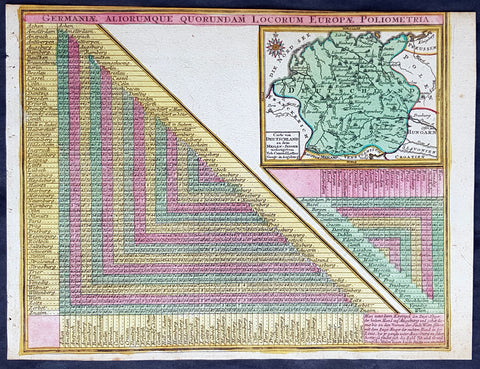
Europe (305)
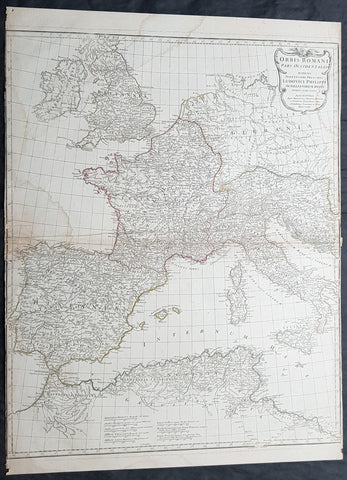
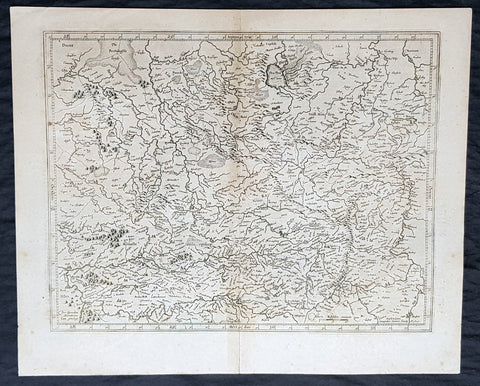
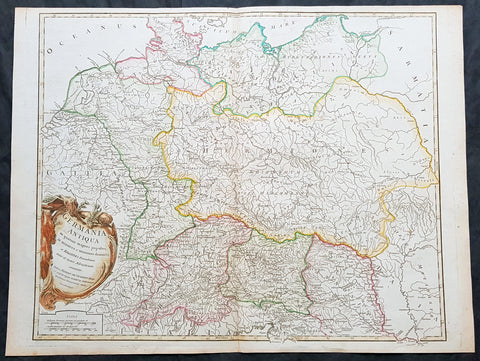
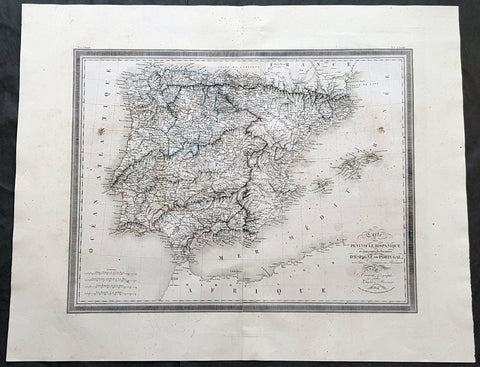
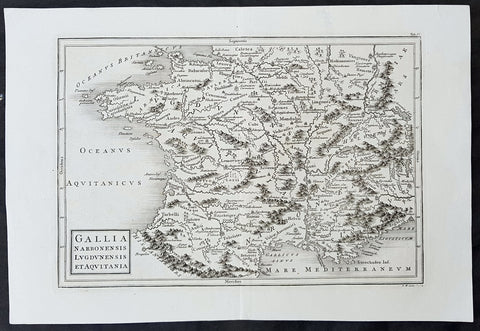
1764 D Anville Large Antique Map of the Western Roman Empire Dalmatia to Britain
- Title : Orbis Romani Pars Occidentalis...Auctor D Anville...MDCCLXIV (1763)
- Size: 29in x 22in (740mm x 560mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1763
- Ref #: 92294
Description:
This large hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Western part of the post Roman Empire, from Eastern Europe to Britain by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D Anville was engraved in 1764 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 22in (740mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 28in x 22in (730mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling in margins, L&R margins cropped close to border
Plate area: - Soiling bottom & top left
Verso: - Soiling
Background:
The Roman Empire was the post-Roman Republic period of the ancient Roman civilization, with a government headed by emperors and large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. The city of Rome was the largest city in the world c. 100 BC – c. AD 400, with Constantinople (New Rome) becoming the largest around AD 500, and the Empire\\\'s population grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world\\\'s population at the time) The 500-year-old republic which preceded it had been severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflict, during which Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and executions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar\\\'s adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the annexation of Egypt. Octavian\\\'s power was then unassailable and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively marking the end of the Roman Republic.
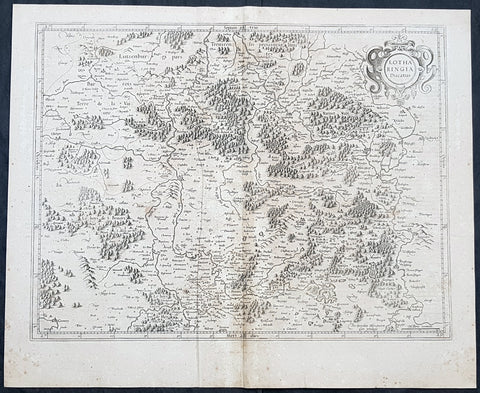
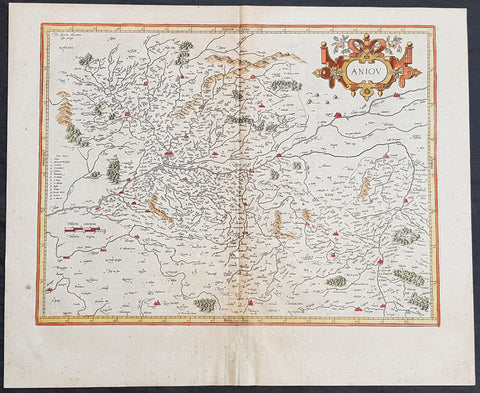
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map Lotharingia Region - Netherlands Germany France
Antique Map
- Title : Lotharingia Ducatus...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26141
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the historical region of Lotharingia region of present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany), Saarland (Germany), and Lorraine (France) by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630\\\'s when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, brown
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning, light creasing
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Lotharingia was a medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire, comprising the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany), Saarland (Germany), and Lorraine (France). It was named after King Lothair II who received this territory after the kingdom of Middle Francia of his father Lothair I was divided among his sons in 855.
Lotharingia was born out of the tripartite division in 855 of the kingdom of Middle Francia, which itself was formed after the threefold division of the Carolingian Empire by the Treaty of Verdun of 843. Conflict between East and West Francia over Lotharingia was based on the fact that these were the old Frankish homelands of Austrasia, so possession of them was of great prestige.
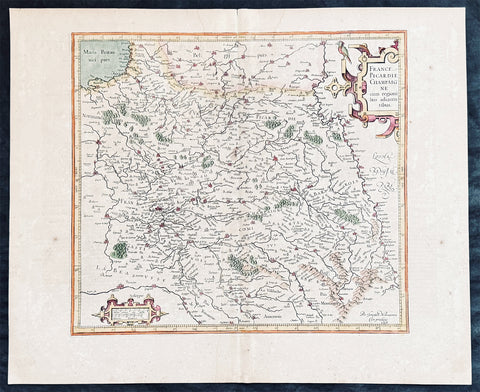
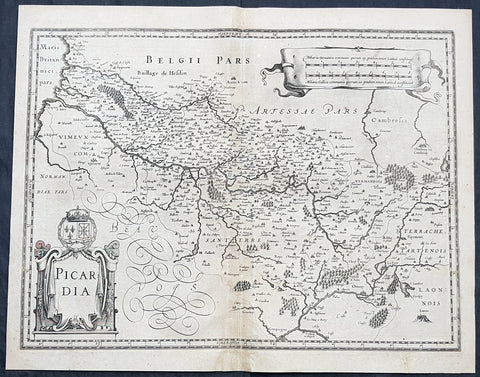
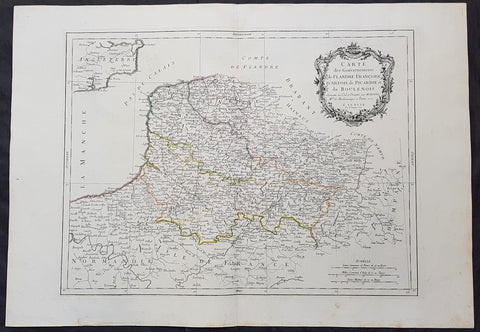
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map the Picardy Region of France
- Title : France Picardie Champagne cum regionibus adiacentibus
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26131
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
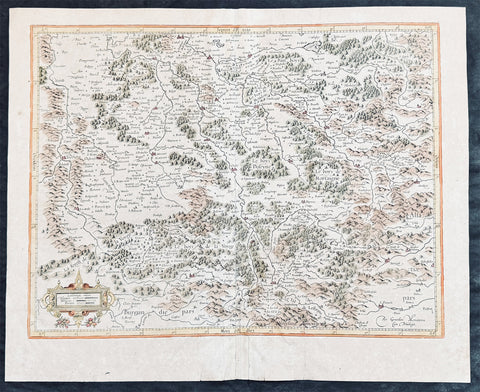
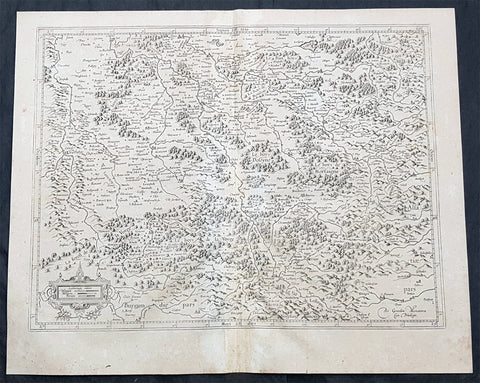
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map the Southern Lorraine Region of France
Antique Map
- Title : La Partie Meridionale de Lorraine...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26142
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map ancient region of southern Lorraine, France by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630\\\'s when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, creasing
Plate area: - Age toning, creasing
Verso: - Age toning, creasing
Background:
Lorraine is a cultural and historical region in north-eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Lorraines name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia, which in turn was named for either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. It later was ruled as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766.
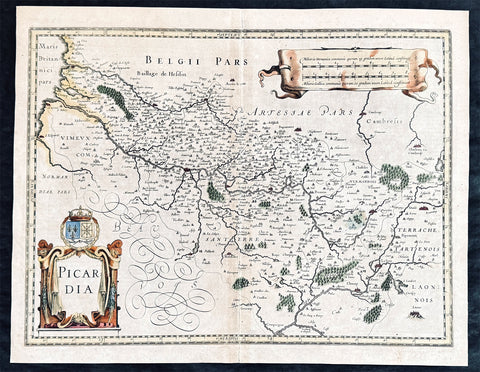
1628 Jan Jansson Antique Map of the Picardy or Picardie Region of France
- Title : Picardia
- Size: 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26133
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Jan Jansson was published in the early 1628 French edition of Janssons Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, brown, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\\\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
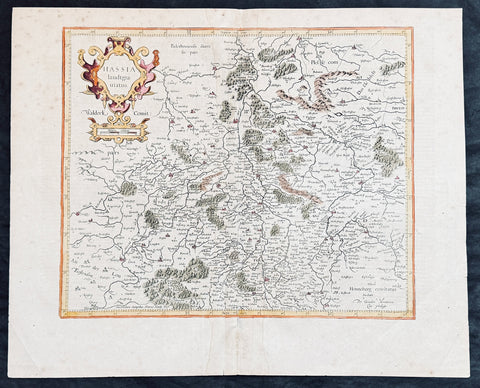
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map State of Hesse, Germany
- Title : Hassia landtgrauiatus...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilego
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26107
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the State of Hesse or Hessia, in central Germany, by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630s by Henricus, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, brown, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Hesse officially the State of Hesse, is a federal state (Land) of the Federal Republic of Germany, with just over six million inhabitants. The state capital is Wiesbaden; the largest city is Frankfurt am Main.
In the 12th century, Hessengau was passed to Thuringia. In the War of the Thuringian Succession (1247–1264), Hesse gained independence and became a Landgraviate within the Holy Roman Empire. It shortly rose to primary importance under Landgrave Philip the Magnanimous, who was one of the leaders of German Protestantism. After Philips death in 1567, the territory was divided among his four sons from his first marriage (Philip was a bigamist) into four lines: Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel), Hesse-Darmstadt, Hesse-Rheinfels, and the also previously existing Hesse-Marburg. As the latter two lines died out quite soon (1583 and 1605, respectively), Hesse-Kassel and Hesse-Darmstadt were the two core states within the Hessian lands. Several collateral lines split off during the centuries, such as in 1622, when Hesse-Homburg split off from Hesse-Darmstadt. In the late 16th century, Kassel adopted Calvinism, while Darmstadt remained Lutheran and subsequently the two lines often found themselves on different sides of a conflict, most notably in the disputes over Hesse-Marburg and in the Thirty Years War, when Darmstadt fought on the side of the Emperor, while Kassel sided with Sweden and France.
The Landgrave Frederick II (1720–1785) ruled as a benevolent despot, from 1760 to 1785. He combined Enlightenment ideas with Christian values, cameralist plans for central control of the economy, and a militaristic approach toward diplomacy.[16] He funded the depleted treasury of the poor nation by loaning 19,000 soldiers in complete military formations to Great Britain to fight in North America during the American Revolutionary War, 1776–1783. These soldiers, commonly known as Hessians, fought under the British flag. The British used the Hessians in several conflicts, including in the Irish Rebellion of 1798. For further revenue, the soldiers were loaned to other places as well. Most were conscripted, with their pay going to the Landgrave.
1744 Georg Mattaus Seutter Antique Map of Germany, Central & NW Europe
Antique Map
- Title : Imperium Romano Germanicum........a Matth. Seutteri...T C Lotter, Geogr.
- Ref #: 93398
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Germany and NW Europe was engraved by Tobias Lotter and was published in the 1744 edition of GM Seutters Atlas Minor Prae cipua Orbis Terrarum Imperia Regna et Provincias...., Augsburg, Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (265mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - None
Background:
Atlas Minor was a series of beautiful maps of all parts of the world. Georg Matthäus Seutter was one of the most and important of the German cartographers of the 18th century, being appointed as the Geographer to the Imperial Court. His son, Albrecht Carl, joined Matthäus and eventually inherited the business. The maps from Atlas Minor were drawn by the two Seutters and engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotte. These maps are highly detailed and engraved with a bold hand with equally strong original hand color in the body of the map as was the 18th century German style. The cartouches were left uncolored in order to emphasize the elaborately detailed illustrations for which German maps are especially prized. These are some of the most decorative and interesting maps of the eighteenth century.
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map Lotharingia Region - Netherlands Germany France
Antique Map
- Title : Lotharingia Ducatus...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26141
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the historical region of Lotharingia region of present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany), Saarland (Germany), and Lorraine (France) by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630\\\'s when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Lotharingia was a medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire, comprising the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany), Saarland (Germany), and Lorraine (France). It was named after King Lothair II who received this territory after the kingdom of Middle Francia of his father Lothair I was divided among his sons in 855.
Lotharingia was born out of the tripartite division in 855 of the kingdom of Middle Francia, which itself was formed after the threefold division of the Carolingian Empire by the Treaty of Verdun of 843. Conflict between East and West Francia over Lotharingia was based on the fact that these were the old Frankish homelands of Austrasia, so possession of them was of great prestige.
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map the Southern Lorraine Region of France
Antique Map
- Title : La Partie Meridionale de Lorraine...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26142
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map ancient region of southern Lorraine, France by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630\\\'s when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Lorraine is a cultural and historical region in north-eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Lorraines name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia, which in turn was named for either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. It later was ruled as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766.
1685 G B Falda & Sandrart Antique Print Villa Gardens Doria Pamphili, Rome Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Prospecto Del Palazzo & Giardino Pamphilio Detto Del Bel Respiro...Architettura del Caualier Alessandro Algardi...Simon Felice delin....Norimburga appresso Gioni. Gac. de Sandart
- Ref #: 93463
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1685
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique print of the Villa & Gardens of Doria Pamphili, Rome was engraved by Simone Felice for the 1685 edition of Giovanni Battista Faldas Li giardini di Roma, disegnati da Giovanni Battista Falda nuovamente dati alle stampe con direttione di Giov. Giacomo de Sandrart (The gardens of Rome, designed by Giovanni Battista Falda again printed with the direction of Giov. Giacomo de Sandrart) published in Nuremberg by Johann von Sandrart.
The work is based on the original series edited by Gian Giacomo de Rossi a few years earlier (the first edition was certainly published after 1677 but before 1683) which included 19 tables of plants and perspective views of the most famous Roman gardens, 14 of which were engraved by GB Falda and 5 by Simon Felice.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Villa Doria Pamphili is a seventeenth-century villa with what is today the largest landscaped public park in Rome, Italy. It is located in the quarter of Monteverde, on the Gianicolo (or the Roman Janiculum), just outside the Porta San Pancrazio in the ancient walls of Rome where the ancient road of the Via Aurelia commences.
It began as a villa for the Pamphili family and when the line died out in the eighteenth century, it passed to Prince Giovanni Andrea IV Doria, and has been known as the Villa Doria Pamphili since.
The nucleus of the villa property, the Villa Vecchia or old villa, already existed before 1630, when it was bought by Pamfilio Pamfili, who had married the heiress Olimpia Maidalchini, to enjoy as a suburban villa. Thereafter he set about buying up neighbouring vineyards to accumulate a much larger holding, which was often known as the Bel Respiro or beautiful breath as it stood on high ground, above the malarial areas of Rome, and offered spectacular views which were a desirable feature of Baroque villa settings.
In 1644 Cardinal Giambattista Pamphili became elected to the papacy and took the name of Innocent X. In accordance with this change in status, the Pamphili aspired to a grander and more expansively sited new villa. Early designs were made, possibly by Virgilio Spada rather than the traditional attribution to Borromini, but these were rejected. Instead the project was placed in the hands of the Bolognese sculptor Alessandro Algardi in 1644, assisted by Giovanni Francesco Grimaldi.
The initial design had a central casino (not the modern usage as a gambling establishment) with wings, but only the central block was built. There is uncertainty as to who the architect was; Algardi was not an architect, and it may be that he had help from Carlo Rainaldi and that the construction was supervised by Grimaldi. The layout has a central circular room around which the other rooms were arranged. Construction began in 1645 and was complete by 1647 although embellishments and the garden layouts were not finished until 1653. The casino, sometimes known as the Casino del Bel Respiro, was designed as a complement to the Pamphili collection of sculptures both ancient and modern, and other Roman antiquities such as vases, sarcophagi and inscriptions; it was only ever intended for display of the collection and the family and guests resided in the older Vecchia Vigna.
As a show case for sculpture, the somewhat crowded Casino facades have rhythmically alternating windows with niches which were elaborately adorned with sculptures, both antique and modern, with busts in hollowed roundels, with panels of bas-reliefs, and reliefs.
The exterior containing statues gives a rich allure that was architecturally somewhat conservative for its date, looking back towards the Villa Medici or the Casina Pio IV, and rather more Mannerist than Baroque. It offered a foretaste of the richly stuccoed and frescoed interiors, where the iconographic program set out to establish the antiquity of the Pamphili, a family then somewhat parvenu in Rome, with origins in Gubbio. Inside, Algardi provided further bas-reliefs and stucco framing for the heroic frescoes drawn from Roman history painted by Grimaldi.
The casino is set into the hill slope such that the main entrance on the north side is at a level above the giardino segreto or secret garden enclosure on its south side, a parterre garden with low clipped hedges. The gardens on the sloping site were laid out from around 1650 by Innocents nephew, Camillo Pamphili, formalizing the slope as a sequence from the parterres that flank the Casino, to a lower level below, framed by the boschi or formalized woodlands that rose above clipped hedges, and eventually arriving at a rusticated grotto in the form of an exedra, from which sculptured figures emerge from the rockwork. The exedra, now grassed, formerly enframed a Fountain of Venus by Algardi, which is preserved in the Villa Vecchia, together with Algardis bas-reliefs of putti representing Love and the Arts that were formerly here. The fountain spilled into a small cascade that let into a short length of formal canal, which was intended to remind the viewer of the similar Canopus at Hadrians Villa— another programmatic connection of the Pamphili with Antiquity.
When Girolamo Pamphili died in 1760 without male heirs, the disputes which broke out among the possible heirs were settled in 1763 when Pope Clement XIII Rezzonico granted to Prince Giovanni Andrea IV Doria the right to take the surname, the arms and the vast properties of the Pamphili; the Princes claim was based on the marriage between Giovanni Andrea III Doria and Anna Pamphili. Since then, the villa has been known as the Villa Doria Pamphili.
Throughout the 18th century, features were regularly added such as fountains and gateways by Gabriele Valvassori and other architects retained by the Pamphili and their heirs. After the Napoleonic era, more sweeping changes were made. The parterres that were formal extensions of the casino were retained but replanted with the patterned planting of colourful carpet bedding supplied from greenhouses by the old villa. (Today the parterres have been replanted in 16th-century style, with panels of scrolling designs in close-clipped greens set in wide gravel walks.) In the sloping outer gardens the changes were more extensive, recasting them in the naturalistic manner of English landscape gardens. The grounds, filled with many surprise features and picturesque incidents, swept down to a small lake at the bottom, which already had an air of atmospheric maturity when it was painted in the 1830s by Alexandre-Gabriel Decamps. In the wooded, natural-appearing landscapes with clumps of characteristic umbrella-like stone pines along horizons stand statues and vases, which evoke a nostalgic antiquity. The 18th-century English landscape gardens such as Stowe and Stourhead that were the inspiration for this style aimed to bring to life the Italian landscapes with Roman ruins painted by Claude and Poussin. A notable difference is that at the Villa Doria Pamphilis giardino inglese the Roman remains are likely to be genuine. The site of the villa contained several Roman tombs that yielded vases, sarcophagi and inscriptions that were added to the Pamphili collection.
Falda, Giovanni Battista 1643 – 1678
Falda was an Italian architect, engraver and artist. He is known for his engravings of both contemporary and antique structures of Rome.
Falda was sent as a boy to Rome, to work in the studio of Bernini, and his draughtsmanship caught the eye of the publisher Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi. He engraved for Le fontane di Roma (Fountains in Rome) and for Palazzi di Roma (Palaces of Rome). The former books was expanded after Faldas death with engravings by Francesco Venturini. The latter was published in 1655 in collaboration with Pietro Ferrerio. He is sometimes known as Falda da Valduggia because of his birthplace.
His works became particularly popular with the first waves of Grand Tour participants during the latter parts of the 17th century and Falda became a commercial success as a result. His works appealed to tourists keen to retain a detailed and accurate representation of those parts of Rome they had visited.
1735 Schubler & Steidlin Antique Baroque Print Musical Ball Regensburg Ger. 1717
Antique Map
- Title : Bal, welche den 26. Sept: 1717 in Sr Durchl: Eminens des Herrn Cardinals residens zu Regensburg, in dem so genamten Lowen-Saal, gehalten worden....NB das Bal Zimmer war mit rohten Tuch belegt
- Ref #: 93443
- Size: 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1735
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original Baroque copper plate engraved antique print, numbered three of three, of an early 18th century Ball, part of the celebrations at the Royal Court in the Cardinal Castle of Regensburg, on September 26, 1717, by Johann Schubler, was engraved by Johann Matthias Steidlin or Steudlin 1717-1754 and published by the Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1735.
A wonderful piece of Baroque art, engraved and published by some of the foremost art engravers and publishers at the beginning of the 18th century.
Professionally matted and can be easily removed if required.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair bottom right signature
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1245 Regensburg became a Free Imperial City and was a trade centre before the shifting of trade routes in the late Middle Ages. In 1486, Regensburg became part of the Duchy of Bavaria, but its independence was restored by the Holy Roman Emperor ten years later. In the city took place the Diet of 1541, was adopted the Protestant Reformation in 1542 and its Town Council remained entirely Lutheran. From 1663 to 1806, the city was the permanent seat of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire, which became known as the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. Thus, Regensburg was one of the central towns of the Empire, attracting visitors in large numbers.
A minority of the population remained Roman Catholic, and Roman Catholics were denied civic rights (Bürgerrecht). Although the Imperial city had adopted the Reformation, the town remained the seat of a Roman Catholic bishop and several abbeys. Three of these, St. Emmeram, Niedermünster and Obermünster, were free imperial estates within the Holy Roman Empire, meaning that they were granted a seat and a vote at the Imperial Diet (Reichstag). So there was the unique situation that the town of Regensburg comprised five independent states (in terms of the Holy Roman Empire): the Protestant city itself, the Roman Catholic bishopric, and the three monasteries. In addition, it was seen as the traditional capital of the region Bavaria (not the state), acted as functional co-capital of the Empire (second to the Emperors court at Vienna) due to the presence of the Perpetual Diet, and it was the residence of the Emperors Commissary-Principal to the same diet, who with one very brief exception was a prince himself (for many years the Prince of Thurn and Taxis, still resident in the town).
Schübler, Johann Jacob 1689 - 1741
Schübler was born in Nuremberg as was known as a versatile German baroque master builder , architectural theorist and writer and mathematician.
Schüblers father Johann Jacob was a braid maker and language teacher, and he also had medical knowledge, which he also used for a fee. He came to Nuremberg from Strasbourg and became resident there by marrying Maria Elisabeth Hengel, the daughter of an independent braid maker. The later master builder Johann Jacob Schübler was the fourth of the couples eight children. Through his father and private tutors, he received careful training, mainly in artistic subjects as well as in old and new languages. Architectural painter Johann Andreas Graff gave him his first drawing lessons . In 1698 he began his apprenticeship as a draftsman in the studio of the portraitist, engraver and art dealerJacob von Sandrart (1630-1708), in addition he was taught by Georg Christoph Eimmart (1638-1705), the long-time director of the important Nuremberg Academy of Painters , a representative of the mathematically oriented artists of the time and founder of the observatory at the Nuremberg castle .
At that time, extensive study trips were common for aspiring artists to complete their training. Between 1705 and 1713, Schüblers years of traveling took him through Germany, Denmark and Norway, the Netherlands and France - with a stopover in 1711 with his parents in Nuremberg. The time around 1700 in Europe was particularly intensive secular and church building activity, numerous elaborate, representative buildings. Schüblers travel destinations were primarily places where the current building activity was concentrated. However, Italy was missing from this program. He made longer stays for scholarly studies in Leipzig and Copenhagen .
After his return in 1713, Schübler remained settled in Nuremberg. Prominent colleagues such as Balthasar Neumann (1687–1753) visited him and he corresponded with well-known artists and scientists. He rejected various offers from foreign employers because they did not seem attractive enough to him. In 1717 he received the order for a gate of honor, which was built to celebrate a princely wedding in the main square of the residential city of Sulzbach . Schübler had an expansive triumphal arch with three stacked columns and niches for allegorical figures built, which was generally praised. A permanent position at the court of the Sulzbach Palatinate Countshowever, did not result from this. So he remained the prevented Builder. Great vocations only reached him towards the end of his life. In 1740 the Danish king invited him to Copenhagen, in 1741 negotiations for a move to Berlin followed to the court of the Prussian king Friedrich II. Both offers came too late for Schübler. He died in September 1741 from a clock-like illness.
Schübler only started his own family at an advanced age. In 1727 he married Margareta Maria Hemme, the daughter of a respected art dealer. At around 40, the bride was even a little older than Schübler herself; she died two years after the marriage, the marriage remained childless. In 1733 Schübler had a second marriage to 26-year-old Margaretha Setzmair. She also came from a long-established, wealthy middle-class family. The couple had two daughters, one of whom died very early, and a son who was born several months after Schüblers death.
In 1734 Schübler was accepted as an external member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin. The small Schüblerstrasse in Nuremberg reminds him of him.
Schüblers actual lifes work consisted of a large number of writings, the publication of which he began around 1715. With his later works in particular, he pursued the intention of scientifically examining the questions of the building industry based on proportion and perspective, thereby making them teachable and learnable for building theorists and practitioners of his time.
Initially, Schübler published smaller masterpieces that appeared in deliveries of six to twelve engravings and contained hardly any text. In it he showed architectural details (e.g. fireplaces , mansard windows , pulpits, altars, confessionals), furniture (beds, desks, clocks, night chairs) and technical objects such as pumping stations and fountains. He drew the originals himself, often with a light color, but hardly ever took over the transfer to the printing plates, even though he knew this technique. For this, he employed a large number of engravers, among them Johann August Corvinus, Johann Matthias Steidlin, Georg Lichtensteger and his own brother Georg Andreas. The objects depicted often appear grotesquely overloaded with decorative elements such as flower threads, sphinxes and the like, but were also not intended for direct implementation. Rather, the executing tradesmen were able to take very different suggestions from a single template. The templates appeared in the publisher Jeremias Wolff in Augsburg, which is renowned throughout Europe .
Schüblers more scientific and literary works were mostly published by Johann Christoph Weigel in Nuremberg. In 1719/20 Perspectiva Pes Picturae was published in two parts , a large-format work of art intended to provide the basis for architectural painting . 1723/24, again in two parts, came out a textbook on the column orders with practical aids for difficult problems, which was reprinted several times. This was followed by publications on the art of sundial (1726) and on the wood-fired parlor ovens(1728). Schüblers main works then appeared within five years. With them he wanted to provide a new, in-depth representation of the entire architecture, with the main areas of the Architectura Civilis and the Architectura Militaris . From the years 1732-35 are the five illustrated volumes of a Synopsis Architecturae Civilis eclecticae , to which the content of the theoretical work Ars inveniendi from 1734 on civil architecture can be assigned. The two volumes of carpentry (Ars Tignaria) date from 1731 and 1736 . The main works include Perspectiva Geometrica Practica .
Schüblers works were widespread, and individual writings had up to 20 editions. The last known new edition dates from 1786. The popularity of his practically applicable proposals ended with the domination of baroque and rococo in architecture. The new general artist lexicon by art historian Georg Kaspar Nagler (1801–1866) already discusses Schüblers works as examples of the aesthetic aberrations of an era that has been overcome and describes them as senseless outbursts of an unregulated imagination.
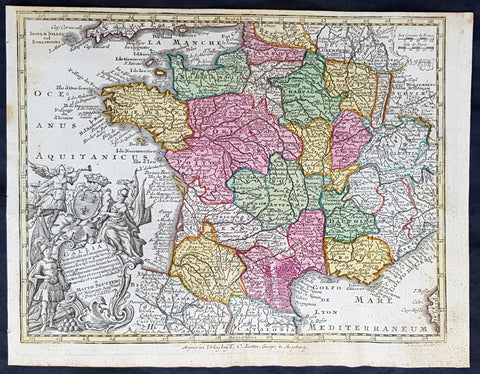
1744 Georg Mattaus Seutter Antique Map of France
Antique Map
- Title : Gallia....a Matth. Seuttero...T C Lotter, Geogr.
- Ref #: 93393
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of France was engraved by Tobias Lotter and was published in the 1744 edition of GM Seutters Atlas Minor Prae cipua Orbis Terrarum Imperia Regna et Provincias...., Augsburg, Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (265mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - None
Background:
Atlas Minor was a series of beautiful maps of all parts of the world. Georg Matthäus Seutter was one of the most and important of the German cartographers of the 18th century, being appointed as the Geographer to the Imperial Court. His son, Albrecht Carl, joined Matthäus and eventually inherited the business. The maps from Atlas Minor were drawn by the two Seutters and engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotte. These maps are highly detailed and engraved with a bold hand with equally strong original hand color in the body of the map as was the 18th century German style. The cartouches were left uncolored in order to emphasize the elaborately detailed illustrations for which German maps are especially prized. These are some of the most decorative and interesting maps of the eighteenth century.
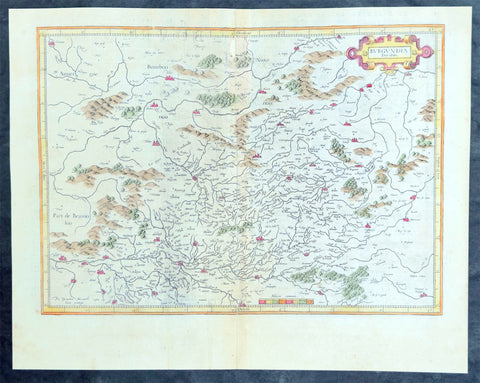
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map of The Burgundy Region of France
- Title : Burgundia Ducatus
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26143
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of of the historical region of the Free County of Burgundy (Franche Comte de Bourgogne) of eastern France by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630\\\'s when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, light creasing
Plate area: - Age toning, light creasing
Verso: - Age toning, light creasing
Background:
Burgundy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of France. It takes its name from the Burgundians, an East Germanic people who moved westwards beyond the Rhine during the late Roman period.
Historically, Burgundy has referred to numerous political entities, including kingdoms and duchies spanning territory from the Mediterranean to the Low Countries.
The first recorded inhabitants of the area that became Burgundy were Celts, who were eventually incorporated in the Roman Empire as Gallo-Romans.
During the 4th century, the Burgundians, a Germanic people, who may have originated in Bornholm (on the Baltic Sea), settled in the western Alps. They founded the Kingdom of the Burgundians, which was conquered in the 6th century by another Germanic tribe, the Franks.
Later, the region was divided between the Duchy of Burgundy (to the west) and the Free County of Burgundy (to the east). The Duchy of Burgundy is the better-known of the two, later becoming the French province of Burgundy, while the County of Burgundy became the French province of Franche-Comté, literally meaning free county.
Burgundys modern existence is rooted in the dissolution of the Frankish Empire. In the 880s, there were four Burgundies, which were the Kingdom of Upper and Lower Burgundy, the duchy and the county.
During the Middle Ages, Burgundy was home to some of the most important Western churches and monasteries, including those of Cluny, Cîteaux, and Vézelay. Cluny, founded in 910, exerted a strong influence in Europe for centuries. The first Cistercian abbey was founded in 1098 in Cîteaux. Over the next century, hundreds of Cistercian abbeys were founded throughout Europe, in a large part due to the charisma and influence of Bernard of Clairvaux. The Abbey of Fontenay, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is today the best-preserved Cistercian abbey in Burgundy. The Abbey of Vezelay, also a UNESCO site, is still a starting point for pilgrimages to Santiago de Compostela. Cluny was almost totally destroyed during the French Revolution.
During the Hundred Years War, King John II of France gave the duchy to his youngest son, Philip the Bold. The duchy soon became a major rival to the crown. The court in Dijon outshone the French court both economically and culturally. In 1477, at the battle of Nancy during the Burgundian Wars, the last duke Charles the Bold was killed in battle, and the Duchy itself was annexed by France and became a province. However the northern part of the empire was taken by the Austrian Habsburgs.
With the French Revolution in the end of the 18th century, the administrative units of the provinces disappeared, but were reconstituted as regions during the Fifth Republic in the 1970s. The modern-day administrative region comprises most of the former duchy.
1628 Jan Jansson Antique Map of the Picardy or Picardie Region of France
- Title : Picardia
- Size: 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26133
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Jan Jansson was published in the early 1628 French edition of Janssons Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\\\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
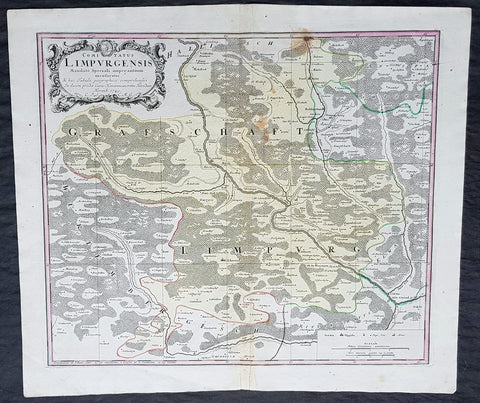
1749 Homann Antique Map Limpurg County, Schwabisch-Hall Baden-Wurtemberg Germany
- Title : Comitatus Limpurgensis Mandato Speciali imperantium mensuratus & hac Tabula geographica comprehensus / In lucem prodit Curis Homannianorum Heredum / Norimb 1749
- Date : 1749
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 20428
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map of Limpurg County in the district of Schwäbisch-Hallin in the state of Baden-Wurtemberg, SW Germany by the Homann Heirs was engraved in 1749 - dated in cartouche - and published in the Homanns 1750 German Atlas.
Limpurg is situated in the present-day district of Schwäbisch-Hall or Ostalbkreis between Schwäbisch-Hall, Schwäbisch Gmünd, Aalen and Ellwangen.
The map centers on the river Kocher, with towns marked such as Schwäbisch-Hall (Comburg), Gaildorf, Abstgemünd and Bühlertann.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 18in (535mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - None
Background:
Baden-Württemberg is formed from the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Hohenzollern, and Württemberg, and also parts of Swabia.
In 100 AD, the Roman Empire invaded and occupied Württemberg, constructing a limes (fortified boundary zone) along its northern borders. Over the course of the third century AD, the Alemanni forced the Romans to retreat west beyond the Rhine and Danube rivers. In 496 AD the Alemanni were defeated by a Frankish invasion led by Clovis I.
The Holy Roman Empire was later established. The majority of people in this region continued to be Roman Catholics, even after the Protestant Reformation influenced populations in northern Germany. In the late-nineteenth and early-twentieth centuries, numerous people emigrated from this mostly rural area to the United States for economic reasons.
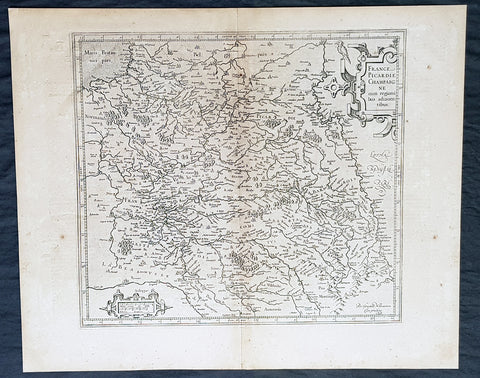
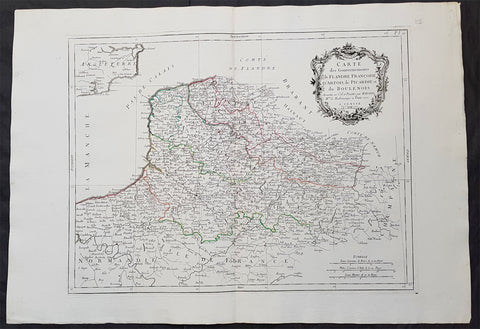
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map the Picardy Region of France
- Title : France Picardie Champagne cum regionibus adiacentibus
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26131
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Westphalia, Germany
- Title : Tabula Seconde Westphalia...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilego...1627
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26109
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the Westphalia region of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630s by Henricus, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
While the Northern Rhineland, Westphalia and Lippe are different historic territories of todays North Rhine-Westphalia, the old border between the former Rhine Province and the Province of Westphalia is also a language border. While in Westphalia and Lippe, people tend to speak West Low German dialects and especially the Westphalian variant of the Low German language, Central German and Low Franconian dialects are being spoken in the Northern Rhineland.
Westphalia is known for the 1648 Peace of Westphalia which ended the Thirty Years War, as the two treaties were signed in Münster and Osnabrück.
It is one of the regions that were part of all incarnations of the German state since the Early Middle Ages: the Holy Roman Empire, the Confederation of the Rhine, the German Confederation, the North German Confederation, the German Empire, the Weimar Republic and National Socialist Germany. After World War II it was a part of the British occupation zone which merged with the American zone to become the Bizone in 1947 and again merged with the French zone to become the Trizone in 1948. The current Federal Republic of Germany was founded on these territories making Westphalia a part of West Germany. It is a part of united Germany since 1990.
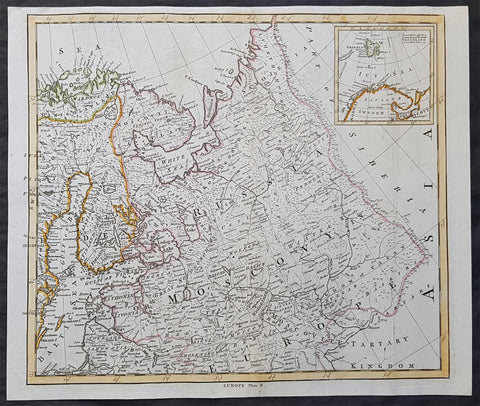
1824 Louis Vivien Large Antique Map of Russia in Europe
- Title : Carte La Russie D Europe...1824
- Size: 27 1/2in x 23in (700mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1824
- Ref #: 40704
Description:
This finely engraved original large antique map of Russia in Europe by Louis Vivien in his Elephant Folio atlas, Atlas Universal
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 23in (700mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West.
Vivien, Louis 1802 - 1896
Louis Vivien , or Vivien de Saint-Martin was a French geographer who was born in Saint-Martin-de-Fontenay and died in Versailles, France in 1896.
He settled in Paris under the Restoration, and became known with his publication of the Electoral and Administrative Map in 1823 and his comprehensive Universal Atlas in 1825, collaborating with Jacques Bibliomappe -Charles Bailleul from 1828. Vivien was foremost a geographer but was also a publisher of works in other fields, including historical books on the General History of the French Revolution and the History of Napoleon. He also translated various English works, such as the novels of Walter Scott .
He also wrote the New Annals of Travels between 1845 and 1854 and briefly the French Athenaeum between 1847 & 1848. He contributed to numerous periodicals such as Le Constitutionnel, Revue contemporaine, Revue germanique & La Presse. He also wrote L Année géographique between 1863 and 1875 before passing the baton to G. Maunoir and Henri Duveyrier.
He is mainly known though, for his three cartographical works, A History of Geographical Discoveries, A New Dictionary of Universal Geography and the Universal Atlas of Geography. The first of these publications he completed after the 1848 Revolution with the latter two completed by Louis Rousselet and Franz Schrader.
Vivien was Honorary President of the Geographical Society, of which he was one of the founder members. He also laureate of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles-Lettres as well as a member of the Asian Society , the Society of Ethnology along with a large number of learned societies and European academies.
Main works of Vivien de Saint-Martin
- General History of the French Revolution, the Empire, the Restoration, the Monarchy of 1830, up to and including 1841 (4 volumes in 2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat Brothers, 1841-1842.
- History of Napoleon and the Empire (2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat brothers, 1844.
- History of geographical discoveries of European nations in various parts of the world (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1845-1846.
- Research on primitive populations and the oldest traditions of the Caucasus , Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1847.
- Studies of Ancient Geography and Asian Ethnography (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1850-1852.
- Historical and geographical description of Asia Minor (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1852.
- Study on the Greek and Latin Geography of India , Paris, Imperial Printing, 1858.
- Study on the geography and the primitive populations of north-west India, according to the Vedic hymns , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1860.
- North Africa in Greek and Roman antiquity, historical and geographical study , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1863.
- History of geography and geographical discoveries from the earliest times to the present day , Paris, Hachette, 1873.
- With Franz Schrader : Universal Atlas of Geography built from the original sources and the most recent documents , Paris, Hachette, 1876-1915.
- With Louis Rousselet : New dictionary of universal geography (9 volumes), Paris, Hachette, 1879-1900.
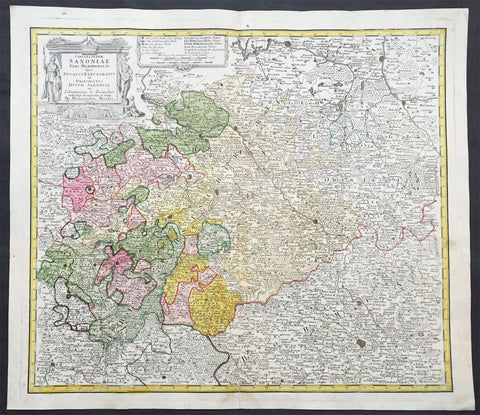
1735 J B Homann Large Antique Map of Old Saxony, Germany - Berlin to Prague
- Title : Circuli Super Saxoniae pars Meridionalis sive Ducatus...Homannianos
- Date : 1735
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 30832
- Size : 23in x 19in (600mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Saxony region of central Germany. The map stretches from Berlin in the north to Prague in the Czech Republic to the south, by J B Homann was published by the Homann Heirs firm in 1735. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (600mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (565mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Saxony is a landlocked federal state of Germany, bordering the federal states of Brandenburg, Saxony Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic.
The history of the state of Saxony spans more than a millennium. It has been a medieval duchy, an electorate of the Holy Roman Empire, a kingdom, and twice a republic.
The area of the modern state of Saxony should not be confused with Old Saxony, the area inhabited by Saxons. Old Saxony corresponds roughly to the modern German states of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and the Westphalian part of North Rhine-Westphalia.
The territory of the Free State of Saxony became part of the Holy Roman Empire by the 10th century, when the dukes of Saxony were also kings (or emperors) of the Holy Roman Empire, comprising the Ottonian, or Saxon, Dynasty. Around this time, the Billungs, a Saxon noble family, received extensive fields in Saxony. The emperor eventually gave them the title of dukes of Saxony. After Duke Magnus died in 1106, causing the extinction of the male line of Billungs, oversight of the duchy was given to Lothar of Supplinburg, who also became emperor for a short time.
In 1137, control of Saxony passed to the Guelph dynasty, descendants of Wulfhild Billung, eldest daughter of the last Billung duke, and the daughter of Lothar of Supplinburg. In 1180 large portions west of the Weser were ceded to the Bishops of Cologne, while some central parts between the Weser and the Elbe remained with the Guelphs, becoming later the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg. The remaining eastern lands, together with the title of Duke of Saxony, passed to an Ascanian dynasty (descended from Eilika Billung, Wulfhild\\\\\\\'s younger sister) and were divided in 1260 into the two small states of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg. The former state was also named Lower Saxony, the latter Upper Saxony, thence the later names of the two Imperial Circles Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg. Both claimed the Saxon electoral privilege for themselves, but the Golden Bull of 1356 accepted only Wittenberg\\\\\\\'s claim, with Lauenburg nevertheless continuing to maintain its claim. In 1422, when the Saxon electoral line of the Ascanians became extinct, the Ascanian Eric V of Saxe-Lauenburg tried to reunite the Saxon duchies.
However, Sigismund, King of the Romans, had already granted Margrave Frederick IV the Warlike of Meissen (House of Wettin) an expectancy of the Saxon electorate in order to remunerate his military support. On 1 August 1425 Sigismund enfeoffed the Wettinian Frederick as Prince-Elector of Saxony, despite the protests of Eric V. Thus the Saxon territories remained permanently separated. The Electorate of Saxony was then merged with the much bigger Wettinian Margraviate of Meissen, however using the higher-ranking name Electorate of Saxony and even the Ascanian coat-of-arms for the entire monarchy. Thus Saxony came to include Dresden and Meissen. In the 18th and 19th centuries Saxe-Lauenburg was colloquially called the Duchy of Lauenburg, which in 1876 merged with Prussia as the Duchy of Lauenburg district.
Saxony-Wittenberg, in modern Saxony-Anhalt, became subject to the margravate of Meissen, ruled by the Wettin dynasty in 1423. This established a new and powerful state, occupying large portions of the present Free State of Saxony, Thuringia, Saxony-Anhalt and Bavaria (Coburg and its environs). Although the centre of this state was far to the southeast of the former Saxony, it came to be referred to as Upper Saxony and then simply Saxony, while the former Saxon territories were now known as Lower Saxony.
In 1485, Saxony was split. A collateral line of the Wettin princes received what later became Thuringia and founded several small states there (see Ernestine duchies). The remaining Saxon state became still more powerful and was known in the 18th century for its cultural achievements, although it was politically weaker than Prussia and Austria, states which oppressed Saxony from the north and south, respectively.
Between 1697 and 1763, the Electors of Saxony were also elected Kings of Poland in personal union.
In 1756, Saxony joined a coalition of Austria, France and Russia against Prussia. Frederick II of Prussia chose to attack preemptively and invaded Saxony in August 1756, precipitating the Third Silesian War (part of the Seven Years\\\\\\\' War). The Prussians quickly defeated Saxony and incorporated the Saxon army into the Prussian army. At the end of the Seven Years\\\\\\\' War, Saxony recovered its independence in the 1763 Treaty of Hubertusburg.
1628 Sebastian Munster & RMD Antique Map View Nordlingen Swabia, Bavaria Germany
- Title : Die Statt Nordlingen
- Ref #: 33587
- Size: 17in x 15in (435mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1628
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German town of Nördlingen in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria,, was engraved by Hans Rudolf Manuel Deutsch (RMD) in 1549 - dated - and published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1628 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Hans Rudolf Manuel Deutsch (1525–1571) was a Swiss artist. He made several of the woodcuts for De re metallica (the metals and mining treatise by Georgius Agricola, the father of mineralogy) and for Sebastian Münsters Cosmographia.
Deutschs father, Niklaus Manuel Deutsch (the Elder), and Deutsch\'s brother, Niklaus Manuel Deutsch the Younger, were also artists. The elder Niklaus had taken the last name Manuel, but all three also commonly used Deutsch as part of their names and signed their paintings with initials ending in D.
Nördlingen is a town in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. The town was the location of two battles during the Thirty Years\' War, which took place between 1618–1648. Today it is one of only three towns in Germany that still has a completely established city wall, the other two being Rothenburg ob der Tauber and Dinkelsbühl.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 15in (435mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 15in (435mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light offsetting
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - Light offsetting
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1574 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the City of Tours, France
- Title : Die Statt Tours
- Ref #: 22614
- Size: 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the French city of Tours, France was published in the French Section of Sebastian Munsters 1574 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Tours is a city in the centre-west of France. It is the administrative centre of the Indre-et-Loire department and the largest city in the Centre-Val de Loire region of France
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
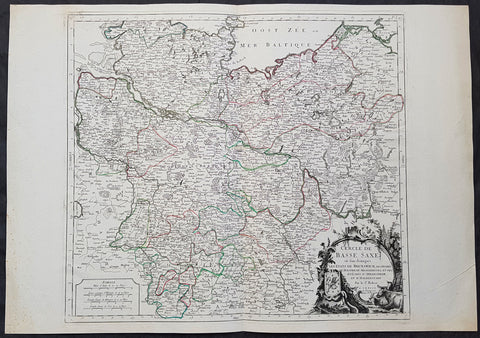
1778 Santini Antique Map Lower Saxon Circle Germany, Holstien Bremen Mecklenburg
- Title : Cercle de Basse Saxe on sont distingues Les Etats de Brunswich Les Duches De Holstien...Par L Sr Robert....A Venise...P Santini...1778
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50203
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Lower Saxon Circle of Northern Germany, was engraved in 1778 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - after Robert De Vaugondy and was published by Francois Santini (active 1776-84) in his 2 volume edition of Atlas Universal 1776-84. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (560mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Lower Saxon Circle was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire. It covered much of the territory of the medieval Duchy of Saxony (except for Westphalia), and was originally called the Saxon Circle (German: Sächsischer Kreis) before later being better differentiated from the Upper Saxon Circle by the more specific name.
An unusual aspect of this circle was that, at various times, the kings of Denmark (in Holstein), Great Britain (in Hanover) and Sweden (in Bremen) were all Princes of a number of Imperial States.
The Lower Saxon Circle included the easternmost part of current Lower Saxony, the northernmost part of Saxony-Anhalt (excluding the Altmark), Mecklenburg, Holstein (excluding Dithmarschen), Hamburg, Bremen, in addition to small areas in Brandenburg and Thuringia. For the most part it was a continuous territory with the exception of small enclaves like Halle and Jüterbog. Nordhausen and Mühlhausen were also areas outside the continuous portion of the imperial circle. Within the circle was the Archbishopric of Verden, which was in personal union with the Archbishopric of Bremen since 1502. The Counties of Schaumburg and Spiegelberg were also part of the personal union, but they were not a part of the Lower Saxon Circle.
By the downfall of the Holy Roman Empire, the circle was 1 240 square miles large, with 2 120 000 inhabitants. With respect to religion, almost all the citizens were Protestant. The exception was the partially Catholic Bishopric of Hildesheim.
During the Early Modern period the Holy Roman Empire was divided into Imperial Circles administrative groupings whose primary purposes were the organization of common defensive structure and the collection of imperial taxes. They were also used as a means of organization within the Imperial Diet and the Imperial Chamber Court. Each circle had a Circle Diet, although not every member of the Circle Diet would hold membership of the Imperial Diet as well.
Six Imperial Circles were introduced at the Diet of Augsburg in 1500. In 1512, three more circles were added, and the large Saxon Circle was split into two, so that from 1512 until the collapse of the Holy Roman Empire in the Napoleonic era, there were ten Imperial Circles. The Crown of Bohemia, the Swiss Confederacy and Italy remained unencircled, as did various minor territories which held imperial immediacy.
1777 F. Santini Antique Map Flanders Artois Hainaut Picardy Regions of Belgium
- Title : Carte Des Gouvernements de Flandre Francois d Artois de Picardie et du Boulenois...P Santini...1777
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1777
- Ref #: 50219
Description:
This large magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique map of Belgium and parts of Northern France made up of the provinces of Flanders, Artois, Hainaut, Picardy was engraved in 1777 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - after Rigobert Bonne in 1771 and was published by Francois Santini (active 1776-84) in his 2 volume edition of Atlas Universal 1776-84.. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Belgium officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Western Europe bordered by France, the Netherlands, Germany and Luxembourg.
Historically, Belgium was part of an area known as the Low Countries, a somewhat larger region than the current Benelux group of states that also included parts of northern France and western Germany. Its name is derived from the Latin word Belgica, after the Roman province of Gallia Belgica. From the end of the Middle Ages until the 17th century, the area of Belgium was a prosperous and cosmopolitan centre of commerce and culture. Between the 16th and early 19th centuries, Belgium served as the battleground between many European powers, earning the moniker the Battlefield of Europe, a reputation strengthened by both world wars. The country emerged in 1830 following the Belgian Revolution when it seceded from the Netherlands.
The Eighty Years War (1568–1648) divided the Low Countries into the northern United Provinces (Belgica Foederata in Latin, the Federated Netherlands) and the Southern Netherlands (Belgica Regia, the Royal Netherlands). The latter were ruled successively by the Spanish (Spanish Netherlands) and the Austrian Habsburgs (Austrian Netherlands) and comprised most of modern Belgium. This was the theatre of most Franco-Spanish and Franco-Austrian wars during the 17th and 18th centuries.
Following the campaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Low Countries—including territories that were never nominally under Habsburg rule, such as the Prince-Bishopric of Liège—were annexed by the French First Republic, ending Austrian rule in the region. The reunification of the Low Countries as the United Kingdom of the Netherlands occurred at the dissolution of the First French Empire in 1815, after the defeat of Napoleon.
1777 F. Santini Antique Map Flanders Artois Hainaut Picardy Regions of Belgium
- Title : Carte Des Gouvernements de Flandre Francois d Artois de Picardie et du Boulenois...P Santini...1777
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1777
- Ref #: 50221
Description:
This large magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique map of Belgium and parts of Northern France made up of the provinces of Flanders, Artois, Hainaut, Picardy was engraved in 1777 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - after Rigobert Bonne in 1771 and was published by Francois Santini (active 1776-84) in his 2 volume edition of Atlas Universal 1776-84.. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Belgium officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Western Europe bordered by France, the Netherlands, Germany and Luxembourg.
Historically, Belgium was part of an area known as the Low Countries, a somewhat larger region than the current Benelux group of states that also included parts of northern France and western Germany. Its name is derived from the Latin word Belgica, after the Roman province of Gallia Belgica. From the end of the Middle Ages until the 17th century, the area of Belgium was a prosperous and cosmopolitan centre of commerce and culture. Between the 16th and early 19th centuries, Belgium served as the battleground between many European powers, earning the moniker the Battlefield of Europe, a reputation strengthened by both world wars. The country emerged in 1830 following the Belgian Revolution when it seceded from the Netherlands.
The Eighty Years War (1568–1648) divided the Low Countries into the northern United Provinces (Belgica Foederata in Latin, the Federated Netherlands) and the Southern Netherlands (Belgica Regia, the Royal Netherlands). The latter were ruled successively by the Spanish (Spanish Netherlands) and the Austrian Habsburgs (Austrian Netherlands) and comprised most of modern Belgium. This was the theatre of most Franco-Spanish and Franco-Austrian wars during the 17th and 18th centuries.
Following the campaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Low Countries—including territories that were never nominally under Habsburg rule, such as the Prince-Bishopric of Liège—were annexed by the French First Republic, ending Austrian rule in the region. The reunification of the Low Countries as the United Kingdom of the Netherlands occurred at the dissolution of the First French Empire in 1815, after the defeat of Napoleon.
1782 J B D Anville Large Antique Map of Western Roman Europe, Britain to Italy
- Title : Germanie, France, Italie, Espagne, Isles Britanniques...Par Le Sr D Anville...MDCCLXXXII
- Size: 27in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1782
- Ref #: 92646
Description:
This large hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Western Roman Britain by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville was engraved in 1782 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D\'Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 27in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Vertical & horizontal folds
Verso: - None
Background:
The Roman Empire was the post-Roman Republic period of the ancient Roman civilization, with a government headed by emperors and large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. The city of Rome was the largest city in the world c. 100 BC – c. AD 400, with Constantinople (New Rome) becoming the largest around AD 500, and the Empire\'s population grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world\'s population at the time) The 500-year-old republic which preceded it had been severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflict, during which Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and executions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar\'s adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the annexation of Egypt. Octavian\'s power was then unassailable and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively marking the end of the Roman Republic.
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of Germania, Germany During Roman Era
- Title : Germania Antiqua in quatuor magnos populos...Autore Robert De Vaugondy
- Size: 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41548
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Ancient Germania, Germany, during the Roman Era by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Germania was the Roman term for the geographical region in north-central Europe inhabited mainly by Germanic peoples.
It extended from the Danube in the south to the Baltic Sea, and from the Rhine in the west to the Vistula. The Roman portions formed two provinces of the Empire, Germania Inferior to the north (present-day southern Netherlands, Belgium, and western Germany), and Germania Superior to the south (Switzerland, southwestern Germany, and eastern France).
Germania was inhabited mostly by Germanic tribes, but also Celts, Balts, Scythians and later on Early Slavs. The population mix changed over time by assimilation, and especially by migration. The ancient Greeks were the first to mention the tribes in the area. Later, Julius Caesar wrote about warlike Germanic tribesmen and their threat to Roman Gaul, and there were military clashes between the Romans and the indigenous tribes. Tacitus wrote the most complete account of Germania that still survives.
The origin of the term Germania is uncertain, but was known by Caesar\'s time, and may be Gaulish in origin.
Germania was inhabited by different tribes, most of them Germanic but also some Celtic, proto-Slavic, Baltic and Scythian peoples. The tribal and ethnic makeup changed over the centuries as a result of assimilation and, most importantly, migrations. The Germanic people spoke several different dialects.
Classical records show little about the people who inhabited the north of Europe before the 2nd century BC. In the 5th century BC, the Greeks were aware of a group they called Celts (Keltoi). Herodotus also mentioned the Scythians but no other tribes. At around 320 BC, Pytheas of Massalia sailed around Britain and along the northern coast of Europe, and what he found on his journeys was so strange that later writers refused to believe him. He may have been the first Mediterranean to distinguish the Germanic people from the Celts. Contact between German tribes and the Roman Empire did take place and was not always hostile. Recent excavations of the Waldgirmes Forum show signs that a civilian Roman town was established there, which has been interpreted to mean that Romans and Germanic tribesmen were living in peace, at least for a while.
Caesar described the cultural differences between the Germanic tribesmen, the Romans, and the Gauls in his book Commentarii de Bello Gallico, where he recalls his defeat of the Suebi tribes at the Battle of Vosges. He describes them at length at the beginning of Book IV and the middle of Book VI. He states that the Gauls, although warlike, had a functional society and could be civilized, but that the Germanic tribesmen were far more savage and were a threat to Roman Gaul and Rome itself. Caesar said the Germanic tribes were nomadic, with no notable settlements and a primitive culture. He used this as one of his justifications for why they had to be conquered. His accounts of barbaric northern tribes could be described as an expression of the superiority of Rome, including Roman Gaul.
Caesars accounts portray the Roman fear of the Germanic tribes and the threat they posed. The perceived menace of the Germanic tribesmen proved accurate. The most complete account of Germania that has been preserved from Roman times is Tacitus Germania.
1812 Las Cases Large Original Antique Map of The Russian Empire, English Text
- Title : The Russian Empire with its gradual Acquisitions traced and Explained
- Size: 28in x 19in (710mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 40259
- Date : 1812
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique map of Russia - within the geographical, political, economic, physical & historical text - was published in the 1812 English edition of Emmanuel Las Cases very large Elephant Folio size The Historical, Geographical & Genealogy Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 28in x 19in (710mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 13in (535mm x 33mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light offsetting
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - Light age toning
1771 J B D Anville Large Original Antique Map of Western Europe & Britain
- Title : Germanie, France, Italie, Espagne, Isles Britanniques...MDCCLXXI
- Size: 25 1/2in x 20in (650mm x 525mm)
- Ref #: 92305
- Date : 1771
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved and highly detailed original antique map of Western Europe and The British Isles by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville was engraved in 1771 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D\'Anville\'s large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 20in (650mm x 525mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing along centerfold
Plate area: - Creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Creasing along centerfold
1628 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of the Duchy of Anjou, Maine-et-Loire, France
- Title : Aniov
- Date : 1628
- Size: 21in x 17in (535mm x 430mm)
- Ref #: 26135
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the French region of the historical province of Anjou (today a greater part of the Maine-et-Loire dept.) centering on the city of Angers & the Loire River was published in the 1628 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (535mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (460mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning along centerfold
Background:
Anjou is a historical province of France straddling the lower Loire River. Its capital was Angers and it was roughly coextensive with the diocese of Angers. It bordered Brittany to the west, Maine to the north, Touraine to the east and Poitou to the south. The adjectival form of Anjou is Angevin and inhabitants of Anjou are known as Angevins. During the Middle Ages, the county of Anjou was a prominent fief of the French crown.
The region takes its name from the Celtic tribe of the Andecavi, who submitted to Roman rule following the Gallic Wars. Under the Romans, the chief fortified settlement of the Andecavi became the city of Juliomagus, the future Angers. The territory of the Andecavi was organized as a civitas (called the civitas Andegavensis or civitas Andegavorum).
Under the Franks, the city of Juliomagus took the name of the ancient tribe and became Angers. Under the Merovingians, the history of Anjou is obscure. It is not recorded as a county (comitatus) until the time of the Carolingians. In the late ninth and early tenth centuries the viscounts (representatives of the counts) usurped comital authority and made Anjou an autonomous hereditary principality. The first dynasty of counts of Anjou, the House of Ingelger, ruled continuously down to 1205. In 1131, Count Fulk V became the King of Jerusalem; then in 1154, his grandson, Henry \'Curtmantle\' became King of England. The territories ruled by Henry and his successors, which stretched from Ireland to the Pyrenees, are often called the Angevin Empire. This empire was broken up by the French king Philip II, who confiscated the dynasty\'s French lands, including Anjou in 1205.
The county of Anjou was united to the royal domain between 1205 and 1246, when it was turned into an apanage for the king\'s brother, Charles I of Anjou. This second Angevin dynasty, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, established itself on the throne of Naples and Hungary. Anjou itself was united to the royal domain again in 1328, but was detached in 1360 as the Duchy of Anjou for the king\'s son, Louis I of Anjou. The third Angevin dynasty, a branch of the House of Valois, also ruled for a time the Kingdom of Naples. The dukes had the same autonomy as the earlier counts, but the duchy was increasingly administered in the same fashion as the royal domain and the royal government often exercised the ducal power while the dukes were away. When the Valois line failed and Anjou was incorporated into the royal domain again in 1480, there was little change on the ground. Anjou remained a province of crown until the French Revolution (1790), when the provinces were reorganized.
1695 De Rossi Large Old, Antique Map of The Champagne Region of France
- Title : Governo generale della Ciampagna diviso nelle sue Parti Principali; da Giaco. Cantelli da Vignola geografo del Sermo Sigr. Duca di Moda.; e dato in luce da Domenico de Rossi erede di Gio. Giaco. de Rossi dalle sue Stampe in Roma alla Pace, con Privil. del S.P. e licenza de Sup. l'Anno 1695
- Ref #: 50224
- Size: 24in x 18 1/2in (610mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1695
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large, beautifully engraved original antique map of the Champagne Region of France by Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi, (1627-1691) in 1695 - dated in title - and was published by Domenico de Rossi in his monumental Atlas Mercurio Geografico overo Guida Geografica in tutte le parti del Mondo.
Background: A fine example of De Rossi's atlas map, similar to Coronelli's maps of the same period, with engraved decorative title. The atlas included 150 engraved outline hand colored maps with decorative title cartouche, on 181 sheets. Maps are dated between 1669 and 1715, issued by Giov. Giac. de Rossi and Domenico de Rossi, they are mainly derived from Cantelli da Vignola's maps, an important seventeenth-century cartographer who pioneered the Italian style of fine bold engraving that would eventually be embraced and expanded upon by Vincenzo Coronelli, and Nicolas Sanson (1600 – 1667) a French cartographer, termed by some the creator of French geography.
Many of the maps were engraved by Baudrand, Franciscus Donia, G.B. Falda, Jean Lhuilier, Vin Mariotti, Gasparo Pietro Santa, Salomon Rogiers, & Giorgio Widman, Lubin, Titi, Ameti, Magini and Mattei.
Giovanni Giacomo De Rossi (1627 - 1691) was an Italian printer and publisher active in 17th century Rome. Giovanni inherited the important Rome based printing business originally founded by his father, Giuseppe de Rossi (1570-1639). By the mid-17th century the Rossi firm was considered the most active and important press in Rome. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24in x 18 1/2in (610mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 20 3/4in x 16 3/4in (525mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1765 Tardieu Large Antique Map Catholic States of Italy
- Title : Etat de L Eglise
- Ref #: 92787
- Size: 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Catholic States of Italy waspublished by the famous French publisher Pierre Francois Tardieu (famous for publishing Diderots Encyclopedie in 1779) in 1765. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Paper size: - 18in x 13 1/2in (460mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1760 Bellin Large Original Antique Map of Kamchatka Peninsula, in Eastern Russia
- Title : Carte Du Kamtschatka Dressee et Gravee par Laurent.
- Ref #: 60969
- Size: 23in x 14 1/2in (585mm x 370mm)
- Date : 1747
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Kamchatka Peninsula, in Eastern Russia by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1760 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23in x 14 1/2in (585mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 12 1/2in (520mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1765 Tardieu Large Antique Map of Italy
- Title : Italie Carte Comparative
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92789
- Size: 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Italy was published by the famous French publisher Pierre Francois Tardieu (famous for publishing Diderots Encyclopedie in 1779) in 1765. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Paper size: - 18in x 13 1/2in (460mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1682 Merian Antique Map Birds Eye View of the Siege of Szczecin, Stettin Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Abbildung der voortrefflichen Langwerenden Belägerung der Statt und Vöstung Alt Stettin . Im Jahr 1677
- Ref #: 93495
- Size: 15 1/2in x 13 1/2in (395mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1682
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map a birds-eye view of the siege of Szczecin or Stettin, Poland in 1677 by Matthaus Merian was published in the 1682 edition of Theatrum Europaeum
During the Thirty Years War, Stettin refused to accept German imperial armies, instead the Pomeranian dukes allied with Sweden. After the Treaty of Stettin (1630) manifested Swedish occupation, Stettin was fortified by the Swedish Empire. After the death of the last Pomeranian duke, Boguslaw XIV, Stettin was awarded to Sweden with the western part of the duchy in the Peace of Westphalia (1648), but remained part of the Holy Roman Empire. The Swedish-Brandenburgian border was settled in the Treaty of Stettin (1653). The King of Sweden became Duke of Pomerania and as such held a seat in the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire. The city was cut off from its main trading area, and was besieged in several wars with Brandenburg which shattered the citys economy, which fell in prolonged economic decline.
In 1654 the last Pomeranian duke Boguslaw XIV was buried in the Ducal Castle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 13 1/2in (395mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 10in (280mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Szczecin/Stettin is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major seaport and Polands seventh-largest city.
Szczecin is located on the river Oder, south of the Szczecin Lagoon and the Bay of Pomerania. The city is situated along the southwestern shore of Dąbie Lake, on both sides of the Oder and on several large islands between the western and eastern branches of the river. Szczecin is adjacent to the town of Police and is the urban centre of the Szczecin agglomeration, an extended metropolitan area that includes communities in the German states of Brandenburg and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
The cities recorded history began in the 8th century as a Lechitic Pomeranian stronghold, built at the site of the Ducal castle. In the 12th century, when Szczecin had become one of Pomeranias main urban centres, it lost its independence to Piast Poland, the Duchy of Saxony, the Holy Roman Empire and Denmark. At the same time, the House of Griffins established themselves as local rulers and the population was Christianized. After the Treaty of Stettin in 1630, the town came under the control of the Swedish Empire and became in 1648 the Capital of Swedish Pomerania until 1720, when it was acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia and then the German Empire. Following World War II Stettin became part of Poland in accordance with the Potsdam Agreement, resulting in the almost complete expulsion of the pre-war German population.
Merian, Matthaus 1593 - 1650
Merian was a Swiss-born engraver who worked in Frankfurt for most of his career, where he also ran a publishing house. He was a member of the patrician Basel Merian family.
Born in Basel, Merian learned the art of copperplate engraving in Zürich. He next worked and studied in Strasbourg, Nancy, and Paris, before returning to Basel in 1615. The following year he moved to Frankfurt, Germany where he worked for the publisher Johann Theodor de Bry, who was the son of renowned engraver and traveler Theodor de Bry.
In 1617, Merian married Maria Magdalena de Bry, daughter of the publisher, and was for a time associated with the de Bry publishing house. In 1620 they moved back to Basel, but three years later returned to Frankfurt. They had four daughters and three sons, including Matthäus Merian the Younger. Maria Magdalena de Bry died in 1645 and the following year Matthäus married Johanna Catharina Hein. Five years later, Matthäus died, leaving his wife with two small children, Anna Maria Sibylla Merian (born 1647) who later became a pioneering naturalist and illustrator and a son, Maximilian, who died before his third birthday.
In 1623 Merian took over the publishing house of his father-in-law after de Brys death. In 1626 he became a citizen of Frankfurt and could henceforth work as an independent publisher. He spent most of his working life in Frankfurt.
Early in his life, he had created detailed town plans in his unique style, e.g. a plan of Basel (1615) and a plan of Paris (1615). With Martin Zeiler (1589 - 1661), a German geographer, and later (circa 1640) with his own son, Matthäus Merian (der Jüngere, i.e.the Younger or Jr.) (1621 - 1687), he produced a series of Topographia. The 21-volume set was collectively known as the Topographia Germaniae. It includes numerous town plans and views, as well as maps of most countries and a World Map—it was such a popular work that it was re-issued in many editions. He also took over and completed the later parts and editions of the Grand Voyages and Petits Voyages, originally started by de Bry in 1590.
Merians work inspired the Suecia Antiqua et Hodierna by Erik Dahlberg. The German travel magazine Merian is named after him.
He was also noted for the finesse of his alchemical illustrations, in books such as the Musaeum Hermeticum (1678) and Atalanta Fugiens (1618).
Matthäus Merian died after several years of illness in 1650 in Langenschwalbach, near Wiesbaden.
After his death, his sons Matthäus Jr. and Caspar took over the publishing house. They continued publishing the Topographia Germaniae and the Theatrum Europaeum under the name Merian Erben (i.e. Merian Heirs).
1725 Gabriel Bodenehr Antique Map Birds Eye View of Szczecin or Stettin, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Stettin
- Ref #: 93494
- Size: 13 1/2in x 8in (335mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1725
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map, a birds eye view of the city of Szczecin or Stettin, Poland along with descriptive text was published in Gabriel Bodenehrs Force d Europe in 1725.
Bodenehr a copper engraver and publisher, bought the numerous copper plates of Johann Stridbeck (1640 – 1716) and revised them and along with his own maps, views and plans published them in several works with different titles.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 8in (335mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 6 1/2in (330mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Szczecin/Stettin is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major seaport and Polands seventh-largest city.
Szczecin is located on the river Oder, south of the Szczecin Lagoon and the Bay of Pomerania. The city is situated along the southwestern shore of Dąbie Lake, on both sides of the Oder and on several large islands between the western and eastern branches of the river. Szczecin is adjacent to the town of Police and is the urban centre of the Szczecin agglomeration, an extended metropolitan area that includes communities in the German states of Brandenburg and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
The cities recorded history began in the 8th century as a Lechitic Pomeranian stronghold, built at the site of the Ducal castle. In the 12th century, when Szczecin had become one of Pomeranias main urban centres, it lost its independence to Piast Poland, the Duchy of Saxony, the Holy Roman Empire and Denmark. At the same time, the House of Griffins established themselves as local rulers and the population was Christianized. After the Treaty of Stettin in 1630, the town came under the control of the Swedish Empire and became in 1648 the Capital of Swedish Pomerania until 1720, when it was acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia and then the German Empire. Following World War II Stettin became part of Poland in accordance with the Potsdam Agreement, resulting in the almost complete expulsion of the pre-war German population.
Bodenehr, Gabriel I fl 1673-1765
Engraver and mapmaker of Augsburg, from a family dynasty of engravers and publishers. Son of Johann Georg Bodenehr (1631-1704), father of Gabriel II (whose work is difficult to distinguish) and brother of Georg Conrad. In 1717 the family took over the Augsburg publishing house of Stridbeck. His works include Atlas Curieux (1704), Curioser Staats und Kriegs Theatrum (1715), and Europens Pracht und Macht (c.1720).
1740 Isaac Tirion Antique Map of Bohemia, Silesia, Moravia - Germany, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Nuova Carta del Regno di Boemia Ducato Di Slesia, Marches Ato Di Moravia e lusazia in Amsterdam da Isac Tirion
- Ref #: 35636
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 14 1/2in x 12 1/2in (365mm x 315mm)
- Date : 1740
- Price: $149US
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the central European countries of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Duchy of Silesia, Marquisate of Moravia, and Lusatia by Isaac Tirion, was published in 1740 in Amsterdam.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 12 1/2in (365mm x 315mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10 1/2in (315mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Bohemia is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia proper as a means of distinction
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1780 Antonio Zatta Antique Map of The Lusatia Region Germany, Poland & Czech Rep
Antique Map
- Title : La Lusazia divisa ne suoi stati di nuova projezione
- Ref #: 35638
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
- Date : 1780
- Price: $149US
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the ancient central European region of Lusatia in between Poland and Germany, and in the south, the Czech Republic by Antonio Zatta (fl. 1775-97) in 1780 - dated - was published in his Atlas Atlante Novissimo
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Lusatia is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the east to the Pulsnitz and Black Elster rivers in the west, and is located within the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg as well as in the Polish voivodeships of Lower Silesia and Lubusz. Lusatia's central rivers are the Spree and the Lusatian Neisse, which constitutes the border between Germany and Poland since 1945 (Oder–Neisse line). The Lusatian Mountains (part of the Sudetes), separate Lusatia from Bohemia (Czech Republic) in the south. Lusatia is traditionally divided into Upper Lusatia (the hilly southern part) and Lower Lusatia (the flat northern part).
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1744 Georg Mattaus Seutter Antique Map of Germany w/ European City Mileage Chart
Antique Map
- Title : Germaniae Aliorumque Quorundam Locorum Europae Poliometria....Cart von Deutsschland...Tob. Conrad Lotter Geogr.
- Ref #: 93404
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Germany, with a mileage index chart with all the major cities of Europe, was engraved by Tobias Lotter and was published in the 1744 edition of GM Seutters Atlas Minor Prae cipua Orbis Terrarum Imperia Regna et Provincias...., Augsburg, Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (265mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - None
Background:
Atlas Minor was a series of beautiful maps of all parts of the world. Georg Matthäus Seutter was one of the most and important of the German cartographers of the 18th century, being appointed as the Geographer to the Imperial Court. His son, Albrecht Carl, joined Matthäus and eventually inherited the business. The maps from Atlas Minor were drawn by the two Seutters and engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotte. These maps are highly detailed and engraved with a bold hand with equally strong original hand color in the body of the map as was the 18th century German style. The cartouches were left uncolored in order to emphasize the elaborately detailed illustrations for which German maps are especially prized. These are some of the most decorative and interesting maps of the eighteenth century.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
Antique Map
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90194
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Cap Richard Delafield Large Antique Schematics German Fortifications
Antique Map
- Title : Theory and Practise of the German Engineers
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90144
- Size: 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of parts of the German Forts in such cities as Coblenz, Posen, Mainz, Luxemburg, Landau & others - during the time of the Crimean War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 18in (615mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds, as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation.
Section C. Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortress on the Upper Rhine; and Bavaria was allowed £600,000 towards erecting another strong place on the Rhine, at Germersheim or some other point.
By 1835 the works about Mainz were completed; the twin fortresses of Koblenz and Ehrenbreitstein, and Cologne had been abundantly strengthened on the side of Prussia; and, on the Bavarian side, the fortress of Germersheim was in a state to defend the passage on the Upper Rhine. The western frontier of Germany had, in this way, been provided with a formidable line of defences against possible hostile actions by their neighbours. The eastern side of Germany has been additionally fortified by the erection of a strong citadel at Posen; and the southern was to be still further protected by the formidable works in course of construction at Brixen in the Tyrol.
The fortress of Ulm became a major strategic fortress able to accommodate 100,000 men and their equipment. Since the Kingdom of Württemberg had no engineering corps King William I appointed Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz, a Prussian major, as the supervisor to oversee the building the fortresses. His plans included the provisions for the prospective development of the city Ulm. Major Theodor von Hildebrandt was appointed to oversee the building of fortresses around Neu-Ulm on the Bavarian side of the Danube
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics Forts City of Lyons, France
Antique Map
- Title : Detached Forts about the City of Lyons
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90123
- Size: 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of various forts in and around the French city of Lyons - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The ceintures de Lyon (Belts of Lyon) were a series of fortifications built between 1830 and 1890 around the city of Lyon, France to protect the city from foreign invasion.
The belts comprised two defensive barriers that included forts, lunettes, ramparts, batteries, and other defensive structures. Many of these structures proved to be ineffective in war due to advancement in weapon technology and the evolution of attack strategies at the time. Some of the fortifications of the ceintures de Lyon have been destroyed, though many remain today.
In 1830 the maréchal de camp, Hubert Rohault de Fleury, commenced a project designed by military engineer Baron Haxo. With a budget of 10,000,000 francs (approximately €67,000,000 as of 2015) allocated for Lyon between 1831 and 1839, this first project included the restoration of the fortifications between Croix Rousse and Fourvière; the construction of two forts on the plateau of Caluire (Fort de Montessuy and Fort de Caluire, connected by the Enceinte de Caluire), facing the Dombes; closing access to the Presquîle by the construction of a south-facing building; building two forts – Fort de la Duchère and Fort de Grange Blanche – to protect access routes towards Paris and Auvergne.
The fortification of the city is divided into three sectors: The north was protected by the wall of Croix-Rousse and the structures between the Rhône and the Saône. The command was situated at fort de Montessuy. The west was covered by the hillfort of Fourvière and the associated forts of Vaise at Sainte-Foy. The command was situated at fort Saint-Irénée. The east was defended by the Redoute du Haut-Rhône and Fort de la Vitriolerie on the left bank of the Rhône. The command was situated at Fort Lamothe.
The work required almost 20,000 workers, which were locally sourced in an attempt to avoid insurrection such as the ongoing unrest of the Lyon silk workers (Canuts) over increased capitalism. Work began in 1831 to build seven structures, each structure requiring between 400 and 500 workers. The scope of this project included the construction of Fort de Montessuy and Fort de Caluire to the north; Fort des Brotteaux, Fort Montluc and Fort du Colombier to the east; the Redoute de la Part-Dieu to the west; and Fort Saint-Irénée, to protect the entire area.
In January 1831, an uprising began at a work site in Charpennes, however it was quickly stopped by the army. Other insurrections took place the same year, a series of Canut revolts, which succeeded in rallying soldiers on the side of the Canuts, resulting in the death of captain Viquesnel, aide-de-camp of Fleury, and the temporary withdrawal of the 20,000 soldiers who eventually retook the city in December 1831.
In 1832, three other structures were built to reinforce the defenses to the east: The Redoute de la Tête dor, Fort La Motte, and the Redoute des Hirondelles. A treaty was signed between the city of Lyon and the War Department, which stipulated that the city had to cede the land necessary for the construction of military buildings to the War Department, while the forts themselves would still belong to the city if the military decided to abandon them. It is thanks to this treaty that the forts of Croix Rousse, Fourvière, Loyasse, Vaise, and Saint-Jean would later be returned to the city.
Construction resumed in 1840. First the Fort de la Vitriolerie in 1840, then Fort de Sainte-Foy-lès-Lyon and the Lunette des Charpennes in 1842, Fort de la Duchère in 1844, the Redoute du Petit Sainte-Foy-lès-Lyon in 1852, and finally the Redoute du haut-Rhône in 1854.
A law was voted in on 10 July 1851, which defined the methods of destruction of these buildings or construction on their land. By 1854, 19 structures including 10 forts had been built around Lyon, creating a nearly 14-kilometre (8.7 mi) fortified perimeter.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1856 Captain Richard Delafield Antique Maps of Genoa & Venice Italy - Art of War
Antique Map
- Title : Harbour Defences plate 19; Defences of Naval Depot and City of Genoa; Defence of Naval Depot and City of Venice
- Ref #: 90119
- Size: 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original lithograph map of Genoa & Venice Italy was engraved by John T Bowen & co. Philadelphia, was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Left fold rejoined, light age toning
Verso: - Left margin rejoined with archival tape
Background:
In the beginning of 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1824 Louis Vivien Large Antique Map of Spain & Portugal
- Title : Carte De La Peninsule Hispanique...1824
- Size: 29in x 23in (740mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1824
- Ref #: 40717
Description:
This finely engraved original large antique map of Spain & Portugal by Louis Vivien in his Elephant Folio atlas, Atlas Universal
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 23in (740mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19in (635mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Many of the original charts and maps drawn by the first Portuguese and Spanish navigators have survived for the very good reason that, on completion of their voyages, pilots were obliged to hand over their manuscript notes to the Casa da India (founded 1504) in Lisbon or to the equivalent Casa de Contrataci6n de las Indias (founded 1504) in Seville. The clear intention was to maintain secrecy over new discoveries and control over the distribution of cartographic material, not always successfully, as it happened; pilots and navigators seem to have changed allegiance with impunity and, in consequence, many of the earliest and most informative charts were compiled as far away as Genoa, Venice, Florence and Ancona, presumably from sources outside the Portuguese and Spanish Casas. It is apparent that few manuscripts reached the printing stage and, indeed, are so rare that any study of them must be regarded as a specialist subject. (Ref Tooley M&B)
Vivien, Louis 1802 - 1896
Louis Vivien , or Vivien de Saint-Martin was a French geographer who was born in Saint-Martin-de-Fontenay and died in Versailles, France in 1896.
He settled in Paris under the Restoration, and became known with his publication of the Electoral and Administrative Map in 1823 and his comprehensive Universal Atlas in 1825, collaborating with Jacques Bibliomappe -Charles Bailleul from 1828. Vivien was foremost a geographer but was also a publisher of works in other fields, including historical books on the General History of the French Revolution and the History of Napoleon. He also translated various English works, such as the novels of Walter Scott .
He also wrote the New Annals of Travels between 1845 and 1854 and briefly the French Athenaeum between 1847 & 1848. He contributed to numerous periodicals such as Le Constitutionnel, Revue contemporaine, Revue germanique & La Presse. He also wrote L Année géographique between 1863 and 1875 before passing the baton to G. Maunoir and Henri Duveyrier.
He is mainly known though, for his three cartographical works, A History of Geographical Discoveries, A New Dictionary of Universal Geography and the Universal Atlas of Geography. The first of these publications he completed after the 1848 Revolution with the latter two completed by Louis Rousselet and Franz Schrader.
Vivien was Honorary President of the Geographical Society, of which he was one of the founder members. He also laureate of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles-Lettres as well as a member of the Asian Society , the Society of Ethnology along with a large number of learned societies and European academies.
Main works of Vivien de Saint-Martin
- General History of the French Revolution, the Empire, the Restoration, the Monarchy of 1830, up to and including 1841 (4 volumes in 2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat Brothers, 1841-1842.
- History of Napoleon and the Empire (2 volumes), Paris, Pourrat brothers, 1844.
- History of geographical discoveries of European nations in various parts of the world (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1845-1846.
- Research on primitive populations and the oldest traditions of the Caucasus , Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1847.
- Studies of Ancient Geography and Asian Ethnography (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1850-1852.
- Historical and geographical description of Asia Minor (2 volumes), Paris, Arthus-Bertrand, 1852.
- Study on the Greek and Latin Geography of India , Paris, Imperial Printing, 1858.
- Study on the geography and the primitive populations of north-west India, according to the Vedic hymns , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1860.
- North Africa in Greek and Roman antiquity, historical and geographical study , Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1863.
- History of geography and geographical discoveries from the earliest times to the present day , Paris, Hachette, 1873.
- With Franz Schrader : Universal Atlas of Geography built from the original sources and the most recent documents , Paris, Hachette, 1876-1915.
- With Louis Rousselet : New dictionary of universal geography (9 volumes), Paris, Hachette, 1879-1900.
1765 T. Bowen & M Postlethweyt Antique Map of European Russia, Baltics, Lapland
- Title : Europe Plate II
- Date : 1765
- Size: 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 01-1584
Description:
This wonderful large detailed original copper plate engraved antique map of European Russia, parts of Lapland, Sweden, Latvia & Lithuania by Thomas Bowen was published in the 1765 edition of Malachy Postlethweyts monumental 2 Volume tomes on Universal Dictionary of Trade & Commerce concentrating on various states of trade, including slavery, between England and America published between 1751 & 1774.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, orange, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West.
Postlethweyt, Malachy 1707 – 1767
Malachy Postlethweyts Dictionary of Trade & Commerce:
A monumental dictionary of trade and commerce. It is based in part on the Dictionnaire universel de Commerce (Paris: 1723-30) of Jacques Savary de Bruslon, under whose name it is often catalogued, but has been adapted by Postlethwayt for a British audience, with substantial enlargements and improvements, and entirely new material relating to England and her colonies. Postlethwayt devoted twenty years to the preparation of the dictionary, which was first published in 1751-55 & includes a description of British affairs in North America since the peace of 1763.
As with his other works, the dictionary demonstrates Postlethway’s deep commitment to the expansion and strengthening of English trade. Included are entries for geographical locations (Africa, Antilles, Canada, Japan, Louisiana, &c.), products (brandy, cardamom, codfish, diamonds, sugar, &c.), trading companies (Dutch East India Company, English African Company, &c.), treaties of commerce, and a vast range of other information of value to merchants (bankruptcy, currency, bills of exchange, brokerage, exportation, landed interest, privateering, &c.). The Dictionary is also important for containing almost the whole substance of Richard Cantillon’s Essay on Commerce, its first appearance in print.
1789 John Harrison Large Antique Map of Western Europe - Italy to Germania to UK
- Title : Germanie, France, Italie, Espange, Isles Britanniques Dans un Age intermediare de L Ancienne Geographie et de la Moderne Drawn & engraved from D Anvilles Atlas for John Harrison...1789
- Date : 1789
- Size: 19in x 16 1/2in (480mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 15645
Description:
This large magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique map of Western Europe, after J B D Anville, was engraved in 1789 - dated in the title - and was published for John Harrisons Ancient & Modern Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 16 1/2in (480mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14in (480mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Roman Empire was the post-Roman Republic period of the ancient Roman civilization, with a government headed by emperors and large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. The city of Rome was the largest city in the world c. 100 BC – c. AD 400, with Constantinople (New Rome) becoming the largest around AD 500, and the Empire\\\'s population grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world\\\'s population at the time) The 500-year-old republic which preceded it had been severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflict, during which Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and executions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar\\\'s adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the annexation of Egypt. Octavian\\\'s power was then unassailable and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively marking the end of the Roman Republic.
1745 Nicolas Tindal Large Antique Map The Battle of Schellenberg, Germany 1704
- Title : Battle of Donawert fought on the 2nd of June 1704 between a detachment of ye Allies and a body of French and Bavarian Troops
- Size: 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1745
- Ref #: 22160
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved military map of the Battle of Schellenberg, also known as the Battle of Donauwörth in the Donau-Ries district of Swabia, in Bavaria, Germany - during the Spanish War of Succession - was engraved by John Basire and published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
The Battle of Schellenberg, also known as the Battle of Donauwörth, was fought on 2 July 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. The engagement was part of the Duke of Marlboroughs campaign to save the Habsburg capital of Vienna from a threatened advance by King Louis XIVs Franco-Bavarian forces ranged in southern Germany. Marlborough had commenced his 400 km march from Bedburg, near Cologne, on 19 May; within five weeks he had linked his forces with those of the Margrave of Baden, before continuing on to the river Danube. Once in southern Germany, the Allies task was to induce Max Emanuel, the Elector of Bavaria, to abandon his allegiance to Louis XIV and rejoin the Grand Alliance; but to force the issue, the Allies first needed to secure a fortified bridgehead and magazine on the Danube, through which their supplies could cross to the south of the river into the heart of the Electors lands. For this purpose, Marlborough selected the town of Donauwörth.
1750 Christop. Cellarius Original Antique Map of France - Gallia
- Title : Gallia Narbonensis Lugdvnensis et Acvitania
- Size: 15in x 10 1/2in (380mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 31353
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map of France by Christoph. Cellarius was published in the 1750 edition of Geographica Antiqua.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10 1/2in (380mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Geographica was one of the most popular geographical publications of the 17th and 18th centuries, lasting well into the 19th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Cellarius, Christopher, 1638-1707
Christopher Cellarius (Keller) was professor of Oriental languages at Halle university and the author of numerous books including his most famous work the atlas Geographica Antiquafirst published in 1686 and being reissued with updated plates until the early 19th century.
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan & View Siege of Dendermonde, Belgium in 1706
- Title : Plan of the City of Dendermonde, and the manner in which it was blocked by the troops of the Allies
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22157
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the Belgium city of Dendermonde and surrounding regions during the siege of Dendermonde in 1706 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Dendermonde is a Belgian city and municipality located in the Flemish province of East Flanders in the Denderstreek. The municipality comprises the city of Dendermonde proper and the towns of Appels, Baasrode, Grembergen, Mespelare, Oudegem, Schoonaarde, and Sint-Gillis-bij-Dendermonde. Dendermonde is located at the mouth of the river Dender, where it flows into the Scheldt. The town has a long-standing (folkloric) feud with Aalst (situated south along the same river), which dates back from the Middle Ages.
The city is an administrative, commercial, educational, and medical centre for the surrounding region. The current Mayor of Dendermonde is Piet Buyse (Christian Democratic and Flemish).
Some interesting La-Tène artifacts were found in Appels, proof that this region of the Scheldt was inhabited in prehistory. Grave sites from the 2nd and 6th century also attest to dense settlement in Gallo-Roman and Merovingian times. In 843, the Treaty of Verdun placed Dendermonde in Lotharingia. After the Norman invasions of 883, however, Baldwin II took over the region and incorporated it into the German part of the newly founded County of Flanders.
Otto II built a fort here in the 10th century, encouraging further settlements in the area. The town received its city charter in 1233 and grew quickly after that thanks to a thriving cloth industry. Several cloisters, chapels and churches, and a fortified defensive wall were built as well. A cloth hall and belfry were erected on the market square in the mid 14th century. The town’s prosperity, however, gave rise to severe competition with cities such as Ghent and to occasional attacks and plunders by neighbours. In 1384, the whole area came under the control of the Valois dukes of Burgundy.
The 16th century saw a decline in Dendermonde’s fortunes. In 1572 Dendermonde was conquered by William the Silent. The same year however Spanish troops under Duke Alexander Farnese of Parma, took over the city, looted and mostly destroyed it. A decade later, the Spaniards built their own fortress between the Dender and the Scheldt. In 1667, it was France’s turn to advance on the city, but the allied troops of the Netherlands and England, under the Duke of Marlborough, caused the heaviest damage in 1706. The city was then fortified by the Austrians against further French ambitions. After a last siege by Louis XV, the city could finally breathe to the point that the fortifications were dismantled a few decades later.