 between Britain & its allies and France and its allies - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Oudenarde (or Oudenaarde) was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 11 July 1708 between the forces of Great Britain, the Dutch Republic and the Holy Roman Empire on the one side and those of France on the other. It took place at Oudenaarde (now in Belgium) and was a great victory for the allies.
Great Britain, the Netherlands, and the Holy Roman Empire were horrified at the thought of a union between Spain and France which caused them to ally against France, beginning the War of the Spanish Succession. The commander of the allied armies was John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, whose chief deputy was the commander of the Empire\'s army Prince Eugène of Savoy, who was his close friend.
Meanwhile, the two French army commanders were very quarrelsome. Louis Joseph, duc de Vendôme was a seasoned, experienced soldier. The Duke of Burgundy had considerably less experience and owed his position to the fact he was the grandson of the King, Louis XIV of France.
Marlborough\'s army consisted of about 80,000 men (113 infantry battalions and 180 cavalry squadrons) just south of Brussels. Eugène\'s forces were assembled at Coblenz. These two areas were somewhat far apart, while the French army\'s 85,000 soldiers (139 battalions and 204 squadrons) were concentrated near Mons.
At this time, the French commanders began quarrelling. Vendôme wanted to attack the city of Huy, which could draw Marlborough in pursuit. The eventual plan adopted, however, (under orders from Louis XIV) was to attack Flanders. The army moved eastward, until they reached the city of Braine-l\'Alleud, which was about 25 km south of Brussels, and also threatened the nearby city of Leuven. Marlborough placed his forces a few miles south of Leuven, in order to cover both threatened cities.
The French army then remained inactive for more than a month. This apparently allowed the extremely behind schedule Eugène to bring his army from the Rhine River. On 5 July, however, the French unexpectedly moved west, taking the cities of Bruges and Ghent (although about 300 British soldiers held out in Ghent for a few days). This extremely demoralized Marlborough and his army, and he did not recover until Eugène was at his side.
The French army had the entire length of the Scheldt River from the French border to the newly taken city of Ghent. Only one British fortress remained: Oudenaarde. If they took that city, Marlborough\'s army would be cut off from the coast, causing them to lose communications with England.
Marlborough detected this objective, and also correctly guessed the method by which the French troops would attempt to take it. They would march down the east bank of the Scheldt (closer to Marlborough\'s troops), while leaving a large covering force between the two opposing armies. The French army marched on 8 July, toward the city of Lessines. However, Marlborough made one of the most inspired forced marches in history, taking the city on 10 July. This forced the French commanders to attempt simply to march across the Scheldt and thereby take the city of Oudenaarde.
Again Marlborough ordered a forced march. This time, though, he ordered 11,000 troops to hold the main crossing point across the Scheldt, under the command of his Quartermaster General, William Cadogan. Cadogan\'s force built 5 additional pontoon bridges to allow Marlborough to get his 80,000-strong army across the river, until French foragers discovered the allied presence around 09:00 AM.
Cadogan, a superb Irish cavalry commander, ordered some dragoons, under Danish General Jørgen Rantzau, to take prisoners from the French advance guard. Many of those troops escaped and alerted Lieutenant General Charles-Armand de Gontaut, duc de Biron, who commanded the vanguard, of the presence of Allied troops on the west bank.
When de Biron advanced, he was disagreeably surprised by the large number of Allied cavalry already across the river, along with the approaching Allied infantry. Although he was ordered to attack by Vendôme, he hesitated upon seeing the reinforced line of 20 battalions (including the four that had been left to guard the pontoon bridges). Biron\'s own forces comprised only 7 battalions and 20 squadrons. He had been given reliable advice that cavalry could not negotiate the marshy terrain in the area and decided not to attempt a crossing. At this time, Eugène, along with 20 squadrons of Prussian cavalry, moved across the river and occupied crucial positions.
While Biron\'s troops were manoeuvring, the leading British infantry brigade had arrived, under the inexperienced but gifted John Campbell, 2nd Duke of Argyll. Cadogan, with authority from Marlborough, attacked Biron\'s 7 battalions (of Swiss mercenaries) with his soldiers (mainly cavalry). The isolated Swiss mercenaries were immediately pushed back and the Allied force destroyed Biron\'s squadrons, until they reached a large mass of French cavalry, at which point they were forced to retire, outnumbered. The force which performed this action was Rantzau\'s cavalry, with the future King George II of England among them.
Burgundy, making another mistake, decided to attack (over protests by Vendôme). The French right wing began to attack the Allied positions near Eine, while the left wing (for an unknown reason) remained stationary near Huise. A very strong position was held by the Allied left wing. 28 cavalry squadrons protected the right flank of Cadogan\'s infantry, which would receive the attack (which proceeded at about 4:00 p.m.).
Burgundy ordered the assault, which landed on Prussian cavalry squadrons under Dubislav Gneomar von Natzmer. Although hard fighting ensued, the attack was dispersed. Then, Vendôme made a dubious decision and led an attack of twelve regiments, fighting hand-to-hand with a half-pike. This meant that while one commander (Burgundy) was in his headquarters, with no view of the battle, the other was fighting, with no possibility of control.
Most historians agree that the weakened Allied right flank would have been destroyed, had the French left wing attacked. Vendôme realized this, asking Burgundy for permission to attack with the left wing. Burgundy sent a messenger with a refusal but the messenger failed to deliver the message. The situation worsened with Vendôme believing that an attack would support his troops, who were lengthening their line, threatening to envelop the Allied left flank. As Argyll\'s regiments approached, they lengthened the Allied line but too slowly and not great enough in extent, to prevent the French from threatening such an envelopment.
Marlborough moved his headquarters to the left flank, giving Eugène command of the right flank (which still checked the left wing of the French army). While the right was under pressure, Marlborough made a brilliant command decision: he placed 18 newly arrived Hessian and Hanoverian battalions in the left flank, while replacing 20 of Prussian General Carl von Lottum\'s battalions, moving them to Eugène\'s support. This moved fresh troops to the critical left, while reinforcing the right flank (and resting Lottum\'s troops). Marlborough then began formulating a new plan of double encirclement. He had the entire Dutch Army, under Field Marshal Count Hendrik Overkirk, an experienced military officer. His force was unable to cross the collapsed pontoon bridges near Oudenaarde, forcing him to use the stone bridges in the city, delaying him for an hour. Marlborough went ahead with his plan, having Eugène\'s cavalry charge towards Burgundy\'s headquarters. The French Household Cavalry, the Maison du Roi, were able to turn them back and Marlborough, with only the 18 Hessian and Hanoverian battalions, was unable to do much other than keep the French right in check. At about 20:30, Overkirk\'s troops had arrived and flanked the French right wing. This was in conjunction with a dual attack by Marlborough and Eugène. Overkirk\'s manoeuvre was successful, with much of the French army being routed or captured but there was not enough daylight to complete the manoeuvre.
The French army retired to Ghent, with its commanders quarreling; only darkness and a few broken pontoon bridges saved the army from destruction. For unknown reasons, about half of the French army was kept in reserve, without participating at all. There was a great mass of French cavalry and infantry in some raised ground north of the Norken River and many of Burgundy\'s troops remained inactive. There were many bad decisions in the French army. The cavalry had remained in reserve, mainly because of the advice that the ground was impassable. The entire left wing (the troops under Burgundy and the large mass north of the Norken) was kept in reserve. They could easily have destroyed the rather weak right wing of the Allied army. Had a concerted attack been carried out, with Vendôme attacking with his main body to envelop the Allied right, while Burgundy attacked with the left (before Overkirk and the rest of Argyll\'s troops arrived), the French army could have easily won. The French army lost about 14–15,000 soldiers (about 8,000 of whom were prisoners) and 25 guns, while the Allies lost fewer than 3,000.
1781 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Original Antique Map of The Black Sea, Anacharsis Yr
- Title : Carte Du Palus Meotide et du Pont Euxin Pour le Voyage du Jeune Anacharsis....MDCCLXXXI
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16467
- Date : 1781
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1781 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece in 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1785 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map of Phocis, Greece - Oracle of Delphi
- Title : La Phocide et La Doride...1787
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16457
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1787 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece in 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8in x 7in (205mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1788 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map of Thessaly region of Greece
- Title : La thessalie...1788
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16454
- Date : 1788
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1788 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1788 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greecein 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map NW Africa Morocco to Senegal Canary Is.
- Title : Partie Occidentale De L Ancien Continent ...M Bonne
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 40900
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1757 Bellin Antique Map of West Africa South Senegal - Saloum Delta, Nat. Park
- Title : Carte D Une Partie de la Coste D Afrique Depuis Tanit Jusqua la Riviere du Senegal
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Ref #: 25792
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Southern Senegal in West Africa including what is today part of the Saloum National Park in the Saloum Delta by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in 1757 in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1757 Bellin Antique Map St Helena Bay, Western Cape South Africa - Vasco da Gama
- Title : Carte de la Baye de Sainte Helene
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 25783
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of St Helena Bay in Western Cape South Africa by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in 1757 in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Historically, Saint Helena Bay is the location where Vasco da Gama, first set foot in South Africa. The date of this event was recorded as November 7, 1497.
The bay was named Bahia de Santa Helena (Portuguese for its current name) after Saint Helena a devout, influential Christian and mother of Constantine I. This location was also the first setting of a battle between the indigenous Khoikhoi people and early European explorers.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1755 Bellin Antique Map South East Africa from The Cape to Tanzania - Hottentots
- Title : Carte de la Coste orientale d Afrique , depuis le cap de Bonne Espérance jusqu\' au cap del Gada . Tirée de la carte françoise de l Océan Oriental puliée ... le Comte de Maurepas en 1740
- Size: 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 92506
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of St Helena Bay in Western Cape South Africa by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in 1757 in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Historically, Saint Helena Bay is the location where Vasco da Gama, first set foot in South Africa. The date of this event was recorded as November 7, 1497.
The bay was named Bahia de Santa Helena (Portuguese for its current name) after Saint Helena a devout, influential Christian and mother of Constantine I. This location was also the first setting of a battle between the indigenous Khoikhoi people and early European explorers.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1755 Bellin Antique Map Cumberland Bay Juan Fernandez Is Chile Selkirk & Crusoe
- Title : Carte Du Nord Est de I\'Isle de Juan Fernandez
- Ref #: 25644
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of map & view of Cumberland Bay and the Capital San Juan Bautista in the NE of Juan Fernandez Island - off the coast of Chile in the Pacific Ocean - the home of the castaway Alexander Selkirk for 4 years - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Alexander Selkirk (1676 - 1721) was a Scottish sailor who spent four years as a castaway when he was marooned on an uninhabited island, Juan Fernández Island off the coast of Chile. It is his travels that provided the inspiration for Daniel Defoe\'s novel Robinson Crusoe.
At an early period he was engaged in buccaneer expeditions to the South Seas and in 1703 joined in with the expedition of famed privateer and explorer William Dampier. While Dampier was captain of the St. George, Selkirk served on the galley Cinque Ports, the St. George\'s companion, as a sailing master serving under Thomas Stradling.
In October 1704, after the ships had parted ways because of a dispute between Stradling and Dampier, the Cinque Ports was brought by Stradling to the uninhabited archipelago of Juan Fernández off the coast of Chile for a mid-expedition restocking of supplies and fresh water. Selkirk had grave concerns by this time about the seaworthiness of this vessel (indeed, the Cinque Ports later foundered, losing most of its hands). He tried to convince some of his crewmates to desert with him, remaining on the island; he was counting on an impending visit by another ship. No one else agreed to come along with him. Stradling declared that he would grant him his wish and leave him alone on Juan Fernández. Selkirk promptly regretted his decision. He chased and called after the boat, to no avail. Selkirk lived the next four years and four months without any human company. All he had brought with him was a musket, gunpowder, carpenter\'s tools, a knife, a Bible, some clothing and rope.
His long-anticipated rescue occurred on 1 February 1709 by way of the Duke, a privateering ship piloted by the above-mentioned William Dampier. Selkirk was discovered by the Duke\'s captain, Woodes Rogers, who referred to him as Governor of the island. Now rescued, he was almost incoherent in his joy. The agile Selkirk, catching two or three goats a day, helped restore the health of Rogers\' men. Rogers eventually made Selkirk his mate, giving him independent command of one of his ships. Rogers\' A cruising voyage round the world: first to the South-Sea, thence to the East-Indies, and homewards by the Cape of Good Hope was published in 1712 and included an account of Selkirk\'s ordeal. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1746 Bellin Antique Map The Course of Sangha River, Cameroon & The Congo, Africa
- Title : Cours De La Riviere De Sanaga ou Senegal
- Size: 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 21201
- Date : 1746
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the course of the Sangha River flowing through Cameroon & The Congo in Central Africa by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1746 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map Saloum River Delta, Senegal West Africa
- Title : Cours de la Riviere de Senegal...
- Ref #: 92505
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Saloum Delta in the Fatck Region of South Senegal, West Africa by Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The Saloum River rises about 105 kilometers east of Kaolack, Senegal, and flows into the Atlantic Ocean. The significant Saloum Delta is located at its mouth, which is protected as Saloum Delta National Park. The river basin lies within the Serer pre-colonial Kingdom of Saloum. Mangrove forests occupy a 5-kilometer belt on either side of the river almost 70 kilometers upstream.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1757 Bellin Antique Map of Sierra Leone & Sherbro Rivers of Sierra Leone, Africa
- Title : Carte de la Coste et Pays voisins das Rivieres des Sierra Leona et de Sherbro
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Ref #: 21174
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the coast and river mouth of the Sierra Leone & the Sherbro Rivers in Sierrra Leone West Africa by Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The Sierra Leone River is a river estuary on the Atlantic Ocean in Western Sierra Leone. It is formed by the Bankasoka River and Rokel River and is between 4 and 10 miles wide (6–16 km) and 25 miles (40 km) long. It holds the major ports of Queen Elizabeth II Quay and Pepel. The estuary is also important for shipping. It is the largest natural harbour in the African continent. Several islands, including Tasso Island (the largest), Tombo Island, and the historically important Bunce Island, are located in the estuary.
Sherbro Island is in the Atlantic Ocean, located in Bonthe District off the Southern Province of Sierra Leone. The Sherbro people make up by far the largest ethnic group in the island.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 6 1/2in (250mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Repair to left of image
Verso: - Repair as noted
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map of Wallis (Uvea) & Funtuna Islands Capt Wallis 1767
- Title : Isles de Wallis
- Size: 10in x 9in (255mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 16102
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Islands of Wallis (Uvea) and Futuna, situated in the South Pacific between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji to the southwest, Tonga to the southeast, Samoa to the east. Futuna was first mapped by Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire during their famous circumnavigation of the globe in 1616 and Wallis (Uvea) being mapped by Captain Samuel Wallis, who saw it while sailing the HMS Dolphin on 16 August 1767, was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 9in (255mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 8in (230mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Wallis or Uvea, is a Polynesian island in the Pacific Ocean belonging to the French overseas collectivity of Wallis and Futuna. It lies north of Tonga, northeast of Fiji, east-northeast of the Hoorn islands, east of Fijis Rotuma, southeast of Tuvalu, southwest of Tokelau and west of Samoa. Its area is almost 100 km2 with almost 11,000 people. Its capital is Matā utu.
The island was renamed Wallis after a Cornish navigator, Captain Samuel Wallis, who saw it while sailing the HMS Dolphin on 16 August 1767, following his discovery of Tahiti.
Futuna was first put on the European maps by Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire during their famous circumnavigation of the globe in 1616. They named the islands Hoornse Eylanden after the Dutch town of Hoorn where they hailed from. This was later translated into French as Isles de Horne. The French were the first Europeans to settle in the territory with the arrival of French missionaries in 1837
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Capt. Philip Carteret (1733-1796)
was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navy\\\\\\\'s circumnavigation expeditions in 1764-66 and 1766-69.
Carteret entered the Navy in 1747, serving aboard the Salisbury, and then under Captain John Byron from 1751 to 1755. Between 1757 and 1758 he was in the Guernsey on the Mediterranean Station. As a lieutenant in the Dolphin he accompanied Byron during his voyage of circumnavigation, from June 1764 to May 1766.
In 1766 he was made a commander and given the command of the Swallow to circumnavigate the world, as consort to the Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis. The two ships were parted shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Carteret discovering Pitcairn Island and the Carteret Islands, which were subsequently named after him. In 1767, he also discovered a new archipelago inside Saint George\\\\\\\'s Channel between New Ireland and New Britain Islands (Papua New Guinea) and named it Duke of York Islands, as well as rediscovered the Solomon Islands first sighted by the Mendana in 1568, and the Juan Fernandez Islands first discovered by Juan Fernandez in 1574. He arrived back in England, at Spithead, on 20 March 1769.
He was promoted to post captain in 1771.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map of Wallis (Uvea) & Funtuna Islands Capt Wallis 1767
- Title : Isles de Wallis
- Size: 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 21598
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Islands of Wallis (Uvea) and Futuna, situated in the South Pacific between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji to the southwest, Tonga to the southeast, Samoa to the east. Futuna was first mapped by Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire during their famous circumnavigation of the globe in 1616 and Wallis (Uvea) being mapped by Captain Samuel Wallis, who saw it while sailing the HMS Dolphin on 16 August 1767, was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 9in (255mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 8in (230mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Wallis or Uvea, is a Polynesian island in the Pacific Ocean belonging to the French overseas collectivity of Wallis and Futuna. It lies north of Tonga, northeast of Fiji, east-northeast of the Hoorn islands, east of Fijis Rotuma, southeast of Tuvalu, southwest of Tokelau and west of Samoa. Its area is almost 100 km2 with almost 11,000 people. Its capital is Matā utu.
The island was renamed Wallis after a Cornish navigator, Captain Samuel Wallis, who saw it while sailing the HMS Dolphin on 16 August 1767, following his discovery of Tahiti.
Futuna was first put on the European maps by Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire during their famous circumnavigation of the globe in 1616. They named the islands Hoornse Eylanden after the Dutch town of Hoorn where they hailed from. This was later translated into French as Isles de Horne. The French were the first Europeans to settle in the territory with the arrival of French missionaries in 1837
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Capt. Philip Carteret (1733-1796)
was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navy\\\\\\\'s circumnavigation expeditions in 1764-66 and 1766-69.
Carteret entered the Navy in 1747, serving aboard the Salisbury, and then under Captain John Byron from 1751 to 1755. Between 1757 and 1758 he was in the Guernsey on the Mediterranean Station. As a lieutenant in the Dolphin he accompanied Byron during his voyage of circumnavigation, from June 1764 to May 1766.
In 1766 he was made a commander and given the command of the Swallow to circumnavigate the world, as consort to the Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis. The two ships were parted shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Carteret discovering Pitcairn Island and the Carteret Islands, which were subsequently named after him. In 1767, he also discovered a new archipelago inside Saint George\\\\\\\'s Channel between New Ireland and New Britain Islands (Papua New Guinea) and named it Duke of York Islands, as well as rediscovered the Solomon Islands first sighted by the Mendana in 1568, and the Juan Fernandez Islands first discovered by Juan Fernandez in 1574. He arrived back in England, at Spithead, on 20 March 1769.
He was promoted to post captain in 1771.
1834 Henry Teesdale Large Antique Map Switzerland divided in Cantons - Beautiful
- Title : 1834 Henry Teesdale Large Antique Map Switzerland divided in Cantons - Beautiful
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50286
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of Switzerland was engraved by John Dower in 1834 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1835 edition of Henry Teesdale\'s A New General Atlas of the World.
As with all the maps published by Teesdale this one is of the highest quality on strong clean & sturdy paper with beautiful original hand colouring. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The establishment of the Old Swiss Confederacy dates to the late medieval period, resulting from a series of military successes against Austria and Burgundy. Swiss independence from the Holy Roman Empire was formally recognized in the Peace of Westphalia in 1648. The country has a history of armed neutrality going back to the Reformation; it has not been in a state of war internationally since 1815 and did not join the United Nations until 2002. Nevertheless, it pursues an active foreign policy and is frequently involved in peace-building processes around the world. In addition to being the birthplace of the Red Cross, Switzerland is home to numerous international organisations, including the second largest UN office. On the European level, it is a founding member of the European Free Trade Association, but notably not part of the European Union, the European Economic Area or the Eurozone. However, it participates in the Schengen Area and the European Single Market through bilateral treaties.
Spanning the intersection of Germanic and Romance Europe, Switzerland comprises four main linguistic and cultural regions: German, French, Italian and Romansh. Although the majority of the population are German speaking, Swiss national identity is rooted in a common historical background, shared values such as federalism and direct democracy, and Alpine symbolism. Due to its linguistic diversity, Switzerland is known by a variety of native names: Schweiz, Suisse, Svizzera and Svizra. On coins and stamps, the Latin name – frequently shortened to Helvetia – is used instead of the four national languages.
Teesdale & co., Henry fl 1828-1843
Teesdale was a prominent London publisher and founding fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. He produced large-scale maps and charts and a number of fine atlases in the early part of the nineteenth century. He employed the most skilled draftsmen and engravers and his maps are renowned for precise detail and fine coloring
1855 US Coast Survey & A D Bache Antique Map of Monterey Bay, California
- Title : US Coast Survey A D Bache Superintendant Map of the Vicinity of Monterey Bay California...By W P Blake esq. 1855
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (290mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 93017
Description:
This original antique lithograph map of Monterey Bay, California by Alexander Dallas Bache (great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin) in 1855 - dated - was published by the official chart-maker of the United Stetes, the office of The US Coast Survey.
Alexander Dallas Bache 1806 – 1867 was an American physicist, scientist, and surveyor who erected coastal fortifications and conducted a detailed survey to map the mid-eastern United States coastline. Originally an army engineer, he later became Superintendent of the U.S. Coast Survey, and built it into the foremost scientific institution in the country before the Civil War.
Alexander Bache was born in Philadelphia, the son of Richard Bache, Jr., and Sophia Burrell Dallas Bache. He came from a prominent family as he was the nephew of Vice-President George M. Dallas and naval hero Alexander J. Dallas. He was the grandson of Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Dallas and was the great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin.
Bache was a professor of natural philosophy and chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania from 1828 to 1841 and again from 1842 to 1843. He spent 1836–1838 in Europe on behalf of the trustees of what became Girard College; he was named president of the college after his return. Abroad, he examined European education systems, and on his return he published a valuable report. From 1839 to 1842, he served as the first president of Central High School of Philadelphia, one of the oldest public high schools in the United States.
In 1843, on the death of Professor Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, Bache was appointed superintendent of the United States Coast Survey. He convinced the United States Congress of the value of this work and, by means of the liberal aid it granted, he completed the mapping of the whole coast by a skillful division of labor and the erection of numerous observing stations. In addition, magnetic and meteorological data were collected. Bache served as head of the Coast Survey for 24 years (until his death).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (290mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (290mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The earliest archaeological evidence of human habitation of the territory of the city of San Francisco dates to 3000 BC. The Yelamu group of the Ohlone people resided in a few small villages when an overland Spanish exploration party, led by Don Gaspar de Portolà, arrived on November 2, 1769, the first documented European visit to San Francisco Bay. Seven years later, on March 28, 1776, the Spanish established the Presidio of San Francisco, followed by a mission, Mission San Francisco de Asís (Mission Dolores), established by the Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza.
Upon independence from Spain in 1821, the area became part of Mexico. Under Mexican rule, the mission system gradually ended, and its lands became privatized. In 1835, Englishman William Richardson erected the first independent homestead, near a boat anchorage around what is today Portsmouth Square. Together with Alcalde Francisco de Haro, he laid out a street plan for the expanded settlement, and the town, named Yerba Buena, began to attract American settlers. Commodore John D. Sloat claimed California for the United States on July 7, 1846, during the Mexican–American War, and Captain John B. Montgomery arrived to claim Yerba Buena two days later. Yerba Buena was renamed San Francisco on January 30 of the next year, and Mexico officially ceded the territory to the United States at the end of the war. Despite its attractive location as a port and naval base, San Francisco was still a small settlement with inhospitable geography.
The California Gold Rush brought a flood of treasure seekers (known as forty-niners, as in 1849). With their sourdough bread in tow, prospectors accumulated in San Francisco over rival Benicia, raising the population from 1,000 in 1848 to 25,000 by December 1849. The promise of great wealth was so strong that crews on arriving vessels deserted and rushed off to the gold fields, leaving behind a forest of masts in San Francisco harbor. Some of these approximately 500 abandoned ships were used at times as storeships, saloons and hotels; many were left to rot and some were sunk to establish title to the underwater lot. By 1851 the harbor was extended out into the bay by wharves while buildings were erected on piles among the ships. By 1870 Yerba Buena Cove had been filled to create new land. Buried ships are occasionally exposed when foundations are dug for new buildings.
California was quickly granted statehood in 1850, and the U.S. military built Fort Point at the Golden Gate and a fort on Alcatraz Island to secure the San Francisco Bay. Silver discoveries, including the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1859, further drove rapid population growth. With hordes of fortune seekers streaming through the city, lawlessness was common, and the Barbary Coast section of town gained notoriety as a haven for criminals, prostitution, and gambling.
Entrepreneurs sought to capitalize on the wealth generated by the Gold Rush. Early winners were the banking industry, with the founding of Wells Fargo in 1852 and the Bank of California in 1864. Development of the Port of San Francisco and the establishment in 1869 of overland access to the eastern U.S. rail system via the newly completed Pacific Railroad (the construction of which the city only reluctantly helped support) helped make the Bay Area a center for trade. Catering to the needs and tastes of the growing population, Levi Strauss opened a dry goods business and Domingo Ghirardelli began manufacturing chocolate. Immigrant laborers made the city a polyglot culture, with Chinese Railroad Workers, drawn to Old Gold Mountain, creating the citys Chinatown quarter. In 1870, Asians made up 8% of the population. The first cable cars carried San Franciscans up Clay Street in 1873. The citys sea of Victorian houses began to take shape, and civic leaders campaigned for a spacious public park, resulting in plans for Golden Gate Park. San Franciscans built schools, churches, theaters, and all the hallmarks of civic life. The Presidio developed into the most important American military installation on the Pacific coast. By 1890, San Franciscos population approached 300,000, making it the eighth-largest city in the United States at the time. Around 1901, San Francisco was a major city known for its flamboyant style, stately hotels, ostentatious mansions on Nob Hill, and a thriving arts scene. The first North American plague epidemic was the San Francisco plague of 1900–1904.
U.S. Coast Survey (Office of Coast Survey)
The Office of Coast Survey is the official chart-maker of the United States. Set up in 1807, it is one of the U.S. governments oldest scientific organizations. In 1878 it was given the name of Coast and Geodetic Survey (C&GS). In 1970 it became part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The agency was established in 1807 when President Thomas Jefferson signed the document entitled An act to provide for surveying the coasts of the United States. While the bills objective was specific—to produce nautical charts—it reflected larger issues of concern to the new nation: national boundaries, commerce, and defence.
The early years were difficult. Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, who was eventually to become the agencys first superintendent, went to England to collect scientific instruments but was unable to return through the duration of the War of 1812. After his return, he worked on a survey of the New York Harbor in 1817, but Congress stepped in to suspend the work because of tensions between civilian and military control of the agency. After several years under the control of the U.S. Army, the Survey of the Coast was reestablished in 1832, and President Andrew Jackson appointed Hassler as superintendent.
The U.S. Coast Survey was a civilian agency but, from the beginning, members of the Navy and Army were detailed to service with the Survey, and Navy ships were also detailed to its use. In general, army officers worked on topographic surveys on the land and maps based on the surveys, while navy officers worked on hydrographic surveys in coastal waters.
Alexander Dallas Bache, great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, was the second Coast Survey superintendent. Bache was a physicist, scientist, and surveyor who established the first magnetic observatory and served as the first president of the National Academy of Sciences. Under Bache, Coast Survey quickly applied its resources to the Union cause during the Civil War. In addition to setting up additional lithographic presses to produce the thousands of charts required by the Navy and other vessels, Bache made a critical decision to send Coast Survey parties to work with blockading squadrons and armies in the field, producing hundreds of maps and charts. Bache detailed these activities in his annual reports to Congress.
Coast Survey cartographer Edwin Hergesheimer created the map showing the density of the slave population in the Southern states.
Bache was also one of four members of the governments Blockade Strategy Board, planning strategy to essentially strangle the South, economically and militarily. On April 16, 1861, President Lincoln issued a proclamation declaring the blockade of ports from South Carolina to Texas. Baches Notes on the Coast provided valuable information for Union naval forces.
Maps were of paramount importance in wartime:
It is certain that accurate maps must form the basis of well-conducted military operations, and that the best time to procure them is not when an attack is impending, or when the army waits, but when there is no hindrance to, or pressure upon, the surveyors. That no coast can be effectively attacked, defended, or blockaded without accurate maps and charts, has been fully proved by the events of the last two years, if, indeed, such a proposition required practical proof.
— Alexander Dallas Bache, 1862 report.
Coast Survey attracted some of the best and brightest scientists and naturalists. It commissioned the naturalist Louis Agassiz to conduct the first scientific study of the Florida reef system. James McNeill Whistler, who went on to paint the iconic Whistlers Mother, was a Coast Survey engraver. The naturalist John Muir was a guide and artist on Survey of the 39th Parallel across the Great Basin of Nevada and Utah.
The agencys men and women (women professionals were hired as early as 1845) led scientific and engineering activities through the decades. In 1926, they started production of aeronautical charts. During the height of the Great Depression, Coast and Geodetic Survey organized surveying parties and field offices that employed over 10,000 people, including many out-of-work engineers.
In World War II, C&GS sent over 1,000 civilian members and more than half of its commissioned officers to serve as hydrographers, artillery surveyors, cartographers, army engineers, intelligence officers, and geophysicists in all theaters of the war. Civilians on the home front produced over 100 million maps and charts for the Allied Forces. Eleven members of the C&GS gave their lives during the war.
1842 William Mather Antique Geology Print of Hudson River, Sullivan County, NY
Antique Map
- Title : Section in Sullivan Co. Catskill Mt Rocks
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93067
Description:
This original hand coloured antique lithograph cross sectional geological map,a view along the Hudson River in Sullivan County, New York by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
Sullivan County is a county in the U.S. state of New York.
When the Province of New York established its first twelve counties in 1683, the present Sullivan County was part of Ulster County. In 1809, Sullivan County was split from Ulster County.
In the late 19th century, the Industrial Revolution and the advent of factories driven by water power along the streams and rivers led to an increase in population attracted to the jobs. Hamlets enlarged into towns. As industry restructured, many of those jobs left before the middle of the twentieth century. The economy changed again after that, shifting to a more tourist-based variety and benefiting from resorts established by European Jewish immigrants and their descendants in what became called the Borscht Belt of the 20th century. Resort hotels featured a wide variety of entertainers, some nationally known. At the beginning of this period, visitors traveled to the area by train, and later by automobile. The areas natural resources also provided a setting for numerous summer camps frequented by the children of immigrants and their descendants.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1842 William Mather Antique Geology Print Hudson River Lakes George to Champlain
Antique Map
- Title : Section from Lake George by Whitehall to E Poultney in VT
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93064
Description:
This original hand coloured antique lithograph cross sectional geological map,a view along the Hudson River from Lake George in NY to Lake Champlain Vermont by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15662
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map The Battle of Blenheim, Germany in 1704
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Glorious Battle of Hochstet gained by the Allies on August 13.th 1704.
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Ref #: 15692-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Blenheim or Hochstadt, fought in Bavaria, Germany in August 1704 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Blenheim (German: Zweite Schlacht bei Höchstädt; French Bataille de Höchstädt), fought on 13 August 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied victory ensured the safety of Vienna from the Franco-Bavarian army, thus preventing the collapse of the Grand Alliance.
Louis XIV of France sought to knock the Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold out of the war by seizing Vienna, the Habsburg capital, and gain a favourable peace settlement. The dangers to Vienna were considerable: the Elector of Bavaria and Marshal Marsins forces in Bavaria threatened from the west, and Marshal Vendômes large army in northern Italy posed a serious danger with a potential offensive through the Brenner Pass. Vienna was also under pressure from Rákóczis Hungarian revolt from its eastern approaches. Realising the danger, the Duke of Marlborough resolved to alleviate the peril to Vienna by marching his forces south from Bedburg to help maintain Emperor Leopold within the Grand Alliance.
A combination of deception and skilled administration – designed to conceal his true destination from friend and foe alike – enabled Marlborough to march 400 kilometres (250 miles) unhindered from the Low Countries to the River Danube in five weeks. After securing Donauwörth on the Danube, Marlborough sought to engage the Electors and Marsins army before Marshal Tallard could bring reinforcements through the Black Forest. However, with the Franco-Bavarian commanders reluctant to fight until their numbers were deemed sufficient, the Duke enacted a policy of plundering in Bavaria designed to force the issue. The tactic proved unsuccessful, but when Tallard arrived to bolster the Electors army, and Prince Eugene arrived with reinforcements for the Allies, the two armies finally met on the banks of the Danube in and around the small village of Blindheim, from which the English Blenheim is derived.
Blenheim was one of the battles that altered the course of the war, which until then was leaning for Louis coalition, and ended French plans of knocking the Emperor out of the war. France suffered as many as 38,000 casualties including the commander-in-chief, Marshal Tallard, who was taken captive to England. Before the 1704 campaign ended, the Allies had taken Landau, and the towns of Trier and Trarbach on the Moselle in preparation for the following years campaign into France itself. The offensive never materialised as the Grand Alliances army had to depart the Moselle to defend Liège from a French counteroffensive. The war would rage on for another decade.
Tindal, Nicolas 1687 – 1774
Nicolas Tindal was the translator and continuer of the History of England published by Paul de Rapin (1661-1725) in 1724. De Rapins publication chronicles the History of Britain from the invasion of the Romans to the death of Charles I. Very few comprehensive histories of England existed at the time and Tindal added his three-volume Continuation, of the Kingdom, from the reigns of James II to George II.
Tindal\\\'s translation of de Rapins History, was first published in 1727. Tindal enlarged the volumes in their second edition (1732) to contain notes, genealogical tables and maps of his own composition. In 1745 Tindal published Tindal’s Continuation of Mr. Rapin’s History of England. Included with this edition was an atlas containing 45 maps, battle and town plans from the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) that were engraved by Richard William Seale and John Basire.
These maps represent battles that took place during the War of Spanish Succession, concluded by the Treaties of Utrecht. The war resulted from a dispute over who should inherit Spain and its possessions after its Habsburg rulers in 1700. The last Habsburg king of Spain, Charles II (d. 1700) had left the throne to his closest relative in female line: Philippe de France, duke of Anjou, grandson of Louis XIV (Felipe V of Spain). The closest relatives in male line, the Habsburgs of Austria, disputed this claim, and many European nations did not want to see French princes reigning over both kingdoms. The Utrecht treaties recognized Felipe V of Spain, but transferred the Spanish possessions in the Netherlands and Italy to Austria and to Savoy. To reach the goal of separating the crowns of France and Spain, the treaties required Felipe V to relinquish all claims to the French throne, and the remaining French princes to relinquish all claims to the Spanish throne.
The War of the Spanish Succession, was also known as Marlboroughs Wars, that was fought in Europe and the Mediterranean, and were the last and the bloodiest of the Wars between England and France under Louis XIV, and the first in which Britain played a major military role in European military affairs.
Paul de Rapin 1661-1725 was born in Castes and educated at the Protestant academy of Saumur. In 1685 after the death of his father he moved to England but after being unable to find employment moved to Holland and enlisted in French volunteers at Utrecht commanded by his cousin Daniel de Rapin. He accompanied the prince of Orange to England in 1688 and participated in the Irish campaigns of the siege of Carrickfergus, Battle of the Boyne and Limerick. Rapin resigned to become tutor to the Earl of Portlands son. He settled in Holland where he began work on The History of England. It was published in Holland in 1724 in 8 volumes. The work was an attempt to be exhaustive in the spirit of the eighteenth century philosophies by treating the subject from prehistoric times up to the date of publication.
1858 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of Bangladesh, Assam, Sri lanka Ceylon
Antique Map
- Title : India The Eastern Provinces by Edward Weller
- Ref #: 70495
- Size: 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1858
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original lithograph hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was engraved by Day & Co. and was published in the 1858 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Weller, Edward 1819 – 1884
Weller was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.
1857 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of Hyderabad & Nagpur Regions of India
Antique Map
- Title : India Nagpoor, Hyderabad
- Ref #: 70490
- Size: 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1857
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original lithograph hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was engraved by Day & Co. and was published in the 1857 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Edward Weller 1819 - 1884; was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.
1857 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of Southern India & Sri Lanka, Ceylon
Antique Map
- Title : India (South Part)
- Ref #: 40996
- Size: 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1857
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original lithograph hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was engraved by Day & Co. and was published in the 1857 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Weller, Edward 1819 – 1884
Weller was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.
1860 Blackie & Son Map British North America - Canada & The Great Lakes
- Title : British North America
- Ref #: 33165
- Size: 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1860
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original map of Canada was engraved by Blackie and Son of Glasgow, Edinburgh and London in ca 1860. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Blue, pink
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 345mm)
Margins: - min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None