Products
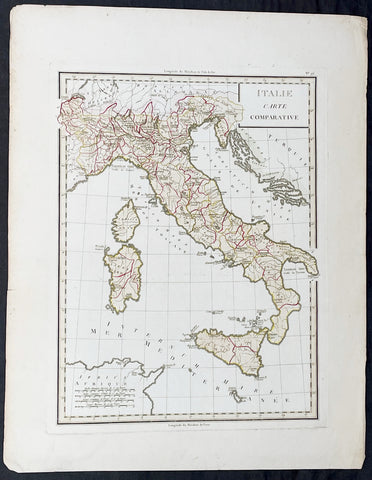
1765 Tardieu Large Antique Map of Italy
- Title : Italie Carte Comparative
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92789
- Size: 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Italy was published by the famous French publisher Pierre Francois Tardieu (famous for publishing Diderots Encyclopedie in 1779) in 1765. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Paper size: - 18in x 13 1/2in (460mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
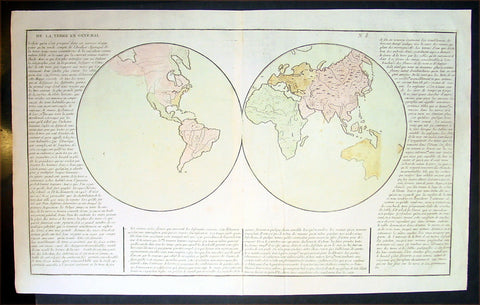
1767 Clouet Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map - Misshapen Australia
- Title : De La Terre En General
- Ref #: 16275
- Size: 23in x 16in (585mm x 410mm)
- Date : 1767
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, large beautifully hand coloured original antique Twin Hemisphere World Map - with an unusually depicted southern coast of Australia and French text on the General views of the World at the time - by Jean Baptiste Louis Clouet (1730-87) was published byMondhare et Jean, Paris in the 1767 edition of Clouets Atlas Geographie moderne avec une introduction. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 16in (585mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 13in (575mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
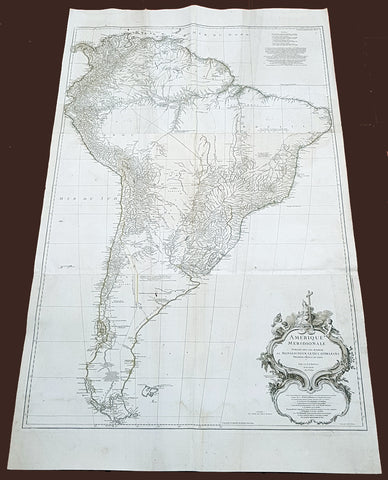
1768 D Anville Large Antique Map of South America
Antique Map
- Title : Amerique Meridionale Publiee Sous Les Auspices...Sr D Anville MDCCXLVIII
- Size: 55in x 32in (1.40m x 810mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1768 (dated)
- Ref #: 92329
Description:
This very large original copper plate engraved antique map of South America was engraved in 1768 by William Delahaye - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 55in x 32in (1.40m x 810mm)
Plate size: - 49in x 30 1/2in (1.30m x 770mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing, light soiling
Plate area: - Creasing, light soiling
Verso: - Creasing, light soiling
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industrys mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
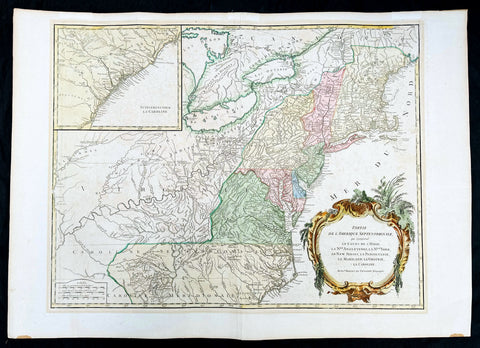
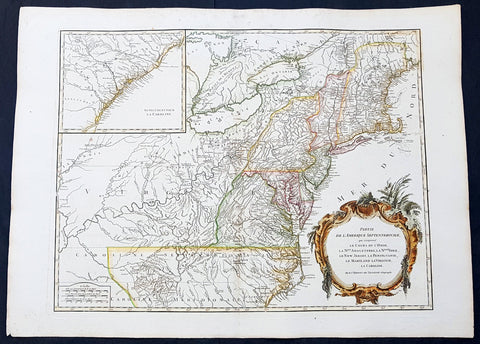
1768 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique 2nd edition Map of Colonial United States
Antique Map
- Title : Partie De L Amerique Septentrionale, qui Comprend Le Cours De L Ohio...Par le Sr Robert de Vaugondy
- Date : 1768
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93504
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 550mm)
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured, scarce 2nd edition antique map of the east coast of the United States, illustrating the course of the Ohio River and stretching from New England to the Carolinas, north to the Great Lakes and south to the Mississippi - with an inset map of The Carolinas - was published in 1768 by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal.
This is one of the best examples of this map I have seen, beautiful hand colour on age toned heavy paper with original margins with a heavy dark ink denoting an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 22in (760mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Second state of the early de Vaugondy map of the British colonies, with changes after the 1763 Treaty of Paris, with Virginia & Carolina extended to the Mississippi and Pennsylvania extended to Lake Erie. The majority of geographical information is based upon John Mitchells great map of North America from the mid 1750s, also drawing from Lewis, Evans on the Middle British Colonies and Joshua Frys and Peter Jeffersons map of Virginia and Maryland. The Mitchell map was the culmination of many years of British surveying in the North American Colonies and was considered one of the best maps of the continent available to Europeans and Americans in the mid-eighteenth century.
De Vaugondys rendition does not copy the full scope of Mitchells map but instead focuses on the colonies stretching from southern Maine to the Carolinas. In the top left corner is an inset of South Carolina and Georgia. De Vaugondy also pays special attention to the river systems and settlements. This map shows some of the earliest accurate information of the trans-Allegheny regions (the Ohio River, Kentucky, Tennessee and Parts of Ohio) and inland areas to the southeast of the Great Lakes and interior of New England.
Maine is still part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. During this era. The dispute between New Hampshire and New York over who controlled the area which is now Vermont has been resolved. The outbreak of the French & Indian War (Seven Years War) briefly suspended interest in the disputed area, and it was not until 1764 that the British crown upheld New Yorks claim to Vermont. Included is a beautiful title cartouche in the Rococo style. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1768 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique 2nd edition Map of Colonial United States
Antique Map
- Title : Partie De L Amerique Septentrionale, qui Comprend Le Cours De L Ohio...Par le Sr Robert de Vaugondy
- Date : 1768
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93129
- Size: 30in x 22in (760mm x 560mm)
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured, scarce 2nd edition antique map of the east coast of the United States, illustrating the course of the Ohio River and stretching from New England to the Carolinas, north to the Great Lakes and south to the Mississippi - with an inset map of The Carolinas - was published in 1768 by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal.
This is one of the best examples of this map I have seen, beautiful hand colour on age toned heavy paper with original margins with a heavy dark ink denoting an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 22in (760mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting in top margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Second state of the early de Vaugondy map of the British colonies, with changes after the 1763 Treaty of Paris, with Virginia & Carolina extended to the Mississippi and Pennsylvania extended to Lake Erie. The majority of geographical information is based upon John Mitchells great map of North America from the mid 1750s, also drawing from Lewis, Evans on the Middle British Colonies and Joshua Frys and Peter Jeffersons map of Virginia and Maryland. The Mitchell map was the culmination of many years of British surveying in the North American Colonies and was considered one of the best maps of the continent available to Europeans and Americans in the mid-eighteenth century.
De Vaugondys rendition does not copy the full scope of Mitchells map but instead focuses on the colonies stretching from southern Maine to the Carolinas. In the top left corner is an inset of South Carolina and Georgia. De Vaugondy also pays special attention to the river systems and settlements. This map shows some of the earliest accurate information of the trans-Allegheny regions (the Ohio River, Kentucky, Tennessee and Parts of Ohio) and inland areas to the southeast of the Great Lakes and interior of New England.
Maine is still part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. During this era. The dispute between New Hampshire and New York over who controlled the area which is now Vermont has been resolved. The outbreak of the French & Indian War (Seven Years War) briefly suspended interest in the disputed area, and it was not until 1764 that the British crown upheld New Yorks claim to Vermont. Included is a beautiful title cartouche in the Rococo style. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
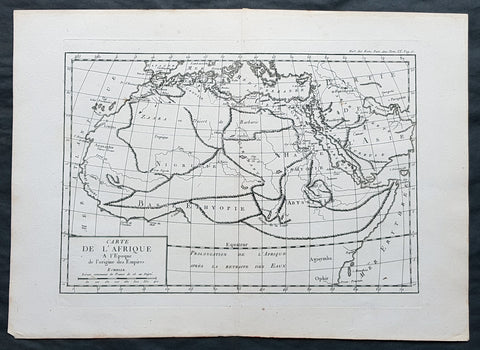
1769 J B D Anville Original Antique Map of Africa as known to the Ancients
- Title : Carte De L Afrique a l Epoque de l origine des Empires
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 32341
- Date : 1769
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville in the 1769 edition of his atlas Geographie Ancienne et Abregee. or Modern and Ancient Geography (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
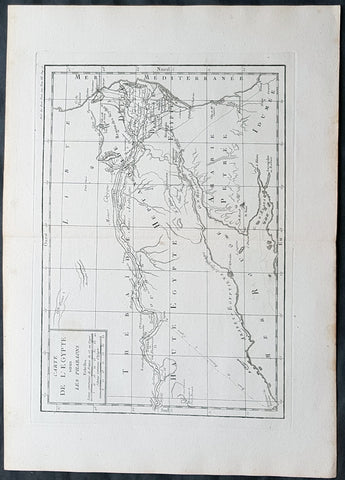
1769 J B D Anville Original Antique Map of Egypt & The Nile in Time of Pharaohs
- Title : Carte De L Egypte sous Les Pharaons
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 32342
- Date : 1769
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D'Anville in the 1769 edition of his atlas Geographie Ancienne et Abregee. or Modern and Ancient Geography (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1769 J B D Anville Original Antique Map of Greece Crete Macedonia Turkey Cyprus
- Title : Carte Generale De La Grece
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 32345
- Date : 1769
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville in the 1769 edition of his atlas Geographie Ancienne et Abregee. or Modern and Ancient Geography (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
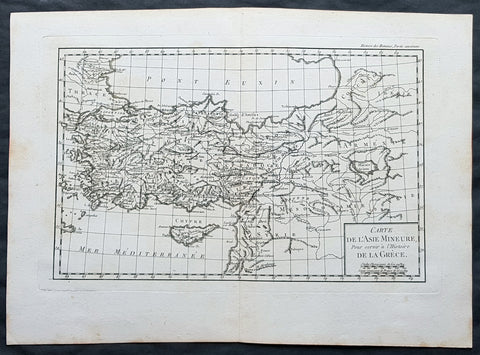
1769 J B D Anville Original Antique Map of Turkey, Cyprus, Asia Minor, Syria
- Title : Carte De L Asie Minerure Pour Servir a L Histoire De La Grece
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 32346
- Date : 1769
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville in the 1769 edition of his atlas Geographie Ancienne et Abregee. or Modern and Ancient Geography (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
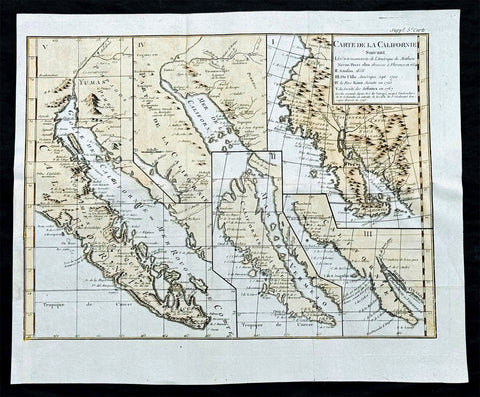
1770 De Vaugondy & Diderot Antique Maps of Cartographical Views of California
Antique Map
- Title : Carte de la Californie suivant / I. La carte manuscrite de l'Amérique de Mathieu Néron Pecci olen dresse à Florence en 1604 / II. Sanson 1656 / III. De L'Isle Amérique Sept. 1700 / IV. le Pere Kino Jesuite en 1705 / V. La Societe des Jésuites en 1767.
- Ref: 93434
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine large historically important original hand coloured, copper-plate engraved antique map, illustrating 5 of the most influential depictions of California and its cartographical evolution between 1604 and 1767.
The map was engraved by the important French cartographer Robert De Vaugondy, for the 1770 edition of the Denis Diderot Encyclopaedie Raisonee des Sciences des Artes.
- The earliest map (upper right corner) is based upon a manuscript map by Mathieu Neron Pecci, drawn in Florence in 1604. This map also forms the basis of a map popularized in 1770 by Rigobert Bonne.
- The second map is Nicholas Sanson's map of California as an Island, based upon his larger map of 1656. This map was probably the single most influential projection of California as an Island.
- The third map map (lower right) is a portion of Guillaume De L'Isles map of America, published in 1700. While not truly peninsular in nature, it was influential in the shift back toward depicting California as a Peninsula.
- The fourth map (upper center) is a portion of Fra. Eusebio Kino's map, generally credited with being the map which dispelled the California as and Island myth. Issued in 1705, the map is based upon Father Kino's overland expedition from the mainland to the top of the Gulf of Cortez.
- The fifth map is one of the most interesting and enduring maps of California and the Baja (left side). Initially issued by the Society of Jesuits in 1767, it was popularized by Isaak Tirion and was perhaps the most interesting of all maps of Baja California in the 2nd half of the 18th Century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12in (405mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin expended from plate mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
This map was 1 of 10 maps to appear in the Supplement to Diderot\'s monumental encyclopedia, one of the most influential and widely distirbuted works of the second half of the 18th Century. Diderot\'s goal was to examine and display the popular geographical conceptions of several different parts of the world where the knowledge of the region\'s geogaphy was still largely unknown and evolving. Other maps treat the Northwest Passage, Northeast Passage and the NW Coast of America, among other topics.
A marvelous amalgam and an essential map for collectors of North American & California maps.
Encyclopaedie Raisonee des Sciences des Artes: At the time of publication these maps of Encyclopedie were some of the most in-depth and accurate maps published of Asia, Canada, California and the NW region of America.
Diderot\'s maps were intended to further an understanding of the Western Coast of America, and NE Asia, during a time period immediately prior to Cook\'s voyage to the region - less than a decade later- where numerous theories abounded on the NW Coast of America.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
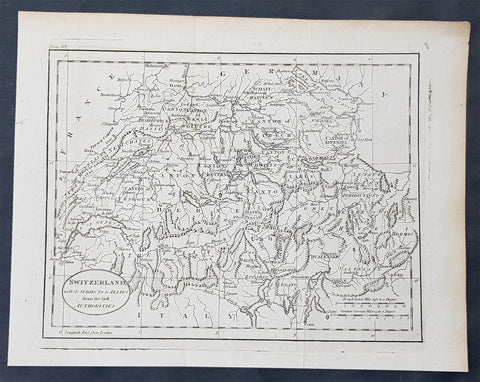
1770 John Cary Original Antique Map of Switzerland
- Title : Switzerland with its Subjects & Allies from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70188
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthries Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
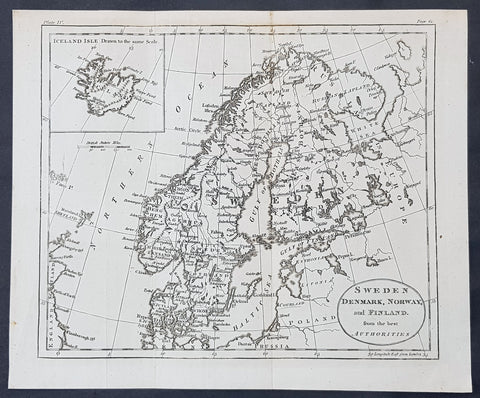
1770 John Cary Original Antique Map Sweden, Denmark, Norway, Finland & Iceland
- Title : Sweden, Denmark, Norway and Finland from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70177
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthrie\'s Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1770 Louis-Joseph Mondhare Antique Print View of St Pauls Cathedral, London England
Antique Map
- Title : Elevation Du Portail De La Cathedrale De St Paul De Londre
- Ref #: 93461
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9in (365mm x 245mm)
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique print of St Pauls Cathedral, London was engraved and published by Louis-Joseph Mondhare in Paris in 1770
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9in (365mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9in (365mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Margins cropped to plate mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The task of designing a replacement structure was officially assigned to Sir Christopher Wren on 30 July 1669. He had previously been put in charge of the rebuilding of churches to replace those lost in the Great Fire. More than 50 City churches are attributable to Wren. Concurrent with designing St Pauls, Wren was engaged in the production of his five Tracts on Architecture.
Wren had begun advising on the repair of the Old St Pauls in 1661, five years before the fire in 1666. The proposed work included renovations to interior and exterior to complement the classical facade designed by Inigo Jones in 1630. Wren planned to replace the dilapidated tower with a dome, using the existing structure as a scaffold. He produced a drawing of the proposed dome which shows his idea that it should span nave and aisles at the crossing. After the Fire, it was at first thought possible to retain a substantial part of the old cathedral, but ultimately the entire structure was demolished in the early 1670s.
In July 1668 Dean William Sancroft wrote to Wren that he was charged by the Archbishop of Canterbury, in agreement with the Bishops of London and Oxford, to design a new cathedral that was Handsome and noble to all the ends of it and to the reputation of the City and the nation. The design process took several years, but a design was finally settled and attached to a royal warrant, with the proviso that Wren was permitted to make any further changes that he deemed necessary. The result was the present St Pauls Cathedral, still the second largest church in Britain, with a dome proclaimed as the finest in the world. The building was financed by a tax on coal, and was completed within its architects lifetime with many of the major contractors engaged for the duration.
The topping out of the cathedral (when the final stone was placed on the lantern) took place on 26 October 1708, performed by Wrens son Christopher Jr and the son of one of the masons. The cathedral was declared officially complete by Parliament on 25 December 1711 (Christmas Day). In fact, construction continued for several years after that, with the statues on the roof added in the 1720s. In 1716 the total costs amounted to £1,095,556 (£165 million in 2019).
On 2 December 1697, 31 years and 3 months after the Great Fire destroyed Old St Pauls, the new cathedral was consecrated for use. The Right Reverend Henry Compton, Bishop of London, preached the sermon. It was based on the text of Psalm 122, I was glad when they said unto me: Let us go into the house of the Lord. The first regular service was held on the following Sunday.
Opinions of Wrens cathedral differed, with some loving it: Without, within, below, above, the eye / Is filled with unrestrained delight, while others hated it: There was an air of Popery about the gilded capitals, the heavy arches ... They were unfamiliar, un-English
Mondhare & Jean (active 1759 - 1829)
Louis-Joseph Mondhare (1734 - Paris 1799) & Pierre Jean (1754 - 1829) were prominent Parisian publishers, engravers, print and map sellers who were active in Paris in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
In 1784 Jean married the daughter of Mondhare, who formed a partnership with his son in law, changing forming a very successful partnership thereafter as Mondhare & Jean.
After Mondhare retirement in 1796, Jean carried on with the publishing & printing business, having inherited all of the printing plates that also included many map plates from the likes of Nolin, Clouet, D Anville , Delsile and others. Both Mondhare and Jean were responsible for the engraving and printing of the very decorative large wall maps by J B Nolin & J B L Clouet, as well as single plate maps and atlases. Mondares premises were located at Rue St Jacques, à lHôtel Saumur later movin
1770 Louis-Joseph Mondhare Antique Print View of St Pauls Cathedral, London UK
Antique Map
- Title : Le Portail de la grande Eglise de St Paul de Londre...a Paris chez Mondhare ru st Jacques
- Ref #: 93460
- Size: 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 235mm)
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique print of St Pauls Cathedral, London was engraved and published by Louis-Joseph Mondhare in Paris in 1770
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 235mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The task of designing a replacement structure was officially assigned to Sir Christopher Wren on 30 July 1669. He had previously been put in charge of the rebuilding of churches to replace those lost in the Great Fire. More than 50 City churches are attributable to Wren. Concurrent with designing St Pauls, Wren was engaged in the production of his five Tracts on Architecture.
Wren had begun advising on the repair of the Old St Pauls in 1661, five years before the fire in 1666. The proposed work included renovations to interior and exterior to complement the classical facade designed by Inigo Jones in 1630. Wren planned to replace the dilapidated tower with a dome, using the existing structure as a scaffold. He produced a drawing of the proposed dome which shows his idea that it should span nave and aisles at the crossing. After the Fire, it was at first thought possible to retain a substantial part of the old cathedral, but ultimately the entire structure was demolished in the early 1670s.
In July 1668 Dean William Sancroft wrote to Wren that he was charged by the Archbishop of Canterbury, in agreement with the Bishops of London and Oxford, to design a new cathedral that was Handsome and noble to all the ends of it and to the reputation of the City and the nation. The design process took several years, but a design was finally settled and attached to a royal warrant, with the proviso that Wren was permitted to make any further changes that he deemed necessary. The result was the present St Pauls Cathedral, still the second largest church in Britain, with a dome proclaimed as the finest in the world. The building was financed by a tax on coal, and was completed within its architects lifetime with many of the major contractors engaged for the duration.
The topping out of the cathedral (when the final stone was placed on the lantern) took place on 26 October 1708, performed by Wrens son Christopher Jr and the son of one of the masons. The cathedral was declared officially complete by Parliament on 25 December 1711 (Christmas Day). In fact, construction continued for several years after that, with the statues on the roof added in the 1720s. In 1716 the total costs amounted to £1,095,556 (£165 million in 2019).
On 2 December 1697, 31 years and 3 months after the Great Fire destroyed Old St Pauls, the new cathedral was consecrated for use. The Right Reverend Henry Compton, Bishop of London, preached the sermon. It was based on the text of Psalm 122, I was glad when they said unto me: Let us go into the house of the Lord. The first regular service was held on the following Sunday.
Opinions of Wrens cathedral differed, with some loving it: Without, within, below, above, the eye / Is filled with unrestrained delight, while others hated it: There was an air of Popery about the gilded capitals, the heavy arches ... They were unfamiliar, un-English
Mondhare & Jean (active 1759 - 1829)
Louis-Joseph Mondhare (1734 - Paris 1799) & Pierre Jean (1754 - 1829) were prominent Parisian publishers, engravers, print and map sellers who were active in Paris in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
In 1784 Jean married the daughter of Mondhare, who formed a partnership with his son in law, changing forming a very successful partnership thereafter as Mondhare & Jean.
After Mondhare retirement in 1796, Jean carried on with the publishing & printing business, having inherited all of the printing plates that also included many map plates from the likes of Nolin, Clouet, D Anville , Delsile and others. Both Mondhare and Jean were responsible for the engraving and printing of the very decorative large wall maps by J B Nolin & J B L Clouet, as well as single plate maps and atlases. Mondares premises were located at Rue St Jacques, à lHôtel Saumur later movin
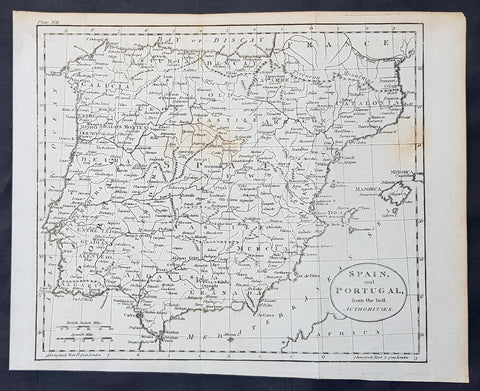
1770 Thomas Kitchin Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & Balearic Islands
- Title : Spain and Portugal from the Best Authorities
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Ref #: 70189
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map by Thomas Kitchen was published in the 1770 edition of the atlas for William Guthrie\'s Geographical Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
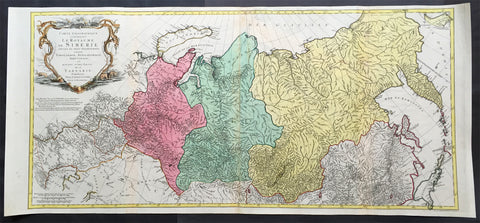
1770 Tobias Lotter Very Large Antique Map of Russia & Siberia
Antique Map
- Title : Carte géographique contenant le royaume de Sibérie
- Ref #: 61039
- Size: 44in x 20 1/2in (1.15m x 520mm)
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This scarce, very large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Russia and Siberia with parts of China was published by Tobias Conrad Lotter in 1770.
Background: Rare, highly detailed map of Russia & Siberia that is subdivided into provinces, namely Tobolsk, Jenissejesk, Irkutsk, and outer parts of the Tartary. In upper right corner inset-map of the Chukchi (Chukotsk) Peninsula. On the left side sheet is a large title cartouche set in a steppe landscape with reindeer sledge, whale and polar bears. Scale ca. 1 : 13,000,000 and engraved by Matthäus Albrecht Lotter for Tobias Conrad Lotter.
In about 1770 a map of Russia & Siberia by Ivan Fomic Truscot (1721-1786, comp. BMC XXII, 353) was published, that comprised the West Siberian states Tobolsk and Yeniseiesk only, but may have been quite available to Lotter, just as also the German edition of the third Russian general map by Truscot and Jacob F. Schmidt of 1776 was published by Lotter in 1784.
The comparison of the Asian north-eastern coast from Japan up to Cape Szalaginskoi (Cape Shelagskiy) together with the offshore islands there results in an astonishing similarity with representation and designation on Rigobert Bonne’s maps of Russia and the Chinese Tartary published by Lattré in Paris in 1771. Especially striking the form of Sakhalin that hitherto – but also still on the Truscot map of 1776 – appears far more stocky, here though shows a slimmer shape considerably closer to reality. Cape Patience known at least since the 1743 Utrecht edition of the map of Russia by Johann Matthias Haas (Augsburg 1684 – Wittenberg/Augsburg 1742) – Kaert van Het geheele Russische Keizerryk – already published by Homann Heirs in Nuremberg in 1730 + 39 here supposedly for the first time shown in unity with Sakhalin and, as the long-stretched southern half beginning west of the cape already recognizable there is missing here, together forming its southern tip.
Of great similarity, too, the still completely bulky representation of Jeso (= Hokkaido), filling up large parts of the Sea of Japan as known sufficiently from numerous, though by far not all maps of the 18th century. The Kurile Islands adjacent in northeastern direction – with rich detail designation, but without the denomination as chain of islands appearing at least in the 1784 edition of Truscot’s general map – with the obscure islands Terre des Etat (Iturup) and Terre de la Compagnie. Both, as also the often furthermore adjacent da Gama Land, had been supposedly finally left by Truscot to the memory of the great time of sometimes only vague discoveries.
Interestingly both islands are designated with hints to Russian maps in question marks. This probably to be seen as a sign for an independent work of Lotter who obviously drew his knowledge from different sources and not just copied a map he had got into his hands for a German edition. Further clue to the dating is, too, the taking over of the Chukchi (Chukotsk) Peninsula in the farest northeast of Asia in the shape practically unchanged since Ivan Kirilov’s (1695 – Samara 1737) general map of 1734 – the first Russian one at all. For at the latest since publishing the Truscot map of 1776 in 1784 Lotter would have known the new shape valid till today.
Likewise Novaya Zemlya here still figuring as undivided island, thus without the Matochkin Strait supposedly recorded by Truscot for the first time. With respect to the independence of his work a recourse to older forms of representation appears not very likely in both cases.
Designed in cone projection, the null meridian runs about 020degrees western longitude of Greenwich through the centre of Iceland. In the west reaching till Novaya Zemlya – Ural Mountains – Kazan – Sea of Azov, the map comprises in the far east still northern Japan , the Kurile Islands and Kamchatka including the offshore Bering Island . Southerly still with at the Caspian Sea , Lake Aral , the headwaters of the Yenisey , the Dalai nuur (Hulun Lake) in northern Mongolia near to the wall of Genghis Chan , the region of today’s Vladivostok and the Tsugari Street . In the Arctic Ocean up to 78 degrees northern latitude. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 44in x 20 1/2in (1.15m x 520mm)
Plate size: - 42in x 19 1/2in (1.0mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Repair to top adjacent to centerfold, no loss
Verso: - Repair as mentioned
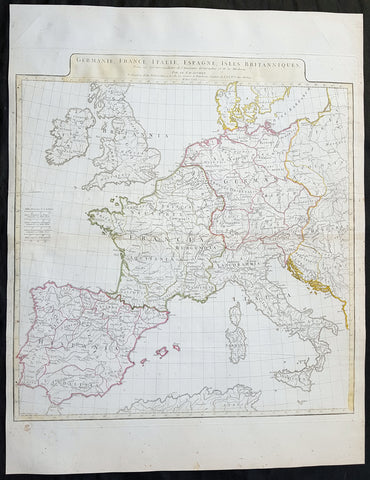
1771 J B D Anville Large Original Antique Map of Western Europe & Britain
- Title : Germanie, France, Italie, Espagne, Isles Britanniques...MDCCLXXI
- Size: 25 1/2in x 20in (650mm x 525mm)
- Ref #: 92305
- Date : 1771
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved and highly detailed original antique map of Western Europe and The British Isles by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D\'Anville was engraved in 1771 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D\'Anville\'s large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 20in (650mm x 525mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing along centerfold
Plate area: - Creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Creasing along centerfold
1772 De Vaugondy Visscher Large Antique Map of California & SW America
Antique Map
- Title : Carte De La Californie Et Des Pays Nord Ouest separes de L'Asie par le Detroit d'Anian…1772
- Date : 1772
- Ref # : 50674
- Size : 20in x 15 3/4in (510mm x 400mm)
Description:
Fascinating study in the comparative cartography of the West Coast of North America, from the Straits of Anian to Cabo San Lucas and the southern tip of Baja California. The work consists of extracts from two maps, both reportedly done by Visscher in the 1612 and 1641 respectively and with information derived from Mercator and Plancius. The larger map prominently shows the Strait of Anian, Anian Regnum, Quivira Regnum, the Sierra Nevada, Nova Albion, Tontonteac Regnum, Tolm Regnum and a coastal detail which includes over 30 coastal place names, including Mendocino, San Miguel (San Diego), Cape Fortuna, I. De Paxaros (Catalina?), and many mythical/ephemeral place names. The smaller map also shows the Straits of Anian, but depicts an open sea above, clearly portending a NW Passage in the Arctic Circle. The NW Coastline differs radically, and only Anian Regnum and Quivira Regnum are located, that later considerably south of the location on the larger map. The smaller map includes a similar number of coastal placenames, but includes several important ones not listed on the larger map, including C. Blanco (3 times), C. de San Francisco and los Farilones, but ommits any significant effort to depict bays.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 15 3/4in (510mm x 400mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (410mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Encyclopaedie Raisonee des Sciences des Artes:
At the time of publication these maps of Encyclopedie were some of the most in-depth and accurate maps published of Asia, Canada, California and the NW region of America.
Diderot's maps were intended to further an understanding of the Western Coast of America, and NE Asia, during a time period immediately prior to Cook's voyage to the region - less than a decade later- where numerous theories abounded on the NW Coast of America. A nice dark impression of this essential map for American map collectors. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1772 John Boydell Antique Print of Moat Island Eight Views of Windsor Great Park
- Title : The Moat Island Published March the 2nd 1772 by John Boydell Engraver in Cheapside London
- Size: 23 1/2in x 13 1/2in (595mm x 340mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1772
- Ref #: 91158-1
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of The Moat Island in Great Windsor Park by Thomas Sandby was engraved by François Vivares and published by John Boydell for the 1772 edition of Eight Views of Windsor Great Park
Thomas Sandby RA 1721 – 1798 was an English draughtsman, watercolour artist, architect and teacher. In 1743 he was appointed private secretary to the Duke of Cumberland, who later appointed him Deputy Ranger of Windsor Great Park, where he was responsible for considerable landscaping work.
Along with his younger brother Paul, he was one of the founding members of the Royal Academy in 1768, and was its first professor of architecture. His most notable architectural work was the Freemason\'s Hall in London (now demolished).
Francois Vivares 1709 – 1780 was a French landscape-engraver, active in England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 13 1/2in (595mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 13 1/2in (595mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling and creasing
Plate area: - Several small tears and holes repaired
Verso: - Repairs as noted
Background:
The set of eight folio plates published in Eight Views of Windsor Great Park executed by Thomas Sandby and his brother Paul with the assistance of several noted English engravers. The 8 views were considered to be the finest set of topographical country house views after Rigauds 1739 Views of Stowe
Thomas Sandby (1721–1798) was an architect who served as draftsman to the Duke of Cumberland at the Battle of Culloden in 1746. With his younger brother Paul, a landscape painter and watercolourist, they were founding members of the Royal Academy in 1768.
Through these engravings, the Duke of Cumberland sought to commemorate his alteration of the park, which had served English royalty since the eleventh century as a hunting and jousting ground and, beginning in the eighteenth century, as a place of formal gardens and walks. (The Duke is pictured in several of the engravings, arriving by carriage, directing workers by a bridge, and discoursing with the King by the river.) The improvements to Windsor Great Park recorded in these engravings include a dam built in 1749, forming an artificial lake, rockwork, a cascade, and a grotto. In 1752, a fifty-ton ships hull was raised from the Thames and fitted up on the artificial lake as a Mandarin Yacht or Chinese Junk. A triangular Gothic belvedere was erected on Shrubs Hill to the south, and a large wooden footbridge was constructed over the water. Renovations were also undertaken at the so-called Great Lodge, which became the Dukes residence at Windsor. In short, these improvements partook of the fashionable taste for picturesque Gothick – that was most noticeably championed by Horace Walpoles contemporary Strawberry Hill villa.
Much of these improvements, which were actually the work of architect Henry Flitcroft, were destroyed by severe floods, which broke the dam at Virginia Water in 1768 and again in 1782. These views therefore provide evidence for the state of the park at that date.
Original sketches and preparatory drawings by Paul and Thomas Sandby related to these engravings survive in the Royal Collection at Windsor Castle, the Victoria and Albert Museum, and the British Museum.
Boydell, John 1720 - 1804
Boydell 1804 was an 18th-century British publisher noted for his reproductions of engravings. He helped alter the trade imbalance between Britain and France in engravings and initiated a British tradition in the art form. A former engraver himself, Boydell promoted the interests of artists as well as patrons and as a result his business prospered.
The son of a land surveyor, Boydell apprenticed himself to William Henry Toms, an artist he admired, and learned engraving. He established his own business in 1746 and published his first book of engravings around the same time. Boydell did not think much of his own artistic efforts and eventually started buying the works of others, becoming a print dealer as well as an artist. He became a successful importer of French prints during the 1750s but was frustrated by their refusal to trade prints in kind. To spark reciprocal trade, he commissioned William Wolletts spectacular engraving of Richard Wilsons The Destruction of the Children of Niobe, which revolutionised the print trade. Ten years later, largely as a result of Boydells initiative, the trade imbalance had shifted, and he was named a fellow of the Royal Society for his efforts.
In the 1790s, Boydell began a large Shakespeare venture that included the establishment of a Shakespeare Gallery, the publication of an illustrated edition of Shakespeares plays, and the release of a folio of prints depicting scenes from Shakespeares works. Some of the most illustrious painters of the day contributed, such as Benjamin West and Henry Fuseli.
Throughout his life, Boydell dedicated time to civic projects: he donated art to government institutions and ran for public office. In 1790 he became Lord Mayor of London. The French Revolutionary Wars led to a cessation in Continental trade at the end of the 1790s. Without this business, Boydells firm declined and he was almost bankrupt at his death in 1804.
In 1751, with his large volume of prints, Boydell moved to larger premises at 90 Cheapside. By 1755, he had published A Collection of One Hundred and Two Views, &C. in England and Wales. This cheap but successful book gave him capital to invest. He became increasingly immersed in the commercial side of the print business and like most print dealers began importing prints to sell. These included print reproductions of landscapes by artists such as Claude Lorrain and Salvator Rosa. The bulk of the imports came from the undisputed masters of engraving during the 18th century: the French. Boydell made a small fortune in the 1750s from these imported prints. His early success was acknowledged in 1760 when he was named a member of the Royal Society.Winifred Friedman, who has written extensively on Boydell, explains that despite this success, [w]hat rankled Boydell was that the French would not extend credit, or exchange prints; he was required to produce hard cash. Boydell took action, and this was the turning point.
In 1761, Boydell decided that he would attempt to trade with the French in kind—something they had refused in the past because of the poor quality of British engravings. To inaugurate this change, he had to have a truly spectacular print. To this end, he hired William Woollett, the foremost engraver in England, to engrave Richard Wilsons Destruction of the Children of Niobe. Woollett had already successfully engraved Claude Lorrains 1663 painting The Father of Psyche Sacrificing at the Temple of Apollo for Boydell in 1760. Boydell paid him approximately £100 for the Niobe engraving, a staggering amount compared to the usual rates. This single act of patronage raised engravers fees throughout London. The print was wildly successful, but more importantly, the French accepted it as payment in kind. In fact, it was the first British print actively desired on the Continent. By 1770, the British were exporting far more prints than they were importing, largely due to Boydell.
Boydells business flourished and he soon hired his nephew, Josiah Boydell, to assist him. Boydells biographer, Sven Bruntjen, hypothesizes that one of the reasons for Boydells early and phenomenal success was his specialisation. Unlike his competitors [who sold manuals, atlases and other assorted books] ... his [business had an] almost exclusive concentration on the sale of reproductive prints. Bruntjen argues that despite the extensive sales of varied types of reproductive prints, it was the contemporary history print which accounted for the major part of Boydells success as a print dealer. Most notable among these was the Death of General Wolfe a 1770 painting by Benjamin West, engraved by Woollett for Boydell in 1776. As early as 1767, Boydell had stopped engraving prints himself and began exclusively relying on commissions and trades and it was from these that he profited.
Boydell had opened up a new market with Niobe and he quickly followed up this success. With a prospering business and capital in reserve, he embarked on several ambitious projects, often simultaneously. In 1769, he began A Collection of Prints, Engraved after the Most Capital Paintings in England. Its last, and ninth volume, was finished in 1792 to great critical and financial success. In 1773, he began A Set of Prints Engraved after the Most Capital Paintings in the Collection of Her Imperial Majesty the Empress of Russia, Lately in the Possession of the Earl of Orford at Houghton in Norfolk, which was finished in 1788.
In addition to these projects and in the middle of his Shakespeare undertaking Boydell experimented with aquatint in An History of the River Thames, published in 1796. Bruntjen writes, although not the first colored aquatint book, [it] was the first major one, and it was to set an example for the type of illustration that was to enjoy widespread popularity in England for some forty years. Boydell also published The Original Work of William Hogarth in 1790 and The Poetical Works of John Milton and The Life of the Poet (i.e., Milton) in 1794.
The productivity and profitability of Boydells firm spurred the British print industry in general. By 1785, annual exports of British prints reached £200,000 while imports fell to £100. Boydell was acknowledged and praised throughout England as the agent of this stunning economic reversal. In 1773 he was awarded the Royal Academy Gold Medal for his services in advancing the print trade. In 1789, at the Royal Academy dinner, the Prince of Wales toasted an English tradesman who patronizes art better than the Grand Monarque, Alderman Boydell, the Commercial Maecenas
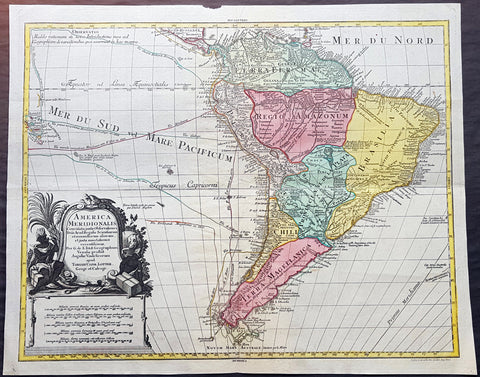
1772 Tobias Lotter Large Antique Map of South America, Drake, Magellan, Le Maire
- Title : America Meridionalis ...Tobiam Conr. Lotter...1772
- Date : 1772
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
- Ref #: 70819
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of South America was engraved by Gustav Conrad Lotter in 1772 - dated at the foot of the map - and published by his father Tobias Conrad Lotter.
The map shows the routes of the voyages by various famous explorers to South America including: Magellan (1520), Drake (1577), le Maire & Schouten (1616), Sarmineto (1570) and others. The map also illustrates various river systems and other speculative information about the unexplored interior of the Continent. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (595mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
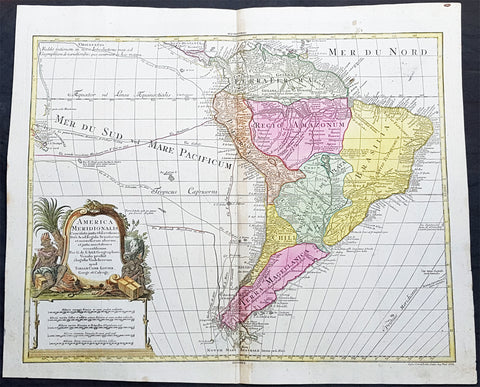
1772 Tobias Lotter Large Antique Map of South America, Magellan, Drake, Le Maire
- Title : America Meridionalis ...Tobiam Conr. Lotter...1772
- Date : 1772
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
- Ref #: 61139
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of South America was engraved by Gustav Conrad Lotter in 1772 - dated at the foot of the map - and published by his father Tobias Conrad Lotter.
The map shows the routes of the voyages by various famous explorers to South America including: Magellan (1520), Drake (1577), le Maire & Schouten (1616), Sarmineto (1570) and others. The map also illustrates various river systems and other speculative information about the unexplored interior of the Continent. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (595mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
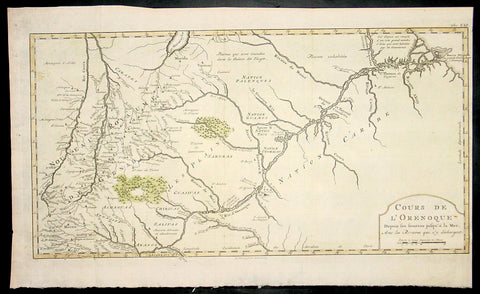
1773 Bellin Antique Map The Course of the Orinoco River South America - Rare
- Title : Cours De L Orenoque...1773
- Ref #: 92803
- Size: 18 1/2in x 11 1/2in (460mm x 295mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Orinoco River, South America, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The mouth of the Orinoco River at the Atlantic Ocean was documented by Columbus on 1 August 1498, during his third voyage. Its source at the Cerro Delgado–Chalbaud, in the Parima range, was not explored until 1951, 453 years later. The source, near the Venezuelan–Brazilian border, at 1,047 metres (3,435 ft) above sea level (02°19′05″N 63°21′42″W), was explored in 1951 by a joint Venezuelan–French team.
The Orinoco Delta, and tributaries in the eastern llanos such as the Apure and Meta, were explored in the 16th century by German expeditions under Ambrosius Ehinger and his successors. In 1531 Diego de Ordaz, starting at the principal outlet in the delta, the Boca de Navios, sailed up the river to the Meta. Antonio de Berrio sailed down the Casanare to the Meta, and then down the Orinoco River and back to Coro. In 1595, after capturing de Berrio to obtain information while conducting an expedition to find the fabled city of El Dorado, the Englishman Sir Walter Raleigh sailed down the river, reaching the savannah country.
Alexander von Humboldt explored the basin in 1800, reporting on the pink river dolphins. He published extensively on the river\'s flora and fauna
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 11 1/2in (460mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 10in (455mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
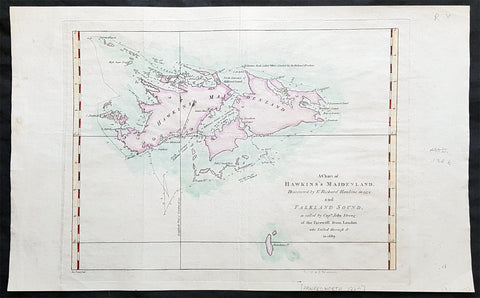
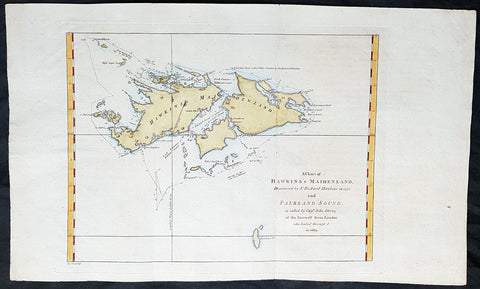
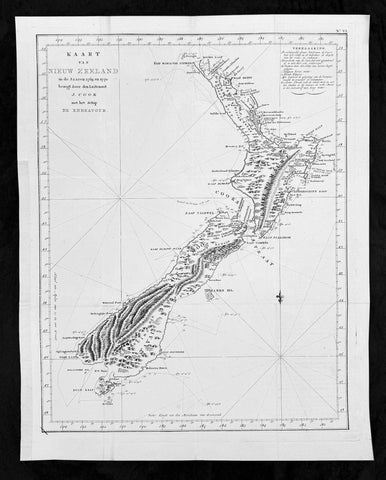
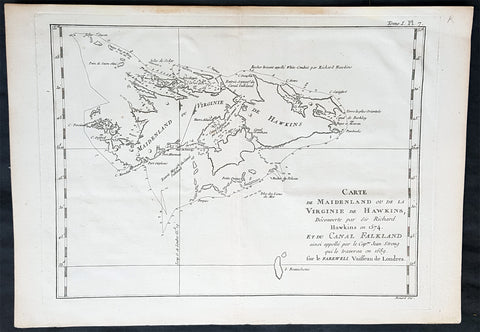
1773 Commodore John Byron 1st Ed Antique Map of The Falkland Islands Sth America
Antique Map
- Title : A chart of Hawkins s Maidenland, discovered by Sr. Richard Hawkins in 1574 and Falkland Sound, so called by Capn. John Strong of the Farewell from London who sailed through it in 1689.
- Ref #: 93384
- Size: 16 1/2in x 10n (405mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the Falkland Islands by Commodore John Byron was engraved by Isaac Noval and published in the 1773 first English edition of John Hawkesworth important book An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor. Drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, Esq; by John Hawkesworth, LL.D. In three volumes. Illustrated with cuts, and a great variety of charts and maps relative to countries now first discovered, or hitherto but imperfectly known. London: printed for W. Strahan; and T. Cadell in the Strand, MDCCLXXIII.
John Hawkesworth (1715 - 1773) was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook, from 1702 to 1771, drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 10n (405mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (310mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Although Fuegians from Patagonia may have visited the Falkland Islands in prehistoric times, the islands were uninhabited when Europeans first discovered them. Claims of discovery date back to the 16th century, but no consensus exists on whether early explorers discovered the Falklands or other islands in the South Atlantic. The first recorded landing on the islands is attributed to English captain John Strong, who, en route to Perus and Chiles littoral in 1690, discovered the Falkland Sound and noted the islands water and game.
The Falklands remained uninhabited until the 1764 establishment of Port Louis on East Falkland by French captain Louis Antoine de Bougainville, and the 1766 foundation of Port Egmont on Saunders Island by British captain John MacBride. Whether or not the settlements were aware of each others existence is debated by historians. In 1766, France surrendered its claim on the Falklands to Spain, which renamed the French colony Puerto Soledad the following year. Problems began when Spain discovered and captured Port Egmont in 1770. War was narrowly avoided by its restitution to Britain in 1771.
Both the British and Spanish settlements coexisted in the archipelago until 1774, when Britains new economic and strategic considerations led it to voluntarily withdraw from the islands, leaving a plaque claiming the Falklands for King George III. Spains Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata became the only governmental presence in the territory. West Falkland was left abandoned, and Puerto Soledad became mostly a prison camp. Amid the British invasions of the Río de la Plata during the Napoleonic Wars in Europe, the islands governor evacuated the archipelago in 1806; Spains remaining colonial garrison followed suit in 1811, except for gauchos and fishermen who remained voluntarily.
Thereafter, the archipelago was visited only by fishing ships; its political status was undisputed until 1820, when Colonel David Jewett, an American privateer working for the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, informed anchored ships about Buenos Aires 1816 claim to Spains territories in the South Atlantic. Since the islands had no permanent inhabitants, in 1823 Buenos Aires granted German-born merchant Luis Vernet permission to conduct fishing activities and exploit feral cattle in the archipelago. Vernet settled at the ruins of Puerto Soledad in 1826, and accumulated resources on the islands until the venture was secure enough to bring settlers and form a permanent colony. Buenos Aires named Vernet military and civil commander of the islands in 1829, and he attempted to regulate sealing to stop the activities of foreign whalers and sealers. Vernets venture lasted until a dispute over fishing and hunting rights led to a raid by the American warship USS Lexington in 1831, when United States Navy commander Silas Duncan declared the dissolution of the islands government.
Buenos Aires attempted to retain influence over the settlement by installing a garrison, but a mutiny in 1832 was followed the next year by the arrival of British forces who reasserted Britains rule. The Argentine Confederation (headed by Buenos Aires Governor Juan Manuel de Rosas) protested against Britains actions and Argentine governments have continued since then to register official protests against Britain. The British troops departed after completing their mission, leaving the area without formal government. Vernets deputy, the Scotsman Matthew Brisbane, returned to the islands that year to restore the business, but his efforts ended after, amid unrest at Port Louis, gaucho Antonio Rivero led a group of dissatisfied individuals to murder Brisbane and the settlements senior leaders; survivors hid in a cave on a nearby island until the British returned and restored order. In 1840, the Falklands became a Crown colony, and Scottish settlers subsequently established an official pastoral community. Four years later, nearly everyone relocated to Port Jackson, considered a better location for government, and merchant Samuel Lafone began a venture to encourage British colonisation.
Stanley, as Port Jackson was soon renamed, officially became the seat of government in 1845. Early in its history, Stanley had a negative reputation due to cargo-shipping losses; only in emergencies would ships rounding Cape Horn stop at the port. Nevertheless, the Falklands geographic location proved ideal for ship repairs and the Wrecking Trade, the business of selling and buying shipwrecks and their cargoes. Aside from this trade, commercial interest in the archipelago was minimal due to the low-value hides of the feral cattle roaming the pastures. Economic growth began only after the Falkland Islands Company, which bought out Lafones failing enterprise in 1851, successfully introduced Cheviot sheep for wool farming, spurring other farms to follow suit. The high cost of importing materials, combined with the shortage of labour and consequent high wages, meant the ship repair trade became uncompetitive. After 1870, it declined as the replacement of sail ships by steamships was accelerated by the low cost of coal in South America; by 1914, with the opening of the Panama Canal, the trade effectively ended. In 1881, the Falkland Islands became financially independent of Britain. For more than a century, the Falkland Islands Company dominated the trade and employment of the archipelago; in addition, it owned most housing in Stanley, which greatly benefited from the wool trade with the UK.
Byron, John 1723 – 1786
Vice-Admiral John Byron (8 November 1723 – 10 April 1786) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer. He earned the nickname Foul-Weather Jack in the press because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sailed in the squadron under George Anson on his voyage around the world, though Byron made it only to southern Chile, where his ship was wrecked. He returned to England with the captain of HMS Wager. He was governor of Newfoundland following Hugh Palliser, who left in 1768. He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764–1766. He fought in battles in the Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral of the White before his death in 1786.
His grandsons include the poet George Gordon Byron and George Anson Byron, admiral and explorer, who were the 6th and 7th Baron Byron, respectively.
Byron was the second son of William Byron, 4th Baron Byron and Frances Berkeley, the daughter of William, 4th Baron Berkeley. After studying at Westminster School he joined the Royal Navy at the age of 14, making his first voyage aboard the HMS Romney in 1738–40.
In 1740, he accompanied George Anson on his voyage around the world as a midshipman aboard one of the several ships in the squadron. On 14 May 1741, HMS Wager under Captain Cheap (as Captain Dandy Kidd had died), was shipwrecked on the coast of Chile on what is now called Wager Island and Byron was one of the survivors. The survivors decided to split in two teams, one to make its way by boat to Rio de Janeiro on the Atlantic coast; the other, including John Byron and the Captain, to sail north along the Spanish colonial coast.
Captain Cheap at Wager Island had a party of 19 men after the deserters rejoined the camp. This included the surgeon Elliot and Lieutenant Hamilton who had been cast adrift with him plus midshipmen John Byron and Campbell who had been in the barge. They rowed up the coast but were punished by continuous rain, headwinds and waves that threatened the boats. One night while the men slept on shore, one of the boats was capsized while at anchor and was swept out to sea with its two boatkeepers. One of the men got ashore but the other drowned. As it was now impossible for them all to fit in the remaining boat, four marines were left ashore with muskets to fend for themselves. The winds prevented them from getting around the headland so they returned to pick up the marines only to find them gone. They returned to Wager Island in early February 1742. With one death on the journey, there were now 13 in the group.
Martín Olleta, a Chono cheftain, guided the men up the coast to the Spanish settlements of Chiloé Island so they set out again. Two men died; after burying the bodies, the six seamen rowed off in the boat never to be seen again while Cheap, Hamilton, Byron, Campbell and the dying Elliot were on shore looking for food. Olleta then agreed to take the remaining four on by canoe for their only remaining possession, a musket. It is likely the party travelled across Presidente Ríos Lake in inland Taitao Peninsula, a lake Chile regarded as officially discovered in 1945. Eventually they made it to be taken prisoner by the Spanish. The Spaniards treated them well and they were eventually taken to the inland capital of Santiago where they were released on parole. The Spaniards heard that Anson had been generous in the treatment of the prisoners he had taken and this kindness was returned.
Byron and the other three men stayed in Santiago till late 1744 and were offered passage on a French ship bound for Spain. Three accepted the passage. Campbell elected to take a mule across the Andes and joined the Spanish Admiral Pizarro in Montevideo on the Asia only to find Isaac Morris and the two seamen who had been abandoned in Freshwater Bay on the Atlantic coast. After time in prison in Spain, Campbell reached Britain in May 1746, followed by the other three two months later.
In England, the official court martial examined only the loss of the Wager in which Baynes, in nominal charge at the time, was acquitted of blame but reprimanded for omissions of duty. Disputes over what happened after the wreck were instead played out as Bulkeley and Cummins, Campbell, Morris, the cooper Young and later Byron published their own accounts, the last of which was the only one that in any way defended Cheap who had since died. Twenty-nine crew members plus seven marines made it back to England.
Byrons account of his adventures and the Wager Mutiny are recounted in The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron (1768). His book sold well enough to be printed in several editions.
Byron was appointed captain of HMS Siren in December 1746.
In 1760, during the Seven Years War, Byron commanded a squadron sent to destroy the fortifications at Louisbourg, Quebec, which had been captured by the British two years before. They wanted to ensure it could not be used by the French in Canada. In July of that year he defeated the French flotilla sent to relieve New France at the Battle of Restigouche.
In early 1764 the British Admiralty determined that it would require a permanent naval settlement off the South American coast, in order to resupply naval vessels seeking to enter the Pacific via Cape Horn. Captain Byron was selected to explore the South Atlantic for a suitable island upon which to establish such a settlement. The South American mainland was controlled by Spain, which was hostile to local expansion of British interests; to disguise Byrons mission it was announced that he had been appointed the new Navy Commander-in-Chief, East Indies. Byron set sail in June 1764, ostensibly to take up the East Indies post. For the voyage he was granted command of the 24-gun frigate HMS Dolphin and the 16-gun sloop HMS Tamar.
Byrons two-vessel flotilla crossed the Atlantic over the winter of 1764 and made its way slowly down the South American coast. The Admiralty had ordered Byron to first seek Pepys Island, reputedly discovered off the Patagonian coast by the corsair Ambrose Cowley in 1683. Byron reached the co-ordinates given by Cowley in January 1765, but there was no sign of the island and the search was swiftly abandoned. On 5 February Byron reached the Patagonian settlement of Port Desire where he resupplied his vessels from the storeship HMS Florida.
Between June 1764 and May 1766, Byron completed his own circumnavigation of the globe as captain of HMS Dolphin. This was the first such circumnavigation that was accomplished in less than 2 years. His actions nearly caused a war between Great Britain and Spain, as both countries had armed fleets ready to contest the sovereignty of the Falkland Islands. Later Byron encountered islands and extant residents of the Tuamotus and Tokelau Islands, and Nikunau in the southern Gilbert Islands; he also visited Tinian in the Northern Marianas Islands. A notable member of Byrons crew was Masters Mate Erasmus Gower whom Byron chose to take a significant part in the ceremony when he took possession of the Falkland Islands. Byron had examined Gower for his lieutenants examination in 1762 and was so impressed that he chose him to accompany him on his own circumnavigation (1764–65) and ensured that he was appointed as lieutenant to Commander Philip Carteret immediately afterwards in the next circumnavigation (1766–69).
In 1769 he was appointed governor of Newfoundland off the mainland of Canada, an office he held for the next three years.
He was promoted to rear admiral on 31 March 1775. In 1779, he served as Commander-in-chief of the Leeward Islands Station during the American War of Independence. After being severely injured during a storm on his way to the West Indies, Byron unsuccessfully attacked a French fleet under the Comte dEstaing at the Battle of Grenada in July 1779. He subsequently resigned his post and returned to England, where he suffered from poor health for the rest of his life.
Byron was briefly Commander-in-Chief, North American Station from 1 October 1779. He was made vice admiral of the white in September 1780.
John Byron died on 1 April 1786 at home in Bolton Row, London. His remains were buried in the Berkeley family vault situated beneath the chancel of the Church of St Mary the Virgin, Twickenham, on 10 April.
Johns life was a great inspiration for his grandson the poet George Gordon Byron, though they never met. The poet both drew from his grandfathers experiences in his writing, using his Narrative for the shipwreck scene in Don Juan, and wrote of the kinship he felt in having such a turbulent, unlucky life: he wrote in an epistle to his half-sister Augusta Leigh that he had no rest at sea, nor I on shore.
1773 Commodore John Byron 1st Ed Antique Map of The Falkland Islands Sth America
Antique Map
- Title : A chart of Hawkins s Maidenland, discovered by Sr. Richard Hawkins in 1574 and Falkland Sound, so called by Capn. John Strong of the Farewell from London who sailed through it in 1689.
- Ref #: 93385
- Size: 16 1/2in x 10n (405mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the Falkland Islands by Commodore John Byron was engraved by Isaac Noval and published in the 1773 first English edition of John Hawkesworth important book An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor. Drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, Esq; by John Hawkesworth, LL.D. In three volumes. Illustrated with cuts, and a great variety of charts and maps relative to countries now first discovered, or hitherto but imperfectly known. London: printed for W. Strahan; and T. Cadell in the Strand, MDCCLXXIII.
John Hawkesworth (1715 - 1773) was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook, from 1702 to 1771, drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 10n (405mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (310mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Although Fuegians from Patagonia may have visited the Falkland Islands in prehistoric times, the islands were uninhabited when Europeans first discovered them. Claims of discovery date back to the 16th century, but no consensus exists on whether early explorers discovered the Falklands or other islands in the South Atlantic. The first recorded landing on the islands is attributed to English captain John Strong, who, en route to Perus and Chiles littoral in 1690, discovered the Falkland Sound and noted the islands water and game.
The Falklands remained uninhabited until the 1764 establishment of Port Louis on East Falkland by French captain Louis Antoine de Bougainville, and the 1766 foundation of Port Egmont on Saunders Island by British captain John MacBride. Whether or not the settlements were aware of each others existence is debated by historians. In 1766, France surrendered its claim on the Falklands to Spain, which renamed the French colony Puerto Soledad the following year. Problems began when Spain discovered and captured Port Egmont in 1770. War was narrowly avoided by its restitution to Britain in 1771.
Both the British and Spanish settlements coexisted in the archipelago until 1774, when Britains new economic and strategic considerations led it to voluntarily withdraw from the islands, leaving a plaque claiming the Falklands for King George III. Spains Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata became the only governmental presence in the territory. West Falkland was left abandoned, and Puerto Soledad became mostly a prison camp. Amid the British invasions of the Río de la Plata during the Napoleonic Wars in Europe, the islands governor evacuated the archipelago in 1806; Spains remaining colonial garrison followed suit in 1811, except for gauchos and fishermen who remained voluntarily.
Thereafter, the archipelago was visited only by fishing ships; its political status was undisputed until 1820, when Colonel David Jewett, an American privateer working for the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, informed anchored ships about Buenos Aires 1816 claim to Spains territories in the South Atlantic. Since the islands had no permanent inhabitants, in 1823 Buenos Aires granted German-born merchant Luis Vernet permission to conduct fishing activities and exploit feral cattle in the archipelago. Vernet settled at the ruins of Puerto Soledad in 1826, and accumulated resources on the islands until the venture was secure enough to bring settlers and form a permanent colony. Buenos Aires named Vernet military and civil commander of the islands in 1829, and he attempted to regulate sealing to stop the activities of foreign whalers and sealers. Vernets venture lasted until a dispute over fishing and hunting rights led to a raid by the American warship USS Lexington in 1831, when United States Navy commander Silas Duncan declared the dissolution of the islands government.
Buenos Aires attempted to retain influence over the settlement by installing a garrison, but a mutiny in 1832 was followed the next year by the arrival of British forces who reasserted Britains rule. The Argentine Confederation (headed by Buenos Aires Governor Juan Manuel de Rosas) protested against Britains actions and Argentine governments have continued since then to register official protests against Britain. The British troops departed after completing their mission, leaving the area without formal government. Vernets deputy, the Scotsman Matthew Brisbane, returned to the islands that year to restore the business, but his efforts ended after, amid unrest at Port Louis, gaucho Antonio Rivero led a group of dissatisfied individuals to murder Brisbane and the settlements senior leaders; survivors hid in a cave on a nearby island until the British returned and restored order. In 1840, the Falklands became a Crown colony, and Scottish settlers subsequently established an official pastoral community. Four years later, nearly everyone relocated to Port Jackson, considered a better location for government, and merchant Samuel Lafone began a venture to encourage British colonisation.
Stanley, as Port Jackson was soon renamed, officially became the seat of government in 1845. Early in its history, Stanley had a negative reputation due to cargo-shipping losses; only in emergencies would ships rounding Cape Horn stop at the port. Nevertheless, the Falklands geographic location proved ideal for ship repairs and the Wrecking Trade, the business of selling and buying shipwrecks and their cargoes. Aside from this trade, commercial interest in the archipelago was minimal due to the low-value hides of the feral cattle roaming the pastures. Economic growth began only after the Falkland Islands Company, which bought out Lafones failing enterprise in 1851, successfully introduced Cheviot sheep for wool farming, spurring other farms to follow suit. The high cost of importing materials, combined with the shortage of labour and consequent high wages, meant the ship repair trade became uncompetitive. After 1870, it declined as the replacement of sail ships by steamships was accelerated by the low cost of coal in South America; by 1914, with the opening of the Panama Canal, the trade effectively ended. In 1881, the Falkland Islands became financially independent of Britain. For more than a century, the Falkland Islands Company dominated the trade and employment of the archipelago; in addition, it owned most housing in Stanley, which greatly benefited from the wool trade with the UK.
Byron, John 1723 – 1786
Vice-Admiral John Byron (8 November 1723 – 10 April 1786) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer. He earned the nickname Foul-Weather Jack in the press because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sailed in the squadron under George Anson on his voyage around the world, though Byron made it only to southern Chile, where his ship was wrecked. He returned to England with the captain of HMS Wager. He was governor of Newfoundland following Hugh Palliser, who left in 1768. He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764–1766. He fought in battles in the Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral of the White before his death in 1786.
His grandsons include the poet George Gordon Byron and George Anson Byron, admiral and explorer, who were the 6th and 7th Baron Byron, respectively.
Byron was the second son of William Byron, 4th Baron Byron and Frances Berkeley, the daughter of William, 4th Baron Berkeley. After studying at Westminster School he joined the Royal Navy at the age of 14, making his first voyage aboard the HMS Romney in 1738–40.
In 1740, he accompanied George Anson on his voyage around the world as a midshipman aboard one of the several ships in the squadron. On 14 May 1741, HMS Wager under Captain Cheap (as Captain Dandy Kidd had died), was shipwrecked on the coast of Chile on what is now called Wager Island and Byron was one of the survivors. The survivors decided to split in two teams, one to make its way by boat to Rio de Janeiro on the Atlantic coast; the other, including John Byron and the Captain, to sail north along the Spanish colonial coast.
Captain Cheap at Wager Island had a party of 19 men after the deserters rejoined the camp. This included the surgeon Elliot and Lieutenant Hamilton who had been cast adrift with him plus midshipmen John Byron and Campbell who had been in the barge. They rowed up the coast but were punished by continuous rain, headwinds and waves that threatened the boats. One night while the men slept on shore, one of the boats was capsized while at anchor and was swept out to sea with its two boatkeepers. One of the men got ashore but the other drowned. As it was now impossible for them all to fit in the remaining boat, four marines were left ashore with muskets to fend for themselves. The winds prevented them from getting around the headland so they returned to pick up the marines only to find them gone. They returned to Wager Island in early February 1742. With one death on the journey, there were now 13 in the group.
Martín Olleta, a Chono cheftain, guided the men up the coast to the Spanish settlements of Chiloé Island so they set out again. Two men died; after burying the bodies, the six seamen rowed off in the boat never to be seen again while Cheap, Hamilton, Byron, Campbell and the dying Elliot were on shore looking for food. Olleta then agreed to take the remaining four on by canoe for their only remaining possession, a musket. It is likely the party travelled across Presidente Ríos Lake in inland Taitao Peninsula, a lake Chile regarded as officially discovered in 1945. Eventually they made it to be taken prisoner by the Spanish. The Spaniards treated them well and they were eventually taken to the inland capital of Santiago where they were released on parole. The Spaniards heard that Anson had been generous in the treatment of the prisoners he had taken and this kindness was returned.
Byron and the other three men stayed in Santiago till late 1744 and were offered passage on a French ship bound for Spain. Three accepted the passage. Campbell elected to take a mule across the Andes and joined the Spanish Admiral Pizarro in Montevideo on the Asia only to find Isaac Morris and the two seamen who had been abandoned in Freshwater Bay on the Atlantic coast. After time in prison in Spain, Campbell reached Britain in May 1746, followed by the other three two months later.
In England, the official court martial examined only the loss of the Wager in which Baynes, in nominal charge at the time, was acquitted of blame but reprimanded for omissions of duty. Disputes over what happened after the wreck were instead played out as Bulkeley and Cummins, Campbell, Morris, the cooper Young and later Byron published their own accounts, the last of which was the only one that in any way defended Cheap who had since died. Twenty-nine crew members plus seven marines made it back to England.
Byrons account of his adventures and the Wager Mutiny are recounted in The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron (1768). His book sold well enough to be printed in several editions.
Byron was appointed captain of HMS Siren in December 1746.
In 1760, during the Seven Years War, Byron commanded a squadron sent to destroy the fortifications at Louisbourg, Quebec, which had been captured by the British two years before. They wanted to ensure it could not be used by the French in Canada. In July of that year he defeated the French flotilla sent to relieve New France at the Battle of Restigouche.
In early 1764 the British Admiralty determined that it would require a permanent naval settlement off the South American coast, in order to resupply naval vessels seeking to enter the Pacific via Cape Horn. Captain Byron was selected to explore the South Atlantic for a suitable island upon which to establish such a settlement. The South American mainland was controlled by Spain, which was hostile to local expansion of British interests; to disguise Byrons mission it was announced that he had been appointed the new Navy Commander-in-Chief, East Indies. Byron set sail in June 1764, ostensibly to take up the East Indies post. For the voyage he was granted command of the 24-gun frigate HMS Dolphin and the 16-gun sloop HMS Tamar.
Byrons two-vessel flotilla crossed the Atlantic over the winter of 1764 and made its way slowly down the South American coast. The Admiralty had ordered Byron to first seek Pepys Island, reputedly discovered off the Patagonian coast by the corsair Ambrose Cowley in 1683. Byron reached the co-ordinates given by Cowley in January 1765, but there was no sign of the island and the search was swiftly abandoned. On 5 February Byron reached the Patagonian settlement of Port Desire where he resupplied his vessels from the storeship HMS Florida.
Between June 1764 and May 1766, Byron completed his own circumnavigation of the globe as captain of HMS Dolphin. This was the first such circumnavigation that was accomplished in less than 2 years. His actions nearly caused a war between Great Britain and Spain, as both countries had armed fleets ready to contest the sovereignty of the Falkland Islands. Later Byron encountered islands and extant residents of the Tuamotus and Tokelau Islands, and Nikunau in the southern Gilbert Islands; he also visited Tinian in the Northern Marianas Islands. A notable member of Byrons crew was Masters Mate Erasmus Gower whom Byron chose to take a significant part in the ceremony when he took possession of the Falkland Islands. Byron had examined Gower for his lieutenants examination in 1762 and was so impressed that he chose him to accompany him on his own circumnavigation (1764–65) and ensured that he was appointed as lieutenant to Commander Philip Carteret immediately afterwards in the next circumnavigation (1766–69).
In 1769 he was appointed governor of Newfoundland off the mainland of Canada, an office he held for the next three years.
He was promoted to rear admiral on 31 March 1775. In 1779, he served as Commander-in-chief of the Leeward Islands Station during the American War of Independence. After being severely injured during a storm on his way to the West Indies, Byron unsuccessfully attacked a French fleet under the Comte dEstaing at the Battle of Grenada in July 1779. He subsequently resigned his post and returned to England, where he suffered from poor health for the rest of his life.
Byron was briefly Commander-in-Chief, North American Station from 1 October 1779. He was made vice admiral of the white in September 1780.
John Byron died on 1 April 1786 at home in Bolton Row, London. His remains were buried in the Berkeley family vault situated beneath the chancel of the Church of St Mary the Virgin, Twickenham, on 10 April.
Johns life was a great inspiration for his grandson the poet George Gordon Byron, though they never met. The poet both drew from his grandfathers experiences in his writing, using his Narrative for the shipwreck scene in Don Juan, and wrote of the kinship he felt in having such a turbulent, unlucky life: he wrote in an epistle to his half-sister Augusta Leigh that he had no rest at sea, nor I on shore.
1773 Cook Antique Maps Tahiti, Raiatea & Huaheine Isles French Polynesia in 1769
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite ; Owharre Harbour in Huaheine ; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea ; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Size: 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 31216
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map, four maps on the one sheet;
1. Matavia Bay, Tahiti (Otaheite) - Windward Islands
2. Ohamaneno (Vaiaau) Harbour Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
3. Owharre (Bourayne Bay) Harbour in Huaheine - Leeward Islands
4. Oopoa (Opoa) Harbour, Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
all located in French Polynesia, South Pacific were complied by Capt James Cook during his first voyage of discovery in 1769, was published in the 1773 edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1773
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (365mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Matavai Bay is located on the north coast of Tahiti, the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia.
The first European known to have visited Tahiti was Lieutenant Samuel Wallis, in Dolphin, who landed on 17 June 1767 in Matavai Bay.
Captain James Cook anchored in the bay on 13 April 1769, on a sandy spit on the northeast end of Matavai Bay - named Point Venus by Cook.
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
Captain Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774.
Huahine is an island located among the Society Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Leeward Islands group (Iles sous le Vent).
Captain Cook arrived Fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour. They met with leading chief Ori (Mato). Cook returned on 3 Sept. 1773 and met with Oris son Teri itaria, the new ari i rahi of the island.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
1773 Grose Large Antique Print View of The London Charter House
- Title : Description of The Charter House
- Ref : 26237
- Size: 15in x 9 1/2in (385mm x 235mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique print of the London Charter House situated in Smithfield London - accompanied with text page - was published by Francis Grose on the 1773 edition of The Antiquities of England and Wales.
The London Charterhouse is a historic complex of buildings in Smithfield, London dating back to the 14th century. It occupies land to the north of Charterhouse Square. The Charterhouse began as (and takes its name from) a Carthusian priory, founded in 1371 and dissolved in 1537.
Substantial fragments remain from this monastic period, but the site was largely rebuilt after 1545 as a large courtyard house. Thus, today it "conveys a vivid impression of the type of large rambling 16th century mansion that once existed all round London". The Charterhouse was further altered and extended after 1611, when it became an almshouseand school, endowed by Thomas Sutton. The almshouse (a home for gentlemen pensioners) still occupies the site today under the name the Charterhouse.
Francis Grose (1731 –1791) was an English antiquary, draughtsman, and lexicographer. He was born at his father's house in Broad Street, St-Peter-le-Poer, London.
Grose had early on shown a keen interest in drawing, having attempted sketches of medieval buildings as far back as 1749, and having taken formal instruction at a drawing school in the mid-1750s. He was not a particularly gifted draughtsman but he mixed in the London artistic milieu and began to exhibit, first at the Society of Artists in 1767–8 and then at the Royal Academy. His interest was in the field of medieval remains, which were beginning to exercise an increasing grip on the public imagination.
In 1772, he published the first part of The Antiquities of England and Wales, a work which he unashamedly aimed at the popular market. Essentially, it targeted those who wanted to know about antiquities but had neither time nor means to visit them in person, and contained small panoramas of medieval ruins, together with an informative text on a separate page. Sometimes the text was taken from books already published, or from information supplied by other antiquaries (both acknowledged); sometimes Grose collated material himself from which he could work up an article. From 1772 onwards, he also toured the country to visit and draw sites for inclusion in The Antiquities. The fourth and last volume came out in June 1776, and Grose almost immediately began work on a supplement.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (385mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1773 Hawkesworth Antique Print Raiatea Island, French Polynesia - Capt Cook 1769
- Title : [A view in the island of Ulietea with a double canoe and a boathouse] ...E. Rooker sculp....No. 3
- Ref : 31816
- Size: 18 1/2in x 10 1/2in (470mm x 265mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print a view of fishing vessels, locals inspecting the days catch and views of the Island of Raiatea (Ulietea) in the Society Isles of French Polynesia, drawn by Sydney Parkinson, on Captain Cooks first visit to the Island in 1769, was engraved by Edward Rooker and published in the 1773 1st English edition of John Hawkesworths An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor. Drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, Esq; by John Hawkesworth, LL.D. In three volumes. Illustrated with cuts, and a great variety of charts and maps relative to countries now first discovered, or hitherto but imperfectly known. London: printed for W. Strahan; and T. Cadell in the Strand, MDCCLXXIII.
..........a double canoe (pahi) with carved figures on bow and stern. Another double canoe in the background at right and a boathouse at left. There are a great number of boathouses all round the bays built with a Catanarian arch, thatched all over; and the boats kept in them are very long, bellying out on the sides, with a very high peak stern, and are used only at particular seasons.....from the account by Sydney Parkinson 1769
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 10 1/2in (470mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 9 1/2in (470mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued, creasing and light soiling along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
A traditional name for the island is Havaii, homeland of the Māori people.
The first European to record sighting Ra iātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Raiātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, traveled with the European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
King Tamatoa VI was the last monarch, reigning from 1884-1888.
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth an English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Edward Rooker 1712 – 1774 was an English engraver, draughtsman and actor.
1774 Capt Cook Antqiue Print of Tahitians Honouring the Dead, Manao Tupapau 1769
- Title : Maniere dont on expose les morts a Otahiti (How the dead are exposed on Tahiti)
- Size: 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 21427
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of how the Dead are left mummified outdoors in an elevated platform in Tahiti, and the ritual of the Spirit of the Dead Watching (Manao tupapau), visited by Captain Cook in HMS Endeavor during his first visit to the Island in 1769, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Sydney Parkinson - was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774.
Ghosts in Polynesian culture
There was widespread belief in ghosts in Polynesian culture, some of which persists today. After death, a person\'s ghost would normally travel to the sky world or the underworld, but some could stay on earth. In many Polynesian legends, ghosts were often involved in the affairs of the living. Ghosts might also cause sickness or even invade the body of ordinary people, to be driven out through strong medicines.
In the reconstructed Proto-Polynesian language, the word qaitu refers to a ghost, the spirit of a dead person, while the word tupuqa has a broader meaning including all supernatural beings. Some of the ancient Māui legends that are common throughout the Polynesian islands include the idea of a double soul inhabiting the body. One was the soul which never forsakes man, and the other the soul that could be separated or charmed away from the body by incantations was the hau.
In some societies, the tattoo marks on the Polynesian\'s face indicated their cult. A spiral symbol meant that the man favoured the sky world, but before ascending there on a whirlwind his ghost had to travel to his people\'s homeland, situated in the navel of the world. Different markings indicated that the ghost chose to live in the underworld. The Hawaiians believed in aumakua, ghosts who did not go down into Po, the land of King Milu. These ghosts remained in the land of the living, guarding their former families.
Of his 1892 Tahitian painting Manao Tupapau, Paul Gauguin said according to Tahitian beliefs, the title Manao Tupapau has a double meaning . . . either she thinks of the ghost or the ghost thinks of her.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt Cook Antqiue Print of Tahitians Honouring the Dead, Manao Tupapau 1769
- Title : Maniere dont on expose les morts a Otahiti (How the dead are exposed on Tahiti)
- Size: 15in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 21733-1
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of how the Dead are left mummified outdoors in an elevated platform in Tahiti, and the ritual of the Spirit of the Dead Watching (Manao tupapau), visited by Captain Cook in HMS Endeavor during his first visit to the Island in 1769, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Sydney Parkinson - was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774.
Ghosts in Polynesian culture
There was widespread belief in ghosts in Polynesian culture, some of which persists today. After death, a person\'s ghost would normally travel to the sky world or the underworld, but some could stay on earth. In many Polynesian legends, ghosts were often involved in the affairs of the living. Ghosts might also cause sickness or even invade the body of ordinary people, to be driven out through strong medicines.
In the reconstructed Proto-Polynesian language, the word qaitu refers to a ghost, the spirit of a dead person, while the word tupuqa has a broader meaning including all supernatural beings. Some of the ancient Māui legends that are common throughout the Polynesian islands include the idea of a double soul inhabiting the body. One was the soul which never forsakes man, and the other the soul that could be separated or charmed away from the body by incantations was the hau.
In some societies, the tattoo marks on the Polynesian\'s face indicated their cult. A spiral symbol meant that the man favoured the sky world, but before ascending there on a whirlwind his ghost had to travel to his people\'s homeland, situated in the navel of the world. Different markings indicated that the ghost chose to live in the underworld. The Hawaiians believed in aumakua, ghosts who did not go down into Po, the land of King Milu. These ghosts remained in the land of the living, guarding their former families.
Of his 1892 Tahitian painting Manao Tupapau, Paul Gauguin said according to Tahitian beliefs, the title Manao Tupapau has a double meaning . . . either she thinks of the ghost or the ghost thinks of her.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt. Cook Antique Print a Portrait of Chief Tynah, Otoo of Tahiti in 1769
- Title : Otoo, Roi de Tahiti
- Ref : 21341
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print a portrait of Chief Tynah (Otoo) of Tahiti Island, met by Captain James Cook during his 1st Voyage of Discovery in 1769, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Sydney Parkinson - and was published in the 1774 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas by John Hawkesworth in An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks. Paris, 1774.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, brown, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt. Cook Antique Print a Portrait of Chief Tynah, Otoo of Tahiti in 1769
- Title : Otoo, Roi de Tahiti
- Ref : 31771
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print a portrait of Chief Tynah (Otoo) of Tahiti Island, met by Captain James Cook during his 1st Voyage of Discovery in 1769, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Sydney Parkinson - and was published in the 1774 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas by John Hawkesworth in An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks. Paris, 1774.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in bottom margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt. Cook, S. Parkinson & G. Stubbs - Antique Print Australian Kangaroo in 1770
Antique Map
- Title : Quadrupede nomme Kanguroo trouve fur la Cote de la N.Hollande
[The Kanguroo, an Animal found on the Coast of New Holland] - Ref : 35016
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Kangaroo, first sketched by Sydney Parkinson onboard HMS Endeavour during Cooks first voyage in 1770, whilst laid up at Endeavour River in northern Queensland, was engraved by Robert Benard, after a painting by the famous English Artist George Stubbs in 1772. This original engraving was published in the 1774 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas by John Hawkesworth in An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks. Paris, 1774.
From Sydney Parkinsons Journal........soon after we arrived in the bay, we laid the ship on a steep bank, on the side of a river; set up tents on shore, unloaded her, carried all the cargo and provisions into them, and there lodged and accommodated our sick.
On the 22d, we examined the ship’s bottom, and found a large hole; through the planks into the hold, which had a piece of coral-rock, half a yard square, sticking in it: the same rock, therefore, that endangered us, yielded us the principal means of our redemption; for, had not this fragment intruded into the leak, in all probability the ship would have sunk.
We lost no time, but immediately set about repairing the ship’s bottom, and in a few days made it sound again. In the mean time, the boats were sent out, in search of another passage, which they found, and returned to the ship on the 3d of July.
On the 4th of July, the ship was carried to the other side of the river, and examined thoroughly; but, being found in good condition, she was soon placed in her former station; where she was loaded, and properly fitted to proceed on the voyage.
During the time we staid here, we picked up a great many natural curiosities from the reef we struck upon, consisting of a variety of curious shells, most of which were entirely new to Mr. Banks and Dr. Solander ...
Of quadrupeds, there are goats, wolves, a small red animal about the size of a squirrel; a spotted one of the viverra kind, and an animal of a kind nearly approaching the mus genus, about the size of a grey-hound, that had a head like a fawn’s; lips and ears, which it throws back, like a hare’s; on the upper jaw six large teeth; on the under one two only; with a short and small neck, near to which are the fore-feet, which have five toes each, and five hooked claws; the hinder legs are long, especially from the last joint, which, from the callosity below it, seems as if it lies flat on the ground when the animal descends any declivity; and each foot had four long toes, two of them behind, placed a great way back, the inner one of which has two claws; the two other toes were in the middle, and resembled a hoof, but one of them was much larger than the other. The tail, which is carried like a grey-hound’s, was almost as long as the body, and tapered gradually to the end. The chief bulk of this animal is behind; the belly being largest, and the back rising toward the posteriors. The whole body is covered with short ash-coloured hair; and the flesh of it tasted like a hare’s, but has a more agreeable flavour................
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
George Stubbs ARA 1724 – 1806 was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. His most famous work is probably Whistlejacket, a painting of a prancing horse commissioned by the 2nd Marquess of Rockingham, which is now in the National Gallery in London. This and two other paintings carried out for Rockingham break with convention in having plain backgrounds. Throughout the 1760s he produced a wide range of individual and group portraits of horses, sometimes accompanied by hounds. He often painted horses with their grooms, whom he always painted as individuals. Meanwhile, he also continued to accept commissions for portraits of people, including some group portraits. From 1761 to 1776 he exhibited at the Society of Artists of Great Britain, but in 1775 he switched his allegiance to the recently founded but already more prestigious Royal Academy of Arts.
Stubbs also painted more exotic animals including lions, tigers, giraffes, monkeys, and rhinoceroses, which he was able to observe in private menageries. His painting of a kangaroo in 1772 after Cooks 1st Voyage to Australia, was the first glimpse of this animal for many 18th-century Britons
1774 Captain James Cook Antique Map, 1st Printed Chart of New Zealand. Dutch Ed. - Scarce
Antique Map
- Title : Kaart van Nieuw Zeeland in de Jaaren 1769 en 1770 bezogt door den Luitenant J Cook met het Schip De Endeavour (Chart of New Zealand explored in 1769 and 1770 by Lieutenant. J. Cook Commander of his Ship Endeavour)
- Date : 1774
- Size: 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35674
Description:
This magnificent large original copper plate engraved scarce antique map, the first printed chart of New Zealand by Captain James Cook, during his circumnavigation of the South Pacific in 1769-70, was published in the 1st Dutch edition of Hawkeworths Voyages in 1774 by Reiner Arrenberg Reizen Rondom de Weereld Ondernomen op Bevell van Zyne Majesteit den Tans Regeerenden Koning van Groot-Brittanje tot Het Doen van Ontdekkingen ... J. Hawkesworth Uit Het Engelsch Vertaalt,
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 394mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty\\\'s choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
1774 Commodore John Byron Antique Map of The Falkland Islands South America
Antique Map
- Title : Carte de Maidenland ou de la Virginie de Hawkins...et du Canal Falklands...Jean Strong...1689.
- Ref #: 93381
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Falkland Islands by Commodore John Byron was engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1774 first French edition of John Hawkesworth important book An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor. Drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, Esq; by John Hawkesworth, LL.D. In three volumes. Illustrated with cuts, and a great variety of charts and maps relative to countries now first discovered, or hitherto but imperfectly known. London: printed for W. Strahan; and T. Cadell in the Strand, MDCCLXXIII.
John Hawkesworth (1715 - 1773) was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook, from 1702 to 1771, drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Background:
Although Fuegians from Patagonia may have visited the Falkland Islands in prehistoric times, the islands were uninhabited when Europeans first discovered them. Claims of discovery date back to the 16th century, but no consensus exists on whether early explorers discovered the Falklands or other islands in the South Atlantic. The first recorded landing on the islands is attributed to English captain John Strong, who, en route to Perus and Chiles littoral in 1690, discovered the Falkland Sound and noted the islands water and game.
The Falklands remained uninhabited until the 1764 establishment of Port Louis on East Falkland by French captain Louis Antoine de Bougainville, and the 1766 foundation of Port Egmont on Saunders Island by British captain John MacBride. Whether or not the settlements were aware of each others existence is debated by historians. In 1766, France surrendered its claim on the Falklands to Spain, which renamed the French colony Puerto Soledad the following year. Problems began when Spain discovered and captured Port Egmont in 1770. War was narrowly avoided by its restitution to Britain in 1771.
Both the British and Spanish settlements coexisted in the archipelago until 1774, when Britains new economic and strategic considerations led it to voluntarily withdraw from the islands, leaving a plaque claiming the Falklands for King George III. Spains Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata became the only governmental presence in the territory. West Falkland was left abandoned, and Puerto Soledad became mostly a prison camp. Amid the British invasions of the Río de la Plata during the Napoleonic Wars in Europe, the islands governor evacuated the archipelago in 1806; Spains remaining colonial garrison followed suit in 1811, except for gauchos and fishermen who remained voluntarily.
Thereafter, the archipelago was visited only by fishing ships; its political status was undisputed until 1820, when Colonel David Jewett, an American privateer working for the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, informed anchored ships about Buenos Aires 1816 claim to Spains territories in the South Atlantic. Since the islands had no permanent inhabitants, in 1823 Buenos Aires granted German-born merchant Luis Vernet permission to conduct fishing activities and exploit feral cattle in the archipelago. Vernet settled at the ruins of Puerto Soledad in 1826, and accumulated resources on the islands until the venture was secure enough to bring settlers and form a permanent colony. Buenos Aires named Vernet military and civil commander of the islands in 1829, and he attempted to regulate sealing to stop the activities of foreign whalers and sealers. Vernets venture lasted until a dispute over fishing and hunting rights led to a raid by the American warship USS Lexington in 1831, when United States Navy commander Silas Duncan declared the dissolution of the islands government.
Buenos Aires attempted to retain influence over the settlement by installing a garrison, but a mutiny in 1832 was followed the next year by the arrival of British forces who reasserted Britains rule. The Argentine Confederation (headed by Buenos Aires Governor Juan Manuel de Rosas) protested against Britains actions and Argentine governments have continued since then to register official protests against Britain. The British troops departed after completing their mission, leaving the area without formal government. Vernets deputy, the Scotsman Matthew Brisbane, returned to the islands that year to restore the business, but his efforts ended after, amid unrest at Port Louis, gaucho Antonio Rivero led a group of dissatisfied individuals to murder Brisbane and the settlements senior leaders; survivors hid in a cave on a nearby island until the British returned and restored order. In 1840, the Falklands became a Crown colony, and Scottish settlers subsequently established an official pastoral community. Four years later, nearly everyone relocated to Port Jackson, considered a better location for government, and merchant Samuel Lafone began a venture to encourage British colonisation.
Stanley, as Port Jackson was soon renamed, officially became the seat of government in 1845. Early in its history, Stanley had a negative reputation due to cargo-shipping losses; only in emergencies would ships rounding Cape Horn stop at the port. Nevertheless, the Falklands geographic location proved ideal for ship repairs and the Wrecking Trade, the business of selling and buying shipwrecks and their cargoes. Aside from this trade, commercial interest in the archipelago was minimal due to the low-value hides of the feral cattle roaming the pastures. Economic growth began only after the Falkland Islands Company, which bought out Lafones failing enterprise in 1851, successfully introduced Cheviot sheep for wool farming, spurring other farms to follow suit. The high cost of importing materials, combined with the shortage of labour and consequent high wages, meant the ship repair trade became uncompetitive. After 1870, it declined as the replacement of sail ships by steamships was accelerated by the low cost of coal in South America; by 1914, with the opening of the Panama Canal, the trade effectively ended. In 1881, the Falkland Islands became financially independent of Britain. For more than a century, the Falkland Islands Company dominated the trade and employment of the archipelago; in addition, it owned most housing in Stanley, which greatly benefited from the wool trade with the UK.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (310mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Byron, John 1723 – 1786:
Vice-Admiral John Byron (8 November 1723 – 10 April 1786) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer. He earned the nickname Foul-Weather Jack in the press because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sailed in the squadron under George Anson on his voyage around the world, though Byron made it only to southern Chile, where his ship was wrecked. He returned to England with the captain of HMS Wager. He was governor of Newfoundland following Hugh Palliser, who left in 1768. He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764–1766. He fought in battles in the Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral of the White before his death in 1786.
His grandsons include the poet George Gordon Byron and George Anson Byron, admiral and explorer, who were the 6th and 7th Baron Byron, respectively.
Byron was the second son of William Byron, 4th Baron Byron and Frances Berkeley, the daughter of William, 4th Baron Berkeley. After studying at Westminster School he joined the Royal Navy at the age of 14, making his first voyage aboard the HMS Romney in 1738–40.
In 1740, he accompanied George Anson on his voyage around the world as a midshipman aboard one of the several ships in the squadron. On 14 May 1741, HMS Wager under Captain Cheap (as Captain Dandy Kidd had died), was shipwrecked on the coast of Chile on what is now called Wager Island and Byron was one of the survivors. The survivors decided to split in two teams, one to make its way by boat to Rio de Janeiro on the Atlantic coast; the other, including John Byron and the Captain, to sail north along the Spanish colonial coast.
Captain Cheap at Wager Island had a party of 19 men after the deserters rejoined the camp. This included the surgeon Elliot and Lieutenant Hamilton who had been cast adrift with him plus midshipmen John Byron and Campbell who had been in the barge. They rowed up the coast but were punished by continuous rain, headwinds and waves that threatened the boats. One night while the men slept on shore, one of the boats was capsized while at anchor and was swept out to sea with its two boatkeepers. One of the men got ashore but the other drowned. As it was now impossible for them all to fit in the remaining boat, four marines were left ashore with muskets to fend for themselves. The winds prevented them from getting around the headland so they returned to pick up the marines only to find them gone. They returned to Wager Island in early February 1742. With one death on the journey, there were now 13 in the group.
Martín Olleta, a Chono cheftain, guided the men up the coast to the Spanish settlements of Chiloé Island so they set out again. Two men died; after burying the bodies, the six seamen rowed off in the boat never to be seen again while Cheap, Hamilton, Byron, Campbell and the dying Elliot were on shore looking for food. Olleta then agreed to take the remaining four on by canoe for their only remaining possession, a musket. It is likely the party travelled across Presidente Ríos Lake in inland Taitao Peninsula, a lake Chile regarded as officially discovered in 1945. Eventually they made it to be taken prisoner by the Spanish. The Spaniards treated them well and they were eventually taken to the inland capital of Santiago where they were released on parole. The Spaniards heard that Anson had been generous in the treatment of the prisoners he had taken and this kindness was returned.
Byron and the other three men stayed in Santiago till late 1744 and were offered passage on a French ship bound for Spain. Three accepted the passage. Campbell elected to take a mule across the Andes and joined the Spanish Admiral Pizarro in Montevideo on the Asia only to find Isaac Morris and the two seamen who had been abandoned in Freshwater Bay on the Atlantic coast. After time in prison in Spain, Campbell reached Britain in May 1746, followed by the other three two months later.
In England, the official court martial examined only the loss of the Wager in which Baynes, in nominal charge at the time, was acquitted of blame but reprimanded for omissions of duty. Disputes over what happened after the wreck were instead played out as Bulkeley and Cummins, Campbell, Morris, the cooper Young and later Byron published their own accounts, the last of which was the only one that in any way defended Cheap who had since died. Twenty-nine crew members plus seven marines made it back to England.
Byrons account of his adventures and the Wager Mutiny are recounted in The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron (1768). His book sold well enough to be printed in several editions.
Byron was appointed captain of HMS Siren in December 1746.
In 1760, during the Seven Years War, Byron commanded a squadron sent to destroy the fortifications at Louisbourg, Quebec, which had been captured by the British two years before. They wanted to ensure it could not be used by the French in Canada. In July of that year he defeated the French flotilla sent to relieve New France at the Battle of Restigouche.
In early 1764 the British Admiralty determined that it would require a permanent naval settlement off the South American coast, in order to resupply naval vessels seeking to enter the Pacific via Cape Horn. Captain Byron was selected to explore the South Atlantic for a suitable island upon which to establish such a settlement. The South American mainland was controlled by Spain, which was hostile to local expansion of British interests; to disguise Byrons mission it was announced that he had been appointed the new Navy Commander-in-Chief, East Indies. Byron set sail in June 1764, ostensibly to take up the East Indies post. For the voyage he was granted command of the 24-gun frigate HMS Dolphin and the 16-gun sloop HMS Tamar.
Byrons two-vessel flotilla crossed the Atlantic over the winter of 1764 and made its way slowly down the South American coast. The Admiralty had ordered Byron to first seek Pepys Island, reputedly discovered off the Patagonian coast by the corsair Ambrose Cowley in 1683. Byron reached the co-ordinates given by Cowley in January 1765, but there was no sign of the island and the search was swiftly abandoned. On 5 February Byron reached the Patagonian settlement of Port Desire where he resupplied his vessels from the storeship HMS Florida.
Between June 1764 and May 1766, Byron completed his own circumnavigation of the globe as captain of HMS Dolphin. This was the first such circumnavigation that was accomplished in less than 2 years. His actions nearly caused a war between Great Britain and Spain, as both countries had armed fleets ready to contest the sovereignty of the Falkland Islands. Later Byron encountered islands and extant residents of the Tuamotus and Tokelau Islands, and Nikunau in the southern Gilbert Islands; he also visited Tinian in the Northern Marianas Islands. A notable member of Byrons crew was Masters Mate Erasmus Gower whom Byron chose to take a significant part in the ceremony when he took possession of the Falkland Islands. Byron had examined Gower for his lieutenants examination in 1762 and was so impressed that he chose him to accompany him on his own circumnavigation (1764–65) and ensured that he was appointed as lieutenant to Commander Philip Carteret immediately afterwards in the next circumnavigation (1766–69).
In 1769 he was appointed governor of Newfoundland off the mainland of Canada, an office he held for the next three years.
He was promoted to rear admiral on 31 March 1775. In 1779, he served as Commander-in-chief of the Leeward Islands Station during the American War of Independence. After being severely injured during a storm on his way to the West Indies, Byron unsuccessfully attacked a French fleet under the Comte dEstaing at the Battle of Grenada in July 1779. He subsequently resigned his post and returned to England, where he suffered from poor health for the rest of his life.
Byron was briefly Commander-in-Chief, North American Station from 1 October 1779. He was made vice admiral of the white in September 1780.
John Byron died on 1 April 1786 at home in Bolton Row, London. His remains were buried in the Berkeley family vault situated beneath the chancel of the Church of St Mary the Virgin, Twickenham, on 10 April.
Johns life was a great inspiration for his grandson the poet George Gordon Byron, though they never met. The poet both drew from his grandfathers experiences in his writing, using his Narrative for the shipwreck scene in Don Juan, and wrote of the kinship he felt in having such a turbulent, unlucky life: he wrote in an epistle to his half-sister Augusta Leigh that he had no rest at sea, nor I on shore.
1774 Comte De Buffon Large Antique Print of Spiders, Scorpion, Centipedes
- Title : Histoire Naturelle, Insectes
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1774
- Ref #: 90535
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print was published in the 1774 quatro edition of Comte de Buffons Histoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du Cabinet du Roi (Natural History, General and Particular, with a Description of the King\'s Cabinet)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Histoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du Cabinet du Roi (Natural History, General and Particular, with a Description of the Kings Cabinet) is an encyclopaedic collection of 36 large (quarto) volumes written between 1749–1804 by the Comte de Buffon, and continued in eight more volumes after his death by his colleagues, led by Bernard Germain de Lacépède. The books cover what was known of the natural sciences at the time, including what would now be called material science, physics, chemistry and technology as well as the natural history of animals.
The Histoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du Cabinet du Roi is the work that the Comte de Buffon (1707–1788) is remembered for. He worked on it for some 50 years, initially at Montbard in his office in the Tour Saint-Louis, then in his library at Petit Fontenet. 36 volumes came out between 1749 and 1789, followed by 8 more after his death, thanks to Bernard Germain de Lacépède. It includes all the knowledge available in his time on the natural sciences, a broad term that includes disciplines which today would be called material science, physics, chemistry and technology. Buffon notes the morphological similarities between men and apes, although he considered apes completely devoid of the ability to think, differentiating them sharply from human beings. Buffons attention to internal anatomy made him an early comparative anatomist. Lintérieur, dans les êtres vivants, est le fond du dessin de la nature, he wrote in his Quadrupèdes, the interior, in living things, is the foundation of natures design.
The Histoire Naturelle, which was meant to address the whole of natural history, actually covers only minerals, birds, and the quadrupeds among animals. It is accompanied by some discourses and a theory of the earth by way of introduction, and by supplements including an elegantly written account of the epochs of nature.
The Suppléments cover a wide range of topics; for example, in (Suppléments IV), there is a Discours sur le style (Discourse on Style) and an Essai darithmétique morale (essay on Moral Arithmetic).
Louis Jean-Marie Daubenton assisted Buffon on the quadrupeds; Philippe Guéneau de Montbeillard worked on the birds. They were joined, from 1767, by Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond, the abbot Gabriel Bexon and Charles-Nicolas-Sigisbert Sonnini de Manoncourt. The whole descriptive and anatomical part of lHistoire des Quadrupèdes was the work of Daubenton and Jean-Claude Mertrud.
Buffon attached much importance to the illustrations; Jacques de Sève illustrated the quadrupeds and François-Nicolas Martinet illustrated the birds. Nearly 2000 plates adorn the work, representing animals with care given both to aesthetics and anatomical accuracy, with dreamlike and mythological settings.
On minerals, Buffon collaborated with André Thouin. Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond and Louis Bernard Guyton de Morveau provided sources for the mineral volumes.
L Histoire Naturelle met immense success, almost as great as Encyclopédie by Diderot, which came out in the same period. The first three volumes of LHistoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du cabinet du Roi were reprinted three times in six weeks.
The encyclopaedia appeared in 36 volumes :
3 volumes in 1749 : De la manière détudier lhistoire naturelle followed by Théorie de la Terre, Histoire Générale des animaux and Histoire Naturelle de lhomme
12 volumes on quadrupeds (1753 to 1767)
9 volumes on birds (1770 to 1783])
5 volumes on minerals (1783 to 1788), the last including Traité de laimant, the last work published by Buffon in his lifetime
7 volumes of supplements (1774 to 1789), including Époques de la nature (from 1778).
LHistoire Naturelle was initially printed at the Imprimerie royale in 36 volumes (1749–1789). In 1764 Buffon bought back the rights to his work. It was continued by Bernard Germain de Lacépède, who described the egg-laying quadrupeds, snakes, fishes and cetaceans in 8 volumes (1788–1804).
Buffon was assisted in the work by Jacques-François Artur (1708–1779), Gabriel Léopold Charles Amé Bexon (1748–1785), Louis Jean-Marie Daubenton (1716–1799), Edme-Louis Daubenton (1732–1786), Jacques de Sève (actif 1742–1788), Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond (1741–1819), Philippe Guéneau de Montbeillard (1720–1785), Louis-Bernard Guyton-Morveau (1737–1816), Bernard Germain de Lacépède (1756–1825), François-Nicolas Martinet (1731–1800), the anatomist Jean-Claude Mertrud (1728–1802), Charles-Nicolas-Sigisbert Sonnini de Manoncourt (1751–1812), and André Thouin (1747–1823).
Each group is introduced with a general essay. This is followed by an article, sometimes of many pages, on each animal (or other item). The article on the wolf begins with the claim that it is one of the animals with a specially strong appetite for flesh; it asserts that the animal is naturally coarse and cowardly (grossier et poltron), but becoming crafty at need, and hardy by necessity, driven by hunger.[4] The language, as in this instance, is elegant and elaborate, even flowery and ornate.[5] Buffon was roundly criticised by his fellow academics for writing a purely popularizing work, empty and puffed up, with little real scientific value.
The species is named in Greek, Latin, Italian, Spanish, German, English, Swedish, and Polish. The zoological descriptions of the species by Gessner, Ray, Linnaeus, Klein and Buffon himself (Canis ex griseo flavescens. Lupus vulgaris. Buffon. Reg. animal. pag. 235) are cited.
The text is written as a continuous essay, without the sections on identification, distribution and behaviour that might have been expected from other natural histories. Parts concern human responses rather than the animal itself, as for example that the wolf likes human flesh, and the strongest wolves sometimes eat nothing else.[6] Measurements may be included; in the case of the wolf, 41 separate measurements are tabulated, in pre-revolutionary French feet and inches[a] starting with the Length of the whole body measured in a straight line from the end of the muzzle to the anus........3 feet. 7 inches. (1.2 m); the Length of the largest claws is given as 10 lines (2.2 cm).
The wolf is illustrated standing in farmland, and as a complete skeleton standing on a stone plinth in a landscape. The account of the species occupies 32 pages including illustrations.
The original edition of the Histoire Naturelle by Buffon comprised 36 volumes in quarto, divided into the following series: Histoire de la Terre et de lHomme, Quadrupèdes, Oiseaux, Minéraux, Suppléments. Buffon edited 35 volumes in his lifetime. Soon after his death, the fifth and final volume of lHistoire des minéraux appeared in 1788 at the Imprimerie des Bâtiments du Roi. The seventh and final volume of Suppléments by Buffon was published posthumously in 1789 through Lacépèdes hands. Lacépède continued the part of the Histoire Naturelle which dealt with animals. A few months before Buffons death, en 1788, Lacépède published, as a continuation, the first volume of his Histoire des Reptiles, on egg-laying quadrupeds. The next year, he wrote a second volume on snakes, published during the French Revolution. Between 1798 and 1803, he brought out the volume Histoire des Poissons. Lacépède made use of the notes and collections left by Philibert Commerson (1727–1773). He wrote Histoire des Cétacés which was printed in 1804. At that point, the Histoire Naturelle, by Buffon and Lacépède, thus contained 44 quarto volumes forming the definitive edition.
Another edition in quarto format was printed by the Imprimerie royale in 36 volumes (1774–1804). It consisted of 28 volumes par Buffon, and 8 volumes by Lacépède. The part containing anatomical articles by Louis Jean-Marie Daubenton was dropped. The supplements were merged into the relevant articles in the main volumes.
The Imprimerie royale also published two editions of the Histoire Naturelle in duodecimo format (1752–1805), occupying 90 or 71 volumes, depending on whether or not they included the part on anatomy. In this print format, the original work by Buffon occupied 73 volumes with the part on anatomy, or 54 volumes without the part on anatomy. The continuation by Lacépède took up 17 duodecimo volumes.
A de luxe edition of Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux (Birds) (1771–1786) was produced by the Imprimerie royale in 10 folio and quarto volumes, with 1008 engraved and hand-coloured plates, executed under Buffons personal supervision by Edme-Louis Daubenton, cousin and brother-in-law of Buffons principal collaborator.
The original edition was arranged as follows:
Natural history, and description of the kings cabinet of curiosities
Volume I : Premier Discours - De la manière détudier et de traiter lhistoire naturelle, Second Discours - Histoire et théorie de la Terre, Preuves de la théorie de la Terre, 1749
Volume II : Histoire générale des Animaux, Histoire Naturelle de lHomme, 1749
Volume III : Description du cabinet du Roi, Histoire Naturelle de lHomme, 1749
Quadrupèdes (Quadrupeds)
Volume IV (Quadrupèdes I) : Discours sur la nature des Animaux, Les Animaux domestiques, 1753
Volume V (Quadrupèdes II) : 1755
Volume VI (Quadrupèdes III) : Les Animaux sauvages, 1756
Volume VII (Quadrupèdes IV) : Les Animaux carnassiers, 1758
Volume VIII (Quadrupèdes V) : 1760
Volume IX (Quadrupèdes VI) : 1761
Volume X (Quadrupèdes VII) : 1763
Volume XI (Quadrupèdes VIII) : 1764
Volume XII (Quadrupèdes IX) : 1764
Volume XIII (Quadrupèdes X) : 1765
Volume XIV (Quadrupèdes XI) : Nomenclature des Singes, De la dégénération des Animaux, 1766
Volume XV (Quadrupèdes XII) : 1767
Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux (Birds) (1770–1783)
Volume XVI (Oiseaux I) : 1770
Volume XVII (Oiseaux II) : 1771
Volume XVIII (Oiseaux III) : 1774
Volume XIX (Oiseaux IV) : 1778
Volume XX (Oiseaux V) : 1778
Volume XXI (Oiseaux VI) : 1779
Volume XXII (Oiseaux VII) : 1780
Volume XXIII (Oiseaux VIII) : 1781
Volume XXIV (Oiseaux IX) : 1783
Histoire Naturelle des Minéraux (Minerals) (1783–1788)
Volume XXV (Minéraux I) : 1783
Volume XXVI (Minéraux II) : 1783
Volume XXVII (Minéraux III) : 1785
Volume XXVIII (Minéraux IV) : 1786
Volume XXIX (Minéraux V) : Traité de lAimant et de ses usages, 1788
Suppléments à lHistoire Naturelle, générale et particulière (Supplements) (1774–1789)
Volume XXX (Suppléments I) : Servant de suite à la Théorie de la Terre, et dintroduction à lHistoire des Minéraux, 1774
Volume XXXI (Suppléments II) : Servant de suite à la Théorie de la Terre, et de préliminaire à lHistoire des Végétaux - Parties Expérimentale & Hypothétique, 1775
Volume XXXII (Suppléments III) : Servant de suite à lHistoire des Animaux quadrupèdes, 1776
Volume XXXIII (Suppléments IV) : Servant de suite à lHistoire Naturelle de lHomme, 1777
Volume XXXIV (Suppléments V) : Des Époques de la nature, 1779
Volume XXXV (Suppléments VI) : Servant de suite à lHistoire des Animaux quadrupèdes, 1782
Volume XXXVI (Suppléments VII) : Servant de suite à lHistoire des Animaux quadrupèdes, 1789
Histoire Naturelle des Quadrupèdes ovipares et des Serpents (Egg-laying Quadrupeds and Snakes) (1788–1789)
The Gecko, 1788
Volume XXXVII (Reptiles I) : Histoire générale et particulière des Quadrupèdes ovipares, 1788
Volume XXXVIII (Reptiles II) : Histoire des Serpents, 1789
Histoire Naturelle des Poissons (Fish) (1798–1803)
Volume XXXIX (Poissons I) : 1798
Volume XXXX (Poissons II) : 1800
Volume XXXXI (Poissons III) : 1802
Volume XXXXII (Poissons IV) : 1802
Volume XXXXIII (Poissons V) : 1803
Histoire Naturelle des Cétacés (Cetaceans) (1804)
Volume XXXXIV (Cétacés) : 1804
1774 Comte De Buffon Large Antique Print of Various American Cactus
- Title : Histoire Naturelle, Fig. 1. Le Cierge du Perou Fig 2. Le Cierge Rampant Fig 3. L Euphorbe
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1774
- Ref #: 90641
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print was published in the 1774 quatro edition of Comte de Buffons Histoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du Cabinet du Roi (Natural History, General and Particular, with a Description of the King\'s Cabinet)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Background:
The Histoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du Cabinet du Roi (Natural History, General and Particular, with a Description of the Kings Cabinet) is an encyclopaedic collection of 36 large (quarto) volumes written between 1749–1804 by the Comte de Buffon, and continued in eight more volumes after his death by his colleagues, led by Bernard Germain de Lacépède. The books cover what was known of the natural sciences at the time, including what would now be called material science, physics, chemistry and technology as well as the natural history of animals.
The Histoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du Cabinet du Roi is the work that the Comte de Buffon (1707–1788) is remembered for. He worked on it for some 50 years, initially at Montbard in his office in the Tour Saint-Louis, then in his library at Petit Fontenet. 36 volumes came out between 1749 and 1789, followed by 8 more after his death, thanks to Bernard Germain de Lacépède. It includes all the knowledge available in his time on the natural sciences, a broad term that includes disciplines which today would be called material science, physics, chemistry and technology. Buffon notes the morphological similarities between men and apes, although he considered apes completely devoid of the ability to think, differentiating them sharply from human beings. Buffons attention to internal anatomy made him an early comparative anatomist. Lintérieur, dans les êtres vivants, est le fond du dessin de la nature, he wrote in his Quadrupèdes, the interior, in living things, is the foundation of natures design.
The Histoire Naturelle, which was meant to address the whole of natural history, actually covers only minerals, birds, and the quadrupeds among animals. It is accompanied by some discourses and a theory of the earth by way of introduction, and by supplements including an elegantly written account of the epochs of nature.
The Suppléments cover a wide range of topics; for example, in (Suppléments IV), there is a Discours sur le style (Discourse on Style) and an Essai darithmétique morale (essay on Moral Arithmetic).
Louis Jean-Marie Daubenton assisted Buffon on the quadrupeds; Philippe Guéneau de Montbeillard worked on the birds. They were joined, from 1767, by Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond, the abbot Gabriel Bexon and Charles-Nicolas-Sigisbert Sonnini de Manoncourt. The whole descriptive and anatomical part of lHistoire des Quadrupèdes was the work of Daubenton and Jean-Claude Mertrud.
Buffon attached much importance to the illustrations; Jacques de Sève illustrated the quadrupeds and François-Nicolas Martinet illustrated the birds. Nearly 2000 plates adorn the work, representing animals with care given both to aesthetics and anatomical accuracy, with dreamlike and mythological settings.
On minerals, Buffon collaborated with André Thouin. Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond and Louis Bernard Guyton de Morveau provided sources for the mineral volumes.
L Histoire Naturelle met immense success, almost as great as Encyclopédie by Diderot, which came out in the same period. The first three volumes of LHistoire Naturelle, générale et particulière, avec la description du cabinet du Roi were reprinted three times in six weeks.
The encyclopaedia appeared in 36 volumes :
3 volumes in 1749 : De la manière détudier lhistoire naturelle followed by Théorie de la Terre, Histoire Générale des animaux and Histoire Naturelle de lhomme
12 volumes on quadrupeds (1753 to 1767)
9 volumes on birds (1770 to 1783])
5 volumes on minerals (1783 to 1788), the last including Traité de laimant, the last work published by Buffon in his lifetime
7 volumes of supplements (1774 to 1789), including Époques de la nature (from 1778).
LHistoire Naturelle was initially printed at the Imprimerie royale in 36 volumes (1749–1789). In 1764 Buffon bought back the rights to his work. It was continued by Bernard Germain de Lacépède, who described the egg-laying quadrupeds, snakes, fishes and cetaceans in 8 volumes (1788–1804).
Buffon was assisted in the work by Jacques-François Artur (1708–1779), Gabriel Léopold Charles Amé Bexon (1748–1785), Louis Jean-Marie Daubenton (1716–1799), Edme-Louis Daubenton (1732–1786), Jacques de Sève (actif 1742–1788), Barthélemy Faujas de Saint-Fond (1741–1819), Philippe Guéneau de Montbeillard (1720–1785), Louis-Bernard Guyton-Morveau (1737–1816), Bernard Germain de Lacépède (1756–1825), François-Nicolas Martinet (1731–1800), the anatomist Jean-Claude Mertrud (1728–1802), Charles-Nicolas-Sigisbert Sonnini de Manoncourt (1751–1812), and André Thouin (1747–1823).
Each group is introduced with a general essay. This is followed by an article, sometimes of many pages, on each animal (or other item). The article on the wolf begins with the claim that it is one of the animals with a specially strong appetite for flesh; it asserts that the animal is naturally coarse and cowardly (grossier et poltron), but becoming crafty at need, and hardy by necessity, driven by hunger.[4] The language, as in this instance, is elegant and elaborate, even flowery and ornate.[5] Buffon was roundly criticised by his fellow academics for writing a purely popularizing work, empty and puffed up, with little real scientific value.
The species is named in Greek, Latin, Italian, Spanish, German, English, Swedish, and Polish. The zoological descriptions of the species by Gessner, Ray, Linnaeus, Klein and Buffon himself (Canis ex griseo flavescens. Lupus vulgaris. Buffon. Reg. animal. pag. 235) are cited.
The text is written as a continuous essay, without the sections on identification, distribution and behaviour that might have been expected from other natural histories. Parts concern human responses rather than the animal itself, as for example that the wolf likes human flesh, and the strongest wolves sometimes eat nothing else.[6] Measurements may be included; in the case of the wolf, 41 separate measurements are tabulated, in pre-revolutionary French feet and inches[a] starting with the Length of the whole body measured in a straight line from the end of the muzzle to the anus........3 feet. 7 inches. (1.2 m); the Length of the largest claws is given as 10 lines (2.2 cm).
The wolf is illustrated standing in farmland, and as a complete skeleton standing on a stone plinth in a landscape. The account of the species occupies 32 pages including illustrations.
The original edition of the Histoire Naturelle by Buffon comprised 36 volumes in quarto, divided into the following series: Histoire de la Terre et de lHomme, Quadrupèdes, Oiseaux, Minéraux, Suppléments. Buffon edited 35 volumes in his lifetime. Soon after his death, the fifth and final volume of lHistoire des minéraux appeared in 1788 at the Imprimerie des Bâtiments du Roi. The seventh and final volume of Suppléments by Buffon was published posthumously in 1789 through Lacépèdes hands. Lacépède continued the part of the Histoire Naturelle which dealt with animals. A few months before Buffons death, en 1788, Lacépède published, as a continuation, the first volume of his Histoire des Reptiles, on egg-laying quadrupeds. The next year, he wrote a second volume on snakes, published during the French Revolution. Between 1798 and 1803, he brought out the volume Histoire des Poissons. Lacépède made use of the notes and collections left by Philibert Commerson (1727–1773). He wrote Histoire des Cétacés which was printed in 1804. At that point, the Histoire Naturelle, by Buffon and Lacépède, thus contained 44 quarto volumes forming the definitive edition.
Another edition in quarto format was printed by the Imprimerie royale in 36 volumes (1774–1804). It consisted of 28 volumes par Buffon, and 8 volumes by Lacépède. The part containing anatomical articles by Louis Jean-Marie Daubenton was dropped. The supplements were merged into the relevant articles in the main volumes.
The Imprimerie royale also published two editions of the Histoire Naturelle in duodecimo format (1752–1805), occupying 90 or 71 volumes, depending on whether or not they included the part on anatomy. In this print format, the original work by Buffon occupied 73 volumes with the part on anatomy, or 54 volumes without the part on anatomy. The continuation by Lacépède took up 17 duodecimo volumes.
A de luxe edition of Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux (Birds) (1771–1786) was produced by the Imprimerie royale in 10 folio and quarto volumes, with 1008 engraved and hand-coloured plates, executed under Buffons personal supervision by Edme-Louis Daubenton, cousin and brother-in-law of Buffons principal collaborator.
The original edition was arranged as follows:
Natural history, and description of the kings cabinet of curiosities
Volume I : Premier Discours - De la manière détudier et de traiter lhistoire naturelle, Second Discours - Histoire et théorie de la Terre, Preuves de la théorie de la Terre, 1749
Volume II : Histoire générale des Animaux, Histoire Naturelle de lHomme, 1749
Volume III : Description du cabinet du Roi, Histoire Naturelle de lHomme, 1749
Quadrupèdes (Quadrupeds)
Volume IV (Quadrupèdes I) : Discours sur la nature des Animaux, Les Animaux domestiques, 1753
Volume V (Quadrupèdes II) : 1755
Volume VI (Quadrupèdes III) : Les Animaux sauvages, 1756
Volume VII (Quadrupèdes IV) : Les Animaux carnassiers, 1758
Volume VIII (Quadrupèdes V) : 1760
Volume IX (Quadrupèdes VI) : 1761
Volume X (Quadrupèdes VII) : 1763
Volume XI (Quadrupèdes VIII) : 1764
Volume XII (Quadrupèdes IX) : 1764
Volume XIII (Quadrupèdes X) : 1765
Volume XIV (Quadrupèdes XI) : Nomenclature des Singes, De la dégénération des Animaux, 1766
Volume XV (Quadrupèdes XII) : 1767
Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux (Birds) (1770–1783)
Volume XVI (Oiseaux I) : 1770
Volume XVII (Oiseaux II) : 1771
Volume XVIII (Oiseaux III) : 1774
Volume XIX (Oiseaux IV) : 1778
Volume XX (Oiseaux V) : 1778
Volume XXI (Oiseaux VI) : 1779
Volume XXII (Oiseaux VII) : 1780
Volume XXIII (Oiseaux VIII) : 1781
Volume XXIV (Oiseaux IX) : 1783
Histoire Naturelle des Minéraux (Minerals) (1783–1788)
Volume XXV (Minéraux I) : 1783
Volume XXVI (Minéraux II) : 1783
Volume XXVII (Minéraux III) : 1785
Volume XXVIII (Minéraux IV) : 1786
Volume XXIX (Minéraux V) : Traité de lAimant et de ses usages, 1788
Suppléments à lHistoire Naturelle, générale et particulière (Supplements) (1774–1789)
Volume XXX (Suppléments I) : Servant de suite à la Théorie de la Terre, et dintroduction à lHistoire des Minéraux, 1774
Volume XXXI (Suppléments II) : Servant de suite à la Théorie de la Terre, et de préliminaire à lHistoire des Végétaux - Parties Expérimentale & Hypothétique, 1775
Volume XXXII (Suppléments III) : Servant de suite à lHistoire des Animaux quadrupèdes, 1776
Volume XXXIII (Suppléments IV) : Servant de suite à lHistoire Naturelle de lHomme, 1777
Volume XXXIV (Suppléments V) : Des Époques de la nature, 1779
Volume XXXV (Suppléments VI) : Servant de suite à lHistoire des Animaux quadrupèdes, 1782
Volume XXXVI (Suppléments VII) : Servant de suite à lHistoire des Animaux quadrupèdes, 1789
Histoire Naturelle des Quadrupèdes ovipares et des Serpents (Egg-laying Quadrupeds and Snakes) (1788–1789)
The Gecko, 1788
Volume XXXVII (Reptiles I) : Histoire générale et particulière des Quadrupèdes ovipares, 1788
Volume XXXVIII (Reptiles II) : Histoire des Serpents, 1789
Histoire Naturelle des Poissons (Fish) (1798–1803)
Volume XXXIX (Poissons I) : 1798
Volume XXXX (Poissons II) : 1800
Volume XXXXI (Poissons III) : 1802
Volume XXXXII (Poissons IV) : 1802
Volume XXXXIII (Poissons V) : 1803
Histoire Naturelle des Cétacés (Cetaceans) (1804)
Volume XXXXIV (Cétacés) : 1804
1774 Cook & Hawkesworth Antique Atlas of Australia, New Zealand 52 Maps & Prints
Antique Map
- Title : Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique, actuellement régnante ; pour faire des découvertes dans l'hémisphère méridional, et successivement exécutés par le Commodore Byron, le Capitaine Carteret, le Capitaine Wallis & le Capitaine Cook dans les vaisseaux. MDCCLXXIV (1774)
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1774
- Ref #: 35632
Description:
This original antique Atlas containing 52 maps and prints, as called for, from some of the foremost explorers of the mid 18th century, including Commodore Byron, Captain Carteret, Captain Wallis & Captain James Cook, was published as the 1st French edition of Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique: (Maps and Figures of Travels undertaken by Order of his Present Reigning British Majesty) in 1774, published after only a year after the 1st English edition by John Hawkesworth.
The 52 prints and maps contained in this atlas chart in maps, prints and plans, the progression in the exploration of the South Seas of the 4 explorers. But there is of course, the standout amongst these 4 explorers and that is of course Captain James Cook.
At the time of the publication of this tome, Cook had returned from his first voyage of exploration to The South Pacific, becoming the first European to survey and chart the coastline of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia. But at this point Cook was not as famous as he was destined to become, after completing 2 more voyages of exploration, and in turn becoming the most famous explorer of his era.
The majority of this atlas contains the prints and maps dedicated to Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery including the two famous maps, one of New Zealand and the other the East Coast of Australia. All voyages can be tracked from the first large folding map of the South Seas, at the beginning of the Atlas, that illustrates the tracks on Cook and the other 3 explorers.
In-4 binding in half-calf, spine with five bands with gilding boxes and title label complete with 52 folding & single plates
Spine & boards in poor condition with lack of leather and scratched covers, contents tights with plates in very good condition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning - Maps & Prints
Plate area: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Verso: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Background:
Capt. Cook First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Vice-Admiral John Byron (1723-1786) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is known for his circumnavigation of the globe aboard the HMS Dolphin, completing one of the first British expeditions to achieve this feat. His account of the voyage, "The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron," influenced subsequent explorations. Byron's naval career included service in the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War.
Rear-Admiral Philip Carteret (1733-1796) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is best known for his role as the captain of HMS Swallow during the first circumnavigation of the globe. Carteret's expedition, which took place from 1766 to 1769, aimed to explore and map uncharted regions of the Pacific Ocean. His discoveries included the Carteret Islands and the Pitcairn Islands. Carteret's voyage greatly contributed to the knowledge of Pacific geography and exploration during that time.
Samuel Wallis (1728-1795) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is renowned for leading the first recorded European expedition to visit Tahiti and for his significant contributions to the exploration of the Pacific Ocean. In 1766, Wallis commanded HMS Dolphin on a voyage funded by the British Admiralty. During the expedition, he discovered and named several islands, including Tahiti, which he encountered in June 1767. Wallis's visit to Tahiti marked the beginning of sustained European contact with the island and its inhabitants. His exploration efforts and subsequent reports greatly expanded European knowledge of the Pacific region. Wallis's achievements laid the foundation for future explorations and influenced subsequent voyages of exploration in the Pacific.
John Hawkesworth 1715 -1775
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cooks view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Cook , Capt. James 1728-1779
James Cook was born on 27 October 1728 in Marton, England. His father was a poor farm labourer who had worked his way up to Overseer. James began as a farm labourer and grocer\\\'s assistant. He soon found employment on the Baltic sea in a Collier (coal transport ship) at the age of 18.
During the war with the French in 1755, James Cook enlisted as an Able Seaman on the Eagle. Within a month he was promoted, because of outstanding ability, to Masters Mate. Four years later he was promoted to Master. In command of his own ship, James Cook performed a crucial charting of the St. Lawrence River, which made possible the great amphibious assault upon Quebec City in 1759. In 1763 he was given command of the schooner Grenville to survey the eastern coasts of Canada over a four year period. These excellent charts were used up until the early part of the 20th century.
James Cook was selected to lead a 1768 expedition to observe the transit of Venus, and to explore new lands in the Pacific Ocean. In his first Pacific voyage, James Cook rounded Cape Horn in the Endeavour and reached Tahiti on 3 June 1769. After recovering a necessary scientific instrument stolen by the natives, the transit of Venus was successfully observed. The Endeavour then spent six months charting New Zealand. James Cook next explored and claimed possession of eastern Australia. Returning to England, on 12 June 1771, via New Guinea, Java and the Cape of Good Hope, the crew suffered an appalling 43% fatality rate. James Cook thus became very concerned about crew health on subsequent voyages. He instituted compulsory dietary reforms that were copied by many other ship captains.
The object of Captain Cook\\\'s second Pacific Ocean voyage was to confirm the existence of a theorized Great Southern Continent. His ship the Resolution, accompanied by the Adventure, departed Plymouth on 13 July 1772 and sailed around the Cape of Good Hope. Beset by ice, he was unable to reach Antarctica. Although its existence was suspected, James Cook demonstrated, by traversing large areas of the south Pacific, that it would have to be a frigid wasteland, and not an economically productive addition to the British empire. James Cook charted many of the South Pacific islands with the incredible accuracy of 3 miles. This accuracy was made possible by a new and highly accurate clock. The two ships returned to England, via Cape Horn, on 29 July 1775. The experimental diets and close attention to cleanliness had a miraculous effect: out of a crew of 118, only one man was lost to disease! Since public interest was high, the many paintings by the artists were widely displayed and published as engravings. James Cook was also awarded the Copley Gold Medal and elected as a fellow of the Royal Society.
The third great voyage is especially significant to the history of the west coast of North America. Captain Cook and his men were primarily searching for the Northwest Passage from the Pacific Ocean to the Atlantic Ocean. They departed Plymouth on 12 July 1776 in the Resolution and the Discovery.
The ships sailed around the Cape of Good Hope to reach the west coast of America in February of 1778. They continued north along the coast in haste to the Bering Sea and Bering Strait in an attempt to pass through the Arctic Ocean during the summer season. Foiled by ice, James Cook returned to Hawaii to prepare for another attempt at the Northwest Passage the next season. Soon after they had departed, a storm damaged the foremast of the Resolution and forced a return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs. Unfortunately, they had previously overstayed their welcome and relations became tense. The theft of a ship\\\'s cutter led Captain Cook to put ashore to demand the return of the boat. A fight broke out and James Cook was killed on 14 Feb 1779 by angry natives. Although his men made another attempt at the Northwest Passage, they were unsuccessful. The expedition did identify the possibilities of trade with the coastal American natives for otter seal furs, which could then be bartered for Chinese goods that were highly prized in England.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map Nendo Isle, Nupani, Solomon Islands - Carteret 1767
- Title : Cote septentrional de la plus grande des isles de la Reine Charlotte; Baye Swallow; Havre Byroni
- Ref : 21589-1
- Size: 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique nautical chart & coastal view of the Island of Nendo (then called Lord Egmonts Island or New Guernsey) along with inset maps of Swallow Bay & Byrons Harbour on Nendo and a view of the nearby volcanic island of Nupani was drawn by Captain Phillip Carteret in July-August 1767 aboard his ship Swallow, accompanying Captain Samuel Wallis during his circumnavigation of the world, was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Capt. Philip Carteret (1733-1796)
was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navy\\\\\\\'s circumnavigation expeditions in 1764-66 and 1766-69.
Carteret entered the Navy in 1747, serving aboard the Salisbury, and then under Captain John Byron from 1751 to 1755. Between 1757 and 1758 he was in the Guernsey on the Mediterranean Station. As a lieutenant in the Dolphin he accompanied Byron during his voyage of circumnavigation, from June 1764 to May 1766.
In 1766 he was made a commander and given the command of the Swallow to circumnavigate the world, as consort to the Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis. The two ships were parted shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Carteret discovering Pitcairn Island and the Carteret Islands, which were subsequently named after him. In 1767, he also discovered a new archipelago inside Saint George\\\\\\\'s Channel between New Ireland and New Britain Islands (Papua New Guinea) and named it Duke of York Islands, as well as rediscovered the Solomon Islands first sighted by the Mendana in 1568, and the Juan Fernandez Islands first discovered by Juan Fernandez in 1574. He arrived back in England, at Spithead, on 20 March 1769.
He was promoted to post captain in 1771.
Nendo is the largest of the Santa Cruz Islands, located in the Temotu province of the Solomon Islands. The island is also known as Santa Cruz, Ndeni, Nitendi or Ndende. The name Santa Cruz was given to the island in 1595 by the Spanish navigator Alvaro de Mendaña, who unsuccessfully started a colony there.
The Nupani Atoll is located about 65 km to the West of the main group of the Reef Islands.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map of Magellan Straits, Bachelor River, Punta Arenas, Chile, Byron 1766
- Title : Baye d Elizabeth; Baye au dessons des Isles vis a vis la Rade d York; Côte depuis la Baye d York a la Baye et au Havre des Trois Isles; Baye St. David
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16027
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map, four maps on the one sheet, of;
1. Elizabeth Bay.
2. York Bay.
3. York Bay-Three Island Bay
4.St. Davids Bay.
all located north of Carlos III island, on Punta Arenas in the Chilean Arctic - from Bachelor River north to York Bay - in the Straits of Magellan, Chile. This chart was compiled by Commodore John Byron, who visited the region in HMS Dolphin on his circumnavigation of the globe, between 1764-66, and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Strait of Magellan
(Estrecho de Magallanes) is a navigable sea route separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Ferdinand Magellan a Portuguese explorer and navigator in the service of Charles I of Spain, became the first European to navigate the strait in 1520 during his circumnavigation of the globe.
Other early explorers included Francis Drake (1578). In February 1696 the first French expedition, under the command of M. de Gennes reached the Strait of Magellan. The expedition is described by the young French explorer, engineer and hydrographer François Froger in his A Relation of a Voyage (1699).
The strait was first carefully explored and thoroughly charted by Phillip Parker King, who commanded the British survey vessel HMS Adventure, and in consort with HMS Beagle spent five years surveying the complex coasts around the strait (1826–1830). A report on the survey was presented at two meetings of the Geographical Society of London in 1831.
Vice-Admiral The Hon. John Byron was a British Royal Navy officer and politician. He was known as Foul-weather Jack because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sailed in the squadron under George Anson on his voyage around the world, though Byron made it to southern Chile, and returned to England with the captain of HMS Wager. He was governor of Newfoundland following Hugh Palliser, who left in 1768. He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764-1766. He fought in battles in The Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral of the White before his death in 1786.
In early 1764 the British Admiralty determined that it would require a permanent naval settlement off the South American coast, in order to resupply naval vessels seeking to enter the Pacific via Cape Horn. Captain Byron was selected to explore the South Atlantic for a suitable island upon which to establish such a settlement. The South American mainland was controlled by Spain, which was hostile to local expansion of British interests; to disguise Byrons mission it was announced that he had been appointed the new commander of the Navys East Indies Station. Byron set sail in June 1764, ostensibly to take up the East Indies post. For the voyage he was granted command of the 24-gun frigate HMS Dolphin and the 20-gun sloop HMS Tamar.
Byron\'s two-vessel flotilla crossed the Atlantic over the winter of 1764 and made its way slowly down the South American coast. The Admiralty had ordered Byron to first seek Pepys Island, reputedly discovered off the Patagonian coast by the corsair Ambrose Cowley in 1683. Byron reached the co-ordinates given by Cowley in January 1765, but there was no sign of the island and the search was swiftly abandoned. On 5 February Byron reached the Patagonian settlement of Port Desire where he resupplied his vessels from the storeship HMS Florida.
Between June 1764 and May 1766, Byron completed his own circumnavigation of the globe as captain of HMS Dolphin. This was the first such circumnavigation that was accomplished in less than 2 years. His actions nearly caused a war between Great Britain and Spain, as both countries had armed fleets ready to contest the sovereignty of the Falkland Islands. Later Byron encountered islands and extant residents of the Tuamotus and Tokelau Islands, and Nikunau in the southern Gilbert Islands; he also visited Tinian in the Northern Marianas Islands.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map of Wallis (Uvea) & Funtuna Islands Capt Wallis 1767
- Title : Isles de Wallis
- Size: 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 21598
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Islands of Wallis (Uvea) and Futuna, situated in the South Pacific between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji to the southwest, Tonga to the southeast, Samoa to the east. Futuna was first mapped by Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire during their famous circumnavigation of the globe in 1616 and Wallis (Uvea) being mapped by Captain Samuel Wallis, who saw it while sailing the HMS Dolphin on 16 August 1767, was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 9in (255mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 8in (230mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Wallis or Uvea, is a Polynesian island in the Pacific Ocean belonging to the French overseas collectivity of Wallis and Futuna. It lies north of Tonga, northeast of Fiji, east-northeast of the Hoorn islands, east of Fijis Rotuma, southeast of Tuvalu, southwest of Tokelau and west of Samoa. Its area is almost 100 km2 with almost 11,000 people. Its capital is Matā utu.
The island was renamed Wallis after a Cornish navigator, Captain Samuel Wallis, who saw it while sailing the HMS Dolphin on 16 August 1767, following his discovery of Tahiti.
Futuna was first put on the European maps by Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire during their famous circumnavigation of the globe in 1616. They named the islands Hoornse Eylanden after the Dutch town of Hoorn where they hailed from. This was later translated into French as Isles de Horne. The French were the first Europeans to settle in the territory with the arrival of French missionaries in 1837
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Capt. Philip Carteret (1733-1796)
was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navy\\\\\\\'s circumnavigation expeditions in 1764-66 and 1766-69.
Carteret entered the Navy in 1747, serving aboard the Salisbury, and then under Captain John Byron from 1751 to 1755. Between 1757 and 1758 he was in the Guernsey on the Mediterranean Station. As a lieutenant in the Dolphin he accompanied Byron during his voyage of circumnavigation, from June 1764 to May 1766.
In 1766 he was made a commander and given the command of the Swallow to circumnavigate the world, as consort to the Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis. The two ships were parted shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Carteret discovering Pitcairn Island and the Carteret Islands, which were subsequently named after him. In 1767, he also discovered a new archipelago inside Saint George\\\\\\\'s Channel between New Ireland and New Britain Islands (Papua New Guinea) and named it Duke of York Islands, as well as rediscovered the Solomon Islands first sighted by the Mendana in 1568, and the Juan Fernandez Islands first discovered by Juan Fernandez in 1574. He arrived back in England, at Spithead, on 20 March 1769.
He was promoted to post captain in 1771.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Capt Wallis attacked in Matavia Bay, Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Le Capitaine Wallis est attaque dans L Dauphin par les Otahitiens (Captain Wallis attacked in The Dolphin by the Tahitians)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25928
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis in his ship the HMS Dolphin being attacked by the Tahitians in Matavai Bay - with one tree hill to the right - in 1767 was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Queen Purea Surrender to Capt Wallis Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Cession de lisle D otahiti au Capitaine Wallis par la Reine Oberea (Surrender of the Island of Taahiti to Capt Wallis by Queen Obera)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25925
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis - the first European to visit Tahiti in 1767 - accepting surrender from Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti, after the battle in Matavia Bay in 1767, was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Queen Purea Surrender to Capt Wallis Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Cession de lisle D otahiti au Capitaine Wallis par la Reine Oberea (Surrender of the Island of Taahiti to Capt Wallis by Queen Obera)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16089-1
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis - the first European to visit Tahiti in 1767 - accepting surrender from Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti, after the battle in Matavia Bay in 1767, was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Queen Purea Surrender to Capt Wallis Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Cession de lisle D otahiti au Capitaine Wallis par la Reine Oberea (Surrender of the Island of Taahiti to Capt Wallis by Queen Obera)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25925
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis - the first European to visit Tahiti in 1767 - accepting surrender from Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti, after the battle in Matavia Bay in 1767, was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Large Antique Map Chart of The Magellan Straits, South America
Antique Map
- Title : Carte Du Detroit De Magellan dans laquelle on a Insere Les Observations et Les Decouvertes Du Capne Byron, du Capne Wallis, et du Capne Carteret
- Ref : 32219
- Size: 30 1/2in x 21 1/2in (775mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large, original copper-plate engraved, antique map, a chart of the Straits of Magellan, South America and the Patagonian & South Chilean shoreline was engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks
A large scale chart with detailed shoreline topography, channels, soundings, shoals, harbors and small islands. There are also anchorages, capes & bays as well as 4 finely engraved landfall approach views of
1.Vue Du Port Famine
2. Cap Beau Tems
3.Cap Des Vierges
4. Rochers blanc. (white rocks).
The tracks and some details in this chart are attributed to the following navigators;
Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis and Captain Carteret.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, brown
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30 1/2in x 21 1/2in (775mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 20in (765mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling to top margin and border, repair to top left corner
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The Strait of Magellan
(Estrecho de Magallanes) is a navigable sea route separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Ferdinand Magellan a Portuguese explorer and navigator in the service of Charles I of Spain, became the first European to navigate the strait in 1520 during his circumnavigation of the globe.
Other early explorers included Francis Drake (1578). In February 1696 the first French expedition, under the command of M. de Gennes reached the Strait of Magellan. The expedition is described by the young French explorer, engineer and hydrographer François Froger in his A Relation of a Voyage (1699).
The strait was first carefully explored and thoroughly charted by Phillip Parker King, who commanded the British survey vessel HMS Adventure, and in consort with HMS Beagle spent five years surveying the complex coasts around the strait (1826–1830). A report on the survey was presented at two meetings of the Geographical Society of London in 1831.
The 3 Voyages, with Captains, ships & tracks who contributed to this map are;
1. 1764-66 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Commodore John Byron, completed the first circumnavigation of the globe under two years.
2. 1766-68 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Captain Samuel Wallis, completed another circumnavigation & was the first European to visit Tahiti & the Society Islands.
3. 1766-68 - HMS Swallow under Command of Captain Philip Carteret, who accompanied HMS Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis to circumnavigate the world.
John Hawkesworth an English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Large Antique Map of Australia & South Seas 1765-71 - Capt Cook
Antique Map
- Title : Carte d une Partie de la Mer du Sud Contenant les Decouvertes de Vaisseaux de sa Majeste, Le Dauphin, Commodore Byron, La Tamar, Capitne. Mouats 1765, Le Dauphin, Capitne. Wallis, Le Swallow, Capitne. Cartaret, 1767, et l Endeavour, Lieutenant Cook 1769
- Ref : 35509
- Size: 28in x 16 3/4in (710mm x 425mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved, large antique map, a chart of the tracks of 5 British ships & explorers to the South Ocean from 1765 to 1771 was engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1774 French translation of John Hawkesworths publication An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks
The 5 Voyages, with Captains, ships & tracks are;
1. 1764-66 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Commodore John Byron, completed the first circumnavigation of the globe under two years.
2. 1764-1766 - HMS Tamar under Command of Captain Patrick Mouat, accompanied Commodore John Byron & HMS Dolphin on 1764-66 circumnavigation of the world.
3. 1766-68 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Captain Samuel Wallis, completed another circumnavigation & was the first European to visit Tahiti & the Society Islands.
4. 1766-68 - HMS Swallow under Command of Captain Philip Carteret, who accompanied HMS Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis to circumnavigate the world.
5. 1769-71 - HMS Endeavour, under Command of Lieutenant James Cook (later Captain) completed a the mapping of Tahiti & the Society Islands, New Zealand & the East Coast of Australia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 28in x 16 3/4in (710mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 26 3/4in x 14 3/4in (680mm x 375mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Commodore John Byron 1723 – 1786 was a British Royal Navy officer and politician.He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764-1766. He fought in battles in The Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral before his death in 1786.
Captain Patrick Mouat. Commanded HMS Tamer on a voyage of discovery with Commodore John Byron between 1764-66. HMS Tamar was a sloop, mounting sixteen guns: ninety men, three lieutenants, and two and twenty petty officers.
Captain Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795 was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean. Was given the command of HMS Dolphin in 1751 as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Third\'s Island in honour of the King in June 1767.
Captain Philip Carteret 1733 – 1796 was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navys circumnavigation expeditions in 1764–66 and 1766–69.
Captain James Cook is considered one of the most talented Surveyors & Map Makers of any age, for Cook, the production of a new chart was his principal reason for going to sea. His charts were aimed at fellow seamen so he incorporated as much information as possible while employing an economy of style and little elaboration. The quality of his charts can be confirmed by the fact that some survey details from Newfoundland to New Zealand & Australias East Coast could still be safely used over one hundred years later. His last piece of the New Zealand hydrographic chart was only removed in the 1990s.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Malachy Postlethwayt Antique 2 Volume Atlas 7 Large Cont Maps North America
Antique Map
- Title : The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commercewith large Improvements Adapting the Same to the Present State of British Affairs in America since the last Treaty of Peace made in the year 1763....MDCCLXXIV
- Ref #: 93529
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: Large Folio
- Date : 1774
Description:
These very large, heavy leather backed original antique dictionary & atlas volumes of early Global Economic Commerce by Malachy Postlethwayt was published in 1774.
The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce in 2 volumes is the 4th edition published in London by W. Strahan, J and F. Rivington, et al., in 1774. The first edition was published between 1751 & 1755. Titles in red and black with engraved vignettes, engraved allegorical frontispiece to volume 1 (offset onto title) and contain 24 engraved folding maps sheets that when assembled make 7 complete very large maps. Occasional minor spotting, contemporary diced calf, re-backed preserving original contrasting morocco labels, extremities repaired.
The seven maps once assembled, to the left, are as follows with titles, cartographers dates and dimensions;:
1. A Correct Map of Europe by Thomas Kitchin after D Anville, 80cm x 70cm, 1774
2. Africa Performed by the Sr D Anville Samuel Bolton after D Anville, 103cm x 94cm, 1774
3. A New and Correct Map of the Coast of Africa, so called Slave Coast Map, Richard Seale 48cm x 38cm, 1774
4. North America Performed under the Patronage of Louis Duke of Orleans Richard Seale after D Anville, 88cm x 86cm, 1774
5. South America Thomas Kitchin after D Anville, 124cm x 75cm, 1774
6. First Part of Asia RW Seale, after D Anville, 83cm x 77cm, 1755
7. Second Part of Asia R W Seale, after D Anville, 96cm x 70cm, 1755
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - Please see above
Plate size: - Please see above
Margins: - Please see above
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see above
Plate area: - Please see above
Verso: - Please see above
Background:
Postlethwayts most noted work, The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, appeared after he had devoted twenty years to its preparation. The first edition was published in London in instalments between 1751 and 1755, and then in subsequent editions as a two-volume set in 1757, 1766, and 1774. This dictionary was a translation, with large additions and improvements, from Jacques Savary des Bruslons Dictionnaire universal de commerce (1723–1730). Postlethwayts dictionary was a huge storehouse of economic facts, laws and theory and his departures from the French version reflected his greater interest in political problems; his more intense economic nationalism; and his exuberant belief in the economic usefulness of experimental philosophy
In the 1757 edition of the Universal Dictionary, Postlethwayt outlined his vision for the establishment of a British mercantile college to benefit those who intended to work as merchants, or in gathering public revenue, or in merchandizing. He proposed that theoretical training for business should occur in formal academies and involve the study of mercantile computations, foreign exchanges and the intrinsic value of foreign coins, double-entry accounting, languages, geography, and public revenues and related laws. Postlethwayts ideas appear to have been influential in developing the statutes and procedures of the Portuguese School of Commerce, established in Lisbon in 1759.
It is documented that Thomas Jefferson gave a copy of this dictonary to his son in law, Thomas Mann Randolph, and as a prolific reader we must assumed also read by Jefferson.
Postlethwayt, Malachy 1707-1767
Malachy Postlethwayt was a prolific English writer and publicist on matters of mercantilist economics in the 1740s and 1750s. Little is known about his upbringing or formal education, although he is believed to be the brother of James Postlethwayt (d. 1761), a writer on finance and demography. Malachy Postlethwayt was elected a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London in 1734. His writings are claimed by Edgar Johnson to have exerted a good deal of influence on the trend of British economic thought.
Postlethwayt was alleged to be propagandist for the mercantilist endeavours of the Royal Africa Company, whose interests were well served by his publications The African Trade, the Great Pillar and Supporter of the British Plantation Trade in North America (1745) and The National and Private Advantages of the African Trade Considered (1746). These works supported a strategy of British commercial and manufacturing expansion through trade with Africa and the colonies, and promoted the importance of slavery for British commerce and industry.
Postlethwayts most noted work, The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, appeared after he had devoted twenty years to its preparation. The first edition was published in London in instalments between 1751 and 1755, and then in subsequent editions as a two-volume set in 1757, 1766, and 1774. This dictionary was a translation, with large additions and improvements, from Jacques Savary des Bruslons Dictionnaire universal de commerce (1723–1730). Postlethwayts dictionary was a huge storehouse of economic facts, laws and theory and his departures from the French version reflected his greater interest in political problems; his more intense economic nationalism; and his exuberant belief in the economic usefulness of experimental philosophy
In the 1757 edition of the Universal Dictionary, Postlethwayt outlined his vision for the establishment of a British mercantile college to benefit those who intended to work as merchants, or in gathering public revenue, or in merchandizing. He proposed that theoretical training for business should occur in formal academies and involve the study of mercantile computations, foreign exchanges and the intrinsic value of foreign coins, double-entry accounting, languages, geography, and public revenues and related laws. Postlethwayts ideas appear to have been influential in developing the statutes and procedures of the Portuguese School of Commerce, established in Lisbon in 1759.
Postlethwayts most important contribution to economic literature is regarded by many to be Britains Commercial Interest Explained and Improved (1757), in which he outlines his concept of physical commerce and the policies England should follow to attain commercial parity with foreign rivals.
Whether Postlethwayts writings were his original thoughts and words is a matter for conjecture. His Universal Dictionary included ideas taken from fifty other past or contemporary writers and that it had scattered throughout it practically all of Richard Cantillons Essai sur la nature du commerce en général (Essay on the Nature of Commerce in General, 1755). Although Postlethwayt was alleged widely to be a plagiarist, this accusation is believed to be exaggerated.
Postlethwayt died suddenly on September 13, 1767, and was buried in the Old Street Churchyard, Clerkenwell, in London.
Postlethwayt also published:
- The African Trade the great Pillar and Support of the British Plantation Trade in America, &c., 1745.
- The Natural and Private Advantages of the African Trade considered, &c., 1746.
- Britains Commercial Interest Explained, Vol. I of his Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, 1747.[5]
- Considerations on the making of Bar Iron with Pitt or Sea Coal Fire, &c. In a Letter to a Member of the House of Commons, London, 1747.
- Considerations on the Revival of the Royal-British Assiento, between his Catholic Majesty and the … South-Sea Company. With an … attempt to unite the African-Trade to that of the South-Sea Company, by Act of Parliament, London, 1749.
- The Merchants Public Counting House, or New Mercantile Institution, &c., London, 1750.
- A Short State of the Progress of the French Trade and Navigation, &c., London, 1756.
- Great Britains True System. … To which is prefixed an Introduction relative to the Forming a New Plan of British Politicks with respect to our Foreign Affairs, &c., London, 1757.
- Britains Commercial Interest explained and improved, in a Series of Dissertations on several important Branches of her Trade and Police. … Also … the Advantages which would accrue … from an Union with Ireland, 2 vols., London, 1757; 2nd edit., With … a clear View of the State of our Plantations in America, &c., London, 1759.
- In Honour to the Administration. The importance of the African Expedition considered, &c., London, 1758
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1774, 1777 & 1785 Capt James Cook 3 Atlas Volumes 1st Editions 204 Maps & Prints
- Title : 1. Figure du Banks 2. Premier Voyage De Cook 3. Troisieme Voyage De Cook
- Ref #: 93498, 93499, 93500
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Date : 1774; 1777; 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
A unique and rare opportunity to acquire all three of Captain James Cooks 1st French edition Atlases (4to, Quatro), published to accompany the publication of his 3 voyages of discovery in 1774, 1777 & 1785. The atlases contain a total of 204 large folding, double page and single page maps and prints. It is very rare to find all three atlases complete and available together at the same time.
The contents of all three atlases are in fine condition, with a fresh, heavy impression and clean paper of all maps and prints.
As stated there are 204 maps and prints 51 in the 1st volume, 66 in the second volume and 87 in the second volume. Please view the images above, that include a few images of the 204 maps and prints as well as an itemized list of each volume.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Some scuffing and wear to boards & spines
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Timeline First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Timeline - Second Voyage 1772 - 1775
In July 1772 Resolution, commanded by Captain Cook, and Discovery, commanded by Lieutenant Furneaux, set sail from Britain, via Madiera (Jul-Aug) and Cape Town, South Africa (Oct-Nov), towards the Antarctic in search of the Great Southern Continent.
During January 1773 the ships took on fresh water, charts of the voyage being marked with:
......Here we watered our Ship with Ice the 1st. Time 26S 44W and Here we compleated our Water/26S 20W but became separated in thick fog: Here we parted company…. and The Resolutions Track after we parted Company on the 8 of February 1773......
The ships became the first known to have crossed the Antarctic Circle (17 January 1773). On 9th January Cook wrote:
.......we hoisted out three Boats and took up as much as yielded about 15 Tons of Fresh Water, the Adventure at the same time got about 8 or 9 and all this was done in 5 or 6 hours time; the pieces we took up and which had broke from the Main Island, were very hard and solid, and some of them too large to be handled so that we were obliged to break them with our Ice Azes before they could be taken into the Boats...... Cook, Journals II, 74.)
The ships met again in New Zealand (February-May 1773) and set off to explore the central Pacific, calling at Tahiti (August), where, from the island of Raiatea, they took aboard Omai who returned with the Adventure to England (7 September).
After visiting Amsterdam and Middelburg, two islands that Cook called the Friendly Islands (Tongan group) (October) the ships became separated and never met again. Both ships returned separately to New Zealand. (November) A boats crew from the Adventure were killed by Maori (17 December) and the ship sailed for Britain, arriving July 1774.
Cook on Resolution attempted another search for the Great Southern Continent (November 1773), crossing the Antarctic Circle on 20th December 1773. However, the ice and cold soon forced him to turn north again and he made another search in the central Pacific for the Great Southern Continent. In January 1774 he turned south again, crossing the Antarctic Circle for the second time. Captain Cooks Journal, 2nd January 1774.
Cook sailed north, arriving at Easter Island in March 1774. Cook was too ill to go ashore but a small party explored the southern part of the island. The artist William Hodges painted a group of the large statues of heads (moia) for which the island has become famous.
Cook then sailed to the Marquesas (March); Tahiti (April) and Raiatea (June); past the Cook Islands and Niue, or Savage Islands as Cook called them; Tonga (June); Vatoa, the only Fijian Island visited by Cook (July); New Hebrides (July-August); New Caledonia (September) and Norfolk Island (October); before returning to New Zealand (October 1774).
Not all the peoples of the islands visited by Cook were friendly and when his ship approached Niue the local people would not let his crew ashore. Cook wrote:
.......The Conduct and aspect of these Islanders occasioned my giving it the Name of Savage Island, it lies in the Latitude of 19 degrees 1 Longitude 169 degrees 37 West, is about 11 Leagues in circuit, of a tolerable height and seemingly covered with wood amongst which were some Cocoa-nutt trees......(Cook, Journals II, 435, 22 June 1774.)
En route for New Zealand, Cook sailed west and explored the islands which he called the New Hebrides, now known as Vanuatu, arriving on 17 July 1774. The people were Melanesian, not Polynesian, and spoke different languages and had different customs. Cook recorded:
........The Men go naked, it can hardly be said they cover their Natural parts, the Testicles are quite exposed, but they wrap a piece of cloth or leafe round the yard (nautical slang for the penis) which they tye up to the belly to a cord or bandage which they wear round the waist just under the Short ribs and over the belly and so tight that it was a wonder to us how they could endure it.......(Cook, Journals II, 464, 23 July 1774)
Cook sailed past or visited nearly all the islands in the group, including landfalls at Malekula, Tanna and Erromango. He later moved on to New Caledonia.
Cooks reception by the New Hebrideans was generally hostile. At Erromango during the landing on 4th August 1774 the marines had to open fire when the natives tried to seize the boat and started to fire missiles. Cook wrote:
....…I was very loath to fire upon such a Multitude and resolved to make the chief a lone fall a Victim to his own treachery…happy for many of these poor people not half our Musquets would go of otherwise many more must have fallen.......(Cook, Journals II, 479, 4th August 1774)
Some of Cooks crew were slightly injured but several natives were wounded and their leader killed. Back on the ship Cook had a gun fired to frighten off the islanders and decided to depart.
Cook left New Zealand to return to Britain via the Southern Ocean in November 1774 and arrived in Tierra del Fuego, South America, in December. Cook took on stores and spent the holiday in what he called Christmas Sound. He described the area:......except those little tufts of shrubbery, the whole country was a barren Tack (or Rock) doomed by Nature to everlasting sterility......(Cook, Ms Journal PRO Adm 55/108)
Cook left South America in early January 1775 and set off across the southern Atlantic for Cape Town, South Africa. On the way he tried to confirm the location of a number of islands charted by Alexander Dalrymple on an earlier voyage. On 17 January 1775 Cook arrived at the cold, bleak, glaciated island he called South Georgia and spent 3 days charting it before sailing on.
Cook headed east and in late January came across the South Sandwich Islands that he again charted and then sailed on to Cape Town, arriving in late March 1775. He then headed across the Atlantic via St. Helena and Ascension Island (May), the Azores (July) and landed at Portsmouth on 30th July 1775.
On his return Cook became a national hero. He was presented to the King, made a member of the Royal Society and received its Copley Medal for achievement. Cook was promoted to post-captain of Greenwich Hospital and wrote up his account of the voyage. This did not mean retirement for Cook who went on his third and final voyage the following year.
The second voyage was one of the greatest journeys of all time. During the three years the ships crews had remained healthy and only four of the Resolutions crew had died. Cook disproved the idea of the Great Southern Continent; had become the first recorded explorer to cross the Antarctic Circle; and had charted many Pacific islands for the first time.
Timeline - Third Voyage 1776 - 1780
In 1776 Cook sailed in a repaired Resolution (July) to search for the North West Passage and to return Omai to his home on Huahine in the Society Islands.
He sailed via the Canary Islands and was joined at Cape Town, South Africa, by the Discovery, commanded by Charles Clerke.
The Discovery was the smallest of Cooks ships and was manned by a crew of sixty-nine. The two ships were repaired and restocked with a large number of livestock and set off together for New Zealand ( December).
Cook sailed across the South Indian Ocean and confirmed the location of Desolation Island, later known as Kerguelen Island. Cook wrote of Christmas Harbour where he first anchored on 25th December 1776:
........I found the shore in a manner covered with Penguins and other birds and Seals…so fearless that we killed as ma(n)y as we chose for the sake of their fat or blubber to make Oil for our lamps and other uses… Here I displayd the British flag and named the harbour Christmas harbour as we entered it on that Festival........(Cook, Journals III, i, 29-32)
Cook sailed east, arriving at Van Diemens Land/Tasmania (January 1777) and Queen Charlottes Sound, New Zealand (February). The Maori were wary at first, expecting Cook to take revenge for the killing of members of the Adventures crew in 1773, but instead Cook befriended the leader of the attack.
The ships stayed for nearly two weeks in New Zealand, restocking with wild celery and scurvy grass and trading with the local Maori who set up a small village in Ship Cove. Cook set off around the islands of the south Pacific (February), visiting the Cook Islands (April); Tongan Islands (July); and Tahiti (August-December 1777)
In 1778 Cook visited the Hawaiian islands, or Sandwich Islands as he named them, for the first time. Cook wrote:
........We no sooner landed, that a trade was set on foot for hogs and potatoes, which the people gave us in exchange for nails and pieces of iron formed into some thing like chisels….At sun set I brought every body on board, having got during the day Nine tons of water….about sixty or eighty Pigs, a few Fowls, a quantity of potatoes and a few plantains and Tara roots.......(Cook, Journals III, i. 269 & 272)
In February 1778 Cook sailed from the Hawaiian Islands across the north Pacific to the Oregan coast of North America. He travelled up the coast in bad weather until he found a safe harbour, Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada. There he refitted the ships, explored the area and developed relations with the local people.
Cook described a village there, probably Yoquot:
….their houses or dwellings are situated close to the shore…Some of these buildings are raised on the side of a bank, theses have a flooring consisting of logs supported by post fixed in the ground….before these houses they make a platform about four feet broad…..so allows of a passage along the front of the building: They assend to this passage (along the front of the building) by steps, not unlike some at our landing places in the River Thames........(Cook, Journals III, i, 306)
Cook left Nootka Sound in April 1778 and sailed north along the Alaskan coast looking for inlets that might lead to the Northwest passage but was then forced to turn south. By July he had rounded the Alaskan Peninsula and was able to sail north again, visiting the Chukotskiy Peninsula, Russia, before heading out into the Bering Sea.
Cook described the summer huts, or yarangas, of the Chukchi people as:
.........pretty large, and circular and brought to a point at the top; the framing was of slight poles and bone, covered with the skins of Sea animals…About the habitations were erected several stages ten or twelve feet high, such as we had observed on some part of the American coast, they were built wholly of bones and seemed to be intended to dry skins, fish &ca. upon, out of reach of their dogs........(Cook, Journals III, I, 413)
After entering the Bering Sea on 11th August 1778, Cook crossed the Arctic Circle and went as far north as latitude 70 degrees 41 North before being forced back by the pack ice off Icy Cape, Alaska. On the ice all around the ships were large numbers of walruses. About a dozen of these huge animals were killed to replenish the supplies of fresh meat and to provide oil for the lamps.
Cook had to turn west and worked his way down the Russian coast, eventually heading south and east into Norton Sound, Alaska, in September 1778. He wrote of their very brief encounter with the inhabitants of Norton Sound:
....…a family of the Natives came near to the place where we were taking off wood…I saw no more than a Man, his wife and child…...(Cook, Journals III, I, 438)
After a short period spent searching for the Northwest Passage Cook realised that it was too late in the year to make any progress and so sailed for warmer winter quarters in the Hawaiian Islands, arriving there in December 1778.
After circumnavigating the big island of Hawaii for over a month the ships finally anchored in Kealakekua Bay on 16th January 1779. The Hawaiians in over 1000 canoes came out to welcome them, the arrival of the ships coinciding with celebrations to mark the religious festival of Makahiki to the god Lono. The Hawaiians seem to have treated Cook as a personification of the god and at first relations were good on this second visit. However, relationships became strained and Cook left the island on 4th February 1779.
When Cook left Hawaii his ships ran into gales which broke a mast, forcing him to return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs on 11th February. This time the native people were less friendly and stole the cutter of the Discovery. The next day, the 14th February 1779, Cook went ashore to take the Hawaiian king into custody pending the return of the cutter but a fight developed and Cook, four of his marines and a number of natives were killed. Cooks remains were buried at sea in Kealakekua Bay.
Charles Clerke took over command of the stunned expedition and explored the other Hawaiian islands before sailing north to search for the North-West Passage. The ships called at Kamchatka, Russia, (April-June) where they were welcomed by the governor, Behm, at Bolsheretsk. Behm took news of the expedition and Cooks death overland to St. Petersburg from where it reached Europe and Britain.
Having made another voyage into the Arctic in search of the Northwest Passage (June-July) the ships returned to Kamchatka in August. In November they set off sailing south along the east coast of Japan, between Taiwan and the Phillipines and arrived at Macao, China, in December.
In January 1780 the expeditions left for home, crossing the Indian Ocean, calling at Cape Town (April-May) and arriving back in Stromness, Orkney, in August but not returning to London until October 1780.
News of Cooks death reached Britain in January 1780, ahead of the return of Resolution and Discovery in October 1780. The voyage was written up and published and Cooks life gradually commemorated in articles, books, medals and monuments.
The achievements of the voyage were overshadowed by the deaths of both Cook and his second-in-command, Clerke. The main purpose of the voyage, the discovery of the Northwest Passage, was not realised but large tracts of the Pacific and Arctic coasts of America and Russia were charted.
Early attempts to summarise the life of Cook appeared in the popular press soon after news of his death reached Britain. Articles in journals such as the Westminster Magazine, published in January 1780, included Biographical Anecdotes of Capt. Cook, charting his life from his birth in Marton, North Yorkshire. The first published biography of Cook, Life of Captain James Cook, by Andrew Kippis, appeared a few years later in 1788.