Australia/Oceania (215)
1785 Capt Cook Antique Print Cook Reception on Lifuka Island, Haapai Tonga, 1777
- Title : Reception Du Capitaine Cook a Hapaee (Reception for Captain Cook in Hapaee)
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 21437
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of the reception for Captain Cook on the island of Lifuka, one of the islands of the Haapai group of Tonga Islands, visited by Captain Cook in 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Captain Cook seated with the chiefs, watching two pairs of combatants, one pair boxing, the other pair fighting with clubs within a large circle of spectators. Some men of Cook\'s company are on the left on the fringe of the crowd.
............presently after a number of men entered the Circle or Area before us, armed with Clubs made of the green branches of the Cocoanut tree, these paraded about for a few minutes and then retired the one half to one side and the other half to the other, and seated themselves before the spectators: but soon after went to single Combat, one or two steping forward from the one side and chalenging those on the other which was done more by actions than words; if the Challenge was expected, which was generally the case, each put himself in a proper attitude and began to engage and continued till one or the other gave out or their weapons were broke….there were Wristling and Boxing matches; the first were performed in the same m[an]ner as at Otahiete, and the second very little different from the method practiced in England. Cook Journals III, i, 107
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Lifuka is an island in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is located within the Haapai Group in the centre of the country, to northeast of the national capital of Nukualofa.
Lifuka is the place where Captain James Cook dubbed Tonga The Friendly Islands. Tofua is where the mutiny on the Bounty occurred in 1789; this active volcanic island lies approximately forty nautical miles west of Lifuka. The Cpt. Bligh voyage stands as the longest successful passage ever recorded in an open boat without modern navigational aids.
Haapai is a group of islands, islets, reefs and shoals with an area of 109.30 square kilometres in the central part of the Kingdom of Tonga, with the Tongatapu group to the south and the Vavau group to the north. Seventeen of the Ha apai islands are populated with altogether 6,616 people.
The first European to visit Ha apai, was Abel Tasman in 1643. Captain James Cook in 1774 and 1777, made several stops on the islands. He gave them the name of Friendly Islands in 1777.
On 18 May 1777, Cook arrived with Omai. They were greeted by Fatafehi Paulaho, King of the Isles or Tui Tonga, the most sacred chief in these islands.
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
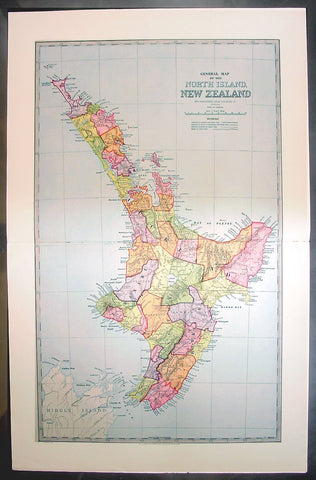
1888 Pic Atlas Large Antique Map of the North Island of New Zealand
- Title : General Map of The North Island of New Zealand
- Ref #: 50321
- Size: 28in x 18in (710mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1888
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique map of the North Island of New Zealand was engraved in 1888 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - by Alex J Scally and was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand publicationThe Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88. Also includes an index to the map on the verso giving names and locations of places on the map.
These maps were some of the best maps published at the time in the "Modern" look. The colour is bright, the engraving extremely fine and the paper heavy and stable.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists.
It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies.
Its publication was one of the most significant cultural projects in nineteenth-century Australia. Writers, artists, academics and politicians came together to prepare a book of unprecedented grandeur and ambition, and a publishing company was established to produce and publish it. The seven hundred engravings on steel and wood contained in the Picturesque Atlas were among the finest engravings to be found anywhere in the world at this time.
The Atlas was a collegial project, staffed by a large number of artists and garnering an unusual number of contributors for one work. Lightly supervised by the former Sydney Morning Herald editor Andrew Garran it was lavishly produced at the Wynyard Square headquarters of the Atlas company. It had the services of the Melburnian journalist and public figure James Smith who wrote much of the Victorian and Tasmanian material, and W.H. Traill wrote extensively about Queensland. It was not, of course, an Atlas is the usual sense of the word, maps playing a comparatively minor role. But use of Atlas in the title, Hughes-d'Aeth notes, gave a sense of the scale of the publication both in terms of comprehensiveness and format. As the author points out, calling it an Atlas carries a promise of the exactitude of the relationship between the subject and its representation, and also bears a sense of the acquisitiveness that shadows the imperial phase of cartography.
There were only thirty maps in the Atlas's 800 pages, but there were hundreds of pictures. This is where much of the ideological work of the Atlas was completed and this is where Paper Nation concentrates its analysis. Its first task is to unravel the linguistic ball of string that is the word 'picturesque'. Though Humphrey Repton and Uvedale Price had their opinions, Hughes-d'Aeth is quite right to pick William Gilpin out of the line-up of suspicious aesthetes, for it was he who really popularised the idea of travelling in search of picturesque views. Paper Nation's dissection of the term picturesque is particularly aware of the term's adaptation to colonial usage, and its mutations through time. The picturesque took on an increasingly acquisitive edge, as admiration of the beauty of the land was joined by a concern to exploit it. A 'deep reverence for production' can be seen in the Picturesque Atlas's many illustrations of mines, factories and agricultural processes. The slag heaps of a mine were now as 'picturesque' as a fern-filled valley, but this does mean that the term was evacuated of all meaning. Rather the aesthetic appropriation of the land and its material exploitation were part of a continuum of colonial attitudes, and it was the duty of the Picturesque Atlas to affirm and re-affirm the rightness of European habitation and progress. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28in x 18in (710mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 28in x 18in (710mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
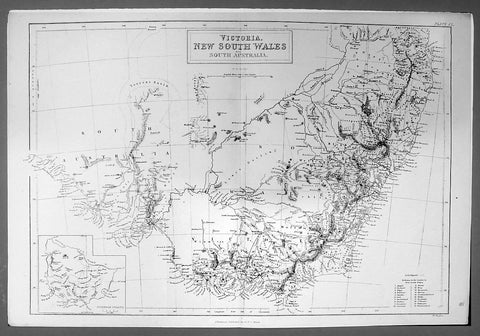
1844 Hughes Antique Australian Map of the States of Victoria & NSW
- Title : Victoria New South Wales and South Australia
- Ref #: 91204
- Size: 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map of the Australian States of NSW, Vic & part of SA was engraved by William Hughes and published by A&C Black in 1844. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1886 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Rainfall Map of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : Map of New South Wales showing Average Annual Rainfall
- Ref : 50340
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
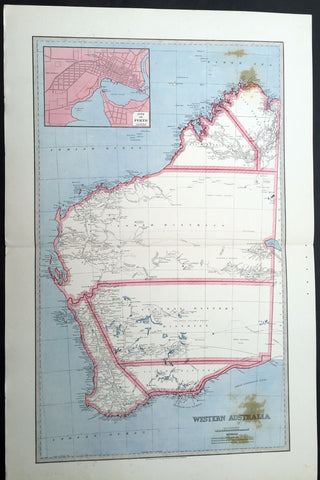
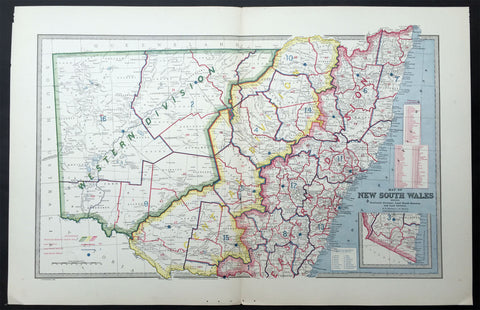
1888 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Map of Western Australia
- Title : Map of New South Wales Showing Territorial Divisions, Land Board Districts and Land Districts
- Ref : 50337
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
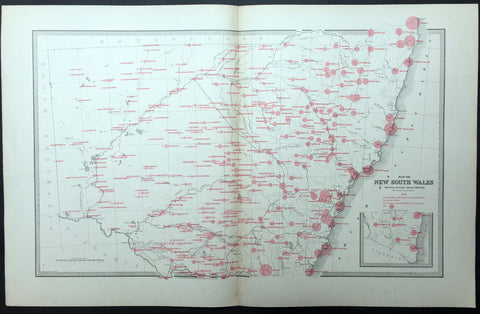
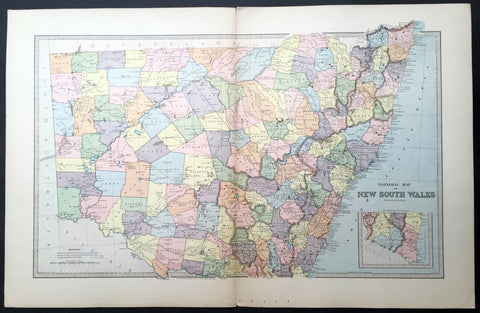
1888 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Map of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : General Map of New South Wales
- Ref : 50339
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Pic Atlas Large Antique Map of NSW, Australia Political & Local Borders
- Title : Map of New South Wales Showing Territorial Divisions, Land Board Districts and Land Districts
- Ref : 50337
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1825 Philippe Vandermaelen Large Antique Map Admiralty or Manus Islands Pacific
Antique Map
-
Title : Iles De L Amiraute
- Ref #: 17005
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
- Date : 1825
Description:
This very large original hand coloured antique lithograph map of the Admiralty or Manus Islands, north of New Guinea, in the South Pacific was published by Philippe Vandermaelen in his revolutionary 1825 Atlas universel de geographie physique, politique, statistique et mineralogique.
Until the publication of this atlas, large detailed maps of this region of Australia & the Pacific were uncommon.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first European to visit the islands was the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Saavedra when trying to return from Tidore to New Spain in the summer of 1528. Saavedra charted Manus as Urays la Grande. Its visit was also reported in 1616 by the Dutch navigator Willem Schouten. The name Admiralty Islands was devised by Captain Philip Carteret of the British Royal Navy in 1767.
Between 1884 and 1914 the area was administered as a German colony. In November 1914, the islands were occupied by troops of the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force landed from the SS Siar. A few shots fired from a machine gun on Siar over the heads of the tiny German garrison at Lorengau were the last shots fired in the battle. After the war, the islands were governed by the Commonwealth of Australia under a League of Nations mandate.
Japanese troops landed on Manus Island on 7 April 1942. In 1944, Japanese forces occupying the islands were attacked and defeated by Allied forces in Operation Brewer. Subsequently, a large American airbase was built at Lombrum near Lorengau.
Vandermaelen, Philippe M G 1795-1869
Vandermaelen was the son of the wealthy soap manufacturer; he abandoned the soap trade and devoted his life to cartography. Entirely self-taught in geometry, astronomy and the geosciences, he began drafting the first sheets of an Atlas universel in 1824. This atlas was published between 1825 and 1827; it was sold in forty instalments of ten maps each and became a great success. The revenue enabled him to set up his own Etablissement géographique de Bruxelles in 1830, which not only produced maps, atlases and globes in large quantities but also housed a natural science museum, botanical gardens, a library, and an impressive collection of maps.
Shortly after the closing of Vandermaelens Institute, the Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) in 1880 acquired a large part of its cartographic collection and production.
Vandermaelens atlas was remarkable: 387 maps on a uniform scale of ca. 1:1.6 million. There was one edition of this very rare atlas, published in 1825-27; the subscription list shows that only 810 copies were sold. The six volumes, of which Africa was in Volume III (60 maps), were issued in instalments during the period 1825-1827.
This folio-size atlas is remarkable for several reasons. It is the first atlas produced by the then new printing process of lithography. It is also the first atlas to show the whole world in 380 maps using a large uniform scale—about 10km to the cm. on a modified conical projection described by Sanson-Flamsteed. Based on a prime meridian through Paris, each map has a drawn-out graticule giving it a trapezoidal form, the underlying intention being construction of a globe with a diameter of 7.755m Eugene Gilbert de Cauwer , his biographer, suggested that Vandernaelen was a worthy follower of Mercator and Ortelius.
Vandermaelen enlisted the assistance of lithographer-printer Hippolyte Ode in this ambitious project which introduced lithography into Belgium and created an upsurge in Belgian publishing. A number of maps were lithographed by Philippe Vandermaelen himself. For many of the areas depicted, these maps are the largest scale maps made at the time, and the most detailed. The lithographs are very well drawn and printed and should be appreciated in the context of lithography, which was a developing art at the time. The maps are handsome and detailed, although some of the place names are somewhat curious and the cartography sometimes imaginary. Nevertheless, the Vandermaelen maps are of great significance in the history of cartography and lithography. Visually, they are arresting and unusual. Vandermaelens maps best are appreciated in the context of its neighbouring maps - they were all meant to be joined .
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1825 Philippe Vandermaelen Large Antique Map of The Solomon Islands
Antique Map
- Title : Oceanique. Partie Des Iles Salomon
- Ref #: 17003
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large original hand coloured antique lithograph map of the Solomon Islands in the South Pacific was published by Philippe Vandermaelen in his revolutionary 1825 Atlas universel de geographie physique, politique, statistique et mineralogique.
Until the publication of this atlas, large detailed maps of this region of Australia & the Pacific were uncommon.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first European to visit the islands was the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, sailing from Peru in 1568. Landing on Santa Isabel on 7 February, Mendaña explored several of the other islands including Makira, Guadalcanal and Malaita. Relations with the native Solomon Islanders were initially cordial, though often soured as time went by. As a result, Mendaña returned to Peru in August 1568. He returned to the Solomons with a larger crew on a second voyage in 1595, aiming to colonise the islands. They landed on Nendö in the Santa Cruz Islands and established a small settlement at Gracioso Bay. However the settlement failed due to poor relations with the native peoples and epidemics of disease amongst the Spanish which caused numerous deaths, with Mendaña himself dying in October. The new commander Pedro Fernandes de Queirós thus decided to abandon the settlement and they sailed north to the Spanish territory of the Philippines. Queirós later returned to the area in 1606, where he sighted Tikopia and Taumako, though this voyage was primarily to Vanuatu in the search of Terra Australis.
Save for Abel Tasmans sighting of the remote Ontong Java Atoll in 1648, no European sailed to the Solomons again until 1767, when the British explorer Philip Carteret sailed by the Santa Cruz Islands, Malaita and, continuing further north, Bougainville and the Bismarck Islands. French explorers also reached the Solomons, with Louis Antoine de Bougainville naming Choiseul in 1768 and Jean-François-Marie de Surville exploring the islands in 1769. In 1788 John Shortland, captaining a supply ship for Britains new Australian colony at Botany Bay, sighted the Treasury and Shortland Islands. That same year the French explorer Jean-François de La Pérouse was wrecked on Vanikoro; a rescue expedition led by Bruni dEntrecasteaux sailed to Vanikoro but found no trace of La Pérouse. The fate of La Pérouse was not confirmed until 1826, when the English merchant Peter Dillon visited Tikopia and discovered items belonging to La Pérouse in the possession of the local people, confirmed by the subsequent voyage of Jules Dumont dUrville in 1828.
Some of the earliest regular foreign visitors to the islands were whaling vessels from Britain, the United States and Australia. They came for food, wood and water from late in the 18th century, establishing a trading relationship with the Solomon Islanders and later taking aboard islanders to serve as crewmen on their ships. Relations between the islanders and visiting seamen was not always good and sometimes there was bloodshed. A knock-on effect of the greater European contact was the spread of diseases to which local peoples had no immunity, as well a shift in the balance of power between coastal groups, who had access to European weapons and technology, and inland groups who did not. In the second half of the 1800s more traders arrived seeking turtleshells, sea cucumbers, copra and sandalwood, occasionally establishing semi-permanent trading stations. However initial attempts at more long-term settlement, such as Benjamin Boyds colony on Guadalcanal in 1851, were unsuccessful.
Vandermaelen, Philippe M G 1795-1869
Vandermaelen was the son of the wealthy soap manufacturer; he abandoned the soap trade and devoted his life to cartography. Entirely self-taught in geometry, astronomy and the geosciences, he began drafting the first sheets of an Atlas universel in 1824. This atlas was published between 1825 and 1827; it was sold in forty instalments of ten maps each and became a great success. The revenue enabled him to set up his own Etablissement géographique de Bruxelles in 1830, which not only produced maps, atlases and globes in large quantities but also housed a natural science museum, botanical gardens, a library, and an impressive collection of maps.
Shortly after the closing of Vandermaelens Institute, the Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) in 1880 acquired a large part of its cartographic collection and production.
Vandermaelens atlas was remarkable: 387 maps on a uniform scale of ca. 1:1.6 million. There was one edition of this very rare atlas, published in 1825-27; the subscription list shows that only 810 copies were sold. The six volumes, of which Africa was in Volume III (60 maps), were issued in instalments during the period 1825-1827.
This folio-size atlas is remarkable for several reasons. It is the first atlas produced by the then new printing process of lithography. It is also the first atlas to show the whole world in 380 maps using a large uniform scale—about 10km to the cm. on a modified conical projection described by Sanson-Flamsteed. Based on a prime meridian through Paris, each map has a drawn-out graticule giving it a trapezoidal form, the underlying intention being construction of a globe with a diameter of 7.755m Eugene Gilbert de Cauwer , his biographer, suggested that Vandernaelen was a worthy follower of Mercator and Ortelius.
Vandermaelen enlisted the assistance of lithographer-printer Hippolyte Ode in this ambitious project which introduced lithography into Belgium and created an upsurge in Belgian publishing. A number of maps were lithographed by Philippe Vandermaelen himself. For many of the areas depicted, these maps are the largest scale maps made at the time, and the most detailed. The lithographs are very well drawn and printed and should be appreciated in the context of lithography, which was a developing art at the time. The maps are handsome and detailed, although some of the place names are somewhat curious and the cartography sometimes imaginary. Nevertheless, the Vandermaelen maps are of great significance in the history of cartography and lithography. Visually, they are arresting and unusual. Vandermaelens maps best are appreciated in the context of its neighbouring maps - they were all meant to be joined .
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
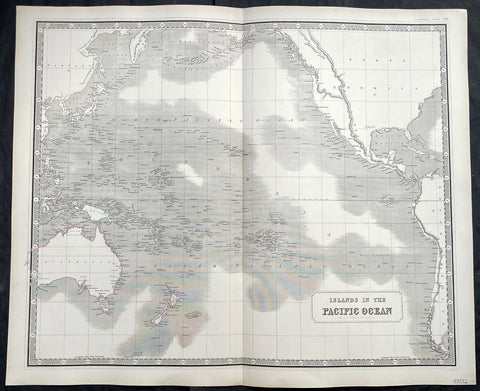
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, North America Pacific
- Title : Islands in the Pacific Ocean
- Size: 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1845
- Ref #: 40960
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique map of Australia, New Zealand, North America and the Pacific Ocean by W & AK Johnston, was published in the 1845 edition of his large General Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\\\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\\\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\\\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
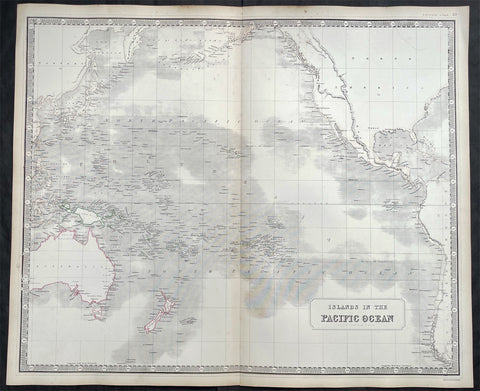
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, North America Pacific
- Title : Islands in the Pacific Ocean
- Size: 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1845
- Ref #: 23805
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original steel plate engraved antique map of Australia, New Zealand, North America and the Pacific Ocean by W & AK Johnston, was published in the 1845 edition of his large General Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (640mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\\\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\\\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\\\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\\\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
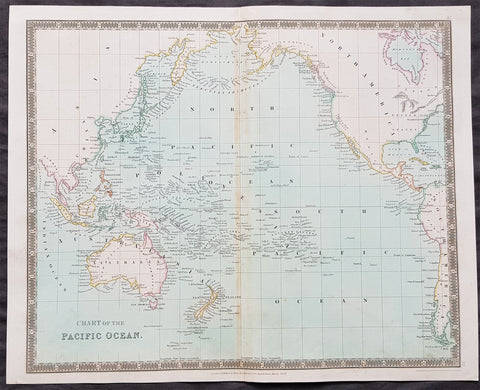
1834 Henry Teesdale Antique Map The Pacific, Australia, New Zealand, Nth America
- Title : Chart of The Pacific Ocean.....London Published by Henry Teesdale & co. High Holborn March 1834
- Ref #: 50303
- Size: 17 1/2in x 14in (445mm x 355mm)
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Pacific Ocean, Australia, New Zealand, to North & South America by John Dower was engraved in 1834 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1835 edition of Henry Teesdales A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Teesdale & co., Henry fl 1828-1843
Teesdale was a prominent London publisher and founding fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. He produced large-scale maps and charts and a number of fine atlases in the early part of the nineteenth century. He employed the most skilled draftsmen and engravers and his maps are renowned for precise detail and fine coloring
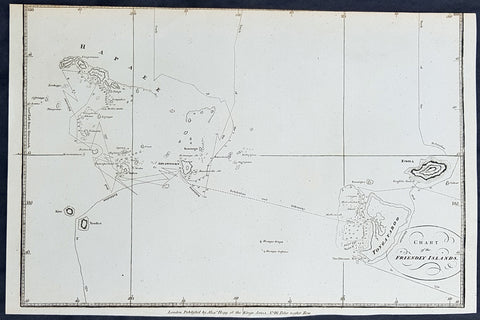
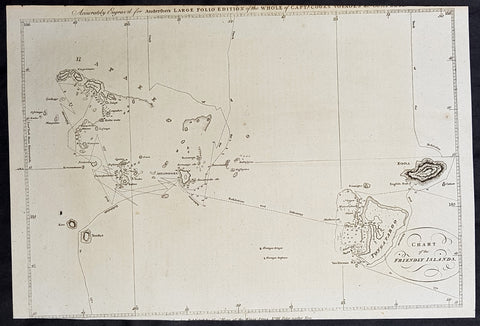
1784 Anderson Antique Map of the Tonga Islands - Capt. Cooks Voyages in 1773 & 1777
- Title : Chart of the Friendly Islands
- Size: 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (360mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 21443
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Tonga Island (Friendly Islands) with the routes taken by Captain James Cook visits to the Islands in his 2nd voyage in 1773 in HMS Resolution & Discovery and his 3rd and last voyage in 1777 in HMS Resolution & Discovery, was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
Exert From Cooks, <i>A Voyage Towards the South Pole, and Round the World, performed in His Majestys Ships the 'Resolution' and 'Adventure', In the Years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775.</i>
......<i>after leaving Raiatea (Society Islands) on 18 September 1773, Cook directed his course towards Amsterdam Island (Tongatapu), discovered by Tasman in 1643, intending to verify Tasman's charting against his own charts. The ships stayed for three days, thoroughly enjoying the reception they had received and called the group the Friendly Islands. On his second visit he headed for the Nomuka, the largest island of the south central group of Tonga.</i>
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (360mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (360mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
1784 Anderson Antique Map of the Tonga Islands - Capt. Cooks Voyages in 1773 & 1777
- Title : Chart of the Friendly Islands
- Size: 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (360mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 32152
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Tonga Island (Friendly Islands) with the routes taken by Captain James Cook visits to the Islands in his 2nd voyage in 1773 in HMS Resolution & Discovery and his 3rd and last voyage in 1777 in HMS Resolution & Discovery, was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
Exert From Cooks, <i>A Voyage Towards the South Pole, and Round the World, performed in His Majestys Ships the 'Resolution' and 'Adventure', In the Years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775.</i>
......<i>after leaving Raiatea (Society Islands) on 18 September 1773, Cook directed his course towards Amsterdam Island (Tongatapu), discovered by Tasman in 1643, intending to verify Tasman's charting against his own charts. The ships stayed for three days, thoroughly enjoying the reception they had received and called the group the Friendly Islands. On his second visit he headed for the Nomuka, the largest island of the south central group of Tonga.</i>
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (360mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (360mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Brown stain top left
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
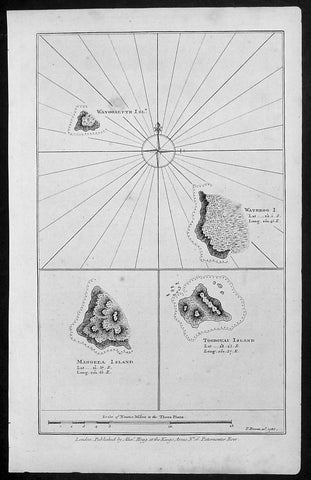
1786 Bowen Antique Map 3 x Cook Islands & 1 x Society Island - Cooks Voyage 1777
- Title : Wanooaette Isl; Wateeoo I; Mangeea Island Toobouai Island
- Size: 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 21697
- Date : 1786
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of three of the Cook Islands, Takutea (Wanooaette) Atiu (Wateeoo) and Mangaia (Mangeea) and a 4th map of the Island of Tubuai (Toobouai) in French Polynesia near Tahiti, visited by Captain Cook in HMS Resolution & Discovery in September 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was published in George Andersons A New, Authentic, and Complete Account of Voyages Round the World, Undertaken and Performed by Royal Authority. Containing a New, Authentic, Entertaining, Instructive, Full and Complete History of Captain Cooks First, Second, Third and Last Voyages.. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1786.
These maps of three Cook Islands :
1.Wanooaette, (Takutea)
2. Wateeoo (Atiu)
3. Mangeea ( Mangaia)
4. inset map of Toobouai (Tubuai) in the Society Islands in French Polynesia
All maps were charted by James Cook in 1777 while sailing for the Society Islands (French Polynesia) with livestock he carried aboard the Discovery and the Resolution. As he sailed toward Tahiti he discovered Toobouai (Tubuai) Island on 13 August 1777 where they stayed for 6 weeks. Relief shown by hachures and soundings.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
George William Anderson
A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... : to which are added genuine narratives of other voyages of discovery round the world, &c. viz. those of Lord Byron, Capt. Wallis, Capt. Carteret, Lord Mulgrave, Lord Anson, Mr. Parkinson, Capt. Lutwidge, Mess. Ives, Middleton, Smith, &c published by Alex. Hogg, 1786.
Spanish ships visited the islands in the 16th century; the first written record of contact with the islands came in 1595 with the sighting of Pukapuka by Spanish sailor Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, who called it San Bernardo (Saint Bernard). Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, a Portuguese captain working for the Spanish crown, made the first recorded European landing in the islands when he set foot on Rakahanga in 1606, calling it Gente Hermosa.
British navigator Captain James Cook arrived in 1773 and 1777 and named the island of Manuae Hervey Island. Later, the name Hervey Islands came to be applied to the entire southern group; the name Cook Islands, in honour of Cook, first appeared on a Russian naval chart published in the 1820s
Takutea, in the Cook Islands, is a small uninhabited island 21 kilometres northwest of Atiu in the southern Cook Islands.
Takutea is the only island in the Cook Islands that never had a permanent population. When Captain James Cook sighted the island on 4 April 1777, and some crew members went ashore, they found some huts, but no evidence of a permanent settlement.
Atiu, also known as Enuamanu (meaning land of the birds), is an island 187 km northeast of Rarotonga, in the Southern Islands group of the Cook Islands Archipelago.
The first recorded European to arrive at Atiu was Captain Cook. He sighted the island on March 31, 1777 and made tentative contact with some of the people over the next few days.
Mangaia (traditionally known as A ua u Enua, which means terraced) is the most southerly of the Cook Islands and the second largest, after Rarotonga.
The first recorded European to arrive at Mangaia was Captain James Cook on 29 March 1777.
Tubuai part of the Society Islands is located 640 km south of Tahiti. Tubuai was first viewed by Europeans when it was mapped by Captain James Cook in 1777, although his party did not disembark. Cook discovered the islands name, Toobouai, from the natives who surrounded his ship in their canoes (a Tahitian named Omai, who was part of Cooks group, translated)
The next Europeans to arrive were the mutineers of the HMS Bounty in 1789. Mutineer Fletcher Christian, in looking for an island on which to permanently hide, had scoured Blighs maps and nautical charts and decided on Tubuai.
Upon arrival at Tubuai, a conflict arose while the mutineers were still on their ship and several islanders were killed in their canoes. The site of this event in the lagoon on the north side of the island is called Baie Sanglant (Bloody Bay)
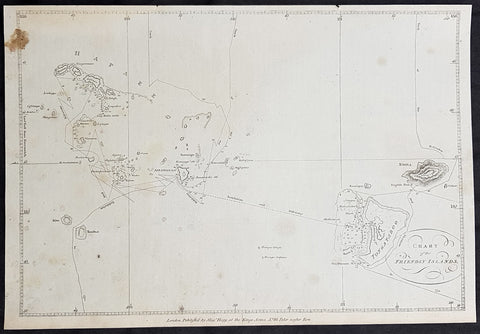
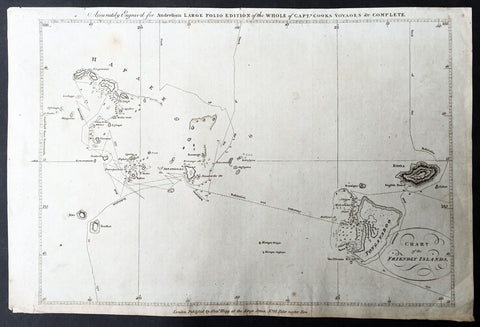
1784 Anderson Antique Map of the Tonga Islands - Capt. Cooks Voyages in 1773 & 1777
- Title : Chart of the Friendly Islands
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 21603
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Tonga Island (Friendly Islands) with the routes taken by Captain James Cook visits to the Islands in his 2nd voyage in 1773 in HMS Resolution & Discovery and his 3rd and last voyage in 1777 in HMS Resolution & Discovery, was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
Exert From Cooks, <i>A Voyage Towards the South Pole, and Round the World, performed in His Majestys Ships the 'Resolution' and 'Adventure', In the Years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775.</i>
......<i>after leaving Raiatea (Society Islands) on 18 September 1773, Cook directed his course towards Amsterdam Island (Tongatapu), discovered by Tasman in 1643, intending to verify Tasman's charting against his own charts. The ships stayed for three days, thoroughly enjoying the reception they had received and called the group the Friendly Islands. On his second visit he headed for the Nomuka, the largest island of the south central group of Tonga.</i>
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top & bottom margins cropped close to borders
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
1784 Anderson Antique Map of the Tonga Islands - Capt. Cooks Voyages in 1773 & 1777
- Title : Chart of the Friendly Islands
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 32181
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Tonga Island (Friendly Islands) with the routes taken by Captain James Cook visits to the Islands in his 2nd voyage in 1773 in HMS Resolution & Discovery and his 3rd and last voyage in 1777 in HMS Resolution & Discovery, was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
Exert From Cooks, <i>A Voyage Towards the South Pole, and Round the World, performed in His Majestys Ships the 'Resolution' and 'Adventure', In the Years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775.</i>
......<i>after leaving Raiatea (Society Islands) on 18 September 1773, Cook directed his course towards Amsterdam Island (Tongatapu), discovered by Tasman in 1643, intending to verify Tasman's charting against his own charts. The ships stayed for three days, thoroughly enjoying the reception they had received and called the group the Friendly Islands. On his second visit he headed for the Nomuka, the largest island of the south central group of Tonga.</i>
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
1784 Capt Cook Antique Print Man called Mourooa of Mangaia in the Cook Islands
- Title : A Man of Mangeea
- Size: 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21605
- Date : 1784
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a man of Mangaia, one of the Cook Islands - visited by Captain James Cook during the third voyage of discovery - after John Webber - was published in the 1784 English publication of Cooks third Voyage.
......Cook reconnoitered the reef surrounding Mangaia, one of the Cook Islands, on 29 March 1777. No landing was made but on the following day, a canoe with paddlers came out to meet the ships.
At length when they had perceived we were going to the Ships they all left us except the man we had in the boat, he tho not without evident signs of fear, accompaned us on board\' Cook\'s Journals III, I, 89.
The portrait was of a native called Mou\'rooa where through Omai\'s services he was questioned about his island.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
John Webber was born in London, of Swiss descent. In the spring of 1776 he showed three works at the Royal Academy\'s annual exhibition, where they attracted the attention of Dr Daniel Solander, President of the Royal Society and a friend and colleague of botanist Joseph Banks. Both had sailed with Captain James Cook on his first voyage of exploration in the Pacific aboard the \'Endeavour\', and were looking for a suitable artist to accompany them on a third trip. Solander recommended Webber to the Admiralty, and he was appointed almost immediately.
The voyage commenced on 12 July 1776. Upon his return to London in 1780, Webber submitted about 200 finished works to the Admiralty, which he had made on the voyage. From autumn 1780 until summer 1784, he re-drew many of the drawings and supervised the engravers and printers who were preparing the images for publication, under the direction of Lord Sandwich
ted.
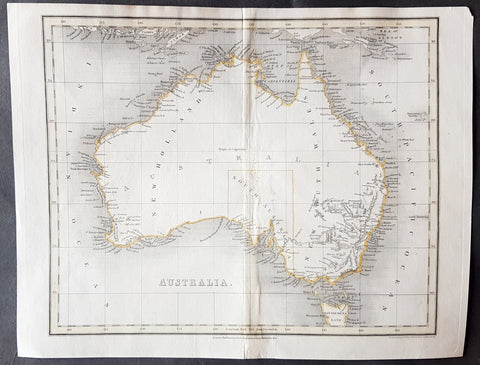
1837 John Dower Original Antique Map of Australia - New Holland
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1837
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 70704
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This fine steel-plate engraved original hand coloured antique map of Australia by John Dower was published by Orr & Smith, London in 1837. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Browning & weak along centerfold
Verso: - Strengthened along centerold
Background:
Interesting early map of Australia with only the state of South Australia delineated. The whole of the east coast is named New South Wales, the city of Melbourne was not noted, few internal details are noted. Western Australia shows significant coastal details but is still named "New Holland"
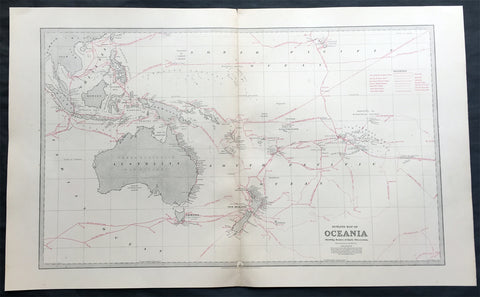
1888 Large Pic Atlas Large Antique Map Oceania Australia, New Zealand
- Title : Oceania, showing the route of the earlier discoverers
- Ref : 50342
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small repair to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
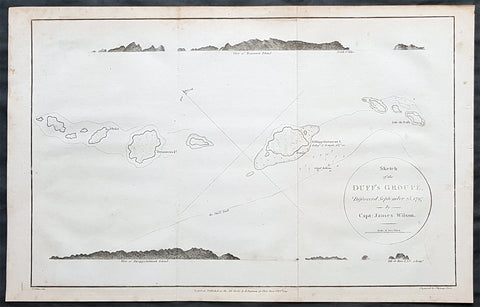
1797 Wilson Large Antique Map of the Duff Isles, Solomon Islands, South Pacific
- Title : 1799 James Wilson Antique Map of Duff or Wilson Islands, Santa Cruz Solomons Is.
- Date : 1799
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90613
- Size: 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 255mm)
Description:
This copper-plate engraved original antique map of Duff or Wilson Islands located northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands in the Solomon Islands province of Temotu, in the South Pacific was engraved in by Thomas foot and was published in the 1799 edition Captain James Wilsons A missionary voyage to the Southern Pacific Ocean, performed in the years 1796, 1797, 1798, in the ship Duff commanded by Captain James Wilson.Compiled from journals of the officers and the missionaries. With a preliminary discourse on the geography and history of the South Sea Islands; and an appendix, including details never before published of the natural and civil state of Otaheite.
Captain James Wilson (1760–1814), commanded the British ship Duff, which the London Missionary Society contracted in 1797 to convey a team of missionaries (consisting of thirty men, six women, and three children) to their postings in Tahiti, Tonga, and the Marquesas Islands. During the voyage, Wilson also surveyed (or confirmed the locations of) numerous islands in the Pacific, including Vanua Balavu, Fulaga and Ogea Levu in Fiji, Mangareva in the Gambier Islands, Pukarua in the Tuamotus, and Satawal, Elato, and Lamotrek, in the Caroline Islands.
Three years after the establishment of the British mission in Tahiti, the directors of the Society appointed a committee to consider a suitable memorial for presentation to Wilson for his services in helping to establish the first mission in the South Seas.
He published an account of his voyage: A Missionary Voyage to the Southern Pacific Ocean in 1799. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soling
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Light soling
Background:
The Duff Islands are a small island group lying to the northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands in the Solomon Islands province of Temotu. They are also sometimes known as the Wilson Islands.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans of the Duff Islands was by the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós where it anchored on 8 April 1606. Its inhabitants named the islands as Taumako. They were charted by Quirós as Nuestra Señora del Socorro (Our Lady of Succour in Spanish).
The Duff Islands were named after missionary ship Duff, captained by James Wilson, which reached them in 1797.
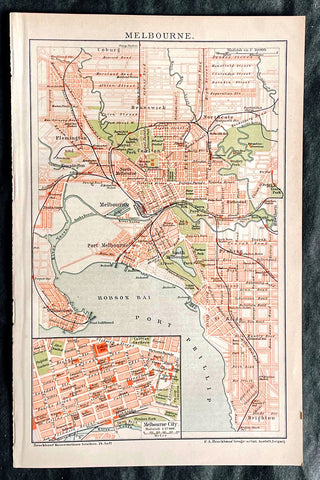
1896 F.A. Brockhaus Antique Map, Street Plan of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Antique Map
- Title : Melbourne
- Ref #: 27012
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
- Date : 1896
Description:
This original antique lithograph street map of Melbourne Australia was engraved and published F.A. Brockhaus for the Brockhaus Konversations Lexikon, Germany, 1896
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Brockhaus, Friedrich Arnold (1772 - 1823)
Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus was a German encyclopedia publisher and editor, famed for publishing the Conversations-Lexikon, which is now published as the Brockhaus encyclopedia.
Brockhaus was educated at the gymnasium of his native Dortmund, and from 1788 to 1793 served an apprenticeship in a mercantile house at Düsseldorf. He then devoted two years at the University of Leipzig to the study of modern languages and literature, after which he set up in Dortmund an emporium for English goods. In 1801, he transferred this business to Arnheim, and in the following year to Amsterdam.
In 1805, having given up his first line of trade, Brockhaus began business as a publisher. Two journals projected by him were not allowed by the government to survive for any length of time, and in 1810 the complications in the affairs of Holland induced him to return homewards. In 1811 he settled at Altenburg. About three years previously he had purchased the copyright of the bankrupt Conversations-Lexikon, an encyclopedia started in 1796, and in 1810-1811 he completed the first edition of this celebrated work. It was widely imitated as a model for encyclopedias, and is still published today, known as the Brockhaus Encyclopedia.
A second edition under Brockhauss editorship was begun in 1812, and was received with universal favour. His business extended rapidly, and in 1818 Brockhaus moved to Leipzig, where he established a large printing-house. Among the more extensive of his many literary undertakings were the critical periodicals — Hermes, the Literarisches Konversationsblatt (afterwards the Blätter für literarische Unterhaltung) and the Zeilgenossen, and some large historical and bibliographical works, such as Friedrich Ludwig Georg von Raumers Geschichte der Hohenstaufen, and Friedrich Adolf Eberts Allgemeines bibliographisches Lexikon.
Brockhaus died in Leipzig. The business was carried on by his sons, Friedrich Brockhaus (1800–1865), who retired in 1850, and Heinrich Brockhaus (1804–1874), under whom it was considerably extended. Heinrich especially rendered great services to literature and science, which the University of Jena recognized by making him, in 1858, honorary Doctor of Philosophy. In the years 1842–1848, Heinrich Brockhaus was member of the Saxon second chamber, as representative for Leipzig, was made honorary citizen of that city in 1872, and died there on 15 November 1874.
His firm continues under the name F.A. Brockhaus AG in his honor. He is also the namesake of 27765 Brockhaus, a main-belt asteroid discovered in 1991.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1825 Philippe Vandermaelen Large Antique Map of Austral Islands French Polynesia
Antique Map
-
Title : Partie De L Archipel Des Iles Basses
- Ref #: 17006
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
- Date : 1825
Description:
This very large original hand coloured antique lithograph map of the Austral Islands in the French Polynesia group of islands in the in the South Pacific was published by Philippe Vandermaelen in his revolutionary 1825 Atlas universel de geographie physique, politique, statistique et mineralogique.
Until the publication of this atlas, large detailed maps of this region of Australia & the Pacific were uncommon.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2in x 21in (725mm x 550mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium (French: Condominium des Nouvelles-Hébrides, lit. Condominium of the New Hebrides) and named for the Hebrides Scottish archipelago, was the colonial name for the island group in the South Pacific Ocean that is now Vanuatu. Native people had inhabited the islands for three thousand years before the first Europeans arrived in 1606 from a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Pedro Fernandes de Queirós. The islands were colonised by both the British and French in the 18th century, shortly after Captain James Cook visited.
The two countries eventually signed an agreement making the islands an Anglo-French condominium that divided New Hebrides into two separate communities: one Anglophone and one Francophone. That divide continued even after independence, with schools teaching in either one language or the other, and with different political parties. The condominium lasted from 1906 until 1980, when New Hebrides gained its independence as the Republic of Vanuatu.
Vandermaelen, Philippe M G 1795-1869
Vandermaelen was the son of the wealthy soap manufacturer; he abandoned the soap trade and devoted his life to cartography. Entirely self-taught in geometry, astronomy and the geosciences, he began drafting the first sheets of an Atlas universel in 1824. This atlas was published between 1825 and 1827; it was sold in forty instalments of ten maps each and became a great success. The revenue enabled him to set up his own Etablissement géographique de Bruxelles in 1830, which not only produced maps, atlases and globes in large quantities but also housed a natural science museum, botanical gardens, a library, and an impressive collection of maps.
Shortly after the closing of Vandermaelens Institute, the Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) in 1880 acquired a large part of its cartographic collection and production.
Vandermaelens atlas was remarkable: 387 maps on a uniform scale of ca. 1:1.6 million. There was one edition of this very rare atlas, published in 1825-27; the subscription list shows that only 810 copies were sold. The six volumes, of which Africa was in Volume III (60 maps), were issued in instalments during the period 1825-1827.
This folio-size atlas is remarkable for several reasons. It is the first atlas produced by the then new printing process of lithography. It is also the first atlas to show the whole world in 380 maps using a large uniform scale—about 10km to the cm. on a modified conical projection described by Sanson-Flamsteed. Based on a prime meridian through Paris, each map has a drawn-out graticule giving it a trapezoidal form, the underlying intention being construction of a globe with a diameter of 7.755m Eugene Gilbert de Cauwer , his biographer, suggested that Vandernaelen was a worthy follower of Mercator and Ortelius.
Vandermaelen enlisted the assistance of lithographer-printer Hippolyte Ode in this ambitious project which introduced lithography into Belgium and created an upsurge in Belgian publishing. A number of maps were lithographed by Philippe Vandermaelen himself. For many of the areas depicted, these maps are the largest scale maps made at the time, and the most detailed. The lithographs are very well drawn and printed and should be appreciated in the context of lithography, which was a developing art at the time. The maps are handsome and detailed, although some of the place names are somewhat curious and the cartography sometimes imaginary. Nevertheless, the Vandermaelen maps are of great significance in the history of cartography and lithography. Visually, they are arresting and unusual. Vandermaelens maps best are appreciated in the context of its neighbouring maps - they were all meant to be joined .
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1856 James Virtue Antique Map of New Zealand and the Colonies of Australia
- Title : New Zealand and the Australian Colonies of Great Britain James S Virtue
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1856
- Ref #: 93052
Description:
This original lithograph antique map of New Zealand and the Colonies of Australia was published by James Virtue in 1856, just after Victorian statehood in 1851 and just prior to Queensland statehood in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A highly detailed map just prior to the gold and population boom of both Australia and New Zealand, with much of Australia unexplored in the center.
Virtue, George & James
George Virtue (1794 – 1868) was a 19th-century London publisher, well known for printing engravings. His publishing house was located at 26 Ivy Lane, Paternoster Row, London, EC
Virtue selected accomplished artists, employed the best engravers, and produced books that were rarely surpassed in elegance and correctness for the period. Chief among his publications were the following, all illustrated by William Henry Bartlett: Switzerland, by William Beattie, 2 vols. 1836; Scotland, by W. Beattie, 1838; The Waldenses, by W. Beattie, 1838; American Scenery, 2 vols. 1840; Description of the Beauties of the Bosphorus, by Julia Pardoe, 1840; and The Danube, its History and Scenery, by W. Beattie, 1844. Virtue created a prodigious business, issuing upwards of twenty thousand copper and steel engravings through his career.
In 1848, Virtue purchased two magazines. One was an art publication, The Art Union, which had been founded in 1839 by Hodgson & Graves, then purchased in 1847 by Chapman & Hall. The second purchase was controlling interest in Sharpe\\\\\\\'s London Magazine, a literary and cultural magazine, Arthur Hall publisher. In 1849, Virtue renamed the art magazine The Art Journal and, in time, it became known as the premier art publication of Great Britain. Also in 1849, he created a new firm with Arthur Hall called Arthur Hall, Virtue & Co
James Sprent Virtue (1829 – 1892) inherited the publishing business from his father, George, after his retirement in 1855
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1830 Sydney Hall Antique Map of Australia, New Holland, Swan River Settlement
- Title : Australia & Islands Adjacent
- Ref #: 35074
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
- Date : 1830
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate original antique map by Sydney Hall was published in the 1830 edition of Halls General Atlas published by Longman & co., London. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1835 Joseph Meyer Antique Print Early View of The Rocks Sydney, Australia
- Title : Sydney in New South Wales
- Ref #: 50668
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1835
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine steel-plate engraved original antique print an early view of The Rocks in Sydney Australia by Joseph Meyer was published in the 1835 edition of Meyers Universum
These are beautiful steel-plate engraved prints, with a high level of detail along with beautifully executed artistry.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australia\'s largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance. The city has played host to many international events, including the 2000 Summer Olympics.
Meyer, Joseph 1796 - 1856
Meyer was a German industrialist and publisher, most noted for his encyclopedia, Meyers Konversations-Lexikon.
Meyer was born at Gotha, Germany, and was educated as a merchant in Frankfurt am Main. He went to London in 1816, but returned to Germany in 1820 after business adventures and stock speculations fell through. Here he invested in enterprises like textile-trade (1820–24). Soon after the first steam-hauled railway had started in December 1835, Meyer started to make business plans how to start the first railways. He also bought some concessions for iron mining. In 1845, he founded the Deutsche Eisenbahnschienen-Compagnie auf Actien (German Railway Rail joint stock company).
Meyer operated very successfully as a publisher, employing a system of serial subscription to publications, which was new at that time. To this end he founded a company, Bibliographisches Institut, in Gotha in 1826. It published several editions of the Bible, works of classical literature (Miniatur-Bibliothek der deutschen Classiker, Groschen-Bibliothek), atlases, the world in pictures on steel engravings Meyers Universum, 1833–61, 17 volumes in 12 languages with 80,000 subscribers all over Europe), and an encyclopaedia, (das Grosse Conversations-Lexikon für die gebildeten Stände;). His company grew substantially, and in 1828 he moved it from Gotha to Hildburghausen, where he died thirty years later.
1859 Aubert Antique Print View of Sydney, Australia from the North to The Rocks
- Title : Sydney (Australie)
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1859
- Ref #: 82027
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique print an view of Sydney NSW from the north across Circular Quay & The Rocks with a view to St James Church on Kings St - across where the Harbour Bridge is now situated - by Pierre Eugene Aubert was published by Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger, Paris in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Crease in right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australia\'s largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance.
Aubert, Pierre Eugene, 1789-1847
A French artist and engraver of the early 19th century, working with the Paris publishers Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger.
1859 Aubert Antique Print View of Sydney, Australia from the North to The Rocks
- Title : Sydney (Australie)
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1859
- Ref #: 82030
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique print an view of Sydney NSW from the north across Circular Quay & The Rocks with a view to St James Church on Kings St - across where the Harbour Bridge is now situated - by Pierre Eugene Aubert was published by Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger, Paris in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Crease in right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australia\'s largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance.
Aubert, Pierre Eugene, 1789-1847
A French artist and engraver of the early 19th century, working with the Paris publishers Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger.
1859 Aubert Antique Print View of Sydney, Australia from the North to The Rocks
- Title : Sydney (Australie)
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1859
- Ref #: 82026
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique print an view of Sydney NSW from the north across Circular Quay & The Rocks with a view to St James Church on Kings St - across where the Harbour Bridge is now situated - by Pierre Eugene Aubert was published by Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger, Paris in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Crease in right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australia\'s largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance.
Aubert, Pierre Eugene, 1789-1847
A French artist and engraver of the early 19th century, working with the Paris publishers Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger.
1859 Aubert Antique Print View of Sydney, Australia from the North to The Rocks
- Title : Sydney (Australie)
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1859
- Ref #: 82028
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique print an view of Sydney NSW from the north across Circular Quay & The Rocks with a view to St James Church on Kings St - across where the Harbour Bridge is now situated - by Pierre Eugene Aubert was published by Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger, Paris in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Crease in right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australia\'s largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance.
Aubert, Pierre Eugene, 1789-1847
A French artist and engraver of the early 19th century, working with the Paris publishers Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger.
1859 Aubert Antique Print View of Sydney, Australia from the North to The Rocks
- Title : Sydney (Australie)
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1859
- Ref #: 82029
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique print an view of Sydney NSW from the north across the Rocks with a view to St James Church on Kings St, across the harbour where the Harbour Bridge now sits, by Pierre Eugene Aubert was published by Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger, Paris in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Crease in right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australia\'s largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance.
Aubert, Pierre Eugene, 1789-1847
A French artist and engraver of the early 19th century, working with the Paris publishers Dufour, Mulat and Boulanger.
1878 Petermann Antique Map of Northern Territory Australia - William McMinn 1876
- Title : Neue Aufnahmen in Nord-Australien Nach. Ringwood & Mc Minn...Gotha: Justus Perthes 1878
- 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1878
- Ref #: 82058
Description:
This scarce original antique lithograph map of north-west Northern Territory, Australia showing Palmerston at Port Darwin, place names and exploration routes, including that of William McMinn in 1876, by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1878 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William McMinn (1844 – 14 February 1884) was an Australian surveyor and architect, based in Adelaide.
He was born in Newry, County Down, Ireland, a son of Joseph McMinn and his wife Martha McMinn (née Hamill), who with their large family emigrated to Adelaide on the Albatross, arriving in September 1850.
After completing school, he was apprenticed to the architect James Macgeorge, but first practiced as a surveyor. He was involved in Boyle Travers Finniss\'s ill-fated 1865 expedition to Northern Australia surveying the area around the Adelaide River. Following the desertion of a majority of the party to Singapore, McMinn and 5 others purchased a 23-foot open boat which they named the Forlorn Hope and sailed it 2,000 miles (3,200 km) to Champion Bay, Geraldton, Western Australia. He was later involved in the 1872 surveying of the Overland Telegraph from Port Augusta to Darwin.
McMinn began practising as an architect in 1867, briefly in partnership with Daniel Garlick, and later with some others, but usually independently. He designed many grand private residences, but also designed or assisted in the design of many of Adelaide\'s grand public buildings. Whilst in partnership with Edward John Woods, he designed the original Venetian Gothic building of the University of Adelaide, considered his greatest work.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print Matavia Bay & Boats in Tahiti French Polynesia 1773
- Title : Vue de Taiti et de plusieurs Pirogues De Cette Isle (View of the Island of Tahiti and canoes)
- Size: 15in x 7 1/2in (380mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21576
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print a view of
Matavia Bay, on the Island of Tahiti, with various canoes & boats, visited by Captain James Cook in August 1773, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
Cooks Journal 1773
On 20th Aug, wrote Cook, Nothing worthy of note happened till the Dusk of the evening when one of the Natives made off with a musquet belonging to the Guard on shore, I was present when this happen\'d and sent two or three of our people after him, this would have signified but little had not some of the natives pursued the thief, knock\'d him down and took from him the Musquet and return\'d it to us.
Three days later I set out accompanied by Captain Furneaux some of the Gentlemen and several of the Natives, we met the Chief... I knew him at first sight and he me, having seen each other several times in 1769 at which time he was but a boy. According to Wales the Capt returned from his Visit to the King, Owhyadoa, having with much difficulty, and expince in presents &c procured three Hogs.
Off to Matavai Bay
The next day, wrote Burney we hove our Anchors up & saild from this place, the Commodore leaving his Cutter behind to try if they could procure any more Hogs - the next day (25th) the Cutter returned about Noon with 10 which were divided between the 2 Ships - at 7 this Evening we Anchored in Matavia Bay in 10 fathoms & Moord with our Small Bower & Stream Anchors.
When the natives came aboard, Cook found several of whom I knew and almost all of them me... In the morning, after having given directions about erecting Tents for the reception of the Sick, Coopers and guard, I set out for Oparre accompanied by Captain Furneaux, some of the gentlemen... as soon as we landed we were conducted to Otoo [Tu], the chief.
When Cook returned, he had the Sick land, Twenty from the Adventure and one from the Resolution, landed a sufficient number of men to guard the Whole and left the command to Lieutt Edgcombe of the Marines. A party of Marines being sent on Shore as a Guard, wrote Wales, I landed my Observatory and Instruments and begun to put them up on the Spot where Mr Green Observed the Transit of Venus in 1769.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 7 1/2in (380mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 7in (370mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print of Manao tupapau or Spirit Watching in Tahiti, 1773
- Title : Un Toupapow, avec un Cadavre dessus avec le principal personnage du deuil en habit de Ceremonie (Manao tupapau Ceremony with a corpse top with the main character of the mourning ceremony dress)
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 21652
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of the Spirit of the Dead Watching (Manao tupapau) in Tahiti with priest and mourners, visited by Captain James Cook in 1773, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
Ghosts in Polynesian culture
There was widespread belief in ghosts in Polynesian culture, some of which persists today. After death, a person\'s ghost would normally travel to the sky world or the underworld, but some could stay on earth. In many Polynesian legends, ghosts were often involved in the affairs of the living. Ghosts might also cause sickness or even invade the body of ordinary people, to be driven out through strong medicines.
In the reconstructed Proto-Polynesian language, the word qaitu refers to a ghost, the spirit of a dead person, while the word tupuqa has a broader meaning including all supernatural beings. Some of the ancient Māui legends that are common throughout the Polynesian islands include the idea of a double soul inhabiting the body. One was the soul which never forsakes man, and the other the soul that could be separated or charmed away from the body by incantations was the hau.
In some societies, the tattoo marks on the Polynesian\'s face indicated their cult. A spiral symbol meant that the man favoured the sky world, but before ascending there on a whirlwind his ghost had to travel to his people\'s homeland, situated in the navel of the world. Different markings indicated that the ghost chose to live in the underworld. The Hawaiians believed in aumakua, ghosts who did not go down into Po, the land of King Milu. These ghosts remained in the land of the living, guarding their former families.
Of his 1892 Tahitian painting Manao Tupapau, Paul Gauguin said according to Tahitian beliefs, the title Manao Tupapau has a double meaning . . . either she thinks of the ghost or the ghost thinks of her.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt Cook Antqiue Print of Tahitians Honouring the Dead, Manao Tupapau 1769
- Title : Maniere dont on expose les morts a Otahiti (How the dead are exposed on Tahiti)
- Size: 15in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 21733-1
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of how the Dead are left mummified outdoors in an elevated platform in Tahiti, and the ritual of the Spirit of the Dead Watching (Manao tupapau), visited by Captain Cook in HMS Endeavor during his first visit to the Island in 1769, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Sydney Parkinson - was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774.
Ghosts in Polynesian culture
There was widespread belief in ghosts in Polynesian culture, some of which persists today. After death, a person\'s ghost would normally travel to the sky world or the underworld, but some could stay on earth. In many Polynesian legends, ghosts were often involved in the affairs of the living. Ghosts might also cause sickness or even invade the body of ordinary people, to be driven out through strong medicines.
In the reconstructed Proto-Polynesian language, the word qaitu refers to a ghost, the spirit of a dead person, while the word tupuqa has a broader meaning including all supernatural beings. Some of the ancient Māui legends that are common throughout the Polynesian islands include the idea of a double soul inhabiting the body. One was the soul which never forsakes man, and the other the soul that could be separated or charmed away from the body by incantations was the hau.
In some societies, the tattoo marks on the Polynesian\'s face indicated their cult. A spiral symbol meant that the man favoured the sky world, but before ascending there on a whirlwind his ghost had to travel to his people\'s homeland, situated in the navel of the world. Different markings indicated that the ghost chose to live in the underworld. The Hawaiians believed in aumakua, ghosts who did not go down into Po, the land of King Milu. These ghosts remained in the land of the living, guarding their former families.
Of his 1892 Tahitian painting Manao Tupapau, Paul Gauguin said according to Tahitian beliefs, the title Manao Tupapau has a double meaning . . . either she thinks of the ghost or the ghost thinks of her.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt Cook Antqiue Print of Tahitians Honouring the Dead, Manao Tupapau 1769
- Title : Maniere dont on expose les morts a Otahiti (How the dead are exposed on Tahiti)
- Size: 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 21427
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of how the Dead are left mummified outdoors in an elevated platform in Tahiti, and the ritual of the Spirit of the Dead Watching (Manao tupapau), visited by Captain Cook in HMS Endeavor during his first visit to the Island in 1769, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Sydney Parkinson - was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774.
Ghosts in Polynesian culture
There was widespread belief in ghosts in Polynesian culture, some of which persists today. After death, a person\'s ghost would normally travel to the sky world or the underworld, but some could stay on earth. In many Polynesian legends, ghosts were often involved in the affairs of the living. Ghosts might also cause sickness or even invade the body of ordinary people, to be driven out through strong medicines.
In the reconstructed Proto-Polynesian language, the word qaitu refers to a ghost, the spirit of a dead person, while the word tupuqa has a broader meaning including all supernatural beings. Some of the ancient Māui legends that are common throughout the Polynesian islands include the idea of a double soul inhabiting the body. One was the soul which never forsakes man, and the other the soul that could be separated or charmed away from the body by incantations was the hau.
In some societies, the tattoo marks on the Polynesian\'s face indicated their cult. A spiral symbol meant that the man favoured the sky world, but before ascending there on a whirlwind his ghost had to travel to his people\'s homeland, situated in the navel of the world. Different markings indicated that the ghost chose to live in the underworld. The Hawaiians believed in aumakua, ghosts who did not go down into Po, the land of King Milu. These ghosts remained in the land of the living, guarding their former families.
Of his 1892 Tahitian painting Manao Tupapau, Paul Gauguin said according to Tahitian beliefs, the title Manao Tupapau has a double meaning . . . either she thinks of the ghost or the ghost thinks of her.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt Cook Antique Print The Remains of Chief Vehiatua II (Tu) Tahiti, 1777
- Title : Le Corps De Thee, Chef De O Taiti, Tel Qu on le Conservoit Apres sa Mort. (The body of Thee, Chief of Tahiti Preserved after his death)
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 31834
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of the mummified remains of Chief Vehiatua II (Tu), laying in state, on the island of Tahiti visited by Captain Cook in 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
.....during his final visit, Cook returned Omai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Omais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua IIs funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ariipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ariipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims....
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt Cook Antique Print of Dancing Girls & Musicians Raiatea Island in 1777
- Title : Vue d L Interieur d une Maison dans i Isle d Ulietea. Representation d une danse a la mode du pays. (View of the inside a house in Isle of Ulieteai. Representation of a dance of the fashion of the country)
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 16087
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of te interior of a long house, dancing girls and musicians on the Island of Raiatea (Ulietea) part of French Polynesia, visited by Captain Cook in 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Cooks Journal 1777
Sep. 29 Mon. Sails for Moorea (Eimeo).
30 Tue. Anchors at Tareu/Papetaai, Moorea.
Oct. 11 Sat. Sails for Fare, Huahine.
12 Sun. Lands at Fare and installs Omai ashore, builds house and plantation.
Nov. 2 Sun. Sails for Raiatea.
3 Mon. Anchors at Haamanino (also in July 1768 and May 1774). Sets up Observatory.
Dec. 8 Mon. Stands off Borabora but stands off and heads MS.
22 Mon. Crosses the Equator.
24 Wed. Sights Christmas Island. Anchors in atoll and collects turtles.
30 Tue. Observes eclipse of Sun (Cook Islet/Eclipse Island).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
A traditional name for the island is Havaii, homeland of the Māori people.
The first European to record sighting Ra\\\\\\\'iātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Ra\\\\\\\'iātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, traveled with the European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
King Tamatoa VI was the last monarch, reigning from 1884-1888.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print of Capt Cook Landing on Eua Island, Tonga in 1773
- Title : Debarquement A Middelburgh L une des Amis (Landing A Middelburgh one of the Friendly Islands)
- Size: 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
- Ref #: 21357
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Cook landing on the Island of Eua - with HMS Resolution in the background - (named Middelburg by the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman in 1643) a small island close the the main island of Tongatapu, in the Kingdom of Tonga, visited by Captain James Cook in 1773, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
As it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands.
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam, the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.
Cooks Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 7in (295mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Eua is a smaller but still major island in the kingdom of Tonga. It is close to Tongatapu, but forms a separate administrative division
Eua was put on the European maps by Abel Tasman who reached it and Tongatapu on 21 January 1643. He called it Middelburg Island, after the capital of the Dutch province of Zeeland. He did not go on land, but proceeded to the Hihifo district of Tongatapu, which he named Amsterdam Island after the capital of the Netherlands.
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Queen Purea Surrender to Capt Wallis Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Cession de lisle D otahiti au Capitaine Wallis par la Reine Oberea (Surrender of the Island of Taahiti to Capt Wallis by Queen Obera)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25925
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis - the first European to visit Tahiti in 1767 - accepting surrender from Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti, after the battle in Matavia Bay in 1767, was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Queen Purea Surrender to Capt Wallis Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Cession de lisle D otahiti au Capitaine Wallis par la Reine Oberea (Surrender of the Island of Taahiti to Capt Wallis by Queen Obera)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16089-1
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis - the first European to visit Tahiti in 1767 - accepting surrender from Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti, after the battle in Matavia Bay in 1767, was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Print Queen Purea Surrender to Capt Wallis Tahiti, 1767
- Title : Cession de lisle D otahiti au Capitaine Wallis par la Reine Oberea (Surrender of the Island of Taahiti to Capt Wallis by Queen Obera)
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25925
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis - the first European to visit Tahiti in 1767 - accepting surrender from Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti, after the battle in Matavia Bay in 1767, was engraved by Robert Benard and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
From the log of Samuel Wallis, Captain of The Dolphin 1767.......
At two in the morning, it being very clear, we made sail again; at day-break we saw the land, at about five leagues distance, and steered directly for it; but at eight o’clock, when we were close under it, the fog obliged us again to lie to, and when it cleared away, we were much surprised to find ourselves surrounded by some hundreds of canoes…. When they came within pistol shot of the ship, they lay by, gazing at us with great astonishment, and by turns conferring with each other. In the mean time we showed them trinkets of various kinds, and invited them on board. Soon after, they drew together, and held a kind of council, to determine what should be done: then they all paddled around the ship, making signs of friendship, and one of them holding up a branch of the plantain tree, made a speech that lasted near a quarter of an hour, and then threw it into the sea. Soon after, as we continued to make signs of invitation, a fine, stout, lively young man ventured on board: he came up by the mizzen chains, and jumped out of the shrouds on top of the awning. We made signs to him to come down upon the quarter-deck, and handed up some trinkets to him: he looked pleased, but would accept of nothing till some of the Indians came alongside, and after much talk, threw a few branches of plantain tree on board the ship. He then accepted our presents, and several others very soon came on board.
As we had no anchorage here, we stood along the shore, sending the boats at the same time to sound at a less distance…. About three o’clock in the afternoon, we brought to, abreast of a large bay, where there was an appearance of anchorage. The boats were immediately sent to sound it, and while they were thus employed, I observed a great number of canoes gather round them. I suspected that the Indians had a design to attack them, and as I was very desirous to prevent mischief, I made the signal for the boats to come aboard, and at the same time, to intimidate the Indians, I fired a nine-pounder over their heads. As soon as the cutter began to stand towards the ship, the Indians in their canoes, though they had been startled by the thunder of our nine-pounder, endeavoured to cut her off. The boat, however, sailing faster than the canoes could paddle, soon got clear of those that were about her; but some others, that were full of men, waylaid her in her course, and threw several stones into her, which wounded some of the people. Upon this, the officer on board fired a musquet, loaded with buck-shot, at the man who threw the first stone, and wounded him in the shoulder. The rest of the people in the canoes, as soon as they perceived their companion wounded, leapt in to the sea, and the other canoes paddled away, in great terror and confusion.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Weapons Tools Hats from New Caledonia - Cook 1774
- Title : Ornemens et Armes de la Nouvelle Caledonie
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 21617
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of various weapons, farming tools and ornaments from the New Caledonia Islands visited by Captain James Cook in September 1774, in HMS Resolution & Adventure, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
The items illustrated are;
1. Lanee - Lance
2. Partie ornee de la Lance sur une plus grande Echelle - Larger scale of Lance handle
3. Chapeau de plumes &c. - Hat with feathers
4. Peigne - Comb
5. Piece de Corde dont ils se servent pour jetter leurs lances - Cord used to launch a spear
6 & 7. Differentes Massues - Two different types of club
8. Pioche pour Cultiver la Terre - Wooden farming hoe
9. Hache - Axe
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Caledonia is a special collective of France in the southwest Pacific Ocean, 1,210 km east of Australia and 20,000 km from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia sub-region, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Chesterfield Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of Pines, and a few remote islets. The Chesterfield Islands are in the Coral Sea. Locals refer to Grande Terre as Le Caillou (the pebble)
British explorer Captain James Cook was the first European to sight New Caledonia, on 4 September 1774, during his second voyage. He named it New Caledonia, as the northeast of the island reminded him of Scotland. The west coast of Grande Terre was approached by Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse in 1788, shortly before his disappearance, and the Loyalty Islands were first visited between 1793 and 1796 when Mare, Lifou, Tiga, and Ouvea were mapped by William Raven. The American whaler encountered the island named then Britania, and today known as Mar (Loyalty Is.) in November 1793. From 1796 until 1840, only a few sporadic contacts with the archipelago were recorded. About fifty American whalers (identified by Robert Langsom from their log books) have been recorded in the region (Grande Terre, Loyalty Is., Walpole and Hunter) between 1793 and 1887. Contacts became more frequent after 1840, because of the interest in sandalwood
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Weapons Tools Hats from New Caledonia - Cook 1774
- Title : Ornemens et Armes de la Nouvelle Caledonie
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16362
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of various weapons, farming tools and ornaments from the New Caledonia Islands visited by Captain James Cook in September 1774, in HMS Resolution & Adventure, during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
The items illustrated are;
1. Lanee - Lance
2. Partie ornee de la Lance sur une plus grande Echelle - Larger scale of Lance handle
3. Chapeau de plumes &c. - Hat with feathers
4. Peigne - Comb
5. Piece de Corde dont ils se servent pour jetter leurs lances - Cord used to launch a spear
6 & 7. Differentes Massues - Two different types of club
8. Pioche pour Cultiver la Terre - Wooden farming hoe
9. Hache - Axe
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Brown spotting to top of image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Caledonia is a special collective of France in the southwest Pacific Ocean, 1,210 km east of Australia and 20,000 km from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia sub-region, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Chesterfield Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of Pines, and a few remote islets. The Chesterfield Islands are in the Coral Sea. Locals refer to Grande Terre as Le Caillou (the pebble)
British explorer Captain James Cook was the first European to sight New Caledonia, on 4 September 1774, during his second voyage. He named it New Caledonia, as the northeast of the island reminded him of Scotland. The west coast of Grande Terre was approached by Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse in 1788, shortly before his disappearance, and the Loyalty Islands were first visited between 1793 and 1796 when Mare, Lifou, Tiga, and Ouvea were mapped by William Raven. The American whaler encountered the island named then Britania, and today known as Mar (Loyalty Is.) in November 1793. From 1796 until 1840, only a few sporadic contacts with the archipelago were recorded. About fifty American whalers (identified by Robert Langsom from their log books) have been recorded in the region (Grande Terre, Loyalty Is., Walpole and Hunter) between 1793 and 1887. Contacts became more frequent after 1840, because of the interest in sandalwood
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1773 Cook Antique Maps Tahiti, Raiatea & Huaheine Isles French Polynesia in 1769
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite ; Owharre Harbour in Huaheine ; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea ; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Size: 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 31216
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map, four maps on the one sheet;
1. Matavia Bay, Tahiti (Otaheite) - Windward Islands
2. Ohamaneno (Vaiaau) Harbour Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
3. Owharre (Bourayne Bay) Harbour in Huaheine - Leeward Islands
4. Oopoa (Opoa) Harbour, Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
all located in French Polynesia, South Pacific were complied by Capt James Cook during his first voyage of discovery in 1769, was published in the 1773 edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1773
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (365mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Matavai Bay is located on the north coast of Tahiti, the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia.
The first European known to have visited Tahiti was Lieutenant Samuel Wallis, in Dolphin, who landed on 17 June 1767 in Matavai Bay.
Captain James Cook anchored in the bay on 13 April 1769, on a sandy spit on the northeast end of Matavai Bay - named Point Venus by Cook.
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
Captain Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774.
Huahine is an island located among the Society Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Leeward Islands group (Iles sous le Vent).
Captain Cook arrived Fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour. They met with leading chief Ori (Mato). Cook returned on 3 Sept. 1773 and met with Oris son Teri itaria, the new ari i rahi of the island.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Map HMS Resolution & Adventure in the Tonga Islands 1773
- Title : Carte Des Isles Des Amis ( Friendly Islands)
- Ref : 21764
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Tonga Islands with the routes taken by HMS Resolution & Adventure, during Captain James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778.
Exert From Cooks diary A Voyage Towards the South Pole.........after leaving Raiatea (Society Islands) on 18 September 1773, Cook directed his course towards Amsterdam Island (Tongatapu), discovered by Tasman in 1643, intending to verify Tasmans charting against his own charts. The ships stayed for three days, thoroughly enjoying the reception they had received and called the group the Friendly Islands. On his second visit he headed for the Nomuka, the largest island of the south central group of Tonga.......
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map Nendo Isle, Nupani, Solomon Islands - Carteret 1767
- Title : Cote septentrional de la plus grande des isles de la Reine Charlotte; Baye Swallow; Havre Byroni
- Ref : 21589-1
- Size: 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique nautical chart & coastal view of the Island of Nendo (then called Lord Egmonts Island or New Guernsey) along with inset maps of Swallow Bay & Byrons Harbour on Nendo and a view of the nearby volcanic island of Nupani was drawn by Captain Phillip Carteret in July-August 1767 aboard his ship Swallow, accompanying Captain Samuel Wallis during his circumnavigation of the world, was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795
was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean.
Wallis was born near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron, and in 1766 was promoted to captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751) as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Thirds Island in honour of the King (June 1767). Wallis himself was ill and remained in his cabin: lieutenant Tobias Furneaux was the first to set foot, hoisting a pennant and turning a turf, taking possession in the name of His Majesty. Dolphin stayed in Matavai Bay in Tahiti for over a month. Wallis went on to name or rename five more islands in the Society Islands and six atolls in the Tuamotu Islands, as well as confirming the locations of Rongerik and Rongelap in the Marshall Islands. He renamed the Polynesian island of Uvea as Wallis after himself, before reaching Tinian in the Mariana Islands. He continued to Batavia, where many of the crew died from dysentery, then via the Cape of Good Hope to England, arriving in May 1768. He was able to pass on useful information to James Cook who was due to depart shortly for the Pacific, and some of the crew from the Dolphin sailed with Cook. In 1780 Wallis was appointed Commissioner of the Admiralty.
Capt. Philip Carteret (1733-1796)
was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navy\\\\\\\'s circumnavigation expeditions in 1764-66 and 1766-69.
Carteret entered the Navy in 1747, serving aboard the Salisbury, and then under Captain John Byron from 1751 to 1755. Between 1757 and 1758 he was in the Guernsey on the Mediterranean Station. As a lieutenant in the Dolphin he accompanied Byron during his voyage of circumnavigation, from June 1764 to May 1766.
In 1766 he was made a commander and given the command of the Swallow to circumnavigate the world, as consort to the Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis. The two ships were parted shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Carteret discovering Pitcairn Island and the Carteret Islands, which were subsequently named after him. In 1767, he also discovered a new archipelago inside Saint George\\\\\\\'s Channel between New Ireland and New Britain Islands (Papua New Guinea) and named it Duke of York Islands, as well as rediscovered the Solomon Islands first sighted by the Mendana in 1568, and the Juan Fernandez Islands first discovered by Juan Fernandez in 1574. He arrived back in England, at Spithead, on 20 March 1769.
He was promoted to post captain in 1771.
Nendo is the largest of the Santa Cruz Islands, located in the Temotu province of the Solomon Islands. The island is also known as Santa Cruz, Ndeni, Nitendi or Ndende. The name Santa Cruz was given to the island in 1595 by the Spanish navigator Alvaro de Mendaña, who unsuccessfully started a colony there.
The Nupani Atoll is located about 65 km to the West of the main group of the Reef Islands.
1784 Anderson Antique Map Capt Cook Exploration of the Society Islands in French Polynesia
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea; Owharre Harbourin Huaheine; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Date : 1784
- Ref # : 32197
- Size : 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map with surveys and depth soundings of four bays and harbours, of various bays & harbours of the Society Islands, French Polynesia made by explorers during the 17th & 18th centuries.
The first map is Matavia Bay, on the island of Tahiti (Otaheite), the second is Fare (Owharre) Harbour on the island of Huahine & the last two are Ohamaneno & Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) harbours on the island of Raiatea (Ulietea) was published in George Andersons 1784 edition of A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1784.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A description of the four Bays & Harbours and their relevance to Capt Cook and other South Seas explorers are;
1.Matavia Bay in Otaheite (Tahiti) - first European to visit Tahiti Capt. Samuel Wallis anchored in Matavai Bay in 1767 as did Louis-Antoine de Bougainville in 1768 & Capt James Cook landed in Matavai Bay in 1769 and returned in his next two voyages.
2. Owharre (Fare) Harbour in Huaheine (Huahine) Captain Cook arrived in fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour
3. Ohamaneno Harbour (Port) in Ulietea (Raiatea)
4. Oopoa (Fa aroa Bay) Harbour in Ulietea (Raiatea)
Raiatea - The first European to record sighting Raiātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva. The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Raiātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, travelled with European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
Tahiti.