Products
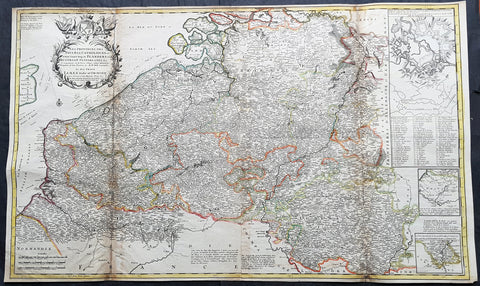
1720 Moll Large Antique Map of The Low Countries, Flanders Netherlands & Belgium
Antique Map
- Title : Les Provinces Des Pays-Bas Catholoiques ou. A Most excat map of Flanders or Austraian Netherlands.....Herman Moll Geogr.
- Size: 40 1/2in x 24in (1.030m x 610mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1720
- Ref #: 61130
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the low country of Flanders region of The Netherlands & Belgium by Herman Moll was published in 1720 in the atlas The World Described, or a New and Correct Sett of Maps by John Bowles, Thomas Bowles, Philip Overton & John King of London.
In the 18th century many large-scale maps were published by the likes of John Senex and Herman Moll, this trend continued until the end of private mapping in the early 19th century when it was replaced by Ordnance Survey maps.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 40 1/2in x 24in (1.030m x 610mm)
Plate size: - 40in x 24in (1.00m x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning along top margin
Plate area: - Age toning along folds
Verso: - Re-enforced & age toning along folds
Background:
Flanders: In 1500, Charles V was born in Ghent. He inherited the Seventeen Provinces (1506), Spain (1516) with its colonies and in 1519 was elected Holy Roman Emperor. The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549, issued by Charles V, established the Low Countries as the Seventeen Provinces (or Spanish Netherlands in its broad sense) as an entity separate from the Holy Roman Empire and from France. In 1556 Charles V abdicated due to ill health (he suffered from crippling gout). Spain and the Seventeen Provinces went to his son, king Philip II of Spain.
Over the first half of the 16th century Antwerp grew to become the second-largest European city north of the Alps by 1560. Antwerp was the richest city in Europe at this time. According to Luc-Normand Tellier It is estimated that the port of Antwerp was earning the Spanish crown seven times more revenues than the Americas.
Meanwhile, Protestantism had reached the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the Lutheran beliefs of the German Hanseatic traders found appeal, perhaps partly for economic reasons. The spread of Protestantism in this city was aided by the presence of an Augustinian cloister (founded 1514) in the St. Andries quarter. Luther, an Augustinian himself, had taught some of the monks, and his works were in print by 1518. The first Lutheran martyrs came from Antwerp. The Reformation resulted in consecutive but overlapping waves of reform: a Lutheran, followed by a militant Anabaptist, then a Mennonite, and finally a Calvinistic movement. These movements existed independently of each other.
Philip II, a devout Catholic and self-proclaimed protector of the Counter-Reformation, suppressed Calvinism in Flanders, Brabant and Holland (what is now approximately Belgian Limburg was part of the Bishopric of Liège and was Catholic de facto). In 1566, the wave of iconoclasm known as the Beeldenstorm was a prelude to religious war between Catholics and Protestants, especially the Anabaptists. The Beeldenstorm started in what is now French Flanders, with open-air sermons (Dutch: hagepreken) that spread through the Low Countries, first to Antwerp and Ghent, and from there further east and north. In total it lasted not even a month.
Subsequently, Philip II sent the Duke of Alba to the Provinces to repress the revolt. Alba recaptured the southern part of the Provinces, who signed the Union of Atrecht, which meant that they would accept the Spanish government on condition of more freedom. But the northern part of the provinces signed the Union of Utrecht and settled in 1581 the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. Spanish troops quickly started fighting the rebels, but before the revolt could be completely defeated, a war between England and Spain had broken out, forcing Philips Spanish troops to halt their advance. Meanwhile, the Spanish armies had already conquered the important trading cities of Bruges and Ghent. Antwerp, which was then the most important port in the world, also had to be conquered. On 17 August 1585, Antwerp fell. This ended the Eighty Years War for the (from now on) Southern Netherlands. The United Provinces (the Northern Netherlands) fought on until 1648 – the Peace of Westphalia.
While Spain was at war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to Philip IIs Spanish troops. They managed to conquer a considerable part of Brabant (the later Noord-Brabant of the Netherlands), and the south bank of the Scheldt estuary (Zeelandic Flanders), before being stopped by Spanish troops. The front line at the end of this war stabilized and became the current border between present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. The Dutch (as they later became known) had managed to reclaim enough of Spanish-controlled Flanders to close off the river Scheldt, effectively cutting Antwerp off from its trade routes.
First the fall of Antwerp to the Spanish and later also the closing of the Scheldt were causes of a considerable emigration of Antverpians. Many of the Calvinist merchants of Antwerp and also of other Flemish cities left Flanders and emigrated to the north. A large number of them settled in Amsterdam, which was at the time a smaller port, of significance only in the Baltic trade. In the following years Amsterdam was rapidly transformed into one of the worlds most important ports. Because of the contribution of the Flemish exiles to this transformation, the exodus is sometimes described as creating a new Antwerp.
Flanders and Brabant, due to these events, went into a period of relative decline from the time of the Thirty Years War. In the Northern Netherlands however, the mass emigration from Flanders and Brabant became an important driving force behind the Dutch Golden Age.
Although arts remained at a relatively impressive level for another century with Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640) and Anthony van Dyck, Flanders experienced a loss of its former economic and intellectual power under Spanish, Austrian, and French rule, with heavy taxation and rigid imperial political control compounding the effects of industrial stagnation and Spanish-Dutch and Franco-Austrian conflict. The Southern Netherlands suffered severely under the War of the Spanish Succession, but under the reign of Empress Maria-Theresia these lands economically flourished again. Influenced by the Enlightenment, the Austrian Emperor Joseph II was the first sovereign who had been in the Southern Netherlands since King Philip II of Spain left them in 1559.
In 1794 the French Republican Army started using Antwerp as the northernmost naval port of France, which country officially annexed Flanders the following year as the départements of Lys, Escaut, Deux-Nèthes, Meuse-Inférieure and Dyle. Obligatory (French) army service for all men aged 16–25 was one of the main reasons for the peoples uprising against the French in 1798, known as the Boerenkrijg (Peasants War), with the heaviest fighting in the Campine area.
After the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte at the 1815 Battle of Waterloo in Waterloo, Brabant, sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands – Belgium minus the East Cantons and Luxembourg – was given by the Congress of Vienna (1815) to the United Netherlands (Dutch: Verenigde Nederlanden), the state that briefly existed under Sovereign Prince William I of Orange Nassau, the latter King William I of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, after the French Empire was driven out of the Dutch territories. The United Kingdom of the Netherlands was born. The Protestant King of the Netherlands, William I rapidly started the industrialisation of the southern parts of the Kingdom. The political system that was set up however, slowly but surely failed to forge a true union between the northern and the southern parts of the Kingdom. The southern bourgeoisie mainly was Roman Catholic, in contrast to the mainly Protestant north; large parts of the southern bourgeoisie also primarily spoke French rather than Dutch.
In 1815 the Dutch Senate was reinstated (Dutch: Eerste Kamer der Staaten Generaal). The nobility, mainly coming from the south, became more and more estranged from their northern colleagues. Resentment grew both between the Roman Catholics from the south and the Protestants from the north and among the powerful liberal bourgeoisie from the south and their more moderate colleagues from the north. On 25 August 1830 (after the showing of the opera La Muette de Portici of Daniel Auber in Brussels) the Belgian Revolution sparked off and became a fact. On 4 October 1830, the Provisional Government (Dutch: Voorlopig Bewind) proclaimed the independence, which was later confirmed by the National Congress that issued a new Liberal Constitution and declared the new state a Constitutional Monarchy, under the House of Saxe-Coburg. Flanders now became part of the Kingdom of Belgium, which was recognized by the major European Powers on 20 January 1831. The de facto dissidence was finally recognized by the United Kingdom of the Netherlands on 19 April 1839.
In 1830, the Belgian Revolution led to the splitting up of the two countries. Belgium was confirmed as an independent state by the Treaty of London of 1839, but deprived of the eastern half of Limburg (now Dutch Limburg), and the Eastern half of Luxembourg (now the Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg). Sovereignty over Zeelandic Flanders, south of the Westerscheldt river delta, was left with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which was allowed to levy a toll on all traffic to Antwerp harbour until 1863.
The Belgian Revolution was not well supported in Flanders and even on 4 October 1830, when the Belgian independence was eventually declared, Flemish authorities refused to take orders from the new Belgian government in Brussels. Only after Flanders was subdued with the aid of a large French military force one month later, under the leadership of the Count de Pontécoulant, did Flanders become a true part of Belgium.
The French-speaking bourgeoisie showed very little respect for the Dutch-speaking part of the population. French became the only official language in Belgium and all secondary and higher education in the Dutch language was abolished.
In 1834, all people even remotely suspected of being Flemish minded or calling for the reunification of the Netherlands were prosecuted and their houses looted and burnt. Flanders, until then a very prosperous European region, was not considered worthwhile for investment and scholarship. A study in 1918 demonstrated that in the first 88 years of its existence, 80% of the Belgian GNP was invested in Wallonia. This led to a widespread poverty in Flanders, forcing roughly 300.000 Flemish to emigrate to Wallonia to start working there in the heavy industry.John SenexMoll
All of these events led to a silent uprising in Flanders against the French-speaking domination. But it was not until 1878 that Dutch was allowed to be used for official purposes in Flanders (see language legislation in Belgium), although French remained the only official language in Belgium.
In 1873, Dutch became the official language in public secondary schools. In 1898 Dutch and French were declared equal languages in laws and Royal orders. In 1930 the first Flemish university was opened. The first official translation of the Belgian constitution in Dutch was not published until 1967.
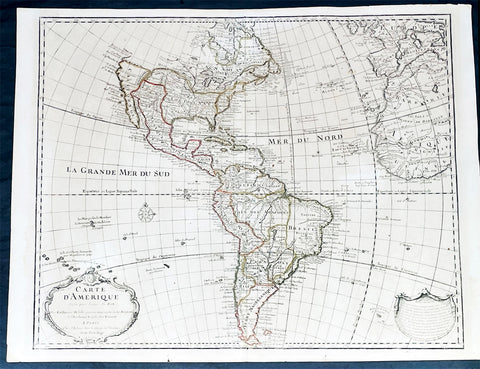
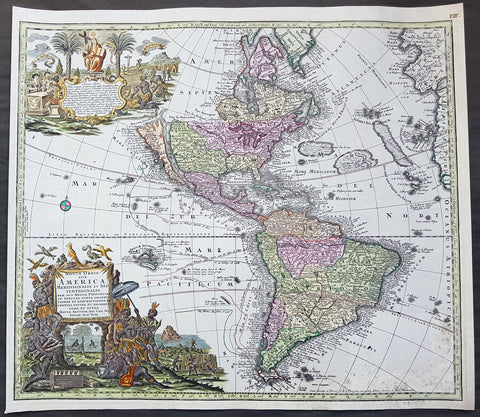
1722 Guillaume Delisle Large Antique Map of America, True Rare 1st Edition
Antique Map
- Title : Carte D Amerique...1722
- Size: 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (675mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 93338
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique, true first edition, map of America was published by Guillaume Delisle in 1722.
Even though this map was published for the better part of the 18th century, the date 1722 in the cartouche, was not updated or removed in most instances. This makes identification of the true 1st editions complicated, but not impossible. The design of the cartouche itself is the defining evidence. I have included an image of the 4 different cartouche designs, from Tooleys The Mapping of America that define the different editions. This map is the first edition, state 2, illustrated in the image as No.2.
This 1st edition is a landmark map and one of the most important maps of America published in the early 18th century. So detailed was it, for its day, that it was copied many times over the next 100 years.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (675mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 19 1/2in (620mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Detailed map of America, showing a blank coastline above Cap Blanc and the mythical entry of D\'Aguilar. The map shows tremendous detail throughout. Nice detail in California and the Southwest. The course of the Mississippi si pushed considerably west of its true location, but the Missouri River is shown in a remarkably accurate fashion, with headwaters in the Northern Rocky Mountains. The map is rich with Indian and other early American details. Decorative cartouche, compass rose and extensive notes throughout the map. First edition, 2nd State of the map. A bit of minor soiling, some lifting at the centerfold near the bottom of the map and a bit of wear at the lower centerfold, but generally a fine dark impression of this important early map.
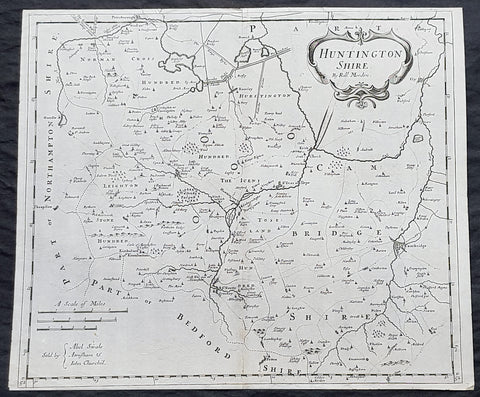
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of Huntington in County of Cambridgeshire England
- Title : Huntington Shire by Robt. Morden...Sold by Abel Swale Awsham & John Churchill
- Size: 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 92680
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the English region of Huntingdonshire, in the county of Cambridgeshire by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
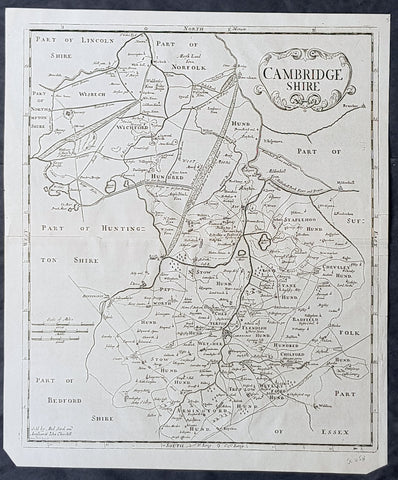
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of Huntington in County of Cambridgeshire England
- Title : Huntington Shire by Robt. Morden...Sold by Abel Swale Awsham & John Churchill
- Size: 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 50149
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the English region of Huntingdonshire, in the county of Cambridgeshire by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
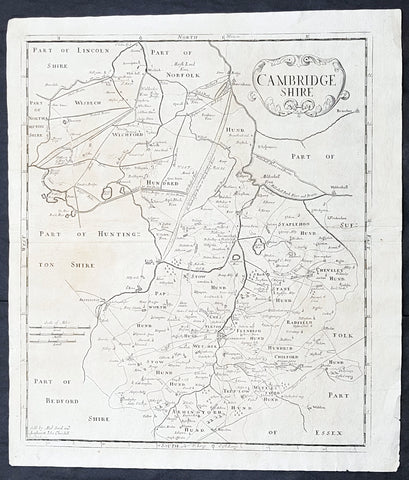
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of the English County of Cambridgeshire
- Title : Cambridgeshire...Sold by Abel Swal and Awsham& John Churchill Sutton Nicholls sculp.
- Size: 16 1/4in x 15in (460mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 40181
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the English county of Cambridgeshire by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16 1/4in x 15in (460mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 14 1/2in (450mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
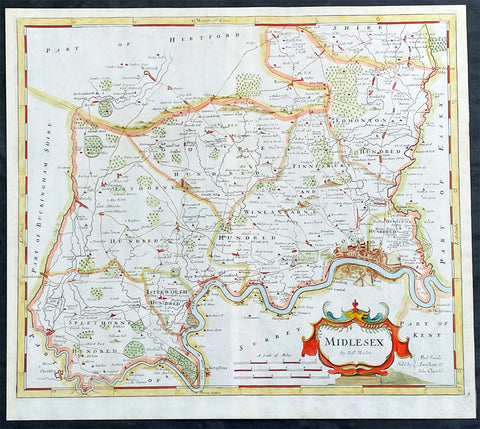
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of The English County of Middlesex, London
Antique Map
- Title : Midlesex
- Date : 1722
- Size: 17 1/2in x 15 1/2in (445mm x 395mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35603
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the county of Middlesex and London by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 15 1/2in (445mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15 1/2in (445mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
These maps are the first county maps to show roads (based on Ogilby’s road maps) and show three scales representing great, middle and small miles as different scales were used in different parts of the country. Morden was employed to replace the outdated maps by Saxton, engraved by Kip and Hole. He based his maps on manuscript sources plus the surveys of Ogilby and Morgan, Seller, Palmer and the coastal charts of Captain Grenville Collins. One innovation was the showing of longitudes measured from the meridian of St. Paul's Cathedral given in the form of time in minutes at the top of the map in Roman numerals and at the bottom in degrees. This was done to clarify local times that were taken from the sun as there was no national standard time. Gibson said:' Where actual Surveys could be had, they were purchased at any rate; and for the rest, one of the best Copies extanct was sent to some of the most knowing Gentlemen in each County; with a request to supply the defects, rectified the positions, and correct the false spellings. And that nothing might be wanting to render them as complete and accurate as might be, this whole business was commited to Mr Robert Morden, a person of know abilities in these matters'..from the Preface of the Britannia.
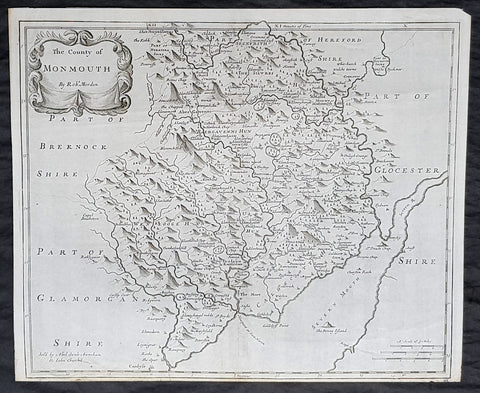
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of the Welsh County of Monmouth
- Title : The county of Monmouth by Robt. Morden...Sold by Abel Swale Awsham & John Churchill
- Size: 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 70317
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Welsh county of Monmouth by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
William Camden 1551 – 1623 was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and herald, best known as author of Britannia, the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Annales, the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.
In 1577, with the encouragement of Abraham Ortelius, Camden began his great work Britannia, a topographical and historical survey of all of Great Britain and Ireland. His stated intention was to restore antiquity to Britaine, and Britain to his antiquity. The first edition, written in Latin, was published in 1586. It proved very popular, and ran through five further editions, of 1587, 1590, 1594, 1600 and 1607, each greatly enlarged from its predecessor in both textual content and illustrations. The 1607 edition included for the first time a full set of English county maps, based on the surveys of Christopher Saxton and John Norden, and engraved by William Kip and William Hole (who also engraved the fine frontispiece). The first English language edition, translated by Philemon Holland, appeared in 1610, again with some additional content supplied by Camden.
Britannia is a county-by-county description of Great Britain and Ireland. It is a work of chorography: a study that relates landscape, geography, antiquarianism, and history. Rather than write a history, Camden wanted to describe in detail the Great Britain of the present, and to show how the traces of the past could be discerned in the existing landscape. By this method, he produced the first coherent picture of Roman Britain.
He continued to collect materials and to revise and expand Britannia throughout his life. He drew on the published and unpublished work of John Leland and William Lambarde, among others, and received the assistance of a large network of correspondents with similar interests. He also travelled throughout Great Britain to view documents, sites, and artefacts for himself: he is known to have visited East Anglia in 1578, Yorkshire and Lancashire in 1582, Devon in 1589, Wales in 1590, Salisbury, Wells and Oxford in 1596, and Carlisle and Hadrians Wall in 1599. His fieldwork and firsthand research set new standards for the time. He even learned Welsh and Old English for the task: his tutor in Old English was Laurence Nowell.
In 1593 Camden became headmaster of Westminster School. He held the post for four years, but left when he was appointed Clarenceux King of Arms. By this time, largely because of the Britannias reputation, he was a well-known and revered figure, and the appointment was meant to free him from the labour of teaching and to facilitate his research. The College of Arms at that time was not only a centre of genealogical and heraldic study, but also a centre of antiquarian study. The appointment, however, roused the jealousy of Ralph Brooke, York Herald, who, in retaliation, published an attack on Britannia, charging Camden with inaccuracy and plagiarism. Camden successfully defended himself against the charges in subsequent editions of the work.
Britannia was recognised as an important work of Renaissance scholarship, not only in England, but across the European Republic of Letters. Camden considered having the 1586 Britannia printed in the Low Countries, and although that did not happen, the third edition of 1590, in addition to its London printing, was also published the same year in Frankfurt, and reprinted there in 1616. In 1612 parts were condemned by the Spanish Inquisition. An abridgement was published in Amsterdam in 1617 and reprinted in 1639; and versions of the text were also included in Joan Blaeus Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (published in Amsterdam in 1645) and in Jan Janssoniuss Novus Atlas (again published in Amsterdam, in 1646)
1723 William Dampier 2 Volumes of World Voyages to America Australia Asia - 20 x Maps & Plates
Antique Map
-
Title : Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l on decrite en particular l Isthme de l Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales...1723
(New Voyage around the world. In which are described in particular the Istmus of America, several Coasts & Islands of the West Indies, the Islands of Cape Verde, the passage through the Land of Fuego, the Southern Coasts of Chili, Peru, & Mexico. . - Size: 8vo
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1723
- Ref #: 93005
Description:
French edition of William Dampier's account of his voyages around the World, in 2 volumes, especially to the South Seas in the years 1683 to 1691. Dampier first sailed to Sierra Leone and from there to the Falkland Islands, Cape Horn, Peru, Guatemala, Mexico, Philippines, Vietnam, China, Indonesia and onto New Guinea. He then went ashore in northern Western Australia, in the Broome region, the region later named after him and then sailed onto Sumatra, the Cape of Good Hope and back to Europe.
Although John Brooke was probably shipwrecked on the Australian coast in 1621, without knowing where exactly he was, Dampier became the first Englishman to set foot in Australia, in the Broome NW region. Even though Dampier spent a good deal of his time as a Buccaneer, he wrote these accounts of his adventures without sensation, concentrating on the hydrographic, geographic and scientific details. This helped him establish his legitimacy, bringing immediate academic acclaim rather than condemnation as a pirate.
Dampier was first person to circumnavigate the world three times between 1679 & 1711. He has also been described as Australias first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the British Admiralty with his book, A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, but was court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage, he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crew mate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Lord Nelson, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace.
These two leather bound Volumes, contain 20 maps & plates (some folding) and was published in Amsterdam by David Paul Marret in 1723 (dated)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 8vo
Plate size: - 8vo
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see below for condition report
Plate area: - Please see below for condition report
Verso: - Please see below for condition report
Background:
The two volumes contain the following titles with 20 maps & plates.
Volume 1.
1. Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l\'on decrite en particular l\'Isthme de l\'Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales, les Isles du Cap Verd, le passage par la Terre del Fuego, les côtes meridionales du Chili, du Perou & du Mexique; l\'Isle de Guam, Mindanao, & des autres Philippines, les isles orientales qui sont prés de Cambodie; de la Chine; Formosa; Luçon, Celebes, &c., la Nouvelle Hollande, les Isles de Sumatra, de Nicobar & de Sainte Helene & le Cap de Bonne Esperance...Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement, de leur negoce, &c....1723
This volume refers to Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa.
Contains Title page, 8 maps & plates total of 340 pages.
a) Mappe-Monde - World map with Dampiers tracks.
b) Maps of the Isthmus of Panama and Central America
c) Print of Natives gathering fruit
d) Print of Dampier loading Gold from the New World
e) Voyage au tour du Monde title page
f) Map of Mexico & southern North America
g) Print of a battle in the East indies
h) Print of a coconut palm in East Indies
2. Suite du Voyage Autour du Monde... Avec un Traite Des Vents qui regnent dans toute..LA ZONE TORRIDE Enrichi de Cartes & de Figures..1723
This volume refers to the continuation of Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa along with a description of global winds and tides.
Contains title page along with 6 maps & plates, 227 pages.
a) Engraved Voyage au Tour Du Monde
b) Print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
c) View of Manila
d) 2nd print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
e) Map of the Philippines islands of Banshee
f) Map of Pulocondor, Malayia
g) Print of Dampiers ship and compass rose
3. Traits des Vents Aliisez ou Reglez des Vents Frais ...1715
This volume refers again to globe winds & tides.
Contains title page 2 maps & 148 pages
a) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
b) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
Volume 2.
1. Voyage Autour Du Monde... Contenant une Description d\'Achin,
Ville de Sumatra, du Royaume de Tonquin & autres Places des Indes,
& de la Baye de Campeche. Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs
habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement,
de leur negoce, &c...1723
This volume refers to the continuation of Dampiers travels in East Indies, SE Asia & Mexico
Contains title page, 4 maps & plates, 264 pages.
a) Royalty in Vietnam
b) Map of central & north America
b) Print of Vietnam
c) Map of Australia & East Indies
2. Voyages de Guillaume Dampier a la Baye de Campeche...1714
This volume refers to Dampiers travel to Campeche, Mexico.
Contains title page and 197 pages.
Condition Report: Two volumes bound in full leather with five raised bands to spines, and title label. Couple of minor chips to top of both spines. The leather is scuffed and little pitted/worn (see photos). Internally there are a couple of small chips to inner edges of front and rear end-papers. Inscription to front end-papers (Gift of W. Wood 1745) and bookplate to inside front board (Lord Sandys). The title page of volume III and following four or so leaves have damp staining, and there is light damp staining throughout Volume I & II. The damp staining has caused the leaves to become softer and little chipped, with some nicks/tears and chips. There is a tear/crease to top inner edge and chip to bottom corner of title page of volume I. Scattered pale foxing/browning. Several of the plates have occasional creases. Four leaves of volume III are gently detaching and two leaves of volume I are missing. A few leaves are a little faded. Overall VG, in readable with firm binding.
Dampier, William 1651 - 1715
Dampier was an English explorer, navigator & buccaneer who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australias first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the Admiralty with his book A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, before being court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crewmate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Horatio Nelson, Charles Darwin.
In 1679, Dampier joined the crew of the buccaneer Captain Bartholomew Sharp on the Spanish Main of Central America, twice visiting the Bay of Campeche, or Campeachy as it was then known, on the north coast of Mexico. This led to his first circumnavigation, during which he accompanied a raid across the Isthmus of Darién in Panama and took part in the capture of Spanish ships on the Pacific coast of that isthmus. The pirates then raided Spanish settlements in Peru before returning to the Caribbean.
Dampier made his way to Virginia, where in 1683 he was engaged by the privateer John Cooke. Cooke entered the Pacific via Cape Horn and spent a year raiding Spanish possessions in Peru, the Galápagos Islands, and Mexico. This expedition collected buccaneers and ships as it went along, at one time having a fleet of ten vessels. Cooke died in Mexico, and a new leader, Edward Davis, was elected captain by the crew.
Dampier transferred to the privateer Charles Swans ship, Cygnet, and on 31 March 1686 they set out across the Pacific to raid the East Indies, calling at Guam and Mindanao. Spanish witnesses saw the predominantly English crew as not only pirates and heretics but also cannibals. Leaving Swan and 36 others behind on Mindanao, the rest of the privateers sailed on to Manila, Poulo Condor, China, the Spice Islands, and New Holland. Contrary to Dampiers later claim that he had not actively participated in actual piratical attacks during this voyage, he was in fact selected in 1687 to command one of the Spanish ships captured by Cygnets crew off Manila.
On 5 January 1688, Cygnet anchored two miles from shore in 29 fathoms on the northwest coast of Australia, near King Sound. Dampier and his ship remained there until March 12, and while the ship was being careened Dampier made notes on the fauna and flora and the indigenous peoples he found there. Among his fellows were a significant number of Spanish sailors, most notably Alonso Ramírez, a native of San Juan, Puerto Rico Later that year, by agreement, Dampier and two shipmates were marooned on one of the Nicobar Islands. They obtained a small canoe which they modified after first capsizing and then, after surviving a great storm at sea, called at Acheen (Aceh) in Sumatra.
Dampier returned to England in 1691 via the Cape of Good Hope, penniless but in possession of his journals. He also had as a source of income a slave known as Prince Jeoly (or Giolo), from Miangas (now Indonesia), who became famous for his tattoos (or paintings as they were known at the time). Dampier exhibited Jeoly in London, thereby also generating publicity for a book based on his diaries.
The publication of the book, A New Voyage Round the World, in 1697 was a popular sensation, creating interest at the Admiralty. In 1699, Dampier was given command of the 26-gun warship HMS Roebuck, with a commission from King William III (who had ruled jointly with Queen Mary II until her death in 1694). His mission was to explore the east coast of New Holland, the name given by the Dutch to what is now Australia, and Dampiers intention was to travel there via Cape Horn.
The expedition set out on 14 January 1699, too late in the season to attempt the Horn, so it headed to New Holland via the Cape of Good Hope instead. Following the Dutch route to the Indies, Dampier passed between Dirk Hartog Island and the Western Australian mainland into what he called Shark Bay on 6 August 1699. He landed and began producing the first known detailed record of Australian flora and fauna. The botanical drawings that were made are believed to be by his clerk, James Brand. Dampier then followed the coast north-east, reaching the Dampier Archipelago and Lagrange Bay, just south of what is now called Roebuck Bay, all the while recording and collecting specimens, including many shells. From there he bore northward for Timor. Then he sailed east and on 3 December 1699 rounded New Guinea, which he passed to the north. He traced the south-eastern coasts of New Hanover, New Ireland and New Britain, charting the Dampier Strait between these islands (now the Bismarck Archipelago) and New Guinea. En route, he paused to collect specimens such as giant clams.
By this time, Roebuck was in such bad condition that Dampier was forced to abandon his plan to examine the east coast of New Holland while less than a hundred miles from it. In danger of sinking, he attempted to make the return voyage to England, but the ship foundered at Ascension Island on 21 February 1701. While anchored offshore the ship began to take on more water and the carpenter could do nothing with the worm-eaten planking. As a result, the vessel had to be run aground. Dampiers crew was marooned there for five weeks before being picked up on 3 April by an East Indiaman and returned home in August 1701.
Although many papers were lost with Roebuck, Dampier was able to save some new charts of coastlines, and his record of trade winds and currents in the seas around Australia and New Guinea. He also preserved a few of his specimens. In 2001, the Roebuck wreck was located in Clarence Bay, Ascension Island, by a team from the Western Australian Maritime Museum. Because of his widespread influence, and also because so little exists that can now be linked to him, it has been argued that the remains of his ship and the objects still at the site on Ascension Island – while the property of Britain and subject to the island governments management – are actually the shared maritime heritage of those parts of the world first visited or described by him. His account of the expedition was published as A Voyage to New Holland in 1703.
The War of the Spanish Succession had broken out in 1701, and English privateers were being readied to act against French and Spanish interests. Dampier was appointed commander of the 26-gun ship St George, with a crew of 120 men. They were joined by the 16-gun Cinque Ports with 63 men, and sailed on 11 September 1703 from Kinsale, Ireland. The two ships made a storm-tossed passage round Cape Horn, arriving at the Juan Fernández Islands off the coast of Chile in February 1704. While watering and provisioning there, they sighted a heavily armed French merchantman, which they engaged in a seven-hour battle but were driven off.
Dampier succeeded in capturing a number of small Spanish ships along the coast of Peru, but released them after removing only a fraction of their cargoes because he believed they would be a hindrance to his greater designs. The greater design he had in mind was a raid on Santa María, a town on the Gulf of Panama rumoured to hold stockpiles of gold from nearby mines. When the force of seamen he led against the town met with unexpectedly strong resistance, however, he withdrew. In May 1704, Cinque Ports separated from St George and, after putting Alexander Selkirk ashore alone on an island for complaining about the vessels seaworthiness, sank off the coast of what is today Colombia. Some of its crew survived being shipwrecked but were made prisoners of the Spanish.
It was now left to St George to make an attempt on the Manila galleon, the main object of the expedition. The ship was sighted on 6 December 1704, probably Nuestra Señora del Rosario. It was caught unprepared and had not run out its guns. But while Dampier and his officers argued over the best way to mount an attack, the galleon got its guns loaded and the battle was joined. St George soon found itself out-sized by the galleons 18- and 24-pounders, and, suffering serious damage, they were forced to break off the attack.
The failure to capture the Spanish galleon completed the break-up of the expedition. Dampier, with about thirty men, stayed in St George, while the rest of the crew took a captured barque across the Pacific to Amboyna in the Dutch settlements. The undermanned and worm-damaged St George had to be abandoned on the coast of Peru. He and his remaining men embarked in a Spanish prize for the East Indies, where they were thrown into prison as pirates by their supposed allies the Dutch but later released. Now without a ship, Dampier made his way back to England at the end of 1707.
In 1708, Dampier was engaged to serve on the privateer Duke, not as captain but as sailing master. Duke beat its way into the South Pacific Ocean round Cape Horn in consort with a second ship, Duchess. Commanded by Woodes Rogers, this voyage was more successful: Selkirk was rescued on 2 February 1709, and the expedition amassed £147,975 (equivalent to £19.9 million today) worth of plundered goods. Most of that came from the capture of a Spanish galleon, Nuestra Señora de la Encarnación y Desengaño, along the coast of Mexico in December 1709.
In January 1710, Dampier crossed the Pacific in Duke, accompanied by Duchess and two prizes. They stopped at Guam before arriving in Batavia. Following a refit at Horn Island (near Batavia) and the sale of one of their prize ships, they sailed for the Cape of Good Hope where they remained for more than three months awaiting a convoy. They left the Cape in company with 25 Dutch and English ships, with Dampier now serving as sailing master of Encarnación. After a further delay at the Texel, they dropped anchor at the Thames in London on 14 October 1711.
Dampier may not have lived to receive all of his share of the expeditions gains. He died in the Parish of St Stephen Coleman Street, London. The exact date and circumstances of his death, and his final resting place, are all unknown. His will was proven on 23 March 1715, and it is generally assumed he died earlier that month, but this is not known with any certainty. (Ref Tooley M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
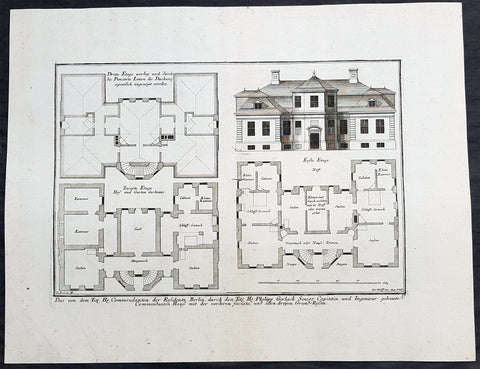
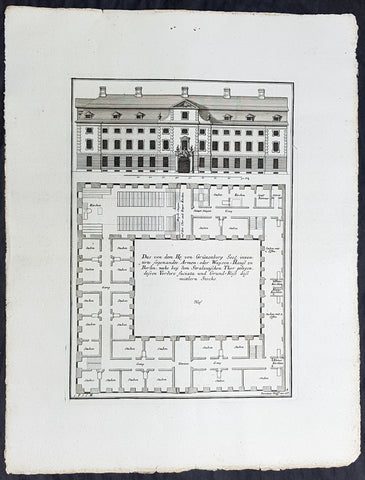
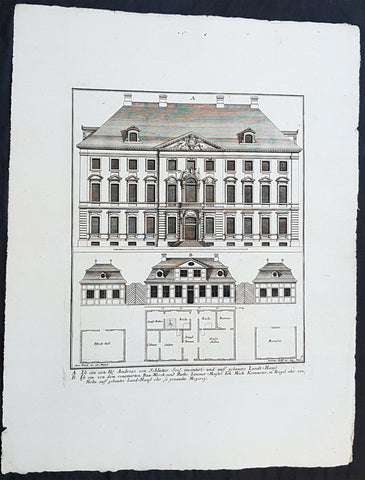
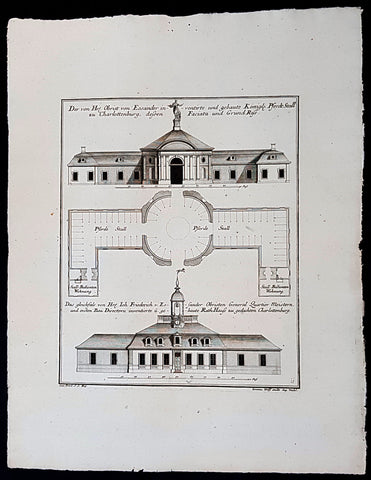
1724 Colen Campbell Antique Architect Print Garden Room Hall Barn, Downton Abbey
Antique Map
- Title : A new Garden Room at Hall Barn near Beaconsfield in the County of Bucks... Vol. 3, pl. 49.
- Ref #: 93462
- Size: 15in x 11 1/2in (380mm x 295mm)
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved of the Garden Room of Hall Barn in Beaconsfield, Buckinghamshire, England, designed by the famous Scottish architect and publisher Colen Campbell was engraved in 1724 - dated - by the Dutch engraver Henry Hulsbergh - and was published in the 1724 edition of Campbells monumental architectural publication Vitruvius Britannicus or The British Architect. London
Hall Barn was also the location used in the filming of the TV series Downton Abbey as the Loxley House.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11 1/2in (380mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Hall Barn is a historic country house located in Beaconsfield, South Bucks district, in Buckinghamshire, England.
The Hall Barn estate was bought by Anne Waller in 1624. The house was built in the late-17th century by her son Edmund Waller, a poet and Member of Parliament at various times between 1624 and 1679. His grandson added the south wing. The estate was sold by his family in 1832 to Sir Gore Ouseley, 1st Baronet, who rebuilt the southern facade and was High Sheriff of Buckinghamshire for 1835.
Edward Levy-Lawson, 1st Baron Burnham bought the estate in 1880 and made a number of renovations and improvement and the estate remains under the management of the Lawson family - Hugh Lawson, 6th Baron Burnham - in the early 21st century.
There were royal visits to the estate, including from the Duke of Cambridge in November 1902. The Princess Royal took the salute at Hall Barn in the 1940s at the Girl Guide County Rally.
During the Second World War, the house was used as a hospital supplies unit. In November 1946, the Hall Barn Estate was reported in Tatler as being the lovely home and venue for the wedding reception for extended family and friends of the newly-wed daughter of the charming Lord and Lady Burnham.
Hall Barn has been used as a filming location for various films and series. In Gosford Park (2001) the opening sequence outside Lady Trenthams home was shot there, and the temple used as the scene for lunch after the shoot. Midsomer Murders Season 7, Episode 4 (2004) Sins of Commission, prominently features the black gatehouse to Hall Barn. It featured in the series Downton Abbey as Loxley House, the home of Sir Anthony Strallan. The location was also used in the 1981 Oscar-winning film Chariots of Fire as the home of the composite character Lord Andrew Lindsay, who memorably practiced his hurdling skills on the lawn by perching filled champagne glasses on each hurdle to determine if hed touched the hurdles or not on each jump. Hall Barn was also featured in the mini-series Sense and Sensibility (2008 miniseries), and used as the location for Delaford House. Black Beauty Film (1994)
Vitruvius Britannicus or The British Architect is from one of the finest works on architecture ever produced. Colen Campbell published the work in London in 1725. The engravings from this work feature illustrations, plans, and cross sections of English country houses and parks.
Campbell was the chief architect to the Prince of Wales. His work served as a design book that led to the construction of many of Britain’s great houses. Vitruvius Britannicus established Palladian architecture as the dominant style England in the 18th century.
Vitruvius Britannicus documented the buildings of some of the greatest architects of the times including Indigo Jones, Sir Christopher Wren, and Colen Campbell himself. The work is essential to the study of 17th and 18th century design and architecture in England.
Campbell, Colen 1676 - 1729
Campbell was a pioneering Scottish architect and architectural writer, credited as a founder of the Georgian style. For most of his career, he resided in Italy and England.
A descendant of the Campbells of Cawdor Castle, he is believed to be the Colinus Campbell who graduated from the University of Edinburgh in July 1695. He initially trained as a lawyer, being admitted to the Faculty of Advocates on 29 July 1702.
He had travelled in Italy from 1695–1702 and is believed to be the Colinus Campbell who signed the visitors book at the University of Padua in 1697. He is believed to have trained in and studied architecture under James Smith, this belief is strengthened by Campbell owning several drawings of buildings designed by Smith.
His major published work, Vitruvius Britannicus, or the British Architect... appeared in three volumes between 1715 and 1725. (Further volumes using the successful title were assembled by Woolfe and Gandon, and published in 1767 and 1771, see below.) Vitruvius Britannicus was the first architectural work to originate in England since John Shutes Elizabethan First Groundes. In the empirical vein, it was not a treatise but basically a catalogue of design, containing engravings of English buildings by Inigo Jones and Sir Christopher Wren, as well as Campbell himself and other prominent architects of the era.
In the introduction that he appended and in the brief descriptions, Campbell belaboured the excesses of Baroque style and declared British independence from foreigners while he dedicated the volume to Hanoverian George I. The third volume (1725) has several grand layouts of gardens and parks, with straight allées, for courts and patterned parterres and radiating rides through wooded plantations, in a Baroque manner that was rapidly becoming old-fashioned.
Buildings were shown in plan, section and elevation, but also some were in a birds-eye perspective. The drawings and designs contained in the book were under way before Campbell was drawn into the speculative scheme. The success of the volumes was instrumental in popularising neo-Palladian Architecture in Great Britain and America during the 18th century. For example, Plate 16 of Vitruvius Britannicus, a rendering of Somerset House in London, was an inspiration for American architect Peter Harrison when he designed the Brick Market in Newport, Rhode Island, in 1761.
Campbell was influenced as a young man by James Smith (ca 1645 – 1731), the pre-eminent Scots architect of his day, and an early neo-Palladian whom Campbell called the most experienced architect of Scotland (Vitruvius Britannicus, ii).
The somewhat promotional volume, with its excellently rendered engravings, came at a propitious moment at the beginning of a boom in country house and villa building among the Whig oligarchy. Campbell was quickly taken up by Lord Burlington, who replaced James Gibbs with Campbell at Burlington House in London and set out to place himself at the center of English neo-Palladian architecture. In 1718, Campbell was appointed deputy to the amateur gentleman who had replaced Wren as Surveyor General of the Royal Board of Works, an appointment that Burlington is certain to have pressed, but a short-lived one. When Benson, the new Surveyor was turned out of office, Campbell went with him.
Later Volumes There are some later volumes also published under the name Vitruvius Brittanicus, but they are not connected to Colen Campbells work, issued between 1715-1725. In 1739 a volume was issued by Badeslade and Rocque, described as Volume 4. However, this had little in common with Campbell, comprising mainly topographical perspective views of houses (54 plates). Between 1765–1771, Woolfe and Gandon published their Volumes 4 & 5 (with 79 plus 75 plates). They discounted Badeslades volume, believing their work to be a more correct continuation of Campbell, hence numbering it as Volume 4. The plates are indeed mostly plans and elevations of buildings largely in the Palladian style, most dating from after 1750. The various Volumes are fully described in Harris.
- Wanstead House, Essex: ca 1713/4 – 20 (illustrated left) In the first volume of Vitruvius Britannicus the most influential designs were two alternatives for a palatial Wanstead House, Essex, for the merchant-banker Sir Richard Child, of which the second design was already under way when the volume was published. (Campbell claimed that Wanstead House had Great Britains first classical portico, but this accolade probably belongs to The Vyne, Hampshire.
- Burlington House, London 1717. Remodelled the front and provided an entrance gateway for Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl of Burlington (Remodelled in 1868 and the gateway demolished.
- Stourhead, Wiltshire, 1721–24, as a seat for the London-based banker Henry Hoare. Wings were added in the later 18th century, and Campbells portico was not executed (though to his design) until 1841. The famous landscape garden round a lake, somewhat apart from the house, was developed after Campbells death, by Henry Flitcroft.
- Pembroke House, Whitehall, London, for Henry Herbert, 9th Earl of Pembroke, 1723, a London house in a prominent location for the heir of Jones Wilton House. It was rebuilt in 1757 and demolished in 1913. Lord Herbert (as he then was) was inspired by it to design the similar Marble Hill at Twickenham for Henrietta Howard, Countess of Suffolk, the mistress of the future George II. (Marble Hill was a 5-bay palladian villa with central pediment, raised on a high basement, with clumped screens of trees and formal turfed terraces descending to the Thames, illustrated right, that manifest the earliest stages of the English landscape garden.
- Houghton Hall, Norfolk, begun 1722, for Sir Robert Walpole, the Whig prime minister. Here Campbell was replaced by Gibbs, who capped the end pavilions with octagonal domes, and by William Kent, who designed the interiors.
- Mereworth Castle, Kent 1722 – 25: Campbells most overtly palladian design, based on Villa La Rotonda, capped with a dome with no drum, through which 24 chimney flues pass to the lantern.
- Waverley Abbey House, Surrey ca 1723–25 for John Aislabie (largely altered)
Title page, Vitruvius Britannicus; or, The British architect, containing the plans, elevations, and sections of the regular buildings, both publick and private in Great Britain, with variety of new designs, written by Colen Campbell
Nos 76 and 78 Brook Street, London W1, 1725 – 26. No. 76, which survives, was Campbells own house, the designs for its interiors published in his Five Orders of architecture, (1729). It carries a blue plaque commemorating him.
Compton Place, Eastbourne, Sussex, 1726 onwards, south front and extensive internal rebuilding for Sir Spencer Compton
Plumptre House, Nottingham 1724 - 30. Remodelled for John Plumptre MP.
Shawfield Mansion, Glasgow (1712) demolished 1792
Wanstead House, Essex (1714–15) demolished 1822
Hedworth House, Chester-le-Street (1726)
Hotham House, Beverley (1716–17) demolished c.1766
Burlington House, London, south front, and west wing (1717) subsequently extended and several occasions
Burlington (Ten Acre Close) Estate, London, layout (1717–18)
Burlington House, Great Gate and Street Wall (1718)
Rolls House, Chancery Lane, London (1718), demolished 1895–96
Ebberston Lodge, Ebberston, Yorkshire, including cascade (1718)
34 Great Burlington Street, London (1718–19)
33 Great Burlington Street, London (1719–20)
32 Great Burlington Street, London (c.1720); this was Campbells own house
31 Great Burlington Street, London (1719–24) rebuilt
Burlington Girls Charity School, Boyle Street, London (1719–21)
Wimbledon Manor House, Surrey, for Sir Theodore Janssen (1720); completion uncertain
Newby Park, (now Baldersby Park), near Topcliffe, Yorkshire (1720–21)
Houghton Hall, Norfolk; one of several architects to work on the building (1721–22)
Stourhead, Wiltshire, the portico part of Campbells design was only added in 1840 (1721–24); interiors destroyed by fire 1902
Mereworth Castle, Kent (1722–23)
Pembroke Lodge, Whitehall, London; executed Henry Herbert, 9th Earl of Pembrokes design (c.1724), demolished 1756
Plumptre House, Nottingham (1724)
Hall Barn, Buckinghamshire, garden buildings: Great Room (only partially survives), Temple of Venus, Obelisk & Doric Pavilion (1724)
Waverley Manor, Surrey (c.1725), extended 1770, damaged by fire and rebuilt 1833
Greenwich Hospital, Greenwich, London; additions to Queen Mary block and Queen Anne block (1726–29)
Compton Place, Eastbourne, remodelled house (1726–29)
76 Brook Street, London, internal alterations (c.1726); became Campbells new home
Hackney House, Hackney, London (c.1727), demolished before 1842
Althorp, Northamptonshire, new stables, loggia gate (c.1729–33)
Studley Royal Park, Yorkshire, the stables (c.1729) built after his death by Roger Morris
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print a View of Carlisle Church in Cumbria, England
- Title : The Cathedral Church of Carlile
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40406
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description: This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
Background: Carlisle Cathedral bears the scars of 900 years spent in this most tumultuous of regions. The scarred exterior and tower, has the effect of making the cathedral look more like a Border castle than a church! The cathedral suffered badly in the Civil War, when Parliamentary troops under General Leslie almost destroyed the nave, leaving only two bays standing.
The original nave was built by secular canons in 1092 as a collegiate church. That early church was built, but by 1123 the Augustinian order had taken over. The choir aisles are late 13th century, but the body of the choir was not completed until a century later.
The transepts and tower date from the 15th century. The glories of Carlisle are the east window, one of the best examples of decorated tracery anywhere, and the delicately carved capitals in the choir, depicting the seasons. The east window is believed to be the work of Ivo de Ragheton, who was also responsible for the west front of York Minster.
The barrel-vaulted choir ceiling is painted in vivid blue with gold trim. Medieval paintings in the north and south aisles and the choir represent the lives of the Apostles and saints Anthony and Cuthbert. The choir stalls and misericords are decorated with wonderful carvings dating from the early 15th century.
This is a finely engraved print being testimony to the beautiful and detailed work produced by Kip whose eye for detail was one of the most acknowledged of his day.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Early
Colours used: - Yellow, brown, green, red
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 19 1/2in (610mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 470mm)
Margins: - min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print of Bath Cathedral, Somerset, England
- Title : The Cathedral Church of Bath
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40401
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
Background:
Bath Abbey stands at the heart of the city of Bath; during the past twelve and a half centuries, three different churches have occupied this site:
An Anglo-Saxon Abbey Church dating from 757, pulled down by the Norman conquerors of England soon after 1066.
A massive Norman cathedral begun about 1090. It was larger than the monastery could afford to maintain and by the end of the 15th century was in ruins.
The present Abbey church founded in 1499, ruined after the dissolution of the monasteries in 1539 by order of Henry VIII.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
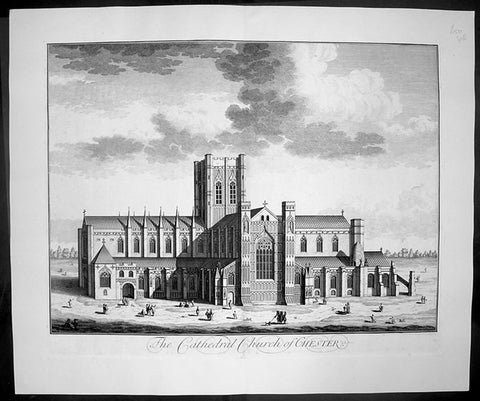
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print of Chester Cathedral Church, Cheshire, England
- Title : The Cathedral Church of Chester
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40412
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description: This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
Background:
Standing on the site of a 10th century Saxon church, the present cathedral at Chester dates from the mid 13th century. Dedicated to St Werburgh, this Christian church was transformed into a Benedictine Abbey in 1092, colonised by a small group of monks from Normandy. Building of the new abbey church began immediately and took the best part of 150 years to complete but little evidence of the first church remains. The traditional sturdy Norman architecture was eventually replaced over the next two centuries by a more elegant Gothic style. Henry VIII dissolved the monastery in 1540 just as the monks of St Werburgh's Abbey were beginning to enjoy their new surroundings. A year later the abbey was given back as a cathedral, the last abbot of St Werburgh's becoming the first Dean of Chester Cathedral.
Over the next two hundred years the cathedral slipped into a bad state of disrepair but was eventually saved from total collapse by the efforts of Sir George Gilbert Scott. His 19th century restoration of Chester Cathedral, both externally and internally, not only put in place essential repairs but also enhanced the appearance of the great church immensely. Most of the stained glass comes from this period and highlights the abbey's dedication to St Werburgh, as well as the long history of the cathedral. On the northern aisle of the nave, at the side of one of the large windows, sits the 'Chester Imp'. A charming little figure in chains, carved by one of the medieval monks, to protect the church from evil spirits.
Most medieval cathedrals have beautifully carved stalls in the quire but the quality of oak carving at Chester Cathedral is quite exceptional. Each stall is topped with an elaborately carved canopy set above a row of small corbels, and below each seat a magnificently carved misericord. This area of the church is so richly carved with such a diverse array of religious artefacts, animals, birds and grotesque figures that it is quite overwhelming.
Apart from the main church many of the monastic buildings from the ancient Benedictine Abbey have been remarkably preserved. The original cloisters, although largely rebuilt during the first half of the 16th century and subsequently restored at the beginning of the 20th century, are a constant reminder of the important part they played in monastic life. All the bays of the undercroft, containing some wonderful vaulting, have been utilised to provide an exhibition centre, gift shop and workshop. The monks' dining room or refectory is still used regularly, as is the superb Chapter House. .
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print of Gloucester Cathedral, England
- Title : The South Prospect of The Cathedral of St Peters Glocester
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40415
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description: This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print of Rochester Cathedral, Kent, England
- Title : The North Prospect of the Cathedral Church of Rochester
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40405
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description: This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
Background:
Being the second oldest cathedral foundation in England, Rochester Cathedrals history goes back to AD604 when Augustine sent Bishop Justus to establish the house founded by King Ethelbert of Kent. Following several invasions by the Danes, the church was in a state of devastation by the time Bishop Gundulf was consecrated in 1077 but immediately he began a major building operation, and introduced a community of Benedictine monks in 1080.
The church suffered misfortune again in the mid 12th century with two serious fires, resulting in a further rebuilding programme. Since that time there has been continuous remodelling, refurbishments and restorations, mainly due to other historical events when the cathedral sustained damage. As a consequence of its very chequered history, Rochester Cathedral displays the varied building styles of each period, from the functional austerity of Gundulf's original structure, through the Romanesque, Gothic and Early English architectural periods, and continuing with renovation and restoration well into the 20th century following war damage.
The sturdy, squat Norman nave contrasts dramatically with the tall, narrow Gothic arches of the crossing. A superbly carved stone archway of the Decorated period (c1345), now enhanced with a solid oak door, leads to the chapter room and is a magnificent feat of craftsmanship. Quite unusually, the Lady Chapel is sited between the nave and the south transept as monastic outbuildings occupied the traditional location at the eastern end of the church when the chapel was added in the late 15th century. Beneath the quire transept is a beautifully preserved and vaulted crypt, with two bays surviving from the original Norman construction. There are also many fragments of medieval ceiling paintings to be found in this lower level sanctuary.
Though one of the smaller Norman cathedrals, Rochester was an important centre for pilgrimage during the 13th century, and even today attracts many visitors who are keen to learn more about its fascinating history. From a photographic perspective, a wonderful view of Rochester cathedral can be seen from the top of Rochester Castle, immediately opposite. We have visited both the Rochester Cathedral and Castle on many occasions, and still manage to uncover more information, or something interesting that we had previously overlooked. Earlier this year, we ventured for the first time into the cloister garth, discovering a substantial section of the ruined Chapter House. On the south side, the entrance arch to the monk's refectory survives and, looking behind it, the 13th century lavatorium and towel recess is still visible.
Johannes Kip was a draughtsman and engraver, who worked first in his native Amsterdam before moving to London at the end of the seventeenth century. He did portraits, views, and book illustrations. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print of St Marys Church The Strand London England
- Title : Admodum Reverendis Amplissimis...Templi St Maria in Vico dicto The Strand
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40399
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description: This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
Background:
The parish of St Mary le Strand may lay a good claim to being one of the oldest parishes in London. It stands dominating a roadway which since prehistory has been the main artery to the west from the City of London. In early Saxon times the Strand area was the very heart of London, for it seems that the City was effectively abandoned by the newly-arrived settlers. The Saxons predominantly inhabited "Lundenwic", an area stretching from Fleet Street to Whitehall and from the Thames to Covent Garden from the sixth to the ninth centuries. Christianity came to this settlement with St Mellitus and his followers in 604, and, despite their brief expulsion in the 620s, became firmly established. We do not know if any of the existing churches in the area date back that far but some, such as St Clement Danes, are known to have existed in later Saxon times.
There is no record of when St Mary le Strand was founded, but the first church, which was dedicated to the Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary, stood just south of the present church on a site now covered by Somerset House. Throughout the Middle Ages, the Bishops of Worcester were the Patrons of the parish and had their London residence on an adjoining site. For throughout the period from the Norman Conquest to the Reformation, the Strand was mainly the home of bishops and princes. Within the parish were the "inns" - large town houses with chapels, stables and accommodation for a large retinue - of the Bishops of Worcester, Llandaff, Coventry and Lichfield. A large part of the parish was absorbed by the building of a great house, the Palace of the Savoy, by Count Peter of Savoy, the uncle of Henry III, in the 1240s. A century later this became the home of John of Gaunt, Earl of Lancaster, and the palace became a centre of culture; among its residents was Geoffrey Chaucer, who was married in the palace chapel. Gaunt's unpopularity, as the king's chief minister, caused the palace to be burned in the Peasant's Revolt. Despite its long absence, the fame of the palace has lasted in the area and was recreated in the nineteenth century by the Savoy Hotel and Theatre.
The site where the present church stands was occupied in medieval times by Strand Cross. The origins of this are unclear. It was not a cross erected in memory of Queen Eleanor - as was Charing Cross - but seems to have dated back at least to Norman times. Perhaps it began as a market cross; by the early fourteenth century it had been rebuilt in a lavish manner, almost certainly following the design of the Eleanor Crosses. Strand Cross was a famous site and it is recorded that in the thirteenth century the local magistrates held their assizes in front of it.
Until the sixteenth century, the Strand was no more than a line of Bishops' palaces on the south side of the roadway stretching all the way to Whitehall. On the north side stood a wall which bounded the Convent - later Covent - Garden, while the churches further away, St Martin's and St Giles, stood "in-the-fields". All this was to change with the Reformation. The bishops' inns around the church were seized by Edward Lord Protector who set about building himself a renaissance palace in what was then the most fashionable part of town. Even with the extensive site that he had now obtained, further space was needed and towards the end of 1548 the Lord Protector's workmen fell upon St Mary's church and demolished it to provide stone for the new palace. Further stone was provided by the demolition of a cloister at St Paul's Cathedral known as Pardon Churchyard and the greater part of the Priory of St John at Clerkenwell. Even by the standards of the time, the demolition of so much sacred property was an outrage. Somerset was never to enjoy living in his new palace; just as it was nearing completion he was overthrown by his political enemies and executed at Tower Hill in 1551.
It is said that Somerset had intended to build a new parish church. If so, all thought of it passed away with his fall. Initially, the parishioners scattered but within a short time we find them gathered in the chapel of St John the Baptist in the Savoy. Here they would remain for the next 175 years. Now known at "St Mary le Savoy", the parishioners chose and paid for their own ministers. The most famous of these was Thomas Fuller, the church historian, who was appointed in 1642, fled during the Civil War and was restored to his living in 1660.
Following the execution of Somerset, his palace had passed to the possession of the Crown. Elizabeth I occasionally lodged there and it was from Somerset House that she set off to give thanks after the defeat of the Armada. Under the Stuarts, extensive improvements were made to the palace, the most impressive being the lavish Roman Catholic chapel built by Charles I's queen, Henrietta Maria.
The roadway in front of Somerset House, where Strand Cross had stood and where the present church was later to stand, was occupied in the early seventeenth century by a windmill used to pump water. In 1634 the first Hackney Carriage stand in England was established here by one Captain Bailey. Here also a maypole was erected which became the most famous maypole in London. Demolished by the Puritans, a new maypole was erected in 1661. Parts of this maypole remained until 1717, when they were removed and presented to Sir Isaac Newton as the base for a telescope.
In 1711, an Act of Parliament was passed for building 50 New Churches in the fast expanding suburbs of London. These were the so-called "Queen Ann Churches"; among them are Hawksmoor's Christ Church Spitalfields, St Anne's Limehouse, and St George's-in-the-East, Archer's St Paul's Depftord and James' St George's, Hanover Square. St Mary le Strand was quick to apply for a church to replace their demolished one and, as the site on the Strand was so prominent, the Commissioners for building the New Churches decided to make the Strand church the most lavish of the churches. Initially, it was intended that there should not be a spire but that a column celebrating the building of the New Churches should stand directly in front of the church.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print of St Marys Church, The Strand, London
- Title : The South West Prospect of St Mary's Church in ye Strand
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40400
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description: This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
Background:
The parish of St Mary le Strand may lay a good claim to being one of the oldest parishes in London. It stands dominating a roadway which since prehistory has been the main artery to the west from the City of London. In early Saxon times the Strand area was the very heart of London, for it seems that the City was effectively abandoned by the newly-arrived settlers. The Saxons predominantly inhabited "Lundenwic", an area stretching from Fleet Street to Whitehall and from the Thames to Covent Garden from the sixth to the ninth centuries. Christianity came to this settlement with St Mellitus and his followers in 604, and, despite their brief expulsion in the 620s, became firmly established. We do not know if any of the existing churches in the area date back that far but some, such as St Clement Danes, are known to have existed in later Saxon times.
There is no record of when St Mary le Strand was founded, but the first church, which was dedicated to the Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary, stood just south of the present church on a site now covered by Somerset House. Throughout the Middle Ages, the Bishops of Worcester were the Patrons of the parish and had their London residence on an adjoining site. For throughout the period from the Norman Conquest to the Reformation, the Strand was mainly the home of bishops and princes. Within the parish were the "inns" - large town houses with chapels, stables and accommodation for a large retinue - of the Bishops of Worcester, Llandaff, Coventry and Lichfield. A large part of the parish was absorbed by the building of a great house, the Palace of the Savoy, by Count Peter of Savoy, the uncle of Henry III, in the 1240s. A century later this became the home of John of Gaunt, Earl of Lancaster, and the palace became a centre of culture; among its residents was Geoffrey Chaucer, who was married in the palace chapel. Gaunt's unpopularity, as the king's chief minister, caused the palace to be burned in the Peasant's Revolt. Despite its long absence, the fame of the palace has lasted in the area and was recreated in the nineteenth century by the Savoy Hotel and Theatre.
The site where the present church stands was occupied in medieval times by Strand Cross. The origins of this are unclear. It was not a cross erected in memory of Queen Eleanor - as was Charing Cross - but seems to have dated back at least to Norman times. Perhaps it began as a market cross; by the early fourteenth century it had been rebuilt in a lavish manner, almost certainly following the design of the Eleanor Crosses. Strand Cross was a famous site and it is recorded that in the thirteenth century the local magistrates held their assizes in front of it.
Until the sixteenth century, the Strand was no more than a line of Bishops' palaces on the south side of the roadway stretching all the way to Whitehall. On the north side stood a wall which bounded the Convent - later Covent - Garden, while the churches further away, St Martin's and St Giles, stood "in-the-fields". All this was to change with the Reformation. The bishops' inns around the church were seized by Edward Lord Protector who set about building himself a renaissance palace in what was then the most fashionable part of town. Even with the extensive site that he had now obtained, further space was needed and towards the end of 1548 the Lord Protector's workmen fell upon St Mary's church and demolished it to provide stone for the new palace. Further stone was provided by the demolition of a cloister at St Paul's Cathedral known as Pardon Churchyard and the greater part of the Priory of St John at Clerkenwell. Even by the standards of the time, the demolition of so much sacred property was an outrage. Somerset was never to enjoy living in his new palace; just as it was nearing completion he was overthrown by his political enemies and executed at Tower Hill in 1551.
It is said that Somerset had intended to build a new parish church. If so, all thought of it passed away with his fall. Initially, the parishioners scattered but within a short time we find them gathered in the chapel of St John the Baptist in the Savoy. Here they would remain for the next 175 years. Now known at "St Mary le Savoy", the parishioners chose and paid for their own ministers. The most famous of these was Thomas Fuller, the church historian, who was appointed in 1642, fled during the Civil War and was restored to his living in 1660.
Following the execution of Somerset, his palace had passed to the possession of the Crown. Elizabeth I occasionally lodged there and it was from Somerset House that she set off to give thanks after the defeat of the Armada. Under the Stuarts, extensive improvements were made to the palace, the most impressive being the lavish Roman Catholic chapel built by Charles I's queen, Henrietta Maria.
The roadway in front of Somerset House, where Strand Cross had stood and where the present church was later to stand, was occupied in the early seventeenth century by a windmill used to pump water. In 1634 the first Hackney Carriage stand in England was established here by one Captain Bailey. Here also a maypole was erected which became the most famous maypole in London. Demolished by the Puritans, a new maypole was erected in 1661. Parts of this maypole remained until 1717, when they were removed and presented to Sir Isaac Newton as the base for a telescope.
In 1711, an Act of Parliament was passed for building 50 New Churches in the fast expanding suburbs of London. These were the so-called "Queen Ann Churches"; among them are Hawksmoor's Christ Church Spitalfields, St Anne's Limehouse, and St George's-in-the-East, Archer's St Paul's Depftord and James' St George's, Hanover Square. St Mary le Strand was quick to apply for a church to replace their demolished one and, as the site on the Strand was so prominent, the Commissioners for building the New Churches decided to make the Strand church the most lavish of the churches. Initially, it was intended that there should not be a spire but that a column celebrating the building of the New Churches should stand directly in front of the church.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1724 Johannes Kip Large Antique Print The Holy Trinity Cathedral, Chichester, England
- Title : The Cathedral Church of the Holy Trinity in Chichester
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40411
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description: This large original copper-plate engraved antique print by Johannes (Jan) Kip, after Leonard Knyff, was published in the 1724 Joseph Smith edition of Britannia Illustrata or Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This beautifully engraved original antique print is testimony to the fine, detailed work produced by Jan Kip.
Britannia Illustrata was first issued in 1707 by David Mortier as a single volume containing 80 topographical etchings by Johannes Kip, after drawings by Leonard Knyff. Many are birds eye views of country seats, but there are also a number of interesting London views. The series was first reissued and expanded into two volumes in 1708-1713, and provided with a second French title Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne.
An expanded edition of Britannia Illustrata was re-published by Joseph Smith in 1724 under its French title, Nouveau Theatre..., containing many of the plates from the original edition by Mortier and also containing may new plates of places, churches, cathedrals and architecture of the landed gentry.
Background:
The cathedral of the Holy Trinity at Chichester was founded in 1075, after the seat of the bishop was transferred to the town from nearby Selsey. It was consecrated in 1108, but a subsequent fire created a need for substantial rebuilding, which was not completed until 1184. The cathedral was reconsecrated in 1199. This was not the last stage in its development, by a long way. Richard de la Wyche, (Saint Richard of Chichester in the Anglican Communion), who was bishop from 1245 to 1253, was buried in the cathedral, where his shrine was a place of pilgrimage, until it was ordered destroyed in 1538, during the first stages of the English Reformation. Further damage to the cathedral had been done by fire after the second consecration, and much rebuilding was carried out in the Early English style. The original wooden ceiling had burnt out, and the sublimely simple present vaulting replaced it. The spire, which was originally built in the 14th century, was of poor-quality local stone, and collapsed suddenly in 1861, miraculously without loss of life. It was immediately rebuilt, by Sir Gilbert Scott, a noted scholarly architect.
The cathedral has many other unique features. Under the floor of the nave are the remains of a Roman mosaic pavement, which can be viewed through a glass window. Also in the interior are the grave of the composer Gustav Holst and the Gothic "Arundel tomb" referred to in a famous poem by Philip Larkin.
Despite its age, the cathedral contains several modern works of art, including tapestries by John Piper and Ursula Benker-Schirmer, a window by Marc Chagall, and a sculpture by Graham Sutherland.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1724 Kip Large Folio Antique Print of Worcester Cathedral, England
- Title : The Cathedral Church of Worcester
- Date : 1724
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40407
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Description:
This finely engraved original large folio antique Cathedral print by Johannes Jan Kip, was engraved by James Collins was published in the 1724 by Joseph Smith monumental work Nouveau Theatre de la Grande Bretagne. This print also appeared in Britannia Illustrata by D. Mortier (brother of Pierre).
This is a finely engraved print being testimony to the beautiful and detailed work produced by Kip whose eye for detail was one of the most acknowledged of his day.
Background:
The history of Worcester goes back a long way. In 672, a council of the English Church was held, Worcester became the centre of five new dioceses formed. In the ninth century invasions from the Danes brought fighting to England, but Worcester being on the edge of the conflict escaped without much damage. In 983, Oswald founded a monastery at Worcester under the Benedictine rule, dedicated to St. Mary the Virgin. Wulfstan, in 1040 became a monk at Worcester and made such an impression, he became Bishop of Worcester in 1062. Wulfstan was the only Anglo-Saxon bishop to remain at his post after the Norman Conquest of 1066. In 1084, Wulfstan began rebuilding Worcester Cathedral, starting with the crypt, some of which still survives. He was canonised in 1203. Building work continued for some time, including rebuilding the two western bays of the nave in 1170 and around 1202 the central tower collapsed and there was a serious fire. In 1216, King John was buried at Worcester and he seems to have a devotion to St. Wulfstan. In 1224, Bishop William de Blois built the Lady Chapel, where he was buried when he died in 1236. In the fourteenth century the nave was completely rebuilt apart from the western bays. The central tower and the cloisters were completed built by 1374.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: -
Colours used: -
General colour appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (670mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1725 Delisle Large Antique Map The West Indies - Antilles, Guadeloupe to Granada
Antique Map
- Title : Carte Des Antilles Francois et des Isles Voisines....
- Ref #: 61038
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1725
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of The West Indian Islands of the Antilles - from Guadeloupe to Granada - by Guillaume de L'Isle was published by Covens & Mortier in 1725 .
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 18in (600mm x 460mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: This map covers the predominately French portion of the West Indies from Guadeloupe to Grenada, including the Grenadines, St. Vincent, Dominica, St. Lucia (Alouise), Barbados, Martinique, and Marie-Galante, among others.
As the title cartouche suggests, Delisle cartographically derived this map almost exclusively from a manuscript produced by Thimothee Peitit, 'Arpenteur Jure de la Martinique' (Royal Surveyor of Martinique). Petit had the challenging task of reconciling local surveys of various islands with the general geography of the West Indies. Delisle copied from Petit's manuscript almost verbatim, a fact that is poignantly illustrated in the erroneous positioning of Grenada, which is both upside-down and situated to the west, rather than to the south, of the lower Grenadines. On Petit's part, this error has been attributed to simply running out of paper combined with an attempt to show the French Antilles within the greater continuity of the Windward Isles. For Delisle this was a major and uncharacteristic misstep that earned considerable critique in scientific and cartographic circles. Nonetheless, this map proved both popular and influential, being slavishly copied extensively by other cartographers of the period (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1725 Gabriel Bodenehr Antique Map Birds Eye View of Szczecin or Stettin, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Stettin
- Ref #: 93494
- Size: 13 1/2in x 8in (335mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1725
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map, a birds eye view of the city of Szczecin or Stettin, Poland along with descriptive text was published in Gabriel Bodenehrs Force d Europe in 1725.
Bodenehr a copper engraver and publisher, bought the numerous copper plates of Johann Stridbeck (1640 – 1716) and revised them and along with his own maps, views and plans published them in several works with different titles.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 8in (335mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 6 1/2in (330mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Szczecin/Stettin is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major seaport and Polands seventh-largest city.
Szczecin is located on the river Oder, south of the Szczecin Lagoon and the Bay of Pomerania. The city is situated along the southwestern shore of Dąbie Lake, on both sides of the Oder and on several large islands between the western and eastern branches of the river. Szczecin is adjacent to the town of Police and is the urban centre of the Szczecin agglomeration, an extended metropolitan area that includes communities in the German states of Brandenburg and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
The cities recorded history began in the 8th century as a Lechitic Pomeranian stronghold, built at the site of the Ducal castle. In the 12th century, when Szczecin had become one of Pomeranias main urban centres, it lost its independence to Piast Poland, the Duchy of Saxony, the Holy Roman Empire and Denmark. At the same time, the House of Griffins established themselves as local rulers and the population was Christianized. After the Treaty of Stettin in 1630, the town came under the control of the Swedish Empire and became in 1648 the Capital of Swedish Pomerania until 1720, when it was acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia and then the German Empire. Following World War II Stettin became part of Poland in accordance with the Potsdam Agreement, resulting in the almost complete expulsion of the pre-war German population.
Bodenehr, Gabriel I fl 1673-1765
Engraver and mapmaker of Augsburg, from a family dynasty of engravers and publishers. Son of Johann Georg Bodenehr (1631-1704), father of Gabriel II (whose work is difficult to distinguish) and brother of Georg Conrad. In 1717 the family took over the Augsburg publishing house of Stridbeck. His works include Atlas Curieux (1704), Curioser Staats und Kriegs Theatrum (1715), and Europens Pracht und Macht (c.1720).
1728 Hermann Moll Large Antique Map and View of Gibraltar - 2nd Spanish Seige
- Title : A New and Exact plan of Gibraltar with all its fortifications as they are at present….
- Ref #: 40838
- Size: 25in x 11in (635mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1727
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map and view of the second Spanish siege of Gibraltar by Herman Moll was published in 1727.
Although undated, the legend at the top left of the map, gives an in-depth explanation to the map including no. 5 that refers to 'Place where at this time Barracks building for a Regiment Ap: 15. 1726. 6. The Great Church.', while the dedication is to David Colyear, 1st Earl of Portmore, Governor of Gibraltar. The plan was presumably engraved either in anticipation of, or during the second Spanish siege; Portmore was in England when the siege began, but sailed there with a relief force, arriving on 1st May, 1727. British command of the sea, coupled with the natural features of the Rock of Gibraltar on the landward side of the peninsula, combined to thwart Spanish ambition, and the siege petered to an end in 1728, with the garrison never seriously troubled.
Background: Gibraltar became part of the Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania following the collapse of the Roman Empire and came under Muslim Moorish rule in 711 AD. It was permanently settled for the first time by the Moors and was renamed Jebel Tariq – the Mount of Tariq, later corrupted into Gibraltar. The Christian Crown of Castile annexed it in 1309, lost it again to the Moors in 1333 and finally regained it in 1462. Gibraltar became part of the unified Kingdom of Spain and remained under Spanish rule until 1704. It was captured during the War of the Spanish Succession by an Anglo-Dutch fleet in the name of Charles VI of Austria, the Habsburg contender to the Spanish throne. At the war's end, Spain ceded the territory to Britain under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht of 1713.
Spain tried to regain control of Gibraltar, which Britain had declared a Crown colony, through military, diplomatic and economic pressure. Gibraltar was besieged and heavily bombarded during three wars between Britain and Spain but the attacks were repulsed on each occasion. By the end of the last siege, in the late 18th century, Gibraltar had faced fourteen sieges in 500 years. In the years after Trafalgar, Gibraltar became a major base in the Peninsular War. The colony grew rapidly during the 19th and early 20th centuries, becoming one of Britain's most important possessions in the Mediterranean. It was a key stopping point for vessels en route to India via the Suez Canal. A large British naval base was constructed there at great expense at the end of the 19th century and became the backbone of Gibraltar's economy.
British control of Gibraltar enabled the Allies to control the entrance to the Mediterranean during the Second World War. It was attacked on several occasions by German, Italian and Vichy French forces, though without causing much damage. The Spanish dictator General Francisco Franco declined to join a Nazi plan to occupy Gibraltar but revived Spain's claim to the territory after the war. As the territorial dispute intensified, Spain closed its border with Gibraltar between 1969 and 1985 and communications links were severed. Spain's position was supported by Latin American countries but was rejected by Britain and the Gibraltarians themselves, who vigorously asserted their right to self-determination. Discussions of Gibraltar's status have continued between Britain and Spain but have not reached any conclusion.
Shortly after Gibraltar's recapture, King Henry IV of Castile declared it Crown property and reinstituted the special privileges which his predecessor had granted during the previous period of Christian rule. Four years after visiting Gibraltar in 1463, he was overthrown by the Spanish nobility and clergy. His half-brother Alfonso was declared king and rewarded Medina Sidonia for his support with the lordship of Gibraltar. The existing governor, a loyalist of the deposed Henry IV, refused to surrender Gibraltar to Medina Sidonia. After a fifteen-month siege from April 1466 to July 1467, Medina Sidonia took control of the town. He died the following year but his son Enrique was confirmed as lord of Gibraltar by the reinstated Henry IV in 1469. In 1474 the new Duke of Medina Sidonia sold Gibraltar to a group of Jewish conversos from Cordova and Seville led by Pedro de Herrera in exchange for maintaining the garrison of the town for two years, after which time the 4,350 conversos were expelled by the Duke. His status was further enhanced by Isabella I of Castile in 1478 with the granting of the Marquisate of Gibraltar.
On 2 January 1492, after five years of war, the Moorish emirate in Spain came to an end with the Catholic Monarchs' capture of Granada. The Jews of Gibraltar were, like those elsewhere in the kingdom, expelled from Spain by order of the monarchs in March that year. Gibraltar was used by Medina Sidonia as a base for the Spanish capture of Melilla in North Africa in 1497. Two years later the Muslims of Granada were ordered to convert to Christianity or leave. Those that did not convert left for North Africa, some of them travelling via Gibraltar.
Gibraltar became Crown property again in 1501 at the order of Isabella and the following year it received a new set of royal arms, which is still used by modern Gibraltar, replacing those of Medina Sidonia. In the Royal Warrant accompanying the arms, Isabella highlighted Gibraltar's importance as "the key between these our kingdoms in the Eastern and Western Seas [the Mediterranean and Atlantic]". The metaphor was represented on the royal arms by a golden key hanging from the front gate of a battlemented fortress. The warrant charged all future Spanish monarchs to "hold and retain the said City for themselves and in their own possession; and that no alienation of it, nor any part of it, nor its jurisdiction ... shall ever be made from the Crown of Castile."
At this point in history, "Gibraltar" meant not just the peninsula but the entire surrounding area including the land on which the towns of La Línea de la Concepción, San Roque, Los Barrios and Algeciras now stand. To the east, Gibraltar was bounded by the Guadiaro River, and its northern boundaries lay in the vicinity of Castellar de la Frontera, Jimena de la Frontera, Alcalá de los Gazules, Medina-Sidonia and Tarifa. From the 16th century, the modern meaning of the name came to be adopted – specifically referring only to the town of Gibraltar and the peninsula on which it stands.
Under Spanish Crown rule, the town of Gibraltar fell into severe decline. The end of Muslim rule in Spain and the Christian capture of the southern ports considerably decreased the peninsula's strategic value. It derived some minor economic value from tuna-fishing and wine-producing industries but its usefulness as a fortress was now limited. It was effectively reduced to the status of an unremarkable stronghold on a rocky promontory and Marbella replaced it as the principal Spanish port in the region.
Gibraltar's inhospitable terrain made it an unpopular place to live. To boost the population, convicts from the kingdom of Granada were offered the possibility of serving their sentence in the Gibraltar garrison as an alternative to prison. Despite its apparent unattractiveness, Juan Alfonso de Guzmán, third Duke of Medina Sidonia, nonetheless sought to regain control of the town. In September 1506, following Isabella's death, he laid siege in the expectation that the gates would quickly be opened to his forces. This did not happen, and after a fruitless four-month blockade he gave up the attempt. Gibraltar received the title of "Most Loyal" from the Spanish crown in recognition of its faithfulness (Ref: M&B, Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 25in x 11in (635mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 11in (635mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small loss to the very right figure in the title cartouche not affecting the map, light creasing along folds as issued
1730 Delisle and Covens & Mortier Foundation Antique Map of North America
Antique Map
- Title : L Amerique Septentrionale dressee sur les Observations de Mrs. De L Academie Royale des Sciences & quelques autres & sur les Memoires les plus recens Par G De L Isle A. Amsterdam Chez I Covens & C Mortier Avec Privilege.
- Ref #: 93501-1
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 540mm)
- Date : 1700 (1730)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This is without doubt one of the most important foundation maps, of North America, published in the early to mid 18th century. This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map by Johannes Covens & Pierre Mortier, after Guillaume Delisle, that was published in 1730 in Atlas nouveau de dicerses cartes choisies des Meilleurs Geographes comme Sanson, G De Lisle &c....A Amsterdam.....
The first edition of this map was mistakenly dedicated to Nicolas Sanson, in the title. This oversight was corrected to Delisle in this 1730 edition.
This map is beautiful with original borders beautiful hand colouring on heavy stable paper.
Covens & Mortier (fl 1721-1866) was an eighteenth century cartographic publishing house. The company was founded by Johannes Covens (1697-1774) and Cornelis Mortier (1699-1783) and was located in Vijgendam in Amsterdam .
The collaboration between the two men began after the death of Pieter Mortier (1661-1711), son of a French political refugee. In 1690, Mortier obtained the privilege of distributing maps and atlases from French publishers, in the Netherlands . His widow continued business until his death in 1719 . His son Cornelis took over the business, under the name of his father.
In November 1721 Cornelis Mortier founded a company with Johannes Covens I. He was married in the same year to Corneliss sister. Thus the company of Covens & Mortier was born.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 540mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
There are many reasons why this rare 1st edition foundation map is important. It contains detail of radical changes both to the interior of North America and helps debunk many fundamentally held ideas of the coastlines. Some of these ideas included The Great lakes, California as an island and previously invented ideas of the interior, NW & NE coastlines.
Specifically the shape of the Great Lakes are changed based on information from the great Italian cartographer Vincenzo Coronelli.
The Mississippi valley is well developed with recent French settlement of d\\\'Iberville at Bilochy and the forts at Bon Secours and St Louis. The map also corrects the error of the western swing of the lower part of the Mississippi River, moving its mouth to essentially its correct position on the Gulf of Mexico.
Delisle has also corrected longitude positions and was the first to revert to a peninsular form for California. He stops his western coast at Cape Mendocin and is the first map to show the Saragossa Sea.
The map also illustrates the routes of explorers such as Cortez, Drake, D\\\'Olivier, Gaeten and Mendana, and indicates the locates of a number of Indian tribes, including the Apaches.
As this is a French map we see many of the French strong points in the NE such as Tadousac, Quebec, Fort Sorel, Montreal & Fort Frontenac included. The English settlements are confined to the east of the Alleghenies, with Fort and River Kinibeki as the border between New England and Arcadia.
Such was the improvement of this map, and the sterling reputation of Delisle, that within a few years other publishers issued their own copies of the map, which continued to appear until the 1780s. The importance of this map cannot be overstated in the progression of American cartography. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1730 Georg M Seutter Original Antique Map of America, Island of California
- Title : Novus Orbis sive America Meridionalis et Septentrionalis
- Date : 1730
- Size: 23 3/4in x 21in (605mm x 535mm)
- Ref #: 70793
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large handsome and beautifully hand coloured original antique map of America - showing California as an Island - was published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730.
One of the best examples of this map I have seen to date with exceptional hand colouring.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 3/4in x 21in (605mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light spotting bottom right of map
Verso: - None
Background:
This is a highly decorative and informative map based on the contemporary European knowledge of America at the beginning of the 18th century. California is shown as an island based on the Sanson-Homann model but with additions including several more rivers on the west coast and two mountains to the north - M. Neges and M.S. Martin and C de Fortuna, C&R de Pins and many others.
The great lakes still show a large degree of ignorance to both shape and location and the NW is left blank. Brazil and the east coast of South America is still largely exaggerated.
The tracks of the early navigators are shown in the Pacific including Fr. Quir, Magellan, Drake and others.
The map also supports two large and highly decorative uncoloured - as published - cartouches which in themselves tell a story of European conquest and ignorance of the local populations.
Religion was a compelling motivation for European imperialism, and the opportunity to convert \"heathen\" Indians provided both a justification and means to conquer the indigenous peoples of the New World. Two Indians kneel reverently before a female figure representing Christianity in the top cartouche, flanked on the right by an altar prepared for Holy Communion and on the left by Europeans at a dining table.
The lower cartouche portrays tranquil Indians surrounded by standard symbols representing the Americas. The seated figure wears a feathered headdress, armband, and skirt. A servant shades him from the sun with a baldachin (parasol), while others in the background and to the left harvest what appears to be sugarcane and tobacco. In the center background someone rests in a hammock suspended between two palm trees while another rows quietly out to sea. A pelican, a cockatiel, and whimsical flying fish, some sporting saw-like beaks, hover above the title. The latter creatures appear to be the artist\'s misconception of a sawfish.
The placement of the two scenes illustrating this work is significant. By depicting numerous symbols associated with Roman Catholicism above a scene of Indians, a subtle message is conveyed: European contact with Indians would yield vast spiritual riches in the form of Christian converts and benefit the indigenous people, who, because they did not practice a Christian faith, were \"beneath\" those who did. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1730 Georg Mattraus Seutter Large Antique Map of Africa
Antique Map
- Title : Africa Iuxta Navigationes..Matth. Seuttero S Caes Maj Geographo Aug.
- Date : 1730
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35011
- Size: 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate antique map of Africa was engraved by Tobais Lotter and published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730 edition of Geographical Atlas or an Accurate Depiction of the Whole World
This striking map of Africa is based largely on Homanns 1715 map. Typical of the period, it presents largely fictitious information in southern Africa, and enormous lakes depicted in central Africa. The Nile is shown originating in the south at lakes Zaire and Zaflan and also continuing further south through a twisted river system with its headwaters in Bed Lac. The splendid decorative cartouche (uncolored) features indigenous people, pyramids and exotic animals, with a fierce dragon perched atop the title.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small restoration to top & bottom margin centerfold. 4 small rejoins to margins, no loss
Plate area: - Restoration to bottom 2in of centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (M&B; Tooley)
1730 Georg Mattraus Seutter Large Antique Map of Africa
Antique Map
- Title : Africa Iuxta Navigationes..Matth. Seuttero S Caes Maj Geographo Aug.
- Date : 1730
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 43003
- Size: 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate antique map of Africa was engraved by Tobais Lotter and published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730 edition of Geographical Atlas or an Accurate Depiction of the Whole World
This striking map of Africa is based largely on Homanns 1715 map. Typical of the period, it presents largely fictitious information in southern Africa, and enormous lakes depicted in central Africa. The Nile is shown originating in the south at lakes Zaire and Zaflan and also continuing further south through a twisted river system with its headwaters in Bed Lac. The splendid decorative cartouche (uncolored) features indigenous people, pyramids and exotic animals, with a fierce dragon perched atop the title.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Two repairs to bottom margin, no loss
Plate area: - Two small professional repairs to center of image, not noticable
Verso: - None
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (M&B; Tooley)
1730 Georg Seutter Antique Map of New England & New York City - Rare 2nd State
Antique Map
- Title : Recens edita totius Novi Belgii, in America Septentrionali siti, delineatio cura et sumtibus Matthaei Seutteri, Sac. Caes Maj. Geographf. August. Vind
- Size: 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1730
- Ref #: 43001
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the NE region of colonial North America, with the famous Restitutio inset birds-eye view of 17th century New York city, was engraved & published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730.
This is the rare second state, identified by the omission of Chalcographi Augustani from the title and the blank shaded are directly below the title (text was added to the shaded area in the 3rd to 6th states) The cartouche and city view are uncoloured as was intended by Seutter along with the beautiful original map colouring.
This map is in exceptional condition with beautiful original colour, with heavy engraving (denoting an early pressing) on clean heavy sturdy paper. The top and left borders have been professionally extended, with no impact on the image.
There are, at the time of listing, nine of these maps for sale online, of states 2 to 6. Of the 9 only 2 are of the rare 2nd state. The average asking price of the nine maps is $4897US.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - T, R & L margins extended
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The map is based upon the Jansson-Visscher New England series of maps, first published by Visscher in 1651. Seutter replaces the original Restitutio view of New York City with a new view of New York entitled Neu Jorck sive Neu Amsterdam, with a key to the view below in Latin. Above the view is an elaborate scene depicting natives, slaves & allegorical deities presenting tributes to the English monarch, George II. The course of the Delaware and Hudson are separated, unlike early editions of the map.
This is the first map in the series to show distinct drawn boundaries between Massachusetts, New England, New York, New Jersey and Pennsylvania, as earlier examples had previously left the delineation of the boundaries to the colorist. Philadelphia is now shown as a set of houses in relief, rather than a ground plan. The map is richly embellished with many animals and other decorations and is without doubt, one of the most decorative 18th century maps of the region.
1730 George Seutter Large Antique Map of Australia, East Indies, SE Asia, China
Antique Map
- Title: India Orientalis cum Adjacentibus Insulis Nova Delineatione ob oculos posita ..Matth. Suettro.
- Date: 1730
- Condition: (A+) Condition
- Ref: 43155
- Size: 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Description: This large, scarce & beautifully hand coloured original map of Australia & SE Asia was published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730. This is one of the best examples of this map I have seen, especially with the colouring. In excellent condition, a must in any Australian or SE Asian collection.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 ½in x 21 ½in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/4in (580mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: The map extends from China, Japan and Persia in the North and in the south stretching from The Maldives east to Northern Australia. Of note, Australia continues to be attached to Nova Guinea, albeit with some hesitation, as the image extends outside the inner neat-line to convey this information - even though 20+ names are confidently engraved around Northern Australia Coastline. The detail throughout Southeast Asia is informative and up-to-date and the print style typically strong. The cartouche is one of Seutter's most ornate, with elaborate scenes from sea, land, jungle and mythology. This map rarely appears on the market, as it was only included in select copies of Seutters atlas. (Ref: Norwich; M&B; Tooley)
1730 Matthaus Seutter Large Antique Map of Norway
Antique Map
- Title : Regnum Norwegiae...Matthaei Seutteri
- Ref #: 17020
- Size: 24 1/2in x 21in (630mm x 530mm)
- Date : 1730
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured antique map of Norway was published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, brown, pink, red, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 21in (630mm x 530mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (590mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Before the fifteenth century the peoples of Southern Europe had little geographical knowledge of the Scandinavian world except from sketchy detail shown in the Catalan Atlas (1375) and on a number of \'portolani\' embracing Denmark and the southern tip of Norway. It was not until 1427 that a manuscript map prepared about that time by Claudius Clavus (b. 1388), a Dane who had spent some time in Rome, made available to scholars a tolerable outline of the northern countries and Greenland. That was to remain the best map available for the rest of the century and it was used as the basis for maps of Scandinavia in early printed editions of Ptolemy. Others by Nicolaus Cusanus (1491) and Ehrhard Etzlaub (c. 1492) followed but, needless to say, these are extremely rare; even the later maps by Olaus Magnus and Marcus Jordan, where they have survived at all, are known only by very few examples. In fact, apart from the rare appearance of an early Ptolemy map, the oldest of Scandinavia which a collector is likely to find are those in Munster\'s Cosmography published in 1544 with many later editions. In the following centuries the comparatively few maps and charts compiled in Scandinavia were usually published in Amsterdam, Antwerp, Paris or Nuremberg, the more important maps often being incorporated in the major Dutch, French and German atlases. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1732 Baldaeus Antique Print a View of Machilipatnam Andhra Pradesh, India
- Title : Masulipatam
- Date : 1732
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25904
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique print a view of the city of Masulipatam (Machilipatnam) on the Malibar Coast in India was published in the 1732 second English edition of Philip Baldaeus "A True and Exact Description of the Most Celebrated East-India Coasts of Malabar and Coromandel; and also of the Isle of Ceylon… London: Awnsham and John Churchill, 1732.
Machilipatnam is a city and the district headquarters of Krishna district, located in Coastal Andhra region of Andhra Pradesh, India. During British rule, the city was their first trading settlement on the Bay of Bengal coast, when it was also known as Masulipatnam or Masula, and as Bandar in folklore, located 72 km to the east of the state capital Vijayawada.
Second edition in English of Baldaeus’ account of his 17th-century travels in south India and Ceylon—one of the first Europeans to publish at length about the region published with 37 copper-engraved views and maps. Father Philippus Baldaeus, Baelde or Philip Balde (October 1632, Delft – 1672, Geervliet) was a Dutch minister. He went to Jaffna, Ceylon with an invading Dutch force during 17th Century. As the first European he documented the life, language and culture of Tamil people, living in the north of the island. It is a great historical record, similar to Mahawamsa, and it was immediately published in Dutch and German (with several beautiful pictures).
Baldaeus had a Flemish origin. His ancestors had left Ypres in 1584. Baldaeus lost both his parents, when he was four years old. His uncle Robertus Junius was a missionary on Dutch Formosa. After studying Oriental languages in Groningen (1649) and theology in Leiden (1650), and discussions with Arnoldus Montanus, he preached from 1655 at Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Jaffanapatnam and Point de Galle, either in Dutch or Portuguese (language). From 1657 he served under Rijklof van Goens, occupying the Coromandel and Negapatnam in 1658. Cornelis Speelman became its first governor. By 1660 the Dutch controlled the whole island except the kingdom of Kandy. When the Dutch occupied the coast of Malabar in 1661, Baldaeus took part. Around 1662 he returned to Ceylon and Baldaeus learned Sanskrit and studied Hinduism.
In 1666 he returned to the Dutch Republic and preached in Geervliet from 1669 until his death at the age of 39 or 40. He left behind a full and faithful account of the civil, religious, and domestic condition of the countries through which he travelled. In this, he introduced also an interesting account of the Hindu mythology, and some specimens of the Tamil language, including the translation of the Lord's Prayer: defective enough it is true, but remarkable as the first treatise, printed in Europe, on any Indian language. The title of the whole work is Description of the East Indian Countries of Malabar, Coromandel, Ceylon, etc. (in Dutch, 1671) The book is dedicated to the bailiff Cornelis de Witt. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, green,
General color appearance: - Fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9 1/2in (360mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1735 Homann Large Antique Map of Oran, Algeria, North Africa
- Title : Topographica Repræsentatio Barbarici Portus et Urbis Munitæ Oran... Nuremberg, 1732
- Ref #: 43187
- Size: 24 1/2in x 21 1/4in (620mm x 540mm)
- Date : 1735
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map and view of the City of Oran & Environs in the North African country of Algeria, as it was being captured by the Spanish in 1732, was published by Homann Heirs in ca 1735.
Background: Chart of the environs of Oran in Algeria, with a panorama of the city and environs, decorated with several sailing battle ships. In 1509 Spain captured Oran from the Moors, but in 1708, with Spain disadvantaged by the War of the Spanish Succession, they were driven out by the Turkish Bey, Mustapha Ben Youssef. In 1732 José Carrillo de Albornoz, 1st Duke of Montemar (1671-1747), recaptured Oran, causing this map to be published, after which the Spanish held the city until 1792. When the Spanish saw no point in keeping it, when it was handed over to the Bey of Algiers(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 21 1/4in (620mm x 540mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1735 J B Homann Large Antique Map of Old Saxony, Germany - Berlin to Prague
- Title : Circuli Super Saxoniae pars Meridionalis sive Ducatus...Homannianos
- Date : 1735
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 30832
- Size : 23in x 19in (600mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Saxony region of central Germany. The map stretches from Berlin in the north to Prague in the Czech Republic to the south, by J B Homann was published by the Homann Heirs firm in 1735. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (600mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (565mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Saxony is a landlocked federal state of Germany, bordering the federal states of Brandenburg, Saxony Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic.
The history of the state of Saxony spans more than a millennium. It has been a medieval duchy, an electorate of the Holy Roman Empire, a kingdom, and twice a republic.
The area of the modern state of Saxony should not be confused with Old Saxony, the area inhabited by Saxons. Old Saxony corresponds roughly to the modern German states of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and the Westphalian part of North Rhine-Westphalia.
The territory of the Free State of Saxony became part of the Holy Roman Empire by the 10th century, when the dukes of Saxony were also kings (or emperors) of the Holy Roman Empire, comprising the Ottonian, or Saxon, Dynasty. Around this time, the Billungs, a Saxon noble family, received extensive fields in Saxony. The emperor eventually gave them the title of dukes of Saxony. After Duke Magnus died in 1106, causing the extinction of the male line of Billungs, oversight of the duchy was given to Lothar of Supplinburg, who also became emperor for a short time.
In 1137, control of Saxony passed to the Guelph dynasty, descendants of Wulfhild Billung, eldest daughter of the last Billung duke, and the daughter of Lothar of Supplinburg. In 1180 large portions west of the Weser were ceded to the Bishops of Cologne, while some central parts between the Weser and the Elbe remained with the Guelphs, becoming later the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg. The remaining eastern lands, together with the title of Duke of Saxony, passed to an Ascanian dynasty (descended from Eilika Billung, Wulfhild\\\\\\\'s younger sister) and were divided in 1260 into the two small states of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg. The former state was also named Lower Saxony, the latter Upper Saxony, thence the later names of the two Imperial Circles Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg. Both claimed the Saxon electoral privilege for themselves, but the Golden Bull of 1356 accepted only Wittenberg\\\\\\\'s claim, with Lauenburg nevertheless continuing to maintain its claim. In 1422, when the Saxon electoral line of the Ascanians became extinct, the Ascanian Eric V of Saxe-Lauenburg tried to reunite the Saxon duchies.
However, Sigismund, King of the Romans, had already granted Margrave Frederick IV the Warlike of Meissen (House of Wettin) an expectancy of the Saxon electorate in order to remunerate his military support. On 1 August 1425 Sigismund enfeoffed the Wettinian Frederick as Prince-Elector of Saxony, despite the protests of Eric V. Thus the Saxon territories remained permanently separated. The Electorate of Saxony was then merged with the much bigger Wettinian Margraviate of Meissen, however using the higher-ranking name Electorate of Saxony and even the Ascanian coat-of-arms for the entire monarchy. Thus Saxony came to include Dresden and Meissen. In the 18th and 19th centuries Saxe-Lauenburg was colloquially called the Duchy of Lauenburg, which in 1876 merged with Prussia as the Duchy of Lauenburg district.
Saxony-Wittenberg, in modern Saxony-Anhalt, became subject to the margravate of Meissen, ruled by the Wettin dynasty in 1423. This established a new and powerful state, occupying large portions of the present Free State of Saxony, Thuringia, Saxony-Anhalt and Bavaria (Coburg and its environs). Although the centre of this state was far to the southeast of the former Saxony, it came to be referred to as Upper Saxony and then simply Saxony, while the former Saxon territories were now known as Lower Saxony.
In 1485, Saxony was split. A collateral line of the Wettin princes received what later became Thuringia and founded several small states there (see Ernestine duchies). The remaining Saxon state became still more powerful and was known in the 18th century for its cultural achievements, although it was politically weaker than Prussia and Austria, states which oppressed Saxony from the north and south, respectively.
Between 1697 and 1763, the Electors of Saxony were also elected Kings of Poland in personal union.
In 1756, Saxony joined a coalition of Austria, France and Russia against Prussia. Frederick II of Prussia chose to attack preemptively and invaded Saxony in August 1756, precipitating the Third Silesian War (part of the Seven Years\\\\\\\' War). The Prussians quickly defeated Saxony and incorporated the Saxon army into the Prussian army. At the end of the Seven Years\\\\\\\' War, Saxony recovered its independence in the 1763 Treaty of Hubertusburg.
1735 Schubler & Steidlin Antique Baroque Print Musical Ball Regensburg Ger. 1717
Antique Map
- Title : Bal, welche den 26. Sept: 1717 in Sr Durchl: Eminens des Herrn Cardinals residens zu Regensburg, in dem so genamten Lowen-Saal, gehalten worden....NB das Bal Zimmer war mit rohten Tuch belegt
- Ref #: 93443
- Size: 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1735
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original Baroque copper plate engraved antique print, numbered three of three, of an early 18th century Ball, part of the celebrations at the Royal Court in the Cardinal Castle of Regensburg, on September 26, 1717, by Johann Schubler, was engraved by Johann Matthias Steidlin or Steudlin 1717-1754 and published by the Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1735.
A wonderful piece of Baroque art, engraved and published by some of the foremost art engravers and publishers at the beginning of the 18th century.
Professionally matted and can be easily removed if required.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair bottom right signature
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1245 Regensburg became a Free Imperial City and was a trade centre before the shifting of trade routes in the late Middle Ages. In 1486, Regensburg became part of the Duchy of Bavaria, but its independence was restored by the Holy Roman Emperor ten years later. In the city took place the Diet of 1541, was adopted the Protestant Reformation in 1542 and its Town Council remained entirely Lutheran. From 1663 to 1806, the city was the permanent seat of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire, which became known as the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. Thus, Regensburg was one of the central towns of the Empire, attracting visitors in large numbers.
A minority of the population remained Roman Catholic, and Roman Catholics were denied civic rights (Bürgerrecht). Although the Imperial city had adopted the Reformation, the town remained the seat of a Roman Catholic bishop and several abbeys. Three of these, St. Emmeram, Niedermünster and Obermünster, were free imperial estates within the Holy Roman Empire, meaning that they were granted a seat and a vote at the Imperial Diet (Reichstag). So there was the unique situation that the town of Regensburg comprised five independent states (in terms of the Holy Roman Empire): the Protestant city itself, the Roman Catholic bishopric, and the three monasteries. In addition, it was seen as the traditional capital of the region Bavaria (not the state), acted as functional co-capital of the Empire (second to the Emperors court at Vienna) due to the presence of the Perpetual Diet, and it was the residence of the Emperors Commissary-Principal to the same diet, who with one very brief exception was a prince himself (for many years the Prince of Thurn and Taxis, still resident in the town).
Schübler, Johann Jacob 1689 - 1741
Schübler was born in Nuremberg as was known as a versatile German baroque master builder , architectural theorist and writer and mathematician.
Schüblers father Johann Jacob was a braid maker and language teacher, and he also had medical knowledge, which he also used for a fee. He came to Nuremberg from Strasbourg and became resident there by marrying Maria Elisabeth Hengel, the daughter of an independent braid maker. The later master builder Johann Jacob Schübler was the fourth of the couples eight children. Through his father and private tutors, he received careful training, mainly in artistic subjects as well as in old and new languages. Architectural painter Johann Andreas Graff gave him his first drawing lessons . In 1698 he began his apprenticeship as a draftsman in the studio of the portraitist, engraver and art dealerJacob von Sandrart (1630-1708), in addition he was taught by Georg Christoph Eimmart (1638-1705), the long-time director of the important Nuremberg Academy of Painters , a representative of the mathematically oriented artists of the time and founder of the observatory at the Nuremberg castle .
At that time, extensive study trips were common for aspiring artists to complete their training. Between 1705 and 1713, Schüblers years of traveling took him through Germany, Denmark and Norway, the Netherlands and France - with a stopover in 1711 with his parents in Nuremberg. The time around 1700 in Europe was particularly intensive secular and church building activity, numerous elaborate, representative buildings. Schüblers travel destinations were primarily places where the current building activity was concentrated. However, Italy was missing from this program. He made longer stays for scholarly studies in Leipzig and Copenhagen .
After his return in 1713, Schübler remained settled in Nuremberg. Prominent colleagues such as Balthasar Neumann (1687–1753) visited him and he corresponded with well-known artists and scientists. He rejected various offers from foreign employers because they did not seem attractive enough to him. In 1717 he received the order for a gate of honor, which was built to celebrate a princely wedding in the main square of the residential city of Sulzbach . Schübler had an expansive triumphal arch with three stacked columns and niches for allegorical figures built, which was generally praised. A permanent position at the court of the Sulzbach Palatinate Countshowever, did not result from this. So he remained the prevented Builder. Great vocations only reached him towards the end of his life. In 1740 the Danish king invited him to Copenhagen, in 1741 negotiations for a move to Berlin followed to the court of the Prussian king Friedrich II. Both offers came too late for Schübler. He died in September 1741 from a clock-like illness.
Schübler only started his own family at an advanced age. In 1727 he married Margareta Maria Hemme, the daughter of a respected art dealer. At around 40, the bride was even a little older than Schübler herself; she died two years after the marriage, the marriage remained childless. In 1733 Schübler had a second marriage to 26-year-old Margaretha Setzmair. She also came from a long-established, wealthy middle-class family. The couple had two daughters, one of whom died very early, and a son who was born several months after Schüblers death.
In 1734 Schübler was accepted as an external member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin. The small Schüblerstrasse in Nuremberg reminds him of him.
Schüblers actual lifes work consisted of a large number of writings, the publication of which he began around 1715. With his later works in particular, he pursued the intention of scientifically examining the questions of the building industry based on proportion and perspective, thereby making them teachable and learnable for building theorists and practitioners of his time.
Initially, Schübler published smaller masterpieces that appeared in deliveries of six to twelve engravings and contained hardly any text. In it he showed architectural details (e.g. fireplaces , mansard windows , pulpits, altars, confessionals), furniture (beds, desks, clocks, night chairs) and technical objects such as pumping stations and fountains. He drew the originals himself, often with a light color, but hardly ever took over the transfer to the printing plates, even though he knew this technique. For this, he employed a large number of engravers, among them Johann August Corvinus, Johann Matthias Steidlin, Georg Lichtensteger and his own brother Georg Andreas. The objects depicted often appear grotesquely overloaded with decorative elements such as flower threads, sphinxes and the like, but were also not intended for direct implementation. Rather, the executing tradesmen were able to take very different suggestions from a single template. The templates appeared in the publisher Jeremias Wolff in Augsburg, which is renowned throughout Europe .
Schüblers more scientific and literary works were mostly published by Johann Christoph Weigel in Nuremberg. In 1719/20 Perspectiva Pes Picturae was published in two parts , a large-format work of art intended to provide the basis for architectural painting . 1723/24, again in two parts, came out a textbook on the column orders with practical aids for difficult problems, which was reprinted several times. This was followed by publications on the art of sundial (1726) and on the wood-fired parlor ovens(1728). Schüblers main works then appeared within five years. With them he wanted to provide a new, in-depth representation of the entire architecture, with the main areas of the Architectura Civilis and the Architectura Militaris . From the years 1732-35 are the five illustrated volumes of a Synopsis Architecturae Civilis eclecticae , to which the content of the theoretical work Ars inveniendi from 1734 on civil architecture can be assigned. The two volumes of carpentry (Ars Tignaria) date from 1731 and 1736 . The main works include Perspectiva Geometrica Practica .
Schüblers works were widespread, and individual writings had up to 20 editions. The last known new edition dates from 1786. The popularity of his practically applicable proposals ended with the domination of baroque and rococo in architecture. The new general artist lexicon by art historian Georg Kaspar Nagler (1801–1866) already discusses Schüblers works as examples of the aesthetic aberrations of an era that has been overcome and describes them as senseless outbursts of an unregulated imagination.
1737 George Vertue Elizabethan Map of London - The "Woodcut" or Ralph Agas Map, 1560
- Title : Civitas Londinum Ano Dni M D L X. Londonium Antiqua
- Ref: 35663
- Size: 78in x 26in (1.93m x 710mm)
- Date : 1737 (1560)
- Condition: (B+) Good Condition
Description:
This large rare original 8 sheet map of Elizabethan London by George Vertue was published in 1737, dated, after an original 8 sheet map first published in 1561, only 2 years after Elizabeth I ascended the throne.
This George Vertue map together with the Braun & Hogenberg map are among the only depictions of Tudor London still available today to collectors. The Braun & Hogenberg map is readily available to collectors. This map rarely appears on the market, with only a small handful sold. Both maps are derived from surveys of Elizabethan London completed in the mid 16th century.
The Braun & Hogenberg single plate map is derived from a very large 15 plate map, referred to as the "Copper-Plate" map produced between 1553 & 1559 whereas this George Vertue map is referred to as the "Woodcut" or "Agas" map and is derived from an 8 sheet map published in 1561. The two maps are referred to as the, "Copperplate" & "Woodcut" maps, because no complete examples of either original 16th century maps have survived and the names of the original surveyors or cartographer are uncertain. There was early speculation by George Vertue, that the "Woodcut" map was compiled by the 16th century Elizabethan surveyor Ralph Agas, but this has since been debunked. But even so, the woodcut map is still referred to as the "Woodcut" "Agas" map.
The 15 plate "Copperplate" map was the first map of the two to be completed, between 1553 and 1559. The 8 plate "Woodcut" map was published shortly afterwards in 1561. In 1962 a single plate of the "Copperplate" was discovered along with two more additional plates, discovered later. No examples of 1561 "Woodcut" map have survived but luckily three later 1633 examples have. They now sit in institutional collections.
The map covers the cities of London and Westminster from the Tower of London in the east to Westminster Abbey in the west. South of the Thames River there are a number of landmarks of Tudor Southwark, including the bull and bear baiting pits and Winchester Palace. London Bridge is shown crossing the river into the City of London. Old St. Paul's Cathedral is depicted in its pre-fire state. The built up suburbs to the north only extend as far as Holborn and Spitalfields, although the hills of Hampstead and Highgate are notionally described in the background.
This map was rescued as 8 separate maps, and professionally restored & joined using contemporary paper, materials and methods. We received the maps in 8 individual frames unprotected by glass. Unfortunately there was some bug damage to a few of the maps, but only to parts of the unprinted areas of the paper, the bugs unwilling to eat the ink. So luckily the vast majority of the printed parts of the maps were saved, with damage minimised to only blank parts of the map, which were restored and filled with dated contemporary paper.
I have included an image of the maps in their 8 original frames prior to removing the maps and restoration, so you can see as they were prior to restoration and joining.
I have found 8 official dealer sales of this map between 1999 and 2017 with a top price of $12,500 in 2017. I know of no copies of this map, currently on the market.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 78in x 26in (1.93m x 710mm)
Plate size: - 78in x 26in (1.93m x 710mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections: (Starting from the top left plate working clockwise)
Plate 1. Some paper loss to the L&T margins, sky paper loss but with no loss to actual ink.
Plate 2. Paper loss to bottom of plate with small loss to actual ink. Left side of plate light loss to paper surface, very slight loss to actual ink. Age toning
Plate 3. Slight loss to paper surface to top and margin, no loss to actual ink
Plate 4. Paper loss to top margin and paper with loss to paper area in the plate, very minimal loss to actual ink surface
Plate 5. None
Plate 6. Loss of paper to top & bottom of plate with some loss to actual ink
Plate 7. Very small localised 2cm diameter loss to top of plate
Plate 8. Paper loss to top & right margin of plate, very minimal loss to ink.
This scarce map has been rescued and restored and although not perfect is a very desirable map.
Background:
The "Woodcut" map of London, formally titled Civitas Londinum, and often referred to as the "Agas" map of London, is one of the earliest true maps (as opposed to panoramic views, such as those of Anton van den Wyngaerde) of the City of London and its environs. The original map probably dated from the early 1560s, but it survives only in later and slightly modified copies. It was printed from woodcut blocks on eight sheets, and in its present state measures approximately 2 feet 4 inches (71 cm) high by 6 feet (180 cm) wide. There has been some damage to the blocks, and it was probably originally fractionally larger.
The Woodcut map is a slightly smaller-scale lightly modified copy of the so-called "Copperplate" map, surveyed between 1553 and 1559, which, however, survives only in part. It also bears a close resemblance to the map of London included in Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg's Civitates Orbis Terrarum, published in Cologne and Amsterdam in 1572, although this is on a greatly reduced one plate scale.
The Woodcut map was traditionally attributed to the surveyor and cartographer Ralph Agas, but this attribution is now considered to be erroneous.
Three impressions of the Woodcut map survive in its earliest known state of c. 1633. They are held in London Metropolitan Archives, the Pepys Library at Magdalene College, Cambridge, and The National Archives at Kew. The three early copies of the map are dated by an inscription to c. 1633. However, it is evident that the map in this form has been updated from an earlier state. The royal arms in the upper left corner are those of the House of Stuart (1603–49), but are clearly an insertion, almost certainly replacing the earlier Tudor arms, which do appear (at a very small scale) on the royal barge, pictured on the Thames. Similarly, the Royal Exchange (erected 1566–70; opened 1571) appears on the map, but is again clearly an insertion. The map is now known to be a close – though slightly less detailed – copy of the "Copperplate" map, surveyed between 1553 and 1559; but one difference between the two maps is that St Paul's Cathedral appears on the Woodcut version without its spire. The spire was lost in a fire in 1561, and so the map cannot be earlier than that date. The Woodcut map is therefore now dated with a reasonable degree of probability to the 1560s. A reference in the Stationers' Register for 1562–3 to the "Carde of London" may possibly refer to it.
The map has also been slightly modified from the Copperplate map by the introduction of a higher degree of perspective to the projection: this is particularly obvious in the northern and western areas (beyond Bishopsgate towards Shoreditch, and in the Westminster and Whitehall area). It is therefore closer to a bird's-eye view of the City, seen from an imaginary viewpoint above the south bank of the Thames, as opposed to the "bird's-flight view" projection of the Copperplate map. Stephen Powys Marks suggests that this adjustment "may be an indication of an appeal to a less sophisticated public than that which would buy the fine copper engraving"
The Woodcut map was traditionally attributed to the surveyor and cartographer Ralph Agas (c. 1540–1621). This attribution has its roots in a claim made by Agas in 1588 to the effect that for ten years past he had been hoping to undertake a survey of London. On the basis of this statement, the late 17th-century engraver of a copy of the map on pewter sheets associated Agas's name with it; and the attribution was then asserted more firmly by the antiquary George Vertue in 1737–8. However, the probable date of the Woodcut map and its relationship to the Copperplate map make it extremely unlikely that Agas – who began practising as a surveyor in about 1566 – played any part in its creation, and the attribution is now treated as highly dubious. Nevertheless, the map is still often referred to as the "Agas" map. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
George Vertue (1684-1756)
Vertue was a prominent early 18th century engraver and antiquarian. His eclectic and artistic tastes drew him into the tastemaking circles in London during his time. He was a contemporary of William Hogarth and together they were members of the Rose and Crown Club. He was also the official engraver for the London Society of Antiquaries. The latter of which was a learned society "charged by its Royal Charter of 1751 with 'the encouragement, advancement and furtherance of the study and knowledge of the antiquities and history of this and other countries'."
As part of his responsibilities, he provided many of the illustrations for the Society's projects, foremost among these was Vetusta Monumenta, an series of publications documenting ancient buildings, arts, and artefacts. Additionally, Vertue undertook his project to re-engrave the "Woodcut" map under the aegis of the Antiquarian Society. This should come as no surprise, as the project was well within the interests of the Society.
In the 1730s and '40s Vertue showed a special interest in Tudor history and printmaking. This is obviously reflected in his copy of the "Woodcut" map. His interest can also be seen in the Historic Prints series of 1740, in which he imitated 16th century images of Henry VIII, Queen Elizabeth, and other royals. Much of his work for Vetusta Monumenta also revolves around Tudor architecture.
Ralph Agas
Ralph Agas (or Radulph Agas) (c. 1540 – 26 November 1621) was an English land surveyor and cartographer. He was born at Stoke-by-Nayland, Suffolk, in about 1540, and lived there throughout his life, although he travelled regularly to London. He began to practise as a surveyor in about 1566, and has been described as "one of the leaders of the emerging body of skilled land surveyors".
Agas is particularly known for his large-scale town map of Oxford (surveyed 1578, published 1588). Early maps of London and Cambridge were also formerly attributed to him, but these attributions are no longer upheld.
Agas was born in Stoke-by-Nayland, in Suffolk, probably between 1540 and 1545. By his own account, he began to practise as a land surveyor in about 1566. He is described at several points in his life as "deformed", "impotent", "lame" and a "cripple", but the precise nature of his disability is not known.
He was ordained, and served from 1578 to 1583 as rector of Gressenhall, Norfolk. He probably abandoned the church after this date in favour of his surveying career.
He appears always to have lived in Suffolk, but travelled regularly to London in term time to obtain orders for surveying work. During his visits he is known to have lodged at inns: in 1596 at the "Flower de Luce", next to the "Sun" near Fleet Bridge; and in 1606 at the sign of the "Helmet" in Holborn, at the end of Fetter Lane.
He died at Stoke-by-Nayland on 26 November 1621, and was buried there the next day.
Agas's regular work consisted of drawing up local estate maps and surveys for a variety of clients. He was one of the first estate surveyors to move beyond the traditional practice of compiling purely written descriptions of landed property, and to consider supplementing these with measured maps.[6] The earliest map that can be attributed to him is one of lands at West Lexham, Norfolk, dated 1575. He subsequently undertook commissions in Bedfordshire, Berkshire, Cambridgeshire, Essex, Gloucestershire, Norfolk, Oxfordshire, Suffolk and Surrey. An estate map he drew of Toddington, Bedfordshire, dated 1581, includes what Paul Harvey has described as "the best picture we have of a small Elizabethan country market-town". He appears to have been patronised by William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley. Another client was Corpus Christi College, Oxford, although the college commissioned only written surveys rather than maps.
Agas is perhaps principally remembered for Oxonia Antiqua Restaurata, a detailed plan – really a "bird's-flight view" – of Oxford. It was drawn in 1578 and engraved and printed in 1588: a copy is held in the Bodleian Library, bequeathed by Richard Rawlinson. The plan was re-engraved by Robert Whittlesey in 1728, at the expense of the university, but this plate was destroyed in the fire at John Nichol's printing-works in 1808.
A town plan of Dunwich in Suffolk is also attributed to Agas. This was engraved for Thomas Gardner's history of the town (1744). The original later came into the possession of the Suffolk antiquary David Elisha Davy
The important early map of London now conventionally known as the "Woodcut" map has traditionally been attributed to Agas. A verse inscribed on the 1588 engraving of Agas's map of Oxford included a claim to the effect that for ten years past he had been hoping to undertake a survey of London, but had not done so. On the dubious evidence of this statement, a link with the Woodcut map was first made by the late 17th-century engraver of a copy of it on pewter sheets; and in 1737–8 George Vertue attributed it confidently and unambiguously to Agas. However, the claim is no longer sustained: the Woodcut map is now dated to the early 1560s, and is known to be based on the slightly earlier "Copperplate" map of the 1550s, making it highly unlikely that Agas played any part in its creation. Nevertheless, the Woodcut map is still often referred to as the "Agas" map.
A map of Cambridge printed in 1592 (of which a unique copy survives in the Bodleian Library) has also been attributed to Agas, but is now thought more likely to be by John Hamond.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1738 J B D Anville Antique Map of North Africa, Spain, Sardinia & Sicily
- Title : Carte de La Partie de L Afrique ou les Carthaginios de L Histoire Ancienne de Mr Rollin..Sr D Anville...1738
- Size: 20in x 12in (510mm x 303mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1738
- Ref #: 70314
Description:
This magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of North Africa, Spain, Sardinia & Sicily - with an inset plan of Carthage by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D Anville in 1738 - dated - was published in Mr Charles Rollins Atlas. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 12in (510mm x 303mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 10 1/2in (495mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\\\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\\\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
1739 Bellin Original Antique Map of SW Africa The Cape to Angola - Hottentots
- Title: Carte Occidentale D Afrique...1739
- Date: 1739
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25563
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map of central and south western coastline of Africa - from the cape to northern Angola - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1739 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 11in (295mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1740 Bellin Antique Coastal Map of South East Africa - South Africa to Zanzibar
- Title : Carte de la Coste Orientale D Afrique...1740
- Date : 1740
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 92509
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map of South and Eastern Coast of Africa from South Africa to Zanzibar by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1740 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Condition:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1740 Guillaume Delisle Original Antique Atlas Title Page for Atlante Novissimo
- Title : Atlante Novissimo De Sig Guglielmo De L Isles
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1740
- Ref #: 70343
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique frontispiece from the Italian version of Guillaume Delisle atlas Atlante Novissimo, was published by Girolamo Albrizzi in 1740.
The architectural columns are flanked by both male & female Roman soldier. At the top of the structure, a pair of putti hold aloft the covering drapes. Within the structure are two internal cartouche, one a vignette view of the city of Venice, where the atlas was published, and above, the symbol for the Society of Jesus.George PhilipDelisle
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1740 Guillaume Delisle Original Antique Atlas Title Page of Atlante Novissimo
- Title : Atlante Novissimo Del Sig. r Guglielmo De L Isle
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 70345
- Date : 1750
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique frontispiece from the Italian version of Guillaume Delisle atlas Atlante Novissimo, was published by Girolamo Albrizzi in 1740.
The architectural columns are flanked by both male & female Roman soldier. At the top of the structure, a pair of putti hold aloft the covering drapes. Within the structure are two internal cartouche, one a vignette view of the city of Venice, where the atlas was published, and above, the symbol for the Society of Jesus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1740 Isaac Tirion Antique Map of Bohemia, Silesia, Moravia - Germany, Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Nuova Carta del Regno di Boemia Ducato Di Slesia, Marches Ato Di Moravia e lusazia in Amsterdam da Isac Tirion
- Ref #: 35636
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 14 1/2in x 12 1/2in (365mm x 315mm)
- Date : 1740
- Price: $149US
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the central European countries of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Duchy of Silesia, Marquisate of Moravia, and Lusatia by Isaac Tirion, was published in 1740 in Amsterdam.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 12 1/2in (365mm x 315mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10 1/2in (315mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Bohemia is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia proper as a means of distinction
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1740 Seutter Large Antique Map of India, Mughal Empire, Tibet, Nepal
- Title : Imperii Magni Mogolis sive Indici Padschach, juxta recentiissimas Navigationes accurata delineato Geographica studio et sumtibus.
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 42008
- Size: 25in x 20 1/2in (630mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of India and the Northern Mughal Empire was published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1740.
Background:
Representing 18th century Germany cartography at it’s finest; this is an absolutely spectacular c. 1740 map of northern India by Matthias Seutter. Showing the extent of the powerful Mughal Empire in the late 17th century, this map details the subcontinent and parts of Central Asia from Persia and Khandhar eastward as far a modern day Burma and Thailand. Extends northward to include parts of Tibet and Nepal and southwards as far as the Malabar Coast and the Gulf of Thailand. Cartographically this map is heavily based upon Hondius and Mercator’s 17th century of the same region entitled India Orientalis. Presented is wonderful combination of surprising accuracy, gross errors, and outright speculation. Generally speaking, this map is cartographically solid detailing numerous cities, river systems and trade routes. Shows Deli, Agra, Kandahar (Candahar), Lahore (Lahor), Pegu, Goa, Kabul (Cabul), Jaisalmer (Gislemere), and many other important and still thriving cities. Also notes several important trade routes including the ancient caravan trail westward from Agra into Persia. Despite this map’s thoroughness, there are a number of cartographic errors, probably the most notable of which is the narrowing of the subcontinent. Usually such lateral misrepresentations are the result of erroneous 16th century longitudinal calculations. In this case, these errors found their way into the Hondius’s map and hence into this one as well. The northernmost regions depicted on this map are highly speculative with regard to physical geography. A number of large lakes, including the apocryphal Lake of Chiamay, are speculated in the northeastern quadrants of the map as the sources of four important Southeast Asian river systems including the Irrawaddy, the Dharla, the Chao Phraya, and the Brahmaputra. The curious Lake of Chiamay (also called Chiam-may or Chian-may), roughly located in the area of Assam but sometimes as far north as Tibet and China, began to appear in maps of this region as early as the 16th century and persisted well into the mid 18th century. Its origins are unknown but may originate in a lost 16th century geography prepared by the Portuguese scholar Jao de Barros. It was speculated to be the source of five important Southeast Asian River systems and was mentioned in the journals of Sven Hedin. There are even records that the King of Siam led an invasionary force to take control of the lake in the 16th century. Nonetheless, the theory of Lake Chimmay was ultimately disproved and it disappeared from maps entirely by the 1760s. Decorated with several extremely attractive allegorical cartouche image. The title cartouche in the lower left hand quadrant shows Poseidon, Hermes, an angel and the goddess Fame admiring the wealth of Asia as represented by jewels, ivory, and precious metals. In the upper left hand quadrant, a distance scale plays second fiddle to a scene of cherubs rummaging through chests full of treasure while exotic peacocks look on. A large trade Caravel rests in the Indian Ocean, lower right quadrant, suggesting the trade riches to be had by daring ship captains willing to sail half way around the world. Engraved by Albrecht Carl Seutter and published by Matthias Seutter c. 1740. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (630mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom & top margin extended from plate-mark & border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Plan Officers Quarters, Royal Arsenal, Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Das von dem Tit. H. Commendanten der Residentz Berlin, durch den Tit. H. Philipp Gerlach Senior Capitain und Ingenieur gebaute Commendaten Hauß mit der vorderen faciata und allen dreyen Grund-Rissen
- Ref #: 93449
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view & plan of officers quarters at the Royal Arsenal in Berlin - plate No.17 of 19 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of a Poorhouse near Stralau Gate Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Das von dem H. von Grünenberg Seel. inventirte sogenandte Armen- oder Waysen-Hauss zu Berlin, nache bey dem Stralauischen Thor gelegen, ....
- Ref #: 93455
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Poorhouse near the old Stralau Gate (Stralauer Tor) in Berlin - plate No. 8 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Berlin Mansions by A. von Schlütter
Antique Map
- Title : A. Ist ein von H. Andreas von Schlütter Seel. inventirt- und auff gebautes Landt-Hauss. B. Ist ein von dem renomirten Bau-Werck- und Raths Zimmer-Meister Joh. Mich. Kemmeter, in Riegel oder Holtz auff gebautes Land-Hauß oder so genandte Meyerey
- Ref #: 93445
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of 18th century Mansions in Berlin designed by Andreas von Schlütter - plate No. 9 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Charlottenburg Palace Stables Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Der von Hr. Obrist von Eosander inventirte und gebaute Königl. Pferdt Stall zu Charlottenburg, dessen Faciata und Grund Riss. - Das gleichfals von Hr. Joh. Friederich v. Eosander Obristen General Quartier Meistern, und ersten Bau Directorn inventierte und gebaute Rath Hauss zu gedachten Charlottenburg
- Ref #: 93453
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Royal Horse Stables at Charlottenburg Palace, Berlin - plate No. 11 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of Charlottenburg Palace Stables Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Ist ein von Hr. Andreas Schlütter Seel. inventirt und aufgebauer Schöner Marstall Datierung
- Ref #: 93447
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view of the facade of the Charlottenburg Palace stables in Berlin - plate No.15 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print of The Royal Arsenal in Berlin Germany
Antique Map
- Title : Das von dem H. Architect und Bau-Meister Nering Seel. angefangne, und von dem unvergleichlichen Architect Ober-Ingenier und Bau-Meistern H. Obrist Both in vollkommenen Perfection Stand gebrachte und von jedermann belobte Herr. Zeug-Haus, dessen vordere faciata
- Ref #: 93454
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print, view & plan of The Royal Arsenal in Berlin Houses - plate No.13 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch Print Plans of Residential Houses in Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Zwey von Hr. von Grünenberg inventirte und gebaute Burgerl. Wohnhäusser mit ihren Faciaten u. Grundrissen
- Ref #: 93450
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print plans of Berlin Houses - plate No. 12 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .
1740 Wolff & Corvinus Antique Arch. Print Jerusalem Church Friedrichstadt.Berlin
Antique Map
- Title : Die von vorgedachten Hr. von Grünenberg invendierte, unter der Direction des Hr. Ioh. Simonetti Hoff Stucator Hoch-Fürstl. Anhaltischen BauMeister aufgebaute so genande Friderich Stättische Kirche sampt dessen Grund u. Faciata.
- Ref #: 93458
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1740
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large rare, original copper-plate engraved antique architectural print of the Parochialkirche (literally the Reformed parochial church) in the Mitte suburb of Berlin - plate No. 7 of 16 - by Johann August Corvinus 1683 - 1738, after Andreas Mayers 1716 - 1782, was published in Eigentliche Abbildung des Prächtigen Königl. Lust Schlosses Charlottenburg, eine Meile von Berlin, sambt dem darhinden im Walde gelegenen schönen Lust Garten
(Set of 16 numbered plates, the first with the title, with plans and views of the buildings and gardens at Charlottenburg, the palace of the King of Prussia on the outskirts of Berlin.) by Jeremias Wolff Erben in 1740.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Berlin straddles the banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Havel (a tributary of the River Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the citys main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel, and Dahme rivers (the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee). Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. About one-third of the citys area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes. The city lies in the Central German dialect area, the Berlin dialect being a variant of the Lusatian-New Marchian dialects.
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes, Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945). Berlin in the 1920s was the third-largest municipality in the world. After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory. East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
The Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, who had succeeded his father George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance. With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlins residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration. Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Poland, and Salzburg.
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the Kingdom of Prussia, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin.
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power. Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years War by the Russian army. Following Frances victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city. In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the citys economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic centre of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighbouring suburbs including Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin. In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded German Empire. In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
Wolff, Jeremais 1663 - 1724
Wolff was an German engraver and publisher. Born in Augsburg, he originally trained as a clock and automat maker, later changing course and opening a small copperplate engraving shop. His success was impressive and became one of the largest European art, print & map publishers in the first half of the 18th century. Wolff employed some of the best engravers of the time and although not an engraver himself, only Wolffs name was recorded on the engravings. Many of his engravers went uncredited for their work. In 1710 Wolff was one of the founder member of the Empire State Academy of Arts in Augsburg.
After his death in 1724, Wolffs publishing business was inherited by his sons and son-in-law, Johann Balthasar Probst (1673–1750) a notable engraver at the time. The firm continued on in Augsburg under the name Jeremias Wolff Erben.
Together with the Nuremberg copperplate engraver Paul Decker , Wolff published a series of engravings showing the war successes of Prince Eugene of Savoy in Italy , southern Germany and the Spanish Netherlands, during the War of the Spanish Succession . The prints are exhibited in the Museum of Military History, in Vienna .