Australia/Oceania (1)
1803 Louis Freycinet Antique Map of The Islands of Timor, Samau & Rote Indonesia
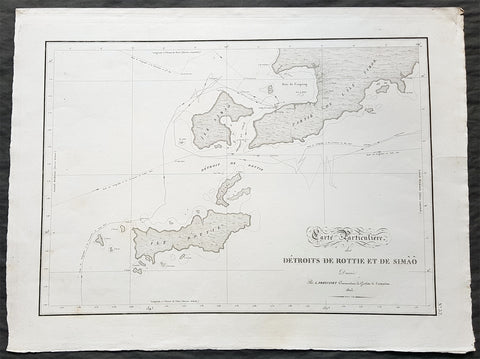
- Title : Carte Particuliere des Detroits De Rottie et de Simao...L Freycienet...le Casuarina 1803..Lambert Sculp.
- Ref #: 42014
- Size: 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1803
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This magnificent large original copper-plate engraved antique map of the islands of Samau, Rote and the southern part of Timor, including the bay and town of Kupang, by Lieutenant Louis Freycinet, in command of the ship Casuarina in 1803, was engraved by Anton Lambart and was published in the 1807 1st edition of François Pérons, Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes (‘Voyage of Discovery to the Southern Lands in three volumes, Paris, 1807–1816.
Also illustrates the tracks of the ships Geographe, the Naturaliste from the earlier voyages in 1801, and the Casuarina tracks of 1803.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15in (545mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nicolas Thomas Baudin 1754 – 1803 was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer.
The Baudin expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland (Australia). The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
Napoléon Bonaparte, as First Consul, formally approved the expedition to the coasts of New Holland, after receiving a delegation consisting of Baudin and eminent members of the Institut National des Sciences et Arts on 25 March 1800. The explicit purpose of the voyage was to be ‘bservation and research relating to Geography and Natural History.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of the continent until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. During their exploration here they lost a longboat and a sailor, Assistant Helmsman Timothée Vasse. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by \'t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted the Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.