Europe (19)
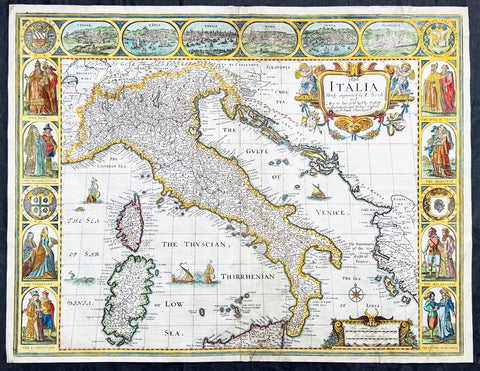
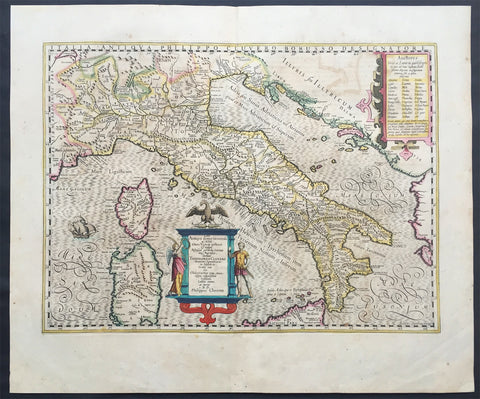
1626 (1676) John Speed Antique Map Italy Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily - Rare state
- Title : 1626 Italia Newly augmented by I. Speed and Are to bee Sold by Tho. Bassett in Fleet Street and Richard Chiswell in St. Puals Church-yard
- Date : 1626 (1676)
- Size: 21 1/4in x 16 1/4in (540mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A-) Good Condition
- Ref: 35655
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Italy by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World.
A very unusual state, as far as I can tell unrecorded, with the date 1626 engraved in the title. This map was first published in 1626 with the date included at the end of the title. This map was published in 1676 by Bassett and Chiswell but for some reason the date, 1626 has been included at the top and beginning of the title, I have been unable to find another example.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/4in x 16 1/4in (540mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15 3/4in (470mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small section of top margin professionally restored about 1/2in into view of Florence
Plate area: - Two rejoins to bottom margin 1in into the border and map, no loss. Light fold bottom right corner
Verso: - Light soiling, repairs as noted
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare, published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
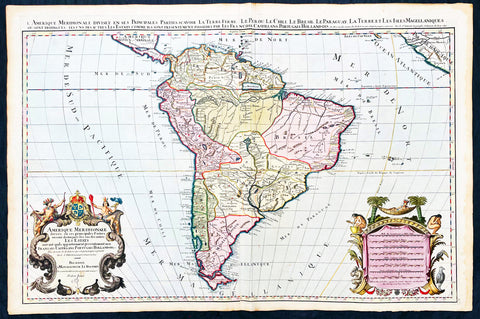
1691 Alex Jaillot Large Antique Map of South America, Gold Imperial Highlights
Antique Map
- Title : Amerique Meridionale Divisee en ses Principales Parties...1691
- Ref #: 35630
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 37 1/2in x 24 3/4in (940mm x 630mm)
- Date: 1691
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured (with gold highlights) antique very large map of South America was engraved in 1691 - dated in Cartouche - and was published by Hubert Jaillot in his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
This map is beautifully hand coloured with gold highlights along country borders and the cartouches indicating it was once part of an Imperial Atlas.
The Imperial atlases were hand coloured using gold highlights and other rare colours which at the time was extremely expensive and available at the time only to royalty and the very rich.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, blue, gold
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 37 1/2in x 24 3/4in (940mm x 630mm)
Plate size: - 35 1/2in x 23in (900mm x 590mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning along margins
Plate area: - Crease along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The map include lines of latitude and longitude, some topographical details, location of settlements, rivers, and lakes (including the lakes Parime, thought to be where the fabulous El Dorado was located) as well as the boundaries of the possessions of the European claimants to South America.
Extremely decorative cartouche with dedication to Le Dauphin, and his coat of arms in top.
After Nicolas Sanson, Hubert Jaillot and Pierre Duval were the most important French cartographers of the seventeenth & eighteenth centuries. Jaillot, originally a sculptor, became interested in geography after his marriage to the daughter of Nicolas Berey (1606-65), a famous map colourist, and went into partnership in Paris with Sanson's sons. There, from about 1669, he undertook the re-engraving, enlarging and re-publishing of the Sanson maps in sheet form and in atlases, sparing no effort to fill the gap in the map trade left by the destruction of Blaeu's printing establishment in Amsterdam in 1672. Many of his maps were printed in Amsterdam (by Pierre Mortier) as well as in Paris. One of his most important works was a magnificent sea atlas, Le Neptune François, published in 1693 and compiled in co-operation with J D Cassini. This was re-published shortly afterwards by Pierre Mortier in Amsterdam with French, Dutch and English texts, the charts having been re-engraved. Eventually, after half a century, most of the plates were used again as the basis for a revised issue published by J N Bellin in 1753.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
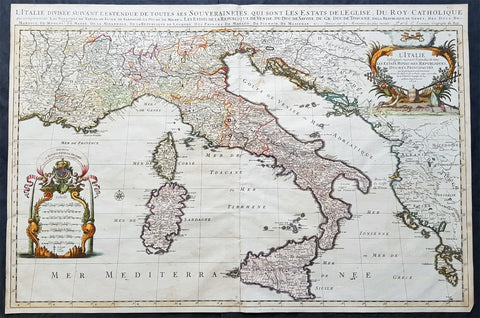
1692 Alexis Jaillot Large Original Antique Map of Italy, Sardinia & Corsica
- Title : L' Italie Divisee Suivant Les l'estendue de tous Les Estats, Royaumes, Republiques, Duches, Principates...1692.
- Size: 35 1/2in x 23 3/4in (900mm x 600mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1692
- Ref #: 35008
Description:
This very large, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Italy by Alexis Hubert Jaillot - after Nicolas Sanson - was engraved in 1692 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche.
Beautifully presented Jaillot map, fantastic colour, clean and heavy paper and a deep clear impression, signifying an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 35 1/2in x 23 3/4in (900mm x 600mm)
Plate size: - 35in x 23in (890mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Very small repairs to margin edges, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by Portolan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare, published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
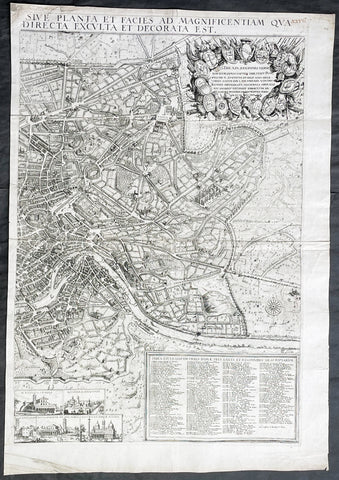
1679 Jacob von Sandrart & Giovanni Battista Falda Large Left Hand Sheet of Rome
Antique Map
- Title : Recentis Romae Ichnographia et Hypsographia Sive Planta et Faies Ad Magnificentiam Qua Prioribus Annis Urbs Ipsa Directa Exculta et Decorata Est.
- Date : 1679
- Size: 26 3/4in x 18 3/4in (680mm x 475mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43188
Description:
This large, original copper plate engraved scarce left hand section of the map of Rome by Jacob Von Sandrart, after Giovanni Battista Falda map, was published in 1679.
This map is based on Giovanni Battista Falda's 12-sheet view of Rome, Nuova Pianta et alzata della citta di Roma, first published in 1676.
Sandrart's view of Rome is rare, we are aware of only 2 examples appearing at auction during the last 25 years.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 3/4in x 18 3/4in (680mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 17in (635mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Jacob von Sandrart's rare and exquisitely engraved view of Rome, one of the finest impressions of the 'Eternal City' made during the great Baroque Era of Art and Architecture.
This finely engraved and lavishly decorative view of Rome takes in all of the 'Eternal City', as it was encompassed by its ancient Aurelian Walls, built during the 2nd Century A.D., on the banks of the River Tiber. Numerous monuments and sites, all of which are still present today, can be seem on the view, including the Coliseum, the Pantheon, the Piazza del Popolo, the Church of San Giovanni Laterno, the Baths of Diocletian, and the Vatican, which is dominated by the Dome of St. Peter's Basilica and the Castel Sant'Angelo. Most notable is the great oval Colonnade that lines the square in front of St. Peter's, which had only been completed in 1666 by the Gianlorenzo Bernini, one of the towering figures of the Baroque Era. The quality of the engraving is exceptionally high, as is the composition of the view, which grants the observer a panoptic view over Rome, while the specific details of the cityscape remain sharply distinguishable.
In the upper left, the title cartouche is surmounted by a portrait of Pope Innocent XI (reigned 1676-89), considered to be a leader of great learning and political acumen. In the upper right corner is a montage featuring the shields of the 14 traditional districts (wards) of Rome. Flowing through the view itself, the River Tiber has its orgins in an allegorical personification of its springs.
In the lower left, a table, 'Index Aedium Antiquitatarum' identifies an amazing 253 ancient buildings and ruins throughout the city. The 'Index Ecclesiarium' in the lower right identifies an incredible 178 churches, although it is not surprising that Rome had by far more houses of worship than any other city in Europe.
In the lower center of the plan are seven views of some of the city's most prominent churches, including St. Peter's Basilica (Vatican), St. Paul's Basilica, San Sebastian Church, San Giovanni Laterno, Sacred Cross of Jerusalem Church, Basilica of St. Lawrence Outside the Walls and the Basilica of Santa Maria Maggiore.
At the time that this view was issued, Rome was enjoying a period of prosperity, and the city's population had reached over 120,000, making it one of the 10 largest cities in Europe. The Roman Catholic Church was on a high, having largely succeeded in driving the Counterreformation, and revenues were pouring in to the Vatican from around the world. This funded the great flourishing of art and architecture in Baroque Rome.
The map was engraved by Jacob von Sandrart (1630-1708), one of the leading fine art engravers of the 17th Century. Born in Frankfurt-am-Main, he apprenticed under his famous uncle Joachim von Sandrart in Amsterdam. He worked in Danzing and Regensburg, and by 1656 had established himself in Nuremberg, where he remained for the rest of his life. Sandrart was highly productive, as over 400 different engravings from his burin are known to survive, although the high quality of his work never wavered. Along with his maps, he is especially well-known for his portraits. Sandrart was the founder and first director of the Nuremberg Academy of Fine Arts (chartered 1662).
Sandrart, Jacob von 1630 - 1708
Jacob von Sandrart was a German engraver primarily active in Nuremberg.
At age ten Sandrart obtained his artistic training from his better-known uncle Joachim von Sandrart in Amsterdam. After spending time in Danzig and Regensburg, he married Regina Christina Eimart, daughter of the engraver Georg Christoph Eimart the elder, on 10 June 1654. The couple settled in Nuremberg in 1656 and remained there for the rest of their lives. His daughter Susanne Maria von Sandrart was also an artist and engraver.
Sandrart was a very prolific artist; over 400 engravings from his hand are extant. He was best known as a portraitist of prominent contemporary citizens of Nuremberg, as an engraver of maps, and as an illustrator of the literary works of Nuremberg writers, especially Sigmund von Birken. Today Sandrart is best remembered as the founder and first director of the Nuremberg Academy of Fine Arts (est. 1662).
1639 Jodocus Hondius Large Antique Map of Italy Sardinia & Corsica
- Title : Italia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43165
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Italy was published in the 1639 French edition of Henricus Hondius & Jan Jansson Atlas Nouvs, after Phillip Cluver.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 14 1/2in (535mm x 365mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy's Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare,published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
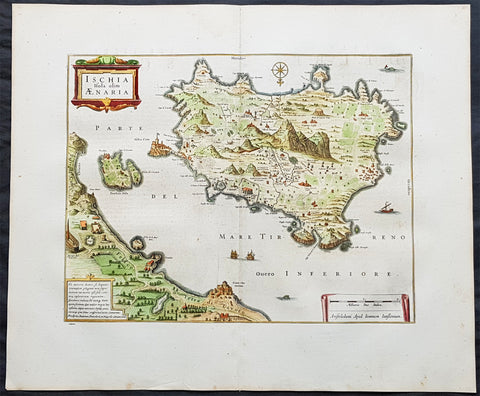
1652 Jansson Large Antique Map Islands of Ischia, Procida & Vivara Naples, Italy
- Title : Ischia Isola olim Aenaria
- Date : 1652
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 61155
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine & beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Italian Islands of Ischia, Procida & Vivara in the the Gulf of Naples in Southern Italy was published in the 1652 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Novus.
Background: Ischia is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, lying at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about 30 kilometres from the city of Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands.
In 6 AD, Augustus restored the island to Naples in exchange for Capri. Ischia suffered from the barbarian invasions, being taken first by the Heruli then by the Ostrogoths, being ultimately absorbed into the Eastern Roman Empire. The Byzantines gave the island over to Naples in 588 and by 661 it was being administered by a Count liege to the Duke of Naples. The area was devastated by the Saracens in 813 and 847; in 1004 it was occupied by Henry II of Germany; the Norman Roger II of Sicily took it in 1130 granting the island to the Norman Aldoyn de Candida created Count d’Ischia; the island was raided by the Pisans in 1135 and 1137 and subsequently fell under the Suebi and then Angevin rule. After the Sicilian Vespers in 1282, the island rebelled, recognizing Peter III of Aragon, but was retaken by the Angevins the following year. It was conquered in 1284 by the forces of Aragon and Charles II of Anjou was unable to successfully retake it until 1299.
As a consequence of the island's last eruption, the population fled to Baia where they remained for 4 years. In 1320 Robert of Anjou and his wife Sancia visited the island and were hosted by Cesare Sterlich, who had been sent by Charles II from the Holy See to govern the island in 1306 and was by this time nearly 100 years of age.
Ischia suffered greatly in the struggles between the Angevin and Durazzo dynasties. It was taken by Carlo Durazzo in 1382, retaken by Louis II of Anjou in 1385 and captured yet again by Ladislaus of Naples in 1386; it was sacked by the fleet of the Antipope John XXIII under the command of Gaspare Cossa in 1410 only to be retaken by Ladislaus the following year. In 1422 Joan II gave the island to her adoptive son Alfonso V of Aragon, though, when he fell into disgrace, she retook it with the help of Genoa in 1424. In 1438 Alfonso reoccupied the castle, kicking out all the men and proclaiming it an Aragonese colony, marrying to his garrison the wives and daughters of the expelled. He set about building a bridge linking the castle to the rest of the island and he carved out a large gallery, both of which are still to be seen today. In 1442, he gave the island to one of his favorites, Lucretia d'Alagno, who in turn entrusted the island's governance to her brother-in-law, Giovanni Torella. Upon the death of Alfonso in 1458, they returned the island to the Angevin side. Ferdinand I of Naples ordered Alessandro Sforza to chase Torella out of the castle and gave the island over, in 1462, to Garceraldo Requesens. In 1464, after a brief Torellan insurrection, Marino Caracciolo was set up as governor.
In February 1495, with the arrival of Charles VIII, Ferdinand II landed on the island and took possession of the castle, and, after having killed the disloyal castellan Giusto di Candida with his own hands, left the island under the control of Innico d'Avalos, marquis of Pescara and Vasto, who ably defended the place from the French flotilla. With him came his sister Costanza and through them they founded the D'Avalos dynasty which would last on the island into the 18th century.
Throughout the 16th century, the island suffered the incursions of pirates and Barbary privateers from North Africa - in 1543 and 1544 Hayreddin Barbarossa laid waste to the island, taking 4,000 prisoners in the process. In 1548 and 1552, Ischia was beset by his successor Dragut Rais. With the increasing rarity and diminishing severity of the piratical attacks later in the century and the construction of better defenses, the islanders began to venture out of the castle and it was then that the historic centre of the town of Ischia was begun. Even so, many inhabitants still ended up slaves to the pirates, the last known being taken in 1796. During the 1647 revolution of Masaniello, there was an attempted rebellion against the feudal landowners. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (460mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1743 D Anville & CA Coypel Large Antique Map of Italy, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica
- Title : L Italie Publiee Sous Les Auspices De Monseigneur Le Duc D Orleans, Premier Prince Du Sang....Par L Sr D Anville...MDCCXLIII
- Date : 1743
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 92312
- Size: 32in x 28in (820mm x 710mm)
Description:
This large scarce original copper-plate engraved antique map of contemporary Italy, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica & Malta by Charles-Antoine Coypel was engraved by Pierre-Alexandre Aveline (1702–1760) (both names engraved under cartouche) in 1743 - dated in cartouche - and was published by Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles in his large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
A scarce and hard to find map with two famous names Charles-Antoine Coypel & Pierre-Alexandre Aveline engraved below the cartouche, I am assuming as both drawer & engraver.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 32in x 28in (820mm x 710mm)
Plate size: - 31 1/2in x 27in (810mm x 690mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (2mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped to border
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Creasing
Background:
Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy\\\'s Geographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi\\\'s maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri \\\'atlases\\\', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy\\\'s position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake\\\'s West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell\\\' Arcano del Mare, published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
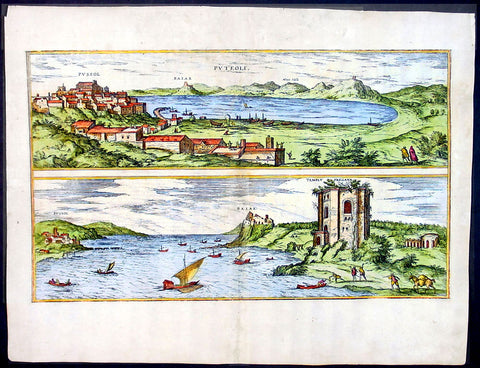
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Map of Pozzuoli Bay Naples Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Puteoli et Baiae
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92687
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique 2 x birds-eye view of the Bay of Pozzuoli -in the Gulf of Naples - with The city of Pozzuoli & the Port Of Baia visible was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The Gulf of Naples is a 10-mile wide gulf located in the south western coast of Italy, (province of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean Sea & is bordered on the north by the cities of Naples and Pozzuoli. To the east is Mount Vesuvius, and on the south by the Sorrentine Peninsula and its main town Sorrento; the Peninsula separates it from the Gulf of Salerno.
Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of Dicaearchia. The Roman colony was established in 194 BC, and took the Latin name Puteoli 'little wells', referring to the many hot springs in the area, most notably Solfatara. This is because Pozzuoli lies in the center of the Campi Flegrei, a caldera.
Puteoli was the great emporium for the Alexandrian grain ships, and other ships from all over the Roman world. It also was the main hub for goods exported from Campania, including blown glass, mosaics, wrought iron, and marble. The Roman naval base at nearby Misenum housed the largest naval fleet in the ancient world. It was also the site of the Roman Dictator Sulla's country villa and the place where he died in 78 BC.
The local volcanic sand, pozzolana formed the basis for the first effective concrete, as it reacted chemically with water. Instead of just evaporating slowly off, the water would turn this sand/lime mix into a mortar strong enough to bind lumps of aggregate into a load-bearing unit. This made possible the cupola of the Pantheon, the first real dome.
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 12in (485mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repair to top centre margin
Plate area: - Small professional repairs & light age toning to centrefold
Verso: - None
1572 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Print View Lake Agnano Cave of Dogs Naples, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Antri Sibillae, Lacus Agnianus
- Ref #: 35013
- Size: 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1572
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique print, a birds eye view of the Italian Volcanic Lake Agnano and the Grotta del cane or Fontana - Cave of the Dogs - located in Pozzuoli, north of Naples, Italy was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The top view of Lake Agnano shows friends Abraham Ortelius & Georg Hoffnagel meeting at the Lake in a way to impress upon the reader the real importance of Nature. These are beautifully engraved with wonderful hand colouring on strong, sturdy paper.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Colour show-through
The Cave of Dogs is a small cave on the eastern side of the Phlegraean Fields near Pozzuoli, Naples. Inside the cave is a fumarole that releases carbon dioxide of volcanic origin. It was a famous if gruesome tourist attraction for travellers on the Grand Tour. The CO2 gas, being denser than air, tends to accumulate in the deeper parts of the cave. Local guides, for a fee, would suspend small animals inside it—usually dogs—until they became unconscious. Because humans inhaled air from a higher level they were not affected. The dogs might be revived by submerging them in the cold waters of the nearby Lake Agnano. Famous tourists who came to see this attraction included Goethe, Alexandre Dumas père, and Mark Twain. The lake became polluted and it was drained in 1870; the spectacle fell into desuetude and the cave was closed. However the area is now being restored by volunteers.
Lago di Agnano or Lake Agnano was a circular lake, some 6½ km in circumference, which occupied the crater of the extinct volcano of Agnano 8 km west of Naples, Italy. It was apparently not formed until the Middle Ages, as it is not mentioned by ancient writers; it was drained in 1870.
On the south bank are the Stufe di San Germano, natural sulphureous vapour baths, and close by is the Grotta del Cane. From the floor of this cave warm carbonic acid gas constantly rises to a height of 18 inches (46 cm): the fumes render a dog insensible in a few seconds. It is mentioned by Pliny the Elder. Remains of an extensive Roman building and some statues have been discovered close by.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Antique Map, a Plan of Rome, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Rome Ancienne et Moderne
- Ref #: 82075
- Size: 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Rome, comparing ancient Rome against contemporary Rome in the early 18th century was published in the 1719 edition of Henri Abraham Chatelains Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13 1/2in (445mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The history of Rome spans 28 centuries. While Roman mythology dates the founding of Rome at around 753 BC, the site has been inhabited for much longer, making it one of the oldest continuously occupied sites in Europe. The cities early population originated from a mix of Latins, Etruscans, and Sabines. Eventually, the city successively became the capital of the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, and is regarded as the birthplace of Western civilization and by some as the first ever metropolis. It was first called The Eternal City by the Roman poet Tibullus in the 1st century BC, and the expression was also taken up by Ovid, Virgil, and Livy. Rome is also called the Caput Mundi (Capital of the World). After the fall of the Western Empire, which marked the beginning of the Middle Ages, Rome slowly fell under the political control of the Papacy, which had settled in the city since the 1st century AD, until in the 8th century it became the capital of the Papal States, which lasted until 1870. Beginning with the Renaissance, almost all the popes since Nicholas V (1447–1455) pursued over four hundred years a coherent architectural and urban program aimed at making the city the artistic and cultural centre of the world. In this way, Rome became first one of the major centres of the Italian Renaissance, and then the birthplace of both the Baroque style and Neoclassicism. Famous artists, painters, sculptors and architects made Rome the centre of their activity, creating masterpieces throughout the city. In 1871, Rome became the capital of the Kingdom of Italy, which, in 1946, became the Italian Republic. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1572 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Print View Lake Agnano Cave of Dogs Naples, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Antri Sibillae, Lacus Agnianus
- Ref #: 35013
- Size: 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1572
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique print, a birds eye view of the Italian Volcanic Lake Agnano and the Grotta del cane or Fontana - Cave of the Dogs - located in Pozzuoli, north of Naples, Italy was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The top view of Lake Agnano shows friends Abraham Ortelius & Georg Hoffnagel meeting at the Lake in a way to impress upon the reader the real importance of Nature. These are beautifully engraved with wonderful hand colouring on strong, sturdy paper.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Colour show-through
The Cave of Dogs is a small cave on the eastern side of the Phlegraean Fields near Pozzuoli, Naples. Inside the cave is a fumarole that releases carbon dioxide of volcanic origin. It was a famous if gruesome tourist attraction for travellers on the Grand Tour. The CO2 gas, being denser than air, tends to accumulate in the deeper parts of the cave. Local guides, for a fee, would suspend small animals inside it—usually dogs—until they became unconscious. Because humans inhaled air from a higher level they were not affected. The dogs might be revived by submerging them in the cold waters of the nearby Lake Agnano. Famous tourists who came to see this attraction included Goethe, Alexandre Dumas père, and Mark Twain. The lake became polluted and it was drained in 1870; the spectacle fell into desuetude and the cave was closed. However the area is now being restored by volunteers.
Lago di Agnano or Lake Agnano was a circular lake, some 6½ km in circumference, which occupied the crater of the extinct volcano of Agnano 8 km west of Naples, Italy. It was apparently not formed until the Middle Ages, as it is not mentioned by ancient writers; it was drained in 1870.
On the south bank are the Stufe di San Germano, natural sulphureous vapour baths, and close by is the Grotta del Cane. From the floor of this cave warm carbonic acid gas constantly rises to a height of 18 inches (46 cm): the fumes render a dog insensible in a few seconds. It is mentioned by Pliny the Elder. Remains of an extensive Roman building and some statues have been discovered close by.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
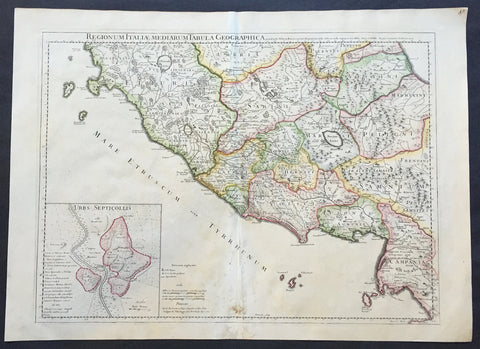
1711 Claude Delisle Large Antique Map of Rome and Regions, Italy
- Title : Regionum Italiae Mediarum Tabula Geographica Par Guill. Delisle.....1711
- Ref #: 31904
- Size: 28in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1711
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of Rome and the regions surrounding the ancient capital was engraved in 1711 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published by Guillaume Delisle in the Atlas Nouveau. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Very heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 18 1/2in (610mm x 470mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to bottom margin
Plate area: - Light creasing and slight discolouration to bottom centerold
Verso: - None
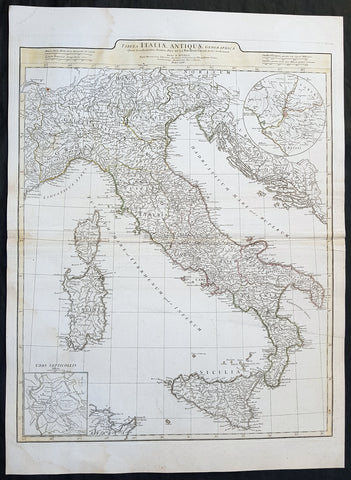
1764 J B D Anville Large Original Antique Map of Italy inset plan of Rome
- Title : Tabula Italiae Antiqua Geographica...MDCCLXIV
- Date : 1764
- Size: 29in x 21in (740mm x 535mm)
- Ref #: 92297
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved and highly detailed original antique map of Italy by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville was engraved in 1764 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D\'Anville\'s large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 21in (740mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning along centerfold
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning along centerfold
Background:
Since classical times, ancient Phoenicians, Carthaginians and Greeks established settlements in the south of Italy, with Etruscans and Celts inhabiting the centre and the north of Italy respectively and various ancient Italian tribes and Italic peoples dispersed throughout the Italian Peninsula and insular Italy. The Italic tribe known as the Latins formed the Roman Kingdom, which eventually became a republic that conquered and assimilated other nearby civilisations. Ultimately the Roman Empire emerged as the dominant power in the Mediterranean basin, conquering much of the ancient world and becoming the leading cultural, political and religious centre of Western civilisation. The legacy of the Roman Empire is widespread and can be observed in the global distribution of civilian law, republican governments, Christianity and the Latin script.
During the Early Middle Ages Italy suffered sociopolitical collapse amid calamitous barbarian invasions, but by the 11th century, numerous rival city-states and maritime republics, mainly in the northern and central regions of Italy, rose to great prosperity through shipping, commerce and banking, laying down the groundwork for modern capitalism.These mostly independent statelets, acting as Europe\'s main spice trade hubs with Asia and the Near East, often enjoyed a greater degree of democracy and wealth in comparison to the larger feudal monarchies that were consolidating throughout Europe at the time, though much of central Italy remained under the control of the theocratic Papal States, while Southern Italy remained largely feudal until the 19th century, partially as a result of a succession of Byzantine, Arab, Norman and Spanish conquests of the region.
The Renaissance began in Italy and spread to the rest of Europe, bringing a renewed interest in humanism, science, exploration and art. Italian culture flourished at this time, producing famous scholars, artists and polymaths such as Leonardo da Vinci, Galileo, Michelangelo and Machiavelli. Italian explorers such as Marco Polo, Christopher Columbus, Amerigo Vespucci and Giovanni da Verrazzano discovered new routes to the Far East and the New World, helping to usher in the European Age of Discovery. Nevertheless, Italy\'s commercial and political power significantly waned with the opening of the Atlantic trade route and the route to the Indian Ocean via the Cape of Good Hope, both of which bypassed the Mediterranean. Furthermore, the Italian city-states constantly engaged one another in bloody warfare, culminating in the Italian Wars of the 15th and 16th centuries that left them exhausted, with no one emerging as a dominant power. The weakened Italian sovereigns soon fell victim to conquest by European powers such as France, Spain and Austria.
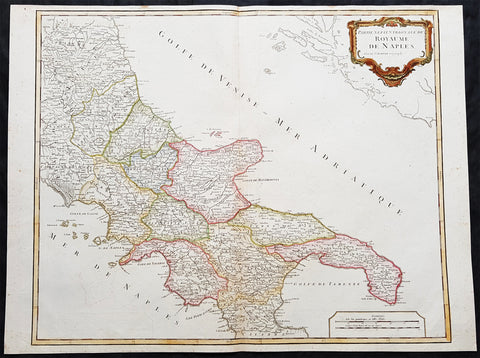
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map Southern Italy Mezzogiorno, 2 Sicilies
- Title : Partie Septentrionale Du Royaume De Naples
- Size: 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 92771
Description:
This magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Southern Italy in the mid to late 18th century by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 19 1/2in (620mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Southern Italy or Mezzogiorno is a macroregion of Italy traditionally encompassing the territories of the former Kingdom of the two Sicilies (all the southern section of the Italian Peninsula and Sicily), with the frequent addition of the island of Sardinia.
In 1442, however, Alfonso V conquered the Kingdom of Naples and unified Sicily and Naples once again as dependencies of the Crown of Aragon. At his death in 1458, the kingdom was again separated and Naples was inherited by Ferrante, Alfonso\'s illegitimate son. When Ferrante died in 1494, Charles VIII of France invaded Italy, using the Angevin claim to the throne of Naples, which his father had inherited on the death of King René\'s nephew in 1481, as a pretext, thus beginning the Italian Wars. Charles VIII expelled Alfonso II of Naples from Naples in 1495, but was soon forced to withdraw due to the support of Ferdinand II of Aragon for his cousin, Alfonso IIs son Ferrantino. Ferrantino was restored to the throne, but died in 1496, and was succeeded by his uncle, Frederick IV. The French, however, did not give up their claim, and in 1501 agreed to a partition of the kingdom with Ferdinand of Aragon, who abandoned his cousin King Frederick. The deal soon fell through, however, and the Crown of Aragon and France resumed their war over the kingdom, ultimately resulting in an Aragonese victory leaving Ferdinand in control of the kingdom by 1504.
The kingdom continued to be a focus of dispute between France and Spain for the next several decades, but French efforts to gain control of it became feebler as the decades went on, and Spanish control was never genuinely endangered. The French finally abandoned their claims to the kingdom by the Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis in 1559. With the Treaty of London (1557) the new client state of Stato dei Presidi (State of Presidi) was established and governed directly by Spain, as part of the Kingdom of Naples.
The administration of the Kingdom of Naples and Sicily, as well as the Duchy of Milan, was then run by the Council of Italy, while Sardinia kept being an integral part of the Council of Aragon until the first years of the XVIII° century, when it was ceded to Austria and eventually Savoy.
After the War of the Spanish Succession in the early 18th century, possession of the kingdom again changed hands. Under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, Naples was given to Charles VI, the Holy Roman Emperor. He also gained control of Sicily in 1720, but Austrian rule did not last long. Both Naples and Sicily were conquered by a Spanish army during the War of the Polish Succession in 1734, and Charles, Duke of Parma, a younger son of King Philip V of Spain was installed as King of Naples and Sicily from 1735. When Charles inherited the Spanish throne from his older half-brother in 1759, he left Naples and Sicily to his younger son, Ferdinand IV. Despite the two kingdoms being in a personal union under the House of Bourbon from 1735 onwards, they remained constitutionally separated.
Being a member of the House of Bourbon, King Ferdinand IV was a natural opponent of the French Revolution and Napoleon. In January 1799, Napoleon Bonaparte, in the name of the French Republic, captured Naples and proclaimed the Parthenopaean Republic, a French client state, as successor to the kingdom. King Ferdinand fled from Naples to Sicily until June of that year. In 1806, Bonaparte, by then French Emperor, again dethroned King Ferdinand and appointed his brother, Joseph Bonaparte, as King of Naples. In the Edict of Bayonne of 1808, Napoleon removed Joseph to Spain and appointed his brother-in-law, Joachim Murat, as King of the Two Sicilies, though this meant control only of the mainland portion of the kingdom. Throughout this Napoleonic interruption, King Ferdinand remained in Sicily, with Palermo as his capital.
After Napoleon\'s defeat, King Ferdinand IV was restored by the Congress of Vienna of 1815 as Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies. He established a concordat with the Papal States, which previously had a claim to the land. There were several rebellions on the island of Sicily against the King Ferdinand II but the end of the kingdom was only brought about by the Expedition of the Thousand in 1860, led by Garibaldi, an icon of the Italian unification, with the support of the House of Savoy and their Kingdom of Sardinia. The expedition resulted in a striking series of defeats for the Sicilian armies against the growing troops of Garibaldi. After the capture of Palermo and Sicily, he disembarked in Calabria and moved towards Naples, while in the meantime the Piedmontese also invaded the Kingdom from the Marche. The last battles fought were that of the Volturnus in 1860 and the siege of Gaeta, where King Francis II had sought shelter, hoping for French help, which never came. The last towns to resist Garibaldi\'s expedition were Messina (which capitulated on 13 March 1861) and Civitella del Tronto (which capitulated on 20 March 1861). The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was dissolved and annexed to the new Kingdom of Italy, founded in the same year. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1685 G B Falda & Sandrart Antique Print Villa Gardens Doria Pamphili, Rome Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Prospecto Del Palazzo & Giardino Pamphilio Detto Del Bel Respiro...Architettura del Caualier Alessandro Algardi...Simon Felice delin....Norimburga appresso Gioni. Gac. de Sandart
- Ref #: 93463
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1685
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique print of the Villa & Gardens of Doria Pamphili, Rome was engraved by Simone Felice for the 1685 edition of Giovanni Battista Faldas Li giardini di Roma, disegnati da Giovanni Battista Falda nuovamente dati alle stampe con direttione di Giov. Giacomo de Sandrart (The gardens of Rome, designed by Giovanni Battista Falda again printed with the direction of Giov. Giacomo de Sandrart) published in Nuremberg by Johann von Sandrart.
The work is based on the original series edited by Gian Giacomo de Rossi a few years earlier (the first edition was certainly published after 1677 but before 1683) which included 19 tables of plants and perspective views of the most famous Roman gardens, 14 of which were engraved by GB Falda and 5 by Simon Felice.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Villa Doria Pamphili is a seventeenth-century villa with what is today the largest landscaped public park in Rome, Italy. It is located in the quarter of Monteverde, on the Gianicolo (or the Roman Janiculum), just outside the Porta San Pancrazio in the ancient walls of Rome where the ancient road of the Via Aurelia commences.
It began as a villa for the Pamphili family and when the line died out in the eighteenth century, it passed to Prince Giovanni Andrea IV Doria, and has been known as the Villa Doria Pamphili since.
The nucleus of the villa property, the Villa Vecchia or old villa, already existed before 1630, when it was bought by Pamfilio Pamfili, who had married the heiress Olimpia Maidalchini, to enjoy as a suburban villa. Thereafter he set about buying up neighbouring vineyards to accumulate a much larger holding, which was often known as the Bel Respiro or beautiful breath as it stood on high ground, above the malarial areas of Rome, and offered spectacular views which were a desirable feature of Baroque villa settings.
In 1644 Cardinal Giambattista Pamphili became elected to the papacy and took the name of Innocent X. In accordance with this change in status, the Pamphili aspired to a grander and more expansively sited new villa. Early designs were made, possibly by Virgilio Spada rather than the traditional attribution to Borromini, but these were rejected. Instead the project was placed in the hands of the Bolognese sculptor Alessandro Algardi in 1644, assisted by Giovanni Francesco Grimaldi.
The initial design had a central casino (not the modern usage as a gambling establishment) with wings, but only the central block was built. There is uncertainty as to who the architect was; Algardi was not an architect, and it may be that he had help from Carlo Rainaldi and that the construction was supervised by Grimaldi. The layout has a central circular room around which the other rooms were arranged. Construction began in 1645 and was complete by 1647 although embellishments and the garden layouts were not finished until 1653. The casino, sometimes known as the Casino del Bel Respiro, was designed as a complement to the Pamphili collection of sculptures both ancient and modern, and other Roman antiquities such as vases, sarcophagi and inscriptions; it was only ever intended for display of the collection and the family and guests resided in the older Vecchia Vigna.
As a show case for sculpture, the somewhat crowded Casino facades have rhythmically alternating windows with niches which were elaborately adorned with sculptures, both antique and modern, with busts in hollowed roundels, with panels of bas-reliefs, and reliefs.
The exterior containing statues gives a rich allure that was architecturally somewhat conservative for its date, looking back towards the Villa Medici or the Casina Pio IV, and rather more Mannerist than Baroque. It offered a foretaste of the richly stuccoed and frescoed interiors, where the iconographic program set out to establish the antiquity of the Pamphili, a family then somewhat parvenu in Rome, with origins in Gubbio. Inside, Algardi provided further bas-reliefs and stucco framing for the heroic frescoes drawn from Roman history painted by Grimaldi.
The casino is set into the hill slope such that the main entrance on the north side is at a level above the giardino segreto or secret garden enclosure on its south side, a parterre garden with low clipped hedges. The gardens on the sloping site were laid out from around 1650 by Innocents nephew, Camillo Pamphili, formalizing the slope as a sequence from the parterres that flank the Casino, to a lower level below, framed by the boschi or formalized woodlands that rose above clipped hedges, and eventually arriving at a rusticated grotto in the form of an exedra, from which sculptured figures emerge from the rockwork. The exedra, now grassed, formerly enframed a Fountain of Venus by Algardi, which is preserved in the Villa Vecchia, together with Algardis bas-reliefs of putti representing Love and the Arts that were formerly here. The fountain spilled into a small cascade that let into a short length of formal canal, which was intended to remind the viewer of the similar Canopus at Hadrians Villa— another programmatic connection of the Pamphili with Antiquity.
When Girolamo Pamphili died in 1760 without male heirs, the disputes which broke out among the possible heirs were settled in 1763 when Pope Clement XIII Rezzonico granted to Prince Giovanni Andrea IV Doria the right to take the surname, the arms and the vast properties of the Pamphili; the Princes claim was based on the marriage between Giovanni Andrea III Doria and Anna Pamphili. Since then, the villa has been known as the Villa Doria Pamphili.
Throughout the 18th century, features were regularly added such as fountains and gateways by Gabriele Valvassori and other architects retained by the Pamphili and their heirs. After the Napoleonic era, more sweeping changes were made. The parterres that were formal extensions of the casino were retained but replanted with the patterned planting of colourful carpet bedding supplied from greenhouses by the old villa. (Today the parterres have been replanted in 16th-century style, with panels of scrolling designs in close-clipped greens set in wide gravel walks.) In the sloping outer gardens the changes were more extensive, recasting them in the naturalistic manner of English landscape gardens. The grounds, filled with many surprise features and picturesque incidents, swept down to a small lake at the bottom, which already had an air of atmospheric maturity when it was painted in the 1830s by Alexandre-Gabriel Decamps. In the wooded, natural-appearing landscapes with clumps of characteristic umbrella-like stone pines along horizons stand statues and vases, which evoke a nostalgic antiquity. The 18th-century English landscape gardens such as Stowe and Stourhead that were the inspiration for this style aimed to bring to life the Italian landscapes with Roman ruins painted by Claude and Poussin. A notable difference is that at the Villa Doria Pamphilis giardino inglese the Roman remains are likely to be genuine. The site of the villa contained several Roman tombs that yielded vases, sarcophagi and inscriptions that were added to the Pamphili collection.
Falda, Giovanni Battista 1643 – 1678
Falda was an Italian architect, engraver and artist. He is known for his engravings of both contemporary and antique structures of Rome.
Falda was sent as a boy to Rome, to work in the studio of Bernini, and his draughtsmanship caught the eye of the publisher Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi. He engraved for Le fontane di Roma (Fountains in Rome) and for Palazzi di Roma (Palaces of Rome). The former books was expanded after Faldas death with engravings by Francesco Venturini. The latter was published in 1655 in collaboration with Pietro Ferrerio. He is sometimes known as Falda da Valduggia because of his birthplace.
His works became particularly popular with the first waves of Grand Tour participants during the latter parts of the 17th century and Falda became a commercial success as a result. His works appealed to tourists keen to retain a detailed and accurate representation of those parts of Rome they had visited.
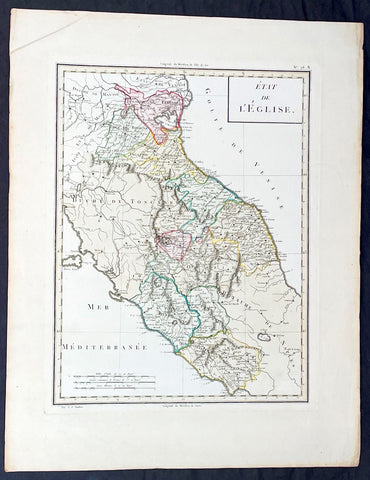
1765 Tardieu Large Antique Map Catholic States of Italy
- Title : Etat de L Eglise
- Ref #: 92787
- Size: 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Catholic States of Italy waspublished by the famous French publisher Pierre Francois Tardieu (famous for publishing Diderots Encyclopedie in 1779) in 1765. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Paper size: - 18in x 13 1/2in (460mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
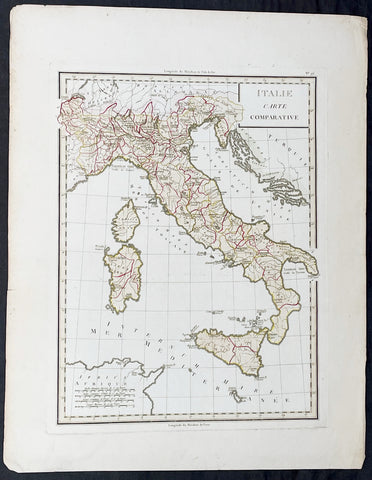
1765 Tardieu Large Antique Map of Italy
- Title : Italie Carte Comparative
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92789
- Size: 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Italy was published by the famous French publisher Pierre Francois Tardieu (famous for publishing Diderots Encyclopedie in 1779) in 1765. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Paper size: - 18in x 13 1/2in (460mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1856 Captain Richard Delafield Antique Maps of Genoa & Venice Italy - Art of War
Antique Map
- Title : Harbour Defences plate 19; Defences of Naval Depot and City of Genoa; Defence of Naval Depot and City of Venice
- Ref #: 90119
- Size: 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original lithograph map of Genoa & Venice Italy was engraved by John T Bowen & co. Philadelphia, was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 9 1/2in (560mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Left fold rejoined, light age toning
Verso: - Left margin rejoined with archival tape
Background:
In the beginning of 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
1802 Lechevalier Antique Map of Italy Greece & Turkey Troy
- Title : Carte Du Golphe Adriatique et De L Archipel pour servir ou Voyage de la Troade
- Ref #: 70207
- Size: 20in x 19in (510mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique map of the voyage of Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier from Italy to the Greece and Turkey - specifically the Biga Peninsular home of the ancient city of Troy in NW Turkey - was published in the Atlas of Charts & Views that accompanied the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier's (1752 - 1836) Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786.
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homer's Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His title, "Voyage de la Troade" was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 19in (510mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 18in (485mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning along fold as issued
Verso: - Light age toning