Europe (305)
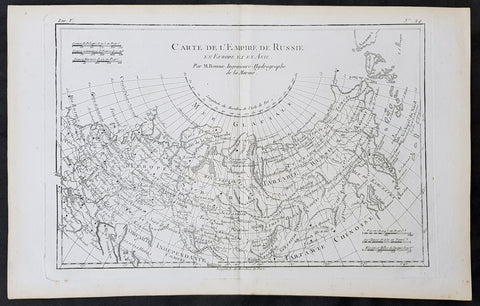
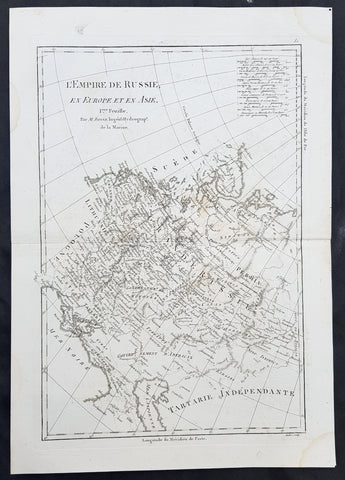
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of The Russian Empire
- Title : Carte De L Empire de Russie en Europe et en Asie...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31674
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
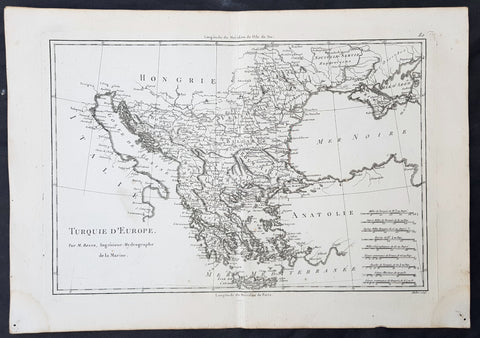
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Turkey in Europe - Greece to Hungary
- Title : Turquie D Europe...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40526
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
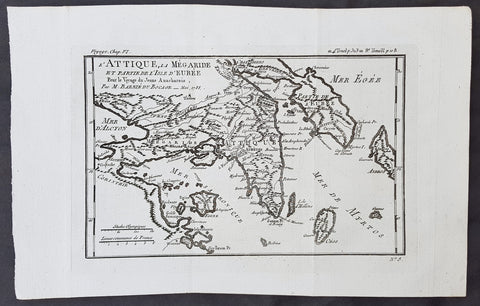
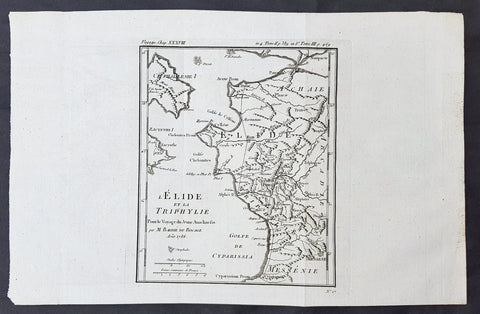
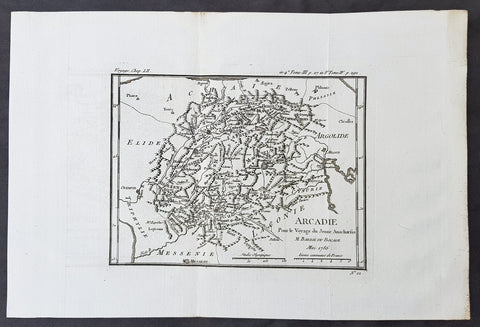
1782 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map of Attica Megaris Thebes Euboea, Greece
- Title : l Attique, la Megaride et partie de l Isle d Eubee, Pour le Voyage du Jeune Anacharsis.....1785
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16463
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1785 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greecein 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8 1/2in x 7 1/2in (215mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
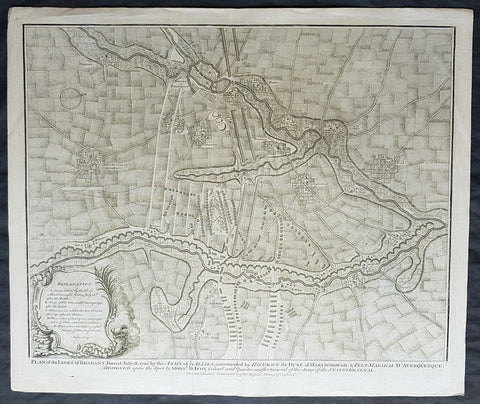
1745 Tindal Original Antique Map Plan of the Battle of Elixheim, Brabant in 1705
- Title : Plan of the Battle lines of Brabant Forced July 18 1705 by the Army of ye Allies commanded by His Grace the Duke of Marlborough & Felt-Marshall D Averquerque Designed upon the spot by Mons D Ivoy Colonel and Quater master General of the Army of the States General
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 01-8714
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Elixheim, in 1705, also known as the Passage of the Lines of Brabant - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Elixheim, 18 July 1705, also known as the Passage of the Lines of Brabant was a battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The Duke of Marlborough successfully broke through the French Lines of Brabant, an arc of defensive fieldworks stretching in a seventy-mile arc from Antwerp to Namur. Although he was unable to bring about a decisive battle, the breaking and subsequent razing of the lines would prove critical to the allied victory at Ramillies the next year.
Early in the campaigning season, Marlborough attempted to launch an invasion of France up the Moselle valley. This effort was halted by a combination of supply shortages and an excellent French defensive position in front of Sierck, and Marlborough and his army were recalled by the Dutch States General when Marshall Villeroi attacked and took the fortress of Huy and threatened Liege. Having rushed back to the Low Countries (and forcing Villeroi to retreat behind his defenses), Marlborough retook Huy, and then planned to break through the lines to bring Villeroi to battle.
On the evening of 17 July Marlborough sent the Dutch troops under Marshal Overkirk in a feint southwards towards Namur, drawing Villeroi and 40,000 men after them. Overnight he marched with his own English and Scottish troops northwards to the small village of Eliksem (Elixheim), and there broke through the lines without resistance. Early the next day, as Overkirk\'s men countermarched northwards to join with Marlborough, a French detachment attacked the small force of allied troops drawn up to the west of the lines, facing south. Following a short but intense cavalry battle, in which Marlborough was often personally engaged, they were driven off, and Villeroi withdrew his army to the west, behind the river Dyle.
Unable to pursue the French with any vigour on the day of the battle due to the exhaustion of his men, who had marched all night and then fought an intense battle, Marlborough nonetheless still hoped to bring Villeroi to battle. He was frustrated in manoeuvering to the west of the lines in the month immediately following the breakthrough. A final effort in early August, using wagons loaded with supplies to remove his dependency on his lines of communication, while successful in forcing Villeroi\'s army to make a stand close to Waterloo, ultimately failed to bring about a battle due to the veto exercised by the Dutch Field Deputies, notably Slangenburg. The Duke was forced to content himself with the capture of the fortress of Leau and the levelling of the Lines of Brabant between Leau and the Meuse.
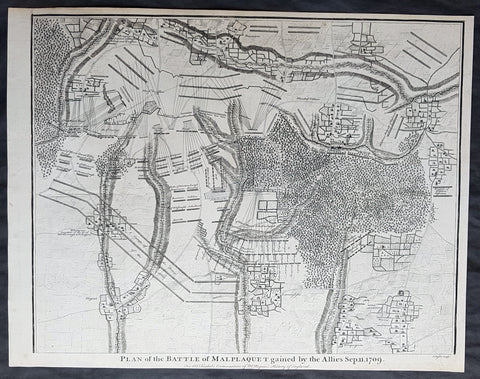
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22154
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
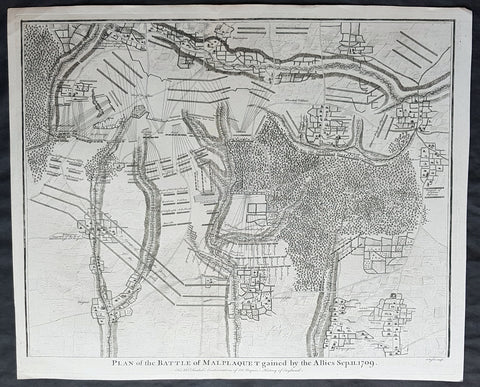
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22173
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
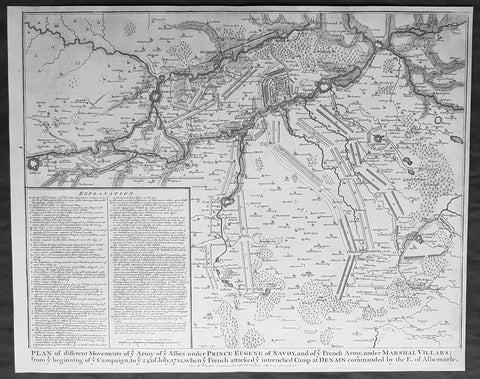
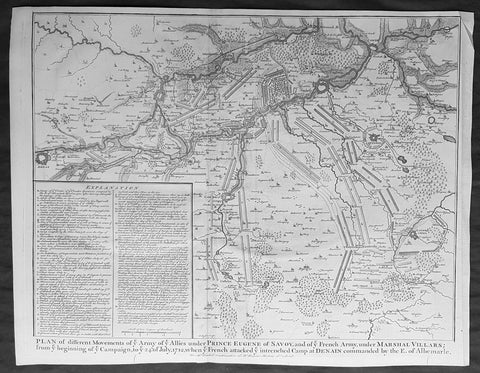
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle Plan of Denain, France in 1712
- Title : Plan of the movements of ye Armies of ye Allies under Prince Eugene of Savoy and of ye French Army under Marshal Villars; from ye beginning of ye campaign to ye 24th July 1712, when ye French attacked ye intrenchement Camp at Denain commanded by the E. of Albemarle
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22155
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan of the Battle of Denain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - centering on the cities of Douai & Bouchain in northern France, was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Denain was fought on 24 July 1712, as part of the War of the Spanish Succession. It resulted in a French victory under Marshal Villars against Dutch and Austrian forces under Prince Eugene of Savoy.
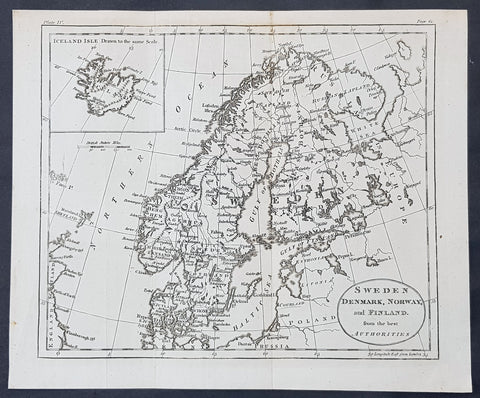
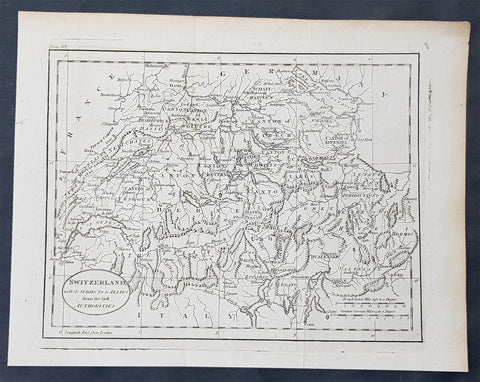
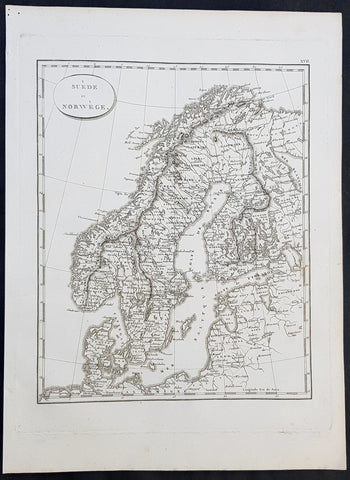
1770 John Cary Original Antique Map Sweden, Denmark, Norway, Finland & Iceland
- Title : Sweden, Denmark, Norway and Finland from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70177
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthrie\'s Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
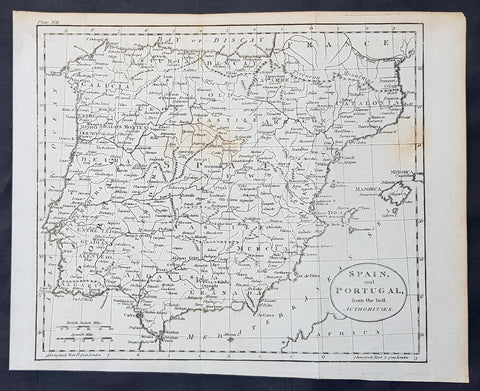
1770 Thomas Kitchin Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & Balearic Islands
- Title : Spain and Portugal from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70189
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthrie\'s Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
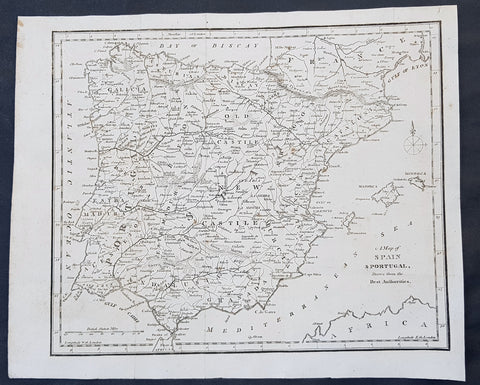
1797 John Cary Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & The Balearic Islands
- Title : A Map of Spain & Portugal Drawn from the Best Authorities
- Size: 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 92755
- Date : 1797
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by John Cary was published in the 1797 edition of Moores Geography
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
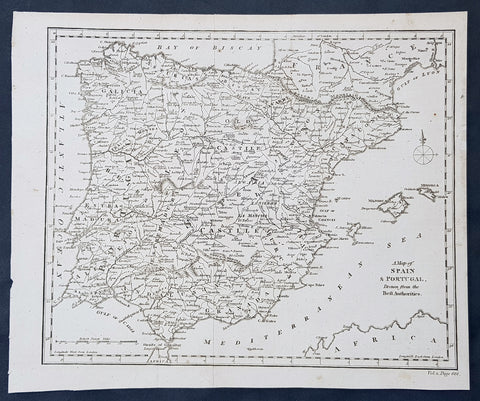
1790 Aaron Arrowsmith Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & Balearic Islands
- Title : A Map of Spain & Portugal Drawn from the Best Authorities
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 30218
- Date : 1790
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Aaron Arrowsmith was published in the 1790 edition of Cruttwells Atlas, to his GazetterJohn Arrowsmithaaron Arrowsmith
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
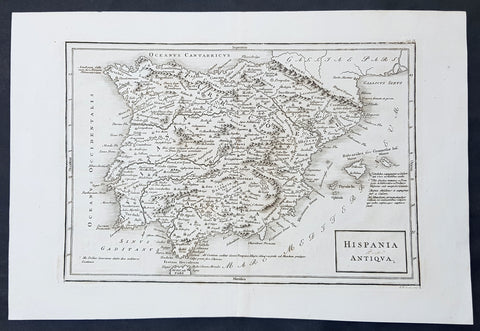
1750 C. Cellarius & RW Seale Original Antique Map of Spain & Balearic Islands
- Title : Hispania Antiqua
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31354
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original copper-plate engraved antique map of Spain by Christopher Cellarius was engraved by RW Seale and published in the 1750 edition of Geographica Antiqua.
Richard William Seale was a prolific engraver of the mid 18th century responsible between 1744-47 for Maps of Continents and Maps for Mr Tindals Continuation of Rapins History of England in 1745. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Geographica was one of the most popular geographical publications of the 17th and 18th centuries, that lasted into the 19th century, a fine map (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
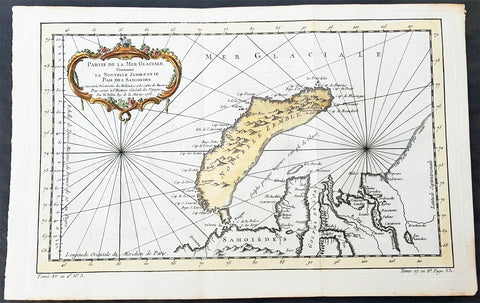
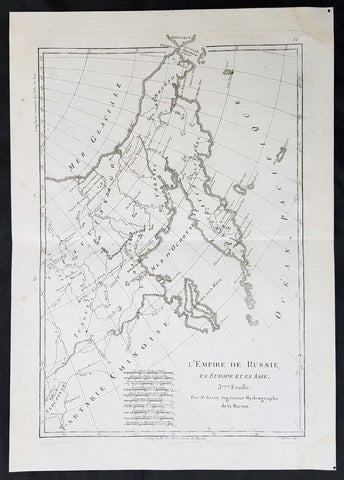
1758 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Russia The Island of Novaya Zemlya
- Title : Partie De La Mer Glaciale Contenant La Nouvelle Zemle...M. Bellin...1758
- Ref #: 60968
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (380mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Novaya Zemlya also known as Nova Zembla (especially in Dutch), is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in northern Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the Northern island. Novaya Zemlya is composed of two islands, the northern Severny Island and the southern Yuzhny Island, which are separated by Matochkin Strait.
The Russians knew of Novaya Zemlya from the 11th century, when hunters from Novgorod visited the area. For western Europeans, the search for the Northern Sea Route in the 16th century led to its exploration. The first visit from a west European was by Hugh Willoughby in 1553, and he met Russian ships from the already established hunting trade. Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya in 1594, and in a subsequent expedition of 1596 rounded the Northern point and wintered on the Northeast coast. (Barentsz died during the expedition, and may have been buried on the Northern island.) During a later voyage by Fyodor Litke in 1821–1824, the west coast was mapped. Henry Hudson was another explorer who passed through Novaya Zemlya while searching for the Northeast Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1574 Munster Large Antique Print - View of The German City of Landau, Bavaria
- Title : Die Statt Landaw
- Ref #: 22668
- Size: 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the Bavarian City of Landau NE of Munich was engraved in 1547 - the date is engraved at the foot of the image - and was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1574 edition of Cosmographia.
Landau or Landau in der Pfalz (pop. 41,821) is an autonomous (kreisfrei) city surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long-standing cultural centre, and a market and shopping town, surrounded by vineyards and wine-growing villages of the Palatinate wine region. Landau lies east of the Palatinate forest, Europe's largest contiguous forest, direct on the German Wine Route.
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle hisCosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographiaappeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications ofCosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: -None
Verso: - None
1797 Laperouse Antique Print View De Kastri Bay, Ulchsky Khabarovsk Kai, Russia
- Title : Tombeaux de la Baie de Castries
- Ref : 21436
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1797
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique print, a view of the very early settlement at De Kastri Bay, in the Ulchsky District of Khabarovsk Kai, Eastern Russia - opposite the Sakhalin Islands - by Jean-François de Galaup, Comte de la Pérouse was published in the 1st edition of the Atlas du voyage de La Perouse, Paris 1797.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repairs to margins, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
De-Kastri was named for the former name of the bay on which it stands. The bay was discovered by La Pérouse on July 25, 1787 and named after the sponsor of the expedition—the then Secretary of State of the French Navy, the Marquis de Castries. The bay is a convenient natural refuge for vessels, giving it strategic importance from a military viewpoint.
The settlement was officially founded in 1853, although the land where it was situated would not officially be Russian territory until the signing of the Treaty of Aigun five years later.
In 1854, the difficult task of defending Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky when it came under siege from the British and French forces during the Crimean War brought to attention the difficulties of supply and defense of the Kamchatka Peninsula, where a large section of the Russian Pacific Fleet was based. It was decided to move the port from Kamchatka without waiting for another attack. In the spring of 1855, the Russian navy\'s weapons and sailors under the leadership of Rear Admiral Vasily Zavoyko headed toward the mouth of the Amur River; however, the river mouth was still covered with ice. It was decided to wait for the break-up, hiding in the Bay of de Castries from the superior forces of French and English. Russian ships were discovered there, but managed to escape to the Amur River in the Strait of Tartary before the arrival of enemy reinforcements. The British and French did not know that Sakhalin was an island, and spent the later years of the war waiting in vain for the Russian fleet at its southern coast.
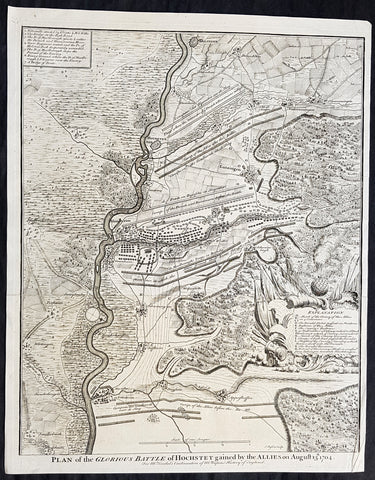
1745 Nicolas Tindal Antique Map The Battle of Blenheim, Germany in 1704
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Glorious Battle of Hochstet gained by the Allies on August 13.th 1704.
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Ref #: 22178
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Blenheim or Hochstadt, fought in Bavaria, Germany in August 1704 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Blenheim (German: Zweite Schlacht bei Höchstädt; French Bataille de Höchstädt), fought on 13 August 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied victory ensured the safety of Vienna from the Franco-Bavarian army, thus preventing the collapse of the Grand Alliance.
Louis XIV of France sought to knock the Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold out of the war by seizing Vienna, the Habsburg capital, and gain a favourable peace settlement. The dangers to Vienna were considerable: the Elector of Bavaria and Marshal Marsins forces in Bavaria threatened from the west, and Marshal Vendômes large army in northern Italy posed a serious danger with a potential offensive through the Brenner Pass. Vienna was also under pressure from Rákóczis Hungarian revolt from its eastern approaches. Realising the danger, the Duke of Marlborough resolved to alleviate the peril to Vienna by marching his forces south from Bedburg to help maintain Emperor Leopold within the Grand Alliance.
A combination of deception and skilled administration – designed to conceal his true destination from friend and foe alike – enabled Marlborough to march 400 kilometres (250 miles) unhindered from the Low Countries to the River Danube in five weeks. After securing Donauwörth on the Danube, Marlborough sought to engage the Electors and Marsins army before Marshal Tallard could bring reinforcements through the Black Forest. However, with the Franco-Bavarian commanders reluctant to fight until their numbers were deemed sufficient, the Duke enacted a policy of plundering in Bavaria designed to force the issue. The tactic proved unsuccessful, but when Tallard arrived to bolster the Electors army, and Prince Eugene arrived with reinforcements for the Allies, the two armies finally met on the banks of the Danube in and around the small village of Blindheim, from which the English Blenheim is derived.
Blenheim was one of the battles that altered the course of the war, which until then was leaning for Louis coalition, and ended French plans of knocking the Emperor out of the war. France suffered as many as 38,000 casualties including the commander-in-chief, Marshal Tallard, who was taken captive to England. Before the 1704 campaign ended, the Allies had taken Landau, and the towns of Trier and Trarbach on the Moselle in preparation for the following years campaign into France itself. The offensive never materialised as the Grand Alliances army had to depart the Moselle to defend Liège from a French counteroffensive. The war would rage on for another decade.
Tindal, Nicolas 1687 – 1774
Nicolas Tindal was the translator and continuer of the History of England published by Paul de Rapin (1661-1725) in 1724. De Rapins publication chronicles the History of Britain from the invasion of the Romans to the death of Charles I. Very few comprehensive histories of England existed at the time and Tindal added his three-volume Continuation, of the Kingdom, from the reigns of James II to George II.
Tindal\\\'s translation of de Rapins History, was first published in 1727. Tindal enlarged the volumes in their second edition (1732) to contain notes, genealogical tables and maps of his own composition. In 1745 Tindal published Tindal’s Continuation of Mr. Rapin’s History of England. Included with this edition was an atlas containing 45 maps, battle and town plans from the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) that were engraved by Richard William Seale and John Basire.
These maps represent battles that took place during the War of Spanish Succession, concluded by the Treaties of Utrecht. The war resulted from a dispute over who should inherit Spain and its possessions after its Habsburg rulers in 1700. The last Habsburg king of Spain, Charles II (d. 1700) had left the throne to his closest relative in female line: Philippe de France, duke of Anjou, grandson of Louis XIV (Felipe V of Spain). The closest relatives in male line, the Habsburgs of Austria, disputed this claim, and many European nations did not want to see French princes reigning over both kingdoms. The Utrecht treaties recognized Felipe V of Spain, but transferred the Spanish possessions in the Netherlands and Italy to Austria and to Savoy. To reach the goal of separating the crowns of France and Spain, the treaties required Felipe V to relinquish all claims to the French throne, and the remaining French princes to relinquish all claims to the Spanish throne.
The War of the Spanish Succession, was also known as Marlboroughs Wars, that was fought in Europe and the Mediterranean, and were the last and the bloodiest of the Wars between England and France under Louis XIV, and the first in which Britain played a major military role in European military affairs.
Paul de Rapin 1661-1725 was born in Castes and educated at the Protestant academy of Saumur. In 1685 after the death of his father he moved to England but after being unable to find employment moved to Holland and enlisted in French volunteers at Utrecht commanded by his cousin Daniel de Rapin. He accompanied the prince of Orange to England in 1688 and participated in the Irish campaigns of the siege of Carrickfergus, Battle of the Boyne and Limerick. Rapin resigned to become tutor to the Earl of Portlands son. He settled in Holland where he began work on The History of England. It was published in Holland in 1724 in 8 volumes. The work was an attempt to be exhaustive in the spirit of the eighteenth century philosophies by treating the subject from prehistoric times up to the date of publication.
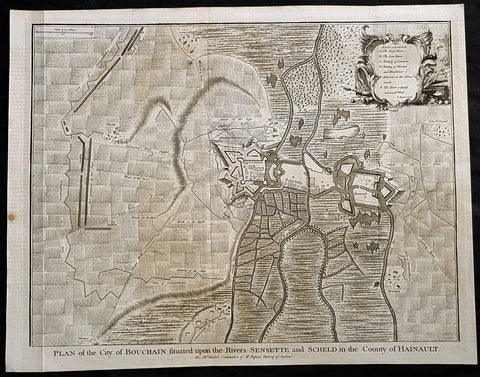
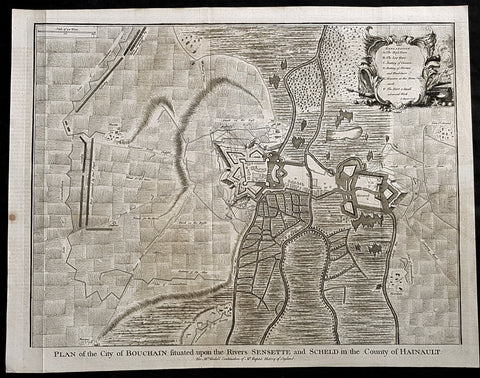
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22156-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
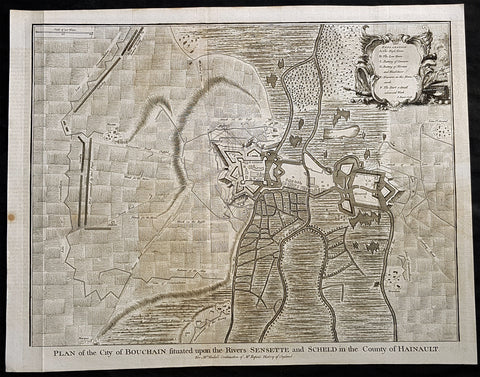
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22156-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
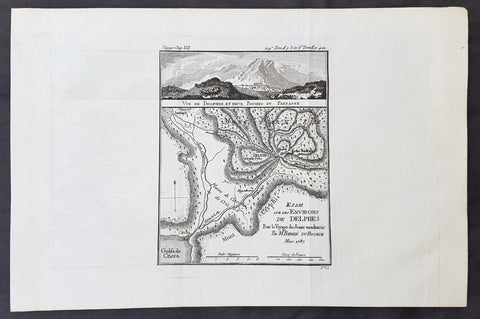
1787 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map & View of Delphi & Mt Parnassus, Greece
- Title : Essai sur Les Environs De Delphes...1787
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16456
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1787 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece in 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8in x 6in (205mm x 155mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1769 J B D Anville Original Antique Map of Greece Crete Macedonia Turkey Cyprus
- Title : Carte Generale De La Grece
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 32345
- Date : 1769
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville in the 1769 edition of his atlas Geographie Ancienne et Abregee. or Modern and Ancient Geography (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22198
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
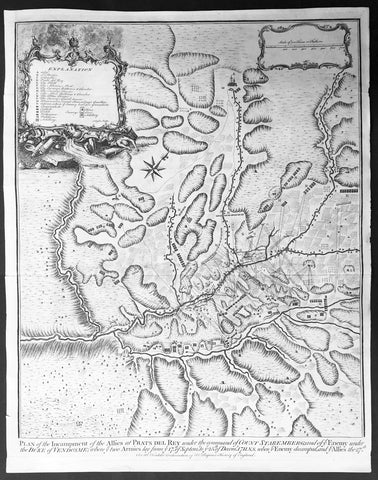
1745 Tindal Antique Map of Spanish & Austrian Armies in Catalonia Spain in 1711
- Title : Plan of the Incampment of the Allies at Prats Del Rey. under the command of Count Staremberg and of ye Enemy under the Duke of Vendsome: wher ye two Armies lay from ye 17th of September to ye 25th of December 1711 N.S. when ye Enemy decamped and ye Allies the 27th.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15657
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the encampments of the Spanish army under Louis-Joseph, duke de Vendome & the Austrian Army under Count Guido Starhemberg in Prado Del Rey in Catalonia, Spain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Duke Louis-Joseph de Vendome , 1654 — 1712 was one of King Louis XIV’s leading generals during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–14).
Vendome was the son of Louis de Vendome, Duke de Mercoeur, by his marriage to Cardinal Jules Mazarin’s niece, Laure Mancini. Vendôme entered the French Army in 1672 and had risen to the rank of lieutenant general by the outbreak of the War of the Grand Alliance (1689–97) between France and the other major powers. He distinguished himself in the victory over the Allies at Steenkirke (1692) and was made commander in Catalonia in 1695; two years later he captured Barcelona.
The dispute over the succession to the Spanish throne brought France and Spain to war with the British, the Austrians, and the Dutch in 1701. Appointed to the command in northern Italy in 1702, Vendôme fought the Austrian commander, Prince Eugene of Savoy, in the bloody but indecisive Battle of Luzzara on August 15. He took Vercelli in 1704 and defeated Prince Eugene at Cassano in August 1705. In May 1706 Vendôme was transferred to the Flanders front, where the British commander John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, had just won an overwhelming victory at Ramillies. Vendôme made limited gains until he was severely defeated by Marlborough and Prince Eugene at Oudenaarde on July 11, 1708. Vendôme subsequently failed to relieve besieged Lille (in northern France), which fell to the Allies in October. Recalled by Louis XIV, he was temporarily disgraced.
Guido Wald Rüdiger, count of Starhemberg1657 – 1737 was an Austrian military officer.
He was a cousin of Ernst Rudiger von Starhemberg (1638-1701), the famous commander of Vienna during the Turkish siege of 1683, and acted as his aide-de-camp during that siege. Guido followed his cousin, and later Prince Eugene of Savoy, in battles against the Turks.
In the War of the Spanish Succession, Starhemberg fought in Italy and Spain. Between 1706 and 1708 he was the commander-in-chief of the imperial army in Hungary, leading military operations against the insurgents of Francis II Rákóczi. In 1708, he was appointed Supreme Commander of the Austrians in Spain.
Together with James Stanhope he succeeded in conquering Madrid in 1710, after previously gaining victories at Almenar and Saragossa. In December, however, he was forced to leave the city by the lack of support by its inhabitants for the Habsburg pretender. After the subsequent defeats at the Battle of Brihuega and the Battle of Villaviciosa (1710), he had to pull back to Catalonia, where he was made viceroy when Archduke Charles returned to Austria.
After the Peace of Utrecht (1713), archduke Charles, now Emperor Charles VI, ordered him to abandon Catalonia. He pulled back with his troops to Genoa on English ships.
When he died in 1737, he was Governor of Slavonia
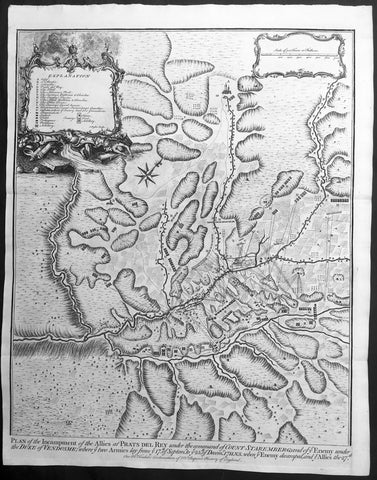
1745 Tindal Antique Map of Spanish & Austrian Armies in Catalonia Spain in 1711
- Title : Plan of the Incampment of the Allies at Prats Del Rey. under the command of Count Staremberg and of ye Enemy under the Duke of Vendsome: wher ye two Armies lay from ye 17th of September to ye 25th of December 1711 N.S. when ye Enemy decamped and ye Allies the 27th.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15687
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, a battle plan of the encampments of the Spanish army under Louis-Joseph, duke de Vendome & the Austrian Army under Count Guido Starhemberg in Prado Del Rey in Catalonia, Spain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapins History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Duke Louis-Joseph de Vendome , 1654 — 1712 was one of King Louis XIV’s leading generals during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–14).
Vendome was the son of Louis de Vendome, Duke de Mercoeur, by his marriage to Cardinal Jules Mazarin’s niece, Laure Mancini. Vendôme entered the French Army in 1672 and had risen to the rank of lieutenant general by the outbreak of the War of the Grand Alliance (1689–97) between France and the other major powers. He distinguished himself in the victory over the Allies at Steenkirke (1692) and was made commander in Catalonia in 1695; two years later he captured Barcelona.
The dispute over the succession to the Spanish throne brought France and Spain to war with the British, the Austrians, and the Dutch in 1701. Appointed to the command in northern Italy in 1702, Vendôme fought the Austrian commander, Prince Eugene of Savoy, in the bloody but indecisive Battle of Luzzara on August 15. He took Vercelli in 1704 and defeated Prince Eugene at Cassano in August 1705. In May 1706 Vendôme was transferred to the Flanders front, where the British commander John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, had just won an overwhelming victory at Ramillies. Vendôme made limited gains until he was severely defeated by Marlborough and Prince Eugene at Oudenaarde on July 11, 1708. Vendôme subsequently failed to relieve besieged Lille (in northern France), which fell to the Allies in October. Recalled by Louis XIV, he was temporarily disgraced.
Guido Wald Rüdiger, count of Starhemberg1657 – 1737 was an Austrian military officer.
He was a cousin of Ernst Rudiger von Starhemberg (1638-1701), the famous commander of Vienna during the Turkish siege of 1683, and acted as his aide-de-camp during that siege. Guido followed his cousin, and later Prince Eugene of Savoy, in battles against the Turks.
In the War of the Spanish Succession, Starhemberg fought in Italy and Spain. Between 1706 and 1708 he was the commander-in-chief of the imperial army in Hungary, leading military operations against the insurgents of Francis II Rákóczi. In 1708, he was appointed Supreme Commander of the Austrians in Spain.
Together with James Stanhope he succeeded in conquering Madrid in 1710, after previously gaining victories at Almenar and Saragossa. In December, however, he was forced to leave the city by the lack of support by its inhabitants for the Habsburg pretender. After the subsequent defeats at the Battle of Brihuega and the Battle of Villaviciosa (1710), he had to pull back to Catalonia, where he was made viceroy when Archduke Charles returned to Austria.
After the Peace of Utrecht (1713), archduke Charles, now Emperor Charles VI, ordered him to abandon Catalonia. He pulled back with his troops to Genoa on English ships.
When he died in 1737, he was Governor of Slavonia
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle Plan of Denain, France in 1712
- Title : Plan of the movements of ye Armies of ye Allies under Prince Eugene of Savoy and of ye French Army under Marshal Villars; from ye beginning of ye campaign to ye 24th July 1712, when ye French attacked ye intrenchement Camp at Denain commanded by the E. of Albemarle
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15689
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan of the Battle of Denain - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - centering on the cities of Douai & Bouchain in northern France, was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Denain was fought on 24 July 1712, as part of the War of the Spanish Succession. It resulted in a French victory under Marshal Villars against Dutch and Austrian forces under Prince Eugene of Savoy.
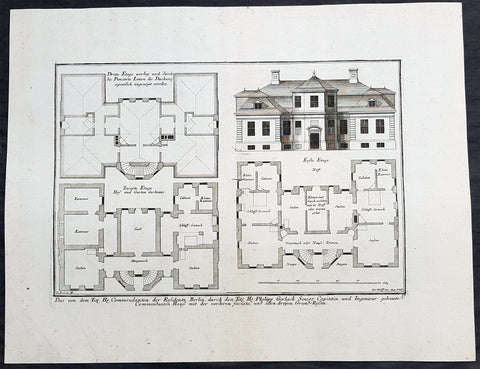
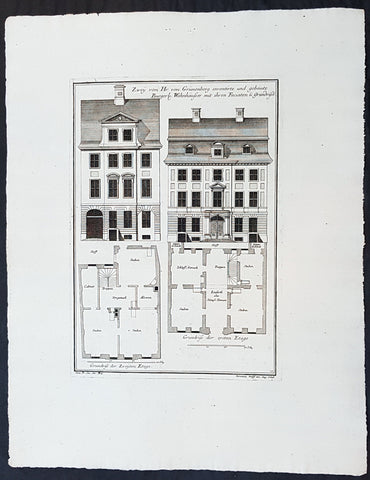
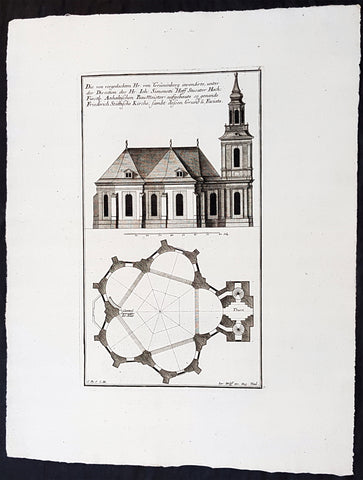
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Plan Officers Quarters, Royal Arsenal, Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Das von dem Tit. H. Commendanten der Residentz Berlin, durch den Tit. H. Philipp Gerlach Senior Capitain und Ingenieur gebaute Commendaten Hauß mit der vorderen faciata und allen dreyen Grund-Rissen
- Ref #: 93449
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view & plan of officers quarters at the Royal Arsenal in Berlin - plate No.17 of 19 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
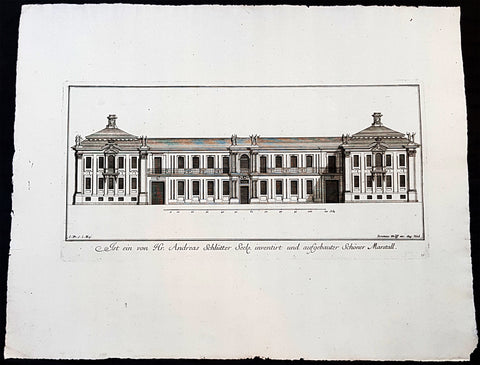
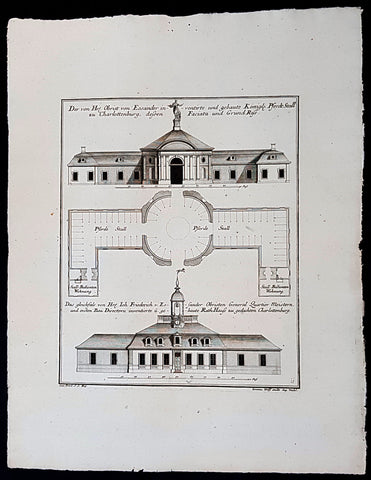
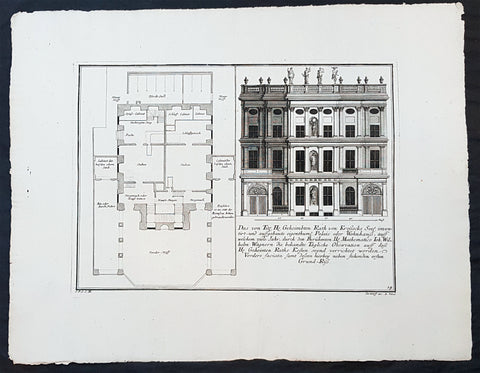
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Charlottenburg Palace Stables Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Ist ein von Hr. Andreas Schlütter Seel. inventirt und aufgebauer Schöner Marstall Datierung
- Ref #: 93447
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view of the facade of the Charlottenburg Palace stables in Berlin - plate No.15 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
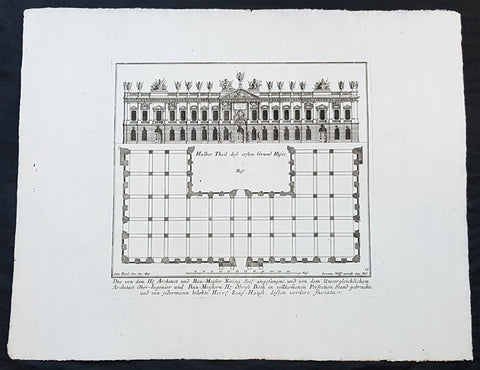
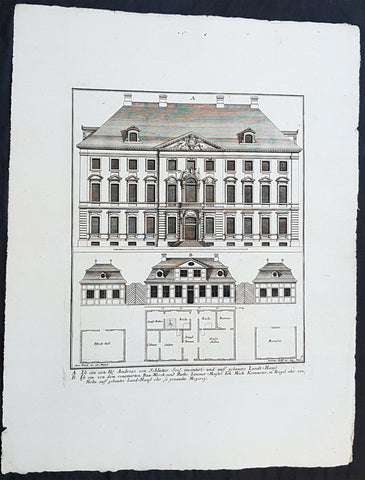
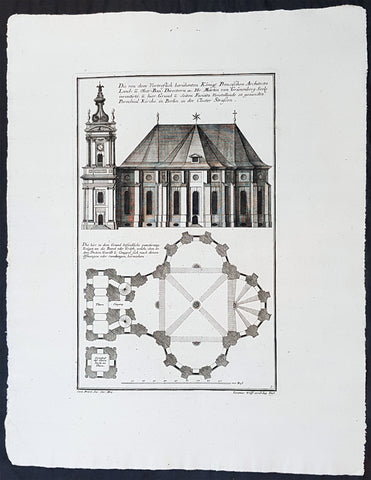
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of The Royal Arsenal in Berlin Germany
Antique Map
- Title : Das von dem H. Architect und Bau-Meister Nering Seel. angefangne, und von dem unvergleichlichen Architect Ober-Ingenier und Bau-Meistern H. Obrist Both in vollkommenen Perfection Stand gebrachte und von jedermann belobte Herr. Zeug-Haus, dessen vordere faciata
- Ref #: 93454
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view & plan of The Royal Arsenal in Berlin Houses - plate No.13 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print Plans of Residential Houses in Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Zwey von Hr. von Grünenberg inventirte und gebaute Burgerl. Wohnhäusser mit ihren Faciaten u. Grundrissen
- Ref #: 93450
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print plans of Berlin Houses - plate No. 12 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Charlottenburg Palace Stables Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Der von Hr. Obrist von Eosander inventirte und gebaute Königl. Pferdt Stall zu Charlottenburg, dessen Faciata und Grund Riss. - Das gleichfals von Hr. Joh. Friederich v. Eosander Obristen General Quartier Meistern, und ersten Bau Directorn inventierte und gebaute Rath Hauss zu gedachten Charlottenburg
- Ref #: 93453
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Royal Horse Stables at Charlottenburg Palace, Berlin - plate No. 11 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Berlin Mansions by A. von Schlütter
Antique Map
- Title : A. Ist ein von H. Andreas von Schlütter Seel. inventirt- und auff gebautes Landt-Hauss. B. Ist ein von dem renomirten Bau-Werck- und Raths Zimmer-Meister Joh. Mich. Kemmeter, in Riegel oder Holtz auff gebautes Land-Hauß oder so genandte Meyerey
- Ref #: 93445
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of 18th century Mansions in Berlin designed by Andreas von Schlütter - plate No. 9 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of a Poorhouse near Stralau Gate Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Das von dem H. von Grünenberg Seel. inventirte sogenandte Armen- oder Waysen-Hauss zu Berlin, nache bey dem Stralauischen Thor gelegen, ....
- Ref #: 93455
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Poorhouse near the old Stralau Gate (Stralauer Tor) in Berlin - plate No. 8 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch. Print Jerusalem Church Friedrichstadt.Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Die von vorgedachten Hr. von Grünenberg invendierte, unter der Direction des Hr. Ioh. Simonetti Hoff Stucator Hoch-Fürstl. Anhaltischen BauMeister aufgebaute so genande Friderich Stättische Kirche sampt dessen Grund u. Faciata.
- Ref #: 93458
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Parochialkirche (literally the Reformed parochial church) in the Mitte suburb of Berlin - plate No. 7 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch. Print of the Parochialkirche in Mitte Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Vordere faciata nebst dem halben Grund Riß der vorigen Parochial-Kirche mit verändertem Thurn wie solcher dermahlen sich würklich presentiert. Frontriß, darunter der halbe Grundriß.
- Ref #: 93459
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Parochialkirche (literally the Reformed parochial church) in the Mitte suburb of Berlin - plate No. 6 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten.
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print Parochialkirche, Mitte, Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Die Von dem Vortreslich beruhmten Konigl. Preusichen Architect Land u. Ober Bau Directorn etc. Hr. Martin von Grunenberg Seel. inventirte, u. hier Grund u. Seiten Faciata Vorstellende so genandte Parochial Kirche in Berlin in der Closter Strassen
- Ref #: 93451
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Parochialkirche (literally the Reformed parochial church) in the Mitte suburb of Berlin - plate No. 5 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print of Berlin Gate, Leipziger Tor
Antique Map
- Title : Das von dem Herrn Baumeister Nering Seel. ausgefuhrte so genandte Leipziger Statt Thor in Berlin
- Ref #: 93452
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of buildings & gardens in 17th & 18th century Berlin - plate No. 3 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print Buildings, Gardens Berlin - No. 14
Antique Map
- Title : Das von Title Hr. Geheimbten Rath von Krossecks Seel. inventirt - und aussgebaute
- Ref #: 93448
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of buildings & gardens in the Charlottenburg suburb of Berlin & Charlottenburg Palace, - plate No. 14 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charlottenburg is an affluent locality of Berlin within the borough of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Established as a town in 1705 and named after late Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, Queen consort of Prussia, it is best known for Charlottenburg Palace, the largest surviving royal palace in Berlin, and the adjacent museums.
Charlottenburg is located in Berlins inner city, west of the Großer Tiergarten park. Its historic core, the former village green of Alt Lietzow, is situated on the southern shore of the Spree River running through the Berlin glacial valley. The Straße des 17. Juni road, former Charlottenburger Chaussee, which runs eastwards from Charlottenburg Gate through the Tiergarten park to Brandenburg Gate, connects Charlottenburg with the historic centre of Berlin-Mitte.
In the north and west, the Berlin Ringbahn and the Bundesautobahn 100 (Stadtring) mark the border with the Charlottenburg-Nord and Westend suburbs. Adjacent in the south is the territory of Wilmersdorf. Charlottenburg also borders on the district of Halensee in the southwest, as well as on Moabit, Hansaviertel and Tiergarten (all part of the Mitte borough) in the east and on Schöneberg in the southeast.
In 1695, Sophia Charlotte of Hanover received Lietzow from her husband, Elector Frederick III of Brandenburg, in exchange for her estates in Caputh and Langerwisch near Potsdam. Frederick had a summer residence built there for Sophie Charlotte by the architect Johann Arnold Nering between 1695 and 1699. After he had crowned himself Frederick I, King in Prussia, the Lützenburg castle was extended into a stately building with a cour dhonneur. The Swedish master builder Johann Friedrich Eosander supervised this work. Sophie Charlotte died in February 1705; shortly afterwards the settlement facing the palace was called Charlottenburg - the palace itself became Schloss Charlottenburg - and chartered as a town on April 5, 1705. The king served as the towns mayor until the historic village of Lietzow was incorporated into Charlottenburg in 1720.
Fredericks successor as king, Frederick William I of Prussia, rarely stayed at the palace, which depressed the small town of Charlottenburg. Frederick William even tried to revoke the towns privileges. With the coronation of his successor Frederick II in 1740 the towns significance increased, as regular celebrations again took place at the palace. Between 1740 and 1747 Georg Wenzeslaus von Knobelsdorff built the eastern New Wing as Fredericks residence. Later, Frederick II preferred the palace of Sanssouci, which he had partly designed himself.
When Frederick II died in 1786, his nephew Frederick William II succeeded him, and Charlottenburg became the favourite royal residence, and remained so for his son and successor Frederick William III (reigned 1797-1840). After the defeat of the Prussian army at Jena in 1806, the French occupied Berlin. Napoleon took over the palace, while his troops made a camp nearby. Charlottenburg became part of the new Prussian Province of Brandenburg in 1815 after the Napoleonic Wars.
In the late 18th century, Charlottenburgs development did not depend only on the crown. The town became a recreational area for the expanding city of Berlin. Its first true inn opened in the 1770s, in the street then called Berliner Straße (now Otto-Suhr-Allee), and many other inns and beer gardens were to follow, popular for weekend parties especially. Berliners seeking leisure and entertainment came by boat, by carriage and later by horse-drawn trams, above all to a large amusement park at the shore of the Spree river called Flora, that went into bankruptcy in 1904.
From the 1860s on the wealthy Bourgeoisie of Berlin discovered Charlottenburg as a residential area, among the first were Gerson von Bleichröder and Ernst Werner von Siemens, who had a villa built in the Berliner Straße in 1862. At the same time industrial companies like Siemens & Halske and Schering erected large factories in the north-east, at the border with the Moabit district of Berlin. In 1877 Charlottenburg received town privileges and until World War I saw an enormous increase of population with 100,000 inhabitants as of 1893 and a population of 306,000 in 1920, being the second largest city within the Province of Brandenburg, after Berlin. In the course of industrialization in the 19th century, much of Charlottenburg was incorporated in a network of streets laid out in the Hobrecht-Plan in an area that came to be known architecturally as the Wilhelmine Ring.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Architectural Print Charlottenburg Palace, Gardens
Antique Map
- Title : Haupt Hof Grund Riss dess Marstalls...Jeremais Wolff exc Aug. Vind
- Ref #: 93446
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of buildings in the Charlottenburg suburb of Berlin & Charlottenburg Palace, - plate No. 4 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charlottenburg is an affluent locality of Berlin within the borough of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Established as a town in 1705 and named after late Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, Queen consort of Prussia, it is best known for Charlottenburg Palace, the largest surviving royal palace in Berlin, and the adjacent museums.
Charlottenburg is located in Berlins inner city, west of the Großer Tiergarten park. Its historic core, the former village green of Alt Lietzow, is situated on the southern shore of the Spree River running through the Berlin glacial valley. The Straße des 17. Juni road, former Charlottenburger Chaussee, which runs eastwards from Charlottenburg Gate through the Tiergarten park to Brandenburg Gate, connects Charlottenburg with the historic centre of Berlin-Mitte.
In the north and west, the Berlin Ringbahn and the Bundesautobahn 100 (Stadtring) mark the border with the Charlottenburg-Nord and Westend suburbs. Adjacent in the south is the territory of Wilmersdorf. Charlottenburg also borders on the district of Halensee in the southwest, as well as on Moabit, Hansaviertel and Tiergarten (all part of the Mitte borough) in the east and on Schöneberg in the southeast.
In 1695, Sophia Charlotte of Hanover received Lietzow from her husband, Elector Frederick III of Brandenburg, in exchange for her estates in Caputh and Langerwisch near Potsdam. Frederick had a summer residence built there for Sophie Charlotte by the architect Johann Arnold Nering between 1695 and 1699. After he had crowned himself Frederick I, King in Prussia, the Lützenburg castle was extended into a stately building with a cour dhonneur. The Swedish master builder Johann Friedrich Eosander supervised this work. Sophie Charlotte died in February 1705; shortly afterwards the settlement facing the palace was called Charlottenburg - the palace itself became Schloss Charlottenburg - and chartered as a town on April 5, 1705. The king served as the towns mayor until the historic village of Lietzow was incorporated into Charlottenburg in 1720.
Fredericks successor as king, Frederick William I of Prussia, rarely stayed at the palace, which depressed the small town of Charlottenburg. Frederick William even tried to revoke the towns privileges. With the coronation of his successor Frederick II in 1740 the towns significance increased, as regular celebrations again took place at the palace. Between 1740 and 1747 Georg Wenzeslaus von Knobelsdorff built the eastern New Wing as Fredericks residence. Later, Frederick II preferred the palace of Sanssouci, which he had partly designed himself.
When Frederick II died in 1786, his nephew Frederick William II succeeded him, and Charlottenburg became the favourite royal residence, and remained so for his son and successor Frederick William III (reigned 1797-1840). After the defeat of the Prussian army at Jena in 1806, the French occupied Berlin. Napoleon took over the palace, while his troops made a camp nearby. Charlottenburg became part of the new Prussian Province of Brandenburg in 1815 after the Napoleonic Wars.
In the late 18th century, Charlottenburgs development did not depend only on the crown. The town became a recreational area for the expanding city of Berlin. Its first true inn opened in the 1770s, in the street then called Berliner Straße (now Otto-Suhr-Allee), and many other inns and beer gardens were to follow, popular for weekend parties especially. Berliners seeking leisure and entertainment came by boat, by carriage and later by horse-drawn trams, above all to a large amusement park at the shore of the Spree river called Flora, that went into bankruptcy in 1904.
From the 1860s on the wealthy Bourgeoisie of Berlin discovered Charlottenburg as a residential area, among the first were Gerson von Bleichröder and Ernst Werner von Siemens, who had a villa built in the Berliner Straße in 1862. At the same time industrial companies like Siemens & Halske and Schering erected large factories in the north-east, at the border with the Moabit district of Berlin. In 1877 Charlottenburg received town privileges and until World War I saw an enormous increase of population with 100,000 inhabitants as of 1893 and a population of 306,000 in 1920, being the second largest city within the Province of Brandenburg, after Berlin. In the course of industrialization in the 19th century, much of Charlottenburg was incorporated in a network of streets laid out in the Hobrecht-Plan in an area that came to be known architecturally as the Wilhelmine Ring.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Wijnendale Flanders Belgium in 1708
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Wynendale, between ye Troops of ye Allies commanded by Major Gen. Webb & those of France under count de la Motte Sep. 28, 1708
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22165
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the The Battle of Wijnendale, Flanders, Belgium in 1708 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Wijnendale was a battle in the War of the Spanish Succession fought on 28 September 1708 near Wijnendale, Flanders, between an allied force protecting a convoy for the Siege of Lille (1708) and forces of Bourbon France and Spain. It ended in a victory for the allies, leading to the taking of Lille.
After their great victory in the Battle of Oudenaarde (11 July 1708), Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy decided to besiege Lille. But Lille was very well defended by modern fortifications designed by Vauban and a garrison of 16,000 men. The allied siege didn\'t go as well as planned and a lack of ammunition was imminent. To make things worst, the supply lines from the east were cut by the French, so the only remaining line of supply was by ship from England to the port of Ostend, some 75 km from Lille.
Marlborough ordered the necessary goods to be shipped to Ostend and a large convoy of 700 slow wagons was organised there to travel further over land to Lille. The convoy was protected by 6,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry under command of general-major John Richmond Webb.
The commander of the French garrison of Bruges, Count de la Mothe, was informed of the convoy and gathered a force of 22,000 to 24,000 men towards Wijnendale to intercept the convoy.
Webb was aware of the advancing French army and knew a confrontation was unavoidable. He drew up a plan to compensate for his numerical disadvantage. Using the wooded landscape around Wijnendale, he chose an open spot, flanked on both sides by woods and hedges. He placed his troops in two long lines, closing off this open space. Later a third line was formed with reinforcements coming from Oudenburg. Meanwhile, behind these lines, the convoy continued slowly towards Lille.
While Webb was deploying his troops, Prussian general Carl von Lottum, with only 150 cavalry harassed the approaching French army, gaining valuable time, and preventing de la Mothe to gather knowledge of the terrain and the plans of the allies.
Having arrived at the open space, de la Mothe, expecting an easy victory, deployed his army as expected. Between 4 and 5 pm the French artillery opened fire. When de la Mothe saw the effects on the enemy were limited, he ordered his infantry forward. The large French force was hampered by the narrow terrain and suffered badly from the fire of the allied first line, which held its ground. Then Webb ordered the Prussian, Hanoverian and Dutch regiments who were hidden in the woods on both flanks, to open fire. Despite suffering heavy casualties, de la Mothe ordered a second attack, which initially pushed the allied first line back. But with the help of the second line and the continuous fire from the flanks, the French were stopped and forced to withdraw and leave the battlefield.
When the battle was as good as won, allied cavalry under command of William Cadogan arrived at the battlefield. He was sent from Lille by Marlborough, who was worried about the convoy.
The toll of this two-hour battle was heavy: 3,000 to 4,000 French and Spanish soldiers were killed or wounded. The allies lost 900 dead and wounded.
The convoy reached Lille intact on 29 September, allowing the siege to continue. Three weeks later, on 22 October, the city was taken.
For political reasons, Marlborough gave in his initial dispatch the credit for the victory to William Cadogan, also a Whig. But Webb subsequently received full credit and the thanks of Parliament for the action, and the following year he was promoted to Lieutenant-General. From this point onwards Webb became the centre of Tory agitation against Marlborough.
1760 J B D Anville Large Antique Map of Roman France
Antique Map
- Title : Gallia Antiqua ex Aevi Romani......D Anville...MDCCLX
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1760 (dated)
- Ref #: 92296
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique map of Roman France was engraved in 1760 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 18 1/4in (595mm x 465mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing, light age toning
Plate area: - Creasing
Verso: - Creasing, light age toning
Background:
In 600 BC, Ionian Greeks, originating from Phocaea, founded the colony of Massalia (present-day Marseille), on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. This makes it Frances oldest city. At the same time, some Gallic Celtic tribes penetrated parts of the current territory of France, and this occupation spread to the rest of France between the 5th and 3rd century BC.
The concept of Gaul emerged at that time; it corresponds to the territories of Celtic settlement ranging between the Rhine, the Atlantic Ocean, the Pyrenees and the Mediterranean. The borders of modern France are roughly the same as those of ancient Gaul, which was inhabited by Celtic Gauls. Gaul was then a prosperous country, of which the southernmost part was heavily subject to Greek and Roman cultural and economic influences.
Around 390 BC the Gallic chieftain Brennus and his troops made their way to Italy through the Alps, defeated the Romans in the Battle of the Allia, and besieged and ransomed Rome. The Gallic invasion left Rome weakened, and the Gauls continued to harass the region until 345 BC when they entered into a formal peace treaty with Rome. But the Romans and the Gauls would remain adversaries for the next centuries, and the Gauls would continue to be a threat in Italy.
Around 125 BC, the south of Gaul was conquered by the Romans, who called this region Provincia Nostra (Our Province), which over time evolved into the name Provence in French. Julius Caesar conquered the remainder of Gaul and overcame a revolt carried out by the Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix in 52 BC. According to Plutarch and the writings of scholar Brendan Woods, the Gallic Wars resulted in 800 conquered cities, 300 subdued tribes, one million men sold into slavery, and another three million dead in battle.
Gaul was divided by Augustus into Roman provinces. Many cities were founded during the Gallo-Roman period, including Lugdunum (present-day Lyon), which is considered the capital of the Gauls. These cities were built in traditional Roman style, with a forum, a theatre, a circus, an amphitheatre and thermal baths. The Gauls mixed with Roman settlers and eventually adopted Roman culture and Roman speech (Latin, from which the French language evolved). The Roman polytheism merged with the Gallic paganism into the same syncretism.
From the 250s to the 280s AD, Roman Gaul suffered a serious crisis with its fortified borders being attacked on several occasions by barbarians. Nevertheless, the situation improved in the first half of the 4th century, which was a period of revival and prosperity for Roman Gaul. In 312, Emperor Constantin I converted to Christianity. Subsequently, Christians, who had been persecuted until then, increased rapidly across the entire Roman Empire. But, from the beginning of the 5th century, the Barbarian Invasions resumed. Teutonic tribes invaded the region from present-day Germany, the Visigoths settling in the southwest, the Burgundians along the Rhine River Valley, and the Franks (from whom the French take their name) in the north.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Western, European Russia, Poland
- Title : L Empire de Russie en Europe et an Asie...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40527
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Eastern Russia, China
- Title : L Empire de Russie en Europe et an Asie...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40528
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1786 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map of Elis Peloponnesos, Greece - Olympia
- Title : L Elide et La Triphylie....1786
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16451
- Date : 1786
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1785 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greecein 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8 1/2in x 7 1/2in (215mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1782 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map of Arcadia Peloponnese, Greece - Tripoli
- Title : l Arcadie, Pour le Voyage du Jeune Anacharsis......1786
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16448
- Date : 1786
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1786 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greecein 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1784 Du Bocage & Barthelemy Antique Map of Plato's Academy in Athens, Greece
- Title : L Helles-Pont...1782
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16462
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage was engraved in 1784 - dated in the title - and was published in the 1787 edition of Jean-Jacques Barthelemy famous Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece or Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greecein 4 volumes.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8 1/2in x 7 1/2in (215mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Jacques Barthelemy 1716 – 1795 was a French writer and numismatist.
Barthelemy was the author of a number of learned works on antiquarian subjects, but the great work on which his fame rests is Travels of Anacharsis the younger in Greece (French: Voyage du jeune Anarcharsis en Grece, 4 vols., 1787). He had begun it in 1757 and had been working on it for thirty years. The hero, a young Scythian descended from the famous philosopher Anacharsis, is supposed to repair to Greece for instruction in his early youth, and after making the tour of her republics, colonies and islands, to return to his native country and write this book in his old age, after the Macedonian hero had overturned the Persian empire. In the manner of modern travellers, he gives an account of the customs, government, and antiquities of the country he is supposed to have visited. A copious introduction supplies whatever may be wanting in respect to historical details, while various dissertations on the music of the Greeks, on the literature of the Athenians, and on the economy, pursuits, ruling passions, manners, and customs of the surrounding states supply ample information on the subjects of which they treat.
Modern scholarship has superseded most of the details in the Voyage, but the author himself did not imagine his book to be a register of accurately ascertained facts. Rather, he intended to afford to his countrymen, in an interesting form, some knowledge of Greek civilisation. The Charicles, or Illustrations of the Private Life of the Ancient Greeks of Wilhelm Adolf Becker is an attempt in a similar direction
1770 John Cary Original Antique Map of Switzerland
- Title : Switzerland with its Subjects & Allies from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70188
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthries Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1804 Jean N Buache Original Antique Map of Scandinavia, Sweden Norway & Baltics
- Title : A Suede et Norwege
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 34191
- Date : 1804
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map was published in the 1804 edition of Jean Nicolas Buache Atlas Geographie Moderne.
The maps in this atlas were illustrated by Jean Nicolas Buache - nephew to Phillipe Buache who was son-in-law to Nicolas Delisle - after maps published by the Scottish publisher John Pinkerton.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1804 Jean N Buache Original Antique Map of Denmark
- Title : Danemarck
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 34190
- Date : 1804
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map was published in the 1804 edition of Jean Nicolas Buache Atlas Geographie Moderne.
The maps in this atlas were illustrated by Jean Nicolas Buache - nephew to Phillipe Buache who was son-in-law to Nicolas Delisle - after maps published by the Scottish publisher John Pinkerton.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Scandinavia, Baltic States & European Russia
- Title : Le Nord De L Europe contenant Le Danemark La Norwege, La Suede et la Laponie avec la Majeure Partie de la Russie Europeenne Par M Bonne
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 31671
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Scandinavia, The Baltic States & European Russia was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None