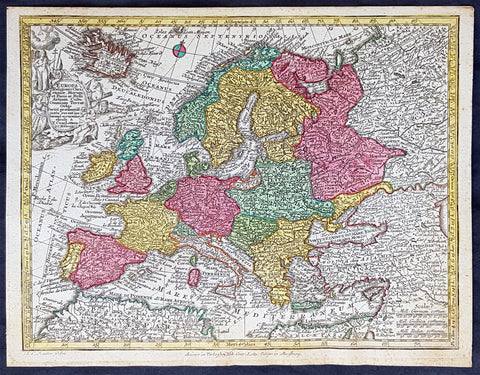
Europe (305)
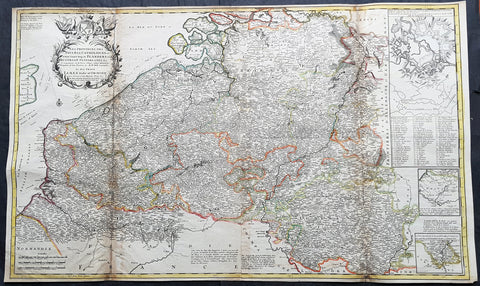
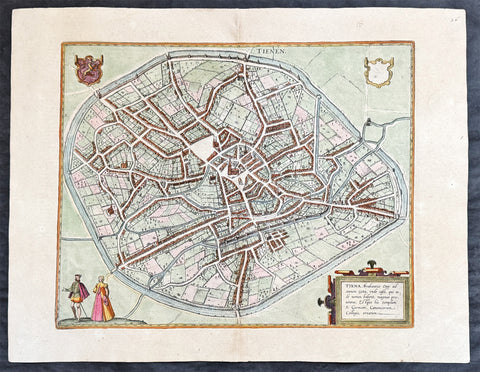
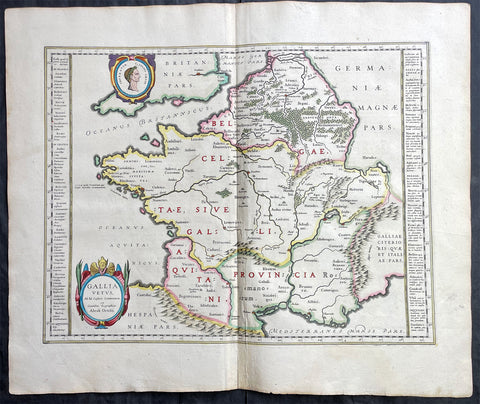
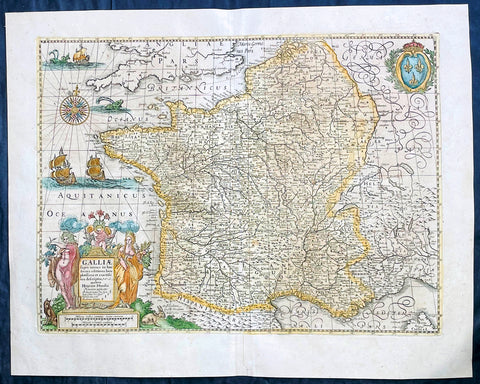
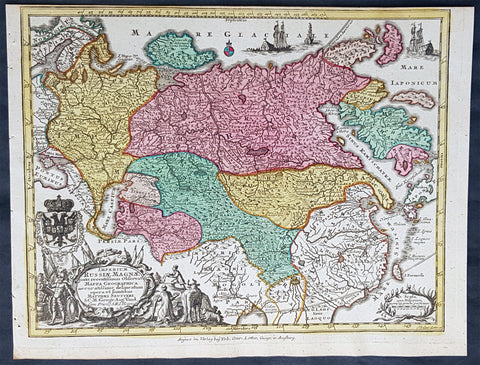
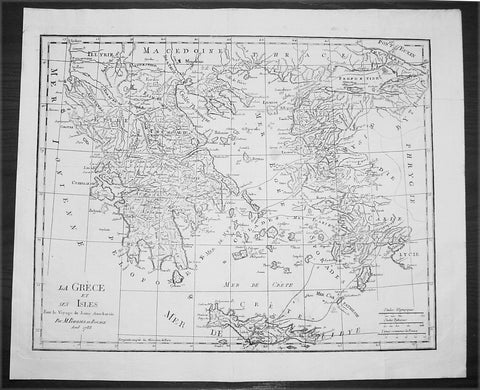
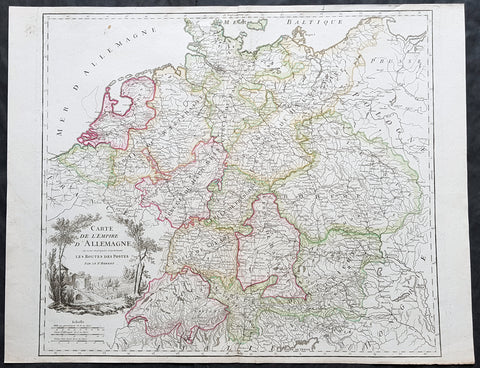
1720 Moll Large Antique Map of The Low Countries, Flanders Netherlands & Belgium
Antique Map
- Title : Les Provinces Des Pays-Bas Catholoiques ou. A Most excat map of Flanders or Austraian Netherlands.....Herman Moll Geogr.
- Size: 40 1/2in x 24in (1.030m x 610mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1720
- Ref #: 61130
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the low country of Flanders region of The Netherlands & Belgium by Herman Moll was published in 1720 in the atlas The World Described, or a New and Correct Sett of Maps by John Bowles, Thomas Bowles, Philip Overton & John King of London.
In the 18th century many large-scale maps were published by the likes of John Senex and Herman Moll, this trend continued until the end of private mapping in the early 19th century when it was replaced by Ordnance Survey maps.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 40 1/2in x 24in (1.030m x 610mm)
Plate size: - 40in x 24in (1.00m x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning along top margin
Plate area: - Age toning along folds
Verso: - Re-enforced & age toning along folds
Background:
Flanders: In 1500, Charles V was born in Ghent. He inherited the Seventeen Provinces (1506), Spain (1516) with its colonies and in 1519 was elected Holy Roman Emperor. The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549, issued by Charles V, established the Low Countries as the Seventeen Provinces (or Spanish Netherlands in its broad sense) as an entity separate from the Holy Roman Empire and from France. In 1556 Charles V abdicated due to ill health (he suffered from crippling gout). Spain and the Seventeen Provinces went to his son, king Philip II of Spain.
Over the first half of the 16th century Antwerp grew to become the second-largest European city north of the Alps by 1560. Antwerp was the richest city in Europe at this time. According to Luc-Normand Tellier It is estimated that the port of Antwerp was earning the Spanish crown seven times more revenues than the Americas.
Meanwhile, Protestantism had reached the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the Lutheran beliefs of the German Hanseatic traders found appeal, perhaps partly for economic reasons. The spread of Protestantism in this city was aided by the presence of an Augustinian cloister (founded 1514) in the St. Andries quarter. Luther, an Augustinian himself, had taught some of the monks, and his works were in print by 1518. The first Lutheran martyrs came from Antwerp. The Reformation resulted in consecutive but overlapping waves of reform: a Lutheran, followed by a militant Anabaptist, then a Mennonite, and finally a Calvinistic movement. These movements existed independently of each other.
Philip II, a devout Catholic and self-proclaimed protector of the Counter-Reformation, suppressed Calvinism in Flanders, Brabant and Holland (what is now approximately Belgian Limburg was part of the Bishopric of Liège and was Catholic de facto). In 1566, the wave of iconoclasm known as the Beeldenstorm was a prelude to religious war between Catholics and Protestants, especially the Anabaptists. The Beeldenstorm started in what is now French Flanders, with open-air sermons (Dutch: hagepreken) that spread through the Low Countries, first to Antwerp and Ghent, and from there further east and north. In total it lasted not even a month.
Subsequently, Philip II sent the Duke of Alba to the Provinces to repress the revolt. Alba recaptured the southern part of the Provinces, who signed the Union of Atrecht, which meant that they would accept the Spanish government on condition of more freedom. But the northern part of the provinces signed the Union of Utrecht and settled in 1581 the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. Spanish troops quickly started fighting the rebels, but before the revolt could be completely defeated, a war between England and Spain had broken out, forcing Philips Spanish troops to halt their advance. Meanwhile, the Spanish armies had already conquered the important trading cities of Bruges and Ghent. Antwerp, which was then the most important port in the world, also had to be conquered. On 17 August 1585, Antwerp fell. This ended the Eighty Years War for the (from now on) Southern Netherlands. The United Provinces (the Northern Netherlands) fought on until 1648 – the Peace of Westphalia.
While Spain was at war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to Philip IIs Spanish troops. They managed to conquer a considerable part of Brabant (the later Noord-Brabant of the Netherlands), and the south bank of the Scheldt estuary (Zeelandic Flanders), before being stopped by Spanish troops. The front line at the end of this war stabilized and became the current border between present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. The Dutch (as they later became known) had managed to reclaim enough of Spanish-controlled Flanders to close off the river Scheldt, effectively cutting Antwerp off from its trade routes.
First the fall of Antwerp to the Spanish and later also the closing of the Scheldt were causes of a considerable emigration of Antverpians. Many of the Calvinist merchants of Antwerp and also of other Flemish cities left Flanders and emigrated to the north. A large number of them settled in Amsterdam, which was at the time a smaller port, of significance only in the Baltic trade. In the following years Amsterdam was rapidly transformed into one of the worlds most important ports. Because of the contribution of the Flemish exiles to this transformation, the exodus is sometimes described as creating a new Antwerp.
Flanders and Brabant, due to these events, went into a period of relative decline from the time of the Thirty Years War. In the Northern Netherlands however, the mass emigration from Flanders and Brabant became an important driving force behind the Dutch Golden Age.
Although arts remained at a relatively impressive level for another century with Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640) and Anthony van Dyck, Flanders experienced a loss of its former economic and intellectual power under Spanish, Austrian, and French rule, with heavy taxation and rigid imperial political control compounding the effects of industrial stagnation and Spanish-Dutch and Franco-Austrian conflict. The Southern Netherlands suffered severely under the War of the Spanish Succession, but under the reign of Empress Maria-Theresia these lands economically flourished again. Influenced by the Enlightenment, the Austrian Emperor Joseph II was the first sovereign who had been in the Southern Netherlands since King Philip II of Spain left them in 1559.
In 1794 the French Republican Army started using Antwerp as the northernmost naval port of France, which country officially annexed Flanders the following year as the départements of Lys, Escaut, Deux-Nèthes, Meuse-Inférieure and Dyle. Obligatory (French) army service for all men aged 16–25 was one of the main reasons for the peoples uprising against the French in 1798, known as the Boerenkrijg (Peasants War), with the heaviest fighting in the Campine area.
After the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte at the 1815 Battle of Waterloo in Waterloo, Brabant, sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands – Belgium minus the East Cantons and Luxembourg – was given by the Congress of Vienna (1815) to the United Netherlands (Dutch: Verenigde Nederlanden), the state that briefly existed under Sovereign Prince William I of Orange Nassau, the latter King William I of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, after the French Empire was driven out of the Dutch territories. The United Kingdom of the Netherlands was born. The Protestant King of the Netherlands, William I rapidly started the industrialisation of the southern parts of the Kingdom. The political system that was set up however, slowly but surely failed to forge a true union between the northern and the southern parts of the Kingdom. The southern bourgeoisie mainly was Roman Catholic, in contrast to the mainly Protestant north; large parts of the southern bourgeoisie also primarily spoke French rather than Dutch.
In 1815 the Dutch Senate was reinstated (Dutch: Eerste Kamer der Staaten Generaal). The nobility, mainly coming from the south, became more and more estranged from their northern colleagues. Resentment grew both between the Roman Catholics from the south and the Protestants from the north and among the powerful liberal bourgeoisie from the south and their more moderate colleagues from the north. On 25 August 1830 (after the showing of the opera La Muette de Portici of Daniel Auber in Brussels) the Belgian Revolution sparked off and became a fact. On 4 October 1830, the Provisional Government (Dutch: Voorlopig Bewind) proclaimed the independence, which was later confirmed by the National Congress that issued a new Liberal Constitution and declared the new state a Constitutional Monarchy, under the House of Saxe-Coburg. Flanders now became part of the Kingdom of Belgium, which was recognized by the major European Powers on 20 January 1831. The de facto dissidence was finally recognized by the United Kingdom of the Netherlands on 19 April 1839.
In 1830, the Belgian Revolution led to the splitting up of the two countries. Belgium was confirmed as an independent state by the Treaty of London of 1839, but deprived of the eastern half of Limburg (now Dutch Limburg), and the Eastern half of Luxembourg (now the Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg). Sovereignty over Zeelandic Flanders, south of the Westerscheldt river delta, was left with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which was allowed to levy a toll on all traffic to Antwerp harbour until 1863.
The Belgian Revolution was not well supported in Flanders and even on 4 October 1830, when the Belgian independence was eventually declared, Flemish authorities refused to take orders from the new Belgian government in Brussels. Only after Flanders was subdued with the aid of a large French military force one month later, under the leadership of the Count de Pontécoulant, did Flanders become a true part of Belgium.
The French-speaking bourgeoisie showed very little respect for the Dutch-speaking part of the population. French became the only official language in Belgium and all secondary and higher education in the Dutch language was abolished.
In 1834, all people even remotely suspected of being Flemish minded or calling for the reunification of the Netherlands were prosecuted and their houses looted and burnt. Flanders, until then a very prosperous European region, was not considered worthwhile for investment and scholarship. A study in 1918 demonstrated that in the first 88 years of its existence, 80% of the Belgian GNP was invested in Wallonia. This led to a widespread poverty in Flanders, forcing roughly 300.000 Flemish to emigrate to Wallonia to start working there in the heavy industry.John SenexMoll
All of these events led to a silent uprising in Flanders against the French-speaking domination. But it was not until 1878 that Dutch was allowed to be used for official purposes in Flanders (see language legislation in Belgium), although French remained the only official language in Belgium.
In 1873, Dutch became the official language in public secondary schools. In 1898 Dutch and French were declared equal languages in laws and Royal orders. In 1930 the first Flemish university was opened. The first official translation of the Belgian constitution in Dutch was not published until 1967.
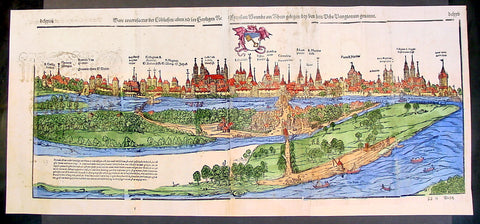
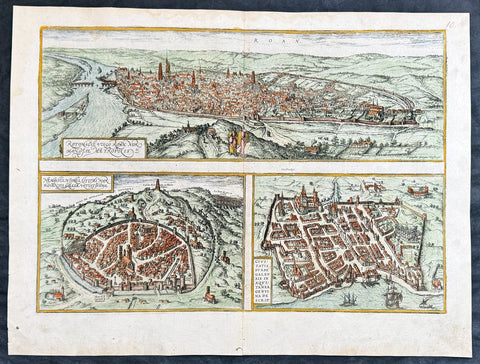
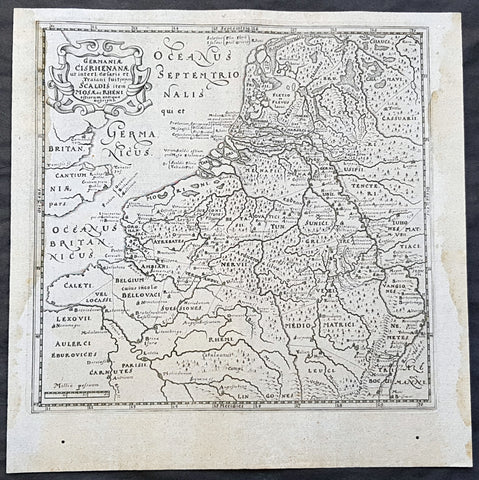
1574 Munster Large Antique Print View of The City of Wormbs, Germany
Antique Map
- Title : Die Statt Wormbs
- Ref #: 22670
- Size: 27in x 13in (685mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large folding original antique print a View of the important German city ofWormbs, south of Hamburg was published in the 1574 release of Sebastian MunstersCosmographia published by Sebastian Petri, Basle.
(This is a reasonably scarce map as the large fold out maps in Cosmographia were easily damaged and lost)
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 13in (685mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 10in (635 x 255m)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: -Folds re-joined small loss, light soiling, light creasing
Verso: - Light soiling, colour show through, half the map backed in archival material
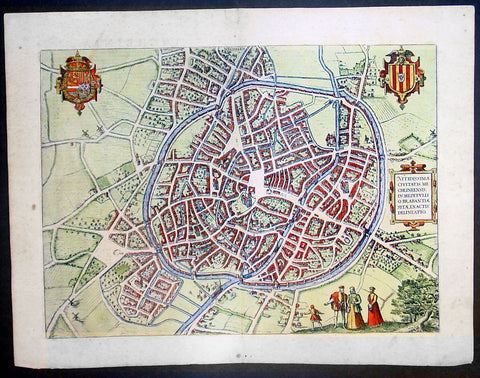
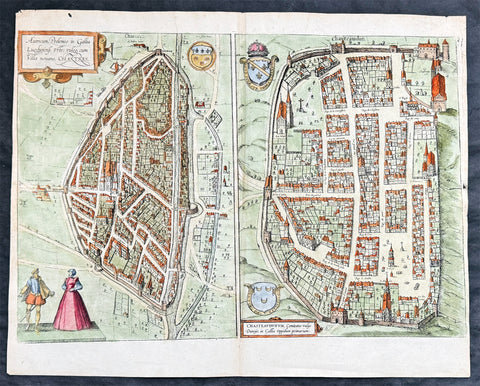
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Large Antique Print a View of Mechelen, Belgium
Antique Map
- Title : Mechelen - Nitidissimae Civitatis Mechlineensis in meditullio Brabantiae sitae, exactis: delineatio
- Ref #: 16247
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map a birds-eye view of the city of Mechelen in the Antwerp province of Flanders, Belgium was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II (1572-1612) intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
Franz Hogenberg's birthplace is illustrated twice. In the view presented in Volume I the cityscape is dominated by the massive tower belonging to the cathedral of Sint-Rombout, which measures almost 100 m in height. Behind the cathedral to the right lies the Onze-Lieve-Vrouwe church built in the Brabantine late Gothic style. In the present plate Mechelen is seen in a bird's-eye view from the northwest. Clearly apparent is the almost circular shape of the inner city, which has already spread beyond the bounds of the canal ringing the old city wall. In the Middle Ages staple rights and the cloth trade brought Mechelen great prosperity. In 1336 the city passed to the Duchy of Brabant, later to Burgundy, and developed into a highly regarded centre of commerce. The collapse of the cloth industry prompted the development of new areas of manufacturing, such as cannon and bell founding. In 1477 Mechelen passed to the Habsburgs and from 1507 to 1530, under the regency of Margaret of Austria, was capital of the Habsburg Netherlands. In 1559 Mechelen became an archbishopric and over the course of the Wars of Religion grew into a centre of the Counter-Reformation. For some time it was also the seat of the highest tribunal of the Habsburg Netherlands. (Taschen)
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13 1/2in (470mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
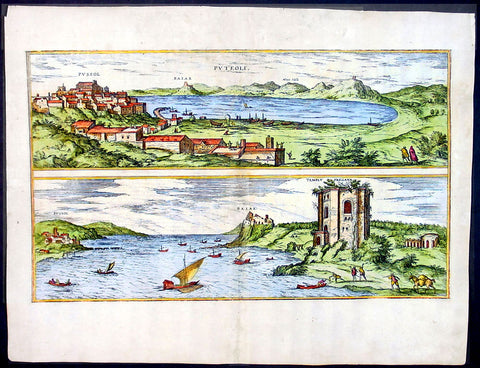
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Map of Pozzuoli Bay Naples Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Puteoli et Baiae
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92687
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique 2 x birds-eye view of the Bay of Pozzuoli -in the Gulf of Naples - with The city of Pozzuoli & the Port Of Baia visible was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The Gulf of Naples is a 10-mile wide gulf located in the south western coast of Italy, (province of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean Sea & is bordered on the north by the cities of Naples and Pozzuoli. To the east is Mount Vesuvius, and on the south by the Sorrentine Peninsula and its main town Sorrento; the Peninsula separates it from the Gulf of Salerno.
Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of Dicaearchia. The Roman colony was established in 194 BC, and took the Latin name Puteoli 'little wells', referring to the many hot springs in the area, most notably Solfatara. This is because Pozzuoli lies in the center of the Campi Flegrei, a caldera.
Puteoli was the great emporium for the Alexandrian grain ships, and other ships from all over the Roman world. It also was the main hub for goods exported from Campania, including blown glass, mosaics, wrought iron, and marble. The Roman naval base at nearby Misenum housed the largest naval fleet in the ancient world. It was also the site of the Roman Dictator Sulla's country villa and the place where he died in 78 BC.
The local volcanic sand, pozzolana formed the basis for the first effective concrete, as it reacted chemically with water. Instead of just evaporating slowly off, the water would turn this sand/lime mix into a mortar strong enough to bind lumps of aggregate into a load-bearing unit. This made possible the cupola of the Pantheon, the first real dome.
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 12in (485mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repair to top centre margin
Plate area: - Small professional repairs & light age toning to centrefold
Verso: - None
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map City Views of Rouen, Nimes & Bordeaux France
- Title : Rotomagus Vulgo Roan Normandie Metropolis / Nemausus, Nismes, Civitas Narbonensis . . . / Civitatis Burdengalensis in Aquitanea, Genuina Descrip (Rouen, Nimes & Bordeaux)
- Size: 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 40168
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique of 3 x maps, birds eye city views of Rouen, Nime, and Bordeaux, France was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius Master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (480mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Rouen: The cities favourable position between the Seine to the south and the hills in the north is clearly illustrated in this view; which is seen from the east from an ideal hill and which also shows the intact city walls from the Roman era. The staffage emphasizes the course taken by the road from Paris leading into the city.
Nimes was a flourishing settlement even in Celtic times and due to its favourable location on the Via Domitia, a major transportation route linking Italy and Spain, was developed into the capital of Narbonensis province. Amongst other things, it was given a 7-km-long city wall and the dominant Tour Magne watchtower (top centre). Also stemming from Roman times is the imposing amphitheatre which could seat some 23,000 spectators and is used for performances even today. Its facade, comprising two storeys, each with 60 arches, is clearly recognizable, even in foreshortening. Above the cathedral and clock tower lies the Maison Carrée, a Roman temple built by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa around 19 B.C. The 49-m-high Pont du Gard aqueduct, mentioned by Braun and visible top right, is an important work of Roman civil engineering.
Bordeaux: The fortifications were built by Charles VII of France only following the reconquest of Bordeaux in 1452. Shown on a smaller scale to the right of the château is the Gothic cathedral of Saint-André with its free-standing clock tower, the Tour Pey-Berland. Outside the city walls lie the ruins of the Roman amphitheatre.
1572 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Print View Lake Agnano Cave of Dogs Naples, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Antri Sibillae, Lacus Agnianus
- Ref #: 35013
- Size: 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1572
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique print, a birds eye view of the Italian Volcanic Lake Agnano and the Grotta del cane or Fontana - Cave of the Dogs - located in Pozzuoli, north of Naples, Italy was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The top view of Lake Agnano shows friends Abraham Ortelius & Georg Hoffnagel meeting at the Lake in a way to impress upon the reader the real importance of Nature. These are beautifully engraved with wonderful hand colouring on strong, sturdy paper.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Colour show-through
The Cave of Dogs is a small cave on the eastern side of the Phlegraean Fields near Pozzuoli, Naples. Inside the cave is a fumarole that releases carbon dioxide of volcanic origin. It was a famous if gruesome tourist attraction for travellers on the Grand Tour. The CO2 gas, being denser than air, tends to accumulate in the deeper parts of the cave. Local guides, for a fee, would suspend small animals inside it—usually dogs—until they became unconscious. Because humans inhaled air from a higher level they were not affected. The dogs might be revived by submerging them in the cold waters of the nearby Lake Agnano. Famous tourists who came to see this attraction included Goethe, Alexandre Dumas père, and Mark Twain. The lake became polluted and it was drained in 1870; the spectacle fell into desuetude and the cave was closed. However the area is now being restored by volunteers.
Lago di Agnano or Lake Agnano was a circular lake, some 6½ km in circumference, which occupied the crater of the extinct volcano of Agnano 8 km west of Naples, Italy. It was apparently not formed until the Middle Ages, as it is not mentioned by ancient writers; it was drained in 1870.
On the south bank are the Stufe di San Germano, natural sulphureous vapour baths, and close by is the Grotta del Cane. From the floor of this cave warm carbonic acid gas constantly rises to a height of 18 inches (46 cm): the fumes render a dog insensible in a few seconds. It is mentioned by Pliny the Elder. Remains of an extensive Roman building and some statues have been discovered close by.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
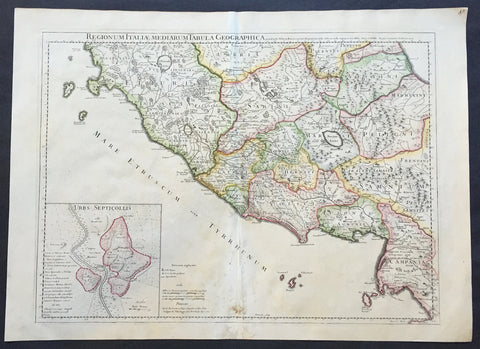
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Antique Map, a Plan of Rome, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Rome Ancienne et Moderne
- Ref #: 82075
- Size: 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Rome, comparing ancient Rome against contemporary Rome in the early 18th century was published in the 1719 edition of Henri Abraham Chatelains Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13 1/2in (445mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The history of Rome spans 28 centuries. While Roman mythology dates the founding of Rome at around 753 BC, the site has been inhabited for much longer, making it one of the oldest continuously occupied sites in Europe. The cities early population originated from a mix of Latins, Etruscans, and Sabines. Eventually, the city successively became the capital of the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, and is regarded as the birthplace of Western civilization and by some as the first ever metropolis. It was first called The Eternal City by the Roman poet Tibullus in the 1st century BC, and the expression was also taken up by Ovid, Virgil, and Livy. Rome is also called the Caput Mundi (Capital of the World). After the fall of the Western Empire, which marked the beginning of the Middle Ages, Rome slowly fell under the political control of the Papacy, which had settled in the city since the 1st century AD, until in the 8th century it became the capital of the Papal States, which lasted until 1870. Beginning with the Renaissance, almost all the popes since Nicholas V (1447–1455) pursued over four hundred years a coherent architectural and urban program aimed at making the city the artistic and cultural centre of the world. In this way, Rome became first one of the major centres of the Italian Renaissance, and then the birthplace of both the Baroque style and Neoclassicism. Famous artists, painters, sculptors and architects made Rome the centre of their activity, creating masterpieces throughout the city. In 1871, Rome became the capital of the Kingdom of Italy, which, in 1946, became the Italian Republic. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
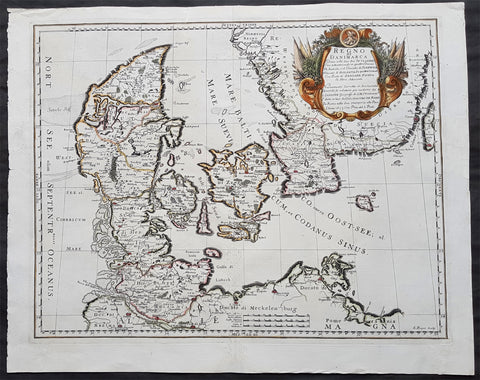
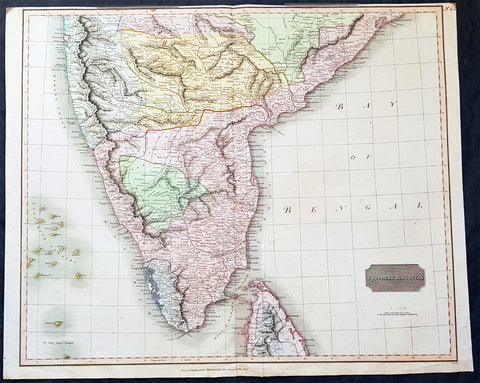
1677 De Rossi Large Original Antique Map of Denmark & Sweden, Schleswig Holstein
- Title : Regno di Danimarca Diuiso nelle Sue due Iutlandie Cioe settentrionale in quattro Diocesi Et Australe, e` il Ducato di...Gio Giacomo De Rossi....L Anno 1677
- Date : 1677
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (575mm x 460mm)
- Ref #: 50610
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
A beautiful and quite scarce original 1677 antique map of Denmark and southern Sweden, was engraved in 1677 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1692 edition of de Rossi's world atlas Mercurio Geografico
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (575mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16in (420mm x 405mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repairs to top & bottom margins
Plate area: - Professional repairs to centerfold
Verso: - Repairs as noted
Background:
Before the fifteenth century the people of Southern Europe had little geographical knowledge of the Scandinavian World except from sketchy detail shown in the Catalan Atlas (1375) and on a number of " portolani" embracing Denmark and the southern tip of Norway. It was not until 1427 that a manuscript map prepared about that time by Claudius Clavus (b.1388) a Dane who spent some time in Rome, made available to scholars a tolerable outline of the northern countries and Greenland. That was to remain the best map available for the rest of the century and it was used as the basis for maps of Scandinavia in early printed editions of Ptolemy. Others by Nicolaus Cusanus (1491) and Ehrhard Etzlaub (c. 1492) followed but, needless to say, these are extremely rare; even the later maps by Olaus Magnus and Marcus Jordan, where they have survived at all , are known only by a very few examples. In fact, apart from the rare appearance of an early Ptolemy map, the oldest of Scandinavia which a collector is likely to find are those of Munster's Cosmograhy first published in 1544. In the following centuries the few maps and charts complied in Scandinavia were usually published in Amsterdam, Antwerp, Paris or Nuremberg, the most important maps often being incorporated in the major Dutch, French & German Atlases. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
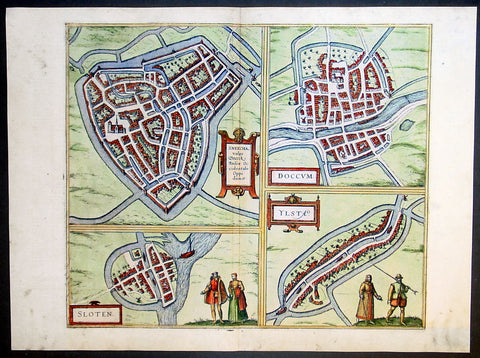
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Print Sneek Dokkum Ylst Frisia Sloten Netherlands
- Title : Sneecha, vulgo Sneeck Frisiae Occidentalis Oppidum. - Doccum - Sloten - Ylsta
- Ref #: 30261
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map a birds-eye view of the towns of Sneek, Dokkum, Ylst and Sloten in Frisia, the Netherlands was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II (1572-1612) intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 14in (420mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
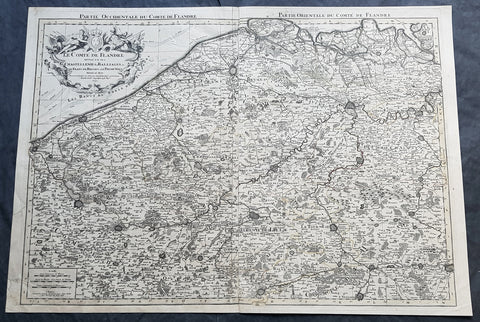
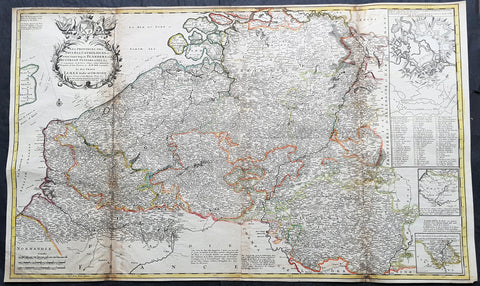
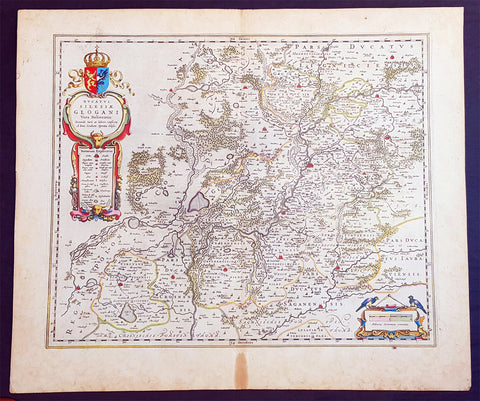
1692 Alexis Jaillot Large Antique Map Flanders Region of Netherlands & Belgium
Antique Map
- Title : Le Comte De Flandre Divisee en ses Chastellenie, Balliages &c.....1692
- Size: 34in x 24in (865mm x 610mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1692
- Ref #: 16384
Description:
This very large, hand coloured original antique map of Flanders region of The Netherlands and Belgium, by Alexis Hubert Jaillot - after Nicolas Sanson - was engraved in 1692 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche.
This large highly detailed map centers on the Brugge to the north, south to Douay west to Dunkirk and east to Dendermonde.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 34in x 24in (865mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 33in x 23in (855mm x 600mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling and creasing in margins
Plate area: - Light uplift along centerfold, light soiling
Verso: - Soiling and creasing
Background:
Flanders: In 1500, Charles V was born in Ghent. He inherited the Seventeen Provinces (1506), Spain (1516) with its colonies and in 1519 was elected Holy Roman Emperor. The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549, issued by Charles V, established the Low Countries as the Seventeen Provinces (or Spanish Netherlands in its broad sense) as an entity separate from the Holy Roman Empire and from France. In 1556 Charles V abdicated due to ill health (he suffered from crippling gout). Spain and the Seventeen Provinces went to his son, king Philip II of Spain.
Over the first half of the 16th century Antwerp grew to become the second-largest European city north of the Alps by 1560. Antwerp was the richest city in Europe at this time. According to Luc-Normand Tellier It is estimated that the port of Antwerp was earning the Spanish crown seven times more revenues than the Americas.
Meanwhile, Protestantism had reached the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the Lutheran beliefs of the German Hanseatic traders found appeal, perhaps partly for economic reasons. The spread of Protestantism in this city was aided by the presence of an Augustinian cloister (founded 1514) in the St. Andries quarter. Luther, an Augustinian himself, had taught some of the monks, and his works were in print by 1518. The first Lutheran martyrs came from Antwerp. The Reformation resulted in consecutive but overlapping waves of reform: a Lutheran, followed by a militant Anabaptist, then a Mennonite, and finally a Calvinistic movement. These movements existed independently of each other.
Philip II, a devout Catholic and self-proclaimed protector of the Counter-Reformation, suppressed Calvinism in Flanders, Brabant and Holland (what is now approximately Belgian Limburg was part of the Bishopric of Liège and was Catholic de facto). In 1566, the wave of iconoclasm known as the Beeldenstorm was a prelude to religious war between Catholics and Protestants, especially the Anabaptists. The Beeldenstorm started in what is now French Flanders, with open-air sermons (Dutch: hagepreken) that spread through the Low Countries, first to Antwerp and Ghent, and from there further east and north. In total it lasted not even a month.
Subsequently, Philip II sent the Duke of Alba to the Provinces to repress the revolt. Alba recaptured the southern part of the Provinces, who signed the Union of Atrecht, which meant that they would accept the Spanish government on condition of more freedom. But the northern part of the provinces signed the Union of Utrecht and settled in 1581 the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. Spanish troops quickly started fighting the rebels, but before the revolt could be completely defeated, a war between England and Spain had broken out, forcing Philips Spanish troops to halt their advance. Meanwhile, the Spanish armies had already conquered the important trading cities of Bruges and Ghent. Antwerp, which was then the most important port in the world, also had to be conquered. On 17 August 1585, Antwerp fell. This ended the Eighty Years War for the (from now on) Southern Netherlands. The United Provinces (the Northern Netherlands) fought on until 1648 – the Peace of Westphalia.
While Spain was at war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to Philip IIs Spanish troops. They managed to conquer a considerable part of Brabant (the later Noord-Brabant of the Netherlands), and the south bank of the Scheldt estuary (Zeelandic Flanders), before being stopped by Spanish troops. The front line at the end of this war stabilized and became the current border between present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. The Dutch (as they later became known) had managed to reclaim enough of Spanish-controlled Flanders to close off the river Scheldt, effectively cutting Antwerp off from its trade routes.
First the fall of Antwerp to the Spanish and later also the closing of the Scheldt were causes of a considerable emigration of Antverpians. Many of the Calvinist merchants of Antwerp and also of other Flemish cities left Flanders and emigrated to the north. A large number of them settled in Amsterdam, which was at the time a smaller port, of significance only in the Baltic trade. In the following years Amsterdam was rapidly transformed into one of the worlds most important ports. Because of the contribution of the Flemish exiles to this transformation, the exodus is sometimes described as creating a new Antwerp.
Flanders and Brabant, due to these events, went into a period of relative decline from the time of the Thirty Years War. In the Northern Netherlands however, the mass emigration from Flanders and Brabant became an important driving force behind the Dutch Golden Age.
Although arts remained at a relatively impressive level for another century with Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640) and Anthony van Dyck, Flanders experienced a loss of its former economic and intellectual power under Spanish, Austrian, and French rule, with heavy taxation and rigid imperial political control compounding the effects of industrial stagnation and Spanish-Dutch and Franco-Austrian conflict. The Southern Netherlands suffered severely under the War of the Spanish Succession, but under the reign of Empress Maria-Theresia these lands economically flourished again. Influenced by the Enlightenment, the Austrian Emperor Joseph II was the first sovereign who had been in the Southern Netherlands since King Philip II of Spain left them in 1559.
In 1794 the French Republican Army started using Antwerp as the northernmost naval port of France, which country officially annexed Flanders the following year as the départements of Lys, Escaut, Deux-Nèthes, Meuse-Inférieure and Dyle. Obligatory (French) army service for all men aged 16–25 was one of the main reasons for the peoples uprising against the French in 1798, known as the Boerenkrijg (Peasants War), with the heaviest fighting in the Campine area.
After the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte at the 1815 Battle of Waterloo in Waterloo, Brabant, sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands – Belgium minus the East Cantons and Luxembourg – was given by the Congress of Vienna (1815) to the United Netherlands (Dutch: Verenigde Nederlanden), the state that briefly existed under Sovereign Prince William I of Orange Nassau, the latter King William I of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, after the French Empire was driven out of the Dutch territories. The United Kingdom of the Netherlands was born. The Protestant King of the Netherlands, William I rapidly started the industrialisation of the southern parts of the Kingdom. The political system that was set up however, slowly but surely failed to forge a true union between the northern and the southern parts of the Kingdom. The southern bourgeoisie mainly was Roman Catholic, in contrast to the mainly Protestant north; large parts of the southern bourgeoisie also primarily spoke French rather than Dutch.
In 1815 the Dutch Senate was reinstated (Dutch: Eerste Kamer der Staaten Generaal). The nobility, mainly coming from the south, became more and more estranged from their northern colleagues. Resentment grew both between the Roman Catholics from the south and the Protestants from the north and among the powerful liberal bourgeoisie from the south and their more moderate colleagues from the north. On 25 August 1830 (after the showing of the opera La Muette de Portici of Daniel Auber in Brussels) the Belgian Revolution sparked off and became a fact. On 4 October 1830, the Provisional Government (Dutch: Voorlopig Bewind) proclaimed the independence, which was later confirmed by the National Congress that issued a new Liberal Constitution and declared the new state a Constitutional Monarchy, under the House of Saxe-Coburg. Flanders now became part of the Kingdom of Belgium, which was recognized by the major European Powers on 20 January 1831. The de facto dissidence was finally recognized by the United Kingdom of the Netherlands on 19 April 1839.
In 1830, the Belgian Revolution led to the splitting up of the two countries. Belgium was confirmed as an independent state by the Treaty of London of 1839, but deprived of the eastern half of Limburg (now Dutch Limburg), and the Eastern half of Luxembourg (now the Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg). Sovereignty over Zeelandic Flanders, south of the Westerscheldt river delta, was left with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which was allowed to levy a toll on all traffic to Antwerp harbour until 1863.
The Belgian Revolution was not well supported in Flanders and even on 4 October 1830, when the Belgian independence was eventually declared, Flemish authorities refused to take orders from the new Belgian government in Brussels. Only after Flanders was subdued with the aid of a large French military force one month later, under the leadership of the Count de Pontécoulant, did Flanders become a true part of Belgium.
The French-speaking bourgeoisie showed very little respect for the Dutch-speaking part of the population. French became the only official language in Belgium and all secondary and higher education in the Dutch language was abolished.
In 1834, all people even remotely suspected of being Flemish minded or calling for the reunification of the Netherlands were prosecuted and their houses looted and burnt. Flanders, until then a very prosperous European region, was not considered worthwhile for investment and scholarship. A study in 1918 demonstrated that in the first 88 years of its existence, 80% of the Belgian GNP was invested in Wallonia. This led to a widespread poverty in Flanders, forcing roughly 300.000 Flemish to emigrate to Wallonia to start working there in the heavy industry.
All of these events led to a silent uprising in Flanders against the French-speaking domination. But it was not until 1878 that Dutch was allowed to be used for official purposes in Flanders (see language legislation in Belgium), although French remained the only official language in Belgium.
In 1873, Dutch became the official language in public secondary schools. In 1898 Dutch and French were declared equal languages in laws and Royal orders. In 1930 the first Flemish university was opened. The first official translation of the Belgian constitution in Dutch was not published until 1967.
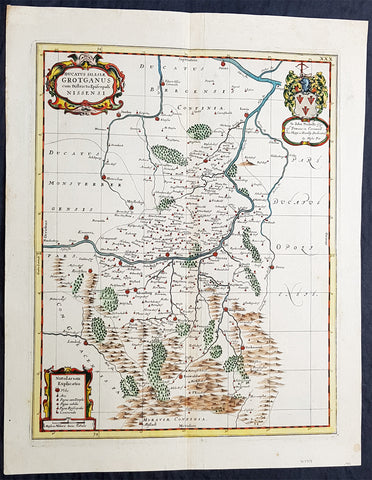
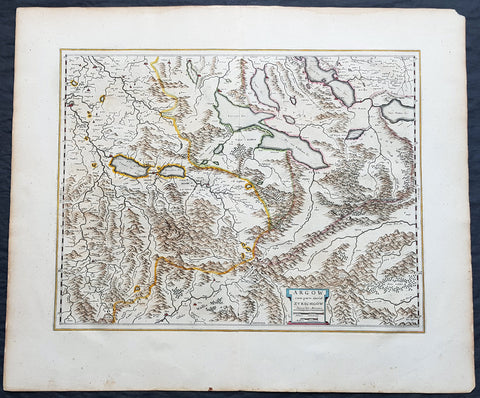
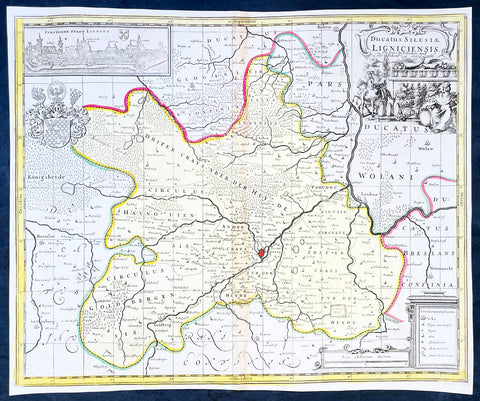
1681 J Jansson & Moses Pitt Rare Antique Map Duchy of Grottkau & Nysa Silesia, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Ducatus Silesiae Grotganus cum Districtu Episcopali Nissensi
- Ref #: 93485
- Size: 23in x 18in (590mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1681
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original rare (not called for in Koeman) hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Duchy of Grottkau and the Diocese of Nysa (Grottkau, Neisse, Brieg and the surrounding area) in the ancient region of Silesia, now in Western Poland by Jan Jansson was published by Moses Pitt in the 1681 edition of Atlas of the World
Moses Pitt 1639–1697 was a bookseller and printer known for the production of his Atlas of the world, a project supported by the Royal Society, and in particular by Christopher Wren. He is also known as the author of The Cry of the Oppressed (1691), an account of the conditions in which imprisoned debtors lived in debtors jails in England.
His work was characterised by its learned content and included authors such as Robert Boyle and Gilbert Burnet. His Atlas was initially intended to be 12 volumes and he continued to undertake other work for the Royal Society. However rising costs, estimated by Pitt at £1000 per volume, contributed to his eventual bankruptcy and only four volumes were ever produced. The second volume had as frontispiece a noted engraved portrait of Queen Catherine of Braganza, by Edward Le Davis.
In Ireland William Molyneux collaborated with Roderic OFlaherty to collect material for the Atlas. While Pitts financial crisis lead to cancellation of the project, much valuable work on early Irish history was collected. Molyneux and OFlaherty struck a friendship and Molyneux assisted when the latters treatise Ogygia was published in London in 1685.
As a result of the Atlas project, Pitt was declared bankrupt. He was taken to the Fleet Prison, and remained there, or in the Kings Bench Prison, for seven years. In 1691, he published The Cry of the Oppressed: Being a True and Tragical Account of the Unparalleld Sufferings of Multitudes of Poor Imprisond Debtors In Most of the Gaols in England, a moving appeal on behalf of prisoners for debt across the country. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18in (590mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 3/4in (510mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Silesia is a historical region of Central Europe mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately 40,000 km2, and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000 inhabitants. Silesia is split into two main sub-regions of Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language.
Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region possesses many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. Silesias largest city and historical capital is Wrocław. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrava and the German city of Görlitz fall within the borders of Silesia.
Silesias borders and national affiliation have changed over time, both when it was a hereditary possession of noble houses and after the rise of modern nation-states. The varied history with changing aristocratic possessions resulted in an abundance of castles, especially in the Jelenia Góra valley. The first known states to hold power in Silesia were probably those of Greater Moravia at the end of the 9th century and Bohemia early in the 10th century. In the 10th century, Silesia was incorporated into the early Polish state, and after its division in the 12th century became a Piast duchy. In the 14th century, it became a constituent part of the Bohemian Crown Lands under the Holy Roman Empire, which passed to the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy in 1526. As a result of the Silesian Wars, the region was annexed by Prussia in 1742.
After World War I, the easternmost part of Upper Silesia was granted to Poland by the Entente Powers after insurrections by Poles and the Upper Silesian plebiscite. The remaining former Austrian parts of Silesia were partitioned to Czechoslovakia, forming part of Czechoslovakias Sudetenland region, and are today part of the Czech Republic. In 1945, after World War II, the bulk of Silesia was transferred to Polish jurisdiction by the Potsdam Agreement between the victorious Allies and became part of Poland, whose Communist government expelled the majority of Silesias previous population. The small Lusatian strip west of the Oder–Neisse line, which had belonged to Silesia since 1815, remained in Germany.
1572 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Print View Lake Agnano Cave of Dogs Naples, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Antri Sibillae, Lacus Agnianus
- Ref #: 35013
- Size: 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1572
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique print, a birds eye view of the Italian Volcanic Lake Agnano and the Grotta del cane or Fontana - Cave of the Dogs - located in Pozzuoli, north of Naples, Italy was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The top view of Lake Agnano shows friends Abraham Ortelius & Georg Hoffnagel meeting at the Lake in a way to impress upon the reader the real importance of Nature. These are beautifully engraved with wonderful hand colouring on strong, sturdy paper.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Colour show-through
The Cave of Dogs is a small cave on the eastern side of the Phlegraean Fields near Pozzuoli, Naples. Inside the cave is a fumarole that releases carbon dioxide of volcanic origin. It was a famous if gruesome tourist attraction for travellers on the Grand Tour. The CO2 gas, being denser than air, tends to accumulate in the deeper parts of the cave. Local guides, for a fee, would suspend small animals inside it—usually dogs—until they became unconscious. Because humans inhaled air from a higher level they were not affected. The dogs might be revived by submerging them in the cold waters of the nearby Lake Agnano. Famous tourists who came to see this attraction included Goethe, Alexandre Dumas père, and Mark Twain. The lake became polluted and it was drained in 1870; the spectacle fell into desuetude and the cave was closed. However the area is now being restored by volunteers.
Lago di Agnano or Lake Agnano was a circular lake, some 6½ km in circumference, which occupied the crater of the extinct volcano of Agnano 8 km west of Naples, Italy. It was apparently not formed until the Middle Ages, as it is not mentioned by ancient writers; it was drained in 1870.
On the south bank are the Stufe di San Germano, natural sulphureous vapour baths, and close by is the Grotta del Cane. From the floor of this cave warm carbonic acid gas constantly rises to a height of 18 inches (46 cm): the fumes render a dog insensible in a few seconds. It is mentioned by Pliny the Elder. Remains of an extensive Roman building and some statues have been discovered close by.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
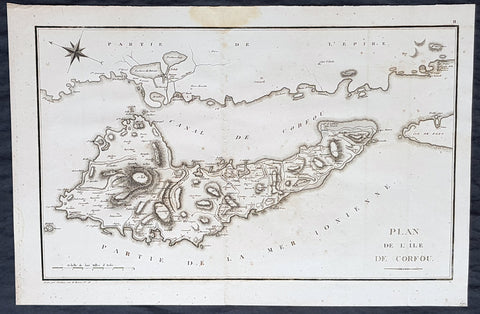
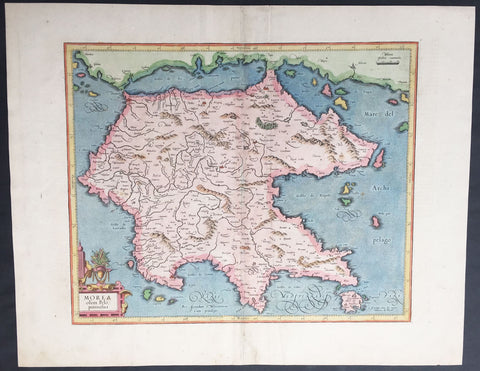
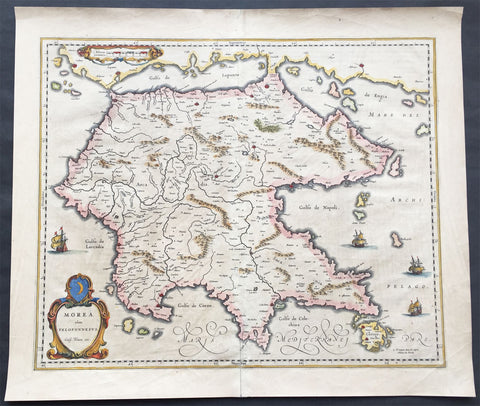
1802 J B Lechevalier & Pierre Tardieu Large Antique Map of Corfu, Greece
- Title : Plan De L Ile De Corfou
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50669-1
- Size: 21in x 14in (535mm x 355mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Greek Island of Corfu was engraved by Pierre Tardieu and was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 14in (535mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 13in (520mm x 335mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Corfu or Kerkyra is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the second largest of the Ionian Islands and, including its small satellite islands, forms the north-westernmost part of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered as a single municipality, which also includes the smaller islands of Ereikoussa, Mathraki and Othonoi. The municipality has an area of 610,9 km2, the island proper 592,8 km2. The principal city of the island and seat of the municipality (pop. 32,095) is also named Corfu. Corfu is home to the Ionian University.
The island is bound up with the history of Greece from the beginnings of Greek mythology. Its history is full of battles and conquests. Ancient Korkyra took part in the Battle of Sybota which was a catalyst for the Peloponnesian War, and, according to Thucydides, the largest naval battle between Greek city states until that time. Thucydides also reports that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers of fifth century BC Greece, along with Athens and Corinth. Medieval castles punctuating strategic locations across the island are a legacy of struggles in the Middle Ages against invasions by pirates and the Ottomans. Two of these castles enclose its capital, which is the only city in Greece to be surrounded in such a way. As a result, Corfu\'s capital has been officially declared a Kastropolis (castle city) by the Greek government. From medieval times and into the 17th century, the island, having successfully repulsed the Ottomans during several sieges, was recognised as a bulwark of the European States against the Ottoman Empire and became one of the most fortified places in Europe. The fortifications of the island were used by the Venetians to defend against Ottoman intrusion into the Adriatic. Corfu eventually fell under British rule following the Napoleonic Wars. Corfu was eventually ceded by the British Empire along with the remaining islands of the United States of the Ionian Islands, and unification with modern Greece was concluded in 1864 under the Treaty of London.
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1720 Moll Large Antique Map of The Low Countries, Flanders Netherlands & Belgium
- Title : Les Provinces Des Pays-Bas Catholoiques ou. A Most excat map of Flanders or Austraian Netherlands.....Herman Moll Geogr.
- Size: 40 1/2in x 24in (1.030m x 610mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1720
- Ref #: 61130
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the low country of Flanders region of The Netherlands & Belgium by Herman Moll was published in 1720 in the atlas The World Described, or a New and Correct Sett of Maps by John Bowles, Thomas Bowles, Philip Overton & John King of London.
In the 18th century many large-scale maps were published by the likes of John Senex and Herman Moll, this trend continued until the end of private mapping in the early 19th century when it was replaced by Ordnance Survey maps.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 40 1/2in x 24in (1.030m x 610mm)
Plate size: - 40in x 24in (1.00m x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning along top margin
Plate area: - Age toning along folds
Verso: - Re-enforced & age toning along folds
Background:
Flanders: In 1500, Charles V was born in Ghent. He inherited the Seventeen Provinces (1506), Spain (1516) with its colonies and in 1519 was elected Holy Roman Emperor. The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549, issued by Charles V, established the Low Countries as the Seventeen Provinces (or Spanish Netherlands in its broad sense) as an entity separate from the Holy Roman Empire and from France. In 1556 Charles V abdicated due to ill health (he suffered from crippling gout). Spain and the Seventeen Provinces went to his son, king Philip II of Spain.
Over the first half of the 16th century Antwerp grew to become the second-largest European city north of the Alps by 1560. Antwerp was the richest city in Europe at this time. According to Luc-Normand Tellier It is estimated that the port of Antwerp was earning the Spanish crown seven times more revenues than the Americas.
Meanwhile, Protestantism had reached the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the Lutheran beliefs of the German Hanseatic traders found appeal, perhaps partly for economic reasons. The spread of Protestantism in this city was aided by the presence of an Augustinian cloister (founded 1514) in the St. Andries quarter. Luther, an Augustinian himself, had taught some of the monks, and his works were in print by 1518. The first Lutheran martyrs came from Antwerp. The Reformation resulted in consecutive but overlapping waves of reform: a Lutheran, followed by a militant Anabaptist, then a Mennonite, and finally a Calvinistic movement. These movements existed independently of each other.
Philip II, a devout Catholic and self-proclaimed protector of the Counter-Reformation, suppressed Calvinism in Flanders, Brabant and Holland (what is now approximately Belgian Limburg was part of the Bishopric of Liège and was Catholic de facto). In 1566, the wave of iconoclasm known as the Beeldenstorm was a prelude to religious war between Catholics and Protestants, especially the Anabaptists. The Beeldenstorm started in what is now French Flanders, with open-air sermons (Dutch: hagepreken) that spread through the Low Countries, first to Antwerp and Ghent, and from there further east and north. In total it lasted not even a month.
Subsequently, Philip II sent the Duke of Alba to the Provinces to repress the revolt. Alba recaptured the southern part of the Provinces, who signed the Union of Atrecht, which meant that they would accept the Spanish government on condition of more freedom. But the northern part of the provinces signed the Union of Utrecht and settled in 1581 the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. Spanish troops quickly started fighting the rebels, but before the revolt could be completely defeated, a war between England and Spain had broken out, forcing Philips Spanish troops to halt their advance. Meanwhile, the Spanish armies had already conquered the important trading cities of Bruges and Ghent. Antwerp, which was then the most important port in the world, also had to be conquered. On 17 August 1585, Antwerp fell. This ended the Eighty Years War for the (from now on) Southern Netherlands. The United Provinces (the Northern Netherlands) fought on until 1648 – the Peace of Westphalia.
While Spain was at war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to Philip IIs Spanish troops. They managed to conquer a considerable part of Brabant (the later Noord-Brabant of the Netherlands), and the south bank of the Scheldt estuary (Zeelandic Flanders), before being stopped by Spanish troops. The front line at the end of this war stabilized and became the current border between present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. The Dutch (as they later became known) had managed to reclaim enough of Spanish-controlled Flanders to close off the river Scheldt, effectively cutting Antwerp off from its trade routes.
First the fall of Antwerp to the Spanish and later also the closing of the Scheldt were causes of a considerable emigration of Antverpians. Many of the Calvinist merchants of Antwerp and also of other Flemish cities left Flanders and emigrated to the north. A large number of them settled in Amsterdam, which was at the time a smaller port, of significance only in the Baltic trade. In the following years Amsterdam was rapidly transformed into one of the worlds most important ports. Because of the contribution of the Flemish exiles to this transformation, the exodus is sometimes described as creating a new Antwerp.
Flanders and Brabant, due to these events, went into a period of relative decline from the time of the Thirty Years War. In the Northern Netherlands however, the mass emigration from Flanders and Brabant became an important driving force behind the Dutch Golden Age.
Although arts remained at a relatively impressive level for another century with Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640) and Anthony van Dyck, Flanders experienced a loss of its former economic and intellectual power under Spanish, Austrian, and French rule, with heavy taxation and rigid imperial political control compounding the effects of industrial stagnation and Spanish-Dutch and Franco-Austrian conflict. The Southern Netherlands suffered severely under the War of the Spanish Succession, but under the reign of Empress Maria-Theresia these lands economically flourished again. Influenced by the Enlightenment, the Austrian Emperor Joseph II was the first sovereign who had been in the Southern Netherlands since King Philip II of Spain left them in 1559.
In 1794 the French Republican Army started using Antwerp as the northernmost naval port of France, which country officially annexed Flanders the following year as the départements of Lys, Escaut, Deux-Nèthes, Meuse-Inférieure and Dyle. Obligatory (French) army service for all men aged 16–25 was one of the main reasons for the peoples uprising against the French in 1798, known as the Boerenkrijg (Peasants War), with the heaviest fighting in the Campine area.
After the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte at the 1815 Battle of Waterloo in Waterloo, Brabant, sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands – Belgium minus the East Cantons and Luxembourg – was given by the Congress of Vienna (1815) to the United Netherlands (Dutch: Verenigde Nederlanden), the state that briefly existed under Sovereign Prince William I of Orange Nassau, the latter King William I of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, after the French Empire was driven out of the Dutch territories. The United Kingdom of the Netherlands was born. The Protestant King of the Netherlands, William I rapidly started the industrialisation of the southern parts of the Kingdom. The political system that was set up however, slowly but surely failed to forge a true union between the northern and the southern parts of the Kingdom. The southern bourgeoisie mainly was Roman Catholic, in contrast to the mainly Protestant north; large parts of the southern bourgeoisie also primarily spoke French rather than Dutch.
In 1815 the Dutch Senate was reinstated (Dutch: Eerste Kamer der Staaten Generaal). The nobility, mainly coming from the south, became more and more estranged from their northern colleagues. Resentment grew both between the Roman Catholics from the south and the Protestants from the north and among the powerful liberal bourgeoisie from the south and their more moderate colleagues from the north. On 25 August 1830 (after the showing of the opera La Muette de Portici of Daniel Auber in Brussels) the Belgian Revolution sparked off and became a fact. On 4 October 1830, the Provisional Government (Dutch: Voorlopig Bewind) proclaimed the independence, which was later confirmed by the National Congress that issued a new Liberal Constitution and declared the new state a Constitutional Monarchy, under the House of Saxe-Coburg. Flanders now became part of the Kingdom of Belgium, which was recognized by the major European Powers on 20 January 1831. The de facto dissidence was finally recognized by the United Kingdom of the Netherlands on 19 April 1839.
In 1830, the Belgian Revolution led to the splitting up of the two countries. Belgium was confirmed as an independent state by the Treaty of London of 1839, but deprived of the eastern half of Limburg (now Dutch Limburg), and the Eastern half of Luxembourg (now the Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg). Sovereignty over Zeelandic Flanders, south of the Westerscheldt river delta, was left with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which was allowed to levy a toll on all traffic to Antwerp harbour until 1863.
The Belgian Revolution was not well supported in Flanders and even on 4 October 1830, when the Belgian independence was eventually declared, Flemish authorities refused to take orders from the new Belgian government in Brussels. Only after Flanders was subdued with the aid of a large French military force one month later, under the leadership of the Count de Pontécoulant, did Flanders become a true part of Belgium.
The French-speaking bourgeoisie showed very little respect for the Dutch-speaking part of the population. French became the only official language in Belgium and all secondary and higher education in the Dutch language was abolished.
In 1834, all people even remotely suspected of being Flemish minded or calling for the reunification of the Netherlands were prosecuted and their houses looted and burnt. Flanders, until then a very prosperous European region, was not considered worthwhile for investment and scholarship. A study in 1918 demonstrated that in the first 88 years of its existence, 80% of the Belgian GNP was invested in Wallonia. This led to a widespread poverty in Flanders, forcing roughly 300.000 Flemish to emigrate to Wallonia to start working there in the heavy industry.John SenexMoll
All of these events led to a silent uprising in Flanders against the French-speaking domination. But it was not until 1878 that Dutch was allowed to be used for official purposes in Flanders (see language legislation in Belgium), although French remained the only official language in Belgium.
In 1873, Dutch became the official language in public secondary schools. In 1898 Dutch and French were declared equal languages in laws and Royal orders. In 1930 the first Flemish university was opened. The first official translation of the Belgian constitution in Dutch was not published until 1967.
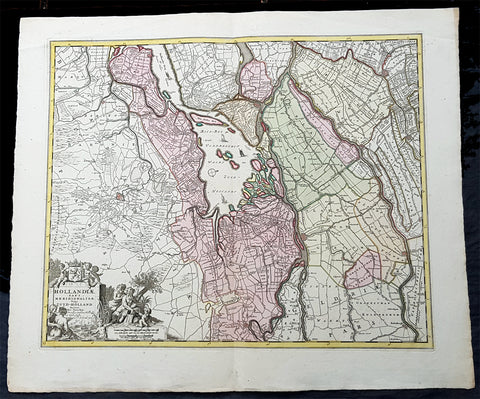
1670 Nicolas Visscher Large Antique Map of South Holland Dordrecht, Gouda, Breda
Antique Map
- Title : Hollandiae Pars Merionalior Vulgo Zuyd-Holland Auctore Nic. Visscher
- Ref #: 93481
- Size: 26 1/2in x 21in (675mm x 515mm)
- Date : 1670
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original large beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of South Holland, from the city of Gouda in the North to Breda in the South and centering on the city of Dordrecht, was published by Nicolas Visscher in 1670.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, brown, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 21in (675mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (565mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first city in South Holland to receive city rights was Dordrecht, which did so in 1220. The city retained a dominant position in the area until it was struck by a series of floods in the late 14th century. The same century also saw a series of civil wars, the Hook and Cod wars, concerning the succession of count William IV. Both his daughter Jacqueline and his brother John, the latter supported by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, claimed the throne. The conflict ended in 1490, with John victorious.
Overall, the area of South Holland remained largely agrarian throughout the late Middle Ages. This changed around 1500, when Holland became Europes most urbanised area. During the Eighty Years War, the area of South Holland was the scene of the Capture of Brielle, the Siege of Leiden and the assassination of William the Silent.
The United Netherlands declared their independence in 1581, and Holland quickly emerged as the countrys dominant province, with important trading cities such as Leiden, Delft, Gouda and Dordrecht. In 1575, the Netherlands first university was founded in Leiden by William the Silent. The Hague, which had originated around the castle of the counts of Holland, became its new political centre. Both the States of Holland and the States General seated in the Binnenhof. The Dutch Golden Age blossomed in the 17th century. The south of Holland, back then often referred to as the Zuiderkwartier (literally South Quarter), was the birthplace and residence of many scientists such as Antoni van Leeuwenhoek and Christiaan Huygens, philosophers such as Baruch Spinoza and Pierre Bayle, as well as painters such as Johannes Vermeer, Rembrandt van Rijn and Jan Steen.
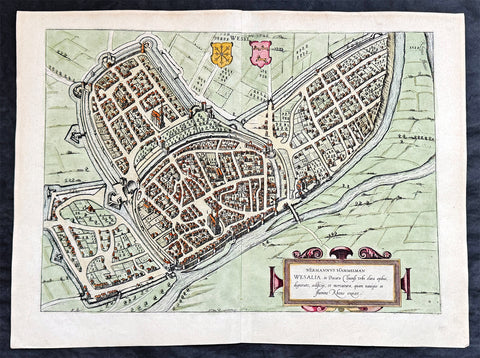
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map View of Wesel North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany
- Title : Hermannus Hammelman Wesalia in Ducatu Cliuensi
- Size: 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 81068-1
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hnd coloured antique map, plan, a birds eye view of city of Wesel in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, pink, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (480mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Wesel is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel district.
The city originated from a Franconian manor that was first recorded in the 8th century. In the 12th century, the Duke of Clèves took possession of Wesel. The city became a member of the Hanseatic League during the 15th century. Wesel was second only to Cologne in the lower Rhine region as an entrepôt. It was an important commercial centre: a clearing station for the trans-shipment and trading of goods.
In 1590 the Spanish captured Wesel after a four-year siege. The city changed hands between the Dutch and Spanish several times during the Eighty Years War. In 1672 a French force under Louis II de Bourbon, Prince de Condé captured the city. Wesel was inherited by the Hohenzollerns of the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1609 but they were unable to take control of Wesel until the Treaty of Nijmegen in 1678. Although the city had been heavily fortified the Prussians evacuated the city during the Seven Years War and it was occupied by the French. It was returned to Prussia at the end of the war. Friedrich Wilhelm von Dossow was the Prussian Governor of Wesel during the 18th century. Wesel was ceded to the French in 1805 under the treaty of Schönbrunn. The French heavily fortified the city constructing a rectangular fort called the Citadelle Napoleon at Büderich and the Citadelle Bonaparte on an island in the Rhine off Wesel. Though blockaded by the Allies in 1813 the city remained in French hands until after the Battle of Waterloo. After the Napoleonic Wars of the early 19th century, the city became part of the Prussian Rhine Province and the Citadelle Napoleon was renamed Fort Blücher.
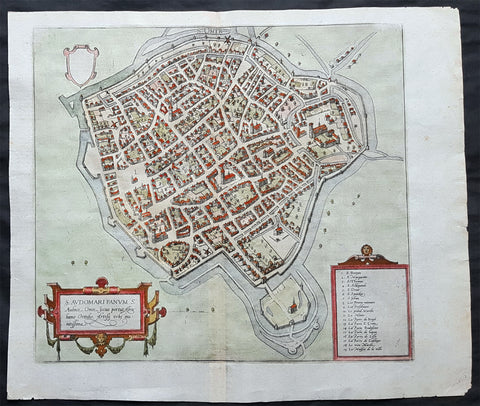
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Original Antique Birds Eye View of St Omer, Calais France
Antique Map
- Title : S. Audomari Fanum. S. Ausmer, Omer, Iccius portus Abrahamo Orttelio, Artesii urbs munitissima
- Date : 1575
- Size: 25in x 21 1/4in (635mm x 540mm)
- Ref #: 30268
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original 1572 antique birds eye view of the Northern French Town of St Omer in the Pas-de-Calais department, was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
This is a bird's-eye view from the south of the town, which is fortified with moats, walls and bastions. Numerous churches stand out, including the Gothic cathedral of Notre-Dame in the lower left-hand corner, with its 50-m-high clock tower. The town goes back to the Benedictine monastery established in AD 657 by Bishop Audomar of Thérouanne. Initially a religious centre, it quickly developed various commercial activities. At the beginning of the 14th century the town was one of the largest in France, the wealthiest in Artois and a centre of European trade.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 15 1/2in (470mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13 1/2in (385mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This is a bird's-eye view from the south of the town, which is fortified with moats, walls and bastions. Numerous churches stand out, including the Gothic cathedral of Notre-Dame in the lower left-hand corner, with its 50-m-high clock tower. The town goes back to the Benedictine monastery established in AD 657 by Bishop Audomar of Thérouanne. Initially a religious centre, it quickly developed various commercial activities. At the beginning of the 14th century the town was one of the largest in France, the wealthiest in Artois and a centre of European trade.
Saint-Omer, is a city in France in the sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department 68 km. The town is named after Saint Audomar, who brought Christianity to the area.
Saint Audomar (died c. 670), better known as Saint Omer, was a Burgundy-born bishop of Thérouanne, after whom nearby Saint-Omer in northern France was named
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN (on verso): "Saint-Audomar, commonly known as Saint-Audmar, and, in the mutilated form read by some, Saint-Omer, a small town in Artois, gets its name from St Audomar, a German, a priest born not far from Constance [...]. Through the recommendation of King Pippin and the bishop of Noyon, he was appointed bishop to the Morini or Flemings. Because he was a man of pious conduct, Adroaldus, a rich and noble man, was later persuaded to present him with the hamlet of Sithieu and the surrounding area to build a monastery there. [...] Through the teachings of these men a large number of people came to the little village of Sithieu and began to build a town, which was later named St Audomar or St Omer in honour of this excellent bishop."
CARTOUCHE LEFT: S. Audomari Fanum, S. Aulmer, Saint-Omer. Iccius portus according to Abraham Ortelius; well-fortified town in Artois.
1650 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of The Cantons of Aargau & Zurich, Switzerland
Antique Map
- Title : Argow cum Parte Merid. Zurchgow
- Ref #: 40331
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Cantons of Zurich & Aargau in North West Switzerland was published in the 1650 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novusafter Gerard Mercator.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the Waldstätte. Two further major steps in the development of the Swiss cantonal system are referred to by the terms Acht Orte (Eight Cantons; between 1353 and 1481) and Dreizehn Orte (Thirteen Cantons,during 1513–1798); they were important intermediate periods of the Ancient Swiss Confederacy.
Each canton, formerly also Ort (from before 1450), or Stand (estate, from c. 1550), was a fully sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848; with a brief period of centralized government during the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803). With the Napoleonic period of the Helvetic Republic the term Kanton was also fully established in German-speaking region.
From 1833, there were 25 cantons, increasing to 26 after the secession of the canton of Jura from Bern in 1979.
The canton of Aargau is one of the more northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare, which is why the canton is called Aar-gau (meaning Aare province). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland.
The canton of Zürich is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. It is the most populated canton in the country. Its capital is the city of Zürich. The official language is German. The local Swiss German dialect, called Züritüütsch, is commonly spoken. In English the name of the canton and its capital is often written without an umlaut.
1575 Abraham Ortelius Antique Map of Saxony Eastern Germany & Western Poland
- Title : Saxoniae Misniae, Thuringiae, Nova Exactissimaq Descriptio
- Size: 20 1/2in x 15 1/2in (520mm x 390mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1587
- Ref #: 30032
Description:
These original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the Saxony region of Germany, historically covering eastern Germany and Western Poland and Silesia (today Obersachsen, Meissen and Thuringen regions) was published in the 1575 French edition of Abraham Ortelius Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/2in (520mm x 390mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 13 1/2in (510mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (4mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Soiling
Background:
Ortelius regional map of Germany, showing the area between Berlin and Braunschweig in the north, to Prague in the south and Silesia in the east. With Chemnitz, Dresden, Leipzig, Wittenberg and Erfurt
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map City View of Tienen, Flemish Brabant, Belgium
- Title : Tiena, Brabantiae Opp: ad amnem Geta, unde casei, qui inde nomen habent, magnus proventus, Estque hic templum S. Germani, Canonicorum Collegio, ornatum
- Size: 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 30256
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique map a birds eye city view of Tienen in Flemish Brabant was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius\\\'s master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (480mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tienen or Thienen is a city and municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in Flanders, Belgium.
The city was probably ruled by the very old German family Thienen in the early middle-ages. This is likely a branch of the Jonckers dynasty. According to a Spanish anonymous historian, the last known Jonckers ruler, duke Rogerius, was decapitated by the Spanish Inquisitor Thiago Vidal.
In the late eighteenth century, under the French name Tirlemont, the city was the site of a small-scale battle during the French Revolutionary Wars. The French Republican army of General Charles François Dumouriez met and turned back the Austrian army of Prince Josias of Coburg on 16 March 1793. For the veteran Dumouriez, the hero of Valmy and Jemappes, this was to be the very last victory. Within a week his army suffered such catastrophic defeats that the victor of Tirlemont defected infamously to the royalists for the rest of his life.
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Birds Eye Views Chartres & Chateaudu Loire France
- Title : Autricum, Prolemeo in Gallia Lugdunensis Urbs; vulgo, cum Villa nouano, Chartres / Chasteaudunum, Comitatus vulgo Dunoys in Gallia Oppidum primorium
- Size: 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 30267
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique print, a birds eye view of cities of Chartres and Chateaudu , in Loire, France was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarumintended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius\'s master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Chartres is a commune and capital of the Eure-et-Loir department in France. It is located about 90 km (56 mi) southwest of Paris.
Chartres was in Gaul one of the principal towns of the Carnutes, a Celtic tribe. In the Gallo-Roman period, it was called Autricum, name derived from the river Autura (Eure), and afterwards civitas Carnutum, city of the Carnutes, from which Chartres got its name. The city was burned by the Normans in 858, and unsuccessfully besieged by them in 911.
During the Middle Ages, it was the most important town of the Beauce. It gave its name to a county which was held by the counts of Blois, and the counts of Champagne, and afterwards by the House of Châtillon, a member of which sold it to the Crown in 1286.
In 1417, during the Hundred Years War, Chartres fell into the hands of the English, from whom it was recovered in 1432.
In 1528, it was raised to the rank of a duchy by Francis I.
In 1568, during the Wars of Religion, Chartres was unsuccessfully besieged by the Huguenot leader, the Prince of Condé. It was finally taken by the royal troops of Henry IV on 19 April 1591. On Sunday, 27 February 1594, the cathedral of Chartres was the site of the coronation of Henry IV after he converted to the Catholic faith, the only king of France whose coronation ceremony was not performed in Reims.
In 1674, Louis XIV raised Chartres from a duchy to a duchy peerage in favor of his nephew, Duke Philippe II of Orléans. The title of Duke of Chartres was hereditary in the House of Orléans, and given to the eldest son of the Duke of Orléans.
In the 1870-1871 Franco-Prussian War, Chartres was seized by the Germans on 2 October 1870, and continued during the rest of the war to be an important centre of operations.
Chateaudun is located about 45 km northwest of Orléans, and about 50 km south-southwest of Chartres. It lies on the river Loir, a tributary of the Sarthe.
1659 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of The Cantons of Aargau & Zurich, Switzerland
Antique Map
- Title : Argow cum Parte Merid. Zurchgow
- Ref #: 30282
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1659
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Cantons of Zurich & Aargau in North West Switzerland was published in the 1659 Spanish edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novusafter Gerard Mercator.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the Waldstätte. Two further major steps in the development of the Swiss cantonal system are referred to by the terms Acht Orte (Eight Cantons; between 1353 and 1481) and Dreizehn Orte (Thirteen Cantons,during 1513–1798); they were important intermediate periods of the Ancient Swiss Confederacy.
Each canton, formerly also Ort (from before 1450), or Stand (estate, from c. 1550), was a fully sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848; with a brief period of centralized government during the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803). With the Napoleonic period of the Helvetic Republic the term Kanton was also fully established in German-speaking region.
From 1833, there were 25 cantons, increasing to 26 after the secession of the canton of Jura from Bern in 1979.
The canton of Aargau is one of the more northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare, which is why the canton is called Aar-gau (meaning Aare province). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland.
The canton of Zürich is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. It is the most populated canton in the country. Its capital is the city of Zürich. The official language is German. The local Swiss German dialect, called Züritüütsch, is commonly spoken. In English the name of the canton and its capital is often written without an umlaut.
1634 Joan Blaeu Large Antique Map of Glogow, Lower Silesia, Poland
- Title : Ducatus Silesiae Glogani Vera Delineatio.
- Ref #: 93486
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1634
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique, rare map of the Duchy of Glogow, in the ancient region of Silesia, Poland - centering on the city of Glogow - was published by Joan Blaeu in the 1634 French edition of Atlas Nouvs,.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16 1/2in (510mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Duchy of Głogów was one of the Duchies of Silesia ruled by the Silesian Piasts. Its capital was Głogów in Lower Silesia.
In 1177, under the rule of Konrad Spindleshanks, the youngest son of High Duke Władysław II the Exile of Poland, the town of Głogów had already become the capital of a duchy in its own right. However, when Konrad died between 1180 and 1190, his duchy was again inherited by his elder brother Bolesław I the Tall, Duke of Wrocław. After the death of Bolesławs grandson Duke Henry II the Pious at the 1241 Battle of Legnica his sons in 1248 divided the Lower Silesian Duchy of Wrocław among themselves. Konrad I, a child when his father died, claimed his rights too and in 1251 and received the northern Głogów territory from his elder brother Bolesław II the Bald, then Duke of Legnica.
Under the rule of Konrads son Henry III the principality became smaller, as fragmentation and division continued, and other, smaller duchies were split from it like Ścinawa (Steinau, Stínava) and Żagań (Sagan, Zaháň) in 1273 as well as the duchies of Oleśnica (Oels, Olešnice) and Wołów (Wohlau, Volov) in 1312. After Henrys son Przemko II had died without heirs in 1331, King John the Blind was able to seize the duchy as a fiefdom of the Kingdom of Bohemia and granted it to the Piast Duke Henry I of Jawor six years later. As Henry I left no issue, King Johns son, Charles IV incorporated one half of Głogów into Crown of Bohemia, granting the remaining half to Duke Henry V of Iron of Żagań in 1349.
When in 1476 the Głogów line of the Piast dynasty became extinct with the death of Henry XI, fights over his succession broke out between his cousin Duke Jan II the Mad of Żagań and Elector Albert III Achilles of Brandenburg, the father of Henrys widow Barbara of Brandenburg. In consequence the duchys northern part of Krosno Odrzańskie (Crossen an der Oder) was incorporated by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1482. The truce however was broken by Duke Jan II, who continued his attacks on the neighbouring territories and in 1480 even invaded the royal Bohemian half of the Głogów duchy. This action finally brought the Bohemian antiking Matthias Corvinus to the scene, who in 1488 conquered Głogów, deposed Jan II and made his son János the duke.
Upon Matthias death in 1490 his territories were reacquired by Bohemian king Vladislaus II Jagiellon, who granted the fief of Głogów to his brothers John I Albert in 1491 and later Sigismund I the Old in 1499, both future kings of Poland. In 1506 the duchy finally became an immediate dominion of the Bohemian Crown, which, after Vladislaus son Louis II Jagiellon had died in 1526, were inherited by Archduke Ferdinand I of Austria and became part of the Habsburg Monarchy.
Głogów remained part of the Crown of Bohemia within the province of Silesia until the end of the First Silesian War in 1742 when, like the majority of Silesia, it became part of Frederick the Greats Kingdom of Prussia (which was definitively confirmed by the Treaty of Aachen in 1748). Even the Seven Years War did not change this status. In 1815 the Duchy (along with other Silesian duchies) ceased to exist due to radical administrative reform. All of Silesia was unified into a single administrative unit, Province of Silesia (Provinz Schlesien).
1638 Joan Blaeu & Abraham Ortelius Antiue Map of France
Antique Map
- Title : Gallia Vetus...Abrah Ortelii
- Date : 1638
- Size: 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70606
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of France, after Abraham Ortelius, was published by Joan Blaeu in the 1638 French edition of Atlas Nouvs,.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1756 J B D Anville Large Antique Map Greece, Crete, Corfu, Aegean Isles Turkey
- Title : Les Cotes De La Grece et L Archipel...MDCCLVI
- Size: 34in x 23in (865m x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1756
- Ref #: 21996
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map of Greece, Crete & the Greek Islands by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville was engraved in 1756 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D\'Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 34in x 23in (865m x 585mm)
Plate size: - 29in x 22in (735mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
While most of mainland Greece and the Aegean islands was under Ottoman control by the end of the 15th century, Cyprus and Crete remained Venetian territory and did not fall to the Ottomans until 1571 and 1670 respectively. The only part of the Greek-speaking world that escaped long-term Ottoman rule was the Ionian Islands, which remained Venetian until their capture by the First French Republic in 1797, then passed to the United Kingdom in 1809 until their unification with Greece in 1864.
While some Greeks in the Ionian Islands and Constantinople lived in prosperity, and Greeks of Constantinople (Phanariotes) achieved positions of power within the Ottoman administration, much of the population of mainland Greece suffered the economic consequences of the Ottoman conquest. Heavy taxes were enforced, and in later years the Ottoman Empire enacted a policy of creation of hereditary estates, effectively turning the rural Greek populations into serfs.
The Greek Orthodox Church and the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople were considered by the Ottoman governments as the ruling authorities of the entire Orthodox Christian population of the Ottoman Empire, whether ethnically Greek or not. Although the Ottoman state did not force non-Muslims to convert to Islam, Christians faced several types of discrimination intended to highlight their inferior status in the Ottoman Empire. Discrimination against Christians, particularly when combined with harsh treatment by local Ottoman authorities, led to conversions to Islam, if only superficially. In the 19th century, many crypto-Christians returned to their old religious allegiance.
The nature of Ottoman administration of Greece varied, though it was invariably arbitrary and often harsh. Some cities had governors appointed by the Sultan, while others (like Athens) were self-governed municipalities. Mountainous regions in the interior and many islands remained effectively autonomous from the central Ottoman state for many centuries.
When military conflicts broke out between the Ottoman Empire and other states, Greeks usually took up arms against the Ottomans, with few exceptions. Prior to the Greek Revolution of 1821, there had been a number of wars which saw Greeks fight against the Ottomans, such as the Greek participation in the Battle of Lepanto in 1571, the Epirus peasants\' revolts of 1600–1601 (led by the Orthodox bishop Dionysios Skylosophos), the Morean War of 1684–1699, and the Russian-instigated Orlov Revolt in 1770, which aimed at breaking up the Ottoman Empire in favor of Russian interests.[89][page needed] These uprisings were put down by the Ottomans with great bloodshed. On the other side, many Greeks were conscripted as Ottoman citizens to serve in the Ottoman army (and especially the Ottoman navy), while also the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, responsible for the Orthodox, remained in general loyal to the empire.
The 16th and 17th centuries are regarded as something of a dark age in Greek history, with the prospect of overthrowing Ottoman rule appearing remote with only the Ionian islands remaining free of Turkish domination. Corfu withstood three major sieges in 1537, 1571 and 1716 all of which resulted in the repulsion of the Ottomans. However, in the 18th century, due to their mastery of shipping and commerce, a wealthy and dispersed Greek merchant class arose. These merchants came to dominate trade within the Ottoman Empire, establishing communities throughout the Mediterranean, the Balkans, and Western Europe. Though the Ottoman conquest had cut Greece off from significant European intellectual movements such as the Reformation and the Enlightenment, these ideas together with the ideals of the French Revolution and romantic nationalism began to penetrate the Greek world via the mercantile diaspora. In the late 18th century, Rigas Feraios, the first revolutionary to envision an independent Greek state, published a series of documents relating to Greek independence, including but not limited to a national anthem and the first detailed map of Greece, in Vienna, and was murdered by Ottoman agents in 1798.
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map Spain, Portugal & The Balearic Islands
- Title : 1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map Spain, Portugal & The Balearic Islands
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41585
Description:
This magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Spain, Portugal & The Balearic Islands by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Many of the original charts and maps drawn by the first Portuguese and Spanish navigators have survived for the very good reason that, on completion of their voyages, pilots were obliged to hand over their manuscript notes to the Casa da India (founded 1504) in Lisbon or to the equivalent Casa de Contrataci6n de las Indias (founded 1504) in Seville. The clear intention was to maintain secrecy over new discoveries and control over the distribution of cartographic material, not always successfully, as it happened; pilots and navigators seem to have changed allegiance with impunity and, in consequence, many of the earliest and most informative charts were compiled as far away as Genoa, Venice, Florence and Ancona, presumably from sources outside the Portuguese and Spanish \\\'Casas\\\'.It is apparent that few manuscripts reached the printing stage and, indeed, are so rare that any study of them must be regarded as a specialist subject. (Ref Tooley M&B)
1638 Jansson Large Antique Map of The Netherlands & Belgium
- Title : Belgii Veteris Typus...Abrahami Ortelii...Petrus Karius
- Ref #: 61036
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of The Netherlands & Belgium was engraved by Peter Karius and was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (480mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing in bottom margin
Plate area: - Centerfold Re-joined
Verso: - Soiling
1623 Mercator Hondius Antique Map of Morea - the Greek Peloponnesus, Greece
- Title : Morea olim Piloponnesus
- Ref #: 35489
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1623
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Morea - the Greek Peloponnesus - was published in the 1623 ofMercators Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerard Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light wear along centerfold
Verso: - Light colour bleed
1640 Blaeu Antique Map of the Peloponnese or Morea Peninsula, Greece
- Title : Morea olim Peloponnesus..Guil. Blaeu exc.
- Date : 1640
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70300
- Size: 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original 1st edition antique map of the southern Greek peninsular of the Peloponnesusor Morea was published in the 1640 Latin edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Nouvs.
The peninsula has been inhabited since prehistoric times. Its modern name derives from ancient Greek mythology, specifically the legend of the hero Pelops who was said to have conquered the entire region. The namePeloponnesos means "Island of Pelops". During the Middle Ages, the peninsula was known as the Morea. According to folk etymology, this is because the Crusaders found it densely planted with mulberry trees (Greek: moreai) used by the flourishing silk industry.
Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map. The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom centerfold re-joined slight separation
Plate area: - Light brush marks across page
Verso: - Light brush marks across page
1639 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of France
Antique Map
- Title : Galliae supera omnes in hac...auctore Henrico Hondio
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 17039
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of France was published by Henricus Hondius & Jan Jansson in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/2in (500mm x 375mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1700 Jan Jansson & Schenk Antique Map of Duchy of Legnica, Silesia South Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Ducatus Silesiae Ligniciensis Pet. Schenk et G Valk
- Ref #: 35636
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 19in x 14 3/4in (480mm x 375mm)
- Date : 1700
- Price: $225US
Description:
This original hand coloured large copper plate engraved antique map of the City and Regions of The Duchy of Legnica (Ligniciensis) in Lower Silesia, southern Poland, after Jan Jansson, was published by Peter Schenk Gerard Valck in 1700.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 14 3/4in (480mm x 375mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (465mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The Duchy of Legnica or Duchy of Liegnitz was one of the Duchies of Silesia. Its capital was Legnica (Liegnitz) in Lower Silesia.
Legnica Castle had become a residence of the Silesian dukes in 1163 and from 1248 was the seat of a principality in its own right, ruled by the Silesian branch of the Piast dynasty until the extinction of the line in 1675. Formed by Bolesław II the Bald, Duke of Lower Silesia at Wrocław, Legnica shared the fate of most of the others Silesian duchies, falling into Bohemian, Austrian and eventually—after the First Silesian War—Prussian spheres of influence.
The town of Legnica became famous for the Battle of Legnica that took place at the nearby village of Legnickie Pole on 9 April 1241, during the Mongol invasion of Poland. A Christian army led by the Polish High Duke Henry II the Pious, supported by the feudal nobility including Poles, Bavarian miners and military orders, was decisively defeated by the Mongols. Although Henry was killed and his forces defeated, their advance into Europe was halted when they turned back to attend to the election of a new Khagan (Grand Khan) following the death of Ögedei Khan in the same year. Minor celebrations are held annually in Legnica to commemorate the battle.
After Henry's death his eldest son Bolesław II the Bald followed him as ruler of Lower Silesia until in 1248 his younger brother Henry III the White came of age and claimed his rights of succession. Backed by the nobility of Wrocław, Henry III forced the duke to cede central parts of Lower Silesia to him, while Bolesław himself retired to Legnica. Furthermore, he came into conflict with his younger brother Konrad, who, originally predestined for an ecclesiastical career as Bishop of Passau, also demanded his distributive share and had to be paid off by Bolesław with the newly created Duchy of Głogów in 1251.
Nevertheless, Bolesław's son Henry V the Fat, who succeeded his father in 1278, was able to enlarge the duchy's territories by defeating his cousin Henry Probus, Duke of Wrocław, and, with support of King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia succeeded him as duke in 1290. Thus, the Lower Silesian duchies of Legnica and Wrocław were re-reunited until 1311.
As after the death of Henry V in 1296 his eldest son Bolesław III the Generous was still a minor, King Wenceslaus took over his guardianship, strengthening the Bohemian influence in Silesia. In 1303 Bolesław III was betrothed to Wenceslaus' daughter Margaret and to no avail tried to follow the extinct Přemyslid dynasty on the Bohemian throne in 1306. He was not able to retain the united duchy and in 1311 Lower Silesia was split again, with Wrocław going to his younger brother Henry VI the Good. Even Bolesław's rule over Legnica was contested by his brother Władysław and in 1329 he had to pay homage to the Bohemian King John of Luxembourg to secure his reign.
As the duchy's capital at the beginning of the 14th century, Legnica was an important city of Central Europe, with a population of approximately 16,000 residents. The city began to expand quickly after the discovery of gold in the Kaczawa.
Piast state from 1329 onwards became a Czech vassal, the political weakness of the duchy continued, caused by domestic conflicts between Bolesław's the Wastefull sons Wenceslaus and Louis the Fair strengthening the influences of the Bohemian monarchs. When in 1419 the Legnica branch of the Silesian Piasts became extinct with the death of Duke Wenceslaus II, the duchy was inherited by Duke Louis II of Brzeg. As Louis himself had no male heirs, Legnica was annexed as a ceased fief by the Bohemian king Sigismund in 1436. A long-standing dispute arose, as the late Duke Louis II had bequeathed his estates to the sons of his step-brother Duke Henry IX of Lubin –though without the consent of the Bohemian overlord. Eventually, in 1455 the duchy was inherited by Frederick I, the son of Louis' daughter Hedwig, who was officially enfeoffed by King Matthias Corvinus in 1469.
Frederick's son Frederick II, Duke from 1499, again inherited the Duchy of Brzeg in 1520. The Protestant Reformation was introduced in the duchy as early as 1522, decisively promoted by the theologians Caspar Schwenckfeld and Valentin Krautwald, and the population quickly turned Lutheran. This led to conflict when, after the death of the Bohemian King Louis II at the Battle of Mohács in 1526, the Lands of the Bohemian Crown including the Legnica fief were incorporated into the Habsburg monarchy of the Catholic king Ferdinand. In turn, Duke Frederick II signed an inheritance pact with the Hohenzollern elector Joachim II Hector of Brandenburg, a cousin of his second wife Sophia. However, King Ferdinand I, rejecting any Hohenzollern influence within the Habsburg lands, declared the agreement null and void.
The struggles continued, though the duchy was officially guaranteed freedom of religion by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia. After the death of the last Piast duke, George William, in 1675, Legnica passed to the direct rule of the Habsburg emperor Leopold I, despite claims raised by Elector Frederick William of Brandenburg referring to the inheritance pact in 1537. For the Prussian king Frederick the Great, the old dispute was a pretext to justify his campaign during the First Silesian War: in 1742 most of Silesia including Legnica was occupied by the Prussian Army after Empress Maria Theresa's defeat in the War of the Austrian Succession. Finally in 1763 the duchy lost most of its privileges after being incorporated into Prussia according to the Peace of Hubertusburg.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1802 J B Lechevalier & Pierre Tardieu Large Antique Map of Corfu, Greece
- Title : Plan De L Ile De Corfou
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70208
- Size: 21in x 14in (535mm x 355mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Greek Island of Corfu was engraved by Pierre Tardieu and was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 14in (535mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 13in (520mm x 335mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Corfu or Kerkyra is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the second largest of the Ionian Islands and, including its small satellite islands, forms the north-westernmost part of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered as a single municipality, which also includes the smaller islands of Ereikoussa, Mathraki and Othonoi. The municipality has an area of 610,9 km2, the island proper 592,8 km2. The principal city of the island and seat of the municipality (pop. 32,095) is also named Corfu. Corfu is home to the Ionian University.
The island is bound up with the history of Greece from the beginnings of Greek mythology. Its history is full of battles and conquests. Ancient Korkyra took part in the Battle of Sybota which was a catalyst for the Peloponnesian War, and, according to Thucydides, the largest naval battle between Greek city states until that time. Thucydides also reports that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers of fifth century BC Greece, along with Athens and Corinth. Medieval castles punctuating strategic locations across the island are a legacy of struggles in the Middle Ages against invasions by pirates and the Ottomans. Two of these castles enclose its capital, which is the only city in Greece to be surrounded in such a way. As a result, Corfu\'s capital has been officially declared a Kastropolis (castle city) by the Greek government. From medieval times and into the 17th century, the island, having successfully repulsed the Ottomans during several sieges, was recognised as a bulwark of the European States against the Ottoman Empire and became one of the most fortified places in Europe. The fortifications of the island were used by the Venetians to defend against Ottoman intrusion into the Adriatic. Corfu eventually fell under British rule following the Napoleonic Wars. Corfu was eventually ceded by the British Empire along with the remaining islands of the United States of the Ionian Islands, and unification with modern Greece was concluded in 1864 under the Treaty of London.
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1744 Georg Mattaus Seutter Antique Map of Europe
Antique Map
- Title : Europa a Matth. Seutteri...T C Lotter, Geogr.
- Ref #: 93388
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
These beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map was engraved by Tobias Lotter and published in the 1744 edition of GM Seutters Atlas Minor Prae cipua Orbis Terrarum Imperia Regna et Provincias...., Augsburg, Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (265mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Atlas Minor was a series of beautiful maps of all parts of the world. Georg Matthäus Seutter was one of the most and important of the German cartographers of the 18th century, being appointed as the Geographer to the Imperial Court. His son, Albrecht Carl, joined Matthäus and eventually inherited the business. The maps from Atlas Minor were drawn by the two Seutters and engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotte. These maps are highly detailed and engraved with a bold hand with equally strong original hand color in the body of the map as was the 18th century German style. The cartouches were left uncolored in order to emphasize the elaborately detailed illustrations for which German maps are especially prized. These are some of the most decorative and interesting maps of the eighteenth century.
1782 G F Frentzel Large Rare Antique Map of Lubsza Forest Brzeg, Opole SW Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Plan Von Dem zum Koniglichen Briegischen Forfst Amt gehorigen Leubuscher Forst RevierSo Auf hoher Ordre Sr Excellence und Einer Konig Prussia Hochlob Breslauischen Krieges und Domainen Cammer special vermessen und in diese Proportion gebracht worden In denen Jahren 1782 et 1783
- Ref #: 93489
- Size: 21in x 16in (530mm x 415mm)
- Date : 1782-83
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This incredibly rare detailed original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map, a survey of the forest near Lubsza in the county of Brzeg in the Opole Province in SW Poland between 1782 & 1783 was engraved by the Leipzig engraver Georg Friedrich Jonas Frentzel.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, brown, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (530mm x 415mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16in (530mm x 415mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (2mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped close to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Lubsza is a village in Brzeg, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Lubsza. It lies approximately 7 kilometres north-east of Brzeg and 41 km north-west of the regional capital Opole. Before 1945 the area was part of Germany
Frentzel, Georg Friedrich Jonas 1754 - 1799
Frentzel was a master-engraver from Leipzig in Germany, specialising in copper engraving. His work was known for its critical level of detail, cumulating in one of the finest revolutionary maps of Boston in 1776 Carte von dem Hafen und der Stadt Boston
1690 N. Visscher Large Antique Map Northern Holland Guelders & Zutphen Amsterdam
Antique Map
- Title : Ducatus Geldriae et Zutphaniae Comitatus...per Nicolaum Visscher
- Ref #: 93482
- Size: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1690
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare hand coloured original antique map of the Duchy of Guelders and the County of Zutphen was published by Nicholas Visscher II in the 1690 edition of Atlas minor sive totius orbis terrarum contracta delinea ex conatibus Nico. Visscher.
A rare and decorative map of Geldern oriented to the west, covering an area from Amsterdam to the west to Vreden in the east and from Montfoort in the south to Campden in the north.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 18 1/2in (565mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guelders or Gueldres is a historical county, later duchy of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
The County of Zutphen, located in modern-day Gelderland, a province of the Netherlands, was formed in the eleventh century as a fief of the Bishop of Utrecht. It was ruled by the Counts of Zutphen between 1018 and 1182, and then formed a personal union with Guelders. Later, it became one of the 4 quarters of Guelders. The name Graafschap (county) is still used for the Achterhoek, the region east of Zutphen, and for the football club De Graafschap from this region.
1662 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Wołow County, Lower Silesia Voivodeship SW Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Ducatus Silesiae Wolanus Authore Jona Sculteto Sprotta Silesio
- Ref #: 93430
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique, rare map of Wolow County, located at the time of publication in the Duchy of Głogow, in Lower Silesia, today SW Poland, was published in Joan Blaeu greatest publication, the first 1662 French edition of Atlas Major,.
As this map was only published over a 10 year period, as most of the plates were destroyed in the disasterous 1672 fire that wiped out the Blaeu publishing house, this map is extremely rare especially with original hand colour, such as this map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Offsetting
Verso: - Offsetting
Background:
Wolow is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in south-western Poland. It is the seat of Wołów County and Gmina Wołów. It lies approximately 38 kilometres north-west of the regional capital Wrocław.
The area around Wołów has been settled since prehistoric times. It became part of the emerging Polish state in the late 10th century under Mieszko I of Poland. The town was first mentioned in 1157 when a wooden castle founded by Senior Duke of Poland Władysław II the Exile is documented, which developed into a castle complex, which was again mentioned in 1202. Two villages developed near the castle, one of them called Wołowo. Probably in the second half of the 13th century the town was founded near Wołowo and partially on the soil of the second village. Wołów received Magdeburg town rights about 1285 at the time of German Ostsiedlung in the region; a Vogt is mentioned in 1288.
At that time Wołów belonged to the Duchy of Głogów, after 1312 to the Duchy of Oleśnica. With the duchy it came under the suzerainty of Bohemia in 1328. From 1473 dates the oldest known seal of the town, which already shows an ox, as do all later seals. Wołów was ruled by local Polish dukes until 1492, and soon after, in 1495, it came into the possession of the Czech Podiebrad family, then in 1517 it came into the hands the Hungarian magnate Johann Thurzó, before returning to Piast rule in 1523, by passing to the Duchy of Legnica. It remained there until the Piast dukes of Legnica-Brzeg-Wołów died out in 1675. As a result of the Thirty Years War, the towns population fell by half.
The Protestant Reformation was introduced to the town in 1522 by duke Frederick II. After the extinction of the local Piasts the duchy passed to the House of Habsburg, which opposed the Protestant denomination in the town, as part of the Counter-Reformation. In 1682 the towns parish church was closed and given to the Catholics. According to the Treaty of Altranstädt the church however was already returned to the Protestants in 1707 and stayed Protestant until 1945. The small Catholic minority in return received a Josephinian curacy.
In 1742 Wołów was annexed by Prussia. The duchy was divided into two districts and the town became county seat of one of the districts. The structure of the town was, until 1700, defined by craft, especially clothiers. As the seat of a duchy and a district administrative function however became more and more important. The industrialization played only a minor role and mostly affected smaller companies of the timber industry. In 1781 the city suffered a fire.
The town was part of Germany from 1871 to 1945. In January 1945 – just before town was taken by the Red Army – the Wehrmacht evacuated the German population westwards.
1744 Georg Mattaus Seutter Antique Map of The Russian Empire, China, Japan
- Title : Imperium Russiae Magnae........a Matth. Seutteri...T C Lotter, Geogr.
- Ref #: 93401
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Russian Empire was engraved by Tobias Lotter and was published in the 1744 edition of GM Seutters Atlas Minor Prae cipua Orbis Terrarum Imperia Regna et Provincias...., Augsburg, Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (265mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Atlas Minor was a series of beautiful maps of all parts of the world. Georg Matthäus Seutter was one of the most and important of the German cartographers of the 18th century, being appointed as the Geographer to the Imperial Court. His son, Albrecht Carl, joined Matthäus and eventually inherited the business. The maps from Atlas Minor were drawn by the two Seutters and engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotte. These maps are highly detailed and engraved with a bold hand with equally strong original hand color in the body of the map as was the 18th century German style. The cartouches were left uncolored in order to emphasize the elaborately detailed illustrations for which German maps are especially prized. These are some of the most decorative and interesting maps of the eighteenth century.
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of the Russian Empire - Poland to Asia
- Title : Partie Occidentale De L Empire De Russie...Sr Robert De Vaugondy
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41592
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Russian Empire - stretching from Poland to Central Asia - by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West. (Ref Tooley M&B)
1857 Dufour Very Large Scarce Old, Antique Map of France - 4ft x 6ft
- Title : Carte Administrative et Physique de la France indiquant Les Canaan Les Riviers Navigable les routes, le Chemis de fer avec leurs stations Dresee par A.H. Dufour Gravee Par CH Dyonnet 1857
- Ref #: 61029
- Size: 62in x 46in (1.5m x 1.15m)
- Date : 1857
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This scarce very large elephant folio 4 sheet - joined - hand coloured original map of France was engraved by Charles Dyonnet in 1857 - dated in the title - for Adolphe Hippolyte Dufour's monumental elephant folio Atlas Physique, Historique et Politique Geographie Moderne published by Pauline Et La Chevalier, Paris.
This uncommon elephant folio map is huge measuring overall 62in x 46in (1.5m x 1.15m) and is incredibly detailed. The map covers the whole of France including Corsica and parts of Spain, Germany and Switzerland.
The first sheet (top left in image) represents north-western France and includes two insets of Nantes and Rouen. The second sheet (top right) represents north-eastern France with an inset of Paris and its environs. The bottom right sheet depicts the south-eastern portions of France and includes two insets, one featuring Marseille and the other featuring Lyon. The last sheet on the bottom left is of southwest France.
An inset on Bordeaux is included and throughout illustrates roads, canals, railways, rivers, cities and other topographical features are noted.
Adolphe Hippolyte Dufour (1795 - 1865), also known as Auguste-Henri Dufour, was a Paris based map and atlas publisher active in the middle to late 19th century. Dufour claimed to be a student of another French cartographer, Emile Lapie. He is known to have worked with numerous other cartographers, publishers and engravers of the period including Charles Dyonnet and Duvotenay. His corpus includes numerous maps and atlases, the most striking of which is probably his monumental elephant folio Atlas Universel physique, historique et politique geographie ancienne et moderne. Dufour's student and successor was Alexandre Vuillemin.
Charles Dyonnet (fl. c. 1822 - c. 1880) was an extremely active Paris based engraver working in the mid to late 19th century. From his offices at 220 Rue St. Jacques, Paris, Dyonnet engraved numerous maps for many of the most prominent 19th French cartographic publishers including Vuillemin, Dufour, Fremin and Duvotenay. From 1850-1861, he held the coveted position of "Graveur du Dépot de la Marine," and in this position engraved numerous French naval and military maps. Dyonnet had a detail oriented and aesthetically minded hand and is responsible from some of the most beautiful French maps to emerge during the 19th century. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 62in x 46in (1.5m x 1.15m)
Paper size: - 62in x 46in (1.5m x 1.15m)
Margins: - Min 1in (24mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Top NE sheet age toning
Verso: - Soiling
1699 Danckerts Antique Map of Germany & Central Europe Poland to France to Italy
- Title : Accuratissima Germaniae Tabula
- Ref #: 16295
- Size: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1699
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of central Europe - centering on the various German States but stretching from Poland in the east to France in the west and Venice to the south - by Justus Danckerts was published in 1699.
In the latter half of the fifteenth century Germany, though nominally still part of the Holy Roman Empire, was a fragmented land, split into a score of principalities and Imperial Cities, fiercely jealous of each other but having in common an extraordinary creative urge which produced builders of great churches and cathedrals, workers in stone and wood, metal engravers, painters and makers of scientific instruments, who were the envy of the world. Of all their achievements, the invention of movable-type printing was to have the most profound effect on human relationships. Printing industries soon grew up in many cities, including Nuremberg and Augsburg where wood engraving already flourished and which, with Basle and Strassburg, were also the centres of geographical knowledge. Not only were local and regional maps produced in considerable variety and quantity, but more particularly the geographers and mathematicians of Nuremberg are famous for their globes of the world, some of which are still preserved.
The most important map of the whole of Germany produced in this period was a manuscript dated c. 1464 by Nicholas Cusanus (Khryfts), Cardinal, humanist and scholar, friend of Toscanelli, the Italian geographer, and one of the most brilliant men of his day. The map covering Germany, Southern Scandinavia and the Baltic was printed in 1491, long after the author's death, and it served as a model for a similar map in the Nuremberg Chronicle. We have written in some detail in Chapter 4 of this famous book, first published in 1493, which contained a great number of woodcut views and maps, but as far as cartography is concerned the printing of Ptolemy's Geographia at Ulm in 1482 (and 1486) - the first edition with woodcut maps - was an event of the greatest importance. The most ambitious editions of the Ptolemy maps appeared in 1513 in Strassburg, containing not only maps of the ancient world but also twenty new ones, including one of the 'New World', based on the latest contemporary.
knowledge. This was produced under the guidance of Martin Waldseemuller, a German cartographer, at St Die' in Lorraine, at that time a noted centre of learning. Other editions followed in the years up to 1 541, overlapping with the newer work of Sebastian Mu'~nster, an eminent mathematician and linguist, who settled in Basle and whose prolific output of atlases and maps contained also many plans and views of the great cities of the time. These in turn were superseded by Braun and Hogenberg's Civitates Orbis Terrarumissued in Cologne between the years 1572 and 1618, which was one of the most famous publications of the period.
In the seventeenth century Dutch supremacy in map making and publishing overshadowed Germany no less than England and France and there was to be no revival until the foundation in Nuremberg about the year 1700 of the printing firm of J. B. Homann, whose business acumen started a resurgence of map publishing. He became a member of the Berlin Academy of Sciences and was appointed Geographer to the Emperor in 1715. The business was continued by his son, Johann Christoph, and was eventually bequeathed to the founder's son-in-law on condition that he continued the business under the name of Homann Heirs. Other notable publishing houses active during the century were run by Matthaus Seutter and Tobias Lotter in the rival city of Augsburg. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss.
1788 Du Bocage Large Antique Map of Greece, Aegean, Western Turkey & Crete
- Title : La Grece et Ses Isles Pour le Voyage du Jeune Aanacharis Par M Barbier Du Bocage Aout 1788
- Date : 1788
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 16471
- Size: 19 1/4in x 16in (490mm x 410mm)
Description:
This fine large original antique map of Greece, The Aegean Islands and the West Coast of Turkey & Crete illustrating the Voyages of the Anacharsis the Younger was engraved in 1788 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in his Voyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece) published between 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage: (1760-1825) was a French geographer and cosmographer who studied under D' Anville and became one of the founders of the Geography Society of Paris. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: - General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/4in x 16in (490mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14 1/2in (470mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1814 John Pinkerton Large Antique Map of Turkey in Europe - Greece to Hungary
- Title : Turkey in Europe....Drawn under the direction of Mr Pinkerton by L Herbert Neele Sculp. 352 Starnd.....London Published 1st Jan 1814 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 16434
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1814
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Turkey in Europe - Greece, Balkans, Romania, Bosnia, Albania, Serbia, Dalmatia - by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1814 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Ottoman Empire also historically known in Western Europe as the Turkish Empire or simply Turkey, was a state that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia and North Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Oghuz Turkish tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe, and with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the 1453 conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, at the height of its power under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was a multinational, multilingual empire controlling most of Southeast Europe, parts of Central Europe, Western Asia, parts of Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, North Africa and the Horn of Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states. Some of these were later absorbed into the Ottoman Empire, while others were granted various types of autonomy during the course of centuries.
With Constantinople as its capital and control of lands around the Mediterranean basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds for six centuries. While the empire was once thought to have entered a period of decline following the death of Suleiman the Magnificent, this view is no longer supported by the majority of academic historians. The empire continued to maintain a flexible and strong economy, society and military throughout the 17th and much of the 18th century. However, during a long period of peace from 1740 to 1768, the Ottoman military system fell behind that of their European rivals, the Habsburg and Russian empires. The Ottomans consequently suffered severe military defeats in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, which prompted them to initiate a comprehensive process of reform and modernisation known as the Tanzimat. Thus, over the course of the 19th century, the Ottoman state became vastly more powerful and organised, despite suffering further territorial losses, especially in the Balkans, where a number of new states emerged. The empire allied with Germany in the early 20th century, hoping to escape from the diplomatic isolation which had contributed to its recent territorial losses, and thus joined World War I on the side of the Central Powers. While the Empire was able to largely hold its own during the conflict, it was struggling with internal dissent, especially with the Arab Revolt in its Arabian holdings. During this time, atrocities were committed by the Ottoman government against the Armenians, Assyrians and Pontic Greeks.
The Empires defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories, which were divided between the United Kingdom and France. The successful Turkish War of Independence against the occupying Allies led to the emergence of the Republic of Turkey in the Anatolian heartland and the abolition of the Ottoman monarchy.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map of Mecklenburg NE Germany Rostock, Wizmar, Parchim
- Title : Meklenburg Ducatus
- Ref #: 50185
- Size: 11 1/2in x 8in (290mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Mecklenburg, north eastern Germany by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mecklenburg is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow.
The name Mecklenburg derives from a castle named Mikilenburg (Old Saxon: big castle, hence its translation into New Latin and Greek: Megalopolis), located between the cities of Schwerin and Wismar. In Slavic language it was known as Veligrad, which also means big castle. It was the ancestral seat of the House of Mecklenburg; for a time the area was divided into Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz among the same dynasty.
Linguistically Mecklenburgers retain and use many features of Low German vocabulary or phonology.
Mecklenburg is the site of many prehistoric dolmen tombs. Its earliest organised inhabitants may have had Celtic origins. By no later than 100 BC the area had been populated by pre-Christian Germanic peoples.
The traditional symbol of Mecklenburg, the grinning steers head (Low German: Ossenkopp, lit.: oxen\'s head, with osse being a synonym for steer and bull in Middle Low German), with an attached hide, and a crown above, may have originated from this period. It represents what early peoples would have worn, i.e. a steers\'s head as a helmet, with the hide hanging down the back to protect the neck from the sun, and overall as a way to instill fear in the enemy.
From the 7th through the 12th centuries, the area of Mecklenburg was taken over by Western Slavic peoples, most notably the Obotrites and other tribes that Frankish sources referred to as Wends. The 11th century founder of the Mecklenburgian dynasty of Dukes and later Grand Dukes, which lasted until 1918, was Nyklot of the Obotrites.
In the late 12th century, Henry the Lion, Duke of the Saxons, conquered the region, subjugated its local lords, and Christianized its people, in a precursor to the Northern Crusades. From 12th to 14th century, large numbers of Germans and Flemings settled the area (Ostsiedlung), importing German law and improved agricultural techniques. The Wends who survived all warfare and devastation of the centuries before, including invasions of and expeditions into Saxony, Denmark and Liutizic areas as well as internal conflicts, were assimilated in the centuries thereafter. However, elements of certain names and words used in Mecklenburg speak to the lingering Slavic influence. An example would be the city of Schwerin, which was originally called Zuarin in Slavic. Another example is the town of Bresegard, the \'gard\' portion of the town name deriving from the Slavic word \'grad\', meaning city or town.
Since the 12th century, the territory remained stable and relatively independent of its neighbours; one of the few German territories for which this is true. During the reformation the Duke in Schwerin would convert to Protestantism and so would follow the Duchy of Mecklenburg.
Like many German territories, Mecklenburg was sometimes partitioned and re-partitioned among different members of the ruling dynasty. In 1621 it was divided into the two duchies of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Güstrow. With the extinction of the Güstrow line in 1701, the Güstrow lands were redivided, part going to the Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, and part going to the new line of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
In 1815, the two Mecklenburgian duchies were raised to Grand Duchies, the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, and subsequently existed separately as such in Germany under enlightened but absolute rule (constitutions being granted on the eve of World War I) until the revolution of 1918. Life in Mecklenburg could be quite harsh. Practices such as having to ask for permission from the Grand Duke to get married, or having to apply for permission to emigrate, would linger late into the history of Mecklenburg (i.e. 1918), long after such practices had been abandoned in other German areas. Even as late as the later half of the 19th century the Grand Duke personally owned half of the countryside. The last Duke abdicated in 1918, as monarchies fell throughout Europe. The Duke\'s ruling house reigned in Mecklenburg uninterrupted (except for two years) from its incorporation into the Holy Roman Empire until 1918. From 1918 to 1933, the duchies were free states in the Weimar Republic.
Traditionally Mecklenburg has always been one of the poorer German areas, and later the poorer of the provinces, or Länder, within a unified Germany. The reasons for this may be varied, but one factor stands out: agriculturally the land is poor and can not produce at the same level as other parts of Germany. The two Mecklenburgs made attempts at being independent states after 1918, but eventually this failed as their dependence on the rest of the German lands became apparent.
1650 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Archbishopric of Madenburg Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
- Title : Magdeburgensis Archiepiscopatus
- Ref #: 40335
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Archbishopric of Madenburg today located in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, on the Elbe River, was published in the 1650 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Roman Catholic archdiocese (969–1552) and Prince-Archbishopric (1180–1680) of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.
Planned since 955 and established in 968, the Roman Catholic archdiocese had de facto turned void since 1557, when the last papally confirmed prince-archbishop, the Lutheran Sigismund of Brandenburg came of age and ascended to the see and the Magdeburg cathedral chapter had adopted Lutheranism in 1567, with most parishioners having preceded in their conversion. All his successors were only administrators of the prince-archbishopric and Lutheran too, except of the Catholic layman Leopold William of Austria (1631–1635). In ecclesiastical respect the remaining Catholics and their parishes and abbeys in the former archdiocese were put under supervision of the Archdiocese of Cologne in 1648 and under the jurisdiction of the Apostolic Vicariate of the Northern Missions in 1670.
In political respect the Erzstift, the archiepiscopal and capitular temporalities, had gained imperial immediacy as prince-archbishopric in 1180. Its territory comprised only some parts of the archdiocesan area, such as the city of Magdeburg, the bulk of the Magdeburg Börde, and the Jerichow Land as an integral whole and exclaves comprising about the Saalkreis including Halle upon Saale, Oebisfelde and environs as well as Jüterbog and environs. The prince-archbishopric maintained its statehood as an elective monarchy until 1680. Then Brandenburg-Prussia acquired Magdeburg prince-archbishopric, and after being secularised, transformed it into the Duchy of Magdeburg, a hereditary monarchy in personal union with Brandenburg.
1711 Claude Delisle Large Antique Map of Rome and Regions, Italy
- Title : Regionum Italiae Mediarum Tabula Geographica Par Guill. Delisle.....1711
- Ref #: 31904
- Size: 28in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1711
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of Rome and the regions surrounding the ancient capital was engraved in 1711 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published by Guillaume Delisle in the Atlas Nouveau. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Very heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 18 1/2in (610mm x 470mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to bottom margin
Plate area: - Light creasing and slight discolouration to bottom centerold
Verso: - None
1816 John Thomson Large Antique Map of Southern India & Northern Sri Lanka
- Title : Southern Hindostan....Drawn & Engraved for Thomsons New General Atlas, 1816
- Date : 1816
- Size: 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 41004
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of South India & northern Sri Lanka by John Thomson was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1816 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons New General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin soiling and cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The cartography of India begins with early charts for navigation and constructional plans for buildings. Indian traditions influenced Tibetan and Islamic traditions, and in turn, were influenced by the British cartographers who solidified modern concepts into India\'s map making
A prominent foreign geographer and cartographer was Hellenistic geographer Ptolemy (90–168) who researched at the library in Alexandria to produce a detailed eight-volume record of world geography. During the Middle Ages, India sees some exploration by Chinese and Muslim geographers, while European maps of India remain very sketchy. A prominent medieval cartographer was Persian geographer Abu Rayhan Biruni (973–1048) who visited India and studied the country\'s geography extensively.
European maps become more accurate with the Age of Exploration and Portuguese India from the 16th century. The first modern maps were produced by Survey of India, established in 1767 by the British East India Company. Survey of India remains in continued existence as the official mapping authority of the Republic of India.
1611 Philipp Cluver Antique Map The Netherlands, Belgium, parts France & Germany
- Title : Germaniae Cisrhenanae ut interl. caesaris et Traiani suit imperii Scaldis item Mosae ac Rheni ostiorum antiqua Descriptio
- Size: 11 1/2in x 11 1/2in (295mm x 295mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1611
- Ref #: 23967
Description:
This fine original wood-block engraved antique map of The Netherlands, Belgium, Northern France and parts of Western Germany was published in the 1611 edition of Philip Cluvers first publication Commentarius de tribus Rheni alveis, et ostiis; item. De Quinque populis quondam accolis; scilicet de Toxandris, Batavis, Caninefatibus, Frisiis, ac Marsacis. (Ref: King; Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 11 1/2in (295mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 10in (255mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to left & right margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Clüver was an antiquary, who was given a special appointment at Leiden as geographer and put in charge of the university\'s library, but his lifes project, it developed, was a general study of the geography of Antiquity, based not only on classical literary sources, but — and this was his contribution — supplemented by wide travels and local inspections. He became virtually the founder of historical geography.
Clüvers first work, in 1611, concerning the lower reaches of the Rhine and its tribal inhabitants in Roman times (Commentarius de tribus Rheni alveis, et ostiis; item. De Quinque populis quondam accolis; scilicet de Toxandris, Batavis, Caninefatibus, Frisiis, ac Marsacis) touched a source of national pride among the Seventeen Provinces, for the Dutch were enjoying a twelve years truce in their Eighty Years War of liberation.
Cluver, Philipp 1580 – 1622
Clüver - also Klüwer, Cluwer, or Cluvier, Latinized as Philippus Cluverius and Philippi Cluverii) - was an Early Modern German geographer and historian.
Clüver was born in Danzig (Gdańsk), in Royal Prussia, a province of the Kingdom of Poland. After spending some time at the Polish court of Sigismund III Vasa, he began the study of law at the University of Leiden (Dutch Republic), but soon he turned his attention to history and geography, which were then taught there by Joseph Scaliger.
Clüver received science education from his father, who was Münzmeister at Danzig (coin master), but when Clüver went into different studies, his father stopped supporting his studies. He therefore travelled from Leiden across Hungary to Bohemia, where he did military service for a few years. While in Bohemia, he translated into Latin a defense by Baron Popel Lobkowitz, who was imprisoned. Upon his return to Leiden, he faced sanctions by the imperial (Habsburg) authorities for this, which however he could avoid with the help of his Leiden friends.
Clüver also travelled in England, Scotland, and France. He did all travel on foot, finally returning to Leiden, where (after 1616) he received a regular pension from the university. He died in Leiden.
Clüver was an antiquary, who was given a special appointment at Leiden as geographer and put in charge of the university\\\'s library, but his lifes project, it developed, was a general study of the geography of Antiquity, based not only on classical literary sources, but — and this was his contribution — supplemented by wide travels and local inspections. He became virtually the founder of historical geography.
Clüver\\\'s first work, in 1611, concerning the lower reaches of the Rhine and its tribal inhabitants in Roman times (Commentarius de tribus Rheni alveis, et ostiis; item. De Quinque populis quondam accolis; scilicet de Toxandris, Batavis, Caninefatibus, Frisiis, ac Marsacis) touched a source of national pride among the Seventeen Provinces, for the Dutch were enjoying a twelve years\\\' truce in their Eighty Years War of liberation.
Clüvers Germaniae antiquae libri tres (Leiden, 1616) depends on Tacitus and other Latin authors. A volume on the antiquities of Sicily, with notes on Sardinia and Corsica (Sicilia Antiqua cum minoribus insulis ei adjacentibus item Sardinia et Corsica), published at Leiden by Louis Elsevier in 1619, is a useful source, with many reference from writers of Antiquity and maps that are often detached and sold to map collectors. His Introductio in universam geographiam, totally 6 parts, (published posthumously from 1624) was the first comprehensive modern geography, and became a standard geographical textbook.
Clüver was also a prolific a writer on mathematical and theological subjects. He is remembered by collectors and historians of cartography for his edition of Ptolemys Geographia (based on Mercators edition of 1578) and for miniature atlases that were reprinted for most of the 17th century. Many of his maps were etched for him by Petrus Bertius.
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of the German States, Bohemia, Austria
- Title : Carte De L Empire D Allemagne..Les Routes Des Postes
- Size: 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41567
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of various individual states of Germany including Austria, Bohemia, Switzerland & The Netherlands by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 territories. The elaborate legal system initiated by a series of Imperial Reforms (approximately 1450–1555) created the Imperial Estates and provided for considerable local autonomy among ecclesiastical, secular, and hereditary states, reflected in Imperial Diet. The House of Habsburg held the imperial crown from 1438 until the death of Charles VI in 1740. Having no male heirs, he had convinced the Electors to retain Habsburg hegemony in the office of the emperor by agreeing to the Pragmatic Sanction. This was finally settled through the War of Austrian Succession; in the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, Charles VI\'s daughter Maria Theresa ruled the Empire as Empress Consort when her husband, Francis I, became Holy Roman Emperor. From 1740, the dualism between the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy and the Kingdom of Prussia dominated the German history.
In 1772, then again in 1793 and 1795, the two dominant German states of Prussia and Austria, along with the Russian Empire, agreed to the Partitions of Poland; dividing among themselves the lands of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. As a result of the partitions, millions of Polish speaking inhabitants fell under the rule of the two German monarchies. However, the annexed territories though incorporated into the Kingdom of Prussia and the Habsburg Realm, were not legally considered as a part of the Holy Roman Empire. During the period of the French Revolutionary Wars, along with the arrival of the Napoleonic era and the subsequent final meeting of the Imperial Diet, most of the secular Free Imperial Cities were annexed by dynastic territories; the ecclesiastical territories were secularised and annexed. In 1806 the Imperium was dissolved; many German states, particularly the Rhineland states, fell under the influence of France. Until 1815, France, Russia, Prussia and the Habsburgs (Austria) competed for hegemony in the German states during the Napoleonic Wars