Products
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Woman of Tanna Isle, Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Tanna
- Ref : 21354
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Woman & Child of the Island of Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 6-20th August 1774
........the Women have all the same ornaments as Men, Nose-Stones, Earrings, Shells on the Breast & Bracelets...their heads covered with a kind of cap made of a Plantain leaf or a Mat-Basket. Few are covered, & even very young Girls have these Caps.......Cooks Journal II
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tanna (sometimes spelled Tana) is an island in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
Tanna was first settled about 400 BC by Melanesians from the surrounding islands. The glowing light of Mount Yasur attracted James Cook, the first European to visit the island, in August 1774, where he landed in an inlet on the southeastern tip of the island that he named Port Resolution after his ship HMS Resolution. He gave the island the name of Tanna, probably from the local name for earth, tana in the Kwamera language.
Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Woman of Tanna Isle, Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Tanna
- Ref : 16354
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Woman & Child of the Island of Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 6-20th August 1774
........the Women have all the same ornaments as Men, Nose-Stones, Earrings, Shells on the Breast & Bracelets...their heads covered with a kind of cap made of a Plantain leaf or a Mat-Basket. Few are covered, & even very young Girls have these Caps.......Cooks Journal II
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tanna (sometimes spelled Tana) is an island in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
Tanna was first settled about 400 BC by Melanesians from the surrounding islands. The glowing light of Mount Yasur attracted James Cook, the first European to visit the island, in August 1774, where he landed in an inlet on the southeastern tip of the island that he named Port Resolution after his ship HMS Resolution. He gave the island the name of Tanna, probably from the local name for earth, tana in the Kwamera language.
Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia, Tahiti 1773
- Title : Potatow, Chef de Tahiti
- Ref : 31772
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia in Tahiti, French Polynesia, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cooks Biography............George Vancouver (midshipman, of later fame) meanwhile, stayed behind to contemplate the role of the red feather in Tahitian society. It happened that Chief Potatau consulted with his wife on how they might obtain some of Cook\'s Oora and according to the plan that somehow reached Georges ears, she would go to Cook in his cabin and offer her services in return for said feathers. But the Captain was unswayed. It was just as well that Georges father was absent on this particular occasion, for he would only have been upset. As it was, his sleep was often disturbed by the sailors running all over the ship with their sexual partners at any hour of the night.
Such was Tahitian zeal for red feathers, Clerke remarked, that they gladly engaged in rather unhallow\'d rites for the sacred jewels in order to offer Propitiation to their Jolly Gods. Such was the maritime zeal for the Tahitian religion that the sailors fairly plundered the ship of its treasures; feathers were ripped from lovely Tongan garments and from delicate fretwork on coconuts; sailors even dyed plain feathers red. Thus valuable artifacts of the South Seas were undone. Nevertheless, among the treasures that came aboard were Potatau\'s monstrous helmets of war of five feet high and several handsome mourning dresses to become in due course part of the collections of ethnology in the Ashmolean Museum and the Bishop Museum. Besides the red feathers, the abundance of pork also attracted the girls; they consumed incredible quantities, reported George, because, as members of a poor class of Tahitians, they were denied pork in their own households. Such were the quantities they consumed, added George with a certain delicacy, that of a sudden they suffered the inconvenience of restlessness, and when they were refused the attention of their lovers, the very decks began to resemble the paths in the islands.........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia, Tahiti 1773
- Title : Potatow, Chef de Tahiti
- Ref : 16353
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia in Tahiti, French Polynesia, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cooks Biography............George Vancouver (midshipman, of later fame) meanwhile, stayed behind to contemplate the role of the red feather in Tahitian society. It happened that Chief Potatau consulted with his wife on how they might obtain some of Cook\'s Oora and according to the plan that somehow reached Georges ears, she would go to Cook in his cabin and offer her services in return for said feathers. But the Captain was unswayed. It was just as well that Georges father was absent on this particular occasion, for he would only have been upset. As it was, his sleep was often disturbed by the sailors running all over the ship with their sexual partners at any hour of the night.
Such was Tahitian zeal for red feathers, Clerke remarked, that they gladly engaged in rather unhallow\'d rites for the sacred jewels in order to offer Propitiation to their Jolly Gods. Such was the maritime zeal for the Tahitian religion that the sailors fairly plundered the ship of its treasures; feathers were ripped from lovely Tongan garments and from delicate fretwork on coconuts; sailors even dyed plain feathers red. Thus valuable artifacts of the South Seas were undone. Nevertheless, among the treasures that came aboard were Potatau\'s monstrous helmets of war of five feet high and several handsome mourning dresses to become in due course part of the collections of ethnology in the Ashmolean Museum and the Bishop Museum. Besides the red feathers, the abundance of pork also attracted the girls; they consumed incredible quantities, reported George, because, as members of a poor class of Tahitians, they were denied pork in their own households. Such were the quantities they consumed, added George with a certain delicacy, that of a sudden they suffered the inconvenience of restlessness, and when they were refused the attention of their lovers, the very decks began to resemble the paths in the islands.........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia, Tahiti 1773
- Title : Potatow, Chef de Tahiti
- Ref : 21415
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia in Tahiti, French Polynesia, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cooks Biography............George Vancouver (midshipman, of later fame) meanwhile, stayed behind to contemplate the role of the red feather in Tahitian society. It happened that Chief Potatau consulted with his wife on how they might obtain some of Cook\'s Oora and according to the plan that somehow reached Georges ears, she would go to Cook in his cabin and offer her services in return for said feathers. But the Captain was unswayed. It was just as well that Georges father was absent on this particular occasion, for he would only have been upset. As it was, his sleep was often disturbed by the sailors running all over the ship with their sexual partners at any hour of the night.
Such was Tahitian zeal for red feathers, Clerke remarked, that they gladly engaged in rather unhallow\'d rites for the sacred jewels in order to offer Propitiation to their Jolly Gods. Such was the maritime zeal for the Tahitian religion that the sailors fairly plundered the ship of its treasures; feathers were ripped from lovely Tongan garments and from delicate fretwork on coconuts; sailors even dyed plain feathers red. Thus valuable artifacts of the South Seas were undone. Nevertheless, among the treasures that came aboard were Potatau\'s monstrous helmets of war of five feet high and several handsome mourning dresses to become in due course part of the collections of ethnology in the Ashmolean Museum and the Bishop Museum. Besides the red feathers, the abundance of pork also attracted the girls; they consumed incredible quantities, reported George, because, as members of a poor class of Tahitians, they were denied pork in their own households. Such were the quantities they consumed, added George with a certain delicacy, that of a sudden they suffered the inconvenience of restlessness, and when they were refused the attention of their lovers, the very decks began to resemble the paths in the islands.........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Oedidee, Bora Bora met by Cook in 1773
- Title : O-Hedidee, Jeune homme de Bolabala
- Ref : 31774
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of O-Hedidee or Oedidee of the island of Bora Bora in the Society Islands, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
O-Hedidee or Oedidee, was a native of Bora Bora, Society Islands, French Polynesia, was about 17 or 18 years of age when he was taken on board the Resolution at Raiatea Island on 17 September 1773. He is described in Hawkesworths account as a young man with curly hair and flattish nose, wearing a gown. Cook wrote: he may be of use to us if we should fall in with and touch at any isles in our rout to the west which was my only motive for taking him on board. Cook Journals II.
O-Hedidee traveled with Cook from Raiatea to New Zealand, Easter Island, and Tahiti, returning to Raiatea on 4 June 1774, having been with the Resolutions company for seven months.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Bora Bora is a 30.55 km2 island group in the Leeward group in the western part of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the Pacific Ocean. The main island, located about 230 kilometres northwest of Papeete, Tahiti is surrounded by a lagoon and a barrier reef. In the center of the island are the remnants of an extinct volcano rising to two peaks, Mount Pahia and Mount Otemanu, the highest point at 727 metres
The island was inhabited by Polynesian settlers around the 4th century C.E. The first European sighting was made by Jakob Roggeveen in 1722.
James Cook sighted the island on 29 July 1769, using a Tahitian navigator, Tupaia. The London Missionary Society arrived in 1820 and founded a Protestant church in 1890. Bora Bora was an independent kingdom until 1888 when its last queen Teriimaevarua III was forced to abdicate by the French who annexed the island as a colony.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Weapons Tools Hats from New Caledonia - Cook 1774
- Title : Ornemens et Armes de la Nouvelle Caledonie
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16362
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of various weapons, farming tools and ornaments from the New Caledonia Islands visited by Captain James Cook in September 1774, in HMS Resolution & Adventure, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
The items illustrated are;
1. Lanee - Lance
2. Partie ornee de la Lance sur une plus grande Echelle - Larger scale of Lance handle
3. Chapeau de plumes &c. - Hat with feathers
4. Peigne - Comb
5. Piece de Corde dont ils se servent pour jetter leurs lances - Cord used to launch a spear
6 & 7. Differentes Massues - Two different types of club
8. Pioche pour Cultiver la Terre - Wooden farming hoe
9. Hache - Axe
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Brown spotting to top of image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Caledonia is a special collective of France in the southwest Pacific Ocean, 1,210 km east of Australia and 20,000 km from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia sub-region, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Chesterfield Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of Pines, and a few remote islets. The Chesterfield Islands are in the Coral Sea. Locals refer to Grande Terre as Le Caillou (the pebble)
British explorer Captain James Cook was the first European to sight New Caledonia, on 4 September 1774, during his second voyage. He named it New Caledonia, as the northeast of the island reminded him of Scotland. The west coast of Grande Terre was approached by Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse in 1788, shortly before his disappearance, and the Loyalty Islands were first visited between 1793 and 1796 when Mare, Lifou, Tiga, and Ouvea were mapped by William Raven. The American whaler encountered the island named then Britania, and today known as Mar (Loyalty Is.) in November 1793. From 1796 until 1840, only a few sporadic contacts with the archipelago were recorded. About fifty American whalers (identified by Robert Langsom from their log books) have been recorded in the region (Grande Terre, Loyalty Is., Walpole and Hunter) between 1793 and 1887. Contacts became more frequent after 1840, because of the interest in sandalwood
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Weapons Tools Hats from New Caledonia - Cook 1774
- Title : Ornemens et Armes de la Nouvelle Caledonie
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 21617
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of various weapons, farming tools and ornaments from the New Caledonia Islands visited by Captain James Cook in September 1774, in HMS Resolution & Adventure, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
The items illustrated are;
1. Lanee - Lance
2. Partie ornee de la Lance sur une plus grande Echelle - Larger scale of Lance handle
3. Chapeau de plumes &c. - Hat with feathers
4. Peigne - Comb
5. Piece de Corde dont ils se servent pour jetter leurs lances - Cord used to launch a spear
6 & 7. Differentes Massues - Two different types of club
8. Pioche pour Cultiver la Terre - Wooden farming hoe
9. Hache - Axe
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Caledonia is a special collective of France in the southwest Pacific Ocean, 1,210 km east of Australia and 20,000 km from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia sub-region, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Chesterfield Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of Pines, and a few remote islets. The Chesterfield Islands are in the Coral Sea. Locals refer to Grande Terre as Le Caillou (the pebble)
British explorer Captain James Cook was the first European to sight New Caledonia, on 4 September 1774, during his second voyage. He named it New Caledonia, as the northeast of the island reminded him of Scotland. The west coast of Grande Terre was approached by Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse in 1788, shortly before his disappearance, and the Loyalty Islands were first visited between 1793 and 1796 when Mare, Lifou, Tiga, and Ouvea were mapped by William Raven. The American whaler encountered the island named then Britania, and today known as Mar (Loyalty Is.) in November 1793. From 1796 until 1840, only a few sporadic contacts with the archipelago were recorded. About fifty American whalers (identified by Robert Langsom from their log books) have been recorded in the region (Grande Terre, Loyalty Is., Walpole and Hunter) between 1793 and 1887. Contacts became more frequent after 1840, because of the interest in sandalwood
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
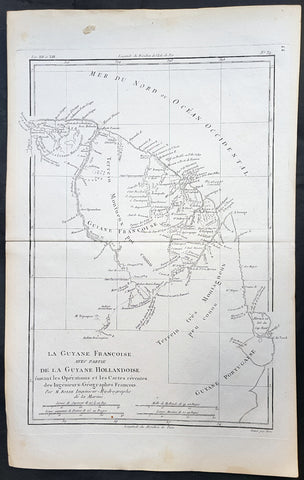
1778 John Mitchell & Antonio Zatta 12 Sheet Antique Map of North America - Rare
Antique Map
- Title : Le Colonie Unite dell' America Settentrle. di Nuova Projezione Ass. Ee. Li Signori Riformatori dello Studio di Padova. Venezia 1778, Presso Antonio Zatta, con Privilegio dell' Eccellentissimo Senato.
- Ref #: 93528
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 52 1/2in x 51in (1.33m x 1.30m)
- Date : 1778
Description:
This impressive very large twelve-sheet joined, original hand coloured important antique map is Antonio Zattas version of John Mitchells 1755 landmark map of North America, published first in 1778. This map is one of a few to be released during the late 18th century copying Mitchells map, in an effort to explain the rapidly changing political & economic situation in North America. Zatta has included many additional notes relating to both the Treaty of 1763 and events in the Revolutionary War. Most importantly, it is the first printed map devoted to the thirteen states, and to use the a name distinguishing them from their previous status as British Colonies. The name United Colonies was used in the Declaration of Independence and was not officially replaced until the Articles of Confederation adopted the name The United States of America.
This is an incredibly important and rare map, especially joined, in excellent condition with original colour. With John Mitchells map is now almost now impossible to find, with the last known sale in 2011 of $175,000US, this map is now one of the few, of that period, that is avaialble.
Zatta published these twelve separate sheets of Mitchells Map of North America, plus three other maps: Il Canada, Le Isole di Terra Nuova e Capo Breton, and La Baja D Hudson in the atlas Atlante Novissimo published from 1779-1785, with a second edition of the Zatta/Mitchell map published in 1791. Zattas version does not cover the far western portions of Mitchells map stretching to the Mississippi. An image of Mitchells map has been included as a point of reference.
Because Mitchells map was immediately recognized as seminal, it was exceedingly popular. Events leading up to the American Revolution only increased that demand. During the midst of the colonists on-going struggle for liberation from England, Zatta published this version which included some additional place names and information on early battles of the American Revolution.
The maps of Venetian publisher Antonio Zatta are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 52 1/2in x 51in (1.33m x 1.30m)
Plate size: - 49 1/2in x 49 1/4in (1.26m x 1.25m)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Light creasing
Background:
A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America by John Mitchell Map is a landmark map by John Mitchell (1711–1768), which was reprinted several times during the second half of the 18th century, in France, Italy & Germany. The Mitchell Map was used as a primary map source during the Treaty of Paris for defining the boundaries of the newly independent United Colonies. The Mitchell Map is the most comprehensive map of eastern North America made during the colonial era, measuring 6.5 feet (2.0 m) wide by 4.5 feet (1.4 m) high.
Mitchell started compiling a first draught map in 1750 from information acquired in London, both in official & private archives. This proved to be inadequate & George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax, accordingly ordered the governors of the 13 British colonies to survey and compile new maps, which most did. These became the basis, along with cartographical information of the French geographer Guillaume Delisle, of his landmark map. Late in 1754, Halifax was using one manuscript copy of Mitchells second map to successfully promote his political position (no compromise with the French) within the British cabinet in the build-up to the Seven Years War, also know as the French and Indian War. Halifax also permitted Mitchell to have the map published: it appeared in April 1755, engraved by Thomas Kitchin and published by Andrew Millar.
The published map bore the title A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America. It bore the copyright date of 13 February 1755, but the map was probably not sold to the public until April or even May. Minor corrections to the maps printing plates were made probably during the printing process (for example, the name and address of the publisher were corrected).
The geographer John Green criticized Mitchell and his map soon after it appeared, emphasizing two failings with respect to Nova Scotia (an area of particular dispute with the French). Mitchell, Green noted, had used neither the astronomical observations for latitude and longitude made by Marquis Joseph Bernard de Chabert in the 1740s nor a 1715 chart of the Nova Scotia coast. In response, Mitchell released a new version of his map, now with two large blocks of text that described all of his data sources; the new version of the map also adjusted the coastline in line with Chaberts work but rejected the 1715 chart as deeply flawed. This version of the map, which Mitchell referred to as the second edition, is commonly thought to have appeared sometime in 1757, but advertisements in the (London) Public Advertiser and Gazetteer and London Daily Advertiser on 23 April 1756 clearly indicate that this new map appeared at that time.
Mitchells map was printed in eight sheets; when assembled, it measures 136 cm by 195 cm (4 feet 6 inches by 6 feet 5 inches; height x width). The initial impressions printed in 1755 have a consistent coloring outlining British colonial claims. Mitchell extended the southern colonies across the entire continent, even over established Spanish territory west of the Mississippi. Mitchell divided up the Iroquois territories (as he understood them, reaching from Lake Champlain [Lac Irocoisia] to the Mississippi, and north of Lake Superior) between Virginia and New York, leaving only a much-reduced territory to the French.
Mitchells map was expensive but it spawned many cheaper variants that trumpeted Halifax and Mitchells powerful colonial vision to the British public. One of these, published in December 1755 by a Society of Anti-Gallicans, restricted the French even further just to Quebec.
The map is liberally sprinkled with text describing and explaining various features, especially in regions that were relatively unknown or which were subject to political dispute. Many notes describe the natural resources and potential for settlement of frontier regions. Others describe Indian tribes. Many Indian settlements are shown, along with important Indian trails.
Since Mitchells main objective was to show the French threat to the British colonies, there is a very strong pro-British bias in the map, especially with regard to the Iroquois. The map makes clear that the Iroquois were not just allies of Britain, but subjects, and that all Iroquois land was therefore British territory. Huge parts of the continent are noted as being British due to Iroquois conquest of one tribe or another. French activity within the Iroquois claimed lands is noted, explicitly or implicitly, as illegal.
In cases where the imperial claims of Britain and France were questionable, Mitchell always takes the British side. Thus many of his notes and boundaries seem like political propaganda today. Some of the claims seem to be outright falsehoods.
The Mitchell Map remained the most detailed map of North America available in the later eighteenth century. Various impressions (and also French copies) were used to establish the boundaries of the new United States of America by diplomats at the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the American Revolutionary War. The maps inaccuracies subsequently led to a number of border disputes, such as in Maine.[clarification needed] Its supposition that the Mississippi River extended north to the 50th parallel (into British territory) resulted in the treaty using it as a landmark for a geographically impossible definition of the border in that region. It was not until 1842, when the Webster-Ashburton Treaty resolved these inconsistencies with fixes such as the one that created Minnesotas Northwest Angle, that the U.S.–Canada border was clearly drawn from Maine to the Oregon Country.
Similarly, during the drafting of the Northwest Ordinance, the maps inaccuracy in depicting where an east–west line drawn through the southernmost point of Lake Michigan would intersect Lake Erie led to a long dispute over the Ohio–Michigan border that culminated in the Toledo War.
Zatta, Antonio fl. 1757-1797
Antonio Zatta was a prominent Italian editor, cartographer, and publisher. Little is known about his life beyond his many surviving published works. It is possible that he was born as early as 1722 and lived as late as 1804. He lived in Venice and his work flourished between 1757 and 1797. He is best known for his atlas, Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785), and for his prolific output of prints and books that were both precisely made and aesthetically pleasing. Zatta clearly had a large network from which to draw information; this is how he was able to publish the first glimpse of the islands visited by Captain Cook in the Atlante Novissimo.
Zattas maps are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. His re-engraving and publication of John Mitchells famous map of North America A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America in 1778, is considered one of the best re-issues of this seminal, landmark map .
......He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.... (Portinaro & Knirsch, The Cartography of North America, 1500-1800, p. 319).
Zatta was among the leaders in the eighteenth-century revival of fine printing in Italy and his choice of the text of Raynal to support his re-issue of Mitchells Map, is not surprising. Anne Palms Chalmers describes Zatta as a sardonic writer with the focus of a certain amount of political controversy (Venetian Book Design in the Eighteenth Century, The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, New Series, Vol. 29, No. 5, January 1971, pp. 226-235). Chalmers describes Zattas printing and design as harmonious in composition with ornament unified by style, quality of line, and tone of printing.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1778 Matthaus Lotter Large Oval World Map showing Capt Cooks 1st Voyage - Rare 1st edition
Antique Map
- Title : Mappe Monde ou carte generale de l`Univers sur une projection nouvelle d`une sphere ovale pour mieux entendre les distances entre l`Europe et Amerique avec le tour du monde du Lieut Cook et Tous Les Decouvertes Nouvelles...MDCCLXXVIII
- Date : 1778 (1st edition)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35629
- Size: 39in x 21in (990mm x 535mm)
Description:
This very large, impressive original copper-plate engraved antique World Map, on an Ortelius Oval Projection, showing the tracks of Captain Cooks 1st Voyage to the South Seas, was engraved and published by Matthäus Albrecht Lotter in 1778, dated in title. The map was re-issued in 1782 & 1787 to include the tracks of Cooks 2nd & 3rd voyages of discovery.
This 1st edition Lotter Oval map is scarce with only a small few available on the open market.
This map was one of the first world maps published to cash in on the publicity over Captain James Cooks Circumnavigation of the world and the first European survey of New Zealand and the East Coast of Australia. Beautifully executed and dominated by New Holland, Australia, for the first time almost complete on a world map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39in x 21in (990mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 37 1/2in x 19 1/4in (955mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
This large world map was one of the first to show the discoveries of the east coast of Australia and New Zealand by James Cook on his first voyage of Discovery. The shadow line from Tasmania west to Western Australia was not filled in until the later discoveries of Bass Strait by Bass and Matthew Flinders in 1797 and the southern coast by Baudin and Flinders in 1803. Also included along the New Holland coastline is the earlier Dutch discoveries of Hartog 1616, the van Leeuwin 1619, Nuyts 1627, de Wit 1628 and Tasman 1642-44. The Trial Islands near present-day Dampier, named after the English ship the Trial, which were incorrectly charted by Gerritsz after the false reports provided by Captain Brookes, are also noted.
Cooks First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cooks command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on HMS Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earths distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research.
Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the HMS Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
The Ortelius Oval Projection is a map projection used for world maps largely in the late 16th and early 17th century. It is neither conformal nor equal-area but instead offers a compromise presentation. It is similar in structure to a pseudocylindrical projection but does not qualify as one because the meridians are not equally spaced along the parallels. The projection\'s first known use was by Battista Agnese (flourished 1535–1564) around 1540, although whether the construction method was truly identical to Ortelius\'s or not is unclear because of crude drafting and printing. The front hemisphere is identical to Petrus Apianus\'s 1524 globular projection.
The projection reached a wide audience via the popular map Typus Orbis Terrarum by Abraham Ortelius beginning in 1570. The projection (and indeed Ortelius maps) were widely copied by other mapmakers such as Giovanni Pietro Maffei, Fernando de Solis, and Matteo Ricci.
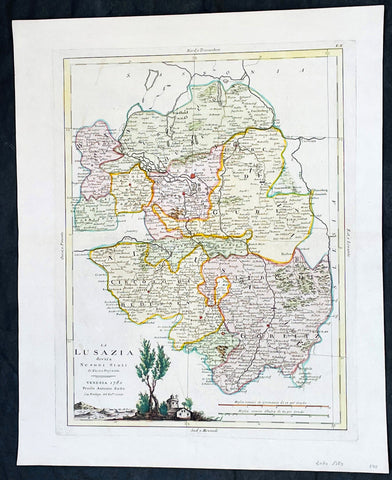
1778 Santini Antique Map Lower Saxon Circle Germany, Holstien Bremen Mecklenburg
- Title : Cercle de Basse Saxe on sont distingues Les Etats de Brunswich Les Duches De Holstien...Par L Sr Robert....A Venise...P Santini...1778
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50203
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Lower Saxon Circle of Northern Germany, was engraved in 1778 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - after Robert De Vaugondy and was published by Francois Santini (active 1776-84) in his 2 volume edition of Atlas Universal 1776-84. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19 1/2in (560mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Lower Saxon Circle was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire. It covered much of the territory of the medieval Duchy of Saxony (except for Westphalia), and was originally called the Saxon Circle (German: Sächsischer Kreis) before later being better differentiated from the Upper Saxon Circle by the more specific name.
An unusual aspect of this circle was that, at various times, the kings of Denmark (in Holstein), Great Britain (in Hanover) and Sweden (in Bremen) were all Princes of a number of Imperial States.
The Lower Saxon Circle included the easternmost part of current Lower Saxony, the northernmost part of Saxony-Anhalt (excluding the Altmark), Mecklenburg, Holstein (excluding Dithmarschen), Hamburg, Bremen, in addition to small areas in Brandenburg and Thuringia. For the most part it was a continuous territory with the exception of small enclaves like Halle and Jüterbog. Nordhausen and Mühlhausen were also areas outside the continuous portion of the imperial circle. Within the circle was the Archbishopric of Verden, which was in personal union with the Archbishopric of Bremen since 1502. The Counties of Schaumburg and Spiegelberg were also part of the personal union, but they were not a part of the Lower Saxon Circle.
By the downfall of the Holy Roman Empire, the circle was 1 240 square miles large, with 2 120 000 inhabitants. With respect to religion, almost all the citizens were Protestant. The exception was the partially Catholic Bishopric of Hildesheim.
During the Early Modern period the Holy Roman Empire was divided into Imperial Circles administrative groupings whose primary purposes were the organization of common defensive structure and the collection of imperial taxes. They were also used as a means of organization within the Imperial Diet and the Imperial Chamber Court. Each circle had a Circle Diet, although not every member of the Circle Diet would hold membership of the Imperial Diet as well.
Six Imperial Circles were introduced at the Diet of Augsburg in 1500. In 1512, three more circles were added, and the large Saxon Circle was split into two, so that from 1512 until the collapse of the Holy Roman Empire in the Napoleonic era, there were ten Imperial Circles. The Crown of Bohemia, the Swiss Confederacy and Italy remained unencircled, as did various minor territories which held imperial immediacy.
1779 J B D Anville Large Antique Map of the Tigris–Euphrates River System Iraq
Antique Map
- Title : L Euphrate et Le Tigre Par Le Sr D Anville..MDCCLXXIX
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1779
- Ref #: 92300
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique map of the Tigris–Euphrates river system was engraved in 1779 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17 1/2in (535mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing, light age toning
Plate area: - Creasing
Verso: - Creasing, light age toning
Background:
The Tigris and Euphrates, with their tributaries, form a major river system in Western Asia. From sources originating in eastern Turkey, they flow by/through Syria through Iraq into the Persian Gulf. The system is part of the Palearctic Tigris–Euphrates ecoregion, which includes Iraq and parts of Turkey, Syria, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Jordan.
From their sources and upper courses in the mountains of eastern Anatolia, the rivers descend through valleys and gorges to the uplands of Syria and northern Iraq and then to the alluvial plain of central Iraq. The rivers flow in a south-easterly direction through the central plain and combine at Al-Qurnah to form the Shatt al-Arab and discharge into the Persian Gulf.
The region has historical importance as part of the Fertile Crescent region, in which civilization is believed to have first emerged.
1779 Thomas Forrest Antique Print Views Maluku, Moluccas Spice Islands Indonesia
Antique Map
- Title : Ternate; Tidor; Motir; Tartar Galley; Macquian; Northmost of the Giaritchas; Macquian;
- Ref : 31727
- Size: 22in x 13 1/2in (560mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1779
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large scarce original copper plate engraved antique print a view of the Indonesian Spice Islands and Thomas Forrests ship the Tartar by Thomas Forrest was published in the 1779 edition of A Voyage to New Guinea and the Moluccas from Balambangan … during the years 1774–5–6
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 13 1/2in (560mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 13 1/2in (560mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin extended
Plate area: - Small loss to image on left border, light offsetting
Verso: - Folds as issued, light offsetting
Background:
This large print that includes Thomas Forrests ship The Tartar, a garay boat from Sulu of about ten tons burden, with two English officers and a crew of eighteen locals, shows views of the Spice or Maluku (Moluccas) Islands of Ternate, Tidore, Makian & Kajoa
Forrest, Thomas 1729 - 1802
Forrest was a Scottish navigator who worked for the British East India Company.
He appears to have served for some time in the Royal Navy, and to have been a midshipman in 1745. Passages in his own writings show that he was employed in Indian waters from 1753 almost continuously. He implies that during part of the Seven Years War he was on the Elizabeth, in the squadron under Admiral Charles Steevens; but this cannot be verified from the pay-book.
In 1762 Forrest had command of a Company ship. In 1770 he was engaged in forming the new settlement at Balambangan which had been recommended by Alexander Dalrymple, and in 1774 he led an exploring mission in the direction of New Guinea. He sailed on 9 December in the Tartar, a garay boat from Sulu of about ten tons burden, with two English officers and a crew of eighteen Malays. In this, accompanied during part of the time by two small boats, he pushed his explorations as far as Geelvink Bay in New Guinea, examining the Sulu Archipelago, the south coast of Mindanao, Mandiolo, Batchian, and particularly Waigeo, of which his was the first good chart. Forrest reached Dorei Harbour,[1] and returned to Achin (present-day Aceh) in March 1776.
In December 1782 Forrest was tasked by governor-general Warren Hastings to gain intelligence of the French fleet, which had left the coast of India and had eluded Sir Edward Hughes the English commander-in-chief. The British surmised that the French were headed for Mauritius; Forrest spotted the ships near Achin and returned the information to Vizagapatam just ahead of the French return. In the following June he sailed again to survey the Andaman Islands, but falling to leeward of them, passed through the Preparis Channel to the Tenasserim coast, which he examined southwards as far as Quedah. In 1790 he made a more thorough examination of the same coast and of its offshore islands, which lay in a long row, leaving a 125-mile-long sheltered passage between them and the mainland. He christened that stretch Forrest Strait.
Forrest is said to have died in India about 1802.
A detailed account of Forrests 1774 voyage was published in 1779 under the title, A Voyage to New Guinea and the Moluccas from Balambangan … during the years 1774–5–6; the volume included a portrait of the author. In 1782 Forrest published at Calcutta A Treatise on the Monsoons in East India, a new edition of which was published in London in 1783.
An account of the first survey voyage came out in 1789 under the title, A Journal of the Esther Brig, Capt. Thomas Forrest, from Bengal to Quedah, in 1783, later edited by Dalrymple, with publishing costs borne by the East India Company. An account of the second survey voyage was published in 1792 as A Voyage from Calcutta to the Mergui Archipelago, with which were included some minor essays and descriptive accounts, as well as a reprint of the Treatise on the Monsoons. This volume is dedicated to William Aldersey, president of the board of trade in Bengal, who was described as Forrests cousin.
1780 Antonio Zatta Antique Map of The Lusatia Region Germany, Poland & Czech Rep
Antique Map
- Title : La Lusazia divisa ne suoi stati di nuova projezione
- Ref #: 35638
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
- Date : 1780
- Price: $149US
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the ancient central European region of Lusatia in between Poland and Germany, and in the south, the Czech Republic by Antonio Zatta (fl. 1775-97) in 1780 - dated - was published in his Atlas Atlante Novissimo
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Lusatia is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the east to the Pulsnitz and Black Elster rivers in the west, and is located within the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg as well as in the Polish voivodeships of Lower Silesia and Lubusz. Lusatia's central rivers are the Spree and the Lusatian Neisse, which constitutes the border between Germany and Poland since 1945 (Oder–Neisse line). The Lusatian Mountains (part of the Sudetes), separate Lusatia from Bohemia (Czech Republic) in the south. Lusatia is traditionally divided into Upper Lusatia (the hilly southern part) and Lower Lusatia (the flat northern part).
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1780 Bonne Antique Map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40849
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
In 1498 French Guiana was first visited by Europeans when Christopher Columbus sailed to the region on his third voyage and named it the \"Land of pariahs\".[citation needed] In 1608 the Grand Duchy of Tuscany did an expedition to the area in order to create an Italian colony for the commerce of Amazonian products to Renaissance Italy, but the sudden death of Ferdinando I de\' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany stopped it.
In 1624 France attempted to settle in the area, but was forced to abandon it in the face of hostility from the Portuguese, who viewed it as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas. However French settlers returned in 1630 and in 1643 managed to establish a settlement at Cayenne along with some small-scale plantations. This second attempt would again be abandoned following Amerindian attacks. In 1658 the Dutch West Indies Company seized French territory to establish the Dutch colony of Cayenne. The French returned once more in 1664, and founded a second settlement at Sinnamary (this was attacked by the Dutch in 1665).
In 1667 the English seized the area. Following the Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667 the area was given back to France. The Dutch briefly occupied it for a period in 1676.
After the Treaty of Paris in 1763, which deprived France of almost all her possessions in the Americas other than Guiana and a few islands, Louis XV sent thousands of settlers to Guiana who were lured there with stories of plentiful gold and easy fortunes to be made. Instead they found a land filled with hostile natives and tropical diseases. One and a half years later only a few hundred survived. These fled to three small islands which could be seen off shore and named them the Iles de Salut (or \"Islands of Salvation\"). The largest was called Royal Island, another St. Joseph (after the patron saint of the expedition), and the smallest of the islands, surrounded by strong currents, Île du Diable (the infamous \"Devil\'s Island\"). When the survivors of this ill-fated expedition returned home, the terrible stories they told of the colony left a lasting impression in France.
In 1794, after the death of Robespierre, 193 of his followers were sent to French Guiana. In 1797 the republican general Pichegru and many deputies and journalists were also sent to the colony. When they arrived they found that only 54 of the 193 deportées sent out three years earlier were left; 11 had escaped, and the rest had died of tropical fevers and other diseases. Pichegru managed to escape to the United States and then returned to France where he was eventually executed for plotting against Napoleon.
Later on, slaves were brought out from Africa and plantations were established along the more disease-free rivers. Exports of sugar, hardwood, Cayenne pepper and other spices brought a certain prosperity to the colony for the first time. Cayenne, the capital, was surrounded by plantations, some of which had several thousand slaves.
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Kerguelen, Desolation Island South Indian Ocean
- Title : Terre De Kerguelen, Appellee par M. Cook, Isle De La Desolation. Par M. Bonne; Plan Du Port Palliser dans la Terre De Kerguelen: Plan Du Havre De Noel dans la Terre De Kerguelen: Isles decouvertes par Mr. Marion Du Fresne en 1772, appellees par M.Cook en 1776, Isles Du Prince Edouard
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40585
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of parts of the Kerguelen Islands, also known as the Desolation Islands, in the southern Indian Ocean, was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
The map also includes three inset maps, the first two of Port Palliser & Noel Bay on Kerguelen Island, with the third inset map of the Prince Edward Islands - part of South Africa.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Two small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Kerguelen’s land was named for Yves de Kerguelen, a French navigator and explorer who sailed around the islands in 1772 along with Marion Du Fresne another French explorer who was in the vicinity in that same year. Capt. James Cook didn’t sight the islands until his 3rd voyage in 1776, having failed in his first attempts on earlier voyages. On Christmas Eve 1776, Cook’s ships the Resolution and the Discovery anchored in a Bay which he called Christmas Harbor, only staying long enough to replenish his water, and as the islands were so bleak and treeless, he called them Desolation Isles. Bonne’s chart was taken from original surveys by Kerguelen, Du Fresne and Capt. James Cook and was finely engraved by Gaspard Andre.
The Kerguelen Islands also known as the Desolation Islands, are a group of islands in the southern Indian Ocean constituting one of the two exposed parts of the mostly submerged Kerguelen Plateau. They are among the most isolated places on Earth, located 450 km (280 mi) northwest of the uninhabited Heard Island and McDonald Islands and more than 3,300 km (2,051 mi) from Madagascar, the nearest populated location (excluding the Alfred Faure scientific station in Ile de la Possession, about 1,340 km (830 mi) from there, and the non-permanent station located in Île Amsterdam, 1,440 km (890 mi) away). The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands, Amsterdam, and Saint Paul Islands, and France\'s Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean are part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands and are administered as a separate district.
Kerguelen Islands appear as the \"Ile de Nachtegal\" on Philippe Buache\'s map from 1754 before the island was officially discovered in 1772. The Buache map has the title Carte des Terres Australes comprises entre le Tropique du Capricorne et le Pôle Antarctique où se voyent les nouvelles découvertes faites en 1739 au Sud du Cap de Bonne Esperance (\'Map of the Southern Lands contained between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Pole, where the new discoveries made in 1739 to the south of the Cape of Good Hope may be seen\'). It is possible this early name was after Abel Tasman\'s ship \"De Zeeuwsche Nachtegaal.\" On the Buache map, \"Ile de Nachtegal\" is located at 43°S, 72°E, about 6 degrees north and 2 degrees east of the accepted location of Grande Terre.
The islands were officially discovered by the French navigator Yves-Joseph de Kerguelen-Trémarec on 12 February 1772. The next day Charles de Boisguehenneuc landed and claimed the island for the French crown. Yves de Kerguelen organised a second expedition in 1773 and arrived at the \"baie de l\'Oiseau\" by December of the same year. On 6 January 1774 he commanded his lieutenant, Henri Pascal de Rochegude, to leave a message notifying any passers-by of the two passages and of the French claim to the islands. Thereafter, a number of expeditions briefly visited the islands, including that of Captain James Cook in December 1776 during his third voyage, who verified and confirmed the passage of de Kerguelen by discovering and annotating the message left by the French navigator.
Soon after their discovery, the archipelago was regularly visited by whalers and sealers (mostly British, American and Norwegian) who hunted the resident populations of whales and seals to the point of near extinction, including fur seals in the 18th century and elephant seals in the 19th century. Since the end of the whaling and sealing era, most of the islands\' species have been able to increase their population again.
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Santa Cruz Isles, Solomon Islands Sth Pacific Lord Howe, Nendo
- Title : Isles De La Reine Charlotte
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40580
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Santa Cruz Island, of the Temotu Province in the Solomon Islands, Nendo Island & Lord Howe Island was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small worm holes in bottom margin
Plate area: - Two small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Map of four island with compass rose. Santa Cruz Island, of Santa Cruz Island, of the Temotu Province in the Solomon Islands, based on Cook\'s discoveries, was named after Queen Charlotte, wife of King George III.
The Isle du Lord Edgemont (present day Nendo Island) and Isle du Lord Howe islands have been only partially engraved to show the explored portions.
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Scandinavia, Baltic States & European Russia
- Title : Le Nord De L Europe contenant Le Danemark La Norwege, La Suede et la Laponie avec la Majeure Partie de la Russie Europeenne Par M Bonne
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 31671
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Scandinavia, The Baltic States & European Russia was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Du Bocage Large Antique Map Plan of Olympia, Greece
- Title : Essai Sur La Topographe d Olympie...1780
- Ref #: 16450
- Size: 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique map a plan of Olympia, Greece - 1st site of the Olympic Games - was engraved in 1780 - dated - and was published by Jean Denis Barbie du Bocage in hisVoyage Anacharsis (The Travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece) published between 1781 - 1788.
Voyage Anacharsis is an illustrative account of the travels of Anacharsis the Younger in Greece, during the middle of the fourth century before the Christian era.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8in (310mm x 200mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1780 Large Delisle Antique Map of Nothern Greece, Macedonia, Thracia, Turkey
- Title : Graeciae Pars Septentrionalis Par Guill. Delisle.....1780
- Ref #: 20404
- Size: 30in x 22in (765mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of Northern Greece, Macedonia, Thracia by Guillaume Delisle was engraved by Philip Bauche and published in 1780 - the date is engraved in the scale cartouche (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Very heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 22in (765mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 18 1/2in (660mm x 470mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light browning to bottom left & right margin corners. Three reapirs to margins, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 R. Bonne Original Antique Map of Mogul Empire, India, Tibet, Tibet & Ganges
- Title : Carte de la Partie superieure D L Inde en Daca du Gange...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31661
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31682
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Caribbean Islands of Guadeloupe & Martinique
- Title : L Isle De La Martinique; Isles De La Guadeloupe...Par M Bonne
- Date : 1780
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40556
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Caribbean Islands of Guadeloupe & Martinique by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Two small worm holes
Plate area: - Two small worm holes
Verso: - Two small worm holes
Background:
Martinique is an insular region of France located in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea.
Guadeloupe is an insular region of France located in the Leeward Islands, part of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of New Guinea, William Dampier 1699 - 5 Harbours
- Title : Carte des Decouvertes du Capt,. Carteret dans La Nlle. Bretagne..Par M Bonne
- Date : 1780
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40581
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Papua New Guinea - and the early discoveries of William Dampier and the later passage of Cooks ship the Endeavor through the straits between Australia and New Guinea, by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
The map also contains the bays, Harbours and coastlines of several Islands of the Pacific including New Ireland, Philippines, Indonesia.(Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 ½in x 11 ½in; (420mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 14 ½in x 10in; (370mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
William Dampier 1651 - 1715 was an English explorer and navigator who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australia\'s first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the Admiralty with his book A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in Western Australia, before being court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crewmate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Horatio Nelson, Charles Darwin, and Alfred Russel Wallace.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31685
- Size: 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40850
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Peru, The Amazon River, South America
- Title : Carte Du Perou avec une partie des pays quien sont al est... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 60565
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of South America French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 16059
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of South America Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 16059
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of the Cape Verde Islands & Plan of Praia
- Title : Isles Du Cap-Verd; Plan de la Rade de la Praya...Par M Bonne
- Ref : 40546
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of the Cape Verde Islands, West Africa with an inset map of the harbour & city of Praia, by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Cape Verde officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country spanning an archipelago of 10 volcanic islands in the central Atlantic Ocean. It forms part of the Macaronesia ecoregion, along with the Azores, Canary Islands, Madeira, and the Savage Isles.
The Cape Verde archipelago was uninhabited until the 15th century, when Portuguese explorers discovered and colonized the islands, establishing the first European settlement in the tropics. Ideally located for the Atlantic slave trade, the islands grew prosperous throughout the 16th and 17th centuries, attracting merchants, privateers, and pirates. The end of slavery in the 19th century led to economic decline and emigration. Cape Verde gradually recovered as an important commercial center and stopover for shipping routes. Incorporated as an overseas department of Portugal in 1951, the islands continued to campaign for independence, which was peacefully achieved in 1975.
Praia is the capital and largest city of Cape Verde, an island nation in the Atlantic Ocean west of Senegal. It lies on the southern coast of Santiago island in the Sotavento Islands group.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of The Straits of Magellan, Chile, South America
- Title : Detroit De Magellan avec les plans des Principaux... Par M. Bonne
- Ref : 40569
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Straits of Magellan, South America - with 14 inset maps of different bays and inlets of the straits - by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - wo small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The Strait of Magellan: (Estrecho de Magallanes) is a navigable sea route separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Ferdinand Magellan a Portuguese explorer and navigator in the service of Charles I of Spain, became the first European to navigate the strait in 1520 during his circumnavigation of the globe.
Other early explorers included Francis Drake (1578). In February 1696 the first French expedition, under the command of M. de Gennes reached the Strait of Magellan. The expedition is described by the young French explorer, engineer and hydrographer François Froger in his A Relation of a Voyage (1699).
The strait was first carefully explored and thoroughly charted by Phillip Parker King, who commanded the British survey vessel HMS Adventure, and in consort with HMS Beagle spent five years surveying the complex coasts around the strait (1826–1830). A report on the survey was presented at two meetings of the Geographical Society of London in 1831.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of West South America Peru & The Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Perou... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40843
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of West South America Peru & The Amazon River
- Title : Perou et Pays Circonvoisins... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40551
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40848
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31681
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 40851
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 16042-1
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 40552
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Large Antique Map of Tahiti
- Title : Carte De L 'Isle O - Taiti...Par M. Bonne...
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 40570
- Size: 15in x 11in (400mm x 275mm)
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 ½in x 11 ½in; (420mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 14 ½in x 10in; (370mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Two very small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map NW Africa Morocco to Senegal Canary Is.
- Title : Partie Occidentale De L Ancien Continent ...M Bonne
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 40900
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Brazil, South America
- Title : Carte de la Partie Meridionale Du Bresil....M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31684
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Eastern Russia, China
- Title : L Empire de Russie en Europe et an Asie...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40528
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Peru, South America
- Title : Perou et Pays Circonvoisins... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40551
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Scandinavia Sweden, Norway & Denmark
- Title : Les Royaumes De Suede De Denmark et de Norwege
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40525
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Scandinavia, Sweden, Norwaty and Denmark was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of The Russian Empire
- Title : Carte De L Empire de Russie en Europe et en Asie...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31674
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Turkey in Europe - Greece to Hungary
- Title : Turquie D Europe...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40526
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Western, European Russia, Poland
- Title : L Empire de Russie en Europe et an Asie...M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40527
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Robert De Vaugondy Antique Twin Hemisphere World Map
Antique Map
- Title : Mappe-Monde par Robert de Vaugondy Geographe ord du Roi
- Size: 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (440mm x 290mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1780
- Ref #: 17060
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique Twin Hemisphere World Map by Robert De Vaugondy was engraved in 1780 - dated in title and published in the same year.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (440mm x 290mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (440mm x 290mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Fine twin hemisphere world map illustrating the known world in the 18th century. Although almost complete there are a few regions of uncertainty. The route taken by Cook on his final voyage is included which reaches from Australia, New Zealand to Hawaii and the very northern reaches of western North America which were surveyed and mapped by Cook extensively. There is some indication of a northern Arctic region there is no mention of the great southern Antarctica regions. A great map showing the world at the beginning of modern era. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)