Maps (791)
1693 Slezer Antique Print View of the Town of Alloa on Firth of Forth Scotland
- Title : The Prospect of the House & of the Town of Alloua
- Ref : 24947
- Size: 18 ½in x 14 ½in (470mm x 370mm)
- Date : 1693
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original important antique print a view of the town of Alloa in Clackmannanshire in eastern Scotland on the Firth of Forth, was published in the first edition of John Slezer's 'Theatrum Scotiae', 1693.
This is an important and rare print as Slezer s Theatrum Scotiae is one of the earliest records of early Scottish towns. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 ½in x 14 ½in (470mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 16 ½in x 11 in (420mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
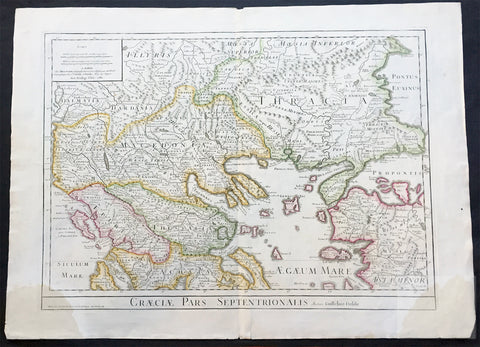
1780 Large Delisle Antique Map of Nothern Greece, Macedonia, Thracia, Turkey
- Title : Graeciae Pars Septentrionalis Par Guill. Delisle.....1780
- Ref #: 20404
- Size: 30in x 22in (765mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of Northern Greece, Macedonia, Thracia by Guillaume Delisle was engraved by Philip Bauche and published in 1780 - the date is engraved in the scale cartouche (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Very heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 22in (765mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 18 1/2in (660mm x 470mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light browning to bottom left & right margin corners. Three reapirs to margins, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
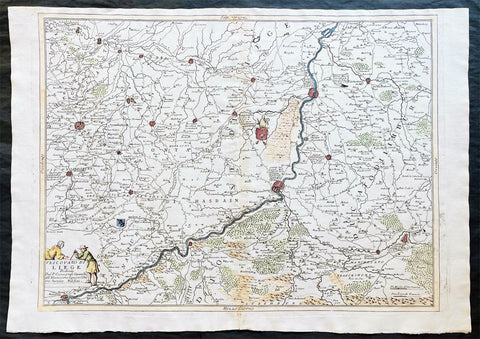
1691 Coronelli Large Antique Map of The Liege Region of Belgium - Maastricht
- Title : Vescovato di Leige
- Ref #: 16271
- Size: 27in x 19 1/2in (685mm x 495mm)
- Date : 1691
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description
This large, fine, scarce & beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Liege Region of Belgium - centering on the Meusa River and the cities of Liege, Maastricht, Namur & Tienen - was published by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli (1650-1718) in 1691.
Coronelli was one of the finest engravers & cartographers of any era, producing some of the most stunning work ever seen. This is evident in this beautiful map. He was a master craftsman with an eye for detail. You can feel the uncompromising accuracy & passion in his work when you study his maps & globes. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 19 1/2in (685mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 19in (620mm x 485mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold
Verso: - 3 small repairs along centerfold
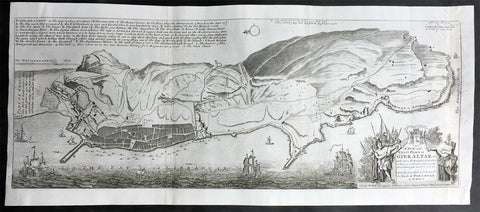
1728 Hermann Moll Large Antique Map and View of Gibraltar - 2nd Spanish Seige
- Title : A New and Exact plan of Gibraltar with all its fortifications as they are at present….
- Ref #: 40838
- Size: 25in x 11in (635mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1727
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map and view of the second Spanish siege of Gibraltar by Herman Moll was published in 1727.
Although undated, the legend at the top left of the map, gives an in-depth explanation to the map including no. 5 that refers to 'Place where at this time Barracks building for a Regiment Ap: 15. 1726. 6. The Great Church.', while the dedication is to David Colyear, 1st Earl of Portmore, Governor of Gibraltar. The plan was presumably engraved either in anticipation of, or during the second Spanish siege; Portmore was in England when the siege began, but sailed there with a relief force, arriving on 1st May, 1727. British command of the sea, coupled with the natural features of the Rock of Gibraltar on the landward side of the peninsula, combined to thwart Spanish ambition, and the siege petered to an end in 1728, with the garrison never seriously troubled.
Background: Gibraltar became part of the Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania following the collapse of the Roman Empire and came under Muslim Moorish rule in 711 AD. It was permanently settled for the first time by the Moors and was renamed Jebel Tariq – the Mount of Tariq, later corrupted into Gibraltar. The Christian Crown of Castile annexed it in 1309, lost it again to the Moors in 1333 and finally regained it in 1462. Gibraltar became part of the unified Kingdom of Spain and remained under Spanish rule until 1704. It was captured during the War of the Spanish Succession by an Anglo-Dutch fleet in the name of Charles VI of Austria, the Habsburg contender to the Spanish throne. At the war's end, Spain ceded the territory to Britain under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht of 1713.
Spain tried to regain control of Gibraltar, which Britain had declared a Crown colony, through military, diplomatic and economic pressure. Gibraltar was besieged and heavily bombarded during three wars between Britain and Spain but the attacks were repulsed on each occasion. By the end of the last siege, in the late 18th century, Gibraltar had faced fourteen sieges in 500 years. In the years after Trafalgar, Gibraltar became a major base in the Peninsular War. The colony grew rapidly during the 19th and early 20th centuries, becoming one of Britain's most important possessions in the Mediterranean. It was a key stopping point for vessels en route to India via the Suez Canal. A large British naval base was constructed there at great expense at the end of the 19th century and became the backbone of Gibraltar's economy.
British control of Gibraltar enabled the Allies to control the entrance to the Mediterranean during the Second World War. It was attacked on several occasions by German, Italian and Vichy French forces, though without causing much damage. The Spanish dictator General Francisco Franco declined to join a Nazi plan to occupy Gibraltar but revived Spain's claim to the territory after the war. As the territorial dispute intensified, Spain closed its border with Gibraltar between 1969 and 1985 and communications links were severed. Spain's position was supported by Latin American countries but was rejected by Britain and the Gibraltarians themselves, who vigorously asserted their right to self-determination. Discussions of Gibraltar's status have continued between Britain and Spain but have not reached any conclusion.
Shortly after Gibraltar's recapture, King Henry IV of Castile declared it Crown property and reinstituted the special privileges which his predecessor had granted during the previous period of Christian rule. Four years after visiting Gibraltar in 1463, he was overthrown by the Spanish nobility and clergy. His half-brother Alfonso was declared king and rewarded Medina Sidonia for his support with the lordship of Gibraltar. The existing governor, a loyalist of the deposed Henry IV, refused to surrender Gibraltar to Medina Sidonia. After a fifteen-month siege from April 1466 to July 1467, Medina Sidonia took control of the town. He died the following year but his son Enrique was confirmed as lord of Gibraltar by the reinstated Henry IV in 1469. In 1474 the new Duke of Medina Sidonia sold Gibraltar to a group of Jewish conversos from Cordova and Seville led by Pedro de Herrera in exchange for maintaining the garrison of the town for two years, after which time the 4,350 conversos were expelled by the Duke. His status was further enhanced by Isabella I of Castile in 1478 with the granting of the Marquisate of Gibraltar.
On 2 January 1492, after five years of war, the Moorish emirate in Spain came to an end with the Catholic Monarchs' capture of Granada. The Jews of Gibraltar were, like those elsewhere in the kingdom, expelled from Spain by order of the monarchs in March that year. Gibraltar was used by Medina Sidonia as a base for the Spanish capture of Melilla in North Africa in 1497. Two years later the Muslims of Granada were ordered to convert to Christianity or leave. Those that did not convert left for North Africa, some of them travelling via Gibraltar.
Gibraltar became Crown property again in 1501 at the order of Isabella and the following year it received a new set of royal arms, which is still used by modern Gibraltar, replacing those of Medina Sidonia. In the Royal Warrant accompanying the arms, Isabella highlighted Gibraltar's importance as "the key between these our kingdoms in the Eastern and Western Seas [the Mediterranean and Atlantic]". The metaphor was represented on the royal arms by a golden key hanging from the front gate of a battlemented fortress. The warrant charged all future Spanish monarchs to "hold and retain the said City for themselves and in their own possession; and that no alienation of it, nor any part of it, nor its jurisdiction ... shall ever be made from the Crown of Castile."
At this point in history, "Gibraltar" meant not just the peninsula but the entire surrounding area including the land on which the towns of La Línea de la Concepción, San Roque, Los Barrios and Algeciras now stand. To the east, Gibraltar was bounded by the Guadiaro River, and its northern boundaries lay in the vicinity of Castellar de la Frontera, Jimena de la Frontera, Alcalá de los Gazules, Medina-Sidonia and Tarifa. From the 16th century, the modern meaning of the name came to be adopted – specifically referring only to the town of Gibraltar and the peninsula on which it stands.
Under Spanish Crown rule, the town of Gibraltar fell into severe decline. The end of Muslim rule in Spain and the Christian capture of the southern ports considerably decreased the peninsula's strategic value. It derived some minor economic value from tuna-fishing and wine-producing industries but its usefulness as a fortress was now limited. It was effectively reduced to the status of an unremarkable stronghold on a rocky promontory and Marbella replaced it as the principal Spanish port in the region.
Gibraltar's inhospitable terrain made it an unpopular place to live. To boost the population, convicts from the kingdom of Granada were offered the possibility of serving their sentence in the Gibraltar garrison as an alternative to prison. Despite its apparent unattractiveness, Juan Alfonso de Guzmán, third Duke of Medina Sidonia, nonetheless sought to regain control of the town. In September 1506, following Isabella's death, he laid siege in the expectation that the gates would quickly be opened to his forces. This did not happen, and after a fruitless four-month blockade he gave up the attempt. Gibraltar received the title of "Most Loyal" from the Spanish crown in recognition of its faithfulness (Ref: M&B, Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 25in x 11in (635mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 11in (635mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small loss to the very right figure in the title cartouche not affecting the map, light creasing along folds as issued
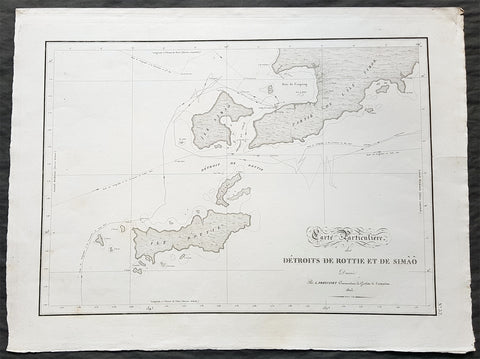
1803 Louis Freycinet Antique Map of The Islands of Timor, Samau & Rote Indonesia
- Title : Carte Particuliere des Detroits De Rottie et de Simao...L Freycienet...le Casuarina 1803..Lambert Sculp.
- Ref #: 42014
- Size: 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1803
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This magnificent large original copper-plate engraved antique map of the islands of Samau, Rote and the southern part of Timor, including the bay and town of Kupang, by Lieutenant Louis Freycinet, in command of the ship Casuarina in 1803, was engraved by Anton Lambart and was published in the 1807 1st edition of François Pérons, Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes (‘Voyage of Discovery to the Southern Lands in three volumes, Paris, 1807–1816.
Also illustrates the tracks of the ships Geographe, the Naturaliste from the earlier voyages in 1801, and the Casuarina tracks of 1803.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15in (545mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nicolas Thomas Baudin 1754 – 1803 was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer.
The Baudin expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland (Australia). The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
Napoléon Bonaparte, as First Consul, formally approved the expedition to the coasts of New Holland, after receiving a delegation consisting of Baudin and eminent members of the Institut National des Sciences et Arts on 25 March 1800. The explicit purpose of the voyage was to be ‘bservation and research relating to Geography and Natural History.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of the continent until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. During their exploration here they lost a longboat and a sailor, Assistant Helmsman Timothée Vasse. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by \'t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted the Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
1856 A H Dufour Very Large Antique Political map of Europe - Mountains
- Title : Carte Generale L Europe Actuelle Dressee A H Dufour Gravee CH Dyonnet..1856
- Ref #: 61020
- Size: 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large, magnificent hand coloured original copper plate antique map of the political borders of Europe in the mid 19th century - with a list of European mountains at the bottom of the map - by Adolphe Hippolyte Dufour was engraved by Charles Dyonnet in 1856 - dated in the title - for Dufours 1860 edition of his monumental elephant folio Atlas Physique, Historique et Politique Geographie Moderne published by Pauline Et La Chevalier, Paris.
The 19th century French cartographer Auguste-Henri Dufour began publishing the dramatic elephant folio Atlas Universel, also occasionally titled Grand Atlas Universal, around 1855. Several editions appeared between its initial publication in the 1850s and a final run c. 1870. The 1863 and 1864 editions in particular are highly desirable among collectors because the United States and North America maps illustrate the proposed, but unrealized, state of Corona (roughly modern day Utah). The atlas contained roughly 40 maps, most of which were engraved by Louis Antoine (the maps) and Deletre (typography) under the supervision of Charles Dyonnet, official engraver of the Depot de la Marine. The Atlas Universal was published in Paris and edited by the firm of Paulin et le Chevalier, 60 Rue Richelieu.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charles Dyonnet 1822 - 1880 was an extremely active Paris based engraver working in the mid to late 19th century. From his offices at 220 Rue St. Jacques, Paris, Dyonnet engraved numerous maps for many of the most prominent 19th French cartographic publishers including Vuillemin, Dufour, Fremin and Duvotenay. From 1850-1861, he held the coveted position of Graveur du Dépot de la Marine, and in this position engraved numerous French naval and military maps. Dyonnet had a detail oriented and aesthetically minded hand and is responsible from some of the most beautiful French maps to emerge during the 19th century. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
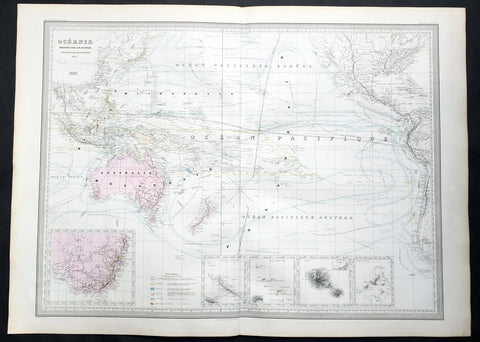
1857 A H Dufour Very Large Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand & South Pacific
- Title : Oceanie Dressee par A H Dufour Gravee CH Dyonnet..1857
- Ref #: 61026
- Size: 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
- Date : 1857
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large, magnificent hand coloured original copper plate antique map of Australia, New Zealand, Oceania & The Pacific, showing the Ocean Currents and 5 inset maps (NSW & Victoria Australia, Gambier Islands, Tahiti, Marquesas Isles & New Caledonia) by Adolphe Hippolyte Dufour was engraved by Charles Dyonnet in 1856 - dated in the title - for Dufours 1860 edition of his monumental elephant folio Atlas Physique, Historique et Politique Geographie Moderne published by Pauline Et La Chevalier, Paris.
The 19th century French cartographer Auguste-Henri Dufour began publishing the dramatic elephant folio Atlas Universel, also occasionally titled Grand Atlas Universal, around 1855. Several editions appeared between its initial publication in the 1850s and a final run c. 1870. The 1863 and 1864 editions in particular are highly desirable among collectors because the United States and North America maps illustrate the proposed, but unrealized, state of Corona (roughly modern day Utah). The atlas contained roughly 40 maps, most of which were engraved by Louis Antoine (the maps) and Deletre (typography) under the supervision of Charles Dyonnet, official engraver of the Depot de la Marine. The Atlas Universal was published in Paris and edited by the firm of Paulin et le Chevalier, 60 Rue Richelieu.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charles Dyonnet 1822 - 1880 was an extremely active Paris based engraver working in the mid to late 19th century. From his offices at 220 Rue St. Jacques, Paris, Dyonnet engraved numerous maps for many of the most prominent 19th French cartographic publishers including Vuillemin, Dufour, Fremin and Duvotenay. From 1850-1861, he held the coveted position of Graveur du Dépot de la Marine, and in this position engraved numerous French naval and military maps. Dyonnet had a detail oriented and aesthetically minded hand and is responsible from some of the most beautiful French maps to emerge during the 19th century. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
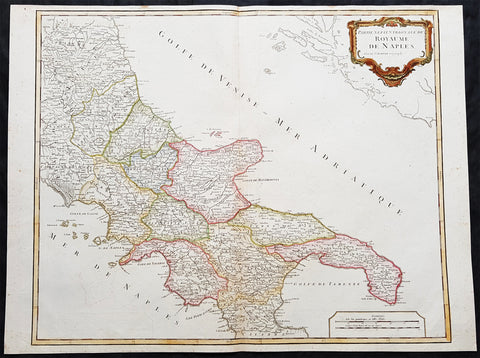
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map Southern Italy Mezzogiorno, 2 Sicilies
- Title : Partie Septentrionale Du Royaume De Naples
- Size: 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 92771
Description:
This magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Southern Italy in the mid to late 18th century by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 19 1/2in (620mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Southern Italy or Mezzogiorno is a macroregion of Italy traditionally encompassing the territories of the former Kingdom of the two Sicilies (all the southern section of the Italian Peninsula and Sicily), with the frequent addition of the island of Sardinia.
In 1442, however, Alfonso V conquered the Kingdom of Naples and unified Sicily and Naples once again as dependencies of the Crown of Aragon. At his death in 1458, the kingdom was again separated and Naples was inherited by Ferrante, Alfonso\'s illegitimate son. When Ferrante died in 1494, Charles VIII of France invaded Italy, using the Angevin claim to the throne of Naples, which his father had inherited on the death of King René\'s nephew in 1481, as a pretext, thus beginning the Italian Wars. Charles VIII expelled Alfonso II of Naples from Naples in 1495, but was soon forced to withdraw due to the support of Ferdinand II of Aragon for his cousin, Alfonso IIs son Ferrantino. Ferrantino was restored to the throne, but died in 1496, and was succeeded by his uncle, Frederick IV. The French, however, did not give up their claim, and in 1501 agreed to a partition of the kingdom with Ferdinand of Aragon, who abandoned his cousin King Frederick. The deal soon fell through, however, and the Crown of Aragon and France resumed their war over the kingdom, ultimately resulting in an Aragonese victory leaving Ferdinand in control of the kingdom by 1504.
The kingdom continued to be a focus of dispute between France and Spain for the next several decades, but French efforts to gain control of it became feebler as the decades went on, and Spanish control was never genuinely endangered. The French finally abandoned their claims to the kingdom by the Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis in 1559. With the Treaty of London (1557) the new client state of Stato dei Presidi (State of Presidi) was established and governed directly by Spain, as part of the Kingdom of Naples.
The administration of the Kingdom of Naples and Sicily, as well as the Duchy of Milan, was then run by the Council of Italy, while Sardinia kept being an integral part of the Council of Aragon until the first years of the XVIII° century, when it was ceded to Austria and eventually Savoy.
After the War of the Spanish Succession in the early 18th century, possession of the kingdom again changed hands. Under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, Naples was given to Charles VI, the Holy Roman Emperor. He also gained control of Sicily in 1720, but Austrian rule did not last long. Both Naples and Sicily were conquered by a Spanish army during the War of the Polish Succession in 1734, and Charles, Duke of Parma, a younger son of King Philip V of Spain was installed as King of Naples and Sicily from 1735. When Charles inherited the Spanish throne from his older half-brother in 1759, he left Naples and Sicily to his younger son, Ferdinand IV. Despite the two kingdoms being in a personal union under the House of Bourbon from 1735 onwards, they remained constitutionally separated.
Being a member of the House of Bourbon, King Ferdinand IV was a natural opponent of the French Revolution and Napoleon. In January 1799, Napoleon Bonaparte, in the name of the French Republic, captured Naples and proclaimed the Parthenopaean Republic, a French client state, as successor to the kingdom. King Ferdinand fled from Naples to Sicily until June of that year. In 1806, Bonaparte, by then French Emperor, again dethroned King Ferdinand and appointed his brother, Joseph Bonaparte, as King of Naples. In the Edict of Bayonne of 1808, Napoleon removed Joseph to Spain and appointed his brother-in-law, Joachim Murat, as King of the Two Sicilies, though this meant control only of the mainland portion of the kingdom. Throughout this Napoleonic interruption, King Ferdinand remained in Sicily, with Palermo as his capital.
After Napoleon\'s defeat, King Ferdinand IV was restored by the Congress of Vienna of 1815 as Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies. He established a concordat with the Papal States, which previously had a claim to the land. There were several rebellions on the island of Sicily against the King Ferdinand II but the end of the kingdom was only brought about by the Expedition of the Thousand in 1860, led by Garibaldi, an icon of the Italian unification, with the support of the House of Savoy and their Kingdom of Sardinia. The expedition resulted in a striking series of defeats for the Sicilian armies against the growing troops of Garibaldi. After the capture of Palermo and Sicily, he disembarked in Calabria and moved towards Naples, while in the meantime the Piedmontese also invaded the Kingdom from the Marche. The last battles fought were that of the Volturnus in 1860 and the siege of Gaeta, where King Francis II had sought shelter, hoping for French help, which never came. The last towns to resist Garibaldi\'s expedition were Messina (which capitulated on 13 March 1861) and Civitella del Tronto (which capitulated on 20 March 1861). The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was dissolved and annexed to the new Kingdom of Italy, founded in the same year. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
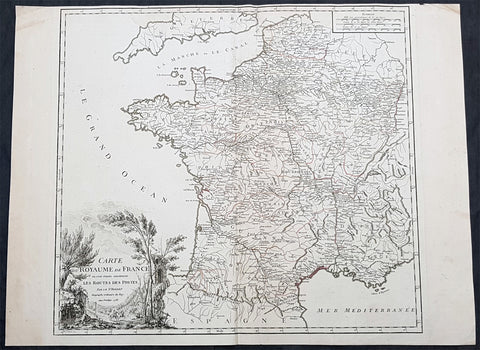
1758 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of France and Postal Roads
- Title : Carte Du Royame de France ou sont tracees exactement Les Routes Des Postes...1758
- Size: 25 1/2in x 19 1/2in (650mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1758
- Ref #: 15819
Description:
This large original hand coloured, antique map of France and the postal roads of the day was engraved in 1758 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and published by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal, Paris 1757.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 19 1/2in (650mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Carolingian dynasty ruled France until 987, when Hugh Capet, Duke of France and Count of Paris, was crowned King of the Franks. His descendants—the Capetians, the House of Valois, and the House of Bourbon—progressively unified the country through wars and dynastic inheritance into the Kingdom of France, which was fully declared in 1190 by Philip II Augustus. The French nobility played a prominent role in most Crusades in order to restore Christian access to the Holy Land. French knights made up the bulk of the steady flow of reinforcements throughout the two-hundred-year span of the Crusades, in such a fashion that the Arabs uniformly referred to the crusaders as Franj caring little whether they really came from France. The French Crusaders also imported the French language into the Levant, making French the base of the lingua franca (litt. Frankish language) of the Crusader states. French knights also made up the majority in both the Hospital and the Temple orders. The latter, in particular, held numerous properties throughout France and by the 13th century were the principal bankers for the French crown, until Philip IV annihilated the order in 1307. The Albigensian Crusade was launched in 1209 to eliminate the heretical Cathars in the southwestern area of modern-day France. In the end, the Cathars were exterminated and the autonomous County of Toulouse was annexed into the crown lands of France. Later kings expanded their domain to cover over half of modern continental France, including most of the north, centre and west of France. Meanwhile, the royal authority became more and more assertive, centred on a hierarchically conceived society distinguishing nobility, clergy, and commoners.
From the 11th century, the House of Plantagenet, the rulers of the County of Anjou, succeeded in establishing its dominion over the surrounding provinces of Maine and Touraine, then progressively built an empire that spanned from England to the Pyrenees and covering half of modern France. Tensions between the kingdom of France and the Plantagenet empire would last a hundred years, until Philip Augustus of France conquered between 1202 and 1214 most of the continental possessions of the empire, leaving England and Aquitaine to the Plantagenets. Following the Battle of Bouvines, the Angevin court retreated to England, but persistent Capetian–Plantagenet rivalry would paved the way for another conflict.
Charles IV the Fair died without an heir in 1328. Under the rules of the Salic law the crown of France could not pass to a woman nor could the line of kingship pass through the female line. Accordingly, the crown passed to Philip of Valois, a cousin of Charles, rather than through the female line to Charles nephew, Edward of Plantagenet, who would soon become Edward III of England. During the reign of Philip of Valois, the French monarchy reached the height of its medieval power. Philips seat on the throne was contested by Edward III of England and in 1337, on the eve of the first wave of the Black Death, England and France went to war in what would become known as the Hundred Years War. The exact boundaries changed greatly with time, but French landholdings of the English Kings remained extensive for decades. With charismatic leaders, such as Joan of Arc and La Hire, strong French counterattacks won back English continental territories. Like the rest of Europe, France was struck by the Black Death; half of the 17 million population of France died.
The French Renaissance saw a spectacular cultural development and the first standardisation of the French language, which would become the official language of France and the language of Europes aristocracy. It also saw a long set of wars, known as the Italian Wars, between France and the House of Habsburg. French explorers, such as Jacques Cartier or Samuel de Champlain, claimed lands in the Americas for France, paving the way for the expansion of the First French colonial empire. The rise of Protestantism in Europe led France to a civil war known as the French Wars of Religion, where, in the most notorious incident, thousands of Huguenots were murdered in the St. Bartholomews Day massacre of 1572. The Wars of Religion were ended by Henry IVs Edict of Nantes, which granted some freedom of religion to the Huguenots. Spanish troops, the terror of Western Europe, assisted the Catholic side during the Wars of Religion in 1589–1594, and invaded northern France in 1597; after some skirmishing in the 1620s and 1630s, Spain and France returned to all-out war between 1635 and 1659. The war cost France 300,000 casualties.
Under Louis XIII, the energetic Cardinal Richelieu promoted the centralisation of the state and reinforced the royal power by disarming domestic power holders in the 1620s. He systematically destroyed castles of defiant lords and denounced the use of private violence (dueling, carrying weapons, and maintaining private army). By the end of 1620s, Richelieu established the royal monopoly of force as the doctrine. During Louis XIVs minority and the regency of Queen Anne and Cardinal Mazarin, a period of trouble known as the Fronde occurred in France. This rebellion was driven by the great feudal lords and sovereign courts as a reaction to the rise of royal absolute power in France.
The monarchy reached its peak during the 17th century and the reign of Louis XIV. By turning powerful feudal lords into courtiers at the Palace of Versailles, Louis XIVs personal power became unchallenged. Remembered for his numerous wars, he made France the leading European power. France became the most populous country in Europe and had tremendous influence over European politics, economy, and culture. French became the most-used language in diplomacy, science, literature and international affairs, and remained so until the 20th century. France obtained many overseas possessions in the Americas, Africa and Asia. Louis XIV also revoked the Edict of Nantes, forcing thousands of Huguenots into exile.
Under Louis XV, Louis XIVs great-grandson, France lost New France and most of its Indian possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years War (1756–63). Its European territory kept growing, however, with notable acquisitions such as Lorraine (1766) and Corsica (1770). An unpopular king, Louis XVs weak rule, his ill-advised financial, political and military decisions – as well as the debauchery of his court– discredited the monarchy, which arguably paved the way for the French Revolution 15 years after his death.
Louis XVI, Louis XVs grandson, actively supported the Americans, who were seeking their independence from Great Britain (realised in the Treaty of Paris (1783)). The financial crisis aggravated by Frances involvement in the American Revolutionary War was one of many contributing factors to the French Revolution. Much of the Enlightenment occurred in French intellectual circles, and major scientific breakthroughs and inventions, such as the discovery of oxygen (1778) and the first hot air balloon carrying passengers (1783), were achieved by French scientists. French explorers, such as Bougainville and Lapérouse, took part in the voyages of scientific exploration through maritime expeditions around the globe. The Enlightenment philosophy, in which reason is advocated as the primary source for legitimacy and authority, undermined the power of and support for the monarchy and helped pave the way for the French Revolution.
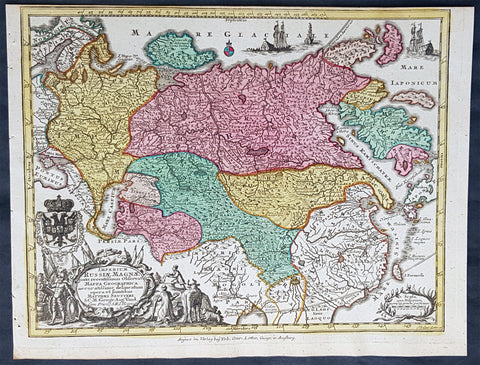
1744 Georg Mattaus Seutter Antique Map of The Russian Empire, China, Japan
- Title : Imperium Russiae Magnae........a Matth. Seutteri...T C Lotter, Geogr.
- Ref #: 93401
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Russian Empire was engraved by Tobias Lotter and was published in the 1744 edition of GM Seutters Atlas Minor Prae cipua Orbis Terrarum Imperia Regna et Provincias...., Augsburg, Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (265mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Atlas Minor was a series of beautiful maps of all parts of the world. Georg Matthäus Seutter was one of the most and important of the German cartographers of the 18th century, being appointed as the Geographer to the Imperial Court. His son, Albrecht Carl, joined Matthäus and eventually inherited the business. The maps from Atlas Minor were drawn by the two Seutters and engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotte. These maps are highly detailed and engraved with a bold hand with equally strong original hand color in the body of the map as was the 18th century German style. The cartouches were left uncolored in order to emphasize the elaborately detailed illustrations for which German maps are especially prized. These are some of the most decorative and interesting maps of the eighteenth century.
1635 Willem Hondius & Anthony van Dyck Portait of Willem Hondius son of Jodocus
Antique Map
- Title : Guilielmus Hondius, Calcographus Hagae Comitis. Ant. van Dyck pinxit, Guil. Hondius sculp
- Date : 1630-40
- Size: 9 3/4in x 7in (250mm x 180mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 91420
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print of Guillaume Hondius, was engraved by himself (Guillaume Hondius) after the famous Flemish painter Anthony van Dyck 1599 - 1641 as part of his Iconographie series of engraved portraits of famous people at the time, between 1630-40.
A wonderfully detailed and charismatic portrait, this exquisite work illustrates the technical mastery and artistic vision of Van Dyck. Guillaume Hondius' stately yet approachable expression reflects Van Dyck's refined ability to comfort and relax his subjects, resulting in a realistic and acute portrait. This piece is intriguing because the subject and the engraver are one and the same, yet the image essentially is still Van Dyck's. Guillaumine Hondius engraves himself through the eyes of Van Dyck, depicted with kind eyes, a broad nose, and a pointy chin. Hondius stands with a calm demeanor, holding up his elaborately draped garment with his left hand and gazing straight out at us.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 3/4in x 7in (250mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 9 3/4in x 7in (250mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Dark age toning
Background:
Anthony van Dyck (also spelled van Dyke) was a renowned Flemish Baroque painter born on March 22, 1599, in Antwerp, Belgium, and died on December 9, 1641, in London, England. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential portrait painters of his time, known for his elegant and refined style.
Van Dyck showed great artistic talent from a young age and began his artistic training under the guidance of Hendrick van Balen, a local painter in Antwerp. Recognizing his potential, his parents enrolled him as an apprentice with Peter Paul Rubens, the leading Flemish painter of the time. Van Dyck spent six years in Rubens' studio, absorbing the master's techniques and developing his own skills.
By the age of 19, van Dyck had already established himself as an accomplished artist and was admitted as a master to the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke. He primarily focused on religious and mythological subjects during his early years, reflecting the influence of Rubens' style. However, van Dyck soon turned his attention to portraiture, a genre that would bring him great success and recognition.
In the early 1620s, van Dyck traveled to Italy, where he spent several years studying the works of Italian Renaissance masters such as Titian and Tintoretto. This period of Italian sojourn greatly influenced his artistic style, leading to a refinement and sophistication in his portraiture. He became particularly renowned for his ability to capture the personality and character of his sitters, employing a sensitive and flattering approach.
Upon his return to Antwerp in 1627, van Dyck's reputation as a portraitist had grown significantly, attracting commissions from aristocrats, nobles, and prominent figures of the time. His portraits exuded a sense of grandeur and elegance, often featuring his subjects in elaborate costumes and settings. Van Dyck's remarkable talent for capturing the likeness and personality of his sitters earned him patrons and clients across Europe.
In 1632, van Dyck was invited to England by King Charles I, who had heard of his remarkable skill as a portrait painter. He was appointed as the court artist and granted a knighthood, becoming Sir Anthony van Dyck. During his time in England, van Dyck produced numerous portraits of the royal family, aristocracy, and influential figures of the British court. His ability to convey grace, poise, and nobility in his subjects revolutionized the art of portraiture in England.
Van Dyck's impact on English art was profound, and he played a crucial role in elevating the status of portrait painting within the art world. His influence extended beyond his lifetime, as many English portraitists were inspired by his style and approach. Van Dyck's legacy can be seen in the works of later artists such as Thomas Gainsborough, Joshua Reynolds, and Thomas Lawrence.
Despite his success, van Dyck's life was plagued by financial troubles and personal difficulties. He led a lavish lifestyle and accumulated significant debts, which he struggled to repay. Moreover, his health deteriorated in his later years, possibly due to the strain of his extensive work. Van Dyck passed away in London at the age of 42, leaving behind a rich artistic legacy.
Anthony van Dyck's mastery of portraiture, characterized by his skillful rendering of his subjects' individuality and his elegant style, has made him one of the most celebrated painters in art history. His works continue to be admired and studied, serving as a testament to his enduring influence and artistic brilliance.
Hondius, Guillaume or Willem (1598/9 - 1658/60)
Willem Hondius was one of seven children of Hendrik Hondius the Elder (1573 – c. 1649) and Sara Jansdochter. His father was one of the most important Dutch reproductive printmakers and publishers in the early 17th century. A connection with the Hondius family of cartographers in Amsterdam is possible but has not been established.
In 1636 Willem visited Danzig in Poland. In 1641 he moved there from The Hague for good. Hondius was supported at the royal court of King Władysław IV Waza. The King awarded him the title of Chalcographus privilegialus (privileged engraver) and Chalcographus Regius (Royal engraver).
He was married twice, first in 1632 in The Hague to Kornelia van den Enden, secondly in 1646 in Danzig to Anna Mackensen, daughter of the Royal Goldsmith.
In August 1651, in the wake of the Khmelnytsky Uprising, Hondius joined the army of Janusz Radziwiłł conquering Kiev. The first ever portrait of the famous Cossack leader Bohdan Khmelnytsky was engraved during this campaign.
Nothing is known of Hondius after 1652, though he may have lived until 1658.
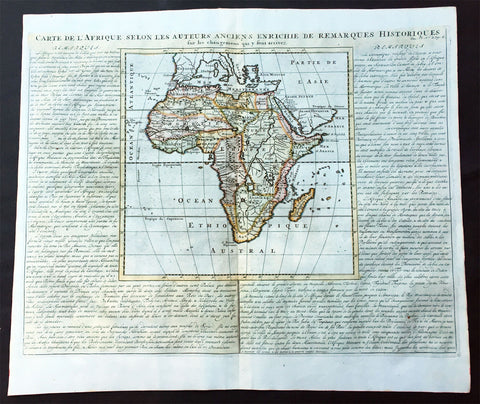
1719 Chatelain Large Old, Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Carte De L Afrique Selon Les Auteurs Anciens Enrichie de Remarques Historiques
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50628
- Size: 20 3/4in x 17 1/2in (530m x 445m)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of antique map of Africa was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 17 1/2in (530m x 445m)
Plate size: - 11in x 11in (280m x 280mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
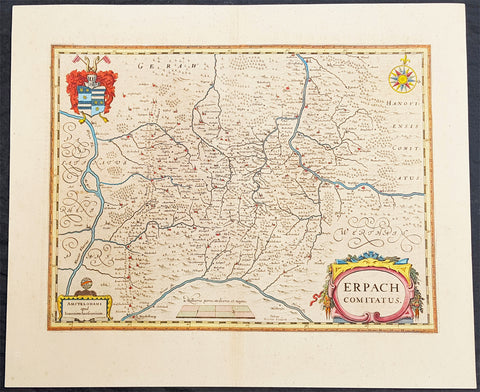
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map Erbach Hesse & Baden-Württemberg Heidelberg Germany
- Title : Erpach Comitatus
- Ref #: 50182
- Size: 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Erbach im Odenwald area in the Baden-Württemberg & Hesse regions of southern Germany, framed by the Neckar River in the south, Rhine River to the west and the Main river to the east (major towns and cities of Heidelberg, Gensheim, Worms, Miltenberg and Oldenburg) by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Erbach is a town and the district seat of the Odenwaldkreis (district) in Hesse, Germany.
Baden-Württemberg is a state in southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the border with France.
Hesseis a federal state (Land) of the Federal Republic of Germany
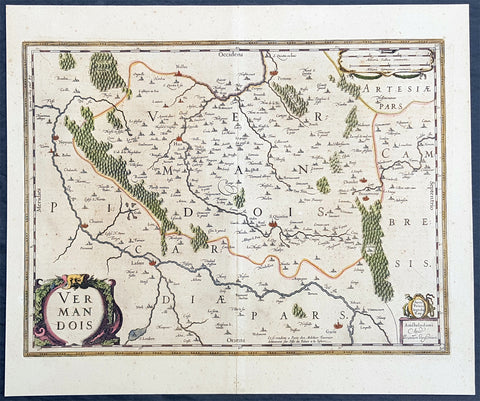
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map the County of Vermandois, Picardy, Northern France
- Title : Vermandois
- Ref #: 50236
- Size: 21 1/2in x 18in (545mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the ancient county of Vermandois now located in the Picardy region of northern France, centering on the city of St Quentin by Jan Jansson was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Vermandois was a French county that appeared in the Merovingian period. Its name derives from that of an ancient tribe, the Viromandui. In the 10th century, it was organised around two castellan domains: St Quentin (Aisne) and Péronne (Somme). In today\'s times, the Vermandois county would fall in the Picardy region of northern France.
Pepin I of Vermandois, the earliest of its hereditary counts, was descended in direct male line from the emperor Charlemagne. More famous was his grandson Herbert II (902–943), who considerably increased the territorial power of the house of Vermandois, and kept the lawful king of France, the unlucky Charles the Simple, prisoner for six years. Herbert II was son of Herbert I, lord of Péronne and St Quentin, who was killed in 902 by an assassin in the pay of Baldwin II, Count of Flanders. His successors, Albert I, Herbert III, Albert II, Otto and Herbert IV, were not as historically significant.
In 1077, the last count of the first house of Vermandois, Herbert IV, received the county of Valois through his wife. His son Eudes (II) the Insane was disinherited by the council of the Barons of France. He was lord of Saint-Simon through his wife, and the county was given to his sister Adela, whose first husband was Hugh the Great, the brother of King Philip I of France. Hugh was one of the leaders of the First Crusade, and died in 1102 at Tarsus in Cilicia. The eldest son of Hugh and Adela was count Raoul I (c. 1120–1152), who married Petronilla of Aquitaine, sister of the queen, Eleanor, and had by her three children: Raoul (Rudolph) II, the Leper (count from 1152–1167); Isabelle, who possessed from 1167 to 1183 the counties of Vermandois, Valois and Amiens conjointly with her husband, Philip, Count of Flanders; and Eleanor. By the terms of a treaty concluded in 1186 with the king, Philip Augustus, the count of Flanders kept the county of Vermandois until his death, in 1191. At this date, a new arrangement gave Eleanor (d. 1213) a life interest in the eastern part of Vermandois, together with the title of countess of St Quentin, and the king entered immediately into possession of Péronne and its dependencies
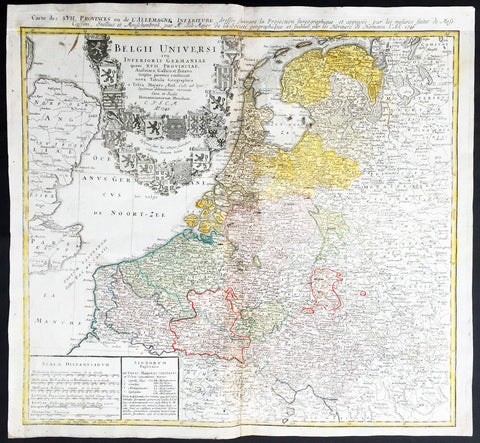
1748 Homann, Mayer Large Old, Antique Map of The Netherlands, Belgium, Holland
- Title : Belgii Universi seu Inferioris Germaniae quam XVII Provinciae Austriaco, Gallico et Batavo sceptro parentes constituunt nova Tabula Geographica a Tobia Majero Math. Cult. ad leges legitimae delineationis revocata Cura et studio Homanniorum Heredum A. 1748
- Ref #: 16422
- Size: 21 1/2in x 20in (545mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1748
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of Holland, The Netherlands and Belgium was engraved in 1748 byJohann Tobias Mayer - dated in Title - and was published by Homann firm in 1750.
Background: A beautifully detailed 1748 Homann Heirs map of Belgium and the Netherlands (Holland). Includes Belgium proper as well as the seven states of the Belgian Federation – what is today Holland or the Netherlands. Also includes parts of England and extends into eastern Germany past the Rhine River.
Title elaborate cartouche in the upper left quadrant, filling the North Sea, features the armorial shields of the Belgian Counties as well as those of the seven states of the federation: Geldern, Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Friesland, Ober Issel, and Groningen.
This map was drawn by Johann Tobias Mayer for inclusion the 1752 Homann Heirs Maior Atlas Scholasticus ex Triginta Sex Generalibus et Specialibus…. Most early Homann atlases were 'made to order' or compiled of individual maps at the request of the buyer. However, this rare atlas, composed of 37 maps and charts, was issued as a 'suggested collection' of essential Homann Heirs maps. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 20in (545mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing along centrefold
Verso: - Re-enforced along centrefold
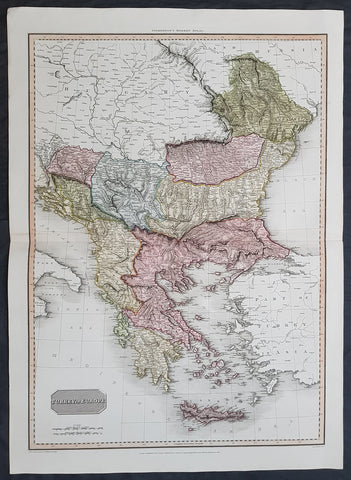
1814 John Pinkerton Large Antique Map of Turkey in Europe - Greece to Hungary
- Title : Turkey in Europe....Drawn under the direction of Mr Pinkerton by L Herbert Neele Sculp. 352 Starnd.....London Published 1st Jan 1814 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 16434
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1814
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Turkey in Europe - Greece, Balkans, Romania, Bosnia, Albania, Serbia, Dalmatia - by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1814 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Ottoman Empire also historically known in Western Europe as the Turkish Empire or simply Turkey, was a state that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia and North Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Oghuz Turkish tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe, and with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the 1453 conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, at the height of its power under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was a multinational, multilingual empire controlling most of Southeast Europe, parts of Central Europe, Western Asia, parts of Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, North Africa and the Horn of Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states. Some of these were later absorbed into the Ottoman Empire, while others were granted various types of autonomy during the course of centuries.
With Constantinople as its capital and control of lands around the Mediterranean basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds for six centuries. While the empire was once thought to have entered a period of decline following the death of Suleiman the Magnificent, this view is no longer supported by the majority of academic historians. The empire continued to maintain a flexible and strong economy, society and military throughout the 17th and much of the 18th century. However, during a long period of peace from 1740 to 1768, the Ottoman military system fell behind that of their European rivals, the Habsburg and Russian empires. The Ottomans consequently suffered severe military defeats in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, which prompted them to initiate a comprehensive process of reform and modernisation known as the Tanzimat. Thus, over the course of the 19th century, the Ottoman state became vastly more powerful and organised, despite suffering further territorial losses, especially in the Balkans, where a number of new states emerged. The empire allied with Germany in the early 20th century, hoping to escape from the diplomatic isolation which had contributed to its recent territorial losses, and thus joined World War I on the side of the Central Powers. While the Empire was able to largely hold its own during the conflict, it was struggling with internal dissent, especially with the Arab Revolt in its Arabian holdings. During this time, atrocities were committed by the Ottoman government against the Armenians, Assyrians and Pontic Greeks.
The Empires defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories, which were divided between the United Kingdom and France. The successful Turkish War of Independence against the occupying Allies led to the emergence of the Republic of Turkey in the Anatolian heartland and the abolition of the Ottoman monarchy.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
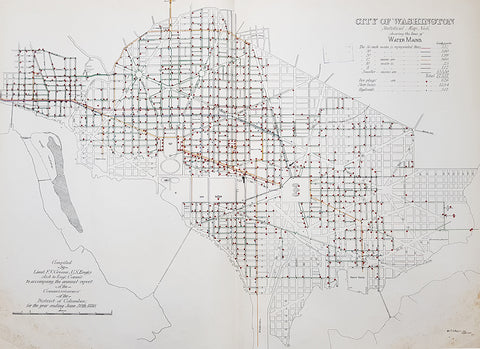
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Location of the Water Mains in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 6 showing the lines of Water Mains...Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16263
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the location of the Water Mains very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
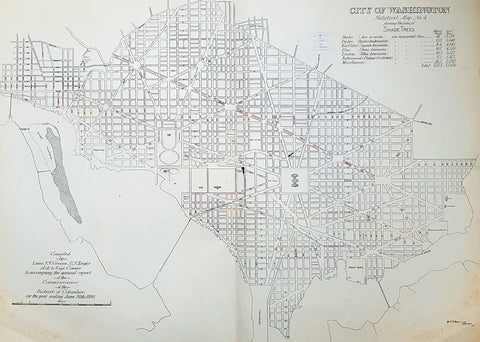
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Lines of Planted Trees in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 4 showing the lines of Shade Trees.....Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16266
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the lines of Trees planted very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
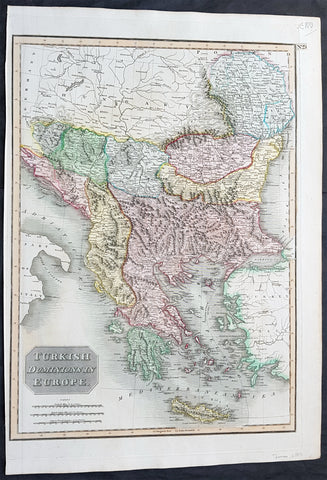
1817 John Thomson Large Antique Map Turkey in Europe Greece to Bosnia & Hungary
- Title : Turkish Dominions in Europe
- Date : 1817
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 390mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 16431
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of Turkey In Europe (Moldova, Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, Bosnia, Croatia, Slovenia, Dalmatia & Greece) by John Thomson was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons New General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 390mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 13 1/2in (510mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - none
Background:
The Ottoman Empire also historically known in Western Europe as the Turkish Empire or simply Turkey, was a state that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia and North Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Oghuz Turkish tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe, and with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the 1453 conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, at the height of its power under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was a multinational, multilingual empire controlling most of Southeast Europe, parts of Central Europe, Western Asia, parts of Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, North Africa and the Horn of Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states. Some of these were later absorbed into the Ottoman Empire, while others were granted various types of autonomy during the course of centuries.
With Constantinople as its capital and control of lands around the Mediterranean basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds for six centuries. While the empire was once thought to have entered a period of decline following the death of Suleiman the Magnificent, this view is no longer supported by the majority of academic historians. The empire continued to maintain a flexible and strong economy, society and military throughout the 17th and much of the 18th century. However, during a long period of peace from 1740 to 1768, the Ottoman military system fell behind that of their European rivals, the Habsburg and Russian empires. The Ottomans consequently suffered severe military defeats in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, which prompted them to initiate a comprehensive process of reform and modernisation known as the Tanzimat. Thus, over the course of the 19th century, the Ottoman state became vastly more powerful and organised, despite suffering further territorial losses, especially in the Balkans, where a number of new states emerged. The empire allied with Germany in the early 20th century, hoping to escape from the diplomatic isolation which had contributed to its recent territorial losses, and thus joined World War I on the side of the Central Powers. While the Empire was able to largely hold its own during the conflict, it was struggling with internal dissent, especially with the Arab Revolt in its Arabian holdings. During this time, atrocities were committed by the Ottoman government against the Armenians, Assyrians and Pontic Greeks.
The Empire\'s defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories, which were divided between the United Kingdom and France. The successful Turkish War of Independence against the occupying Allies led to the emergence of the Republic of Turkey in the Anatolian heartland and the abolition of the Ottoman monarchy.
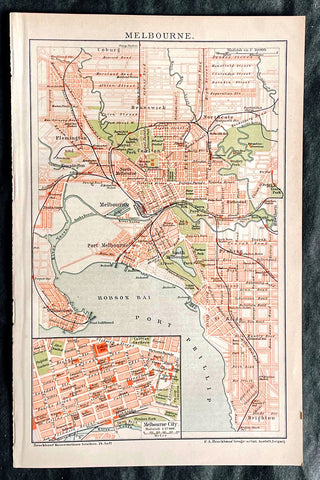
1896 F.A. Brockhaus Antique Map, Street Plan of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Melbourne
- Ref #: 27012
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
- Date : 1896
Description:
This original antique lithograph street map of Melbourne Australia was engraved and published F.A. Brockhaus for the Brockhaus Konversations Lexikon, Germany, 1896
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Brockhaus, Friedrich Arnold (1772 - 1823)
Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus was a German encyclopedia publisher and editor, famed for publishing the Conversations-Lexikon, which is now published as the Brockhaus encyclopedia.
Brockhaus was educated at the gymnasium of his native Dortmund, and from 1788 to 1793 served an apprenticeship in a mercantile house at Düsseldorf. He then devoted two years at the University of Leipzig to the study of modern languages and literature, after which he set up in Dortmund an emporium for English goods. In 1801, he transferred this business to Arnheim, and in the following year to Amsterdam.
In 1805, having given up his first line of trade, Brockhaus began business as a publisher. Two journals projected by him were not allowed by the government to survive for any length of time, and in 1810 the complications in the affairs of Holland induced him to return homewards. In 1811 he settled at Altenburg. About three years previously he had purchased the copyright of the bankrupt Conversations-Lexikon, an encyclopedia started in 1796, and in 1810-1811 he completed the first edition of this celebrated work. It was widely imitated as a model for encyclopedias, and is still published today, known as the Brockhaus Encyclopedia.
A second edition under Brockhauss editorship was begun in 1812, and was received with universal favour. His business extended rapidly, and in 1818 Brockhaus moved to Leipzig, where he established a large printing-house. Among the more extensive of his many literary undertakings were the critical periodicals — Hermes, the Literarisches Konversationsblatt (afterwards the Blätter für literarische Unterhaltung) and the Zeilgenossen, and some large historical and bibliographical works, such as Friedrich Ludwig Georg von Raumers Geschichte der Hohenstaufen, and Friedrich Adolf Eberts Allgemeines bibliographisches Lexikon.
Brockhaus died in Leipzig. The business was carried on by his sons, Friedrich Brockhaus (1800–1865), who retired in 1850, and Heinrich Brockhaus (1804–1874), under whom it was considerably extended. Heinrich especially rendered great services to literature and science, which the University of Jena recognized by making him, in 1858, honorary Doctor of Philosophy. In the years 1842–1848, Heinrich Brockhaus was member of the Saxon second chamber, as representative for Leipzig, was made honorary citizen of that city in 1872, and died there on 15 November 1874.
His firm continues under the name F.A. Brockhaus AG in his honor. He is also the namesake of 27765 Brockhaus, a main-belt asteroid discovered in 1991.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of New South Wales, Australia with inset plan of Sydney
- Title : New South Wales..1833 Baldwin & Craddock
- Size: 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 21290
Description:
This fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique maps of New South Wales - with an inset plan of Sydney Town - was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833- date engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, Alvin Jewett JohnsonAmerica, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1662 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Mansfeld Land, in SW Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
- Title : Mansfelda Comitatus Auctore Tilemanno Stella Sig.
- Ref #: 50180
- Size: 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the ancient region of Mansfeld Land located in the in southwestern region of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany - centering on the city of Mansfeld - by was published in the 1662 Latin edition edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Major.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 16 1/2in (495mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Mansfeld Land is a region in the southwestern corner of the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. The region derives its name from the counts of Mansfeld, who ruled this region for about 1,000 years.
The House of Mansfeld, whose members belonged to the Saxon nobility and served as counts in the Hassegau, was first documented in a 973 deed. The counts built Mansfeld Castle, whose foundations date back to the late 11th century, when one Hoyer of Mansfeld served as field marshal to Emperor Henry V. The first reference of the fortress coincides with the extinction of the elder line in 1229. The estates were inherited by the Lords of Querfurt, who also adopted the comital title, calling themselves Counts of Mansfeld from that time on.
The settlement of Mansfeld received town privileges in 1400, and grew through the development of copper and silver mining, an activity in which Hans Luder from Möhra, father to Martin Luther and Mansfeld citizen from 1484, was employed as a master smelter. Luthers family had arrived into a modest prosperity, he himself attended the local school between 1488 and 1496. The building known as Luther\'s School had to be torn down and rebuilt in 2000 due to structural problems. His parents house is preserved and today a museum. Luther also acted as an altar server at the St George parish church.
The Counts of Mansfeld had already lost Imperial immediacy in 1580. When the comital line finally became extinct in 1780, the estates around Mansfeld were incorporated into the Prussian Duchy of Magdeburg. The town retained the status of an independent city (Immediatstadt), it was temporarily part of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Westphalia and after the 1815 Congress of Vienna belonged to the Prussian Province of Saxony.
1649 Blaeu Antique Map View of Thérouanne, Tarwanna or Tervanna Northern France
- Title : Teroana morinorum metropolis olim, diruta a Carolo V. Anno 1553
- Ref #: Tav
- Size: 21 1/2in x 13in (545mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1649
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map a view of the city of Tarwanna or Tervanna (today the town of Thérouanne, France) the capital of the ancient Belgian tribe of the Morini, was published in the 1649 edition of John Blaeus Toonneel der Steeden (Views of Dutch Cities)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 13in (545mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 7 1/2in (270mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Thérouanne is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France. At the time of the Gauls, Tarwanna or Tervanna was the capital of the Belgian tribe of the Morini. After the Romans conquered Gaul, they too made the city the capital of the Civitas Morinorum district.
In the 7th century, probably around 639, Saint Audomar (Saint Omer) established the bishopric of Terwaan or Terenburg, the diocese of Thérouanne, which during the Middle Ages controlled a large part of the left bank of the river Scheldt. Territorially it was part of the county of Artois which belonged to the county of Flanders.
Thanks to that ecclesiastical control of some of the most prosperous cities north of the Alps, like Arras and Ypres, the bishopric was able to build a cathedral which was at the time the largest in France.
The town was captured by the Emperor Maximilian and Henry VIII from the French in 1513 after the battle of the Spurs. In 1553 Charles V besieged Thérouanne, then a French enclave in the Holy Roman Empire, in revenge for a defeat by the French at the siege of Metz. After he captured the city he ordered it to be razed, the roads to be broken up, and the area to be ploughed and salted Only a small commune which lay outside the city walls, then named Saint-Martin-Outre-Eaux, was left standing, and later (probably around 1800) took over the name Thérouanne. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
1638 Joducus Hondius Antique Map of the Lorraine Region of NE France - Grand Est
- Title : Lorraine Vers Le Midy
- Ref #: 50250
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the ancient Lorraine region of France - centering on the Moselle River with the city of Nancy to the north Faucogney-et-la-Mer to the south & the Meuse River to the west - by Gerard Mercator was published by Jodocus Hondius in the 1638 edition of Mercators Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (500mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Lorraine is a cultural and historical region in north-eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Lorraines name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia, which in turn was named for either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. It later was ruled as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766.
1628 Henricus Hondius Antique Map The Province of Quercy, Lot, Cahors, SW France
- Title : Quercy - Cadurcium
- Ref #: 26140
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (490mm x 340mm)
- Date : 1628
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the ancient province of Quercy located in southwest France - centering on the city of Cahors & the River Lot - was published in the 1628 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (490mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning along centerfold
Background:
Quercy is a former province of France located in the countrys southwest, bounded on the north by Limousin, on the west by Périgord and Agenais, on the south by Gascony and Languedoc, and on the east by Rouergue and Auvergne.
Under the Romans Quercy was part of Aquitania prima, and Christianity was introduced during the 4th century. Early in the 6th century it fell under the authority of the Franks, and in the 7th century became part of the autonomous Duchy of Aquitaine. At the end of the 10th century its rulers were the powerful counts of Toulouse. During the wars between England and France in the reign of Henry II, the English placed garrisons in the county, and by the 1259 Treaty of Paris lower Quercy was ceded to England. The monarchs of both England and France confirmed and added to the privileges of the towns and the district, each thus hoping to attach the inhabitants to his own interest. In 1360, by the Treaty of Bretigny, the whole county passed to England, but in 1440 the English were finally expelled. In the 16th century Quercy was a stronghold of the Protestants, and the scene of a savage religious warfare. The civil wars of the reign of Louis XIII largely took place around Montauban.
1638 Jansson Old, Antique Map of the Dauphine Region of France, Grenoble
- Title : Nova et acurrata Descriptio Delphinatus vulgo Dauphine
- Ref #: 50244
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Dauphine region of southern France - centering on the city of Grenoble - with the Rhone River to the west and north with Savoy & Piedmont to the east was published by Jan Jansson in the 1638 edition ofAtlas Novus. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/4in (520mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1638 Willem Blaeu Antique Map of Mansfeld Land, in SW Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
- Title : Mansfelda Comitatus
- Ref #: 70078
- Size: 22 1/2in x 17in (570mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the ancient region of Mansfeld Land located in the in southwestern region of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany - centering on the city of Mansfeld - by was published in the 1638 Latin edition edition of Willem Blaeus Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 17in (570mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 16 1/4in (495mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mansfeld Land is a region in the southwestern corner of the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. The region derives its name from the counts of Mansfeld, who ruled this region for about 1,000 years.
The House of Mansfeld, whose members belonged to the Saxon nobility and served as counts in the Hassegau, was first documented in a 973 deed. The counts built Mansfeld Castle, whose foundations date back to the late 11th century, when one Hoyer of Mansfeld served as field marshal to Emperor Henry V. The first reference of the fortress coincides with the extinction of the elder line in 1229. The estates were inherited by the Lords of Querfurt, who also adopted the comital title, calling themselves Counts of Mansfeld from that time on.
The settlement of Mansfeld received town privileges in 1400, and grew through the development of copper and silver mining, an activity in which Hans Luder from Möhra, father to Martin Luther and Mansfeld citizen from 1484, was employed as a master smelter. Luthers family had arrived into a modest prosperity, he himself attended the local school between 1488 and 1496. The building known as Luther\'s School had to be torn down and rebuilt in 2000 due to structural problems. His parents house is preserved and today a museum. Luther also acted as an altar server at the St George parish church.
The Counts of Mansfeld had already lost Imperial immediacy in 1580. When the comital line finally became extinct in 1780, the estates around Mansfeld were incorporated into the Prussian Duchy of Magdeburg. The town retained the status of an independent city (Immediatstadt), it was temporarily part of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Westphalia and after the 1815 Congress of Vienna belonged to the Prussian Province of Saxony.
1757 Nicolas Bellin Antique Map, Plan of the City of Buenos Aires, Argentina
- Title : Plan De La Ville de Buenos - Ayres
- Ref #: 61102
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* a plan of the Capital City of Argentina Buenos Aires by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in the 1757 French & Dutch edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Background: Seaman Juan Díaz de Solís, navigating in the name of Spain, was the first European to reach the Río de la Plata in 1516. His expedition was cut short when he was killed during an attack by the native Charrúa tribe in what is now Uruguay.
The city of Buenos Aires was first established as Ciudad de Nuestra Señora Santa María del Buen Ayre (literally "City of Our Lady Saint Mary of the Fair Winds") after Our Lady of Bonaria (Patroness Saint of Sardinia) on 2 February 1536 by a Spanish expedition led by Pedro de Mendoza. The settlement founded by Mendoza was located in what is today the San Telmo district of Buenos Aires, south of the city center.
More attacks by the indigenous people forced the settlers away, and in 1542 the site was abandoned. A second (and permanent) settlement was established in 11 June 1580 by Juan de Garay, who arrived by sailing down the Paraná River from Asunción (now the capital of Paraguay). He dubbed the settlement "Santísima Trinidad" and its port became "Puerto de Santa María de los Buenos Aires.
From its earliest days, Buenos Aires depended primarily on trade. During most of the 17th and 18th centuries, Spanish ships were menaced by pirates, so they developed a complex system where ships with military protection were dispatched to Central America, cross the land, from there to Lima, Peru and from it to the inner cities of the viceroyalty. Because of this, products took a very long time to arrive in Buenos Aires, and the taxes generated by the transport made them prohibitive. This scheme frustrated the traders of Buenos Aires, and a thriving contraband industry developed. This also instilled a deep resentment in porteños towards the Spanish authorities.
Sensing these feelings, Charles III of Spain progressively eased the trade restrictions and finally declared Buenos Aires an open port in the late 18th century. The capture of Porto Bello by British forces also fueled the need to foster commerce via the Atlantic route, to the detriment of Lima-based trade. One of his rulings was to split a region from the Viceroyalty of Perú and create instead the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, with Buenos Aires as the capital. However, Charles's placating actions did not have the desired effect, and the porteños, some of them versed in the ideology of the French Revolution, became even more convinced of the need for independence from Spain. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 7 1/2in (290mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1682 Du Val Original Antique Map of North Pole, North America, Europe, Russia
- Title : Terres Arctiques.. Septemtrional et Boreales.
- Date : 1682
- Size: 6 1/2in x 6in (160mm x 155mm)
- Ref #: 22138
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original 1682 antique map of the North Pole by Pierre Du Val was published in his 1682 miniature atlas, 'Géographie Universelle'.Jacques Nicholas Bellindu
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 6 1/2in x 6in (160mm x 155mm)
Plate size: - 5in x 4in (125mm x 100mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A driving force for the exploration of the Arctic was the desire of European monarchs to find an alternate trading route to China, via either a Northwest Passage along the coast of North America, or a Northeast Passage along the coast of Siberia. A number of expeditions sought such routes in the 1500-1700s, which resulted in the discovery of much of northern North America, but no viable passage.
In 1524, under the direction of the king of France, Giovanni da Verrazano took the entrance to Hudson River (now New York City) to be the entrance for the passage, and ten years later Jacques Cartier likewise discovered the St. Lawrence estuary. The first Englishman to seek the passage was Martin Frobisher in three voyages up to 60°N between 1576 and 1578. On his first voyage, relations with the natives quickly became hostile, and a prisoner was brought back to England. John Davis followed in 1585, 1586, and 1587 charting the strait west of Greenland that now bears his name.
Financed by the Dutch, in 1609 the Englishman Henry Hudson followed Verrazano's course, and explored the river that now bears his name. The following year he discovered the vast inlet (now called Hudson Bay) beyond Davis Strait. Robert Bylot and navigator William Baffin undertook two expeditions in 1615 and 1616, exploring the north coast of Greenland up to 78°N and then along the Canadian archipelago to Lancaster Sound. Convinced it was only a bay, Baffin concluded that no Northwest Passage existed, and interest in searching for one waned for the next 200 years.
Other explorers were drawn to search for a Northeast Passage connecting the White Sea and Bering Sea. The Dutch navigator William Barents led three expeditions east of Novaya Zemlya, and on the third expedition in 1596 claimed Spitsbergen. From the early 16th century, Russian navigators used shallow draft vessels with reinforced bottoms (kochi) to cross the Kara Sea and explore the Ob and Yenisey rivers. Yermak's Cossacks expanded the Russian presence eastward, crossing the Ural Mountains in 1581. In 1601, Mangazeya town was founded at Taz River between the Ob and Yenisey rivers, and dozens of boats from Pomor lands began annual navigations.
Throughout the first quarter of the 17th century, a great number of merchants, trappers and Cossacks moved east and north, settled East Siberia and explored the northern Siberian coast. In 1610, the Yenisey River was navigated to its northern estuary and the coast to the estuary of the Pyasina was explored. Cape Chelyuskin was overtaken from the west in 1617, Yakutian Cossacks Ivan Rebrov and Ilya Perfilyev headed down to the Lena River estuary and made the first sea voyage to the Yana River in 1633, and in 1639, the Pacific shore was reached by Ivan Moskvitin and his detachment of Cossacks. In a 15-year timespan, all Siberian river estuaries from Khatanga to Kolyma had been discovered and a large part of the Northeast Passage from the White Sea to Kolyma estuary had been covered. Semen Dezhnev traversed the final segment in 1648, leading 90 Cossacks on a journey from the Kolyma to Anadyr Rivers, discovering the strait between Asia and America (proving that they were different continents) and passing the cape which now bears his name.
1829 Friedrich Wilhelm Streit Large Antique Map of European Russia
- Title : Charte von dem Europaeisch Russischen Reiche entworsen u. gezeichnet von FW Streit...Leipzig J C Hinrichssche...1829
- Ref #: 32211
- Size: 20in x 16 1/2in (510mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1829
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Russian Empire in Europe - from Finland to the Caspian Sea - by Friedrich Wilhelm Streit was published in 1829 by Johann Conrad Hinrichssche, dated in the title.
Friedrich Wilhelm Streit 1772 - 1839 was a Prussian cartographer., engineer and mathematician. He was a Prussian Army Major and member of the Academie of useful sciences, Erfurt and the society for geography, Berlin. From 1807 to 1808 he was director of the Geographical Institute in Weimar .(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 16 1/2in (510mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16 1/2in (510mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia, Swan River Colony & Van Diemens Land
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 32682
Description:
This original antique map of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Blind Library stamp
Verso: - Re-enforced on verso along margins
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1833 SDUK Antique Map of New South Wales w/ inset Map of Sydney Town, Australia
- Title : New South Wales...Sydney from the New South Wales Almanack...Sep 1833
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 32681
Description:
This fine original antique map of New South Wales, Australia - with an inset plan of Sydney Town - was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning, left T&B corners cropped
Plate area: - Blind Library stamp
Verso: - Re-enforced on verso along margins
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1628 Henricus Hondius Antique Map Beauvais Region of Northern France, Oise River
- Title : Beauvaisis Comitatus Belovacium
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 50230
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Beauvais region of Northern France - centering on the city of Beauvais & the Oise River running through the cities of Noyon, Compiègne, Creil, by Henricus Hondius was published by Henricus Hondius & Jan Jansson in the 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Beauvais is a city and commune in northern France. It serves as the capital of the Oise département, in the Hauts-de-France region. Beauvais is located approximately 75 kilometres from Paris.
Beauvais was known to the Romans by the Gallo-Roman name of Caesaromagus (magos is Common Celtic for field). The post-Renaissance Latin rendering is Bellovacum from the Belgic tribe the Bellovaci, whose capital it was. In the ninth century it became a countship, which about 1013 passed to the bishops of Beauvais, who became peers of France from the twelfth century. At the coronations of kings the Bishop of Beauvais wore the royal mantle and went, with the Bishop of Langres, to raise the king from his throne to present him to the people.
De Bello Gallico II 13 reports that as Julius Caesar was approaching a fortified town called Bratuspantium in the land of the Bellovaci, its inhabitants surrendered to him when he was about 5 Roman miles away. Its name is Gaulish for place where judgements are made, from *bratu-spantion. Some say that Bratuspantium is Beauvais. Others theorize that it is Vendeuil-Caply or Bailleul sur Thérain.
From 1004 to 1037, the Count of Beauvais was Odo II, Count of Blois.
In a charter dated 1056/1060, Eudo of Brittany granted land in pago Belvacensi (Beauvais, Picardy) to the Abbey of Angers Saint-Aubin
In 1346 the town had to defend itself against the English, who again besieged it in 1433. The siege which it endured in 1472 at the hands of the Duke of Burgundy, was rendered famous by the heroism of the towns women, under the leadership of Jeanne Hachette, whose memory is still celebrated by a procession on 27 June (the feast of Sainte Angadrême), during which women take precedence over men.
An interesting hoard of coins from the High Middle Ages became known as the Beauvais Hoard, because some of the British and European coins found with the lot were from the French abbey located in Beauvais. The hoard, which contained a variety of rare and extremely rare Anglo-Norman pennies, English and foreign coins, was reputed to have been found in or near Paris.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1650 Joan Blaeu Antique Map Archbishopic of Madenburg in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
- Title : Magdeburgensis Archiepiscopatus...Amstelaedami J Blaeu excudebat
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1650
- Ref #: 70075
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Archbishopric of Madenburg today located in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, on the Elbe River, was published in the 1650 edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Roman Catholic archdiocese (969–1552) and Prince-Archbishopric (1180–1680) of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.
Planned since 955 and established in 968, the Roman Catholic archdiocese had de facto turned void since 1557, when the last papally confirmed prince-archbishop, the Lutheran Sigismund of Brandenburg came of age and ascended to the see and the Magdeburg cathedral chapter had adopted Lutheranism in 1567, with most parishioners having preceded in their conversion. All his successors were only administrators of the prince-archbishopric and Lutheran too, except of the Catholic layman Leopold William of Austria (1631–1635). In ecclesiastical respect the remaining Catholics and their parishes and abbeys in the former archdiocese were put under supervision of the Archdiocese of Cologne in 1648 and under the jurisdiction of the Apostolic Vicariate of the Northern Missions in 1670.
In political respect the Erzstift, the archiepiscopal and capitular temporalities, had gained imperial immediacy as prince-archbishopric in 1180. Its territory comprised only some parts of the archdiocesan area, such as the city of Magdeburg, the bulk of the Magdeburg Börde, and the Jerichow Land as an integral whole and exclaves comprising about the Saalkreis including Halle upon Saale, Oebisfelde and environs as well as Jüterbog and environs. The prince-archbishopric maintained its statehood as an elective monarchy until 1680. Then Brandenburg-Prussia acquired Magdeburg prince-archbishopric, and after being secularised, transformed it into the Duchy of Magdeburg, a hereditary monarchy in personal union with Brandenburg.
1740 Guillaume Delisle Original Antique Atlas Title Page for Atlante Novissimo
- Title : Atlante Novissimo De Sig Guglielmo De L Isles
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1740
- Ref #: 70343
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique frontispiece from the Italian version of Guillaume Delisle atlas Atlante Novissimo, was published by Girolamo Albrizzi in 1740.
The architectural columns are flanked by both male & female Roman soldier. At the top of the structure, a pair of putti hold aloft the covering drapes. Within the structure are two internal cartouche, one a vignette view of the city of Venice, where the atlas was published, and above, the symbol for the Society of Jesus.George PhilipDelisle
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1756 D Anville Large Antique Map of Greece & The Aegean Islands & Crete
- Title : Les Cotes de la Grece et L Archipel par le D Anville...MDCCLVI (1756)
- Size: 31in x 24in (790mm x 610mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1756
- Ref #: 92313
Description:
This large hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Aegean Islands of Greece, south to Crete by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D Anville was engraved in 1756 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 31in x 24in (790mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 29in x 24in (770mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling in margins
Plate area: - Soiling bottom of image
Verso: - Soiling
Background:
The Aegean Islands are the group of islands in the Aegean Sea, with mainland Greece to the west and north and Turkey to the east; the island of Crete delimits the sea to the south, those of Rhodes, Karpathos and Kasos to the southeast. The ancient Greek name of the Aegean Sea, Archipelago (ἀρχιπέλαγος, archipelagos) was later applied to the islands it contains and is now used more generally, to refer to any island group.
The vast majority of the Aegean Islands belong to Greece, being split among nine administrative regions. The only sizable possessions of Turkey in the Aegean Sea are Imbros (Gökçeada) and Tenedos (Bozcaada), in the northeastern part of the Sea. Various smaller islets off Turkeys western coast are also under Turkish sovereignty.
1845 Sydney Hall Large Antique World Map insets Singapore, Hong Kong, Cape, TAS
- Title : 1845 Sydney Hall Large Antique World Map insets Singapore, Hong Kong, Cape, TAS
- Size: 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Date : 1843
- Ref #: 32258-1
Description:
This large original steel-plate antique world map - with 5 inset maps of Hong Kong, Van Diemens Land, Calcutta, Singapore & the Colony Of Good Hope - by Sydney Hall was published by Longman & co. in 1845. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small loss to top centerfold, into border
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape, light soiling
Background:
A highly detailed and attractive map of the world, with seven inset maps of British colonies: Hong Kong, Van Diemens Land, Calcutta, Singapore & the Colony Of Good Hope. A note on the Pitcairn Islands records their colonisation by the mutineers from the Bounty.
Also prominent in North America is an independent Texas along with an extended Mexico into the SW and California regions.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of New Guinea, William Dampier 1699 - 5 Harbours
- Title : Carte des Decouvertes du Capt,. Carteret dans La Nlle. Bretagne..Par M Bonne
- Date : 1780
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40581
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Papua New Guinea - and the early discoveries of William Dampier and the later passage of Cooks ship the Endeavor through the straits between Australia and New Guinea, by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
The map also contains the bays, Harbours and coastlines of several Islands of the Pacific including New Ireland, Philippines, Indonesia.(Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 ½in x 11 ½in; (420mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 14 ½in x 10in; (370mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
William Dampier 1651 - 1715 was an English explorer and navigator who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australia\'s first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the Admiralty with his book A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in Western Australia, before being court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crewmate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Horatio Nelson, Charles Darwin, and Alfred Russel Wallace.
1774 Commodore John Byron Antique Map of The Falkland Islands South America
Antique Map
- Title : Carte de Maidenland ou de la Virginie de Hawkins...et du Canal Falklands...Jean Strong...1689.
- Ref #: 93381
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Falkland Islands by Commodore John Byron was engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1774 first French edition of John Hawkesworth important book An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor. Drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, Esq; by John Hawkesworth, LL.D. In three volumes. Illustrated with cuts, and a great variety of charts and maps relative to countries now first discovered, or hitherto but imperfectly known. London: printed for W. Strahan; and T. Cadell in the Strand, MDCCLXXIII.
John Hawkesworth (1715 - 1773) was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook, from 1702 to 1771, drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Background:
Although Fuegians from Patagonia may have visited the Falkland Islands in prehistoric times, the islands were uninhabited when Europeans first discovered them. Claims of discovery date back to the 16th century, but no consensus exists on whether early explorers discovered the Falklands or other islands in the South Atlantic. The first recorded landing on the islands is attributed to English captain John Strong, who, en route to Perus and Chiles littoral in 1690, discovered the Falkland Sound and noted the islands water and game.
The Falklands remained uninhabited until the 1764 establishment of Port Louis on East Falkland by French captain Louis Antoine de Bougainville, and the 1766 foundation of Port Egmont on Saunders Island by British captain John MacBride. Whether or not the settlements were aware of each others existence is debated by historians. In 1766, France surrendered its claim on the Falklands to Spain, which renamed the French colony Puerto Soledad the following year. Problems began when Spain discovered and captured Port Egmont in 1770. War was narrowly avoided by its restitution to Britain in 1771.
Both the British and Spanish settlements coexisted in the archipelago until 1774, when Britains new economic and strategic considerations led it to voluntarily withdraw from the islands, leaving a plaque claiming the Falklands for King George III. Spains Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata became the only governmental presence in the territory. West Falkland was left abandoned, and Puerto Soledad became mostly a prison camp. Amid the British invasions of the Río de la Plata during the Napoleonic Wars in Europe, the islands governor evacuated the archipelago in 1806; Spains remaining colonial garrison followed suit in 1811, except for gauchos and fishermen who remained voluntarily.
Thereafter, the archipelago was visited only by fishing ships; its political status was undisputed until 1820, when Colonel David Jewett, an American privateer working for the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, informed anchored ships about Buenos Aires 1816 claim to Spains territories in the South Atlantic. Since the islands had no permanent inhabitants, in 1823 Buenos Aires granted German-born merchant Luis Vernet permission to conduct fishing activities and exploit feral cattle in the archipelago. Vernet settled at the ruins of Puerto Soledad in 1826, and accumulated resources on the islands until the venture was secure enough to bring settlers and form a permanent colony. Buenos Aires named Vernet military and civil commander of the islands in 1829, and he attempted to regulate sealing to stop the activities of foreign whalers and sealers. Vernets venture lasted until a dispute over fishing and hunting rights led to a raid by the American warship USS Lexington in 1831, when United States Navy commander Silas Duncan declared the dissolution of the islands government.
Buenos Aires attempted to retain influence over the settlement by installing a garrison, but a mutiny in 1832 was followed the next year by the arrival of British forces who reasserted Britains rule. The Argentine Confederation (headed by Buenos Aires Governor Juan Manuel de Rosas) protested against Britains actions and Argentine governments have continued since then to register official protests against Britain. The British troops departed after completing their mission, leaving the area without formal government. Vernets deputy, the Scotsman Matthew Brisbane, returned to the islands that year to restore the business, but his efforts ended after, amid unrest at Port Louis, gaucho Antonio Rivero led a group of dissatisfied individuals to murder Brisbane and the settlements senior leaders; survivors hid in a cave on a nearby island until the British returned and restored order. In 1840, the Falklands became a Crown colony, and Scottish settlers subsequently established an official pastoral community. Four years later, nearly everyone relocated to Port Jackson, considered a better location for government, and merchant Samuel Lafone began a venture to encourage British colonisation.
Stanley, as Port Jackson was soon renamed, officially became the seat of government in 1845. Early in its history, Stanley had a negative reputation due to cargo-shipping losses; only in emergencies would ships rounding Cape Horn stop at the port. Nevertheless, the Falklands geographic location proved ideal for ship repairs and the Wrecking Trade, the business of selling and buying shipwrecks and their cargoes. Aside from this trade, commercial interest in the archipelago was minimal due to the low-value hides of the feral cattle roaming the pastures. Economic growth began only after the Falkland Islands Company, which bought out Lafones failing enterprise in 1851, successfully introduced Cheviot sheep for wool farming, spurring other farms to follow suit. The high cost of importing materials, combined with the shortage of labour and consequent high wages, meant the ship repair trade became uncompetitive. After 1870, it declined as the replacement of sail ships by steamships was accelerated by the low cost of coal in South America; by 1914, with the opening of the Panama Canal, the trade effectively ended. In 1881, the Falkland Islands became financially independent of Britain. For more than a century, the Falkland Islands Company dominated the trade and employment of the archipelago; in addition, it owned most housing in Stanley, which greatly benefited from the wool trade with the UK.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (310mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Byron, John 1723 – 1786:
Vice-Admiral John Byron (8 November 1723 – 10 April 1786) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer. He earned the nickname Foul-Weather Jack in the press because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sailed in the squadron under George Anson on his voyage around the world, though Byron made it only to southern Chile, where his ship was wrecked. He returned to England with the captain of HMS Wager. He was governor of Newfoundland following Hugh Palliser, who left in 1768. He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764–1766. He fought in battles in the Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral of the White before his death in 1786.
His grandsons include the poet George Gordon Byron and George Anson Byron, admiral and explorer, who were the 6th and 7th Baron Byron, respectively.
Byron was the second son of William Byron, 4th Baron Byron and Frances Berkeley, the daughter of William, 4th Baron Berkeley. After studying at Westminster School he joined the Royal Navy at the age of 14, making his first voyage aboard the HMS Romney in 1738–40.
In 1740, he accompanied George Anson on his voyage around the world as a midshipman aboard one of the several ships in the squadron. On 14 May 1741, HMS Wager under Captain Cheap (as Captain Dandy Kidd had died), was shipwrecked on the coast of Chile on what is now called Wager Island and Byron was one of the survivors. The survivors decided to split in two teams, one to make its way by boat to Rio de Janeiro on the Atlantic coast; the other, including John Byron and the Captain, to sail north along the Spanish colonial coast.
Captain Cheap at Wager Island had a party of 19 men after the deserters rejoined the camp. This included the surgeon Elliot and Lieutenant Hamilton who had been cast adrift with him plus midshipmen John Byron and Campbell who had been in the barge. They rowed up the coast but were punished by continuous rain, headwinds and waves that threatened the boats. One night while the men slept on shore, one of the boats was capsized while at anchor and was swept out to sea with its two boatkeepers. One of the men got ashore but the other drowned. As it was now impossible for them all to fit in the remaining boat, four marines were left ashore with muskets to fend for themselves. The winds prevented them from getting around the headland so they returned to pick up the marines only to find them gone. They returned to Wager Island in early February 1742. With one death on the journey, there were now 13 in the group.
Martín Olleta, a Chono cheftain, guided the men up the coast to the Spanish settlements of Chiloé Island so they set out again. Two men died; after burying the bodies, the six seamen rowed off in the boat never to be seen again while Cheap, Hamilton, Byron, Campbell and the dying Elliot were on shore looking for food. Olleta then agreed to take the remaining four on by canoe for their only remaining possession, a musket. It is likely the party travelled across Presidente Ríos Lake in inland Taitao Peninsula, a lake Chile regarded as officially discovered in 1945. Eventually they made it to be taken prisoner by the Spanish. The Spaniards treated them well and they were eventually taken to the inland capital of Santiago where they were released on parole. The Spaniards heard that Anson had been generous in the treatment of the prisoners he had taken and this kindness was returned.
Byron and the other three men stayed in Santiago till late 1744 and were offered passage on a French ship bound for Spain. Three accepted the passage. Campbell elected to take a mule across the Andes and joined the Spanish Admiral Pizarro in Montevideo on the Asia only to find Isaac Morris and the two seamen who had been abandoned in Freshwater Bay on the Atlantic coast. After time in prison in Spain, Campbell reached Britain in May 1746, followed by the other three two months later.
In England, the official court martial examined only the loss of the Wager in which Baynes, in nominal charge at the time, was acquitted of blame but reprimanded for omissions of duty. Disputes over what happened after the wreck were instead played out as Bulkeley and Cummins, Campbell, Morris, the cooper Young and later Byron published their own accounts, the last of which was the only one that in any way defended Cheap who had since died. Twenty-nine crew members plus seven marines made it back to England.
Byrons account of his adventures and the Wager Mutiny are recounted in The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron (1768). His book sold well enough to be printed in several editions.
Byron was appointed captain of HMS Siren in December 1746.
In 1760, during the Seven Years War, Byron commanded a squadron sent to destroy the fortifications at Louisbourg, Quebec, which had been captured by the British two years before. They wanted to ensure it could not be used by the French in Canada. In July of that year he defeated the French flotilla sent to relieve New France at the Battle of Restigouche.
In early 1764 the British Admiralty determined that it would require a permanent naval settlement off the South American coast, in order to resupply naval vessels seeking to enter the Pacific via Cape Horn. Captain Byron was selected to explore the South Atlantic for a suitable island upon which to establish such a settlement. The South American mainland was controlled by Spain, which was hostile to local expansion of British interests; to disguise Byrons mission it was announced that he had been appointed the new Navy Commander-in-Chief, East Indies. Byron set sail in June 1764, ostensibly to take up the East Indies post. For the voyage he was granted command of the 24-gun frigate HMS Dolphin and the 16-gun sloop HMS Tamar.
Byrons two-vessel flotilla crossed the Atlantic over the winter of 1764 and made its way slowly down the South American coast. The Admiralty had ordered Byron to first seek Pepys Island, reputedly discovered off the Patagonian coast by the corsair Ambrose Cowley in 1683. Byron reached the co-ordinates given by Cowley in January 1765, but there was no sign of the island and the search was swiftly abandoned. On 5 February Byron reached the Patagonian settlement of Port Desire where he resupplied his vessels from the storeship HMS Florida.
Between June 1764 and May 1766, Byron completed his own circumnavigation of the globe as captain of HMS Dolphin. This was the first such circumnavigation that was accomplished in less than 2 years. His actions nearly caused a war between Great Britain and Spain, as both countries had armed fleets ready to contest the sovereignty of the Falkland Islands. Later Byron encountered islands and extant residents of the Tuamotus and Tokelau Islands, and Nikunau in the southern Gilbert Islands; he also visited Tinian in the Northern Marianas Islands. A notable member of Byrons crew was Masters Mate Erasmus Gower whom Byron chose to take a significant part in the ceremony when he took possession of the Falkland Islands. Byron had examined Gower for his lieutenants examination in 1762 and was so impressed that he chose him to accompany him on his own circumnavigation (1764–65) and ensured that he was appointed as lieutenant to Commander Philip Carteret immediately afterwards in the next circumnavigation (1766–69).
In 1769 he was appointed governor of Newfoundland off the mainland of Canada, an office he held for the next three years.
He was promoted to rear admiral on 31 March 1775. In 1779, he served as Commander-in-chief of the Leeward Islands Station during the American War of Independence. After being severely injured during a storm on his way to the West Indies, Byron unsuccessfully attacked a French fleet under the Comte dEstaing at the Battle of Grenada in July 1779. He subsequently resigned his post and returned to England, where he suffered from poor health for the rest of his life.
Byron was briefly Commander-in-Chief, North American Station from 1 October 1779. He was made vice admiral of the white in September 1780.
John Byron died on 1 April 1786 at home in Bolton Row, London. His remains were buried in the Berkeley family vault situated beneath the chancel of the Church of St Mary the Virgin, Twickenham, on 10 April.
Johns life was a great inspiration for his grandson the poet George Gordon Byron, though they never met. The poet both drew from his grandfathers experiences in his writing, using his Narrative for the shipwreck scene in Don Juan, and wrote of the kinship he felt in having such a turbulent, unlucky life: he wrote in an epistle to his half-sister Augusta Leigh that he had no rest at sea, nor I on shore.
1757 Bellin Large Antique Map of Guyana, South America
- Title: Carte de la Guyana...1757
- Date: 1757
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 60940
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Guyana, South America by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a sovereign state on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Suriname to the east and Venezuela to the west.
There are nine indigenous tribes residing in Guyana: the Wai Wai, Macushi, Patamona, Lokono, Kalina, Wapishana, Pemon, Akawaio and Warao. Historically the Lokono and Kalina tribes dominated Guyana. Although Christopher Columbus sighted Guyana during his third voyage (in 1498), and Sir Walter Raleigh wrote an account of its discovery in 1596, the Dutch were the first to establish colonies: Essequibo (1616), Berbice (1627), and Demerara (1752). After the British assumed control in 1796, the Dutch formally ceded the area in 1814. In 1831 the three separate colonies became a single British colony known as British Guiana.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1756 Bellin Antique Map of Paraguay & Brazil, South America
- Title: Carte Du Paraguay...1756
-
Date: 1756
Condition : (A+) Fine Condition - Ref: 60939
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Paraguay South America, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1756 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The first Europeansto explore the country were Spanish explorers in 1516. The Spanish explorer Juan de Salazar de Espinosa founded the settlement of Asunción on 15 August 1537. The city eventually became the center of a Spanish colonial province of Paraguay.
An attempt to create an autonomous Christian Indian nation was undertaken by Jesuit missions and settlements in this part of South America in the eighteenth century, which included portions of Uruguay, Argentina, and Brazil. They developed Jesuit reductions to bring Guarani populations together at Spanish missions and protect them from virtual slavery by Spanish settlers and Portuguese slave raiders, the Bandeirantes. In addition to seeking their conversion to Christianity. Catholicism in Paraguay was influenced by the indigenous peoples; the syncretic religion has absorbed native elements. The reducciones flourished in eastern Paraguay for about 150 years, until the expulsion of the Jesuits by the Spanish Crown in 1767. The ruins of two 18th-century Jesuit Missions of La Santísima Trinidad de Paraná and Jesús de Tavarangue have been designated as World Heritage Sites by UNESCO.
In western Paraguay Spanish settlement and Christianity were strongly resisted by the nomadic Guaycuru and other nomads from the 16th century onward. Most of these peoples were absorbed into the mestizo population in the 18th and 19th centuries.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 8 1/2in (330mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1750 Bellin & Condamine Antique Map The Course of the Amazon River South America
- Title : Carte Du Cours Du Maragnon ou De La Grande Riviere Des Amazones...1743 et 1744...par M de la Condamine
- Ref: 50686
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map of the course of the Amazon River - according to the discoveries of the French explorer Charles-Marie La Condamine - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine-François Prevost's monumental 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague between 1747 & 1780.
Charles-Marie La Condamine (1701 - 1774) was a French mathematician and surveyor who took part in an expedition to South America to measure a degree of latitude.
La Condamine was born in Paris. He was trained for the military profession, but turned his attention to science and geographical exploration. After taking part in a scientific expedition in the Levant (1731), he became a member with Louis Godin and Pierre Bouguer of the expedition sent to Peru in 1735 to determine the length of a degree of the meridian in the neighborhood of the equator.
His associations with his principals were unhappy; the expedition was beset by many difficulties, and finally La Condamine separated from the rest and made his way from Quito down the Amazon, ultimately reaching Cayenne. His was the first scientific exploration of the Amazon. He returned to Paris in 1744 and published the results of his measurements and travels with a map of the Amazon in M' de l'Acadme des Sciences, 1745 (English translation 1745-1747). This included the first descriptions by a European of the Casiquiare canal and the curare arrow poison prepared by the Amerindians.
(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Margins cropped to margins
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1888 Pic Atlas Large Antique Map of NSW, Australia Political & Local Borders
- Title : Map of New South Wales Showing Territorial Divisions, Land Board Districts and Land Districts
- Ref : 50337
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Map of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : General Map of New South Wales
- Ref : 50339
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Map of Western Australia
- Title : Map of New South Wales Showing Territorial Divisions, Land Board Districts and Land Districts
- Ref : 50337
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1886 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Rainfall Map of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : Map of New South Wales showing Average Annual Rainfall
- Ref : 50340
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1720 Chatelain Antique Map of England & Wales
- Title : Nouvelle Carte De L Angleterre Dans Laquelle Lon Observe Lez Comtez Les Archives
- Ref #: 16370
- Size: 25 1/2in x 20 1/2in (650m x 430m)
- Date : 1720
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of England & Wales - with side text on all the different counties - by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1720 was published in his famous Atlas Historique.
This is a magnificent map with bright hand colouring, clean strong sturdy paper and a heavy clear impression.
The Atlas Historique published by Henri Chatelain was part of a major work of its time, an encyclopedia in seven volumes, including geography as one of its main subjects. The text was by Nicholas Gueudeville and the maps by Chatelain. The Atlas included one of the finest map of America (four sheets) surrounded by vignettes and decorative insets. The Atlas Historique was completed between 1705 and 1720, further issues were published up to 1739. The series was published in Amsterdam, with Chatelain’s maps based on those of G. Delisle. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 20 1/2in (650m x 430m)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635m x 495mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1744 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Hudsons Bay & Surrounds, Canada
- Title : Karte Von Der Hudsons Bay Durch N Bellin..1744
- Ref #: 41156
- Size: 14in x 9 1/2in (355mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Hudsons Bay, Canada by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1744 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Hudson Bay is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of 1,230,000 km2 (470,000 sq mi). It drains a very large area, about 3,861,400 km2 (1,490,900 sq mi), that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, Ontario, Quebec and parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay\'s southern arm is called James Bay.
English explorers and colonists named Hudson Bay after Sir Henry Hudson who explored the bay beginning August 2, 1610 on his ship Discovery.:170 On his fourth voyage to North America, Hudson worked his way around Greenland\'s west coast and into the bay, mapping much of its eastern coast. Discovery became trapped in the ice over the winter, and the crew survived onshore at the southern tip of James Bay. When the ice cleared in the spring, Hudson wanted to explore the rest of the area, but the crew mutinied on June 22, 1611. They left Hudson and others adrift in a small boat. No one knows the fate of Hudson or the crew members stranded with him, but historians see no evidence that they survived for long afterwards.
In 1668, Nonsuch reached the bay and traded for beaver pelts, leading to the creation of the Hudson\'s Bay Company (HBC) which still bears the historic name. The HBC negotiated a trading monopoly from the English crown for the Hudson Bay watershed, called Rupert\'s Land. France contested this grant by sending several military expeditions to the region, but abandoned its claim in the Treaty of Utrecht (April 1713).
During this period, the Hudson\'s Bay Company built several factories (forts and trading posts) along the coast at the mouth of the major rivers (such as Fort Severn, Ontario; York Factory and Churchill, Manitoba). The strategic locations were bases for inland exploration. More importantly, they were trading posts with the indigenous peoples who came to them with furs from their trapping season. The HBC shipped the furs to Europe and continued to use some of these posts well into the 20th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9 1/2in (355mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.