Johannes Jansson (1588 - 1664)
Profile :
Johannes Janssonius, more commonly known to us as Jan Jansson, was born in Arnhem where his father was a bookseller and publisher (Jan Janszoon the Elder).
In 1612 he married the daughter of the cartographer and publisher Jodocus Hondius, and then set up in business in Amsterdam as a book publisher. In 1616 he published his first maps of France and Italy and from then onwards he produced a very large number of maps, perhaps not quite rivaling those of the Blaeu family but running a very close second in quantity and quality.
From about 1630 to 1638 he was in partnership with his brother-in-law, Henricus Hondius, issuing further editions of the Mercator/Hondius atlases to which his name was added. On the death of Henricus he took over the business, expanding the atlas still further, until eventually he published an 11-volume Atlas Major on a scale similar to Blaeu's Atlas Major.
The first full edition of Jansson's English County Maps was published in 1646 but some years earlier he issued a number of British maps in the Mercator/Hondius/Jansson series of atlases (1636-44); the maps were printed from newly engraved plates and are different from the later 1646 issue and are now rarely seen (see Appendix B for further details). In general appearance Jansson's maps are very similar to those of Blaeu and, in fact, were often copied from them, but they tend to be more flamboyant and decorative.
After Jansson's death his heirs published a number of maps in an Atlas Contractus in 1666, later still many of the plates of his British maps were acquired by Pieter Schenk and Gerard Valck who published them again in 1683 as separate maps
Jan Jansson (41)
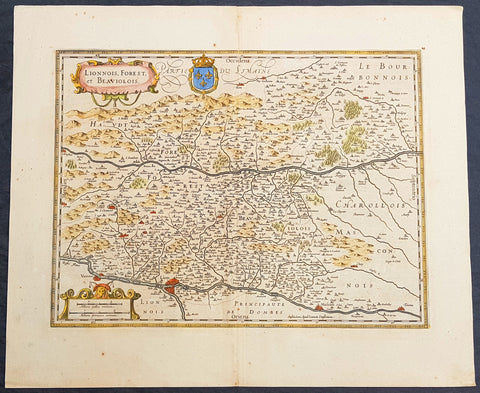
1619 Jan Jansson Antique Map Loire & Rhone Rivers, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France
- Title : Lionnois, Forest et Beaviolois
- Ref #: 50247
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1619
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of France - centering on the Loire & Rhone Rivers and the cities of Lyon, Vienne & Macon - by Jan Jansson - was published in the 1619 edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Lyon is the third-largest city and second-largest urban area of France. It is located in the country\'s east-central part at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône.
Fernand Braudel remarked, Historians of Lyon are not sufficiently aware of the bi-polarity between Paris and Lyon, which is a constant structure in French development...from the late Middle Ages to the Industrial Revolution. In the late 15th century, the fairs introduced by Italian merchants made Lyon the economic counting house of France. Even the Bourse (treasury), built in 1749, resembled a public bazaar where accounts were settled in the open air. When international banking moved to Genoa, then Amsterdam, Lyon remained the banking centre of France.
During the Renaissance, the cities development was driven by the silk trade, which strengthened its ties to Italy. Italian influence on Lyons architecture is still visible among historic buildings. In the later 1400s and 1500s Lyon was also a key centre of literary activity and book publishing, both of French writers (such as Maurice Scève, Antoine Heroet, and Louise Labé) and of Italians in exile (such as Luigi Alamanni and Gian Giorgio Trissino).
In 1572, Lyon was a scene of mass violence by Catholics against Protestant Huguenots in the St. Bartholomew\'s Day Massacre. Two centuries later, Lyon was again convulsed by violence when, during the French Revolution, the citizenry rose up against the National Convention and supported the Girondins. The city was besieged by Revolutionary armies for over two months before surrendering in October 1793. Many buildings were destroyed, especially around the Place Bellecour, while Jean-Marie Collot d\'Herbois and Joseph Fouché administered the execution of more than 2,000 people. The Convention ordered that its name be changed to Liberated City and a plaque was erected that proclaimed Lyons made war on Liberty; Lyons no longer exists. A decade later, Napoleon ordered the reconstruction of all the buildings demolished during this period.
The Convention was not the only target within Lyon during the 1789-1799 French Revolution. After the National Convention faded into history, the French Directory appeared and days after the September 4, 1797, Coup of 18 Fructidor, a Directory\'s commissioner was assassinated in Lyon.
The city became an important industrial town during the 19th century. In 1831 and 1834, the canuts (silk workers) of Lyon staged two major uprisings for better working conditions and pay. In 1862, the first of Lyon\'s extensive network of funicular railways began operation.
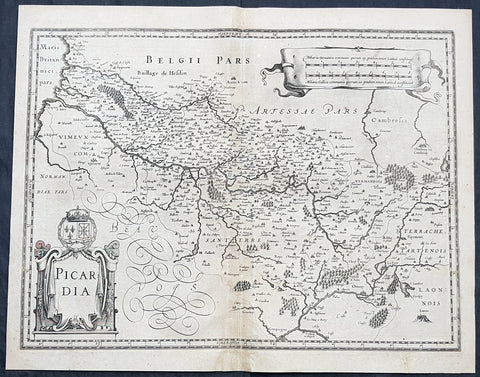
1628 Jan Jansson Antique Map of the Picardy or Picardie Region of France
- Title : Picardia
- Size: 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26133
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Jan Jansson was published in the early 1628 French edition of Janssons Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\\\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
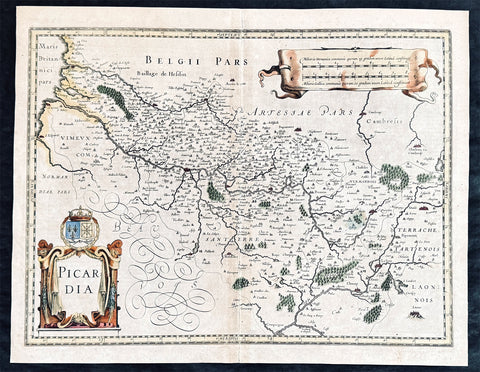
1628 Jan Jansson Antique Map of the Picardy or Picardie Region of France
- Title : Picardia
- Size: 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26133
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Jan Jansson was published in the early 1628 French edition of Janssons Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, brown, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\\\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
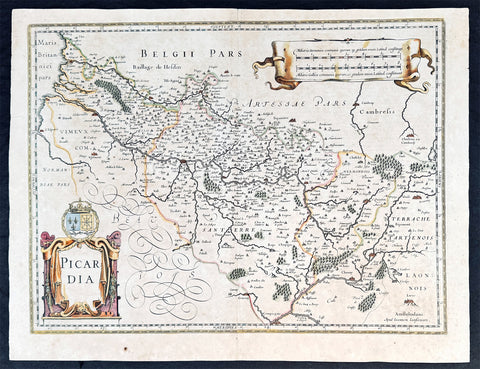
1628 Jan Jansson Antique Map of the Picardy Region of France
- Title : Picardia
- Size: 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 50241
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Jan Jansson was published in the early 1628 Latin edition of Janssons Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - later
Colors used: - Green, blue, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\\\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
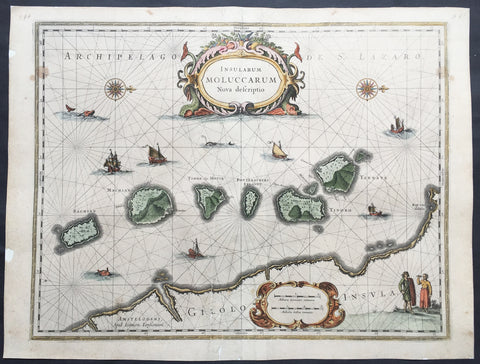
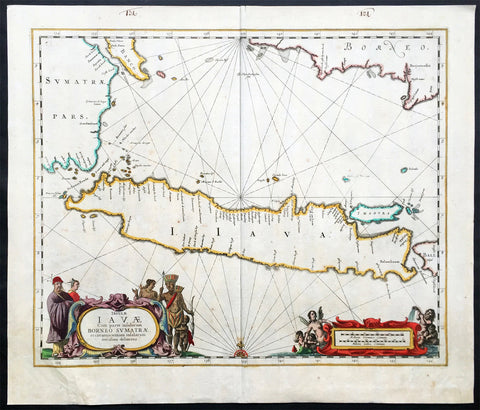
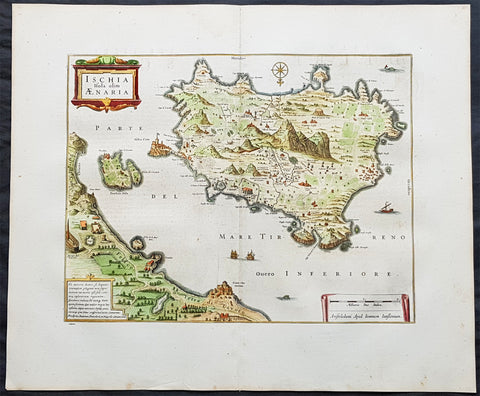
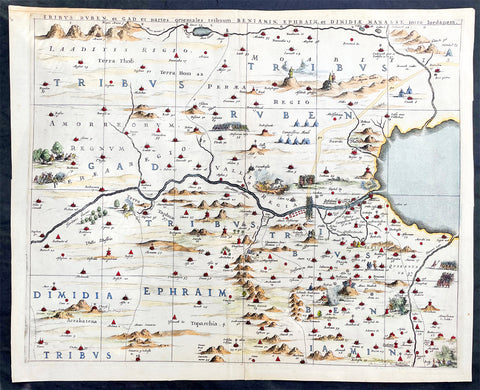
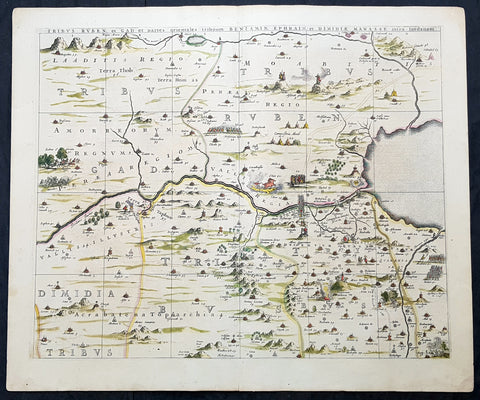
1633 Jan Jansson Old, Antique Map of The Maluku or Spice Islands, Indonesia
Antique Map
- Title : Insularum Moluccarum Nova descriptio
- Ref #: 42018
- Size: 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1633
- Condition: (B+) Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Maluku or Spice Islands of Indonesia was published by Jan Jansson in the 1633 edition of Atlas Novus.
Background: The Maluku Islands (also known as the Moluccas, Moluccan Islands, the Spice Islands) are an archipelago in Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Geographically they are located east of Sulawesi (Celebes), west of New Guinea, and north of Timor. The islands were also historically known as the Spice Islands by the Chinese and Europeans, but this term has also been applied to other islands. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top and bottom margin, slight separation into border
Plate area: - Repairs adjacent to bottom centrefold, slight separation
Verso: - Map professionally backed onto archival paper
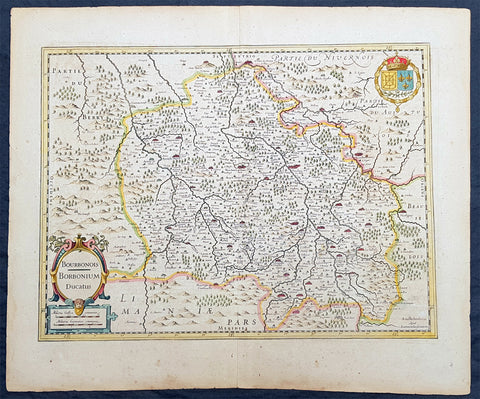
1636 Jan Jansson Antique Map of The Bourbon or Bourbonnais Region Central France
- Title : Boubonoius; Borbonium Ducatus
- Ref #: 41641
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (490mm x 340mm)
- Date : 1636
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Bourbon or Bourbonnais Region of central France was published in the rare 1636 English edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
There was only one English edition of Mercators Atlas published in 1636 by Jansson & Hondius. These maps - with English text on the verso - are now understandably scarce.
The text running for two pages on the back of the map generally describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (490mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background:
Bourbonnais was a historic province in the centre of France that corresponded to the modern département of Allier, along with part of the département of Cher. Its capital was Moulins.
The title of the ruler of Bourbonnais between 913 and 1327, was Sire de Bourbon (or Seigneur de Bourbon). The first lord of Bourbonnais known by name was Adhémar (or Aymon I of Bourbon). Aymon\'s father was Aymar (894-953), sire of Souvigny, his only son with Ermengarde.Aymar lived during the reign of Charles the Simple who, in 913, gave him fiefs on the Allier River in which would become Bourbonnais. He acquired the castle of Bourbon (today Bourbon-l\'Archambault). Almost all early lords took the name d\'Archambaud, after the palace, but later the family became known as the \"House of Bourbon\".
The first House of Bourbon ended in 1196, with the death of Archambault VII, who had only one heir, Mathilde of Bourbon. She married Guy II of Dampierre, who added Montlucon to the possessions of the lords of Bourbon. The second house of Bourbon started in 1218, with Archambault VIII, son of Guy II and Mahaut, and brother of William II of Dampierre. He was followed by his son Archambaut IX, who died in Cyprus in 1249, during a crusade. The House of Burgundy then acquired Bourbonnais.
In 1272, Beatrice of Burgundy (1258-1310), Lady of Bourbon, married Robert de France (1256-1318), Count of Clermont, son of king Louis IX (Saint-Louis). Thus began the long-lasting House of Bourbon, which would provide the kings of France from Henry IV to Louis-Phillipe in 1848, when France abolished its monarchy.
The Bourbons had concluded an alliance with the royal power. They put their forces at the service of the king, thus benefitting from the geographic position of Bourbonnais, located between the royal fidemesne and the duchies of Aquitaine and Auvergne. This alliance, as well as the marriage of Béatrix de Bourgogne and Robert de France, aided the rise and prosperity of the province. In 1327, King Charles (le Bel) elevated Boubonnais to the status of a duchy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
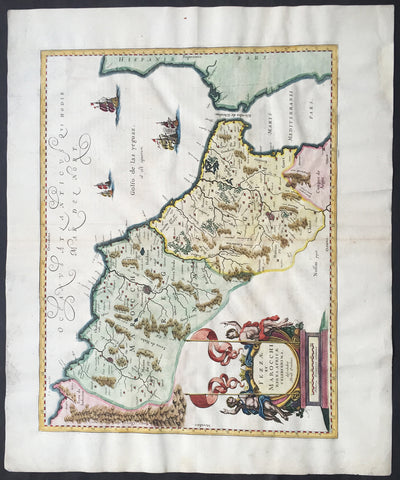
1638 Jan Jansson Large, Old Antique Map of Africa Morocco, Gibraltar & NW Africa
- Title : Fezzae et Marocchi Regna Africae Celeberrima
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92950
- Size: 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
Description:
This fine large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Morocco & the Straits of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean was published by Jan Jansson in the 1638 Latin edition of Atlas Novus.
Background: Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in left margin, reapir to top and bottom margin not affecting the image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
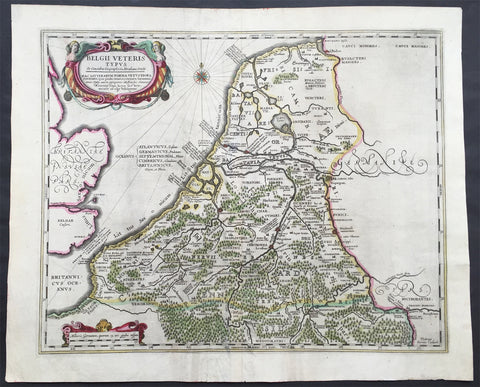
1638 Jansson Large Antique Map of The Netherlands & Belgium
- Title : Belgii Veteris Typus...Abrahami Ortelii...Petrus Karius
- Ref #: 61036
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of The Netherlands & Belgium was engraved by Peter Karius and was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (480mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing in bottom margin
Plate area: - Centerfold Re-joined
Verso: - Soiling
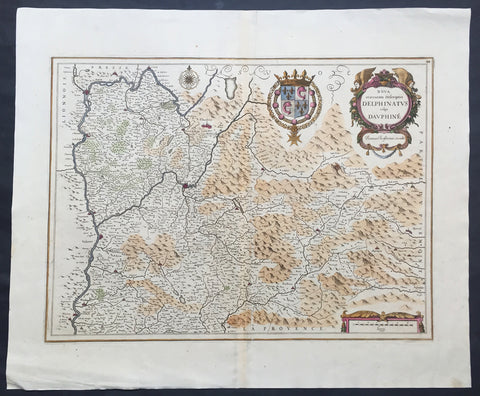
1638 Jansson Old, Antique Map of the Dauphine Region of France, Grenoble
- Title : Nova et acurrata Descriptio Delphinatus vulgo Dauphine
- Ref #: 50244
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Dauphine region of southern France - centering on the city of Grenoble - with the Rhone River to the west and north with Savoy & Piedmont to the east was published by Jan Jansson in the 1638 edition ofAtlas Novus. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/4in (520mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
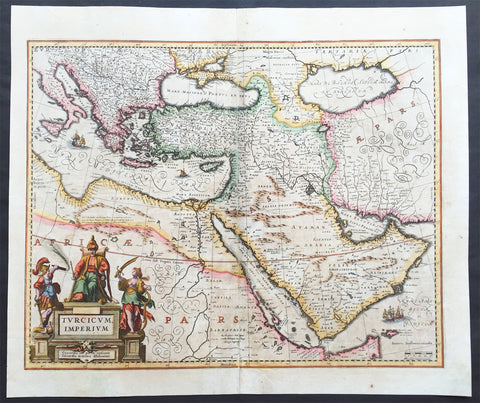
1638 Jansson Old, Antique Map of the Turkish Empire, Saudi Arabia, Middle East
- Title : Turcicum Imperium
- Ref #: 61009
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautiful, old original antique map* of The Turkish Empire in Europe, Africa & Asia centering on Saudi Arabia by Jan Jansson was published in the 1638 Latin edition for Mercator's Atlas by both Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
Background: This is the standard 17th century view of the Turkish Empire, including the Balkans in south-eastern Europe, the North African littoral, the Levant and the Arabian Peninsula in addition to the area of Modern Turkey & Persia.
Much of the place name information on this map is derived from the maps published in 1561 by the Italian mapmaker, Giacomo Gastaldi, whose maps exercised great influence over later European mapmakers, throughout the 17th century.
Formidable though the barrier presented by the Turkish Empire in the Near East was, by the early years of the 17th century it was beginning to show signs of decadence and weakness, especially after the defeat of the Turkish navy at the hands of the combined Christian forces of Western Europe at the battle of Lepanto in 1571, from which Turkish naval power never fully recovered.
Centered on the palace of the Sultans at Constantinople, the administration of the empire was passed down through local rulers, the Beys, Deys and Pashas, who never lost an opportunity to enrich themselves and to develop often considerable powers of their own.
Further defeats of the Turks occurred in 1669 when Candia (Crete) was taken by the Venetians, and in 1683 when they suffered a humiliating defeat outside Wien (Vienna) at the north-western extremity of European Turkey. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early & Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Several small repairs to margins, no loss
Plate area: - Centerfold re-joined light uplift along centerfold, light age toning
Verso: - Repairs as noted
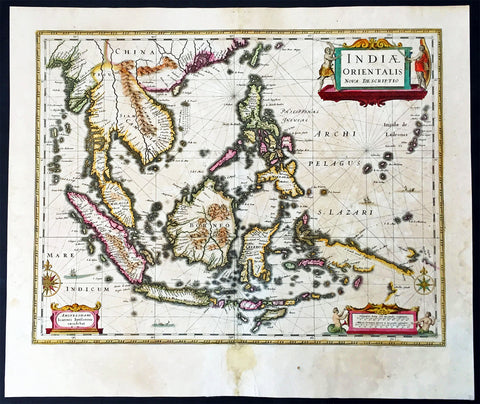
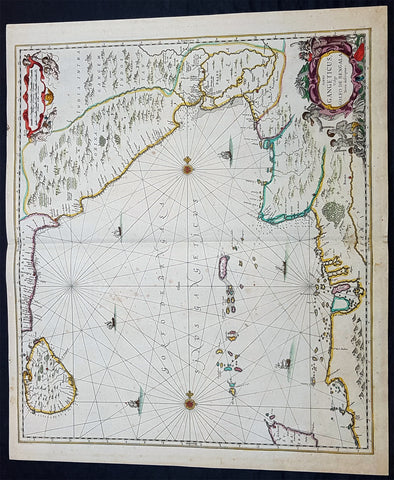
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of East Indies, Australia - Voyage of Dufken, Spice Islands
Antique Map
- Title : Indiae Orientalis Nova Descriptio
- Ref #: 43144
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautiful, very significant original antique map of SE Asia, the East Indies PNG and significantly a small portion of the west coast of Australia's Cape York Peninsular was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning, bottom centerfold restored
Plate area: - Uniform age toning, centerfold re-joined
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background: This landmark map is the first published record of the discoveries made by the Dutch ship Dufken on route to Cape York in Australia. New Guinea ("Landt vande Papuos") is marked the (Is)land next to it is called ÔNieu ZeelandtÕ and the island Duyfkens is named after the ship Duyfken.
With the first publication of this map 27 years had passed since the voyage of the Dufken and its discoveries of PNG and NW Australia had been completed. The Dutch East India Company had suppressed the discoveries until it was sure how profitable or not Australia would be.
Jansson & Hondius were the first to published this map in 1630 and it is believed the information was leaked from the Blaeu firm - the official cartographers to the Dutch East India Company. Surprisingly Blaeu did not publish a similar map for another two years. It must have been incredibly galling for Blaeu to have known of the discoveries for nearly thirty years and then to have been beaten to publication by his fiercest rival Jansson & Hondius.
Given this information this is an incredibly significant map of this imporatant region being the first map published with concrete first hand knowledge of the area which prior had been mapped based mainly on speculation or second hand knowledge.
The text running for two pages on the back of the map generally describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
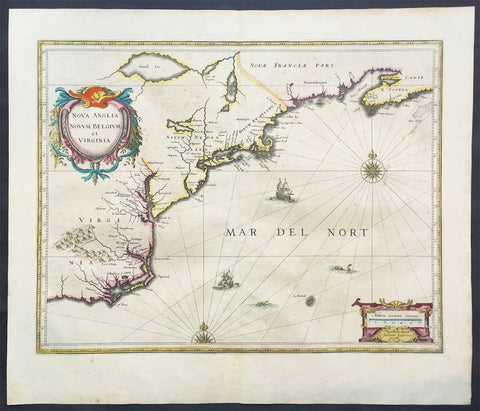
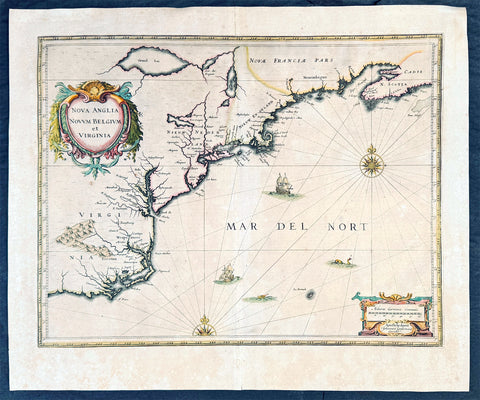
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
Antique Map
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Ref: 43134
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured, important original antique map of the north east regions of the United States from Virginia, Chesapeake Bay, to New York & New England by Jan Jansson was published in the 1639 French edition of the Jansson, Hondius Atlas.
A beautiful map with sturdy, clean paper original wide margins and beautiful original hand colouring.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Very light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
A beautiful original 17th map of Virginia, New York and New England which was derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. This version is enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, with de Laets narrative on the verso (De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the namesManbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam)
The nomenclature on this map is virtually identical to the De Laet map, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630's the families of Blaeu and Jansson produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, the first one published in 1636 - entitled Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia.
The second edition in which the title of the map was changed to Nova Belgium et Anglia Nova (to give more weight to Dutch claims in North America) within a new square cartouche was first published in 1647.
State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden; AMPR)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
Antique Map
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93508
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper plate engraved antique landmark 1st edition map of the NE region of North America, the original colonial states from Virginia to New England, was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas
A magnificent early map of NE North America published only 19 years after the landing of the Pilgrims at Plymouth Rock, Massachusetts.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 384mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning, old archival tape on verso
Background:
This influential map is derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. Enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, it carries de Laets narrative on the reverse. De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the names Manbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam. The nomenclature is virtually identical, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630s the families of Blaeu and Hondius - Jansson of ten produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, the latter relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, this one first published in 1636, the second edition was published in 1647 renamed Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova within a new square cartouche. State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden)
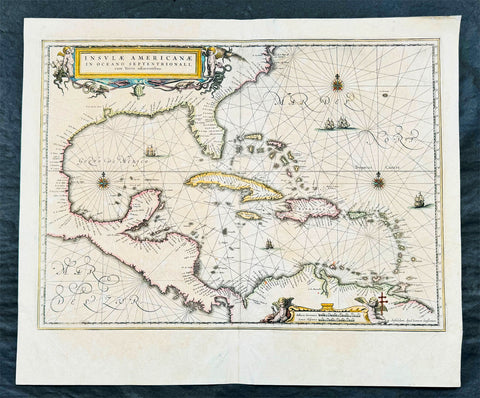
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America, Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean
Antique Map
- Title : Insulae Americanae in Oceano Septentrionali cum terris adiacentibus
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 43142
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Gulf of Mexico, The Caribbean, Virginia to Florida to Texas and Central America, Venezuela was published in the 1639 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Nouvs.
This map has been re-joined along the centerold and has some uplift along the centerfold and has been priced accordingly.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595.
After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 andcontinued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/4in (525mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Light uniform age toning, centerfold re-joined with light uplift
Verso: - Light age toning
Background: Cartographically this map draws on the extremely rare chart by Hessel Gerritsz, c.1631. The area of coverage is exactly the same with the exception of the addition of the west coast of Central America. The nomenclature of the North American part is virtually identical, the only notable addition being the naming of Virginia. It reflects the firsthand knowledge of Gerritsz during his voyage to South America and the West Indies undertaken in 1628. The distance between Chesapeake Bay and Albemarle Sound is accurately portrayed at 1°; even in Gerritsz's acclaimed NOVA ANGLIA ..., for de Laet, 1630, this distance is over 2°. It seems likely that a Spanish chart was used as the nomenclature along the south-east coast lacks any of the French influences often seen at the time.(Ref: Burden; Tooley, Koeman)
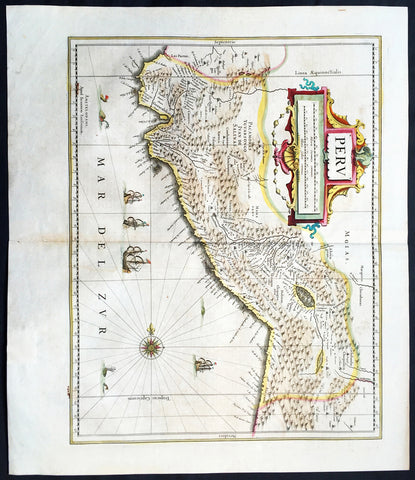
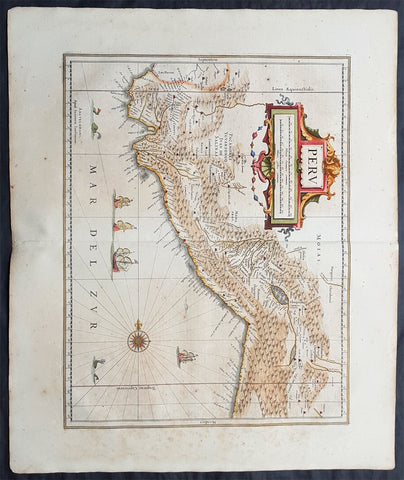
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of Peru, South America
Antique Map
- Title : Peru
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43147
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the ancient South American country of Peru was published in the 1639 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Nouvs.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Jansson in this map shows the Pacific coast of South America from Ecuador - at the left hand side - as far south as the Atacama desert in the northern reaches of Chile.
Although the interior terrain is not mapped with any particular degree of accuracy, this map nevertheless conveys a vivid impression of the difficult terrain of the Andes in Peru.
As early as 1520, Spanish settlers in Panama had heard tales of a powerful civilisation rich in gold that lay to the south, and in 1522 an expedition was organised to find this land and the people called Biru or Piru in the south. In 1524 Francisco Pizarro led the first of his expeditions that led ultimately to the discovery & conquest of the Inca Empire which extended over wide areas of modern Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and part of Chile. Pizarro obtained from Atahuallpa, the head of the Inca Empire, a huge ransom of silver and gold that made Spain rich almost beyond the most inventive dreams of the Spanish conquerors, and once the mountain city of Cuzco was captured in 1533, the Spanish hold over much of South America was virtually complete.
A beautiful map with a fine impression on clean heavy paper with beautiful hand colouring. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
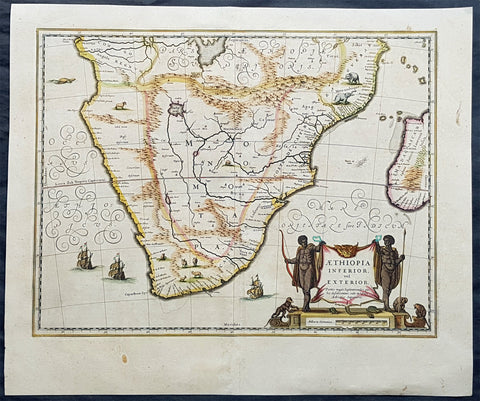
1639 Jan Jansson Large Original, Antique Map of South Africa
Antique Map
- Title : Aethiopia Inferior vel Exterior...
- Date : 1639
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 43145
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the southern & central parts of Africa, with the south-west coast of Madagascar, was published by Jan Jansson in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Gerardi Mercators Atlantis Novi.
Background: This handsome map formed the standard for the depiction of South Africa throughout the 17th century, covering the region from Congo-Zanzibar to the Cape. Both Blaeu & Jansson based this map on Portuguese exploration, most detail is confined to the coastlines. There are two large lakes in the interior, one unnamed and the other called Zachef, which is the lake out of which the Zambere (Zambesi River) flows, probably based on reports of Lake Ngami, which was not conclusively discovered until the mid 19th century. The interior shows the mythical Mountains of the Moon or Lunae Montes. Indigenous animals including elephants and monkeys are illustrated, while large galleons sail the sea. The dramatic title cartouche is drawn on an ox hide held up by natives, with monkeys and turtles at their feet.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Norwich; Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom margin centerfold re-joined, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1639 Jan Jansson Original Antique Map of Peru, South America
Antique Map
- Title : Peru
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70709
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique and very important map of Peru, South America by Jan Jansson was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Jansson in this map shows the Pacific coast of South America from Ecuador - at the left hand side - as far south as the Atacama desert in the northern reaches of Chile.
Although the interior terrain is not mapped with any particular degree of accuracy, this map nevertheless conveys a vivid impression of the difficult terrain of the Andes in Peru.
As early as 1520, Spanish settlers in Panama had heard tales of a powerful civilisation rich in gold that lay to the south, and in 1522 an expedition was organised to find this land and the people called Biru or Piru in the south. In 1524 Francisco Pizarro led the first of his expeditions that led ultimately to the discovery & conquest of the Inca Empire which extended over wide areas of modern Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and part of Chile. Pizarro obtained from Atahuallpa, the head of the Inca Empire, a huge ransom of silver and gold that made Spain rich almost beyond the most inventive dreams of the Spanish conquerors, and once the mountain city of Cuzco was captured in 1533, the Spanish hold over much of South America was virtually complete.
A beautiful map with a fine impression on clean heavy paper with beautiful hand colouring. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
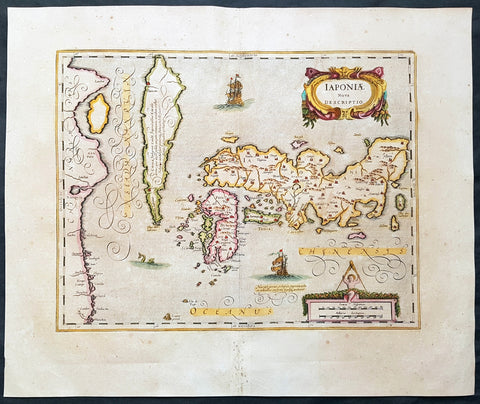
1639 Jansson & Hondius Large Antique Map of Japan, Korea & China - Japoniae Nova Descriptio
- Title : Japoniae Nova Descriptio
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
- Ref #: 43136
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique, early scarce map of Japan & Korea (as an Island) with parts of eastern China was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerardi Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13 3/4in (445mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, light spotting
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning, bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss
Background: This map published by Jansson is taken directly from the Jodocus Hondius map - first published in 1606 - of Japan which faithfully followed the Ortelius/Teixeira style. Jansson has added an explanation for Korea, saying he was not yet certain whether it was an island or part of the mainland. The rest of Jansson's changes were ornamental, replacing the bottom Chinese Junk with a European ship & monster as well as changing the title and scale cartouches.
Luis Teixeira'a map, which was published by Ortelius in 1595, began a process that would last for three centuries, in which Western printed maps of Japan increasingly approached geographical reality. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
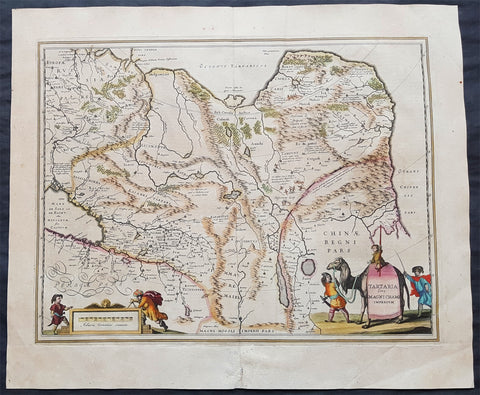
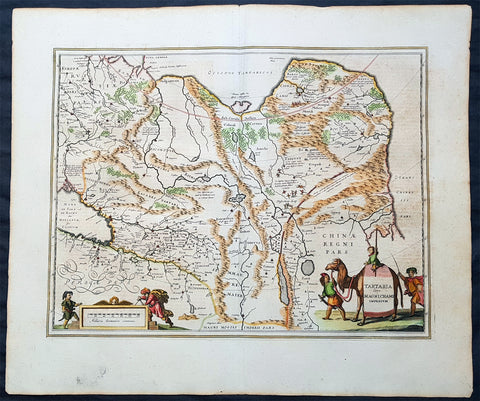
1639 Jansson Large Antique Map of Tartary, Siberian Russia, China, Central Asia
Antique Map
- Title : Tartaria sive Magni Chami Imperium
- Ref #: 43149
- Size: 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This handsome hand coloured original antique map of China, Tartary (Russian Siberia) & Central Asia was published by Jan Jansson in the 1639 French edition of Atlas Novus.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning
Verso: - Uniform age toning, bottom centerfold re-joined
Background: This handsome map shows all of eastern Asia between the Caspian Sea and a good portion of northern China and Manchuria both from outside and within the confines of The Great Wall.
This map of north-eastern Asia is dated when Tartary vaguely meant those regions to the north of Persia and China. The name Siberia only began to be applied with the gradual eastward expansion of the Russian Cossacks into those areas hinted at in the accounts of Marco Polo from three centuries earlier.
The Mythical and legendary nature of the geography of this vast interior is illustrated by the inclusion of devils and dragons in the Desertum Lop to the left of the Great Wall. (Ref Tooley M&B)
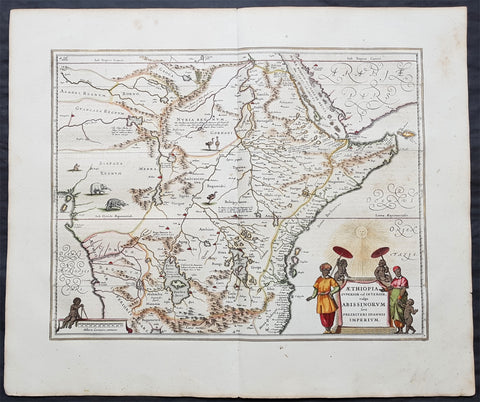
1639 Jansson Original Antique Map of Africa - The Myth of Emperor Prestor John
Antique Map
- Title : Aethiopia Superior vel Interior; vulgo Abissinorum sive Presbiteri Ioannis Imperium
- Date : 1639
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 70712
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Central and NE Africa - the mythical land of Emperor Prestor John - was published in the 1639 French Edition of Mercator's Atlas publsihed by Mercators successors Jan Jansson & Henricus Hondius.
This map was first published by Gerard Mercators son Rumold in the 1606 Latin edition of his fathers atlas and remained unchanged until the plate was re-designed for the 1636 edition of the Atlas by Jansson & Hondius and remained in service until 1680.
This map is in stunning condition on bright heavy stable paper. with original margins and beautiful original colour.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/4in (495mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Rumours of the mythical Emperor Prestor John began in Europe around 1150AD, that somewhere in Asia there was a powerful Christian Emperor named Presbyter Johannes (with the court title of Gurkhan), who had founded the kingdom of Kara Khitai. He had broken the power of the Musselman in his own domain after a fierce and bloody fight. The mysterious Priest-King became a symbol of hope in the Christian world beset by Mongol hordes. Pope Alexander III resolved to make contact with Presbyter John, and his first step was to address a letter to him (dated 27th September 1177). The Pope's physician was dispatched to deliver the letter in person. He never returned. Pope Innocent IV was even more determined than his predecessor, and decided to convert the Barbarians instead of conquer them. Dominican and Franciscan missionaries as well as civil ambassadors of peace plodded back and forth between the Pope, the King of France and the Mogul Khan. These travelers soon learned that His Highness Presbyter Johannes and the Christian kingdom in deepest Asia were popular myths. But the popular fancy was not easily dispelled, and instead of allowing the bubble to be punctured, the people merely transferred the kingdom of Presbyter John to Africa - especially Abyssinia. No-one knew very much about Abyssinia. A few die hards like John de Plano Carpini and Marco Polo persisted in the belief that Presbyter John still reigned in his splendor deep in the heart of the Orient. On the larger map in Higdens Polychronicon the empire of Presbyter John was located in the lower Scythia within the limits of Europe, but the map of Marino Sanuto it was placed in further India. It was moved again to Central Asia and ended up in Abyssinia. The legend persisted, however, and four hundred years after Pope Alexander III wrote his letter to Presbyter Johannes, Abraham Ortelius, a Dutch map publisher issued a separate map titled Presbyteri Johannis Siv Abissinorum Iperii Descripto .
(Ref: M&B, Tooley; Norwich)
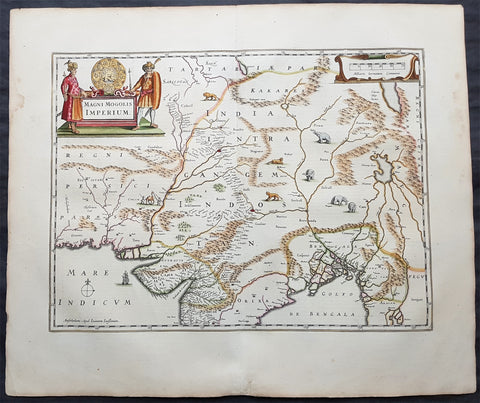
1639 Jansson Original Antique Map The Mughal or Mogul Empire India, Tibet, Nepal
- Title : Magni Mogolis Imperium
- Date : 1639
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 70711
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique and very important map of Mughal Empire of Northern India, Tibet, Nepal and central Asia by Jan Jansson was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/2in (495mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map centers on the Mughal capital of Agra, with the map covering, roughly, from Kabul to Orissa and Deccan, and from Persia to Bengal. It depicts the empire prior to the conquest of Orissa and Deccan, most likely during the reign of Shah Jahan, of Taj Mahal fame. Relief is shown pictorially. An elaborate title cartouche appears in the upper left quadrant. The map is embellished with images of tigers, elephants, caravans, and galleons.
There is much of interest. In particular, is the map detailed breakdown of the caravan network between Gujarat and Agra, between Agra and the desert outpost of Jaisalmer, and between Agra and the Silk Road center of Kabul. While the map does not show roads, for surely none as such existed at the time, it does show the network of towns, waystations and caravanserai built to support the bustling trade system.
The apocryphal Lake of Chiamay appears just north of the Bay of Bengal as the source of four important Southeast Asian river systems including the Irrawaddy, the Dharla, the Chao Phraya, and the Brahmaputra. The curious Lake of Chiamay (also called Chiam-may or Chian-may), roughly located in the area of Assam but sometimes as far north as Tibet and China, began to appear in maps of this region as early as the 16th century and persisted well into the mid 18th century. Its origins are unknown but may originate in a lost 16th century geography prepared by the Portuguese scholar Jao de Barros. It was speculated to be the source of five important Southeast Asian River systems and was mentioned in the journals of Sven Hedin. There are even records that the King of Siam led an invasionary force to take control of the lake in the 16th century. Nonetheless, the theory of Lake Chiamay was ultimately disproved and it disappeared from maps entirely by the 1760s.
There are two states of this map, the present example being the first state, first issued in 1638 by Henricus Hondius, and the second state a few years later in 1641 by Jan Jannson. With the exception of the signature imprint, the plates are identical. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
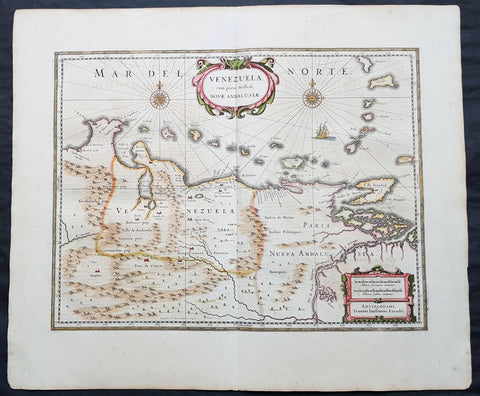
1639 Jansson Scarce Original Antique Map of Venezuela, A. de Berrio & W Raleigh
- Title : Venezuela, cum Parte Australi Novae Andalusiae
- Date : 1639
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 70710
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of what is today modern Venezuela, northern South America was published in the 1639 French Edition of Mercator's Atlas by Mercators successors Jan Jansson & Henricus Hondius.
This map is in stunning condition on bright heavy stable paper. with original margins and beautiful original colour.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map, showing the area of modern Venezuela to the north of the Orinoco valley is another of the early group of maps added to Mercators atlas by Jansson and Hondius, after Joan Blaeus map of the 1630's. It extends from Lago de Maracaibo in the west to the Island of Trinidad in the east and also shows the Dutch held is lands of Curacao, Aruba and Bonaire which served as the base of the Geotroyeerde West Indische Compahnie or Netherlands West Indian Company, since 1634.
Of the three great rivers of South America, the Orinoco was, and remains, the most difficult to navigate. It was the last to yield any of its secrets even though, on his third voyage in 1498, Columbus had noted the strong currents of fresh water from the Orinoco and believed himself to be at the mouth of one of the four rivers of Paradise>
Throughout the sixteenth century, attempts were made to search for the legendary kingdom of El Dorado, but it was not until the three Orinoco voyages of Antonio de Berrio between 1584 and 1591, all starting out from bases in Nueva Granada, that any useful knowledge of the interior was gathered. Berrio never found El Dorado, but he made several discoveries of the river valleys of the interior. By a curious twist of fate, Berrio, whilst waiting in Trinidad for further orders from Spain, was captured by Sir Walter Raleigh, to whom he divulged his knowledge of the region, as well as a great deal of intended misinformation
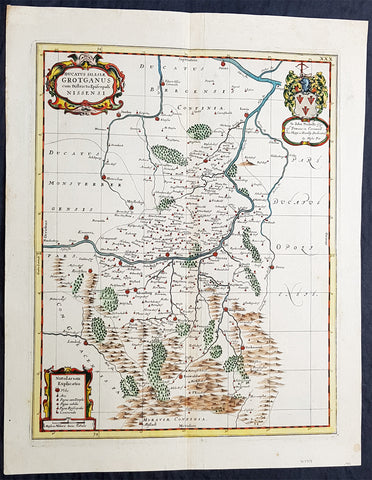
1640 Jansson Old, Antique German Atlas Title Page
- Title : Theatrum Exhibens Illustriores Principesque Germaniae
- Date : 1640
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 80014
- Size: 19 1/2in x 12in (495mm x 305mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique Atlas Title Page was published by Jan Jansson for the in the 1640 edition of Jansson's German Atlas. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 12in (495mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9in (370mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Blind stamp and old ink notation in top margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
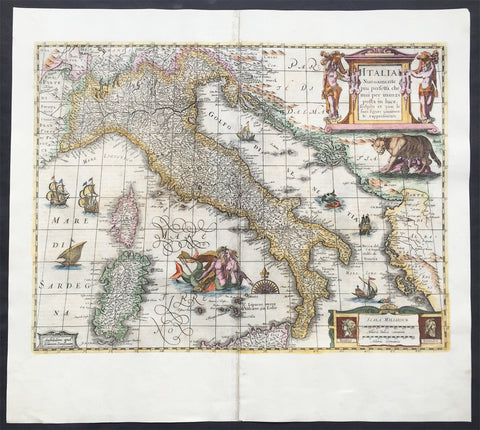
1644 Jan Jansson & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Italy, Sardinia, Corsica
- Title : Italia Nuouamente piu perfetta chemai per inanzi posta
- Ref #: 61008
- Size: 21 1/2in x 19in (545mm x 490mm)
- Date : 1644
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Italy, Sicily, Sardinia & the Adriatic Coast by Jan Jansson was published in the 1644 German edition of Mercator's atlas by Jansson and Hondius.
This map is richly embellished with cartouches, sailing vessels, sea monsters and a wonderful rendering of Neptune and his mate. The image of the two mer-people embracing with bare chests is a hold over from the controversial images present in the first edition of Ortelius' modern map of Italy. Includes portraits of Romulus and Remus in the lower right corner. In subsequent years, Jansson would replace Hondius's name with his own in the bottom left corner.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 19in (545mm x 490mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/2in (500mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Centrefold re-joined
Plate area: - Centrefold re-joined
Verso: - Centrefold re-joined
Background: Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy'sGeographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare,published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
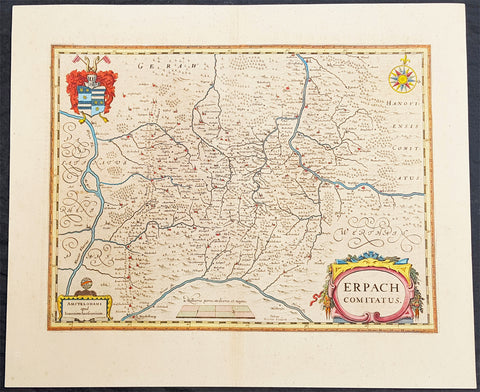
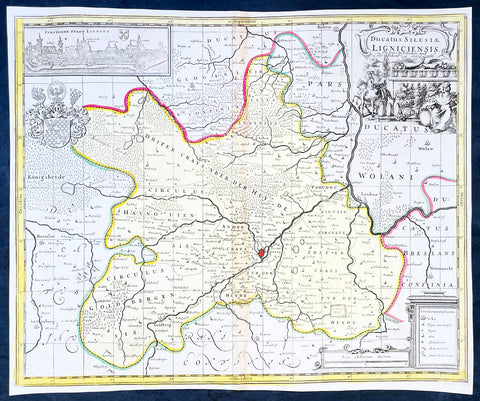
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map Erbach Hesse & Baden-Württemberg Heidelberg Germany
- Title : Erpach Comitatus
- Ref #: 50182
- Size: 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Erbach im Odenwald area in the Baden-Württemberg & Hesse regions of southern Germany, framed by the Neckar River in the south, Rhine River to the west and the Main river to the east (major towns and cities of Heidelberg, Gensheim, Worms, Miltenberg and Oldenburg) by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Erbach is a town and the district seat of the Odenwaldkreis (district) in Hesse, Germany.
Baden-Württemberg is a state in southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the border with France.
Hesseis a federal state (Land) of the Federal Republic of Germany
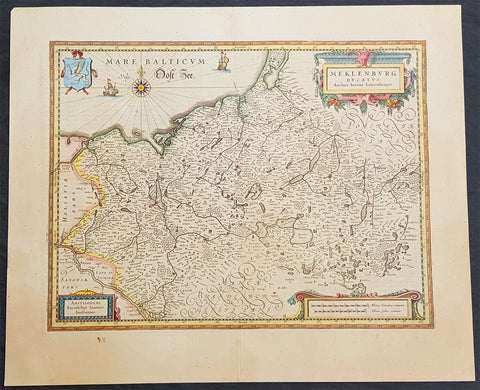
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map of Mecklenburg NE Germany Rostock, Wizmar, Parchim
- Title : Meklenburg Ducatus
- Ref #: 50185
- Size: 11 1/2in x 8in (290mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Mecklenburg, north eastern Germany by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mecklenburg is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow.
The name Mecklenburg derives from a castle named Mikilenburg (Old Saxon: big castle, hence its translation into New Latin and Greek: Megalopolis), located between the cities of Schwerin and Wismar. In Slavic language it was known as Veligrad, which also means big castle. It was the ancestral seat of the House of Mecklenburg; for a time the area was divided into Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz among the same dynasty.
Linguistically Mecklenburgers retain and use many features of Low German vocabulary or phonology.
Mecklenburg is the site of many prehistoric dolmen tombs. Its earliest organised inhabitants may have had Celtic origins. By no later than 100 BC the area had been populated by pre-Christian Germanic peoples.
The traditional symbol of Mecklenburg, the grinning steers head (Low German: Ossenkopp, lit.: oxen\'s head, with osse being a synonym for steer and bull in Middle Low German), with an attached hide, and a crown above, may have originated from this period. It represents what early peoples would have worn, i.e. a steers\'s head as a helmet, with the hide hanging down the back to protect the neck from the sun, and overall as a way to instill fear in the enemy.
From the 7th through the 12th centuries, the area of Mecklenburg was taken over by Western Slavic peoples, most notably the Obotrites and other tribes that Frankish sources referred to as Wends. The 11th century founder of the Mecklenburgian dynasty of Dukes and later Grand Dukes, which lasted until 1918, was Nyklot of the Obotrites.
In the late 12th century, Henry the Lion, Duke of the Saxons, conquered the region, subjugated its local lords, and Christianized its people, in a precursor to the Northern Crusades. From 12th to 14th century, large numbers of Germans and Flemings settled the area (Ostsiedlung), importing German law and improved agricultural techniques. The Wends who survived all warfare and devastation of the centuries before, including invasions of and expeditions into Saxony, Denmark and Liutizic areas as well as internal conflicts, were assimilated in the centuries thereafter. However, elements of certain names and words used in Mecklenburg speak to the lingering Slavic influence. An example would be the city of Schwerin, which was originally called Zuarin in Slavic. Another example is the town of Bresegard, the \'gard\' portion of the town name deriving from the Slavic word \'grad\', meaning city or town.
Since the 12th century, the territory remained stable and relatively independent of its neighbours; one of the few German territories for which this is true. During the reformation the Duke in Schwerin would convert to Protestantism and so would follow the Duchy of Mecklenburg.
Like many German territories, Mecklenburg was sometimes partitioned and re-partitioned among different members of the ruling dynasty. In 1621 it was divided into the two duchies of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Güstrow. With the extinction of the Güstrow line in 1701, the Güstrow lands were redivided, part going to the Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, and part going to the new line of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
In 1815, the two Mecklenburgian duchies were raised to Grand Duchies, the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, and subsequently existed separately as such in Germany under enlightened but absolute rule (constitutions being granted on the eve of World War I) until the revolution of 1918. Life in Mecklenburg could be quite harsh. Practices such as having to ask for permission from the Grand Duke to get married, or having to apply for permission to emigrate, would linger late into the history of Mecklenburg (i.e. 1918), long after such practices had been abandoned in other German areas. Even as late as the later half of the 19th century the Grand Duke personally owned half of the countryside. The last Duke abdicated in 1918, as monarchies fell throughout Europe. The Duke\'s ruling house reigned in Mecklenburg uninterrupted (except for two years) from its incorporation into the Holy Roman Empire until 1918. From 1918 to 1933, the duchies were free states in the Weimar Republic.
Traditionally Mecklenburg has always been one of the poorer German areas, and later the poorer of the provinces, or Länder, within a unified Germany. The reasons for this may be varied, but one factor stands out: agriculturally the land is poor and can not produce at the same level as other parts of Germany. The two Mecklenburgs made attempts at being independent states after 1918, but eventually this failed as their dependence on the rest of the German lands became apparent.
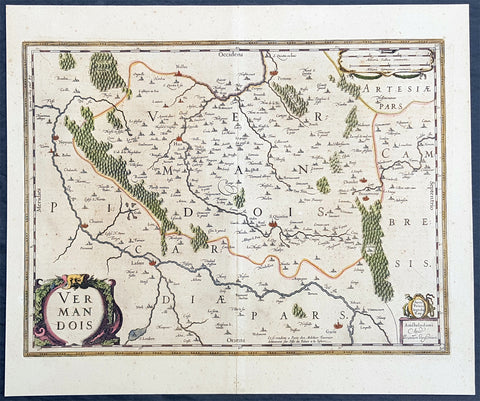
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map the County of Vermandois, Picardy, Northern France
- Title : Vermandois
- Ref #: 50236
- Size: 21 1/2in x 18in (545mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the ancient county of Vermandois now located in the Picardy region of northern France, centering on the city of St Quentin by Jan Jansson was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Vermandois was a French county that appeared in the Merovingian period. Its name derives from that of an ancient tribe, the Viromandui. In the 10th century, it was organised around two castellan domains: St Quentin (Aisne) and Péronne (Somme). In today\'s times, the Vermandois county would fall in the Picardy region of northern France.
Pepin I of Vermandois, the earliest of its hereditary counts, was descended in direct male line from the emperor Charlemagne. More famous was his grandson Herbert II (902–943), who considerably increased the territorial power of the house of Vermandois, and kept the lawful king of France, the unlucky Charles the Simple, prisoner for six years. Herbert II was son of Herbert I, lord of Péronne and St Quentin, who was killed in 902 by an assassin in the pay of Baldwin II, Count of Flanders. His successors, Albert I, Herbert III, Albert II, Otto and Herbert IV, were not as historically significant.
In 1077, the last count of the first house of Vermandois, Herbert IV, received the county of Valois through his wife. His son Eudes (II) the Insane was disinherited by the council of the Barons of France. He was lord of Saint-Simon through his wife, and the county was given to his sister Adela, whose first husband was Hugh the Great, the brother of King Philip I of France. Hugh was one of the leaders of the First Crusade, and died in 1102 at Tarsus in Cilicia. The eldest son of Hugh and Adela was count Raoul I (c. 1120–1152), who married Petronilla of Aquitaine, sister of the queen, Eleanor, and had by her three children: Raoul (Rudolph) II, the Leper (count from 1152–1167); Isabelle, who possessed from 1167 to 1183 the counties of Vermandois, Valois and Amiens conjointly with her husband, Philip, Count of Flanders; and Eleanor. By the terms of a treaty concluded in 1186 with the king, Philip Augustus, the count of Flanders kept the county of Vermandois until his death, in 1191. At this date, a new arrangement gave Eleanor (d. 1213) a life interest in the eastern part of Vermandois, together with the title of countess of St Quentin, and the king entered immediately into possession of Péronne and its dependencies
1646 Jan Jansson Large Antique Map The Island of Bermuda
- Title : Mappa Aestivarum Insularum, alias Barmudas Dictarum ... Accurate Descripta
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93340
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Island of Bermuda by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin of Mercators Atlas by Henricus Hondius & Janson. One of the best examples of this map we have had in some time with original hand colouring, original margins heavy paper and a heavy impression, beautiful map.
A much sought after map of Bermuda, with decorative cartouche, compass rose with the Island divided into lots and tribes, listed at the base of the map.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 3/4in (520mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Like all 17th century maps of Bermuda this map is based ultimately on the survey made by John Norwood of the Bermuda Company in 1618 in the form as published by the English map-maker John Speed in 1627. Although discovered in 1515 by Spaniard Juan de Bermudez, after whom the island is supposedly named, it was the shipwreck of a party of Virginia colonists in 1610 led by Sir George Somers that gave Bermuda its first known inhabitants. The Latin title reflects this fact, for Aestivarum Insularum means summers (or Somers) Islands. The experience of Somers and his men inspired William Shakespeare, who dispatched Ariel to "fetch dew from the still-vext Bermoothes" and populated the islands with the cast of The Tempest.
The place names and the list of Proprietors given below the map itself all recall the original members of the Bermuda Company, the latter being listed as eight tribes (or parishes). In 1610, the Virginia Company, in a True Declaration of the Estate of the Colonie of Virginia, said of Bermuda: These Islands of Bermudos, have evere beene accounted as an inchaunted pile of rocks, and a desert inhabitation for Divels; but all the Faities of the rockes were but flocks of Birds, and all the Divels that haunted the woods, were but heards of Swine. In the upper left-hand and right-hand corners of the map appear the adjacent coasts of the North American colonies of Virginia and New England with, just below the cartouche a tiny outline of Bermuda itself, intended to show its correct proportion and position against the mainland.(Ref Tooley M&B)
1646 Jan Jansson Large, Old Antique Map of Portugal - Portugallia et Algarbia
- Title : Portugallia et Algarbia quae olim Lusitania
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 81055
- Size: 24in x 19in (610mm x 480mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Portugal was published by Jan Jansson in the 1646 Latin edition of Atlas Novus. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 19in (610mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1650 Jan Jansson & Nicolaas Blankaert 3 x Large Antique Maps Europe, Asia & Africa
Antique Map
- Title : Europa Antiqua cum finitimis; Asia antiqua cum finitimis; Africae Antiquae, et quarundam...
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50489, 50490, 50492
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (565mm x 510mm) each
Description:
In 1650 Jan Jansson published three maps of the ancient world, Europe, Asia & Africa, after much considered and detailed work by the Leyden scholar of antiquities Nicolass Blanckaert 1624 - 1703, Latin Nicolaus Blancardus. These three highly detailed maps were only published in limited release and so are incredibly rare, especially as a set.
Nicolaas Blanckaert was a respected expert on the ancient world specialising on the Roman World and Alexander the Great. Three incredibly rare maps in exceptional condition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (565mm x 510mm) each
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15in (510mm x 380mm); 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm); 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Alexander III of Macedon 356 – 323 BC, commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king (basileus) of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon and a member of the Argead dynasty. He was born in Pella in 356 BC and succeeded his father Philip II to the throne at the age of 20. He spent most of his ruling years on an unprecedented military campaign through Asia and northeast Africa, and by the age of thirty, he had created one of the largest empires of the ancient world, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered one of historys most successful military commanders.
During his youth, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle until age 16. After Philips assassination in 336 BC, he succeeded his father to the throne and inherited a strong kingdom and an experienced army. Alexander was awarded the generalship of Greece and used this authority to launch his fathers pan-Hellenic project to lead the Greeks in the conquest of Persia. In 334 BC, he invaded the Achaemenid Empire (Persian Empire) and began a series of campaigns that lasted 10 years. Following the conquest of Anatolia, Alexander broke the power of Persia in a series of decisive battles, most notably the battles of Issus and Gaugamela. He subsequently overthrew Persian King Darius III and conquered the Achaemenid Empire in its entirety. At that point, his empire stretched from the Adriatic Sea to the Beas River.
Alexander endeavoured to reach the ends of the world and the Great Outer Sea and invaded India in 326 BC, winning an important victory over the Pauravas at the Battle of the Hydaspes. He eventually turned back at the demand of his homesick troops, dying in Babylon in 323 BC, the city that he planned to establish as his capital, without executing a series of planned campaigns that would have begun with an invasion of Arabia. In the years following his death, a series of civil wars tore his empire apart, resulting in the establishment of several states ruled by the Diadochi, Alexanders surviving generals and heirs.
Alexanders legacy includes the cultural diffusion and syncretism which his conquests engendered, such as Greco-Buddhism. He founded some twenty cities that bore his name, most notably Alexandria in Egypt. Alexanders settlement of Greek colonists and the resulting spread of Greek culture in the east resulted in a new Hellenistic civilization, aspects of which were still evident in the traditions of the Byzantine Empire in the mid-15th century AD and the presence of Greek speakers in central and far eastern Anatolia until the Greek genocide of the 1920s. Alexander became legendary as a classical hero in the mould of Achilles, and he features prominently in the history and mythic traditions of both Greek and non-Greek cultures. He was undefeated in battle and became the measure against which military leaders compared themselves. Military academies throughout the world still teach his tactics. He is often ranked among the most influential people in history.
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa and West Asia ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus to the military anarchy of the third century, it was a principate with Italy as metropole of the provinces and its city of Rome as sole capital (27 BC – 286 AD). Although fragmented briefly during the military crisis, the empire was forcibly reassembled, then ruled by multiple emperors who shared rule over the Western Roman Empire (based in Milan and later in Ravenna) and over the Eastern Roman Empire (based in Nicomedia and later in Constantinople). Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until 476 AD, when it sent the imperial insignia to Constantinople (Byzantium - Ancient Greek: Βυζάντιον, Byzántion) following the capture of Ravenna by the barbarians of Odoacer and the subsequent deposition of Romulus Augustus. The fall of the Western Roman Empire to Germanic kings, along with the hellenization of the Eastern Roman Empire into the Byzantine Empire, conventionally marks the end of Ancient Rome and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
The predecessor state of the Roman Empire, the Roman Republic (which had replaced Romes monarchy in the 6th century BC) became severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflicts. In the mid-1st century BC Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and proscriptions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesars adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC. The following year Octavian conquered Ptolemaic Egypt, ending the Hellenistic period that had begun with the conquests of Alexander the Great of Macedon in the 4th century BC. Octavians power then became unassailable, and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively making him the first Roman emperor.
The first two centuries of the Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana (Roman Peace). Rome reached its greatest territorial expanse during the reign of Trajan (98–117 AD). A period of increasing trouble and decline began with the reign of Commodus (177-192). In the 3rd century the Empire underwent a crisis that threatened its existence, as the Gallic Empire and Palmyrene Empire broke away from the Roman state, and a series of short-lived emperors, often from the legions, led the empire. The empire was reunified under Aurelian (r. 270–275). In an effort to stabilize the Empire, Diocletian set up two different imperial courts in the Greek East and Latin West in 286. Christians rose to positions of power in the 4th century following the Edict of Milan of 313. Shortly after, the Migration Period, involving large invasions by Germanic peoples and by the Huns of Attila, led to the decline of the Western Roman Empire. With the fall of Ravenna to the Germanic Herulians and the deposition of Romulus Augustulus in 476 AD by Odoacer, the Western Roman Empire finally collapsed – the (Eastern Roman) Emperor Zeno formally abolished it in 480 AD. Nonetheless, some states in the territories of the former Western Roman Empire would later claim to have inherited the supreme power of the emperors of Rome, most notably the Holy Roman Empire. The Eastern Roman Empire, identified by modern historians under the name of the Byzantine Empire, survived for another millennium until the Empires last remains collapsed when Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks of Sultan Mehmed II in 1453.
Due to the Roman Empires vast extent and long endurance, the institutions and culture of Rome had a profound and lasting influence on the development of language, religion, art, architecture, philosophy, law, and forms of government in the territory it governed, and far beyond. The Latin language of the Romans evolved into the Romance languages of the medieval and modern world, while Medieval Greek became the language of the Eastern Roman Empire. The Empires adoption of Christianity led to the formation of medieval Christendom. Greek and Roman art had a profound impact on the Italian Renaissance. Romes architectural tradition served as the basis for Romanesque, Renaissance and Neoclassical architecture, and also had a strong influence on Islamic architecture. The corpus of Roman law has its descendants in many legal systems of the world today, such as the Napoleonic Code, while Romes republican institutions have left an enduring legacy, influencing the Italian city-states republics of the Medieval period, as well as the early United States and other modern democratic republics.
1650 Jan Jansson Antique Map Island of Java, Indonesia - Dutch East India Co
Antique Map
- Title: Insulae Java Cum Parte insularum Borneo Sumatrae
- Date: 1650
- Ref: 60603
- Size: 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large elegant & very impressive hand coloured original antique map, a sea chart of the Indonesian Island of Java including Sumatra, Borneo and Bali was published by Jan Jansson in the 1650 Edition of his "Water World" atlas Atlantis Majoris.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 3/4in (520mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair & ink notations
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Java & the port of Batavia was at the time of publication of the utmost importance to the Dutch East India Company and its domination of the Spice Trade.
This elegant chart focuses on the islands coast with the lack of detail on the interior correctly reflecting the lack of knowledge (or possible lack of importance) to the Dutch, who's primary concern was the sea and sea charts used in the trade of the ever lucrative Spice Trade.
The Dutch capital in the East Indies is Batavia (Jakarta) located on the NW coast. The beautiful chart is richly embellished with two fine cartouche featuring local Javanese warrior and Chinese merchants flanking the title and Neptune and mermaids surrounding the scale of miles... The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia. It was the second multinational corporation in the world (the British East India Company was founded two years earlier) and the first company to issue stock. It was also arguably the first mega-corporation, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, coin money, and establish colonies.
Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asian trade on 4,785 ships, and netted for their efforts more than 2.5 million tons of Asian trade goods. By contrast, the rest of Europe combined sent only 882,412 people from 1500 to 1795, and the fleet of the English (later British) East India Company, the VOC’s nearest competitor, was a distant second to its total traffic with 2,690 ships and a mere one-fifth the tonnage of goods carried by the VOC. The VOC enjoyed huge profits from its spice monopoly through most of the 17th century.
Having been set up in 1602, to profit from the Malukan spice trade, in 1619 the VOC established a capital in the port city of Batavia (now Jakarta) on the Indonesian Island of Java. Over the next two centuries the Company acquired additional ports as trading bases and safeguarded their interests by taking over surrounding territory. It remained an important trading concern and paid an 18% annual dividend for almost 200 years.
Weighed down by corruption in the late 18th century, the Company went bankrupt and was formally dissolved in 1800, its possessions and the debt being taken over by the government of the Dutch Batavian Republic. The VOC's territories became the Dutch East Indies and were expanded over the course of the 19th century to include the whole of the Indonesian archipelago, and in the 20th century would form Indonesia. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1650 Jan Jansson Large Rare Antique Map of India and The Bay of Bengal
Antique Map
- Title : Sinus Gangeticus Vulgo Golfo De Bengala
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 60604
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Description:
This exceedingly impressive hand coloured original antique map of the Bay of Bengal, India - stretching from Sri Lanka to the west coast of Thailand - was published by Jan Jansson in the 1650 Edition of his "Water World" atlas Atlantis Majoris. There were far fewer editions of this atlas published than Janssons more prevalent Atlas Novus.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 19in (545mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Very light spotting
Verso: - Very light spotting
Background:
Maps of India, much distorted in shape, appear in most world atlases from the time of Ptolemy, the earliest usually showing India as a relatively small extension of Southern Asia, dominated by the very large island of Taprobana (Ceylon). In later sixteenth-century maps de Jode, Ortelius and Mercator gave a much improved outline of both lands but India was still shown too small in relation to the whole continent. Most publishers in the seventeenth century continued to issue maps but with little improvement in detail until about 1719 when a French Jesuit priest, Father Jean Bouchet, compiled an accurate map of South India, subsequently used by G. Delisle (1723), Homann Heirs (1735) and by J. B. B. d'Anville, then the French East India Company's cartographer, as the basis for his greatly improved maps in 1737 and 1752.
In the next decade Alexander Dalrymple published a collection of newly surveyed coastal charts and plans of ports and, about the same time, in 1764, James Rennell, a young British Army officer who showed a remarkable aptitude for surveying, was appointed - at the age of 21- Surveyor General of Bengal; he immediately set in motion a comprehensive survey of the Company's lands, subsequently publishing maps of Bengal and other provinces which eventually formed The &ngal Atlas (1779). His other works included a Map of Hindoustan (1782-85) and The Provinces of Delhi, Agra etc and the Indian Peninsula (1788-94). These maps by Reunell provided the basis for a Trigonometrical Survey of India which was initiated in 1802 and for splendid maps published in London by Cary, the Arrowsmiths (1804-22) and the Wylds. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1652 Jan Jansson Antique Map of East & Central Asia, China to Russia - Tartary
Antique Map
- Title : Tartaria sive Magni Chami Imperium
- Date : 1652
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 61166
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This handsome beautifully hand coloured original antique map of huge region of east & central Asia from China, to Central Asia, The Caspian Sea & parts of European Russia was published by Jan Jansson in the 1652 French edition of Atlas Novus.
Background: This handsome map maps the whole of eastern Central Asia from the Caspian Sea to the Great Wall, Northern China and Manchuria.
This map is dated from a time when Tartaria vaguely meant those regions to the north of Persia, west of China & to the east of Russia. The name Siberia only began to be applied with the gradual eastward expansion of the Russian Cossacks into those areas hinted at in the accounts of Marco Polo from three centuries earlier.
The Mythical and legendary nature of the geography of this vast interior is emphasised by the inclusion of devils and dragons in the Desertum Lop to the left of the Great Wall.
The rest of the map is full of detail both real and myth, some of which is no doubt borrowed from the writings of Marco Polo considered at the time one of the foremost expert on China and Central Asia.
The newly discovered northern coastline of Nova Zembla is shown with a notation concerning the Dutch expedition led by Willem Barents in 1594-96. Interesting in Siberia, Ung quae Gog and Sumongul quae Mogog, which refers to the mythological lands of Gog and Magog. These lands, noted in the Bible as being situated in the remotest parts of the earth, were originally depicted on maps just north of Israel. The map extends west to include the Caspien Sea and Russia, but the primary focus of the map is Tartaria, Central Asia, China and Asiatic Russia. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1652 Jansson Large Antique Map Islands of Ischia, Procida & Vivara Naples, Italy
- Title : Ischia Isola olim Aenaria
- Date : 1652
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 61155
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine & beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Italian Islands of Ischia, Procida & Vivara in the the Gulf of Naples in Southern Italy was published in the 1652 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Novus.
Background: Ischia is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, lying at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about 30 kilometres from the city of Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands.
In 6 AD, Augustus restored the island to Naples in exchange for Capri. Ischia suffered from the barbarian invasions, being taken first by the Heruli then by the Ostrogoths, being ultimately absorbed into the Eastern Roman Empire. The Byzantines gave the island over to Naples in 588 and by 661 it was being administered by a Count liege to the Duke of Naples. The area was devastated by the Saracens in 813 and 847; in 1004 it was occupied by Henry II of Germany; the Norman Roger II of Sicily took it in 1130 granting the island to the Norman Aldoyn de Candida created Count d’Ischia; the island was raided by the Pisans in 1135 and 1137 and subsequently fell under the Suebi and then Angevin rule. After the Sicilian Vespers in 1282, the island rebelled, recognizing Peter III of Aragon, but was retaken by the Angevins the following year. It was conquered in 1284 by the forces of Aragon and Charles II of Anjou was unable to successfully retake it until 1299.
As a consequence of the island's last eruption, the population fled to Baia where they remained for 4 years. In 1320 Robert of Anjou and his wife Sancia visited the island and were hosted by Cesare Sterlich, who had been sent by Charles II from the Holy See to govern the island in 1306 and was by this time nearly 100 years of age.
Ischia suffered greatly in the struggles between the Angevin and Durazzo dynasties. It was taken by Carlo Durazzo in 1382, retaken by Louis II of Anjou in 1385 and captured yet again by Ladislaus of Naples in 1386; it was sacked by the fleet of the Antipope John XXIII under the command of Gaspare Cossa in 1410 only to be retaken by Ladislaus the following year. In 1422 Joan II gave the island to her adoptive son Alfonso V of Aragon, though, when he fell into disgrace, she retook it with the help of Genoa in 1424. In 1438 Alfonso reoccupied the castle, kicking out all the men and proclaiming it an Aragonese colony, marrying to his garrison the wives and daughters of the expelled. He set about building a bridge linking the castle to the rest of the island and he carved out a large gallery, both of which are still to be seen today. In 1442, he gave the island to one of his favorites, Lucretia d'Alagno, who in turn entrusted the island's governance to her brother-in-law, Giovanni Torella. Upon the death of Alfonso in 1458, they returned the island to the Angevin side. Ferdinand I of Naples ordered Alessandro Sforza to chase Torella out of the castle and gave the island over, in 1462, to Garceraldo Requesens. In 1464, after a brief Torellan insurrection, Marino Caracciolo was set up as governor.
In February 1495, with the arrival of Charles VIII, Ferdinand II landed on the island and took possession of the castle, and, after having killed the disloyal castellan Giusto di Candida with his own hands, left the island under the control of Innico d'Avalos, marquis of Pescara and Vasto, who ably defended the place from the French flotilla. With him came his sister Costanza and through them they founded the D'Avalos dynasty which would last on the island into the 18th century.
Throughout the 16th century, the island suffered the incursions of pirates and Barbary privateers from North Africa - in 1543 and 1544 Hayreddin Barbarossa laid waste to the island, taking 4,000 prisoners in the process. In 1548 and 1552, Ischia was beset by his successor Dragut Rais. With the increasing rarity and diminishing severity of the piratical attacks later in the century and the construction of better defenses, the islanders began to venture out of the castle and it was then that the historic centre of the town of Ischia was begun. Even so, many inhabitants still ended up slaves to the pirates, the last known being taken in 1796. During the 1647 revolution of Masaniello, there was an attempted rebellion against the feudal landowners. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (460mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1658 Jansson & Hornius Large Antique Map of the Holy Land, Israel, Palestine XII Tribes
Antique Map
- Title : (Situs Terrae Promissionis)
- Ref #: HL
- Size: 71in x 36in (1.801m x 910mm)
- Date : 1658
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large (71in, 1.8m) & very important rare map of the Holy Land, Featuring the Twelve Tribes of Israel by Jan Jansson & George Hornius 8-sheet map of the Holy Land was published in 1658. The map is oriented with east at the top and provides one of the finest large-scale depictions of the Holy Land available in the seventeenth century.
The map is based on Christian van Adricham's 1590 map Situs Terrae Promissionis. Jansson version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Jansson’s Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The single map appears occasionally on the market, but rarely complete sets joined with old color.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abraham's journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 71in x 36in (1.801m x 910mm)
Plate size: - 71in x 36in (1.801m x 910mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Verso: - Folds and joins re-enforced with contemporary paper
Background:
Titles and description of the six individual maps:
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
Tribuum Ephraim, Beniamin, et Dimidiae Manasse intra Iordanem partes occidentales, et partes septentrionales Dan et Iuda. This second panel shows the lands of Ephraim, Benjamin, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan river. More Biblical scenes include a scene where Jonas is cast from a sailing ship into the open jaws of a whale. Also, the panel shows the lands of Palestine and numerous armies.
Tribus Aser, et partes occidentales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. One of two enlarged panels in this series, this map shows the lands of Asher and the western reaches of Zebulon and Issachar. More Biblical illustrations include St. George and the Dragon, the city of Tyre, Nazareth, and the Tabernacle of Abraham.
Dimidia Tribus Manasse Ultra Iordanem, Tribus Neptalim et partes orientales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. The second enlarged panel details the parts of Manasseh lying on the western shores of the Jordan River, the tribe of Naphtali, and parts of the lands of Zebulon and Issachar. This sheet includes the Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberius), as well as several scenes from the life of Jesus, such as his walking on water, Jesus preaching from onboard a boat, and other. The large inset map in the upper left quadrant, entitled Peregrinatio Abrahae, shows the route followed by Abraham from Ur into Canaan.
Pars maxima Tribus Iusa Versus Orientem. This southeastern-most sheet depicts much of the Dead Sea, as well as the lands claimed by the tribe of Judah. It also features the smoking ruins of Sodom, Gomorrah, Adaima, and Seboim. In the upper right, there is a large inset, Itinera et Mansiones Deserti, which shows the route taken by the Hebrews as they fled from Egypt. Finally, it also shows the parting of the Red Sea.
Tribus Simeon et pars meridionalis Tribus Dan, et orientalis Tribus Idua. Usually considered the last in the series, this panel is mountainous, depicting the lands of Simeon, as well as parts of Dan and Judah. It also identifies the lands of the Philistines and timber lands rich in cedar.
Maps of the Holy Land and the early history of Israel
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh.
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
George Hornius
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the “Hornius Map.” Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Hornius’s first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Hornius’s historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Jansson’s Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Hornius’s works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map of the Tribes of Simeon, Dan & Juda
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Simeon et pars meridionalis Tribus Dan, et Oriemtalis Tribus Juda
- Ref #: 50600
- Size: 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map one of six, of the Tribes of Simeon, Dan, & Juda, located to the South West of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major and was based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #6 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
The six panels are individually titled:
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
Tribuum Ephraim, Beniamin, et Dimidiae Manasse intra Iordanem partes occidentales, et partes septentrionales Dan et Iuda. This second panel shows the lands of Ephraim, Benjamin, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan river. More Biblical scenes include a scene where Jonas is cast from a sailing ship into the open jaws of a whale. Also, the panel shows the lands of Palestine and numerous armies.
Tribus Aser, et partes occidentales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. One of two enlarged panels in this series, this map shows the lands of Asher and the western reaches of Zebulon and Issachar. More Biblical illustrations include St. George and the Dragon, the city of Tyre, Nazareth, and the Tabernacle of Abraham.
Dimidia Tribus Manasse Ultra Iordanem, Tribus Neptalim et partes orientales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. The second enlarged panel details the parts of Manasseh lying on the western shores of the Jordan River, the tribe of Naphtali, and parts of the lands of Zebulon and Issachar. This sheet includes the Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberius), as well as several scenes from the life of Jesus, such as his walking on water, Jesus preaching from onboard a boat, and other. The large inset map in the upper left quadrant, entitled Peregrinatio Abrahae, shows the route followed by Abraham from Ur into Canaan.
Pars maxima Tribus Iusa Versus Orientem. This southeastern-most sheet depicts much of the Dead Sea, as well as the lands claimed by the tribe of Judah. It also features the smoking ruins of Sodom, Gomorrah, Adaima, and Seboim. In the upper right, there is a large inset, Itinera et Mansiones Deserti, which shows the route taken by the Hebrews as they fled from Egypt. Finally, it also shows the parting of the Red Sea.
Tribus Simeon et pars meridionalis Tribus Dan, et orientalis Tribus Idua. Usually considered the last in the series, this panel is mountainous, depicting the lands of Simeon, as well as parts of Dan and Judah. It also identifies the lands of the Philistines and timber lands rich in cedar.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12in (405mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map Tribes Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Ruben, et Gad parties orientales tribumum Beniamin, Ephraim, et Dimidiae, Manasse, intra Jordanem
- Ref #: 61037
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, one of six, of the Tribes of Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh located to the north and east of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major, based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #1 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map Tribes Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Ruben, et Gad parties orientales tribumum Beniamin, Ephraim, et Dimidiae, Manasse, intra Jordanem
- Ref #: 17016
- Size: 23in x 18 1/2in (580mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, one of six, of the Tribes of Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh located to the north and east of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major, based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #1 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (580mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map Tribes Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Ruben, et Gad parties orientales tribumum Beniamin, Ephraim, et Dimidiae, Manasse, intra Jordanem
- Ref #: 61037
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, one of six, of the Tribes of Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh located to the north and east of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major, based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #1 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1681 J Jansson & Moses Pitt Rare Antique Map Duchy of Grottkau & Nysa Silesia, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Ducatus Silesiae Grotganus cum Districtu Episcopali Nissensi
- Ref #: 93485
- Size: 23in x 18in (590mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1681
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original rare (not called for in Koeman) hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Duchy of Grottkau and the Diocese of Nysa (Grottkau, Neisse, Brieg and the surrounding area) in the ancient region of Silesia, now in Western Poland by Jan Jansson was published by Moses Pitt in the 1681 edition of Atlas of the World
Moses Pitt 1639–1697 was a bookseller and printer known for the production of his Atlas of the world, a project supported by the Royal Society, and in particular by Christopher Wren. He is also known as the author of The Cry of the Oppressed (1691), an account of the conditions in which imprisoned debtors lived in debtors jails in England.
His work was characterised by its learned content and included authors such as Robert Boyle and Gilbert Burnet. His Atlas was initially intended to be 12 volumes and he continued to undertake other work for the Royal Society. However rising costs, estimated by Pitt at £1000 per volume, contributed to his eventual bankruptcy and only four volumes were ever produced. The second volume had as frontispiece a noted engraved portrait of Queen Catherine of Braganza, by Edward Le Davis.
In Ireland William Molyneux collaborated with Roderic OFlaherty to collect material for the Atlas. While Pitts financial crisis lead to cancellation of the project, much valuable work on early Irish history was collected. Molyneux and OFlaherty struck a friendship and Molyneux assisted when the latters treatise Ogygia was published in London in 1685.
As a result of the Atlas project, Pitt was declared bankrupt. He was taken to the Fleet Prison, and remained there, or in the Kings Bench Prison, for seven years. In 1691, he published The Cry of the Oppressed: Being a True and Tragical Account of the Unparalleld Sufferings of Multitudes of Poor Imprisond Debtors In Most of the Gaols in England, a moving appeal on behalf of prisoners for debt across the country. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18in (590mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 3/4in (510mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Silesia is a historical region of Central Europe mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately 40,000 km2, and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000 inhabitants. Silesia is split into two main sub-regions of Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language.
Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region possesses many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. Silesias largest city and historical capital is Wrocław. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrava and the German city of Görlitz fall within the borders of Silesia.
Silesias borders and national affiliation have changed over time, both when it was a hereditary possession of noble houses and after the rise of modern nation-states. The varied history with changing aristocratic possessions resulted in an abundance of castles, especially in the Jelenia Góra valley. The first known states to hold power in Silesia were probably those of Greater Moravia at the end of the 9th century and Bohemia early in the 10th century. In the 10th century, Silesia was incorporated into the early Polish state, and after its division in the 12th century became a Piast duchy. In the 14th century, it became a constituent part of the Bohemian Crown Lands under the Holy Roman Empire, which passed to the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy in 1526. As a result of the Silesian Wars, the region was annexed by Prussia in 1742.
After World War I, the easternmost part of Upper Silesia was granted to Poland by the Entente Powers after insurrections by Poles and the Upper Silesian plebiscite. The remaining former Austrian parts of Silesia were partitioned to Czechoslovakia, forming part of Czechoslovakias Sudetenland region, and are today part of the Czech Republic. In 1945, after World War II, the bulk of Silesia was transferred to Polish jurisdiction by the Potsdam Agreement between the victorious Allies and became part of Poland, whose Communist government expelled the majority of Silesias previous population. The small Lusatian strip west of the Oder–Neisse line, which had belonged to Silesia since 1815, remained in Germany.
1700 Jan Jansson & Schenk Antique Map of Duchy of Legnica, Silesia South Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Ducatus Silesiae Ligniciensis Pet. Schenk et G Valk
- Ref #: 35636
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 19in x 14 3/4in (480mm x 375mm)
- Date : 1700
- Price: $225US
Description:
This original hand coloured large copper plate engraved antique map of the City and Regions of The Duchy of Legnica (Ligniciensis) in Lower Silesia, southern Poland, after Jan Jansson, was published by Peter Schenk Gerard Valck in 1700.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 14 3/4in (480mm x 375mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (465mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The Duchy of Legnica or Duchy of Liegnitz was one of the Duchies of Silesia. Its capital was Legnica (Liegnitz) in Lower Silesia.
Legnica Castle had become a residence of the Silesian dukes in 1163 and from 1248 was the seat of a principality in its own right, ruled by the Silesian branch of the Piast dynasty until the extinction of the line in 1675. Formed by Bolesław II the Bald, Duke of Lower Silesia at Wrocław, Legnica shared the fate of most of the others Silesian duchies, falling into Bohemian, Austrian and eventually—after the First Silesian War—Prussian spheres of influence.
The town of Legnica became famous for the Battle of Legnica that took place at the nearby village of Legnickie Pole on 9 April 1241, during the Mongol invasion of Poland. A Christian army led by the Polish High Duke Henry II the Pious, supported by the feudal nobility including Poles, Bavarian miners and military orders, was decisively defeated by the Mongols. Although Henry was killed and his forces defeated, their advance into Europe was halted when they turned back to attend to the election of a new Khagan (Grand Khan) following the death of Ögedei Khan in the same year. Minor celebrations are held annually in Legnica to commemorate the battle.
After Henry's death his eldest son Bolesław II the Bald followed him as ruler of Lower Silesia until in 1248 his younger brother Henry III the White came of age and claimed his rights of succession. Backed by the nobility of Wrocław, Henry III forced the duke to cede central parts of Lower Silesia to him, while Bolesław himself retired to Legnica. Furthermore, he came into conflict with his younger brother Konrad, who, originally predestined for an ecclesiastical career as Bishop of Passau, also demanded his distributive share and had to be paid off by Bolesław with the newly created Duchy of Głogów in 1251.
Nevertheless, Bolesław's son Henry V the Fat, who succeeded his father in 1278, was able to enlarge the duchy's territories by defeating his cousin Henry Probus, Duke of Wrocław, and, with support of King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia succeeded him as duke in 1290. Thus, the Lower Silesian duchies of Legnica and Wrocław were re-reunited until 1311.
As after the death of Henry V in 1296 his eldest son Bolesław III the Generous was still a minor, King Wenceslaus took over his guardianship, strengthening the Bohemian influence in Silesia. In 1303 Bolesław III was betrothed to Wenceslaus' daughter Margaret and to no avail tried to follow the extinct Přemyslid dynasty on the Bohemian throne in 1306. He was not able to retain the united duchy and in 1311 Lower Silesia was split again, with Wrocław going to his younger brother Henry VI the Good. Even Bolesław's rule over Legnica was contested by his brother Władysław and in 1329 he had to pay homage to the Bohemian King John of Luxembourg to secure his reign.
As the duchy's capital at the beginning of the 14th century, Legnica was an important city of Central Europe, with a population of approximately 16,000 residents. The city began to expand quickly after the discovery of gold in the Kaczawa.
Piast state from 1329 onwards became a Czech vassal, the political weakness of the duchy continued, caused by domestic conflicts between Bolesław's the Wastefull sons Wenceslaus and Louis the Fair strengthening the influences of the Bohemian monarchs. When in 1419 the Legnica branch of the Silesian Piasts became extinct with the death of Duke Wenceslaus II, the duchy was inherited by Duke Louis II of Brzeg. As Louis himself had no male heirs, Legnica was annexed as a ceased fief by the Bohemian king Sigismund in 1436. A long-standing dispute arose, as the late Duke Louis II had bequeathed his estates to the sons of his step-brother Duke Henry IX of Lubin –though without the consent of the Bohemian overlord. Eventually, in 1455 the duchy was inherited by Frederick I, the son of Louis' daughter Hedwig, who was officially enfeoffed by King Matthias Corvinus in 1469.
Frederick's son Frederick II, Duke from 1499, again inherited the Duchy of Brzeg in 1520. The Protestant Reformation was introduced in the duchy as early as 1522, decisively promoted by the theologians Caspar Schwenckfeld and Valentin Krautwald, and the population quickly turned Lutheran. This led to conflict when, after the death of the Bohemian King Louis II at the Battle of Mohács in 1526, the Lands of the Bohemian Crown including the Legnica fief were incorporated into the Habsburg monarchy of the Catholic king Ferdinand. In turn, Duke Frederick II signed an inheritance pact with the Hohenzollern elector Joachim II Hector of Brandenburg, a cousin of his second wife Sophia. However, King Ferdinand I, rejecting any Hohenzollern influence within the Habsburg lands, declared the agreement null and void.
The struggles continued, though the duchy was officially guaranteed freedom of religion by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia. After the death of the last Piast duke, George William, in 1675, Legnica passed to the direct rule of the Habsburg emperor Leopold I, despite claims raised by Elector Frederick William of Brandenburg referring to the inheritance pact in 1537. For the Prussian king Frederick the Great, the old dispute was a pretext to justify his campaign during the First Silesian War: in 1742 most of Silesia including Legnica was occupied by the Prussian Army after Empress Maria Theresa's defeat in the War of the Austrian Succession. Finally in 1763 the duchy lost most of its privileges after being incorporated into Prussia according to the Peace of Hubertusburg.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.