Sold (332)
1789 Jean Baptiste Lamarck Antique Concology Print, Terebratula Lamp Shells Plate 245
- Title : Terebratule, Terebratula
- Size: 11in x 8in (280mm x 200mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1789
- Ref #: 23876
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique Conchology or Shell print by Jean Baptiste Lamarck was drawn by Henri Joseph Redoute (1766 - 1852) - younger brother of the famous illustrator P J Redoute - engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1789 edition of Tableau encyclopédique et méthodique des trois règnes de la nature(1782-1832) by the French publisher Charles Joseph Panckoucke.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 11in x 8in (280mm x 200mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tableau encyclopédique et méthodique des trois regnes de la nature was an illustrated encyclopedia of plants, animals and minerals, notable for including the first scientific descriptions of many species, and for its attractive engravings. It was published in Paris by Charles Joseph Panckoucke, from 1788 on. Although its several volumes can be considered a part of the greater Encyclopédie méthodique, they were titled and issued separately.
Encyclopédie méthodique par ordre des matières (Methodical Encyclopedia by Order of Subject Matter) was published between 1782 and 1832 by the French publisher Charles Joseph Panckoucke, his son-in-law Henri Agasse, and the latter´s wife, Thérèse-Charlotte Agasse. Arranged by disciplines, it was a revised and much expanded version, in roughly 210 to 216 volumes (different sets were bound differently), of the alphabetically arranged Encyclopédie, edited by Denis Diderot and Jean le Rond d Alembert.
Two sets of Diderots Encyclopédie and its supplements were cut up into articles. Each subject category was entrusted to a specialized editor, whose job was to collect all articles relating to his subject and exclude those belonging to others. Great care was to be taken of those articles that were of a doubtful nature, which were not to be omitted. For certain topics, such as air (which belonged equally to chemistry, physics and medicine), the methodical arrangement had the unexpected effect of breaking up a single article into several parts. Each volume was to have its own introduction, a table of contents, and a history of the Encyclopédie. The whole work was to be linked together by a Vocabulaire universel (Vol. 1 – 4), with references to all locations where each word appears.
The prospectus, issued early in 1782, proposed three editions, each with seven volumes of 250 to 300 plates:
84 volumes;
43 volumes, with 3 columns per page; and
53 volumes of about 100 sheets, with 2 columns per page.
The publication was continued by Henri Agasse, Panckouckes son-in-law, from 1794 to 1813, and then by the latters widow, Mme Agasse, until 1832, when it was completed in 102 livraisons or 337 parts, forming roughly 166½ volumes of text (depending on how the parts were bound) as well as 51 illustrated parts containing 6,439 plates. The number of pages totalled 124,210 pages, of which 5,458 pages were plates. To save money, the plates belonging to architecture were not published. Pharmacy (separated from chemistry), minerals, education, Ponts et chausses were not published as had been announced.
Many dictionaries have a classed index of articles. The one in Oeconomie politique is an excellent example, giving the contents of each article, so that any passage can be found easily.
When completed, the encyclopedia suffered at least one great weakness. As the Vocabulaire Universel, the key and index to the entire work, was not published, it was difficult to carry out any research or to find all the articles on any particular subject. The original parts had often been subdivided, and had been so added onto by other dictionaries, supplements, and appendices that an exact account could not be given of the work, which contained 88 alphabets, 83 indexes, 166 introductions, discourses, prefaces, etc. Overall, probably no more an unmanageable body of dictionaries has ever been published, except Jacques Paul Mignes Encyclopédie théologique, Paris, 1844–1875, with 168 volumes, 101 dictionaries, and 119,059 pages.
The Encyclopédie méthodique par ordre des matières occupied a thousand workers in production, and 2,250 contributors.
Lamarck, Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, Chevalier de1744 – 1829
Lamarck was a pioneer French biologist, who is best known for his idea that acquired characters are inheritable, an idea known as Lamarckism, which is controverted by modern evolutionary theorygenetics.
Lamarck was the youngest of 11 children in a family of the lesser nobility. His family intended him for the priesthood, but, after the death of his father and the expulsion of the Jesuits from France, Lamarck embarked on a military career in 1761. As a soldier garrisoned in the south of France, he became interested in collecting plants. An injury forced him to resign in 1768, but his fascination for botany endured, and it was as a botanist that he first built his scientific reputation.
Lamarck gained attention among the naturalists in Paris at the Jardin et Cabinet du Roi (the kings garden and natural history collection, known informally as the Jardin du Roi) by claiming he could create a system for identifying the plants of France that would be more efficient than any system currently in existence, including that of the great Swedish naturalist Carolus Linnaeus. This project appealed to Georges-Louis Leclerc, comte de Buffon, who was the director of the Jardin du Roi and Linnaeuss greatest rival. Buffon arranged to have Lamarcks work published at government expense, and Lamarck received the proceeds from the sales. The work appeared in three volumes under the title Flore française (1778; French Flora). Lamarck designed the Flore française specifically for the task of plant identification and used dichotomous keys, which are classification tools that allow the user to choose between opposing pairs of morphological characters (see taxonomy: The objectives of biological classification) to achieve this end.
With Buffons support, Lamarck was elected to the Academy of Sciences in 1779. Two years later Buffon named Lamarck correspondent of the Jardin du Roi, evidently to give Lamarck additional status while he escorted Buffons son on a scientific tour of Europe. This provided Lamarck with his first official connection, albeit an unsalaried one, with the Jardin du Roi. Shortly after Buffons death in 1788, his successor, Flahault de la Billarderie, created a salaried position for Lamarck with the title of botanist of the King and keeper of the Kings herbaria.
Between 1783 and 1792 Lamarck published three large botanical volumes for the Encyclopédie méthodique (Methodical Encyclopaedia) , a massive publishing enterprise begun by French publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke in the late 18th century. Lamarck also published botanical papers in the Mémoires of the Academy of Sciences. In 1792 he cofounded and coedited a short-lived journal of natural history, the Journal dhistoire naturelle.
Lamarcks career changed dramatically in 1793 when the former Jardin du Roi was transformed into the Muséum National dHistoire Naturelle (National Museum of Natural History). In the changeover, all 12 of the scientists who had been officers of the previous establishment were named as professors and coadministrators of the new institution; however, only two professorships of botany were created. The botanists Antoine-Laurent de Jussieu and René Desfontaines held greater claims to these positions, and Lamarck, in a striking shift of responsibilities, was made professor of the insects, worms, and microscopic animals. Although this change of focus was remarkable, it was not wholly unjustified, as Lamarck was an ardent shell collector. Lamarck then set out to classify this large and poorly analyzed expanse of the animal kingdom. Later he would name this group animals without vertebrae and invent the term invertebrate. By 1802 Lamarck had also introduced the term biology.
This challenge would have been enough to occupy the energies of most naturalists; however, Lamarcks intellectual aspirations ran well beyond that of reforming invertebrate classification. In the 1790s he began promoting the broad theories of physics, chemistry, and meteorology that he had been nurturing for almost two decades. He also began thinking about Earths geologic history and developed notions that he would eventually publish under the title of Hydrogéologie (1802). In his physico-chemical writings, he advanced an old-fashioned, four-element theory that was self-consciously at odds with the revolutionary advances of the emerging pneumatic chemistry of Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier. His colleagues at the Institute of France (the successor to the Academy of Sciences) saw Lamarcks broad theorizing as unscientific system building. Lamarck in turn became increasingly scornful of scientists who preferred small facts to larger, more important ones. He began to characterize himself as a naturalist-philosopher, a person more concerned with the broader processes of nature than the details of the chemists laboratory or naturalists closet.
In 1800 Lamarck first set forth the revolutionary notion of species mutability during a lecture to students in his invertebrate zoology class at the National Museum of Natural History. By 1802 the general outlines of his broad theory of organic transformation had taken shape. He presented the theory successively in his Recherches sur lorganisation des corps vivans (1802; Research on the Organization of Living Bodies), his Philosophie zoologique (1809; Zoological Philosophy), and the introduction to his great multivolume work on invertebrate classification, Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres (1815–22; Natural History of Invertebrate Animals) . Lamarcks theory of organic development included the idea that the very simplest forms of plant and animal life were the result of spontaneous generation. Life became successively diversified, he claimed, as the result of two very different sorts of causes. He called the first the power of life, or the cause that tends to make organization increasingly complex, whereas he classified the second as the modifying influence of particular circumstances (that is, the effects of the environment). He explained this in his Philosophie zoologique : The state in which we now see all the animals is on the one hand the product of the increasing composition of organization, which tends to form a regular gradation, and on the other hand that of the influences of a multitude of very different circumstances that continually tend to destroy the regularity in the gradation of the increasing composition of organization.
With this theory, Lamarck offered much more than an account of how species change. He also explained what he understood to be the shape of a truly natural system of classification of the animal kingdom. The primary feature of this system was a single scale of increasing complexity composed of all the different classes of animals, starting with the simplest microscopic organisms, or infusorians, and rising up to the mammals. The species, however, could not be arranged in a simple series. Lamarck described them as forming lateral ramifications with respect to the general masses of organization represented by the classes. Lateral ramifications in species resulted when they underwent transformations that reflected the diverse, particular environments to which they had been exposed.
By Lamarcks account, animals, in responding to different environments, adopted new habits. Their new habits caused them to use some organs more and some organs less, which resulted in the strengthening of the former and the weakening of the latter. New characters thus acquired by organisms over the course of their lives were passed on to the next generation (provided, in the case of sexual reproduction, that both of the parents of the offspring had undergone the same changes). Small changes that accumulated over great periods of time produced major differences. Lamarck thus explained how the shapes of giraffes, snakes, storks, swans, and numerous other creatures were a consequence of long-maintained habits. The basic idea of the inheritance of acquired characters had originated with Anaxagoras, Hippocrates, and others, but Lamarck was essentially the first naturalist to argue at length that the long-term operation of this process could result in species change.
Later in the century, after English naturalist Charles Darwin advanced his theory of evolution by natural selection, the idea of the inheritance of acquired characters came to be identified as a distinctively Lamarckian view of organic change (though Darwin himself also believed that acquired characters could be inherited). The idea was not seriously challenged in biology until the German biologist August Weismann did so in the 1880s. In the 20th century, since Lamarcks idea failed to be confirmed experimentally and the evidence commonly cited in its favour was given different interpretations, it became thoroughly discredited. Epigenetics, the study of the chemical modification of genes and gene-associated proteins, has since offered an explanation for how certain traits developed during an organisms lifetime can be passed along to its offspring.
Lamarck made his most important contributions to science as a botanical and zoological systematist, as a founder of invertebrate paleontology, and as an evolutionary theorist. In his own day, his theory of evolution was generally rejected as implausible, unsubstantiated, or heretical. Today he is primarily remembered for his notion of the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Nonetheless, Lamarck stands out in the history of biology as the first writer to set forth—both systematically and in detail—a comprehensive theory of organic evolution that accounted for the successive production of all the different forms of life on Earth.
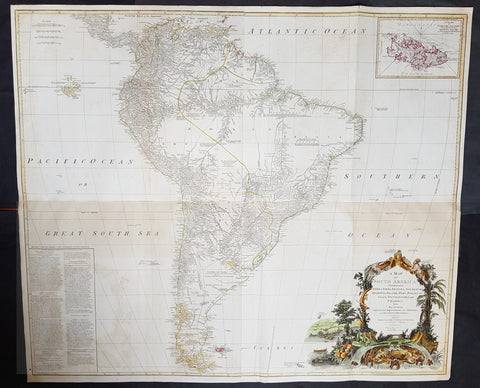
1794 Laurie, Whittle & Kitchin Very Large Original Antique Map of South America - Rare
- Title : A Map of South America containing Tierra-Firma, Guayana, New Granada, Amazonia, Brasil, Peru, Paraguay, Chaco, Tucuman, Chili and Patagonia from M. d'Anville with Several Imporvements and Additions, and The Newest Discoveries.
- Date : 1794
- Size: 48in x 41in (1.22m x 1.10m)
- Ref #: 16257
- Condition: (+) Very Good Condition
Description: This very large, incredibly important, highly detailed beautifully hand coloured original antique map of South America, with contributions from two prominent 18th century cartographers, Thomas Kitchin & Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D'Anville, was updated and published by Laurie & Whittle in 1794, dated in the title cartouche, for the Elephant Folio General Atlas.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - Off white
Age of map colour: - Original & early
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 48in x 41in (1.22m x 1.10m)
Plate size: - 47in x 40in (1.19m x 1.04m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair to bottom margin,
Plate area: - Folds as issued, offsetting & browning to bottom half of image
Verso: - Folds as issued, light browning
Background:
This is probably the most important two panel wall map of South America produced in the 18th century. Largely based upon the earlier D'Anville map, this map has been enlarged and expanded by the English publishing house of Laurie and Whittle. Depicts the continent in full with an inset of the Falkland Islands. This map is unique in that it is a serious attempt to compile all of the accurate scientific knowledge of the South American continent available at the time. Offers a smorgasbord of factual, speculative, and historical detail.
This extraordinary and highly decorative map bears up to almost endless perusal and volumes could be composed upon its content. The cartographer attempts to depict both known and unknown parts of the continent with actual data reported by both contemporary and historic travelers. In most cases it is extremely difficult to identify specific sources as much of the data is vague and uncertain.
Our survey of this map beings with the coast which Spanish and Portuguese navigators had mapped with considerable accuracy as early as the late 16th century. This, like most early maps of the area, contrasts a detailed mapping of the coast with a speculative discussion of the interior, particularly Patagonia and the Amazon Basin. Offers a fairly accurate discussion of both the east and west coasts with exceptional detail in the populated Andean regions of Venezuela, Columbia, Ecuador (Labeled Quito), and Peru. Notes Cuzco, Lima, Quito, Valladolid, Arequipa, Trujillo and other important trading centers of the region. In Portuguese controlled Brazil, Rio de Janeiro, San Salvador and San Sebastian are noted.
It is in the interior that this map becomes exceptionally fascinating. In the northern part of the continent D'Anville maps a number of confusions associated with the English adventurer Sir Walter Raleigh's search for El Dorado. Believing El Dorado to lie in the northern part of the Amazon, Raleigh sailed down the Orinoco River just before the onset of the rainy season. Reaching a remote tribal village, Raleigh noted canoes arriving bearing gold, silver, and other treasures. Asked where the gold came from, the natives replied, 'Manoa,' the term for the tribe to which the river traders belonged. Manoa, the natives claimed could be reached following a long river voyage southward to a Great Lake, called Parima. Raleigh and his associates immediately associated Manoa and Lake Parima with the golden kingdom of El Dorado, though they never visited the city or lake. Subsequent maps, including this one, mapped El Dorado and Lake Parima in this location for several hundred years. Both Raleigh and the natives were describing an actual event known to occur annually in the region. Rains would annually swell the Amazon and Orinoco river systems creating a linkage in the Parima flood plain, which, during heavy rains, can resemble a massive lake. The Manoa were a large and populous trading nation active pre-colonial days whose vast empire, based in the Amazon Basin, extended form the Andes to the Orinoco. Curiously, in addition to noting the city of Manoa on Lake Parima, D'Anville also correctly maps the center of the ancient Manoan civilization between the Amazon tributaries Rio Negro and Rio Yapura. Sadly the Manoa and many of the other populous South American indigenous nations noted by the earliest explores to the region vanished, brought low by European epidemics.
A similar error appears far to the south where the Paraguay rivers empties into the Laguna de Xarayes. The Xarayes, a corruption of 'Xaraies' meaning 'Masters of the River,' were an indigenous people occupying what are today parts of Brazil's Matte Grosso and the Pantanal. When Spanish and Portuguese explorers first navigated up the Paraguay River, as always in search of El Dorado, they encountered the vast Pantanal flood plain at the height of its annual inundation. Understandably misinterpreting the flood plain as a gigantic inland sea, they named it after the local inhabitants, the Xaraies. The Laguna de los Xarayes almost immediately began to appear on early maps of the region and, at the same time, almost immediately took on a legendary aspect. Later missionaries and chroniclers, particularly Diaz de Guzman, imagined an island in this lake and curiously identified it as an 'Island of Paradise,'
...an island [of the Paraguay River] more than ten leagues [56 km] long, two or three [11-16 km] wide. A very mild land rich in a thousand types of wild fruit, among them grapes, pears and olives: the Indians created plantations throughout, and throughout the year sow and reap with no difference in winter or summer, ... the Indians of that island are of good will and are friends to the Spaniards; Orejon they call them, and they have their ears pierced with wheels of wood ... which occupy the entire hole. They live in round houses, not as a village, but each apart though keep up with each other in much peace and friendship. They called of old this island Land of Paradise for its abundance and wonderful qualities.
To the north of the 'Island of Paradise' appeared the 'Puerto de los Reyes' which was considered to be a gateway to the Amazon and the Kingdom of El Dorado. D'Anville, to his credit, shows the 'Laguna' and it's island in a much reduced form compared to earlier cartographers and also comments that its existence is 'dubious.'
Far to the south Patagonia is crisscrossed with a number of speculative rivers based upon assumptions from earlier cartographers. D'Anville notes several questionable river passes that suggest a possible navigable communication between the east and west coasts of the continent. Speculation on such a pass fueled the famous South Sea Company, one of the modern world's first stock bubbles, but when no such pass was discovered, the bubble burst.
D'Anville also notes several offshore discoveries including the Galapagos, which he calls the Inchanted Islands, the Isle of Georgia, the Juan Fernandez islands, the Falkands, and some curious land masses just west of the Galapagos labeled 'Isles known to the Spanish.' Curiously, he also notes a 'a Bank of Sounding Discovered by Capt. Hook in 1767.' We know of no navigator by the name of Captain Hook except Peter Pan's fictional nemesis. Most likely this is a misprinted reference to Captain Cook, who was active in the Atlantic at this time. One can only wonder if J.M. Barrie had this map handy when imagining his fictional villain.
Prepared from work by D'Anville and published by Laurie & Whittle in Kitchin's 1794 General Atlas.
1797 John Russell Old, Antique Map of The Great Lakes & Canada, North America
- Title : British Colonies in North America from the best Authorities
- Ref : 70195
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1797
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique map of Canada and the Great Lakes was engraved in 1797 - dated at foot of map - by John Russell and published by Charles Dilly & John Robinson, London. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (260mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (260mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
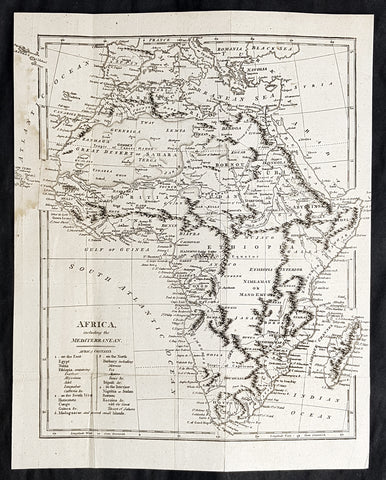
1798 Arron Arrowsmith Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africa including the Mediterranean
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1798
- Ref #: 30202
Description:
This highly detailed original copper-plate engraved antique map by Aaron Arrowsmith was published in the 1798 edition of Clement Crutwells Atlas to Crutwells Universal Gazatteer.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Clement Cruttwell (1743 - 1808) was an English compiler of religious works and gazetteers.
Cruttwell was born at Wokingham, Berkshire in 1743. He enrolled at St Mary Hall, Oxford on 14 December 1780. He commenced his career as a surgeon at Bath, where he published his Advice to Lying-in Women in 1779. He soon afterwards took orders. He published Bishop Thomas Wilsons Bible and an autobiography in 1785. He then began his Concordance of the Parallel Texts of Scripture (1790), which he printed in his own house, and on its completion his health was so broken down that he went to the baths of Saint-Amand for a cure. His Gazetteer of France (1793) and Gazetteer of the Netherlands (1794) were succeeded by his Universal Gazetteer (1798), an enormous compilation, of which the entire edition was quickly sold out. He was engaged on a second edition of this great work, which was to contain thirty thousand fresh articles, when he died suddenly while on the way to his native town, at Froxfield in Wiltshire, on 5 August 1808.
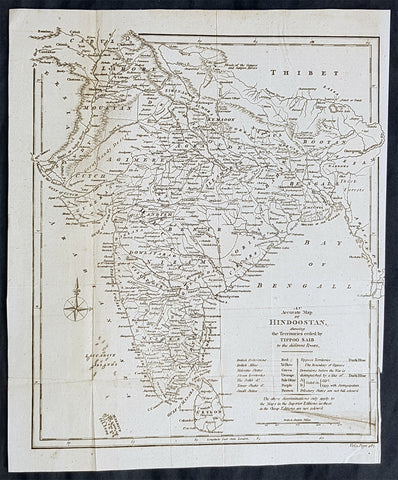
1798 Arron Arrowsmith Antique Map of India or Hindoostan
- Title : An accurtae map of Hindoostan
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1798
- Ref #: 30212
Description:
This highly detailed original copper-plate engraved antique map by Aaron Arrowsmith was published in the 1798 edition of Clement Crutwells Atlas to Crutwells Universal Gazatteer.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
Clement Cruttwell (1743 - 1808) was an English compiler of religious works and gazetteers.
Cruttwell was born at Wokingham, Berkshire in 1743. He enrolled at St Mary Hall, Oxford on 14 December 1780. He commenced his career as a surgeon at Bath, where he published his Advice to Lying-in Women in 1779. He soon afterwards took orders. He published Bishop Thomas Wilsons Bible and an autobiography in 1785. He then began his Concordance of the Parallel Texts of Scripture (1790), which he printed in his own house, and on its completion his health was so broken down that he went to the baths of Saint-Amand for a cure. His Gazetteer of France (1793) and Gazetteer of the Netherlands (1794) were succeeded by his Universal Gazetteer (1798), an enormous compilation, of which the entire edition was quickly sold out. He was engaged on a second edition of this great work, which was to contain thirty thousand fresh articles, when he died suddenly while on the way to his native town, at Froxfield in Wiltshire, on 5 August 1808.
1798 John Stockdale Original Antique Map Plan of The Canadian City of Quebec
- Title : A Plan of the City of Quebec
- Size: 10 1/2in x 7 1/2in (265mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 15651
- Date : 1798
- Condition: (A)Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique map of the city of Quebec with reference to many buildings and places of interest by John Stockdale in 1798 was published in Isaac Welds 1799 edition of Travels Through the States of North America and the Provinces of Upper and Lower Canada During the Years 1795, 1796 and 1797
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 7 1/2in (265mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 7 1/2in (265mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to border & extended
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
An interesting & detailed map of Quebec issued near the end of the eighteenth century. The map was published in Isaac Weld\'s work describing his travels through North America between 1795 and 1797. This map focuses on the scene of General Wolfe\'s great victory at the end of the French and Indian War. Quebec has always been scenic, and those with interests in the region had every reason to believe that it would be of central interest in any forthcoming clash between Great Britain and the United States.
1798 W H Hall Large Antique Print Various 18th century Navigational Instruments
- Title : Elements of Navigation....Halls Encyclopedia...C. Cooke
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90688
- Size: 15in x 9in (380mm x 230mm)
- Date: 1798
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print was was published by William Henry Hall in the 1798 edition of The new royal encyclopedia; or, complete modern universal dictionary of arts and sciences on a new and improved plan.... printed by Charles Cooke, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 9in (380mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 9in (380mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
In the European medieval period, navigation was considered part of the set of seven mechanical arts, none of which were used for long voyages across open ocean. Polynesian navigation is probably the earliest form of open-ocean navigation, it was based on memory and observation recorded on scientific instruments like the Marshall Islands Stick Charts of Ocean Swells. Early Pacific Polynesians used the motion of stars, weather, the position of certain wildlife species, or the size of waves to find the path from one island to another.
Maritime navigation using scientific instruments such as the mariners astrolabe first occurred in the Mediterranean during the Middle Ages. Although land astrolabes were invented in the Hellenistic period and existed in classical antiquity and the Islamic Golden Age, the oldest record of a sea astrolabe is that of Majorcan astronomer Ramon Llull dating from 1295. The perfecting of this navigation instrument is attributed to Portuguese navigators during early Portuguese discoveries in the Age of Discovery. The earliest known description of how to make and use a sea astrolabe comes from Spanish cosmographer Martín Cortés de Albacars Arte de Navegar (The Art of Navigation) published in 1551, based on the principle of the archipendulum used in constructing the Egyptian pyramids.
Open-seas navigation using the astrolabe and the compass started during the Age of Discovery in the 15th century. The Portuguese began systematically exploring the Atlantic coast of Africa from 1418, under the sponsorship of Prince Henry. In 1488 Bartolomeu Dias reached the Indian Ocean by this route. In 1492 the Spanish monarchs funded Christopher Columbuss expedition to sail west to reach the Indies by crossing the Atlantic, which resulted in the Discovery of the Americas. In 1498, a Portuguese expedition commanded by Vasco da Gama reached India by sailing around Africa, opening up direct trade with Asia. Soon, the Portuguese sailed further eastward, to the Spice Islands in 1512, landing in China one year later.
The first circumnavigation of the earth was completed in 1522 with the Magellan-Elcano expedition, a Spanish voyage of discovery led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan and completed by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano after the formers death in the Philippines in 1521. The fleet of seven ships sailed from Sanlúcar de Barrameda in Southern Spain in 1519, crossed the Atlantic Ocean and after several stopovers rounded the southern tip of South America. Some ships were lost, but the remaining fleet continued across the Pacific making a number of discoveries including Guam and the Philippines. By then, only two galleons were left from the original seven. The Victoria led by Elcano sailed across the Indian Ocean and north along the coast of Africa, to finally arrive in Spain in 1522, three years after its departure. The Trinidad sailed east from the Philippines, trying to find a maritime path back to the Americas, but was unsuccessful. The eastward route across the Pacific, also known as the tornaviaje (return trip) was only discovered forty years later, when Spanish cosmographer Andrés de Urdaneta sailed from the Philippines, north to parallel 39°, and hit the eastward Kuroshio Current which took its galleon across the Pacific. He arrived in Acapulco on October 8, 1565.
Hall, William Henry
Hall was responsible for a significant publication in the middle of the 18th century The new royal encyclopedia; or, complete modern universal dictionary of arts and sciences on a new and improved plan . containing a digest and display of the whole theory and practice of the liberal and mechanical arts comprising a general repository of ancient and modern literature . including all the material information that is contained in Chamber s Cyclopedia, the Encyclopædia Britannica, and the French Encyclopædie . first published in 1788 going into many re-issues over the next 50 years.
The three volume set contained 153 copper-plate prints and maps, including some folding maps. Contained many brief encyclopedic entries in alphabetical orders plus longer, mainly illustrated, sections (systems or treatises) on a variety of subjects: Aerology; Aerostation (hot air balloons); Agriculture; Algebra; Amphibiology; Anatomy; Annuities; Architecture; Arithmetic; Astronomy (includes plates of telescopes); Book-Keeping; Botany; Brewing; Chronology; Chymistry; Comparative Anatomy; Concology; Dialling; Distillation; Drawing; Earth; Earthquakes; Electricity; Entomology; Farriery; Fencing; Fluxions; Fortification; Gardening; Geography (this section includes six folding maps); Geometry; Globes; Grammar; Heraldry; Hydrostatics and Hydraulics (one plate included a diving bell); Icthyology; Knighthood; Logic; Mammalia (included a plate showing whales); Mechanics; Medicine; Mensuration and Gauging; Miscroscopic Apparatus (microscopes); Midwifery; Military Affairs; Music; Natural History; Naval Affairs; Navigation (includes a folding map showing Cooks voyages); Optics; Oratory; Ornithology; Peerage; Perspective; Pneumatics; Projectiles; Steam Engines; Surgery; Surveying; Trigonometry; Vermeology; Volcanos; and War. Hard to find a complete set, as many have been broken up for their handsome copper plate engravings and maps.
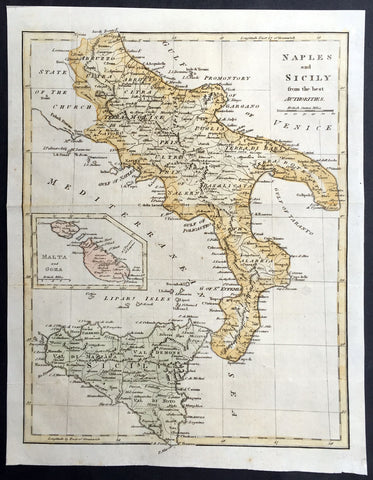
1799 Cary, Moores Old, Antique map of Southern Italy Sicily - Malta & Goza Isles
- Title : Naples and Sicily from the best Authorities
- Ref #: 92750
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1799
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Southern Italy & Sicily - with an inset map of the Islands of Malta & Goza - by John Cary was published in the 1799 edition of Henry Moore's A New and Comprehensive System of Universal Geography, printed by Macdonald and Son, London. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1799 Le Barbier Large Antique Print Consecration of Cora to the Sun Cult, Mexico
- Title : Consécration de Cora au culte du Soleil
- Ref #: 40446
- Size: 21in x 18 1/2in (535mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1799
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully engraved large original antique print of the Consecration of Cora to the Sun Cult after Jean Jacques Francois Le Barbier was engraved by Louis-François Marriage in ca 1799.
Louis-François Mariage is a French dotted engraver who was active in Paris between 1785 and 1828. He sometimes signed his inverted surname, Egairam .
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 18 1/2in (535mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 18 1/2in (535mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling, small re-join to bottom margin
Plate area: - Small repair to top of image, no loss
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
The Cora are an indigenous ethnic group of Western Central Mexico which live in the municipality El Nayar in the Mexican state of Nayarit and in a few settlements in the neighboring state of Jalisco. They call themselves náayerite whence the name of the present day Mexican state of Nayarit.
The Cora live in the rugged mountain and canyon country of Nayarit and across the border in neighboring Jalisco, Durango, and Sinaloa. In the early 18th century they were an anomaly in that they had never permitted Catholic missionaries to live in their country. They had become a pagan island in a sea of Christian Indians and Hispanic culture. In 1716, a Spanish expedition to attempt to bring the Cora under Spanish control failed. However, in 1722, the Spanish returned in force and the Cora yielded. According to Spanish accounts many of them became Christian and practice, up until the present, Catholic-derived customs.
The Cora religion is a syncretism between the pre-Conquest religion and Catholicism.
The ancestral Cora religion has three principal divinities. The supreme god is the sun god, Tayau, our father. He travels across the sky during the day, sitting down in his golden throne at noon. Clouds are believed to be smoke from his pipe. In earlier times the priests of Tayau, the tonatí, were the highest authority of the Cora communities. His wife is Tetewan, the underworld goddess associated with the moon, rain, and the west. Her alternate names are Hurima and Nasisa. Their son, Sautari, the flower picker, is associated with maize and the afternoon. Other names for him are Hatsikan, big brother, Tahás, and Ora. He is also associated with Jesus Christ.
Some Cora myths clearly have Mesoamerican origins; for example, the myth of the creation of the fifth sun. Others are shared with the geographically and linguistically adjacent Huichol; for example, the myth of the human race being the offspring of a man and a dog-woman who were the only survivors of a mythical cataclysmic deluge.
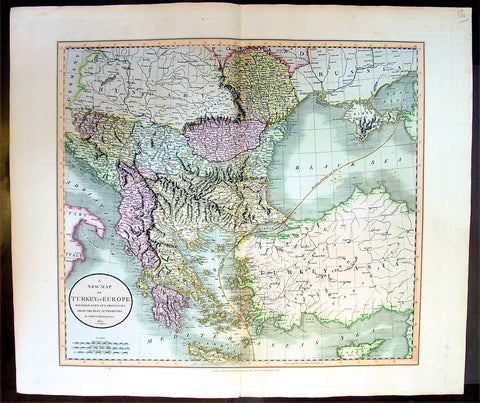
1801 Cary Antique map of Turkey in Europe - Greece, Balkans, Bosnia, Moldavia
- Title : A New Map of Turkey in Europe, Divided into its Provinces, from the Best Authorities 1801
- Ref #: 16433
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1801
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Ottoman Empire in Europe from Greece, The Balkans to Hungary by John Cary was engraved in 1801 - the date is engraved in the title - and was published in Cary's large New Universal Atlas.
An exceptionally beautiful example of John Cary’s important 1801 map of Turkey in Europe. Covers from the Adriatic eastward to Crimea and Southwards as far as Crete and Cyprus. While technically a map of Ottoman holdings in Europe, this map is essentially a map of Greece and the Balkans. Includes the modern day countries of Turkey, Greece, Albania, Macedonia, Rumania, Bulgaria, Moldova, Serbia, Bosnia, Croatia and Montenegro. Notes the line of Division between Europe and Asia as it passes through the Black Sea and the Aegean. All in all, one of the most interesting and attractive atlas maps of Greece and the Balkans to appear in first years of the 19th century. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1804 Jean N Buache Original Antique Map of Spain, Portugal & Balearic Islands
- Title : Espagne et Portugal
- Size: 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
- Ref #: 34186
- Date : 1804
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map was published in the 1804 edition of Jean Nicolas Buache Atlas Geographie Moderne.
The maps in this atlas were illustrated by Jean Nicolas Buache - nephew to Phillipe Buache who was son-in-law to Nicolas Delisle - after maps published by the Scottish publisher John Pinkerton.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
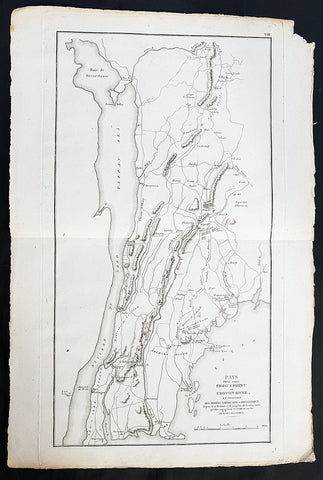
1807 John Marshall Antique Map Battle of Pells Point in The Bronx, NYC in 1776
- Title: Pays Situe Entre Frogs Point et Croton River, et Position Des Armees Americaine et Brittannique....1776
- Date: 1807
- Ref: 33645
- Size: 18in x 12in (460mm x 305mm)
- Condition: - (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Battle of Pells Point, also known as the Battle of Pelham, a conflict that took place in what is now part of Pelham Bay Park in the Bronx, New York City the golf courses of Split Rock Golf Course & Pelham Bay Golf Course in The Bronx, New York City, in October 1776 during the American Revolutionary War, was published in the 1807 French edition of John Marshall\'s The Life of George Washington.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18in x 12in (460mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 10in (460mm x 255m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Pell\'s Point (October 18, 1776), also known as the Battle of Pelham, was a skirmish fought between British and American troops during the New York and New Jersey campaign of the American Revolutionary War. The conflict took place in what is now part of Pelham Bay Park in the Bronx, New York City the golf courses of Split Rock Golf Course & Pelham Bay Golf Course in The Bronx, New York City and the towns of Pelham Manor and Pelham in Westchester County, NY.
On October 12, British forces landed at Throgs Neck in order to execute a flanking maneuver that would trap Gen. George Washington, commander-in-chief of the American revolutionary forces, and the main body of the Continental Army on the island of Manhattan. The Americans thwarted the landing, and Gen. Sir William Howe, commander-in-chief of British forces in North America, looked for another location along Long Island Sound to disembark his troops. On October 18, he landed 4,000 men at Pelham, 3 miles north of Throgs Neck. Inland were 750 men of a brigade under the command of the American Col. John Glover. Glover positioned his troops behind a series of stone walls and attacked the British advance units. As the British overran each position, the American troops fell back and reorganized behind the next wall. After several such attacks, the British broke off, and the Americans retreated.
The battle delayed British movements long enough for Washington to move the main army to White Plains and avoid being surrounded on Manhattan. After losing to the British in a battle at White Plains, and losing Fort Washington, Washington retreated across New Jersey to Pennsylvania.
At dawn, the British began to land on the shore, Clinton\'s advance guard of 4,000 British light infantry and Hessian jägers landing first. Inland, opposing them, was a brigade of some 750 men under the command of John Glover. Glover was atop a hill with a telescope when he noticed the British ships. (hill on the west side of the Hutchinson River Parkway and the Hutchinson River on East Sanford Blvd. in Mount Vernon, NY on the opposite side of the Hutchinson River Parkway and Pelham Memorial High School) Glover sent an officer, Major William Lee, to report to Charles Lee, Washington\'s second in command, and ask for orders. However, Lee did not give any orders, and in the absence of orders Glover chose to attack. Glover turned out his brigade, which consisted of the 14th, 13th, 3rd and the 26th Continental Regiments. Glover left the 150 men of the 14th Continentals behind in reserve. Glover had not closed half the distance when he ran into approximately 30 skirmishers. Glover ordered a Captain and his 40-man company forward as an advance guard to hold the British in check, while Glover organized the rest of the force.
Glover prepared an ambush by placing the main body in staggered positions behind the stone walls that lined either side of the laneway leading from the beachhead to the interior. Glover instructed each of the regiments to hold their position as long as they could and then to fall back to a position in the rear, while the next unit took up the fighting. Glover then rode up to take command of the advance guard. The advance guard and the British began to engage each other, both sides taking casualties. After a little while the British were reinforced, and Glover ordered a retreat, which was done without confusion. The British troops began to advance at the retreating Americans. However, the 200 troops of the 13th Continentals that Glover had stationed behind the stone wall stood up and fired at the British when there were only 30 yards away. The ambush worked, and the column of British troops took heavy losses and fell back to the main body of the invading army.
The British waited half an hour before attacking again. This time when they attacked, they attacked with all 4,000 men and seven cannon. The British bombarded the American position behind the stone wall as their infantry advanced. The cannon fire was ineffective, and when the British were 50 yards away the Americans fired a volley which stopped the British infantry. The British returned fire, and musket and rifle fire ensued for 20 minutes, the British supported by cannon, at which point the lead American regiment fell back under cover of the next reserve regiment. The 3rd Continental Regiment was stationed behind the stone wall on the opposite side of the road.
The British attacked the position of the 3rd Continentals, and an engagement ensued. Both sides kept up constant fire, the Americans breaking the British lines several times. However, after 17 volleys, the British numbers began to overwhelm the Americans, and Glover ordered a withdrawal to another stone wall on the crest of a hill while the next regiment in line, the 26th Continentals, engaged the British.
A reconnaissance party of 30 men was sent out from behind the third stone wall to see if the British would try and flank the American position. The party ran into the British, who had continued to advance, and they fell back to the stone wall. The Americans behind the wall fired one volley before Glover gave the order to retreat. The Americans retreated across a bridge over the Hutchinson stream, their retreat covered by the 150 men of the 14th Continentals who engaged in an artillery duel with the British. Howe camped on a hill on the opposite side of the stream but made no attempt to cross the stream.
The next day, Glover and his force retreated to the town of Yonkers. American casualties were 8 killed and 13 wounded. British and Hessian casualties are not known. Howes official dispatch listed British casualties as 3 killed and 20 wounded, although the report did not include Hessian casualties. As the Hessians made up the majority of the landing force, it is reasonable to expect they made up the majority of the casualties. Over the next few days, from knowledge collected from British deserters, the Americans estimated that the British lost between 800 and 1,000 killed or wounded, likely an exaggeration. Colonel Loammi Baldwin, (an officer and fruit fancier whose fame came in the Baldwin apple) who was present at the battle, estimated that the Americans had killed 200 British and Hessians, but historian David McCullough says this was undoubtedly an exaggeration. Historian George Athan Billias argues in support of Baldwin\'s estimates, due in part to the corroborating admission of another British deserter. Regardless, the combined British and Hessian casualties were almost certainly larger than those of the Americans.
With the British advance delayed, the main American army under Washington was able to safely evacuate from Harlem (on the island of Manhattan) to White Plains. Howe slowly moved his army through New Rochelle and Scarsdale. On October 28, he sent 13,000 men to attack the Americans, resulting in a minor victory over Washington at the Battle of White Plains. Fort Washington, the last American stronghold on Manhattan, fell on November 16. With these defeats, Washington and his army retreated across New Jersey and into Pennsylvania, paving the way for the Battles of Trenton and Princeton.
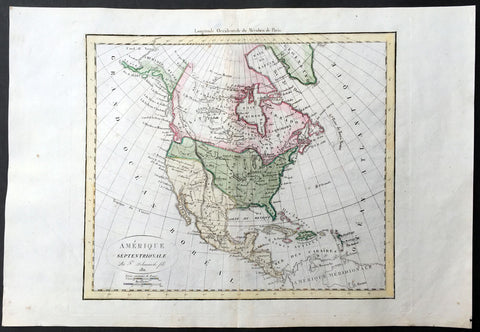
1811 Delamarche Antique Map of North America, Russian Alaska
- Title : Amerique Septentrionale Par F Delmarche fils 1811
- Ref #: 35093
- Size: 18in x 12 1/2in (460mm x 310mm)
- Date : 1811
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique Map of North America by Robert De Vaugondy was published by Charles Francois Delamarche, De Vaugondy's successor, in 1811 - dated in the title.
Great early 19th century map of North America showing French Spanish and English possessions of North America. Alaska is shown as Russian Territory. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, green, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper Size: - 18in x 12 1/2in (460mm x 310mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 11 3/4in (330mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
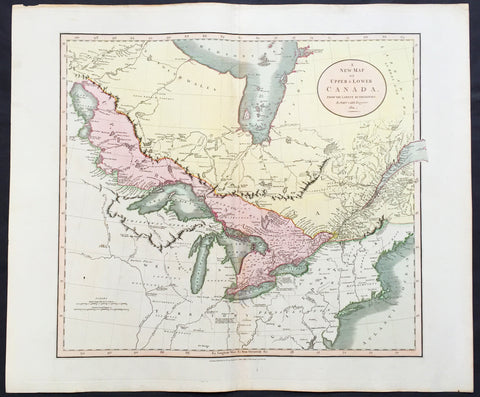
1811 John Cary Large Old, Antique Map of The Great Lakes of North America
- Title : A New Map of Upper & Lower Canada by John Cary...1811
- Ref #: 61107
- Size: 26in x 21 1/2in (660mm x 550mm)
- Date : 1811
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Great Lakes of North America was engraved by John Cary in 1811 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in Cary's New Universal Atlas. (Ref Tooley M&B)
John Cary (1745 - 1835) many regard Cary as one of the finest English cartographers of his time. His maps are not as decorative in the 17th century sense, but he came to on the scene at a time when the large-scale English county maps had recently become available. His fine craftsmanship and ability as an engraver enabled him to produce not only fine English county maps but also world atlases, road maps, town and canal plans sea charts and terrestrial and celestial globes.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 21 1/2in (660mm x 550mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1817 Capt. Frederick L Norden Antique Atlas of Egypt & Nubia - 1 Map & 22 Prints
- Title : Atlas de Norden...Chez M.Me Lepetit...1817
- Ref #: 91614
- Size: 8vo
- Date : 1817
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original antique Atlas, Voyage d'Egypte et de Nubie, travels to Egypt and Nubia by the Dane, Captain Frederick Louis Norden was translated and published in Paris by M Henry & Breton in the 1817 - dated - edition of Biblio Portative Des Voyages Traduite De L Anglais Par MM. Henry et Breton Tome XIII (Portable Travel Library. Translated from the English by MM Henry and Breton Volume 13)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy, stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Atlas size: - 8vo
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
The atlas covers have been removed with front title page partially detached & damaged. Pages are generally clean, with some age toning, overall VG. Size 8vo, each page size is 7in x 5in (180mm x 125mm)
1. Cours du Nil Depuis le Sennaar
2. Vue de Ville d Alexandrie....
3. Vue de la Ville et du Port Neuf d Alexandrie....
4. Vue de la Vieille Alexandrie
5. A: Chateau d Aboukir B: Vue de cote de l Orient meridional C: Plan du Chateau vec son port
6. Fig1: Vue de la villede Rosette Fig 2: Chateau de Rosette Fig 3: Vue du village de Deruth
7. Perspective du Vieux Caire
8. Vue du vieux Caire et d'une Pyramide dans le lointain
9. Vue de la ville de Gize ci-devant Memphis....
10. Coupe du Mokian
11. Plan de l ile de Rodda
12. Village de Dair Etun
13. Vue des Pyramides proche du Caire
14. Vue des Pyramides de Memphis
15. Maisons ordinaires des Arabec
16. Ruines di Palais de Memmon
17. Portail antique plien de Hieroglyphes en couleur et ...
18. Ancien Temple au milieu de la ville d Esnay
19. Deux coupes sur la longueur des superbes..Ruines du temple d Tsia
20. Fig 1: Les Deux Colosses en particular Fig 2: Portail principal des antiquities de Luxor
21. Statues colossales et Ruines du Palais de Memnon
22. Vue des Tombeaux pres d Essouan
23. Maniere de Battre les ris et de porter lEau en Egypte
Frederick Norden sailed to Egypt in 1737-38 to survey the architecture, agriculture, and other curiosities of the country. He was the first European to penetrate as far as Derr in Nubia, and produced the first coherent maps of the country. Seventeen years later, long after Norden’s death, his maps and drawings were published by the Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters, under order of Frederick V of Denmark, as Voyage d’Egypte et de Nubie (1755). Two years later, the physician and naturalist Peter Templeman completed an English translation, which was published in two folio volumes.
Frederic Louis Norden (1708 –1742) was a Danish naval captain and explorer.
Also known as Frederick, Frederik, Friderick, Ludwig, Ludvig and Lewis, the name used on the first publication of his famous Voyage d'Egypte et de Nubie (Copenhagen, 1755) is Frederic Louis Norden. His name is often shortened F. L. Norden.
Norden made a voyage through Egypt all the way down to Sudan in 1737–1738, on the request of King Christian VI of Denmark. Norden made abundant notes, observations and drawings of everything around him, including people, pharaonic monuments, architecture, installations, maps etc., all of which was published in the posthumous Voyage d'Egypte et de Nubie.
On 8 January 1741 he became a Fellow of the Royal Society of London, where his name was registered as Frederic Lewis Norden.
1817 J. Thomson Large Antique Map Turkey in Asia, Armenia, Iraq, Syria Palestine, Cyprus
- Title : Turkey in Asia
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 20in (685mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 16432
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of Turkey In Asia ( turkey, Armenia, Iraq, Afghanistan, Syria & Palestine - by John Thomson was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons New General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20 1/2in (635mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
The Ottoman Empire also historically known in Western Europe as the Turkish Empire or simply Turkey, was a state that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia and North Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Oghuz Turkish tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe, and with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the 1453 conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, at the height of its power under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was a multinational, multilingual empire controlling most of Southeast Europe, parts of Central Europe, Western Asia, parts of Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, North Africa and the Horn of Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states. Some of these were later absorbed into the Ottoman Empire, while others were granted various types of autonomy during the course of centuries.
With Constantinople as its capital and control of lands around the Mediterranean basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds for six centuries. While the empire was once thought to have entered a period of decline following the death of Suleiman the Magnificent, this view is no longer supported by the majority of academic historians. The empire continued to maintain a flexible and strong economy, society and military throughout the 17th and much of the 18th century. However, during a long period of peace from 1740 to 1768, the Ottoman military system fell behind that of their European rivals, the Habsburg and Russian empires. The Ottomans consequently suffered severe military defeats in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, which prompted them to initiate a comprehensive process of reform and modernisation known as the Tanzimat. Thus, over the course of the 19th century, the Ottoman state became vastly more powerful and organised, despite suffering further territorial losses, especially in the Balkans, where a number of new states emerged. The empire allied with Germany in the early 20th century, hoping to escape from the diplomatic isolation which had contributed to its recent territorial losses, and thus joined World War I on the side of the Central Powers. While the Empire was able to largely hold its own during the conflict, it was struggling with internal dissent, especially with the Arab Revolt in its Arabian holdings. During this time, atrocities were committed by the Ottoman government against the Armenians, Assyrians and Pontic Greeks.
The Empire\'s defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories, which were divided between the United Kingdom and France. The successful Turkish War of Independence against the occupying Allies led to the emergence of the Republic of Turkey in the Anatolian heartland and the abolition of the Ottoman monarchy.
1820 J W Lewin Antique Print Early View of Sydney Cove
- Title : Vue de la ville de Sydney
- Ref #: 61012
- Size: 7 3/4in x 4 1/2in (195mm x 115mm)
- Date : 1820
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This wonderful hand coloured original antique print an early view Sydney Cove, - attributed to a drawing, now lost, by the artist John William Lewin in ca 1820 - was published in the 1826 of Nouvelles Annales Des Voyages, De La Geographie et de L Histoire, ou Recueil, volume II.
Background:
This is an early panorama of Sydney Cove only 32 years after the first European settlement of Sydney Cove. In the foreground is an octagonal two-storey, yellow, sandstone house, built by Governor Macquarie in 1812 for his favourite boatman and former water bailiff, Billy Blue. The drawing of this little house – now the site of the Sydney Opera House — is out of all proportion to its actual modest size. Billy or William Blue (1767–1834) was an African-Jamaican who had been given a seven-year sentence in London for stealing raw sugar. To the left of the house is a sandy beach where the Circular Quay ferry wharves now stand. Facing the beach is First Government House where the Museum of Sydney is now situated.
On the western shore is the Rocks district, with two windmills on the ridge. Known as Tallawoladah by the Cadigal people, the Rocks became the convicts' side of the town. They built traditional vernacular houses, first of wattle and daub, with thatched roofs, later of weatherboards or rubble stone, roofed with timber shingles. They took in lodgers – the newly arrived convicts – who slept in kitchens and skillions. Some emancipists also had convict servants. After November 1790, large numbers of Aboriginal people also came into the town to visit and to live. By 1823, about 1,200 people lived in The Rocks, most of them emancipists and convicts and their children.
To the left of The Rocks area is a long, low, military barracks, built between 1792 and 1818 around Barracks Square/the Parade Ground – which is now Wynyard Park. It was from here that, in 1808, the New South Wales Corps marched to arrest Governor Macquarie's predecessor Governor William Bligh (1754–1817), an event later known as the Rum Rebellion. Heading east is St. Philip's Church – the earliest Christian church (Church of England) in Australia – erected in stone in 1810 on Church Hill – now Lang Park.[34] In 1798, the original wattle and daub church – on what is now the corner of Bligh and Hunter Streets – was burnt down, allegedly by disgruntled convicts in response to a decree by the second NSW Governor (1795–1800), John Hunter, that all colony residents, including officers and convicts, attend Sunday services. The jail had earlier suffered a similar fate.
Further along the ridge to the east is Fort Phillip, flying the Union Jack, on Windmill (later Observatory) Hill where the Sydney Observatory is now located. Fort Phillip was commissioned in 1804 by the third NSW Governor (1800–1806), Philip Gidley King, partly as a response to external threats and partly due to the internal unrest reflected in Australia's only major convict rebellion at Castle Hill in March 1804. This was dubbed the Battle of Vinegar Hill as most of the convict rebels were Irish. Windmill Hill was chosen as a fort location as it was the highest point above the colony, affording commanding views of the Harbour approaches from east and west, theriver and road to Parramatta, surrounding country and of the entire town below.
On the waterfront below Fort Phillip is the yellow, four-storey, Commissariat Stores, constructed by convicts for Governor Macquarie in 1810 and 1812. One of the largest buildings constructed in the colony at the time, it is now the site of the Museum of Contemporary Art. The foreshore buildings on the extreme right are the warehouse and 'Wharf House' residence of merchant, Robert Campbell (1769–1846) who was to become one of the colony's biggest landholders. This is now the site of the Sydney Harbour Bridge pylons and is just to the left of Dawes Point. Three British Sailing ships, flying either the red ensign of the Merchant Navy or (more likely) the white ensign of the Royal Navy, are anchored in the Cove along with four sailboats and five canoes.
The Sydney Cove panorama on the Museum punchbowl can be dated between 1812 and 1818. The vantage point is from beneath Dawes Point, shown with its flagstaff and before the Dawes Point fortifications built 1818 to 1821. Looking directly into Campbell's Cove, the immediate focal points are Robert Campbell's warehouse and the 'Wharf House' roof of his residence. To the right of Campbell's Wharf are extensive stone walls marking boundaries between properties in this part of the Rocks district.
First Government House can be seen at the head of Sydney Cove in the distance and around the eastern shore a small rendition of Billy Blue's 1812 house. The Governor and civil personnel lived on the more orderly eastern slopes of the Tank Stream, compared to the disorderly western side where convicts lived. The Tank Stream was the fresh water course emptying into Sydney Cove and supplied the fledgling colony until 1826. Further along is Bennelong Point – with no sign of Fort Macquarie [built from December 1817 – and Garden Island – the colony's first food source. The distant vista of the eastern side of the Harbour goes almost as far as the Macquarie Lighthouse – Australia's first lighthouse – built between 1816–18 on South Head. There are seven Sailing ships flying the white ensign of the British Royal Navy in the Harbour, along with three sailboats and two canoes.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, orange, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 7 3/4in x 4 1/2in (195mm x 115mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1824 Kelly Old, Antique Print of a North American Indian in War Dress & Tomahawk
- Title : American Indian
- Ref : 91230
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8in (270mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1824
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This wonderful hand coloured original antique print of a North American Indian in war dress was published in the 1824 edition of A New And Complete System Of Universal Geography, Or An Authentic History And Interesting Description Of The Whole World And Its Inhabitants by Christopher Kelly and was printed by Rider and Weed in Little Britain, London
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, black, gold
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (270mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8in (270mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
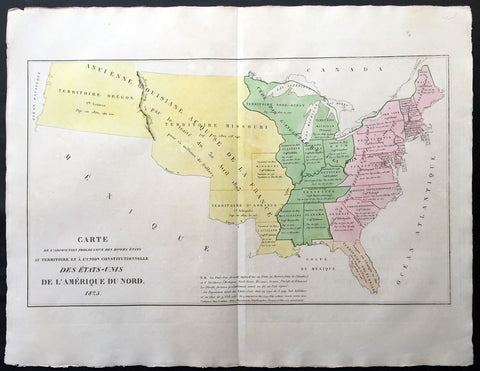
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Antique Map United States America - Oregon Territories
- Title : Carte De L'Adjonction Progressive De Divers Etats Au Territoire et A L'Union Constitutionnelle Des Etats-Unis Dd L' Amerique Du Nord 1825
- Ref #: 70004
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the United States and its territories was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
A beautifully hand coloured map and somewhat scarce early map of the United States. Most of the states are formed east of the Mississippi with the NW and Michigan Territories yet to gain statehood. To the west of the Mississippi are the states of Missouri and Louisiana with the vast territories of Arkansas, Missouri and Oregon north of the Missouri River. Each state is engraved with the date of statehood as well as the size of the population in 1790 & 1820.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases'Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None
1825 Carey & Lea Buchon Large Antique Map of East Canada & The Great Lakes
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique Des Possessions Anglaises
- Ref #: 70003
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None
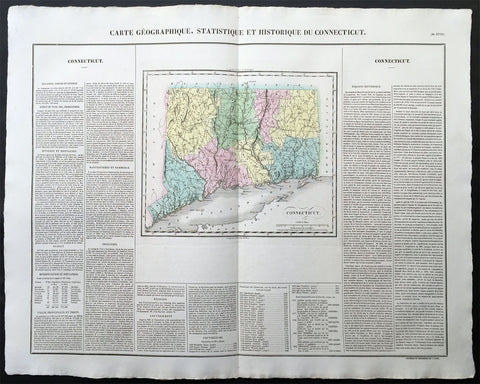
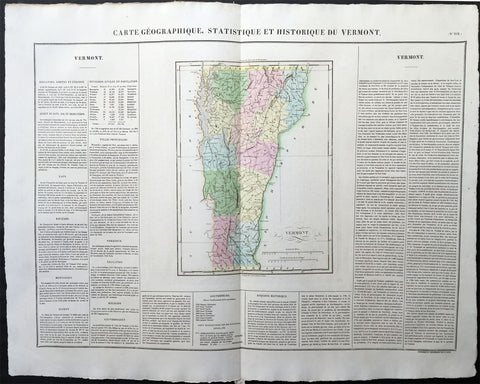
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of Connecticut, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique Du Connecticut
- Ref #: 70008
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None
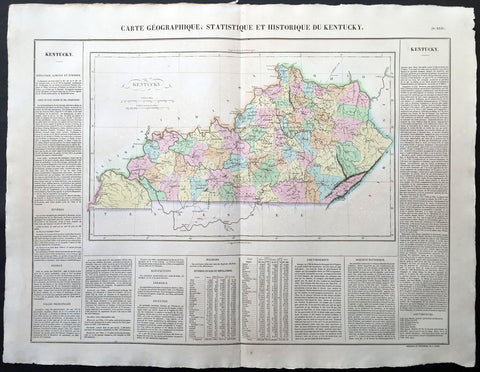
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of Kentucky, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique Du Kentucky
- Ref #: 70020
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
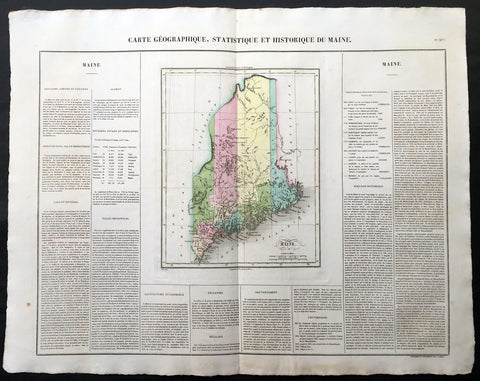
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of Maine, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique Du Maine
- Ref #: 70005
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of New Jersey, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique Du New-Jersey
- Ref #: 70011
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of Ohio, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique De Ohio
- Ref #: 70019
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of Vermont, USA
-
Title: Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique Du Vermont
- Ref: 70009
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date: 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None
1826 (1834) Brue Large Antique Map of Australia and New Zealand
-
Title : Carte de L'Australie...1826...1834
- Date : 1826 (1834)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35092
- Size: 26in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique early map of Australia & New Zealand - with an inset map of the colony of New South Wales - was engraved in 1826 with an update in 1834 - dated in the title - was published by Adrien Brue (1786 - 1832) in his atlas Universel de Geographie. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 16in (560mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - Light soiling
1830 Wyld Large Folding Antique Map Eastern Europe, Russia to Turkey, Ukraine
- Title :
- Ref #: 80506
- Size: 63in x 33in (1.6m x 840mm)
- Date : 1830
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This extremely large large original antique folding map (dissected into 56 sections on linen) of eastern Europe, Russia & Turkey - the eastern part of a huge two part map of Europe - was published in ca 1830 by James Wyld, Charing Cross East London.
This is a huge map and highly detailed stretching from Scandinavia in the north to Cyprus in the south and Lithuania and the Hungarian Empire in the west to Russia & Central Asia in the east with an amazing amount of detail. (Ref: M&B; Tooley;Clancy)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 63in x 33in (1.6m x 840mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
1833 SDUK Antique Map of New South Wales w/ inset Plan of Sydney Town
- Title : New South Wales ...from the MS Maps in the Colonial Office
- Ref : 31989
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Date : 1833
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique map of New South Wales with an inset plan of Sydney Town was engraved in 1833 by J&C Walker - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1835 Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge(SDUK) Atlas.
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes in cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford.
This is a finely engraved map with beautiful original colour t on strong, clean paper. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original & heavy
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1834 - 1840 SDUK Antique Maps of Russia x 12 Maps - Complete Set
- Title : Russia
- Ref #: 24733
- Size: 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1834 - 1840
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
These twelve finely engraved hand coloured original antique maps of Russia - a complete set - were engraved between 1834 & 1840 by J & C Walker - the dates are engraved at the foot of each map - and were published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
The maps included are;
#1 Russia General map
#2 Olonetz, Iaroslavl, Arkhangel
#3 Estonia, Livonia
#4 Novogrod, Tver, Smolensk
#5 Vilna, Grodno, Volhynia, Podolia
#6 Kalouga, Orlov, Orel, Kharkov, Ukraine
#7 Novogrod, Orenbourg, Astrkhan
#8 Podolia, Bessarabia, Kherson, Crimea
#9 Caucasus, Circassia, Astrakhan, Georgia
#10 Western Siberia, Tartary, Khiva, Bokhara
#11 Eastern Siberia
#12 Siberia & Chinese Tartary
The SDUK produced two landmark publications in cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford.
This is a finely engraved map with beautiful original colour t on strong, clean paper. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 345mm)ea.
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1834 Brue Large Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Carte Generale De L Afrique...1828...1834
- Ref #: 34266
- Size: 26in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured originalantique map of Africa - was engraved in 1834 - the date is engraved in the title - and was published in Adrien Brue's (1786 - 1832) Universel de Geographie. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 16in (560mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light offsetting
Verso: - None
1836 Brue Very Large Antique Map of Prussia - Poland To Germany
- Title : Carte Generale De La Monarchie Prussienne...1836
- Ref #: 34249
- Size: 26in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1836
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured originalantique map of Prussia stretching from Poland into Germany - was engraved in 1836 - the date is engraved in the title - and was published in Adrien Brue's (1786 - 1832) Universel de Geographie.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 21in (660mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 16in (560mm x 410mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1834 Heck Antique Map The Republic of Mexico & Texas, w/ California & Missouri Territories
- Title : Carte des Republiques Unies du Mexique J G Heck 1834
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 61005
- Size: 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (445mm x 290mm)
Description:
This original antique map of the Republic of Mexico - from California, Missouri, Texas to Central America and the Indian Territories - with parts of the early US, during the early 18th century was published in the Atlas Geographe. Astronome. Et Hystorique by Johann Georg Heck, Paris in 1834 - dated in the title.
In this map, Mexico is shown divided into several provinces that include Texas and Upper California. Routes from Natchitoches and Austin to points south are depicted, as well as several trails leading from Jefferson and St. Charles, Missouri to Santa Fe. The 1819 Adams-Onis Treaty line acts as the border between Upper California and the Oregon Territory. Native American districts are also depicted in the northern portion of the map. Within the Great Basin the mythical Lake Teguayo is shown below Lake Timpanagos with several notations including "desert country, inhabited by few" and "country of many free Indian tribes."
This is overall, an unusual and scarce map showing the Republic of Mexico and continuous parts of the United States during a very interesting time of territorial expansion in North America. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original color:
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, orange.
General color appearance: - Authentic & beautiful
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (445mm x 290mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 11 1/2in (445mm x 290mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1837 John Dower Original Antique Map of Van Diemens Land - Tasmania, Australia
- Title : Van Diemens Land
- Date : 1837
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 70705
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine steel-plate engraved original hand coloured antique map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania by John Dower was published by Orr & Smith, London in 1837. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Van Diemens Land—which thus far had existed as a territory within the colony of New South Wales—was proclaimed a separate colony, with its own judicial establishment and Legislative Council, on 3 December 1825. Transportation to the island ceased in 1853 and the colony was renamed Tasmania in 1856, partly to differentiate the burgeoning society of free settlers from the island\'s convict past.
A convict ploughing team breaking up new ground at the farm at Port Arthur.
The Legislative Council of Van Diemens Land drafted a new constitution which it passed in 1854. The following year the Privy Council approved the colony changing its name from Van Diemens Land to Tasmania, and in 1856 the newly elected bicameral parliament sat for the first time, establishing Tasmania as a self-governing colony of the British Empire.
The colony suffered from economic fluctuations, but for the most part was prosperous, experiencing steady growth. With few external threats and strong trade links with the Empire, Tasmania enjoyed many fruitful periods in the late 19th century, becoming a world-centre of shipbuilding. It raised a local defence force that eventually played a significant role in the Second Boer War in South Africa, and Tasmanian soldiers in that conflict won the first two Victoria Crosses awarded to Australians.
In 1901 the Colony of Tasmania united with the five other Australian colonies to form the Commonwealth of Australia. Tasmanians voted in favour of federation with the largest majority of all the Australian colonies.
1838 Basire Antique Rare British Postal Map Uniform Penny Post, Sir Rowland Hill
- Title : Sketch of the Post Office Map February 1838.
- Size: 35 1/2in x 28 1/2in (900mm x 725mm)
- Ref #: 70822
- Date : 1838
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original hand coloured and incredibly rare antique map of England and Wales, illustrating the Post Office Reform proposed by Sir Rowland Hill in 1837 was engraved by James Basire in 1838, dated in the title.
This original map of England and Wales was commissioned by the House of Commons for the reform of the post service in the late 1830s. The map shows the mail delivery routes throughout the country (distinguishing rail, coach, horse and foot deliveries) and indicates all post office towns and Penny Post sub-offices. The circles radiating from the City of Leicester indicate the distances regulating the rates of postage.
In my research of this map, I have only been able to find one other example that currently resides in the British library.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, black
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 35 1/2in x 28 1/2in (900mm x 725mm)
Plate size: - 35 1/2in x 28 1/2in (900mm x 725mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uplift of the map in left margin, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Soiling top right of image
Verso: - Map was originally folding and has been professionally backed onto archival linen
Background:
The Uniform Penny Post was a component of the comprehensive reform of the Royal Mail, the UK\'s official postal service, that took place in the 19th century. The reforms were a government initiative to eradicate the abuse and corruption of the existing service. Under the reforms, the postal service became a government monopoly, but it also became more accessible to the British population at large through setting a charge of one penny for carriage and delivery between any two places in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland irrespective of distance.
Richard Cobden and John Ramsey McCulloch, both advocates of free trade, attacked the Conservative government\'s policies of privilege and protection, including their archaic postal system. McCulloch, in 1833, advanced the view that nothing contributes more to facilitate commerce than the safe, speedy and cheap conveyance of letters.
The campaign for cheap postage was actually initiated by Robert Wallace, who in 1835 argued, before a governmental commission set up to investigate the problems, that greater use of the mailing system would lead to increased revenue for the government.
Sir Rowland Hill expounded his concept for the reformed service at a meeting of the commission on February 13, 1837, and published a famous pamphlet Post Office Reform: its Importance and Practicability late that year. In 1838 Hill made a proposal to parliament in which he suggested that the postage on all letters received in a post-town, and delivered in the same, or any other post-town in the British Isles, shall be at the uniform rate of one penny per half ounce\". However, Hill did not include a specific timetable for the introduction of a \"penny post\" in his proposal, nor did he suggest a plan for its implementation. Nonetheless, Hill\'s 1838 proposal paved the way for the 1840 Act which introduced the Uniform Penny Post.
In his proposal, Hill also called for official pre-printed envelopes and adhesive postage stamps as alternative ways of getting the sender to pay for postage, at a time when prepayment was optional. Previously, postage had depended on distance and the number of sheets of paper; now, one penny would assure delivery of an envelope and the letter it enclosed anywhere in the country provided together they satisfied the weight condition. This was a lower rate than before, when the cost of postage was usually more than 4d (four pence). The reform did not settle the issue of who paid for the postage, as it still remained optional for a number of years in spite of Hill\'s efforts as Secretary to the Post Office to alter the situation.
As of 2013 the value of one penny in 1840 ranges from 32p (GBP) to 4.89 (GBP); the latter based on mean income. It would appear that the cost to an established semi-skilled man of sending a letter in 1840 can be represented by approximately 1.00 (GBP) in 2013 values.
This however was a lower cost than previously and made postal communication more affordable to the increasing numbers of people capable of reading and writing as a consequence of public education. Financially, the penny post scheme was a disaster. More than thirty years elapsed before revenues were back to the pre-1840 level. The real benefits were the encouragement and support that the availability of cheap letterpost communication gave to the development of transport links, education, commerce and social cohesion.
1838 Sydney Hall Antique Map of The United States of America
- Title : United States
- Ref #: 35077
- Size: 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
- Date : 1838
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the United States stretching as far west as Missouri was engraved by Sydney Hall and was published in his 1838 General Atlas by Chapman & Hall , London. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, blue.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 8 1/2in (265mm x 210mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small ink smudge at bottom of map
Verso: - None
1843 John Arrowsmith Antique Map of South Australia, Kangaroo Is to Lake Torrens
- Title : South Australia Shewing the Divisons into Counties of the Settled Portions of the Province from Surveys of Capt. Frome R. Eng. Surv. Gen. of the Colony 1842...John Arrowsmith 10 Soho Square....London Pub. 10th July 1843.
- Size: 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1843
- Ref #: 82037
Description:
This rare, large lithograph hand coloured early colonial antique map of SE South Australia from Lake Torrens to Kangaroo Island by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1843 - dated - and was published in The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers requiring very few published for the Colonial papers. These maps are very hard, if not impossible, to be be found for sale on the open market.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin extended from border
Plate area: - Folds as issued, left fold re-enforced on verso. Light age toning
Verso: - Left fold re-enforced on verso
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1844 Johnston Large Antique Map of Australia
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 23806
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original antique lithograph map of Australia - with coloured outlines to the counties in NSW & WA - was published by W & AK Johnston in General Atlas,1844.
At the bottom of the map is atext box outlining the period of settlements in Australia from Botany Bay in 1788, WA 1829, SA 1836 & the colony of Victoria begun some 8 years ealier in 1838.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century, this large map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map of New South Wales & Victoria, Australia Felix
- Title : Colony of New South Wales and Australia Felix
- Ref #: 16298
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original antique map of NSW & SE Australia stretching from the 10 year old Settlement of Melbourne in the south to the 31st parallel in the north, by W & AK Johnston, was published in the 1845 edition of the General Atlas.
A large, highly detailed regional map of New South Wales and Australia Felix the SE area which quickly became the state of Victoria. The map, with this title, lasted for only a few years, before both NSW and Victoria were quickly settled. The map provides a very early depiction of the region, pre-dating the discovery of gold.
Also of great interest are the exploration routes by Mitchell (1836) in Red, Tyer's & Townsend's (1840) in Yellow and Streletsky's (Strzelecki) (1840) in Blue.
The 18 counties of NSW are highlighted in beautiful hand colour with extensive detail of towns, tracks and rivers. Historical note included below the title.Decorative Piano Key border and a fine example, on thick heavy paper.
Johnston was one of the master publishers of fine engraved and lithographed maps during the 19th century - this map is no exception. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1851 Tallis Antique Map of South Australia
- Title : Part of South Australia
- Ref #: 22126
- Size: 14in x 10 ½in (355mm x 265mm)
- Date : 1851
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of South Australia - with several vignettes of Adelaide, Aboriginals and various wildlife - was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10 ½in (355mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 10 ½in (355mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
1851 Tallis Antique Map of Victoria or Port Phillip, Australia
- Title : Victoria or Port Phillip
- Ref #: 35089
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1851
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Victoria - Port Phillip - was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 270mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1853 John Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map of The River Murray & Victoria, Australia
- Title : Sketch of South Eastern Australia shewing the River Murray and Southern Branches
- Size: 21in x 13in (535mm x 330mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1853
- Ref #: 82044
Description:
This rare, large lithograph hand coloured early map of the State of Victoria centering on the river Murray and branches by John Arrowsmith was published in 1853 for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have had very low numbers published and are very hard, if not impossible, to be be found for sale on the open market.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 13in (535mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 13in (535mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1854 (1813) Valentine, Grimm Large Old, Antique Map of New York City in 1742
- Title : A Plan of the City and Environs of New York as they were in the Years 1742 - 1743 and 1744. Drawn by D... G...in the 76th year of his age who had at this time a perfect & correct recollection of every part of the same
- Ref #: 35102
- Size: 23 1/2in x 18 1/2in (600mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1854 (1813)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This hand coloured original, antique highly detailed map* of New York City in the 1740's by David Grimm in 1813, was engraved by George Hayward in 1854 - dated in title - and was presented to the New York Historical Society edition of D. T. Valentine's Manual in 1854.
The map features a reference chart of governmental, religious and public buildings, as well as as rivers, farms and wells. Also includes ships sailing in the north and East river. The top of the map are illustrations of religious houses and building and at the bottom of the map is a illustration of Fort George.
Illustration of this map can be found at the New York City Library.
http://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/2af29660-0f61-0132-6b5f-58d385a7b928 (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 18 1/2in (600mm x 470mm)
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 18 1/2in (600mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning, brown stain top left corner of map
Verso: - Light age toning
1854 Arrowsmith & Selwyn Rare Antique Goldfields Map Mt Alexander & Castlemaine, Victoria
- Title : Geological Sketch of the Country in the Vicinty of Mt Alexander By AR Selwyn Geol Surv. for the Colony of Victoria
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (540x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1854
- Ref #: 82048
Description:
This rare, large lithograph geological map of Mount Alexander, the town of Castlemaine & environs, NW of Melbourne, Australia by John Arrowsmith - after the Geological Surveyor of Victoria, Alfred Selwyn - was published in 1854 for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
A very important geological map pertaining to the local goldfields around Mt Alexander and Castlemaine. Being a prominent local landmark, the mountain has its name associated with the surrounding district once known as the Mount Alexander goldfields. The first European to climb the peak was Major Thomas Mitchell on 28 September 1836 during his journey of exploration through Australia Felix. Overlander Edward John Eyre camped the north-west slope of Mount Alexander on 8 February 1838. Alexander Tolmer established a gold escort route between Mount Alexander and Adelaide to serve South Australian gold miners in the early 1850s (the first arrived in Adelaide on 20 March 1852 with around 600 lb of gold, the second, with 1,620 lb on 4 May 1852; it also carried mail between diggers and their Adelaide families)
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have had very low numbers published and are very hard, if not impossible, to be be found for sale on the open market.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (540x 430mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (540x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1855 A D Bache Rare Antique Map, Views Farallon Islands San Francisco California
- Title : US Coast Survey A D Buache Superintendant Sketch of South Farallon Island Pacific Ocean...1855
- Size: 15 1/2in x 14in (395mm x 355mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 93011
Description:
This large rare, original antique lithograph early map of Farallon Islands, off the coast of San Francisco (with views of the islands) California by Alexander Dallas Bache (great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin) in 1855 - dated - was published by the official chart-maker of the United States, the office of The US Coast Survey.
The Office of the Coast Survey, founded in 1807 by President Thomas Jefferson and Secretary of Commerce Albert Gallatin, is the oldest scientific organization in the U.S. Federal Government. Jefferson created the Survey of the Coast, as it was then called, in response to a need for accurate navigational charts of the new nation\'s coasts and harbors.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 14in (395mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 14in (395mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light age toning
Verso: - Some folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The Farallon Islands, or Farallones (from the Spanish farallón meaning \"pillar\" or \"sea cliff\"), are a group of islands and sea stacks in the Gulf of the Farallones, off the coast of San Francisco, California, United States. The islands are also sometimes referred to by mariners as the Devil\'s Teeth Islands, in reference to the many treacherous underwater shoals in their vicinity.[2] The islands lie 30 miles (48 km) outside the Golden Gate and 20 miles (32 km) south of Point Reyes, and are visible from the mainland on clear days. The islands are part of the City and County of San Francisco. The only inhabited portion of the islands is on Southeast Farallon Island (SEFI), where researchers from Point Blue Conservation Science and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service stay.
U.S. Coast Survey (Office of Coast Survey)
The Office of Coast Survey is the official chart-maker of the United States. Set up in 1807, it is one of the U.S. governments oldest scientific organizations. In 1878 it was given the name of Coast and Geodetic Survey (C&GS). In 1970 it became part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The agency was established in 1807 when President Thomas Jefferson signed the document entitled An act to provide for surveying the coasts of the United States. While the bills objective was specific—to produce nautical charts—it reflected larger issues of concern to the new nation: national boundaries, commerce, and defence.
The early years were difficult. Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, who was eventually to become the agencys first superintendent, went to England to collect scientific instruments but was unable to return through the duration of the War of 1812. After his return, he worked on a survey of the New York Harbor in 1817, but Congress stepped in to suspend the work because of tensions between civilian and military control of the agency. After several years under the control of the U.S. Army, the Survey of the Coast was reestablished in 1832, and President Andrew Jackson appointed Hassler as superintendent.
The U.S. Coast Survey was a civilian agency but, from the beginning, members of the Navy and Army were detailed to service with the Survey, and Navy ships were also detailed to its use. In general, army officers worked on topographic surveys on the land and maps based on the surveys, while navy officers worked on hydrographic surveys in coastal waters.
Alexander Dallas Bache, great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, was the second Coast Survey superintendent. Bache was a physicist, scientist, and surveyor who established the first magnetic observatory and served as the first president of the National Academy of Sciences. Under Bache, Coast Survey quickly applied its resources to the Union cause during the Civil War. In addition to setting up additional lithographic presses to produce the thousands of charts required by the Navy and other vessels, Bache made a critical decision to send Coast Survey parties to work with blockading squadrons and armies in the field, producing hundreds of maps and charts. Bache detailed these activities in his annual reports to Congress.
Coast Survey cartographer Edwin Hergesheimer created the map showing the density of the slave population in the Southern states.
Bache was also one of four members of the governments Blockade Strategy Board, planning strategy to essentially strangle the South, economically and militarily. On April 16, 1861, President Lincoln issued a proclamation declaring the blockade of ports from South Carolina to Texas. Baches Notes on the Coast provided valuable information for Union naval forces.
Maps were of paramount importance in wartime:
It is certain that accurate maps must form the basis of well-conducted military operations, and that the best time to procure them is not when an attack is impending, or when the army waits, but when there is no hindrance to, or pressure upon, the surveyors. That no coast can be effectively attacked, defended, or blockaded without accurate maps and charts, has been fully proved by the events of the last two years, if, indeed, such a proposition required practical proof.
— Alexander Dallas Bache, 1862 report.
Coast Survey attracted some of the best and brightest scientists and naturalists. It commissioned the naturalist Louis Agassiz to conduct the first scientific study of the Florida reef system. James McNeill Whistler, who went on to paint the iconic Whistlers Mother, was a Coast Survey engraver. The naturalist John Muir was a guide and artist on Survey of the 39th Parallel across the Great Basin of Nevada and Utah.
The agencys men and women (women professionals were hired as early as 1845) led scientific and engineering activities through the decades. In 1926, they started production of aeronautical charts. During the height of the Great Depression, Coast and Geodetic Survey organized surveying parties and field offices that employed over 10,000 people, including many out-of-work engineers.
In World War II, C&GS sent over 1,000 civilian members and more than half of its commissioned officers to serve as hydrographers, artillery surveyors, cartographers, army engineers, intelligence officers, and geophysicists in all theaters of the war. Civilians on the home front produced over 100 million maps and charts for the Allied Forces. Eleven members of the C&GS gave their lives during the war.
Alexander Dallas Bache 1806 – 1867 was an American physicist, scientist, and surveyor who erected coastal fortifications and conducted a detailed survey to map the mid-eastern United States coastline. Originally an army engineer, he later became Superintendent of the U.S. Coast Survey, and built it into the foremost scientific institution in the country before the Civil War.
Alexander Bache was born in Philadelphia, the son of Richard Bache, Jr., and Sophia Burrell Dallas Bache. He came from a prominent family as he was the nephew of Vice-President George M. Dallas and naval hero Alexander J. Dallas. He was the grandson of Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Dallas and was the great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin.
Bache was a professor of natural philosophy and chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania from 1828 to 1841 and again from 1842 to 1843. He spent 1836–1838 in Europe on behalf of the trustees of what became Girard College; he was named president of the college after his return. Abroad, he examined European education systems, and on his return he published a valuable report. From 1839 to 1842, he served as the first president of Central High School of Philadelphia, one of the oldest public high schools in the United States.
In 1843, on the death of Professor Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, Bache was appointed superintendent of the United States Coast Survey. He convinced the United States Congress of the value of this work and, by means of the liberal aid it granted, he completed the mapping of the whole coast by a skillful division of labor and the erection of numerous observing stations. In addition, magnetic and meteorological data were collected. Bache served as head of the Coast Survey for 24 years (until his death).
1855 US Coast Survey & A D Bache Antique Map of Drakes Bay or Puerto de Los Reyes, California
- Title : US Coast Survey A D Bache Superintendant Preliminary Survey of Point Reyes and Drakes Bay California...By W P Blake esq. 1855
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 93012
Description:
This original antique lithograph map of Drakes Bay or Puerto de Los Reyes, California, located approximately 30 miles northwest of San Francisco, by Alexander Dallas Bache (great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin) in 1855 - dated - was published by the official chart-maker of the United States, the office of The US Coast Survey.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
An uncommon 1855 map of Drakes Bay or Puerto de Los Reyes, California. Located approximately 30 miles northwest of San Francisco, Drakes Bay has long been considered the most likely landing site of the englishman Sir Francis Drake on his historic 1579 circumnavigation of the world. The map features numerous depth soundings and excellent inland topographical detail. A note in the lower left quadrant discusses the soundings. Drawn on a scale of 1:40,000. The Geographical positioning for this chart was the work of George Davidson. The Topography was accomplished by J. S. Lawson. The hydrography was completed by a party under the command of J. Alden. The whole was compiled under the exacting direction of A. D. Bache, Superintendent of the Coast Survey.
U.S. Coast Survey (Office of Coast Survey)
The Office of Coast Survey is the official chart-maker of the United States. Set up in 1807, it is one of the U.S. governments oldest scientific organizations. In 1878 it was given the name of Coast and Geodetic Survey (C&GS). In 1970 it became part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The agency was established in 1807 when President Thomas Jefferson signed the document entitled An act to provide for surveying the coasts of the United States. While the bills objective was specific—to produce nautical charts—it reflected larger issues of concern to the new nation: national boundaries, commerce, and defence.
The early years were difficult. Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, who was eventually to become the agencys first superintendent, went to England to collect scientific instruments but was unable to return through the duration of the War of 1812. After his return, he worked on a survey of the New York Harbor in 1817, but Congress stepped in to suspend the work because of tensions between civilian and military control of the agency. After several years under the control of the U.S. Army, the Survey of the Coast was reestablished in 1832, and President Andrew Jackson appointed Hassler as superintendent.
The U.S. Coast Survey was a civilian agency but, from the beginning, members of the Navy and Army were detailed to service with the Survey, and Navy ships were also detailed to its use. In general, army officers worked on topographic surveys on the land and maps based on the surveys, while navy officers worked on hydrographic surveys in coastal waters.
Alexander Dallas Bache, great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, was the second Coast Survey superintendent. Bache was a physicist, scientist, and surveyor who established the first magnetic observatory and served as the first president of the National Academy of Sciences. Under Bache, Coast Survey quickly applied its resources to the Union cause during the Civil War. In addition to setting up additional lithographic presses to produce the thousands of charts required by the Navy and other vessels, Bache made a critical decision to send Coast Survey parties to work with blockading squadrons and armies in the field, producing hundreds of maps and charts. Bache detailed these activities in his annual reports to Congress.
Coast Survey cartographer Edwin Hergesheimer created the map showing the density of the slave population in the Southern states.
Bache was also one of four members of the governments Blockade Strategy Board, planning strategy to essentially strangle the South, economically and militarily. On April 16, 1861, President Lincoln issued a proclamation declaring the blockade of ports from South Carolina to Texas. Baches Notes on the Coast provided valuable information for Union naval forces.
Maps were of paramount importance in wartime:
It is certain that accurate maps must form the basis of well-conducted military operations, and that the best time to procure them is not when an attack is impending, or when the army waits, but when there is no hindrance to, or pressure upon, the surveyors. That no coast can be effectively attacked, defended, or blockaded without accurate maps and charts, has been fully proved by the events of the last two years, if, indeed, such a proposition required practical proof.
— Alexander Dallas Bache, 1862 report.
Coast Survey attracted some of the best and brightest scientists and naturalists. It commissioned the naturalist Louis Agassiz to conduct the first scientific study of the Florida reef system. James McNeill Whistler, who went on to paint the iconic Whistlers Mother, was a Coast Survey engraver. The naturalist John Muir was a guide and artist on Survey of the 39th Parallel across the Great Basin of Nevada and Utah.
The agencys men and women (women professionals were hired as early as 1845) led scientific and engineering activities through the decades. In 1926, they started production of aeronautical charts. During the height of the Great Depression, Coast and Geodetic Survey organized surveying parties and field offices that employed over 10,000 people, including many out-of-work engineers.
In World War II, C&GS sent over 1,000 civilian members and more than half of its commissioned officers to serve as hydrographers, artillery surveyors, cartographers, army engineers, intelligence officers, and geophysicists in all theaters of the war. Civilians on the home front produced over 100 million maps and charts for the Allied Forces. Eleven members of the C&GS gave their lives during the war.
Alexander Dallas Bache 1806 – 1867 was an American physicist, scientist, and surveyor who erected coastal fortifications and conducted a detailed survey to map the mid-eastern United States coastline. Originally an army engineer, he later became Superintendent of the U.S. Coast Survey, and built it into the foremost scientific institution in the country before the Civil War.
Alexander Bache was born in Philadelphia, the son of Richard Bache, Jr., and Sophia Burrell Dallas Bache. He came from a prominent family as he was the nephew of Vice-President George M. Dallas and naval hero Alexander J. Dallas. He was the grandson of Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Dallas and was the great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin.
Bache was a professor of natural philosophy and chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania from 1828 to 1841 and again from 1842 to 1843. He spent 1836–1838 in Europe on behalf of the trustees of what became Girard College; he was named president of the college after his return. Abroad, he examined European education systems, and on his return he published a valuable report. From 1839 to 1842, he served as the first president of Central High School of Philadelphia, one of the oldest public high schools in the United States.
In 1843, on the death of Professor Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, Bache was appointed superintendent of the United States Coast Survey. He convinced the United States Congress of the value of this work and, by means of the liberal aid it granted, he completed the mapping of the whole coast by a skillful division of labor and the erection of numerous observing stations. In addition, magnetic and meteorological data were collected. Bache served as head of the Coast Survey for 24 years (until his death).
1855 US Coast Survey & A D Bache Antique Map of Golden Gate Entrance to San Francisco Bay
- Title : US Coast Survey A D Bache Superintendant Map of the Vicinity of the Golden Gate San Francisco Bay California...By W P Blake esq. 1855
- Size: 11 1/2in x 9in (290mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 93013
Description:
This original antique lithograph map of the Golden Gate, entrance to San Francisco Bay, prior to the bridge, by Alexander Dallas Bache (great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin) in 1855 - dated - was published by the official chart-maker of the United Stetes, the office of The US Coast Survey.
Alexander Dallas Bache 1806 – 1867 was an American physicist, scientist, and surveyor who erected coastal fortifications and conducted a detailed survey to map the mid-eastern United States coastline. Originally an army engineer, he later became Superintendent of the U.S. Coast Survey, and built it into the foremost scientific institution in the country before the Civil War.
Alexander Bache was born in Philadelphia, the son of Richard Bache, Jr., and Sophia Burrell Dallas Bache. He came from a prominent family as he was the nephew of Vice-President George M. Dallas and naval hero Alexander J. Dallas. He was the grandson of Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Dallas and was the great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin.
Bache was a professor of natural philosophy and chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania from 1828 to 1841 and again from 1842 to 1843. He spent 1836–1838 in Europe on behalf of the trustees of what became Girard College; he was named president of the college after his return. Abroad, he examined European education systems, and on his return he published a valuable report. From 1839 to 1842, he served as the first president of Central High School of Philadelphia, one of the oldest public high schools in the United States.
In 1843, on the death of Professor Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, Bache was appointed superintendent of the United States Coast Survey. He convinced the United States Congress of the value of this work and, by means of the liberal aid it granted, he completed the mapping of the whole coast by a skillful division of labor and the erection of numerous observing stations. In addition, magnetic and meteorological data were collected. Bache served as head of the Coast Survey for 24 years (until his death).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (290mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9in (290mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The earliest archaeological evidence of human habitation of the territory of the city of San Francisco dates to 3000 BC. The Yelamu group of the Ohlone people resided in a few small villages when an overland Spanish exploration party, led by Don Gaspar de Portolà, arrived on November 2, 1769, the first documented European visit to San Francisco Bay. Seven years later, on March 28, 1776, the Spanish established the Presidio of San Francisco, followed by a mission, Mission San Francisco de Asís (Mission Dolores), established by the Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza.
Upon independence from Spain in 1821, the area became part of Mexico. Under Mexican rule, the mission system gradually ended, and its lands became privatized. In 1835, Englishman William Richardson erected the first independent homestead, near a boat anchorage around what is today Portsmouth Square. Together with Alcalde Francisco de Haro, he laid out a street plan for the expanded settlement, and the town, named Yerba Buena, began to attract American settlers. Commodore John D. Sloat claimed California for the United States on July 7, 1846, during the Mexican–American War, and Captain John B. Montgomery arrived to claim Yerba Buena two days later. Yerba Buena was renamed San Francisco on January 30 of the next year, and Mexico officially ceded the territory to the United States at the end of the war. Despite its attractive location as a port and naval base, San Francisco was still a small settlement with inhospitable geography.
The California Gold Rush brought a flood of treasure seekers (known as forty-niners, as in 1849). With their sourdough bread in tow, prospectors accumulated in San Francisco over rival Benicia, raising the population from 1,000 in 1848 to 25,000 by December 1849. The promise of great wealth was so strong that crews on arriving vessels deserted and rushed off to the gold fields, leaving behind a forest of masts in San Francisco harbor. Some of these approximately 500 abandoned ships were used at times as storeships, saloons and hotels; many were left to rot and some were sunk to establish title to the underwater lot. By 1851 the harbor was extended out into the bay by wharves while buildings were erected on piles among the ships. By 1870 Yerba Buena Cove had been filled to create new land. Buried ships are occasionally exposed when foundations are dug for new buildings.
California was quickly granted statehood in 1850, and the U.S. military built Fort Point at the Golden Gate and a fort on Alcatraz Island to secure the San Francisco Bay. Silver discoveries, including the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1859, further drove rapid population growth. With hordes of fortune seekers streaming through the city, lawlessness was common, and the Barbary Coast section of town gained notoriety as a haven for criminals, prostitution, and gambling.
Entrepreneurs sought to capitalize on the wealth generated by the Gold Rush. Early winners were the banking industry, with the founding of Wells Fargo in 1852 and the Bank of California in 1864. Development of the Port of San Francisco and the establishment in 1869 of overland access to the eastern U.S. rail system via the newly completed Pacific Railroad (the construction of which the city only reluctantly helped support) helped make the Bay Area a center for trade. Catering to the needs and tastes of the growing population, Levi Strauss opened a dry goods business and Domingo Ghirardelli began manufacturing chocolate. Immigrant laborers made the city a polyglot culture, with Chinese Railroad Workers, drawn to Old Gold Mountain, creating the citys Chinatown quarter. In 1870, Asians made up 8% of the population. The first cable cars carried San Franciscans up Clay Street in 1873. The citys sea of Victorian houses began to take shape, and civic leaders campaigned for a spacious public park, resulting in plans for Golden Gate Park. San Franciscans built schools, churches, theaters, and all the hallmarks of civic life. The Presidio developed into the most important American military installation on the Pacific coast. By 1890, San Franciscos population approached 300,000, making it the eighth-largest city in the United States at the time. Around 1901, San Francisco was a major city known for its flamboyant style, stately hotels, ostentatious mansions on Nob Hill, and a thriving arts scene. The first North American plague epidemic was the San Francisco plague of 1900–1904.
U.S. Coast Survey (Office of Coast Survey)
The Office of Coast Survey is the official chart-maker of the United States. Set up in 1807, it is one of the U.S. governments oldest scientific organizations. In 1878 it was given the name of Coast and Geodetic Survey (C&GS). In 1970 it became part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The agency was established in 1807 when President Thomas Jefferson signed the document entitled An act to provide for surveying the coasts of the United States. While the bills objective was specific—to produce nautical charts—it reflected larger issues of concern to the new nation: national boundaries, commerce, and defence.
The early years were difficult. Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler, who was eventually to become the agencys first superintendent, went to England to collect scientific instruments but was unable to return through the duration of the War of 1812. After his return, he worked on a survey of the New York Harbor in 1817, but Congress stepped in to suspend the work because of tensions between civilian and military control of the agency. After several years under the control of the U.S. Army, the Survey of the Coast was reestablished in 1832, and President Andrew Jackson appointed Hassler as superintendent.
The U.S. Coast Survey was a civilian agency but, from the beginning, members of the Navy and Army were detailed to service with the Survey, and Navy ships were also detailed to its use. In general, army officers worked on topographic surveys on the land and maps based on the surveys, while navy officers worked on hydrographic surveys in coastal waters.
Alexander Dallas Bache, great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, was the second Coast Survey superintendent. Bache was a physicist, scientist, and surveyor who established the first magnetic observatory and served as the first president of the National Academy of Sciences. Under Bache, Coast Survey quickly applied its resources to the Union cause during the Civil War. In addition to setting up additional lithographic presses to produce the thousands of charts required by the Navy and other vessels, Bache made a critical decision to send Coast Survey parties to work with blockading squadrons and armies in the field, producing hundreds of maps and charts. Bache detailed these activities in his annual reports to Congress.
Coast Survey cartographer Edwin Hergesheimer created the map showing the density of the slave population in the Southern states.
Bache was also one of four members of the governments Blockade Strategy Board, planning strategy to essentially strangle the South, economically and militarily. On April 16, 1861, President Lincoln issued a proclamation declaring the blockade of ports from South Carolina to Texas. Baches Notes on the Coast provided valuable information for Union naval forces.
Maps were of paramount importance in wartime:
It is certain that accurate maps must form the basis of well-conducted military operations, and that the best time to procure them is not when an attack is impending, or when the army waits, but when there is no hindrance to, or pressure upon, the surveyors. That no coast can be effectively attacked, defended, or blockaded without accurate maps and charts, has been fully proved by the events of the last two years, if, indeed, such a proposition required practical proof.
— Alexander Dallas Bache, 1862 report.
Coast Survey attracted some of the best and brightest scientists and naturalists. It commissioned the naturalist Louis Agassiz to conduct the first scientific study of the Florida reef system. James McNeill Whistler, who went on to paint the iconic Whistlers Mother, was a Coast Survey engraver. The naturalist John Muir was a guide and artist on Survey of the 39th Parallel across the Great Basin of Nevada and Utah.
The agencys men and women (women professionals were hired as early as 1845) led scientific and engineering activities through the decades. In 1926, they started production of aeronautical charts. During the height of the Great Depression, Coast and Geodetic Survey organized surveying parties and field offices that employed over 10,000 people, including many out-of-work engineers.
In World War II, C&GS sent over 1,000 civilian members and more than half of its commissioned officers to serve as hydrographers, artillery surveyors, cartographers, army engineers, intelligence officers, and geophysicists in all theaters of the war. Civilians on the home front produced over 100 million maps and charts for the Allied Forces. Eleven members of the C&GS gave their lives during the war.
1855 Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map Land Parcels in Van Diemens Land, TAS Australia
- Title : North Western Portion of Tasmania Newly Opened...Accompanying my report of the 16th April 1855
- Size: 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 82041
Description:
This rare map of land opened for purchase North-West of Hobart, Tasmania - from Hamilton along the Derwent River to Lake St Clair and south to Lake Peeder, with a hand coloured reference to the land parcels - by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1855 - dated - and was published for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have numbered only in the 100s.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.