Products
1639 Mercator & Hondius Large Antique Map of Greece, Aegean Islands & Turkey
Antique Map
- Title : Nova Totius Graeciae descriptio
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Ref #: 43151
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Greece, Aegean Islands & Turkey was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerardi Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14 1/2in (470mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom & top margin centre-fold re-joined, no loss
Plate area: - Repair to left side of image, no loss
Verso: - Repairs as noted
Background:
From the early days of map-making, cartographers have always had a keen interest he mapping of Greece and of the particular continental and insular Greek areas. In other words the "Greek chorography", as it is often called had been a cartographic item of special importance, both in manuscript and printed cartography, the later having produced an impressive number of Greek maps. All of these have been include in almost all the European Atlases and travel books, since the first printed edition of Ptolemy's Geographia in 1447. This prominent presence of Greece in the field of European cartography is due to various historic, political and cultural reasons. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
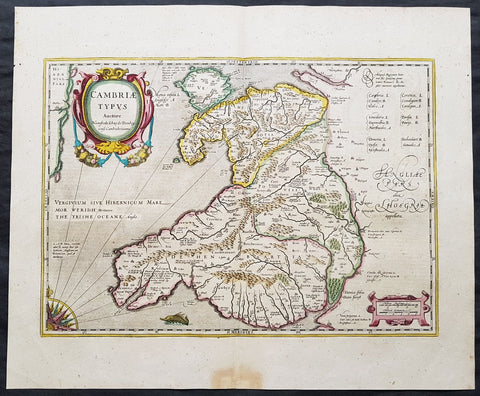
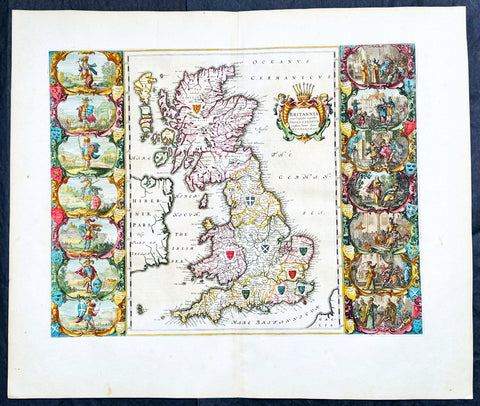
1639 Mercator & Hondius Large Old, Antique Map of Wales, GB - Humphrey Llwyd
- Title : Cambriae Typus Auctore Humfredo Lhuydo Denbigiense Cambrobritanno
- Date : 1639
- Size: 23in x 19in (590mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 43139
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Wales - dedicated to its original creator the Welsh cartographer Lhuyd Humphrey - by Gerard Mercator was published by Jodocus Hondius in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas.
One of the best examples I seen of this map to date, beautiful original hand colour with strong sturdy paper with a deep strong impression.
Humphrey Llwyd (also spelled Lhuyd) (1527–1568) was a Welsh cartographer , author, antiquary and Member of Parliament. He was a leading member of the Renaissance period in Wales along with other such men as Thomas Salisbury and William Morgan.
Llwyd was born in Denbigh, the county seat of the then county of Denbighshire at Foxhall, his family's estate. His father, Robert Llwyd, was descended from Harry Rossendale, henchman and grantee of the Earl of Lincoln. The first of the family that came to Wales from England appears to have been Foulk Rosindale, from whom Foxhall, or Foulk's Hall, was called. He married into the family of the Llwyd's of Aston, and probably from where his descendants derived their name, as well as their extraction from Einion Evell of the 12th Century. Einion Evell, Lord of part of Cynllaith, resided at Llwyn y Macn, in the parish of Oswestry. He and his twin brother, Cynwrig Evell, Lord of Y Glwyegl in Maelor Gymraeg, were the illegitimate sons of Madog ab Maredydd, Prince of Powys, by Eva, daughter of Madog (ab Einion Hael) ab Urien of Macn Gwynedd, ab Eginirab Lies ab Idnerth Benvras, Lord of Maesbrwg.
As a young man, he was educated at Brasenose College, Oxford and fared so well in the sciences and engineering that he was given a position as a physician to the Earl of Arundel during the Earl's tenure as Chancellor of the university. He was MP for East Grinstead during Elizabeth I's first parliament (1559).
In 1563, Llwyd returned to Denbigh and lived at Denbigh Castle at the permission of Sir John Salusbury who was then the Lord of the Manor of Denbigh. That year, he was elected MP for Denbigh Boroughs during Elizabeth's second Parliament where he promoted an act allowing the translation of the Bible into Welsh.
From 1566 he toured Europe, including Brussels, Augsburg, Milan, Padua and Venice. In Antwerp, he learnt from, and collaborated with, map maker Abraham Ortelius. In 1567, when Llwyd returned to Denbigh, he was given a stipend from the Crown to create the first printed map of Wales.
Llwyd died in 1568 and is buried in Whitchurch, a small chapel on the outskirts of Denbigh
Jodocus Hondius (1563 - 1612), one of the most notable engravers of his time, is known for his work in association with many of the cartographers and publishers prominent at the end of the sixteenth and the beginning of the seventeenth century.
In 1604 Hondius bought the plates of Mercator's Atlas which, in spite of its excellence, had not competed successfully with the continuing demand of the Ortelius Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
To meet this competition Hondius added about 40 maps to Mercator's original number and from 1606 published enlarged editions in many languages, still under Mercator's name but with his own name as publisher. These atlases have become known as the Mercator/Hondius series. The following year the maps were re-engraved in miniature form and issued as a pocket Atlas Minor.
After the death of Jodocus Hondius the Elder in 1612, work on the two atlases, folio and miniature, was carried on by his widow and sons, Jodocus II and Henricus, and eventually in conjunction with Jan Jansson in Amsterdam. In all, from 1606 onwards, nearly 50 editions with increasing numbers of maps with texts in the main European languages were printed. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (590mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14in (500mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning to bottom of margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
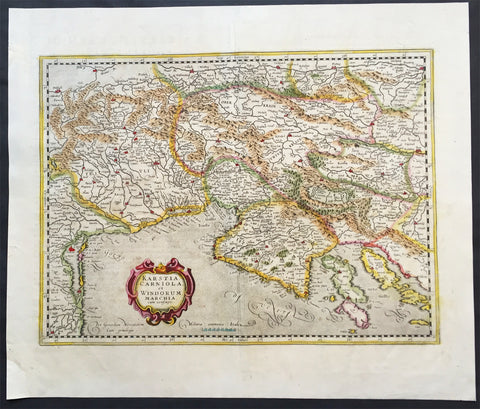
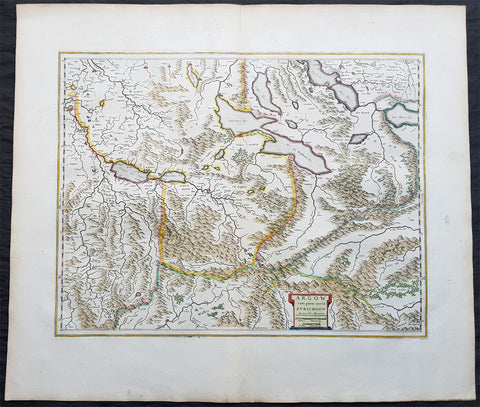
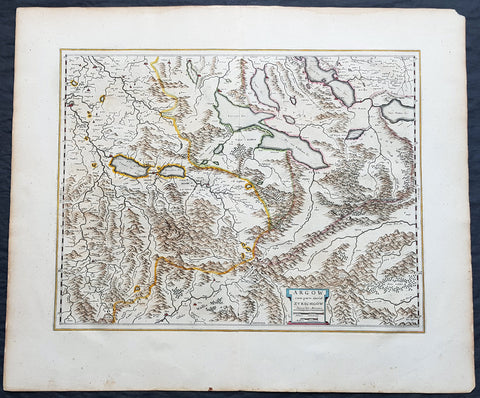
1639 Mercator Hondius Antique Map of Gulf of Venice, Istra, Italy, Slovenia
- Title : Karstia, Carniola, Histria et Windorum Marchia
- Ref #: 43152
- Size: 21 1/2in x 18 1/2in (550mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of northern Adriatic Sea and the Gulf of Venice centered on Istria, showing present-day north-eastern Italy, a large part of Slovenia and northern Croatia - extending from Venice to the Island of Arbe and from Doblach to Pettau on the Dravus River - engraved by Gerard Mercator, was published by 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 18 1/2in (550mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14 1/2in (470mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin corner repaired, no affect on image
Plate area: - Creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
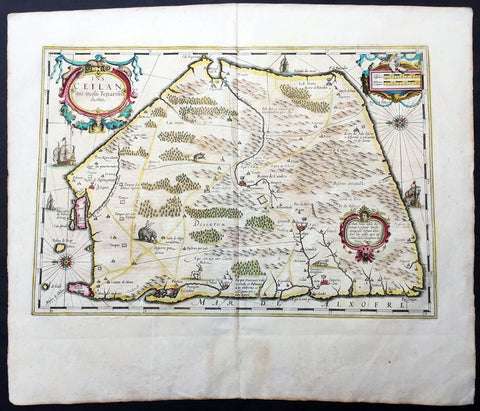
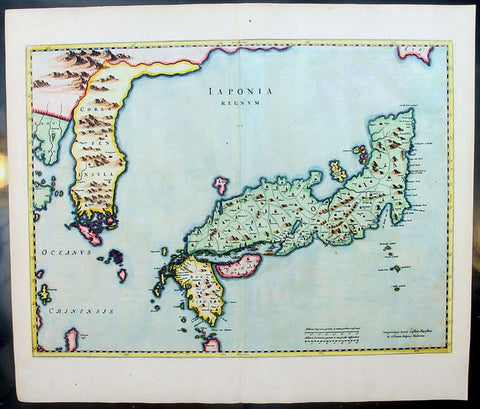
1639 Mercator Hondius Antique Map of Sri Lanka, India - Ceylon
- Title : Ins. Ceilan quae incolis Tenarifin dicture
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43138
- Size: 22 3/4in x 19 3/4in (580mm x 500mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of the Island of Ceylon - Sri Lanka was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercator's atlas by Jansson and Hondius.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 andcontinued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Background: Maps of India & Ceylon, much distorted in shape, appear in most world atlases from the time of Ptolemy. The earliest usually showing India as a relatively small extension of Southern Asia, dominated by the very large island of Taprobana (Ceylon). In later sixteenth-century maps de Jode, Ortelius and Mercator gave a much improved outline of both lands but India was still shown too small in relation to the whole continent. Most publishers in the seventeenth century continued to issue maps but with little improvement in detail until about 1719 when a French Jesuit priest, Father Jean Bouchet, compiled an accurate map of South India, subsequently used by G. Delisle (1723), Homann Heirs (1735) and by J. B. B. d'Anville, then the French East India Company's cartographer, as the basis for his greatly improved maps in 1737 and 1752.
In the next decade Alexander Dalrymple published a collection of newly surveyed coastal charts and plans of ports and, about the same time, in 1764, James Rennell, a young British Army officer who showed a remarkable aptitude for surveying, was appointed - at the age of 21- Surveyor General of Bengal; he immediately set in motion a comprehensive survey of the Company's lands, subsequently publishing maps of Bengal and other provinces which eventually formed The &ngal Atlas (1779). His other works included a Map of Hindoustan (1782-85) and The Provinces of Delhi, Agra etc and the Indian Peninsula (1788-94). These maps by Reunell provided the basis for a Trigonometrical Survey of India which was initiated in 1802 and for splendid maps published in London by Cary, the Arrowsmiths (1804-22) and the Wylds.
Jodocus Hondius (1563 - 1612), one of the most notable engravers of his time, is known for his work in association with many of the cartographers and publishers prominent at the end of the sixteenth and the beginning of the seventeenth century.
In 1604 Hondius bought the plates of Mercator's Atlas which, in spite of its excellence, had not competed successfully with the continuing demand of the Ortelius Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
To meet this competition Hondius added about 40 maps to Mercator's original number and from 1606 published enlarged editions in many languages, still under Mercator's name but with his own name as publisher. These atlases have become known as the Mercator/Hondius series. The following year the maps were re-engraved in miniature form and issued as a pocket Atlas Minor.
After the death of Jodocus Hondius the Elder in 1612, work on the two atlases, folio and miniature, was carried on by his widow and sons, Jodocus II and Henricus, and eventually in conjunction with Jan Jansson in Amsterdam. In all, from 1606 onwards, nearly 50 editions with increasing numbers of maps with texts in the main European languages were printed.(Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 3/4in x 19 3/4in (580mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 13 3/4in (500mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
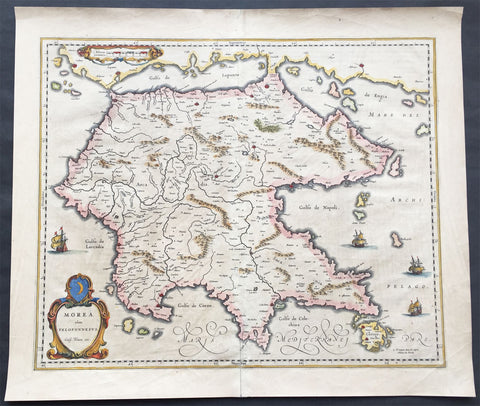
1640 Blaeu Antique Map of the Peloponnese or Morea Peninsula, Greece
- Title : Morea olim Peloponnesus..Guil. Blaeu exc.
- Date : 1640
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70300
- Size: 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original 1st edition antique map of the southern Greek peninsular of the Peloponnesusor Morea was published in the 1640 Latin edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Nouvs.
The peninsula has been inhabited since prehistoric times. Its modern name derives from ancient Greek mythology, specifically the legend of the hero Pelops who was said to have conquered the entire region. The namePeloponnesos means "Island of Pelops". During the Middle Ages, the peninsula was known as the Morea. According to folk etymology, this is because the Crusaders found it densely planted with mulberry trees (Greek: moreai) used by the flourishing silk industry.
Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map. The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom centerfold re-joined slight separation
Plate area: - Light brush marks across page
Verso: - Light brush marks across page
1640 Jansson Old, Antique German Atlas Title Page
- Title : Theatrum Exhibens Illustriores Principesque Germaniae
- Date : 1640
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 80014
- Size: 19 1/2in x 12in (495mm x 305mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique Atlas Title Page was published by Jan Jansson for the in the 1640 edition of Jansson's German Atlas. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 12in (495mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 9in (370mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Blind stamp and old ink notation in top margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
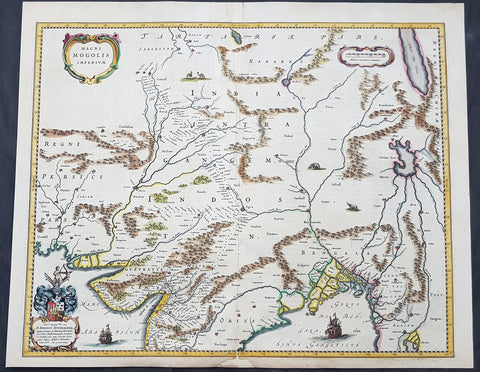
1640 Joan Blaeu Antique Map Mughal Empire of Northern India, Tibet, Nepal, Asia
- Title : Magni Mogolis Imperium
- Size: 22in x 18in (560mm x 465mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1640
- Ref #: 42017
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Mughal Empire of Northern India, Tibet, Nepal and central Asia was published by Joan Blaeu in the 1640 edition of Atlas Nouvs
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 465mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (515mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small section of bottom margin restored
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Centerfold re-enforced
Background:
This map centers on the Mughal capital of Agra, with the map covering, roughly, from Kabul to Orissa and Deccan, and from Persia to Bengal. It depicts the empire prior to the conquest of Orissa and Deccan, most likely during the reign of Shah Jahan, of Taj Mahal fame. Relief is shown pictorially. An elaborate title cartouche appears in the upper left quadrant. The map is embellished with images of tigers, elephants, caravans, and galleons.
There is much of interest. In particular, is the map detailed breakdown of the caravan network between Gujarat and Agra, between Agra and the desert outpost of Jaisalmer, and between Agra and the Silk Road center of Kabul. While the map does not show roads, for surely none as such existed at the time, it does show the network of towns, waystations and caravanserai built to support the bustling trade system.
The apocryphal Lake of Chiamay appears just north of the Bay of Bengal as the source of four important Southeast Asian river systems including the Irrawaddy, the Dharla, the Chao Phraya, and the Brahmaputra. The curious Lake of Chiamay (also called Chiam-may or Chian-may), roughly located in the area of Assam but sometimes as far north as Tibet and China, began to appear in maps of this region as early as the 16th century and persisted well into the mid 18th century. Its origins are unknown but may originate in a lost 16th century geography prepared by the Portuguese scholar Jao de Barros. It was speculated to be the source of five important Southeast Asian River systems and was mentioned in the journals of Sven Hedin. There are even records that the King of Siam led an invasionary force to take control of the lake in the 16th century. Nonetheless, the theory of Lake Chiamay was ultimately disproved and it disappeared from maps entirely by the 1760s.
There are two states of this map, the present example being the first state, first issued in 1638 by Henricus Hondius, and the second state a few years later in 1641 by Jan Jannson. With the exception of the signature imprint, the plates are identical. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
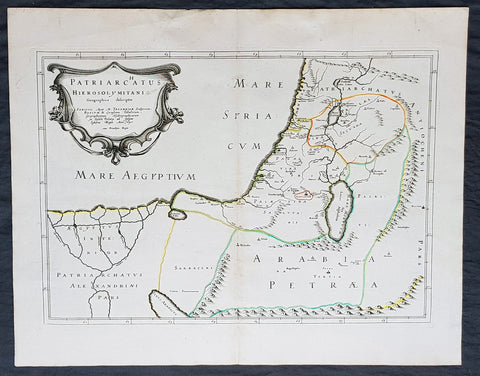
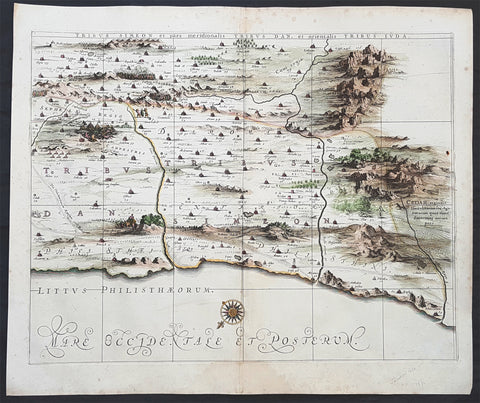
1640 Nicolas Sanson Antique Map of The Holy Land, Egypt, Saudi - Knights Templar
- Title : Patriachatus Hierosolymitani....Aput M Tavernier....1640
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 460mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1640
- Ref #: 40692
Description:
This fine original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the Holy Land, Egypt, part of Saudi Arabia and the connection to the Nights Templar (Latin: Militaris Templi Hierosolymitani) in the middle ages was engraved by Michael Tavernier in 1640 - dated in the cartouche - and was published by Nicolas Sanson in the 1653 edition of Geographia sacra, sive notitia antiqua dioecesium omnium partriarchalium, metropoliticarum, et episcopalium veteris ecclesiae. notae et animadversions Lucae Holstenii.
This is a wonderful map with original outline hand colour on strong sturdy clean paper and a heavy impression.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Templars became a favoured charity throughout Christendom and grew rapidly in membership and power. They were prominent in Christian finance. Templar knights, in their distinctive white mantles with a red cross, were among the most skilled fighting units of the Crusades. Non-combatant members of the order, who formed as much as 90% of the orders members, managed a large economic infrastructure throughout Christendom, developing innovative financial techniques that were an early form of banking, building its own network of nearly 1,000 commanderies and fortifications across Europe and the Holy Land, and arguably forming the worlds first multinational corporation.
The Templars were closely tied to the Crusades; when the Holy Land was lost, support for the order faded. Rumours about the Templars secret initiation ceremony created distrust, and King Philip IV of France – deeply in debt to the order – took advantage of this distrust to destroy them and erase his debt. In 1307, he had many of the orders members in France arrested, tortured into giving false confessions, and burned at the stake. Pope Clement V disbanded the order in 1312 under pressure from King Philip. The abrupt reduction in power of a significant group in European society gave rise to speculation, legend, and legacy through the ages.
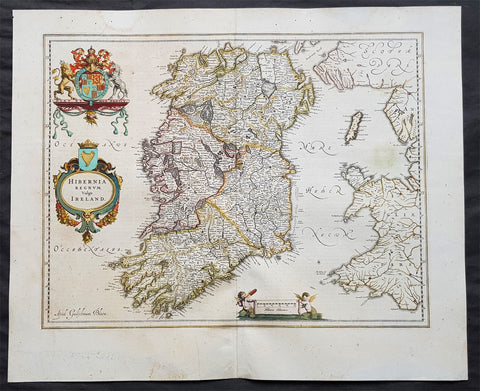
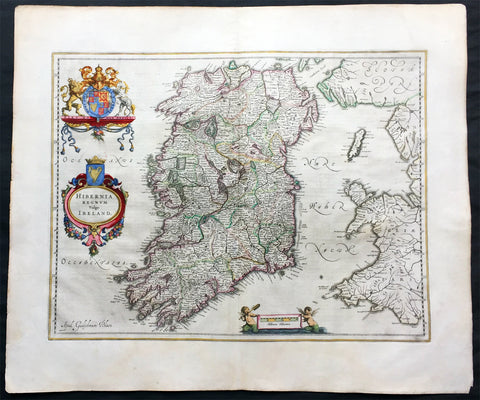
1642 Blaeu Large Old, Antique Map of Ireland - Hibernia Regnum
- Title: Hibernia Regnum Vulgo Ireland
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
- Ref # : 61159
- Date: 1642
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This superbly hand coloured original antique map of Ireland - Hibernia - was published in the 1642 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Novus.
Background:
This is Willem Blaeu's highly decorative general map of Ireland and is coloured to show in outline the ancient provinces of Connaught, Leinster, Munster and Ulster each of which together with the map of Carlow, was given a separate map in a section at the end of the atlas volume devoted to Scotland.
The map, which Blaeu first issued in 1635 (twenty years prior to the publication of the Scotland and Ireland volume) was based on that published by John Speed in 1611 in his Theatre of the Empire of Great Briatine. In its turn Speed's map was copied Hondius and Blaeu's great rival Jan Jansson. It was the latter version that Willem Blaeu used. His beautifully balanced design is complemented by the Royal arms and the relatively simple title cartouche at the left hand side. (Ref: Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19in (600mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Bottom section of centerfold re-joined, no loss
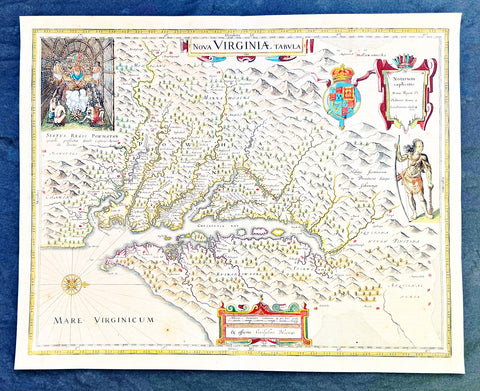
1642 Blaeu, Hondius & John Smith Antique Map of Virginia, America - Pocahontas
- Title : Nova Virginiae Tabula
- Date : 1642
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35667
- Size: 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Description:
This superb original antique hand coloured map of Chesapeake Bay, Virginia was published in the 1642 Dutch edition of Mercators Atlas.
This map by Blaeu comes directly from John Smiths map of Virginia. Blaeu bought this plate from Joducus Hondius who had engraved it directly from John Smith map. It is the only map on the market that is unchanged from Smiths map.
Although this map bears the name of Willem Blaeu, it comes from the plate stock of the Amsterdam publisher Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1629. Blaeu then issued the map in his Atlantis Appendix and in most editions of the firms atlases thereafter.
The map is a version of the map by the Englishman Captain John Smith in 1612. His map was the first to depict with reasonable accuracy Chesapeake Bay with its tributaries and became the accepted prototype map for most subsequent maps of the colony published either in Britain or Europe during the remainder of the 17th century.
Captain Smiths maps acted as a promotional piece for the vast area of North America called Virginia and it exerted a great influence of the history of English colonisation in America.
John Smith (1579-1631) was the foremost English settler in Virginia. His many adventures included being captured several times, defeating an Indian chief in hand to hand combat as well as the celebrated incident in which Pocahontas saved him from Powhatan who is himself the subject of the portrait at the upper left hand corner of Blaeus map.
While the geographical detail of the map shows information accurate at the time of Smiths travels, earlier descriptions of Virginia are recalled. When Smiths map appeared in 1612, the engraver turned to an engraving by the German Theodor de Bry based on the drawings made by John White in the 1580s for the portrait of Powhatan, and the figure of an Indian in war paint at the right to represent the Susquehanna chief. All of these elements were combined by the Amsterdam engraver Dirk Grijp for the Dutch version of Smiths map as issued by the Hondius firm in 1618. Thus, when Blaeu purchased the plate it was already a decade old and it was issued unchanged except for his imprint and a few very small retouches until the 1660s. The Blaeu derivative was the most popular version of Captain Smith Map published during the seventeenth century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning, light crease along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
This is one of the most important seventeenth century maps of the Chesapeake Bay region. The early settlement of Jamestown Iamestowne is noted along with a number of other place names, both in English and Native American. The map was derived from Capt. John Smith\'s map of 1612 and was the first to depict the bay and its tributaries with any accuracy.
Capt John Smith's fine survey work, as well as reports from indigenous American Indian tribes, and fanciful wishful thinking, combine to make this one of the most interesting maps of America to emerge in the 17th century. Philip D. Burden, the author of The Mapping of America, considers this map, Nova Virginiae Tabula, to be \'one of the most important maps of America ever produced and certainly one of the greatest influence.\' Oriented to the west, this map covers from Cape Henry to the Susquehanna River and inland as far as the Appellation Mountains. The Chesapeake Bay is shown in full as are many of its river estuaries, though topographically this map places a number of mountain ranges where there are in fact none.
To fully understand this map one must first realize that most Europeans believed the Pacific, or at least some great bay that led to the Pacific, lay just a few days travel inland. In the minds of most Europeans of the period, the trade potential for the Virginia colony was entirely dependent upon it being a practical access point to the riches of Asia. Thus the significance of large and mysterious body of water appearing in the land of the Massawomecks, in the upper right quadrant, becomes apparent. Of course, much of this land was entirely unexplored by the European settlers in Jamestown, shown here on the Powhatan River (James River), who relied heavily upon American Indian reports for much of their cartographic knowledge of the Virginia hinterlands. The Massawomecks themselves were a rival of the Powhatan and made their home near the headwaters of the Potomac. These, like many other indigenous groups of the region made only a brief and frequently violent appearance during the 17th century before entirely disappearing, mostly from disease and war, in the early 18th century.
In the upper left quadrant there is an image of the American Indian chief of the Powhatan sitting enthroned before a great fire in his long house. One of the more popular legends regarding John Smith was his capture and trial before the chief of the Powahatan. Smith was convinced that his liberation had something to do with the youthful daughter of Chief Powahatan, Pocahontas, taking a liking to him. Although this grew into a fictitious legend of its own, the truth is more likely that Powhatan saw Smith and his Englishmen as potential allies against the rival American Indian groups, such as the Massawomecks, that were pressing hard against his borders.
There are a number of different editions of this map and its publication by various map houses in various states made it the first widely distributed map of the Virginia colony and of John Smith\'s important map. There was, however, a scandal relating to its publication. The map was originally drawn and engraved in 1618 by Jodocus Hondius based upon the first edition of John Smith\'s 1612 map. When Jodocus died in 1629, he and his brother, Henricus Hondius, while collaborating on the Hondius Atlas Major, had established and maintained separate business for some 10 years. Jodocus\' death enabled the competing cartographer, Willem Blaeu to acquire a large number of Jodocus\' map plates, which he promptly published in 1630 as the Atlantis Appendix. Henricus, in the meantime, had been counting on Jodocus\' new plates to enhance his own, by then outdated, Hondius Atlas Major. A surviving contract dated March 2, 1630 reveals that Henricus Hondius and his partner Joannes Janssonius hired engravers to produce a number of new map plates copying the work of Jodocus – now in the hands of the Blaeu firm. This map was among the most important of that group and accounts for variants of this map being issued by competing Blaeu and Hondius firms.
The History of Virginia begins with documentation by the first Spanish explorers to reach the area in the 1500s, when it was occupied chiefly by Algonquian, Iroquoian, and Siouan peoples. After a failed English attempt to settle Virginia in the 1580s by Walter Raleigh permanent English settlement began in Virginia with Jamestown, Virginia, in 1607. The Virginia Company colony was looking for gold but failed and the colonists could barely feed themselves. The famine during the harsh winter of 1609 forced the colonists to eat leather from their clothes and boots and resort to cannibalism.[1] The colony nearly failed until tobacco emerged as a profitable export. It was grown on plantations, using primarily indentured servants for the intensive hand labor involved. After 1662, the colony turned black slavery into a hereditary racial caste. By 1750, the primary cultivators of the cash crop were West African slaves. While the plantations thrived because of the high demand for tobacco, most white settlers raised their families on subsistence farms. Warfare with the Virginia Indian nations had been a factor in the 17th century; after 1700 there was continued conflict with natives east of the Alleghenies, especially in the French and Indian War (1754-1763), when the tribes were allied with the French. The westernmost counties including Wise and Washington only became safe with the death of Bob Benge in 1794.
The Virginia Colony became the wealthiest and most populated British colony in North America, with an elected General Assembly. The colony was dominated by rich planters who were also in control of the established Anglican Church. Baptistand Methodist preachers brought the Great Awakening, welcoming black members and leading to many evangelical and racially integrated churches. Virginia planters had a major role in gaining independence and in the development of democratic-republican ideals of the United States. They were important in the Declaration of Independence, writing the Constitutional Convention (and preserving protection for the slave trade), and establishing the Bill of Rights. The state of Kentucky separated from Virginia in 1792. Four of the first five presidents were Virginians: George Washington, the "Father of his country"; and after 1800, "The Virginia Dynasty" of presidents for 24 years: Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and James Monroe.
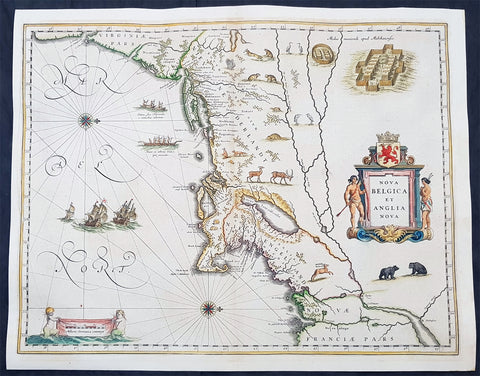
1642 Joan Blaeu Antique Map New England & NE America, Virginia New York to Maine
- Title : Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova
- Size: 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1642
- Ref #: 93080
Description:
This beautiful, original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of New England & NE America, centering on New York and Manhattan stretching from Virginia to Maine, by Joan Blaeu was published in the 1642 edition of Atlas Novus
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning, printers crease in left margin into border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas published at the time. It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map is the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Niev Nederland.
It has been noted that the time difference between 1614, the date of the manuscript, and Blaeus map whose first appearance is in 1635, appears long for such an important advance. It would seem highly feasible that Blaeu, who published many separately issued maps, would have wanted to produce one like this sooner. However, evidence points to the fact that it could not have been made before 1630. The Stokes Collection in New York possesses an example of the map on thicker paper without text on the reverse which could well be a proof issue of some kind.
There are features on Blaeus map that differ from the Block chart. Some of these could be accounted for by the fact that the surviving figurative map is not the original, and that the copyist omitted some place names that are referred to in the text of de Laets work. Block drew on Champlains map of 1612 for the depiction of the lake named after him, but it is here called Lacus Irocoisiensis. … The lack of interrelation between the Dutch or English colonies and the French, led for some time to the eastward displacement of this lake when its true position would be north of the Hudson River.
Some nomenclature has its origins in Blaeus second Paskaert of c.1630, and others, such as Manatthans, in de Laet. The colony of Nieu Pleimonth is identified. This and other English names along that part of the coast are largely derived from Smith\\\'s New England, 1616. Cape Cod is here improved over the Block manuscript by being reconnected to the mainland, the narrow strait having been removed. The coastline between here and Narragansett Bay, which can be clearly recognized, is not so accurate. Adriaen Blocx Eylandt leads us to the Versche Rivier, or Connecticut River, which Block ascended as far as was possible. t Lange Eyland is named; however, it is incorrectly too far east, being applied to what is possibly Fishers Island. De Groote bay marks Long Island Sound. The Hudson River is still not named as such, but is littered with Dutch settlements, and the failed Fort Nassau is here depicted renamed as Fort Orange. He does, however, improve on the direction of its flow. Blaeu separates the sources of the Hudson and Delaware Rivers which had been causing some confusion. Nieu Amsterdam is correctly marked as a fort at the tip of an island separated on the east side by Hellegat, or the East River. The coastline south of Sandy Hook also shows signs of improvement.
The whole map is adorned by deer, foxes, bears, egrets, rabbits, cranes and turkeys. Beavers, polecats and otters appear on a printed map for the first time. The Mohawk Indian village top right is derived from the de Bry-White engravings.
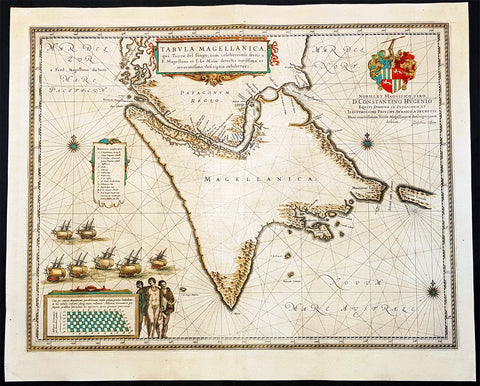
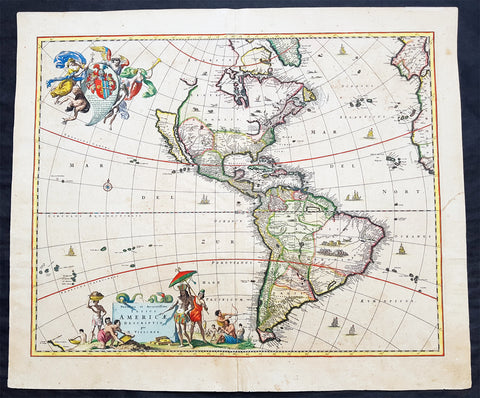
1642 Joan Blaeu Large Antique Map of Tierra Del Fuego & the Magellan Straits, South America
- Title : Tabula Magellanica qua Tierrae del Fuego
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1642
- Ref #: 93352
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the Tierra Del Fuego & the Magellan Straits at the very bottom of South America, was published in the 1642 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Nouvs.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Ferdinand Magellan became the first European to navigate the strait in 1520, during his global circumnavigation voyage. Because Magellan\'s ships entered it on November 1, All Saints\' Day, it was originally named Estrecho de Todos los Santos (Strait of All Saints). Later the Spanish king changed the name to Estrecho de Magallanes in honor of Magellan. Since its discovery the Spanish Empire and the Kingdom of Chile saw it as its southern boundary. The first Spanish colonization attempt was led by Pedro Sarmiento de Gamboa who founded Nombre de Jesús and Rey Don Felipe on its northern shores. The cities suffered severe food shortages, and years afterwards in 1587 the English navigator Sir Thomas Cavendish landed at the site of Rey Don Felipe and found only ruins of the settlement. He renamed the place Port Famine. Other early explorers included Francis Drake among others.
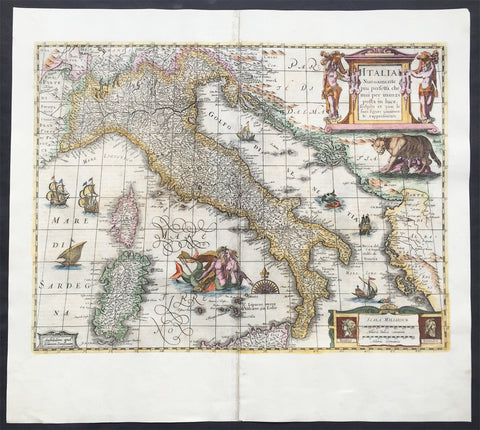
1644 Jan Jansson & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Italy, Sardinia, Corsica
- Title : Italia Nuouamente piu perfetta chemai per inanzi posta
- Ref #: 61008
- Size: 21 1/2in x 19in (545mm x 490mm)
- Date : 1644
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Italy, Sicily, Sardinia & the Adriatic Coast by Jan Jansson was published in the 1644 German edition of Mercator's atlas by Jansson and Hondius.
This map is richly embellished with cartouches, sailing vessels, sea monsters and a wonderful rendering of Neptune and his mate. The image of the two mer-people embracing with bare chests is a hold over from the controversial images present in the first edition of Ortelius' modern map of Italy. Includes portraits of Romulus and Remus in the lower right corner. In subsequent years, Jansson would replace Hondius's name with his own in the bottom left corner.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 19in (545mm x 490mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/2in (500mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Centrefold re-joined
Plate area: - Centrefold re-joined
Verso: - Centrefold re-joined
Background: Since classical times the countries bordering the enclosed waters of the Mediterranean had been well versed in the use of maps and sea charts and in Italy, more than anywhere else, the traditional knowledge was kept alive during the many hundreds of years following the collapse of the Roman Empire. By the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries the seamen of Venice, Genoa and Amalfi traded to far countries, from the Black Sea ports and the coasts of Palestine and Egypt in the East to Flanders and the southern coasts of England and Ireland in the West, their voyages guided by portulan charts and the use of the newly invented compass. For a time Italian supremacy in cartography passed to Aragon and the Catalan map makers based on Majorca, but by the year 1400 the power and wealth of the city states of Venice, Genoa, Florence and Milan surpassed any in Europe. Florence, especially, under the rule of the Medici family, became not only a great trading and financial centre but also the focal point of the rediscovery of the arts and learning of the ancient world. In this milieu a number of manuscript world maps were produced, of which one by Fra Mauro (c. 1459) is the most notable, but the event of the greatest importance in the history of cartography occurred in the year 1400 when a Florentine, Palla Strozzi, brought from Constantinople a Greek manuscript copy of Claudius Ptolemy'sGeographia, which, 1,250 years after its compilation, came as a revelation to scholars in Western Europe. In the following fifty years or so manuscript copies, translated into Latin and other languages, became available in limited numbers but the invention of movable-type printing transformed the scene: the first copy without maps being printed in 1475 followed by many with copper-engraved maps, at Bologna in 1477, Rome 1478, 1490, 1507 and 1508, and Florence 1482.
About the year 1485 the first book of sea charts, compiled by Bartolommeo dalli Sonetti, was printed in Venice and in the first part of the sixteenth century a number of world maps were published, among them one compiled in 1506 by Giovanni Contarini, engraved by Francesco Rosselli, which was the first printed map to show the discoveries in the New World. In the following years there were many attractive and unusual maps of Islands (Isolano) by Bordone, Camocio and Porcacchi, but more important was the work of Giacomo (Jacopo) Gastaldi, a native of Piedmont who started life as an engineer in the service of the Venetian Republic before turning to cartography as a profession. His maps, produced in great variety and quantity, were beautifully drawn copperplate engravings and his style and techniques were widely copied by his contemporaries. From about 1550 to 1580 many of Gastaldi's maps appeared in the collections of maps known as Lafreri 'atlases', a term applied to groups of maps by different cartographers brought together in one binding. As the contents of such collections varied considerably they were no doubt assembled at the special request of wealthy patrons and are now very rare indeed.
About this time, for a variety of historical and commercial reasons, Italy's position as the leading trading and financial nation rapidly declined and with it her superiority in cartography was lost to the vigorous new states in the Low Countries. That is not to say, of course, that Italian skills as map makers were lost entirely for it was not until 1620 that the first printed maps of Italy by an Italian, Giovanni Magini, appeared, and much later in the century there were fine maps by Giacomo de Rossi and Vincenzo Coronelli, the latter leading a revival of interest in cartography at the end of the century. Coronelli was also famous for the construction of magnificent large-size globes and for the foundation in Venice in 1680 of the first geographical society.
In the eighteenth century the best-known names are Antonio Zatta, Rizzi-Zannoni and Giovanni Cassini.
We ought to mention the work of Baptista Boazio who drew a series of maps in A Summarie and True Discourse of Sir Francis Drake's West Indian Voyage, published in 1588-89, and who is especially noted for a very fine map of Ireland printed in 1599 which was incorporated in the later editions of the Ortelius atlases. It is perhaps appropriate also to refer to two English map makers who spent many years in exile in Italy: the first, George Lily, famous for the splendid map of the British Isles issued in Rome in 1546, and the second, Robert Dudley, who exactly one hundred years later was responsible for the finest sea atlas of the day, Dell' Arcano del Mare,published in Florence. Both of these are described in greater detail elsewhere in this handbook. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
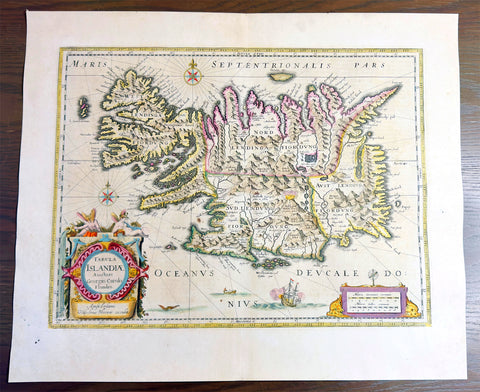
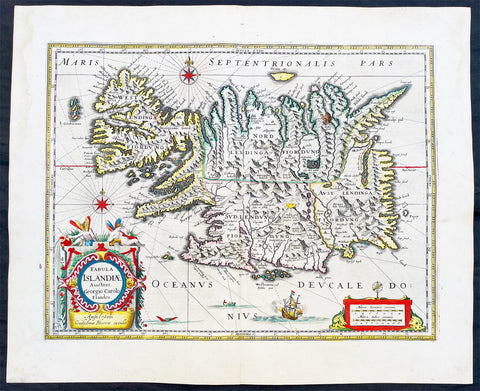
1644 Willem Blaeu Antique Map of Iceland - Beautiful Original Hand Colouring
Antique Map
- Title :Tabula Islandia Auctore Georgio Carolo Flandro
- Ref #: 35625
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (590mm x 510mm)
- Date: 1644
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map, with beautiful original hand colouring by Willem Blaeu, was engraved by Jodocus Hondius after Joris Carolus, and was published by Guillaume Blaeus in the 1644 Latin edition of Atlas Nouvs.
This is beautiful example of this early map of Iceland with fresh original hand colouring, on uniform aged paper with original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (590mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light scraping to L & R margins
Plate area: - Uniform aged toning
Verso: - Uniform aged toning
Background:
This map of Iceland is perhaps the most familiar of all the outlines of the island ever published. The author is stated to be one Joris Carolus, a Dutch navigator from Enkhuizen, whose map was first engraved and prepared by Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1628, whose plates were bought by Willem Blaeu in 1629. Iceland bears the imprint of Willem Blaeu who issued it in his Appendix of 1630.
The Carolus map was copied by virtually all mapmakers throughout the rest of the 17th century and well into the 18th. Some of the information is derived from a map made famous by the Flemish cartographer Abraham Ortelius, the Islandia of Gudhbrandur Thorlaksson (1541 - 1627) Bishop of Holar, who had studied mathematics and astronomy as well as theology, while other information, such as place names, is derived from Gerard Mercator's map of 1595.
Willem Blaeu reprinted the map without change in his subsequent atlas editions, as did Joan after him, including the great atlas of 1662. In the southern southern part is shown the lively impression of Hekla in full eruption, described as mons perpetuo ardens while immediately to the west, the Bishopric of Skalholt is marked. To the south a note by Eiapialla hokel (Eyjafjallajokull) states that here may be found falcones albi or white falcons, presumably referring to the gyr falcon.
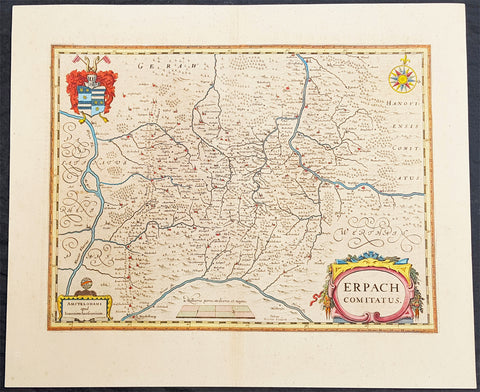
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map Erbach Hesse & Baden-Württemberg Heidelberg Germany
- Title : Erpach Comitatus
- Ref #: 50182
- Size: 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Erbach im Odenwald area in the Baden-Württemberg & Hesse regions of southern Germany, framed by the Neckar River in the south, Rhine River to the west and the Main river to the east (major towns and cities of Heidelberg, Gensheim, Worms, Miltenberg and Oldenburg) by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Erbach is a town and the district seat of the Odenwaldkreis (district) in Hesse, Germany.
Baden-Württemberg is a state in southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the border with France.
Hesseis a federal state (Land) of the Federal Republic of Germany
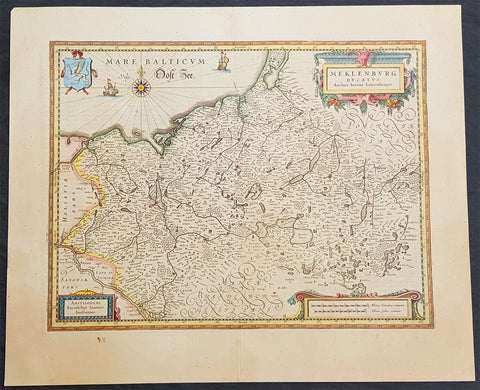
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map of Mecklenburg NE Germany Rostock, Wizmar, Parchim
- Title : Meklenburg Ducatus
- Ref #: 50185
- Size: 11 1/2in x 8in (290mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Mecklenburg, north eastern Germany by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mecklenburg is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow.
The name Mecklenburg derives from a castle named Mikilenburg (Old Saxon: big castle, hence its translation into New Latin and Greek: Megalopolis), located between the cities of Schwerin and Wismar. In Slavic language it was known as Veligrad, which also means big castle. It was the ancestral seat of the House of Mecklenburg; for a time the area was divided into Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz among the same dynasty.
Linguistically Mecklenburgers retain and use many features of Low German vocabulary or phonology.
Mecklenburg is the site of many prehistoric dolmen tombs. Its earliest organised inhabitants may have had Celtic origins. By no later than 100 BC the area had been populated by pre-Christian Germanic peoples.
The traditional symbol of Mecklenburg, the grinning steers head (Low German: Ossenkopp, lit.: oxen\'s head, with osse being a synonym for steer and bull in Middle Low German), with an attached hide, and a crown above, may have originated from this period. It represents what early peoples would have worn, i.e. a steers\'s head as a helmet, with the hide hanging down the back to protect the neck from the sun, and overall as a way to instill fear in the enemy.
From the 7th through the 12th centuries, the area of Mecklenburg was taken over by Western Slavic peoples, most notably the Obotrites and other tribes that Frankish sources referred to as Wends. The 11th century founder of the Mecklenburgian dynasty of Dukes and later Grand Dukes, which lasted until 1918, was Nyklot of the Obotrites.
In the late 12th century, Henry the Lion, Duke of the Saxons, conquered the region, subjugated its local lords, and Christianized its people, in a precursor to the Northern Crusades. From 12th to 14th century, large numbers of Germans and Flemings settled the area (Ostsiedlung), importing German law and improved agricultural techniques. The Wends who survived all warfare and devastation of the centuries before, including invasions of and expeditions into Saxony, Denmark and Liutizic areas as well as internal conflicts, were assimilated in the centuries thereafter. However, elements of certain names and words used in Mecklenburg speak to the lingering Slavic influence. An example would be the city of Schwerin, which was originally called Zuarin in Slavic. Another example is the town of Bresegard, the \'gard\' portion of the town name deriving from the Slavic word \'grad\', meaning city or town.
Since the 12th century, the territory remained stable and relatively independent of its neighbours; one of the few German territories for which this is true. During the reformation the Duke in Schwerin would convert to Protestantism and so would follow the Duchy of Mecklenburg.
Like many German territories, Mecklenburg was sometimes partitioned and re-partitioned among different members of the ruling dynasty. In 1621 it was divided into the two duchies of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Güstrow. With the extinction of the Güstrow line in 1701, the Güstrow lands were redivided, part going to the Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, and part going to the new line of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
In 1815, the two Mecklenburgian duchies were raised to Grand Duchies, the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, and subsequently existed separately as such in Germany under enlightened but absolute rule (constitutions being granted on the eve of World War I) until the revolution of 1918. Life in Mecklenburg could be quite harsh. Practices such as having to ask for permission from the Grand Duke to get married, or having to apply for permission to emigrate, would linger late into the history of Mecklenburg (i.e. 1918), long after such practices had been abandoned in other German areas. Even as late as the later half of the 19th century the Grand Duke personally owned half of the countryside. The last Duke abdicated in 1918, as monarchies fell throughout Europe. The Duke\'s ruling house reigned in Mecklenburg uninterrupted (except for two years) from its incorporation into the Holy Roman Empire until 1918. From 1918 to 1933, the duchies were free states in the Weimar Republic.
Traditionally Mecklenburg has always been one of the poorer German areas, and later the poorer of the provinces, or Länder, within a unified Germany. The reasons for this may be varied, but one factor stands out: agriculturally the land is poor and can not produce at the same level as other parts of Germany. The two Mecklenburgs made attempts at being independent states after 1918, but eventually this failed as their dependence on the rest of the German lands became apparent.
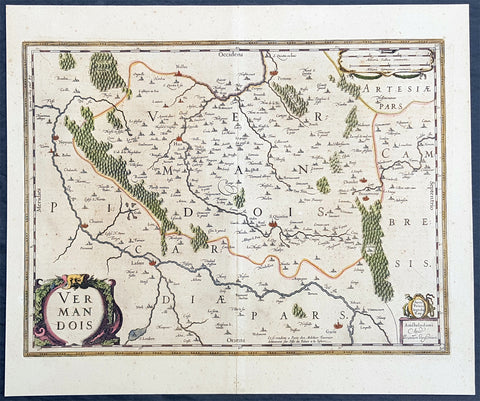
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Map the County of Vermandois, Picardy, Northern France
- Title : Vermandois
- Ref #: 50236
- Size: 21 1/2in x 18in (545mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the ancient county of Vermandois now located in the Picardy region of northern France, centering on the city of St Quentin by Jan Jansson was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (480mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Vermandois was a French county that appeared in the Merovingian period. Its name derives from that of an ancient tribe, the Viromandui. In the 10th century, it was organised around two castellan domains: St Quentin (Aisne) and Péronne (Somme). In today\'s times, the Vermandois county would fall in the Picardy region of northern France.
Pepin I of Vermandois, the earliest of its hereditary counts, was descended in direct male line from the emperor Charlemagne. More famous was his grandson Herbert II (902–943), who considerably increased the territorial power of the house of Vermandois, and kept the lawful king of France, the unlucky Charles the Simple, prisoner for six years. Herbert II was son of Herbert I, lord of Péronne and St Quentin, who was killed in 902 by an assassin in the pay of Baldwin II, Count of Flanders. His successors, Albert I, Herbert III, Albert II, Otto and Herbert IV, were not as historically significant.
In 1077, the last count of the first house of Vermandois, Herbert IV, received the county of Valois through his wife. His son Eudes (II) the Insane was disinherited by the council of the Barons of France. He was lord of Saint-Simon through his wife, and the county was given to his sister Adela, whose first husband was Hugh the Great, the brother of King Philip I of France. Hugh was one of the leaders of the First Crusade, and died in 1102 at Tarsus in Cilicia. The eldest son of Hugh and Adela was count Raoul I (c. 1120–1152), who married Petronilla of Aquitaine, sister of the queen, Eleanor, and had by her three children: Raoul (Rudolph) II, the Leper (count from 1152–1167); Isabelle, who possessed from 1167 to 1183 the counties of Vermandois, Valois and Amiens conjointly with her husband, Philip, Count of Flanders; and Eleanor. By the terms of a treaty concluded in 1186 with the king, Philip Augustus, the count of Flanders kept the county of Vermandois until his death, in 1191. At this date, a new arrangement gave Eleanor (d. 1213) a life interest in the eastern part of Vermandois, together with the title of countess of St Quentin, and the king entered immediately into possession of Péronne and its dependencies
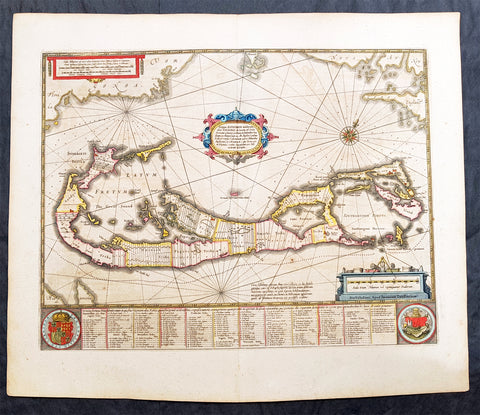
1646 Jan Jansson Large Antique Map The Island of Bermuda
- Title : Mappa Aestivarum Insularum, alias Barmudas Dictarum ... Accurate Descripta
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93340
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Island of Bermuda by Jan Jansson was published in the 1646 Latin of Mercators Atlas by Henricus Hondius & Janson. One of the best examples of this map we have had in some time with original hand colouring, original margins heavy paper and a heavy impression, beautiful map.
A much sought after map of Bermuda, with decorative cartouche, compass rose with the Island divided into lots and tribes, listed at the base of the map.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 3/4in (520mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Like all 17th century maps of Bermuda this map is based ultimately on the survey made by John Norwood of the Bermuda Company in 1618 in the form as published by the English map-maker John Speed in 1627. Although discovered in 1515 by Spaniard Juan de Bermudez, after whom the island is supposedly named, it was the shipwreck of a party of Virginia colonists in 1610 led by Sir George Somers that gave Bermuda its first known inhabitants. The Latin title reflects this fact, for Aestivarum Insularum means summers (or Somers) Islands. The experience of Somers and his men inspired William Shakespeare, who dispatched Ariel to "fetch dew from the still-vext Bermoothes" and populated the islands with the cast of The Tempest.
The place names and the list of Proprietors given below the map itself all recall the original members of the Bermuda Company, the latter being listed as eight tribes (or parishes). In 1610, the Virginia Company, in a True Declaration of the Estate of the Colonie of Virginia, said of Bermuda: These Islands of Bermudos, have evere beene accounted as an inchaunted pile of rocks, and a desert inhabitation for Divels; but all the Faities of the rockes were but flocks of Birds, and all the Divels that haunted the woods, were but heards of Swine. In the upper left-hand and right-hand corners of the map appear the adjacent coasts of the North American colonies of Virginia and New England with, just below the cartouche a tiny outline of Bermuda itself, intended to show its correct proportion and position against the mainland.(Ref Tooley M&B)
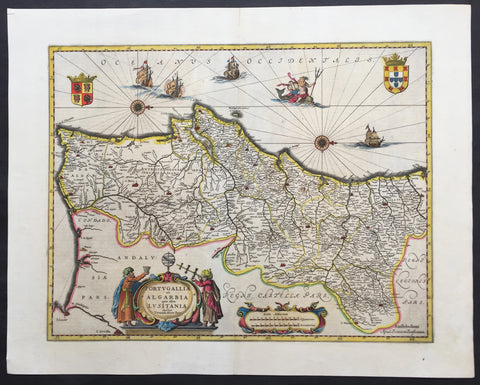
1646 Jan Jansson Large, Old Antique Map of Portugal - Portugallia et Algarbia
- Title : Portugallia et Algarbia quae olim Lusitania
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 81055
- Size: 24in x 19in (610mm x 480mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Portugal was published by Jan Jansson in the 1646 Latin edition of Atlas Novus. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 19in (610mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1646 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Ireland - Hibernia Regnum
- Title: Hibernia Regnum Vulgo Ireland
- Date: 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 50673
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Description:
This superbly hand coloured original antique map of Ireland - Hibernia - was published in the 1646 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Novus.
One of the best I have seen to date, the original colouring is superb and the paper is heavy and stable with original margins.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Very bottom of margin re-joined, not affecting image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This is Willem Blaeu's highly decorative general map of Ireland and is coloured to show in outline the ancient provinces of Connaught, Leinster, Munster and Ulster each of which together with the map of Carlow, was given a separate map in a section at the end of the atlas volume devoted to Scotland.
The map, which Blaeu first issued in 1635 (twenty years prior to the publication of the Scotland and Ireland volume) was based on that published by John Speed in 1611 in his Theatre of the Empire of Great Briatine. In its turn Speed's map was copied Hondius and Blaeu's great rival Jan Jansson. It was the latter version that Willem Blaeu used. His beautifully balanced design is complemented by the Royal arms and the relatively simple title cartouche at the left hand side. (Ref: Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
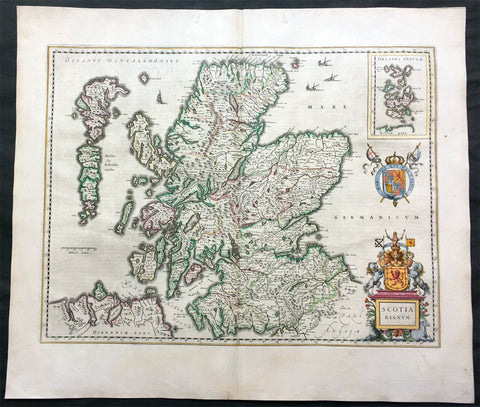
1646 Joan Blaeu Large Antique Map of Scotland - Scotia Regnum
Antique Map
- Title : Scotia Regnum
- Ref #: 61001
- Size: 22 3/4in x 19 3/4in (580mm x 500mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Scotland was published in the 1646 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Novus.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 3/4in x 19 3/4in (580mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: When the Blaeu's published Volume V - GB & Ireland - of Atlas Novus, Scotland became one of the best-mapped countries in the world. Volume V contained forty-eight plates showing forty-nine separate maps of Scotland (plus a map of Ptolemy British Isles and six maps of Ireland). The first two plates from the atlas show the entire country ancient and modern, whilst the remaining forty-six plates cover most Scotland in forty-seven regional maps. In total the regional maps locate some 20,000 different place names. A clue as to the reason for this extraordinary explosion of geographical information is to be found on thirty-six of the regional maps, which all carry engraved credits to Timothy Pont (1524-1606)
Pont was responsible for surveying the greater part of Scotland between 1583-1600, the resulting Pont Manuscript maps were never published but were put to good use some fifty to seventy years later by Robert Gordon and Joan Blaeu. (Ref: Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
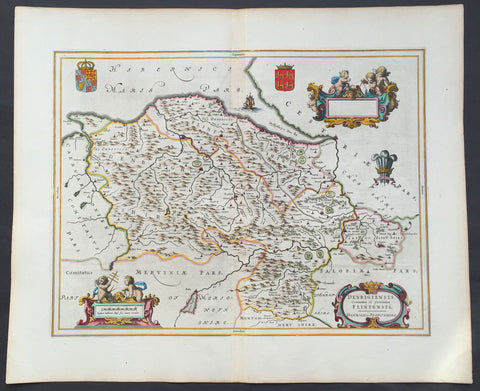
1647 Blaeu Antique Map of The Welsh Counties of Denbigh & Flintshire
- Title : Denbigiensis comitatus et Comitatus Flintensis - Denbigh et Flintshire
- Ref #: 31034
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1647
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Welsh counties of Denbigh & Flintshire was published in the 1647 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus.
Blaeu's reference for the topographical data for this map derive from John Speeds maps of Great Britain from the 1611 Empire of Great Britaine - the beautiful decoration, though, is distinctly Blaeus.
Background: Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map.
The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1647 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Iceland - Beautiful Original Hand Colouring
- Title :Tabula Islandia Auctore Georgio Carolo Flandro
- Ref #: 17042
- Size: 23 1/2in x 19in (590mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1647
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This is possibly one the best original hand coloured maps of Iceland by Blaeu, we have had the pleasure to offer.
This map, by Willem Blaeu, was engraved by Jodocus Hondius after Joris Carolus, and was published by Willem Blaeus son, Joan, in the 1647 German edition of Atlas Nouvs
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19in (590mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in left margin
Plate area: - Small stain top right of map
Verso: - None
Background:
This map of Iceland is perhaps the most familiar of all the outlines of the island ever published. The author is stated to be one Joris Carolus, a Dutch navigator from Enkhuizen, whose map was first engraved and prepared by Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1628, whose plates were bought by Willem Blaeu in 1629. Iceland bears the imprint of Willem Blaeu who issued it in his Appendix of 1630.
The Carolus map was copied by virtually all mapmakers throughout the rest of the 17th century and well into the 18th. Some of the information is derived from a map made famous by the Flemish cartographer Abraham Ortelius, the Islandia of Gudhbrandur Thorlaksson (1541 - 1627) Bishop of Holar, who had studied mathematics and astronomy as well as theology, while other information, such as place names, is derived from Gerard Mercator's map of 1595.
Willem Blaeu reprinted the map without change in his subsequent atlas editions, as did Joan after him, including the great atlas of 1662. In the southern southern part is shown the lively impression of Hekla in full eruption, described as mons perpetuo ardens while immediately to the west, the Bishopric of Skalholt is marked. To the south a note by Eiapialla hokel (Eyjafjallajokull) states that here may be found falcones albi or white falcons, presumably referring to the gyr falcon.
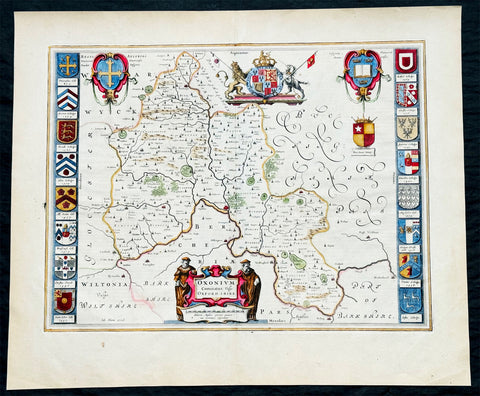
1647 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of the English County of Oxfordshire, Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : Oxonium Comitatus, Vulgo Oxfordshire
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92846
- Size: 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
- Date : 1647
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of the English county of Oxfordshire was published in the 1647 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus.
There is also the added bonus on the verso of the map with an early depiction of Stonehenge engraving to text.
Background:
This along with John Speeds map, is one of the most decorative of Oxfordshire. The basic cartographic information is derived from Speed's map, but presented with Blaeu typical elegance & decoration. These include coats-of-arms of the Oxford colleges along the sides, each expertly coloured, as well crests of nobility, the Royal coat-of-arms, and a title cartouche flanked by two Oxford scholars.
Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map. The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1647 Olivarius Vredius Antique Map of Roman Europe Flanders, Germany, France
- Title : Francorum Primae Sedes...Incisum Bruges a Joe F Jois...Olivario Vredio...1647
- Ref #: 60040
- Size: 16 1/2in x 14in (420mm x 355mm)
- Date : 1647
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine scarce beautifully engraved original antique map of central & western Roman Europe centering on what is today Belgium, the Southern Netherlands, Northern France and Western Germany - was engraved in 1647 - dated - and published by Olivarius Vredius (Olivier de Wree)in the 1652 edition of Historiae Comitum Flandriae
Historiae Comitum Flandriae was an important historical work on the origin and early history of Flanders by the well-known historian Olivarius Vredius - Olivier de Wree - (1596-1652) from Bruges. Vredius belongs to the most prominent representatives of late-Belgian humanism and his historical works are still considered to be of high value. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 14in (420mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 11in (320mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light blue underlining some names, light creasing
Verso: - None
1648 Joan Blaeu Antique Rare Atlas of England & Wales - Complete 58 Maps, Magnificent
Antique Map
- Title : Guil. et Joannis Blaeu. Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive Atlas novus, pars quarta [England and Wales]
- Size: Large Folio - 20 1/2in x 14in (510mm x 355mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1646 (1648)
- Ref #: 3025
Description:
A unique & rare opportunity to acquire an original & complete atlas of England & Wales, Latin edition, by Joan & Guillem. Blaeu, in exceptional original condition. This original antique atlas is dated 1648 on the title page containing 58 maps of England & Wales as listed for the 1646 edition.
In my thirty plus years collecting and dealing with Antiquarian maps and Atlas, I occasionally come across an item that is of exceptional quality and condition. This Atlas is one of them. Even though this Atlas is 376 years old, the contents within are in exceptional condition and as they would have been when first pressed and bound. All 58 maps & descriptive text in the 460 pages are clean, heavy, sturdy with heavy clear ink denoting a early fresh printing with new copper-plates. The external original Dutch Vellum & Gilt boards are clean, stiff and great condition, as is the binding itself. To find an atlas like this, in absolute original condition, is exceptionally rare and this is only one I have ever seen in this fine condition.
Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive Atlas novus, pars quarta [England and Wales], Amsterdam: apud Johannem Blaeu, 1648, Koeman 2:301.
Contents
- Blank front page
- Engraved Title Page 1648.
- Dedication to King Charles.
- Joannes Blaeu Lectori S.P.D dated MDCXLV (1645)
- Lectori, Guilielmus Cambdenus & Poem to Britannia
- 460 pages containing 58 maps and descriptive text.
- Index Page
- Blank end page
Koeman 2:301 (volume 11 pp. 234- 238)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm) Page size
Plate size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm) Page size
Margins: - Min 1in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Joan Blaeus atlas of England (first edition 1645) consists mainly of copies of the maps in John Speeds Theatre of the Empire of Great Briatine (first edition 1611-12) and the text of Camdens Britannia (first edition, 1607). The title page is derived from that of Speeds Theatre. The volume includes 58 maps, most of which are copies of maps of various edition of Speeds Theatre.
The volume was published in five languages Latin, French, Dutch, German and Spanish. The dates of the forward are: 1st September 1645 (Latin) 1st October 1645 (French), 1st March 1646 (German), and 12th November 1647 (Dutch) The Spanish edition does not have a forward. The atlas of England was added as the fourth volume of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum and later as the fifth volume of Blaeus Atlas Major, separate editions also exist.
The numerous variants of each language edition of this atlas seldom to correspond to the changes in the editions of the Theatrum and Atlas Major For this reason the volume is treated as a separate atlas with its own bibliographical number.
If one considers only the main body of the book - that is, the maps with their descriptive texts - then there are only a few edition of this atlas.
1649 Blaeu Antique Map View of Thérouanne, Tarwanna or Tervanna Northern France
- Title : Teroana morinorum metropolis olim, diruta a Carolo V. Anno 1553
- Ref #: Tav
- Size: 21 1/2in x 13in (545mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1649
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map a view of the city of Tarwanna or Tervanna (today the town of Thérouanne, France) the capital of the ancient Belgian tribe of the Morini, was published in the 1649 edition of John Blaeus Toonneel der Steeden (Views of Dutch Cities)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 13in (545mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 7 1/2in (270mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Thérouanne is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France. At the time of the Gauls, Tarwanna or Tervanna was the capital of the Belgian tribe of the Morini. After the Romans conquered Gaul, they too made the city the capital of the Civitas Morinorum district.
In the 7th century, probably around 639, Saint Audomar (Saint Omer) established the bishopric of Terwaan or Terenburg, the diocese of Thérouanne, which during the Middle Ages controlled a large part of the left bank of the river Scheldt. Territorially it was part of the county of Artois which belonged to the county of Flanders.
Thanks to that ecclesiastical control of some of the most prosperous cities north of the Alps, like Arras and Ypres, the bishopric was able to build a cathedral which was at the time the largest in France.
The town was captured by the Emperor Maximilian and Henry VIII from the French in 1513 after the battle of the Spurs. In 1553 Charles V besieged Thérouanne, then a French enclave in the Holy Roman Empire, in revenge for a defeat by the French at the siege of Metz. After he captured the city he ordered it to be razed, the roads to be broken up, and the area to be ploughed and salted Only a small commune which lay outside the city walls, then named Saint-Martin-Outre-Eaux, was left standing, and later (probably around 1800) took over the name Thérouanne. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
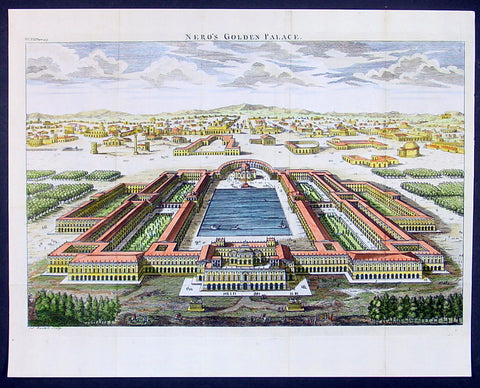
1650 Fuller Antique Print a View of Neros Palace Rome
- Title : Neros Golden Palace
- Ref : 24312
- Size: 17in X 13in (435mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved hand coloured original antique print a view of Neros Golden Palace in Rome was published in 1650 by Thomas Fuller in his unique book of the Holy Land A Pisagh-Sight of Palestine
Fuller, a loyalist during the English Civil War of the mid 17th century, wrote Pisagh-Sightduring a forced exile in Waltham.
The book was an early success and confirmed the genial divines contention the “the booksellers have always done well by me”. His earlier studies in poetry and history and his droll humor contribute to the geographical description in “Pisagh-Sight” while the cartography in the book is derived from that of Adrichom sixty years before.
The book contained 21 wonderfully engraved maps on the Holy Land and displayed unusual charm in their Vignettes and scenes. For all its lively and playful erudition, Pisagh-Sight is one of the great books on the topography of the Holy Land. (Ref: Nebenzahl; Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, orange, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in X 13in (435mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1650 Jan Jansson & Nicolaas Blankaert 3 x Large Antique Maps Europe, Asia & Africa
Antique Map
- Title : Europa Antiqua cum finitimis; Asia antiqua cum finitimis; Africae Antiquae, et quarundam...
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50489, 50490, 50492
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (565mm x 510mm) each
Description:
In 1650 Jan Jansson published three maps of the ancient world, Europe, Asia & Africa, after much considered and detailed work by the Leyden scholar of antiquities Nicolass Blanckaert 1624 - 1703, Latin Nicolaus Blancardus. These three highly detailed maps were only published in limited release and so are incredibly rare, especially as a set.
Nicolaas Blanckaert was a respected expert on the ancient world specialising on the Roman World and Alexander the Great. Three incredibly rare maps in exceptional condition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (565mm x 510mm) each
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15in (510mm x 380mm); 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm); 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Alexander III of Macedon 356 – 323 BC, commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king (basileus) of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon and a member of the Argead dynasty. He was born in Pella in 356 BC and succeeded his father Philip II to the throne at the age of 20. He spent most of his ruling years on an unprecedented military campaign through Asia and northeast Africa, and by the age of thirty, he had created one of the largest empires of the ancient world, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered one of historys most successful military commanders.
During his youth, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle until age 16. After Philips assassination in 336 BC, he succeeded his father to the throne and inherited a strong kingdom and an experienced army. Alexander was awarded the generalship of Greece and used this authority to launch his fathers pan-Hellenic project to lead the Greeks in the conquest of Persia. In 334 BC, he invaded the Achaemenid Empire (Persian Empire) and began a series of campaigns that lasted 10 years. Following the conquest of Anatolia, Alexander broke the power of Persia in a series of decisive battles, most notably the battles of Issus and Gaugamela. He subsequently overthrew Persian King Darius III and conquered the Achaemenid Empire in its entirety. At that point, his empire stretched from the Adriatic Sea to the Beas River.
Alexander endeavoured to reach the ends of the world and the Great Outer Sea and invaded India in 326 BC, winning an important victory over the Pauravas at the Battle of the Hydaspes. He eventually turned back at the demand of his homesick troops, dying in Babylon in 323 BC, the city that he planned to establish as his capital, without executing a series of planned campaigns that would have begun with an invasion of Arabia. In the years following his death, a series of civil wars tore his empire apart, resulting in the establishment of several states ruled by the Diadochi, Alexanders surviving generals and heirs.
Alexanders legacy includes the cultural diffusion and syncretism which his conquests engendered, such as Greco-Buddhism. He founded some twenty cities that bore his name, most notably Alexandria in Egypt. Alexanders settlement of Greek colonists and the resulting spread of Greek culture in the east resulted in a new Hellenistic civilization, aspects of which were still evident in the traditions of the Byzantine Empire in the mid-15th century AD and the presence of Greek speakers in central and far eastern Anatolia until the Greek genocide of the 1920s. Alexander became legendary as a classical hero in the mould of Achilles, and he features prominently in the history and mythic traditions of both Greek and non-Greek cultures. He was undefeated in battle and became the measure against which military leaders compared themselves. Military academies throughout the world still teach his tactics. He is often ranked among the most influential people in history.
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa and West Asia ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus to the military anarchy of the third century, it was a principate with Italy as metropole of the provinces and its city of Rome as sole capital (27 BC – 286 AD). Although fragmented briefly during the military crisis, the empire was forcibly reassembled, then ruled by multiple emperors who shared rule over the Western Roman Empire (based in Milan and later in Ravenna) and over the Eastern Roman Empire (based in Nicomedia and later in Constantinople). Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until 476 AD, when it sent the imperial insignia to Constantinople (Byzantium - Ancient Greek: Βυζάντιον, Byzántion) following the capture of Ravenna by the barbarians of Odoacer and the subsequent deposition of Romulus Augustus. The fall of the Western Roman Empire to Germanic kings, along with the hellenization of the Eastern Roman Empire into the Byzantine Empire, conventionally marks the end of Ancient Rome and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
The predecessor state of the Roman Empire, the Roman Republic (which had replaced Romes monarchy in the 6th century BC) became severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflicts. In the mid-1st century BC Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and proscriptions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesars adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC. The following year Octavian conquered Ptolemaic Egypt, ending the Hellenistic period that had begun with the conquests of Alexander the Great of Macedon in the 4th century BC. Octavians power then became unassailable, and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively making him the first Roman emperor.
The first two centuries of the Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana (Roman Peace). Rome reached its greatest territorial expanse during the reign of Trajan (98–117 AD). A period of increasing trouble and decline began with the reign of Commodus (177-192). In the 3rd century the Empire underwent a crisis that threatened its existence, as the Gallic Empire and Palmyrene Empire broke away from the Roman state, and a series of short-lived emperors, often from the legions, led the empire. The empire was reunified under Aurelian (r. 270–275). In an effort to stabilize the Empire, Diocletian set up two different imperial courts in the Greek East and Latin West in 286. Christians rose to positions of power in the 4th century following the Edict of Milan of 313. Shortly after, the Migration Period, involving large invasions by Germanic peoples and by the Huns of Attila, led to the decline of the Western Roman Empire. With the fall of Ravenna to the Germanic Herulians and the deposition of Romulus Augustulus in 476 AD by Odoacer, the Western Roman Empire finally collapsed – the (Eastern Roman) Emperor Zeno formally abolished it in 480 AD. Nonetheless, some states in the territories of the former Western Roman Empire would later claim to have inherited the supreme power of the emperors of Rome, most notably the Holy Roman Empire. The Eastern Roman Empire, identified by modern historians under the name of the Byzantine Empire, survived for another millennium until the Empires last remains collapsed when Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks of Sultan Mehmed II in 1453.
Due to the Roman Empires vast extent and long endurance, the institutions and culture of Rome had a profound and lasting influence on the development of language, religion, art, architecture, philosophy, law, and forms of government in the territory it governed, and far beyond. The Latin language of the Romans evolved into the Romance languages of the medieval and modern world, while Medieval Greek became the language of the Eastern Roman Empire. The Empires adoption of Christianity led to the formation of medieval Christendom. Greek and Roman art had a profound impact on the Italian Renaissance. Romes architectural tradition served as the basis for Romanesque, Renaissance and Neoclassical architecture, and also had a strong influence on Islamic architecture. The corpus of Roman law has its descendants in many legal systems of the world today, such as the Napoleonic Code, while Romes republican institutions have left an enduring legacy, influencing the Italian city-states republics of the Medieval period, as well as the early United States and other modern democratic republics.
1650 Jan Jansson Antique Map Island of Java, Indonesia - Dutch East India Co
Antique Map
- Title: Insulae Java Cum Parte insularum Borneo Sumatrae
- Date: 1650
- Ref: 60603
- Size: 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large elegant & very impressive hand coloured original antique map, a sea chart of the Indonesian Island of Java including Sumatra, Borneo and Bali was published by Jan Jansson in the 1650 Edition of his "Water World" atlas Atlantis Majoris.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (585mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 3/4in (520mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair & ink notations
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Java & the port of Batavia was at the time of publication of the utmost importance to the Dutch East India Company and its domination of the Spice Trade.
This elegant chart focuses on the islands coast with the lack of detail on the interior correctly reflecting the lack of knowledge (or possible lack of importance) to the Dutch, who's primary concern was the sea and sea charts used in the trade of the ever lucrative Spice Trade.
The Dutch capital in the East Indies is Batavia (Jakarta) located on the NW coast. The beautiful chart is richly embellished with two fine cartouche featuring local Javanese warrior and Chinese merchants flanking the title and Neptune and mermaids surrounding the scale of miles... The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia. It was the second multinational corporation in the world (the British East India Company was founded two years earlier) and the first company to issue stock. It was also arguably the first mega-corporation, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, coin money, and establish colonies.
Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asian trade on 4,785 ships, and netted for their efforts more than 2.5 million tons of Asian trade goods. By contrast, the rest of Europe combined sent only 882,412 people from 1500 to 1795, and the fleet of the English (later British) East India Company, the VOC’s nearest competitor, was a distant second to its total traffic with 2,690 ships and a mere one-fifth the tonnage of goods carried by the VOC. The VOC enjoyed huge profits from its spice monopoly through most of the 17th century.
Having been set up in 1602, to profit from the Malukan spice trade, in 1619 the VOC established a capital in the port city of Batavia (now Jakarta) on the Indonesian Island of Java. Over the next two centuries the Company acquired additional ports as trading bases and safeguarded their interests by taking over surrounding territory. It remained an important trading concern and paid an 18% annual dividend for almost 200 years.
Weighed down by corruption in the late 18th century, the Company went bankrupt and was formally dissolved in 1800, its possessions and the debt being taken over by the government of the Dutch Batavian Republic. The VOC's territories became the Dutch East Indies and were expanded over the course of the 19th century to include the whole of the Indonesian archipelago, and in the 20th century would form Indonesia. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1650 Jan Jansson Large Rare Antique Map of India and The Bay of Bengal
Antique Map
- Title : Sinus Gangeticus Vulgo Golfo De Bengala
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 60604
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Description:
This exceedingly impressive hand coloured original antique map of the Bay of Bengal, India - stretching from Sri Lanka to the west coast of Thailand - was published by Jan Jansson in the 1650 Edition of his "Water World" atlas Atlantis Majoris. There were far fewer editions of this atlas published than Janssons more prevalent Atlas Novus.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (600mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 19in (545mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Very light spotting
Verso: - Very light spotting
Background:
Maps of India, much distorted in shape, appear in most world atlases from the time of Ptolemy, the earliest usually showing India as a relatively small extension of Southern Asia, dominated by the very large island of Taprobana (Ceylon). In later sixteenth-century maps de Jode, Ortelius and Mercator gave a much improved outline of both lands but India was still shown too small in relation to the whole continent. Most publishers in the seventeenth century continued to issue maps but with little improvement in detail until about 1719 when a French Jesuit priest, Father Jean Bouchet, compiled an accurate map of South India, subsequently used by G. Delisle (1723), Homann Heirs (1735) and by J. B. B. d'Anville, then the French East India Company's cartographer, as the basis for his greatly improved maps in 1737 and 1752.
In the next decade Alexander Dalrymple published a collection of newly surveyed coastal charts and plans of ports and, about the same time, in 1764, James Rennell, a young British Army officer who showed a remarkable aptitude for surveying, was appointed - at the age of 21- Surveyor General of Bengal; he immediately set in motion a comprehensive survey of the Company's lands, subsequently publishing maps of Bengal and other provinces which eventually formed The &ngal Atlas (1779). His other works included a Map of Hindoustan (1782-85) and The Provinces of Delhi, Agra etc and the Indian Peninsula (1788-94). These maps by Reunell provided the basis for a Trigonometrical Survey of India which was initiated in 1802 and for splendid maps published in London by Cary, the Arrowsmiths (1804-22) and the Wylds. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1650 Joan Blaeu Antique Map Archbishopic of Madenburg in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
- Title : Magdeburgensis Archiepiscopatus...Amstelaedami J Blaeu excudebat
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1650
- Ref #: 70075
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Archbishopric of Madenburg today located in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, on the Elbe River, was published in the 1650 edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Roman Catholic archdiocese (969–1552) and Prince-Archbishopric (1180–1680) of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.
Planned since 955 and established in 968, the Roman Catholic archdiocese had de facto turned void since 1557, when the last papally confirmed prince-archbishop, the Lutheran Sigismund of Brandenburg came of age and ascended to the see and the Magdeburg cathedral chapter had adopted Lutheranism in 1567, with most parishioners having preceded in their conversion. All his successors were only administrators of the prince-archbishopric and Lutheran too, except of the Catholic layman Leopold William of Austria (1631–1635). In ecclesiastical respect the remaining Catholics and their parishes and abbeys in the former archdiocese were put under supervision of the Archdiocese of Cologne in 1648 and under the jurisdiction of the Apostolic Vicariate of the Northern Missions in 1670.
In political respect the Erzstift, the archiepiscopal and capitular temporalities, had gained imperial immediacy as prince-archbishopric in 1180. Its territory comprised only some parts of the archdiocesan area, such as the city of Magdeburg, the bulk of the Magdeburg Börde, and the Jerichow Land as an integral whole and exclaves comprising about the Saalkreis including Halle upon Saale, Oebisfelde and environs as well as Jüterbog and environs. The prince-archbishopric maintained its statehood as an elective monarchy until 1680. Then Brandenburg-Prussia acquired Magdeburg prince-archbishopric, and after being secularised, transformed it into the Duchy of Magdeburg, a hereditary monarchy in personal union with Brandenburg.
1650 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Archbishopric of Madenburg Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
- Title : Magdeburgensis Archiepiscopatus
- Ref #: 40335
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Archbishopric of Madenburg today located in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, on the Elbe River, was published in the 1650 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Roman Catholic archdiocese (969–1552) and Prince-Archbishopric (1180–1680) of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.
Planned since 955 and established in 968, the Roman Catholic archdiocese had de facto turned void since 1557, when the last papally confirmed prince-archbishop, the Lutheran Sigismund of Brandenburg came of age and ascended to the see and the Magdeburg cathedral chapter had adopted Lutheranism in 1567, with most parishioners having preceded in their conversion. All his successors were only administrators of the prince-archbishopric and Lutheran too, except of the Catholic layman Leopold William of Austria (1631–1635). In ecclesiastical respect the remaining Catholics and their parishes and abbeys in the former archdiocese were put under supervision of the Archdiocese of Cologne in 1648 and under the jurisdiction of the Apostolic Vicariate of the Northern Missions in 1670.
In political respect the Erzstift, the archiepiscopal and capitular temporalities, had gained imperial immediacy as prince-archbishopric in 1180. Its territory comprised only some parts of the archdiocesan area, such as the city of Magdeburg, the bulk of the Magdeburg Börde, and the Jerichow Land as an integral whole and exclaves comprising about the Saalkreis including Halle upon Saale, Oebisfelde and environs as well as Jüterbog and environs. The prince-archbishopric maintained its statehood as an elective monarchy until 1680. Then Brandenburg-Prussia acquired Magdeburg prince-archbishopric, and after being secularised, transformed it into the Duchy of Magdeburg, a hereditary monarchy in personal union with Brandenburg.
1650 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of The Cantons of Aargau & Zurich, Switzerland
Antique Map
- Title : Argow cum Parte Merid. Zurchgow
- Ref #: 40331
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1650
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Cantons of Zurich & Aargau in North West Switzerland was published in the 1650 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novusafter Gerard Mercator.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the Waldstätte. Two further major steps in the development of the Swiss cantonal system are referred to by the terms Acht Orte (Eight Cantons; between 1353 and 1481) and Dreizehn Orte (Thirteen Cantons,during 1513–1798); they were important intermediate periods of the Ancient Swiss Confederacy.
Each canton, formerly also Ort (from before 1450), or Stand (estate, from c. 1550), was a fully sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848; with a brief period of centralized government during the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803). With the Napoleonic period of the Helvetic Republic the term Kanton was also fully established in German-speaking region.
From 1833, there were 25 cantons, increasing to 26 after the secession of the canton of Jura from Bern in 1979.
The canton of Aargau is one of the more northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare, which is why the canton is called Aar-gau (meaning Aare province). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland.
The canton of Zürich is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. It is the most populated canton in the country. Its capital is the city of Zürich. The official language is German. The local Swiss German dialect, called Züritüütsch, is commonly spoken. In English the name of the canton and its capital is often written without an umlaut.
1652 Jan Jansson Antique Map of East & Central Asia, China to Russia - Tartary
Antique Map
- Title : Tartaria sive Magni Chami Imperium
- Date : 1652
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 61166
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This handsome beautifully hand coloured original antique map of huge region of east & central Asia from China, to Central Asia, The Caspian Sea & parts of European Russia was published by Jan Jansson in the 1652 French edition of Atlas Novus.
Background: This handsome map maps the whole of eastern Central Asia from the Caspian Sea to the Great Wall, Northern China and Manchuria.
This map is dated from a time when Tartaria vaguely meant those regions to the north of Persia, west of China & to the east of Russia. The name Siberia only began to be applied with the gradual eastward expansion of the Russian Cossacks into those areas hinted at in the accounts of Marco Polo from three centuries earlier.
The Mythical and legendary nature of the geography of this vast interior is emphasised by the inclusion of devils and dragons in the Desertum Lop to the left of the Great Wall.
The rest of the map is full of detail both real and myth, some of which is no doubt borrowed from the writings of Marco Polo considered at the time one of the foremost expert on China and Central Asia.
The newly discovered northern coastline of Nova Zembla is shown with a notation concerning the Dutch expedition led by Willem Barents in 1594-96. Interesting in Siberia, Ung quae Gog and Sumongul quae Mogog, which refers to the mythological lands of Gog and Magog. These lands, noted in the Bible as being situated in the remotest parts of the earth, were originally depicted on maps just north of Israel. The map extends west to include the Caspien Sea and Russia, but the primary focus of the map is Tartaria, Central Asia, China and Asiatic Russia. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1652 Jansson Antique Map of Japan - Korea as an Island, China - Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : Japonia nova Descriptio
- Date : 1652
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35644
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique, early scarce map of Japan & Korea (as an Island) with parts of eastern China was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerardi Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
A beautiful map with sturdy, clean paper original wide margins and beautiful original hand colouring.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13 1/2in (445mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Uplift along centerfold
Verso: - Re-enforced along centerfold
Background:
This map published by Jansson is taken directly from the Jodocus Hondius map - first published in 1606 - of Japan which faithfully followed the Ortelius/Teixeira style. Jansson has added an explanation for Korea, saying he was not yet certain whether it was an island or part of the mainland. The rest of Jansson's changes were ornamental, replacing the bottom Chinese Junk with a European ship & monster as well as changing the title and scale cartouches.
Luis Teixeira'a map, which was published by Ortelius in 1595, began a process that would last for three centuries, in which Western printed maps of Japan increasingly approached geographical reality.
1652 Jansson Large Antique Map Islands of Ischia, Procida & Vivara Naples, Italy
- Title : Ischia Isola olim Aenaria
- Date : 1652
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Ref #: 61155
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine & beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Italian Islands of Ischia, Procida & Vivara in the the Gulf of Naples in Southern Italy was published in the 1652 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Novus.
Background: Ischia is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, lying at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about 30 kilometres from the city of Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands.
In 6 AD, Augustus restored the island to Naples in exchange for Capri. Ischia suffered from the barbarian invasions, being taken first by the Heruli then by the Ostrogoths, being ultimately absorbed into the Eastern Roman Empire. The Byzantines gave the island over to Naples in 588 and by 661 it was being administered by a Count liege to the Duke of Naples. The area was devastated by the Saracens in 813 and 847; in 1004 it was occupied by Henry II of Germany; the Norman Roger II of Sicily took it in 1130 granting the island to the Norman Aldoyn de Candida created Count d’Ischia; the island was raided by the Pisans in 1135 and 1137 and subsequently fell under the Suebi and then Angevin rule. After the Sicilian Vespers in 1282, the island rebelled, recognizing Peter III of Aragon, but was retaken by the Angevins the following year. It was conquered in 1284 by the forces of Aragon and Charles II of Anjou was unable to successfully retake it until 1299.
As a consequence of the island's last eruption, the population fled to Baia where they remained for 4 years. In 1320 Robert of Anjou and his wife Sancia visited the island and were hosted by Cesare Sterlich, who had been sent by Charles II from the Holy See to govern the island in 1306 and was by this time nearly 100 years of age.
Ischia suffered greatly in the struggles between the Angevin and Durazzo dynasties. It was taken by Carlo Durazzo in 1382, retaken by Louis II of Anjou in 1385 and captured yet again by Ladislaus of Naples in 1386; it was sacked by the fleet of the Antipope John XXIII under the command of Gaspare Cossa in 1410 only to be retaken by Ladislaus the following year. In 1422 Joan II gave the island to her adoptive son Alfonso V of Aragon, though, when he fell into disgrace, she retook it with the help of Genoa in 1424. In 1438 Alfonso reoccupied the castle, kicking out all the men and proclaiming it an Aragonese colony, marrying to his garrison the wives and daughters of the expelled. He set about building a bridge linking the castle to the rest of the island and he carved out a large gallery, both of which are still to be seen today. In 1442, he gave the island to one of his favorites, Lucretia d'Alagno, who in turn entrusted the island's governance to her brother-in-law, Giovanni Torella. Upon the death of Alfonso in 1458, they returned the island to the Angevin side. Ferdinand I of Naples ordered Alessandro Sforza to chase Torella out of the castle and gave the island over, in 1462, to Garceraldo Requesens. In 1464, after a brief Torellan insurrection, Marino Caracciolo was set up as governor.
In February 1495, with the arrival of Charles VIII, Ferdinand II landed on the island and took possession of the castle, and, after having killed the disloyal castellan Giusto di Candida with his own hands, left the island under the control of Innico d'Avalos, marquis of Pescara and Vasto, who ably defended the place from the French flotilla. With him came his sister Costanza and through them they founded the D'Avalos dynasty which would last on the island into the 18th century.
Throughout the 16th century, the island suffered the incursions of pirates and Barbary privateers from North Africa - in 1543 and 1544 Hayreddin Barbarossa laid waste to the island, taking 4,000 prisoners in the process. In 1548 and 1552, Ischia was beset by his successor Dragut Rais. With the increasing rarity and diminishing severity of the piratical attacks later in the century and the construction of better defenses, the islanders began to venture out of the castle and it was then that the historic centre of the town of Ischia was begun. Even so, many inhabitants still ended up slaves to the pirates, the last known being taken in 1796. During the 1647 revolution of Masaniello, there was an attempted rebellion against the feudal landowners. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (460mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1655 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Japan, Korea & parts of China - Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : Japonia Regnum
- Date : 1655
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92811
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Japan & Korea - the seventeenth and last of the maps provided by the Jesuit priest Martino Martini to Joan Blaeu - was published by Joan Blaeu in his 1665 edition of Atlas Simenis.
Martinis map was to provide the most accurate depiction of the general outlines of the principle islands of Japan - Honshu, Kyushu and Shikoku - for more than a century. The map was copied extensively by other mapmakers throughout the remainder of the seventeenth century and was replaced during the eighteenth century by maps that were in nearly all respects considerably inferior, albeit rather more flamboyant in design. Martinis first hand knowledge of the Chinese mainland enabled him to draw Korea correctly, for the first time on a printed map, as a peninsular even though little interior detail is shown. However what lay to the north of Japan was a mystery, not only Europeans, but also to the Japanese and Chinese as well. Even as early as 1613, William Adams, an Englishman living in Japan for many years, had written back to England recommending Japan as a base for "discouerie to the northward...never hath bin better menes to discouer". As with his general map of China, Martini here provides information on the internal administrative divisions in Japan; each of the feudal fiefdoms is shown, with the chief town in each, while some evidence of the activity of Jesuit missions, since the arrival of Francis Xavier in 1549, can be gathered from the town symbols surmounted by a small cross. This is one of the finest maps of Japan ever published, the engraving is strong, paper excellent and clean with beautiful original hand colour. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early color
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic & beautiful
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 16 3/4in (570mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1658 Jansson & Hornius Large Antique Map of the Holy Land, Israel, Palestine XII Tribes
Antique Map
- Title : (Situs Terrae Promissionis)
- Ref #: HL
- Size: 71in x 36in (1.801m x 910mm)
- Date : 1658
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large (71in, 1.8m) & very important rare map of the Holy Land, Featuring the Twelve Tribes of Israel by Jan Jansson & George Hornius 8-sheet map of the Holy Land was published in 1658. The map is oriented with east at the top and provides one of the finest large-scale depictions of the Holy Land available in the seventeenth century.
The map is based on Christian van Adricham's 1590 map Situs Terrae Promissionis. Jansson version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Jansson’s Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The single map appears occasionally on the market, but rarely complete sets joined with old color.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abraham's journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 71in x 36in (1.801m x 910mm)
Plate size: - 71in x 36in (1.801m x 910mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Verso: - Folds and joins re-enforced with contemporary paper
Background:
Titles and description of the six individual maps:
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
Tribuum Ephraim, Beniamin, et Dimidiae Manasse intra Iordanem partes occidentales, et partes septentrionales Dan et Iuda. This second panel shows the lands of Ephraim, Benjamin, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan river. More Biblical scenes include a scene where Jonas is cast from a sailing ship into the open jaws of a whale. Also, the panel shows the lands of Palestine and numerous armies.
Tribus Aser, et partes occidentales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. One of two enlarged panels in this series, this map shows the lands of Asher and the western reaches of Zebulon and Issachar. More Biblical illustrations include St. George and the Dragon, the city of Tyre, Nazareth, and the Tabernacle of Abraham.
Dimidia Tribus Manasse Ultra Iordanem, Tribus Neptalim et partes orientales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. The second enlarged panel details the parts of Manasseh lying on the western shores of the Jordan River, the tribe of Naphtali, and parts of the lands of Zebulon and Issachar. This sheet includes the Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberius), as well as several scenes from the life of Jesus, such as his walking on water, Jesus preaching from onboard a boat, and other. The large inset map in the upper left quadrant, entitled Peregrinatio Abrahae, shows the route followed by Abraham from Ur into Canaan.
Pars maxima Tribus Iusa Versus Orientem. This southeastern-most sheet depicts much of the Dead Sea, as well as the lands claimed by the tribe of Judah. It also features the smoking ruins of Sodom, Gomorrah, Adaima, and Seboim. In the upper right, there is a large inset, Itinera et Mansiones Deserti, which shows the route taken by the Hebrews as they fled from Egypt. Finally, it also shows the parting of the Red Sea.
Tribus Simeon et pars meridionalis Tribus Dan, et orientalis Tribus Idua. Usually considered the last in the series, this panel is mountainous, depicting the lands of Simeon, as well as parts of Dan and Judah. It also identifies the lands of the Philistines and timber lands rich in cedar.
Maps of the Holy Land and the early history of Israel
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh.
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
George Hornius
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the “Hornius Map.” Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Hornius’s first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Hornius’s historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Jansson’s Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Hornius’s works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1658 Joan Blaeu Antique Heptarchy Map of Great Britain & Ireland - Magnificent
Antique Map
- Title : Britannia prout divisa suit temporibus Anglo-Saxonum præsertim durante illorum Heptarchia
- Date : 1658
- Size: 26in x 22in (660mm x 560mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35658
Description:
This beautifully engraved, hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique Heptarchy Map of Great Britain, during part of the Saxon Period (approx. 400 to 600AD) was published by Joan Blaeu in the only Spanish edition of Atlas Nouvs in 1658.
This is one of the best examples of the most beautiful maps ever published of the British Isles, I have seen for sometime. The map has magnificent fresh hand colouring, along with a deep heavy impression on clean heavy paper, with original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 22in (660mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map is based on the 1611 Heptarchy map published by John Speed. The side panels show historical scenes in Saxon history between 456 and 662 A.D.
The unknown engraver of this Blaeu Map has re-created each of the 14 scenes as an unmistakable Dutch miniature in the dramatic style of the greater paintings of the time. Blaeus map is considered by some, the finest of the three edition released by Speed, Blaeu and Jansson.
On the left panel are seven full length figures of the first aspiring Saxon Kings with their escutcheons, forces or townships; Hengist - Kent 456; Ella - South Saxon 478; Cherdin - West Saxon 519; Erkenwin - East Saxon 527; Ida - Northumberland 582; Uffa - East Anglia 546; Creda - Mercian 575. On the right there are scenes showing the conversion of Saxon Sovereigns to Christianity: Ethelbert (Kent 595) receiving religious instruction from St Augustine; Sebert (East Saxon 604) re-consecrating the temples of Diana & Apollo - now St Pauls, London, and St Peters, Westminster; Erpenwald (East Anglia, 624) embracing baptism by the armed extortion of King Edwin of Northumberland; Edwin (Northumberland, 627) stirred by a vision to receive the Faith; Kengils (West Saxon, 635) converted by the preaching of St Bernius; Peada (Mercia, 650) receiving the Faith by the persuasion of King Osway of Northumberland but also being murdered by his own mothers (some say his wife's) procurement; finally Ethelwolfe (South Saxon 662) being baptized at Oxford by St Berinus.
Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map.
The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Shirley; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Splendid map of Anglo-Saxon Britain flanked by intricately rendered portraits of the kings through the 5th through 7th centuries. The monarchs to the left are those of the pre-Christian era, while those on the right are depicted receiving Christianity or being martyred for its sake.
This is often called the Heptarchy Map, as it presents England during the time following the Anglo Saxon conquest of southern England, approximately 500 to 850 A.D. known as the Heptarchy Era. (The word itself refers to the seven kingdoms that would eventually combine to form the Kingdom of England in the 10th century.)
To the left are the seven full length figures of the first aspiring Saxon Kings with their escutcheons, armies or townships;
1. Hengist - Kent 456AD
2. Ella - South Saxon 478AD
3. Cherdin - West Saxon 519AD
4. Erkenwin - East Saxon 527AD
5. Ida - Northumberland 582AD
6. Uffa - East Angle 546AD
7. Creda - Mercian 575AD
On the right there are scenes showing the conversion of Saxon sovereigns to Christianity:
1. Ethelbert - Kent 595AD receiving religious instruction from St Augustine
2. Sebert - East saxon604AD re-consecrating the temples of Diana and Apollo that later become St Pauls London and St Peters Westminster
3. Epenwald - East Angle 624AD embracing baptism by the armed exhortation of King Edwin of Northumberland
4. Edwin - Northumberland 627AD stirred by a vision to receive the faith
5. Kengils West Saxon 635AD converted by the preaching of St Berinus
6. Peada Mercia 650 receiving the Faith by the persuasion of King Osway of Northumberland but also being murdered by his own mothers, some say his wifes, procurement.
7. Ethenwolfe South Saxon 662AD being baptised at Oxford by St Berinus
(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1658 Visscher Large Antique Map of America
- Title : Novissima et Accuratissima Totius Americae Descriptio per N. Visscher
- Ref #: 50683
- Size: 24in x 20 1/4in (610mm x 515mm)
- Date : 1658
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large rare beautifully hand coloured original antique 1st edition map of America was published by Nicholas Visscher in ca 1658.
This is an important map, derived from Blaeu's earlier wall map, that would prove influential to many future maps of the western hemisphere, with similar maps issued by De Wit, Danckerts, Allard, and Ottens to the end of the 17th century.
Background:
Various dates have been attributed to this map from 1658 to 1680. The earliest date derives from its presence in the third volume of Jan Jansson's Novus Atlas dated 1658. However, it is not present in all examples and other maps have borne dates as late as 1680. The heirs of Jan Jansson who died in 1664, appear to have issued the volumes with old title pages on a continuous basis.
Although the map did not provide much in the way of cartographic advances after Blaeu, it had a large influence on future cartographers drawing upon either its geography or the distinctive cartouches. One of the most recognisable features is the large open lake in the place of the western Great Lakes. The single lake to its east most probably represents that of Ontario, but is named Lac Contenant. This like much of the map is derived from Joan Blaeu's wall map of the world, 1648. The use of Real de Nueva Mogulcorrectly placed on the east bank of the Rio del Norte is taken directly from Blaeu. One are where Visscher breaks from this is his depiction of the west coast. He uses an older model, that of Briggs, 1625 although with a broader north coast to California as an Island, a feature that was not found in any of Viscchers earlier works. He continues the mainland coastline north-north -east towards the Strait of Anian, which separates it from ANIAN.
The title is decorated with a scene showing the panning of gold or silver, with a native standing by under an umbrella. The cartouche top left bears a dedication to Cornelis Witsen, mayor of Amsterdam who financed many trips to the New World and depicts three angels helping a native Indian to heaven while the devil is fading away. (Burden; M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/4in (610mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/4in (545mm x 440mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning, center-fold re-joined, no loss
Verso: - Uniform age toning, light spotting
1659 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of The Cantons of Aargau & Zurich, Switzerland
Antique Map
- Title : Argow cum Parte Merid. Zurchgow
- Ref #: 30282
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1659
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Cantons of Zurich & Aargau in North West Switzerland was published in the 1659 Spanish edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novusafter Gerard Mercator.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the Waldstätte. Two further major steps in the development of the Swiss cantonal system are referred to by the terms Acht Orte (Eight Cantons; between 1353 and 1481) and Dreizehn Orte (Thirteen Cantons,during 1513–1798); they were important intermediate periods of the Ancient Swiss Confederacy.
Each canton, formerly also Ort (from before 1450), or Stand (estate, from c. 1550), was a fully sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848; with a brief period of centralized government during the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803). With the Napoleonic period of the Helvetic Republic the term Kanton was also fully established in German-speaking region.
From 1833, there were 25 cantons, increasing to 26 after the secession of the canton of Jura from Bern in 1979.
The canton of Aargau is one of the more northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare, which is why the canton is called Aar-gau (meaning Aare province). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland.
The canton of Zürich is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. It is the most populated canton in the country. Its capital is the city of Zürich. The official language is German. The local Swiss German dialect, called Züritüütsch, is commonly spoken. In English the name of the canton and its capital is often written without an umlaut.
1659 Joan Blaeu Large Antique Map of Jersey and Guernsey British Channel Islands
Antique Map
- Title : Sarnia Insula Vulgo Garnsey: et Insula Caesarrea vernacule Jarsey
- Date : 1659
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43170
- Size: 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
Description:
This original large hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Channel Islands Jersey and Guernsey and smaller islands was published in the 1659 Spanish edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Novus.
This map is in beautiful condition, large margins, strong sturdy clean paper and bright fresh original colouring.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15 1/2in (480mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Very light crease along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background: The Channel Islands (Norman: Îles d'la Manche, French: Îles Anglo-Normandes orÎles de la Manche) are an archipelago of British Crown Dependencies in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two separate bailiwicks: the Bailiwick of Jersey and the Bailiwick of Guernsey. They are considered the remnants of the Duchy of Normandy, and are not part of the United Kingdom. They have a total population of about 168,000 and their respective capitals, Saint Helier and Saint Peter Port, have populations of 33,500 and 16,488, respectively. The total area of the islands is 194 km.
Both Bailiwicks have been administered separately since the late 13th century; each has its own independent laws, elections, and representative bodies (although in modern times, politicians from the islands' legislatures are in regular contact). Any institution common to both is the exception rather than the rule.
Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map. The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
1662 Blaeu & Barlaeus Complete Set of 13 x Antique Maps of South America
Antique Map
- Titles:
1. Terra Firma
2. Venezuela
3. Guiana
4. Peru
5. Chili
6. Brasilia
7. Paraquaria
8. Tabula Magellanica
9. Preafecturae Paranambucae Prs Borealis
10. Praefecturae De Paraiba et Rio Grande
11. Praefectura De Ciriii vel Seregippe
12. Praefectura Paranambucae Pars Meridionalis
13. Sinus Omnium Sanctoru - Sizes: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)ea
- Condition: (A) Very Good to Fine Condition
- Date: 1662
- Ref #: BlaeuSA 1662
Description:
This is a unique opportunity to acquire a complete set of the 13 maps of South America, including the 4 rare uniform Blaeu-Barleus maps of the Coast of Brazil, published by Joan Blaeu in his monumental & rare 1st 1662 Atlas, Latin edition of Atlas Major.
All paper in imprinted with a large Elephant watermark donating german paper from the 1660s.
The maps cover the full geographical area from North to South, South America from Panama to Tierra Firma. Please see the background section below for details of each map. All maps have wide original margins & colour on strong sturdy paper.
Joan Blaeus 11 volumes of Atlas Major, is considered by many to be the greatest atlas set ever published. It excels in comprehensiveness, engraving, color, and overall production. The first edition was published in Latin in 1662 and was subsequently published in French, Dutch, German, and Spanish over the next 10 years.
On the 23rd of February 1672, a fire broke out in central Amsterdam, that ended the reign of one of the greatest & most prolific publishers of printed maps and atlases in publishing history. The Blaeu family had reached its zenith 10 years previously, with the publication of its greatest achievement, the Atlas Major or Great Atlas, consisting of 11 volumes, with geographical detail reflecting many of the achievements of the Golden Age of the United Netherlands. Blaeus Atlas Major were the most expensive books printed in the 17th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - Various, pls see below
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm) min
Imperfections:
Margins: - Pls see below
Plate area: - Pls see below
Verso: - Pls see below
Background:
1. Terra Firma - This regional map of the north eastern corner of South America belongs to the early group of plates printed by Willem Blaeu from 1630 onwards. It covers modern Colombia, part of Venezuela and Panama.
Plate: 19in x 14 1/2in.
Condition: Very light age toning
2. Venezuela - This map showing the area of modern Venezuela to the north of the Orinoco valley is another of the early plates of the 1630s. It extends from Lago dee Maracaibo in the west to the Island of Trinidad in the east and also shows the Dutch held Islands of Curacao, Aruba and Bonaire which served as a base of the Geotroyeerde West Indische Compaagnie (or Netherlands West Indian Company) since 1634.
Plate: 18 3/4in x 14 1/2in
Condition: Age toning, printers crease along centerfold, 8 small worm holes.
3. Guiana - This handsome map, another of the Blaeu maps of 1630, extendends from the Isla Margarita in the north-west to the coast of Northern Brazil near Sao Luis east of the Amazonas delta. The interior is dominated by a large island sea , the Parime Lacus, on whose north wesstern shores lies the fabled city of Manoa, de el Dorado, golden City of the Inca.
Plate: 19 1/4in x 14 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
4. Peru - Here willem Blaeu, this map being part of Pacific Coast of South America from Ecuador (at the left hand side) as far south as the Atacama desert in the northern reaches of Chile.
Plate: 19 1/4in x 14 3/4in
Condition: Light age toning
5. Chili - This is another of Willem Blaeus early group f maps showing the coastal region of Central Chile from Copiapo in the north as far as a point to the south of the island of Chiloe.
Plate: 16 3/4in x 14in
Condition: Light age toning
6. Brasilia - Oriented west to the top of the plate, this general map of Brazil was an early product of Joan Blaeu himself, made after he had assumed full control of the publishing house following the death of his father a few years earlier.
This plate was made to replace the De Laet derivative which Willem had acquired from the Hondius plate stock in 1629 and is considerably more detailed than its earlier name sake.
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/4in
Condition: Light age toning
7. Paraquaria - First map of Paraguay published first in this 1662 Atlas Major and so rare only published for 10 years or so.
Plate: 21 1/2in x 19 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
8. Tabula Magellanica - Beautifully engraved map of the Magellan Straits first published in 1635
Plate: 19in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
9. Preafecturae Paranambucae Prs Borealis
10. Praefecturae De Paraiba et Rio Grande
11. Praefectura De Ciriii vel Seregippe
12. Praefectura Paranambucae Pars Meridionalis
These 4 beautiful uniform maps are quite unlike any other maps found in Blaeu's Atlas Major.
Although they first appeared in the atlas for in 1662, these 4 maps first appeared in another earlier work published by Blaeu, the Rerum per octennium in Brasilia (1647) by the Remonstrant theologian Casper van Baerle (or Barlaeus) who died very soon afterwards in 1648.
Barlaeus great work, still one of the most valuable sources for Brazilian history, was published under the auspices of the Dutch governor in Brazil, Johan Maurits of Nassau Siegen, whose governorship from 1637 to 1644 Barlaeus describes in a eulogistic but nevertheless impartial account compiled from official sources.
The large pictorial vignettes of this group of maps illustrate much about local life and conditions of the time: in Preafecturae Paranambucae Prs Borealis & Praefecturae De Paraiba et Rio Grandea is shown processions of Indians from a mission, illustrated after paintings of the artist Frans Janszoon Post (1612 - 1680) who was with Johan Maurits in Brazil during the years 1637 - 1644. The buildings depicted have not been identified with any certainty but must have been in or near Pernambuco
Plates:
(9) 21in x 16 1/2in
(10) 21in x 16 1/2in
(11) 21in x 16 1/2in
(12) 17 1/2in x 16 1/2in
Conditions:
(9) Light age toning
(10) Light age toning
(11) Light age toning
(12) Light age toning
13. Sinus Omnium Sanctoru
Beautiful map of the Bahia De Todos Sanctos (All Saints Bay) in Brazil, with a large inset plan of the City of Sao Salvador.
Plate: 20in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Age toning
Caspar Barlaeus (1584 – 1648) was a Dutch polymath and Renaissance humanist, a theologian, poet, and historian.
Born Caspar (Kaspar) van Baerle in Antwerp, Barlaeus' parents fled the city when it was occupied by Spanish troops shortly after his birth. They settled in Zaltbommel, where his father eventually would become head of the Latin school. Caspar studied theology and philosophy at the University of Leiden. After his study, he preached for 1.5 years in the village of Nieuwe-Tonge, before returning to Leiden in 1612 as an under-regent of a college. From 1617 he also was professor in philosophy at the university. Because of his remonstrant sympathies, he was forced out of this job in 1619. He then studied and graduated in medicines (in Caen), but never practiced professionally.
From 1631, he was professor of philosophy and rhetoric at the Amsterdam Athenaeum, Athenaeum Illustre), which is commonly regarded as the predecessor of the University of Amsterdam; the Athenaeum had its seat in the fourteenth-century Agnietenkapel. In January 1632, Barlaeus, along with Gerard Vossius, held his inaugural speech at the Amsterdam Atheneum. Barlaeus later encouraged Martinus Hortensius to lecture –and give an inaugural speech- at the same Institution. One of his huge patrons was Amsterdam burgomaster Andries de Graeff, his neighbor at Oudezijds Achterburgwal.
Barlaeus suffered from mental illness including the delusion that he was made of glass (the Glass delusion) though Gill Speak refers to his glass delusion as ‘unsubstantiated’
Barlaeus published many volumes of poetry, particularly Latin poetry. He also wrote the eulogy that accompanies the 1622 portrait of cartographer Willem Blaeu.
Barlaeus was involved in various aspects of cartography and history. He translated Antonio de Herrera's Description of the West Indies in 1622. In 1627, Barlaeus provided the text for the atlas of Italy created by Jodocus Hondius. In 1647, he wrote an account of the Dutch colonial empire in Brazil, inspired by the leadership of John Maurice of Nassau (Johan Maurits) at Recife. The Rerum per octennium in Brasilia et alibi nuper gestarum sub praefectura, as it is called, contains numerous maps and plates of the region. The engravings of Brazilian northeastern locales, fleets, battles, and maps were for 160 years the main references to Brazilian landscapes available in Europe, and are well known by Brazilians today as the most important examples of pre-national art. Franciscus Plante wrote a similar work in the same year called Mauritias, and included the maps already published in Barlaeus' work. These were maps of Ceará, Pernambuco, Paraíba, and Pernambuco Borealá. Plante also incorporated a portrait of John Maurice that had already been included in Barlaeus' work.
In 1638, Barlaeus wrote Medicea Hospes, sive descriptio publicae gratulationis, qua ... Mariam de Medicis, excepit senatus populusque Amstelodamensis. Published by Willem Blaeu, it includes two large folding engraved views of the ceremonies on the occasion of the French queen mother Marie de Medici's triumphal entry into Amsterdam in 1638. Considered an important moment in Dutch history, Marie's visit lent de facto international recognition of the newly formed Dutch Republic. Marie de Medici actually traveled to the Netherlands as exile, but spectacular displays and water pageants took place in the city's harbor in celebration of her visit. There was a procession led by two mounted trumpeters; a large temporary structure erected on an artificial island in the Amstel River was built especially for the festival. This building was designed to display a series of dramatic tableaux in tribute to her once she set foot on the floating island and entered its pavilion.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map of the Tribes of Simeon, Dan & Juda
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Simeon et pars meridionalis Tribus Dan, et Oriemtalis Tribus Juda
- Ref #: 50600
- Size: 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map one of six, of the Tribes of Simeon, Dan, & Juda, located to the South West of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major and was based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #6 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
The six panels are individually titled:
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
Tribuum Ephraim, Beniamin, et Dimidiae Manasse intra Iordanem partes occidentales, et partes septentrionales Dan et Iuda. This second panel shows the lands of Ephraim, Benjamin, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan river. More Biblical scenes include a scene where Jonas is cast from a sailing ship into the open jaws of a whale. Also, the panel shows the lands of Palestine and numerous armies.
Tribus Aser, et partes occidentales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. One of two enlarged panels in this series, this map shows the lands of Asher and the western reaches of Zebulon and Issachar. More Biblical illustrations include St. George and the Dragon, the city of Tyre, Nazareth, and the Tabernacle of Abraham.
Dimidia Tribus Manasse Ultra Iordanem, Tribus Neptalim et partes orientales tribuum Zabulon et Isachar. The second enlarged panel details the parts of Manasseh lying on the western shores of the Jordan River, the tribe of Naphtali, and parts of the lands of Zebulon and Issachar. This sheet includes the Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberius), as well as several scenes from the life of Jesus, such as his walking on water, Jesus preaching from onboard a boat, and other. The large inset map in the upper left quadrant, entitled Peregrinatio Abrahae, shows the route followed by Abraham from Ur into Canaan.
Pars maxima Tribus Iusa Versus Orientem. This southeastern-most sheet depicts much of the Dead Sea, as well as the lands claimed by the tribe of Judah. It also features the smoking ruins of Sodom, Gomorrah, Adaima, and Seboim. In the upper right, there is a large inset, Itinera et Mansiones Deserti, which shows the route taken by the Hebrews as they fled from Egypt. Finally, it also shows the parting of the Red Sea.
Tribus Simeon et pars meridionalis Tribus Dan, et orientalis Tribus Idua. Usually considered the last in the series, this panel is mountainous, depicting the lands of Simeon, as well as parts of Dan and Judah. It also identifies the lands of the Philistines and timber lands rich in cedar.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12in (405mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map Tribes Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Ruben, et Gad parties orientales tribumum Beniamin, Ephraim, et Dimidiae, Manasse, intra Jordanem
- Ref #: 61037
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, one of six, of the Tribes of Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh located to the north and east of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major, based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #1 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map Tribes Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Ruben, et Gad parties orientales tribumum Beniamin, Ephraim, et Dimidiae, Manasse, intra Jordanem
- Ref #: 17016
- Size: 23in x 18 1/2in (580mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, one of six, of the Tribes of Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh located to the north and east of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major, based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #1 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (580mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.
1662 Hornius & Jansson Antique Holy Land Map Tribes Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh
Antique Map
- Title : Tribus Ruben, et Gad parties orientales tribumum Beniamin, Ephraim, et Dimidiae, Manasse, intra Jordanem
- Ref #: 61037
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1662
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, important & scarce hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, one of six, of the Tribes of Ruben, Gad, Benjamin, Ephraim & Manasseh located to the north and east of the Dead Sea was published by Jan Jansson & Georguis Hornius (1620-1670) in the 1662 French Edition of Atlas Major, based on the 1590 map of Christian van Adricham, Situs Terrae Promissionis.
This map is #1 of 6 published by Jansson that combined measures 66in long by 37in wide (1.68m x 940mm) Please see the B&W image to see combined maps.
Tribus Ruben, et Gad et partes orientales tribuum Beniamin, Ephraim, et dimidiae Manasse intra Iordenem. This is usually thought to the be the first panel in the series. It includes several vignettes, such as Jesus and Satan arguing on a mountaintop, Moses looking across the Jordan, the entry point of the Hebrews into the land of Milk and Honey, and a stairway ascending to heaven. This panel shows the lands controlled by Ruben and Gad, as well as the eastern lands of Benjamin, Ephraim, and part of Manasseh beyond the Jordan River. It also shows the western part of the Dead Sea.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Jan Jansson based his map on Christian van Adrichams Situs Terrae Promissionis of ca. 1590. This version is both expanded and carries additional vignettes and details. Georgius Hornius wrote the text that accompanied the map in volume six of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio.
The map shows the region divided into domains of the Twelve Tribes of Israel on both sides of the Jordan River, with the shoreline running from Sidon to Alexandria. The Cison Torrens (Kishon River) is shown as connecting the Sea of Galilee with the Mediterranean Sea, and there are many rivers, some of which do not exist; for example, there is a river connecting Jerusalem with the Dead Sea. In the Dead Sea, four burning cities are shown: Sodom, Gomorra, Seboim, and Adama.
The map is intricately engraved to show topographical features, major roads, towns and villages. It is also richly embellished with dozens of biblical illustrations. Inset maps in the top corners depict Abrahams journey (left) and the wandering of the Israelites through the desert (right).
Maps of the Holy Land, a popular genre in the early modern period, allowed users to better understand events from religious traditions. For the mapmaker, the relationship between religion and geography acted as a powerful storytelling tool, allowing viewers to spatialize religious stories. The maps show the centrality of religion to early modern European culture, as well as an enduring interest in historical geography.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel, shown here, descended from the twelve sons of Jacob. According to Deuteronomy, the twelve sons were Reuben, Simeon, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Benjamin, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Ephraim, and Manasseh..
In the tenth century BCE, the Israelites made up of about 300 highland villages with a population of approximately 40,000 people. These villages would begin to conglomerate in the ninth century BCE. The kingdom formed by their joining was referred to by its neighbors as the House of David. After the kingdoms of Samaria and Judah were destroyed, the resulting Babylonian captivity caused a merging of the south Levantine groups into a unified cultural identity.
This unified kingdom would ultimately not last, however. Tensions between the tribes of Israel mounted over a disagreement as to the location of the mountain on which Moses attempted to sacrifice Isaac. Eventually, the tensions exploded when the Hasmonean King destroyed the temple of another tribe, which caused the lower Levant to devolve into chaos. This civil conflict would last until the Roman Empire invaded, with future emperor Vespasian leading an army into Israel under the pretense of restoring order. This resulted in Roman dominance over the lower Levant until the Muslim conquests of the seventh century CE.
Although published by Jan Jansson, the map was made in collaboration with Georgius Hornius (1620-1670). Indeed, it is often called the Hornius Map. Hornius was a renowned cartographer and historian who published maps as well. His family was forced to flee to Nuremberg during the religious violence of the Thirty Years War. He would eventually attend the University of Altdorf, studying religion and medicine there.
Horniuss first notable work was a history of the English Civil War, which he witnessed firsthand as a traveler. In 1648 he completed his doctorate in Leiden; by this time, his historical works had drawn the attention of many universities which sought him as a professor. He eventually decided to accept a professorship at the University of Harderwijk where he quickly became rector in 1652, a position he would hold until his death in 1670.
Horniuss historical works were influential, propagating the idea of universal history, which was an understanding of history as a whole, concurrent unit. He also prepared the text for portions of Janssons Novus Atlas, Accuratissimia Orbis Antiqui Delineatio, including the text that accompanied this map. Horniuss works would continue to be relevant after his death, with many posthumous editions of his writings published.