Maps (791)
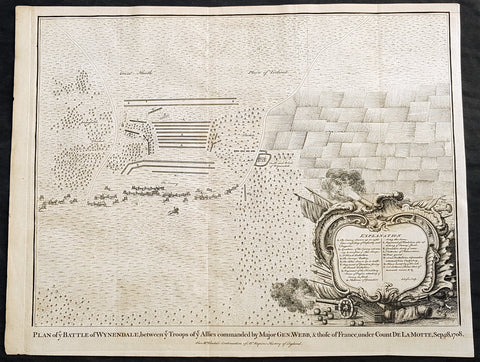
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15662
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
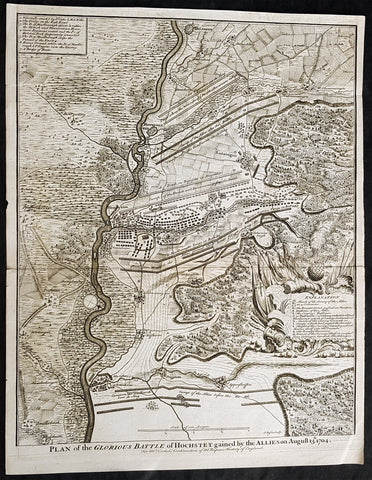
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map The Battle of Blenheim, Germany in 1704
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Glorious Battle of Hochstet gained by the Allies on August 13.th 1704.
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Ref #: 15692-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Blenheim or Hochstadt, fought in Bavaria, Germany in August 1704 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Blenheim (German: Zweite Schlacht bei Höchstädt; French Bataille de Höchstädt), fought on 13 August 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied victory ensured the safety of Vienna from the Franco-Bavarian army, thus preventing the collapse of the Grand Alliance.
Louis XIV of France sought to knock the Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold out of the war by seizing Vienna, the Habsburg capital, and gain a favourable peace settlement. The dangers to Vienna were considerable: the Elector of Bavaria and Marshal Marsins forces in Bavaria threatened from the west, and Marshal Vendômes large army in northern Italy posed a serious danger with a potential offensive through the Brenner Pass. Vienna was also under pressure from Rákóczis Hungarian revolt from its eastern approaches. Realising the danger, the Duke of Marlborough resolved to alleviate the peril to Vienna by marching his forces south from Bedburg to help maintain Emperor Leopold within the Grand Alliance.
A combination of deception and skilled administration – designed to conceal his true destination from friend and foe alike – enabled Marlborough to march 400 kilometres (250 miles) unhindered from the Low Countries to the River Danube in five weeks. After securing Donauwörth on the Danube, Marlborough sought to engage the Electors and Marsins army before Marshal Tallard could bring reinforcements through the Black Forest. However, with the Franco-Bavarian commanders reluctant to fight until their numbers were deemed sufficient, the Duke enacted a policy of plundering in Bavaria designed to force the issue. The tactic proved unsuccessful, but when Tallard arrived to bolster the Electors army, and Prince Eugene arrived with reinforcements for the Allies, the two armies finally met on the banks of the Danube in and around the small village of Blindheim, from which the English Blenheim is derived.
Blenheim was one of the battles that altered the course of the war, which until then was leaning for Louis coalition, and ended French plans of knocking the Emperor out of the war. France suffered as many as 38,000 casualties including the commander-in-chief, Marshal Tallard, who was taken captive to England. Before the 1704 campaign ended, the Allies had taken Landau, and the towns of Trier and Trarbach on the Moselle in preparation for the following years campaign into France itself. The offensive never materialised as the Grand Alliances army had to depart the Moselle to defend Liège from a French counteroffensive. The war would rage on for another decade.
Tindal, Nicolas 1687 – 1774
Nicolas Tindal was the translator and continuer of the History of England published by Paul de Rapin (1661-1725) in 1724. De Rapins publication chronicles the History of Britain from the invasion of the Romans to the death of Charles I. Very few comprehensive histories of England existed at the time and Tindal added his three-volume Continuation, of the Kingdom, from the reigns of James II to George II.
Tindal\\\'s translation of de Rapins History, was first published in 1727. Tindal enlarged the volumes in their second edition (1732) to contain notes, genealogical tables and maps of his own composition. In 1745 Tindal published Tindal’s Continuation of Mr. Rapin’s History of England. Included with this edition was an atlas containing 45 maps, battle and town plans from the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) that were engraved by Richard William Seale and John Basire.
These maps represent battles that took place during the War of Spanish Succession, concluded by the Treaties of Utrecht. The war resulted from a dispute over who should inherit Spain and its possessions after its Habsburg rulers in 1700. The last Habsburg king of Spain, Charles II (d. 1700) had left the throne to his closest relative in female line: Philippe de France, duke of Anjou, grandson of Louis XIV (Felipe V of Spain). The closest relatives in male line, the Habsburgs of Austria, disputed this claim, and many European nations did not want to see French princes reigning over both kingdoms. The Utrecht treaties recognized Felipe V of Spain, but transferred the Spanish possessions in the Netherlands and Italy to Austria and to Savoy. To reach the goal of separating the crowns of France and Spain, the treaties required Felipe V to relinquish all claims to the French throne, and the remaining French princes to relinquish all claims to the Spanish throne.
The War of the Spanish Succession, was also known as Marlboroughs Wars, that was fought in Europe and the Mediterranean, and were the last and the bloodiest of the Wars between England and France under Louis XIV, and the first in which Britain played a major military role in European military affairs.
Paul de Rapin 1661-1725 was born in Castes and educated at the Protestant academy of Saumur. In 1685 after the death of his father he moved to England but after being unable to find employment moved to Holland and enlisted in French volunteers at Utrecht commanded by his cousin Daniel de Rapin. He accompanied the prince of Orange to England in 1688 and participated in the Irish campaigns of the siege of Carrickfergus, Battle of the Boyne and Limerick. Rapin resigned to become tutor to the Earl of Portlands son. He settled in Holland where he began work on The History of England. It was published in Holland in 1724 in 8 volumes. The work was an attempt to be exhaustive in the spirit of the eighteenth century philosophies by treating the subject from prehistoric times up to the date of publication.
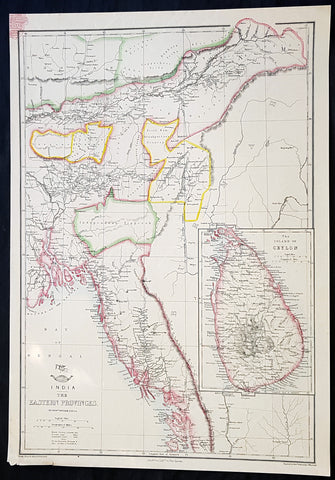
1858 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of Bangladesh, Assam, Sri lanka Ceylon
Antique Map
- Title : India The Eastern Provinces by Edward Weller
- Ref #: 70495
- Size: 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1858
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original lithograph hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was engraved by Day & Co. and was published in the 1858 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Weller, Edward 1819 – 1884
Weller was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.
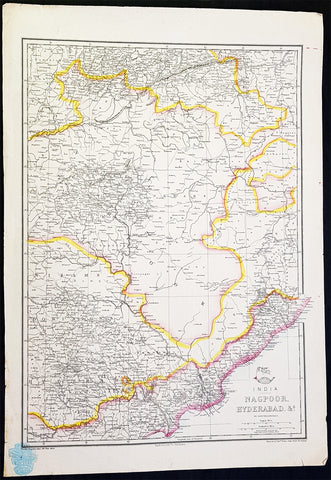
1857 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of Hyderabad & Nagpur Regions of India
Antique Map
- Title : India Nagpoor, Hyderabad
- Ref #: 70490
- Size: 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1857
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original lithograph hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was engraved by Day & Co. and was published in the 1857 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Edward Weller 1819 - 1884; was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.
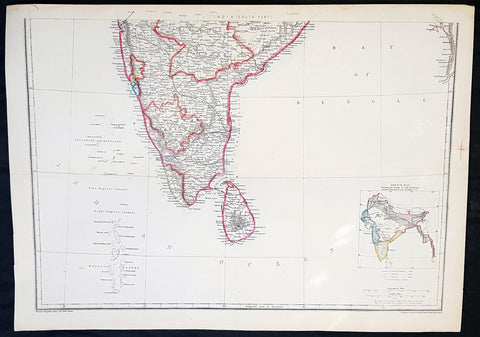
1857 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of Southern India & Sri Lanka, Ceylon
Antique Map
- Title : India (South Part)
- Ref #: 40996
- Size: 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1857
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original lithograph hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was engraved by Day & Co. and was published in the 1857 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Weller, Edward 1819 – 1884
Weller was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.
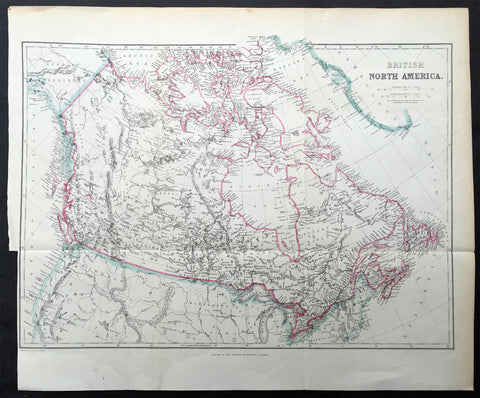
1860 Blackie & Son Map British North America - Canada & The Great Lakes
- Title : British North America
- Ref #: 33165
- Size: 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1860
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original map of Canada was engraved by Blackie and Son of Glasgow, Edinburgh and London in ca 1860. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Blue, pink
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 345mm)
Margins: - min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1785 Du Bocage Large Antique Map of The Environs of Athens to Piraeus, Greece
- Title : Plan Des Environs D Athenes...1785
- Ref #: 16464
- Size: 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique map or plan of The Environs of Athens, Greece to Piraeus, was engraved in 1785 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in his Voyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece) published between 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 8 1/2in x 7in (215mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
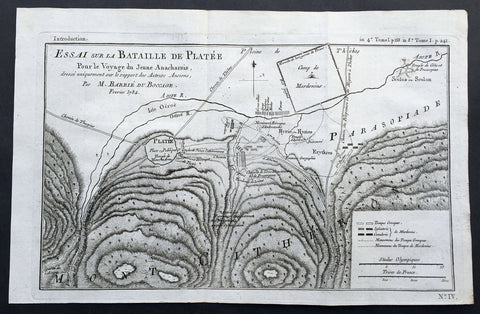
1784 Du Bocage Large Antique Map of The Battle of Platea City of Plataea Boeotia
- Title : Essai sur la Bataille de Platee...1784
- Ref #: 16469
- Size: 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique map or plan of the Battle of Platea, Greece near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, was engraved in 1784 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in his Voyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece) publishedbetween 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9in (360mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1784 Du Bocage Large Antique Map of The Bosphorus Straits, Turkey
- Title : Plan Du Bosphore de Thrace...1784
- Ref #: 16466
- Size: 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique map Bosphorus Straits, Turkey was engraved in 1784 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in his Voyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece) publishedbetween 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 220mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
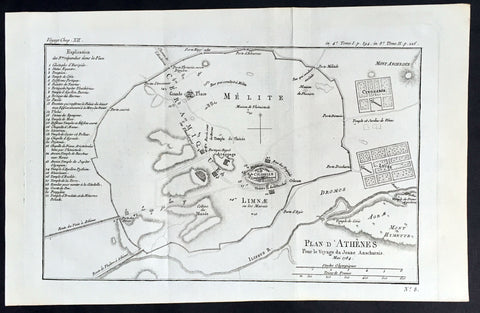
1784 Du Bocage Large Antique Map Plan of The City of Athens, Greece
- Title : Plan D Athenes...1784
- Ref #: 16460
- Size: 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique map a plan of Athens, Greece was engraved in 1784 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in his Voyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece) publishedbetween 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (350mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
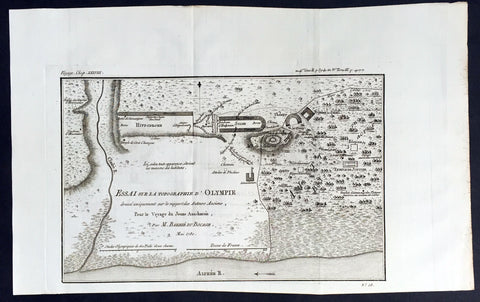
1780 Du Bocage Large Antique Map Plan of Olympia, Greece
- Title : Essai Sur La Topographe d Olympie...1780
- Ref #: 16450
- Size: 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique map a plan of Olympia, Greece - 1st site of the Olympic Games - was engraved in 1780 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in hisVoyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece) published between 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8in (310mm x 200mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
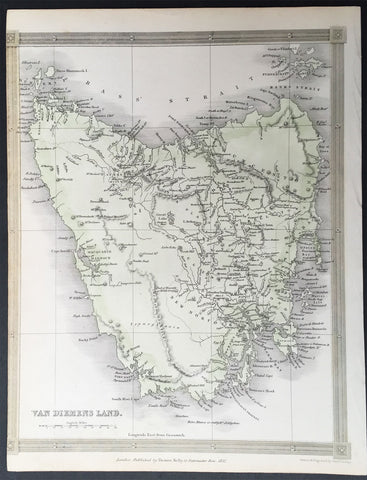
1837 Thomas Kelly Antique Map of Van Diemens Land - Tasmania, Australia
- Title : Van Diemens Land
- Ref #: 91205
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1837
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine large original detailed antique map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania, Australia was engraved in 1837 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published by Thomas Kelly for Barclays English Dictionary. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1783 Du Bocage Antique Map of Sparta and Surrounding Area, Greece
- Title : Essai Sur la Topographie De Sparte Et De Ses Environs.... 1783.
- Ref #: 16447
- Size: 15 1/2in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1783
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique map of Sparta and surrounding area, Greece - was engraved in 1783 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in his Voyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece)published between 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage (1760 - 1825)and his son Jean-Guillaume Barbie du Bocage (1795 - 1848) were French cartographers and cosmographers active in Paris during late 18th and early 19th centuries. The elder Barbie du Bocage, Jean Denis, was trained as a cartographer and engraver in the workshops of mapmaking legend J. B. B. d'Anville. At some point Jean Denis held the post of Royal Librarian of France and it was through is associations with d'Anville that the d'Anville collection of nearly 9000 maps was acquired by French Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The younger Barbie du Bocage, Jean-Guillaume, acquired a position shortly afterwards at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and, in time, became its head, with the title of Geographe du Ministere des Affaires Etrangeres. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8in (310mm x 200mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1784 Anderson Antique Coastal Views of the Admiralty Isles of PNG & Mindanao Islands - Capt Cook 1767
- Title : Three Views of the Admiralty Isles; Two islands seen 24th September 1767; Seen the 26 of September 1767, Joseph Freewills Islands; An island seen from the mast head & this view taken there September 29th 1767, S. 50W; An island seen from the mast head & this view taken October 12th 1767. Current Island, N.E. 1/2 E; Seen only from the mast head where this view was taken October 15, 1767. St. Andrews Islands; Three islands seen from our anchoring place in the Bay at the south end of Mindinao.
- Date : 1784
- Ref # : 21696
- Size : 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique 8 nautical chart & coastal view of the Admiralty Islands, off the coast of north PNG, along with St Andrews & Joseph Freewill Islands sighted by James Cook from September to October 1767 and the last view being a coastal view of southern Mindanao Islands in the Philippines, was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
1.2.3 Three Views of the Admiralty Isles
4. Two islands seen 24th September 1767
5. Seen the 26 of September 1767, Joseph Freewills Islands
6. An island seen from the mast head & this view taken there September 29th 1767, S. 50W.
7. An island seen from the mast head & this view taken October 12th 1767. Current Island, N.E. 1/2 E.
8. Seen only from the mast head where this view was taken October 15, 1767. St. Andrews Islands
9. Three islands seen from our anchoring place in the Bay at the south end of Mindinao.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island.
Mindanao is the second largest island in the Philippines. Mindanao and the smaller islands surrounding it make up the island group of the same name.
Cooks First Voyage (1768–71) In 1766, the Admiralty engaged Cook to command a scientific voyage to the Pacific Ocean. The purpose of the voyage was to observe and record the transit of Venus across the Sun for the benefit of a Royal Society inquiry into a means of determining longitude. Cook, at the age of 39, was promoted to lieutenant to grant him sufficient status to take the command. For its part the Royal Society agreed that Cook would receive a one hundred guinea gratuity in addition to his Naval pay.
The expedition sailed aboard HMS Endeavour, departing England on 26 August 1768. Cook and his crew rounded Cape Horn and continued westward across the Pacific to arrive at Tahiti on 13 April 1769, where the observations of the Venus Transit were made. However, the result of the observations was not as conclusive or accurate as had been hoped. Once the observations were completed, Cook opened the sealed orders which were additional instructions from the Admiralty for the second part of his voyage: to search the south Pacific for signs of the postulated rich southern continent of Terra Australis. Cook then sailed to New Zealand and mapped the complete coastline, making only some minor errors. He then voyaged west, reaching the south-eastern coast of Australia on 19 April 1770, and in doing so his expedition became the first recorded Europeans to have encountered its eastern coastline.
On 23 April he made his first recorded direct observation of indigenous Australians at Brush Island near Bawley Point, noting in his journal: “...and were so near the Shore as to distinguish several people upon the Sea beach they appear\\\'d to be of a very dark or black Colour but whether this was the real colour of their skins or the Clothes they might have on I know not. On 29 April Cook and crew made their first landfall on the mainland of the continent at a place now known as the Kurnell Peninsula. Cook originally christened the area as \\\"Stingray Bay\\\", but later he crossed this out and named it Botany Bay after the unique specimens retrieved by the botanists Joseph Banks and Daniel Solander. It is here that James Cook made first contact with an aboriginal tribe known as the Gweagal.
After his departure from Botany Bay he continued northwards. He stopped at Bustard Bay (now known as Seventeen Seventy or 1770) at 8 o’clock on 23 May 1770. On 24 May Cook and Banks and others went ashore. Continuing north, on 11 June a mishap occurred when HMS Endeavour ran aground on a shoal of the Great Barrier Reef, and then nursed into a river mouth on 18 June 1770. The ship was badly damaged and his voyage was delayed almost seven weeks while repairs were carried out on the beach (near the docks of modern Cooktown, Queensland, at the mouth of the Endeavour River). The voyage then continued, sailing through Torres Strait and on 22 August Cook landed on Possession Island, where he claimed the entire coastline that he had just explored as British territory. He returned to England via Batavia (modern Jakarta, Indonesia), where many in his crew succumbed to malaria, and then the Cape of Good Hope, arriving at the island of Saint Helena on 12 July 1771.
Cook\\\'s journals were published upon his return, and he became something of a hero among the scientific community. Among the general public, however, the aristocratic botanist Joseph Banks was a greater hero. Banks even attempted to take command of Cook\\\'s second voyage, but removed himself from the voyage before it began, and Johann Reinhold Forster and his son Georg Forster were taken on as scientists for the voyage. Cook\\\'s son George was born five days before he left for his second voyage.
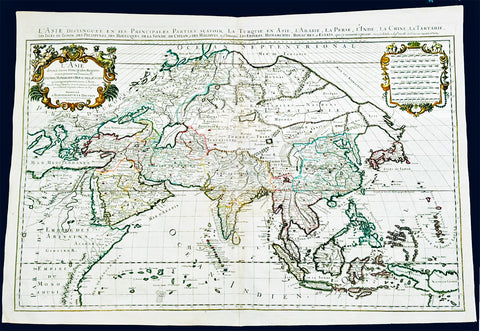
1719 Jaillot Very Large Antique Map of Asia China, SE Asia, Middle East, Russia
Antique Map
- Title : L' Asie divisee en ses Principales Regions....Hubert Jaillot
- Ref #: 35656
- Size: 37in x 25in (940mm x 635mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Asia was engraved in 1719 - dated in title - and was published by Hubert Jaillot in the last edition of his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
Background: After Nicolas Sanson, Hubert Jaillot and Pierre Duval were the most important French cartographers of the seventeenth & eighteenth centuries. Jaillot, originally a sculptor, became interested in geography after his marriage to the daughter of Nicolas Berey (1606-65), a famous map colourist, and went into partnership in Paris with Sanson's sons. There, from about 1669, he undertook the re-engraving, enlarging and re-publishing of the Sanson maps in sheet form and in atlases, sparing no effort to fill the gap in the map trade left by the destruction of Blaeu's printing establishment in Amsterdam in 1672. Many of his maps were printed in Amsterdam (by Pierre Mortier) as well as in Paris. One of his most important works was a magnificent sea atlas, Le Neptune François, published in 1693 and compiled in co-operation with J D Cassini. This was re-published shortly afterwards by Pierre Mortier in Amsterdam with French, Dutch and English texts, the charts having been re-engraved. Eventually, after half a century, most of the plates were used again as the basis for a revised issue published by J N Bellin in 1753.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Condition:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown, gold.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 37in x 25in (940mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 22 1/2in (875mm x 570mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning
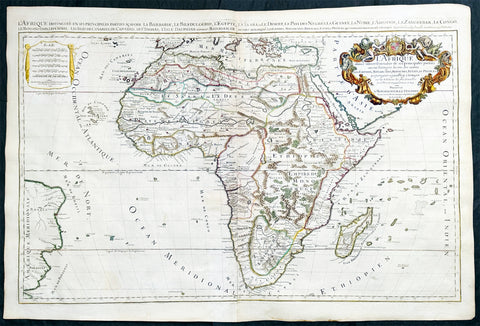
1719 Jaillot Very Large Antique Map of Africa
Antique Map
- Title : L'Afrique Divisee Suivant l'Estendue de ses Principales Parties...Alexis Hubert Jaillot. 1719
- Ref #: 35657
- Size: 37in x 25in (940mm x 635mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Africa was engraved in 1719 - dated in title - and was published by Hubert Jaillot in the last edition of his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
Background: After Nicolas Sanson, Hubert Jaillot and Pierre Duval were the most important French cartographers of the seventeenth & eighteenth centuries. Jaillot, originally a sculptor, became interested in geography after his marriage to the daughter of Nicolas Berey (1606-65), a famous map colourist, and went into partnership in Paris with Sanson's sons. There, from about 1669, he undertook the re-engraving, enlarging and re-publishing of the Sanson maps in sheet form and in atlases, sparing no effort to fill the gap in the map trade left by the destruction of Blaeu's printing establishment in Amsterdam in 1672. Many of his maps were printed in Amsterdam (by Pierre Mortier) as well as in Paris. One of his most important works was a magnificent sea atlas, Le Neptune François, published in 1693 and compiled in co-operation with J D Cassini. This was re-published shortly afterwards by Pierre Mortier in Amsterdam with French, Dutch and English texts, the charts having been re-engraved. Eventually, after half a century, most of the plates were used again as the basis for a revised issue published by J N Bellin in 1753.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Condition:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown, gold.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 37in x 25in (940mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 22 1/2in (875mm x 570mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning
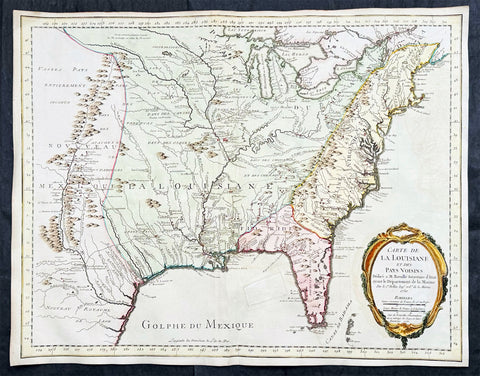
1750 (1755) Nicolas Bellin Very Scarce Large Antique Map of North America
Antique Map
- Title : Carte de La Louisiane et Des Pays Voisins Dediee a M. Rouille Secretairr 'd Etat ayant le Departement de la Marine . . . 1750 . . . Sur de Nouvelle Observations on a corrigee les Lacs, et leurs Enviorns. 1755.
- Date : 1750 (1755)
- Size: 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35661
Description:
This large original very scarce hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of North America by Nicolas Bellin, in 1750 - dated - and updated in 1755, was published as a single map by Nicolas Bellin in Paris.
Extremely important, large and scarce 1755 map of North America issued at the outbreak of the French and Indian War (1754 - 1763). Centered on the vast Mississippi Valley, the map covers from the Rio Grande to the Atlantic Seaboard and from Lake Superior to the Florida Keys. While first issued in 1750, the present map has been updated considerably to represent French, English, and Spanish claims at the outbreak of the French and Indian War. Most of the most important battle sites are forts are noted, including Fort Duquesne, Fort Necessity, Fr. Le Boeuf, Fort Presqu'Isle, and Fort St. Frederic, among others.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early & later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small professional restoration in GOM
Verso: - None
Background:
The map presents the much of the modern United States as the French understood it at the outbreak of the war. Spanish territory is red, English territory is yellow, and French territory is green. The British are here restricted to the coastal lands east of the Appalachian Mountains, and bounded on the south by the Altamaha River, which forms the boundary with Spanish Florida. French Territorial claims are expansive, encompassing roughly 2/3rds of the land and controlling the most valuable waterways, including the Great Lakes, the Ohio, and the Mississippi. Forts, mission settlements, mines, and trading posts dot the Mississippi Valley, but in truth, most of these were, by this time, only loosely manned or altogether abandoned - hardly an argument for effective occupation.
This map features a wealth of cartographic information drawn in part from the Guilaume de L'Isle map of 1718, but has been expanded considerably with new information from the the Chaussegros de Lery manuscripts and Pierre-Francois-Xavier de Charlevoix s Histoire et description generale de la Nouvelle France. Of note is the curious mountain range running through Michigan.
The inclusion of Fort Necessity is significant, as it suggests this map was issued just months after the construction of the fort and George Washington's disastrous defeat there. It underscores how quickly information moved - even through the outback of the New World and active war. For this map to have been made, news of the events, as well as cartographic reconnaissance, would have had to move rapidly from Fort Duquesne, down the Ohio River, then down the full length of the Mississippi, then across the Atlantic to Paris. There Bellin would have had to study the work, reconcile it with his older maps, update and re-engrave them accordingly, and then get the map to the presses for distribution. The whole is a remarkable accomplishment, but may explain somewhat this maps scarcity, as in a short time, much of the data he would be irreverent.
The map is dedicated to Antoine-Louis Rouillé, comte de Jouy (1689 - 1761). Rouillé replaced Jean-Frédéric Phélypeaux, 1st Count of Maurepas (1701 - 1781), Bellin's former patron, as Secretary of State for the Navy (Ministère de la Marine) on July 24, 1754, just in time for the French and Indian War. Bellin, who worked under the Navy Department, would have been highly motivated to engender Rouillé patronage and good well, making the dedication unsurprising.
The map was separately published in Paris, France by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin. It is dedicated to M. Rouillé. It represents the second state of the map, 1755, issued during the French and Indian War. Examples are extremely scarce. We have identified only three examples, including this map, in the last 20 years of market history. The map is further not identified in Cumming, Karpinski, Ehrenberg, or Phillips. The OCLC notes examples in 8 institutions, but upon closer inspection many of these appear to be digital resources and do not represent any actual holdings.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
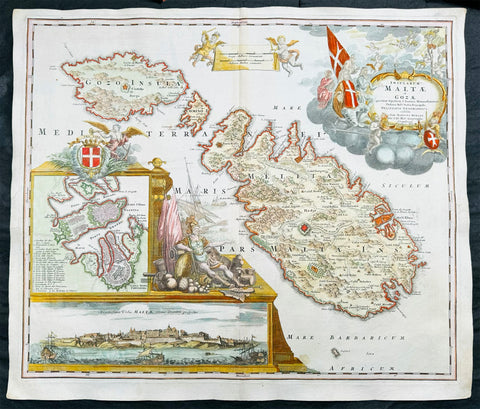
1720 Homann Large Antique Map of The Islands of Malta - Gozo, Comino, Valletta
Antique Map
- Title : Insularum Maltae et Gozae quae sunt Equitum S. Ioannis Hierosolimitani Ordinis Melit. Sed
- Date : 1720
- Size: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43169
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of the Mediterranean Islands of Malta, Gozo and Comino by J B Homann was published in 1720.
This is one of the best examples of this map I have seen to date. The paper is heavy and clean, original colouring is fresh and beautifully applied with original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (590mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of the most superbly embellished and desirable maps of Malta. Homann's magnificent map of Malta, includes detailed topographical information and many place names. The elaborate title cartouche depicts the knights of Malta in prayer before an image of the crucified Christ. At lower left is a panorama of Valetta from the sea and a further inset map of Valletta with a key of buildings and sites. To the right of the insets is a second elaborate embellishment comprising the Maltese coat of arms and the figure of a Knight of Malta Collections (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
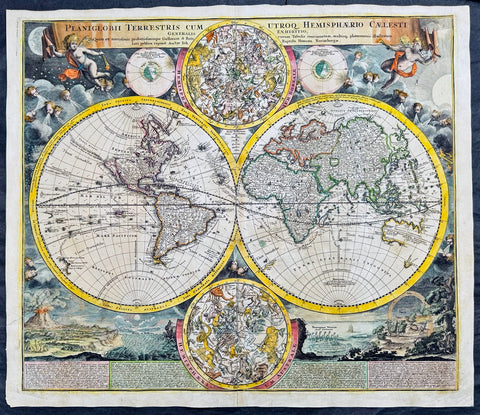
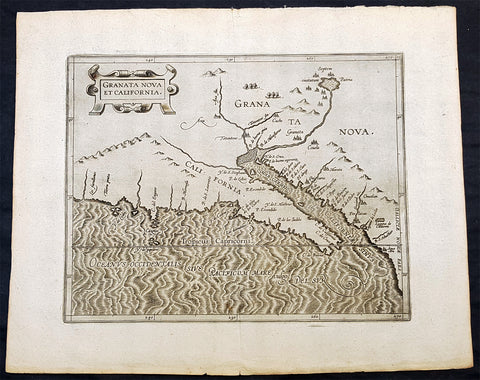
1707 Homann Rare Ist Edition Twin Hemisphere World Antique Map, California Isle.
Antique Map
- Title : Planiglobii Terrestris Cum Utroq. Hemisphaerio Caelesti Generalis Exhibitio.
- Date : 1707
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 61006
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original scarce first edition copper plate engraved antique twin hemisphere world map by Johann Baptist Homann was engraved in 1707 and published in Homanns 1710 edition of Neuer Atlas.
Later editions of the map is commonly misidentified as first editions. In later editions the words Cum Priviligo (Imperial privilege or permission) are engraved in the title, this privilege was later awarded to the Homanns and included in all future maps. In later editions California is shown as a peninsular and not an Island as shown in this map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/4in x 19 1/4in (515mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Professional paper rejoin left margin 2in into image, no loss. Light age toning
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
The map evokes the Dutch maps of the previous century, featuring an insular California and a depiction of Australia and the South Pacific that resembles that of Abel Tasman. Homann nonetheless incorporated a significant detail from the state-of-the-art maps of the Parisian geographer Guillaume De l'Isle, and the English polymath Edmund Halley. The map is a rich compendium of explorers' routes, including Magellan, Tasman, Gaetani, and Chaumont, as well as the extremely current voyages of Dampier (whose discovery of Nova Britannia near New Guinea is shown with a date of 1700). Above and below the cruxes of the main hemispheres are a pair of celestial hemispheres. At the bottom is a beautifully engraved panorama illustrating volcanoes, earthquakes, the tides, marine vortices, rain, and rainbows. These themes are significant in that they are neither mythological nor allegorical: they are plainly discussed natural phenomena. The map, then, is a visual representation of a shift to a more modern, scientific approach to the study of the world that would be typical of the 18th century.
Homann describes his sources as 'the latest and most approved maps of the French and the Dutch'. The bulk of Asia, Africa, and Europe appear to derive from the c. 1700 Peter Schenk Haemisphaeriorum Tabula Carthesiana, while the labeling scheme shows a strong similarity to the c. 1700 Danckerts De Werelt Caart. The primary French source is certainly Guillaume de l'Isle's 1700 Mappe-Monde. The explorers' tracks, the illustration of the Sargasso Sea, and an astonishing (and erroneous) sighting of Antarctica all derive from De l'Isle. Likewise with the treatment of the Pacific Northwest coast and Asiatic northeast, including the channel separating Terra Iesso from the mainland. Otherwise, the general models of Asia, Africa, and South America closely follow the c. 1700 Schenk.
The mapping of North America, here, is very different from either the Schenk or the 1700 De l'Isle. Although Homann retained California as an Island, the map was quite up to date. It presents a largely correct delineation of the Great Lakes and the Mississippi. The northwest part of Canada and the course of the Mississippi reveal the likely source: De l'Isle's 1703 Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France (including the Baron Lahontan's spurious geography) and De l'Isle's Carte du Mexique et de la Floride. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
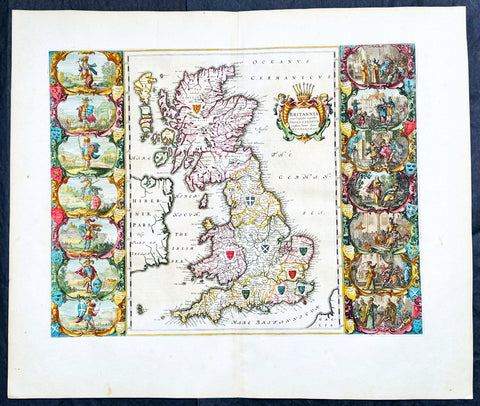
1658 Joan Blaeu Antique Heptarchy Map of Great Britain & Ireland - Magnificent
Antique Map
- Title : Britannia prout divisa suit temporibus Anglo-Saxonum præsertim durante illorum Heptarchia
- Date : 1658
- Size: 26in x 22in (660mm x 560mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35658
Description:
This beautifully engraved, hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique Heptarchy Map of Great Britain, during part of the Saxon Period (approx. 400 to 600AD) was published by Joan Blaeu in the only Spanish edition of Atlas Nouvs in 1658.
This is one of the best examples of the most beautiful maps ever published of the British Isles, I have seen for sometime. The map has magnificent fresh hand colouring, along with a deep heavy impression on clean heavy paper, with original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 22in (660mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map is based on the 1611 Heptarchy map published by John Speed. The side panels show historical scenes in Saxon history between 456 and 662 A.D.
The unknown engraver of this Blaeu Map has re-created each of the 14 scenes as an unmistakable Dutch miniature in the dramatic style of the greater paintings of the time. Blaeus map is considered by some, the finest of the three edition released by Speed, Blaeu and Jansson.
On the left panel are seven full length figures of the first aspiring Saxon Kings with their escutcheons, forces or townships; Hengist - Kent 456; Ella - South Saxon 478; Cherdin - West Saxon 519; Erkenwin - East Saxon 527; Ida - Northumberland 582; Uffa - East Anglia 546; Creda - Mercian 575. On the right there are scenes showing the conversion of Saxon Sovereigns to Christianity: Ethelbert (Kent 595) receiving religious instruction from St Augustine; Sebert (East Saxon 604) re-consecrating the temples of Diana & Apollo - now St Pauls, London, and St Peters, Westminster; Erpenwald (East Anglia, 624) embracing baptism by the armed extortion of King Edwin of Northumberland; Edwin (Northumberland, 627) stirred by a vision to receive the Faith; Kengils (West Saxon, 635) converted by the preaching of St Bernius; Peada (Mercia, 650) receiving the Faith by the persuasion of King Osway of Northumberland but also being murdered by his own mothers (some say his wife's) procurement; finally Ethelwolfe (South Saxon 662) being baptized at Oxford by St Berinus.
Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map.
The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Shirley; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Splendid map of Anglo-Saxon Britain flanked by intricately rendered portraits of the kings through the 5th through 7th centuries. The monarchs to the left are those of the pre-Christian era, while those on the right are depicted receiving Christianity or being martyred for its sake.
This is often called the Heptarchy Map, as it presents England during the time following the Anglo Saxon conquest of southern England, approximately 500 to 850 A.D. known as the Heptarchy Era. (The word itself refers to the seven kingdoms that would eventually combine to form the Kingdom of England in the 10th century.)
To the left are the seven full length figures of the first aspiring Saxon Kings with their escutcheons, armies or townships;
1. Hengist - Kent 456AD
2. Ella - South Saxon 478AD
3. Cherdin - West Saxon 519AD
4. Erkenwin - East Saxon 527AD
5. Ida - Northumberland 582AD
6. Uffa - East Angle 546AD
7. Creda - Mercian 575AD
On the right there are scenes showing the conversion of Saxon sovereigns to Christianity:
1. Ethelbert - Kent 595AD receiving religious instruction from St Augustine
2. Sebert - East saxon604AD re-consecrating the temples of Diana and Apollo that later become St Pauls London and St Peters Westminster
3. Epenwald - East Angle 624AD embracing baptism by the armed exhortation of King Edwin of Northumberland
4. Edwin - Northumberland 627AD stirred by a vision to receive the faith
5. Kengils West Saxon 635AD converted by the preaching of St Berinus
6. Peada Mercia 650 receiving the Faith by the persuasion of King Osway of Northumberland but also being murdered by his own mothers, some say his wifes, procurement.
7. Ethenwolfe South Saxon 662AD being baptised at Oxford by St Berinus
(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
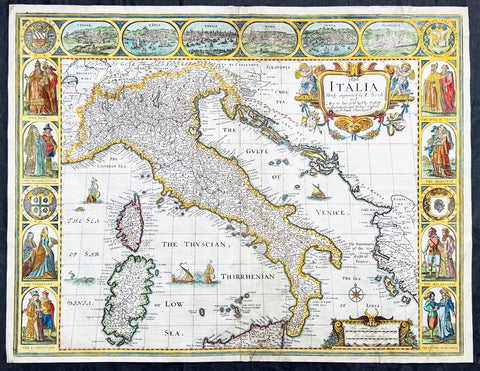
1626 (1676) John Speed Antique Map Italy Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily - Rare state
- Title : 1626 Italia Newly augmented by I. Speed and Are to bee Sold by Tho. Bassett in Fleet Street and Richard Chiswell in St. Puals Church-yard
- Date : 1626 (1676)
- Size: 21 1/4in x 16 1/4in (540mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A-) Good Condition
- Ref: 35655
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Italy by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World.
A very unusual state, as far as I can tell unrecorded, with the date 1626 engraved in the title. This map was first published in 1626 with the date included at the end of the title. This map was published in 1676 by Bassett and Chiswell but for some reason the date, 1626 has been included at the top and beginning of the title, I have been unable to find another example.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/4in x 16 1/4in (540mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15 3/4in (470mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small section of top margin professionally restored about 1/2in into view of Florence
Plate area: - Two rejoins to bottom margin 1in into the border and map, no loss. Light fold bottom right corner
Verso: - Light soiling, repairs as noted
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare, published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
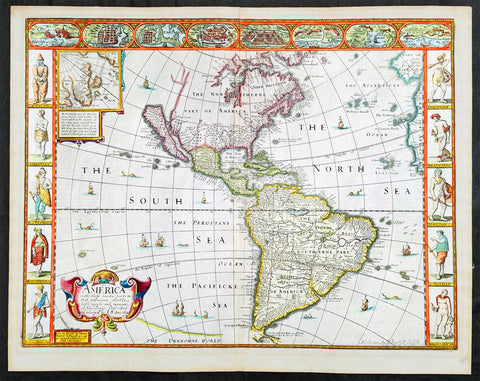
1626 (1676) John Speed Antique Map of America - Beautiful Condition
Antique Map
- Title : America with those known parts in that unknowne world both people and manner of buildings discribed and inlarged by I.S. Ano 1626.
- Date : 1626 (1676)
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35654
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of America by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World.
One of the best examples of this map I have seen. Beautiful original condition with original hand colour, clean heavy impression on sturdy clean paper with original margins, which is very rare.
This 1626 map of America is the fourth or 1676 state and is one of the most iconic maps of America, surrounded by decorative vignettes illustrating the indigenous peoples and cities of the Americas. This map is both beautiful and important. It features a number of first, including being the first atlas map to depict California as an island and to accurately depict the east coast of North America. Cartographically it follows on the earlier maps of the Dutchman Abraham Goos, the engraver, with updates to reflect the 1625 Briggs vision of an insular California
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/4in x 15 1/2in (515mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 3/4in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Old archival hinge paper top of verso, not affecting the map.
Background:
This is the first atlas map to represent California as an island. The idea of an insular California first appeared as a work of fiction in Garci Rodriguez de Montalvo's c. 1510 romance Las Sergas de Esplandian, where he writes
.....Know, that on the right hand of the Indies there is an island called California very close to the side of the Terrestrial Paradise; and it is peopled by black women, without any man among them, for they live in the manner of Amazons.....
Baja California was subsequently discovered in 1533 by Fortun Ximenez, who had been sent to the area by Hernan Cortez. When Cortez himself traveled to Baja, he must have had Montalvo's novel in mind, for he immediately claimed the 'Island of California' for the Spanish King. By the late 16th and early 17th century ample evidence had been amassed, through explorations of the region by Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarcon and others, that California was in fact a peninsula. However, by this time other factors were in play. Francis Drake had sailed north and claimed 'New Albion' (identified here on the northwest coast of California Island) near modern day Washington or Vancouver for England. The Spanish thus needed to promote Cortez's claim on the 'Island of California' to preempt English claims on the western coast of North America. Henry Briggs, an English mathematician, began promoting the idea of an insular California in 1622, citing the journals of Friar Antonio de la Ascension, who accompanied the 1602-03 Sebastian Vizcaino expedition. The significant influence of the Spanish crown on European cartographers caused a major resurgence of the Insular California theory. Just before this map was made Eusebio Kino, a Jesuit missionary, traveled overland from Mexico to California, proving conclusively the peninsularity of California. Even so, it was ultimately a 1747 royal decree from King Ferdinand VII of Spain that finally forced cartographers to give up on the alluring idea.
Other elements of interest in North America are the complete absence of the Great Lakes - which in 1626 had yet to be conceived of by any European cartographers. The Straits of Anian appear tenuously in the extreme northwest, just above California. Just east of the 'o' in 'California', on the continental mainland, there is a curious ghosted in lake called the 'Lagueo de Oro.' We have found no references or explanation for this. None of the legendary kingdoms of gold, Quivara, Teguayo, Cibola, etc. are noted. The western portions of the Hudson Bay are unmapped - suggestive of their unexplored status. The addition of Long Island and Boston, in notably darker print, are important updates over the earliest editions.
South America offers much of interest including the mythical Lake Parimia, in Guiana. The legend of Parima is associated with the English adventurer Sir Walter Raleigh's search for El Dorado. Believing El Dorado to lie in the northern part of the Amazon, Raleigh sailed down the Orinoco River just before the onset of the rainy season. Reaching a remote tribal village, Raleigh noted canoes arriving bearing gold, silver, and other treasures. Asked where the gold came from, the natives replied, 'Manoa', the term for the tribe to which the river traders belonged. Manoa, the natives claimed could be reached following a long river voyage southward to a Great Lake, called Parima. Raleigh and his associates immediately associated Manoa and Lake Parima with the golden kingdom of El Dorado, though they never visited the city or lake. Subsequent maps, including this one, mapped el Dorado and Lake Parima in this location for several hundred years. Both Raleigh and the natives were describing an actual event known to occur annually in the region. Rains would annually swell the Amazon and Orinoco river systems creating a linkage in the Rupununu flood plain, which, during heavy rains, can resemble a massive lake. The Manoa were a large and populous trading nation active in pre-colonial days whose vast empire, based in the Amazon Basin, extended form the Andes to the Orinoco. Curiously, in addition to noting the city of Manoa on Lake Parima, D'Anville also correctly maps the center of the ancient Manoan civilization between the Amazon tributaries Rio Negro and Rio Yapura. Sadly the Manoa and many of the other populous South American indigenous nations noted by the earliest explores to the region vanished, brought low by European epidemics.
Another mythical lake, Eupana, appears further south connecting the Rio de la Plata and the Paraguay River to the R. Real, thus turning eastern Brazil into an island. This is a update over many earlier maps which connected Eupana directly to the Amazon. Far in the south Speed presents us ith another anomaly, the Straits of Le Maire, which separates Tierra de Fuego from another mysterious stretch of land labeled 'States Land.' The is in fact the modern island of Isla de los Estados, the southeastern most point in South America. Jacob le Maire and his pilot Willem Schouten passed to between this island and Tierra del Fuego on their 1615 voyage around Cape Horn and into the Pacific.
In the high Arctic, near Iceland and Greenland, the supposed islands of Frisland and Brasil are noted. Frisland is little more than a double mapping of Iceland. Brasil, also known as Hy-Brasil, is a phantom island north Atlantic just west of Ireland. In Irish myths it was said to be cloaked in mist, except for one day every seven years, when it became visible but still could not be reached. Little is known of this origins of this myth, but it appears on maps in various forms from about 1325. The last known appearance was in 1865 when it appeared on a nautical chart as 'Brasil Rock.' Some speculate that it may be an early reference to Porcupine Bank, a shoal in the Atlantic Ocean about 200 kilometres (120 mi) west of Ireland.
Speed's map of America is especially noteworthy for its surrounded vignettes. To either side of the map proper there are various vignettes illustrating the indigenous peoples of the America. These includes natives of Greenland, Virginia, Florida, Mexico, New England, Peru, Brazil, and Tierra del Feugo.n Along the top of the map there are eight city views: Havanna, Santo Domingo, Cartagena, Mexico City, Cuzco, the isle of Moca, Rio de Janeiro, and Olinda.
This map was engraved for John Speed by Abraham Goos. It is the fourth state of the map issued by Thomas Bassett of Fleet Street and Richard Chiswell of St. Paul's Churchyard. Bassett, Chiswell, and others continued to republish Speed's work well after his death. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, Burden)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
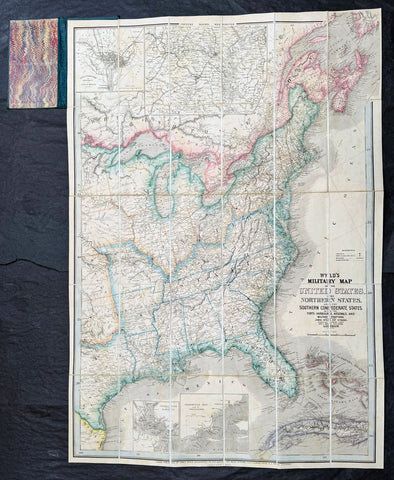
1865 James Wyld Large Antique Folding American Civil War Map - Extremely Rare
Antique Map
- Title : Wyld's Military Map Of The United States, The Northern States, And The Southern Confederate States: With The Forts, Harbours, Arsenals And Military Positions. James Wyld, 457 Strand; Charing Cross East And 2, Royal Exchange London. ......London, Published By James Wyld, Geographer To The Queen
- Date : 1865
- Size: 34 1/2in x 24in (875mm x 610mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35660
Description:
A very rare map of the United States first issued in 1861, during the Secession Crises that preceded the outbreak of the American Civil War, with this rare edition issued in January 1865 - dated at the foot of the map, only 4 months before the end of the war..
There are a few 1861 editions of this map for sale, currently on the market, but I have been unable to find an 1865 edition, either currently on the market or sold in the past.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 34 1/2in x 24in (875mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 24in (875mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Wyld was particularly masterful at capturing political events throughout the world as they happened and leveraging his impressive publishing operation to quickly produce and distribute pertinent to the invested public. In this case, the map distinguishes between the 'Northern States' (orange border) and the 'Southern Confederate States' (blue border). Wyld here erroneously conflates slaveholding states with Confederate secessionist states - in particular, Missouri, Kentucky, Delaware, and Maryland, which allowed slavery but remained loyal to the Union. Arsenals, forts, and military posts highlighted and keyed, underscoring that 'war' was very much in the air. The map is also noteworthy for recognizes the apocryphal territory 'Chippewa', roughly corresponding to modern-day North Dakota.
This map is scarce to the market. Known institutions holdings at the Boston Public Library, the Library of Congress, Bibliothèque nationale de France, the David Rumsey Collection, among others. (Ref: M&B; Tooley; Clancy) (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, Burden)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
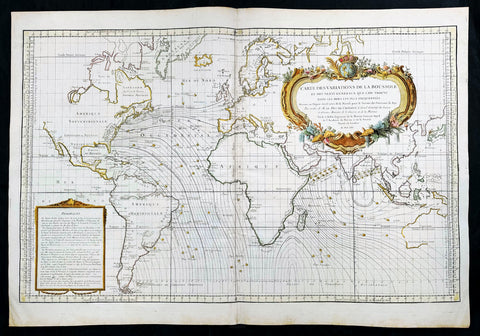
1765 Bellin Large Antique World Map of Global Winds & Magnetic Variations
Antique Map
- Title : Carte des Variations de la Boussole et des Vents Generaux que l'on Trouve dans les Mers les Plus Frequentees
- Date : 1765
- Size: 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35665
Description:
This original very large hand coloured copper plate engraved antique world map, illustrating global magnetic and ocean wind variations, was engraved in 1765 - dated- and published by Jacques Nicholas Bellin, Paris.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 23in (875mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
An elegantly designed and precisely drafted sea chart of the oceans sailed by French navigators in the 18th century. Drawn by J. N. Bellin, who during his over fifty years of work in the French Hydrographic Service was appointed the first Ingenieur hydrographe de la Marine. This chart extends from California to Japan and focuses on the Atlantic and Indian oceans. The French sphere of influence in the West Indies, Africa, and India, would have generated this interest in compass and wind variations applied to a Mercator projection covering most of the world.
By 1765, France had lost most of its overseas empire in America following the Seven Years War (French and Indian War in America), so knowledge of the sea routes was important to holding what was left. Besides a wealth of hydrographic information, including little wind heads throughout, this beautiful map features an exquisite title cartouche featuring the French crown surmounting the globe. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, Burden)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
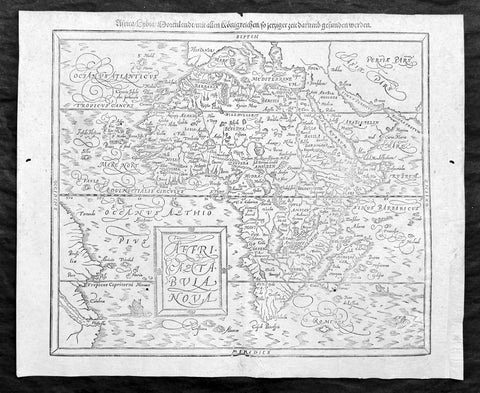
1588 Sebastian Munster Antique Map of Africa
Antique Map
- Title : Africae tabula nova / Africa, Lybia, Morenlandt, mit allen Königreichen so jetziger zeit darumb gefunden werden
- Ref: 35664
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 340mm)
- Date : 1588
Description:
A great example of the original wood-block engraved antique map of the whole continent of Africa published by Sebastian Munster in the 1588 edition of Cosmographia.
This is Munsters 2nd map of Africa, after the Abraham Ortelius continental map of 1574. The woodblock map is elegantly engraved in the style of copper engravings. It depicts the continent with a jagged coastline with several prominent bays. In the interior there are several large lakes, including the twin lakes source of the Nile. The coast of Brazil appears in the lower left corner. Two small ships, a sea monster and a block-style title cartouche decorate the map. German text and illustration on verso.
The Cosmographia or Cosmography was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world.
It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century and passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Die Newe Welt oder Inseln, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically unique.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia, with numerous illustrations.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small extension to bottom right corner margin, repair to bottom centerfold, not affecting image.
Plate area: - 2 very small worm holes
Verso: - Repairs as noted
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle(c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
Sebastian Petri re-release of Cosomgraphia in 1588 produced some fine woodcut maps in the copperplate style. The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1737 George Vertue Elizabethan Map of London - The "Woodcut" or Ralph Agas Map, 1560
- Title : Civitas Londinum Ano Dni M D L X. Londonium Antiqua
- Ref: 35663
- Size: 78in x 26in (1.93m x 710mm)
- Date : 1737 (1560)
- Condition: (B+) Good Condition
Description:
This large rare original 8 sheet map of Elizabethan London by George Vertue was published in 1737, dated, after an original 8 sheet map first published in 1561, only 2 years after Elizabeth I ascended the throne.
This George Vertue map together with the Braun & Hogenberg map are among the only depictions of Tudor London still available today to collectors. The Braun & Hogenberg map is readily available to collectors. This map rarely appears on the market, with only a small handful sold. Both maps are derived from surveys of Elizabethan London completed in the mid 16th century.
The Braun & Hogenberg single plate map is derived from a very large 15 plate map, referred to as the "Copper-Plate" map produced between 1553 & 1559 whereas this George Vertue map is referred to as the "Woodcut" or "Agas" map and is derived from an 8 sheet map published in 1561. The two maps are referred to as the, "Copperplate" & "Woodcut" maps, because no complete examples of either original 16th century maps have survived and the names of the original surveyors or cartographer are uncertain. There was early speculation by George Vertue, that the "Woodcut" map was compiled by the 16th century Elizabethan surveyor Ralph Agas, but this has since been debunked. But even so, the woodcut map is still referred to as the "Woodcut" "Agas" map.
The 15 plate "Copperplate" map was the first map of the two to be completed, between 1553 and 1559. The 8 plate "Woodcut" map was published shortly afterwards in 1561. In 1962 a single plate of the "Copperplate" was discovered along with two more additional plates, discovered later. No examples of 1561 "Woodcut" map have survived but luckily three later 1633 examples have. They now sit in institutional collections.
The map covers the cities of London and Westminster from the Tower of London in the east to Westminster Abbey in the west. South of the Thames River there are a number of landmarks of Tudor Southwark, including the bull and bear baiting pits and Winchester Palace. London Bridge is shown crossing the river into the City of London. Old St. Paul's Cathedral is depicted in its pre-fire state. The built up suburbs to the north only extend as far as Holborn and Spitalfields, although the hills of Hampstead and Highgate are notionally described in the background.
This map was rescued as 8 separate maps, and professionally restored & joined using contemporary paper, materials and methods. We received the maps in 8 individual frames unprotected by glass. Unfortunately there was some bug damage to a few of the maps, but only to parts of the unprinted areas of the paper, the bugs unwilling to eat the ink. So luckily the vast majority of the printed parts of the maps were saved, with damage minimised to only blank parts of the map, which were restored and filled with dated contemporary paper.
I have included an image of the maps in their 8 original frames prior to removing the maps and restoration, so you can see as they were prior to restoration and joining.
I have found 8 official dealer sales of this map between 1999 and 2017 with a top price of $12,500 in 2017. I know of no copies of this map, currently on the market.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 78in x 26in (1.93m x 710mm)
Plate size: - 78in x 26in (1.93m x 710mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections: (Starting from the top left plate working clockwise)
Plate 1. Some paper loss to the L&T margins, sky paper loss but with no loss to actual ink.
Plate 2. Paper loss to bottom of plate with small loss to actual ink. Left side of plate light loss to paper surface, very slight loss to actual ink. Age toning
Plate 3. Slight loss to paper surface to top and margin, no loss to actual ink
Plate 4. Paper loss to top margin and paper with loss to paper area in the plate, very minimal loss to actual ink surface
Plate 5. None
Plate 6. Loss of paper to top & bottom of plate with some loss to actual ink
Plate 7. Very small localised 2cm diameter loss to top of plate
Plate 8. Paper loss to top & right margin of plate, very minimal loss to ink.
This scarce map has been rescued and restored and although not perfect is a very desirable map.
Background:
The "Woodcut" map of London, formally titled Civitas Londinum, and often referred to as the "Agas" map of London, is one of the earliest true maps (as opposed to panoramic views, such as those of Anton van den Wyngaerde) of the City of London and its environs. The original map probably dated from the early 1560s, but it survives only in later and slightly modified copies. It was printed from woodcut blocks on eight sheets, and in its present state measures approximately 2 feet 4 inches (71 cm) high by 6 feet (180 cm) wide. There has been some damage to the blocks, and it was probably originally fractionally larger.
The Woodcut map is a slightly smaller-scale lightly modified copy of the so-called "Copperplate" map, surveyed between 1553 and 1559, which, however, survives only in part. It also bears a close resemblance to the map of London included in Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg's Civitates Orbis Terrarum, published in Cologne and Amsterdam in 1572, although this is on a greatly reduced one plate scale.
The Woodcut map was traditionally attributed to the surveyor and cartographer Ralph Agas, but this attribution is now considered to be erroneous.
Three impressions of the Woodcut map survive in its earliest known state of c. 1633. They are held in London Metropolitan Archives, the Pepys Library at Magdalene College, Cambridge, and The National Archives at Kew. The three early copies of the map are dated by an inscription to c. 1633. However, it is evident that the map in this form has been updated from an earlier state. The royal arms in the upper left corner are those of the House of Stuart (1603–49), but are clearly an insertion, almost certainly replacing the earlier Tudor arms, which do appear (at a very small scale) on the royal barge, pictured on the Thames. Similarly, the Royal Exchange (erected 1566–70; opened 1571) appears on the map, but is again clearly an insertion. The map is now known to be a close – though slightly less detailed – copy of the "Copperplate" map, surveyed between 1553 and 1559; but one difference between the two maps is that St Paul's Cathedral appears on the Woodcut version without its spire. The spire was lost in a fire in 1561, and so the map cannot be earlier than that date. The Woodcut map is therefore now dated with a reasonable degree of probability to the 1560s. A reference in the Stationers' Register for 1562–3 to the "Carde of London" may possibly refer to it.
The map has also been slightly modified from the Copperplate map by the introduction of a higher degree of perspective to the projection: this is particularly obvious in the northern and western areas (beyond Bishopsgate towards Shoreditch, and in the Westminster and Whitehall area). It is therefore closer to a bird's-eye view of the City, seen from an imaginary viewpoint above the south bank of the Thames, as opposed to the "bird's-flight view" projection of the Copperplate map. Stephen Powys Marks suggests that this adjustment "may be an indication of an appeal to a less sophisticated public than that which would buy the fine copper engraving"
The Woodcut map was traditionally attributed to the surveyor and cartographer Ralph Agas (c. 1540–1621). This attribution has its roots in a claim made by Agas in 1588 to the effect that for ten years past he had been hoping to undertake a survey of London. On the basis of this statement, the late 17th-century engraver of a copy of the map on pewter sheets associated Agas's name with it; and the attribution was then asserted more firmly by the antiquary George Vertue in 1737–8. However, the probable date of the Woodcut map and its relationship to the Copperplate map make it extremely unlikely that Agas – who began practising as a surveyor in about 1566 – played any part in its creation, and the attribution is now treated as highly dubious. Nevertheless, the map is still often referred to as the "Agas" map. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
George Vertue (1684-1756)
Vertue was a prominent early 18th century engraver and antiquarian. His eclectic and artistic tastes drew him into the tastemaking circles in London during his time. He was a contemporary of William Hogarth and together they were members of the Rose and Crown Club. He was also the official engraver for the London Society of Antiquaries. The latter of which was a learned society "charged by its Royal Charter of 1751 with 'the encouragement, advancement and furtherance of the study and knowledge of the antiquities and history of this and other countries'."
As part of his responsibilities, he provided many of the illustrations for the Society's projects, foremost among these was Vetusta Monumenta, an series of publications documenting ancient buildings, arts, and artefacts. Additionally, Vertue undertook his project to re-engrave the "Woodcut" map under the aegis of the Antiquarian Society. This should come as no surprise, as the project was well within the interests of the Society.
In the 1730s and '40s Vertue showed a special interest in Tudor history and printmaking. This is obviously reflected in his copy of the "Woodcut" map. His interest can also be seen in the Historic Prints series of 1740, in which he imitated 16th century images of Henry VIII, Queen Elizabeth, and other royals. Much of his work for Vetusta Monumenta also revolves around Tudor architecture.
Ralph Agas
Ralph Agas (or Radulph Agas) (c. 1540 – 26 November 1621) was an English land surveyor and cartographer. He was born at Stoke-by-Nayland, Suffolk, in about 1540, and lived there throughout his life, although he travelled regularly to London. He began to practise as a surveyor in about 1566, and has been described as "one of the leaders of the emerging body of skilled land surveyors".
Agas is particularly known for his large-scale town map of Oxford (surveyed 1578, published 1588). Early maps of London and Cambridge were also formerly attributed to him, but these attributions are no longer upheld.
Agas was born in Stoke-by-Nayland, in Suffolk, probably between 1540 and 1545. By his own account, he began to practise as a land surveyor in about 1566. He is described at several points in his life as "deformed", "impotent", "lame" and a "cripple", but the precise nature of his disability is not known.
He was ordained, and served from 1578 to 1583 as rector of Gressenhall, Norfolk. He probably abandoned the church after this date in favour of his surveying career.
He appears always to have lived in Suffolk, but travelled regularly to London in term time to obtain orders for surveying work. During his visits he is known to have lodged at inns: in 1596 at the "Flower de Luce", next to the "Sun" near Fleet Bridge; and in 1606 at the sign of the "Helmet" in Holborn, at the end of Fetter Lane.
He died at Stoke-by-Nayland on 26 November 1621, and was buried there the next day.
Agas's regular work consisted of drawing up local estate maps and surveys for a variety of clients. He was one of the first estate surveyors to move beyond the traditional practice of compiling purely written descriptions of landed property, and to consider supplementing these with measured maps.[6] The earliest map that can be attributed to him is one of lands at West Lexham, Norfolk, dated 1575. He subsequently undertook commissions in Bedfordshire, Berkshire, Cambridgeshire, Essex, Gloucestershire, Norfolk, Oxfordshire, Suffolk and Surrey. An estate map he drew of Toddington, Bedfordshire, dated 1581, includes what Paul Harvey has described as "the best picture we have of a small Elizabethan country market-town". He appears to have been patronised by William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley. Another client was Corpus Christi College, Oxford, although the college commissioned only written surveys rather than maps.
Agas is perhaps principally remembered for Oxonia Antiqua Restaurata, a detailed plan – really a "bird's-flight view" – of Oxford. It was drawn in 1578 and engraved and printed in 1588: a copy is held in the Bodleian Library, bequeathed by Richard Rawlinson. The plan was re-engraved by Robert Whittlesey in 1728, at the expense of the university, but this plate was destroyed in the fire at John Nichol's printing-works in 1808.
A town plan of Dunwich in Suffolk is also attributed to Agas. This was engraved for Thomas Gardner's history of the town (1744). The original later came into the possession of the Suffolk antiquary David Elisha Davy
The important early map of London now conventionally known as the "Woodcut" map has traditionally been attributed to Agas. A verse inscribed on the 1588 engraving of Agas's map of Oxford included a claim to the effect that for ten years past he had been hoping to undertake a survey of London, but had not done so. On the dubious evidence of this statement, a link with the Woodcut map was first made by the late 17th-century engraver of a copy of it on pewter sheets; and in 1737–8 George Vertue attributed it confidently and unambiguously to Agas. However, the claim is no longer sustained: the Woodcut map is now dated to the early 1560s, and is known to be based on the slightly earlier "Copperplate" map of the 1550s, making it highly unlikely that Agas played any part in its creation. Nevertheless, the Woodcut map is still often referred to as the "Agas" map.
A map of Cambridge printed in 1592 (of which a unique copy survives in the Bodleian Library) has also been attributed to Agas, but is now thought more likely to be by John Hamond.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1642 Blaeu, Hondius & John Smith Antique Map of Virginia, America - Pocahontas
- Title : Nova Virginiae Tabula
- Date : 1642
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35667
- Size: 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Description:
This superb original antique hand coloured map of Chesapeake Bay, Virginia was published in the 1642 Dutch edition of Mercators Atlas.
This map by Blaeu comes directly from John Smiths map of Virginia. Blaeu bought this plate from Joducus Hondius who had engraved it directly from John Smith map. It is the only map on the market that is unchanged from Smiths map.
Although this map bears the name of Willem Blaeu, it comes from the plate stock of the Amsterdam publisher Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1629. Blaeu then issued the map in his Atlantis Appendix and in most editions of the firms atlases thereafter.
The map is a version of the map by the Englishman Captain John Smith in 1612. His map was the first to depict with reasonable accuracy Chesapeake Bay with its tributaries and became the accepted prototype map for most subsequent maps of the colony published either in Britain or Europe during the remainder of the 17th century.
Captain Smiths maps acted as a promotional piece for the vast area of North America called Virginia and it exerted a great influence of the history of English colonisation in America.
John Smith (1579-1631) was the foremost English settler in Virginia. His many adventures included being captured several times, defeating an Indian chief in hand to hand combat as well as the celebrated incident in which Pocahontas saved him from Powhatan who is himself the subject of the portrait at the upper left hand corner of Blaeus map.
While the geographical detail of the map shows information accurate at the time of Smiths travels, earlier descriptions of Virginia are recalled. When Smiths map appeared in 1612, the engraver turned to an engraving by the German Theodor de Bry based on the drawings made by John White in the 1580s for the portrait of Powhatan, and the figure of an Indian in war paint at the right to represent the Susquehanna chief. All of these elements were combined by the Amsterdam engraver Dirk Grijp for the Dutch version of Smiths map as issued by the Hondius firm in 1618. Thus, when Blaeu purchased the plate it was already a decade old and it was issued unchanged except for his imprint and a few very small retouches until the 1660s. The Blaeu derivative was the most popular version of Captain Smith Map published during the seventeenth century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning, light crease along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
This is one of the most important seventeenth century maps of the Chesapeake Bay region. The early settlement of Jamestown Iamestowne is noted along with a number of other place names, both in English and Native American. The map was derived from Capt. John Smith\'s map of 1612 and was the first to depict the bay and its tributaries with any accuracy.
Capt John Smith's fine survey work, as well as reports from indigenous American Indian tribes, and fanciful wishful thinking, combine to make this one of the most interesting maps of America to emerge in the 17th century. Philip D. Burden, the author of The Mapping of America, considers this map, Nova Virginiae Tabula, to be \'one of the most important maps of America ever produced and certainly one of the greatest influence.\' Oriented to the west, this map covers from Cape Henry to the Susquehanna River and inland as far as the Appellation Mountains. The Chesapeake Bay is shown in full as are many of its river estuaries, though topographically this map places a number of mountain ranges where there are in fact none.
To fully understand this map one must first realize that most Europeans believed the Pacific, or at least some great bay that led to the Pacific, lay just a few days travel inland. In the minds of most Europeans of the period, the trade potential for the Virginia colony was entirely dependent upon it being a practical access point to the riches of Asia. Thus the significance of large and mysterious body of water appearing in the land of the Massawomecks, in the upper right quadrant, becomes apparent. Of course, much of this land was entirely unexplored by the European settlers in Jamestown, shown here on the Powhatan River (James River), who relied heavily upon American Indian reports for much of their cartographic knowledge of the Virginia hinterlands. The Massawomecks themselves were a rival of the Powhatan and made their home near the headwaters of the Potomac. These, like many other indigenous groups of the region made only a brief and frequently violent appearance during the 17th century before entirely disappearing, mostly from disease and war, in the early 18th century.
In the upper left quadrant there is an image of the American Indian chief of the Powhatan sitting enthroned before a great fire in his long house. One of the more popular legends regarding John Smith was his capture and trial before the chief of the Powahatan. Smith was convinced that his liberation had something to do with the youthful daughter of Chief Powahatan, Pocahontas, taking a liking to him. Although this grew into a fictitious legend of its own, the truth is more likely that Powhatan saw Smith and his Englishmen as potential allies against the rival American Indian groups, such as the Massawomecks, that were pressing hard against his borders.
There are a number of different editions of this map and its publication by various map houses in various states made it the first widely distributed map of the Virginia colony and of John Smith\'s important map. There was, however, a scandal relating to its publication. The map was originally drawn and engraved in 1618 by Jodocus Hondius based upon the first edition of John Smith\'s 1612 map. When Jodocus died in 1629, he and his brother, Henricus Hondius, while collaborating on the Hondius Atlas Major, had established and maintained separate business for some 10 years. Jodocus\' death enabled the competing cartographer, Willem Blaeu to acquire a large number of Jodocus\' map plates, which he promptly published in 1630 as the Atlantis Appendix. Henricus, in the meantime, had been counting on Jodocus\' new plates to enhance his own, by then outdated, Hondius Atlas Major. A surviving contract dated March 2, 1630 reveals that Henricus Hondius and his partner Joannes Janssonius hired engravers to produce a number of new map plates copying the work of Jodocus – now in the hands of the Blaeu firm. This map was among the most important of that group and accounts for variants of this map being issued by competing Blaeu and Hondius firms.
The History of Virginia begins with documentation by the first Spanish explorers to reach the area in the 1500s, when it was occupied chiefly by Algonquian, Iroquoian, and Siouan peoples. After a failed English attempt to settle Virginia in the 1580s by Walter Raleigh permanent English settlement began in Virginia with Jamestown, Virginia, in 1607. The Virginia Company colony was looking for gold but failed and the colonists could barely feed themselves. The famine during the harsh winter of 1609 forced the colonists to eat leather from their clothes and boots and resort to cannibalism.[1] The colony nearly failed until tobacco emerged as a profitable export. It was grown on plantations, using primarily indentured servants for the intensive hand labor involved. After 1662, the colony turned black slavery into a hereditary racial caste. By 1750, the primary cultivators of the cash crop were West African slaves. While the plantations thrived because of the high demand for tobacco, most white settlers raised their families on subsistence farms. Warfare with the Virginia Indian nations had been a factor in the 17th century; after 1700 there was continued conflict with natives east of the Alleghenies, especially in the French and Indian War (1754-1763), when the tribes were allied with the French. The westernmost counties including Wise and Washington only became safe with the death of Bob Benge in 1794.
The Virginia Colony became the wealthiest and most populated British colony in North America, with an elected General Assembly. The colony was dominated by rich planters who were also in control of the established Anglican Church. Baptistand Methodist preachers brought the Great Awakening, welcoming black members and leading to many evangelical and racially integrated churches. Virginia planters had a major role in gaining independence and in the development of democratic-republican ideals of the United States. They were important in the Declaration of Independence, writing the Constitutional Convention (and preserving protection for the slave trade), and establishing the Bill of Rights. The state of Kentucky separated from Virginia in 1792. Four of the first five presidents were Virginians: George Washington, the "Father of his country"; and after 1800, "The Virginia Dynasty" of presidents for 24 years: Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and James Monroe.
1626 (1676) John Speed Antique Map of China - Island of Korea, Japan.
Antique Map
- Title : The Kingdome of China newly augumented by J.S. 1626
- Date : 1626 (1676)
- Size: 21 3/4in x 17in (550mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35668
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of China including the Island of Korea & Japan along with parts of SE & Central Asia by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 3/4in x 17in (550mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 3/4in (520mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 3/4in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold, two light angled crease along top, slight uplift along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning, re-enforced along centerfold and top corners.
Background:
The Kingdome of China, one of the first English-language maps of China. Note the
generally correct outline of the Ming China, with many provinces labeled (Cantam/Guangdong, Quancii/Guangxi, Chequiam/Zhejiang, Quicheu/Guizhou, Fuquam/en:Huguang/ Huguang, Honao/Henan, Xanton/Shandong, Xiamxii and Sancii (Shanxi and Shaanxi?). “Xuntien alias Quinzay” more or less corresponds to Beijing (the name Shuntian Prefecture was indeed in use). However, north of China proper, John Speed had also placed Cathaya, the Chief Kingdome of Great Cam, with the capital Cambalu (Khanbaliq - i.e., in fact, the same Beijing). This kind of duplication was common on the maps of the period, as geographers had not apparently yet fully identified Marco Polo’s Cathay with the China then known to Europeans, and Cambalu with Beijing. The Great Wall is depicted on the map, along with several annotations. Korea is shown as an Island. Japan is also shown using a very curious depiction. The map includes a portion
of India within the Ganges region, extending well into Central Asia. In addition to the
wonderful land-views showing a sailing land craft, manner of execution (crucifixion)
and city views of Macao and Quinzay and the costumed figures of Chinese, Japanese
and Pegu men and women, there are interesting notes throughout the map on various historical and mythical aspects of China, including a region where men are seduced by wonderful illusions and dirt is spun into cloth. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1853 - 1857 Elephant Folio Album w/ 328 Antique Maps & Prints of The Crimea War - Unique
Antique Map
- Title : Crimean War Maps, Prints & Views
- Date : 1853 - 57
- Size: 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) Elephant Folio
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35600
Description:
This is a unique and very comprehensive visual record of the Crimean War (1853 - 1856 & 57) in a huge Elephant Folio Album.
The album consists of 163 double pages with 328 original maps, prints and views of the War tipped in chronological order. These are mainly from the Illustrated London News, from the Wars beginning in 1853 to its end in 1856 through to the Coronation of Alexander II in 1857 and some of the first recipients of the Victoria Cross.
My impression is that the album was professionally organised and assembled possibly by a political or historical organisation of the time, in the mid 19th century.
This album is extremely large measuring 28 inches x 18 inches (62cm x 46cm) when closed and weighs approx. 14 Kg.
The Album contains; (in more detail directly below)
- 71 views of various battles during the conflict.
- 94 Portraits & prints of the leaders, generals, & personnel who were in charge and soldiers, sailors who participated in the war.
- 47 views of various cities and towns from the participating countries England, Russia, Crimea, Turkey etc.
- 63 prints of naval fleets, battleships, sea battles, landings & evacuations..
- 15 Maps of various regions and conflicts
- 25 victory scenes in Britain
- 39 prints of portraits and views of the Coronation of Alexander II
- 4 Pages of recipients from both Army & Navy, of the first Victoria Cross.
Battle Views (Battle of Kars, Kinburn, Sebastopol, Malakoff, Tchernaya, Sveaborg, Gheisk, Hango-Head, Narva, Balaclava, Inkerman, Charge of Light Cavalry Balaclava, Alma, Odessa, Crondstat, Citate, Oltenitza, Kalafat)
Prints of leaders, generals and soldiers (British, Russian, Turkish, Greek, French, Austrian, Peace Talks Paris, Congress of Vienna, Allied Naval Command, Marshall Pelissier, Wounded, Hospitals, Sir De Lacy Evans, Nicolas Emperor of Russia, Royal Marines, Lord Raglan, Napoleon III, Commanders of Allied Armies in the East, Sultan of Turkey, Marshal St Arnaud, French Cavalry, French Infantry, British Infantry, British Navy, Sir Charles Napier, Rear Admiral Corry, & Plumridge, British Cavalry & Artillery Officers, Scots Guards, Royal marines, British Cavalry, Coldstream Guards, Grenadier Guards, Omer Pacha, General Prim)
Views of cities & towns (Balaclava, Kars, Sebastopol, Sveaborg, Helsingborg, Kiel, Copenhagen, Crondstat, St Petersberg, Kerch, Inkermann, Eupatoria, Alma, Coast of Crimea, Varna Bay, Odessa and Coast, Constantinople, Oltenitza, Sinope)
Fleets, battleships & sea battles (HMS Wellington, Steamers, British Fleet, Baltic Fleet, Gun Boats, Nystad, Sebastopol, Spithead, Portsmouth, Flying Squadron, Trafalgar and Resolution, landing French Troops at Gallipoli, Duke of Wellingtons Flagship, Turkish Fleet in Biospheres, English & French Fleet in Besika Bay, HMS Neptune)
Maps (Crimea & Black Sea region, Russia-Turkey, Constantinople, Austria-Russia, Spithead review of Fleet, Sea of Azoff, Kerch, River Alma to Balaklava, Plan of Sebastopol, Seat of War in the Crimea, Sebastopol & Balaklava, Picturesque map of the seat of war, Battle of Alma, The Ottoman Empire)
Florence Nightingale (Treating wounded, visiting wounded Balaclava)
Victory Scenes in England (illuminations, Parades, Queen, Brighton, Hyde Park, Awarding Medals, The Guards, Fireworks, Landing in Kalamita Bay)
The Album is huge Elephant Folio measuring 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) and weighing about 13kg (29lbs) The contemporary half morocco boards are worn, rubbed and detached from the internals that on the whole are clean and tight with occasional spotting and repairs with no loss.
Also included with the album is the following loose prints, maps and newspaper clippings;
- 47 prints and views from ILN on the British Expedition into Abyssinia in 1868.
- 39 prints, views and maps from the ILN and The Graphic on the 1882 Anglo-Egyptian War.
- 60 Newspaper clipping from 1882 of The Times, Evening Standard, Daily News and other papers again on the Anglo Egyptian War.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable.
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) each
Plate size: - 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) each
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
External Boards: - Worn, slit spine, scuffing detached from internals
Internal pages: - Overall clean, some spotting, light offsetting to some pages, several small repairs without loss
Background: The Crimean War was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between the Russian Empire and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom, and Sardinia-Piedmont.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the decline of the Ottoman Empire (the "Eastern Question"), the expansion of the Russian Empire in the preceding Russo-Turkish Wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a disagreement over the rights of Christian minorities in Palestine, then part of the Ottoman Empire, with the French promoting the rights of Roman Catholics, and Russia promoting those of the Eastern Orthodox Church.
The churches worked out their differences with the Ottomans and came to an agreement, but both the French Emperor Napoleon III and the Russian Tsar Nicholas I refused to back down. Nicholas issued an ultimatum that demanded the Orthodox subjects of the Ottoman Empire be placed under his protection. Britain attempted to mediate and arranged a compromise to which Nicholas agreed. When the Ottomans demanded changes to the agreement, Nicholas recanted and prepared for war.
In July 1853, Russian troops occupied the Danubian Principalities (now part of Romania but then under Ottoman suzerainty). On 16 October 1853, having obtained promises of support from France and Britain, the Ottomans declared war on Russia. Led by Omar Pasha, the Ottomans fought a strong defensive campaign and stopped the Russian advance at Silistra (now in Bulgaria). A separate action on the fort town of Kars, in the Ottoman Empire, led to a siege, and an Ottoman attempt to reinforce the garrison was destroyed by a Russian fleet at the Battle of Sinop in November 1853.
Fearing the growth of influence of the Russian Empire, the British and French fleets entered the Black Sea in January 1854. They moved north to Varna in June 1854 and arrived just in time for the Russians to abandon Silistra. In the Baltic, near the Russian capital of Saint Petersburg, an Anglo-French fleet instituted a naval blockade and bottled up the outnumbered Russian Baltic Fleet, causing economic damage to Russia by blockading trade while also forcing the Russians to keep a large army guarding St. Petersburg from a potential allied attack.
After a minor skirmish at Köstence (now Constanța), the allied commanders decided to attack Russia's main naval base in the Black Sea, Sevastopol, in Crimea. After extended preparations, allied forces landed on the peninsula in September 1854 and marched their way to a point south of Sevastopol after they had won the Battle of the Alma on 20 September 1854. The Russians counterattacked on 25 October in what became the Battle of Balaclava and were repulsed, but the British Army's forces were seriously depleted as a result. A second Russian counterattack at Inkerman ended in a stalemate.
By 1855, the Italian Kingdom of Sardinia sent an expeditionary force to Crimea, siding with France, Britain and the Ottoman Empire. The front settled into the Siege of Sevastopol, involving brutal conditions for troops on both sides. Smaller military actions took place in the Caucasus (1853–1855), the White Sea (July–August 1854) and the North Pacific (1854–1855).
Sevastopol finally fell after eleven months, after the French assaulted Fort Malakoff. Isolated and facing a bleak prospect of invasion by the West if the war continued, Russia sued for peace in March 1856. France and Britain welcomed the development, owing to the conflict's domestic unpopularity. The Treaty of Paris, signed on 30 March 1856, ended the war. It forbade Russia to base warships in the Black Sea. The Ottoman vassal states of Wallachia and Moldavia became largely independent. Christians in the Ottoman Empire gained a degree of official equality, and the Orthodox Church regained control of the Christian churches in dispute.
The Crimean War was one of the first conflicts in which military forces used modern technologies such as explosive naval shells, railways and telegraphs. The war was also one of the first to be documented extensively in written reports and in photographs. The war quickly became a symbol of logistical, medical and tactical failures and of mismanagement. The reaction in Britain led to a demand for the professionalisation of medicine, most famously achieved by Florence Nightingale, who gained worldwide attention for pioneering modern nursing while she treated the wounded.
The Crimean War marked a turning point for the Russian Empire. The war weakened the Imperial Russian Army, drained the treasury and undermined Russia's influence in Europe. The empire would take decades to recover. Russia's humiliation forced its educated elites to identify its problems and recognise the need for fundamental reforms. They saw rapid modernisation as the sole way to recover the empire's status as a European power. The war thus became a catalyst for reforms of Russia's social institutions, including the abolition of serfdom and overhauls in the justice system, local self-government, education and military service. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
The Illustrated London News (ILN)
In 1842, Herbert Ingram, a young printer and newsagent from Nottingham, arrived in London. As a newsagent he noticed that when on the rare occasions that newspapers included woodcuts, their sales increased. He therefore came to the conclusion that it would be possible to make a good profit from a magazine that included a large number of illustrations.
Herbert Ingram discussed the proposal with his friend, Mark Lemon, the editor of Punch magazine. With Lemon as his chief adviser, the first edition of the Illustrated London News appeared on 14th May 1842. Costing sixpence, the magazine had sixteen pages and thirty-two woodcuts. The first edition included pictures of the war in Afghanistan, a train crash in France, a steamboat explosion in Canada and a fancy dress ball at Buckingham Palace.
Ingram was a staunch Liberal who favored social reform. He announced in the London Illustrated News that the concern of the magazine would be \\\"with the English poor\\\" and the \\\"three essential elements of discussion with us will be the poor laws, the factory laws, and the working of the mining system\\\". Later Herbert Ingram was to become MP for Boston and until his death in 1860 continued his campaign for social reform in the House of Commons.
The London Illustrated News was an immediate success and the first edition sold 26,000 copies. Within a few months it was selling over 65,000 copies a week. Special events were important to the success of the London Illustrated News. The magazine did very well during the Exhibition 1851 and over 150,000 copies were sold of the edition that reported the funeral of the Duke of Wellington. The Crimean War caused a further boast to sales and by 1863 it was selling over 300,000 copies a week. This was far higher than other journals. For example, newspapers such as the Daily News only sold 6,000 copies at this time, and even the largest selling newspaper, The Times only sold 70,000 copies. In the Christmas Number of The Illustrated London News, 1855, the first pictures in color were published.
In the year 1879, The ILLUSTRATED LONDON NEWS claimed to be the fastest woodcut-printing establishment in the world. The Ingram Rotary machine had been invented. It printed both sides of the paper at once and turned out 6,500 copies per hour. It required only four men to operate it, whereas thirty men and five machines were needed previously
 The ILN held a commanding position in the market place. It was seriously challenged by The GRAPHIC in 1870. Although it never reached the circulation of the ILN. it did take a good market share until the turn of the century.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1648 Joan Blaeu Antique Rare Atlas of England & Wales - Complete 58 Maps, Magnificent
Antique Map
- Title : Guil. et Joannis Blaeu. Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive Atlas novus, pars quarta [England and Wales]
- Size: Large Folio - 20 1/2in x 14in (510mm x 355mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1646 (1648)
- Ref #: 3025
Description:
A unique & rare opportunity to acquire an original & complete atlas of England & Wales, Latin edition, by Joan & Guillem. Blaeu, in exceptional original condition. This original antique atlas is dated 1648 on the title page containing 58 maps of England & Wales as listed for the 1646 edition.
In my thirty plus years collecting and dealing with Antiquarian maps and Atlas, I occasionally come across an item that is of exceptional quality and condition. This Atlas is one of them. Even though this Atlas is 376 years old, the contents within are in exceptional condition and as they would have been when first pressed and bound. All 58 maps & descriptive text in the 460 pages are clean, heavy, sturdy with heavy clear ink denoting a early fresh printing with new copper-plates. The external original Dutch Vellum & Gilt boards are clean, stiff and great condition, as is the binding itself. To find an atlas like this, in absolute original condition, is exceptionally rare and this is only one I have ever seen in this fine condition.
Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive Atlas novus, pars quarta [England and Wales], Amsterdam: apud Johannem Blaeu, 1648, Koeman 2:301.
Contents
- Blank front page
- Engraved Title Page 1648.
- Dedication to King Charles.
- Joannes Blaeu Lectori S.P.D dated MDCXLV (1645)
- Lectori, Guilielmus Cambdenus & Poem to Britannia
- 460 pages containing 58 maps and descriptive text.
- Index Page
- Blank end page
Koeman 2:301 (volume 11 pp. 234- 238)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm) Page size
Plate size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm) Page size
Margins: - Min 1in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Joan Blaeus atlas of England (first edition 1645) consists mainly of copies of the maps in John Speeds Theatre of the Empire of Great Briatine (first edition 1611-12) and the text of Camdens Britannia (first edition, 1607). The title page is derived from that of Speeds Theatre. The volume includes 58 maps, most of which are copies of maps of various edition of Speeds Theatre.
The volume was published in five languages Latin, French, Dutch, German and Spanish. The dates of the forward are: 1st September 1645 (Latin) 1st October 1645 (French), 1st March 1646 (German), and 12th November 1647 (Dutch) The Spanish edition does not have a forward. The atlas of England was added as the fourth volume of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum and later as the fifth volume of Blaeus Atlas Major, separate editions also exist.
The numerous variants of each language edition of this atlas seldom to correspond to the changes in the editions of the Theatrum and Atlas Major For this reason the volume is treated as a separate atlas with its own bibliographical number.
If one considers only the main body of the book - that is, the maps with their descriptive texts - then there are only a few edition of this atlas.
1639 Henricus Hondius Antique 1st Edition Map of North America California Island
Antique Map
- Title : America Septentrionalis
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43161-1
- Size: 23in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique rare 1st state map of North America, with California as an Island, by Henricus Hondius was published in the 1639 French edition.
There were only 3 publications of this map by Hondius in the 1630s & 40s with Jan Jansson replacing the map with his signature in 1641.
The now seldom seen first state of an important, early Dutch map of North America. It one of the first Dutch atlas maps to show California as an island, preceded only by the Hondius Hondius world map of 1633. A note on the map recounting the story of the origin of the California-as-an-island refers to a Dutch captain who obtained a map of California depicted as an island from a captured Spanish ship. The note even provides the dimensions of the island. The Hondius map was an important conduit for bringing the island myth into the cartographic mainstream. Further, Tooley noted the map was also first attempt in Holland to add lakes connected to the St. Lawrence. One of these lakes on the map is in the approximate shape and position of Lake Ontario.
This was also one of a very few, early Dutch maps specifically of North America (as opposed to the entire Western Hemisphere). Aside from the rare De Jode map of 1593, this is the only folio-sized map of North America produced during the entire Dutch Golden Age.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (500mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin extended from plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Henricus Hondius beautifully engraved map of North America had significant influence in perpetuating the theory of California as an island. This was of the influence of his powerful Dutch publishing house with no earlier maps representing California as an island maps having such a wide audience. The 1630s were a decade of constant development in the houses of Blaeu, Hondius & Jansson. It is interesting to note that Blaeu never produced a single sheet map of North America; producing a map of just the whole American continent, first produced in 1617. Also during this decade Joannes Janssonius became an active partner of Hondius, and although this map does not bear his mark, it is believe it was his creation, based on the very similar South American, at the same time, displaying his name.
Cartographically this map is a careful composition of many different sources. The depiction and nomenclature of the west, along with that of California, derive directly from the Henry Briggs The North Part of America, 1625. A legend placed strategically over the north-west coastline offers the opportunity to discontinue a coastline least understood. An unnamed lake still feeds a Rio del Norto flowing incorrectly south-west into what should be the headwaters of the Gulf of California. On the east bank of this river is Real de Nueua Mexico, or Santa Fe. The Gulf of Mexico and the Florida peninsula originate from the Hessel Gerritsz chart of c.1631.
The east coast, however, is harder to define; the south-east appears to be quite generic in form. It is the area north of here that does not appear to be from a particular source. The Chesapeake Bay area is defined in about as much detail as the scale and style of the map will allow, Iames Towne being clearly identified. NOVUM BELGIUM is unlike any other before it, the area between the Zuitt Reuier (Delaware River) and the Noort R (Hudson River) being greatly elongated on a north-east to south-west axis. New Amsterdam is curiously not designated although Fort Orange is present. For New England just a select few names have been chosen from John Smiths map of the area, 1616. The Gulf of St. Lawrence appears to follow de Laet more than Champlain. The latter is used to depict a single great Lake; however, its name, Lac des Iroquois, is borrowed from one nearby. Interestingly the author chose not use Champlains more recent 1632 map but the earlier 1612 Carte Geographique De La Nouvelle France; To avoid unknown territory he does not venture the river system further west, unlike Champlain. Along the Atlantic coast of Labrador we find for the first time much Dutch Nomenclature, reflecting their increased whaling activities in these waters. Hudson Bay is clearly derived from Briggs, 1625, except for the west coast where he introduces the cartography of Thomas James, 1633. The addition of a fox here could be seen as a veiled reference to Luke Foxe, whose own map of the previous year bears just such an animal.
1597 Cornelis Wytfliet Antique Map Early Important Map of California & SW America
Antique Map
- Title : Granata Nova et California
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1597
- Ref #: 41716
Description:
A fine original antique, and incredibly important map the first to focus on California & the SW was published by Cornelis van Wytfliet in the 1597 edition of Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum.
The first printed map devoted to California and the south-west of the present day United States. One of the most interesting features is the depiction of so many fabled places largely from Spanish sources. Most notable amongst these are the seven cities of Cibola. The seven cities originated from the narrative of Fray Marcos de Niza in 1539. Some of the other nomenclature originates from Coronados epic exploration. The outline map is fairly accurate and is derived largely from Petrus Plancius large world map of 1592. The main coastal irregularity is the westward slant of the Californian coastline. Bearing in mind that it would be shown as part of an island in twenty five years, this is quite forgivable. No other states of the map are known and all issues are without text on the back (Burden 106).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/4in x 9 1/4in (285mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1597 Cornelis van Wytfliet published his Augmentum to Ptolemys Geography. Dedicated to Philip III of Spain it is a history of the New World to date, recording its discovery, natural history etc. For the book Wytfliet had engraved nineteen maps, by whom we do not know, one of the world and eighteen regional maps of the Americas. As such this book can be truly called the first atlas of the New World, America.
Wytfliet, Cornelis van d. 1597
Cornelius Wytfliet or Cornelis van Wytfliet was a geographer from Leuven in the Habsburg Netherlands, best known for producing the first atlas of the Americas.
Cornelius was the son of Catherine Huybrechts and her husband, Gregorius Wytfliet, who was advocate fiscal of Leuven University from 1557 to 1594. After graduating Licentiate in Laws from the University of Leuven, Wytfliet moved to Brussels and became secretary to the Council of Brabant. He died in or shortly after 1597, when his Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum (a work adding new discoveries to Ptolemys description of the world) was published
1723 William Dampier 2 Volumes of World Voyages to America Australia Asia - 20 x Maps & Plates
Antique Map
-
Title : Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l on decrite en particular l Isthme de l Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales...1723
(New Voyage around the world. In which are described in particular the Istmus of America, several Coasts & Islands of the West Indies, the Islands of Cape Verde, the passage through the Land of Fuego, the Southern Coasts of Chili, Peru, & Mexico. . - Size: 8vo
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1723
- Ref #: 93005
Description:
French edition of William Dampier's account of his voyages around the World, in 2 volumes, especially to the South Seas in the years 1683 to 1691. Dampier first sailed to Sierra Leone and from there to the Falkland Islands, Cape Horn, Peru, Guatemala, Mexico, Philippines, Vietnam, China, Indonesia and onto New Guinea. He then went ashore in northern Western Australia, in the Broome region, the region later named after him and then sailed onto Sumatra, the Cape of Good Hope and back to Europe.
Although John Brooke was probably shipwrecked on the Australian coast in 1621, without knowing where exactly he was, Dampier became the first Englishman to set foot in Australia, in the Broome NW region. Even though Dampier spent a good deal of his time as a Buccaneer, he wrote these accounts of his adventures without sensation, concentrating on the hydrographic, geographic and scientific details. This helped him establish his legitimacy, bringing immediate academic acclaim rather than condemnation as a pirate.
Dampier was first person to circumnavigate the world three times between 1679 & 1711. He has also been described as Australias first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the British Admiralty with his book, A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, but was court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage, he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crew mate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Lord Nelson, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace.
These two leather bound Volumes, contain 20 maps & plates (some folding) and was published in Amsterdam by David Paul Marret in 1723 (dated)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 8vo
Plate size: - 8vo
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see below for condition report
Plate area: - Please see below for condition report
Verso: - Please see below for condition report
Background:
The two volumes contain the following titles with 20 maps & plates.
Volume 1.
1. Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l\'on decrite en particular l\'Isthme de l\'Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales, les Isles du Cap Verd, le passage par la Terre del Fuego, les côtes meridionales du Chili, du Perou & du Mexique; l\'Isle de Guam, Mindanao, & des autres Philippines, les isles orientales qui sont prés de Cambodie; de la Chine; Formosa; Luçon, Celebes, &c., la Nouvelle Hollande, les Isles de Sumatra, de Nicobar & de Sainte Helene & le Cap de Bonne Esperance...Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement, de leur negoce, &c....1723
This volume refers to Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa.
Contains Title page, 8 maps & plates total of 340 pages.
a) Mappe-Monde - World map with Dampiers tracks.
b) Maps of the Isthmus of Panama and Central America
c) Print of Natives gathering fruit
d) Print of Dampier loading Gold from the New World
e) Voyage au tour du Monde title page
f) Map of Mexico & southern North America
g) Print of a battle in the East indies
h) Print of a coconut palm in East Indies
2. Suite du Voyage Autour du Monde... Avec un Traite Des Vents qui regnent dans toute..LA ZONE TORRIDE Enrichi de Cartes & de Figures..1723
This volume refers to the continuation of Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa along with a description of global winds and tides.
Contains title page along with 6 maps & plates, 227 pages.
a) Engraved Voyage au Tour Du Monde
b) Print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
c) View of Manila
d) 2nd print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
e) Map of the Philippines islands of Banshee
f) Map of Pulocondor, Malayia
g) Print of Dampiers ship and compass rose
3. Traits des Vents Aliisez ou Reglez des Vents Frais ...1715
This volume refers again to globe winds & tides.
Contains title page 2 maps & 148 pages
a) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
b) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
Volume 2.
1. Voyage Autour Du Monde... Contenant une Description d\'Achin,
Ville de Sumatra, du Royaume de Tonquin & autres Places des Indes,
& de la Baye de Campeche. Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs
habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement,
de leur negoce, &c...1723
This volume refers to the continuation of Dampiers travels in East Indies, SE Asia & Mexico
Contains title page, 4 maps & plates, 264 pages.
a) Royalty in Vietnam
b) Map of central & north America
b) Print of Vietnam
c) Map of Australia & East Indies
2. Voyages de Guillaume Dampier a la Baye de Campeche...1714
This volume refers to Dampiers travel to Campeche, Mexico.
Contains title page and 197 pages.
Condition Report: Two volumes bound in full leather with five raised bands to spines, and title label. Couple of minor chips to top of both spines. The leather is scuffed and little pitted/worn (see photos). Internally there are a couple of small chips to inner edges of front and rear end-papers. Inscription to front end-papers (Gift of W. Wood 1745) and bookplate to inside front board (Lord Sandys). The title page of volume III and following four or so leaves have damp staining, and there is light damp staining throughout Volume I & II. The damp staining has caused the leaves to become softer and little chipped, with some nicks/tears and chips. There is a tear/crease to top inner edge and chip to bottom corner of title page of volume I. Scattered pale foxing/browning. Several of the plates have occasional creases. Four leaves of volume III are gently detaching and two leaves of volume I are missing. A few leaves are a little faded. Overall VG, in readable with firm binding.
Dampier, William 1651 - 1715
Dampier was an English explorer, navigator & buccaneer who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australias first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the Admiralty with his book A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, before being court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crewmate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Horatio Nelson, Charles Darwin.
In 1679, Dampier joined the crew of the buccaneer Captain Bartholomew Sharp on the Spanish Main of Central America, twice visiting the Bay of Campeche, or Campeachy as it was then known, on the north coast of Mexico. This led to his first circumnavigation, during which he accompanied a raid across the Isthmus of Darién in Panama and took part in the capture of Spanish ships on the Pacific coast of that isthmus. The pirates then raided Spanish settlements in Peru before returning to the Caribbean.
Dampier made his way to Virginia, where in 1683 he was engaged by the privateer John Cooke. Cooke entered the Pacific via Cape Horn and spent a year raiding Spanish possessions in Peru, the Galápagos Islands, and Mexico. This expedition collected buccaneers and ships as it went along, at one time having a fleet of ten vessels. Cooke died in Mexico, and a new leader, Edward Davis, was elected captain by the crew.
Dampier transferred to the privateer Charles Swans ship, Cygnet, and on 31 March 1686 they set out across the Pacific to raid the East Indies, calling at Guam and Mindanao. Spanish witnesses saw the predominantly English crew as not only pirates and heretics but also cannibals. Leaving Swan and 36 others behind on Mindanao, the rest of the privateers sailed on to Manila, Poulo Condor, China, the Spice Islands, and New Holland. Contrary to Dampiers later claim that he had not actively participated in actual piratical attacks during this voyage, he was in fact selected in 1687 to command one of the Spanish ships captured by Cygnets crew off Manila.
On 5 January 1688, Cygnet anchored two miles from shore in 29 fathoms on the northwest coast of Australia, near King Sound. Dampier and his ship remained there until March 12, and while the ship was being careened Dampier made notes on the fauna and flora and the indigenous peoples he found there. Among his fellows were a significant number of Spanish sailors, most notably Alonso Ramírez, a native of San Juan, Puerto Rico Later that year, by agreement, Dampier and two shipmates were marooned on one of the Nicobar Islands. They obtained a small canoe which they modified after first capsizing and then, after surviving a great storm at sea, called at Acheen (Aceh) in Sumatra.
Dampier returned to England in 1691 via the Cape of Good Hope, penniless but in possession of his journals. He also had as a source of income a slave known as Prince Jeoly (or Giolo), from Miangas (now Indonesia), who became famous for his tattoos (or paintings as they were known at the time). Dampier exhibited Jeoly in London, thereby also generating publicity for a book based on his diaries.
The publication of the book, A New Voyage Round the World, in 1697 was a popular sensation, creating interest at the Admiralty. In 1699, Dampier was given command of the 26-gun warship HMS Roebuck, with a commission from King William III (who had ruled jointly with Queen Mary II until her death in 1694). His mission was to explore the east coast of New Holland, the name given by the Dutch to what is now Australia, and Dampiers intention was to travel there via Cape Horn.
The expedition set out on 14 January 1699, too late in the season to attempt the Horn, so it headed to New Holland via the Cape of Good Hope instead. Following the Dutch route to the Indies, Dampier passed between Dirk Hartog Island and the Western Australian mainland into what he called Shark Bay on 6 August 1699. He landed and began producing the first known detailed record of Australian flora and fauna. The botanical drawings that were made are believed to be by his clerk, James Brand. Dampier then followed the coast north-east, reaching the Dampier Archipelago and Lagrange Bay, just south of what is now called Roebuck Bay, all the while recording and collecting specimens, including many shells. From there he bore northward for Timor. Then he sailed east and on 3 December 1699 rounded New Guinea, which he passed to the north. He traced the south-eastern coasts of New Hanover, New Ireland and New Britain, charting the Dampier Strait between these islands (now the Bismarck Archipelago) and New Guinea. En route, he paused to collect specimens such as giant clams.
By this time, Roebuck was in such bad condition that Dampier was forced to abandon his plan to examine the east coast of New Holland while less than a hundred miles from it. In danger of sinking, he attempted to make the return voyage to England, but the ship foundered at Ascension Island on 21 February 1701. While anchored offshore the ship began to take on more water and the carpenter could do nothing with the worm-eaten planking. As a result, the vessel had to be run aground. Dampiers crew was marooned there for five weeks before being picked up on 3 April by an East Indiaman and returned home in August 1701.
Although many papers were lost with Roebuck, Dampier was able to save some new charts of coastlines, and his record of trade winds and currents in the seas around Australia and New Guinea. He also preserved a few of his specimens. In 2001, the Roebuck wreck was located in Clarence Bay, Ascension Island, by a team from the Western Australian Maritime Museum. Because of his widespread influence, and also because so little exists that can now be linked to him, it has been argued that the remains of his ship and the objects still at the site on Ascension Island – while the property of Britain and subject to the island governments management – are actually the shared maritime heritage of those parts of the world first visited or described by him. His account of the expedition was published as A Voyage to New Holland in 1703.
The War of the Spanish Succession had broken out in 1701, and English privateers were being readied to act against French and Spanish interests. Dampier was appointed commander of the 26-gun ship St George, with a crew of 120 men. They were joined by the 16-gun Cinque Ports with 63 men, and sailed on 11 September 1703 from Kinsale, Ireland. The two ships made a storm-tossed passage round Cape Horn, arriving at the Juan Fernández Islands off the coast of Chile in February 1704. While watering and provisioning there, they sighted a heavily armed French merchantman, which they engaged in a seven-hour battle but were driven off.
Dampier succeeded in capturing a number of small Spanish ships along the coast of Peru, but released them after removing only a fraction of their cargoes because he believed they would be a hindrance to his greater designs. The greater design he had in mind was a raid on Santa María, a town on the Gulf of Panama rumoured to hold stockpiles of gold from nearby mines. When the force of seamen he led against the town met with unexpectedly strong resistance, however, he withdrew. In May 1704, Cinque Ports separated from St George and, after putting Alexander Selkirk ashore alone on an island for complaining about the vessels seaworthiness, sank off the coast of what is today Colombia. Some of its crew survived being shipwrecked but were made prisoners of the Spanish.
It was now left to St George to make an attempt on the Manila galleon, the main object of the expedition. The ship was sighted on 6 December 1704, probably Nuestra Señora del Rosario. It was caught unprepared and had not run out its guns. But while Dampier and his officers argued over the best way to mount an attack, the galleon got its guns loaded and the battle was joined. St George soon found itself out-sized by the galleons 18- and 24-pounders, and, suffering serious damage, they were forced to break off the attack.
The failure to capture the Spanish galleon completed the break-up of the expedition. Dampier, with about thirty men, stayed in St George, while the rest of the crew took a captured barque across the Pacific to Amboyna in the Dutch settlements. The undermanned and worm-damaged St George had to be abandoned on the coast of Peru. He and his remaining men embarked in a Spanish prize for the East Indies, where they were thrown into prison as pirates by their supposed allies the Dutch but later released. Now without a ship, Dampier made his way back to England at the end of 1707.
In 1708, Dampier was engaged to serve on the privateer Duke, not as captain but as sailing master. Duke beat its way into the South Pacific Ocean round Cape Horn in consort with a second ship, Duchess. Commanded by Woodes Rogers, this voyage was more successful: Selkirk was rescued on 2 February 1709, and the expedition amassed £147,975 (equivalent to £19.9 million today) worth of plundered goods. Most of that came from the capture of a Spanish galleon, Nuestra Señora de la Encarnación y Desengaño, along the coast of Mexico in December 1709.
In January 1710, Dampier crossed the Pacific in Duke, accompanied by Duchess and two prizes. They stopped at Guam before arriving in Batavia. Following a refit at Horn Island (near Batavia) and the sale of one of their prize ships, they sailed for the Cape of Good Hope where they remained for more than three months awaiting a convoy. They left the Cape in company with 25 Dutch and English ships, with Dampier now serving as sailing master of Encarnación. After a further delay at the Texel, they dropped anchor at the Thames in London on 14 October 1711.
Dampier may not have lived to receive all of his share of the expeditions gains. He died in the Parish of St Stephen Coleman Street, London. The exact date and circumstances of his death, and his final resting place, are all unknown. His will was proven on 23 March 1715, and it is generally assumed he died earlier that month, but this is not known with any certainty. (Ref Tooley M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1774 Captain James Cook Antique Map, 1st Printed Chart of New Zealand. Dutch Ed. - Scarce
Antique Map
- Title : Kaart van Nieuw Zeeland in de Jaaren 1769 en 1770 bezogt door den Luitenant J Cook met het Schip De Endeavour (Chart of New Zealand explored in 1769 and 1770 by Lieutenant. J. Cook Commander of his Ship Endeavour)
- Date : 1774
- Size: 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35674
Description:
This magnificent large original copper plate engraved scarce antique map, the first printed chart of New Zealand by Captain James Cook, during his circumnavigation of the South Pacific in 1769-70, was published in the 1st Dutch edition of Hawkeworths Voyages in 1774 by Reiner Arrenberg Reizen Rondom de Weereld Ondernomen op Bevell van Zyne Majesteit den Tans Regeerenden Koning van Groot-Brittanje tot Het Doen van Ontdekkingen ... J. Hawkesworth Uit Het Engelsch Vertaalt,
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 394mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty\\\'s choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
1710 Herman Moll Large Antique Map of England & Wales - Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : The South Part of Great Britain called England & Wales...by Herman Moll 1710
- Size: 39in x 24in (1.0m x 610mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1710
- Ref #: 80662
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of England & Wales was engraved in 1710 by Herman Moll - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by John Bowles of London.
Striking large format, one off published, map of England and Wales. The map is embellished with two large cartouches and an extensive table locating all ye Cities, Market Towns, Boroughs and whateve Places in South Britain have ye Election of Members of Parliament.
The map is elaborately colored by counties, with 5 sailing ships to the right of Northumberland. Includes a dedication to Right Honourable FRANCIS, Lord Viscount Rialton in the cartouche at the right side of the map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39in x 24in (1.0m x 610mm)
Plate size: - 38in x 23in (970mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds
Verso: - Repairs along folds
Background:
English Cartography: When considering the work of English map makers we tend, perhaps, to think too much in terms of county maps, dominated by the names of Saxton and Speed, but we should not underrate the contribution to the sum of geographical knowledge made in other spheres, such as the sea charts of Edward Wright, Robert Dudley and Greenvile Collins, the discoveries of James Cook, the road maps of Ogilby and Cary, the meteorological and magnetic charts compiled by Edmund Halley, to mention only a few.
In 1558 Queen Elizabeth came to the throne in the midst of a fast changing world. In 1563 a nineteen sheet map, copies of which survive only in manuscript form, was completed by Laurence Nowell, and no doubt, the issue of Mercators large-scale map of the British Isles in 1564 had an important influence on the thought of the period. A few years later a national survey was commissioned privately, although probably at the instigation of Lord Burghley, the Lord Treasurer, but subsequently was completed with royal encouragement. The outcome was Christopher Saxtons Atlas of EngIand and Wales, started about 1570 and published in 1579 - the first printed set of county maps and the first countrywide atlas on such a splendid scale produced anywhere. A Welsh antiquarian, Humphrey Lhuyd completed a set of surveys that were even more successful than Saxton in which he had produced fine manuscript maps of England and Wales which were used by Ortelius in editions of his Atlas from 1573 onwards.
The earliest maps of the 17th century, attributed to William Smith of the College of Heralds, covered only twelve counties based on Saxton/Norden and were presumably intended to be part of a complete new atlas. They were printed in the Low Countries in 1602-3 and were soon followed by maps for the Latin edition of Camdens Britannia dated 1607. In 1610-11 the first edition of John Speeds famous county Atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published and immediately replaced Saxtons in popular appeal. Although Speed assembled much of his material from the earlier works of Saxton, Norden and others, a considerable part of the up-to-date information, especially relating to the inset town plans depicted on his maps, was obtained first hand. The maps undoubtedly owed much of their popularity to the splendid engravings of high quality made in the workshops in Amsterdam of Jodocus Hondius to whom Speed sent his manuscripts, the plates subsequently being returned to London for printing.
In 1645, Volume IV of the famous Blaeu World Atlas covering the counties of England and Wales was published in Amsterdam. These maps have always been esteemed as superb examples of engraving and design, the calligraphy being particularly splendid, but nevertheless they were nearly all based on Saxton and Speed and added little to geographical knowledge.
Not until the latter part of the century do we find an English map maker of originality with the capacity to put new ideas into practice. John Ogilby, one of the more colourful figures associated with cartography, started life as a dancing master and finished as Kings Cosmographer and Geographic Printer. After publishing a small number of county maps, somewhat on the lines of John Norden he issued in 1675 the Britannia, the first practical series of detailed maps of the post roads of England and Wales on a standard scale of 1,760 yards to the mile. Up to the end of the century and beyond, reprints and revisions of Saxtons and Speeds atlases continued to appear and the only other noteworthy county maps were Richard Blomes Britannia (1673), John Overtons Atlas (c. 1670) and Robert Mordens maps for an English translation of Camdens Britannia published in 1695.
Another noted cartographer of the day was Captain Greenvile Collins, and of his work in surveying the coasts of Great Britain culminating in the issue in 1693 of the Great Britains Coasting Pilot. Apart from these charts, English cartographers published during the century a number of world atlases. Speed was the first Englishman to produce a world atlas with the issue in 1627 of his A Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World. Other atlases appeared later in the century by Peter Heylin, John Seller, William Berry, Moses Pitt and Richard Blome, whilst Ogilby found time to issue maps of Africa, America and Asia. Far more important, from the purely scientific point of view, was the work of Edmund Halley, Astronomer Royal, who compiled and issued meteorological and magnetic charts in 1688 and 1701 respectively.
At the beginning of the eighteenth century the Dutch map trade was finally in decline, the French in the ascendant and the English to a great extent still dominated by Saxton and Speed except, as we have shown, in the spheres of sea charts and road maps. There were atlases by John Senex, the Bowles family, Emanuel and Thomas Bowen, Thomas Badeslade and the unique birds-eye perspective views of the counties, The British Monarchy by George Bickham. In 1750-60 Bowen and Kitchins The Large English Atlas containing maps on a rather larger scale than hitherto was published.
In 1759 the Society for the encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce offered an award of £100 for the best original surveys on this scale and by the end of the century about thirty counties had been re-surveyed. These maps, many of which formed, in later years, the basis for the first issues of county maps by the Ordnance Survey Office were not only decorative but a tremendous improvement geographically on earlier local maps. As a consequence, the skills and expertise of the new-style cartographers soon enabled them to cover the world as well as the domestic market. Thomas Jefferys was such a man; he was responsible for a number of the new 1 in. to 1 mile county surveys and he issued an edition of Saxtons much battered 200-year-old plates of the county maps, but he is better known for many fine maps of North America and the West Indies. His work was continued on the same lines by William Faden, trading as Faden and Jefferys. Other publishers such as Sayer and Bennett and their successors Laurie and Whittle published a prodigious range of maps, charts and atlases in the second half of the century. A major influence at this time was John Cary who, apart from organizing the first re-survey of post roads since Ogilby and subsequently printing the noted Travellers Companion, was a prolific publisher of atlases and maps of every kind of all parts of the world. After starting work with Cary, and taking part in the new road survey, Aaron Arrowsmith set up in his own business and went on to issue splendid large-scale maps of many parts of the world. Both Carys and Arrowsmiths plates were used by other publishers until far into the next century and, in turn, their work was taken up and developed by James Wyld (Elder and Younger) and Tallis and Co.
Later into the 19th century some of the better known cartographers and publishers were by Henry Teesdale (1829-30), Christopher and John Greenwood, surveyors, Thomas Moule, a writer on heraldry and antiques (1830-36) and John Walker (1837) but by about the middle of the century few small-scale publishers survived and their business passed into the hands of large commercial concerns such as Bartholomews of Edinburgh and Philips of London who continue to this day. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
1755 (1768) Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique 2nd edition Map of Colonial United States
Antique Map
- Title : Partie De L Amerique Septentrionale, qui Comprend Le Cours De L Ohio...Par le Sr Robert de Vaugondy
- Date : 1755 (1768)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93514
- Size: 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured, scarce 2nd edition antique map of the east coast of the United States, illustrating the course of the Ohio River and stretching from New England to the Carolinas, north to the Great Lakes and south to the Mississippi - with an inset map of The Carolinas - was published in 1768 - dated 1755 in the cartouche - by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal.
This map is all original with hand colour on age toned heavy paper with original margins with a heavy dark ink denoting an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Second state of the early de Vaugondy map of the British colonies, with changes after the 1763 Treaty of Paris, with Virginia & Carolina extended to the Mississippi and Pennsylvania extended to Lake Erie. The majority of geographical information is based upon John Mitchells great map of North America from the mid 1750s, also drawing from Lewis, Evans on the Middle British Colonies and Joshua Frys and Peter Jeffersons map of Virginia and Maryland. The Mitchell map was the culmination of many years of British surveying in the North American Colonies and was considered one of the best maps of the continent available to Europeans and Americans in the mid-eighteenth century.
De Vaugondys rendition does not copy the full scope of Mitchells map but instead focuses on the colonies stretching from southern Maine to the Carolinas. In the top left corner is an inset of South Carolina and Georgia. De Vaugondy also pays special attention to the river systems and settlements. This map shows some of the earliest accurate information of the trans-Allegheny regions (the Ohio River, Kentucky, Tennessee and Parts of Ohio) and inland areas to the southeast of the Great Lakes and interior of New England.
Maine is still part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. During this era. The dispute between New Hampshire and New York over who controlled the area which is now Vermont has been resolved. The outbreak of the French & Indian War (Seven Years War) briefly suspended interest in the disputed area, and it was not until 1764 that the British crown upheld New Yorks claim to Vermont. Included is a beautiful title cartouche in the Rococo style. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1785 De Vaugondy & Jefferson Antique Early Map of The United States of America
- Title : Etats-Unis de l'Amerique Septentrionale avec les Isles Royale, de Terre Neuve de St. Jean, l'Acadie &c. 1785 M. Robert de Vaugondy....Boudet....
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93513
- Size: 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved very important, early & scarce antique early map of the United States (Etats-Unis De L Amerique), during what is know as the Confederation Period, by Robert De Vaugondy was published by the French printer Antoine Boudet (1715 - 1787) for the supplement of de Vaugondys Atlas Universal
This scarce first state map is very important to the formation of the United States of America. The map is the first to describe what is know as the Jeffersonian Ordinance, showing the new international borders of the fledgling United States, the inclusion of the original 13 states in the bottom right text box (the first map to do so) along with the inclusion of Michigan, ratified under the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
The successor to De Vaugondy, Charles Francois Delamarche (1740 - 1817) was a known correspondent to Thomas Jefferson and along with the printer Boudet would have played an important part in the publication of this map. The Ordinance of 1784 was a plan to outline the new territories and states, that would eventually make up the foundation of the United States, ratified by the Treaty of Paris. Given that this map was engraved in 1785 or possibly earlier and that Delamarche was a friend of Jefferson, it is not a stretch to believe that he was one of the first, if not the first, to map the new country of the United States (Etats-Unis De L Amerique)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (670mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25 1/2in x 19 1/2in (650mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The Confederation Period was the era of United States history in the 1780s after the American Revolution and prior to the ratification of the United States Constitution. In 1781, the United States ratified the Articles of Confederation and prevailed in the Battle of Yorktown, the last major land battle between British and American forces in the American Revolutionary War. American independence was confirmed with the 1783 signing of the Treaty of Paris. The fledgling United States faced several challenges, many of which stemmed from the lack of a strong national government and unified political culture. The period ended in 1789 following the ratification of the United States Constitution, which established a new, more powerful, national government.
The Articles of Confederation established a loose confederation of states with a weak federal government. An assembly of delegates acted on behalf of the states they represented. This unicameral body, officially referred to as the United States in Congress Assembled, had little authority, and could not accomplish anything independent of the states. It had no chief executive, and no court system. Congress lacked the power to levy taxes, regulate foreign or interstate commerce, or effectively negotiate with foreign powers. The weakness of Congress proved self-reinforcing, as the leading political figures of the day served in state governments or foreign posts. The failure of the national government to handle the challenges facing the United States led to calls for reform and frequent talk of secession.
The Treaty of Paris left the United States with a vast territory spanning from the Atlantic Ocean to the Mississippi River. Settlement of the trans-Appalachian territories proved difficult, in part due to the resistance of Native Americans and the neighboring foreign powers of Great Britain and Spain. The British refused to evacuate US territory, while the Spanish used their control of the Mississippi River to stymie Western settlement. In 1787, Congress passed the Northwest Ordinance, which set an important precedent by establishing the first organized territory under the control of the national government.
After Congressional efforts to amend the Articles failed, numerous national leaders met in Philadelphia in 1787 to establish a new constitution. The new constitution was ratified in 1788, and the new federal government began meeting in 1789, marking the end of the Confederation Period. Some historians believe that the 1780s were a bleak, terrible time for the US, while others have argued that the period was actually stable and relatively prosperous.
1827 Dumont D Urville Large Antique Early Map of New Zealand
Antique Map
- Title : Carte Generale de la Partie De La Nouvelle Zelande Reconnue par le Capitaine de Fregate Dumont D Urville Dressee par Mr Loottin Enseigue de v au Expedition de la Corvette de S M L Astrolobe Janvier, Fevrier, Mars, 1827
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1827
- Ref #: 42011
Description:
This magnificent large original & scarce copper-plate engraved antique map of the North Island & part of the South Island of New Zealand by Dumont D Urville and Lieutenant Victor Lottin, aboard the ship The Astrolabe during the first D Urville voyage to the South Seas 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Alphonse Chassant, 1808-1907 and published in the 1836 edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Fantastic & rare map by D Urville & Lottin with surveys made of the north, south east coasts of New Zealands North Island & the north west part of the South Island, between January and March 1827.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
On 25 April 1826, Dumont d Urville, with the rank of commander, sailed from Toulon as chief of the ship formerly named the Coquille, renamed Astrolabe, on a voyage of exploration and scientific inquiry which lasted till 24 March 1829. On 10 January 1827 the Astrolabe came in sight of the north-west coast of the South Island of New Zealand. On 14 January the ship passed the entrance to the modern Golden Bay, which had been visited by Abel Tasman. The ship anchored off the west side of Tasman Bay. This bay had not been investigated at close quarters previously. In the following days d Urville established that it was a great deal bigger than Cooks mapping indicated, and his officers surveyed and charted it. Adele Island, Pepin Island, and Croisilles Harbour are modern names derived from those given by d Urville. On 23 January d Urville made for a channel which he had noticed at a distance some time before, and which seemed to him to communicate between Tasman Bay and Cooks Admiralty Bay. This was the channel culminating in French Pass and dividing D Urville Island from the mainland. Victor Lottin and Gressien, two of d Urville\'s officers, on the same day saw the pass at close quarters from two of the ships boats. On 25 January d Urville went through the pass into Admiralty Bay in a ship\'s boat. On 28 January the Astrolabe made the hazardous passage into Admiralty Bay. The investigation of Tasman Bay and the discovery of French Pass and the insularity of D Urville Island were significant contributions by d Urville to the discovery of New Zealands coastline.
From Cook Strait d Urville went north along the coast to Whangarei Harbour, which was surveyed and charted on 21–23 February 1827. The Astrolabe then doubled back to Hauraki Gulf, passing between the main coastal islands on the west side of the gulf on 25–27 February. The Astrolabe had been preceded in this passage by the Prince Regent in 1820, but the surveys and charts made under d Urville\'s command were notable contributions to the cartography of New Zealands coast. Lottin crossed the isthmus on 26 February and made a survey of Manukau Harbour, discovered in 1820 by Samuel Marsden. From Hauraki Gulf d Urville proceeded to North Cape and then to the Bay of Islands, leaving New Zealand in March 1827.
Lottin, Victor Charles 1795 - 1858. Lottin was a French frigate captain and geographer who took part in the voyage made around the world by the Astrolabe, under the command of Dumont-d Urville. He served as a lieutenant on the research expedition to Iceland and Greenland. During these two excursions, Lottin drew several maps and gathered a large quantity of objects of natural history, and made mention of the aurora borealis, inserted in the Annales Maritimes (1839). He was a member of the Academy of Sciences, Section of Geography and Navigation (elected in 1852) and a Knight of the Legion of Honour.
He died at Versailles on 18 February 1858.
1720 Herman Moll Large Antique Map of The Netherlands - 7 x Town Plans Amsterdam
Antique Map
- Title : A New and Exact Map of the United Provinces, or Netherlands &c. According to the Newest and Most Exact Observations by Herman Moll Geographer
- Size: 41in x 25in (1.04m x 635mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1720
- Ref #: 93007
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Netherlands by Herman Moll was published in 1720 in the atlas The World Described, or a New and Correct Sett of Maps by John Bowles, Thomas Bowles, Philip Overton & John King of London.
In the 18th century many large-scale maps were published by the likes of John Senex and Herman Moll, this trend continued until the end of private mapping in the early 19th century when it was replaced by Ordnance Survey maps.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 41in x 25in (1.02m x 635mm)
Plate size: - 39 1/4in x 24 1/2in (1.00m x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Backed onto contemporary paper
Background:
An attractive, large scale map of The Netherlands or the United Provinces by the highly regarded cartographer and engraver Herman Moll. on the right-hand side views of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Middelburg, Utrecht, Groningen, Het Loo Palace and a plan of the ancient Roman Castle at the mouth of the Rhine river Arx Britannica (Huis Britten, Brittenberg). The upper left corner of the map has an inset map of the coasts, sands and banks of the North Sea, the stretch of water that lies between England and The Netherlands. Moll dedicates his map to ‘The Right Hon Charles Lord Viscount of Townsend &c one of his Majesty’s Principal Secretaries of State’
This magnificent map was printed by John Bowles of Cornhill, London and published in Moll’s 1719 New and Complete Atlas, but it may also have been separately issued earlier. Moll came to London probably from Bremen around 1678 and by 1688 he had his own shop in Vanley\'s Court in London\'s Blackfriars, between 1691 and 1710 at the corner of Spring Gardens and Charing Cross, when he moved to Beech Street where he remained until his death. In 1701 he published his first work A System of Geography. He was publishing atlases and separately issued maps, and from 1710 was also known as a maker of pocket globes. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, M&B)
1730 Georg Seutter Antique Map of New England & New York City - Rare 2nd State
Antique Map
- Title : Recens edita totius Novi Belgii, in America Septentrionali siti, delineatio cura et sumtibus Matthaei Seutteri, Sac. Caes Maj. Geographf. August. Vind
- Size: 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1730
- Ref #: 43001
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the NE region of colonial North America, with the famous Restitutio inset birds-eye view of 17th century New York city, was engraved & published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730.
This is the rare second state, identified by the omission of Chalcographi Augustani from the title and the blank shaded are directly below the title (text was added to the shaded area in the 3rd to 6th states) The cartouche and city view are uncoloured as was intended by Seutter along with the beautiful original map colouring.
This map is in exceptional condition with beautiful original colour, with heavy engraving (denoting an early pressing) on clean heavy sturdy paper. The top and left borders have been professionally extended, with no impact on the image.
There are, at the time of listing, nine of these maps for sale online, of states 2 to 6. Of the 9 only 2 are of the rare 2nd state. The average asking price of the nine maps is $4897US.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - T, R & L margins extended
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The map is based upon the Jansson-Visscher New England series of maps, first published by Visscher in 1651. Seutter replaces the original Restitutio view of New York City with a new view of New York entitled Neu Jorck sive Neu Amsterdam, with a key to the view below in Latin. Above the view is an elaborate scene depicting natives, slaves & allegorical deities presenting tributes to the English monarch, George II. The course of the Delaware and Hudson are separated, unlike early editions of the map.
This is the first map in the series to show distinct drawn boundaries between Massachusetts, New England, New York, New Jersey and Pennsylvania, as earlier examples had previously left the delineation of the boundaries to the colorist. Philadelphia is now shown as a set of houses in relief, rather than a ground plan. The map is richly embellished with many animals and other decorations and is without doubt, one of the most decorative 18th century maps of the region.
1550 Munster Rare Antique World Map - early depiction of America, Post Columbus
Antique Map
- Title : Das Erst General Inhaltend die Beschreibung und den Cirkel des Gantzen Erdtriche und
- Ref #: 35671
- Size: 16 1/2in x 12 3/4in (415mm x 315mm)
- Date : 1550
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This wood-block engraved original antique oval World Map was engraved by David Kandel, initials engraved bottom left "DK" and was published in the 1550 edition of Cosmographia by Sebastian Munster.
One of the most recognizable maps of the 16th century considered the first map to identify the Pacific Ocean, as here, 'Mare Pacificum.' This is the world of the educated 16th century European, divided into Asia, Europe, India, Africa and America. The southern latitudes are inhabited by a variety of sea monsters and sailing ships.
One of the best examples I have seen of this map for sometime, nice heavy impression on clean sturdy paper with original margins.
The American continent is barely recognizable, only a scant 58 years after European discovery by Christopher Columbus. North America is defined as Terra Florida showing an enormous inlet extending towards the eastern seaboard in the vicinity of modern day North Carolina named Verrazano's Sea. Apparently Verrazano, coasting the Outer Banks, observed the Pamlico Sound and assumed that beyond the narrow coastal banks, an open sea gave direct access to the pacific - wishful thinking at best. Verrazano's Sea appears so dramatically on few maps, but persisted in lesser forms for nearly a century.
South America with tentacle like protrusions in all directions, is largely amorphous, but the Rio de la Plata and the Strait of Magellan are clear. Tierra del Fuego is enormous, with no mention of greater Terra Australias, an interesting omission by Munster.
Europe is vaguely recognizable and connected, via an arctic peninsula, to Greenland and North America.
Asia/Pacific extends eastward far enough to reappear just north of America. Ceylon is not present, but a landmass bearing roughly the shape and position of Sumatra is identified as Tapobrana (a term more commonly associated with Ceylon). Japan appears as Zipangri.
Unlike many other world maps of the time, Munster has left out the concept of a 'Terra Australis Incognita' altogether choosing to show ocean instead.
Africa follows the Ptolemaic model with the Nile finding its source in a mountain range and two associated lakes.
The whole is surrounded by twelve named and prominent wind heads - one for each direction.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 12 1/2in (400mm x 310mm)
Plate size: - 15 3/4in x 12 1/2in (400mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small knicks to margin edges
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: This wood-cut engraved World map was prepared for the 1550 edition of Sebastian Münster's Cosmographia to replace the earlier World map by Sebastian Munster which had appeared in the editions of the Geographia and Cosmographia from 1540 onwards. The publisher, from 1552, was Heinrich Petri, Münster's son-in-law.
This "new world" map is on an oval projection, similar in many respects to the previous Munster world map, but with the woodcutter's initials "DK" added, identified as those of the engraver David Kandel, in the lower left-hand corner.
The titles of the wind-heads are now in banners and the east and west winds, unlike the 1540 version, do not protrude inside the oval circumference. North America still retains its unusual shape almost bisected by water but the earlier note indicating a route to the Moluccas has been omitted...."
The map was first issued in the 1550 edition of Cosmographia, and appeared in all subsequent editions through to 1578, with the title varying according to the language of the edition. On the verso the wood block is the title and text, in Latin.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographia appeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
1794 Thomas Pownall & Kitchin Large Post Revolutionary War Map of North America
Antique Map
- Title : A New Map of North America with the West India Islands, divided according to the Preliminary Articles of Peace, Singed at Versailles, 20, jan 1783, wherein are particularly Distinguished The United States, and the Several Provinces, Governments & ca which Compose the British Dominions, Laid down according to the Latest Surveys, and Corrected from the Original Materials of Goverr. Pownall, Membr. of Parlimt....1794
- Size: 47in x 41in (1.20m x 1.050m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1794
- Ref #: 35672
Description:
A large, extraordinary important, original rare copper-plate engraved map of North America by Governor Thomas Pownell, was engraved & updated by Thomas Kitchin in 1794 - dated in cartouche - and published in A general atlas, describing the whole universe: being a complete collection of the most approved maps extant; corrected with the greatest care, and augmented from the latest discoveries by Laurie and Whittle (active 1794 - 1858) London.
This map was first issued by Emmanuel Bowen and John Gibson in 1755 and went through numerous iterations over the next 40 years. This edition was issued shortly after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The map details the newly formed United States of America in Green, the British & French dominions in Canada in Red, plus the extensive Spanish territories of from Florida, Louisiana Mexico and Central America. As one might expect from a map of this size, the detail throughout is extraordinary.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 47in x 41in (1.20m x 1.050m)
Plate size: - 46in x 40in (1.10m x 990mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light toning & offsetting
Verso: - Age toning.
Background:
This monumental 1794 map of North America by Governor Thomas Pownell was issued shortly after the end of the American Revolutionary War. The United States at this time extended from the Pacific to the Mississippi River and from Georgia to the Great Lakes and Maine. The early state boundaries roughly conform to their original colonial charters. Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina are drawn with indefinite western borders, suggesting claims to further unexplored land beyond the Appellation Mountains. By this time most of the boundary issues in the New England states had been resolved, though there remained some vagaries regarding the Massachusetts Connecticut border and, though Vermont is noted textually, its boundaries are not drawn in. At this time there were also some unresolved issues regarding the national borders between Maine and Nova Scotia. In Pennsylvania, the western border displays some surveying confusions that would not be resolved until the early 1800s and the creation of Ohio.
It is beyond the old colonial centers where this map really gets interesting. Pownall offers copious notations on the lands and territories between the Appellation range and this Mississippi River. In some cases he offers commentary on the various indigenous tribes including the Creeks, Chickasaws, Chocktaws, Senekas, Eriez, Delawares, Shawnee, Iroquois, Algonquians, Ottawas and others. The cartographer was clearly concerned with the development of these western regions and offers copious commentary on fit sites for factories, the alliances and temperaments of tribes, and the navigability of various river systems, particularly the Mississippi and Ohio.
The Great Lakes are mapped with considerable accuracy though several apocryphal islands do appear in Lake Superior. The most notable of these are Phelipeaux and Pontchartrain. Phelipeaux Island first appeared in French maps of this region in the 1740s. Later it was mentioned as a boundary marker in the 1783 Treaty of Paris which ended the American Revolutionary War. The nonexistence of these islands was not conclusively proven until about 1820.
To the west of the Mississippi we pass into the largely unknown lands of the Great Plains. In what is roughly modern day Missouri, between Memphis and St. Louis, there is an interesting note suggesting that this region is Full of Mines, with a secondary note suggesting that these mines gave rise to the Mississippi Scheme of 1719. This refers to the Mississippi Company (Compagnie du Mississippi) or, as it was more commonly known the Indies Company (Compagnie d Occident). This organization was part of a French investment plan comparable to the South Seas Company which was developing contemporaneously in England. The Mississippi Companys charter was to trade the riches of the Louisiana Territory. The main proponent of the Mississippi Company, John Law, greatly exaggerated the wealth of Louisiana by describing a rich mining region easily accessible along the Mississippi from New Orleans. This resulted in a stock buying rush which disproportionately overvalued Mississippi Company stock, resulting in one of the world\'s first Bubble Economies.
Further North, along the northern border between the United States and British America (Canada), Rain Lake, the Lake of the Woods, and Lake Winnepeg are noted. This region was a hotbed of exploration throughout the 18th century. French and English concerns in the New World were desperate for access to the Pacific and the rich Asian markets. These markets had long been dominated by the Spanish who had easy access to the Pacific via Mexico and South America. The French and English set their hopes on a Northwest Passage. By the late 18th century the search for a route through the high Arctic had long been abandoned. Instead, explorers and theoretical cartographers believed that a water route might be found among the elaborate network of lakes and rivers that meandered through central Canada. Our map shows evidence of some of this exploration, particularly the travels of the Quebec born Pierre de La Verendrye and his sons around Lake Alimipigon, the Lake of the Woods (Lake Minitti) and Lake Winnipeg (Lake Ouinipigon).
As we progress even further west, passing out of Louisiana into the Spanish holdings we begin to see significant mapping - both conjectural and factual. The Spanish had long been passively active in the exploration of New Mexico. Though no concerted effort had been put forth to map the region, various missionaries and territorial governors had, over roughly 200 years of occupation added considerable data, both fact and fiction to the cartographic picture. Numerous American Indian groups are noted including the Pimas, the Apaches ,the Navajo and others. Along the Rio del Norte or upper Rio Grande there are a quantity mission stations including the regional capital of Santa Fe.
Just to the west of these missions we begin to enter more mythical territory and both Cibola and Teguayo are noted. Cibola and Teguayo are both associated with the legendary Seven Cities of Gold. It was believed that in 1150 when Merida, Spain, was conquered by Moors ,the city\'s seven bishops fled to unknown lands taking with them much of the city\'s riches. Each Bishop supposedly founded a great city in a far away place. With the discovery of the New World and the fabulous riches plundered by Cortez and Pizarro, the Seven Cities became associated with New World legends. Coronado, hearing tales of the paradise-like mythical Aztec homeland of Azatlan somewhere to the north of Mexico , determined to hunt for these cities in what is today the American southwest. In time indigenous legends of rich and prosperous lands became attached to the seven cities. Two of these appear on our map - Cibola and Teguayo.
The gulf of Mexico, the West Indies, and the Caribbean are charted with considerable and typical accuracy. Notes numerous offshore shoals, reefs, and other dangers - especially around the Bahamas. Also describes several important shipping routes, particularly the former routes of Spanish galleons from Veracruz to Havana, the route from Cartagena to Havana, and the route from Cartagena to Europe.
There are also two particularly interesting insets. The first, in the upper left quadrant, depicts the Canadian arctic, particularly the Hudson and Baffin Bays. Notes all of the most recent discoveries in this region and offers interesting notes such as If there is Northwest Passage it appears to be through one of these inlets. In the northwestern quadrant of this inset, the supposed discoveries of Admiral de Fonte are included, despite a notation that they are Imaginary.
The second inset of interest in located in the lower left quadrant. This smaller maps depicts the northern parts of the Gulf of California and the Colorado River Delta based upon the explorations of the Jesuit Father Eusebius Francis Kino. The actual cartography of this region has been vague since the mid 17th century when it was postulated that California must be an Island. It was not until Kino\'s historic expedition, recorded here, that Baja California was conclusively proven to be a peninsula.
A magnificent title cartouche appears in the upper right quadrant. The cartouche, which angles around Bermuda, depicts two stylized American Indians surrounded by the presumed flora and fauna of the new world. These include a small monkey, a parrot, and a jaguar. Above the cartouche is a textual quotation from Article III of the Treaty of Paris, affirming the rights of the United States to access the rich cod fields of Newfoundland\'s Grand Banks.
The Treaty of Paris, signed in Paris by representatives of King George III of Great Britain and representatives of the United States of America on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War. The treaty set the boundaries between the British Empire in North America and the United States, on lines exceedingly generous to the latter. Details included fishing rights and restoration of property and prisoners of war.
This treaty and the separate peace treaties between Great Britain and the nations that supported the American cause—France, Spain, and the Dutch Republic—are known collectively as the Peace of Paris. Only Article 1 of the treaty, which acknowledges the United States existence as free, sovereign, and independent states, remains in force.
Thomas Pownall 1722 - 1805 was a British scholar, statesman and soldier active in the colonial administration of North America just prior to the American Revolutionary War. Pownell was born in England and educated at Trinity College, Cambridge. After graduation he was employed by his brother, John Pownall, at the office of the Lords Commissioners of Trade and Plantations, which oversaw British economic interests in its North American colonies. In 1753, Pownall was appointed secretary to the governor of New York, Sir Danvers Osborne. Osborne, himself having be only recently appointed to the position, committed suicide shortly after taking office. Despite this setback, Pownall remained in America and devoted himself to studying and researching the colonies. In the process Pownall became close lifelong friends with Benjamin Franklin and other New World luminaries. He also published several notable works on the colonial administration of North America. In 1757 Pownall was appointed Governor of the Massachusetts Bay colony. In this position he frequently found himself at odds with the restrictive policies of the Board of Trade. It was not long before he was pushed out of office and, declining the governorship of Jamaica, reassigned to South Carolina. Despite nominally holding the governorship of South Carolina, Pownall never visited the colony. Instead he returned to England where he eventually became a member of Parliament. In Parliament, he advocated for reduced taxes towards the colonies - had he been heeded, the American Revolution may have never happened. Pownall retired from public life around 1780, but continued to pursue his scholarly interests. Pownalls research contributed significantly to several important maps and scholarly work on North America.
Laurie and Whittle 1794 - 1858 based in London, were map and atlas publishers active in the late 18th and early 19th century. Generally considered to be the successors to the Robert Sayer firm, Laurie and Whittle was founded by Robert Laurie (c. 1755 - 1836) and James Whittle (1757-1818). Robert Laurie was a skilled mezzotint engraver and is known to have worked with Robert Sayer on numerous projects. James Whittle was a well-known London socialite and print seller whose Fleet Street shop was a popular haunt for intellectual luminaries. The partnership began taking over the general management of Sayers firm around 1787; however, they did not alter the Sayer imprint until after Sayers death in 1794. Apparently Laurie did most of the work in managing the firm and hence his name appeared first in the Laurie and Whittle imprint. Together Laurie and Whittle published numerous maps and atlases, often bringing in other important cartographers of the day, including Kitchin, Faden, Jefferys and others to update and modify their existing Sayer plates. Robert Laurie retired in 1812, leaving the day to day management of the firm to his son, Richard Holmes Laurie (1777 - 1858). Under R. H. Laurie and James Whittle, the firm renamed itself Whittle and Laurie. Whittle diedin 1818, and thereafter the firm continued under the imprint of R. H. Laurie. After Lauries death the publishing house and its printing stock came under control of Alexander George Findlay, who had long been associated with Laurie and Whittle. Since, Laurie and Whittle has passed through numerous permeations, with part of the firm still extant as an English publisher of maritime or nautical charts, Imray, Laurie, Norie and Wilson Ltd. The firm remains the oldest surviving chart publisher in Europe.
1573 Abraham Ortelius Antique Map Italy, Sardinia - Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : Italiae Novissima Descriptio Avctore Jacobo Castaldo Pedemontano Descriptio
- Ref #: 35675
- Size: 22in x 16in (560mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1573
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map of Italy was published in the 1573 Latin edition of Abraham Ortelius Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
There was only a total of 40 maps of Italy published by Ortelius in this edition of Theatrum.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 16in (560mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 14 1/2in (520mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom section of centerfold re-joined without loss
Background:
A beautiful example of Ortelius' map of Italy, the first of two states showing 'modern' Italy, as opposed to the similar map of ancient Italy Ortelius included in his Parergon, and encompasses the entirety of the Italian peninsula, as well as Corsica, parts of Sardinia and Sicily, and adjoining sections of France, Istria and Dalmatia (modern Croatia), Albania, and Serbia. Principal towns and cities are picked out in red, and the rest of the map is beautifully ornamented in full hand colour. Rivers, mountains, and lakes are shown pictorially, and the waters of the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic Seas are populated by sailing ships and sea monsters, including a Triton and a Nereid embracing. The title is enclosed in a decorative strapwork cartouche at top right, a scale at bottom right is surmounted by a crouching Siren, and the cardinal points are emblazoned on banderoles.
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map, Champagne Region of France
- Title : Champagne...Comitatus Campania
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26134
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Champagne by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, blue, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map, Champagne Region of France
1638 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Alsace Region, France
- Title : Alsatia inferior..Per Gerardam Mercatorem Cum privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1638
- Ref #: 92839
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Alsace by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1638 German edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Alsace is a cultural and historical region in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland.
As in much of Europe, the prosperity of Alsace came to an end in the 14th century by a series of harsh winters, bad harvests, and the Black Death. These hardships were blamed on Jews, leading to the pogroms of 1336 and 1339. In 1349, Jews of Alsace were accused of poisoning the wells with plague, leading to the massacre of thousands of Jews during the Strasbourg pogrom. Jews were subsequently forbidden to settle in the town. An additional natural disaster was the Rhine rift earthquake of 1356, one of Europes worst which made ruins of Basel. Prosperity returned to Alsace under Habsburg administration during the Renaissance.
Holy Roman Empire central power had begun to decline following years of imperial adventures in Italian lands, often ceding hegemony in Western Europe to France, which had long since centralized power. France began an aggressive policy of expanding eastward, first to the rivers Rhône and Meuse, and when those borders were reached, aiming for the Rhine. In 1299, the French proposed a marriage alliance between Philip IV of Frances sister Blanche and Albert I of Germanys son Rudolf, with Alsace to be the dowry; however, the deal never came off. In 1307, the town of Belfort was first chartered by the Counts of Montbéliard. During the next century, France was to be militarily shattered by the Hundred Years War, which prevented for a time any further tendencies in this direction. After the conclusion of the war, France was again free to pursue its desire to reach the Rhine and in 1444 a French army appeared in Lorraine and Alsace. It took up winter quarters, demanded the submission of Metz and Strasbourg and launched an attack on Basel.
In 1469, following the Treaty of St. Omer [fr], Upper Alsace was sold by Archduke Sigismund of Austria to Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy. Although Charles was the nominal landlord, taxes were paid to Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor. The latter was able to use this tax and a dynastic marriage to his advantage to gain back full control of Upper Alsace (apart from the free towns, but including Belfort) in 1477 when it became part of the demesne of the Habsburg family, who were also rulers of the empire. The town of Mulhouse joined the Swiss Confederation in 1515, where it was to remain until 1798.
By the time of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century, Strasbourg was a prosperous community, and its inhabitants accepted Protestantism in 1523. Martin Bucer was a prominent Protestant reformer in the region. His efforts were countered by the Roman Catholic Habsburgs who tried to eradicate heresy in Upper Alsace. As a result, Alsace was transformed into a mosaic of Catholic and Protestant territories. On the other hand, Mömpelgard (Montbéliard) to the southwest of Alsace, belonging to the Counts of Württemberg since 1397, remained a Protestant enclave in France until 1793.
This situation prevailed until 1639, when most of Alsace was conquered by France to keep it out of the hands of the Spanish Habsburgs, who by secret treaty in 1617 had gained a clear road to their valuable and rebellious possessions in the Spanish Netherlands, the Spanish Road. Beset by enemies and seeking to gain a free hand in Hungary, the Habsburgs sold their Sundgau territory (mostly in Upper Alsace) to France in 1646, which had occupied it, for the sum of 1.2 million Thalers. When hostilities were concluded in 1648 with the Treaty of Westphalia, most of Alsace was recognized as part of France, although some towns remained independent. The treaty stipulations regarding Alsace were complex. Although the French king gained sovereignty, existing rights and customs of the inhabitants were largely preserved. France continued to maintain its customs border along the Vosges mountains where it had been, leaving Alsace more economically oriented to neighbouring German-speaking lands. The German language remained in use in local administration, in schools, and at the (Lutheran) University of Strasbourg, which continued to draw students from other German-speaking lands. The 1685 Edict of Fontainebleau, by which the French king ordered the suppression of French Protestantism, was not applied in Alsace. France did endeavour to promote Catholicism. Strasbourg Cathedral, for example, which had been Lutheran from 1524 to 1681, was returned to the Catholic Church. However, compared to the rest of France, Alsace enjoyed a climate of religious tolerance.
France consolidated its hold with the 1679 Treaties of Nijmegen, which brought most remaining towns under its control. France seized Strasbourg in 1681 in an unprovoked action. These territorial changes were recognised in the 1697 Treaty of Ryswick that ended the War of the Grand Alliance.
The year 1789 brought the French Revolution and with it the first division of Alsace into the départements of Haut- and Bas-Rhin. Alsatians played an active role in the French Revolution. On 21 July 1789, after receiving news of the Storming of the Bastille in Paris, a crowd of people stormed the Strasbourg city hall, forcing the city administrators to flee and putting symbolically an end to the feudal system in Alsace. In 1792, Rouget de Lisle composed in Strasbourg the Revolutionary marching song La Marseillaise (as Marching song for the Army of the Rhine), which later became the anthem of France. La Marseillaise was played for the first time in April of that year in front of the mayor of Strasbourg Philippe-Frédéric de Dietrich. Some of the most famous generals of the French Revolution also came from Alsace, notably Kellermann, the victor of Valmy, Kléber, who led the armies of the French Republic in Vendée and Westermann, who also fought in the Vendée.
At the same time, some Alsatians were in opposition to the Jacobins and sympathetic to the restoration of the monarchy pursued by the invading forces of Austria and Prussia who sought to crush the nascent revolutionary republic. Many of the residents of the Sundgau made pilgrimages to places like Mariastein Abbey, near Basel, in Switzerland, for baptisms and weddings. When the French Revolutionary Army of the Rhine was victorious, tens of thousands fled east before it. When they were later permitted to return (in some cases not until 1799), it was often to find that their lands and homes had been confiscated. These conditions led to emigration by hundreds of families to newly vacant lands in the Russian Empire in 1803–4 and again in 1808. A poignant retelling of this event based on what Goethe had personally witnessed can be found in his long poem Hermann and Dorothea.
In response to the hundred day restoration of Napoleon I of France in 1815, Alsace along with other frontier provinces of France was occupied by foreign forces from 1815 to 1818, including over 280,000 soldiers and 90,000 horses in Bas-Rhin alone. This had grave effects on trade and the economy of the region since former overland trade routes were switched to newly opened Mediterranean and Atlantic seaports.
The population grew rapidly, from 800,000 in 1814 to 914,000 in 1830 and 1,067,000 in 1846. The combination of economic and demographic factors led to hunger, housing shortages and a lack of work for young people. Thus, it is not surprising that people left Alsace, not only for Paris – where the Alsatian community grew in numbers, with famous members such as Baron Haussmann – but also for more distant places like Russia and the Austrian Empire, to take advantage of the new opportunities offered there: Austria had conquered lands in Eastern Europe from the Ottoman Empire and offered generous terms to colonists as a way of consolidating its hold on the new territories. Many Alsatians also began to sail to the United States, settling in many areas from 1820 to 1850. In 1843 and 1844, sailing ships bringing immigrant families from Alsace arrived at the port of New York. Some settled in Texas and Illinois, many to farm or to seek success in commercial ventures: for example, the sailing ships Sully (in May 1843) and Iowa (in June 1844) brought families who set up homes in northern Illinois and northern Indiana. Some Alsatian immigrants were noted for their roles in 19th-century American economic development. Others ventured to Canada to settle in southwestern Ontario, notably Waterloo County.
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
Antique Map
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93508
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper plate engraved antique landmark 1st edition map of the NE region of North America, the original colonial states from Virginia to New England, was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas
A magnificent early map of NE North America published only 19 years after the landing of the Pilgrims at Plymouth Rock, Massachusetts.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 384mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning, old archival tape on verso
Background:
This influential map is derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. Enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, it carries de Laets narrative on the reverse. De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the names Manbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam. The nomenclature is virtually identical, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630s the families of Blaeu and Hondius - Jansson of ten produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, the latter relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, this one first published in 1636, the second edition was published in 1647 renamed Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova within a new square cartouche. State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden)
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map View of Wesel North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany
- Title : Hermannus Hammelman Wesalia in Ducatu Cliuensi
- Size: 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 81068-1
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hnd coloured antique map, plan, a birds eye view of city of Wesel in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, pink, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (480mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Wesel is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel district.
The city originated from a Franconian manor that was first recorded in the 8th century. In the 12th century, the Duke of Clèves took possession of Wesel. The city became a member of the Hanseatic League during the 15th century. Wesel was second only to Cologne in the lower Rhine region as an entrepôt. It was an important commercial centre: a clearing station for the trans-shipment and trading of goods.
In 1590 the Spanish captured Wesel after a four-year siege. The city changed hands between the Dutch and Spanish several times during the Eighty Years War. In 1672 a French force under Louis II de Bourbon, Prince de Condé captured the city. Wesel was inherited by the Hohenzollerns of the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1609 but they were unable to take control of Wesel until the Treaty of Nijmegen in 1678. Although the city had been heavily fortified the Prussians evacuated the city during the Seven Years War and it was occupied by the French. It was returned to Prussia at the end of the war. Friedrich Wilhelm von Dossow was the Prussian Governor of Wesel during the 18th century. Wesel was ceded to the French in 1805 under the treaty of Schönbrunn. The French heavily fortified the city constructing a rectangular fort called the Citadelle Napoleon at Büderich and the Citadelle Bonaparte on an island in the Rhine off Wesel. Though blockaded by the Allies in 1813 the city remained in French hands until after the Battle of Waterloo. After the Napoleonic Wars of the early 19th century, the city became part of the Prussian Rhine Province and the Citadelle Napoleon was renamed Fort Blücher.
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Birds Eye Views Chartres & Chateaudu Loire France
- Title : Autricum, Prolemeo in Gallia Lugdunensis Urbs; vulgo, cum Villa nouano, Chartres / Chasteaudunum, Comitatus vulgo Dunoys in Gallia Oppidum primorium
- Size: 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 30267
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique print, a birds eye view of cities of Chartres and Chateaudu , in Loire, France was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarumintended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius\'s master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Chartres is a commune and capital of the Eure-et-Loir department in France. It is located about 90 km (56 mi) southwest of Paris.
Chartres was in Gaul one of the principal towns of the Carnutes, a Celtic tribe. In the Gallo-Roman period, it was called Autricum, name derived from the river Autura (Eure), and afterwards civitas Carnutum, city of the Carnutes, from which Chartres got its name. The city was burned by the Normans in 858, and unsuccessfully besieged by them in 911.
During the Middle Ages, it was the most important town of the Beauce. It gave its name to a county which was held by the counts of Blois, and the counts of Champagne, and afterwards by the House of Châtillon, a member of which sold it to the Crown in 1286.
In 1417, during the Hundred Years War, Chartres fell into the hands of the English, from whom it was recovered in 1432.
In 1528, it was raised to the rank of a duchy by Francis I.
In 1568, during the Wars of Religion, Chartres was unsuccessfully besieged by the Huguenot leader, the Prince of Condé. It was finally taken by the royal troops of Henry IV on 19 April 1591. On Sunday, 27 February 1594, the cathedral of Chartres was the site of the coronation of Henry IV after he converted to the Catholic faith, the only king of France whose coronation ceremony was not performed in Reims.
In 1674, Louis XIV raised Chartres from a duchy to a duchy peerage in favor of his nephew, Duke Philippe II of Orléans. The title of Duke of Chartres was hereditary in the House of Orléans, and given to the eldest son of the Duke of Orléans.
In the 1870-1871 Franco-Prussian War, Chartres was seized by the Germans on 2 October 1870, and continued during the rest of the war to be an important centre of operations.
Chateaudun is located about 45 km northwest of Orléans, and about 50 km south-southwest of Chartres. It lies on the river Loir, a tributary of the Sarthe.