Australia/Oceania (215)
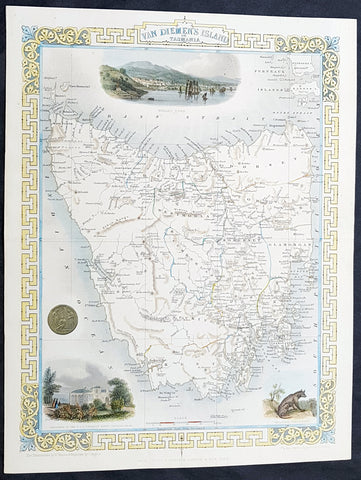
1851 John Tallis Beautiful Antique Map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Van Diemens Land or Tasmania...John Tallis
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1851
- Ref #: 93054
Description:
This original steel plate engraved beautifully hand coloured antique map Van Diemens Land or Tasmania, Australia with vignettes of Hobart, Circular Head and Tasmanian Tiger, by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first reported sighting of Tasmania by a European was on 24 November 1642 by Dutch explorer Abel Tasman, who landed at todays Blackman Bay. More than a century later, in 1772, a French expedition led by Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne landed at (nearby but different) Blackmans Bay, and the following year Tobias Furneaux became the first Englishman to land in Tasmania when he arrived at Adventure Bay, which he named after his ship HMS Adventure. Captain James Cook also landed at Adventure Bay in 1777. Matthew Flinders and George Bass sailed through Bass Strait in 1798–99, determining for the first time that Tasmania was an island.
Sealers and whalers based themselves on Tasmanias islands from 1798, and in August 1803 New South Wales Governor Philip King sent Lieutenant John Bowen to establish a small military outpost on the eastern shore of the Derwent River in order to forestall any claims to the island by French explorers who had been exploring the southern Australian coastline. Bowen, who led a party of 49, including 21 male and three female convicts, named the camp Risdon. Several months later a second settlement was established by Captain David Collins, with 308 convicts, 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) to the south in Sullivans Cove on the western side of the Derwent, where fresh water was more plentiful. The latter settlement became known as Hobart Town or Hobarton, later shortened to Hobart, after the British Colonial Secretary of the time, Lord Hobart. The settlement at Risdon was later abandoned. Left on their own without further supplies, the Sullivans Cove settlement suffered severe food shortages and by 1806 its inhabitants were starving, with many resorting to scraping seaweed off rocks and scavenging washed-up whale blubber from the shore to survive.
A smaller colony was established at Port Dalrymple on the Tamar River in the islands north in October 1804 and several other convict-based settlements were established, including the particularly harsh penal colonies at Port Arthur in the southeast and Macquarie Harbour on the West Coast. Tasmania was eventually sent 75,000 convicts—four out of every ten people transported to Australia. By 1819 the Aboriginal and British population reached parity with about 5000 of each, although among the colonists men outnumbered women four to one. Wealthy middle-class free settlers began arriving in large numbers from 1820, lured by the promise of land grants and free convict labour. Settlement in the islands northwest corner was monopolised by the Van Diemens Land Company, which sent its first surveyors to the district in 1826. By 1830 one-third of Australias non-Indigenous population lived in Van Diemens Land and the island accounted for about half of all land under cultivation and exports.
Van Diemens Land—which thus far had existed as a territory within the colony of New South Wales—was proclaimed a separate colony, with its own judicial establishment and Legislative Council, on 3 December 1825. Transportation to the island ceased in 1853 and the colony was renamed Tasmania in 1856, partly to differentiate the burgeoning society of free settlers from the islands convict past.
The Legislative Council of Van Diemens Land drafted a new constitution which it passed in 1854. The following year the Privy Council approved the colony changing its name from Van Diemens Land to Tasmania, and in 1856 the newly elected bicameral parliament sat for the first time, establishing Tasmania as a self-governing colony of the British Empire.
The colony suffered from economic fluctuations, but for the most part was prosperous, experiencing steady growth. With few external threats and strong trade links with the Empire, Tasmania enjoyed many fruitful periods in the late 19th century, becoming a world-centre of shipbuilding. It raised a local defence force that eventually played a significant role in the Second Boer War in South Africa, and Tasmanian soldiers in that conflict won the first two Victoria Crosses awarded to Australians.
In 1901 the Colony of Tasmania united with the five other Australian colonies to form the Commonwealth of Australia. Tasmanians voted in favour of federation with the largest majority of all the Australian colonies.
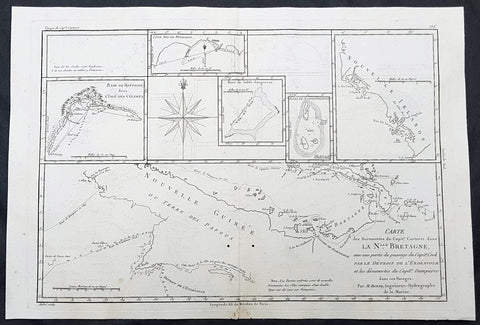
1842 D Urville & Goupil Antique Print of Men of Santa Isabel Isle, Solomon Isle.
- Title : Naturels D Isabelle (Isle Solomon)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31745
Description:
This magnificent, large original antique lithograph print of profiles of 4 different men of the island of Santa Isabel of the Solomon Islands, visited in November & December 1838 by Dumont D Urville, drawn by Ernest Goupil, artist/draftsman aboard the Astrolabe during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayoti and was published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Ernest Goupil was a French painter, draftsman and watercolourist He is known for the illustrations made as official painter for Dumont D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas. In Voyage to the South Pole and in Oceania on corvettes l\'Astrobale and Zélée, executed by order of the king during the years 1837-1838-1839-1840, his drawings are transposed on stone, most notably by Emile Lassalle , Pharamond Blanchard and Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot . Dumont d\'Urville relates: On the Zélée , Mr. Goupil fills his cartons with precious paintings, and on the Astrolabe , the young surgeon Le Breton, who has a remarkable talent in this genre, also performs at my asks for charming drawings.
Some drawings were sent to the Minister of the Navy and were shown to the King, who wanted to see them transposed into painting by the marine painter Théodore Gudin , but Goupil would not have given his consent.
In August 1839 in Samarang Java , the crew is struck by a violent epidemic, and after two months of suffering, Ernest Goupil succumbs and died on January 1 , 1840 ijn Hobart-town where he was buried with full military honours.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (530mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (530mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Santa Isabel Island (also known as Isabel, Ysabel and Mahaga) is the longest in the Solomon Islands, the third largest in terms of surface area, and the largest in the group of islands in Isabel Province.
The first European contact to the Solomon Islands was made at Santa Isabel Island, by the Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña on 7 February 1568. It was charted as Santa Isabel de la Estrella (St. Elizabeth of the Star of Bethlehem in Spanish). A settlement was established by the Spaniards, and a small boat (known in the accounts as the brigantine) was built to survey and chart the surrounding sea and islands. These local explorations led by Maestre de Campo Pedro Ortega Valencia and Alférez Hernando Enríquez resulted in the discoveries of the islands of Malaita, Guadalcanal, Savo, Vangunu, Choiseul, Makira, Ulawa, Malaupaina, Malaulalo, Ali\'ite, and Ugi Island. The Spanish immediately came into contact with Solomon Islanders and at first the relationship was cordial. However, the Spanish expedition\'s need for fresh food and water quickly led to tension and conflict, the Solomon Islanders’ subsistence economy being unable to provide continuous supplies to the Spanish.
Having found no gold and little food, and beset by attacks and sickness, the Spanish colonists shifted their colony to the site of today\'s Honiara on Guadalcanal, and the settlement on Santa Isabel was abandoned.
Santa Isabel islanders suffered attacks from blackbirding in the nineteenth century (the often brutal recruitment or kidnapping of labourers for the sugar plantations in Queensland and Fiji).
In April 1885 a German Protectorate was declared over the North Solomon Islands, including Santa Isabel Island. In 1900, under the terms of Treaty of Berlin (14 November 1899), Germany transferred the North Solomon Islands (except for Bougainville and its surrounding islands) to the British Solomon Islands Protectorate in exchange for the British giving up all claims to Samoa. Missionaries settled on Santa Isabel Island under both protectorates, converting most of the population to Christianity. In the early 20th century several British and Australian firms began large-scale coconut planting.
1842 D Urville & Marescot Antique Print King Mapou-Teoa & Envoy of Mangareva Gambier
- Title : Antonio Mapoua; Koloupo (Isles Manga Reva)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31747
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of King Mapou-Teoa and his envoy who boarded D Urvilles ship the Astrolabe in August 1838, by Jacques Marescot-Duthilleul, one of the artists,draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot and published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Jacques, Marie, Eugene Marescot Duthilleul1809 - 1839 Lieutenant in the French navy and artist who accompanied Dumont D Urville on the Corvette The Astrolabe on D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas, Australia and Antarctica between 1837 and 1840. He was responsible for a number of exquisite drawings of peoples and views during the voyage that were later used for lithograph prints for publication
In 1837, a new mission of exploration in the southern Pacific Ocean was entrusted by King Louis-Philippe to Captain Dumont d Urville. This mission included improvement of scientific knowledge on the islands of the South Pacific and Indonesia, and exploration of the Antarctic continent.
The first phase of the expedition was the crossing the Sea of Weddel sea ice, on the coast of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. The second phase between May 1838 &o December 1839 consisting of visits to many South Pacific Islands: Marquesas, Polynesia, Fiji, Solomon Islands, New Guinea, Carolinas, Marianas, Moluccas and finally Sunda Islands.
At the end of this second phase, after eighteen months of difficult navigation in unhealthy climates, the sanitary condition of the crews of the two corvettes reached a critical state. During the last voyage from Sumatra (Lampang Bay) to Hobart Tasmania, eighteen patients died, including Lieutenant Marescot-Duthilleul.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mangareva is the central and largest island of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. It is surrounded by smaller islands: Taravai in the southwest, Aukena and Akamaru in the southeast, and islands in the north.
Mangareva was once heavily forested and supported a large population that traded with other islands via canoes. However, excessive logging by the islanders during the 10th to the 15th centuries resulted in deforestation of the island, with disastrous results for its environment and economy.
The first European to arrive at Mangareva was British Captain James Wilson in 1797 on the ship Duff. Wilson named the island group in honour of Admiral James Gambier, who had helped him to equip his vessel.
Mangareva along with its dependencies in the Gambier Islands were ruled by a line of kings and later regents that ruled until the French formally annexed the islands in 1881. A French protectorate was requested on 16 February 1844 by King Maputeoa but was never ratified by the French government. On 4 February 1870, Prince Regent Arone Teikatoara and the Mangarevan government formally withdrew the protectorate request and asked the French to not intervene in the kingdom\'s affairs. After Father Honoré Laval was removed to Tahiti, the native government changed its stance and an agreement between Prince Regent Arone and the French colonial authority in Tahiti was signed reaffirming the protectorate status on 30 November 1871. The Gambier Islands were finally annexed on 21 February 1881 under Prince Regent Bernardo Putairi and approved by the President of France on 30 January 1882.
1842 D Urville & Marescot Antique Print of Envoys of Mangareva Isle, Gambier Is.
- Title : Mama-Houi; Tima-Temouo (Isles Maga Reva)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31746
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of Envoys of Mangreva Island, Gambier Island visited by Dumont D Urvilles & his ship the Astrolabe in August 1838, by Jacques Marescot-Duthilleul, one of the artists,draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot and published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Jacques, Marie, Eugene Marescot Duthilleul1809 - 1839 Lieutenant in the French navy and artist who accompanied Dumont D Urville on the Corvette The Astrolabe on D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas, Australia and Antarctica between 1837 and 1840. He was responsible for a number of exquisite drawings of peoples and views during the voyage that were later used for lithograph prints for publication
In 1837, a new mission of exploration in the southern Pacific Ocean was entrusted by King Louis-Philippe to Captain Dumont d Urville. This mission included improvement of scientific knowledge on the islands of the South Pacific and Indonesia, and exploration of the Antarctic continent.
The first phase of the expedition was the crossing the Sea of Weddel sea ice, on the coast of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. The second phase between May 1838 &o December 1839 consisting of visits to many South Pacific Islands: Marquesas, Polynesia, Fiji, Solomon Islands, New Guinea, Carolinas, Marianas, Moluccas and finally Sunda Islands.
At the end of this second phase, after eighteen months of difficult navigation in unhealthy climates, the sanitary condition of the crews of the two corvettes reached a critical state. During the last voyage from Sumatra (Lampang Bay) to Hobart Tasmania, eighteen patients died, including Lieutenant Marescot-Duthilleul.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mangareva is the central and largest island of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. It is surrounded by smaller islands: Taravai in the southwest, Aukena and Akamaru in the southeast, and islands in the north.
Mangareva was once heavily forested and supported a large population that traded with other islands via canoes. However, excessive logging by the islanders during the 10th to the 15th centuries resulted in deforestation of the island, with disastrous results for its environment and economy.
The first European to arrive at Mangareva was British Captain James Wilson in 1797 on the ship Duff. Wilson named the island group in honour of Admiral James Gambier, who had helped him to equip his vessel.
Mangareva along with its dependencies in the Gambier Islands were ruled by a line of kings and later regents that ruled until the French formally annexed the islands in 1881. A French protectorate was requested on 16 February 1844 by King Maputeoa but was never ratified by the French government. On 4 February 1870, Prince Regent Arone Teikatoara and the Mangarevan government formally withdrew the protectorate request and asked the French to not intervene in the kingdom\'s affairs. After Father Honoré Laval was removed to Tahiti, the native government changed its stance and an agreement between Prince Regent Arone and the French colonial authority in Tahiti was signed reaffirming the protectorate status on 30 November 1871. The Gambier Islands were finally annexed on 21 February 1881 under Prince Regent Bernardo Putairi and approved by the President of France on 30 January 1882.
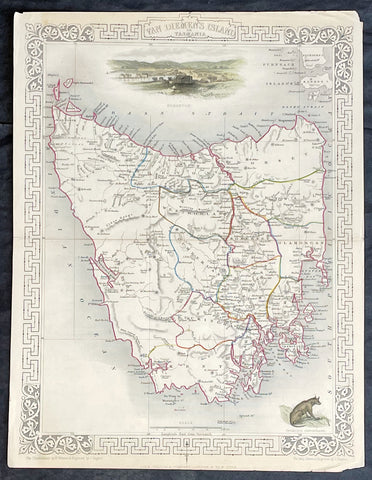
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Van Diemens Land or Tasmania
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35519
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Tasmania, Australia with vignettes of Hobart and Tasmanian Tiger was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
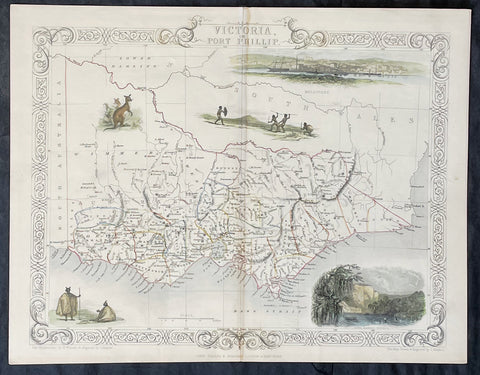
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Victoria or Port Phillip, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Victoria or Port Phillip
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35503
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Victoria, Australia with vignettes of Glenelg River, Aboriginals and Kangaroos was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
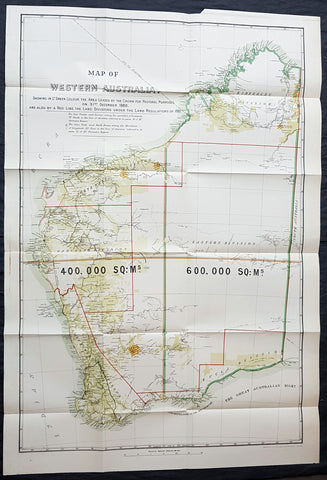
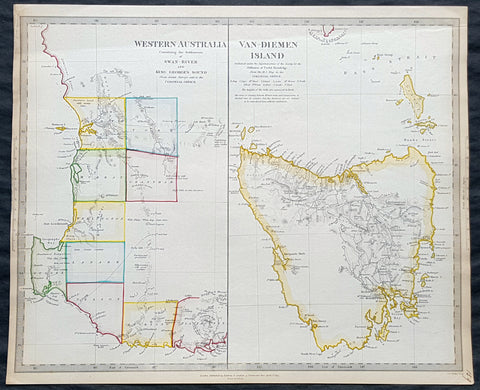
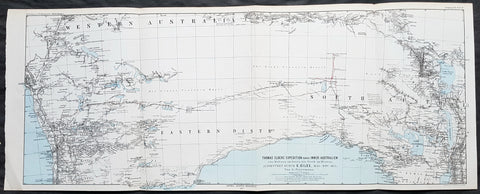
1890 John Forrest Large Antique Map Western Australia Pastoral Leases, Explorers
- Title : MAP OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA. SHOWING IN LT GREEN COLOUR THE AREA LEASED BY THE CROWN FOR PASTORAL PURPOSES ON 31ST DECEMBER 1888. AND ALSO BY A RED LINE THE LAND DIVISION UNDER THE LAND REGULATIONS OF 1887.
- Size: 39in x 27in (980mm x 685mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1890
- Ref #: 82035
Description:
This very large folding scarce original antique chromolithographic map of Western Australia for John Forrest was published by Judd & Co. London in 1890.
An extremely important map of Western Australia, issued in the year of independence for the then Surveyor General and later 1st premier of the state, John Forrest. Shown in green are the pastoral lease granted by the crown, Land Divisions drawn up for Statute in red lines and the tracks of explorers throughout WA since settlement.
This map was intended as a visual reference for the Summary of Land Regulations presented to the Houses of Parliament in 1889 in respect to the proposed introduction of Responsible Government in Western Australia. The map was drawn for the Commissioner of Lands, John Forrest. Covered in blue paper covers, detached, with advertisements.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39in x 27in (980mm x 685mm)
Plate size: - 39in x 27in (980mm x 685mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, blue covers detached
Verso: - None
Background:
Western Australia is a state occupying the entire western third of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, and the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australias largest state, with a total land area of 2,529,875 square kilometres and the second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia\'s Sakha Republic. The state has about 2.6 million inhabitants – around 11% of the national total – of whom the vast majority (92%) live in the south-west corner, 73% of the population living in the Perth area, leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated.
The first European visitor to Western Australia was the Dutch explorer Dirk Hartog, who visited the Western Australian coast in 1616. The first European settlement of Western Australia occurred following the landing by Major Edmund Lockyer on 26 December 1826 of an expedition on behalf of the New South Wales colonial government. He established a convict-supported military garrison at King George III Sound, at present-day Albany, and on 21 January 1827 formally took possession of the western third of the continent for the British Crown. This was followed by the establishment of the Swan River Colony in 1829, including the site of the present-day capital, Perth.
York was the first inland settlement in Western Australia. Situated 97 kilometres east of Perth, it was settled on 16 September 1831.
Western Australia achieved responsible government in 1890, and federated with the other British colonies in Australia in 1901. Today its economy mainly relies on mining, agriculture and tourism. The state produces 46% of Australia\'s exports.Western Australia is the second-largest iron ore producer in the world.
Forrest, John 1847 – 1918
Forrest was an Australian explorer, the first Premier of Western Australia and a cabinet minister in Australia\\\'s first federal parliament.
As a young man, he won fame as an explorer by leading three expeditions into the interior of Western Australia, for which he was awarded the 1876 Royal Geographical Societys Patrons Medal.
He was appointed Surveyor General in 1883 and in 1890 became the first Premier of Western Australia, its only premier as a self-governing colony. Forrest\\\'s premiership gave the state ten years of stable administration during a period of rapid development and demographic change. He pursued a policy of large-scale public works and extensive land settlement, and he helped to ensure that Western Australia joined the federation of Australian states. After federation, he moved to federal politics, where he was at various times postmaster-general, Minister for Defence, Minister for Home Affairs, Treasurer and acting Prime Minister. He was affiliated with the Protectionist Party from 1901 to 1906, the Western Australian Party from 1906 to 1909, the Commonwealth Liberal Party from 1909 to 1917, then the Nationalist Party of Australia from 1917 to 1918.
Shortly before his death, Forrest was informed that the King had approved his elevation to the British peerage as Baron Forrest of Bunbury
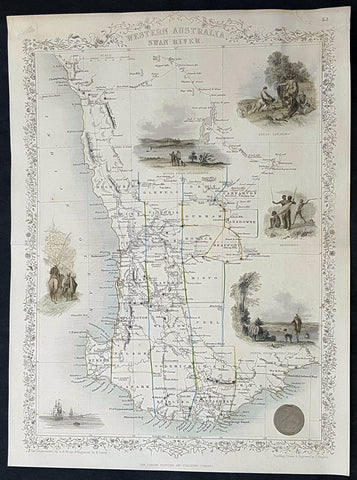
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Western Australia or the Swan River Colony
Antique Map
- Title : Western Australia Swan River
- Size: 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1851
- Ref #: 93056
Description:
This original hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of Western Australia, the Swan River Colony with vignettes of Perth from Kings Park, Swan River, Aboriginals and Sheep Farming by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Very light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
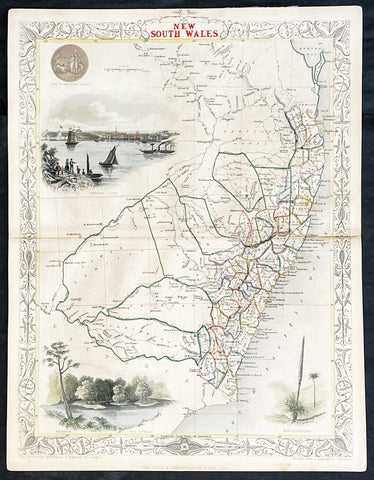
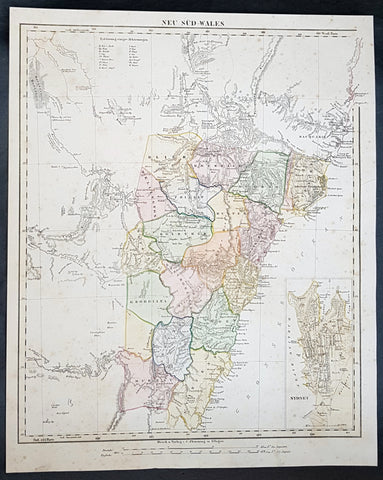
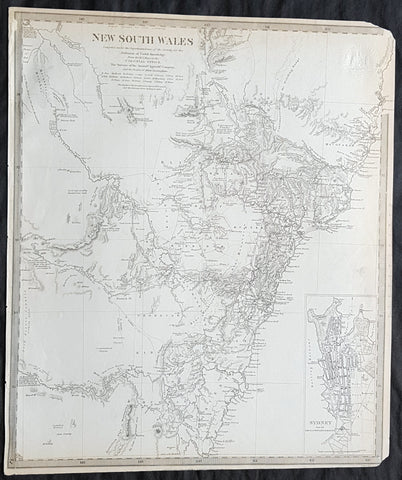
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of New South Wales, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : New South Wales
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 1554
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of New South Wales, Australia with vignettes of Sydney Harbour and The Murray was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
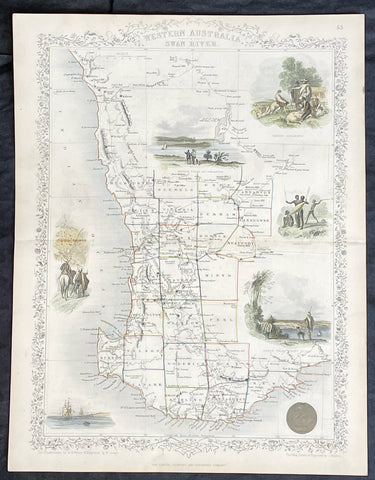
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Western Australia or The Swan River Settlement
Antique Map
- Title : Western Australia Swan River
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35523
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Western Australia or The Swan River Settlement, Australia with vignettes of Perth, Fremantle, Aboriginals and settlers was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
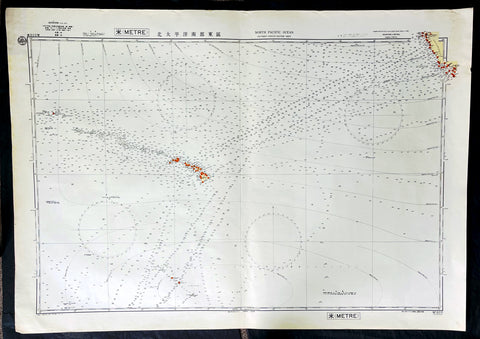
1939 Japanese Safety Agency Large Antique Map of Hawaii, Pacific - Pearl Harbor
Antique Map
- Title : North Pacific Ocean Southern Portion Eastern Sheet, Compiled from the United States and the British Charts to 1939
- Date : 1939
- Size: 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27101
Description:
This original very large lithograph map, a sea chart, with depth soundings, of The Central Pacific, centering on the Hawaiian Islands was complied by the Maritime Safety Agency Japan (MSAJ) from American & British charts. The maps centers on the Hawaiian Islands east to California and south to the Christmas Islands.
The importance of this map cannot be overstated in the context of time and would have no doubt been used by the Japanese carrier group and their attack on Pearl Harbour in 1941.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
Plate size: - 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Hawaii, just before 8:00 a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II on the side of the Allies the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning.
The attack was preceded by months of negotiations between the U.S. and Japan over the future of the Pacific. Japanese demands included that the U.S. end its sanctions against Japan, cease aiding China in the Second Sino-Japanese war, and allow Japan to access the resources of the Dutch East Indies. Anticipating a negative response from the US, Japan sent out its naval attack groups in November 1941 just prior to receiving the Hull note—the U.S. demand that Japan withdraw from China and French Indochina.
Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the U.S.-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire in Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong.
The attack commenced at 7:48 a.m. Hawaiian Time (6:18 p.m. GMT). The base was attacked by 353 Imperial Japanese aircraft (including fighters, level and dive bombers, and torpedo bombers) in two waves, launched from six aircraft carriers. Of the eight U.S. Navy battleships present, all were damaged, with four sunk. All but USS Arizona were later raised, and six were returned to service and went on to fight in the war. The Japanese also sank or damaged three cruisers, three destroyers, an anti-aircraft training ship, and one minelayer. More than 180 US aircraft were destroyed. A total of 2,403 Americans were killed and 1,178 others were wounded, making it the deadliest event ever recorded in Hawaii. Important base installations such as the power station, dry dock, shipyard, maintenance, and fuel and torpedo storage facilities, as well as the submarine piers and headquarters building (also home of the intelligence section) were not attacked. Japanese losses were light: 29 aircraft and five midget submarines lost, and 64 servicemen killed. Kazuo Sakamaki, the commanding officer of one of the submarines, was captured.
Japan announced declarations of war on the United States and the British Empire later that day (December 8 in Tokyo), but the declarations were not delivered until the following day. The British government declared war on Japan immediately after learning that their territory had also been attacked, while the following day (December 8) the United States Congress declared war on Japan. On December 11, though they had no formal obligation to do so under the Tripartite Pact with Japan, Germany and Italy each declared war on the U.S., which responded with a declaration of war against Germany and Italy. There were numerous historical precedents for the unannounced military action by Japan, but the lack of any formal warning (required by part III of the Hague Convention of 1907), particularly while negotiations were still apparently ongoing, led President Franklin D. Roosevelt to proclaim December 7, 1941, a date which will live in infamy. Because the attack happened without a declaration of war and without explicit warning, the attack on Pearl Harbor was later judged in the Tokyo Trials to be a war crime.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Victoria, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Victoria The Gold Districts are coloured (sic yellow)
- Date : 1855
- Size: 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27096
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of Victoria, Australia (with an inset map of the Mt Alexander & Castlemaine regions) by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of South Eastern Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Victoria. New South Wales and South Australia...Gold Deposits..
- Date : 1855
- Size: 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27097
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of South Eastern Australia by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
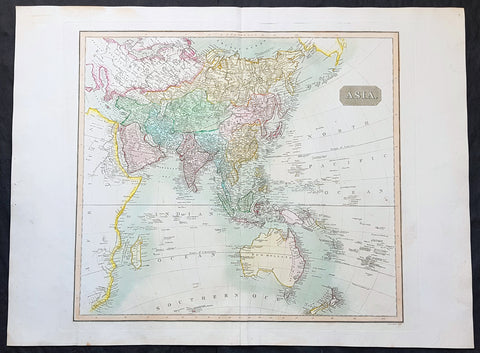
1817 John Thomson Large Antique Map of Asia, New Holland, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : Asia
- Date : 1817
- Size: 28in x 21in (710mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92965
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of Asia, Australia, New Zealand & The South Pacific by John Thomson was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28in x 21in (710mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australias national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
The indigenous population, estimated to have been between 750,000 and 1,000,000 in 1788, declined for 150 years following settlement, mainly due to infectious disease. Thousands more died as a result of frontier conflict with settlers. A government policy of assimilation beginning with the Aboriginal Protection Act 1869 resulted in the removal of many Aboriginal children from their families and communities—often referred to as the Stolen Generations—a practice which may also have contributed to the decline in the indigenous population. As a result of the 1967 referendum, the Federal governments power to enact special laws with respect to a particular race was extended to enable the making of laws with respect to Aborigines.[68] Traditional ownership of land (native title) was not recognised in law until 1992, when the High Court of Australia held in Mabo v Queensland (No 2) that the legal doctrine that Australia had been terra nullius (land belonging to no one) did not apply to Australia at the time of British settlement.
A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s and the Eureka Rebellion against mining licence fees in 1854 was an early expression of civil disobedience. Between 1855 and 1890, the six colonies individually gained responsible government, managing most of their own affairs while remaining part of the British Empire. The Colonial Office in London retained control of some matters, notably foreign affairs, defence and international shipping.
1835 Henry Teesdale Large Antique Map of Van Diemens Land, Tasmania, Australia
- Title : Van-Diemens Land
- Ref #: 80010
- Size: 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Tasmania, Van-Diemens Land with the original 11 counties - was engraved by John Dower in 1834 and was published in the 1835 edition of Henry Teesdale's A New General Atlas of the World.
As with all the maps published by Teesdale this one is of the highest quality on strong clean & sturdy paper with beautiful original hand colouring. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first reported sighting of Tasmania by a European was on 24 November 1642 by the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman, who named the island Anthoonij van Diemenslandt, after his sponsor, the Governor of the Dutch East Indies. The name was later shortened to Van Diemen's Land by the British. In 1772, a French expedition led by Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne landed on the island. Captain James Cook also sighted the island in 1777, and numerous other European seafarers made landfalls, adding a colourful array to the names of topographical features.
The first settlement was by the British at Risdon Cove on the eastern bank of the Derwent estuary in 1803, by a small party sent from Sydney, under Lt. John Bowen. An alternative settlement was established by Capt. David Collins 5 km to the south in 1804 in Sullivans Cove on the western side of the Derwent, where fresh water was more plentiful. The latter settlement became known as Hobart Town, later shortened to Hobart, after the British Colonial Secretary of the time, Lord Hobart. The settlement at Risdon was later abandoned.
Teesdale & co., Henry fl 1828-1843
Teesdale was a prominent London publisher and founding fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. He produced large-scale maps and charts and a number of fine atlases in the early part of the nineteenth century. He employed the most skilled draftsmen and engravers and his maps are renowned for precise detail and fine coloring
C1842 D Urville & Goupil Antique Print Chief Pea, Daughter & Wife of Apia, Samoa
- Title : Chef D Apia (Ise Opoulou): Jeune Fille D Apia (Ile Opoulou): Femme De Lefouga (Iles Hapai)
- Size: 22in x 14in (560mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31754
Description:
This magnificent, large original antique lithograph print of Pea the High Chief of the village of Apia on the Island of Upolu, Samoa along with and his daughter & wife visited in September 1838 by Dumont D Urville, by Ernest Goupil, the senior artist/draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayotiand was published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Ernest Goupil was a French painter, draftsman and watercolourist He is known for the illustrations made as official painter for Dumont D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas. In Voyage to the South Pole and in Oceania on corvettes l\'Astrobale and Zélée, executed by order of the king during the years 1837-1838-1839-1840, his drawings are transposed on stone, most notably by Emile Lassalle , Pharamond Blanchard and Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot . Dumont d\'Urville relates: On the Zélée , Mr. Goupil fills his cartons with precious paintings, and on the Astrolabe , the young surgeon Le Breton, who has a remarkable talent in this genre, also performs at my asks for charming drawings.
Some drawings were sent to the Minister of the Navy and were shown to the King, who wanted to see them transposed into painting by the marine painter Théodore Gudin , but Goupil would not have given his consent.
In August 1839 in Samarang Java , the crew is struck by a violent epidemic, and after two months of suffering, Ernest Goupil succumbs and died on January 1 , 1840 ijn Hobart-town where he was buried with full military honours.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 14in (560mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 14in (560mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Apia is the capital and the largest city of Samoa. From 1900 to 1919, it was the capital of German Samoa. The city is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa\'s second largest island. Apia is the only city in Samoa and falls within the political district (itūmālō) of Tuamasaga.
Apia was originally a small village from which the country\'s capital took its name. Apia village still exists within the larger modern capital of Apia which has grown into a sprawling urban area with many villages. Like every other settlement in the country, Apia village has its own matai chiefly leaders and fa\'alupega (genealogy and customary greetings) according to fa a Samoa.
The modern capital Apia was founded in the 1850s and has been the official capital of Samoa since 1959.
The harbor was also the site of an infamous 15 March 1889 naval standoff in which seven ships from Germany, the US, and Britain refused to leave harbor while a typhoon was clearly approaching, lest the first moved would lose face. All the ships were sunk, except the British cruiser Calliope, which barely managed to leave port at 1 mile per hour and ride out the storm. Nearly 200 American and German lives were lost, as well as six ships sunk or damaged beyond repair.
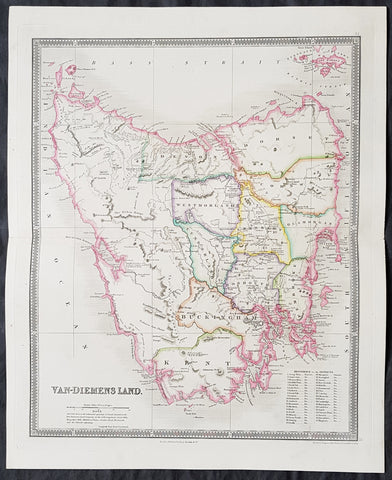
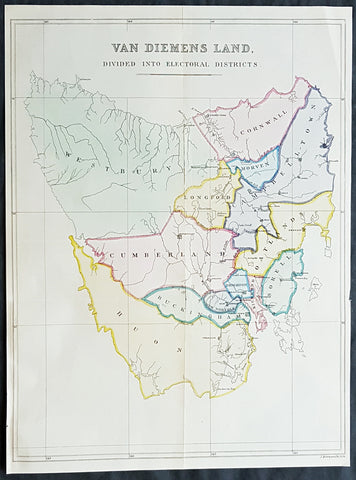
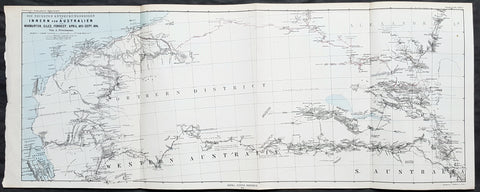
1852 John Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map The First Electoral Districts of Tasmania
- Title : Van Diemens Land Divided into Electoral Districts
- Size: 18 1/2in x 13 3/4in (470mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1852
- Ref #: 82040
Description:
This rare lithograph map of the electoral districts of Van Diemens Land (Tasmania) by John Arrowsmith was published in 1852 - 4 years prior to the first sitting of the state parliament in 1856 - for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have had very low numbers published and are very hard, if not impossible, to be be found for sale on the open market.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 13 3/4in (470mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13 3/4in (470mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Bottom left margin extended
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
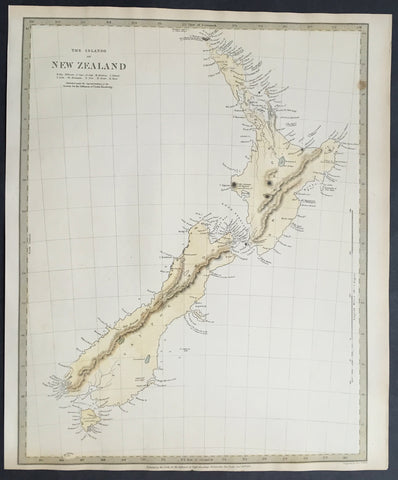
1838 SDUK Large Antique Map of New Zealand - 1st edition
Antique Map
- Title :The Islands of New Zealand....Published by the SDUK...Nov 26th 1838
- Ref #: 61040
- Size: 16in x 13in (400mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1838
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original hand coloured antique map* of New Zealand was engraved in 1838 (1st edition) - dated at the bottom of the map - by J & C W Walker and was published in the Baldwin & Cradock edition of theSociety For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
Background: The map covers the entire island country from Cape Reinga (C. Maria Van Diemen) to Stewart Island. Various cities, towns, rivers, mountains, bays and several other topographical details are noted with relief shown by hachure.
In 1840, after the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, the British annexed New Zealand as part of the Australian colony of New South Wales. However, it separated from New South Wales to become a colony in its own right in 1841. This map was originally copyrighted in 1838, but was issued in Volume two of Chapman and Hall's 1844 edition of Maps of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes in cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford.
This is a finely engraved map with beautiful original colour t on strong, clean paper. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (400mm x 330mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1774 Capt. Cook, S. Parkinson & G. Stubbs - Antique Print Australian Kangaroo in 1770
Antique Map
- Title : Quadrupede nomme Kanguroo trouve fur la Cote de la N.Hollande
[The Kanguroo, an Animal found on the Coast of New Holland] - Ref : 35016
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Kangaroo, first sketched by Sydney Parkinson onboard HMS Endeavour during Cooks first voyage in 1770, whilst laid up at Endeavour River in northern Queensland, was engraved by Robert Benard, after a painting by the famous English Artist George Stubbs in 1772. This original engraving was published in the 1774 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas by John Hawkesworth in An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks. Paris, 1774.
From Sydney Parkinsons Journal........soon after we arrived in the bay, we laid the ship on a steep bank, on the side of a river; set up tents on shore, unloaded her, carried all the cargo and provisions into them, and there lodged and accommodated our sick.
On the 22d, we examined the ship’s bottom, and found a large hole; through the planks into the hold, which had a piece of coral-rock, half a yard square, sticking in it: the same rock, therefore, that endangered us, yielded us the principal means of our redemption; for, had not this fragment intruded into the leak, in all probability the ship would have sunk.
We lost no time, but immediately set about repairing the ship’s bottom, and in a few days made it sound again. In the mean time, the boats were sent out, in search of another passage, which they found, and returned to the ship on the 3d of July.
On the 4th of July, the ship was carried to the other side of the river, and examined thoroughly; but, being found in good condition, she was soon placed in her former station; where she was loaded, and properly fitted to proceed on the voyage.
During the time we staid here, we picked up a great many natural curiosities from the reef we struck upon, consisting of a variety of curious shells, most of which were entirely new to Mr. Banks and Dr. Solander ...
Of quadrupeds, there are goats, wolves, a small red animal about the size of a squirrel; a spotted one of the viverra kind, and an animal of a kind nearly approaching the mus genus, about the size of a grey-hound, that had a head like a fawn’s; lips and ears, which it throws back, like a hare’s; on the upper jaw six large teeth; on the under one two only; with a short and small neck, near to which are the fore-feet, which have five toes each, and five hooked claws; the hinder legs are long, especially from the last joint, which, from the callosity below it, seems as if it lies flat on the ground when the animal descends any declivity; and each foot had four long toes, two of them behind, placed a great way back, the inner one of which has two claws; the two other toes were in the middle, and resembled a hoof, but one of them was much larger than the other. The tail, which is carried like a grey-hound’s, was almost as long as the body, and tapered gradually to the end. The chief bulk of this animal is behind; the belly being largest, and the back rising toward the posteriors. The whole body is covered with short ash-coloured hair; and the flesh of it tasted like a hare’s, but has a more agreeable flavour................
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
George Stubbs ARA 1724 – 1806 was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. His most famous work is probably Whistlejacket, a painting of a prancing horse commissioned by the 2nd Marquess of Rockingham, which is now in the National Gallery in London. This and two other paintings carried out for Rockingham break with convention in having plain backgrounds. Throughout the 1760s he produced a wide range of individual and group portraits of horses, sometimes accompanied by hounds. He often painted horses with their grooms, whom he always painted as individuals. Meanwhile, he also continued to accept commissions for portraits of people, including some group portraits. From 1761 to 1776 he exhibited at the Society of Artists of Great Britain, but in 1775 he switched his allegiance to the recently founded but already more prestigious Royal Academy of Arts.
Stubbs also painted more exotic animals including lions, tigers, giraffes, monkeys, and rhinoceroses, which he was able to observe in private menageries. His painting of a kangaroo in 1772 after Cooks 1st Voyage to Australia, was the first glimpse of this animal for many 18th-century Britons
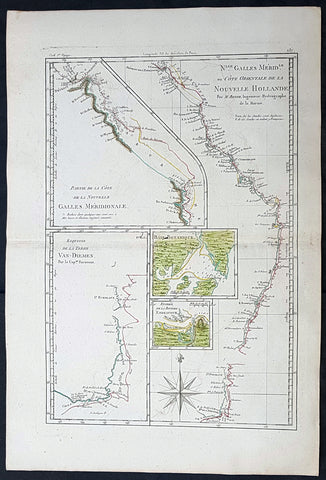
1785 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Australia, Botany Bay, Tasmania & Queensland
Antique Map
- Title : Nlle. Galles Merid. ou Cote Orientale de la Nouvelle Hollande Par M Bonne...Baie Botanique; Entree de la Riviere Endeavour; Esquisse de la Terre Van Diemen...
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 285mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1785
- Ref #: 93127
Description:
This original hand coloured antique copper-plate engraved map of the discoveries of Captain James Cook and the east coast of Australia in 1770 was published in 1785 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 285mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Interesting map illustrating the discoveries in Australia by Captain Cook in 1770 and all the place names along the coastline. The map also 4 inset maps of Botany Bay, the Endeavour River QLD, the SE coast of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania and the northern coastline of QLD.
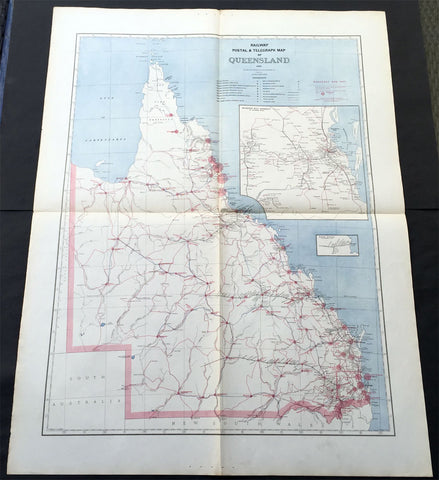
1888 Picturesque Atlas of Australia Large Antique Railway Map of Queensland
- Title : Railway Postal & Telegraph Map of Queensland
- Ref #: 50329
- Size: 34in x 26in (865mm x 660mm)
- Date : 1888
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large fine original antique lithograph layered coloured map of Queensland showing the extent of Railway and postal lines, was engraved in 1888 - the date is engraved in the title - with index page - by Alex J Scally - was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
These maps were some of the best maps published at the time in the "Modern" look. The colour is bright, the engraving extremely fine and the paper heavy and stable.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 34in x 26in (865mm x 660mm)
Plate size: - 34in x 26in (865mm x 660mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
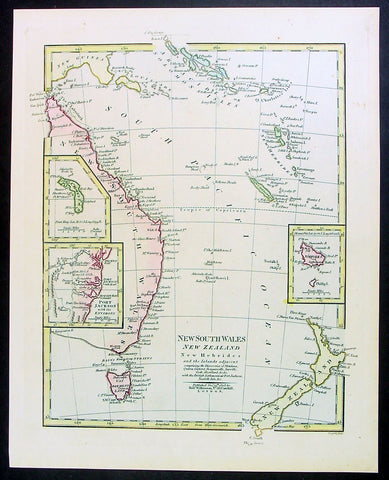
1808 Wilkinson Antique Map of East Coast of Australia, New Zealand, inset Sydney
- Title : New South Wales New Zealand New Hebrides...Published Dec 12th 1808
- Ref #: 9003
- Size: 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1808
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the east coast of Australia, New Zealand and the Solomon Islands - with inset maps of Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island & Port Jackson - was published in 1808 by Robert Wilkinson - the date is included in the title - in his wideley acclaimed General Atlas of the World published between 1794 and 1816.
This is a finely engraved copper-plate map with beautiful original hand colouring on strong stable paper. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10in (320mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
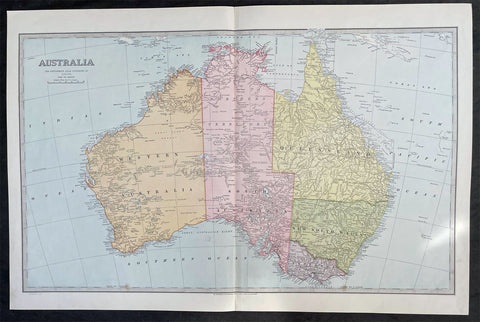
1888 Pic Atlas Scally Large Antique Map of Australia
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1888
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31986
- Size: 25 1/2in x 17in (650mm x 430mm)
Description:
This large steel-plate engraved original antique lithograph map of Australia - engraved by Alex J Scally in 1888, dated at the foot of the map - was published in The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia, 1886-88. A beautiful large pre-federation antique map of Australia, highly detailed in fine condition.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 17in (650mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
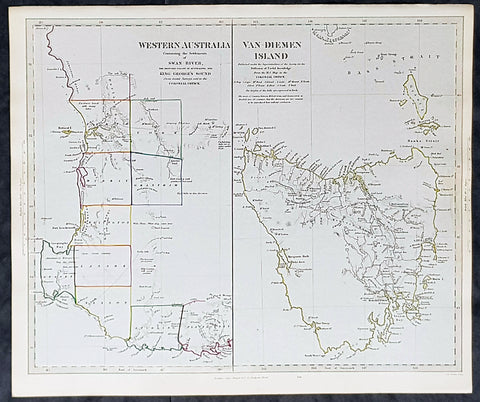
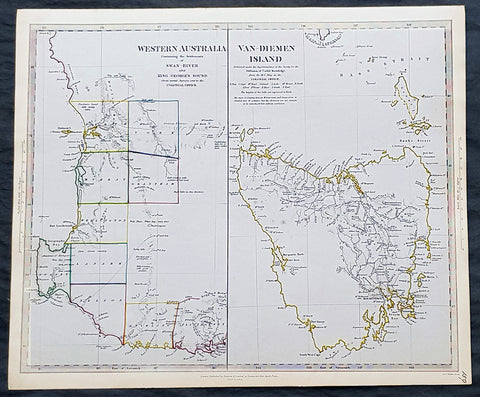
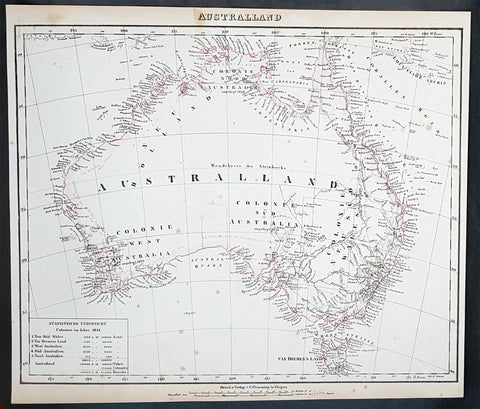
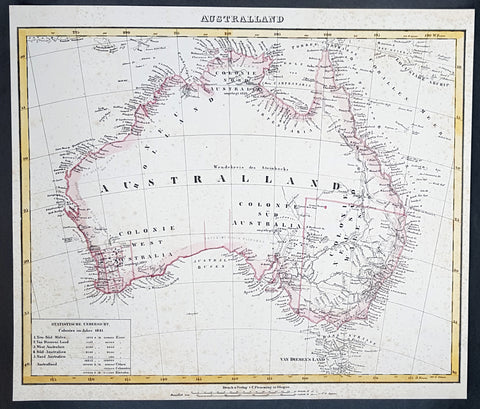
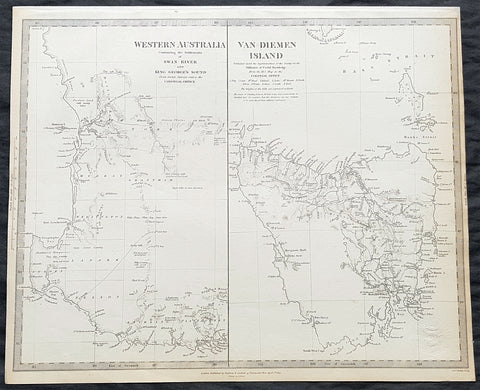
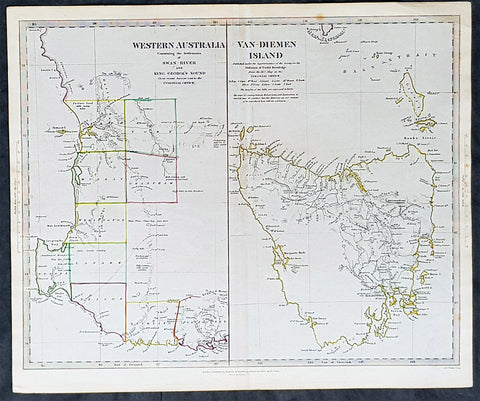
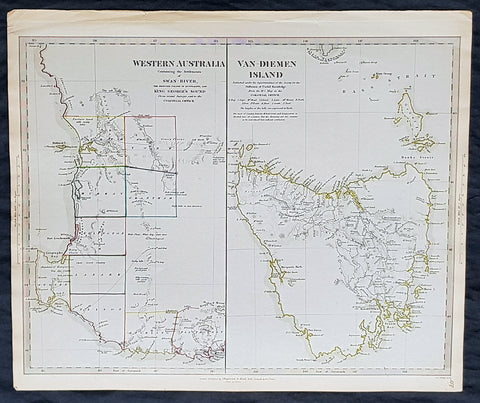
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia & Van Diemens Land, Tasmania
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 31973
Description:
This fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique maps of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, Alvin Jewett JohnsonAmerica, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia & Van Diemens Land, Tasmania
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 24670
Description:
This fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique maps of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, Alvin Jewett JohnsonAmerica, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1845 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of Australia - Population of 213,500
- Title : Australland...1841
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40972
- Size: 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, with a population census of the entire country in 1841, by Friedrich Handtke in 1845, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1845 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of Australia - Population of 213,500
- Title : Australland...1841
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 31977
- Size: 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, with a population census of the entire country in 1841, by Friedrich Handtke in 1845, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning & spotting
Plate area: - Age toning & spotting
Verso: - Age toning & spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
- Title : Neu Sud-Wales
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 31992
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of New South Wales, with an inset of a plan of Sydney Town by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
A golden age of a new kind began in New South Wales and Sydney in 1851 with the announcement of the discovery of payable gold at Ophir near Bathurst by Edward Hargraves. In that year New South Wales had about 200,000 people, a third of them within a days ride of Sydney, the rest scattered along the coast and through the pastoral districts, from the Port Phillip District in the south to Moreton Bay in the north. The gold rushes of the 1850s brought a huge influx of settlers, although initially the majority of them went to the richest gold fields at Ballarat and Bendigo, in the Port Phillip District, which in 1851 was separated to become the colony of Victoria.
Hill End, also near Bathurst N.S.W. was a locality that grew, boomed and faded with the N.S.W. Gold Rush. Called \'Bald Hills\' in 1850, \'Forbes in 1860 and finally Hill End in 1862, it was part of the Tambaroora district. At its peak, its population was 7,000. Completely reliant on mining, the town\'s decline was dramatic once the gold ran out. Hill End is famed for the unearthing of the Holtermann Specimen (correctly, the Beyers Holtermann Specimen), being the largest single mass of gold ever discovered in the world, a record that stands today. Found in 1872 at the Star Hope Mine, this single mass of quartz and gold weighed 630 lbs and when crushed produced an estimated 3,000 troy oz (205 lbs or 93 kg) of gold, thus holding more processed gold than from the largest nugget ever found, that being the Welcome Stranger from the Victorian Goldfields. Holtermann recognizing the significance of the find attempted to preserve it by buying it from the Company of which he was one of a number of directors. His efforts were in vain. It is reported that a larger mass was discovered a few days later in the same mine but was broken up underground.
Victoria soon had a larger population than New South Wales, and its upstart capital, Melbourne, outgrew Sydney. But the New South Wales gold fields also attracted a flood of prospectors, and by 1857 the colony had more than 300,000 people. Inland towns like Bathurst, Goulburn, Orange and Young flourished. Gold brought great wealth but also new social tensions. Multiethnic migrants came to New South Wales in large numbers for the first time. Young became the site of an infamous anti-Chinese miner riot in 1861 and the official Riot Act was read to the miners on 14 July – the only official reading in the history of New South Wales.[27] Despite some tension, the influx of migrants also brought fresh ideas from Europe and North America to New South Wales – Norwegians introduced Skiing in Australia to the hills above the Snowy Mountains gold rush town of Kiandra around 1861. A famous Australian son was also born to a Norwegian miner in 1867, when the bush balladeer Henry Lawson was born at the Grenfell goldfields.
In 1858, a new gold rush began in the far north, which led in 1859 to the separation of Queensland as a new colony. New South Wales thus attained its present borders, although what is now the Northern Territory remained part of the colony until 1863, when it was handed over to South Australia.
The separation and rapid growth of Victoria and Queensland mark the real beginning of New South Wales as a political and economic entity distinct from the other Australian colonies. Rivalry between New South Wales and Victoria was intense throughout the second half of the 19th century, and the two colonies developed in radically different directions. Once the easy gold ran out by about 1860, Victoria absorbed the surplus labour force from the gold fields in manufacturing, protected by high tariff walls. Victoria became the Australian stronghold of protectionism, liberalism and radicalism. New South Wales, which was less radically affected demographically by the gold rushes, remained more conservative, still dominated politically by the squatter class and its allies in the Sydney business community. New South Wales, as a trading and exporting colony, remained wedded to free trade.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Large Antique Map of Tahiti
- Title : Carte De L 'Isle O - Taiti...Par M. Bonne...
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 40570
- Size: 15in x 11in (400mm x 275mm)
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 ½in x 11 ½in; (420mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 14 ½in x 10in; (370mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Two very small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1816 John Thomson Large Antique Map of Southern India & Northern Sri Lanka
- Title : Southern Hindostan....Drawn & Engraved for Thomsons New General Atlas, 1816
- Date : 1816
- Size: 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 41004
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of South India & northern Sri Lanka by John Thomson was engraved by Samuel Neele in 1816 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons New General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin soiling and cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The cartography of India begins with early charts for navigation and constructional plans for buildings. Indian traditions influenced Tibetan and Islamic traditions, and in turn, were influenced by the British cartographers who solidified modern concepts into India\'s map making
A prominent foreign geographer and cartographer was Hellenistic geographer Ptolemy (90–168) who researched at the library in Alexandria to produce a detailed eight-volume record of world geography. During the Middle Ages, India sees some exploration by Chinese and Muslim geographers, while European maps of India remain very sketchy. A prominent medieval cartographer was Persian geographer Abu Rayhan Biruni (973–1048) who visited India and studied the country\'s geography extensively.
European maps become more accurate with the Age of Exploration and Portuguese India from the 16th century. The first modern maps were produced by Survey of India, established in 1767 by the British East India Company. Survey of India remains in continued existence as the official mapping authority of the Republic of India.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia, Swan River Colony & Van Diemens Land
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 31974
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique map of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1785 Capt Cook Antique Print Statues in a Heiau, Island of Kauai Hawaii in 1778
- Title : Interieur D Un Morais D Atooi (Interior of a Morais in Atooi)
- Size: 16in x 10in (405mm x 260mm)
- Ref #: 21478
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of statues inside of a Hawaiian Heiau - temple - on the Island of Kauai (Atooi) Hawaii, visited by Captain Cook in 1778, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Captain Cook arrived at Atooi (Kauai) on 19th January 1778 and stayed until 23rd January 1778.
On the 21st January, Cook accompanied by John Webber, proceeded inland from their beach side anchorage to Waimea, on the south coast of Kauai. Their intention was to examine elevated objects visible from the ship. It proved to be a morai, or temple similar to ones they had seen in Tahiti and other South Pacific islands. This structure was nearly 20-feet high and covered in a thin, light-grey cloth, which likely had ceremonial significance. The temple rested on a platform and consisted of thousands of rough-edged lava rock piled in a tight, mortarless fashion. In the center is the spindly-legged oracle tower, where the priest (kahuna) might seek counsel or pray. Carved figures with tapa and leaf offerings are seen outside thatched huts topped with pili, the tall grass that grew throughout the lowlands. In his journal, Cook took particular note of several stone objects he had observed:
...........about the middle of the Morai, there were three of these places in line. We were told three chiefs had been buried there, and before them was another that was oblong. This they called Tanga (taboo or kapu in Hawaiian) and gave us clearly to understand that three human sacrifices had been buried there, that is, one at the burial of each chief. Cooks Journals - January 21, 1778
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10in (405mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9 1/2in (280mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Kauai is geologically the oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands.
In 1778, Captain James Cook arrived at Waimea Bay, the first European known to have reached the Hawaiian islands. He named the archipelago after his patron the 6th Earl of Sandwich, George Montagu
Hawaii is the 50th and most recent state to have joined the United States of America, having received statehood on August 21, 1959. Hawaii is the only U.S. state located in Oceania and the only one composed entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean. Hawaii is the only U.S. state located outside North America.
It is possible that Spanish explorers arrived in the Hawaiian Islands in the 16th century—200 years before Captain James Cook\\\'s first documented visit in 1778. Ruy López de Villalobos commanded a fleet of six ships that left Acapulco in 1542 bound for the Philippines with a Spanish sailor named Juan Gaetano aboard as pilot. Depending on the interpretation, Gaetanos reports describe an encounter with either Hawaii or the Marshall Islands. If de Villalobos crew spotted Hawaii, Gaetano would be considered the first European to see the islands. Some scholars have dismissed these claims due to a lack of credibility.
Spanish archives contain a chart that depicts islands at the same latitude as Hawaii but with a longitude ten degrees east of the islands. In this manuscript, the island of Maui is named La Desgraciada (The Unfortunate Island), and what appears to be Hawaii Island is named La Mesa (The Table). Islands resembling Kahoolawe, Lanai, and Molokai are named Los Monjes (The Monks). For two-and-a-half centuries, Spanish galleons crossed the Pacific from Mexico along a route that passed south of Hawaii on their way to Manila. The exact route was kept secret to protect the Spanish trade monopoly against competing powers.
The 1778 arrival of British explorer James Cook was the first documented contact by a European explorer with Hawaii. Cook named the archipelago as the Sandwich Islands in honor of his sponsor John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich. Cook published the islands location and rendered the native name as Owyhee. This spelling lives on in Owyhee County, Idaho. It was named after three native Hawaiian members of a trapping party who went missing in that area. The Owyhee Mountains were also named for them
Cook visited the Hawaiian Islands twice. As he prepared for departure after his second visit in 1779, a quarrel ensued as Cook took temple idols and fencing as firewood and a minor chief and his men took a ship\\\'s boat. Cook abducted the King of Hawaii Island, Kalani ōpu u, and held him for ransom aboard his ship in order to gain return of Cook\\\'s boat. This tactic had worked in Tahiti and other islands. Instead, Kalani ōpu u s supporters fought back, killing Cook and four marines as Cooks party retreated along the beach to their ship. They departed without the ships boat.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Cook Antique Print HMS Resolution & Discovery, Prince William Sound, Alaska
- Title : Vue de Lanse Fermee de l entree Du Prince Guillaume (Entrance & view of the Prince William)
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31839
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Cooks ships HMS Resolution and Discovery anchored in Snug Corner Cove, Prince William Sound, Alaska, visited by Captain Cook in 1778, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
May 1778.........On the 12th at nine in the morning, wrote Ledyard, we entered an inlet… at six in the evening perceiving bad weather approaching… both ships anchored… The pinnace of the Resolution with the first lieutenant, some other gentlemen and myself went to the opposite shore to shoot some wild fowl. The first lieutenant was John Gore. The inlet was named Sandwich Sound by Cook, after the Earl of Sandwich, First Lord of the Admiralty, but in the published version of his journal the name appeared as Prince Williams Sound, after George IIIs third son, Duke of Clarence, later William IV. The ships had anchored off Cape Hinchinbrook, named after the country seat of the Earl of Sandwich.
Some local inhabitants appeared and came aboard the ships. Clerke gave them a Glass Bowl, with which they seem\'d much delighted, and toss\'d me, in spight of all my motions to the contrary, one of their Frocks, which was made of Water fowl Skins, and exceedingly well calculated, to keep out both Wet & Cold; then, both Boats put off and made for the Shore, paddling & singing with all the Jollity imaginable. We either found these good folks on of their Jubilee Days, or they are a very happy Race.
They sailed on until Cook found a fine bay or rather harbour which he later called a very snug place and named Snug Corner Bay. Samwell on 14th wrote we secured the Ship with the small Anchor; in carrying this out in the Launch one of the Sailors was so unfortunate as to get his Leg entangled in the Buoy rope which carried him down with the Anchor, however he disengaged himself when he got to the bottom & came up again & saved his Life tho\' he had his Leg broke in a very dangerous Manner.
We heeled the ship to port wrote Gilbert, to examine the leak on the starboard buttock… it being close below the wale and occasioned by some of the seems being very open and the oakum quite rotten and great part of it got out. In two days we repaired this defect being obliged to put two and half inch rope along the seams which were too wide for caulking.
On 18th King noted two boats, one with Mr Gore & the other with the Master, were sent away, the first to explore the Inlet to the Noward: the other to the N end of the Island near us to make observations on the tides. William Bligh was master on the Resolution. They returned by Dusk, Mr Gore had proceeded up the Inlet & perceivd that it took a direction to the NE, & he thought that it bid fair for opening a communication to some other Sea; but the mate that was with him form\'d a very contrary opinion… the Captn judg\'d it the Wisest way to lose no more time, being certain that if we were amongst Islands, we shoud soon come to more Passages. Henry Roberts was the masters mate referred to here. Cook had sent him and others to sketch out the parts they examined
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins cropped close to borders
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Prince William Sound is located on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula, its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. Other settlements on the sound contain numerous small islands, including Cordova and Whittier plus the Alaska native villages of Chenega and Tatitlek.
James Cook entered Prince William Sound in 1778 and named it Sandwich Sound, after his patron the Earl of Sandwich. The name was changed to honour King George III third son, Prince William Henry, then aged 13 and serving as a midshipman in the Royal Navy.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1683 Mallet Antique Map of Australia Cape York Peninsula Gulf of Carpenteria PNG
- Title : Nouvelle Guinee et Carpentarie
- Ref #: 50601
- Size: 8in x 6in (205mm x 152mm)
- Date : 1682
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This hand coloured original antique very early map of Cape York Peninsula, the Gulf of Carpenteria and New Guinea - depicted before the Torres Strait was charted - was published as part of the 1683 edition of Alain Manesson Mallet's 1630 - 1706 Description de l' Univers.
Background:
The first detailed published map to show any part of Queensland (Tully). Shows New Guinea , the east coast of Cape York Peninsula and part of Arnhem Land.
Although not a particularly large map, the significance of Mallet's map of Carpentaria and New Guinea is underrated. It is essentially the first map to concentrate specifically on the Dutch discoveries in Queensland by Jan Cartenszoon in the Pera and the Arnhem that left Ambon on 21 January 1623 and reached the western side of Cape York Peninsula on 12 April. Although De Jode's rare and famous map 'Novae Guineae Forma & Situs', published almost a century earlier also charts the same area, it shows a fictitious Queensland based on the contemporary beliefs of a 'Terra Australis Incongita', or unknown southland.
Mallet names 'Coen R', one of the rivers discovered and named by Carstensz in 1623. No other Australian place names are shown except 'Carpentarie' on the Cape York Peninsula . Mallet places an interesting reference at the entrance of the Gulf of Carpentaria, "Les onze mille vierges", referring to the eleven thousand virgins of Cologne . A text carved into stone at the Church of Saint Ursula refers to the martyrdom of virgins.
Mallet was a French Engineer who in his early days took service with the Portuguese Army. He later returned to France and served Louis XIV. In 1683 he published Description de l' Univers which contained many hundreds of maps, plans and views. A German edition was published in 1686.
This is a beautifully engraved and hand coloured print in excellent condition. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 8in x 6in (205mm x 152mm)
Plate size: - 6 1/2in x 5in (165mm x 127 mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None
1857 A H Dufour Very Large Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand & South Pacific
- Title : Oceanie Dressee par A H Dufour Gravee CH Dyonnet..1857
- Ref #: 61026
- Size: 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
- Date : 1857
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large, magnificent hand coloured original copper plate antique map of Australia, New Zealand, Oceania & The Pacific, showing the Ocean Currents and 5 inset maps (NSW & Victoria Australia, Gambier Islands, Tahiti, Marquesas Isles & New Caledonia) by Adolphe Hippolyte Dufour was engraved by Charles Dyonnet in 1856 - dated in the title - for Dufours 1860 edition of his monumental elephant folio Atlas Physique, Historique et Politique Geographie Moderne published by Pauline Et La Chevalier, Paris.
The 19th century French cartographer Auguste-Henri Dufour began publishing the dramatic elephant folio Atlas Universel, also occasionally titled Grand Atlas Universal, around 1855. Several editions appeared between its initial publication in the 1850s and a final run c. 1870. The 1863 and 1864 editions in particular are highly desirable among collectors because the United States and North America maps illustrate the proposed, but unrealized, state of Corona (roughly modern day Utah). The atlas contained roughly 40 maps, most of which were engraved by Louis Antoine (the maps) and Deletre (typography) under the supervision of Charles Dyonnet, official engraver of the Depot de la Marine. The Atlas Universal was published in Paris and edited by the firm of Paulin et le Chevalier, 60 Rue Richelieu.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 33in x 24in (840mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charles Dyonnet 1822 - 1880 was an extremely active Paris based engraver working in the mid to late 19th century. From his offices at 220 Rue St. Jacques, Paris, Dyonnet engraved numerous maps for many of the most prominent 19th French cartographic publishers including Vuillemin, Dufour, Fremin and Duvotenay. From 1850-1861, he held the coveted position of Graveur du Dépot de la Marine, and in this position engraved numerous French naval and military maps. Dyonnet had a detail oriented and aesthetically minded hand and is responsible from some of the most beautiful French maps to emerge during the 19th century. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1803 Louis Freycinet Antique Map of The Islands of Timor, Samau & Rote Indonesia
- Title : Carte Particuliere des Detroits De Rottie et de Simao...L Freycienet...le Casuarina 1803..Lambert Sculp.
- Ref #: 42014
- Size: 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1803
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This magnificent large original copper-plate engraved antique map of the islands of Samau, Rote and the southern part of Timor, including the bay and town of Kupang, by Lieutenant Louis Freycinet, in command of the ship Casuarina in 1803, was engraved by Anton Lambart and was published in the 1807 1st edition of François Pérons, Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes (‘Voyage of Discovery to the Southern Lands in three volumes, Paris, 1807–1816.
Also illustrates the tracks of the ships Geographe, the Naturaliste from the earlier voyages in 1801, and the Casuarina tracks of 1803.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 16 1/2in (570mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15in (545mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nicolas Thomas Baudin 1754 – 1803 was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer.
The Baudin expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland (Australia). The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
Napoléon Bonaparte, as First Consul, formally approved the expedition to the coasts of New Holland, after receiving a delegation consisting of Baudin and eminent members of the Institut National des Sciences et Arts on 25 March 1800. The explicit purpose of the voyage was to be ‘bservation and research relating to Geography and Natural History.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of the continent until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. During their exploration here they lost a longboat and a sailor, Assistant Helmsman Timothée Vasse. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by \'t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted the Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
1785 Capt Cook Antique Print Interior of a Heiau, Island of Kauai Hawaii in 1778
- Title : Cimetiere D Atooi (Cemetery in Atooi)
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (390mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 21441
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of the inside of a Hawaiian Heiau - temple - on the Island of Kauai (Atooi) Hawaii, visited by Captain Cook in 1778, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Captain Cook arrived at Atooi (Kauai) on 19th January 1778 and stayed until 23rd January 1778.
On the 21st January, Cook accompanied by John Webber, proceeded inland from their beach side anchorage to Waimea, on the south coast of Kauai. Their intention was to examine elevated objects visible from the ship. It proved to be a morai, or temple similar to ones they had seen in Tahiti and other South Pacific islands. This structure was nearly 20-feet high and covered in a thin, light-grey cloth, which likely had ceremonial significance. The temple rested on a platform and consisted of thousands of rough-edged lava rock piled in a tight, mortarless fashion. In the center is the spindly-legged oracle tower, where the priest (kahuna) might seek counsel or pray. Carved figures with tapa and leaf offerings are seen outside thatched huts topped with pili, the tall grass that grew throughout the lowlands. In his journal, Cook took particular note of several stone objects he had observed:
...........about the middle of the Morai, there were three of these places in line. We were told three chiefs had been buried there, and before them was another that was oblong. This they called Tanga (taboo or kapu in Hawaiian) and gave us clearly to understand that three human sacrifices had been buried there, that is, one at the burial of each chief. Cooks Journals - January 21, 1778
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (390mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Kauai is geologically the oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands.
In 1778, Captain James Cook arrived at Waimea Bay, the first European known to have reached the Hawaiian islands. He named the archipelago after his patron the 6th Earl of Sandwich, George Montagu
Hawaii is the 50th and most recent state to have joined the United States of America, having received statehood on August 21, 1959. Hawaii is the only U.S. state located in Oceania and the only one composed entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean. Hawaii is the only U.S. state located outside North America.
It is possible that Spanish explorers arrived in the Hawaiian Islands in the 16th century—200 years before Captain James Cook\\\'s first documented visit in 1778. Ruy López de Villalobos commanded a fleet of six ships that left Acapulco in 1542 bound for the Philippines with a Spanish sailor named Juan Gaetano aboard as pilot. Depending on the interpretation, Gaetanos reports describe an encounter with either Hawaii or the Marshall Islands. If de Villalobos crew spotted Hawaii, Gaetano would be considered the first European to see the islands. Some scholars have dismissed these claims due to a lack of credibility.
Spanish archives contain a chart that depicts islands at the same latitude as Hawaii but with a longitude ten degrees east of the islands. In this manuscript, the island of Maui is named La Desgraciada (The Unfortunate Island), and what appears to be Hawaii Island is named La Mesa (The Table). Islands resembling Kahoolawe, Lanai, and Molokai are named Los Monjes (The Monks). For two-and-a-half centuries, Spanish galleons crossed the Pacific from Mexico along a route that passed south of Hawaii on their way to Manila. The exact route was kept secret to protect the Spanish trade monopoly against competing powers.
The 1778 arrival of British explorer James Cook was the first documented contact by a European explorer with Hawaii. Cook named the archipelago as the Sandwich Islands in honor of his sponsor John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich. Cook published the islands location and rendered the native name as Owyhee. This spelling lives on in Owyhee County, Idaho. It was named after three native Hawaiian members of a trapping party who went missing in that area. The Owyhee Mountains were also named for them
Cook visited the Hawaiian Islands twice. As he prepared for departure after his second visit in 1779, a quarrel ensued as Cook took temple idols and fencing as firewood and a minor chief and his men took a ship\\\'s boat. Cook abducted the King of Hawaii Island, Kalani ōpu u, and held him for ransom aboard his ship in order to gain return of Cook\\\'s boat. This tactic had worked in Tahiti and other islands. Instead, Kalani ōpu u s supporters fought back, killing Cook and four marines as Cooks party retreated along the beach to their ship. They departed without the ships boat.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of New South Wales, Australia with inset plan of Sydney
- Title : New South Wales..1833 Baldwin & Craddock
- Size: 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 21290
Description:
This fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique maps of New South Wales - with an inset plan of Sydney Town - was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833- date engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13 1/2in (405mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, Alvin Jewett JohnsonAmerica, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of New Guinea, William Dampier 1699 - 5 Harbours
- Title : Carte des Decouvertes du Capt,. Carteret dans La Nlle. Bretagne..Par M Bonne
- Date : 1780
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40581
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Papua New Guinea - and the early discoveries of William Dampier and the later passage of Cooks ship the Endeavor through the straits between Australia and New Guinea, by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
The map also contains the bays, Harbours and coastlines of several Islands of the Pacific including New Ireland, Philippines, Indonesia.(Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 ½in x 11 ½in; (420mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 14 ½in x 10in; (370mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
William Dampier 1651 - 1715 was an English explorer and navigator who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australia\'s first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the Admiralty with his book A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in Western Australia, before being court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crewmate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Horatio Nelson, Charles Darwin, and Alfred Russel Wallace.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of New South Wales w/ inset Map of Sydney Town, Australia
- Title : New South Wales...Sydney from the New South Wales Almanack...Sep 1833
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 32681
Description:
This fine original antique map of New South Wales, Australia - with an inset plan of Sydney Town - was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning, left T&B corners cropped
Plate area: - Blind Library stamp
Verso: - Re-enforced on verso along margins
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia, Swan River Colony & Van Diemens Land
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 32682
Description:
This original antique map of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Blind Library stamp
Verso: - Re-enforced on verso along margins
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Capt Wallis attacked in Matavia Bay, Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Le Capitaine Wallis est attaque dans L Dauphin par les Otahitiens (Captain Wallis attacked in The Dolphin by the Tahitians)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25928
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis in his ship the HMS Dolphin being attacked by the Tahitians in Matavai Bay - with one tree hill to the right - in 1767 was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print Aboriginal Woman of Bruny Island, Tasmania in 1777
- Title : Une Femme De La Terre De Van-Diemens
- Ref : 50609
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Indigenous Woman & child of Adventure Bay, Bruny Island, Tasmania (Van Diemens Land) encountered by Captain Cook in during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery in 1777, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Adventure Bay
from Cooks Journal......on the 24th (March 1777) at 3 AM we made the Coast of Van Diemen land wrote Cook. Anderson remarked that though now the middle of summer here a spot or two of snow was seen on the highest hills… At ten we passd a point supposd to be the boundary of Stone Bay where Abel Tasman anchord, i.e. Storm Bay. According to David Samwell, surgeons first mate on the Resolution, both Ships anchored in Adventure Bay in Van Diemens Land, this Bay was so called by Captn Furneaux who had anchored here in the Adventure last Voyage.
The next day Cook and Clerke sent parties, one to cut wood and the other grass. Clerke wrote of his party from the Discovery The Guard I had sent with the Parties on shore which consisted of the following Marines, Hamlet Thompson, Geo: Moody, Ben: Harriot, Jos: Pool & Willm Broom, stole some Liquor & made themselves exceedingly drunk, for which they receivd a dozen lashes each in the Morning. The Privates were all from the Plymouth division of marines. Hamlet Thompson was from the 6th Company, George Moody from the 70th, John Herriott the 12th, James Poole the 33rd and William Broom the 36th. According to Thomas Edgar, Master, they made themselves so Beastly Drunk that they were put motionless in the Boat, and when brought on board were oblig\'d to be hoisted into the Ship.
William Bayly, astronomer on the Discovery, wrote In the morning I carried my Tent observatory & Instruments on Shore & set all up, but was not able to get any observations it being cloudy all day, in the evening Capt Cook Sent for me & told me he had Altered his mind relative to his stay, & ordered me to pack all up & carry the whole on board again, as he intend[ed] to sail for New Zealand in a day or two.
John Henry Martin, seaman on the Discovery, described the natives. They have few, or no wants, & seemed perfectly Happy, if one might judge from their behaviour, for they frequently woud burst out, into the most immoderate fits of Laughter & when one Laughed every one followed his example Emediately.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Adventure Bay is the name of both a township and a geographical feature on the eastern side of Bruny Island, Tasmania.
The first European to sight the bay was explorer Abel Tasman, who sought to anchor his vessel Heemskerck there in 1642. Instead, Heemskerck was driven back offshore by a storm, in token of which Tasman named the place Storm Bay. Captain Tobias Furneaux renamed it in March 1773, in honour of his ship HMS Adventure, which he had anchored in the bay for five days after becoming separated from Captain James Cook\'s HMS Resolution during Cook\'s second voyage to the Pacific search of Terra Australis Incognita. Furneaux\'s log made clear the bay was an excellent anchorage for resupplying vessels:....to the SW of the first watering place there is a large lagoon which I believe has plenty of fish in it for one of our Gentlemen caught upwards of 2 dozen trout, and shot a possum which was the only animal we saw. There are a great many gum trees and of a vast thickness and height, one of which measured in circumference 26 feet and the height under the branches was 20 feet.
Others among Furneaux\'s crew spotted evidence of what they believed were small deer but were more likely kangaroos. Furneaux also noted signs of an Aboriginal settlement in the form of several huts or wigwams on shore, with several bags of grass in which they carry their shellfish. - but the branches of which the huts were made were split and torn and there was not the least appearance of any people.
Reliably mapped and offering an abundance of water, fresh water and game, Adventure Bay quickly became a popular anchorage for European explorers. Cooks Resolution watered there in 1777, followed by William Bligh aboard HMS Bounty in 1788 and HMS Providence in 1792. Others who resupplied their vessels in the bay in this period included Bruni d Entrecasteaux aboard Recherché in 1792 and 1793, and Nicolas Baudin in the corvette Géographe in 1802. Matthew Flinders also tried to enter the bay with Norfolk in 1798.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773 English writer and book editor.
He is said to have been clerk to an attorney, and was certainly self-educated. In 1744, he succeeded Samuel Johnson as compiler of the parliamentary debates for the Gentleman\\\'s Magazine, and from 1746 to 1749 he contributed poems signed Greville, or H Greville, to that journal. In company with Johnson and others he started a periodical called The Adventurer, which ran to 140 issues, of which 70 were from the pen of Hawkesworth himself.
On account of what was regarded as his powerful defense of morality and religion, Hawkesworth was rewarded by the archbishop of Canterbury with the degree of LL.D, In 1754–1755 he published an edition (12 vols) of Swifts works, with a life prefixed which Johnson praised in his Lives of the Poets. A larger edition (27 vols) appeared in 1766–1779. He adapted Dryden\\\'s Amphitryon for the Drury Lane stage in 1756, and Southernes Oronooko in 1759. He wrote the libretto of an oratorio Zimri in 1760, and the next year Edgar and Emmeline: a Fairy Tale was produced at Drury Lane. His Almoran and Hamet (1761) was first drafted as a play[citation needed], and a tragedy based on it by S J Pratt, The Fair Circassian (1781), met with some success.
He was commissioned by the Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work, An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore Byrone John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook (from 1702 to 1771) drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Hawkesworth was a close imitator of Johnson both in style and thought, and was at one time on very friendly terms with him. It is said that he presumed on his success, and lost Johnsons friendship as early as 1756.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print Aboriginal Man of Bruny Island, Tasmania in 1777
- Title : Un Homme De La Terre De Van-Diemens
- Ref : 43195
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Indigenous Man of Adventure Bay, Bruny Island, Tasmania (Van Diemens Land) encountered by Captain Cook in during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery in 1777, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Adventure Bay
from Cooks Journal......on the 24th (March 1777) at 3 AM we made the Coast of Van Diemen land wrote Cook. Anderson remarked that though now the middle of summer here a spot or two of snow was seen on the highest hills… At ten we passd a point supposd to be the boundary of Stone Bay where Abel Tasman anchord, i.e. Storm Bay. According to David Samwell, surgeons first mate on the Resolution, both Ships anchored in Adventure Bay in Van Diemens Land, this Bay was so called by Captn Furneaux who had anchored here in the Adventure last Voyage.
The next day Cook and Clerke sent parties, one to cut wood and the other grass. Clerke wrote of his party from the Discovery The Guard I had sent with the Parties on shore which consisted of the following Marines, Hamlet Thompson, Geo: Moody, Ben: Harriot, Jos: Pool & Willm Broom, stole some Liquor & made themselves exceedingly drunk, for which they receivd a dozen lashes each in the Morning. The Privates were all from the Plymouth division of marines. Hamlet Thompson was from the 6th Company, George Moody from the 70th, John Herriott the 12th, James Poole the 33rd and William Broom the 36th. According to Thomas Edgar, Master, they made themselves so Beastly Drunk that they were put motionless in the Boat, and when brought on board were oblig\'d to be hoisted into the Ship.
William Bayly, astronomer on the Discovery, wrote In the morning I carried my Tent observatory & Instruments on Shore & set all up, but was not able to get any observations it being cloudy all day, in the evening Capt Cook Sent for me & told me he had Altered his mind relative to his stay, & ordered me to pack all up & carry the whole on board again, as he intend[ed] to sail for New Zealand in a day or two.
John Henry Martin, seaman on the Discovery, described the natives. They have few, or no wants, & seemed perfectly Happy, if one might judge from their behaviour, for they frequently woud burst out, into the most immoderate fits of Laughter & when one Laughed every one followed his example Emediately.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Adventure Bay is the name of both a township and a geographical feature on the eastern side of Bruny Island, Tasmania.
The first European to sight the bay was explorer Abel Tasman, who sought to anchor his vessel Heemskerck there in 1642. Instead, Heemskerck was driven back offshore by a storm, in token of which Tasman named the place Storm Bay. Captain Tobias Furneaux renamed it in March 1773, in honour of his ship HMS Adventure, which he had anchored in the bay for five days after becoming separated from Captain James Cook\'s HMS Resolution during Cook\'s second voyage to the Pacific search of Terra Australis Incognita. Furneaux\'s log made clear the bay was an excellent anchorage for resupplying vessels:....to the SW of the first watering place there is a large lagoon which I believe has plenty of fish in it for one of our Gentlemen caught upwards of 2 dozen trout, and shot a possum which was the only animal we saw. There are a great many gum trees and of a vast thickness and height, one of which measured in circumference 26 feet and the height under the branches was 20 feet.
Others among Furneaux\'s crew spotted evidence of what they believed were small deer but were more likely kangaroos. Furneaux also noted signs of an Aboriginal settlement in the form of several huts or wigwams on shore, with several bags of grass in which they carry their shellfish. - but the branches of which the huts were made were split and torn and there was not the least appearance of any people.
Reliably mapped and offering an abundance of water, fresh water and game, Adventure Bay quickly became a popular anchorage for European explorers. Cooks Resolution watered there in 1777, followed by William Bligh aboard HMS Bounty in 1788 and HMS Providence in 1792. Others who resupplied their vessels in the bay in this period included Bruni d Entrecasteaux aboard Recherché in 1792 and 1793, and Nicolas Baudin in the corvette Géographe in 1802. Matthew Flinders also tried to enter the bay with Norfolk in 1798.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773 English writer and book editor.
He is said to have been clerk to an attorney, and was certainly self-educated. In 1744, he succeeded Samuel Johnson as compiler of the parliamentary debates for the Gentleman\\\'s Magazine, and from 1746 to 1749 he contributed poems signed Greville, or H Greville, to that journal. In company with Johnson and others he started a periodical called The Adventurer, which ran to 140 issues, of which 70 were from the pen of Hawkesworth himself.
On account of what was regarded as his powerful defense of morality and religion, Hawkesworth was rewarded by the archbishop of Canterbury with the degree of LL.D, In 1754–1755 he published an edition (12 vols) of Swifts works, with a life prefixed which Johnson praised in his Lives of the Poets. A larger edition (27 vols) appeared in 1766–1779. He adapted Dryden\\\'s Amphitryon for the Drury Lane stage in 1756, and Southernes Oronooko in 1759. He wrote the libretto of an oratorio Zimri in 1760, and the next year Edgar and Emmeline: a Fairy Tale was produced at Drury Lane. His Almoran and Hamet (1761) was first drafted as a play[citation needed], and a tragedy based on it by S J Pratt, The Fair Circassian (1781), met with some success.
He was commissioned by the Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work, An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore Byrone John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook (from 1702 to 1771) drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Hawkesworth was a close imitator of Johnson both in style and thought, and was at one time on very friendly terms with him. It is said that he presumed on his success, and lost Johnsons friendship as early as 1756.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia & Van Diemens Island, Tasmania
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 11-1084
Description:
This fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique maps of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 and was published in the Charles Knight edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, Alvin Jewett JohnsonAmerica, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia & Van Diemens Island, Tasmania
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 11-1074
Description:
This fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique maps of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (410mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, Alvin Jewett JohnsonAmerica, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1876 Petermann Antique Map Western & South Australia - Warburton, Giles, Forrest
- Title : Die Neuesten Entdeckungsreisen im Inner-Australien von Warburton, Giles, Forrest, April 1873 - Sept 1874
- Size: 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1876
- Ref #: 82055
Description:
This early folding original antique lithograph map of Western & South Australia and Alexandria land (Northern Territory) with the tracks of 3 explorers - in 1873 & 1874 - Peter Egerton-Warburton, Ernest Giles & Alexander Forrest by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1876 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Colonel Peter Egerton-Warburton CMG (1813–1889), was a British military officer, Commissioner of Police for South Australia, and an Australian explorer. In 1872 he sealed his legacy through a particularly epic expedition from Adelaide crossing the arid centre of Australia to the coast of Western Australia via Alice Springs.
William Ernest Powell Giles (1835 – 1897) best known as Ernest Giles, was an Australian explorer who led five major expeditions in central Australia.
Alexander Forrest CMG (1849 – 1901) was an explorer and surveyor of Western Australia, and later also a member of parliament.
1876 Petermann Antique Map Expedition Ernest Giles Western & South Australia, 1875
- Title : Thomas Elders Expedition durch Inner-Australien vom Beltana im Osten bis Perth im Westen, Ausgefuhrt Durch E. Giles Mai - Nov 1875
- Size: 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1876
- Ref #: 82054
Description:
This early folding original antique lithograph map of Western & South Australia - from Perth to Lake Torrens South Australia covering the 3rd & 4th expedition of the explorer Ernest Giles in 1875 by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1877 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
William Ernest Powell Giles 1835 – 1897 best known as Ernest Giles, was an Australian explorer who led five major expeditions in central Australia.
Giles did not attempt an organised expedition until 1872, when with two other men he left Chambers Pillar, South Australia (now in the Northern Territory), on 22 August and traversed much previously untrodden country to the north-west and west. Finding their way barred by Lake Amadeus and that their horses were getting very weak, a return was made to the Finke River and then to Charlotte Waters and Adelaide, where Giles arrived in January 1873. Giles looked upon his expedition as a failure, but he had done well considering the size and equipment of his party.
Giles friend Baron von Mueller raised a subscription so that a new expedition could be made. The services of William Tietkens as first assistant were obtained, and with two other men a start was made on 4 August 1873. The journey began considerably south from the previous expedition and from the Alberga River a generally western course was traversed. A month later in the Musgrave Ranges a fine running river was found and named the Ferdinand and by 3 October 1873 the party was approaching longitude 128 East. The country was extremely dry and though tested in various directions it was a constant struggle to get enough water to keep the horses going. Early in November, having passed longitude 126, a partial return was made and on 20 December 1873 the neighbourhood of Mount Scott was reached. A turn to the north and then west was made and the farthest westerly point was reached on 23 April 1874. Giles and one of the men, Alfred Gibson, had been scouting ahead when the latter\'s horse died. Giles gave him his own horse with instructions to follow their tracks back and obtain assistance. Giles made his way back to their depot on foot in eight days, almost completely exhausted, to find that Gibson had not reached the camp. A search was made for him for several days without success. The stores were almost finished, nothing further could be done, and on 21 May 1874 the return journey began. Giles named the desert Gibson Desert after his companion. On 24 June 1874 they were on a good track to the Finke River and on 13 July 1874 Charlotte Waters was reached. Giles had again failed to cross the continent, but in the circumstances all had been done that was possible.
Giles was the first European to see the rock formations of The Olgas, now known by their Aboriginal name of Kata Tjuta, and Lake Amadeus. He had wanted to name these Mt Mueller and Lake Ferdinand respectively, to honour his benefactor Baron Ferdinand von Mueller, however Mueller prevailed on him to instead honour the King Amadeus of Spain and Queen Olga of Württemberg. Giles supposedly discovered Uluru (formerly Ayers Rock), but was beaten to the claim by a competing explorer, William Gosse.
Early in 1875 Giles prepared his diaries for publication under the title Geographic Travels in Central Australia, and on 13 March 1875, with the generous help of Sir Thomas Elder, he began his third expedition. Proceeding considerably to the north from Fowler\'s Bay the country was found to be very dry. Retracing his steps Giles turned east, and eventually going round the north side of Lake Torrens reached Elder\'s station at Beltana. There the preparations for his fourth journey were made, and with Tietkens again his lieutenant, and with what Giles had always wanted, a caravan of camels, a start was made on 6 May. Port Augusta was reached on 23 May and, after taking a northerly course to clear the lakes, a generally westerly course was followed. Some water was carried, and the party was saved the continual excursions in search of water for horses that had caused so much difficulty during previous expeditions. Towards the end of September over 323 miles (520 km) had been covered in 17 days without finding water, when on 25 September the native Tommy found an abundant supply in a small hollow between sand dunes at Queen Victoria Spring, and the party was saved. After a rest of nine days the journey was resumed on 6 October the course being still west. Ten days later the expedition was attacked by a large body of aborigines and Giles was compelled to fire on them. On 4 November they met a white stockman at Tootra out-camp, east of Bindi Bindi. Their course was west to Walebing Station, then south-west and on 11 November they arrived at New Norcia where they were welcomed by Bishop Salvado. On 17 November 1875 the party arrived at Guildford and Perth the next day, where they received an enthusiastic reception.
Giles stayed for two months at Perth. Tietkens and Jess Young, another member of the expedition, went back to Adelaide by sea, and on 13 January 1876 Giles began the return journey taking a course generally about 400 miles north of the last journey. He arrived at Adelaide in September 1876 after a good journey during which the camels were found to be invaluable.