Products
1802 J B Lechevalier Antique Print Bronze Figure, Vases in Achilles Tomb Turkey
- Title : Figure de bronze et vases cineraires, trouves dans le tombeau d Achille
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70228
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Bronze Figure and a pair of Vases found in the Tomb of Achilles located in the ancient Greek city of Achilleion in the Troad region of Çanakkale, now in NW modern Turkey, was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 7in x 5in (180mm x 130mm) each plate
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Achilleion was an ancient Greek city in the south-west of the Troad region of Anatolia. It has been located on a promontory known as Beşika Burnu (cradle promontory) about 8 km south of Sigeion. Beşika Burnu is 2 km south of the modern village of Yeniköy in the Ezine district of Çanakkale Province, Turkey. The site considered in classical antiquity to be the tomb of Achilles is a short distance inland at a tumulus known as Beşiktepe. Achilleion in the Troad is not to be confused with Achilleion near Smyrna and Achilleion in the territory of Tanagra.
The otherwise obscure polis of Achilleion was most famous in classical antiquity for its association with Achilles, after whom it was named (the place of Achilles). According to some sources, while passing by Ilion in 334 BC Alexander the Great sacrificed at the Tomb of Achilles. This story became famous, and in the mid-1st century BC it is mentioned by the politician and writer Cicero in his Pro Archia Poeta. In AD 216 the Emperor Caracalla emulated Alexander when, on passing Ilion on his way to a war against Parthia, he held funeral games around the tumulus. Following the abandonment of the settlement at Achilleion in the late Hellenistic period, writers began to associate the tomb with nearby Sigeion to the north.
The first mention of Achilleion is as a fortified settlement from which Mytilene conducted its attacks on Athenian controlled Sigeion to the north in the early 6th century BCE. It is not clear whether Achilleion had been settled earlier, but the ceramic record also begins at this point, suggesting that it had not. Recent excavations have established that the walls of the settlement also date to the first half of the 6th century BCE, further corroborating the literary accounts of Herodotus and Strabo regarding its origins. Achilleion remained under Mytilenaean control until Athens brought an end to the Mytilenaean revolt in 427 BCE and took over all the so-called Actaean cities in the Troad. Achilleion appears in the Athenian tribute lists for 425/4 and 422/1 BCE, indicating that it had joined the Delian League. The legend AX (ACH) which some bronze coins found in this region bear is thought to refer to Ach (illeion) and suggest that c. 350 - 300 BCE the city minted its own coins. King Lysimachus synoecized Ilion with many surrounding communities including Achilleion during his reign (306 - 281 BCE), effectively ending Achilleions political independence. The testimony of Demetrius of Scepsis, who hailed from a nearby town in the Troad, indicates that there was still a hamlet known as Achilleion on the site in the mid-2nd century BCE. It is to around this time that the latest ceramic finds from Achilleion date, suggesting that the site became uninhabited soon afterwards.
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
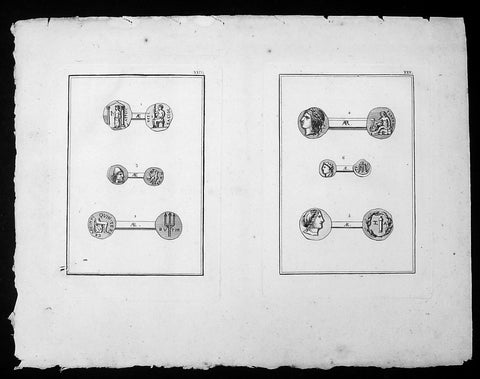
1802 J B Lechevalier Antique Print of Ancient Greek Coins Jupiter, Diane, Apollo
- Title : Plates XXIV & XXV
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70229
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique prints of ancient Greek coins (details below) found in the ancient Greek province of Çanakkale in the NW of modern Turkey, was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
Each plate contains 3 coins;
Plate XXIV
1. Apdeyc - Jupiter debout dans un Temple Distyle (Jupiter standing in a Distinct Temple)
2. Graecinus, Qvin Tert. - Une figure assise, dont on ne voit que la partie inserieure (A seated figure, whose only part is visible)
3. Tete d Ulysse - Barbue et couverte du Pileus (Head of Ulysses - Bearded and Covered Pileus)
Plate XXV
1. Tete d Appolon lauree (Head of Appolo laurel)
2. Tete de Diane ( Head of Diane)
3. Tete de femme (Head of a woman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 7in x 5in (180mm x 130mm) each plate
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1802 J B Lechevalier Antique Print Temple Apollo Ruins Gülpınar Çanakkale Turkey
- Title : Ruines Du Temple D Apollon Thymbreen; Inscription Trouvee dans les Ruines du Temple d Apollon
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70222
- Size: 19 1/4in x 14in (495mm x 355mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print view of the ruins of the Temple of Apollo in the ancient city of Hamaxitus in the Troad region of NW Turkey - with Greek inscription from the temple - was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Hamaxitus was an ancient Greek city in the south-west of the Troad region of Anatolia which was considered to mark the boundary between the Troad and Aeolis. Its surrounding territory was known in Greek as Ἁμαξιτία (Hamaxitia) and included the temple of Apollo Smintheus, the salt pans at Tragasai, and the Satnioeis river (modern Tuzla Çay). It has been located on a rise called Beşiktepe near the village of Gülpınar (previously Külahlı) in the Ayvacık district of Çanakkale Province, Turkey
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1802 J B Lechevalier Antique Print Temple of Poseidon Cape Sounion Attica Greece
- Title : Vue Du Temple De Minerve-Suniade
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70213
- Size: 19 1/4in x 14in (495mm x 355mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print view of the ruins of the Temple of Poseidon, on the cliffs on Cape Sounion, Attica Peninsula, Greece, south of Athens was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 11in (445mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Cape Sounion is the promontory at the southernmost tip of the Attic peninsula, 8 kilometres south of the town of Lavrio (ancient Thoricus), and 70 kilometres southeast of Athens. It is part of Lavreotiki municipality, East Attica, Greece.
Cape Sounion is noted for its Temple of Poseidon, one of the major monuments of the Golden Age of Athens. Its remains are perched on the headland, surrounded on three sides by the sea.
The original, Archaic-period temple of Poseidon on the site was built of tufa. The Sounion Kouros, discovered in 1906 in a pit east of the temple alongside fragments of other statues, was probably one of a number of votive statues dedicated to Poseidon which probably stood in front of the gods sanctuary. The archaic temple was probably destroyed in 480 BC by Persian troops during Xerxes I\'s invasion of Greece. After they defeated Xerxes in the naval Battle of Salamis, the Athenians placed an entire captured enemy trireme (warship with three banks of oars) at Sounion as a trophy dedicated to Poseidon.
The temple of Poseidon at Sounion was constructed in 444–440 BC. This was during the ascendancy of the Athenian statesman Pericles, who also rebuilt the Parthenon in Athens. It was built on the ruins of a temple dating from the Archaic period. It is perched above the sea at a height of almost 60 metres. The design of the temple is a typical hexastyle, i.e., it had a front portico with six columns. Only some columns of the Sounion temple stand today, but when intact it would have closely resembled the contemporary and well-preserved Temple of Hephaestus beneath the Acropolis, which may have been designed by the same architect.
As with all Greek temples, the Poseidon building was rectangular, with a colonnade on all four sides. The total number of original columns was 36: 15 columns still stand today. The columns are of the Doric Order. They were made of locally quarried white marble. They were 6.10 m high, with a diameter of 1 m (3.1 ft) at the base and 79 cm at the top. At the center of the temple, colonnade would have been the hall of worship (naos), a windowless rectangular room, similar to the partly intact hall at the Temple of Hephaestus. It would have contained, at one end facing the entrance, the cult image, a colossal, ceiling-height (6 metres (20 ft)) bronze statue of Poseidon.
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1802 J B Lechevalier Antique Print The Sarcophagus of the Greek Author, Homer
- Title : Sarcophage Grec, Appele Le Tombeau D Homere
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 70216
- Size: 19 1/4in x 14in (495mm x 355mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Greek Sarcophagus, believe to be that of the ancient Greek Philosopher Homer, was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 10 3/4in (445mm x 275mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Homer is the legendary author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems that are the central works of ancient Greek literature. The Iliad is set during the Trojan War, the ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Greek kingdoms. It focuses on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles lasting a few weeks during the last year of the war. The Odyssey focuses on the journey home of Odysseus, king of Ithaca, around 20 years after the fall of Troy. Many accounts of Homer\'s life circulated in classical antiquity, the most widespread being that he was a blind bard from Ionia, a region of central coastal Anatolia in present-day Turkey. Modern scholars consider them legends.
The Homeric Question—concerning by whom, when, where and under what circumstances the Iliad and Odyssey were composed—continues to be debated. Broadly speaking, modern scholarly opinion falls into two groups. One holds that most of the Iliad and (according to some) the Odyssey are the works of a single poet of genius. The other considers the Homeric poems to be the result of a process of working and reworking by many contributors, and that Homer is best seen as a label for an entire tradition. It is generally accepted that the poems were composed at some point around the late eighth or early seventh century BC.
The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language which shows a mixture of features of the Ionic and Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems were originally transmitted orally. From antiquity until the present day, the influence of the Homeric epics on Western civilization has been great, inspiring many of its most famous works of literature, music, art and film. The Homeric epics were the greatest influence on ancient Greek culture and education; to Plato, Homer was simply the one who has taught Greece – ten Hellada pepaideuken
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
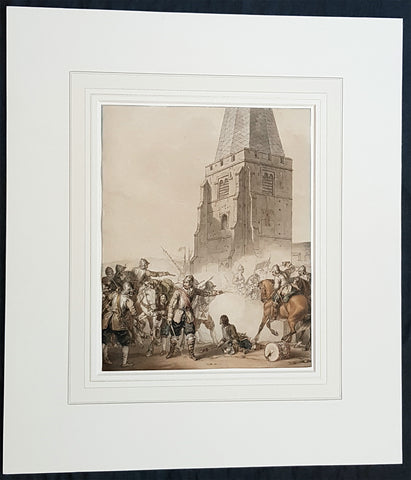
1802 J B Lechevalier Antique Print Tomb of Hector, Ophryneion in Troad, Turkey
- Title : Vue Des Tombeaux D Hector et D Aisyetes
- Date : 1802
- Size: 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
- Ref: 70226
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print a view of the Tombs of Hector & Aesyetes located in the ancient Greek city of Ophryneion in the Troad region of Çanakkale, now in NW modern Turkey, was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 10 3/4in (445mm x 275mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Ophryneion was an ancient Greek city in the northern Troad region of Anatolia. Its territory was bounded to the west by Rhoiteion and to the east by Dardanos. It was located about 1.5 km north-east of the village of İntepe (previously known as Erenköy) in Çanakkale Province, Turkey. The city was situated on the steep brow of a hill overlooking the Dardanelles, hence the origin of its Ancient Greek name ὀφρῦς (ophrus), meaning \'brow of a hill\', crag
In Greek mythology, Aesyetes was a Trojan hero and father of Alcathous. His tomb was the vantage point which Polites, son of Priam, used to scout the Greek camp during the Trojan War.
Aesyetes was also given as the father of Antenor by Cleomestra.
In Greek mythology and Roman mythology, Hector was a Trojan prince and the greatest fighter for Troy in the Trojan War. As the first-born son of King Priam and Queen Hecuba, who was a descendant of Dardanus and Tros, the founder of Troy, he was a prince of the royal house and the heir apparent to his fathers throne. He was married to Andromache, with whom he had an infant son, Scamandrius (whom the people of Troy called Astyanax). He acted as leader of the Trojans and their allies in the defence of Troy, killing 31,000 Greek fighters, offers Hyginus. During the European Middle Ages, Hector figures as one of the Nine Worthies noted by Jacques de Longuyon, known not only for his courage but also for his noble and courtly nature. Indeed, Homer places Hector as peace-loving, thoughtful as well as bold, a good son, husband and father, and without darker motives. James Redfield describes Hector as a martyr to loyalties, a witness to the things of this world, a hero ready to die for the precious imperfections of ordinary life.
The most valuable historical evidence for the Battle of Troy are treaties and letters mentioned in Hittite cuneiform texts of the same approximate era, which mention an unruly Western Anatolian warlord named Piyama-Radu (possibly Priam) and his successor Alaksandu (possibly Alexander, the nickname of Paris) both based in Wilusa (possibly Ilion/Ilios), as well as the god Apaliunas (possibly Apollo).
Other such pieces of evidence are names of Trojan heroes in Linear B tablets. Twenty out of fifty-eight men\'s names also known from Homer, including E-ko-to (Hector) are Trojan warriors and some, including Hector, are in a servile capacity. No such conclusion that they are the offspring of Trojan captive women is warranted. Generally the public has to be content with the knowledge that these names existed in Greek in Mycenaean times, although Page hypothesizes that Hector may very well be ... a familiar Greek form impressed on a similar-sounding foreign name.
When Pausanias visited Thebes in Boeotia, in the second century AD, he was shown Hector\'s tomb and was told that the bones had been transported to Thebes according to a Delphic oracle. Moses I. Finley observes this typical bit of fiction must mean that there was an old Theban hero Hector, a Greek, whose myths antedated the Homeric poems. Even after Homer had located Hector in Troy for all time, the Thebans held on to their hero, and the Delphic oracle provided the necessary sanction.
The pseudepigraphical writer Dares Phrygius states that Hector \"spoke with a slight lisp. His complexion was fair, his hair curly. His eyes would blink attractively. His movements were swift. His face, with its beard, was noble. He was handsome, fierce, and high-spirited, merciful to the citizens, and deserving of love
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1802 J B Lechevalier Antique Print View of Tomb of Ajax Troy in Troad, NW Turkey
- Title : Vue Du Tombeau D'Ajax
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70224
- Size: 19 1/4in x 14in (495mm x 355mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print view of the Tomb of Ajax the Great near in the ancient Greek city of Troy in the Troad region of NW Turkey was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 11in (445mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Ajax or Aiasis a Greek hero, the son of King Telamon and Periboea, and the half-brother of Teucer. He plays an important role, and is portrayed as a towering figure and a warrior of great courage in Homers Iliad and in the Epic Cycle, a series of epic poems about the Trojan War. He is also referred to as Telamonian Ajax (Αἴας ὁ Τελαμώνιος, in Etruscan recorded as Aivas Tlamunus), Greater Ajax, or Ajax the Great, which distinguishes him from Ajax, son of Oileus (Ajax the Lesser).
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade.....was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
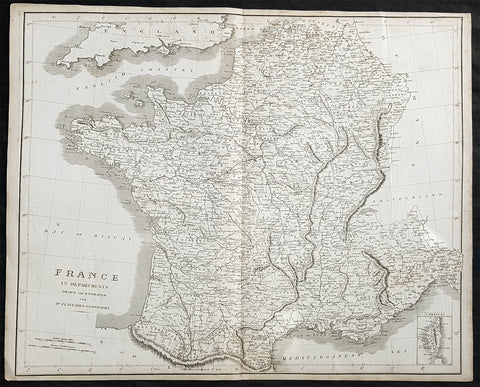
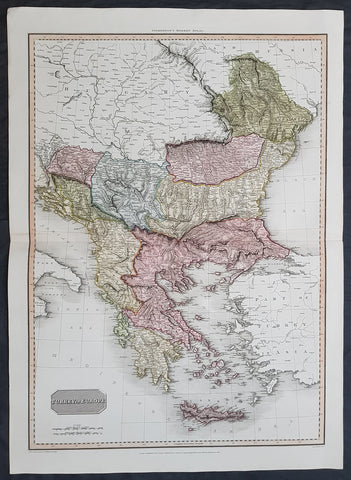
1802 Lechevalier Antique Map of Italy Greece & Turkey Troy
- Title : Carte Du Golphe Adriatique et De L Archipel pour servir ou Voyage de la Troade
- Ref #: 70207
- Size: 20in x 19in (510mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique map of the voyage of Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier from Italy to the Greece and Turkey - specifically the Biga Peninsular home of the ancient city of Troy in NW Turkey - was published in the Atlas of Charts & Views that accompanied the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier's (1752 - 1836) Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786.
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homer's Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His title, "Voyage de la Troade" was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 19in (510mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 18in (485mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning along fold as issued
Verso: - Light age toning
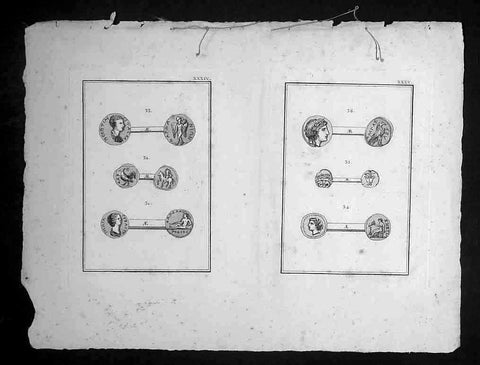
1802 Lechevalier Antique Print of Ancient Greek & Troy Coins - Apollo, Ganymede.
- Title : Plates XXXIV & XXXV
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70231
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique prints of ancient Greek, Roman & Troy coins (details below) found in the ancient Greek province of Çanakkale, now in the NW of modern Turkey, was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
Each plate contains 3 coins;
Plate XXXIV
31. Tete d Julia Domna (The head of Julia Domna)
32. Un guerrier a cheval (A horse warrior)
33. Tete de Geta (Head of Geta)
Plate XXXV
34. Tete de femme voilee (Head of a woman)
35. Tete de Meduse, de face (Head & face of Medusa)
36. Tete de lauree d apollon (Head of Apollo)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 7in x 5in (180mm x 130mm) each plate
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade..... was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1802 Lechevalier Large Antique Print View of Xanthos or Kinik, Antalya Turkey
- Title : Vue Des Sources Du Scamandre
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70225
- Size: 19 1/4in x 14in (495mm x 355mm)
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print view of the source of the Karamenderes (Scamander) River that flowed beneath the ancient Greek city of Troy located in the Troad region of Çanakkale in NW Turkey, was published in the 1802 edition of Jean-Baptiste Lechevaliers of Voyage de la Troade, fait dans les années 1785 et 1786
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 11in (445mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Karamenderes is the modern name of the river Scamander, along the lower course of which, according to the Iliad, the battles of the Trojan War were fought. It flows entirely within the Turkish province of Çanakkale.
Scamander was the name of a river god in Greek mythology.
Scamander fought on the side of the Trojans during the Trojan War (Iliad XX, 73/74; XXI), after the Greek hero Achilles insulted him. Scamander was also said to have attempted to kill Achilles three times, and the hero was only saved due to the intervention of Hera, Athena and Hephaestus. In this context, he is the personification of the Scamander River that flowed from Mount Ida across the plain beneath the city of Troy, joining the Hellespont north of the city. The Achaeans, according to Homer, had set up their camp near its mouth, and their battles with the Trojans were fought on the plain of Scamander. In Iliad XXII (149ff), Homer states that the river had two springs: one produced warm water; the other yielded cold water, regardless of the season.
According to Homer, he was called Xanthos by gods and Scamander by men, which might indicate that the former name refers to the god and the latter one to the river itself
Jean-Baptiste Lechevalier was the secretary of the Ambassador of France in Constantinople. In the year 1788 he visited the plain of Troy, and was enthusiastically in favour of the theory that the site of Homers Troy was to be found at the village of Bunarbashi. His publication about Troy Voyage de la Troade..... was first published in 1799.
The Troad, also known as Troas, is the historical name of the Biga peninsula (Biga Yarımadası, Τρωάς) in the northwestern part of Anatolia, Turkey. This region now is part of the Çanakkale province of Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander (Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Grenikos, Kebren, Simoeis, Rhesos, Rhodios, Heptaporos and Aisepos were seven rivers of the Troad and the names of the river gods that inhabited each river.
Troy (Ancient Greek: Τροία, Troia or Τροίας, Troias, Truva or Troya) was a city in the far northwest of the region known in late Classical antiquity as Asia Minor, now known as Anatolia in modern Turkey, just south of the southwest mouth of the Dardanelles strait and northwest of Mount Ida. The present-day location is known as Hisarlik. It was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name λιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa.
A new capital called Ilium (from Greek: λιον, Ilion) was founded on the site in the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus. It flourished until the establishment of Constantinople, became a bishopric and declined gradually in the Byzantine era, but is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
In 1865, English archaeologist Frank Calvert excavated trial trenches in a field he had bought from a local farmer at Hisarlik, and in 1868, Heinrich Schliemann, a wealthy German businessman and archaeologist, also began excavating in the area after a chance meeting with Calvert in Çanakkale. These excavations revealed several cities built in succession. Schliemann was at first skeptical about the identification of Hisarlik with Troy, but was persuaded by Calvert and took over Calverts excavations on the eastern half of the Hisarlik site, which was on Calvert\'s property. Troy VII has been identified with the city called Wilusa by the Hittites (the probable origin of the Greek λιον) and is generally (but not conclusively) identified with Homeric Troy.
Today, the hill at Hisarlik has given its name to a small village near the ruins, which supports the tourist trade visiting the Troia archaeological site. It lies within the province of Çanakkale, some 30 km south-west of the provincial capital, also called Çanakkale. The nearest village is Tevfikiye. The map here shows the adapted Scamander estuary with Ilium a little way inland across the Homeric plain. Due to Troys location near the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Black Sea, it was a central hub for the military and trade(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
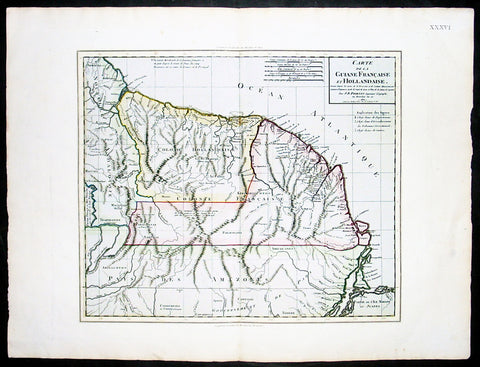
1802 Poirson Large Antique Map of French & Dutch Guyana
- Title : Carte De La Guiane Francaise et Hollandaise...J B Poirson...1802
- Ref #: 92520
- Size: 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America, was engraved by Jean Baptiste Poirson in 1802 - the date is engraved in the Title.
J.B. Poirson (1760-1831) was a French geographer & engineer who published a number of Atlases - including the Malte-Brun Atlas - between 1790 & 1830. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (500mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1803 Louis Freycinet Antique Map of The Islands of Timor, Samau & Rote Indonesia
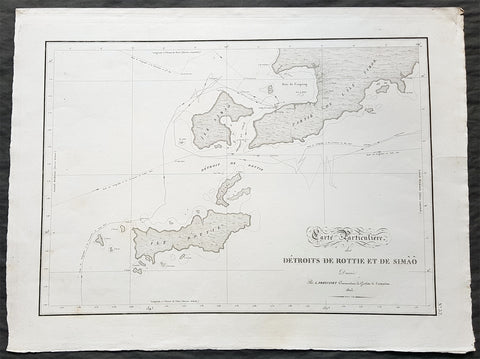
- Title : Carte Particuliere des Detroits De Rottie et de Simao...L Freycienet...le Casuarina 1803..Lambert Sculp.
- Ref #: 42014
- Size: 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1803
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This magnificent large original copper-plate engraved antique map of the islands of Samau, Rote and the southern part of Timor, including the bay and town of Kupang, by Lieutenant Louis Freycinet, in command of the ship Casuarina in 1803, was engraved by Anton Lambart and was published in the 1807 1st edition of François Pérons, Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes (‘Voyage of Discovery to the Southern Lands in three volumes, Paris, 1807–1816.
Also illustrates the tracks of the ships Geographe, the Naturaliste from the earlier voyages in 1801, and the Casuarina tracks of 1803.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15in (545mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nicolas Thomas Baudin 1754 – 1803 was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer.
The Baudin expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland (Australia). The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
Napoléon Bonaparte, as First Consul, formally approved the expedition to the coasts of New Holland, after receiving a delegation consisting of Baudin and eminent members of the Institut National des Sciences et Arts on 25 March 1800. The explicit purpose of the voyage was to be ‘bservation and research relating to Geography and Natural History.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of the continent until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. During their exploration here they lost a longboat and a sailor, Assistant Helmsman Timothée Vasse. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by \'t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted the Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
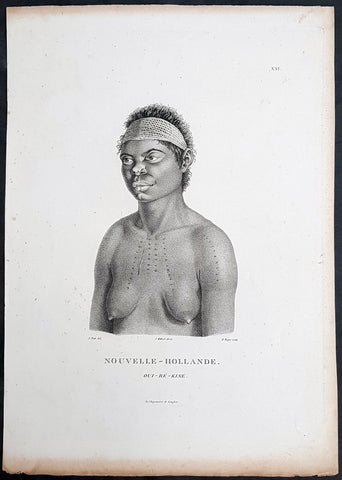
1803 Mayer Large Antique Print of a Woman & Child of Karaman, Turkey
- Title : Woman of Caramania
- Date : 1803
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92705
- Size: 19 1/2in x 13in (485mm x 330mm)
Description:
This large fine beautifully coloured original early antique aquatint of a woman and children of the ancient southern Turkish region of Caramania (Karaman) was engraved in 1803 - the date is engraved at the foot of the image - and was published in Luigi Mayer's "Views in Egypt, Palestine and Other Parts of the Ottoman Empire" R Bowyer, Historic Gallery Pall Mall.
This engraving is characteristic of those made during Regency period, a time of exploration of the Middle East spurred by Napoleon's explorations and conquests in Egypt. Often these expeditions were published as books, containing descriptions and illustrations of the ancient architecture, customs and culture of indigenous peoples.
Italian orientalist Luigi Mayer, active in the 18th and begin 19th century travelled extensively in the middle east. His work "Views in Egypt, Palestine and Other Parts of the Ottoman Empire" was published between 1801 and 1804 with historical observations, and incidental illustrations of the manners and customs of the natives of that country. During Mayer’s time, while Britain and France were vying for control of colonial territories, Views in Egypt captivated and informed audiences in Europe about the country’s prevailing culture and even political structures. "Mamalukes exercising in the Square of Muurad Bey’s Palace," for instance, provides a valuable visual record of the military elite’s training exercises, and perhaps a hint of the Ottoman ruler’s efforts to impose centralized authority. Such highly descriptive drawings continue to make the volume an invaluable primary source.
The aquatint engraver, Thomas Milton studied under William Woollett, and was extolled by scholar W. Bell Scott as having "a unique power of distinguishing the foliage of trees and the texture of bodies, especially water, as it never had been done before, and never will be done again." (Ref: Abbey, Travel, 369. Blackmer 1097. Colas 2018-2022. Gay 2145. Hiler, pp. 577-8. HBS 15571)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Haevy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2 in x 13in (460mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15 in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: None
Plate area: None
Verso: None
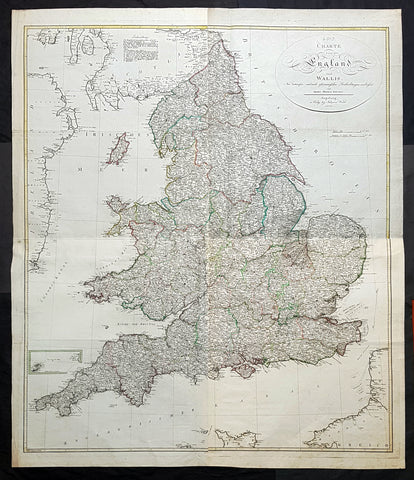
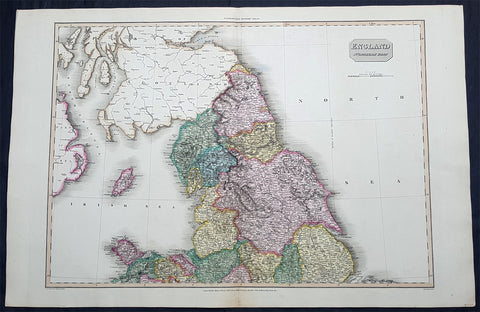
1803 Thomas Kitchen & Johannes Walch Large Antique Wall Map of England & Wales
Antique Map
- Titles: Carte von England und Wallli...Herren Thomas Kitchin Augsburg in Verlag bey Johannes Walch 1803
Sizes: 53in x 45in (1.345m x 1.120m) - Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date: 1803
- Ref #: 93420
Description:
This very large original copper plate engraved antique wall map of England & Wales after the English cartographer Thomas Kitchin was engraved and published by the German publisher Johannes Walch in 1803, dated.
First published by Kitchin in London in 1760, this incredibly large, detailed & scarce map is a credit to Kitchin, one of the foremost cartographers of the 18th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 53in x 45in (1.345m x 1.120m)
Plate size: - 50 1/2in x 43in (1.280m x 1.090m)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Johann Walch 1757 - 1815 was a German painter, draftsman, engraver, cartographer and publisher. Walch was the son of the merchant and amateur painter and copper engraver Sebastian Walch (1721–1788) and his wife Katharina Zorn, daughter of the butcher Martin Zorn. He received training as a miniature painter in Augsburg, Geneva and three years at the Vienna Art Academy . This was followed by a two-year trip to Italy. Before 1785 he settled in Augsburg, where on January 16, 1786 he married Anna Regina Will the eldest daughter of the copper engraver and publisher Johann Martin Will , who was based in Augsburg, and was married in the publishing house worked with his father-in-law. As a result, the publisher increasingly turned to map production .
In 1789 he inherited from Gustav Conrad Lotter (1746–1776) map material from the map publishers Matthäus Seutter and Tobias Conrad Lotter, almost 25,000 individual map sheets and 208 copper plates. After Wills death in 1806, he inherited Willschen Verlag , which he developed into a major map publisher (Joh. Walchsche Landkarte Handlung). This gave rise to the print shop named Joh. Walch . His son Johann Sebastian Walch (1787-1840) continued the publishing house.
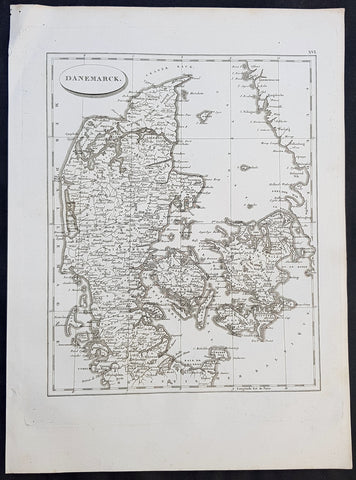
1804 Jean N Buache Original Antique Map of Denmark
- Title : Danemarck
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 34190
- Date : 1804
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map was published in the 1804 edition of Jean Nicolas Buache Atlas Geographie Moderne.
The maps in this atlas were illustrated by Jean Nicolas Buache - nephew to Phillipe Buache who was son-in-law to Nicolas Delisle - after maps published by the Scottish publisher John Pinkerton.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
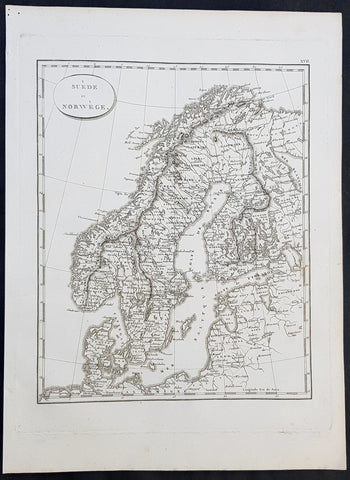
1804 Jean N Buache Original Antique Map of Scandinavia, Sweden Norway & Baltics
- Title : A Suede et Norwege
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 34191
- Date : 1804
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map was published in the 1804 edition of Jean Nicolas Buache Atlas Geographie Moderne.
The maps in this atlas were illustrated by Jean Nicolas Buache - nephew to Phillipe Buache who was son-in-law to Nicolas Delisle - after maps published by the Scottish publisher John Pinkerton.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1806 John Barrow Antique Atlas Travel Book to Vietnam via Brazil & South Africa
Antique Map
- Title : A Voyage to Cochinchina, in the years 1792 and 1793. to which is annexed an account of a journey, made in the years 1801 and 1802, to the residence of the chief of the Booshuana Nation, being the remotest point in the interior of Southern Africa
- Size: 4to (10 1/2in x 8 1/4in)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1806
- Ref #: 61010
Description:
This rare publication of the first English edition of Sir Johns Barrows voyages to Cochin-China, (Vietnam) via Rio de Janeiro, the South African Cape & Batavia, Java in 1792 & 93, was published by Strahan and Preston for T. Cadell and T. Davies, London in 1806. 447 pages with 19 hand coloured plates & 2 hand coloured maps, as called for.
The book has been beautifully rebound in half calf with gilt text to spine & new end papers. Library stamps to the back of each plate & pages TP, 1, 101, 401 & 447. Staining to title page to page 23 & light browning to several pages after, repair to page 311 with browning.
Plates & maps in VG condition in fresh condition and beautiful hand colouring. 447 pages containing 19 hand colored prints, including one folding view of Rio, by T. Medland after Samuel Daniell and W. Alexander, and two folding hand coloured maps, the first a plan of the harbor and town of Rio de Janeiro, the second a Chart of the Cape & Southern Africa.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 7 1/2in (280mm x 190mm) Plates
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm) Fold out plates
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning, repair to page 311
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
A Voyage to Cochinchina, in the years 1792 and 1793 first edition of the first illustrated English work on Vietnam. A description of the outward voyage of Lord Macartneys embassy to China. The voyage visited Madeira, the Canary Islands, and Rio de Janeiro; a description of that city and of Brazil in general is given. Touching at Tristan da Cunha, the ship rounded the Cape and eventually reached Cochin China via the city of Batavia on Java. The volume is also of Cook interest, as it describes finding Captain Cooks Resolution transformed into a smuggling whaler under the French flag. The substance of the sketch of Cochinchina is taken from a manuscript memoir drawn up by Captain Barissy, a French naval officer who, having several years commanded a frigate in the service of the King of Cochinchina and being an able and intelligent man, had the means and the opportunity of collecting accurate information .
The African part of the volume - which might perhaps, with more propriety, have formed an appendix to Barrows South African travels - relates to his two missions into the interior in order to reconcile the Kaffirs and Boers and to obtain more accurate topographical knowledge of the colony. He visited most parts of the Cape Colony, including the countries of the Kaffirs, Hottentots and Bushmen. He conducted the first census of Cape Colony, undertook a few amateur geological surveys, and contrived an interview with Shaka, king of the Zulus (Howgego). The son of a Lancashire journeyman tanner, Barrow was initially educated in the local grammar school, subsequently working as as a clerk in a Liverpool iron foundry, as a landsman on a Greenland whaler, and as a mathematics teacher in a Greenwich academy preparing young men for a naval career (ODNB). At this time he gave private tuition to Thomas Staunton, son of Sir George Staunton, to whom, as he later admitted, he was indebted for all the good fortune of his life, which began with his service as comptroller of household to Lord Macartneys embassy. Today, Barrow is perhaps best known for his Mutiny on the Bounty (1831) but, during his lifetime, his accounts of his travels in eastern Asia and southern Africa, published between 1801 and 1807, were better known and more influential. These established new standards for travel writing His interests ranged widely, but the great bulk of his output had a geographical focus, usually with an underlying imperial theme and a belief in progress and the superiority of British civilization Collectively, these activities established his pre-eminence within British geography. The account is superbly illustrated with aquatints of views, types, and natural history specimens, Abbey commending the aquatinting as of excellent quality. Bookplate of Charles Constant de Rebecque to the front pastedown, together with a modern collectors plate. A Swiss, a cousin of Benjamin Consant, Constant de Rebecque acted as an agent for the HEIC, making three trips to China for them, and publishing an account of his travels, Récits de Trois Voyages à la Chine.
Cochinchina is a historical exonym for part or the whole of Vietnam, depending on the contexts, but it was commonly used to refer to the region south of the Gianh River. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Vietnam was divided between the Trịnh lords to the north and the Nguyễn lords to the south. The two domains bordered each other on the Son–Gianh River. The northern section was called Tonkin by Europeans, and the southern part, Đàng Trong, was called Cochinchina by most Europeans and Quinam by the Dutch
Barrow, Sir John 1764 - 1848
Barrow, 1st Baronet, was an English civil servant, geographer, linguist and writer. Barrows legacy has been met with mixed analysis. Some historians regard Barrow as an instrument of imperialism who portrayed Africa as a resource rich land devoid of any human or civilized elements. Nonetheless, other historians consider Barrow to have promoted humanitarianism and rights for South Africans.
Barrow was born the only child of Roger Barrow, a tanner in the village of Dragley Beck, in the parish of Ulverston, Lancashire. He was schooled at Town Bank grammar school, Ulverston, but left at age 13 to found a Sunday school for the poor.
Barrow was employed as superintending clerk of an iron foundry at Liverpool. At only 16, he went on a whaling expedition to Greenland. By his twenties, he was teaching mathematics, in which he had always excelled, at a private school in Greenwich.
Barrow taught mathematics to the son of Sir George Leonard Staunton; through Stauntons interest, he was attached on the first British embassy to China from 1792 to 1794 as comptroller of the household to Lord Macartney. He soon acquired a good knowledge of the Chinese language, on which he subsequently contributed articles to the Quarterly Review; and the account of the embassy published by Sir George Staunton records many of Barrows valuable contributions to literature and science connected with China.
Barrow ceased to be officially connected with Chinese affairs after the return of the embassy in 1794, but he always took much interest in them, and on critical occasions was frequently consulted by the British government.
Some historians attribute the stagnation thesis to Barrow; that China was an extremely civilized nation that was in a process of decay by the time of European contact.
In 1797, Barrow accompanied Lord Macartney as private secretary in his important and delicate mission to settle the government of the newly acquired colony of the Cape of Good Hope. Barrow was entrusted with the task of reconciling the Boer settlers and the native Black population and of reporting on the country in the interior. In the course of the trip, he visited all parts of the colony; when he returned, he was appointed auditor-general of public accounts. He then decided to settle in South Africa, married, and bought a house in 1800 in Cape Town. However, the surrender of the colony at the peace of Amiens (1802) upset this plan.
During his travels through South Africa, Barrow compiled copious notes and sketches of the countryside that he was traversing. The outcome of his journeys was a map which, despite its numerous errors, was the first published modern map of the southern parts of the Cape Colony. Barrows descriptions of South Africa greatly influenced Europeans understanding of South Africa and its peoples. William John Burchell (1781–1863) was particularly scathing: As to the miserable thing called a map, which has been prefixed to Mr. Barrows quarto, I perfectly agree with Professor Lichtenstein, that it is so defective that it can seldom be found of any use.
Barrow returned to Britain in 1804 and was appointed Second Secretary to the Admiralty by Viscount Melville, a post which he held for forty years – apart from a short period in 1806–1807 when there was a Whig government in power. Lord Grey took office as Prime Minister in 1830, and Barrow was especially requested to remain in his post, starting the principle that senior civil servants stay in office on change of government and serve in a non-partisan manner. Indeed, it was during his occupancy of the post that it was renamed Permanent Secretary. Barrow enjoyed the esteem and confidence of all the eleven chief lords who successively presided at the Admiralty board during that period, and more especially of King William IV while lord high admiral, who honoured him with tokens of his personal regard.
In his position at the Admiralty, Barrow was a great promoter of Arctic voyages of discovery, including those of John Ross, William Edward Parry, James Clark Ross and John Franklin. The Barrow Strait in the Canadian Arctic as well as Point Barrow and the city of Barrow in Alaska are named after him. He is reputed to have been the initial proposer of Saint Helena as the new place of exile for Napoleon Bonaparte following the Battle of Waterloo in 1815. Barrow was a fellow of the Royal Society and received the degree of LL.D from the University of Edinburgh in 1821. A baronetcy was conferred on him by Sir Robert Peel in 1835. He was also a member of the Raleigh Club, a forerunner of the Royal Geographical Society.
Barrow retired from public life in 1845 and devoted himself to writing a history of the modern Arctic voyages of discovery (1846), as well as his autobiography, published in 1847. He died suddenly on 23 November 1848. The Sir John Barrow monument was built in his honour on Hoad Hill overlooking his home town of Ulverston, though locally it is more commonly called Hoad Monument. Mount Barrow and Barrow Island in Australia are believed to have been named for him.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print of a Sydney & Port Jackson Aboriginal Warrior
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Nelle Galles Du Sud. Nourou-gal-derri & avancant pour combattre
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91240
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Aboriginal warrior of Port Jackson carrying a spear & shield, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes in 1807.
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - 2 small repair to left margin, no loss
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print of a Sydney & Port Jackson Aboriginal Warrior
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Nelle Galles Du Sud. Nourou-gal-derri & avancant pour combattre
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93087
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Aboriginal warrior of Port Jackson carrying a spear & shield, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes in 1807.
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting to left and bottom margins, not affecting the image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print Sydney Aboriginal Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan - Bennelong
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Gnoung-a-gnoung-a Mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91239
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print, of the brother in law of the famous Port Jackson Aborginal leader Bennelong, Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, or Anganángan, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 by Nicolas-Martin Petit, was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan
It is over 200 years since the death of an adventurous young Aboriginal Australian who crossed the vast Pacific Ocean to North America and returned to Sydney. From the deck of an English storeship he glimpsed many strange places, visiting Norfolk Island, Hawaii, Nootka Sound (now Vancouver, Canada) and the Spanish colonies of San Francisco, Santa Barbara and San Diego on the Californian coast.
The voyager was Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, whose wife Warreeweer was the younger sister of the Wangal leader Woollarawarre Bennelong, at that time being feted in London society. The distance Gnung-a Gnung-a traversed was some 16,000 miles (25,750 kilometres) as the crow flies, but much further in a sailing ship driven by unpredictable winds.
On the first day he ventured into the convict settlement at Sydney Cove, in November 1790, Gnung-a Gnung-a adopted the name Collins from Acting Judge Advocate David Collins, who often mentions him in An Account of the English Colony in New South Wales, published in London in 1798.
It was the idea of Major Francis Grose, acting governor of New South Wales after the departure of Captain Arthur Phillip in 1792, to embark a native of this country on HM storeship Daedalus for the purpose of acquiring our language, wrote David Collins. The 350-ton capacity vessel was ordered to resupply provisions for the expedition to the north-west coast of North America commanded by Captain George Vancouver (1757–1798). In the navy ships HMS Discovery and HMS Chatham, Captain Vancouver was to complete the survey made by Captain James Cook.
Voyage to America
HMS Daedalus sailed from Port Jackson on 1 July 1793, passing west of the Society Islands (French Polynesia) to Owhyee (Hawaii). The commander, Lieutenant James Hanson, missed a rendezvous with Vancouvers ships at Nootka Sound on 8 October, but anchored with the two survey ships off San Francisco Bay on 21 October. The three British ships followed the coast of todays California to San Diego, leaving on 9 December 1793 and arriving at Hilo in Hawaii on 8 January 1794.
The Hawaiian King Kamehameha, who warmly welcomed Vancouver, was so impressed by the good-natured, handsome Aboriginal man on the expedition that he wanted to buy him, offering in exchange canoes, weapons and curiosities.
Gnung-a Gnung-a got on well with everyone on Daedalus and Hanson was pleased by his good nature and his willingness to do whatever was asked of him. During his month in Hawaii, he often went ashore with his shipmates. Wherever he went he readily adopted the manners of those around him, Hanson later told Collins, who remarked, with ironic humour, that...........
when at Owhyee, having discovered that favours from the females were to be procured at the easy exchange for a looking-glass, a nail, or a knife, he was not backward in presenting his little offering, and was as well received as any of the white people in the ship. It was noticed too that he always displayed some taste in selecting the object of his attentions.......
Return to Sydney
Home in Sydney Town, Gnung-a Gnung-a fought and wounded a very fine young fellow called Wyatt, who had taken up with his wife during his absence and Warreeweer became the prize of the victor.
During a ritual revenge combat in December 1795, Pemulwuy, leader of the Georges River Bidjigal near Botany Bay, launched a spear at Gnung-a Gnung-a that remained fixed in his back. The English surgeons could not extract the spear and thought he was unlikely to recover. Gnung-a Gnung-a, however, left the hospital and walked about for several weeks with the spear protruding from his back. At last, wrote Collins in a footnote..........
we heard that his wife, or one of his male friends, had fixed their teeth in the wood and drawn it out after which he recovered, and was able again to go into the field. His wife War-re-weer showed by an uncommon attention her great attachment to him.......
Before this unexpected recovery, David Collins wrote a brief appreciation of his namesake:
He was much esteemed by every white man who knew him, as well on account of his personal bravery, of which we had witnessed many distinguishing proofs, as on account of a gentleness of manners which strongly marked his disposition, and shaded off the harsher lines that his uncivilised life now and then forced into the fore-ground.
While in Sydney with a scientific expedition commanded by Nicholas Baudin in 1802, the young French artist Nicolas-Martin Petit met Gnung-a Gnung-a and sketched a striking portrait that he captioned Gnoung-a gnoung-a, mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
A report in the Sydney Gazette of Sunday 15 January 1809 said that the body of Collins (Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan) had been found beside the Dry Store, site of the present Sirius Park in Bridge Street, Sydney. The newspaper said he had been known for the docility of his temper, and the high estimation in which he was universally held among the native tribes.
On the night of Thursday 12 January 1809, Gnung-a Gnung-as children, others he had adopted, and his brother Old Phillip, faced a salvo of spears in the ritual ordeal that followed death in Aboriginal society. The date of his death was not recorded, but it was customary to keep an overnight vigil over a dead body before burial and the subsequent revenge combat, so it was probably 11 January.
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan is one of many Aboriginal men and women who sailed from Sydney in English ships and played a significant role in Australias early maritime history.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print Sydney Aboriginal Wárrgan, Bennelong's Sister
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Oui-re-kine
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91238
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print, of the (half) sister of the famous Port Jackson Aborginal leader Bennelong, Oui-ré-kine – Wárrgan (Crow), also referred to as Worogan, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit, and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
The sitter – identified by artist Nicolas-Martin Petit as Oui-ré-kine – Wárrgan (Crow), also referred to as Worogan. In his writings about the Eora people he knew, astronomer and collector of Sydney languages William Dawes counted Wárrgan with Bennelongs sisters, although she might have been a half-sister or other relative of Bennelongs. Her husband Yeranibe (Euranabie) was the son of Maugoran, a leader of the Burramattagal clan, making Wárrgan a sister-in-law to Bidgee Bidgee, another of Petits Sydney sitters. In 1801, Wárrgan and Yeranibe joined the Lady Nelson which, under the command of James Grant, voyaged to Jervis Bay before making a survey of Bass Strait. In The Narrative of a Voyage of Discovery performed in His Majestys vessel the Lady Nelson (1803–1804), Grant related an incident wherein Wárrgan demonstrated the use of a waddy and a woomera, and how incisions were made on the body using a shell. Both Wárrgan and Yeranibe spoke English, and acted as Grant’s interpreters.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Arra Maida
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93085
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida, visited by the Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Bara-Ourou
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Bara-Ourou
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93088
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Bara-Ourou, portrait of a young man 28-30 years of age, visited by Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Grou Agara
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Grou Agara
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93086
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Grou Agara, visited by the Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal, Ourlaga
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Ourlaga
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93089
Description:
This exquisite, rare original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Ourlaga, visited by Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1808 Dr Playfair Large Old, Antique Map of France - Gallia
- Title : Gallia Drawn & Engraved Dr Playfairs Geography
- Ref #: 31155
- Size: 23 1/2in x 19in (595mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1808
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved map of France was engraved in 1808 by B Smith - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1808 edition of Dr Playfair's General Atlas. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19in (595mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 19in (595mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1808 Jean Henri Cless Antique Print of The Cartographer Guillaume Delisle
Antique Map
- Title : Guillaue De L Isle Geb. zu Paris d. 28 Febr. 1675 gest. ebendas d. 25 Jan 1726
- Date : 1808
- Size: 7in x 4 1/2in (180mm x 115mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 91417
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of the famous cartographer Guillaume Delisle, by Jean Henri Cless was published in 1808 in Allgemeine Geographische Ephemeriden' (Universal Geographical Ephemerides (i.e. encyclopedia) by Friedrich Bertuch
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 7in x 4 1/2in (180mm x 115mm)
Plate size: - 5 1/2in x 3 1/2in (140mm x 90mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Following the long period of Dutch domination, the Homann family became the most important map publishers in Germany in the eighteenth century, the business being founded by J.B. Homann in Nuremberg about the year 1702. Soon after publishing his first atlas in 1707 he became a member of the Berlin academy of Sciences and in 1715 he was appointed Geographer to the Emperor. After the founder's death in 1724, the firm was continued under the direction of his son until 1730 and was then bequeathed to his heirs on the condition that it trades under the name of Homann Heirs. The firm remained in being until the next century and had a wide influence on map publishing in Germany. Apart from the atlases the firm published a very large number of individual maps.
The Homman's produced a Neuer Atlas in 1714, a Grosser Atlas in 1737, and an Atlas Maior with about 300 maps in 1780. They also issued a special Atlas of Germany with full sized plans of principal cities, school atlases and an Atlas of Silesia in 1750 with 20 maps.
Cless, Jean Henri 1774- 1812
A pupil of Jacques-Louis David , he began to be active around 1800 and exhibited in Paris at the Salons from 1804 to 1808.
According to the Thieme-Becker 2 artistic dictionary , he returned to Alsace in 1811 , where many private collections hold his works.
Cless was also a draftsman and miniaturist .
1808 Samuel Neele Large Antique Map of Belgium & Southern Netherlands
- Title : Belgium or the Netherlands divided into Departments
- Date : 1808
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 24329-1
- Size: 20in x 16in (510mm x 405mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Belgium & the southern Netherlands was engraved by John Neele in 1808 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and published in the 1810 edition of The Modern Royal Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 16½in x 15in (420mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Light creasing, light wear along bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The name Belgium is derived from Gallia Belgica, a Roman province in the northernmost part of Gaul that before Roman invasion in 100 BC, was inhabited by the Belgae, a mix of Celtic and Germanic peoples. A gradual immigration by Germanic Frankish tribes during the 5th century brought the area under the rule of the Merovingian kings. A gradual shift of power during the 8th century led the kingdom of the Franks to evolve into the Carolingian Empire.
The Treaty of Verdun in 843 divided the region into Middle and West Francia and therefore into a set of more or less independent fiefdoms which, during the Middle Ages, were vassals either of the King of France or of the Holy Roman Emperor.
Many of these fiefdoms were united in the Burgundian Netherlands of the 14th and 15th centuries. Emperor Charles V extended the personal union of the Seventeen Provinces in the 1540s, making it far more than a personal union by the Pragmatic Sanction of 1549 and increased his influence over the Prince-Bishopric of Liège.
The Eighty Years\' War (1568–1648) divided the Low Countries into the northern United Provinces (Belgica Foederata in Latin, the Federated Netherlands) and the Southern Netherlands (Belgica Regia, the Royal Netherlands). The latter were ruled successively by the Spanish (Spanish Netherlands) and the Austrian Habsburgs (Austrian Netherlands) and comprised most of modern Belgium. This was the theatre of most Franco-Spanish and Franco-Austrian wars during the 17th and 18th centuries.
Following the campaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Low Countries—including territories that were never nominally under Habsburg rule, such as the Prince-Bishopric of Liège—were annexed by the French First Republic, ending Austrian rule in the region. The reunification of the Low Countries as the United Kingdom of the Netherlands occurred at the dissolution of the First French Empire in 1815, after the defeat of Napoleon.
Neele, Samuel John 1758–1824
Samuel John Neele was a cartographer, copper-plate engraver and printer with business in the Strand, London.
Also father of Henry Neele the English poet and literary scholar.
1808 Wilkinson Antique Map of East Coast of Australia, New Zealand, inset Sydney
- Title : New South Wales New Zealand New Hebrides...Published Dec 12th 1808
- Ref #: 9003
- Size: 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1808
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the east coast of Australia, New Zealand and the Solomon Islands - with inset maps of Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island & Port Jackson - was published in 1808 by Robert Wilkinson - the date is included in the title - in his wideley acclaimed General Atlas of the World published between 1794 and 1816.
This is a finely engraved copper-plate map with beautiful original hand colouring on strong stable paper. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10in (320mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1810 John Augustus Atkinson Original Water Colour Art of an English War Skirmish
Antique Map
- Title : (A Civil War Skirmish)
- Ref #: 93444
- Size: 17in x 15in (430mm x 365mm)
- Date : 1810
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully executed original pen, pencil and watercolour picture of an English Civil War battle scene was painted by John Augustus Atkinson in ca 1810.
Atkinson was known for his battle scene art works during his time at the St Petersburg Court in Russia as well as his Napoleonic battle scenes from the early 19th century.
Atkinson is held in high esteem as a watercolourist, and was elected as a member of the Society of Painters in Water Colours in 1808. He has works of art held at many prestigious museums in Russia, Europe and the UK, such as the Tate, Royal Watercolour Society, National Maritime Museum and many more listed below. He also sells on the open market with this piece last sold in 2004.
Professionally matted and can be easily removed if required.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 15in (430mm x 365mm)
Plate size: - 9 3/4in x 8in (247mm x 203mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (Roundheads) and Royalists (Cavaliers) principally over the manner of Englands governance and part of the wider Wars of the Three Kingdoms. The first (1642–1646) and second (1648–1649) wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third (1649–1651) saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The war ended with Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651.
Unlike other civil wars in England, which were mainly fought over who should rule, these conflicts were also concerned with how the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland were to be governed. The outcome was threefold: the trial and execution of Charles I (1649); the exile of his son, Charles II (1651); and the replacement of English monarchy with, at first, the Commonwealth of England (1649–1653) and then the Protectorate, which as the Commonwealth of England, Scotland, and Ireland unified the British Isles under the personal rule of Oliver Cromwell (1653–1658) and briefly his son Richard (1658–1659). The execution of Charles I was particularly notable given that an English king had never been executed before. In England, the monopoly of the Church of England on Christian worship was ended, while in Ireland the victors consolidated the established Protestant Ascendancy. Constitutionally, the wars established the precedent that an English monarch cannot govern without Parliaments consent, although the idea of Parliamentary sovereignty was only legally established as part of the Glorious Revolution in 1688.
Atkinson, John Augustus 1775 - 1830
Atkinson was an English artist, engraver and watercolourist.
He was born in London and at the age of 9, in 1784, went to live with his uncle, the famous engraver James Walker, in St Petersburg, Russia. Walker was engraver to the empress Catherine the Great 1729 - 1796 and encouraged Atkinson to study art, seeing a talent in him. Atkinson was well placed in St Petersburg to study art, being surrounded by the many collections of Catherine and the Russian Nobility, the richest in Europe. It is known that Atkinson was encouraged by Catherine herself along with and her son & later Emperor of Russia Paul I 1754 - 1801. Paul later commissioned Atkinson to paint large pieces from Russian history that can be seen in many Museums today around the world.
After the death of Paul in 1801, Atkinson returned to England and in 1803 published A Picturesque Representation of the Manners, Customs, and Amusements of the Russians, in 100 plates, drawn and etched by himself. He also painted in watercolours and in 1808 was elected to the Society of Painters in Water Colours. Many of his works, during the Napoleonic wars, were of naval subjects. He painted many battle scenes including a Battle of Waterloo, which was engraved by John Burnet.
His last contribution to the Royal Academy exhibition was in 1829. He died on 25 March 1830 in London.
Selected Works
• Carriage on Sledges 1803 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• A Russian Village 1804 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• Golubtza 1804 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• Village Amusements 1804 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• Scene from Tom Jones Courtauld Institute of Art, London
• The Slack Rope Courtauld Institute of Art, London
• A Belgian Waggon with Four Horses Tate Gallery, London
• Illustrations to Ossian The Huntington Library, California
• Heaving a Lead 1807 National Maritime Museum
• Greenwich Pensioners 1808 National Maritime Museum
• Skating, 1810 Tyne & Wear Museums, England
• Ships of the Reign of King Edward IV 1812 - Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco
• 42nd Highlanders at Waterloo Courtauld Institute of Art, London
• British Sailors Boarding a Man of War 1815 National Maritime Museum
1811 John Pinkerton Very Large Antique Map of The North of England - Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : England Northern Part....Published March 25th 1811 by Cadell & Davies
- Ref #: 93422
- Size: 33 1/2in x 22 1/2in (850mm x 570mm)
- Date : 1811
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large & magnificent, beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Northern England by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1811 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in the large elephant folio Pinkertons Modern Atlas, published between 1809 & 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 33 1/2in x 22 1/2in (850mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 30 1/2in x 22 1/2in (775mm x 570mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1812 Conrad Malte Brun Large Quatro Antique World Atlas with 75 Maps
Antique Map
- Title : Atlas Complet du précis de la Geographie universelle. Dressé conformément au Texte de cet Ouvrage et sous les Yeux de L'Auteur, par M. Lapie. (Cet Atlas est formé de 75 Cartes)
- Size: Large Quarto - 14 1/2in x 11in (370mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1812
- Ref #: 31573
Description:
This original large quatro, antique 1st edition atlas by Conrad Matle-Brun Atlas Complet du précis de la Geographie universelle containing 75 hand coloured maps, as called for, was published by Francois Buisson in 1812.
This fine world atlas contains 3 double page and 72 single page maps with original hand colouring on clean heavy paper with a heavy impression. The binding & spine is tight, with worn boards. A beautiful intact clean atlas, now how to find.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 355mm) double page maps
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm) single page maps
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Malte-Brun, Conrad 1775 - 1826
Malte-Brun was born Malthe Conrad Bruun - sometimes referred to simply as Malte-Brun - was a Dano-French geographer and journalist. His second son, Victor Adolphe Malte-Brun, was also a geographer. Today he is perhaps best remembered for coining the name for the geographic region Oceania (French Oceanie) around 1812.
Born in Thisted to an administrator of Danish crown lands, Malte-Brun was originally destined for a career as a pastor, but chose instead to attend classes at the University of Copenhagen, and became a supporter of the French Revolution and an activist in favor of freedom of the press. Following the harsh censorship laws instituted by the Danish ruler crown prince Frederick in September 1799, he was indicted because of his many pamphlets which contained outright criticism of the government, which the new censorship laws forbade. A particular cause for offence was a pamphlet he published in 1795 entitled Catechism of the Aristocrat.
The case of Peter Andreas Heiberg, who for similar crimes had been sentenced to exile at Christmas of 1799, did not make Malte-Brun optimistic about his prospects. He had already left the country prior to the court sentence (which was first carried late 1800) and had settled first in Sweden, later in the Free City of Hamburg.
At some point during his exile, he started using his Danish first name, Malthe, as part of his surname, Bruun.
Malte-Brun arrived in France in November 1799, and began work on a geography treatise meant as a gift to his adoptive country. A poem on the death of Andreas Peter Bernstorff which he published during his exile procured for him permission to return to Denmark. But another pamphlet against the aristocracy subjected him to a new prosecution, and he left his country, and finally took up his residence in Paris. In December 1800, the Danish courts pronounced sentence of perpetual banishment against him, which was rescinded about the time of his death. Malte-Brun\'s geography treatise was written with the help of Edme Mentelle, a professor at the Ale Normale; together, they produced Gaographie mathamatique, physique et politique de toutes les parties du monde (6 vols., published between 1803 and 1812).
He was a regular contributor to Journal des dabats. At first opposed the consular government, but subsequently became a zealous imperialist, and after the fall of Napoleon an equally zealous monarchist, publishing in 1824 Traita de la lagitimita considae comme base du droit public de l Europe chratienne.
Aside from his political writings, he devoted himself especially to geographical studies. He was the founder of Les Annales des Voyages (in 1807) and Les Annales des Voyages, de la Gaographie et de l Histoire (in 1819), which encouraged observations and reports as a basis for research. He became well known after contributing Tableau de la Pologne, a treatise on the geography of Poland (in 1807) as the First Empire troops established French tutelage in the region). In 1822-1824, he served as the first general secretary of the newly founded Sociata de Gaographie. Malte-Brun was the first person to suggest importing camels into Australia. See Australian feral camel.
He died in Paris in 1826 as he was drafting the final version of his major work, the Pracis de Gaographie Universelle ou Description de toutes les parties du monde. This appeared in eight volumes (1810 - 29), the last two volumes being by Huot. Malte-Bruns name was given to streets in both Paris (20th arrondissement) and Thisted.
1812 Las Cases Large Original Antique Map of The Russian Empire, English Text
- Title : The Russian Empire with its gradual Acquisitions traced and Explained
- Size: 28in x 19in (710mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 40259
- Date : 1812
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique map of Russia - within the geographical, political, economic, physical & historical text - was published in the 1812 English edition of Emmanuel Las Cases very large Elephant Folio size The Historical, Geographical & Genealogy Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 28in x 19in (710mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 13in (535mm x 33mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light offsetting
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - Light age toning
1812 Pinkerton Large Antique Stereographic Projection Map of Northern Hemisphere
- Title : Northern Hemisphere....Neele Sculp. 352 Strand.....London Published October 1st 1812 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 60542
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1812
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique stereographic projection style map of the Northern Hemisphere, North America, Canada, Europe, Asia, Africa & The North Pole by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1812 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In geometry, the stereographic projection is a particular mapping (function) that projects a sphere onto a plane. The projection is defined on the entire sphere, except at one point: the projection point. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective. It is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet. It is neither isometric nor area-preserving: that is, it preserves neither distances nor the areas of figures.
Intuitively, then, the stereographic projection is a way of picturing the sphere as the plane, with some inevitable compromises. Because the sphere and the plane appear in many areas of mathematics and its applications, so does the stereographic projection; it finds use in diverse fields including complex analysis, cartography, geology, and photography. In practice, the projection is carried out by computer or by hand using a special kind of graph paper called a stereographic net, shortened to stereonet, or Wulff net.
The stereographic projection was known to Hipparchus, Ptolemy and probably earlier to the Egyptians. It was originally known as the planisphere projection. Planisphaerium by Ptolemy is the oldest surviving document that describes it. One of its most important uses was the representation of celestial charts. The term planisphere is still used to refer to such charts.
In the 16th and 17th century, the equatorial aspect of the stereographic projection was commonly used for maps of the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. It is believed that already the map created in 1507 by Gualterius Lud was in stereographic projection, as were later the maps of Jean Roze (1542), Rumold Mercator (1595), and many others. In star charts, even this equatorial aspect had been utilised already by the ancient astronomers like Ptolemy.
François d\'Aguilon gave the stereographic projection its current name in his 1613 work Opticorum libri sex philosophis juxta ac mathematicis utiles (Six Books of Optics, useful for philosophers and mathematicians alike).
In 1695, Edmond Halley, motivated by his interest in star charts, published the first mathematical proof that this map is conformal. He used the recently established tools of calculus, invented by his friend Isaac Newton.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
1812 Pinkerton Large Antique Stereographic Projection Map of Southern Hemisphere
- Title : Southern Hemisphere....Drawn Under the Direction of Mr Pinkerton by L Herbert Neele Sculp. 352 Starnd.....London Published August 31st 1812 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 60540
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1812
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique stereographic projection style map of the Southern Hemisphere, Australia, New Zealand & Antarctica by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1812 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In geometry, the stereographic projection is a particular mapping (function) that projects a sphere onto a plane. The projection is defined on the entire sphere, except at one point: the projection point. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective. It is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet. It is neither isometric nor area-preserving: that is, it preserves neither distances nor the areas of figures.
Intuitively, then, the stereographic projection is a way of picturing the sphere as the plane, with some inevitable compromises. Because the sphere and the plane appear in many areas of mathematics and its applications, so does the stereographic projection; it finds use in diverse fields including complex analysis, cartography, geology, and photography. In practice, the projection is carried out by computer or by hand using a special kind of graph paper called a stereographic net, shortened to stereonet, or Wulff net.
The stereographic projection was known to Hipparchus, Ptolemy and probably earlier to the Egyptians. It was originally known as the planisphere projection. Planisphaerium by Ptolemy is the oldest surviving document that describes it. One of its most important uses was the representation of celestial charts. The term planisphere is still used to refer to such charts.
In the 16th and 17th century, the equatorial aspect of the stereographic projection was commonly used for maps of the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. It is believed that already the map created in 1507 by Gualterius Lud was in stereographic projection, as were later the maps of Jean Roze (1542), Rumold Mercator (1595), and many others. In star charts, even this equatorial aspect had been utilised already by the ancient astronomers like Ptolemy.
François d\'Aguilon gave the stereographic projection its current name in his 1613 work Opticorum libri sex philosophis juxta ac mathematicis utiles (Six Books of Optics, useful for philosophers and mathematicians alike).
In 1695, Edmond Halley, motivated by his interest in star charts, published the first mathematical proof that this map is conformal. He used the recently established tools of calculus, invented by his friend Isaac Newton.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
1814 Dr Playfairs Large Antique Map of France in Departments
Antique Map
- Title : France in Departments Drawn and Engraved for Dr Playfairs Geography.
- Size: 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1814
- Ref #: 31154
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved map of France was published in the 1814 edition of A System of Geography Ancient and Modern (1810–14) (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
Playfair, Rev James Octavius 1738 - 1819
Rev Playfair was a Scottish minister and author and an eminent figure in the Scottish Enlightenment. He was born at West Bendochy in Perthshire the son of George Playfair (d. 1786), a farmer, and his wife, Jean Roger (d. 1804).[1]
He studied at St Andrews University and then became minister of Newtyle (1770–77) and Meigle (1777–1800). He was then appointed Principal of St Andrews University in 1800. During this period he was also minister of St Leonard\\\'s Church in St Andrews.
In 1779 St Andrews awarded him an honorary doctorate (DD). In 1787 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposers were John Playfair (a distant cousin) and Alexander Fraser Tytler.[2]
He was the official histiographer of the then Prince of Wales.
He died at Dalmarnock near Glasgow. He is buried in Glasgow but is also memorialised on the grave of his wife in the churchyard of St Andrews Cathedral.
Publications:
1. A System of Chronology (1782)
2. A System of Geography Ancient and Modern (1810–14)
3. General Atlas Ancient and Modern (1814)
4. A Geographical and Statistical Description of Scotland (1819)
1814 John Pinkerton Large Antique Map of Turkey in Europe - Greece to Hungary
- Title : Turkey in Europe....Drawn under the direction of Mr Pinkerton by L Herbert Neele Sculp. 352 Starnd.....London Published 1st Jan 1814 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 16434
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1814
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Turkey in Europe - Greece, Balkans, Romania, Bosnia, Albania, Serbia, Dalmatia - by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1814 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Ottoman Empire also historically known in Western Europe as the Turkish Empire or simply Turkey, was a state that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia and North Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Oghuz Turkish tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe, and with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the 1453 conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, at the height of its power under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was a multinational, multilingual empire controlling most of Southeast Europe, parts of Central Europe, Western Asia, parts of Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, North Africa and the Horn of Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states. Some of these were later absorbed into the Ottoman Empire, while others were granted various types of autonomy during the course of centuries.
With Constantinople as its capital and control of lands around the Mediterranean basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds for six centuries. While the empire was once thought to have entered a period of decline following the death of Suleiman the Magnificent, this view is no longer supported by the majority of academic historians. The empire continued to maintain a flexible and strong economy, society and military throughout the 17th and much of the 18th century. However, during a long period of peace from 1740 to 1768, the Ottoman military system fell behind that of their European rivals, the Habsburg and Russian empires. The Ottomans consequently suffered severe military defeats in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, which prompted them to initiate a comprehensive process of reform and modernisation known as the Tanzimat. Thus, over the course of the 19th century, the Ottoman state became vastly more powerful and organised, despite suffering further territorial losses, especially in the Balkans, where a number of new states emerged. The empire allied with Germany in the early 20th century, hoping to escape from the diplomatic isolation which had contributed to its recent territorial losses, and thus joined World War I on the side of the Central Powers. While the Empire was able to largely hold its own during the conflict, it was struggling with internal dissent, especially with the Arab Revolt in its Arabian holdings. During this time, atrocities were committed by the Ottoman government against the Armenians, Assyrians and Pontic Greeks.
The Empires defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories, which were divided between the United Kingdom and France. The successful Turkish War of Independence against the occupying Allies led to the emergence of the Republic of Turkey in the Anatolian heartland and the abolition of the Ottoman monarchy.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
1814 John Thomson Large Antique Map of The Russian Empire
- Title : Russian Empire ...John Thomson....1814
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (720mm x 530mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1814
- Ref #: 31910
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of The Russian Empire by John Thomson in 1814 - dated at the foot of the map - was published in the large 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Light
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (720mm x 530mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
It is scarcely necessary to look at a map of Russia - with which we must include Siberia - to visualize the daunting task facing Russian map makers. Indeed, considering the vastness of their territory and the lack of skilled cartographers, it is surprising that relatively good maps were available for engraving and printing in most of the well known sixteenth and seventeenth century atlases. Generally, maps of that time were based on material brought back from Moscow by visitors from the West.
1814 William Alexander Antique Print of a Chinese Soldier with Matchlock Rifle
- Title : China - Plate 13....Published Jan. 1814 by J Murray, Albenarle Street (Plate XIII A Soldier with his Matchlock)
- Date : 1814
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25464-1
- Size: 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Chinese soldier with his Matchlock rifle - accompanied by text - by William Alexander was published in the 1st 1814 - dated - edition of Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7in (240mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1792, Alexander was appointed as one of the draughtsmen to the Macartney Embassy to China. He accompanied the Earl of Macartney to Peking where he made drawings for the plates which accompanied Sir George Stauntons account of the embassy, published in 1797.
In 1805 he published The Costume of China, illustrated by 48 coloured engravings, after his travels to China with The Earl of Macartney. The work was so well-received that in 1814 he published another book titled Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions. This publication was re-issued over the next twenty years in various languages including French.
Alexander, William 1767 – 1816
Alexander was an English painter, illustrator and engraver. The hallmarks of his work, usually executed in watercolours, were clearness and harmony of colour, simplicity and taste in composition, grace of outline, and delicacy of execution. He accompanied the Macartney Embassy to China in 1792. Prints of his work were reproduced from engravings. One his of works was used to illustrate Cadell & Davies Britannia depicta.
Alexander was born in Maidstone, Kent, the son of Harry Alexander, a coachmaker. He was educated at Maidstone Grammar School, but in 1782, at the age of 15, moved to London to study art - first under William Pars, and subsequently Julius Caesar Ibbetson. In February 1784, he was admitted to the Royal Academy Schools. He assiduously applied himself to the mastery of his profession, obtaining the notice and approbation of Sir Joshua Reynolds.
In 1792, he was appointed as one of the draughtsmen to the Macartney Embassy to China. He accompanied the Earl of Macartney to Peking where he made drawings for the plates which accompanied Sir George Stauntons account of the embassy (published in 1797) In 1794 he returned to England and married Jane Wogan the following year. She died soon afterwards.
His other principal works were: Views of Headlands, Islands, etc. taken during the Voyage to China (1798); drawings based on Daniells sketches, for Vancouvers Voyage to the North Pacific Ocean (1798); and the descriptive plates to Sir John Barrows Travels in China (1804), and Voyage to Cochin China (1806). In 1805 he published The Costume of China, illustrated by 48 coloured engravings. The work was so well-received that in 1814 he published another book titled Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions.
Besides his works as a draughtsman, he made several engravings - the principal one of which is a representation of the Festival given by the Earl of Romney to the Kentish Volunteers, on 1 August 1799, from his own drawing.
In 1802, Alexander was appointed professor of drawing at the Military College at Great Marlow, resigning in May 1808 to take up the post of assistant keeper of antiquities in the British Museum. In the years 1810, 1812, and 1815, he made drawings of the terra cottas and marbles in the Museum which were engraved and published in three volumes - the accompanying text being provided by Taylor Combe (keeper of the Department of Antiquities). Alexander had completed drawings for a fourth volume before his death.
He died at the house of his uncle in Maidstone in July 1816, and was buried in Boxley churchyard. He was described in one of his obituaries as a man of mild and unassuming manners, rich in the knowledge of art, and of unsullied integrity.
1814 William Alexander Antique Print of Chinese Family Eating a Meal
- Title : China - Plate 10....Published Jan. 1814 by J Murray, Albenarle Street
- Date : 1814
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25462
- Size: 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Chinese family eating by the side of the road - by William Alexander was published in the 1st 1814 - dated - edition of Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7in (240mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1792, Alexander was appointed as one of the draughtsmen to the Macartney Embassy to China. He accompanied the Earl of Macartney to Peking where he made drawings for the plates which accompanied Sir George Stauntons account of the embassy, published in 1797.
In 1805 he published The Costume of China, illustrated by 48 coloured engravings, after his travels to China with The Earl of Macartney. The work was so well-received that in 1814 he published another book titled Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions. This publication was re-issued over the next twenty years in various languages including French.
Alexander, William 1767 – 1816
Alexander was an English painter, illustrator and engraver. The hallmarks of his work, usually executed in watercolours, were clearness and harmony of colour, simplicity and taste in composition, grace of outline, and delicacy of execution. He accompanied the Macartney Embassy to China in 1792. Prints of his work were reproduced from engravings. One his of works was used to illustrate Cadell & Davies Britannia depicta.
Alexander was born in Maidstone, Kent, the son of Harry Alexander, a coachmaker. He was educated at Maidstone Grammar School, but in 1782, at the age of 15, moved to London to study art - first under William Pars, and subsequently Julius Caesar Ibbetson. In February 1784, he was admitted to the Royal Academy Schools. He assiduously applied himself to the mastery of his profession, obtaining the notice and approbation of Sir Joshua Reynolds.
In 1792, he was appointed as one of the draughtsmen to the Macartney Embassy to China. He accompanied the Earl of Macartney to Peking where he made drawings for the plates which accompanied Sir George Stauntons account of the embassy (published in 1797) In 1794 he returned to England and married Jane Wogan the following year. She died soon afterwards.
His other principal works were: Views of Headlands, Islands, etc. taken during the Voyage to China (1798); drawings based on Daniells sketches, for Vancouvers Voyage to the North Pacific Ocean (1798); and the descriptive plates to Sir John Barrows Travels in China (1804), and Voyage to Cochin China (1806). In 1805 he published The Costume of China, illustrated by 48 coloured engravings. The work was so well-received that in 1814 he published another book titled Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions.
Besides his works as a draughtsman, he made several engravings - the principal one of which is a representation of the Festival given by the Earl of Romney to the Kentish Volunteers, on 1 August 1799, from his own drawing.
In 1802, Alexander was appointed professor of drawing at the Military College at Great Marlow, resigning in May 1808 to take up the post of assistant keeper of antiquities in the British Museum. In the years 1810, 1812, and 1815, he made drawings of the terra cottas and marbles in the Museum which were engraved and published in three volumes - the accompanying text being provided by Taylor Combe (keeper of the Department of Antiquities). Alexander had completed drawings for a fourth volume before his death.
He died at the house of his uncle in Maidstone in July 1816, and was buried in Boxley churchyard. He was described in one of his obituaries as a man of mild and unassuming manners, rich in the knowledge of art, and of unsullied integrity.
1814 William Alexander Antique Print of Chinese Mandarin Servant on Horseback
- Title : China - Plate 18....Published Jan. 1814 by J Murray, Albenarle Street (Plate XVIII A Mandarins Servant on Horseback)
- Date : 1814
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25461
- Size: 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Mandarins servant on horseback by William Alexander was published in the 1st 1814 - dated - edition of Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7in (240mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1792, Alexander was appointed as one of the draughtsmen to the Macartney Embassy to China. He accompanied the Earl of Macartney to Peking where he made drawings for the plates which accompanied Sir George Stauntons account of the embassy, published in 1797.
In 1805 he published The Costume of China, illustrated by 48 coloured engravings, after his travels to China with The Earl of Macartney. The work was so well-received that in 1814 he published another book titled Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions. This publication was re-issued over the next twenty years in various languages including French.
Alexander, William 1767 – 1816
Alexander was an English painter, illustrator and engraver. The hallmarks of his work, usually executed in watercolours, were clearness and harmony of colour, simplicity and taste in composition, grace of outline, and delicacy of execution. He accompanied the Macartney Embassy to China in 1792. Prints of his work were reproduced from engravings. One his of works was used to illustrate Cadell & Davies Britannia depicta.
Alexander was born in Maidstone, Kent, the son of Harry Alexander, a coachmaker. He was educated at Maidstone Grammar School, but in 1782, at the age of 15, moved to London to study art - first under William Pars, and subsequently Julius Caesar Ibbetson. In February 1784, he was admitted to the Royal Academy Schools. He assiduously applied himself to the mastery of his profession, obtaining the notice and approbation of Sir Joshua Reynolds.
In 1792, he was appointed as one of the draughtsmen to the Macartney Embassy to China. He accompanied the Earl of Macartney to Peking where he made drawings for the plates which accompanied Sir George Stauntons account of the embassy (published in 1797) In 1794 he returned to England and married Jane Wogan the following year. She died soon afterwards.
His other principal works were: Views of Headlands, Islands, etc. taken during the Voyage to China (1798); drawings based on Daniells sketches, for Vancouvers Voyage to the North Pacific Ocean (1798); and the descriptive plates to Sir John Barrows Travels in China (1804), and Voyage to Cochin China (1806). In 1805 he published The Costume of China, illustrated by 48 coloured engravings. The work was so well-received that in 1814 he published another book titled Picturesque Representations of the Dress and Manners of the Chinese, illustrated in fifty colored engravings, with descriptions.
Besides his works as a draughtsman, he made several engravings - the principal one of which is a representation of the Festival given by the Earl of Romney to the Kentish Volunteers, on 1 August 1799, from his own drawing.
In 1802, Alexander was appointed professor of drawing at the Military College at Great Marlow, resigning in May 1808 to take up the post of assistant keeper of antiquities in the British Museum. In the years 1810, 1812, and 1815, he made drawings of the terra cottas and marbles in the Museum which were engraved and published in three volumes - the accompanying text being provided by Taylor Combe (keeper of the Department of Antiquities). Alexander had completed drawings for a fourth volume before his death.
He died at the house of his uncle in Maidstone in July 1816, and was buried in Boxley churchyard. He was described in one of his obituaries as a man of mild and unassuming manners, rich in the knowledge of art, and of unsullied integrity.
1815 Swoboda & Hartl Antique Early Map of New Holland Australia, Ulimaroa Scarce
Antique Map
- Title : Generalcharte von Australien nach dem entwurfe des H.Joseph Marx Freiherrn v. Liechtenstern
- Date : 1815
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 16258
- Size: 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original & scarce antique map of New Holland also named Ulimaroa, New Zealand and the South Pacific by Franz Swoboda and Martin Hartl was published in Vienna in 1815 - dated.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Paper size: - 27in x 20 3/4in (685mm x 525mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (7mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Vertical crease right image
Verso: - None
This map is typical of the affect of Cooks discoveries on European cartography. Australia regularly became a focus on regional maps. The name "Ulimaroa" was often used, mainly by German & Austrian cartographers, at this time. It was term Cook learned from the New Zealand Maoris before discovering the east coast of Australia during his first voyage of discovery. When this map was printed there was a strong belief that the Australian continent was possibly divided by an internal sea strait, separating the east from the west coasts. It was explorers such as Flinders and Baudin who set out to find this elusive passage and if so the possible point at which a ship could enter.
Only a few years before in 1798 Flinders and Bass had proved that there was a strait dividing Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) from the rest of the continent so now the race was on to find the other passage. On Swoboda’s map a line has been drawn from the bottom of Carpentaria to the eastern part of present day Victoria. This line represented two things, the potential shape of the eastern landmass split by the sea and the extent to English territory in the newly settled colonies, only 17 years old. The Southern Coastline is not shown as even though Flinders had by 1803 mapped the entire region he was in 1805 still under house arrest on the islands of Mauritius by the French, he would not publish his discoveries until 1814. Therefore this map shows Australia at a pivotal point in its history when most of the continent was still open for settlement by other nations and the coastlines and mysteries were still to be confirmed. (Ref: Clancy; M&B; Tooley)
1816 John Thompson Large Antique Map Grenada, Tobago, Curacao Trinidad Caribbean
Antique Map
- Title : West India Islands: Grenada; Tobago; Curacao; Trinadad.
- Date : 1816
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35612
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands Grenada, Tobago, Curacao & Trinidad was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
1816 John Thomson Large Antique Map of Southern India & Northern Sri Lanka
- Title : Southern Hindostan....Drawn & Engraved for Thomsons New General Atlas, 1816
- Date : 1816
- Size: 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 41004
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of South India & northern Sri Lanka by John Thomson was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1816 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons New General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin soiling and cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The cartography of India begins with early charts for navigation and constructional plans for buildings. Indian traditions influenced Tibetan and Islamic traditions, and in turn, were influenced by the British cartographers who solidified modern concepts into India\'s map making
A prominent foreign geographer and cartographer was Hellenistic geographer Ptolemy (90–168) who researched at the library in Alexandria to produce a detailed eight-volume record of world geography. During the Middle Ages, India sees some exploration by Chinese and Muslim geographers, while European maps of India remain very sketchy. A prominent medieval cartographer was Persian geographer Abu Rayhan Biruni (973–1048) who visited India and studied the country\'s geography extensively.
European maps become more accurate with the Age of Exploration and Portuguese India from the 16th century. The first modern maps were produced by Survey of India, established in 1767 by the British East India Company. Survey of India remains in continued existence as the official mapping authority of the Republic of India.
1817 Capt. Frederick L Norden Antique Atlas of Egypt & Nubia - 1 Map & 22 Prints
- Title : Atlas de Norden...Chez M.Me Lepetit...1817
- Ref #: 91614
- Size: 8vo
- Date : 1817
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original antique Atlas, Voyage d'Egypte et de Nubie, travels to Egypt and Nubia by the Dane, Captain Frederick Louis Norden was translated and published in Paris by M Henry & Breton in the 1817 - dated - edition of Biblio Portative Des Voyages Traduite De L Anglais Par MM. Henry et Breton Tome XIII (Portable Travel Library. Translated from the English by MM Henry and Breton Volume 13)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy, stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Atlas size: - 8vo
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
The atlas covers have been removed with front title page partially detached & damaged. Pages are generally clean, with some age toning, overall VG. Size 8vo, each page size is 7in x 5in (180mm x 125mm)
1. Cours du Nil Depuis le Sennaar
2. Vue de Ville d Alexandrie....
3. Vue de la Ville et du Port Neuf d Alexandrie....
4. Vue de la Vieille Alexandrie
5. A: Chateau d Aboukir B: Vue de cote de l Orient meridional C: Plan du Chateau vec son port
6. Fig1: Vue de la villede Rosette Fig 2: Chateau de Rosette Fig 3: Vue du village de Deruth
7. Perspective du Vieux Caire
8. Vue du vieux Caire et d'une Pyramide dans le lointain
9. Vue de la ville de Gize ci-devant Memphis....
10. Coupe du Mokian
11. Plan de l ile de Rodda
12. Village de Dair Etun
13. Vue des Pyramides proche du Caire
14. Vue des Pyramides de Memphis
15. Maisons ordinaires des Arabec
16. Ruines di Palais de Memmon
17. Portail antique plien de Hieroglyphes en couleur et ...
18. Ancien Temple au milieu de la ville d Esnay
19. Deux coupes sur la longueur des superbes..Ruines du temple d Tsia
20. Fig 1: Les Deux Colosses en particular Fig 2: Portail principal des antiquities de Luxor
21. Statues colossales et Ruines du Palais de Memnon
22. Vue des Tombeaux pres d Essouan
23. Maniere de Battre les ris et de porter lEau en Egypte
Frederick Norden sailed to Egypt in 1737-38 to survey the architecture, agriculture, and other curiosities of the country. He was the first European to penetrate as far as Derr in Nubia, and produced the first coherent maps of the country. Seventeen years later, long after Norden’s death, his maps and drawings were published by the Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters, under order of Frederick V of Denmark, as Voyage d’Egypte et de Nubie (1755). Two years later, the physician and naturalist Peter Templeman completed an English translation, which was published in two folio volumes.
Frederic Louis Norden (1708 –1742) was a Danish naval captain and explorer.
Also known as Frederick, Frederik, Friderick, Ludwig, Ludvig and Lewis, the name used on the first publication of his famous Voyage d'Egypte et de Nubie (Copenhagen, 1755) is Frederic Louis Norden. His name is often shortened F. L. Norden.
Norden made a voyage through Egypt all the way down to Sudan in 1737–1738, on the request of King Christian VI of Denmark. Norden made abundant notes, observations and drawings of everything around him, including people, pharaonic monuments, architecture, installations, maps etc., all of which was published in the posthumous Voyage d'Egypte et de Nubie.
On 8 January 1741 he became a Fellow of the Royal Society of London, where his name was registered as Frederic Lewis Norden.
1817 John Barrow Original Antique Atlas of Travels in China in 1797 - 21 Prints
- Title : Bibliotheque Portative Des Voyages Traduite De L Anglais Par MM. Henry et Breton Tome XLII - Atlas De Barrow - Paris Chez M.Me V Lepetit....1817
- Date : 1817
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 91572
- Size: 8vo
Description:
This original antique Atlas of the travels of Sir John Barrow in China, who accompanied Ambassador Lord Macartney during his travels in 1797, contains 21 coloured and B&W copper-plate engraved antique prints - was translated and published in Paris by M Henry & Breton in the 1817 - dated - edition of <i>Biblio Portative Des Voyages Traduite De L Anglais Par MM. Henry et Breton Tome XLII</i> (Portable Travel Library. Translated from the English by MM Henry and Breton Volume 42)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 7in x 5in (180mm x 125mm)
Plate size: - 7in x 5in (180mm x 125mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
The atlas covers have been removed with front title page - partially detached. The pages are generally clean with light aging to borders, overall VG, 8vo, each page size is 7in x 5in (180mm x 125mm)
This atlas contains 21 coloured & B&W copper-plate engraved prints, listed below.
1. Portrait de Van-ta-gin
2. Jonque pour les Voyages de long cours (Chinese Junks)
3. Chinois et Hottentot
4. Brouette a Voile (Wheelbarrow with sail)
5. Porte de Pakin
6. Palias de Yuen-min-Yuen
7. Parc oriental de Ge-hol
8. Jardins du Palais Imperial a Pekin
9. Caracteres Chinois & Medailles (Chinese Writing Characters & Money)
10. Artillerie, Mousquets &c. (Chinese Weapons)
11. Artillerie
13. Cloche de Pekin Gongs Cymbals &c.
14. Tcha ou Cangue, Exposition (Punishment of Prisoners)
15. Armes offensives & defensives (Chinese Weapons)
16. Ta ou Pagode (Chinese Pagoda)
17. Dame Chinoise avec son fils (Chinese Mother & Son)
18. Palais d un Mandarin
19. Village et Paysans (Village & Peasants)
20. Bateau passant sur un glacis (boats on a slipway)
21. Moulin a Riz (Rice thrasher)
Sir John Barrow (1764-1848),“Barrow'sTravels in China. an Investigation Into the Origin and Authenticity in "Travels in China, by J. Barrow" Preceded by a Inquiry Into the Nature of the "Powerful Motive" and Influence on His Duties at the Chinese Capital, in 1793”.
Barrow an English statesman, was born in the village of Dragley Beck in the parish of Ulverston in Lancashire, on the ,9th of June 1764. He started in life as superintending clerk of an iron foundry at Liverpool and afterwards taught mathematics at a school in Greenwich. Through the interest of Sir George Staunton, to whose son he taught mathematics, he was attached on the first British embassy to China as comptroller of the household to Lord Macartney. He soon acquired a good knowledge of the Chinese language, on which he subsequently contributed interesting articles to theQuarterly Review; and the account of the embassy published by Sir George Staunton records many of Barrow's valuable contributions to literature and science connected with China.
Although Barrow ceased to be officially connected with Chinese affairs after the return of the embassy in 1794, he always took much interest in them, and on critical occasions was frequently consulted by the British government. In 1797 he accompanied Lord Macartney, as private secretary, in his important and delicate mission to settle the government of the newly acquired colony of the Cape of Good Hope. Barrow was entrusted with the task of reconciling the Boers and Kaffirs and of reporting on the country in the interior. On his return from his journey, in the course of which he visited all parts of the colony, he was appointed auditor-general of public accounts. He now decided to settle in South Africa, married Anne Maria Triiter, and in 1800 bought a house in Cape Town. But the surrender of the colony at the peace of Amiens (1802) upset this plan. He returned to England in 1804, was appointed by Lord Melville second secretary to the admiralty, a post which he held for forty years. He enjoyed the esteem and confidence of all the eleven chief lords who successively presided at the admiralty board during that period, and more especially of King William IV. while lord high admiral, who honoured him with tokens of his personal regard. Barrow was a fellow of the Royal Society, and in 1821 received the degree of LL.D. from Edinburgh University. A baronetcy was conferred on him by Sir Robert Peel in 1835. He retired from public life in 1845 and devoted himself to writing a history of the modern Arctic voyages of discovery (1846), of which he was a great promoter, as well as his autobiography, published in 1847. He died suddenly on the 23rd of November 1848.
Besides the numerous articles in theQuarterly Review already mentioned, Barrow published among other works, Travels in China (1804); Travels into the Interior of South Africa (1806); and lives of Lord Macartney (1807), Lord Anson (1839), Lord Howe (1838). He was also the author of several valuable contributions to the seventh edition of the Encyclopaedia Britannica. Seememoir of John Barlow, by G. F. Staunton (1852). (Ref Clancy; Tooley; M&B)
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Is. St Christopher St Lucia Nevis
Antique Map
- Title : West India Islands: St Christopher; St Lucia; Nevis
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35609
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Islands of Martinique & Dominica
Antique Map
- Title : West India Islands: Martinico (Cul de Sac Royal); Dominica
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35606
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands of Martinique and Dominica was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Age toning