Products
1835 Joseph Meyer Antique Print Early View of The Rocks Sydney, Australia
- Title : Sydney in New South Wales
- Ref #: 50668
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1835
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine steel-plate engraved original antique print an early view of The Rocks in Sydney Australia by Joseph Meyer was published in the 1835 edition of Meyers Universum
These are beautiful steel-plate engraved prints, with a high level of detail along with beautifully executed artistry.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australia\'s largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance. The city has played host to many international events, including the 2000 Summer Olympics.
Meyer, Joseph 1796 - 1856
Meyer was a German industrialist and publisher, most noted for his encyclopedia, Meyers Konversations-Lexikon.
Meyer was born at Gotha, Germany, and was educated as a merchant in Frankfurt am Main. He went to London in 1816, but returned to Germany in 1820 after business adventures and stock speculations fell through. Here he invested in enterprises like textile-trade (1820–24). Soon after the first steam-hauled railway had started in December 1835, Meyer started to make business plans how to start the first railways. He also bought some concessions for iron mining. In 1845, he founded the Deutsche Eisenbahnschienen-Compagnie auf Actien (German Railway Rail joint stock company).
Meyer operated very successfully as a publisher, employing a system of serial subscription to publications, which was new at that time. To this end he founded a company, Bibliographisches Institut, in Gotha in 1826. It published several editions of the Bible, works of classical literature (Miniatur-Bibliothek der deutschen Classiker, Groschen-Bibliothek), atlases, the world in pictures on steel engravings Meyers Universum, 1833–61, 17 volumes in 12 languages with 80,000 subscribers all over Europe), and an encyclopaedia, (das Grosse Conversations-Lexikon für die gebildeten Stände;). His company grew substantially, and in 1828 he moved it from Gotha to Hildburghausen, where he died thirty years later.
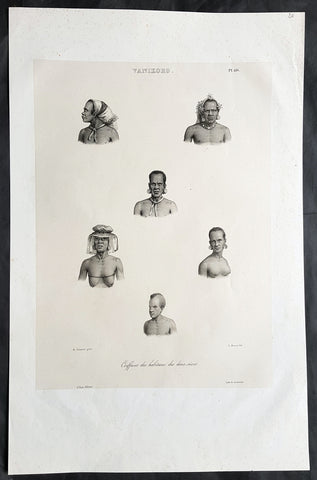
1836 D Urville & Sainson Antique Print Men & Women of Vanikoro Isle, Solomon Is.
- Title : Vanikoro. Coiffures des habitans des deux sexes
- Size: 20 1/2in x 13 1/2in (520mm x 345mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1836
- Ref #: 31751
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of hair styles of the men & woman of the island of Vanikoro, part of the Solomon Islands in the south Pacific (and last resting place of the ill fated La Perouse expedition), by Louis Auguste de Sainson, artist on the Astrolabe, during the first of Dumont D Urvilles voyages to the South Seas, between 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Antoine Maurin 1793 - 1860 and published in the 1836 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Louis Auguste de Sainson, (1800-1848). Sainson was a French draftsman & artist who specialized in natural history and geography. He accompanied the expedition of the corvette L Astrolabe as a naturalist directed by Jules Dumont d\'Urville between 1826-1829.
He began his naval career in a secretarial position at the French Atlantic port of Rochefort, working there from 1825 till 1826. He then volunteered to join the Astrolabe as a draughtsman, after being recommended to the expedition by Quoy, one of the naturalists on the expedition, joining the ship at Toulon on 7 February 1826.
He was responsible for the bulk of the drawings produced during the expedition, with over 500 in three years. Many of his drawings paintings and prints now reside in Australian, New Zealand & French museums.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 13 1/2in (520mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 13 1/2in (520mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Vanikoro (sometimes wrongly named Vanikolo) is an island in the Santa Cruz group, located 118 kilometres to the Southeast of the main Santa Cruz group. It is part of the Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands.
The first sighting of Vanikoro by Europeans was in September 1595, by the second Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mendaña. It was sighted by Lorenzo Barreto, while in command of one of the smaller vessels on a voyage around the then Santa Cruz, which is today\'s Nendo Island.
The French explorer Jean-François de La Pérouse was stranded on Vanikoro after both his vessels, La Boussole and the Astrolabe, struck the then unknown reefs of the island in 1788. It is reported that some of the men were killed by the local inhabitants, while the surviving sailors built a smaller vessel and left the island, but were never seen again. Those that remained on the island died before search parties of Dumont D Urville arrived in 1826.
1836 D Urville & Sainson Antique Print of Vanikoro & Tikopia Islands, Solomon Isands
- Title : Tikopia et Vanikoro: Costumes des habitans de Vanikoro: Costumes des habitans de Tikopia
- Size: 19 1/2in x 13in (495mm x 330mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1836
- Ref #: 31735
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of the peoples of the island of Vanikoro & Tikopia, part of the Solomon Islands in the south Pacific (and last resting place of the ill fated La Perouse expedition), by Louis Auguste de Sainson, artist on the Astrolabe, during the first of Dumont D Urvilles voyages to the South Seas, between 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Antoine Maurin 1793 - 1860 and published in the 1836 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Louis Auguste de Sainson, (1800-1848). Sainson was a French draftsman & artist who specialized in natural history and geography. He accompanied the expedition of the corvette L Astrolabe as a naturalist directed by Jules Dumont d\'Urville between 1826-1829.
He began his naval career in a secretarial position at the French Atlantic port of Rochefort, working there from 1825 till 1826. He then volunteered to join the Astrolabe as a draughtsman, after being recommended to the expedition by Quoy, one of the naturalists on the expedition, joining the ship at Toulon on 7 February 1826.
He was responsible for the bulk of the drawings produced during the expedition, with over 500 in three years. Many of his drawings paintings and prints now reside in Australian, New Zealand & French museums.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 13in (495mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 13in (495mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Vanikoro (sometimes wrongly named Vanikolo) is an island in the Santa Cruz group, located 118 kilometres to the Southeast of the main Santa Cruz group. It is part of the Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands.
The first sighting of Vanikoro by Europeans was in September 1595, by the second Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mendaña. It was sighted by Lorenzo Barreto, while in command of one of the smaller vessels on a voyage around the then Santa Cruz, which is today\'s Nendo Island.
The French explorer Jean-François de La Pérouse was stranded on Vanikoro after both his vessels, La Boussole and the Astrolabe, struck the then unknown reefs of the island in 1788. It is reported that some of the men were killed by the local inhabitants, while the surviving sailors built a smaller vessel and left the island, but were never seen again. Those that remained on the island died before search parties of Dumont D Urville arrived in 1826.
Tikopia is a small high island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Solomon Islands of Melanesia, but is culturally Polynesian. The first Europeans arrived on 22 April 1606 as part of the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernandes de Queirós.
In 1964, explorers found artefacts from the shipwreck of the expedition of Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse.
1836 Dumont D Urville Large Antique Print Monument to La Perouse Solomon Islands
- Title : Inauguration du Monument
- Size: 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1836
- Ref #: 31734-1
Description:
This large original antique lithograph print of Dumont D Urville Inauguration of a monument to Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse on the island of Vanikoro, part of the Solomon Islands in the south Pacific (the last resting place of La Perouse & his crew), by Louis Auguste de Sainson, the artist on the Astrolabe, during the first of Dumont D Urvilles first voyage to the South Seas between 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Antoine Maurin 1793 - 1860 and published in the 1836 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Louis Auguste de Sainson, (1800-1848). Sainson was a French draftsman & artist who specialized in natural history and geography. He accompanied the expedition of the corvette L Astrolabe as a naturalist directed by Jules Dumont d\\\'Urville between 1826-1829.
He began his naval career in a secretarial position at the French Atlantic port of Rochefort, working there from 1825 till 1826. He then volunteered to join the Astrolabe as a draughtsman, after being recommended to the expedition by Quoy, one of the naturalists on the expedition, joining the ship at Toulon on 7 February 1826.
He was responsible for the bulk of the drawings produced during the expedition, with over 500 in three years. Many of his drawings paintings and prints now reside in Australian, New Zealand & French museums.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Re-join to bottom margin
Plate area: - 9in & 2in re-join to bottom to centre of image
Verso: - Repair as noted, light spotting
Background:
Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse (1741 – 1788) was a French Naval officer and explorer whose expedition vanished in Oceania.
Lapérouse was appointed in 1785 by Louis XVI and by the Secretary of State of the Navy, the Marquis de Castries, to lead an expedition around the world. Many countries were initiating voyages of scientific explorations at that time.
The expeditions aims were to complete the Pacific discoveries of James Cook (whom Lapérouse greatly admired), correct and complete maps of the area, establish trade contacts, open new maritime routes and enrich French science and scientific collections. His ships were LAstrolabe (under Fleuriot de Langle) and La Boussole, both 500 tons. They were storeships reclassified as frigates for the occasion. Their objectives were geographic, scientific, ethnological, economic (looking for opportunities for whaling or fur trading), and political (the eventual establishment of French bases or colonial cooperation with their Spanish allies in the Philippines). They were to explore both the north and south Pacific, including the coasts of the Far East and of Australia, and send back reports through existing European outposts in the Pacific.
La Perouse visited Australia, arriving off Botany Bay on 24 January 1788. There Lapérouse encountered a British convoy (known later as the First Fleet) led by Captain Arthur Phillip RN, who was to establish the penal colony of New South Wales. While it had been intended that the colony would be located at Botany Bay, Phillip had quickly decided that the site was unsuitable and the colony would instead be established at Sydney Cove in Port Jackson. High winds – which had hindered Lapérouses ships in entering Botany Bay – delayed the relocation until 26 January (later commemorated as Australia Day).
The French were received courteously and spent six weeks at the British colony (their last recorded landfall). While Lapérouse and Phillip did not meet, French and British officers visited each other formally on at least 11 occasions, and offered each other assistance and supplies. During their stay, the French established an observatory and a garden, held masses, and made geological observations. Lapérouse also took the opportunity to send journals, charts and letters back to Europe, with the British merchant ship Alexander. The chaplain from L Astrolabe, Father Louis Receveur, never recovered from injuries he had sustained in a clash with indigenous people in the Samoan Islands and died at Botany Bay on 17 February; Receveur was buried on shore at Frenchmans Cove.
On 10 March, after taking on sufficient wood and fresh water, the French expedition left New South Wales – bound for New Caledonia, Santa Cruz, the Solomons, the Louisiades, and the western and southern coasts of Australia. While Lapérouse had reported in a letter from Port Jackson that he expected to be back in France by June 1789, neither he nor any members of his expedition were seen again by Europeans.
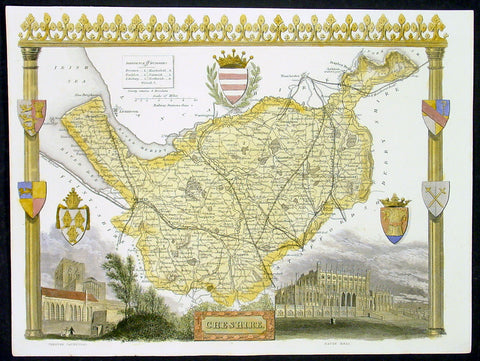
1836 Moule Antique Map The English County of Cheshire
- Title : Cheshire
- Date : 1836
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92439
- Size: 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Description:
This finely engraved original beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the English county of Cheshire by Thomas Moule was published in the 1836 edition of Barclays Dictionary. Moules maps were some of the the last original decorative maps published in the 19th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
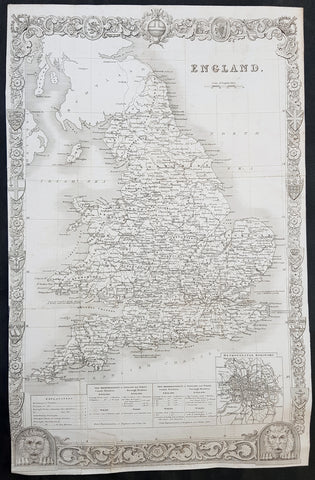
1836 Thomas Moule Large Original Antique Map of England & Wales
- Title : England
- Size: 17in x 11in (430mm x 280mm)
- Ref #: 31112
- Date : 1836
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique map of England was engraved for the 1836 edition of Thomas Moules English Counties Delineatedby W. Schmollinger.
Inset plan of Metorpolitan Boroughs of London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (430mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 11in (430mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - Folds as issued, repair to bottom border & left bottom fold
Verso: - Re-enforced along folds
Background:
When considering the work of English map makers we tend, perhaps, to think too much in terms of county maps, dominated by the names of Saxton and Speed, but we should not underrate the contribution to the sum of geographical knowledge made in other spheres, such as the sea charts of Edward Wright, Robert Dudley and Greenvile Collins, the discoveries of James Cook, the road maps of Ogilby and Cary, the meteorological and magnetic charts compiled by Edmund Halley, to mention only a few.
In 1558 Queen Elizabeth came to the throne in the midst of a fast changing world. In 1563 a nineteen sheet map, copies of which survive only in manuscript form, was completed by Laurence Nowell, and no doubt, the issue of Mercator\'s large-scale map of the British Isles in 1564 had an important influence on the thought of the period. A few years later a national survey was commissioned privately, although probably at the instigation of Lord Burghley, the Lord Treasurer, but subsequently was completed with royal encouragement. The outcome was Christopher Saxton\'s Atlas of EngIand and Wales, started about 1570 and published in 1579 - the first printed set of county maps and the first countrywide atlas on such a splendid scale produced anywhere. A Welsh antiquarian, Humphrey Lhuyd completed a set of surveys that were even more successful than Saxton in which he had produced fine manuscript maps of England and Wales which were used by Ortelius in editions of his Atlas from 1573 onwards.
The earliest maps of the 17th century, attributed to William Smith of the College of Heralds, covered only twelve counties based on Saxton/Norden and were presumably intended to be part of a complete new atlas. They were printed in the Low Countries in 1602-3 and were soon followed by maps for the Latin edition of Camden\'s Britannia dated 1607. In 1610-11 the first edition of John Speed\'s famous county Atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published and immediately replaced Saxton\'s in popular appeal. Although Speed assembled much of his material from the earlier works of Saxton, Norden and others, a considerable part of the up-to-date information, especially relating to the inset town plans depicted on his maps, was obtained first hand. The maps undoubtedly owed much of their popularity to the splendid engravings of high quality made in the workshops in Amsterdam of Jodocus Hondius to whom Speed sent his manuscripts, the plates subsequently being returned to London for printing.
In 1645, Volume IV of the famous Blaeu World Atlas covering the counties of England and Wales was published in Amsterdam. These maps have always been esteemed as superb examples of engraving and design, the calligraphy being particularly splendid, but nevertheless they were nearly all based on Saxton and Speed and added little to geographical knowledge.
Not until the latter part of the century do we find an English map maker of originality with the capacity to put new ideas into practice. John Ogilby, one of the more colourful figures associated with cartography, started life as a dancing master and finished as King\'s Cosmographer and Geographic Printer. After publishing a small number of county maps, somewhat on the lines of John Norden he issued in 1675 the Britannia, the first practical series of detailed maps of the post roads of England and Wales on a standard scale of 1,760 yards to the mile. Up to the end of the century and beyond, reprints and revisions of Saxton\'s and Speed\'s atlases continued to appear and the only other noteworthy county maps were Richard Blome\'s Britannia (1673), John Overton\'s Atlas (c. 1670) and Robert Morden\'s maps for an English translation of Camden\'s Britannia published in 1695.
Another noted cartographer of the day was Captain Greenvile Collins, and of his work in surveying the coasts of Great Britain culminating in the issue in 1693 of the Great Britain\'s Coasting Pilot. Apart from these charts, English cartographers published during the century a number of world atlases. Speed was the first Englishman to produce a world atlas with the issue in 1627 of his A Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World. Other atlases appeared later in the century by Peter Heylin, John Seller, William Berry, Moses Pitt and Richard Blome, whilst Ogilby found time to issue maps of Africa, America and Asia. Far more important, from the purely scientific point of view, was the work of Edmund Halley, Astronomer Royal, who compiled and issued meteorological and magnetic charts in 1688 and 1701 respectively.
At the beginning of the eighteenth century the Dutch map trade was finally in decline, the French in the ascendant and the English to a great extent still dominated by Saxton and Speed except, as we have shown, in the spheres of sea charts and road maps. There were atlases by John Senex, the Bowles family, Emanuel and Thomas Bowen, Thomas Badeslade and the unique bird\'s-eye perspective views of the counties, The British Monarchy by George Bickham. In 1750-60 Bowen and Kitchin\'s The Large English Atlas containing maps on a rather larger scale than hitherto was published.
In 1759 the Society for the encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce offered an award of £100 for the best original surveys on this scale and by the end of the century about thirty counties had been re-surveyed. These maps, many of which formed, in later years, the basis for the first issues of county maps by the Ordnance Survey Office were not only decorative but a tremendous improvement geographically on earlier local maps. As a consequence, the skills and expertise of the new-style cartographers soon enabled them to cover the world as well as the domestic market. Thomas Jefferys was such a man; he was responsible for a number of the new 1 in. to 1 mile county surveys and he issued an edition of Saxton\'s much battered 200-year-old plates of the county maps, but he is better known for many fine maps of North America and the West Indies. His work was continued on the same lines by William Faden, trading as Faden and Jefferys. Other publishers such as Sayer and Bennett and their successors Laurie and Whittle published a prodigious range of maps, charts and atlases in the second half of the century. A major influence at this time was John Cary who, apart from organizing the first re-survey of post roads since Ogilby and subsequently printing the noted Travellers\' Companion, was a prolific publisher of atlases and maps of every kind of all parts of the world. After starting work with Cary, and taking part in the new road survey, Aaron Arrowsmith set up in his own business and went on to issue splendid large-scale maps of many parts of the world. Both Cary\'s and Arrowsmith\'s plates were used by other publishers until far into the next century and, in turn, their work was taken up and developed by James Wyld (Elder and Younger) and Tallis and Co.
Later into the 19th century some of the better known cartographers and publishers were by Henry Teesdale (1829-30), Christopher and John Greenwood, surveyors, Thomas Moule, a writer on heraldry and antiques (1830-36) and John Walker (1837) but by about the middle of the century few small-scale publishers survived and their business passed into the hands of large commercial concerns such as Bartholomews of Edinburgh and Philips of London who continue to this day. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
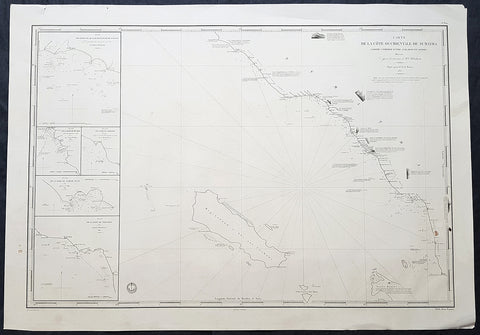
1837 Depot De Marine Large Antique Map Sea Chart of Aceh, Sumatra, Indonesia
- Title : Carte de la Cote Occidentale De Sumatra..1837
- Size: 38in x 26 1/2in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1837
- Ref #: 30142
Description:
This very large highly detailed original antique map, Sea Chart of the South west coast of Aceh on the North-West tip of the Island of Sumatra, Indonesia was engraved in 1837 - the date is engraved in the title - and was published by The French Admiralty - Depot General de la Marine.
At the time of publication Baron Duperre was head of the French Admiralty. This sea chart would have been one of the actual charts used by the French navy during the many voyages of discovery launched by the French in the 18th & 19th centuries.
The map stretches from the town of Singkil on the south coast to the town of Meulaboh in the north. Off the coast is the Island of Simeulue. Inset are 5 inset maps of ports and harbours along the SW Aceh coastline.
1. Qualh-Battoo et De Soosoo (Susu)
2. Baie De Muckie
3. De Labon et Hadje (Labuan)
4. Baie Tampat Tuan (Tapak Tuan)
5. Baie De Troumon (Trumon)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 38in x 26 1/2in (330mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 38in x 26 1/2in (330mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Aceh is a province of Indonesia. The territory is located at the northern end of Sumatra. Its capital is Banda Aceh. It is close to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India and separated from them by the Andaman Sea. Its population has the highest percentage of Muslims in Indonesia, who mostly live according to Sharia customs and laws.
The Sultanate of Aceh was established by Sultan Ali Mughayat Syah in 1511.
In 1584–88 the Bishop of Malacca, D. João Ribeiro Gaio, based on information provided by a former captive called Diogo Gil, wrote the Roteiro das Cousas do Achem (Lisboa 1997) – a description of the Sultanate.
Later, during its golden era, in the 17th century, its territory and political influence expanded as far as Satun in southern Thailand, Johor in Malay Peninsula, and Siak in what is today the province of Riau. As was the case with most non-Javan pre-colonial states, Acehnese power expanded outward by sea rather than inland. As it expanded down the Sumatran coast, its main competitors were Johor and Portuguese Malacca on the other side of the Straits of Malacca. It was this seaborne trade focus that saw Aceh rely on rice imports from north Java rather than develop self sufficiency in rice production.
After the Portuguese occupation of Malacca in 1511, many Islamic traders passing the Malacca Straits shifted their trade to Banda Aceh and increased the Acehnese rulers\' wealth. During the reign of Sultan Iskandar Muda in the 17th century, Aceh\'s influence extended to most of Sumatra and the Malay Peninsula. Aceh allied itself with the Ottoman Empire and the Dutch East India Company in their struggle against the Portuguese and the Johor Sultanate. Acehnese military power waned gradually thereafter, and Aceh ceded its territory of Pariaman in Sumatra to the Dutch in the 18th century.
By the early nineteenth century, however, Aceh had become an increasingly influential power due to its strategic location for controlling regional trade. In the 1820s it was the producer of over half the world\'s supply of black pepper. The pepper trade produced new wealth for the Sultanate and for the rulers of many smaller nearby ports that had been under Aceh\'s control, but were now able to assert more independence. These changes initially threatened Acehs integrity, but a new sultan Tuanku Ibrahim, who controlled the kingdom from 1838 to 1870, reasserted power over nearby ports.
Under the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 the British ceded their colonial possessions on Sumatra to the Dutch. In the treaty, the British described Aceh as one of their possessions, although they had no actual control over the Sultanate. Initially, under the agreement the Dutch agreed to respect Aceh\'s independence. In 1871, however, the British dropped previous opposition to a Dutch invasion of Aceh, possibly to prevent France or the United States from gaining a foothold in the region. Although neither the Dutch nor the British knew the specifics, there had been rumors since the 1850s that Aceh had been in communication with the rulers of France and of the Ottoman Empire
Depot des cartes et plans de la Marine
The Naval Hydrographic and Oceanographic Service is a French public establishment of an administrative nature, administered by the Ministry of Defence. It is the successor to the Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine, founded in 1720 which became the Naval Hydrographic Service in 1886 and the Naval and Oceanographic Service in 1971.
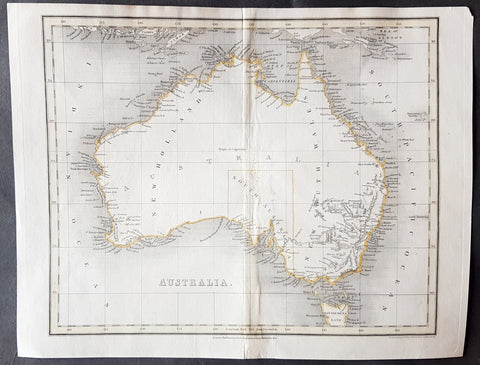
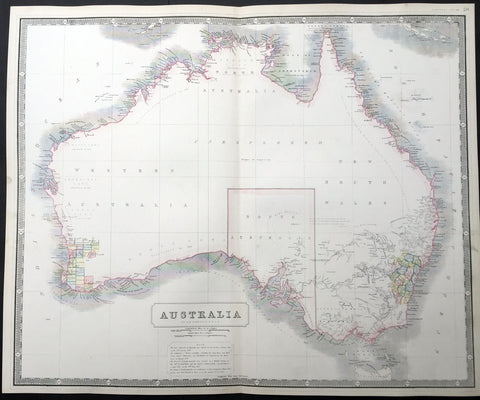
1837 John Dower Original Antique Map of Australia - New Holland
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1837
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 70704
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This fine steel-plate engraved original hand coloured antique map of Australia by John Dower was published by Orr & Smith, London in 1837. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Browning & weak along centerfold
Verso: - Strengthened along centerold
Background:
Interesting early map of Australia with only the state of South Australia delineated. The whole of the east coast is named New South Wales, the city of Melbourne was not noted, few internal details are noted. Western Australia shows significant coastal details but is still named "New Holland"
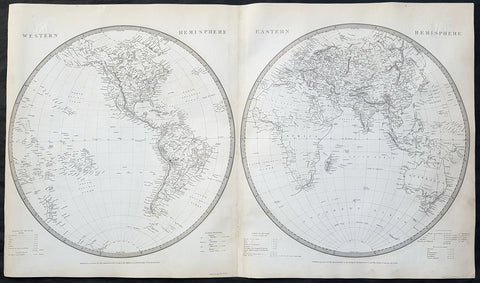
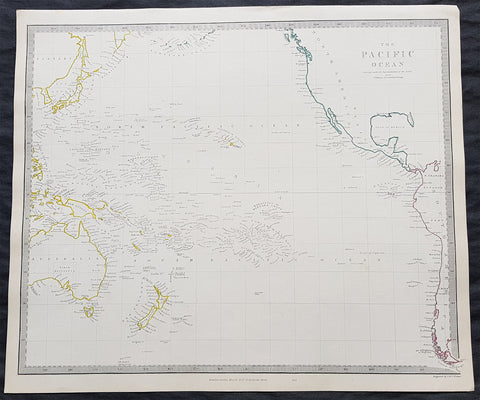
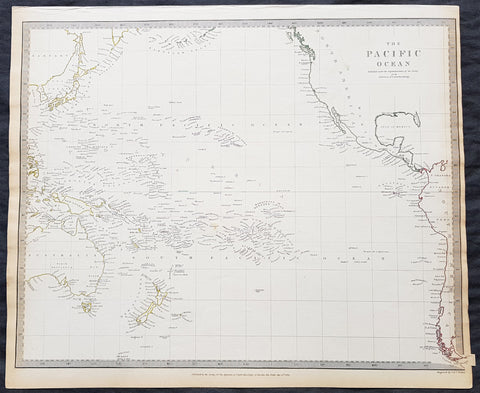
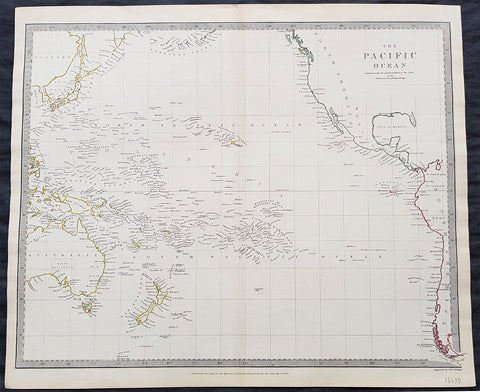
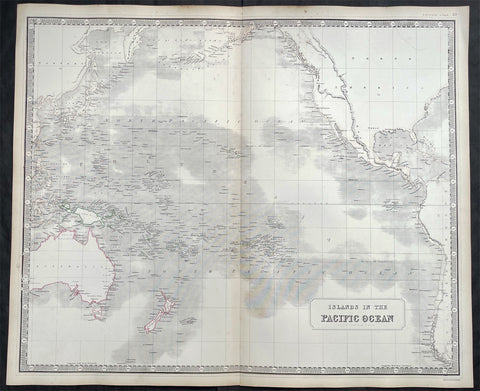
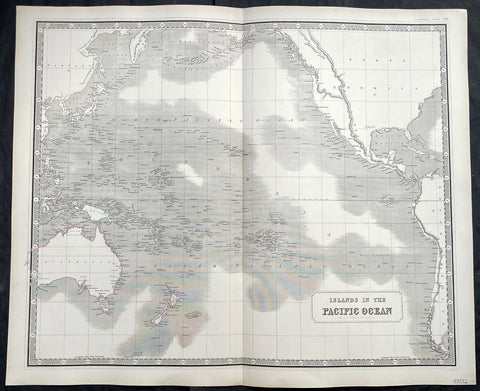
1837 SDUK Large Original Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map
- Title : Western Hemisphere; Eastern Hemisphere
- Date : 1837
- Size: 26 1/2in x 15 1/2in (675mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 32528
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique twin hemisphere world map was engraved by J & C Walker and was published by the SDUK in 1837.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 15 1/2in (675mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 15 1/2in (675mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Blind library stamp
Verso: - Centerfold re-joined
Background:
The map depicts the Western and Eastern Hemispheres offering a fascinating snapshot of the world during a period of rapid globalization and discovery. Both maps note towns, rivers, mountains, deserts, islands, and various other important topographical details. Elevation throughout is rendered by hachure.
The map of the Western Hemisphere covers North America, South America, West Indies and most of Polynesia, including New Zealand. The Antarctic continent, first sighted in 1820, but neglected during the first half of the 19th century, does not appear on the map.
The map of the Eastern Hemisphere includes the entirety of Asia, Europe and Africa as well as Australia and much of the Pacific. The interior of Australia is largely blank though the coastal colonies are noted. These include Mediterranean North Africa, Egypt, Abyssinia, the western Niger valley, the Congo, South Africa, and the lands of Mozambique and Zimbabwe.
This map is part of a Series of Maps, Modern and Ancient, issued by subscription. Each folder in the series would contain a set of two maps bound together. These two maps were issued in folder no. XCII. Original folder includes the names of committee members of the ‘Society’, maps already published, the contents and the printer and publication details. These maps were engraved by J. and C. Walker. This folder was printed by William Clowes and Sons for the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge in their September 30, 1841 subscriber’s edition folder. The folder at the time was priced at 1 shilling plain or 1 shilling 6 pence for colored maps.
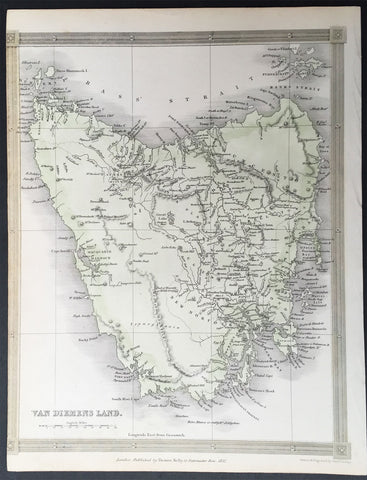
1837 Thomas Kelly Antique Map of Van Diemens Land - Tasmania, Australia
- Title : Van Diemens Land
- Ref #: 91205
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Date : 1837
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine large original detailed antique map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania, Australia was engraved in 1837 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published by Thomas Kelly for Barclays English Dictionary. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
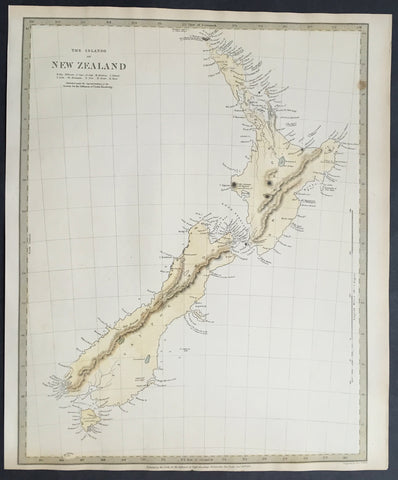
1838 SDUK Large Antique Map of New Zealand - 1st edition
Antique Map
- Title :The Islands of New Zealand....Published by the SDUK...Nov 26th 1838
- Ref #: 61040
- Size: 16in x 13in (400mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1838
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original hand coloured antique map* of New Zealand was engraved in 1838 (1st edition) - dated at the bottom of the map - by J & C W Walker and was published in the Baldwin & Cradock edition of theSociety For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
Background: The map covers the entire island country from Cape Reinga (C. Maria Van Diemen) to Stewart Island. Various cities, towns, rivers, mountains, bays and several other topographical details are noted with relief shown by hachure.
In 1840, after the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, the British annexed New Zealand as part of the Australian colony of New South Wales. However, it separated from New South Wales to become a colony in its own right in 1841. This map was originally copyrighted in 1838, but was issued in Volume two of Chapman and Hall's 1844 edition of Maps of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes in cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford.
This is a finely engraved map with beautiful original colour t on strong, clean paper. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (400mm x 330mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
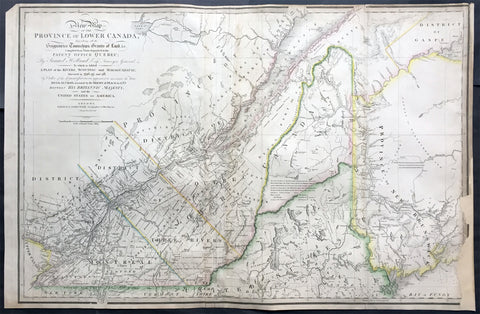
1839 James Wyld Large Antique Map Provinces of Lower Canada, St Lawrence River
Antique Map
- Title : A New Map of the Province of Lower Canada, Describing all the Seigneuries, Townships, Grants of Land, &c. Compiled from Plans deposited in the Patent Office Quebec: by Samuel Holland, Esq. Surveyor General
- Ref #: 50391
- Size: 35 1/4in x 23 1/4in (895mm x 590mm)
- Date : 1839
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This large, rare hand coloured original antique map of the provinces of Lower Canada and The St Lawrence River was engraved in 1839 - dated in title - and was published by James Wyld, Charing Cross, London.
This map has undergone some repairs and is priced accordingly. Currently this map is priced as high as $1500.
Background:
This boldly engraved map extends westward to include Lake St. Francis and the extreme tip of Upper Canada, eastward to part of New Brunswick showing the River St. John and beyond, and south to just below the Canadian border with New York and Vermont. It is filled with towns and settlements and individual named townships, roads and trails. It includes several interesting notations and delineates the "Boundary awarded to the King of Holland." Samuel Holland was originally a Dutch surveyor who fought on the side of the British during the French and Indian Wars and served as Surveyor General for the Province of Quebec and the Northern District of America. An infrequently seen issue.
This updated example of this important map of the Lower Province of Canada, first issued by Faden in 1813, which identifies in manuscript the location of the disputed lands southeast of the St. Lawrence River, the so-called "English Line" and "American Line," which would be the subject of an early boundary dispute between the two countries.
The original Faden map included information concerning over 100 land grants on either side of the St. Lawrence River, including the names of Land Owners. Faden's orginal map showed the surveys conducted in 1796-98 along the Scoudiac and Magaguadavic Rivers, in order to ascertain the true location of the St. Croix River. In the present map, there is significant new information and topographcal details, showing the remarkable advancement in the surveying of the region in the 12 years after the publication of Faden's map of 1813.
This new addition includes the District of Maine, Moosehad Lake, Penobscot River and the Bowding County Township and Bingham's Purchase. Whereas the original Faden map had no topographical detail, the present map is a dramatic improvement.
In addition to the topographical improvements, there is now an annotation in the centre of the map identifying the boundary dispute in the region, relating to the existence of two St. Croix Rivers in the region.
The second article of the Treaty of Peace between the US and Britain included the setting of the boundary between the two nations, "From the northwest angle of Nova Scotia, viz., that angle which is formed by a line drawn due north from the source of St. Croix River to the highlands . . ." It later became apparent that there was more than one St. Croix River. A further treaty provision in 1794 appointed a boundary commission, which determined in 1798 that the intended St. Croix was the Schoodiac River and its northern branch Cheputnaticook. The Treaty of Ghent, concluded on December 24, 1814, agreed to provide for a final adjustment of the boundaries described in the Treaty of 1783 that had not yet been determined, which included the boundary line from the source of the River St. Croix to the most north-western point of the Lake of the Woods.
A further commission was appointed to settle the boundary from the St. Croix to the St. Lawrence. Joseph Bouchette and John Lawrence were hired to conduct the surveys and the reports submitted for resolution to a third nation and ultimately resolved by the Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1842.
The present map shows the two boundary claims at a time when they were not yet fully resolved. (Ref: M&B; Tooley; Clancy)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 35 1/4in x 23 1/4in (895mm x 590mm)
Plate size: - 35 1/4in x 23 1/4in (895mm x 590mm)
Margins: - min. 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling, repair to bottom right margin , border into image
Plate area: Light soiling, creasing along left fold
Verso: - Light soiling, repairs as noted
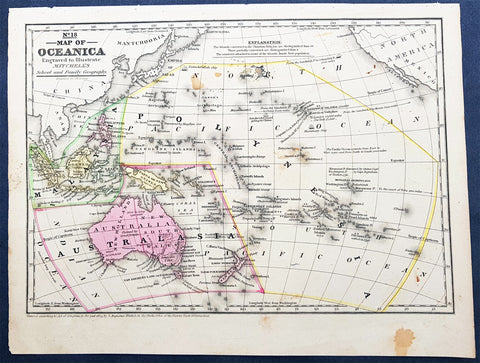
1839 Samuel Augustus Mitchell Antique Map of New Holland, New Zealand & Oceania
- Title : No 18 Map of Oceania...Entered according to Act of Congress in the year 1839 by S Augustus Mitchell
- Date : 1839
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 32148
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Description:
This detailed original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of New Holland - Australia, New Zealand, Polynesia & Micronesia, Oceania by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in 1839 - dated - was published in Mitchells School and Family Geography
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Early map of Australia and Oceania, the east coast is still referred to as NSW, with no sign of development of Melbourne or Victoria with New Zealand listing early Cook & Maori place names.
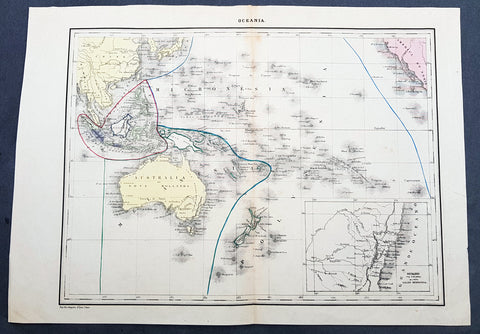
1840 P & A Lapie Antique Map of New Holland, New Zealand & Central Coast of NSW
- Title : Oceania
- Date : 1840
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 21425
- Size: 17in x 12in (430mm x 305mm)
Description:
This detailed original hand coloured lithograph map of Australia, New Zealand, Polynesia & Micronesia - Oceania - with an inset map of part of the coast of Sydney, NSW from Double Bay to Shoal Bay by Pierre & Alexandrie Lapie was published as a single map Kaeppelin & Co. in 1840.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 12in (430mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 12in (430mm x 305mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Early map of Australia and Oceania, the east coast is still referred to as NSW, with no sign of development of Melbourne or Victoria with New Zealand listing early Cook & Maori place names. The inset map of the central NSW coast is still largely lacking in detail past Bathurst, with Australia Felix noted in the south.
Lapie, Pierre & Alexandre
Pierre M. Lapie 1779 - 1850 and his son Alexandre Emile Lapie 1809 - 1850 were French cartographers and engravers active in the early part of the 19th century. The Lapies were commissioned officers in the French army holding the ranks of Colonel and Captain, respectively. Alexander enjoyed the title of First Geographer to the King, and this title appears on several of his atlases. Both father and son were exceptional engravers and fastidious cartographers. Working separately and jointly they published four important atlases, an 1811 Atlas of the French Empire (Alexander), the 1812 Atlas Classique et Universel (Pierre), the Atlas Universel de Geographie Ancienne et Modern (joint issue), and the 1848 Atlas Militaire (Alexander). They also issued many smaller maps and independent issues. All of these are products of exceptional beauty and detail. Despite producing many beautiful maps and atlases, the work of the Lapie family remains largely underappreciated by most modern collectors and map historians. The later 19th century cartographer A. H. Dufour claimed to be a student of Lapie, though it is unclear if he was referring to the father or the son. The work of the Lapie firm, with its precise engraving and informational density, strongly influenced the mid-19th century German commercial map publishers whose maps would eventually dominate the continental market.
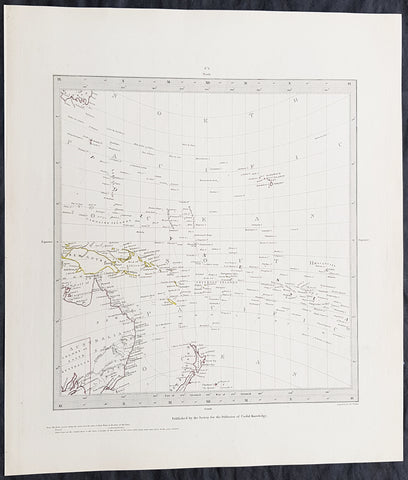
1840 SDUK Antique Gnomonic Map East Australia, New Zealand South Pacific
- Title : Published by the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 24676-1
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique Gnomonic Map of eastern Australia, New Zealand & The South Pacific was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
A gnomonic map projection displays all great circles as straight lines, resulting in any line segment on a gnomonic map showing a geodesic, the shortest route between the segment\'s two endpoints. This is achieved by casting surface points of the sphere onto a tangent plane, each landing where a ray from the center of the sphere passes through the point on the surface and then on to the plane. No distortion occurs at the tangent point, but distortion increases rapidly away from it. Less than half of the sphere can be projected onto a finite map. Consequently a rectilinear photographic lens cannot image more than 180 degrees.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Gnomonic Map East Australia, New Zealand South Pacific
- Title : Published by the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0974
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique Gnomonic Map of eastern Australia, New Zealand & The South Pacific was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
A gnomonic map projection displays all great circles as straight lines, resulting in any line segment on a gnomonic map showing a geodesic, the shortest route between the segment\'s two endpoints. This is achieved by casting surface points of the sphere onto a tangent plane, each landing where a ray from the center of the sphere passes through the point on the surface and then on to the plane. No distortion occurs at the tangent point, but distortion increases rapidly away from it. Less than half of the sphere can be projected onto a finite map. Consequently a rectilinear photographic lens cannot image more than 180 degrees.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
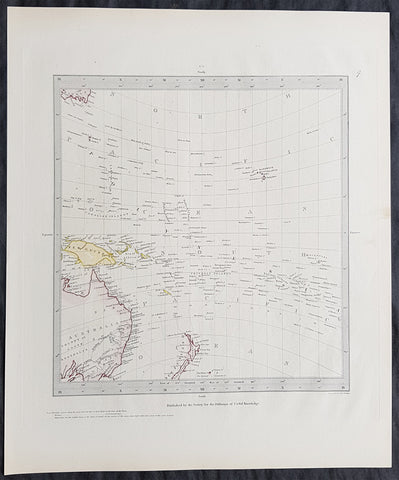
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0944
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
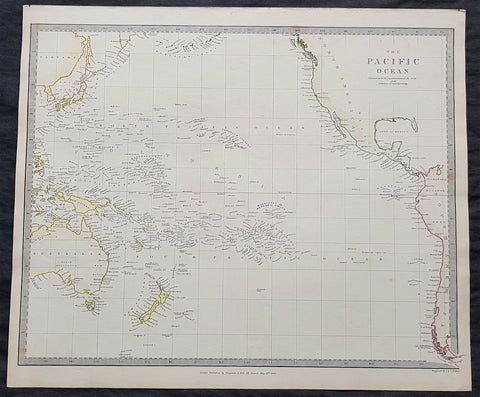
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 24668
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
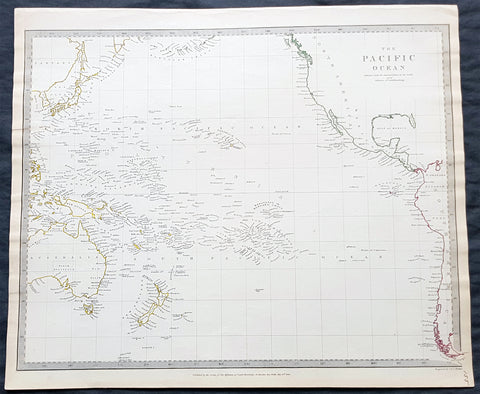
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0954-1
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
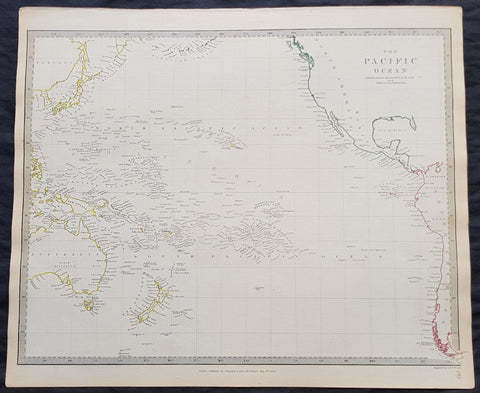
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0964
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 91362
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 31980
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
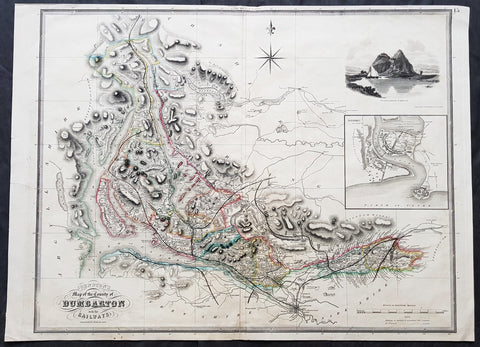
1841 Johnston Large Antique Map The County of Dumbarton, Dunbartonshire Scotland
- Title : 1841 Johnston Large Antique Map The County of Dumbarton, Dunbartonshire Scotland
- Size: 29in x 21in (740mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1841
- Ref #: 70481
Description:
This large original hand coloured steel-plate engraved antique map of the Scottish region of Dumbarton in the county of Dunbartonshire centering on Glasgow and the river Clyde - with an inset image of Dumbarton Castle and another of Dumbarton Town - was published by W & A.K. Johnston in 1841.
The map centers on Loch Lomond, the River Clyde and the city of Glasgow.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 21in (740mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling, several small repairs to margins into border, no loss
Plate area: - Light soiling, centerfold re-joined
Verso: - Soiling, repairs as noted
Background:
Dunbartonshire or the County of Dumbarton is a historic county, lieutenancy area and registration county in the west central Lowlands of Scotland lying to the north of the River Clyde.
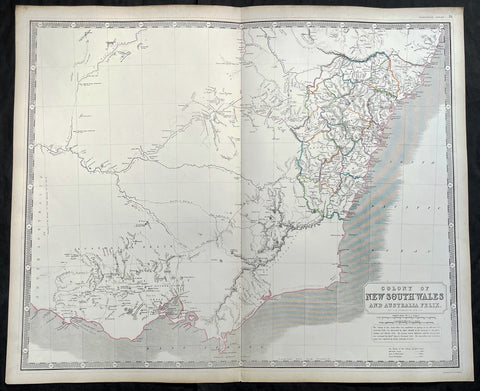
1841 Macarthur Antique Octavo Book on Colonial Policy in Australia, Map of NSW
Antique Map
- Title : Colonial Policy of 1840 and 1841, as illustrated by the Governor's Despatches, and Proceedings of the Legislative Council of New South Wales. By Major Macarthur.
- Ref #: 17045
- Size: Octavo
- Date : 1841
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
Fine original antique Octavo book with 79 pages and a single lithographed hand coloured map of eastern Australia & Van Diemens Land; uncut copy in half calf with gilt lettering by Edward Macarthur, advocating for immigration and trade for the colony of Australia, published by John Murray, London in 1841, dated.
This is the first of two books by Sir Edward Macarthurs advocating immigration to the colony of Australia. The eldest son of John and Elizabeth, Edward Macarthur was born at Bath in 1789, and accompanied his parents to New South Wales in 1790. As one of the first free settlers in the colony, he was a strong advocate of immigration, and served as Thomas Macqueens agent in arranging the first shipment of free immigrants in 1824, which gave great stimulus to agriculture.
The map illustrates a division of New South Wales and the subsequent creation of a smaller colony. Titled Eastern Australia or Territory of New South Wales, the map is captioned 'territory to which the Colony might be reduced by Bill of the last session' with reference debate in the House of Commons knocked down by Sir Robert Peel.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - Octavo
Plate size: - Octavo
Margins: - Octavo
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Sir Edward Macarthur (1789-1872), soldier, was born on 16 March 1789 at Bath, England, the eldest son of Captain John Macarthur and his wife Elizabeth. He went to Sydney with his parents in 1790 and spent his boyhood there and at Elizabeth Farm, Parramatta. Sent to England in 1799 to be educated he returned to Sydney in 1806. With his father he took part in the deposition of Governor William Bligh in 1808. He soon left for London taking his father's version of the rebellion and the first bale of merino wool to be exported from the colony. He obtained a commission in the 60th Regiment and served at Corunna and in Sicily. As a lieutenant in the 39th Regiment he took part in Wellington's campaigns of 1812-14 and was present at Vittoria, the Pyrénées and the battles in southern France. After brief service in Canada he joined the army of occupation in France.
In 1824 Macarthur went to New South Wales as the agent of T. P. Macqueen. He was impressed by the dispersion of the garrison from Moreton Bay to Hobart Town in the face of runaway convicts and 'hostile tribes'. In London he placed detailed proposals for a colonial militia before Under-Secretary Horton but the plan was rejected by Governor (Sir) Ralph Darling in 1827. Macarthur competently represented Australian interests in London. He presented a petition from New South Wales in 1840. He advocated emigration in two small books, Colonial Policy of 1840 and 1841, as Illustrated by the Governor's Despatches, and the Proceedings of the Legislative Council of New South Wales (London, 1841) and Brief Remarks on Colonization (London, 1846). He personally arranged the migration of German vinedressers to the Macarthur properties at Camden and also sought to develop coastal steamship services. After serving as secretary in the Lord Chamberlain's Office in 1843-46 he was on the military staff in Ireland. In 1851 he was posted to Sydney as deputy adjutant general. Promoted colonel in 1854, he moved with the headquarters to Melbourne. He accompanied the commander-in-chief, Major-General Sir Robert Nickle, to Eureka on 5 December. They talked freely with the miners and as a result of their investigations Nickle advised that martial law be withdrawn.
After Nickle died in May 1855 and Governor Hotham in December, Macarthur took over command of the forces and became administrator. He inherited a confused political situation and was coolly received by the press. However, his impartiality and his willingness to leave things to his ministers helped him, and when he handed over to Sir Henry Barkly on 23 December 1856 he had won the esteem of parliament and the people of Melbourne. Emily, wife of Hugh Childers, described him as 'if not a brilliant statesman, an industrious, kind-hearted, Christian gentleman'. In 1858 Macarthur chaired a royal commission on the defences of the colony. In 1860 he returned to England and was appointed K.C.B. in 1862. In that year he married Sarah (d.1889), daughter of Lieutenant-Colonel W. S. Neill. Promoted lieutenant-general in 1866, he died childless in London on 4 January 1872 and was buried in the Brompton cemetery. He was survived by his wife. His goods were valued for probate at £4000.
Macarthur, Edward (1789 - 1872)
Macarthur was a lieutenant-general in the British Army, Commander-in-chief of British forces in Australia from 1855, and an administrator of the Colony of Victoria for 12 months, following the death of the Governor, Sir Charles Hotham.
Macarthur was the eldest son of John Macarthur, and his wife Elizabeth (née Veal). He was born at Bath, Somerset, England, and arrived at Sydney with his parents in the ships Neptune and Scarborough in 1790, part of the Second Fleet. Edward Macarthur is believed to be the only passenger on those ships of whom a photograph exists, although taken later in life. In 1799, the young Edward was sent to England to be educated.
Macarthur returned to Australia in 1806 and took part with his father in the deposing of Governor William Bligh. Bligh, in his dispatch to Viscount Castlereagh of 30 April 1808, requested that two of the rebels Charles Grimes and Edward Macarthur who have gone home in the Dart may be secured, in order to be tried in due time. On Macarthurs arrival in England, he entered the army as an ensign in the 60th regiment, serving at Corunna and in Sicily. In 1809, he was promoted to the rank of lieutenant. As part of the 39th Regiment he took part in the Duke of Wellingtons campaigns in the Peninsular War and in France. In 1820 or 1829 he became a captain. In 1824 he paid a visit of 10 months to Australia as an agent of Thomas Potter Macqueen. After Macarthurs return to England, he was for some years secretary to the Lord Chamberlain. In 1826 he was promoted to the rank of major and in 1837 he was on the staff in Ireland.
Macarthur retained his interest in Australia. On 3 July 1839, he addressed a long communication to the Right Hon. Henry Labouchère, suggesting that regular lines of steamers should be established in Australia to trade between the various ports. That was referred to the governor, Sir George Gipps who, in May 1840, replied that government aid was unnecessary, because a large company had been formed to establish a line of steamers, of which James Macarthur (Edwards brother) was chairman. Edward Macarthur also promoted emigration in two small books: Colonial Policy of 1840 and 1841, as Illustrated by the Governors Despatches, and the Proceedings of the Legislative Council of New South Wales (London, 1841) and Brief Remarks on Colonization (London, 1846).
In August 1840, Macarthur protested against the regulations that people wanting to take up land in the Port Phillip district should have to proceed to Melbourne where all charts of land were kept for public inspection. He was made a Lieutenant-Colonel in 1841, and afterwards went to New South Wales as deputy adjutant-general. He was promoted to colonel in 1854.
On 5 December 1854, Macarthur travelled with the commander-in-chief of British forces in Australia, Major-General Sir Robert Nickle, to the site of the Eureka Rebellion. There they talked with the miners openly and, as a result of their investigations, Nickle advised the withdrawal of martial law. Macarthur was appointed commander-in-chief of British forces in Australia in 1855, to replace Nickle. On 1 January 1856, after the death of Governor of Victoria, Sir Charles Hotham, Macarthur was administrator of the colony of Victoria for 12 months.
Macarthur returned to London in 1860. In 1862, he was created a Knight Commander of the KCB and, in the same year, was given the colonelcy of the 100th (Prince of Waless Royal Canadian) Regiment of Foot, a position he held until his death.
He died in London on 4 January 1872 and was buried in Brompton Cemetery. In 1862, at the age of 73, he had married Sarah (daughter of Lieutenant-Colonel W. S. Neill), who survived him. There were no children.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1842 D Urville & Goupil Antique Print of Men of Santa Isabel Isle, Solomon Isle.
- Title : Naturels D Isabelle (Isle Solomon)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31745
Description:
This magnificent, large original antique lithograph print of profiles of 4 different men of the island of Santa Isabel of the Solomon Islands, visited in November & December 1838 by Dumont D Urville, drawn by Ernest Goupil, artist/draftsman aboard the Astrolabe during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayoti and was published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Ernest Goupil was a French painter, draftsman and watercolourist He is known for the illustrations made as official painter for Dumont D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas. In Voyage to the South Pole and in Oceania on corvettes l\'Astrobale and Zélée, executed by order of the king during the years 1837-1838-1839-1840, his drawings are transposed on stone, most notably by Emile Lassalle , Pharamond Blanchard and Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot . Dumont d\'Urville relates: On the Zélée , Mr. Goupil fills his cartons with precious paintings, and on the Astrolabe , the young surgeon Le Breton, who has a remarkable talent in this genre, also performs at my asks for charming drawings.
Some drawings were sent to the Minister of the Navy and were shown to the King, who wanted to see them transposed into painting by the marine painter Théodore Gudin , but Goupil would not have given his consent.
In August 1839 in Samarang Java , the crew is struck by a violent epidemic, and after two months of suffering, Ernest Goupil succumbs and died on January 1 , 1840 ijn Hobart-town where he was buried with full military honours.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (530mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (530mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Santa Isabel Island (also known as Isabel, Ysabel and Mahaga) is the longest in the Solomon Islands, the third largest in terms of surface area, and the largest in the group of islands in Isabel Province.
The first European contact to the Solomon Islands was made at Santa Isabel Island, by the Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña on 7 February 1568. It was charted as Santa Isabel de la Estrella (St. Elizabeth of the Star of Bethlehem in Spanish). A settlement was established by the Spaniards, and a small boat (known in the accounts as the brigantine) was built to survey and chart the surrounding sea and islands. These local explorations led by Maestre de Campo Pedro Ortega Valencia and Alférez Hernando Enríquez resulted in the discoveries of the islands of Malaita, Guadalcanal, Savo, Vangunu, Choiseul, Makira, Ulawa, Malaupaina, Malaulalo, Ali\'ite, and Ugi Island. The Spanish immediately came into contact with Solomon Islanders and at first the relationship was cordial. However, the Spanish expedition\'s need for fresh food and water quickly led to tension and conflict, the Solomon Islanders’ subsistence economy being unable to provide continuous supplies to the Spanish.
Having found no gold and little food, and beset by attacks and sickness, the Spanish colonists shifted their colony to the site of today\'s Honiara on Guadalcanal, and the settlement on Santa Isabel was abandoned.
Santa Isabel islanders suffered attacks from blackbirding in the nineteenth century (the often brutal recruitment or kidnapping of labourers for the sugar plantations in Queensland and Fiji).
In April 1885 a German Protectorate was declared over the North Solomon Islands, including Santa Isabel Island. In 1900, under the terms of Treaty of Berlin (14 November 1899), Germany transferred the North Solomon Islands (except for Bougainville and its surrounding islands) to the British Solomon Islands Protectorate in exchange for the British giving up all claims to Samoa. Missionaries settled on Santa Isabel Island under both protectorates, converting most of the population to Christianity. In the early 20th century several British and Australian firms began large-scale coconut planting.
1842 D Urville & Marescot Antique Print King Mapou-Teoa & Envoy of Mangareva Gambier
- Title : Antonio Mapoua; Koloupo (Isles Manga Reva)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31747
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of King Mapou-Teoa and his envoy who boarded D Urvilles ship the Astrolabe in August 1838, by Jacques Marescot-Duthilleul, one of the artists,draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot and published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Jacques, Marie, Eugene Marescot Duthilleul1809 - 1839 Lieutenant in the French navy and artist who accompanied Dumont D Urville on the Corvette The Astrolabe on D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas, Australia and Antarctica between 1837 and 1840. He was responsible for a number of exquisite drawings of peoples and views during the voyage that were later used for lithograph prints for publication
In 1837, a new mission of exploration in the southern Pacific Ocean was entrusted by King Louis-Philippe to Captain Dumont d Urville. This mission included improvement of scientific knowledge on the islands of the South Pacific and Indonesia, and exploration of the Antarctic continent.
The first phase of the expedition was the crossing the Sea of Weddel sea ice, on the coast of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. The second phase between May 1838 &o December 1839 consisting of visits to many South Pacific Islands: Marquesas, Polynesia, Fiji, Solomon Islands, New Guinea, Carolinas, Marianas, Moluccas and finally Sunda Islands.
At the end of this second phase, after eighteen months of difficult navigation in unhealthy climates, the sanitary condition of the crews of the two corvettes reached a critical state. During the last voyage from Sumatra (Lampang Bay) to Hobart Tasmania, eighteen patients died, including Lieutenant Marescot-Duthilleul.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mangareva is the central and largest island of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. It is surrounded by smaller islands: Taravai in the southwest, Aukena and Akamaru in the southeast, and islands in the north.
Mangareva was once heavily forested and supported a large population that traded with other islands via canoes. However, excessive logging by the islanders during the 10th to the 15th centuries resulted in deforestation of the island, with disastrous results for its environment and economy.
The first European to arrive at Mangareva was British Captain James Wilson in 1797 on the ship Duff. Wilson named the island group in honour of Admiral James Gambier, who had helped him to equip his vessel.
Mangareva along with its dependencies in the Gambier Islands were ruled by a line of kings and later regents that ruled until the French formally annexed the islands in 1881. A French protectorate was requested on 16 February 1844 by King Maputeoa but was never ratified by the French government. On 4 February 1870, Prince Regent Arone Teikatoara and the Mangarevan government formally withdrew the protectorate request and asked the French to not intervene in the kingdom\'s affairs. After Father Honoré Laval was removed to Tahiti, the native government changed its stance and an agreement between Prince Regent Arone and the French colonial authority in Tahiti was signed reaffirming the protectorate status on 30 November 1871. The Gambier Islands were finally annexed on 21 February 1881 under Prince Regent Bernardo Putairi and approved by the President of France on 30 January 1882.
1842 D Urville & Marescot Antique Print of Envoys of Mangareva Isle, Gambier Is.
- Title : Mama-Houi; Tima-Temouo (Isles Maga Reva)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31746
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of Envoys of Mangreva Island, Gambier Island visited by Dumont D Urvilles & his ship the Astrolabe in August 1838, by Jacques Marescot-Duthilleul, one of the artists,draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot and published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Jacques, Marie, Eugene Marescot Duthilleul1809 - 1839 Lieutenant in the French navy and artist who accompanied Dumont D Urville on the Corvette The Astrolabe on D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas, Australia and Antarctica between 1837 and 1840. He was responsible for a number of exquisite drawings of peoples and views during the voyage that were later used for lithograph prints for publication
In 1837, a new mission of exploration in the southern Pacific Ocean was entrusted by King Louis-Philippe to Captain Dumont d Urville. This mission included improvement of scientific knowledge on the islands of the South Pacific and Indonesia, and exploration of the Antarctic continent.
The first phase of the expedition was the crossing the Sea of Weddel sea ice, on the coast of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. The second phase between May 1838 &o December 1839 consisting of visits to many South Pacific Islands: Marquesas, Polynesia, Fiji, Solomon Islands, New Guinea, Carolinas, Marianas, Moluccas and finally Sunda Islands.
At the end of this second phase, after eighteen months of difficult navigation in unhealthy climates, the sanitary condition of the crews of the two corvettes reached a critical state. During the last voyage from Sumatra (Lampang Bay) to Hobart Tasmania, eighteen patients died, including Lieutenant Marescot-Duthilleul.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mangareva is the central and largest island of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. It is surrounded by smaller islands: Taravai in the southwest, Aukena and Akamaru in the southeast, and islands in the north.
Mangareva was once heavily forested and supported a large population that traded with other islands via canoes. However, excessive logging by the islanders during the 10th to the 15th centuries resulted in deforestation of the island, with disastrous results for its environment and economy.
The first European to arrive at Mangareva was British Captain James Wilson in 1797 on the ship Duff. Wilson named the island group in honour of Admiral James Gambier, who had helped him to equip his vessel.
Mangareva along with its dependencies in the Gambier Islands were ruled by a line of kings and later regents that ruled until the French formally annexed the islands in 1881. A French protectorate was requested on 16 February 1844 by King Maputeoa but was never ratified by the French government. On 4 February 1870, Prince Regent Arone Teikatoara and the Mangarevan government formally withdrew the protectorate request and asked the French to not intervene in the kingdom\'s affairs. After Father Honoré Laval was removed to Tahiti, the native government changed its stance and an agreement between Prince Regent Arone and the French colonial authority in Tahiti was signed reaffirming the protectorate status on 30 November 1871. The Gambier Islands were finally annexed on 21 February 1881 under Prince Regent Bernardo Putairi and approved by the President of France on 30 January 1882.
1842 William Mather Antique Cross Section Geology Print The Island of New York
Antique Map
- Title : Geological Section, on the Island of New York.....
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93063
Description:
This original hand coloured antique lithograph of 3 cross sectional geological maps, views on the Island of New York by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1842 William Mather Antique Geology Print Digging of New York & Harlem Railroad
Antique Map
- Title : View of the Cut of Harlem Rail Road North of the Tunnel
- Size: 18 1/2 in x 11in (460mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93062
Description:
This original antique coloured lithograph plate depicting a cross sectional geological part view of the New York and Harlem Railroad and the Park Avenue or Murray Hill Tunnel by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
The view depicts about 400 yards of rail in two views, a north view and a south view. Each view is split into approximately equal distances of 200 yards each. In the views, the cross section of the ground through which the tunnel was cut is illustrated, comprised mostly of layers of diluvial loam and gneiss. Some granite veins run through the gneiss, which are colored red.
The New York and Harlem Railroad (now the Metro-North Railroads Harlem Line) was one of the first railroads in the United States, and was the worlds first street railway. Designed by John Stephenson, it was opened in stages between 1832 and 1852 between Lower Manhattan to and beyond Harlem. Horses initially pulled railway carriages, followed by a conversion to steam engines, then one to battery-powered Julien electric traction cars. In 1907 the then leaseholders of the line, New York City Railway, a streetcar operator, went into receivership. Following a further receivership in 1932 the New York Railways Corporation converted the line to bus operation. The Murray Hill Tunnel now carries a lane of road traffic, but not the buses.
The line became part of the New York Central Railroad system with trackage rights granted to the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad into Manhattan. It is now part of the Metro-North Railroad system, and the only Manhattan trackage of that system.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2 in x 11in (460mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2 in x 11in (460mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1842 William Mather Antique Geology Print Entrance to Howes Cavern Cobleskill NY
Antique Map
- Title : Howes Cave Cobleskill N.Y.
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93069
Description:
This original antique lithograph of the entrance to Howes Cavern in Cobleskill, New York by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
A beautiful black and white lithograph, the entrance to the cave is situated in the foreground, with what appears to be stones and beams marking the way in. Trees cover the hillside, creating the image of a wild, untamed wilderness. Today, Howes Cave is known by another name: Howe Caverns and is located in the town of Howes Cave in Schoharie County. Howe Caverns is the second most visited natural attraction in New York State, following Niagara Falls.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1842 William Mather Antique Geology Print Hudson River Lakes George to Champlain
Antique Map
- Title : Section from Lake George by Whitehall to E Poultney in VT
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93064
Description:
This original hand coloured antique lithograph cross sectional geological map,a view along the Hudson River from Lake George in NY to Lake Champlain Vermont by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1842 William Mather Antique Geology Print of Balls Cave, Schoharie County, NY
Antique Map
- Title : Balls Cave, Schoharie Court House....
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93065
Description:
This original antique coloured lithograph plate depicting a cross sectional geological part view Balls Cave, Schoharie County, New York state by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
Balls Cave was located in Schoharie County about two miles from the courthouse in Schoharie. It was discovered and explored by John Gebhard and John Bonny in 1831 and 1832. Soon after the cave was discovered, Gebhard and Bonny provided a description of the cave which was subsequently published in the newspapers of the day. A stream ran through the cave, so Gebhard and Bonny kept a boat for use during their explorations. Per Mather, the cave is chiefly remarkable for its extent and beautiful stalactites and stalagmites.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1842 William Mather Antique Geology Print of Hudson River, Sullivan County, NY
Antique Map
- Title : Section in Sullivan Co. Catskill Mt Rocks
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 93067
Description:
This original hand coloured antique lithograph cross sectional geological map,a view along the Hudson River in Sullivan County, New York by the Endicott company, was published in the 1842 edition of William Mathers Geology of New York
Sullivan County is a county in the U.S. state of New York.
When the Province of New York established its first twelve counties in 1683, the present Sullivan County was part of Ulster County. In 1809, Sullivan County was split from Ulster County.
In the late 19th century, the Industrial Revolution and the advent of factories driven by water power along the streams and rivers led to an increase in population attracted to the jobs. Hamlets enlarged into towns. As industry restructured, many of those jobs left before the middle of the twentieth century. The economy changed again after that, shifting to a more tourist-based variety and benefiting from resorts established by European Jewish immigrants and their descendants in what became called the Borscht Belt of the 20th century. Resort hotels featured a wide variety of entertainers, some nationally known. At the beginning of this period, visitors traveled to the area by train, and later by automobile. The areas natural resources also provided a setting for numerous summer camps frequented by the children of immigrants and their descendants.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1836 William Williams Mather was appointed geologist of the first district, or 21 counties, of New York State. This work required seven years, and his final report was a quarto of 671 pages, with forty-six colored plates, a great undertaking for the early days of geological research. From 1837 to 1840, he also superintended the geological survey of the state of Ohio, and made elaborate reports (2 vols., Columbus, 1838). In 1838/9 he made a report upon the geological reconnaissance of the state of Kentucky.
Mather, William W. 1804 - 1859
Mather was an important American geologist and natural historian. Mather was born in Brooklyn, Connecticut to an old New England family. In 1823, as a young man, he entered the West Point military academy after which he served as a 2nd Lieutenant in the Seventh Infantry. His interest in Chemistry and mineralogy soon called him back to West Point where he acted as an Assistant Professor of Geology. After resigning from the Army in 1834 with a rank of 1st Lieutenant, Mather accepted a position as Professor of Chemistry at the University of Louisiana. Later he was employed as Professor of Natural History and Sciences at the University of Ohio, was appointed Geologist of the First Geological District of New York for Governor William H. Seward, and was the State Geologist of both Ohio and Kentucky. In 1847 Mather became president of the University of Ohio. During his long career Mather made copious notes regarding his geological explorations, published profusely, and had a lively and extensive correspondence - much of which remains accessible to this day. Mather reports on one humorous incident in Long Island where, while collecting rock specimens, he had a run-in with a local farmer. The famer, observing the care with which Mather collected and cataloged his rock specimens, assumed that Mather had, in fact, discovered gold! Mather died in Columbus, Ohio on February 26, 1859. Today the W.W. Mather Medal is an important Geologic Reserach commendation. (Collections of the Minnesota Historical Society, p. 133.)
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), George\\\'s younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes \\\"it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality.\\\" The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1843 Baron Von Humboldt Large Old, Antique Map of Texas & Mexico, Mining - Rare
Antique Map
- Title : Carte des principaux Districts de Mines Du Mexique Reduite d apres celle de Mr. le Baron A de Humbold
- Ref #: 61108
- Size: 22in x 14in (560mm x 360mm)
- Date : 1843
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, scarce original, antique map* showing the location of Mines in Texas and Mexico in the early part of the 19th century by Baron Humboldt was engraved by Dutos in 1843. This map is scarce with no other example available currently on the market.
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a Prussian geographer, naturalist, explorer, and influential proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher, and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt (1767–1835). Humboldt's quantitative work on botanical geography laid the foundation for the field of biogeography. Humboldt's advocacy of long-term systematic geophysical measurement laid the foundation for modern geomagnetic and meteorological monitoring.
Between 1799 and 1804, Humboldt travelled extensively in Latin America, exploring and describing it for the first time from a modern scientific point of view. His description of the journey was written up and published in an enormous set of volumes over 21 years. Humboldt was one of the first people to propose that the lands bordering the Atlantic Ocean were once joined (South America and Africa in particular). Humboldt resurrected the use of the word cosmos from the ancient Greek and assigned it to his multi-volume treatise, Kosmos, in which he sought to unify diverse branches of scientific knowledge and culture. This important work also motivated a holistic perception of the universe as one interacting entity. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 14in (560mm x 360mm)
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (390mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, light spotting
Plate area: - Light uplift along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning, light spotting
1843 James Hall Large Antique Geological Map of the United States & Great Lakes
Antique Map
- Title : Geological Map of the Middle and Western States by James Hall
- Date : 1843
- Size: 32 1/2in x 24in (825mm x 610mm)
- Ref #: 93061
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original steel plate engraved, hand coloured antique Geological map from the Mississippi River to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Straits of Michilimackinac (Michillimaoinac) and Montreal, Canada to Virginia, Kentucky, and Missouri by James Hall was published in the 1843 edition of Halls Geology of New York. Part IV. Comprising the Survey of the Fourth Geological District
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 32 1/2in x 24in (825mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 32 1/2in x 24in (825mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The New York System of Geology
Hall’s map can be regarded as a landmark work as it was one of the earliest known maps to employ the New York System, of stratigraphic nomenclature developed by Hall and others at the New York Geological Survey. The system emphasized the importance of paleontology for delineating geological units and introduced the concept of type locality, a primary reference location used for defining the characteristics of geological formations. This map is the first regional application of the system, which evolved into the standard nomenclature used today for North America and much of the rest of the world.
Hall, James 1811 - 1898
Hall was an American paleontologist and geologist. Born in Hingham, Massachusetts, Hall was the oldest of four children born to James Hall Sr. and Sousanna Dourdain Hall, who had emigrated from England two years earlier. Hall attended the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, from which he graduated with honors in 1832 and he received a masters degree from the same institution the following year. After completing his masters degree, Hall stayed at Rensselaer and taught chemistry and later geology. In 1836, Hall was appointed to the team working on a geological and natural history of New York. That first year he was assigned as Ebenezer Emmonss assistant, for who he studied iron deposits in the Adirondack Mountains. The following year, after the survey was reorganized, Hall was put in charge of the Fourth District, in western New York. After completing the survey in 1841, Hall was named the first state paleontologist of New York. Hall published the findings of the survey in 1843 as Geology of New York Part IV. This work received much acclaim and became a classic in the field. Thanks to this success, Hall had established a solid reputation and spent the rest of his life studying stratigraphic geology and invertebrate paleontology. Hall constructed a laboratory in Albany, New York, which quickly became an important institution for aspiring geologists and paleontologists to study and train. Today, this laboratory is known as the James Hall Office and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1976. Following the survey of New York, Hall participated in a geological survey of northern Michigan and Wisconsin in 1850, and served as state geologist for Iowa from 1855 until 1858 and for Wisconsin from 1857 until 1860. In 1866, Hall was appointed the director of the New York State Museum of Natural History in Albany, and was appointed State Geologist of New York in 1893. Hall was a founding member of the National Academy of Sciences and served as the first president of the Geological Society of America. In 1838, Hall married Sarah Aikin, with whom he had two daughters and two sons. Sarah passed away in 1895.
Endicott and Company (fl. c. 1828 - 1891) was a New York based family run lithography firm that flourished throughout the 19th century. The firm was founded by George and William Endicott, brothers who were born in Canton, Massachusetts. George Endicott (June 14, 1802 - 1848) trained as a lithographer under Pendleton Lithography from January of 1826. He later worked as superintendent of Senefelder Company until the summer of 1828. Afterwards, in 1830, he relocated to Baltimore and partnered with Moses Swett. Endicott and Swett relocated to New York City in December of 1831. They remained partners until July of 1834 when the relationship dissolved. George set up shop on his own account at 359 Broadway. William Endicott (1815 - 1851), Georges younger brother of 14 years, joined the firm in 1840 and was made a partner in 1845, after which the name of the firm was changed to G. and W. Endicott. George Endicott died shortly afterward, in 1848, but William continued operating the firm as William Endicott and Co. until his own 1851 death at just 35 years. The firm was carried on by his widow Sara Munroe Endicott until it was taken over by her son, Francis Endicott, who ran the firm from 1852 to 1886. George Endicott, Jr. subsequently ran the firm from 1887 to 1891. Peters, in his important work on American lithography America on Stone writes it is hard to summarize the Endicotts. They did everything and did it well . . . [they] worked with and for Currier and Ives, yet in spite of all that much of their work lacks real individuality. The Endicott firm was responsible for many 19th century views and plans of New York City and state as well as plans of Sacramento, California, and the Midwest.
1844 Hughes Antique Australian Map of the States of Victoria & NSW
- Title : Victoria New South Wales and South Australia
- Ref #: 91204
- Size: 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map of the Australian States of NSW, Vic & part of SA was engraved by William Hughes and published by A&C Black in 1844. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1844 W & AK Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia - South Australia Settlement
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 23806
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of Australia - with coloured outlines to the counties in NSW & WA - was published by W & AK Johnston in General Atlas,1844.
At the bottom of the map is a text box outlining the period of settlements in Australia from Botany Bay in 1788, WA 1829, SA 1836 & the colony of Victoria begun some 8 years earlier in 1838.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century, this large map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1844 W & AK Johnston Large Early Antique Map of Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 30143
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original antique lithograph map of Australia - with coloured outlines to the counties in NSW & WA - was published by W & AK Johnston in General Atlas,1844.
At the bottom of the map is atext box outlining the period of settlements in Australia from Botany Bay in 1788, WA 1829, SA 1836 & the colony of Victoria begun some 8 years ealier in 1838.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century, this large map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1845 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of Australia - Population of 213,500
- Title : Australland...1841
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 31977
- Size: 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, with a population census of the entire country in 1841, by Friedrich Handtke in 1845, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning & spotting
Plate area: - Age toning & spotting
Verso: - Age toning & spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1845 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of Australia - Population of 213,500
- Title : Australland...1841
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40972
- Size: 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, with a population census of the entire country in 1841, by Friedrich Handtke in 1845, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map Florida, Caribbean, Cuba, Haiti, Central America
Antique Map
- Title : West India Islands
- Date : 1845
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35619
Description:
This large original hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of West Indian, Caribbean Islands, was published by W & AK Johnston in his General Atlas, 1845.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, North America Pacific
- Title : Islands in the Pacific Ocean
- Size: 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1845
- Ref #: 23805
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique map of Australia, New Zealand, North America and the Pacific Ocean by W & AK Johnston, was published in the 1845 edition of his large General Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\\\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\\\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\\\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, North America Pacific
- Title : Islands in the Pacific Ocean
- Size: 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1845
- Ref #: 40960
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique map of Australia, New Zealand, North America and the Pacific Ocean by W & AK Johnston, was published in the 1845 edition of his large General Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\\\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\\\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\\\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map of New South Wales & Victoria, Australia Felix
Antique Map
- Title : Colony of New South Wales and Australia Felix
- Ref #: 35088
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original antique map of NSW & SE Australia stretching from the 10 year old Settlement of Melbourne in the south to the 31st parallel in the north, by W & AK Johnston, was published in the 1845 edition of the General Atlas.
A large, highly detailed regional map of New South Wales and Australia Felix the SE area which quickly became the state of Victoria. The map, with this title, lasted for only a few years, before both NSW and Victoria were quickly settled. The map provides a very early depiction of the region, pre-dating the discovery of gold.
Also of great interest are the exploration routes by Mitchell (1836) in Red, Tyer's & Townsend's (1840) in Yellow and Streletsky's (Strzelecki) (1840) in Blue.
The 18 counties of NSW are highlighted in beautiful hand colour with extensive detail of towns, tracks and rivers. Historical note included below the title.Decorative Piano Key border and a fine example, on thick heavy paper.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century - this map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1845 Sydney Hall Large Antique World Map insets Singapore, Hong Kong, Cape, TAS
- Title : 1845 Sydney Hall Large Antique World Map insets Singapore, Hong Kong, Cape, TAS
- Size: 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Date : 1843
- Ref #: 32258-1
Description:
This large original steel-plate antique world map - with 5 inset maps of Hong Kong, Van Diemens Land, Calcutta, Singapore & the Colony Of Good Hope - by Sydney Hall was published by Longman & co. in 1845. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (500mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small loss to top centerfold, into border
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape, light soiling
Background:
A highly detailed and attractive map of the world, with seven inset maps of British colonies: Hong Kong, Van Diemens Land, Calcutta, Singapore & the Colony Of Good Hope. A note on the Pitcairn Islands records their colonisation by the mutineers from the Bounty.
Also prominent in North America is an independent Texas along with an extended Mexico into the SW and California regions.
1845-63 John Gould Large Antique Print of Tree Kangaroo The Mammals of Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Dendrolagus Inustus, Mull....H C Richter del et lith....C Hullmandel Imp.
- Ref #: 93442
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
- Date : 1845–63
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare original hand coloured lithograph antique print of The Grizzled Tree Kangaroo, by the artist HC Richter was printed by Charles Joseph Hullmandel 1789 – 1850 in the famous Naturalists John Goulds The Mammals of Australiapublished between 1845–63.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Mammals of Australia is a three-volume work written and published by John Gould between 1845–63. It contains 182 illustrations by the author and its artist H. C. Richter. It was intended to be a complete survey of the novel species of mammals, such as the marsupials, discovered in the colonies of Australia.
The author, John Gould, best known for The Birds of Australia and other major works of ornithology, visited Australia in 1838. In his introduction, Gould says:.....It was not until I arrived in the country, and found myself surrounded by objects as strange as if I had been transported to another planet, that I conceived the idea of devoting a portion of my attention to the mammalian class of its extraordinary fauna......During his short stay he made observations on the natural history and employed his skills as a taxidermist to obtain specimens.
The publication of this major work by Gould followed his A Monograph of the Macropodidae or Family of Kangaroos in 1841. This work was the first comprehensive survey of Australian mammals, and gave an account of their classification and description. Gould also included the indigenous names for the species from the lists he made while in Australia. He used these names to make requests of the local peoples for his specimens, and recorded the regions where the names were used. This conserved a number of common names, such as dibbler (Parantechinus apicalis), which were later recommended by authorities.
The large lithographs reproduced the artwork of Richter, after the drawings and watercolours made in Australia by Gould and his wife, Elizabeth. (The contribution by Elizabeth Gould was uncredited). These were hand-coloured by a group of artists, led by Gabriel Bayfield, that required the completion of 26,572 plates. The illustrations produced during their visit to Australia were supplemented by the preserved specimens returned to England and detailed the characteristics of the species. These illustrations have become iconic images of the mammals of Australia. Among the best known of the illustrations from the work are the two of Thylacinus cynocephalus (Tasmanian tiger), copied since its publication and the most frequently reproduced, made more recognizable by Cascade Brewerys appropriation for its label in 1987. The government of Tasmania published a monochromatic reproduction of the same image in 1934, the author Louisa Anne Meredith also copied it for Tasmanian Friends and Foes (1881).
The Mammals of Australia was published by subscription in the format Imperial Folio; 13 parts in three volumes were issued from 1845 until 1863. To these the author added An Introduction to The Mammals of Australia (1863) in a separate work. This provided corrections and updates, a new preface, introduction, and a list of the mammals of the three volumes. The first two volumes were complete surveys of orders Marsupiata (marsupials), and, with Rodentia in the third, it formed the sum of known mammalian species of Australia. With the addition of those contained in the later Introduction the total of species described reached 166. The same work notes the exclusion of marine mammals such as whales from the volumes, but reprints a manuscript by Charles Coxen on the dugong.
Beyond the scientific value of this comprehensive survey, the document is cited in reference to its subjects conservation. Some of the species included in the work, such as Onychogalea lunata (crescent nailtail wallaby), have since succumbed to changes in land use since European colonisation.
The work was received with acclaim, but the high cost of production, especially of the coloured plates, reduced its accessibility. The original listed price was £41 for the complete set of volumes. The public curiosity for the unique fauna of Australia was met by this handsomely illustrated and comprehensive survey, and it spawned imitations in Australia. The curator of the Australian Museum, Gerard Krefft, produced the more affordable The Mammals of Australia (1871); intended for educational purposes and influenced by Goulds illustrations. Gracius Broinowskis abandoned work, Birds and Mammals of Australia (1884), so closely imitated the plates that an injunction was threatened by its publisher.
Gould, John FRS 1804 – 1881
Gould was an English ornithologist and bird artist. He published a number of monographs on birds, illustrated by plates that he produced with the assistance of his wife, Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists including Edward Lear, Henry Constantine Richter, Joseph Wolf and William Matthew Hart. He has been considered the father of bird study in Australia and the Gould League in Australia is named after him. His identification of the birds now nicknamed Darwins finches played a role in the inception of Darwins theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work is referenced in Charles Darwins book, On the Origin of Species.
Gould was born in Lyme Regis the first son of a gardener. He and the boy probably had a scanty education. Shortly afterwards his father obtained a position on an estate near Guildford, Surrey, and then in 1818 Gould became foreman in the Royal Gardens of Windsor. He was for some time under the care of J. T. Aiton, of the Royal Gardens of Windsor. The young Gould started training as a gardener, being employed under his father at Windsor from 1818 to 1824, and he was subsequently a gardener at Ripley Castle in Yorkshire. He became an expert in the art of taxidermy. In 1824 he set himself up in business in London as a taxidermist, and his skill helped him to become the first Curator and Preserver at the museum of the Zoological Society of London in 1827.
Goulds position brought him into contact with the countrys leading naturalists. This meant that he was often the first to see new collections of birds given to the Zoological Society of London. In 1830 a collection of birds arrived from the Himalayas, many not previously described. Gould published these birds in A Century of Birds from the Himalaya Mountains (1830–1832). The text was by Nicholas Aylward Vigors and the illustrations were drawn and lithographed by Goulds wife Elizabeth Coxen Gould. Most of Goulds work were rough sketches on paper from which other artists created the lithographic plates.
This work was followed by four more in the next seven years, including Birds of Europe in five volumes. It was completed in 1837; Gould wrote the text, and his clerk, Edwin Prince, did the editing. The plates were drawn and lithographed by Elizabeth Coxen Gould. A few of the illustrations were made by Edward Lear as part of his Illustrations of the Family of Psittacidae in 1832. Lear, however, was in financial difficulty, and he sold the entire set of lithographs to Gould. The books were published in a very large size, imperial folio, with magnificent coloured plates. Eventually 41 of these volumes were published, with about 3000 plates. They appeared in parts at £3 3s. a number, subscribed for in advance, and in spite of the heavy expense of preparing the plates, Gould succeeded in making his ventures pay, realising a fortune. This was a busy period for Gould who also published Icones Avium in two parts containing 18 leaves of bird studies on 54 cm plates as a supplement to his previous works. No further monographs were published as in 1838 he and his wife moved to Australia to work on the Birds of Australia. Shortly after their return to England, his wife died in 1841. Elizabeth Gould completed 84 plates for Birds of Australia before her death.
When Charles Darwin presented his mammal and bird specimens collected during the second voyage of HMS Beagle to the Zoological Society of London on 4 January 1837, the bird specimens were given to Gould for identification. He set aside his paying work and at the next meeting on 10 January reported that birds from the Galápagos Islands which Darwin had thought were blackbirds, gross-bills and finches were in fact a series of ground Finches which are so peculiar as to form an entirely new group, containing 12 species. This story made the newspapers. In March, Darwin met Gould again, learning that his Galápagos wren was another species of finch and the mockingbirds he had labelled by island were separate species rather than just varieties, with relatives on the South American mainland. Subsequently, Gould advised that the smaller southern Rhea specimen that had been rescued from a Christmas dinner was a separate species which he named Rhea darwinii, whose territory overlapped with the northern rheas. Darwin had not bothered to label his finches by island, but others on the expedition had taken more care. He now sought specimens collected by captain Robert FitzRoy and crewmen. From them he was able to establish that the species were unique to islands, an important step on the inception of his theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work on the birds was published between 1838 and 1842 in five numbers as Part 3 of Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle, edited by Charles Darwin. Elizabeth Gould illustrated all the plates for Part 3.
In 1838 the Goulds sailed to Australia, intending to study the birds of that country and be the first to produce a major work on the subject. They took with them the collector John Gilbert. They arrived in Tasmania in September, making the acquaintance of the governor Sir John Franklin and his wife. Gould and Gilbert collected on the island. In February 1839 Gould sailed to Sydney, leaving his pregnant wife with the Franklins. He travelled to his brother-in-laws station at Yarrundi, spending his time searching for bowerbirds in the Liverpool Range. In April he returned to Tasmania for the birth of his son. In May he sailed to Adelaide to meet Charles Sturt, who was preparing to lead an expedition to the Murray River. Gould collected in the Mount Lofty range, the Murray Scrubs and Kangaroo Island, returning again to Hobart in July. He then travelled with his wife to Yarrundi. They returned home to England in May 1840.
The result of the trip was The Birds of Australia (1840–48). It included a total of 600 plates in seven volumes; 328 of the species described were new to science and named by Gould. He also published A Monograph of the Macropodidae, or Family of Kangaroos (1841–1842) and the three volume work The Mammals of Australia (1849–1861).
Elizabeth died in 1841 after the birth of their eighth child, Sarah, and Goulds books subsequently used illustrations by a number of artists, including Henry Constantine Richter, William Matthew Hart and Joseph Wolf.
Throughout his professional life Gould had a strong interest in hummingbirds. He accumulated a collection of 320 species, which he exhibited at the Great Exhibition of 1851. Despite his interest, Gould had never seen a live hummingbird. In May 1857 he travelled to the United States with his second son, Charles. He arrived in New York too early in the season to see hummingbirds in that city, but on 21 May 1857, in Bartrams Gardens in Philadelphia, he finally saw his first live one, a ruby-throated hummingbird. He then continued to Washington D.C. where he saw large numbers in the gardens of the Capitol. Gould attempted to return to England with live specimens, but, as he was not aware of the conditions necessary to keep them, they only lived for two months at most.
Gould published: A Monograph of the Trochilidae or Humming Birds with 360 plates (1849–61); The Mammals of Australia (1845–63), Handbook to the Birds of Australia (1865), The Birds of Asia (1850–83), The Birds of Great Britain (1862–73) and The Birds of New Guinea and the adjacent Papuan Islands (1875–88).
The University of Glasgow, which owns a copy of Birds of Great Britain, describes John Gould as the greatest figure in bird illustration after Audubon, and auctioneers Sotherans describe the work as Goulds pride and joy.
Gould had already published some of the illustrations in Birds of Europe, but Birds of Great Britain represents a development of his aesthetic style in which he adds illustrations of nests and young on a large scale.
Sotherans Co. reports that Gould published the book himself, producing 750 copies, which remain sought after both as complete volumes, and as individual plates, currently varying in price from £450 – £850. The University of Glasgow records that the volumes were issued in London in 25 parts, to make the complete set, between 1863 and 1873, and each set contained 367 coloured lithographs.
Gould undertook an ornithological tour of Scandinavia in 1856, in preparation for the work, taking with him the artist Henry Wolf who drew 57 of the plates from Goulds preparatory sketches. According to The University of Glasgow Goulds skill was in rapidly producing rough sketches from nature (a majority of the sketches were drawn from newly killed specimens) capturing the distinctiveness of each species. Gould then oversaw the process whereby his artists worked his sketches up into the finished drawings, which were made into coloured lithographs by engraver William Hart.
There were problems: the stone engraving of the snowy owl in volume I was dropped and broken at an early stage in the printing. Later issues of this plate show evidence of this damage and consequently the early issue – printed before the accident – are considered more desirable.
The lithographs were hand coloured. In the introduction for the work, Gould states every sky with its varied tints and every feather of each bird were coloured by hand; and when it is considered that nearly two hundred and eighty thousand illustrations in the present work have been so treated, it will most likely cause some astonishment to those who give the subject a thought.
The work has gathered critical acclaim: according to Mullens and Swann, Birds of Great Britain is the most sumptuous and costly of British bird books, whilst Wood describes it as a magnificent work. Isabella Tree writes that it was seen – perhaps partly because its subject was British, as the culmination of [his] ... genius
1845-63 John Gould Large Antique Print The Mammals of Australia - Tree Kangaroo
Antique Map
- Title : Dendrolagus Ursinus, Mull....H C Richter del et lith....C Hullmandel Imp.
- Ref #: 93441
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
- Date : 1845–63
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare original hand coloured lithograph antique print of The Ursine Tree Kangaroo, by the artist HC Richter was printed by Charles Joseph Hullmandel 1789 – 1850 in the famous Naturalists John Goulds The Mammals of Australiapublished between 1845–63.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Mammals of Australia is a three-volume work written and published by John Gould between 1845–63. It contains 182 illustrations by the author and its artist H. C. Richter. It was intended to be a complete survey of the novel species of mammals, such as the marsupials, discovered in the colonies of Australia.
The author, John Gould, best known for The Birds of Australia and other major works of ornithology, visited Australia in 1838. In his introduction, Gould says:.....It was not until I arrived in the country, and found myself surrounded by objects as strange as if I had been transported to another planet, that I conceived the idea of devoting a portion of my attention to the mammalian class of its extraordinary fauna......During his short stay he made observations on the natural history and employed his skills as a taxidermist to obtain specimens.
The publication of this major work by Gould followed his A Monograph of the Macropodidae or Family of Kangaroos in 1841. This work was the first comprehensive survey of Australian mammals, and gave an account of their classification and description. Gould also included the indigenous names for the species from the lists he made while in Australia. He used these names to make requests of the local peoples for his specimens, and recorded the regions where the names were used. This conserved a number of common names, such as dibbler (Parantechinus apicalis), which were later recommended by authorities.
The large lithographs reproduced the artwork of Richter, after the drawings and watercolours made in Australia by Gould and his wife, Elizabeth. (The contribution by Elizabeth Gould was uncredited). These were hand-coloured by a group of artists, led by Gabriel Bayfield, that required the completion of 26,572 plates. The illustrations produced during their visit to Australia were supplemented by the preserved specimens returned to England and detailed the characteristics of the species. These illustrations have become iconic images of the mammals of Australia. Among the best known of the illustrations from the work are the two of Thylacinus cynocephalus (Tasmanian tiger), copied since its publication and the most frequently reproduced, made more recognizable by Cascade Brewerys appropriation for its label in 1987. The government of Tasmania published a monochromatic reproduction of the same image in 1934, the author Louisa Anne Meredith also copied it for Tasmanian Friends and Foes (1881).
The Mammals of Australia was published by subscription in the format Imperial Folio; 13 parts in three volumes were issued from 1845 until 1863. To these the author added An Introduction to The Mammals of Australia (1863) in a separate work. This provided corrections and updates, a new preface, introduction, and a list of the mammals of the three volumes. The first two volumes were complete surveys of orders Marsupiata (marsupials), and, with Rodentia in the third, it formed the sum of known mammalian species of Australia. With the addition of those contained in the later Introduction the total of species described reached 166. The same work notes the exclusion of marine mammals such as whales from the volumes, but reprints a manuscript by Charles Coxen on the dugong.
Beyond the scientific value of this comprehensive survey, the document is cited in reference to its subjects conservation. Some of the species included in the work, such as Onychogalea lunata (crescent nailtail wallaby), have since succumbed to changes in land use since European colonisation.
The work was received with acclaim, but the high cost of production, especially of the coloured plates, reduced its accessibility. The original listed price was £41 for the complete set of volumes. The public curiosity for the unique fauna of Australia was met by this handsomely illustrated and comprehensive survey, and it spawned imitations in Australia. The curator of the Australian Museum, Gerard Krefft, produced the more affordable The Mammals of Australia (1871); intended for educational purposes and influenced by Goulds illustrations. Gracius Broinowskis abandoned work, Birds and Mammals of Australia (1884), so closely imitated the plates that an injunction was threatened by its publisher.
Gould, John FRS 1804 – 1881
Gould was an English ornithologist and bird artist. He published a number of monographs on birds, illustrated by plates that he produced with the assistance of his wife, Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists including Edward Lear, Henry Constantine Richter, Joseph Wolf and William Matthew Hart. He has been considered the father of bird study in Australia and the Gould League in Australia is named after him. His identification of the birds now nicknamed Darwins finches played a role in the inception of Darwins theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work is referenced in Charles Darwins book, On the Origin of Species.
Gould was born in Lyme Regis the first son of a gardener. He and the boy probably had a scanty education. Shortly afterwards his father obtained a position on an estate near Guildford, Surrey, and then in 1818 Gould became foreman in the Royal Gardens of Windsor. He was for some time under the care of J. T. Aiton, of the Royal Gardens of Windsor. The young Gould started training as a gardener, being employed under his father at Windsor from 1818 to 1824, and he was subsequently a gardener at Ripley Castle in Yorkshire. He became an expert in the art of taxidermy. In 1824 he set himself up in business in London as a taxidermist, and his skill helped him to become the first Curator and Preserver at the museum of the Zoological Society of London in 1827.
Goulds position brought him into contact with the countrys leading naturalists. This meant that he was often the first to see new collections of birds given to the Zoological Society of London. In 1830 a collection of birds arrived from the Himalayas, many not previously described. Gould published these birds in A Century of Birds from the Himalaya Mountains (1830–1832). The text was by Nicholas Aylward Vigors and the illustrations were drawn and lithographed by Goulds wife Elizabeth Coxen Gould. Most of Goulds work were rough sketches on paper from which other artists created the lithographic plates.
This work was followed by four more in the next seven years, including Birds of Europe in five volumes. It was completed in 1837; Gould wrote the text, and his clerk, Edwin Prince, did the editing. The plates were drawn and lithographed by Elizabeth Coxen Gould. A few of the illustrations were made by Edward Lear as part of his Illustrations of the Family of Psittacidae in 1832. Lear, however, was in financial difficulty, and he sold the entire set of lithographs to Gould. The books were published in a very large size, imperial folio, with magnificent coloured plates. Eventually 41 of these volumes were published, with about 3000 plates. They appeared in parts at £3 3s. a number, subscribed for in advance, and in spite of the heavy expense of preparing the plates, Gould succeeded in making his ventures pay, realising a fortune. This was a busy period for Gould who also published Icones Avium in two parts containing 18 leaves of bird studies on 54 cm plates as a supplement to his previous works. No further monographs were published as in 1838 he and his wife moved to Australia to work on the Birds of Australia. Shortly after their return to England, his wife died in 1841. Elizabeth Gould completed 84 plates for Birds of Australia before her death.
When Charles Darwin presented his mammal and bird specimens collected during the second voyage of HMS Beagle to the Zoological Society of London on 4 January 1837, the bird specimens were given to Gould for identification. He set aside his paying work and at the next meeting on 10 January reported that birds from the Galápagos Islands which Darwin had thought were blackbirds, gross-bills and finches were in fact a series of ground Finches which are so peculiar as to form an entirely new group, containing 12 species. This story made the newspapers. In March, Darwin met Gould again, learning that his Galápagos wren was another species of finch and the mockingbirds he had labelled by island were separate species rather than just varieties, with relatives on the South American mainland. Subsequently, Gould advised that the smaller southern Rhea specimen that had been rescued from a Christmas dinner was a separate species which he named Rhea darwinii, whose territory overlapped with the northern rheas. Darwin had not bothered to label his finches by island, but others on the expedition had taken more care. He now sought specimens collected by captain Robert FitzRoy and crewmen. From them he was able to establish that the species were unique to islands, an important step on the inception of his theory of evolution by natural selection. Goulds work on the birds was published between 1838 and 1842 in five numbers as Part 3 of Zoology of the Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle, edited by Charles Darwin. Elizabeth Gould illustrated all the plates for Part 3.
In 1838 the Goulds sailed to Australia, intending to study the birds of that country and be the first to produce a major work on the subject. They took with them the collector John Gilbert. They arrived in Tasmania in September, making the acquaintance of the governor Sir John Franklin and his wife. Gould and Gilbert collected on the island. In February 1839 Gould sailed to Sydney, leaving his pregnant wife with the Franklins. He travelled to his brother-in-laws station at Yarrundi, spending his time searching for bowerbirds in the Liverpool Range. In April he returned to Tasmania for the birth of his son. In May he sailed to Adelaide to meet Charles Sturt, who was preparing to lead an expedition to the Murray River. Gould collected in the Mount Lofty range, the Murray Scrubs and Kangaroo Island, returning again to Hobart in July. He then travelled with his wife to Yarrundi. They returned home to England in May 1840.
The result of the trip was The Birds of Australia (1840–48). It included a total of 600 plates in seven volumes; 328 of the species described were new to science and named by Gould. He also published A Monograph of the Macropodidae, or Family of Kangaroos (1841–1842) and the three volume work The Mammals of Australia (1849–1861).
Elizabeth died in 1841 after the birth of their eighth child, Sarah, and Goulds books subsequently used illustrations by a number of artists, including Henry Constantine Richter, William Matthew Hart and Joseph Wolf.
Throughout his professional life Gould had a strong interest in hummingbirds. He accumulated a collection of 320 species, which he exhibited at the Great Exhibition of 1851. Despite his interest, Gould had never seen a live hummingbird. In May 1857 he travelled to the United States with his second son, Charles. He arrived in New York too early in the season to see hummingbirds in that city, but on 21 May 1857, in Bartrams Gardens in Philadelphia, he finally saw his first live one, a ruby-throated hummingbird. He then continued to Washington D.C. where he saw large numbers in the gardens of the Capitol. Gould attempted to return to England with live specimens, but, as he was not aware of the conditions necessary to keep them, they only lived for two months at most.
Gould published: A Monograph of the Trochilidae or Humming Birds with 360 plates (1849–61); The Mammals of Australia (1845–63), Handbook to the Birds of Australia (1865), The Birds of Asia (1850–83), The Birds of Great Britain (1862–73) and The Birds of New Guinea and the adjacent Papuan Islands (1875–88).
The University of Glasgow, which owns a copy of Birds of Great Britain, describes John Gould as the greatest figure in bird illustration after Audubon, and auctioneers Sotherans describe the work as Goulds pride and joy.
Gould had already published some of the illustrations in Birds of Europe, but Birds of Great Britain represents a development of his aesthetic style in which he adds illustrations of nests and young on a large scale.
Sotherans Co. reports that Gould published the book himself, producing 750 copies, which remain sought after both as complete volumes, and as individual plates, currently varying in price from £450 – £850. The University of Glasgow records that the volumes were issued in London in 25 parts, to make the complete set, between 1863 and 1873, and each set contained 367 coloured lithographs.
Gould undertook an ornithological tour of Scandinavia in 1856, in preparation for the work, taking with him the artist Henry Wolf who drew 57 of the plates from Goulds preparatory sketches. According to The University of Glasgow Goulds skill was in rapidly producing rough sketches from nature (a majority of the sketches were drawn from newly killed specimens) capturing the distinctiveness of each species. Gould then oversaw the process whereby his artists worked his sketches up into the finished drawings, which were made into coloured lithographs by engraver William Hart.
There were problems: the stone engraving of the snowy owl in volume I was dropped and broken at an early stage in the printing. Later issues of this plate show evidence of this damage and consequently the early issue – printed before the accident – are considered more desirable.
The lithographs were hand coloured. In the introduction for the work, Gould states every sky with its varied tints and every feather of each bird were coloured by hand; and when it is considered that nearly two hundred and eighty thousand illustrations in the present work have been so treated, it will most likely cause some astonishment to those who give the subject a thought.
The work has gathered critical acclaim: according to Mullens and Swann, Birds of Great Britain is the most sumptuous and costly of British bird books, whilst Wood describes it as a magnificent work. Isabella Tree writes that it was seen – perhaps partly because its subject was British, as the culmination of [his] ... genius
1846 Louis Dussieux Large Antique Map of The Political Boundaries of France
- Title : 1846 Louis Dussieux Large Antique Map of The Political Boundaries of France
- Size: 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1846
- Ref #: 32414
Description:
This large hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map was published by Louis Dussieux in the 1846 edition of Atlas Generale
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 27 1/2in x 20 1/2in (700mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Dussieux, Louis 1815 - 1894
Dussieux was a French Geographer, prolific during the mid 19th century. After winning prizes in competitions of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles Letters in 1839 and 1840, he was appointed recorder of military history and geography at the Saint - Cyr Special School in 1842 and became the professor of history in 1850. In 1843 he was appointed correspondent for the Historical Monuments Committee.