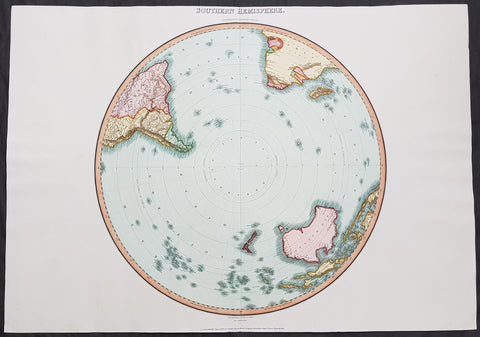
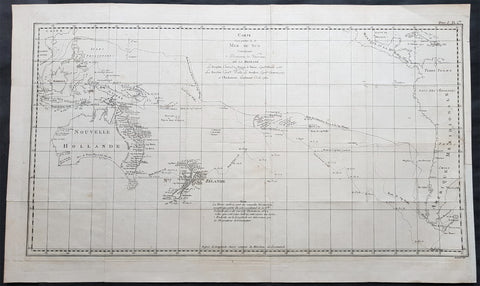
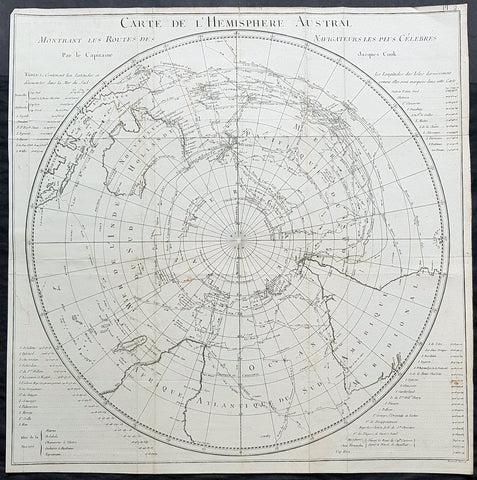
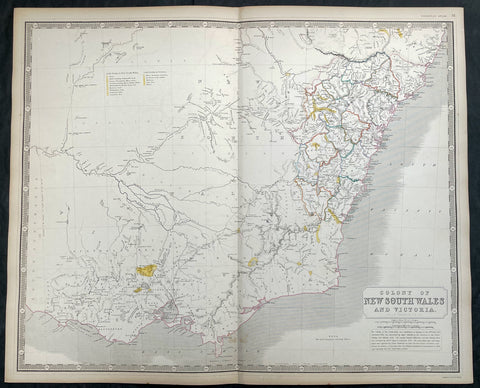
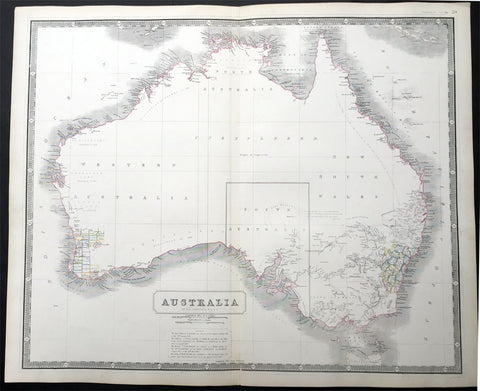
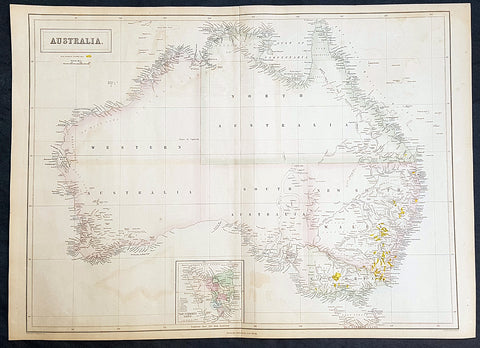
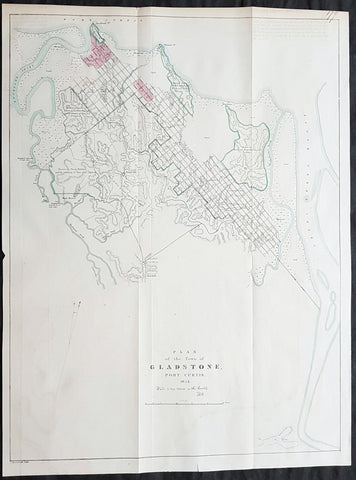
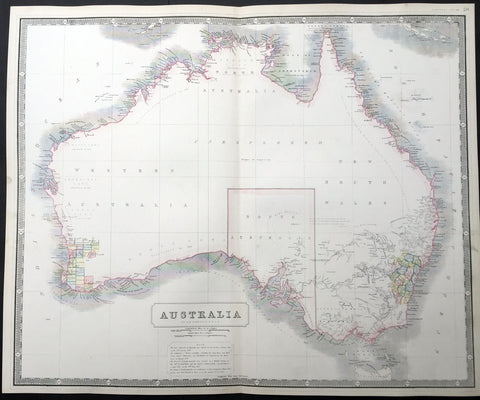
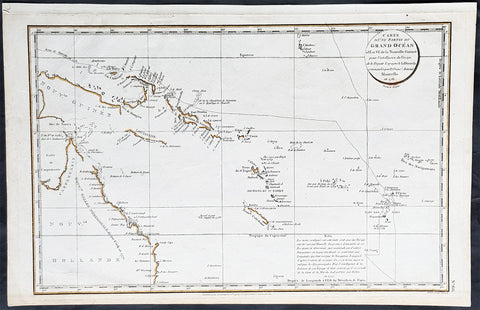
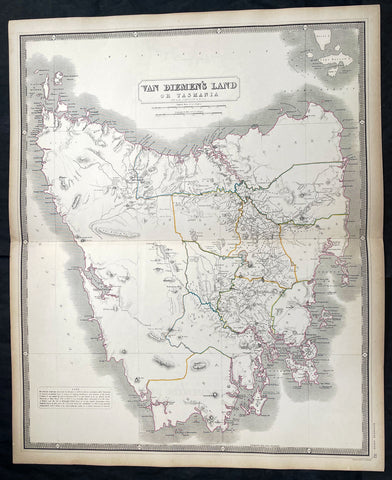
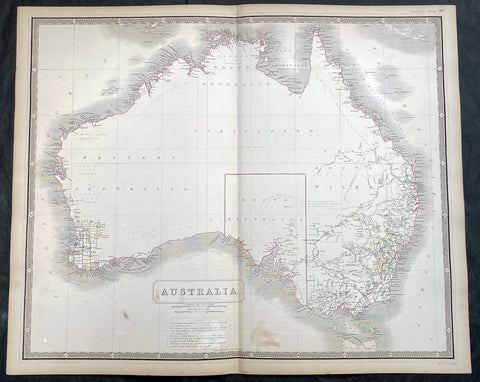
Australia/Oceania (215)
1774, 1777 & 1785 Capt James Cook 3 Atlas Volumes 1st Editions 204 Maps & Prints
- Title : 1. Figure du Banks 2. Premier Voyage De Cook 3. Troisieme Voyage De Cook
- Ref #: 93498, 93499, 93500
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Date : 1774; 1777; 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
A unique and rare opportunity to acquire all three of Captain James Cooks 1st French edition Atlases (4to, Quatro), published to accompany the publication of his 3 voyages of discovery in 1774, 1777 & 1785. The atlases contain a total of 204 large folding, double page and single page maps and prints. It is very rare to find all three atlases complete and available together at the same time.
The contents of all three atlases are in fine condition, with a fresh, heavy impression and clean paper of all maps and prints.
As stated there are 204 maps and prints 51 in the 1st volume, 66 in the second volume and 87 in the second volume. Please view the images above, that include a few images of the 204 maps and prints as well as an itemized list of each volume.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Some scuffing and wear to boards & spines
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Timeline First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Timeline - Second Voyage 1772 - 1775
In July 1772 Resolution, commanded by Captain Cook, and Discovery, commanded by Lieutenant Furneaux, set sail from Britain, via Madiera (Jul-Aug) and Cape Town, South Africa (Oct-Nov), towards the Antarctic in search of the Great Southern Continent.
During January 1773 the ships took on fresh water, charts of the voyage being marked with:
......Here we watered our Ship with Ice the 1st. Time 26S 44W and Here we compleated our Water/26S 20W but became separated in thick fog: Here we parted company…. and The Resolutions Track after we parted Company on the 8 of February 1773......
The ships became the first known to have crossed the Antarctic Circle (17 January 1773). On 9th January Cook wrote:
.......we hoisted out three Boats and took up as much as yielded about 15 Tons of Fresh Water, the Adventure at the same time got about 8 or 9 and all this was done in 5 or 6 hours time; the pieces we took up and which had broke from the Main Island, were very hard and solid, and some of them too large to be handled so that we were obliged to break them with our Ice Azes before they could be taken into the Boats...... Cook, Journals II, 74.)
The ships met again in New Zealand (February-May 1773) and set off to explore the central Pacific, calling at Tahiti (August), where, from the island of Raiatea, they took aboard Omai who returned with the Adventure to England (7 September).
After visiting Amsterdam and Middelburg, two islands that Cook called the Friendly Islands (Tongan group) (October) the ships became separated and never met again. Both ships returned separately to New Zealand. (November) A boats crew from the Adventure were killed by Maori (17 December) and the ship sailed for Britain, arriving July 1774.
Cook on Resolution attempted another search for the Great Southern Continent (November 1773), crossing the Antarctic Circle on 20th December 1773. However, the ice and cold soon forced him to turn north again and he made another search in the central Pacific for the Great Southern Continent. In January 1774 he turned south again, crossing the Antarctic Circle for the second time. Captain Cooks Journal, 2nd January 1774.
Cook sailed north, arriving at Easter Island in March 1774. Cook was too ill to go ashore but a small party explored the southern part of the island. The artist William Hodges painted a group of the large statues of heads (moia) for which the island has become famous.
Cook then sailed to the Marquesas (March); Tahiti (April) and Raiatea (June); past the Cook Islands and Niue, or Savage Islands as Cook called them; Tonga (June); Vatoa, the only Fijian Island visited by Cook (July); New Hebrides (July-August); New Caledonia (September) and Norfolk Island (October); before returning to New Zealand (October 1774).
Not all the peoples of the islands visited by Cook were friendly and when his ship approached Niue the local people would not let his crew ashore. Cook wrote:
.......The Conduct and aspect of these Islanders occasioned my giving it the Name of Savage Island, it lies in the Latitude of 19 degrees 1 Longitude 169 degrees 37 West, is about 11 Leagues in circuit, of a tolerable height and seemingly covered with wood amongst which were some Cocoa-nutt trees......(Cook, Journals II, 435, 22 June 1774.)
En route for New Zealand, Cook sailed west and explored the islands which he called the New Hebrides, now known as Vanuatu, arriving on 17 July 1774. The people were Melanesian, not Polynesian, and spoke different languages and had different customs. Cook recorded:
........The Men go naked, it can hardly be said they cover their Natural parts, the Testicles are quite exposed, but they wrap a piece of cloth or leafe round the yard (nautical slang for the penis) which they tye up to the belly to a cord or bandage which they wear round the waist just under the Short ribs and over the belly and so tight that it was a wonder to us how they could endure it.......(Cook, Journals II, 464, 23 July 1774)
Cook sailed past or visited nearly all the islands in the group, including landfalls at Malekula, Tanna and Erromango. He later moved on to New Caledonia.
Cooks reception by the New Hebrideans was generally hostile. At Erromango during the landing on 4th August 1774 the marines had to open fire when the natives tried to seize the boat and started to fire missiles. Cook wrote:
....…I was very loath to fire upon such a Multitude and resolved to make the chief a lone fall a Victim to his own treachery…happy for many of these poor people not half our Musquets would go of otherwise many more must have fallen.......(Cook, Journals II, 479, 4th August 1774)
Some of Cooks crew were slightly injured but several natives were wounded and their leader killed. Back on the ship Cook had a gun fired to frighten off the islanders and decided to depart.
Cook left New Zealand to return to Britain via the Southern Ocean in November 1774 and arrived in Tierra del Fuego, South America, in December. Cook took on stores and spent the holiday in what he called Christmas Sound. He described the area:......except those little tufts of shrubbery, the whole country was a barren Tack (or Rock) doomed by Nature to everlasting sterility......(Cook, Ms Journal PRO Adm 55/108)
Cook left South America in early January 1775 and set off across the southern Atlantic for Cape Town, South Africa. On the way he tried to confirm the location of a number of islands charted by Alexander Dalrymple on an earlier voyage. On 17 January 1775 Cook arrived at the cold, bleak, glaciated island he called South Georgia and spent 3 days charting it before sailing on.
Cook headed east and in late January came across the South Sandwich Islands that he again charted and then sailed on to Cape Town, arriving in late March 1775. He then headed across the Atlantic via St. Helena and Ascension Island (May), the Azores (July) and landed at Portsmouth on 30th July 1775.
On his return Cook became a national hero. He was presented to the King, made a member of the Royal Society and received its Copley Medal for achievement. Cook was promoted to post-captain of Greenwich Hospital and wrote up his account of the voyage. This did not mean retirement for Cook who went on his third and final voyage the following year.
The second voyage was one of the greatest journeys of all time. During the three years the ships crews had remained healthy and only four of the Resolutions crew had died. Cook disproved the idea of the Great Southern Continent; had become the first recorded explorer to cross the Antarctic Circle; and had charted many Pacific islands for the first time.
Timeline - Third Voyage 1776 - 1780
In 1776 Cook sailed in a repaired Resolution (July) to search for the North West Passage and to return Omai to his home on Huahine in the Society Islands.
He sailed via the Canary Islands and was joined at Cape Town, South Africa, by the Discovery, commanded by Charles Clerke.
The Discovery was the smallest of Cooks ships and was manned by a crew of sixty-nine. The two ships were repaired and restocked with a large number of livestock and set off together for New Zealand ( December).
Cook sailed across the South Indian Ocean and confirmed the location of Desolation Island, later known as Kerguelen Island. Cook wrote of Christmas Harbour where he first anchored on 25th December 1776:
........I found the shore in a manner covered with Penguins and other birds and Seals…so fearless that we killed as ma(n)y as we chose for the sake of their fat or blubber to make Oil for our lamps and other uses… Here I displayd the British flag and named the harbour Christmas harbour as we entered it on that Festival........(Cook, Journals III, i, 29-32)
Cook sailed east, arriving at Van Diemens Land/Tasmania (January 1777) and Queen Charlottes Sound, New Zealand (February). The Maori were wary at first, expecting Cook to take revenge for the killing of members of the Adventures crew in 1773, but instead Cook befriended the leader of the attack.
The ships stayed for nearly two weeks in New Zealand, restocking with wild celery and scurvy grass and trading with the local Maori who set up a small village in Ship Cove. Cook set off around the islands of the south Pacific (February), visiting the Cook Islands (April); Tongan Islands (July); and Tahiti (August-December 1777)
In 1778 Cook visited the Hawaiian islands, or Sandwich Islands as he named them, for the first time. Cook wrote:
........We no sooner landed, that a trade was set on foot for hogs and potatoes, which the people gave us in exchange for nails and pieces of iron formed into some thing like chisels….At sun set I brought every body on board, having got during the day Nine tons of water….about sixty or eighty Pigs, a few Fowls, a quantity of potatoes and a few plantains and Tara roots.......(Cook, Journals III, i. 269 & 272)
In February 1778 Cook sailed from the Hawaiian Islands across the north Pacific to the Oregan coast of North America. He travelled up the coast in bad weather until he found a safe harbour, Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada. There he refitted the ships, explored the area and developed relations with the local people.
Cook described a village there, probably Yoquot:
….their houses or dwellings are situated close to the shore…Some of these buildings are raised on the side of a bank, theses have a flooring consisting of logs supported by post fixed in the ground….before these houses they make a platform about four feet broad…..so allows of a passage along the front of the building: They assend to this passage (along the front of the building) by steps, not unlike some at our landing places in the River Thames........(Cook, Journals III, i, 306)
Cook left Nootka Sound in April 1778 and sailed north along the Alaskan coast looking for inlets that might lead to the Northwest passage but was then forced to turn south. By July he had rounded the Alaskan Peninsula and was able to sail north again, visiting the Chukotskiy Peninsula, Russia, before heading out into the Bering Sea.
Cook described the summer huts, or yarangas, of the Chukchi people as:
.........pretty large, and circular and brought to a point at the top; the framing was of slight poles and bone, covered with the skins of Sea animals…About the habitations were erected several stages ten or twelve feet high, such as we had observed on some part of the American coast, they were built wholly of bones and seemed to be intended to dry skins, fish &ca. upon, out of reach of their dogs........(Cook, Journals III, I, 413)
After entering the Bering Sea on 11th August 1778, Cook crossed the Arctic Circle and went as far north as latitude 70 degrees 41 North before being forced back by the pack ice off Icy Cape, Alaska. On the ice all around the ships were large numbers of walruses. About a dozen of these huge animals were killed to replenish the supplies of fresh meat and to provide oil for the lamps.
Cook had to turn west and worked his way down the Russian coast, eventually heading south and east into Norton Sound, Alaska, in September 1778. He wrote of their very brief encounter with the inhabitants of Norton Sound:
....…a family of the Natives came near to the place where we were taking off wood…I saw no more than a Man, his wife and child…...(Cook, Journals III, I, 438)
After a short period spent searching for the Northwest Passage Cook realised that it was too late in the year to make any progress and so sailed for warmer winter quarters in the Hawaiian Islands, arriving there in December 1778.
After circumnavigating the big island of Hawaii for over a month the ships finally anchored in Kealakekua Bay on 16th January 1779. The Hawaiians in over 1000 canoes came out to welcome them, the arrival of the ships coinciding with celebrations to mark the religious festival of Makahiki to the god Lono. The Hawaiians seem to have treated Cook as a personification of the god and at first relations were good on this second visit. However, relationships became strained and Cook left the island on 4th February 1779.
When Cook left Hawaii his ships ran into gales which broke a mast, forcing him to return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs on 11th February. This time the native people were less friendly and stole the cutter of the Discovery. The next day, the 14th February 1779, Cook went ashore to take the Hawaiian king into custody pending the return of the cutter but a fight developed and Cook, four of his marines and a number of natives were killed. Cooks remains were buried at sea in Kealakekua Bay.
Charles Clerke took over command of the stunned expedition and explored the other Hawaiian islands before sailing north to search for the North-West Passage. The ships called at Kamchatka, Russia, (April-June) where they were welcomed by the governor, Behm, at Bolsheretsk. Behm took news of the expedition and Cooks death overland to St. Petersburg from where it reached Europe and Britain.
Having made another voyage into the Arctic in search of the Northwest Passage (June-July) the ships returned to Kamchatka in August. In November they set off sailing south along the east coast of Japan, between Taiwan and the Phillipines and arrived at Macao, China, in December.
In January 1780 the expeditions left for home, crossing the Indian Ocean, calling at Cape Town (April-May) and arriving back in Stromness, Orkney, in August but not returning to London until October 1780.
News of Cooks death reached Britain in January 1780, ahead of the return of Resolution and Discovery in October 1780. The voyage was written up and published and Cooks life gradually commemorated in articles, books, medals and monuments.
The achievements of the voyage were overshadowed by the deaths of both Cook and his second-in-command, Clerke. The main purpose of the voyage, the discovery of the Northwest Passage, was not realised but large tracts of the Pacific and Arctic coasts of America and Russia were charted.
Early attempts to summarise the life of Cook appeared in the popular press soon after news of his death reached Britain. Articles in journals such as the Westminster Magazine, published in January 1780, included Biographical Anecdotes of Capt. Cook, charting his life from his birth in Marton, North Yorkshire. The first published biography of Cook, Life of Captain James Cook, by Andrew Kippis, appeared a few years later in 1788.
1774 Cook & Hawkesworth Antique Atlas of Australia, New Zealand 52 Maps & Prints
Antique Map
- Title : Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique, actuellement régnante ; pour faire des découvertes dans l'hémisphère méridional, et successivement exécutés par le Commodore Byron, le Capitaine Carteret, le Capitaine Wallis & le Capitaine Cook dans les vaisseaux. MDCCLXXIV (1774)
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1774
- Ref #: 35632
Description:
This original antique Atlas containing 52 maps and prints, as called for, from some of the foremost explorers of the mid 18th century, including Commodore Byron, Captain Carteret, Captain Wallis & Captain James Cook, was published as the 1st French edition of Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique: (Maps and Figures of Travels undertaken by Order of his Present Reigning British Majesty) in 1774, published after only a year after the 1st English edition by John Hawkesworth.
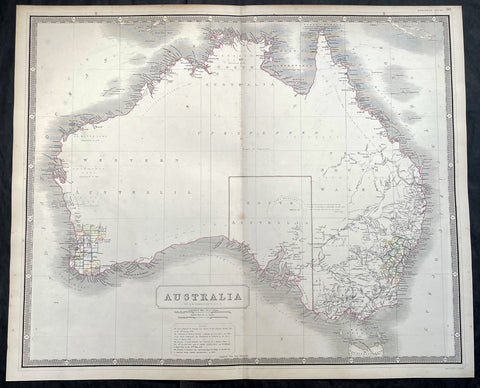
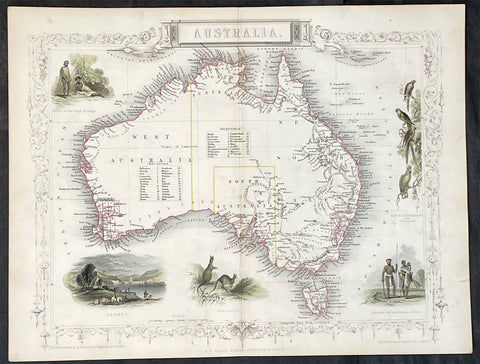
The 52 prints and maps contained in this atlas chart in maps, prints and plans, the progression in the exploration of the South Seas of the 4 explorers. But there is of course, the standout amongst these 4 explorers and that is of course Captain James Cook.
At the time of the publication of this tome, Cook had returned from his first voyage of exploration to The South Pacific, becoming the first European to survey and chart the coastline of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia. But at this point Cook was not as famous as he was destined to become, after completing 2 more voyages of exploration, and in turn becoming the most famous explorer of his era.
The majority of this atlas contains the prints and maps dedicated to Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery including the two famous maps, one of New Zealand and the other the East Coast of Australia. All voyages can be tracked from the first large folding map of the South Seas, at the beginning of the Atlas, that illustrates the tracks on Cook and the other 3 explorers.
In-4 binding in half-calf, spine with five bands with gilding boxes and title label complete with 52 folding & single plates
Spine & boards in poor condition with lack of leather and scratched covers, contents tights with plates in very good condition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning - Maps & Prints
Plate area: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Verso: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Background:
Capt. Cook First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Vice-Admiral John Byron (1723-1786) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is known for his circumnavigation of the globe aboard the HMS Dolphin, completing one of the first British expeditions to achieve this feat. His account of the voyage, "The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron," influenced subsequent explorations. Byron's naval career included service in the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War.
Rear-Admiral Philip Carteret (1733-1796) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is best known for his role as the captain of HMS Swallow during the first circumnavigation of the globe. Carteret's expedition, which took place from 1766 to 1769, aimed to explore and map uncharted regions of the Pacific Ocean. His discoveries included the Carteret Islands and the Pitcairn Islands. Carteret's voyage greatly contributed to the knowledge of Pacific geography and exploration during that time.
Samuel Wallis (1728-1795) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is renowned for leading the first recorded European expedition to visit Tahiti and for his significant contributions to the exploration of the Pacific Ocean. In 1766, Wallis commanded HMS Dolphin on a voyage funded by the British Admiralty. During the expedition, he discovered and named several islands, including Tahiti, which he encountered in June 1767. Wallis's visit to Tahiti marked the beginning of sustained European contact with the island and its inhabitants. His exploration efforts and subsequent reports greatly expanded European knowledge of the Pacific region. Wallis's achievements laid the foundation for future explorations and influenced subsequent voyages of exploration in the Pacific.
John Hawkesworth 1715 -1775
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cooks view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Cook , Capt. James 1728-1779
James Cook was born on 27 October 1728 in Marton, England. His father was a poor farm labourer who had worked his way up to Overseer. James began as a farm labourer and grocer\\\'s assistant. He soon found employment on the Baltic sea in a Collier (coal transport ship) at the age of 18.
During the war with the French in 1755, James Cook enlisted as an Able Seaman on the Eagle. Within a month he was promoted, because of outstanding ability, to Masters Mate. Four years later he was promoted to Master. In command of his own ship, James Cook performed a crucial charting of the St. Lawrence River, which made possible the great amphibious assault upon Quebec City in 1759. In 1763 he was given command of the schooner Grenville to survey the eastern coasts of Canada over a four year period. These excellent charts were used up until the early part of the 20th century.
James Cook was selected to lead a 1768 expedition to observe the transit of Venus, and to explore new lands in the Pacific Ocean. In his first Pacific voyage, James Cook rounded Cape Horn in the Endeavour and reached Tahiti on 3 June 1769. After recovering a necessary scientific instrument stolen by the natives, the transit of Venus was successfully observed. The Endeavour then spent six months charting New Zealand. James Cook next explored and claimed possession of eastern Australia. Returning to England, on 12 June 1771, via New Guinea, Java and the Cape of Good Hope, the crew suffered an appalling 43% fatality rate. James Cook thus became very concerned about crew health on subsequent voyages. He instituted compulsory dietary reforms that were copied by many other ship captains.
The object of Captain Cook\\\'s second Pacific Ocean voyage was to confirm the existence of a theorized Great Southern Continent. His ship the Resolution, accompanied by the Adventure, departed Plymouth on 13 July 1772 and sailed around the Cape of Good Hope. Beset by ice, he was unable to reach Antarctica. Although its existence was suspected, James Cook demonstrated, by traversing large areas of the south Pacific, that it would have to be a frigid wasteland, and not an economically productive addition to the British empire. James Cook charted many of the South Pacific islands with the incredible accuracy of 3 miles. This accuracy was made possible by a new and highly accurate clock. The two ships returned to England, via Cape Horn, on 29 July 1775. The experimental diets and close attention to cleanliness had a miraculous effect: out of a crew of 118, only one man was lost to disease! Since public interest was high, the many paintings by the artists were widely displayed and published as engravings. James Cook was also awarded the Copley Gold Medal and elected as a fellow of the Royal Society.
The third great voyage is especially significant to the history of the west coast of North America. Captain Cook and his men were primarily searching for the Northwest Passage from the Pacific Ocean to the Atlantic Ocean. They departed Plymouth on 12 July 1776 in the Resolution and the Discovery.
The ships sailed around the Cape of Good Hope to reach the west coast of America in February of 1778. They continued north along the coast in haste to the Bering Sea and Bering Strait in an attempt to pass through the Arctic Ocean during the summer season. Foiled by ice, James Cook returned to Hawaii to prepare for another attempt at the Northwest Passage the next season. Soon after they had departed, a storm damaged the foremast of the Resolution and forced a return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs. Unfortunately, they had previously overstayed their welcome and relations became tense. The theft of a ship\\\'s cutter led Captain Cook to put ashore to demand the return of the boat. A fight broke out and James Cook was killed on 14 Feb 1779 by angry natives. Although his men made another attempt at the Northwest Passage, they were unsuccessful. The expedition did identify the possibilities of trade with the coastal American natives for otter seal furs, which could then be bartered for Chinese goods that were highly prized in England.
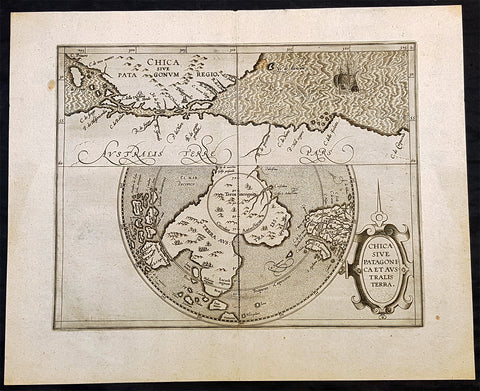
1597 Cornelis Wytfliet Antique Map Early Important Map of Australia, South America Terra Australis
- Title : Chica Sive Patagonica et Australis Terra
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1597
- Ref #: 41718
Description:
A fine original antique, and incredibly important map of Patagonia & the Magellan Straits but more importantly one of the first maps to depict a distinctive outline of Australia - depicted here as part of Terra Australis the Great Southern Land - and was published by Cornelis van Wytfliet in the 1597 edition of Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum.
Wytfliets famous map of the southern continent from the first atlas of the Americas, Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum, sive Occidentis Notitia in 1597.
In the top part of the map, Patagonia is separated by a strait from a large southern continent named Australis Terrae Pars. The naming of C. Della Victoria and the illustration of Magellans ship, Victoria, indicates, although not names on the map, as the Strait of Magellan. The lower portion of the map is a polar projection, showing Terra Australis as the large landmass made up of four peninsulas, one reaching towards New Guinea which is shown as an island. This and the other peninsula to the west is one of the earliest and clearest indications of cartographical knowledge of Northern Australia, specifically Northern Queensland, the Gulf of Carpentaria & parts of the Northern Territory.
Gunter Schilder discusses this map at length and points to its significance to Major Collingridge and others as proof that Australia had already been discovered in the sixteenth century....
Wytfliet notes The Australis Terra is the most southern of all lands; it is separated from New Guinea by a narrow strait; its shores are hitherto but little known, since, after one voyage and another, that route has been deserted, and seldom is the country visited unless when sailors are driven there by storms. The Australis Terra begins at two or three degrees from the equator, and is maintained by some to be of so great an extent that if it were thoroughly explored it would be regarded as a fifth part of the world.
Wyfliets depiction of a narrow strait separating Australis Terra from New Guinea, predates that of Torress discovery in 1606. Torress passage was not known to the world until the end of the 18th century, when Dalrymple discovered Torress journal of the voyage amongst archives in Manila.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/4in x 9 1/4in (285mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1597 Cornelis van Wytfliet published his Augmentum to Ptolemys Geography. Dedicated to Philip III of Spain it is a history of the New World to date, recording its discovery, natural history etc. For the book Wytfliet had engraved nineteen maps, by whom we do not know, one of the world and eighteen regional maps of the Americas. As such this book can be truly called the first atlas of the New World, America.
Wytfliet, Cornelis van d. 1597
Cornelius Wytfliet or Cornelis van Wytfliet was a geographer from Leuven in the Habsburg Netherlands, best known for producing the first atlas of the Americas.
Cornelius was the son of Catherine Huybrechts and her husband, Gregorius Wytfliet, who was advocate fiscal of Leuven University from 1557 to 1594. After graduating Licentiate in Laws from the University of Leuven, Wytfliet moved to Brussels and became secretary to the Council of Brabant. He died in or shortly after 1597, when his Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum (a work adding new discoveries to Ptolemy\\\'s description of the world) was published
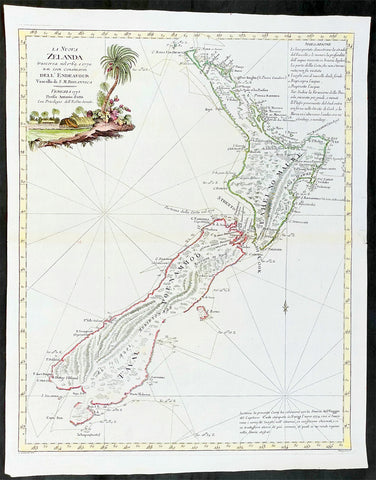
1778 Antonio Zatta Antique Map of New Zealand af. Captain James Cook - Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : La Nuova Zelanda trascorsa nel 1769 e 1770 d'al Cook Comandante dell' Endeavour Vascello di S. M. Britannica . . . 1778
- Ref #: 93527
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Date : 1778
Description:
This impressive original hand coloured copper-plate engraved very early antique map of New Zealand, after Captain James Cook, was engraved in 1778 (the first edition with a second dated 1791) was published by Antonio Zatta in his 1779 edition of Atlante Novissimo
This is a beautifully engraved map after Captain James Cooks surveys of 1769. Cook published the first compete map of NZ in 1774, with this more decorative map being published by Zatta some 4 years later. The map contains all of Cooks coastal survey detail with some details of the interior of the islands. Also included are the tracks of Cooks ship HMS Endeavour as he surveyed the coast as well as his approach and exit from New Zealand. Beautiful original hand colour, with a heavy impression denoting an early pressing.
The maps of Venetian publisher Antonio Zatta are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (455mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
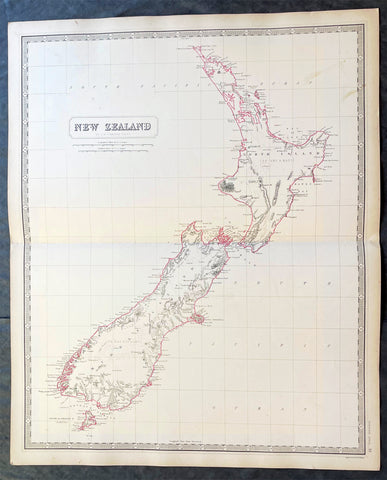
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land "Nieuw Zeeland" after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasman's place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including 'Cape Maria van Diemen' (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the 'Three Kings' islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty's choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via "Secret Instructions" to be opened once at sea.
Cook's party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cook's intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavour's voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cook's crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavour's return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cook's second voyage, and was related to Cook's wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawke's Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavor's crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cook's "Banke's Island" is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the "Isle Solander" to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cook's first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cook's chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cook's very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
Zatta, Antonio fl. 1757 - 1797
Antonio Zatta was a prominent Italian editor, cartographer, and publisher. Little is known about his life beyond his many surviving published works. It is possible that he was born as early as 1722 and lived as late as 1804. He lived in Venice and his work flourished between 1757 and 1797. He is best known for his atlas, Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785), and for his prolific output of prints and books that were both precisely made and aesthetically pleasing. Zatta clearly had a large network from which to draw information; this is how he was able to publish the first glimpse of the islands visited by Captain Cook in the Atlante Novissimo.
Zattas maps are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. His re-engraving and publication of John Mitchells famous map of North America A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America in 1778, is considered one of the best re-issues of this seminal, landmark map .
......He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.... (Portinaro & Knirsch, The Cartography of North America, 1500-1800, p. 319).
Zatta was among the leaders in the eighteenth-century revival of fine printing in Italy and his choice of the text of Raynal to support his re-issue of Mitchells Map, is not surprising. Anne Palms Chalmers describes Zatta as a sardonic writer with the focus of a certain amount of political controversy (Venetian Book Design in the Eighteenth Century, The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, New Series, Vol. 29, No. 5, January 1971, pp. 226-235). Chalmers describes Zattas printing and design as harmonious in composition with ornament unified by style, quality of line, and tone of printing.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
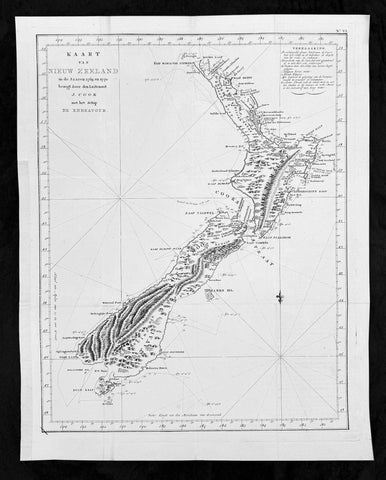
1774 Captain James Cook Antique Map, 1st Printed Chart of New Zealand. Dutch Ed. - Scarce
Antique Map
- Title : Kaart van Nieuw Zeeland in de Jaaren 1769 en 1770 bezogt door den Luitenant J Cook met het Schip De Endeavour (Chart of New Zealand explored in 1769 and 1770 by Lieutenant. J. Cook Commander of his Ship Endeavour)
- Date : 1774
- Size: 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35674
Description:
This magnificent large original copper plate engraved scarce antique map, the first printed chart of New Zealand by Captain James Cook, during his circumnavigation of the South Pacific in 1769-70, was published in the 1st Dutch edition of Hawkeworths Voyages in 1774 by Reiner Arrenberg Reizen Rondom de Weereld Ondernomen op Bevell van Zyne Majesteit den Tans Regeerenden Koning van Groot-Brittanje tot Het Doen van Ontdekkingen ... J. Hawkesworth Uit Het Engelsch Vertaalt,
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 394mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty\\\'s choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
1753 Diderot & Bellin Antique Atlas History of Early Voyages to Australia w/ Map
Antique Atlas
- s Diderot & Nicolas BellinTitle : Histoire Generale Des Voyages ou Nouvelle Collection De Toutes Les Relations de Voyages Par Mer et Par Terre, Qui ont ete publiees jusqu a present dans les differentes Langues de toutes les nations connues.....Tome Quarante - Deuxieme A Paris Chez Didot....MDCCLIII
(General History of Travels or New Collection of all Travel reports by Sea and land, which have been published unitl now in the different languages of all known nations....volume 42...Didots...1753) - Ref #: 51002
- Size: 12mo (7in x 4in)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original antique atlas of early voyages of discovery to the South Seas and significantly Australia was published by the famous French writer & publisher of the French Enlightenment Denis Diderot in his significant publication Historie Generale Des Voyages in 1753 - dated.
The atlas contains 381 pages, one of the earliest complete copper plate maps of Australia (13in x 10in) by Nicolas Bellin along with 2 copper plate prints of plants by Dampier in the late 17th century. The atlas has original marbled end papers contained within contemporary mottled calf bindings, gilt spines in compartments with morocco labels.
This atlas is in beautiful fine condition, clean crisp paper, fine map and prints contained within a beautiful tight calf bindings and spine.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Book size: - 12mo (7in x 4in)
Imperfections:
Margins: - See above
Plate area: - See above
Verso: - See above
A significant publication which includes accounts of many early voyages to Asia & the southern hemisphere. The voyages include
1. Introduction
2. Francois Plesart 1629 - 1630
3. Abel Tasman 1642 - 1643
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
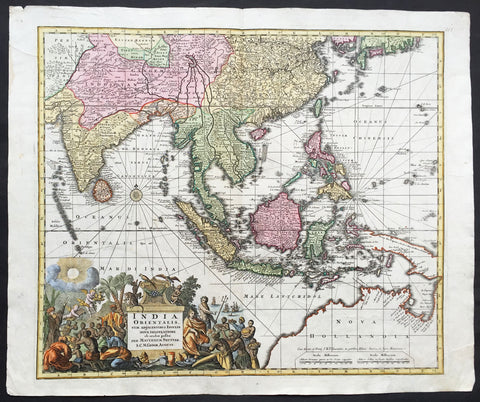
1730 George Seutter Large Antique Map of Australia, East Indies, SE Asia, China
Antique Map
- Title: India Orientalis cum Adjacentibus Insulis Nova Delineatione ob oculos posita ..Matth. Suettro.
- Date: 1730
- Condition: (A+) Condition
- Ref: 43155
- Size: 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Description: This large, scarce & beautifully hand coloured original map of Australia & SE Asia was published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730. This is one of the best examples of this map I have seen, especially with the colouring. In excellent condition, a must in any Australian or SE Asian collection.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/4in (580mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: The map extends from China, Japan and Persia in the North and in the south stretching from The Maldives east to Northern Australia. Of note, Australia continues to be attached to Nova Guinea, albeit with some hesitation, as the image extends outside the inner neat-line to convey this information - even though 20+ names are confidently engraved around Northern Australia Coastline. The detail throughout Southeast Asia is informative and up-to-date and the print style typically strong. The cartouche is one of Seutter's most ornate, with elaborate scenes from sea, land, jungle and mythology. This map rarely appears on the market, as it was only included in select copies of Seutters atlas. (Ref: Norwich; M&B; Tooley)
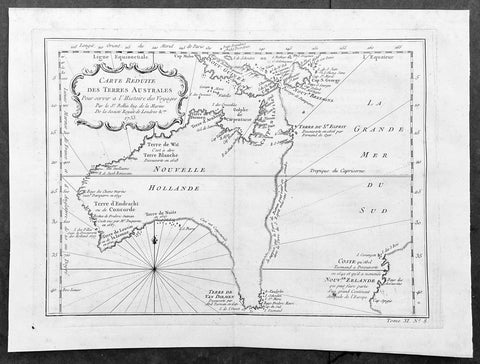
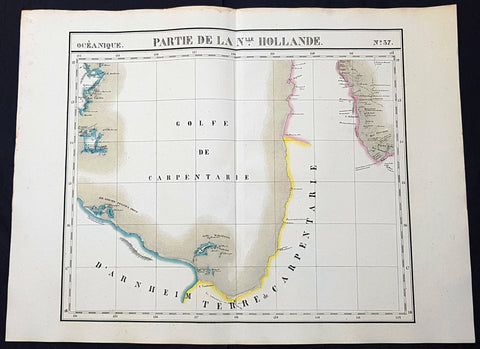
1753 Bellin Antique Map of Australia & New Zealand - Carte Reduite.....Australes
Antique Map
- Title : Carte Reduite des Terres Australes pour Servir a l'Histoire des Voyages...1753
- Ref #: 17027
- Size: 13 1/2in x 10in (340mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of Australia - one of the earliest, near complete maps, dedicated to the Island Continent - was engraved in 1753 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin - date engraved in the title -and was published in Antoine Prevosts Histoire Generale Des Voyages.
Background: This is one of the few 18th century maps to focus on the Australian continent prior to Cook's famous first voyage from 1768-1771. Mainland Australia is connected to both Tasmania (Terre de Van Diemen) and Papua New Guinea (Nouv. Guinee). Along the imaginary eastern coastline is a note that reads: "I suppose that the land of Diemen can join with the land of the Holy Ghost, but this is without proof." A partial coastline of New Zealand is shown peeking out of the corner of the map, with a note that it was discovered by Abel Tasman in 1642 and speculation that it might be part of a great southern continent. This is an important map of Australia depicting the interesting theories made prior to exploration of the region later in the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 10in (340mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 8 1/2in (295mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
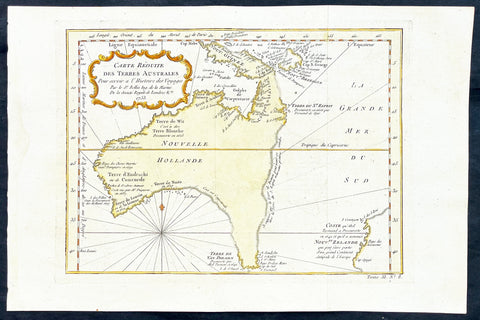
1753 Bellin Antique Map of Australia & New Zealand - Carte Reduite.....Australes
Antique Map
- Title : Carte Reduite des Terres Australes pour Servir a l'Histoire des Voyages...1753
- Ref #: 17040
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Australia - one of the earliest, near complete maps, dedicated to the Island Continent - was engraved in 1753 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin - date engraved in the title -and was published in the 1753 edition of Prevosts Histoire Generale Des Voyages.
Background: This is one of the few 18th century maps to focus on the Australian continent prior to Cook's famous first voyage from 1768-1771. Mainland Australia is connected to both Tasmania (Terre de Van Diemen) and Papua New Guinea (Nouv. Guinee). Along the imaginary eastern coastline is a note that reads: "I suppose that the land of Diemen can join with the land of the Holy Ghost, but this is without proof." A partial coastline of New Zealand is shown peeking out of the corner of the map, with a note that it was discovered by Abel Tasman in 1642 and speculation that it might be part of a great southern continent. This is an important map of Australia depicting the interesting theories made prior to exploration of the region later in the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 8 1/2in (295mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
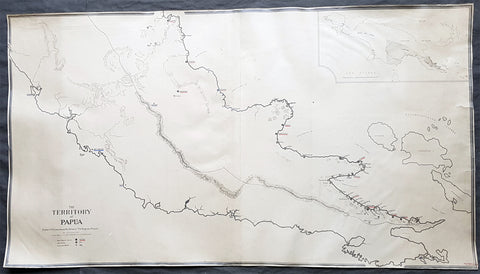
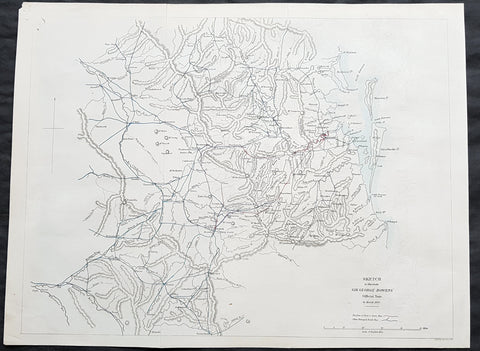
1930 Evan Gill Antique Map of Missions in PNG - Brother to Eric & MacDonald Gill - Unique
- Title : The Territory of Papua Eastern Portion shoqing the Stations of The Anglican Missions...Evan R Gill 1930.
- Size: 34in x 19in (865mm x 485mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1930
- Ref #: 92580
Description:
This unique manuscript original antique map of Papua New Guinea ,and the Stations of the Anglican Missions in the eastern portion of the country, was drawn by Evan Robertson Gill, brother of the Arts and Crafts artist Eric Gill and map-maker Macdonald - Max - Gill in 1930 - dated.
The maps is also signed and addressed on the verso of the map by Evan.
This map was purchased a number of years ago but its significance only became apparent later with the direct connection to Evans (in)famous brother Eric and his equally well known brother MacDonald Gill, known as Max, and his famous map of the London Underground map known as the Wonderground Map.
Our research has been unable to find any other maps by Evan but we were understandably excited once the connection was made to his three brothers from the artistic and PNG missionary connection.
The map must have been commissioned by Evans brother Archdeacon Stephen Romney Gill, missionary in PNG during the first half of the 20th century, who famously survived in the Lae area of New Guinea, near the Kokoda trail, during the occupation of PNG by the Japanese in 1942/3.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 34in x 19in (865mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 34in x 19in (865mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repairs to tears in left margin, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Repairs to tears in left margin, no loss
Background:
Gill, Evan Robertson 1892 - 1968. Gill was born in Brighton England one of thirteen children. His father Arthur Gill was a clergyman with a family background of missionary work in the South Seas. Evan had three well known brothers Eric Gill the (in)famous Arts and Crafts artist, Macdonald Gill (Max) the decorative map maker - famous for designing the 1914 Wonderground Map of the London Underground - and Stephen Romney Gill 1886 - 1954, Anglican Archdeacon in Papua New Guinea in the early 20th century and during the occupation of PNG by the Japanese in 1942/3.
His brothers Stephen & Dr Cecil Gill, were missionaries in Papua New Guinea from 1905 until the 1950s after their Grandfather George Gill & Great Uncle William Gill, both missionaries in the Cook Islands.
Leslie MacDonald Gill 1884 – 1947 commonly known as MacDonald Gill or Max Gill, was a noted early-twentieth century graphic designer, cartographer, artist and architect.
Born in Brighton, Gill was the younger brother of Eric Gill, one of the leading figures of the Arts and Crafts movement.
In 1914 his Wonderground Map, commissioned by Frank Pick, and hung at every station, helped to save the London Underground by presenting an accurate map which also had a humorous side in cartoon style. Produced in poster form, it was also made available for sale to members of the public and proved to be very popular. Elder brother Eric, who at that time was engaged in a commission for Westminster Cathedral, was included at the bottom of the map. Gill showed three works at the first annual exhibition of the newly-formed Society of Graphic Art in 1921.
He was the designer of the standard upper case lettering used on headstones and war memorials by the Imperial War Graves Commission. But it is perhaps his illustrated maps for which he is most well known. These maps have featured in a series of exhibitions including Magnificent Maps exhibition in 2010 at the British Library, an exhibition MacDonald Gill, Out of the Shadows in 2011 at the University of Brighton and at the Mind the Map exhibition in 2012 at the London Transport Museum.
Arthur Eric Rowton Gill 1882 – 1940 was an English sculptor, typeface designer, and print-maker, who was associated with the Arts and Crafts movement. He is a controversial figure, with his well-known religious views and subject matter generally viewed as being at odds with his sexual behaviour.
Gill was born in 1882 in Hamilton Road, Brighton and grew up in the Brighton suburb of Preston Park. One of twelve children, he was the elder brother of MacDonald Max Gill (1884–1947), the graphic artist. In 1897 the family moved to Chichester. He studied at Chichester Technical and Art School, and in 1900 moved to London to train as an architect with the practice of W.D. Caroe, specialists in ecclesiastical architecture.
Frustrated with his training, he took evening classes in stone-masonry at the Westminster Technical Institute and in calligraphy at the Central School of Arts and Crafts, where Edward Johnston, creator of the London Underground typeface, became a strong influence. In 1903 he gave up his architectural training to become a calligrapher, letter-cutter and monumental mason.
Working from Ditchling in Sussex, where he lived with his wife, in 1910 Gill began direct carving of stone figures. These included Madonna and Child (1910), which English painter and art critic Roger Fry described in 1911 as a depiction of pathetic animalism, and Ecstasy (1911). Such semi-abstract sculptures showed Gill\'s appreciation of medieval ecclesiastical statuary, Egyptian, Greek and Indian sculpture, as well as the Post-Impressionism of Cézanne, van Gogh and Gauguin.
His first public success was Mother and Child (1912). A self-described disciple of the Ceylonese philosopher and art historian Ananda Coomaraswamy, Gill was fascinated during this period by Indian temple sculpture. Along with his friend and collaborator Jacob Epstein, Gill planned the construction in the Sussex countryside of a colossal, hand-carved monument in imitation of the large-scale Jain structures at Gwalior Fort in Madhya Pradesh, to which he had been introduced by William Rothenstein.
In 1914 Gill produced sculptures for the stations of the cross in Westminster Cathedral. In the same year he met the typographer Stanley Morison. After the war, together with Hilary Pepler and Desmond Chute, Gill founded The Guild of St Joseph and St Dominic at Ditchling. There his pupils included David Jones, who soon began a relationship with Gills daughter, Petra.
Gill designed several war memorials after the First World War, including the Grade II* listed Trumpington War Memorial. Commissioned to produce a war memorial for the University of Leeds, Gill produced a frieze depicting Jesus driving the money-changers from the temple, showing contemporary Leeds merchants as the money-changers. Gill contended that the money men were a key cause of the war. This is at the Michael Sadler Building at the University.
In 1924, Gill moved to Capel-y-ffin in Powys, Wales, where he established a new workshop, to be followed by Jones and other disciples. In 1928, he set up a printing press and lettering workshop in Speen, Buckinghamshire. He took on a number of apprentices, including David Kindersley, who in turn became a successful sculptor and engraver, and his nephew, John Skelton, noted as an important letterer and sculptor. Other apprentices included Laurie Cribb, Donald Potter and Walter Ritchie. Others in the household included Gills two sons-in-law, Petra\'s husband Denis Tegetmeier and Joanna\'s husband Rene Hague.
In 1928–9, Gill carved three of eight relief sculptures on the theme of winds for Charles Holdens headquarters for the London Electric Railway (now Transport for London) at 55 Broadway, St James. He carved a statue of the Virgin and Child for the west door of the chapel at Marlborough College.
In 1932, Gill produced a group of sculptures, Prospero and Ariel and others for the BBCs Broadcasting House in London. In 1934, Gill visited Jerusalem where he worked at the Palestine Archaeological Museum (now the Rockefeller Museum). He carved a stone bas-relief of the meeting of Asia and Africa above the front entrance together with ten stone reliefs illustrating different cultures and a gargoyle fountain in the inner courtyard. He also carved stone signage throughout the museum in English, Hebrew and Arabic.
Gill was commissioned to produce a sequence of seven bas-relief panels for the façade of The People\'s Palace, now the Great Hall of Queen Mary University of London, which opened in 1936. In 1937, he designed the background of the first George VI definitive stamp series for the post office. In 1938 Gill produced The Creation of Adam, three bas-reliefs in stone for the Palace of Nations, the League of Nations building in Geneva, Switzerland. During this period he was made a Royal Designer for Industry, the highest British award for designers, by the Royal Society of Arts and became a founder-member of the Faculty of Royal Designers for Industry when it was established in 1938. In April 1937, Gill was elected an Associate member of the Royal Academy.
Gills only complete work of architecture was St Peter the Apostle Roman Catholic Church in Gorleston, built in 1938–39.
1815 Swoboda & Hartl Antique Early Map of New Holland Australia, Ulimaroa Scarce
Antique Map
- Title : Generalcharte von Australien nach dem entwurfe des H.Joseph Marx Freiherrn v. Liechtenstern
- Date : 1815
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 16258
- Size: 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original & scarce antique map of New Holland also named Ulimaroa, New Zealand and the South Pacific by Franz Swoboda and Martin Hartl was published in Vienna in 1815 - dated.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Paper size: - 27in x 20 3/4in (685mm x 525mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (7mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Vertical crease right image
Verso: - None
This map is typical of the affect of Cooks discoveries on European cartography. Australia regularly became a focus on regional maps. The name "Ulimaroa" was often used, mainly by German & Austrian cartographers, at this time. It was term Cook learned from the New Zealand Maoris before discovering the east coast of Australia during his first voyage of discovery. When this map was printed there was a strong belief that the Australian continent was possibly divided by an internal sea strait, separating the east from the west coasts. It was explorers such as Flinders and Baudin who set out to find this elusive passage and if so the possible point at which a ship could enter.
Only a few years before in 1798 Flinders and Bass had proved that there was a strait dividing Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) from the rest of the continent so now the race was on to find the other passage. On Swoboda’s map a line has been drawn from the bottom of Carpentaria to the eastern part of present day Victoria. This line represented two things, the potential shape of the eastern landmass split by the sea and the extent to English territory in the newly settled colonies, only 17 years old. The Southern Coastline is not shown as even though Flinders had by 1803 mapped the entire region he was in 1805 still under house arrest on the islands of Mauritius by the French, he would not publish his discoveries until 1814. Therefore this map shows Australia at a pivotal point in its history when most of the continent was still open for settlement by other nations and the coastlines and mysteries were still to be confirmed. (Ref: Clancy; M&B; Tooley)
1812 Pinkerton Large Antique Stereographic Projection Map of Southern Hemisphere
- Title : Southern Hemisphere....Drawn Under the Direction of Mr Pinkerton by L Herbert Neele Sculp. 352 Starnd.....London Published August 31st 1812 by Cadell & Davies Strand & Longman. Hurst. Rees.Orme & Brown. Paternaster Row
- Ref #: 60540
- Size: 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
- Date : 1812
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique stereographic projection style map of the Southern Hemisphere, Australia, New Zealand & Antarctica by John Pinkerton was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1812 - dated at the foot of the map - and published in Pinkertons large elephant folio Modern Atlas, published between 1809 - 14. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 31in x 22in (790mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In geometry, the stereographic projection is a particular mapping (function) that projects a sphere onto a plane. The projection is defined on the entire sphere, except at one point: the projection point. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective. It is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet. It is neither isometric nor area-preserving: that is, it preserves neither distances nor the areas of figures.
Intuitively, then, the stereographic projection is a way of picturing the sphere as the plane, with some inevitable compromises. Because the sphere and the plane appear in many areas of mathematics and its applications, so does the stereographic projection; it finds use in diverse fields including complex analysis, cartography, geology, and photography. In practice, the projection is carried out by computer or by hand using a special kind of graph paper called a stereographic net, shortened to stereonet, or Wulff net.
The stereographic projection was known to Hipparchus, Ptolemy and probably earlier to the Egyptians. It was originally known as the planisphere projection. Planisphaerium by Ptolemy is the oldest surviving document that describes it. One of its most important uses was the representation of celestial charts. The term planisphere is still used to refer to such charts.
In the 16th and 17th century, the equatorial aspect of the stereographic projection was commonly used for maps of the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. It is believed that already the map created in 1507 by Gualterius Lud was in stereographic projection, as were later the maps of Jean Roze (1542), Rumold Mercator (1595), and many others. In star charts, even this equatorial aspect had been utilised already by the ancient astronomers like Ptolemy.
François d\'Aguilon gave the stereographic projection its current name in his 1613 work Opticorum libri sex philosophis juxta ac mathematicis utiles (Six Books of Optics, useful for philosophers and mathematicians alike).
In 1695, Edmond Halley, motivated by his interest in star charts, published the first mathematical proof that this map is conformal. He used the recently established tools of calculus, invented by his friend Isaac Newton.
Pinkerton, John 1758 – 1826
Pinkerton was a Scottish antiquarian, cartographer, author, numismatist, historian, and early advocate of Germanic racial supremacy theory.
He was born in Edinburgh, as one of three sons to James Pinkerton. He lived in the neighbourhood of that city for some of his earliest childhood years, but later moved to Lanark. His studious youth brought him extensive knowledge of the Classics, and it is known that in his childhood years he enjoyed translating Roman authors such as Livy. He moved on to Edinburgh University, and after graduating, remained in the city to take up an apprenticeship in Law. However, his scholarly and literary inclinations led him to abandon the legal profession. It had been during his brief legal career though that he had begun writing, his Elegy on Craigmillar Castle being first published in 1776.
Pinkerton was a celebrated master of the Edinburgh school of cartography which lasted from roughly 1800 to 1830. Pinkerton, along with John Thomson & Co. and John Cary, redefined cartography by exchanging the elaborate cartouches and fantastical beasts used in the 18th century for more accurate detail. Pinkertons main work was the \\\"Pinkerton\\\'s Modern Atlas\\\" published from 1808 through 1815 with an American version by Dobson & Co. in 1818. Pinkerton maps are today greatly valued for their quality, size, colouration, and detail.
1854 Arrowsmith Rare Antique Geological Map from Queensland to NSW Australia
- Title : Sketch of the Country bewteen The River Condamine and the Nandawah Mounatins
- Size: 26in x 12 1/2in (660mm x 315mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1854
- Ref #: 82047
Description:
This rare, large lithograph hand coloured geological map from the Condamine River, Queensland south to the Nandewar Range, Warrabah NSW, Australia by John Arrowsmith was published in 1854 for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
A very important geological map illustrating coal deposits near the Horton River NSW and gold deposits north through to Queensland.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have had very low numbers published and are very hard, if not impossible, to be be found for sale on the open market.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 12 1/2in (660mm x 315mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 12 1/2in (660mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1795 (1806) Canzler Large Antique Map Australia, Ulimaroa, New Zealand SE Asia
Antique Map
- Title : Karte vom Funften Erdtheil oder Polynaesien-Inselwelt oder Australien oder Sudindien (Map of the fifth earth or Polynesia or Australia or South India.)
- Size: 24 1/4in x 20 1/2in (615mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1795 (1806)
- Ref #: 93121
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved, antique map of Australia, New Zealand and SE Asia by Friedrich Gottlieb Canzler in 1795, was published by the Homann Firm in 1806.
A distinct map with the short lived alternative name of Ulimaroa for New Holland, given by Canzler after Daniel Djurberg mistakenly interperated the New Zealand Maori word, Olhemaroa, from Cooks diary, for Australia. The real interpretation being Long Hand, the Maori name for New Caledonia.
There are two records in Cooks diary relating to Ulimaroa....
5th Feb 1769....This place we concluded to be the land difcovered by Tafman, which he called Cape Maria Van Diemen, and finding thefe people fo intelligent, we inquired farther, if they knew of any country befides their own: they anfwered, that they never had vifisted any other, but that their anceftors had told them, that to the N.W. by N., or N.N.W. there was a country of great extent, called Ulimaroa, which people had failed in a very large canoe
5th Feb 1770.....When we were under fail, our old man aTopaa came on board to take his leave of us, and as we were ftill defirous of making farther enquiries whether any memory of Tafman had been preferved among thefe people, Tupia was directed to afk him whether he had ever heard that fuch a veffel as ours had vifited the country. To this he replied in the negative, but faid, that his anceftors had told him there had once come to this place a fmall veffel, from a distant country, called Ulimaroa, in which were four men, who, upon coming on fhore, were all killed: upon being afked where this diftant land lay, he pointed to the northward. Of Ulimaroa we had heard fome-thing before, from people about the Bay of Iflands, who faid that their anceftors had vifisted it; and Tupia had alfo talked to us of Ulimaroa.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/4in x 20 1/2in (615mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 19in (620mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Ulimaroa was a name given to Australia by the Swedish geographer and cartographer Daniel Djurberg in 1776. Djurberg adapted the name from Olhemaroa, a Māori word found in Hawkesworths edition of Captain James Cook and Sir Joseph Banks journals which is thought to have been a misunderstood translation — the Māori were actually referring to Grand Terre, the largest island of New Caledonia. Djurberg believed the name meant something like big red land, whereas modern linguists believe it meant long hand — echoing the geography of Grand Terre. The spurious name continued to be reproduced on certain European maps, particularly some Austrian, Czech, German and Swedish maps, until around 1820, including in Carl Almqvists 1817 novel Parjumouf Saga ifrån Nya Holland (Stockholm, 1817).
Canzler, Friedrich Gottlieb 1764-1811
Friedrich Gottlieb Canzler was born in Wolgast, Sweden in 1764. He graduated from the school in his hometown and from 1781 to 1783 the Sundische Gymnasium in Stralsund . He then studied history , geography , statistics and the Swedish language at the University of Göttingen . After completing his studies, he also received his doctorate and habilitation in Göttingen, and worked as a Privatdozent for history, geography, statistics and cameralistics .
In addition, he published in Göttingen from July 1789 to February 1791 the General Political State Newspaper for all Stands, for which he ran his own university and newspaper printing plant, and founded in 1797 an Academic Reading Museum. Two years later he was appointed Professor of Statistics, State Economics, Cameral, Financial and Commerz Sciences at the University of Greifswald where he worked until his death in 1811.
Selected Works:
- New magazine for recent history, Earth and ethnology. Leipzig 1790
- English language teaching for Germans. Göttingen 1796
- General Litteraturarchiv for history, geography and statistics. Leipzig 1792-1798 (as publisher)
- Map of the fifth earth or Polynesia or Australia or South India. Nuremberg 1795, 1805 and 1806 (as well as 1813 with corrections by Christian Gottlieb Reichard)
- Front India or Hindostan or East India on the side of the Ganges. Nuremberg 1804
1855 Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map Land Parcels in Van Diemens Land, TAS Australia
- Title : North Western Portion of Tasmania Newly Opened...Accompanying my report of the 16th April 1855
- Size: 16 1/4in x 12in (415mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 82042
Description:
This rare map of land opened for purchase North-West of Hobart, Tasmania - from Hamilton along the Derwent River to Lake St Clair and south to Lake Peeder, with a hand coloured reference to the land parcels - by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1855 - dated - and was published for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have numbered only in the 100s.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light offsetting
Verso: - Light offsetting
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1774 Hawkesworth Large Antique Map of Australia & South Seas 1765-71 - Capt Cook
Antique Map
- Title : Carte d une Partie de la Mer du Sud Contenant les Decouvertes de Vaisseaux de sa Majeste, Le Dauphin, Commodore Byron, La Tamar, Capitne. Mouats 1765, Le Dauphin, Capitne. Wallis, Le Swallow, Capitne. Cartaret, 1767, et l Endeavour, Lieutenant Cook 1769
- Ref : 35509
- Size: 28in x 16 3/4in (710mm x 425mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved, large antique map, a chart of the tracks of 5 British ships & explorers to the South Ocean from 1765 to 1771 was engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1774 French translation of John Hawkesworths publication An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks
The 5 Voyages, with Captains, ships & tracks are;
1. 1764-66 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Commodore John Byron, completed the first circumnavigation of the globe under two years.
2. 1764-1766 - HMS Tamar under Command of Captain Patrick Mouat, accompanied Commodore John Byron & HMS Dolphin on 1764-66 circumnavigation of the world.
3. 1766-68 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Captain Samuel Wallis, completed another circumnavigation & was the first European to visit Tahiti & the Society Islands.
4. 1766-68 - HMS Swallow under Command of Captain Philip Carteret, who accompanied HMS Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis to circumnavigate the world.
5. 1769-71 - HMS Endeavour, under Command of Lieutenant James Cook (later Captain) completed a the mapping of Tahiti & the Society Islands, New Zealand & the East Coast of Australia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 28in x 16 3/4in (710mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 26 3/4in x 14 3/4in (680mm x 375mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Commodore John Byron 1723 – 1786 was a British Royal Navy officer and politician.He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764-1766. He fought in battles in The Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral before his death in 1786.
Captain Patrick Mouat. Commanded HMS Tamer on a voyage of discovery with Commodore John Byron between 1764-66. HMS Tamar was a sloop, mounting sixteen guns: ninety men, three lieutenants, and two and twenty petty officers.
Captain Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795 was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean. Was given the command of HMS Dolphin in 1751 as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Third\'s Island in honour of the King in June 1767.
Captain Philip Carteret 1733 – 1796 was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navys circumnavigation expeditions in 1764–66 and 1766–69.
Captain James Cook is considered one of the most talented Surveyors & Map Makers of any age, for Cook, the production of a new chart was his principal reason for going to sea. His charts were aimed at fellow seamen so he incorporated as much information as possible while employing an economy of style and little elaboration. The quality of his charts can be confirmed by the fact that some survey details from Newfoundland to New Zealand & Australias East Coast could still be safely used over one hundred years later. His last piece of the New Zealand hydrographic chart was only removed in the 1990s.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt James Cook Antique Map The Southern Hemisphere, Australia, Antarctica
Antique Map
- Title : Carte De L Hemisphere Austral Montrant les Routes des Navigateurs les plus Celebree par le Capitaine Jacques Cook
- Ref : 42004
- Size: 22in x 21 1/2in (560mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved, antique map, a chart of the Southern Hemisphere, was engraved by Robert Benard and is dedicated to the discoveries in the South Seas and Antarctic Regions of Captain James Cook during his second Voyage of Discovery between 1772 & 1775. By comparison the tracks of 11 other explorers are included, from the 16th to the 18th centuries. The map by Captain James Cook was published in the 1778 French edition of A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
This map is unique in another way, as the English edition of this map was used as a prop, by Nathaniel Dance, in his 1776 portrait of Captain James Cook. Please also see above for the portrait.
The 11 other explorers and their tracks around the Southern Hemisphere are;
1. Mendana in 1595
2. Quiros in 1606
3. Le Maire & Schouten in 1616
4. Tasman in 1642
5. Halley in 1700
6. Roggewein in 1722
7. Bouvet in 1738-39
8. Byron in 1765
9. Wallis in 1767
10. Bougainville in 1768
11. Surville in 1769
12. Cooks first and second voyages.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 21 1/2in (560mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 21 1/2in (560mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair without loss to left of image
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Background:
This map by James Cook, was published as the premier map of his second voyage to the Southern Hemisphere, dispelling forever the myth of the Great Southern Land and showing the true cartographic nature of the southern hemisphere dominated by Australia & New Zealand. The map on a South Polar Projection also shows South America, the South Atlantic Ocean, South Africa, Madagascar, Australia - with Tasmania still joined to the mainland - New Zealand and the southern Pacific Ocean with islands.
Engraved within the explorer\\\'s tracks are the dates of their voyages and ships tracks are particularly noted around the Antarctic Circle with notations of ice fields seen during the voyages.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1876 Thomas & Tayler Scarce Antique Goldfields & Minerals Map of New South Wales
Antique Map
- Title : Sketch Map of New South Wales showing the Localities of the Principal Minerals 1876
- Ref #: 27011
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 18in x 15 1/2in (455mm x 400mm)
- Date : 1876
Description:
This original, incredibly scarce & important, antique lithograph map of New South Wales, illustrating the location of the Principle Minerals of that state, was drawn by John Tayler, engraved by G W Sharp and published by Thomas Richards in 1876 - dated, Sydney
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 15 1/2in (455mm x 400mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 15 1/2in (455mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The map shows New South Wales' new (and current) boundaries, with the state's 'Pastoral Districts' delineated; railways from Ports Hunter and Jackson are shown, along with their proposed extensions inland. Roads and telegraph lines are also indicated. Relief is shown by hachure. An inset map in the lower left shows the state's location on the Australian continent. These features are shared by the authors' other maps of New South Wales, the 1871 Map of New South Wales and the 1878 Sketch map of New South Wales showing the principal agricultural districts. Specific to this map, areas printed in color show the regions understood to be rich in minerals: Kerosene shale, coal, tin, iron, silver, copper, gold and 'diamonds and other gems.' The data on the map reflects the experience of some twenty years of prospecting in New South Wales, but predate the first systematic geological survey of the state, which would not be completed until 1880. The map specifies that the gold fields are 'proclaimed' gold fields, that is to say, permissible for prospectors. No prospector's claim was valid unless it fell within the limits of a 'proclaimed' field, which was officially recognized by the state and administered by a commissioner. The earlier 1873 edition of this map distinguishes between 'proclaimed' and 'unproclaimed' fields; in the present edition, the 'unproclaimed' fields have disappeared entirely. By 1876, control of gold mining in the state had passed from the Department of Lands to a new administration, the Department of Mines; in conjunction with this, mining had become less of a prospector-driven, 'gold rush' affair and more the province of mining companies employing more sophisticated processes, capable of extracting wealth from existing claims in which lower-capitalized operations were ineffective.
John Tayler 1861 - 1875 was an Australian cartographer and draftsman, employed by the NSW Surveyor Generals Office. His 1871 Map of New South Wales appears to have provided the basis for the bulk of the maps of the state produced prior to the Geological survey of 1880.
Richards, Thomas (1831 - 1898)
Thomas Richards, government printer, was born on 21 December 1831 in Pitt Street, Sydney, son of James Richards, builder, and his wife Mary, née OBrien. He was baptized a Catholic. His parents died in his infancy and he was reared by his aunt, the daughter of a sergeant-major in the First Fleet, and educated at Ebenezer on the Hawkesbury River. Having answered an advertisement for an intelligent youth, on 1 January 1845 he was engaged as an apprentice in the Government Printing Office, where he advanced as clerk, proof-reader, compositor, pressman, overseer and, in 1854, superintendent. In June 1859 he became government printer and inspector of stamps at a salary of £500, which had been reduced from his predecessors £850, but was raised to £600 in 1863; he had a staff of seventy. As he lacked London experience his appointment was unpopular. From 1 July 1879 he was also registrar of copyright.
During Richardss innovative administration, with increasing volume of work, the office expanded its functions and techniques. In 1863 he introduced photo-lithography and, after he had observed plant in Victoria in 1864, he added stereo-typing and electro-typing. In 1868 following the establishment of extra branches a new fast process of photo-lithography was invented by John Sharkey whose experiments were encouraged and assisted by Richards. The Sydney Morning Herald praised the gems of photo-lithographic art the Printing Office displayed at the 1870 Intercolonial Exhibition at Sydney. Later Richards initiated helio-type or photo-mechanical printing, introduced a perforating machine and invented a method of drying stamps with heat from gas. He devised an arithmotype bars system for numbering debentures which was adopted in all the colonies and England; he alleged the Bank of England took the patent without acknowledgment.
Frequently working long hours, Richards was criticized by some politicians for his administration and his publication of documents of allegedly limited public interest. He defended himself adequately before the 1870 select committee on the Government Printing Office, resisting suggestions of reductions in salaries and praising his men for the finest examples of the modern technique of photo-lithography seen in the colonies; and he admitted ambitions to produce an Australian geography and natural history, a year-book and dictionary of names for New South Wales. Looking back in 1891 he wrote, I had opposed to me a truculent minister, a truculent under-secretary and a truculent newspaper proprietor … I beat them but came out of the fray wounded in mind body and estate. He also had trouble with trade unions in difficult industrial times for heads of government departments and in 1875 antagonized the Trades and Labor Council by threatening to close the Office against all union men.
In 1877 Richards represented the government on an English committee to celebrate the quatercentenary of Caxtons introduction of printing. With twelve months leave he also studied advanced methods and bought new machinery. At the 1878 Paris Universal Exhibition he won a silver and two bronze medals and at the 1880 Melbourne International Exhibition he won five high diplomas for printing, bookbinding and photography. The 1883 Amsterdam Exhibition awarded him a gold and a silver medal, and the Printing Office was commended at other important exhibitions from 1862 to 1886. In 1882 Richards compiled, edited and printed the highly regarded New South Wales in 1881, which was translated into French; next year the office produced An Epitome of the Official History of New South Wales.
On 23 April 1861 Richards had joined the Volunteer Rifles as a second lieutenant. A good shot and member of the New South Wales Rifle Association, in 1885 he became lieutenant-colonel of the first regiment, Volunteer Infantry; he resigned next year. In November 1886, because of rapidly failing eyesight, Richards retired as government printer on a pension of £480; he left a staff of 400 and an office with sixty-one new departments. On 31 August 1898 he died at Manly and was buried in the Anglican cemetery there. On 29 January 1865, with Anglican rites, he had married Zara Bell, by whom he had three daughters and two sons who survived him.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map of New South Wales & Victoria, Australia Felix
Antique Map
- Title : Colony of New South Wales and Australia Felix
- Ref #: 35088
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original antique map of NSW & SE Australia stretching from the 10 year old Settlement of Melbourne in the south to the 31st parallel in the north, by W & AK Johnston, was published in the 1845 edition of the General Atlas.
A large, highly detailed regional map of New South Wales and Australia Felix the SE area which quickly became the state of Victoria. The map, with this title, lasted for only a few years, before both NSW and Victoria were quickly settled. The map provides a very early depiction of the region, pre-dating the discovery of gold.
Also of great interest are the exploration routes by Mitchell (1836) in Red, Tyer's & Townsend's (1840) in Yellow and Streletsky's (Strzelecki) (1840) in Blue.
The 18 counties of NSW are highlighted in beautiful hand colour with extensive detail of towns, tracks and rivers. Historical note included below the title.Decorative Piano Key border and a fine example, on thick heavy paper.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century - this map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1856 A K Johnston Large Antique Goldfields Map of Victoria & New South Wales
Antique Map
- Title : Colony of New South Wales and Victoria by A K Johnston
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27001
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
This original large hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of NSW & Victoria - was published by A K Johnston in the 1856 edition of his National atlas of historical, commercial, and political geography.
A important and interesting map, showing some of the earliest and most important goldfields in both NSW & Victoria, illustrated in yellow with legend. the map is also one of the earliest to show the separation of the state of Victoria from New South Wales in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\\\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\\\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\\\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1844 W & AK Johnston Large Early Antique Map of Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 30143
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original antique lithograph map of Australia - with coloured outlines to the counties in NSW & WA - was published by W & AK Johnston in General Atlas,1844.
At the bottom of the map is atext box outlining the period of settlements in Australia from Botany Bay in 1788, WA 1829, SA 1836 & the colony of Victoria begun some 8 years ealier in 1838.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century, this large map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Australia - 1st Gold Rush
- Title : Australia
- Size: 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 93000
Description:
This large original steel-plate engraved rare antique map of Australia, with early Goldfields marked in yellow, by the famous Scottish cartographer John Bartholomew was published by A&C Black in 1855.
Rare large, highly detailed, antique Goldfields map of Australia, published prior to Queensland statehood in 1859 and during the first Australian gold rush of the 1850s.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.Jacques Nicholas Bellin
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1841 Macarthur Antique Octavo Book on Colonial Policy in Australia, Map of NSW
Antique Map
- Title : Colonial Policy of 1840 and 1841, as illustrated by the Governor's Despatches, and Proceedings of the Legislative Council of New South Wales. By Major Macarthur.
- Ref #: 17045
- Size: Octavo
- Date : 1841
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
Fine original antique Octavo book with 79 pages and a single lithographed hand coloured map of eastern Australia & Van Diemens Land; uncut copy in half calf with gilt lettering by Edward Macarthur, advocating for immigration and trade for the colony of Australia, published by John Murray, London in 1841, dated.
This is the first of two books by Sir Edward Macarthurs advocating immigration to the colony of Australia. The eldest son of John and Elizabeth, Edward Macarthur was born at Bath in 1789, and accompanied his parents to New South Wales in 1790. As one of the first free settlers in the colony, he was a strong advocate of immigration, and served as Thomas Macqueens agent in arranging the first shipment of free immigrants in 1824, which gave great stimulus to agriculture.
The map illustrates a division of New South Wales and the subsequent creation of a smaller colony. Titled Eastern Australia or Territory of New South Wales, the map is captioned 'territory to which the Colony might be reduced by Bill of the last session' with reference debate in the House of Commons knocked down by Sir Robert Peel.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - Octavo
Plate size: - Octavo
Margins: - Octavo
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Sir Edward Macarthur (1789-1872), soldier, was born on 16 March 1789 at Bath, England, the eldest son of Captain John Macarthur and his wife Elizabeth. He went to Sydney with his parents in 1790 and spent his boyhood there and at Elizabeth Farm, Parramatta. Sent to England in 1799 to be educated he returned to Sydney in 1806. With his father he took part in the deposition of Governor William Bligh in 1808. He soon left for London taking his father's version of the rebellion and the first bale of merino wool to be exported from the colony. He obtained a commission in the 60th Regiment and served at Corunna and in Sicily. As a lieutenant in the 39th Regiment he took part in Wellington's campaigns of 1812-14 and was present at Vittoria, the Pyrénées and the battles in southern France. After brief service in Canada he joined the army of occupation in France.
In 1824 Macarthur went to New South Wales as the agent of T. P. Macqueen. He was impressed by the dispersion of the garrison from Moreton Bay to Hobart Town in the face of runaway convicts and 'hostile tribes'. In London he placed detailed proposals for a colonial militia before Under-Secretary Horton but the plan was rejected by Governor (Sir) Ralph Darling in 1827. Macarthur competently represented Australian interests in London. He presented a petition from New South Wales in 1840. He advocated emigration in two small books, Colonial Policy of 1840 and 1841, as Illustrated by the Governor's Despatches, and the Proceedings of the Legislative Council of New South Wales (London, 1841) and Brief Remarks on Colonization (London, 1846). He personally arranged the migration of German vinedressers to the Macarthur properties at Camden and also sought to develop coastal steamship services. After serving as secretary in the Lord Chamberlain's Office in 1843-46 he was on the military staff in Ireland. In 1851 he was posted to Sydney as deputy adjutant general. Promoted colonel in 1854, he moved with the headquarters to Melbourne. He accompanied the commander-in-chief, Major-General Sir Robert Nickle, to Eureka on 5 December. They talked freely with the miners and as a result of their investigations Nickle advised that martial law be withdrawn.
After Nickle died in May 1855 and Governor Hotham in December, Macarthur took over command of the forces and became administrator. He inherited a confused political situation and was coolly received by the press. However, his impartiality and his willingness to leave things to his ministers helped him, and when he handed over to Sir Henry Barkly on 23 December 1856 he had won the esteem of parliament and the people of Melbourne. Emily, wife of Hugh Childers, described him as 'if not a brilliant statesman, an industrious, kind-hearted, Christian gentleman'. In 1858 Macarthur chaired a royal commission on the defences of the colony. In 1860 he returned to England and was appointed K.C.B. in 1862. In that year he married Sarah (d.1889), daughter of Lieutenant-Colonel W. S. Neill. Promoted lieutenant-general in 1866, he died childless in London on 4 January 1872 and was buried in the Brompton cemetery. He was survived by his wife. His goods were valued for probate at £4000.
Macarthur, Edward (1789 - 1872)
Macarthur was a lieutenant-general in the British Army, Commander-in-chief of British forces in Australia from 1855, and an administrator of the Colony of Victoria for 12 months, following the death of the Governor, Sir Charles Hotham.
Macarthur was the eldest son of John Macarthur, and his wife Elizabeth (née Veal). He was born at Bath, Somerset, England, and arrived at Sydney with his parents in the ships Neptune and Scarborough in 1790, part of the Second Fleet. Edward Macarthur is believed to be the only passenger on those ships of whom a photograph exists, although taken later in life. In 1799, the young Edward was sent to England to be educated.
Macarthur returned to Australia in 1806 and took part with his father in the deposing of Governor William Bligh. Bligh, in his dispatch to Viscount Castlereagh of 30 April 1808, requested that two of the rebels Charles Grimes and Edward Macarthur who have gone home in the Dart may be secured, in order to be tried in due time. On Macarthurs arrival in England, he entered the army as an ensign in the 60th regiment, serving at Corunna and in Sicily. In 1809, he was promoted to the rank of lieutenant. As part of the 39th Regiment he took part in the Duke of Wellingtons campaigns in the Peninsular War and in France. In 1820 or 1829 he became a captain. In 1824 he paid a visit of 10 months to Australia as an agent of Thomas Potter Macqueen. After Macarthurs return to England, he was for some years secretary to the Lord Chamberlain. In 1826 he was promoted to the rank of major and in 1837 he was on the staff in Ireland.
Macarthur retained his interest in Australia. On 3 July 1839, he addressed a long communication to the Right Hon. Henry Labouchère, suggesting that regular lines of steamers should be established in Australia to trade between the various ports. That was referred to the governor, Sir George Gipps who, in May 1840, replied that government aid was unnecessary, because a large company had been formed to establish a line of steamers, of which James Macarthur (Edwards brother) was chairman. Edward Macarthur also promoted emigration in two small books: Colonial Policy of 1840 and 1841, as Illustrated by the Governors Despatches, and the Proceedings of the Legislative Council of New South Wales (London, 1841) and Brief Remarks on Colonization (London, 1846).
In August 1840, Macarthur protested against the regulations that people wanting to take up land in the Port Phillip district should have to proceed to Melbourne where all charts of land were kept for public inspection. He was made a Lieutenant-Colonel in 1841, and afterwards went to New South Wales as deputy adjutant-general. He was promoted to colonel in 1854.
On 5 December 1854, Macarthur travelled with the commander-in-chief of British forces in Australia, Major-General Sir Robert Nickle, to the site of the Eureka Rebellion. There they talked with the miners openly and, as a result of their investigations, Nickle advised the withdrawal of martial law. Macarthur was appointed commander-in-chief of British forces in Australia in 1855, to replace Nickle. On 1 January 1856, after the death of Governor of Victoria, Sir Charles Hotham, Macarthur was administrator of the colony of Victoria for 12 months.
Macarthur returned to London in 1860. In 1862, he was created a Knight Commander of the KCB and, in the same year, was given the colonelcy of the 100th (Prince of Waless Royal Canadian) Regiment of Foot, a position he held until his death.
He died in London on 4 January 1872 and was buried in Brompton Cemetery. In 1862, at the age of 73, he had married Sarah (daughter of Lieutenant-Colonel W. S. Neill), who survived him. There were no children.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1882 Edward Stanford Large Folding Antique Map Eastern Australia, QLD, NSW, Vic
Antique Map
- Title : Queensland & New South Wales....London Published by Edward Stanford ...March 20th 1882
- Ref : 17064
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (680mm x 570mm)
- Date : 1882.
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original hand coloured folding canvas backed antique map of Vicoria, New South Wales & Queensland in Eastern Australia, illustrating Tracks of Travellers, Roads, Railways & Telegraph was published by Edward Stanford, London in 1882, dated at the foot of the map. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, red, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (680mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (680mm x 570mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Stanford, Edward 1827-1904
Stanford was a prominent British mapmaker and publisher. A native of Holborn in the heart of London, Edward was apprenticed to a printer and stationer at the age of 14. After his first master died, he worked with several others, including Trelawny W. Saunders of Charing Cross. Saunders oversaw young Edward’s early career, ensuring that he became a Fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. Associations with the Society eventually brought Sanders much business and gave him a reputation as a publisher of explorers. As testament to this reputation, the Stanford Range in British Columbia was named for him by John Palliser.
Stanford briefly partnered with Saunders in 1852 before striking out on his own in 1853. He was an agent for the Ordnance Survey, the Admiralty, the Geological Survey, the Trigonometrical Survey of India, and the India Office. He also controlled the maps of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge, another lucrative source of income. In 1857, Stanford founded his namesake Geographical Establishment, with Saunders and A. K. Johnston as engravers. Thereafter, Stanford was known for his library maps, particularly those of Africa and Asia.
Although he had authored many maps, the Harrow Atlas of Modern Geography and a similar volume on classical geography, Stanford is better remembered today as the leader of a successful map business. Ever in search of more inventory, he acquired the plates and stock of John Arrowsmith, heir of the Arrowmsith family firm, in 1874. By 1881 he employed 87 people at his premises at 6 Charing Cross Road, Saunders’ old address. As he aged, he phased in his son Edward Jr. to run the business. He died in 1904. The business survived him, and the Stanford’s shop is still a prominent London landmark today.
Stanford premises were located in the Strand, London from 1853 to 1884 and then Cockspur St from 1885 to 1901 locating to its present location in Covent Garden.
1854 John Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map, Early Town Plan of Gladstone, Queensland
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the Town of Gladstone Port Curtis 1854 (Water is very scarce in this locality)
- Size: 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1854
- Ref #: 82046
Description:
Description:
This large, rare & important map, a very early plan of the Queensland town of Gladstone by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1854 - dated - and was published for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have numbered only in the 100s.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
Gladstone is a city in the Gladstone Region, Queensland, Australia. It is approximately 550 km (340 mi) by road north of Brisbane and 100 km south-east of Rockhampton. Situated between the Calliope and Boyne Rivers, Gladstone is home to Queensland\'s largest multi-commodity shipping port.
Before European settlement, the Gladstone region was home of the Toolooa (or Tulua), Meerooni and Baiali (or Byellee) Aboriginal tribes.
In May 1770, the HM Bark Endeavour, under the command of James Cook, sailed by the entrance to Gladstone Harbour under the cover of darkness. Matthew Flinders, during his 1801–1803 circumnavigation of Australia, became the first recorded European to sight the harbour in August 1802. He named the harbour Port Curtis, after Admiral Roger Curtis, a man who was of assistance to Flinders a year earlier at the Cape of Good Hope. John Oxley conducted further exploration of the harbour and surrounding countryside in November 1823. Oxley was dismissive of the region, noting the harbour was difficult to enter, the countryside was too dry, and the timber useless for construction purposes.
Nevertheless, in 1847 the British attempted to establish the new colony of North Australia at Port Curtis. Colonel George Barney was chosen to lead this experiment in colonisation and his expedition was eventful. On 25 January 1847, the Lord Auckland, carrying 87 soldiers and convicts, arrived off the southern entrance of Port Curtis and promptly ran aground on shoals off the southern tip of Facing Island. The settlers spent seven weeks on the island before being rescued by the supply ship Thomas Lowry and delivered the intended site of settlement, the region now known as Barney Point. On 30 January at a proclamation ceremony, Barney was sworn in as Lieutenant Governor of the colony of North Australia. The convict settlement lasted barely two months and cost the Imperial government ₤15,000. A change of government in Britain ordered the withdrawal of Barney and the settlers. However, interest in the region remained.
By 1853, Francis MacCabe was surveying the site of a new town on the shores of Port Curtis under the protection of several detachments of Native Police. Maurice O\'Connell was appointed government resident the following year, resulting in an influx of free settlers as land became available throughout the region. In 1863, the town became a Municipality with Richard Hetherington elected Gladstones first mayor. The fledgling town was named after the British Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone and has a 19th-century marble statue on display in its town museum.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print of a Sydney & Port Jackson Aboriginal Warrior
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Nelle Galles Du Sud. Nourou-gal-derri & avancant pour combattre
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91240
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Aboriginal warrior of Port Jackson carrying a spear & shield, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes in 1807.
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - 2 small repair to left margin, no loss
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1844 W & AK Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia - South Australia Settlement
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 23806
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of Australia - with coloured outlines to the counties in NSW & WA - was published by W & AK Johnston in General Atlas,1844.
At the bottom of the map is a text box outlining the period of settlements in Australia from Botany Bay in 1788, WA 1829, SA 1836 & the colony of Victoria begun some 8 years earlier in 1838.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century, this large map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print of a Sydney & Port Jackson Aboriginal Warrior
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Nelle Galles Du Sud. Nourou-gal-derri & avancant pour combattre
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93087
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Aboriginal warrior of Port Jackson carrying a spear & shield, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes in 1807.
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting to left and bottom margins, not affecting the image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1773 Hawkesworth Antique Print Raiatea Island, French Polynesia - Capt Cook 1769
- Title : [A view in the island of Ulietea with a double canoe and a boathouse] ...E. Rooker sculp....No. 3
- Ref : 31816
- Size: 18 1/2in x 10 1/2in (470mm x 265mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print a view of fishing vessels, locals inspecting the days catch and views of the Island of Raiatea (Ulietea) in the Society Isles of French Polynesia, drawn by Sydney Parkinson, on Captain Cooks first visit to the Island in 1769, was engraved by Edward Rooker and published in the 1773 1st English edition of John Hawkesworths An account of the voyages undertaken by the order of His present Majesty for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor. Drawn up from the journals which were kept by the several commanders, and from the papers of Joseph Banks, Esq; by John Hawkesworth, LL.D. In three volumes. Illustrated with cuts, and a great variety of charts and maps relative to countries now first discovered, or hitherto but imperfectly known. London: printed for W. Strahan; and T. Cadell in the Strand, MDCCLXXIII.
..........a double canoe (pahi) with carved figures on bow and stern. Another double canoe in the background at right and a boathouse at left. There are a great number of boathouses all round the bays built with a Catanarian arch, thatched all over; and the boats kept in them are very long, bellying out on the sides, with a very high peak stern, and are used only at particular seasons.....from the account by Sydney Parkinson 1769
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 10 1/2in (470mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 9 1/2in (470mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued, creasing and light soiling along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
A traditional name for the island is Havaii, homeland of the Māori people.
The first European to record sighting Ra iātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Raiātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, traveled with the European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
King Tamatoa VI was the last monarch, reigning from 1884-1888.
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth an English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Edward Rooker 1712 – 1774 was an English engraver, draughtsman and actor.
1798 Laperouse & Mourelle Antique Early Map of Queensland, PNG, Fiji etc in 1781
Antique Map
- Title : Carte D Une Partie Du Grand Ocean a l E. et S.E. de la Nouvelle Guinee pour l intelligence du Voyage de la Fregate Espagnole la Princesa commandee par D. Franco. Antonio Maurelle. en 1781..... Published as the (act) directs Novr. 1st 1798, by G.G. & J. Robinson
- Ref #: 31555
- Size: 16 3/4in x 11in (425mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1798
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique early map of Queensland, New Guinea, Fiji, French Polynesia & other South Pacific Islands - tracking the voyages of Francisco Antonio Mourelle in the region in 1781 was engraved in 1798 - dated - and was published in the 1st English edition of the Atlas du voyage de La Perouse G.G & J. Robinson, London in 1799.
La Perouse set sail from France in 1785 to continue the discoveries of Captain Cook. He was shipwrecked in 1788 but his narrative, maps, and views survived and were first published in 1797.
Interesting chart of Eastern Australia and part of the south-western Pacific, showing the routes taken by the Spanish explorer Don Francisco Antonio Maurelle in 1781 along the northern coast of New Guinea and across the Pacific to Fiji and Tonga, including a maunscript grid added in a contemporary hand.
Maurelle was credited with the discovery of the Hermit Islands on this voyage. The map includes the north-eastern coast of Australia, and parts of the coast of New Guinea. The map shows the 1781 route of his ship The Princesa through the Bismarck Archipelago north of New Guinea, through the Archipel de Salomos [i.e. Solomon Islands] and then east across the Pacific to the Iles de Amis [i.e. the Friendly Islands, now Tonga] where he discovered I. Vavao [ i.e. Vavau] with one of the best anchorages in the South Pacific.
The map includes the Iles de Navigateurs [i.e. Samoa], I. Fidji [i.e. Fiji], Iles de Esprit [i.e. Vanuatu or the New Hebrides Isles], and Nouvelle Caledonie [i.e. New Caledonia]. Many small islands are depicted with notes regarding their sightings by Abel Tasman, William Bligh and Maurelle.
A note on the chart states that the publisher has placed the islands according to the longitude of other navigators, rather than on Maurelles figures which were considered estimates only, and also, that Maurelles chart was based on a French chart by Jacques Nicolas Bellin published in 1742.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 3/4in x 11in (425mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mourelle de la Rúa, Francisco Antonio 1750 – 1820
Mourelle was a Galician naval officer and explorer serving the Spanish crown. He was born in 1750 at San Adrián de Corme (Corme Aldea, Ponteceso), near La Coruña, Galicia
1775 voyage Mourelle served the Spanish navy in the Guyanas, Trinidad, and the Antilles before becoming stationed at New Spain\'s Pacific Ocean naval base at San Blas, Mexico in 1774. He joined the 1775 expedition of Bruno de Heceta and Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra, serving as Quadra\'s pilot on the schooner Sonora. On July 29, at around 49 degrees north latitude, the Sonora became separated from Heceta\'s ship Santiago. Heceta soon returned south while Quadra and Mourelle continued north, eventually reaching 58 degrees 30 minutes north latitude. They found and anchored in Bucareli Bay. Then they sailed south, arriving at Monterey, California, on October 7, and San Blas on November 20, 1775.
Mourelle\'s journal was somehow taken clandestinely to London where it was translated and published. Captain James Cook made use of the information in Mourelle\'s journal during his travels in the Pacific Northwest.
1779 voyage Mourelle again served as the pilot of Quadra, and second in command of the ship Favorita, during the 1779 expedition commanded by Ignacio de Arteaga. Leaving San Blas on February 11, 1779, the expedition reached 61 degrees north and Hinchinbrook Island at the head of the Gulf of Alaska. From there they sailed southwest along the Kenai Peninsula. The ships returned to San Blas on November 21, 1779.
Later career During his service at San Blas, Mourelle traveled extensively throughout the Pacific Ocean. From 1781 on the La Princessa, he attempted to find a southern route from the Philippines to Mexico, mapping 29 of the 50 islands in the Hermit Islands, Ninigo Islands and Tench Island in New Guinea, and Ontong Java in the Solomon Islands . He visited Tonga and travelled through the Ellice Islands (now Tuvalu). Keith S. Chambers and Doug Munro (1980) identify Niutao as the island that Mourelle named on May 5, 1781, thus solving what Europeans had called The Mystery of Gran Cocal. Due to contrary winds, he returned via Guam and took the northern route across the Pacific to Mexico. He was also familiar with the Philippines and Canton, China.
Mourelle was to command the Mexicana for a 1792 voyage to explore the Strait of Georgia but Alessandro Malaspina had one of his own officers, Cayetano Valdés, placed in command of the Mexicana. Dionisio Alcalá Galiano commanded the Sutil, the twin companion of the Mexicana.
Mourelle was transferred to Spain in 1793. He was promoted to frigate captain in the same year as the Action of 19 January 1799 where he took a leading role. He became ship\'s captain in 1806, and commodore in 1811. He commanded a squadron in 1818 that was to put down a rebellion in the Rio de la Plata, but the endeavor never got underway. Mourelle died on May 24, 1820, at the age of 64.
1856 A K Johnston Large Antique Map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Van Diemens Land or Tasmania by A K Johnston
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27002
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
This original large hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map was published by A K Johnston in the 1856 edition of his National atlas of historical, commercial, and political geography.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1856 A K Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia, early Separation of Victoria
Antique Map
- Title : Australia by A K Johnston
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27000
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Description:
This original large hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of Australia - with coloured outlines to the counties in NSW & WA - was published by A K Johnston in the 1856 edition of his National atlas of historical, commercial, and political geography.
A important and interesting map illustrating the boundary of South Australia, as well as the county boundaries in both Western Australia and New South Wales. One of the first maps to illustrate the separation of the state of Victoria from New South Wales in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\\\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\\\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\\\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1856 A K Johnston Large Antique Map of New Zealand
Antique Map
- Title : New Zealand by A K Johnston
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27003
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Description:
This original large hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of New Zealand was published by A K Johnston in the 1856 edition of his National atlas of historical, commercial, and political geography.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiraltys choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
1856 A K Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia, early Separation of Victoria
Antique Map
- Title : Australia by A K Johnston
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93439
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Description:
This original large hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of Australia - with coloured outlines to the counties in NSW & WA - was published by A K Johnston in the 1856 edition of his National atlas of historical, commercial, and political geography.
A important and interesting map illustrating the boundary of South Australia, as well as the county boundaries in both Western Australia and New South Wales. One of the first maps to illustrate the separation of the state of Victoria from New South Wales in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\\\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\\\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\\\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print Sydney Aboriginal Wárrgan, Bennelong's Sister
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Oui-re-kine
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91238
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print, of the (half) sister of the famous Port Jackson Aborginal leader Bennelong, Oui-ré-kine – Wárrgan (Crow), also referred to as Worogan, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit, and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
The sitter – identified by artist Nicolas-Martin Petit as Oui-ré-kine – Wárrgan (Crow), also referred to as Worogan. In his writings about the Eora people he knew, astronomer and collector of Sydney languages William Dawes counted Wárrgan with Bennelongs sisters, although she might have been a half-sister or other relative of Bennelongs. Her husband Yeranibe (Euranabie) was the son of Maugoran, a leader of the Burramattagal clan, making Wárrgan a sister-in-law to Bidgee Bidgee, another of Petits Sydney sitters. In 1801, Wárrgan and Yeranibe joined the Lady Nelson which, under the command of James Grant, voyaged to Jervis Bay before making a survey of Bass Strait. In The Narrative of a Voyage of Discovery performed in His Majestys vessel the Lady Nelson (1803–1804), Grant related an incident wherein Wárrgan demonstrated the use of a waddy and a woomera, and how incisions were made on the body using a shell. Both Wárrgan and Yeranibe spoke English, and acted as Grant’s interpreters.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35511
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Australia with vignettes of Sydney Harbour, Aboriginals, Parrots and Kangaroos was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1784 Cook 1st edition Antique Print HMS Resolution & Discovery Xmas Bay, Kerguelen Isle 1776
Antique Map
- Title : A view of Christmas Harbour in Kerguelens Land
- Ref : 31726
- Size: 20in x 14 1/2in (510mm x 370mm)
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of HMS Resolution & Discovery anchored in Christmas Bay, on Kerguelen Islands on Christmas day in 1776, was engraved by James Newton (1748-1804) after a painting by Cooks onboard artist John Webber, during Cooks 3rd & last voyage of Discovery was published in the 1784 1st English edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. London 1784.
Cook wrote..........I found the shore in a manner covered with Penguins and other birds and Seals…so fearless that we killed as ma(n)y as we chose for the sake of their fat or blubber to make Oil for our lamps and other uses… Here I displayd the British flag and named the harbour Christmas harbour as we entered it on that Festival..... (Journals III, i, 29-32)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 14 1/2in (510mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (410mm x 270mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Single heavy vertical crease along top of image, pressed out
Verso: - None
Background:
The Kerguelen Islands, sometimes called the Desolation Islands, are located in the southern Indian Ocean and were discovered by the French navigator Yves de Kerguelen-Trémarec in 1772. On Christmas Day, 1776 Cook’s ships Resolution and Discovery anchored in Oiseau Bay, which he named Christmas Harbour. Cook\'s men discovered a bottle containing a message in Latin left by Kerguelen\'s men. Cook wrote in his log: “I could have very properly called the island Desolation Island to signalise its sterility, but in order not to deprive M. de Kerguelen of the glory of having discovered it, I have called it Kerguelen Land.”
The Kerguelen Islands or the Kerguelen Archipelago are located in the southern Indian Ocean. The main island, Grande Terre, is 6,675 km² and it is surrounded by another 300 smaller islands and islets, forming an archipelago of 7,215 km². The climate is cold and very windy and the seas are usually rough. The islands are part of a submarine large igneous province called the Kerguelen Plateau.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\\\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\\\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
1777 Capt Cook Antique Print View of Cook Landing on Malakula Island, Vanuatu in 1774
Antique Map
- Title : The Landing at Mallicolo one of the New Hebrides...Published Feb 1st 1777 by Wm. Strahan
- Ref : 91223
- Size: 19in x 12 ½in (485mm x 320mm)
- Date : 1777
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain James Cook & his men landing on the Island of Malakula (Mallicolo) in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by James Basire - after William Hodges - and was published in Captain James Cooks 1777 edition of A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775. printed by William Strahan, New Street, Shoe Lane, & Thos. Cadell, in the Strand, London 1777.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 ½in (485mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 12in (480mm x 305mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Two very small worm holes
Verso: - None
Background:
Malakula Island also spelled Malekula, is the second-largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, in the Pacific Ocean region of Melanesia.
First discovered by the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós in 1606 and visited by Captain James Cook in 1774.
Vanuatu officially the Republic of Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island in 1606. Since the Portuguese and Spanish monarchies had been unified under the king of Spain in 1580 (following the vacancy of the Portuguese throne, which lasted for sixty years, until 1640, when the Portuguese monarchy was restored), Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queiros, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition.
James Basire 1730–1802, also known as James Basire Sr., was an English engraver. He is the most significant of a family of engravers, and noted for his apprenticing of the young William Blake.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal, Ourlaga
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Ourlaga
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93089
Description:
This exquisite, rare original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Ourlaga, visited by Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Bara-Ourou
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Bara-Ourou
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93088
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Bara-Ourou, portrait of a young man 28-30 years of age, visited by Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Grou Agara
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Grou Agara
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93086
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Grou Agara, visited by the Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Arra Maida
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93085
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida, visited by the Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print Sydney Aboriginal Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan - Bennelong
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Gnoung-a-gnoung-a Mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91239
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print, of the brother in law of the famous Port Jackson Aborginal leader Bennelong, Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, or Anganángan, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 by Nicolas-Martin Petit, was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan
It is over 200 years since the death of an adventurous young Aboriginal Australian who crossed the vast Pacific Ocean to North America and returned to Sydney. From the deck of an English storeship he glimpsed many strange places, visiting Norfolk Island, Hawaii, Nootka Sound (now Vancouver, Canada) and the Spanish colonies of San Francisco, Santa Barbara and San Diego on the Californian coast.
The voyager was Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, whose wife Warreeweer was the younger sister of the Wangal leader Woollarawarre Bennelong, at that time being feted in London society. The distance Gnung-a Gnung-a traversed was some 16,000 miles (25,750 kilometres) as the crow flies, but much further in a sailing ship driven by unpredictable winds.
On the first day he ventured into the convict settlement at Sydney Cove, in November 1790, Gnung-a Gnung-a adopted the name Collins from Acting Judge Advocate David Collins, who often mentions him in An Account of the English Colony in New South Wales, published in London in 1798.
It was the idea of Major Francis Grose, acting governor of New South Wales after the departure of Captain Arthur Phillip in 1792, to embark a native of this country on HM storeship Daedalus for the purpose of acquiring our language, wrote David Collins. The 350-ton capacity vessel was ordered to resupply provisions for the expedition to the north-west coast of North America commanded by Captain George Vancouver (1757–1798). In the navy ships HMS Discovery and HMS Chatham, Captain Vancouver was to complete the survey made by Captain James Cook.
Voyage to America
HMS Daedalus sailed from Port Jackson on 1 July 1793, passing west of the Society Islands (French Polynesia) to Owhyee (Hawaii). The commander, Lieutenant James Hanson, missed a rendezvous with Vancouvers ships at Nootka Sound on 8 October, but anchored with the two survey ships off San Francisco Bay on 21 October. The three British ships followed the coast of todays California to San Diego, leaving on 9 December 1793 and arriving at Hilo in Hawaii on 8 January 1794.
The Hawaiian King Kamehameha, who warmly welcomed Vancouver, was so impressed by the good-natured, handsome Aboriginal man on the expedition that he wanted to buy him, offering in exchange canoes, weapons and curiosities.
Gnung-a Gnung-a got on well with everyone on Daedalus and Hanson was pleased by his good nature and his willingness to do whatever was asked of him. During his month in Hawaii, he often went ashore with his shipmates. Wherever he went he readily adopted the manners of those around him, Hanson later told Collins, who remarked, with ironic humour, that...........
when at Owhyee, having discovered that favours from the females were to be procured at the easy exchange for a looking-glass, a nail, or a knife, he was not backward in presenting his little offering, and was as well received as any of the white people in the ship. It was noticed too that he always displayed some taste in selecting the object of his attentions.......
Return to Sydney
Home in Sydney Town, Gnung-a Gnung-a fought and wounded a very fine young fellow called Wyatt, who had taken up with his wife during his absence and Warreeweer became the prize of the victor.
During a ritual revenge combat in December 1795, Pemulwuy, leader of the Georges River Bidjigal near Botany Bay, launched a spear at Gnung-a Gnung-a that remained fixed in his back. The English surgeons could not extract the spear and thought he was unlikely to recover. Gnung-a Gnung-a, however, left the hospital and walked about for several weeks with the spear protruding from his back. At last, wrote Collins in a footnote..........
we heard that his wife, or one of his male friends, had fixed their teeth in the wood and drawn it out after which he recovered, and was able again to go into the field. His wife War-re-weer showed by an uncommon attention her great attachment to him.......
Before this unexpected recovery, David Collins wrote a brief appreciation of his namesake:
He was much esteemed by every white man who knew him, as well on account of his personal bravery, of which we had witnessed many distinguishing proofs, as on account of a gentleness of manners which strongly marked his disposition, and shaded off the harsher lines that his uncivilised life now and then forced into the fore-ground.
While in Sydney with a scientific expedition commanded by Nicholas Baudin in 1802, the young French artist Nicolas-Martin Petit met Gnung-a Gnung-a and sketched a striking portrait that he captioned Gnoung-a gnoung-a, mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
A report in the Sydney Gazette of Sunday 15 January 1809 said that the body of Collins (Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan) had been found beside the Dry Store, site of the present Sirius Park in Bridge Street, Sydney. The newspaper said he had been known for the docility of his temper, and the high estimation in which he was universally held among the native tribes.
On the night of Thursday 12 January 1809, Gnung-a Gnung-as children, others he had adopted, and his brother Old Phillip, faced a salvo of spears in the ritual ordeal that followed death in Aboriginal society. The date of his death was not recorded, but it was customary to keep an overnight vigil over a dead body before burial and the subsequent revenge combat, so it was probably 11 January.
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan is one of many Aboriginal men and women who sailed from Sydney in English ships and played a significant role in Australias early maritime history.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1854 John Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map, Early Town Plan of Gladstone, Queensland
- Title : Plan of the Town of Gladstone Port Curtis 1854 (Water is very scarce in this locality)
- Size: 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1854
- Ref #: 82045
Description:
This large, rare & important map, a very early plan of the Queensland town of Gladstone by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1854 - dated - and was published for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have numbered only in the 100s.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
Gladstone is a city in the Gladstone Region, Queensland, Australia. It is approximately 550 km (340 mi) by road north of Brisbane and 100 km south-east of Rockhampton. Situated between the Calliope and Boyne Rivers, Gladstone is home to Queensland\'s largest multi-commodity shipping port.
Before European settlement, the Gladstone region was home of the Toolooa (or Tulua), Meerooni and Baiali (or Byellee) Aboriginal tribes.
In May 1770, the HM Bark Endeavour, under the command of James Cook, sailed by the entrance to Gladstone Harbour under the cover of darkness. Matthew Flinders, during his 1801–1803 circumnavigation of Australia, became the first recorded European to sight the harbour in August 1802. He named the harbour Port Curtis, after Admiral Roger Curtis, a man who was of assistance to Flinders a year earlier at the Cape of Good Hope. John Oxley conducted further exploration of the harbour and surrounding countryside in November 1823. Oxley was dismissive of the region, noting the harbour was difficult to enter, the countryside was too dry, and the timber useless for construction purposes.
Nevertheless, in 1847 the British attempted to establish the new colony of North Australia at Port Curtis. Colonel George Barney was chosen to lead this experiment in colonisation and his expedition was eventful. On 25 January 1847, the Lord Auckland, carrying 87 soldiers and convicts, arrived off the southern entrance of Port Curtis and promptly ran aground on shoals off the southern tip of Facing Island. The settlers spent seven weeks on the island before being rescued by the supply ship Thomas Lowry and delivered the intended site of settlement, the region now known as Barney Point. On 30 January at a proclamation ceremony, Barney was sworn in as Lieutenant Governor of the colony of North Australia. The convict settlement lasted barely two months and cost the Imperial government ₤15,000. A change of government in Britain ordered the withdrawal of Barney and the settlers. However, interest in the region remained.
By 1853, Francis MacCabe was surveying the site of a new town on the shores of Port Curtis under the protection of several detachments of Native Police. Maurice O\'Connell was appointed government resident the following year, resulting in an influx of free settlers as land became available throughout the region. In 1863, the town became a Municipality with Richard Hetherington elected Gladstones first mayor. The fledgling town was named after the British Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone and has a 19th-century marble statue on display in its town museum.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1861 Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map of Queensland, Brisbane to Toowoomba & Warwick - Bowen
- Title : Sketch to illustrate Sir George Bowens offical Tour to March 1860
- Size: 17in x 13in (430mm x 330mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1861
- Ref #: 82051
Description:
This incredibly rare & important map of the first Governor of Queensland Tour west of Queensland - from Brisbane to Toowoomba and south to Warwick in March 1860 - by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1861 - dated at the foot of the map - a year after the granting of Statehood of Queensland in 1859 - and was published for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London. The importance & rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have numbered only in the 100s.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
Sir George Ferguson Bowen, GCMG 1821 – 1899 was a British author and colonial administrator whose appointments included postings to the Ionian Islands, Queensland, New Zealand, Victoria, Mauritius and Hong Kong.
In 1859, Bowen was appointed the first Governor of Queensland, a colony that had just been separated from New South Wales. Bowen\'s influence in Queensland was greater than that of the governors in other Australian colonies in a large part due to Robert Herbert, who accompanied Bowen from England, and later became colonial secretary and then first Premier of Queensland in 1860–66. Bowen was interested in the exploration of Queensland and in the establishment of a volunteer force, but incurred some unpopularity by refusing to sanction the issue of inconvertible paper money during the financial crisis of 1866. But overall, he was quite popular in Queensland, so that the citizens requested an extension of his five-year term as governor, resulting in his staying for further two years.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 13in (430mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 13in (430mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Australia...Gold Areas marked thus....
- Date : 1855
- Size: 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50227
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of Australia by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1824 Louis Freycinet Antique Print of Yellow Bellied Wood Shrike of Timor, 1818
- Title : Choucari Vert; (Graucalus Viridis)
- Ref #: 31742
- Size: 18in x 12in (460mm x 305mm)
- Date : 1824
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This magnificent large hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique print of The Yellow Bellied Wood Shrike of Timor (Plate no. 21) by Florent Prévost (visited by Freycinet in November 1818) was engraved by Jean-Louis-Denis Coutant (1776-1831) and published in the 1824 1st edition of Louis De Freycinets Atlas of Mammals, Birds etc Voyage autour du monde fait par ordre du Roi sur les corvettes de S. M. l\'Uranie et la Physicienne, pendant les années 1817, 1818, 1819 et 1820
These magnificent large hand coloured 1st edition engravings are extremely scarce and a must for ny collection.
Florent Prévost (1794 – 1870) was a French naturalist and illustrator. He was assistant naturalist at the Muséum National d Histoire Naturelle. He was the author of various zoological works, including Les Pigeons par Madame Knip (1843) and, with C. L. Lemaire, Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux d\'Europe (1845). He did illustrative work in books by Coenraad Jacob Temminck (1778–1858), Charles Lucien Bonaparte (1803–1857) and Georges-Louis Leclerc de Buffon (1707–1788).
He worked on the birds from the voyage of La Venus with Marc Athanese Parfait Oeillet Des Murs, and on the birds and mammals brought back from the French expedition to Abyssinia between 1839 and 1843.
Prevost\'s ground sparrow (Melozone biarcuatum), Prevost\'s squirrel (Callosciurus prevostii), and Gerard\'s water snake (Gerarda prevostiana) are named after him
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 12in (460mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 ½in (330mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling & spotting
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling & spotting
Background:
After the Restoration the French government gave Freycinet, then a captain, command of another expedition to circumnavigate the globe and conduct research into the shape of the earth, meteorology and terrestrial magnetism. He sailed from Toulon on 17 September 1817 in L Uranie with his wife Rose who secreted herself aboard, and who wrote a separate account of the voyage. After refreshing at the Cape of Good Hope and Mauritius he landed at Shark Bay, Western Australia on 12 September 1818 where he set up an observatory, thoroughly surveyed the inlets and the coastal districts and removed the plate left by Willem de Vlamingh, which he had found and re-erected in 1801. He then sailed north to Timor. His accounts and description of the landscape and life and customs of that and other islands in the East Indies captivated the attention of people in Europe much more than his Australian reports, and a widespread interest developed in the expedition. Leaving Timor on 27 November he sailed via the Moluccas, the Carolines, the Marianas, and the Sandwich Islands and reached Port Jackson on 19 November 1819, the scientists on board adding constantly to their store of information on hydrography, botany, cartography and anthropology. After spending Christmas ashore, they sailed on 26 December and, falling in with the westerlies, set a course for Cape Horn.
On 13 February 1820 L Uranie was wrecked on the Falkland Islands; the scientific records and notes were saved before the vessel foundered, but 2500 of the 4175 plant specimens were lost. Freycinet returned to France in November 1820 and died on 18 August 1842.
There is no evidence in the expedition\'s records or French governmental archives to suggest that there were political objectives in this circumnavigation but, though its purpose was to engage in scientific discovery, this first major voyage undertaken by the restored Bourbons did show the French flag in distant seas and foreshadowed a series of other expeditions which were not wholly scientific.
1825 Philippe Vandermaelen Large Antique Map The Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Partie De La Nlle. Hollande
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1825
- Ref #: 93125
Description:
This very large original hand coloured antique lithograph map of the Gulf of Carpentaria was published by Philippe Vandermaelen in his revolutionary 1825 Atlas universel de geographie physique, politique, statistique et mineralogique.
Until the publication of this atlas, large detailed maps of this region of remote Australia were uncommon. The clean detailed lines and added hand colouring make this one of the most desirable early maps of northern Queensland and the NT.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first European explorer to visit the region (and Australia) was the Dutch Willem Janszoon (whose name is also written as Jansz) in 1605–6. His fellow countryman, Jan Carstenszoon (or Carstensz), visited in 1623 and named the gulf in honour of Pieter de Carpentier, at that time the Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies. Abel Tasman also explored the coast in 1644. The region was later explored and charted by Matthew Flinders in 1802 and 1803.
The first overland expedition to reach the Gulf was the Burke and Wills expedition, led by Robert O Hara Burke and William John Wills which left Melbourne, Victoria in August 1860 and reached the mouth of the Bynoe River in February 1861.