James Cook (1728-1779)
Profile:
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) was a British explorer, navigator, and cartographer who is known for his extensive voyages to the Pacific Ocean. Born in Marton, Yorkshire, England, Cook began his maritime career as an apprentice at the age of 17. He served as a naval officer during the Seven Years' War, mapping the coastlines of Newfoundland and St. Lawrence River.
In 1768, Cook was selected to lead an expedition to the Pacific Ocean to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, and to search for the fabled southern continent. During this voyage, he charted the east coast of Australia, claiming it for Britain and naming it New South Wales. Cook's second voyage, from 1772 to 1775, was dedicated to exploring the southern oceans, circumnavigating Antarctica and proving that it was a continent.
Cook's third voyage, from 1776 to 1779, was his most famous. He was tasked with finding a northwest passage to connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. While he did not find the passage, he did explore the coast of Alaska and made detailed maps of the region. Cook was also the first European to visit Hawaii, where he was initially welcomed, but was later killed in a skirmish with locals.
Cook was known for his excellent navigational skills and his ability to prevent scurvy among his crew by introducing fresh food and lemon juice into their diets. He also made significant contributions to the field of cartography, creating accurate maps of the Pacific and the coastlines he explored.
Cook's voyages had a significant impact on the scientific and cultural understanding of the world. His accurate maps and charts greatly improved navigational methods and were used by sailors for many years to come. Cook's legacy also includes his interactions with the people he encountered during his voyages, which played a significant role in shaping the understanding of different cultures in Europe.
Cook's First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cook's command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on the Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earth's distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research. Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere.
Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
Cook's Second Voyage (1772-1775)
Based on the success of his first voyage, Cook was appointed by the Admiralty to lead a second expedition. Two ships were employed with Cook commanding the Resolution and Captain Tobias Furneaux in charge of the Adventure. The purpose was to circumnavigate the globe as far south as possible to confirm the location of a southern continent. Cook proved that there was no "Terra Australis," which supposedly was located between New Zealand and South America. Cook was convinced, however, that there was land beyond the southern ice fields.
In his pursuit of this idea, this expedition was the first European voyage to cross the Antarctic Circle. In addition, in two great sweeps through the Southern latitudes, Cook made an incredible number of landfalls including New Zealand, Easter Island, the Marquesas, Tahiti and the Society Islands, the Tonga Islands, the New Hebrides, New Caledonia, and a number of smaller islands. In addition to these navigational accomplishments and the accompanying expansion of geographical knowledge, the expedition also recorded a vast amount of information regarding the Pacific islands and peoples, proved the value of the chronometer as an instrument for calculating longitude, and improved techniques for preventing scurvy.
Cook's Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook's third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century.
England's growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route. Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook's death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook's death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years.
Captain James Cook (28)
1774, 1777 & 1785 Capt James Cook 3 Atlas Volumes 1st Editions 204 Maps & Prints
- Title : 1. Figure du Banks 2. Premier Voyage De Cook 3. Troisieme Voyage De Cook
- Ref #: 93498, 93499, 93500
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Date : 1774; 1777; 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
A unique and rare opportunity to acquire all three of Captain James Cooks 1st French edition Atlases (4to, Quatro), published to accompany the publication of his 3 voyages of discovery in 1774, 1777 & 1785. The atlases contain a total of 204 large folding, double page and single page maps and prints. It is very rare to find all three atlases complete and available together at the same time.
The contents of all three atlases are in fine condition, with a fresh, heavy impression and clean paper of all maps and prints.
As stated there are 204 maps and prints 51 in the 1st volume, 66 in the second volume and 87 in the second volume. Please view the images above, that include a few images of the 204 maps and prints as well as an itemized list of each volume.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Some scuffing and wear to boards & spines
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Timeline First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Timeline - Second Voyage 1772 - 1775
In July 1772 Resolution, commanded by Captain Cook, and Discovery, commanded by Lieutenant Furneaux, set sail from Britain, via Madiera (Jul-Aug) and Cape Town, South Africa (Oct-Nov), towards the Antarctic in search of the Great Southern Continent.
During January 1773 the ships took on fresh water, charts of the voyage being marked with:
......Here we watered our Ship with Ice the 1st. Time 26S 44W and Here we compleated our Water/26S 20W but became separated in thick fog: Here we parted company…. and The Resolutions Track after we parted Company on the 8 of February 1773......
The ships became the first known to have crossed the Antarctic Circle (17 January 1773). On 9th January Cook wrote:
.......we hoisted out three Boats and took up as much as yielded about 15 Tons of Fresh Water, the Adventure at the same time got about 8 or 9 and all this was done in 5 or 6 hours time; the pieces we took up and which had broke from the Main Island, were very hard and solid, and some of them too large to be handled so that we were obliged to break them with our Ice Azes before they could be taken into the Boats...... Cook, Journals II, 74.)
The ships met again in New Zealand (February-May 1773) and set off to explore the central Pacific, calling at Tahiti (August), where, from the island of Raiatea, they took aboard Omai who returned with the Adventure to England (7 September).
After visiting Amsterdam and Middelburg, two islands that Cook called the Friendly Islands (Tongan group) (October) the ships became separated and never met again. Both ships returned separately to New Zealand. (November) A boats crew from the Adventure were killed by Maori (17 December) and the ship sailed for Britain, arriving July 1774.
Cook on Resolution attempted another search for the Great Southern Continent (November 1773), crossing the Antarctic Circle on 20th December 1773. However, the ice and cold soon forced him to turn north again and he made another search in the central Pacific for the Great Southern Continent. In January 1774 he turned south again, crossing the Antarctic Circle for the second time. Captain Cooks Journal, 2nd January 1774.
Cook sailed north, arriving at Easter Island in March 1774. Cook was too ill to go ashore but a small party explored the southern part of the island. The artist William Hodges painted a group of the large statues of heads (moia) for which the island has become famous.
Cook then sailed to the Marquesas (March); Tahiti (April) and Raiatea (June); past the Cook Islands and Niue, or Savage Islands as Cook called them; Tonga (June); Vatoa, the only Fijian Island visited by Cook (July); New Hebrides (July-August); New Caledonia (September) and Norfolk Island (October); before returning to New Zealand (October 1774).
Not all the peoples of the islands visited by Cook were friendly and when his ship approached Niue the local people would not let his crew ashore. Cook wrote:
.......The Conduct and aspect of these Islanders occasioned my giving it the Name of Savage Island, it lies in the Latitude of 19 degrees 1 Longitude 169 degrees 37 West, is about 11 Leagues in circuit, of a tolerable height and seemingly covered with wood amongst which were some Cocoa-nutt trees......(Cook, Journals II, 435, 22 June 1774.)
En route for New Zealand, Cook sailed west and explored the islands which he called the New Hebrides, now known as Vanuatu, arriving on 17 July 1774. The people were Melanesian, not Polynesian, and spoke different languages and had different customs. Cook recorded:
........The Men go naked, it can hardly be said they cover their Natural parts, the Testicles are quite exposed, but they wrap a piece of cloth or leafe round the yard (nautical slang for the penis) which they tye up to the belly to a cord or bandage which they wear round the waist just under the Short ribs and over the belly and so tight that it was a wonder to us how they could endure it.......(Cook, Journals II, 464, 23 July 1774)
Cook sailed past or visited nearly all the islands in the group, including landfalls at Malekula, Tanna and Erromango. He later moved on to New Caledonia.
Cooks reception by the New Hebrideans was generally hostile. At Erromango during the landing on 4th August 1774 the marines had to open fire when the natives tried to seize the boat and started to fire missiles. Cook wrote:
....…I was very loath to fire upon such a Multitude and resolved to make the chief a lone fall a Victim to his own treachery…happy for many of these poor people not half our Musquets would go of otherwise many more must have fallen.......(Cook, Journals II, 479, 4th August 1774)
Some of Cooks crew were slightly injured but several natives were wounded and their leader killed. Back on the ship Cook had a gun fired to frighten off the islanders and decided to depart.
Cook left New Zealand to return to Britain via the Southern Ocean in November 1774 and arrived in Tierra del Fuego, South America, in December. Cook took on stores and spent the holiday in what he called Christmas Sound. He described the area:......except those little tufts of shrubbery, the whole country was a barren Tack (or Rock) doomed by Nature to everlasting sterility......(Cook, Ms Journal PRO Adm 55/108)
Cook left South America in early January 1775 and set off across the southern Atlantic for Cape Town, South Africa. On the way he tried to confirm the location of a number of islands charted by Alexander Dalrymple on an earlier voyage. On 17 January 1775 Cook arrived at the cold, bleak, glaciated island he called South Georgia and spent 3 days charting it before sailing on.
Cook headed east and in late January came across the South Sandwich Islands that he again charted and then sailed on to Cape Town, arriving in late March 1775. He then headed across the Atlantic via St. Helena and Ascension Island (May), the Azores (July) and landed at Portsmouth on 30th July 1775.
On his return Cook became a national hero. He was presented to the King, made a member of the Royal Society and received its Copley Medal for achievement. Cook was promoted to post-captain of Greenwich Hospital and wrote up his account of the voyage. This did not mean retirement for Cook who went on his third and final voyage the following year.
The second voyage was one of the greatest journeys of all time. During the three years the ships crews had remained healthy and only four of the Resolutions crew had died. Cook disproved the idea of the Great Southern Continent; had become the first recorded explorer to cross the Antarctic Circle; and had charted many Pacific islands for the first time.
Timeline - Third Voyage 1776 - 1780
In 1776 Cook sailed in a repaired Resolution (July) to search for the North West Passage and to return Omai to his home on Huahine in the Society Islands.
He sailed via the Canary Islands and was joined at Cape Town, South Africa, by the Discovery, commanded by Charles Clerke.
The Discovery was the smallest of Cooks ships and was manned by a crew of sixty-nine. The two ships were repaired and restocked with a large number of livestock and set off together for New Zealand ( December).
Cook sailed across the South Indian Ocean and confirmed the location of Desolation Island, later known as Kerguelen Island. Cook wrote of Christmas Harbour where he first anchored on 25th December 1776:
........I found the shore in a manner covered with Penguins and other birds and Seals…so fearless that we killed as ma(n)y as we chose for the sake of their fat or blubber to make Oil for our lamps and other uses… Here I displayd the British flag and named the harbour Christmas harbour as we entered it on that Festival........(Cook, Journals III, i, 29-32)
Cook sailed east, arriving at Van Diemens Land/Tasmania (January 1777) and Queen Charlottes Sound, New Zealand (February). The Maori were wary at first, expecting Cook to take revenge for the killing of members of the Adventures crew in 1773, but instead Cook befriended the leader of the attack.
The ships stayed for nearly two weeks in New Zealand, restocking with wild celery and scurvy grass and trading with the local Maori who set up a small village in Ship Cove. Cook set off around the islands of the south Pacific (February), visiting the Cook Islands (April); Tongan Islands (July); and Tahiti (August-December 1777)
In 1778 Cook visited the Hawaiian islands, or Sandwich Islands as he named them, for the first time. Cook wrote:
........We no sooner landed, that a trade was set on foot for hogs and potatoes, which the people gave us in exchange for nails and pieces of iron formed into some thing like chisels….At sun set I brought every body on board, having got during the day Nine tons of water….about sixty or eighty Pigs, a few Fowls, a quantity of potatoes and a few plantains and Tara roots.......(Cook, Journals III, i. 269 & 272)
In February 1778 Cook sailed from the Hawaiian Islands across the north Pacific to the Oregan coast of North America. He travelled up the coast in bad weather until he found a safe harbour, Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada. There he refitted the ships, explored the area and developed relations with the local people.
Cook described a village there, probably Yoquot:
….their houses or dwellings are situated close to the shore…Some of these buildings are raised on the side of a bank, theses have a flooring consisting of logs supported by post fixed in the ground….before these houses they make a platform about four feet broad…..so allows of a passage along the front of the building: They assend to this passage (along the front of the building) by steps, not unlike some at our landing places in the River Thames........(Cook, Journals III, i, 306)
Cook left Nootka Sound in April 1778 and sailed north along the Alaskan coast looking for inlets that might lead to the Northwest passage but was then forced to turn south. By July he had rounded the Alaskan Peninsula and was able to sail north again, visiting the Chukotskiy Peninsula, Russia, before heading out into the Bering Sea.
Cook described the summer huts, or yarangas, of the Chukchi people as:
.........pretty large, and circular and brought to a point at the top; the framing was of slight poles and bone, covered with the skins of Sea animals…About the habitations were erected several stages ten or twelve feet high, such as we had observed on some part of the American coast, they were built wholly of bones and seemed to be intended to dry skins, fish &ca. upon, out of reach of their dogs........(Cook, Journals III, I, 413)
After entering the Bering Sea on 11th August 1778, Cook crossed the Arctic Circle and went as far north as latitude 70 degrees 41 North before being forced back by the pack ice off Icy Cape, Alaska. On the ice all around the ships were large numbers of walruses. About a dozen of these huge animals were killed to replenish the supplies of fresh meat and to provide oil for the lamps.
Cook had to turn west and worked his way down the Russian coast, eventually heading south and east into Norton Sound, Alaska, in September 1778. He wrote of their very brief encounter with the inhabitants of Norton Sound:
....…a family of the Natives came near to the place where we were taking off wood…I saw no more than a Man, his wife and child…...(Cook, Journals III, I, 438)
After a short period spent searching for the Northwest Passage Cook realised that it was too late in the year to make any progress and so sailed for warmer winter quarters in the Hawaiian Islands, arriving there in December 1778.
After circumnavigating the big island of Hawaii for over a month the ships finally anchored in Kealakekua Bay on 16th January 1779. The Hawaiians in over 1000 canoes came out to welcome them, the arrival of the ships coinciding with celebrations to mark the religious festival of Makahiki to the god Lono. The Hawaiians seem to have treated Cook as a personification of the god and at first relations were good on this second visit. However, relationships became strained and Cook left the island on 4th February 1779.
When Cook left Hawaii his ships ran into gales which broke a mast, forcing him to return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs on 11th February. This time the native people were less friendly and stole the cutter of the Discovery. The next day, the 14th February 1779, Cook went ashore to take the Hawaiian king into custody pending the return of the cutter but a fight developed and Cook, four of his marines and a number of natives were killed. Cooks remains were buried at sea in Kealakekua Bay.
Charles Clerke took over command of the stunned expedition and explored the other Hawaiian islands before sailing north to search for the North-West Passage. The ships called at Kamchatka, Russia, (April-June) where they were welcomed by the governor, Behm, at Bolsheretsk. Behm took news of the expedition and Cooks death overland to St. Petersburg from where it reached Europe and Britain.
Having made another voyage into the Arctic in search of the Northwest Passage (June-July) the ships returned to Kamchatka in August. In November they set off sailing south along the east coast of Japan, between Taiwan and the Phillipines and arrived at Macao, China, in December.
In January 1780 the expeditions left for home, crossing the Indian Ocean, calling at Cape Town (April-May) and arriving back in Stromness, Orkney, in August but not returning to London until October 1780.
News of Cooks death reached Britain in January 1780, ahead of the return of Resolution and Discovery in October 1780. The voyage was written up and published and Cooks life gradually commemorated in articles, books, medals and monuments.
The achievements of the voyage were overshadowed by the deaths of both Cook and his second-in-command, Clerke. The main purpose of the voyage, the discovery of the Northwest Passage, was not realised but large tracts of the Pacific and Arctic coasts of America and Russia were charted.
Early attempts to summarise the life of Cook appeared in the popular press soon after news of his death reached Britain. Articles in journals such as the Westminster Magazine, published in January 1780, included Biographical Anecdotes of Capt. Cook, charting his life from his birth in Marton, North Yorkshire. The first published biography of Cook, Life of Captain James Cook, by Andrew Kippis, appeared a few years later in 1788.
1774 Cook & Hawkesworth Antique Atlas of Australia, New Zealand 52 Maps & Prints
Antique Map
- Title : Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique, actuellement régnante ; pour faire des découvertes dans l'hémisphère méridional, et successivement exécutés par le Commodore Byron, le Capitaine Carteret, le Capitaine Wallis & le Capitaine Cook dans les vaisseaux. MDCCLXXIV (1774)
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1774
- Ref #: 35632
Description:
This original antique Atlas containing 52 maps and prints, as called for, from some of the foremost explorers of the mid 18th century, including Commodore Byron, Captain Carteret, Captain Wallis & Captain James Cook, was published as the 1st French edition of Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique: (Maps and Figures of Travels undertaken by Order of his Present Reigning British Majesty) in 1774, published after only a year after the 1st English edition by John Hawkesworth.
The 52 prints and maps contained in this atlas chart in maps, prints and plans, the progression in the exploration of the South Seas of the 4 explorers. But there is of course, the standout amongst these 4 explorers and that is of course Captain James Cook.
At the time of the publication of this tome, Cook had returned from his first voyage of exploration to The South Pacific, becoming the first European to survey and chart the coastline of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia. But at this point Cook was not as famous as he was destined to become, after completing 2 more voyages of exploration, and in turn becoming the most famous explorer of his era.
The majority of this atlas contains the prints and maps dedicated to Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery including the two famous maps, one of New Zealand and the other the East Coast of Australia. All voyages can be tracked from the first large folding map of the South Seas, at the beginning of the Atlas, that illustrates the tracks on Cook and the other 3 explorers.
In-4 binding in half-calf, spine with five bands with gilding boxes and title label complete with 52 folding & single plates
Spine & boards in poor condition with lack of leather and scratched covers, contents tights with plates in very good condition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning - Maps & Prints
Plate area: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Verso: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Background:
Capt. Cook First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Vice-Admiral John Byron (1723-1786) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is known for his circumnavigation of the globe aboard the HMS Dolphin, completing one of the first British expeditions to achieve this feat. His account of the voyage, "The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron," influenced subsequent explorations. Byron's naval career included service in the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War.
Rear-Admiral Philip Carteret (1733-1796) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is best known for his role as the captain of HMS Swallow during the first circumnavigation of the globe. Carteret's expedition, which took place from 1766 to 1769, aimed to explore and map uncharted regions of the Pacific Ocean. His discoveries included the Carteret Islands and the Pitcairn Islands. Carteret's voyage greatly contributed to the knowledge of Pacific geography and exploration during that time.
Samuel Wallis (1728-1795) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is renowned for leading the first recorded European expedition to visit Tahiti and for his significant contributions to the exploration of the Pacific Ocean. In 1766, Wallis commanded HMS Dolphin on a voyage funded by the British Admiralty. During the expedition, he discovered and named several islands, including Tahiti, which he encountered in June 1767. Wallis's visit to Tahiti marked the beginning of sustained European contact with the island and its inhabitants. His exploration efforts and subsequent reports greatly expanded European knowledge of the Pacific region. Wallis's achievements laid the foundation for future explorations and influenced subsequent voyages of exploration in the Pacific.
John Hawkesworth 1715 -1775
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cooks view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Cook , Capt. James 1728-1779
James Cook was born on 27 October 1728 in Marton, England. His father was a poor farm labourer who had worked his way up to Overseer. James began as a farm labourer and grocer\\\'s assistant. He soon found employment on the Baltic sea in a Collier (coal transport ship) at the age of 18.
During the war with the French in 1755, James Cook enlisted as an Able Seaman on the Eagle. Within a month he was promoted, because of outstanding ability, to Masters Mate. Four years later he was promoted to Master. In command of his own ship, James Cook performed a crucial charting of the St. Lawrence River, which made possible the great amphibious assault upon Quebec City in 1759. In 1763 he was given command of the schooner Grenville to survey the eastern coasts of Canada over a four year period. These excellent charts were used up until the early part of the 20th century.
James Cook was selected to lead a 1768 expedition to observe the transit of Venus, and to explore new lands in the Pacific Ocean. In his first Pacific voyage, James Cook rounded Cape Horn in the Endeavour and reached Tahiti on 3 June 1769. After recovering a necessary scientific instrument stolen by the natives, the transit of Venus was successfully observed. The Endeavour then spent six months charting New Zealand. James Cook next explored and claimed possession of eastern Australia. Returning to England, on 12 June 1771, via New Guinea, Java and the Cape of Good Hope, the crew suffered an appalling 43% fatality rate. James Cook thus became very concerned about crew health on subsequent voyages. He instituted compulsory dietary reforms that were copied by many other ship captains.
The object of Captain Cook\\\'s second Pacific Ocean voyage was to confirm the existence of a theorized Great Southern Continent. His ship the Resolution, accompanied by the Adventure, departed Plymouth on 13 July 1772 and sailed around the Cape of Good Hope. Beset by ice, he was unable to reach Antarctica. Although its existence was suspected, James Cook demonstrated, by traversing large areas of the south Pacific, that it would have to be a frigid wasteland, and not an economically productive addition to the British empire. James Cook charted many of the South Pacific islands with the incredible accuracy of 3 miles. This accuracy was made possible by a new and highly accurate clock. The two ships returned to England, via Cape Horn, on 29 July 1775. The experimental diets and close attention to cleanliness had a miraculous effect: out of a crew of 118, only one man was lost to disease! Since public interest was high, the many paintings by the artists were widely displayed and published as engravings. James Cook was also awarded the Copley Gold Medal and elected as a fellow of the Royal Society.
The third great voyage is especially significant to the history of the west coast of North America. Captain Cook and his men were primarily searching for the Northwest Passage from the Pacific Ocean to the Atlantic Ocean. They departed Plymouth on 12 July 1776 in the Resolution and the Discovery.
The ships sailed around the Cape of Good Hope to reach the west coast of America in February of 1778. They continued north along the coast in haste to the Bering Sea and Bering Strait in an attempt to pass through the Arctic Ocean during the summer season. Foiled by ice, James Cook returned to Hawaii to prepare for another attempt at the Northwest Passage the next season. Soon after they had departed, a storm damaged the foremast of the Resolution and forced a return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs. Unfortunately, they had previously overstayed their welcome and relations became tense. The theft of a ship\\\'s cutter led Captain Cook to put ashore to demand the return of the boat. A fight broke out and James Cook was killed on 14 Feb 1779 by angry natives. Although his men made another attempt at the Northwest Passage, they were unsuccessful. The expedition did identify the possibilities of trade with the coastal American natives for otter seal furs, which could then be bartered for Chinese goods that were highly prized in England.
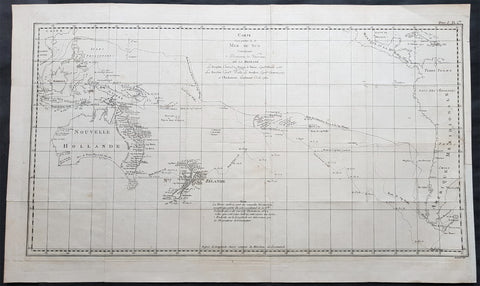
1774 Hawkesworth Large Antique Map of Australia & South Seas 1765-71 - Capt Cook
Antique Map
- Title : Carte d une Partie de la Mer du Sud Contenant les Decouvertes de Vaisseaux de sa Majeste, Le Dauphin, Commodore Byron, La Tamar, Capitne. Mouats 1765, Le Dauphin, Capitne. Wallis, Le Swallow, Capitne. Cartaret, 1767, et l Endeavour, Lieutenant Cook 1769
- Ref : 35509
- Size: 28in x 16 3/4in (710mm x 425mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved, large antique map, a chart of the tracks of 5 British ships & explorers to the South Ocean from 1765 to 1771 was engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1774 French translation of John Hawkesworths publication An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks
The 5 Voyages, with Captains, ships & tracks are;
1. 1764-66 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Commodore John Byron, completed the first circumnavigation of the globe under two years.
2. 1764-1766 - HMS Tamar under Command of Captain Patrick Mouat, accompanied Commodore John Byron & HMS Dolphin on 1764-66 circumnavigation of the world.
3. 1766-68 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Captain Samuel Wallis, completed another circumnavigation & was the first European to visit Tahiti & the Society Islands.
4. 1766-68 - HMS Swallow under Command of Captain Philip Carteret, who accompanied HMS Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis to circumnavigate the world.
5. 1769-71 - HMS Endeavour, under Command of Lieutenant James Cook (later Captain) completed a the mapping of Tahiti & the Society Islands, New Zealand & the East Coast of Australia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 28in x 16 3/4in (710mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 26 3/4in x 14 3/4in (680mm x 375mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Commodore John Byron 1723 – 1786 was a British Royal Navy officer and politician.He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764-1766. He fought in battles in The Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral before his death in 1786.
Captain Patrick Mouat. Commanded HMS Tamer on a voyage of discovery with Commodore John Byron between 1764-66. HMS Tamar was a sloop, mounting sixteen guns: ninety men, three lieutenants, and two and twenty petty officers.
Captain Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795 was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean. Was given the command of HMS Dolphin in 1751 as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Third\'s Island in honour of the King in June 1767.
Captain Philip Carteret 1733 – 1796 was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navys circumnavigation expeditions in 1764–66 and 1766–69.
Captain James Cook is considered one of the most talented Surveyors & Map Makers of any age, for Cook, the production of a new chart was his principal reason for going to sea. His charts were aimed at fellow seamen so he incorporated as much information as possible while employing an economy of style and little elaboration. The quality of his charts can be confirmed by the fact that some survey details from Newfoundland to New Zealand & Australias East Coast could still be safely used over one hundred years later. His last piece of the New Zealand hydrographic chart was only removed in the 1990s.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
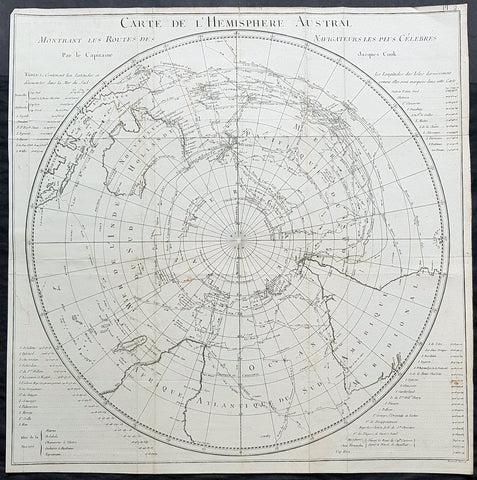
1778 Capt James Cook Antique Map The Southern Hemisphere, Australia, Antarctica
Antique Map
- Title : Carte De L Hemisphere Austral Montrant les Routes des Navigateurs les plus Celebree par le Capitaine Jacques Cook
- Ref : 42004
- Size: 22in x 21 1/2in (560mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved, antique map, a chart of the Southern Hemisphere, was engraved by Robert Benard and is dedicated to the discoveries in the South Seas and Antarctic Regions of Captain James Cook during his second Voyage of Discovery between 1772 & 1775. By comparison the tracks of 11 other explorers are included, from the 16th to the 18th centuries. The map by Captain James Cook was published in the 1778 French edition of A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
This map is unique in another way, as the English edition of this map was used as a prop, by Nathaniel Dance, in his 1776 portrait of Captain James Cook. Please also see above for the portrait.
The 11 other explorers and their tracks around the Southern Hemisphere are;
1. Mendana in 1595
2. Quiros in 1606
3. Le Maire & Schouten in 1616
4. Tasman in 1642
5. Halley in 1700
6. Roggewein in 1722
7. Bouvet in 1738-39
8. Byron in 1765
9. Wallis in 1767
10. Bougainville in 1768
11. Surville in 1769
12. Cooks first and second voyages.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 21 1/2in (560mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 21 1/2in (560mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair without loss to left of image
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Background:
This map by James Cook, was published as the premier map of his second voyage to the Southern Hemisphere, dispelling forever the myth of the Great Southern Land and showing the true cartographic nature of the southern hemisphere dominated by Australia & New Zealand. The map on a South Polar Projection also shows South America, the South Atlantic Ocean, South Africa, Madagascar, Australia - with Tasmania still joined to the mainland - New Zealand and the southern Pacific Ocean with islands.
Engraved within the explorer\\\'s tracks are the dates of their voyages and ships tracks are particularly noted around the Antarctic Circle with notations of ice fields seen during the voyages.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt. Cook, S. Parkinson & G. Stubbs - Antique Print Australian Kangaroo in 1770
Antique Map
- Title : Quadrupede nomme Kanguroo trouve fur la Cote de la N.Hollande
[The Kanguroo, an Animal found on the Coast of New Holland] - Ref : 35016
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Kangaroo, first sketched by Sydney Parkinson onboard HMS Endeavour during Cooks first voyage in 1770, whilst laid up at Endeavour River in northern Queensland, was engraved by Robert Benard, after a painting by the famous English Artist George Stubbs in 1772. This original engraving was published in the 1774 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas by John Hawkesworth in An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks. Paris, 1774.
From Sydney Parkinsons Journal........soon after we arrived in the bay, we laid the ship on a steep bank, on the side of a river; set up tents on shore, unloaded her, carried all the cargo and provisions into them, and there lodged and accommodated our sick.
On the 22d, we examined the ship’s bottom, and found a large hole; through the planks into the hold, which had a piece of coral-rock, half a yard square, sticking in it: the same rock, therefore, that endangered us, yielded us the principal means of our redemption; for, had not this fragment intruded into the leak, in all probability the ship would have sunk.
We lost no time, but immediately set about repairing the ship’s bottom, and in a few days made it sound again. In the mean time, the boats were sent out, in search of another passage, which they found, and returned to the ship on the 3d of July.
On the 4th of July, the ship was carried to the other side of the river, and examined thoroughly; but, being found in good condition, she was soon placed in her former station; where she was loaded, and properly fitted to proceed on the voyage.
During the time we staid here, we picked up a great many natural curiosities from the reef we struck upon, consisting of a variety of curious shells, most of which were entirely new to Mr. Banks and Dr. Solander ...
Of quadrupeds, there are goats, wolves, a small red animal about the size of a squirrel; a spotted one of the viverra kind, and an animal of a kind nearly approaching the mus genus, about the size of a grey-hound, that had a head like a fawn’s; lips and ears, which it throws back, like a hare’s; on the upper jaw six large teeth; on the under one two only; with a short and small neck, near to which are the fore-feet, which have five toes each, and five hooked claws; the hinder legs are long, especially from the last joint, which, from the callosity below it, seems as if it lies flat on the ground when the animal descends any declivity; and each foot had four long toes, two of them behind, placed a great way back, the inner one of which has two claws; the two other toes were in the middle, and resembled a hoof, but one of them was much larger than the other. The tail, which is carried like a grey-hound’s, was almost as long as the body, and tapered gradually to the end. The chief bulk of this animal is behind; the belly being largest, and the back rising toward the posteriors. The whole body is covered with short ash-coloured hair; and the flesh of it tasted like a hare’s, but has a more agreeable flavour................
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
George Stubbs ARA 1724 – 1806 was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. His most famous work is probably Whistlejacket, a painting of a prancing horse commissioned by the 2nd Marquess of Rockingham, which is now in the National Gallery in London. This and two other paintings carried out for Rockingham break with convention in having plain backgrounds. Throughout the 1760s he produced a wide range of individual and group portraits of horses, sometimes accompanied by hounds. He often painted horses with their grooms, whom he always painted as individuals. Meanwhile, he also continued to accept commissions for portraits of people, including some group portraits. From 1761 to 1776 he exhibited at the Society of Artists of Great Britain, but in 1775 he switched his allegiance to the recently founded but already more prestigious Royal Academy of Arts.
Stubbs also painted more exotic animals including lions, tigers, giraffes, monkeys, and rhinoceroses, which he was able to observe in private menageries. His painting of a kangaroo in 1772 after Cooks 1st Voyage to Australia, was the first glimpse of this animal for many 18th-century Britons
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print Aboriginal Woman of Bruny Island, Tasmania in 1777
- Title : Une Femme De La Terre De Van-Diemens
- Ref : 50609
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Indigenous Woman & child of Adventure Bay, Bruny Island, Tasmania (Van Diemens Land) encountered by Captain Cook in during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery in 1777, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Adventure Bay
from Cooks Journal......on the 24th (March 1777) at 3 AM we made the Coast of Van Diemen land wrote Cook. Anderson remarked that though now the middle of summer here a spot or two of snow was seen on the highest hills… At ten we passd a point supposd to be the boundary of Stone Bay where Abel Tasman anchord, i.e. Storm Bay. According to David Samwell, surgeons first mate on the Resolution, both Ships anchored in Adventure Bay in Van Diemens Land, this Bay was so called by Captn Furneaux who had anchored here in the Adventure last Voyage.
The next day Cook and Clerke sent parties, one to cut wood and the other grass. Clerke wrote of his party from the Discovery The Guard I had sent with the Parties on shore which consisted of the following Marines, Hamlet Thompson, Geo: Moody, Ben: Harriot, Jos: Pool & Willm Broom, stole some Liquor & made themselves exceedingly drunk, for which they receivd a dozen lashes each in the Morning. The Privates were all from the Plymouth division of marines. Hamlet Thompson was from the 6th Company, George Moody from the 70th, John Herriott the 12th, James Poole the 33rd and William Broom the 36th. According to Thomas Edgar, Master, they made themselves so Beastly Drunk that they were put motionless in the Boat, and when brought on board were oblig\'d to be hoisted into the Ship.
William Bayly, astronomer on the Discovery, wrote In the morning I carried my Tent observatory & Instruments on Shore & set all up, but was not able to get any observations it being cloudy all day, in the evening Capt Cook Sent for me & told me he had Altered his mind relative to his stay, & ordered me to pack all up & carry the whole on board again, as he intend[ed] to sail for New Zealand in a day or two.
John Henry Martin, seaman on the Discovery, described the natives. They have few, or no wants, & seemed perfectly Happy, if one might judge from their behaviour, for they frequently woud burst out, into the most immoderate fits of Laughter & when one Laughed every one followed his example Emediately.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Adventure Bay is the name of both a township and a geographical feature on the eastern side of Bruny Island, Tasmania.
The first European to sight the bay was explorer Abel Tasman, who sought to anchor his vessel Heemskerck there in 1642. Instead, Heemskerck was driven back offshore by a storm, in token of which Tasman named the place Storm Bay. Captain Tobias Furneaux renamed it in March 1773, in honour of his ship HMS Adventure, which he had anchored in the bay for five days after becoming separated from Captain James Cook\'s HMS Resolution during Cook\'s second voyage to the Pacific search of Terra Australis Incognita. Furneaux\'s log made clear the bay was an excellent anchorage for resupplying vessels:....to the SW of the first watering place there is a large lagoon which I believe has plenty of fish in it for one of our Gentlemen caught upwards of 2 dozen trout, and shot a possum which was the only animal we saw. There are a great many gum trees and of a vast thickness and height, one of which measured in circumference 26 feet and the height under the branches was 20 feet.
Others among Furneaux\'s crew spotted evidence of what they believed were small deer but were more likely kangaroos. Furneaux also noted signs of an Aboriginal settlement in the form of several huts or wigwams on shore, with several bags of grass in which they carry their shellfish. - but the branches of which the huts were made were split and torn and there was not the least appearance of any people.
Reliably mapped and offering an abundance of water, fresh water and game, Adventure Bay quickly became a popular anchorage for European explorers. Cooks Resolution watered there in 1777, followed by William Bligh aboard HMS Bounty in 1788 and HMS Providence in 1792. Others who resupplied their vessels in the bay in this period included Bruni d Entrecasteaux aboard Recherché in 1792 and 1793, and Nicolas Baudin in the corvette Géographe in 1802. Matthew Flinders also tried to enter the bay with Norfolk in 1798.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773 English writer and book editor.
He is said to have been clerk to an attorney, and was certainly self-educated. In 1744, he succeeded Samuel Johnson as compiler of the parliamentary debates for the Gentleman\\\'s Magazine, and from 1746 to 1749 he contributed poems signed Greville, or H Greville, to that journal. In company with Johnson and others he started a periodical called The Adventurer, which ran to 140 issues, of which 70 were from the pen of Hawkesworth himself.
On account of what was regarded as his powerful defense of morality and religion, Hawkesworth was rewarded by the archbishop of Canterbury with the degree of LL.D, In 1754–1755 he published an edition (12 vols) of Swifts works, with a life prefixed which Johnson praised in his Lives of the Poets. A larger edition (27 vols) appeared in 1766–1779. He adapted Dryden\\\'s Amphitryon for the Drury Lane stage in 1756, and Southernes Oronooko in 1759. He wrote the libretto of an oratorio Zimri in 1760, and the next year Edgar and Emmeline: a Fairy Tale was produced at Drury Lane. His Almoran and Hamet (1761) was first drafted as a play[citation needed], and a tragedy based on it by S J Pratt, The Fair Circassian (1781), met with some success.
He was commissioned by the Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work, An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore Byrone John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook (from 1702 to 1771) drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Hawkesworth was a close imitator of Johnson both in style and thought, and was at one time on very friendly terms with him. It is said that he presumed on his success, and lost Johnsons friendship as early as 1756.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print Aboriginal Man of Bruny Island, Tasmania in 1777
- Title : Un Homme De La Terre De Van-Diemens
- Ref : 43195
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Indigenous Man of Adventure Bay, Bruny Island, Tasmania (Van Diemens Land) encountered by Captain Cook in during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery in 1777, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Adventure Bay
from Cooks Journal......on the 24th (March 1777) at 3 AM we made the Coast of Van Diemen land wrote Cook. Anderson remarked that though now the middle of summer here a spot or two of snow was seen on the highest hills… At ten we passd a point supposd to be the boundary of Stone Bay where Abel Tasman anchord, i.e. Storm Bay. According to David Samwell, surgeons first mate on the Resolution, both Ships anchored in Adventure Bay in Van Diemens Land, this Bay was so called by Captn Furneaux who had anchored here in the Adventure last Voyage.
The next day Cook and Clerke sent parties, one to cut wood and the other grass. Clerke wrote of his party from the Discovery The Guard I had sent with the Parties on shore which consisted of the following Marines, Hamlet Thompson, Geo: Moody, Ben: Harriot, Jos: Pool & Willm Broom, stole some Liquor & made themselves exceedingly drunk, for which they receivd a dozen lashes each in the Morning. The Privates were all from the Plymouth division of marines. Hamlet Thompson was from the 6th Company, George Moody from the 70th, John Herriott the 12th, James Poole the 33rd and William Broom the 36th. According to Thomas Edgar, Master, they made themselves so Beastly Drunk that they were put motionless in the Boat, and when brought on board were oblig\'d to be hoisted into the Ship.
William Bayly, astronomer on the Discovery, wrote In the morning I carried my Tent observatory & Instruments on Shore & set all up, but was not able to get any observations it being cloudy all day, in the evening Capt Cook Sent for me & told me he had Altered his mind relative to his stay, & ordered me to pack all up & carry the whole on board again, as he intend[ed] to sail for New Zealand in a day or two.
John Henry Martin, seaman on the Discovery, described the natives. They have few, or no wants, & seemed perfectly Happy, if one might judge from their behaviour, for they frequently woud burst out, into the most immoderate fits of Laughter & when one Laughed every one followed his example Emediately.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Adventure Bay is the name of both a township and a geographical feature on the eastern side of Bruny Island, Tasmania.
The first European to sight the bay was explorer Abel Tasman, who sought to anchor his vessel Heemskerck there in 1642. Instead, Heemskerck was driven back offshore by a storm, in token of which Tasman named the place Storm Bay. Captain Tobias Furneaux renamed it in March 1773, in honour of his ship HMS Adventure, which he had anchored in the bay for five days after becoming separated from Captain James Cook\'s HMS Resolution during Cook\'s second voyage to the Pacific search of Terra Australis Incognita. Furneaux\'s log made clear the bay was an excellent anchorage for resupplying vessels:....to the SW of the first watering place there is a large lagoon which I believe has plenty of fish in it for one of our Gentlemen caught upwards of 2 dozen trout, and shot a possum which was the only animal we saw. There are a great many gum trees and of a vast thickness and height, one of which measured in circumference 26 feet and the height under the branches was 20 feet.
Others among Furneaux\'s crew spotted evidence of what they believed were small deer but were more likely kangaroos. Furneaux also noted signs of an Aboriginal settlement in the form of several huts or wigwams on shore, with several bags of grass in which they carry their shellfish. - but the branches of which the huts were made were split and torn and there was not the least appearance of any people.
Reliably mapped and offering an abundance of water, fresh water and game, Adventure Bay quickly became a popular anchorage for European explorers. Cooks Resolution watered there in 1777, followed by William Bligh aboard HMS Bounty in 1788 and HMS Providence in 1792. Others who resupplied their vessels in the bay in this period included Bruni d Entrecasteaux aboard Recherché in 1792 and 1793, and Nicolas Baudin in the corvette Géographe in 1802. Matthew Flinders also tried to enter the bay with Norfolk in 1798.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773 English writer and book editor.
He is said to have been clerk to an attorney, and was certainly self-educated. In 1744, he succeeded Samuel Johnson as compiler of the parliamentary debates for the Gentleman\\\'s Magazine, and from 1746 to 1749 he contributed poems signed Greville, or H Greville, to that journal. In company with Johnson and others he started a periodical called The Adventurer, which ran to 140 issues, of which 70 were from the pen of Hawkesworth himself.
On account of what was regarded as his powerful defense of morality and religion, Hawkesworth was rewarded by the archbishop of Canterbury with the degree of LL.D, In 1754–1755 he published an edition (12 vols) of Swifts works, with a life prefixed which Johnson praised in his Lives of the Poets. A larger edition (27 vols) appeared in 1766–1779. He adapted Dryden\\\'s Amphitryon for the Drury Lane stage in 1756, and Southernes Oronooko in 1759. He wrote the libretto of an oratorio Zimri in 1760, and the next year Edgar and Emmeline: a Fairy Tale was produced at Drury Lane. His Almoran and Hamet (1761) was first drafted as a play[citation needed], and a tragedy based on it by S J Pratt, The Fair Circassian (1781), met with some success.
He was commissioned by the Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work, An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore Byrone John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook (from 1702 to 1771) drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Hawkesworth was a close imitator of Johnson both in style and thought, and was at one time on very friendly terms with him. It is said that he presumed on his success, and lost Johnsons friendship as early as 1756.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait A Man of Malakula Island Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Homme de L Isle de Mallicolo
- Ref : 31831
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, portrait of a Man of the Island of Malakula (Mallicolo) in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in September 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Journal July, 1774
Arrival at The New Hebrides
On 17th Cook saw land bearing SW and later on decided this was the Australia Del Espiritu Santo of Quiros or what M. D. Bougainville calls the Great Cyclades. The island was Maewo. The next day its northern end was rounded in a gale and the ship sailed south between it and the island called by Bougainville the Isle of Lepers - Omba.
On 20th they crossed Patteson Passage with a view of geting to the South to explore the lands which lies there, and sailed down the west coast of Pentecost Isle (Raga). To the south they saw the island of Ambrin and behind it Paama and Epi. On 22nd, approaching Mallicollo (Malekula) we perceived a creek which had the appearence of a good harbour. Cook sent Lieutt [Richard] Pickersgill and the Master [Joseph Gilbert] in two Armd boats to Sound and look for Anchorage. The following day a good many [natives] came round us, some came in Canoes and others swam off\'... four I took into the Cabbin and made them various presents. Later, after some misunder-standing some natives began to Shoot Arrows... a Musquet discharged in the air and a four pounder over their heads sent them all off in the utmost confusion; those in the Cabbin leaped out of the Windows... About 9 o\'Clock we landed in the face of about 4 or 500 Men who were assembled on the Shore, armd with Bows and Arrows, clubs and Spears, but they made not the least opposission, on the contrary one Man gave his Arms to a nother and Met us in the water with a green branch in his hand, which [he] exchanged for the one I held in my hand. Just before departing Cook remarked they have not so much as a name for a Dog, consequently can have none, for which reason we left them a Dog and a Bitch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Malakula Island also spelled Malekula, is the second-largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, in the Pacific Ocean region of Melanesia.
Discovered by the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós in 1606 and visited by Captain Cook in 1774.
Vanuatu officially the Republic of Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island in 1606. Since the Portuguese and Spanish monarchies had been unified under the king of Spain in 1580 (following the vacancy of the Portuguese throne, which lasted for sixty years, until 1640, when the Portuguese monarchy was restored), Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queiros, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait A Man of Malakula Island Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Homme de L Isle de Mallicolo
- Ref : 31773
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, portrait of a Man of the Island of Malakula (Mallicolo) in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in September 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Journal July, 1774
Arrival at The New Hebrides
On 17th Cook saw land bearing SW and later on decided this was the Australia Del Espiritu Santo of Quiros or what M. D. Bougainville calls the Great Cyclades. The island was Maewo. The next day its northern end was rounded in a gale and the ship sailed south between it and the island called by Bougainville the Isle of Lepers - Omba.
On 20th they crossed Patteson Passage with a view of geting to the South to explore the lands which lies there, and sailed down the west coast of Pentecost Isle (Raga). To the south they saw the island of Ambrin and behind it Paama and Epi. On 22nd, approaching Mallicollo (Malekula) we perceived a creek which had the appearence of a good harbour. Cook sent Lieutt [Richard] Pickersgill and the Master [Joseph Gilbert] in two Armd boats to Sound and look for Anchorage. The following day a good many [natives] came round us, some came in Canoes and others swam off\'... four I took into the Cabbin and made them various presents. Later, after some misunder-standing some natives began to Shoot Arrows... a Musquet discharged in the air and a four pounder over their heads sent them all off in the utmost confusion; those in the Cabbin leaped out of the Windows... About 9 o\'Clock we landed in the face of about 4 or 500 Men who were assembled on the Shore, armd with Bows and Arrows, clubs and Spears, but they made not the least opposission, on the contrary one Man gave his Arms to a nother and Met us in the water with a green branch in his hand, which [he] exchanged for the one I held in my hand. Just before departing Cook remarked they have not so much as a name for a Dog, consequently can have none, for which reason we left them a Dog and a Bitch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Malakula Island also spelled Malekula, is the second-largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, in the Pacific Ocean region of Melanesia.
Discovered by the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós in 1606 and visited by Captain Cook in 1774.
Vanuatu officially the Republic of Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island in 1606. Since the Portuguese and Spanish monarchies had been unified under the king of Spain in 1580 (following the vacancy of the Portuguese throne, which lasted for sixty years, until 1640, when the Portuguese monarchy was restored), Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queiros, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Woman of New Caledonia Visit in 1774
- Title : Femme de la Noule. Caledonie
- Ref : 91210
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, portrait of a Woman of the Islands of New Caledonia in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in September 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 4-13th Sep. 1774
4th Sun. Sights Cape Colnett (New Caledonia).
5th Mon. Enters reef (Amoss Passage) between Cook Reef and Balade Reef, anchors off Observatory Isle (Pudiu), visited by inhabitants.
6th Tue. Goes ashore with armed boats, rows along coast, returns to ship. Visited by natives, meets Chief, Teeabooma. Wales and Pickersgill land on Isle, Cook goes to help. Observatory set up for eclipse of Sun.
7th Wed. Eclipse, cloudy at first, observations made. Returns to ship, goes ashore again and returns. Simon Monk, ship’s butcher, dies after fall down fore-hatchway previous night.
8th Thu. Goes ashore. Excursion to west. The Forsters and Cook are ill with eating poisoned fish, liver and roe (Toadfish).
9th Fri. Exchanges presents with Teeabooma but still indisposed.
10th Sat. Forster ashore botanising.
12th Mon. Cutter is damaged when Gilbert and Pickersgill are returning from a visit to the north-west of island. Repairs made.
13th Tue. Takes possession of island in name of King George III, naming it New Caledonia. Sails back through reef and heads NW. along coast, outside Cook Reef, passes Great False Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Caledonia is a special collective of France in the southwest Pacific Ocean, 1,210 km east of Australia and 20,000 km from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia sub-region, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Chesterfield Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of Pines, and a few remote islets. The Chesterfield Islands are in the Coral Sea. Locals refer to Grande Terre as Le Caillou (the pebble)
British explorer Captain James Cook was the first European to sight New Caledonia, on 4 September 1774, during his second voyage. He named it New Caledonia, as the northeast of the island reminded him of Scotland. The west coast of Grande Terre was approached by Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse in 1788, shortly before his disappearance, and the Loyalty Islands were first visited between 1793 and 1796 when Mare, Lifou, Tiga, and Ouvea were mapped by William Raven. The American whaler encountered the island named then Britania, and today known as Mar (Loyalty Is.) in November 1793. From 1796 until 1840, only a few sporadic contacts with the archipelago were recorded. About fifty American whalers (identified by Robert Langsom from their log books) have been recorded in the region (Grande Terre, Loyalty Is., Walpole and Hunter) between 1793 and 1887. Contacts became more frequent after 1840, because of the interest in sandalwood
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Woman of Tanna Isle, Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Tanna
- Ref : 31782
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Woman & Child of the Island of Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 6-20th August 1774
........the Women have all the same ornaments as Men, Nose-Stones, Earrings, Shells on the Breast & Bracelets...their heads covered with a kind of cap made of a Plantain leaf or a Mat-Basket. Few are covered, & even very young Girls have these Caps.......Cooks Journal II
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tanna (sometimes spelled Tana) is an island in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
Tanna was first settled about 400 BC by Melanesians from the surrounding islands. The glowing light of Mount Yasur attracted James Cook, the first European to visit the island, in August 1774, where he landed in an inlet on the southeastern tip of the island that he named Port Resolution after his ship HMS Resolution. He gave the island the name of Tanna, probably from the local name for earth, tana in the Kwamera language.
Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print Portrait Princess of Tahuata, Marquesas Isles, 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Ste. Christine
- Ref : 31806
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Princess of Tahuata Island, Santa Cristina, in the Marquesas Islands, South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary (1774)
Apr. 7 Thu. Sights Hood’s Island (Fatu Huku), St. Pedro (Motare). La Dominica (Hiva Oa), St. Christina (Tahuata).
Apr 8 Fri. Sails along southern coast of Hiva Oa looking for anchorage. Anchors in Resolution (formerly Madre de Dios) Bay (Vaitahu Bay). Canoes arrive, gifts are exchanged. Natives killed after an iron stanchion is stolen.
Apr 9 Sat. Goes ashore, gifts exchanged, food obtained.
Apr 10 Sun. Goes ashore to south end of Bay and visits house of dead man. Gifts exchanged.
Apr 11 Mon. Goes ashore to south, again. Finds trade becoming expensive because of lavish gifts by his “gentlemen”.
Apr 12 Tue. Sails towards St. Dominica. No anchorage visible. Heads SW away from islands.
Apr 13 Wed. Sights last of the five main islands, Magdalena (Fatu Hiva).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahuata is the smallest of the inhabited Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mandaña on 22 July 1595. They charted the island as Santa Cristina. They landed at Vaitahu that they named Madre de Dios (Gods Mother in Spanish). According to the Spanish accounts Tahuata had fowls, fish, sugar cane, plantains, nuts and fruits. The existent town was built on two sides of a rectangular space, the houses being of timber and intertwined canes. A building which the Spaniards supposed to be a religious one stood outside the town, in a space enclosed by palisades, and containing some ill-carved images before which were offerings and provisions. The people had large and well constructed sailing canoes. Their tools were made of shells and fish bones. They used slings, stones, and lances as weapons.
Tahuata was visited by Captain James Cook in 1774 and Admiral Dupetit-Thouars in 1842, who signed the treaty annexing the Marquesas Islands to France.
The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the southern Pacific Ocean.
The first Europeans to reach the Marquesas may have been the crew of San Lesmes, a Spanish vessel which disappeared in a storm in June 1526; it was part of an expedition headed by García Jofre de Loaísa. The Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña reached them seventy years later on 21 July 1595. He named them after his patron, García Hurtado de Mendoza, 5th Marquis of Cañete (Spanish: Marqués de Cañete), who served as Viceroy of Peru from 1590 to 1596. |Mendaña visited first Fatu Hiva and then Tahuata before continuing on to the Solomon Islands. His expedition charted the four southernmost Marquesas as Magdalena (Fatu Hiva), Dominica (Hiva ʻOa), San Pedro (Moho Tani), and Santa Cristina (Tahuata).
In the late 16th century European explorers estimated the population at more than 100,000. Europeans and Americans were impressed with how easy life appeared to be in the islands, which had a rich habitat and environment. In 1791 the American maritime fur trader Joseph Ingraham first visited the northern Marquesas while commanding the brig Hope. He named them the Washington Islands. In 1813 Commodore David Porter claimed Nuku Hiva for the United States, but the United States Congress never ratified that claim.
In 1842 France conducted a successful military operation on behalf of the native chief Iotete, who claimed he was king of the whole island of Tahuata. The government laid claim to the whole group and established a settlement on Nuku Hiva. That settlement was abandoned in 1857, but France re-established control over the group in 1870. It later incorporated the Marquesas into French Polynesia.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait Chief of Tahuata, Marquesas Isles in 1774
- Title : Chef De L Isle de Ste. Christine
- Ref : 31807
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief of Tahuata Island, Santa Cristina, in the Marquesas Islands, South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary (1774)
Apr. 7 Thu. Sights Hood’s Island (Fatu Huku), St. Pedro (Motare). La Dominica (Hiva Oa), St. Christina (Tahuata).
Apr 8 Fri. Sails along southern coast of Hiva Oa looking for anchorage. Anchors in Resolution (formerly Madre de Dios) Bay (Vaitahu Bay). Canoes arrive, gifts are exchanged. Natives killed after an iron stanchion is stolen.
Apr 9 Sat. Goes ashore, gifts exchanged, food obtained.
Apr 10 Sun. Goes ashore to south end of Bay and visits house of dead man. Gifts exchanged.
Apr 11 Mon. Goes ashore to south, again. Finds trade becoming expensive because of lavish gifts by his “gentlemen”.
Apr 12 Tue. Sails towards St. Dominica. No anchorage visible. Heads SW away from islands.
Apr 13 Wed. Sights last of the five main islands, Magdalena (Fatu Hiva).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahuata is the smallest of the inhabited Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mandaña on 22 July 1595. They charted the island as Santa Cristina. They landed at Vaitahu that they named Madre de Dios (Gods Mother in Spanish). According to the Spanish accounts Tahuata had fowls, fish, sugar cane, plantains, nuts and fruits. The existent town was built on two sides of a rectangular space, the houses being of timber and intertwined canes. A building which the Spaniards supposed to be a religious one stood outside the town, in a space enclosed by palisades, and containing some ill-carved images before which were offerings and provisions. The people had large and well constructed sailing canoes. Their tools were made of shells and fish bones. They used slings, stones, and lances as weapons.
Tahuata was visited by Captain James Cook in 1774 and Admiral Dupetit-Thouars in 1842, who signed the treaty annexing the Marquesas Islands to France.
The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the southern Pacific Ocean.
The first Europeans to reach the Marquesas may have been the crew of San Lesmes, a Spanish vessel which disappeared in a storm in June 1526; it was part of an expedition headed by García Jofre de Loaísa. The Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña reached them seventy years later on 21 July 1595. He named them after his patron, García Hurtado de Mendoza, 5th Marquis of Cañete (Spanish: Marqués de Cañete), who served as Viceroy of Peru from 1590 to 1596. |Mendaña visited first Fatu Hiva and then Tahuata before continuing on to the Solomon Islands. His expedition charted the four southernmost Marquesas as Magdalena (Fatu Hiva), Dominica (Hiva ʻOa), San Pedro (Moho Tani), and Santa Cristina (Tahuata).
In the late 16th century European explorers estimated the population at more than 100,000. Europeans and Americans were impressed with how easy life appeared to be in the islands, which had a rich habitat and environment. In 1791 the American maritime fur trader Joseph Ingraham first visited the northern Marquesas while commanding the brig Hope. He named them the Washington Islands. In 1813 Commodore David Porter claimed Nuku Hiva for the United States, but the United States Congress never ratified that claim.
In 1842 France conducted a successful military operation on behalf of the native chief Iotete, who claimed he was king of the whole island of Tahuata. The government laid claim to the whole group and established a settlement on Nuku Hiva. That settlement was abandoned in 1857, but France re-established control over the group in 1870. It later incorporated the Marquesas into French Polynesia.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Oedidee, Bora Bora met by Cook in 1773
- Title : O-Hedidee, Jeune homme de Bolabala
- Ref : 31774
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of O-Hedidee or Oedidee of the island of Bora Bora in the Society Islands, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
O-Hedidee or Oedidee, was a native of Bora Bora, Society Islands, French Polynesia, was about 17 or 18 years of age when he was taken on board the Resolution at Raiatea Island on 17 September 1773. He is described in Hawkesworths account as a young man with curly hair and flattish nose, wearing a gown. Cook wrote: he may be of use to us if we should fall in with and touch at any isles in our rout to the west which was my only motive for taking him on board. Cook Journals II.
O-Hedidee traveled with Cook from Raiatea to New Zealand, Easter Island, and Tahiti, returning to Raiatea on 4 June 1774, having been with the Resolutions company for seven months.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Bora Bora is a 30.55 km2 island group in the Leeward group in the western part of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the Pacific Ocean. The main island, located about 230 kilometres northwest of Papeete, Tahiti is surrounded by a lagoon and a barrier reef. In the center of the island are the remnants of an extinct volcano rising to two peaks, Mount Pahia and Mount Otemanu, the highest point at 727 metres
The island was inhabited by Polynesian settlers around the 4th century C.E. The first European sighting was made by Jakob Roggeveen in 1722.
James Cook sighted the island on 29 July 1769, using a Tahitian navigator, Tupaia. The London Missionary Society arrived in 1820 and founded a Protestant church in 1890. Bora Bora was an independent kingdom until 1888 when its last queen Teriimaevarua III was forced to abdicate by the French who annexed the island as a colony.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia, Tahiti 1773
- Title : Potatow, Chef de Tahiti
- Ref : 31772
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia in Tahiti, French Polynesia, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cooks Biography............George Vancouver (midshipman, of later fame) meanwhile, stayed behind to contemplate the role of the red feather in Tahitian society. It happened that Chief Potatau consulted with his wife on how they might obtain some of Cook\'s Oora and according to the plan that somehow reached Georges ears, she would go to Cook in his cabin and offer her services in return for said feathers. But the Captain was unswayed. It was just as well that Georges father was absent on this particular occasion, for he would only have been upset. As it was, his sleep was often disturbed by the sailors running all over the ship with their sexual partners at any hour of the night.
Such was Tahitian zeal for red feathers, Clerke remarked, that they gladly engaged in rather unhallow\'d rites for the sacred jewels in order to offer Propitiation to their Jolly Gods. Such was the maritime zeal for the Tahitian religion that the sailors fairly plundered the ship of its treasures; feathers were ripped from lovely Tongan garments and from delicate fretwork on coconuts; sailors even dyed plain feathers red. Thus valuable artifacts of the South Seas were undone. Nevertheless, among the treasures that came aboard were Potatau\'s monstrous helmets of war of five feet high and several handsome mourning dresses to become in due course part of the collections of ethnology in the Ashmolean Museum and the Bishop Museum. Besides the red feathers, the abundance of pork also attracted the girls; they consumed incredible quantities, reported George, because, as members of a poor class of Tahitians, they were denied pork in their own households. Such were the quantities they consumed, added George with a certain delicacy, that of a sudden they suffered the inconvenience of restlessness, and when they were refused the attention of their lovers, the very decks began to resemble the paths in the islands.........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait A Man of Malakula Island Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Homme de L Isle de Mallicolo
- Ref : 21347
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, portrait of a Man of the Island of Malakula (Mallicolo) in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in September 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Journal July, 1774
Arrival at The New Hebrides
On 17th Cook saw land bearing SW and later on decided this was the Australia Del Espiritu Santo of Quiros or what M. D. Bougainville calls the Great Cyclades. The island was Maewo. The next day its northern end was rounded in a gale and the ship sailed south between it and the island called by Bougainville the Isle of Lepers - Omba.
On 20th they crossed Patteson Passage with a view of geting to the South to explore the lands which lies there, and sailed down the west coast of Pentecost Isle (Raga). To the south they saw the island of Ambrin and behind it Paama and Epi. On 22nd, approaching Mallicollo (Malekula) we perceived a creek which had the appearence of a good harbour. Cook sent Lieutt [Richard] Pickersgill and the Master [Joseph Gilbert] in two Armd boats to Sound and look for Anchorage. The following day a good many [natives] came round us, some came in Canoes and others swam off\'... four I took into the Cabbin and made them various presents. Later, after some misunder-standing some natives began to Shoot Arrows... a Musquet discharged in the air and a four pounder over their heads sent them all off in the utmost confusion; those in the Cabbin leaped out of the Windows... About 9 o\'Clock we landed in the face of about 4 or 500 Men who were assembled on the Shore, armd with Bows and Arrows, clubs and Spears, but they made not the least opposission, on the contrary one Man gave his Arms to a nother and Met us in the water with a green branch in his hand, which [he] exchanged for the one I held in my hand. Just before departing Cook remarked they have not so much as a name for a Dog, consequently can have none, for which reason we left them a Dog and a Bitch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Malakula Island also spelled Malekula, is the second-largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, in the Pacific Ocean region of Melanesia.
Discovered by the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós in 1606 and visited by Captain Cook in 1774.
Vanuatu officially the Republic of Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island in 1606. Since the Portuguese and Spanish monarchies had been unified under the king of Spain in 1580 (following the vacancy of the Portuguese throne, which lasted for sixty years, until 1640, when the Portuguese monarchy was restored), Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queiros, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Woman of New Caledonia Visit in 1774
- Title : Femme de la Noule. Caledonie
- Ref : 21327
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, portrait of a Woman of the Islands of New Caledonia in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in September 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 4-13th Sep. 1774
4th Sun. Sights Cape Colnett (New Caledonia).
5th Mon. Enters reef (Amoss Passage) between Cook Reef and Balade Reef, anchors off Observatory Isle (Pudiu), visited by inhabitants.
6th Tue. Goes ashore with armed boats, rows along coast, returns to ship. Visited by natives, meets Chief, Teeabooma. Wales and Pickersgill land on Isle, Cook goes to help. Observatory set up for eclipse of Sun.
7th Wed. Eclipse, cloudy at first, observations made. Returns to ship, goes ashore again and returns. Simon Monk, ship’s butcher, dies after fall down fore-hatchway previous night.
8th Thu. Goes ashore. Excursion to west. The Forsters and Cook are ill with eating poisoned fish, liver and roe (Toadfish).
9th Fri. Exchanges presents with Teeabooma but still indisposed.
10th Sat. Forster ashore botanising.
12th Mon. Cutter is damaged when Gilbert and Pickersgill are returning from a visit to the north-west of island. Repairs made.
13th Tue. Takes possession of island in name of King George III, naming it New Caledonia. Sails back through reef and heads NW. along coast, outside Cook Reef, passes Great False Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Caledonia is a special collective of France in the southwest Pacific Ocean, 1,210 km east of Australia and 20,000 km from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia sub-region, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Chesterfield Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of Pines, and a few remote islets. The Chesterfield Islands are in the Coral Sea. Locals refer to Grande Terre as Le Caillou (the pebble)
British explorer Captain James Cook was the first European to sight New Caledonia, on 4 September 1774, during his second voyage. He named it New Caledonia, as the northeast of the island reminded him of Scotland. The west coast of Grande Terre was approached by Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse in 1788, shortly before his disappearance, and the Loyalty Islands were first visited between 1793 and 1796 when Mare, Lifou, Tiga, and Ouvea were mapped by William Raven. The American whaler encountered the island named then Britania, and today known as Mar (Loyalty Is.) in November 1793. From 1796 until 1840, only a few sporadic contacts with the archipelago were recorded. About fifty American whalers (identified by Robert Langsom from their log books) have been recorded in the region (Grande Terre, Loyalty Is., Walpole and Hunter) between 1793 and 1887. Contacts became more frequent after 1840, because of the interest in sandalwood
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print of a Man of the Tanna Island, Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Homme De L Isle de Tanna
- Ref : 21353
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Man of the Island of Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 6-20th August 1774
........the Women have all the same ornaments as Men, Nose-Stones, Earrings, Shells on the Breast & Bracelets...their heads covered with a kind of cap made of a Plantain leaf or a Mat-Basket. Few are covered, & even very young Girls have these Caps.......Cooks Journal II
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tanna (sometimes spelled Tana) is an island in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
Tanna was first settled about 400 BC by Melanesians from the surrounding islands. The glowing light of Mount Yasur attracted James Cook, the first European to visit the island, in August 1774, where he landed in an inlet on the southeastern tip of the island that he named Port Resolution after his ship HMS Resolution. He gave the island the name of Tanna, probably from the local name for earth, tana in the Kwamera language.
Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print of a Man of the Tanna Island, Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Homme De L Isle de Tanna
- Ref : 16344-1
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Man of the Island of Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 6-20th August 1774
........the Women have all the same ornaments as Men, Nose-Stones, Earrings, Shells on the Breast & Bracelets...their heads covered with a kind of cap made of a Plantain leaf or a Mat-Basket. Few are covered, & even very young Girls have these Caps.......Cooks Journal II
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tanna (sometimes spelled Tana) is an island in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
Tanna was first settled about 400 BC by Melanesians from the surrounding islands. The glowing light of Mount Yasur attracted James Cook, the first European to visit the island, in August 1774, where he landed in an inlet on the southeastern tip of the island that he named Port Resolution after his ship HMS Resolution. He gave the island the name of Tanna, probably from the local name for earth, tana in the Kwamera language.
Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Woman of Tanna Isle, Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Tanna
- Ref : 16354
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Woman & Child of the Island of Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 6-20th August 1774
........the Women have all the same ornaments as Men, Nose-Stones, Earrings, Shells on the Breast & Bracelets...their heads covered with a kind of cap made of a Plantain leaf or a Mat-Basket. Few are covered, & even very young Girls have these Caps.......Cooks Journal II
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tanna (sometimes spelled Tana) is an island in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
Tanna was first settled about 400 BC by Melanesians from the surrounding islands. The glowing light of Mount Yasur attracted James Cook, the first European to visit the island, in August 1774, where he landed in an inlet on the southeastern tip of the island that he named Port Resolution after his ship HMS Resolution. He gave the island the name of Tanna, probably from the local name for earth, tana in the Kwamera language.
Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Woman of Tanna Isle, Vanuatu in 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Tanna
- Ref : 21354
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Woman & Child of the Island of Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary, 6-20th August 1774
........the Women have all the same ornaments as Men, Nose-Stones, Earrings, Shells on the Breast & Bracelets...their heads covered with a kind of cap made of a Plantain leaf or a Mat-Basket. Few are covered, & even very young Girls have these Caps.......Cooks Journal II
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tanna (sometimes spelled Tana) is an island in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
Tanna was first settled about 400 BC by Melanesians from the surrounding islands. The glowing light of Mount Yasur attracted James Cook, the first European to visit the island, in August 1774, where he landed in an inlet on the southeastern tip of the island that he named Port Resolution after his ship HMS Resolution. He gave the island the name of Tanna, probably from the local name for earth, tana in the Kwamera language.
Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print Portrait Princess of Tahuata, Marquesas Isles, 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Ste. Christine
- Ref : 21399
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Princess of Tahuata Island, Santa Cristina, in the Marquesas Islands, South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary (1774)
Apr. 7 Thu. Sights Hood’s Island (Fatu Huku), St. Pedro (Motare). La Dominica (Hiva Oa), St. Christina (Tahuata).
Apr 8 Fri. Sails along southern coast of Hiva Oa looking for anchorage. Anchors in Resolution (formerly Madre de Dios) Bay (Vaitahu Bay). Canoes arrive, gifts are exchanged. Natives killed after an iron stanchion is stolen.
Apr 9 Sat. Goes ashore, gifts exchanged, food obtained.
Apr 10 Sun. Goes ashore to south end of Bay and visits house of dead man. Gifts exchanged.
Apr 11 Mon. Goes ashore to south, again. Finds trade becoming expensive because of lavish gifts by his “gentlemen”.
Apr 12 Tue. Sails towards St. Dominica. No anchorage visible. Heads SW away from islands.
Apr 13 Wed. Sights last of the five main islands, Magdalena (Fatu Hiva).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahuata is the smallest of the inhabited Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mandaña on 22 July 1595. They charted the island as Santa Cristina. They landed at Vaitahu that they named Madre de Dios (Gods Mother in Spanish). According to the Spanish accounts Tahuata had fowls, fish, sugar cane, plantains, nuts and fruits. The existent town was built on two sides of a rectangular space, the houses being of timber and intertwined canes. A building which the Spaniards supposed to be a religious one stood outside the town, in a space enclosed by palisades, and containing some ill-carved images before which were offerings and provisions. The people had large and well constructed sailing canoes. Their tools were made of shells and fish bones. They used slings, stones, and lances as weapons.
Tahuata was visited by Captain James Cook in 1774 and Admiral Dupetit-Thouars in 1842, who signed the treaty annexing the Marquesas Islands to France.
The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the southern Pacific Ocean.
The first Europeans to reach the Marquesas may have been the crew of San Lesmes, a Spanish vessel which disappeared in a storm in June 1526; it was part of an expedition headed by García Jofre de Loaísa. The Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña reached them seventy years later on 21 July 1595. He named them after his patron, García Hurtado de Mendoza, 5th Marquis of Cañete (Spanish: Marqués de Cañete), who served as Viceroy of Peru from 1590 to 1596. |Mendaña visited first Fatu Hiva and then Tahuata before continuing on to the Solomon Islands. His expedition charted the four southernmost Marquesas as Magdalena (Fatu Hiva), Dominica (Hiva ʻOa), San Pedro (Moho Tani), and Santa Cristina (Tahuata).
In the late 16th century European explorers estimated the population at more than 100,000. Europeans and Americans were impressed with how easy life appeared to be in the islands, which had a rich habitat and environment. In 1791 the American maritime fur trader Joseph Ingraham first visited the northern Marquesas while commanding the brig Hope. He named them the Washington Islands. In 1813 Commodore David Porter claimed Nuku Hiva for the United States, but the United States Congress never ratified that claim.
In 1842 France conducted a successful military operation on behalf of the native chief Iotete, who claimed he was king of the whole island of Tahuata. The government laid claim to the whole group and established a settlement on Nuku Hiva. That settlement was abandoned in 1857, but France re-established control over the group in 1870. It later incorporated the Marquesas into French Polynesia.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print Portrait Princess of Tahuata, Marquesas Isles, 1774
- Title : Femme De L Isle de Ste. Christine
- Ref : 16349
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of a Princess of Tahuata Island, Santa Cristina, in the Marquesas Islands, South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary (1774)
Apr. 7 Thu. Sights Hood’s Island (Fatu Huku), St. Pedro (Motare). La Dominica (Hiva Oa), St. Christina (Tahuata).
Apr 8 Fri. Sails along southern coast of Hiva Oa looking for anchorage. Anchors in Resolution (formerly Madre de Dios) Bay (Vaitahu Bay). Canoes arrive, gifts are exchanged. Natives killed after an iron stanchion is stolen.
Apr 9 Sat. Goes ashore, gifts exchanged, food obtained.
Apr 10 Sun. Goes ashore to south end of Bay and visits house of dead man. Gifts exchanged.
Apr 11 Mon. Goes ashore to south, again. Finds trade becoming expensive because of lavish gifts by his “gentlemen”.
Apr 12 Tue. Sails towards St. Dominica. No anchorage visible. Heads SW away from islands.
Apr 13 Wed. Sights last of the five main islands, Magdalena (Fatu Hiva).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahuata is the smallest of the inhabited Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mandaña on 22 July 1595. They charted the island as Santa Cristina. They landed at Vaitahu that they named Madre de Dios (Gods Mother in Spanish). According to the Spanish accounts Tahuata had fowls, fish, sugar cane, plantains, nuts and fruits. The existent town was built on two sides of a rectangular space, the houses being of timber and intertwined canes. A building which the Spaniards supposed to be a religious one stood outside the town, in a space enclosed by palisades, and containing some ill-carved images before which were offerings and provisions. The people had large and well constructed sailing canoes. Their tools were made of shells and fish bones. They used slings, stones, and lances as weapons.
Tahuata was visited by Captain James Cook in 1774 and Admiral Dupetit-Thouars in 1842, who signed the treaty annexing the Marquesas Islands to France.
The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the southern Pacific Ocean.
The first Europeans to reach the Marquesas may have been the crew of San Lesmes, a Spanish vessel which disappeared in a storm in June 1526; it was part of an expedition headed by García Jofre de Loaísa. The Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña reached them seventy years later on 21 July 1595. He named them after his patron, García Hurtado de Mendoza, 5th Marquis of Cañete (Spanish: Marqués de Cañete), who served as Viceroy of Peru from 1590 to 1596. |Mendaña visited first Fatu Hiva and then Tahuata before continuing on to the Solomon Islands. His expedition charted the four southernmost Marquesas as Magdalena (Fatu Hiva), Dominica (Hiva ʻOa), San Pedro (Moho Tani), and Santa Cristina (Tahuata).
In the late 16th century European explorers estimated the population at more than 100,000. Europeans and Americans were impressed with how easy life appeared to be in the islands, which had a rich habitat and environment. In 1791 the American maritime fur trader Joseph Ingraham first visited the northern Marquesas while commanding the brig Hope. He named them the Washington Islands. In 1813 Commodore David Porter claimed Nuku Hiva for the United States, but the United States Congress never ratified that claim.
In 1842 France conducted a successful military operation on behalf of the native chief Iotete, who claimed he was king of the whole island of Tahuata. The government laid claim to the whole group and established a settlement on Nuku Hiva. That settlement was abandoned in 1857, but France re-established control over the group in 1870. It later incorporated the Marquesas into French Polynesia.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait Chief of Tahuata, Marquesas Isles in 1774
- Title : Chef De L Isle de Ste. Christine
- Ref : 16348
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief of Tahuata Island, Santa Cristina, in the Marquesas Islands, South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary (1774)
Apr. 7 Thu. Sights Hood’s Island (Fatu Huku), St. Pedro (Motare). La Dominica (Hiva Oa), St. Christina (Tahuata).
Apr 8 Fri. Sails along southern coast of Hiva Oa looking for anchorage. Anchors in Resolution (formerly Madre de Dios) Bay (Vaitahu Bay). Canoes arrive, gifts are exchanged. Natives killed after an iron stanchion is stolen.
Apr 9 Sat. Goes ashore, gifts exchanged, food obtained.
Apr 10 Sun. Goes ashore to south end of Bay and visits house of dead man. Gifts exchanged.
Apr 11 Mon. Goes ashore to south, again. Finds trade becoming expensive because of lavish gifts by his “gentlemen”.
Apr 12 Tue. Sails towards St. Dominica. No anchorage visible. Heads SW away from islands.
Apr 13 Wed. Sights last of the five main islands, Magdalena (Fatu Hiva).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahuata is the smallest of the inhabited Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mandaña on 22 July 1595. They charted the island as Santa Cristina. They landed at Vaitahu that they named Madre de Dios (Gods Mother in Spanish). According to the Spanish accounts Tahuata had fowls, fish, sugar cane, plantains, nuts and fruits. The existent town was built on two sides of a rectangular space, the houses being of timber and intertwined canes. A building which the Spaniards supposed to be a religious one stood outside the town, in a space enclosed by palisades, and containing some ill-carved images before which were offerings and provisions. The people had large and well constructed sailing canoes. Their tools were made of shells and fish bones. They used slings, stones, and lances as weapons.
Tahuata was visited by Captain James Cook in 1774 and Admiral Dupetit-Thouars in 1842, who signed the treaty annexing the Marquesas Islands to France.
The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the southern Pacific Ocean.
The first Europeans to reach the Marquesas may have been the crew of San Lesmes, a Spanish vessel which disappeared in a storm in June 1526; it was part of an expedition headed by García Jofre de Loaísa. The Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña reached them seventy years later on 21 July 1595. He named them after his patron, García Hurtado de Mendoza, 5th Marquis of Cañete (Spanish: Marqués de Cañete), who served as Viceroy of Peru from 1590 to 1596. |Mendaña visited first Fatu Hiva and then Tahuata before continuing on to the Solomon Islands. His expedition charted the four southernmost Marquesas as Magdalena (Fatu Hiva), Dominica (Hiva ʻOa), San Pedro (Moho Tani), and Santa Cristina (Tahuata).
In the late 16th century European explorers estimated the population at more than 100,000. Europeans and Americans were impressed with how easy life appeared to be in the islands, which had a rich habitat and environment. In 1791 the American maritime fur trader Joseph Ingraham first visited the northern Marquesas while commanding the brig Hope. He named them the Washington Islands. In 1813 Commodore David Porter claimed Nuku Hiva for the United States, but the United States Congress never ratified that claim.
In 1842 France conducted a successful military operation on behalf of the native chief Iotete, who claimed he was king of the whole island of Tahuata. The government laid claim to the whole group and established a settlement on Nuku Hiva. That settlement was abandoned in 1857, but France re-established control over the group in 1870. It later incorporated the Marquesas into French Polynesia.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait Chief of Tahuata, Marquesas Isles in 1774
- Title : Chef De L Isle de Ste. Christine
- Ref : 21328
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief of Tahuata Island, Santa Cristina, in the Marquesas Islands, South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Diary (1774)
Apr. 7 Thu. Sights Hood’s Island (Fatu Huku), St. Pedro (Motare). La Dominica (Hiva Oa), St. Christina (Tahuata).
Apr 8 Fri. Sails along southern coast of Hiva Oa looking for anchorage. Anchors in Resolution (formerly Madre de Dios) Bay (Vaitahu Bay). Canoes arrive, gifts are exchanged. Natives killed after an iron stanchion is stolen.
Apr 9 Sat. Goes ashore, gifts exchanged, food obtained.
Apr 10 Sun. Goes ashore to south end of Bay and visits house of dead man. Gifts exchanged.
Apr 11 Mon. Goes ashore to south, again. Finds trade becoming expensive because of lavish gifts by his “gentlemen”.
Apr 12 Tue. Sails towards St. Dominica. No anchorage visible. Heads SW away from islands.
Apr 13 Wed. Sights last of the five main islands, Magdalena (Fatu Hiva).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahuata is the smallest of the inhabited Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mandaña on 22 July 1595. They charted the island as Santa Cristina. They landed at Vaitahu that they named Madre de Dios (Gods Mother in Spanish). According to the Spanish accounts Tahuata had fowls, fish, sugar cane, plantains, nuts and fruits. The existent town was built on two sides of a rectangular space, the houses being of timber and intertwined canes. A building which the Spaniards supposed to be a religious one stood outside the town, in a space enclosed by palisades, and containing some ill-carved images before which were offerings and provisions. The people had large and well constructed sailing canoes. Their tools were made of shells and fish bones. They used slings, stones, and lances as weapons.
Tahuata was visited by Captain James Cook in 1774 and Admiral Dupetit-Thouars in 1842, who signed the treaty annexing the Marquesas Islands to France.
The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collective of France in the southern Pacific Ocean.
The first Europeans to reach the Marquesas may have been the crew of San Lesmes, a Spanish vessel which disappeared in a storm in June 1526; it was part of an expedition headed by García Jofre de Loaísa. The Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña reached them seventy years later on 21 July 1595. He named them after his patron, García Hurtado de Mendoza, 5th Marquis of Cañete (Spanish: Marqués de Cañete), who served as Viceroy of Peru from 1590 to 1596. |Mendaña visited first Fatu Hiva and then Tahuata before continuing on to the Solomon Islands. His expedition charted the four southernmost Marquesas as Magdalena (Fatu Hiva), Dominica (Hiva ʻOa), San Pedro (Moho Tani), and Santa Cristina (Tahuata).
In the late 16th century European explorers estimated the population at more than 100,000. Europeans and Americans were impressed with how easy life appeared to be in the islands, which had a rich habitat and environment. In 1791 the American maritime fur trader Joseph Ingraham first visited the northern Marquesas while commanding the brig Hope. He named them the Washington Islands. In 1813 Commodore David Porter claimed Nuku Hiva for the United States, but the United States Congress never ratified that claim.
In 1842 France conducted a successful military operation on behalf of the native chief Iotete, who claimed he was king of the whole island of Tahuata. The government laid claim to the whole group and established a settlement on Nuku Hiva. That settlement was abandoned in 1857, but France re-established control over the group in 1870. It later incorporated the Marquesas into French Polynesia.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia, Tahiti 1773
- Title : Potatow, Chef de Tahiti
- Ref : 21415
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia in Tahiti, French Polynesia, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cooks Biography............George Vancouver (midshipman, of later fame) meanwhile, stayed behind to contemplate the role of the red feather in Tahitian society. It happened that Chief Potatau consulted with his wife on how they might obtain some of Cook\'s Oora and according to the plan that somehow reached Georges ears, she would go to Cook in his cabin and offer her services in return for said feathers. But the Captain was unswayed. It was just as well that Georges father was absent on this particular occasion, for he would only have been upset. As it was, his sleep was often disturbed by the sailors running all over the ship with their sexual partners at any hour of the night.
Such was Tahitian zeal for red feathers, Clerke remarked, that they gladly engaged in rather unhallow\'d rites for the sacred jewels in order to offer Propitiation to their Jolly Gods. Such was the maritime zeal for the Tahitian religion that the sailors fairly plundered the ship of its treasures; feathers were ripped from lovely Tongan garments and from delicate fretwork on coconuts; sailors even dyed plain feathers red. Thus valuable artifacts of the South Seas were undone. Nevertheless, among the treasures that came aboard were Potatau\'s monstrous helmets of war of five feet high and several handsome mourning dresses to become in due course part of the collections of ethnology in the Ashmolean Museum and the Bishop Museum. Besides the red feathers, the abundance of pork also attracted the girls; they consumed incredible quantities, reported George, because, as members of a poor class of Tahitians, they were denied pork in their own households. Such were the quantities they consumed, added George with a certain delicacy, that of a sudden they suffered the inconvenience of restlessness, and when they were refused the attention of their lovers, the very decks began to resemble the paths in the islands.........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt. Cook Antique Print Portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia, Tahiti 1773
- Title : Potatow, Chef de Tahiti
- Ref : 16353
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, a portrait of Chief Potatau of Punaauia in Tahiti, French Polynesia, met by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in 1773, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cooks Biography............George Vancouver (midshipman, of later fame) meanwhile, stayed behind to contemplate the role of the red feather in Tahitian society. It happened that Chief Potatau consulted with his wife on how they might obtain some of Cook\'s Oora and according to the plan that somehow reached Georges ears, she would go to Cook in his cabin and offer her services in return for said feathers. But the Captain was unswayed. It was just as well that Georges father was absent on this particular occasion, for he would only have been upset. As it was, his sleep was often disturbed by the sailors running all over the ship with their sexual partners at any hour of the night.
Such was Tahitian zeal for red feathers, Clerke remarked, that they gladly engaged in rather unhallow\'d rites for the sacred jewels in order to offer Propitiation to their Jolly Gods. Such was the maritime zeal for the Tahitian religion that the sailors fairly plundered the ship of its treasures; feathers were ripped from lovely Tongan garments and from delicate fretwork on coconuts; sailors even dyed plain feathers red. Thus valuable artifacts of the South Seas were undone. Nevertheless, among the treasures that came aboard were Potatau\'s monstrous helmets of war of five feet high and several handsome mourning dresses to become in due course part of the collections of ethnology in the Ashmolean Museum and the Bishop Museum. Besides the red feathers, the abundance of pork also attracted the girls; they consumed incredible quantities, reported George, because, as members of a poor class of Tahitians, they were denied pork in their own households. Such were the quantities they consumed, added George with a certain delicacy, that of a sudden they suffered the inconvenience of restlessness, and when they were refused the attention of their lovers, the very decks began to resemble the paths in the islands.........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1774 Capt. Cook Antique Print a Portrait of Chief Tynah, Otoo of Tahiti in 1769
- Title : Otoo, Roi de Tahiti
- Ref : 21341
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print a portrait of Chief Tynah (Otoo) of Tahiti Island, met by Captain James Cook during his 1st Voyage of Discovery in 1769, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Sydney Parkinson - and was published in the 1774 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas by John Hawkesworth in An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks. Paris, 1774.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, brown, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.