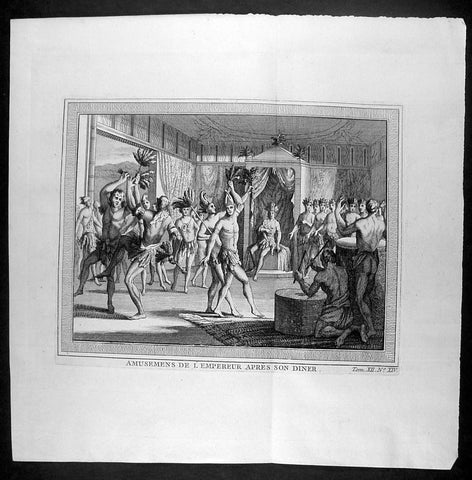
America (163)
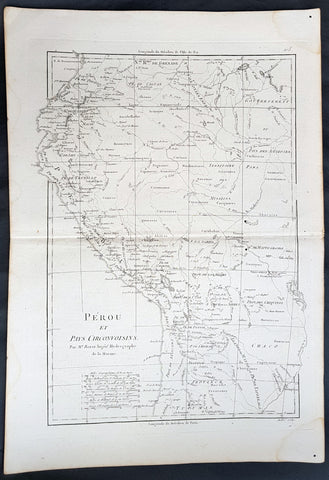
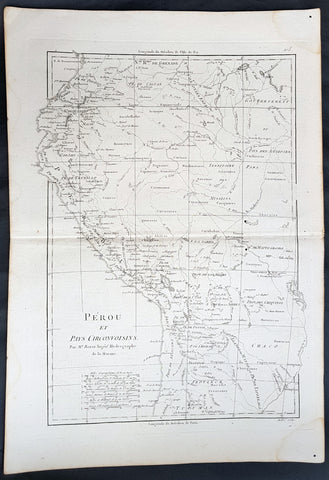
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of West South America Peru & The Amazon River
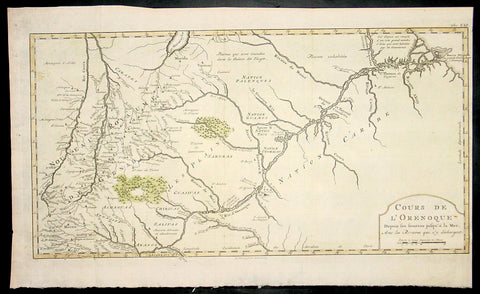
- Title : Perou et Pays Circonvoisins... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40551
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
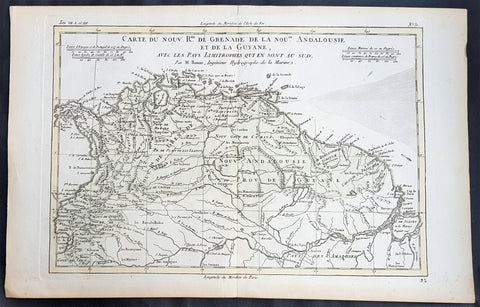
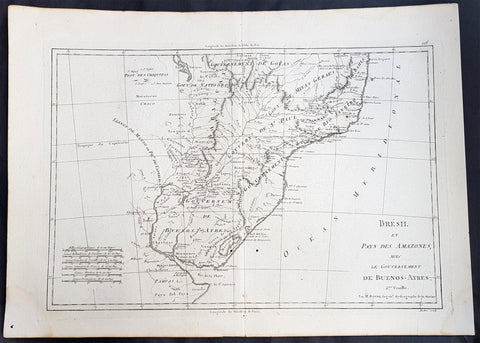
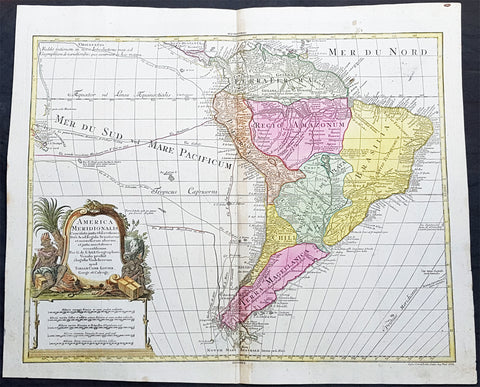
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31681
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
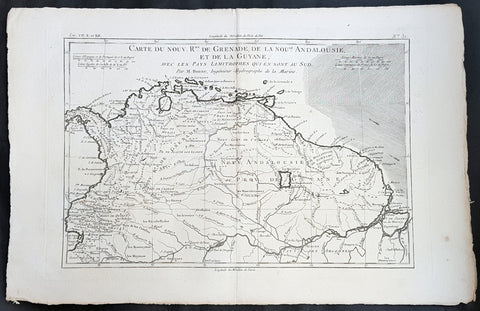
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40848
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
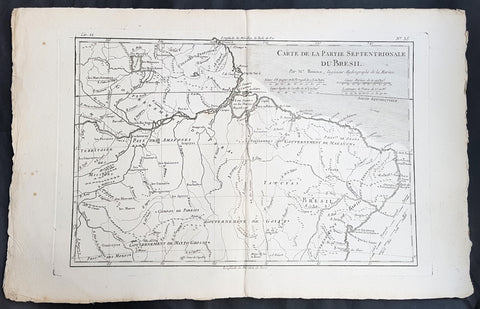
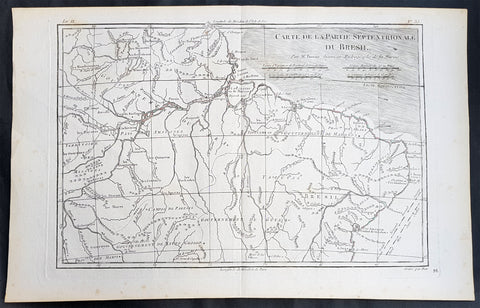
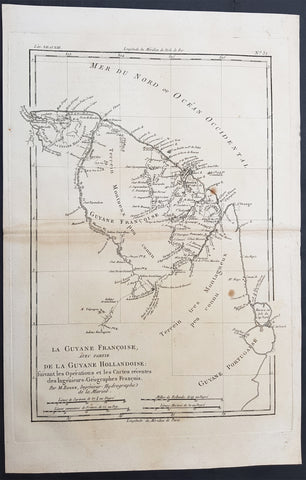
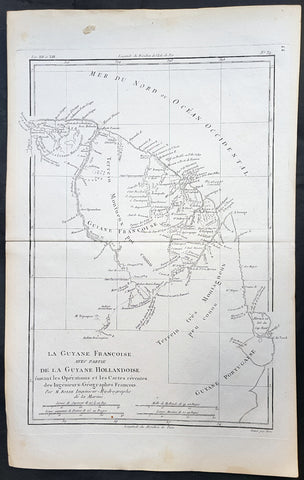
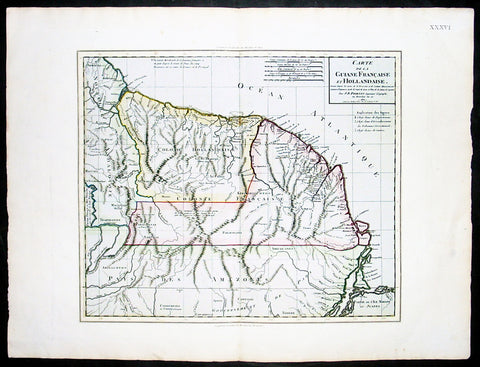
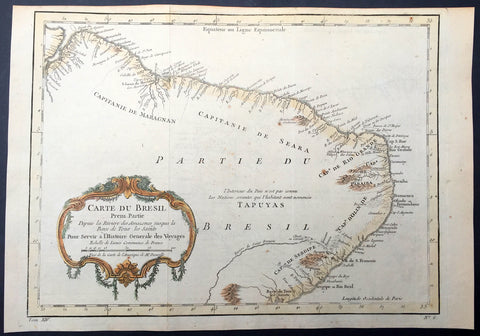
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40850
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31685
- Size: 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
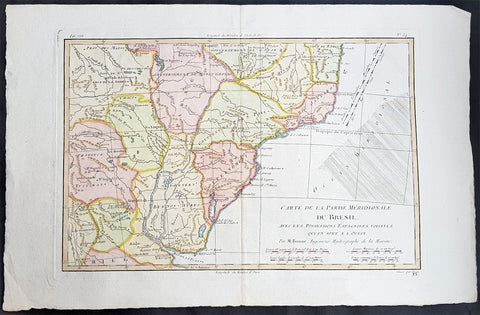
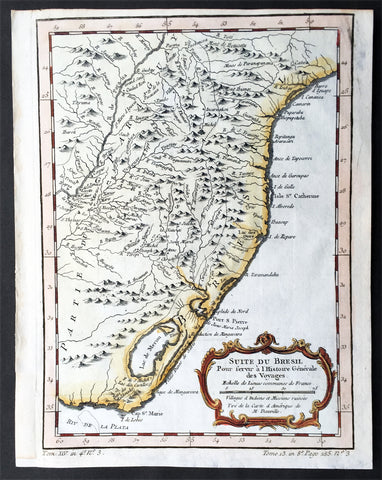
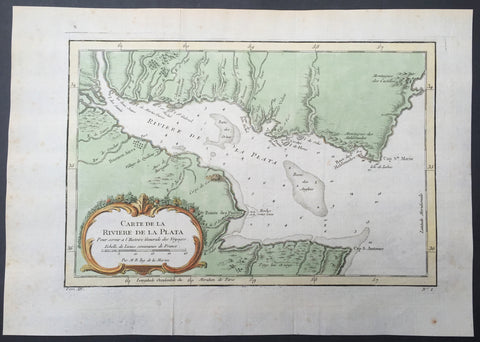
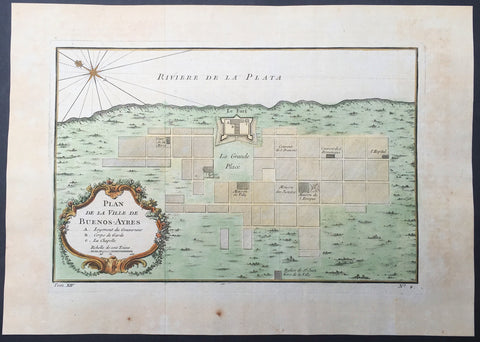
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 40552
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
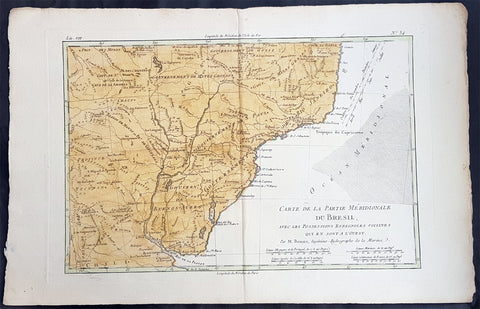
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 16042-1
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Southern Brazil, Uruguay, River Plate Argentina
- Title : Carte De La Parties Meridionale Du Bresil...Par M Bonne
- Ref #: 40851
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of southern Brazil, Uraguay to the Rio De la Plata in Argentina by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Río de la Plata River Plate is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or freshwater sea. The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario. The area was also visited by Francis Drakes fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near todays Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a Sierra de la Plata in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river Río de la Plata (River of Silver).
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
Conflict in the region intensified after the independence of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in the first quarter of the 19th century. Interests in the territories and the navigation rights over the Platine region played a major role in many armed conflicts throughout the century, including the Argentine civil wars, the Cisplatine and Platine wars, and the Paraguayan War. The river was blockaded by extra-regional powers 1838–1840 and 1845–1850.
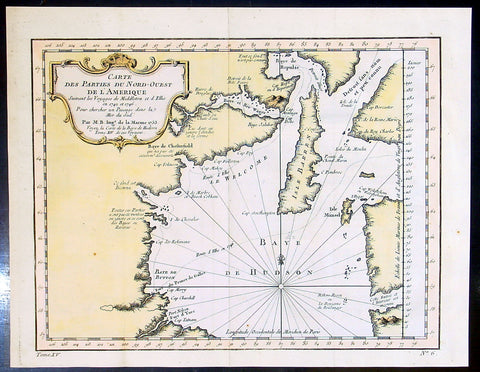
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Caribbean Islands of Guadeloupe & Martinique
- Title : L Isle De La Martinique; Isles De La Guadeloupe...Par M Bonne
- Date : 1780
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 40556
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Caribbean Islands of Guadeloupe & Martinique by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Two small worm holes
Plate area: - Two small worm holes
Verso: - Two small worm holes
Background:
Martinique is an insular region of France located in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea.
Guadeloupe is an insular region of France located in the Leeward Islands, part of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean.
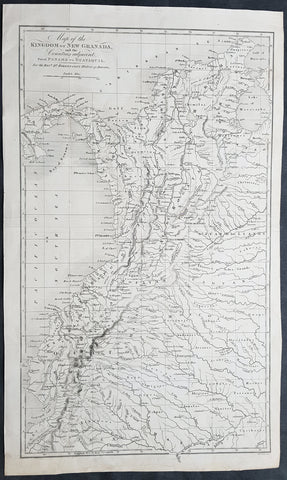
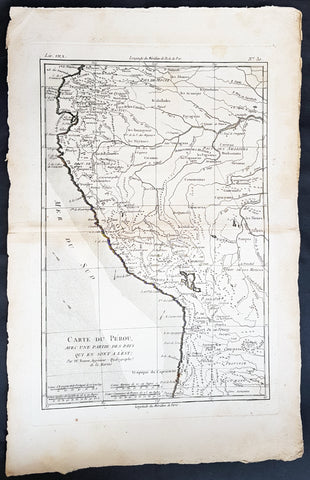
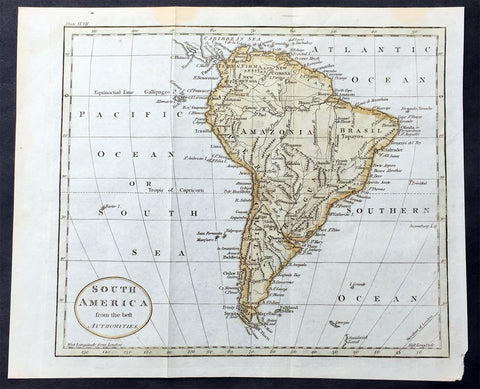
1824 William Robertson Large Antique Map of NW South America - Panama to Peru
- Title : Map of the Kingdom of New Granada and the Countries adjacent from Panama to Guayquil
- Date : 1824
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 01-9624
- Size: 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (445mm x 270mm)
Description:
This large highly detailed original copper-plate engraved antique map of north west South America - from Panama to Peru - was engraved by Sydney Hall and published in the 1824 edition of the Rev. Dr Robertsons The History of America. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (445mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (445mm x 270mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
Robertson , William 1721 - 1793
Rev Robertson was a Scottish historian, minister in the Church of Scotland, and Principal of the University of Edinburgh. The thirty years during which he presided over the University perhaps represent the highest point in its history. He made significant contributions to the writing of Scottish history and the history of Spain and Spanish America.
Robertson was born at the manse of Borthwick, Midlothian, the son of Robertson the local minister.
He was educated at Borthwick Parish School and Dalkeith Grammar School. He was the son of William Robertson and his wife Eleanor Pitcairn. He married his cousin Mary Nesbit in 1751. The family moved to Edinburgh when his father became appointed minister of Old Greyfriars Kirk.
He studied divinity at Edinburgh University (1733–41), and was licensed to preach in 1741. He was granted a Doctor of Divinity in 1759. He became minister at Gladsmuir (East Lothian) in 1743 and in 1759 at Lady Yester\\\'s Kirk and Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh. A staunch Presbyterian and Whig, he volunteered to defend the city against the Jacobites led by Prince Charles Edward Stuart in 1745.
In 1754 he was an original member of The Select Society, also referred to as the Edinburgh Select Society.
Robertson became royal chaplain to George III (1761), principal of the University of Edinburgh (1762), Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland in 1763, and Historiographer Royal in 1764, reviving a role within the Royal household in Scotland that had been in abeyance from 1709 until 1763. He was also a member of The Poker Club.
One of his most notable works is his History of Scotland 1542–1603, begun in 1753 and first published in 1759. Robertson also contributed to the history of Spain and Spanish America in his History of America (1777), the first sustained attempt to describe the discovery, conquest and settlement of Spanish America since Herreras Décadas and his biography of Charles V. In that work he had provided a masterly survey of the progress of European society, in which he traced the erosion of the feudal system caused by the rise of free towns, the revival of learning and Roman law, and by the emergence of royal authority and the balance of power between states. It was the development of commerce, assisted by law and private property, which was held to be chiefly responsible for the advance in civilisation.
He was a significant figure in the Scottish Enlightenment and also of the moderates in the Church of Scotland.
In 1783 he was a founding member of the Royal Society of Edinburgh.
He died of jaundice on 11 June 1793, at Grange House in south Edinburgh (the huge now-demolished mansion which gave its name to the Grange district. Robertson is buried at Greyfriars Kirkyard, Edinburgh. The grave is within a very large stone mausoleum. second only to William Adam\\\'s mausoleum immediately to the south. Both stand to the south-west of the church, near the entrance to the Covenanters Prison.
Publications
- The Situation of the World at the Time of Christ\\\'s Appearance (sermon) (1755)
The History of Scotland 1542-1603 (1759) (3 vols.)
- History of the Reign of the Emperor Charles V (1769) (4 vols.)
- The History of America (1777, 1796) (3 vols.)
- An Historical Disquisition Concerning the Knowledge Which the Ancients Had of India (1791)
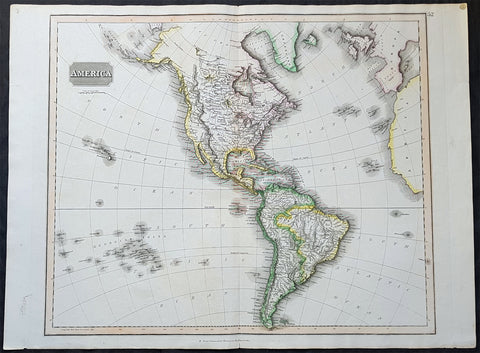
1817 John Thomson Large Antique Map of North & South America, Hawaiian Islands
- Title : America...Drawn & Engraved for Thomsons New General Atlas
- Date : 1817
- Size: 28in x 21 1/2in (710mm x 550mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35020
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of America drawn & engraved by John Thomson was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28in x 21 1/2in (710mm x 550mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The exploration of North America by non-indigenous people was a continuing effort to map and explore the continent of North America. It spanned centuries, and consisted of efforts by numerous people and expeditions from various foreign countries to map the continent. The European colonization of the Americas followed.
There were numerous Spanish explorers and conquistadors who explored the Southwest of North America (including present-day west and central United States) and cross the continent (east to west) in its southern regions, mainly from the second quarter to the middle of the 16th century, such as Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca and Francisco Vásquez de Coronado, but also the North American Southeast and south-central regions, s Soto]].
In 1608 Samuel de Champlain founded what is now Quebec City, which would become the first permanent settlement and the capital of New France. He took personal administration over the city and its affairs, and sent out expeditions to explore the interior. Champlain himself discovered Lake Champlain in 1609. By 1615, he had travelled by canoe up the Ottawa River through Lake Nipissing and Georgian Bay to the centre of Huron country near Lake Simcoe. During these voyages, Champlain aided the Wendat (aka Hurons) in their battles against the Iroquois Confederacy. As a result, the Iroquois would become enemies of the French and be involved in multiple conflicts.
From 1679 to 1682 René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle explored the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada, and the entire course of Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico.
From 1697 to 1702 Eusebio Kino explored the Sonoran Desert and on his journey to the Colorado River Delta discovered an overland route to Baja California that was then commonly believed to be an island. In 1683 Kino lead the first European overland crossing of Baja California.
European exploration of western Canada was largely motivated by the fur trade and the search for the elusive Northwest Passage. Hudson\'s Bay Company explorer Henry Kelsey has the distinction of being the first European to see the northern Great Plains in 1690.
Anthony Henday was the first to have seen the Rocky Mountains, in 1754, but curiously did not mention it in his journals. From his westernmost geographic position (roughly near the town of Olds, Alberta, halfway between Calgary and Red Deer, Alberta) the Rockies should have been quite conspicuous, but he was likely trying to disguise the disappointing fact that an unknown range of seemingly impassible mountains now stood between the HBC and the Pacific. Samuel Hearne found the Coppermine River in 1769-71 in his failed search for copper ore deposits. Burned by these shortfalls, the HBC largely quit exploration.
The North West Company, on the other hand, used a business model that required constant expansion into untapped areas. Under the auspices of the NWC, Alexander Mackenzie discovered the Mackenzie River in 1789 and was the first European to reach the North-American Pacific overland, via the Bella Coola River, in 1793. Simon Fraser reached the Pacific in 1808 via the Fraser River.
David Thompson, widely regarded as the greatest land geographer that ever lived, traveled over 90,000 km during his lifetime. In 1797, Thompson was sent south by his employers to survey part of the Canada-U.S. boundary along the water routes from Lake Superior to Lake of the Woods to satisfy unresolved questions of territory arising from the Jay Treaty between Great Britain and the United States. By 1798 Thompson had completed a survey of 6,750 km (4,190 mi) from Grand Portage, through Lake Winnipeg, to the headwaters of the Assiniboine and Mississippi Rivers, as well as two sides of Lake Superior. In 1798, the company sent him to Red Deer Lake (in present-day Alberta) to establish a trading post. The English translation of Lac La Biche-Red Deer Lake-first appeared on the Mackenzie map of 1793. Thompson spent the next few seasons trading based in Fort George (now in Alberta), and during this time led several expeditions into the Rocky Mountains. In 1811/1812 he followed the Columbia River to the Pacific, and in 1814 used his notes and measurements to draft the first European-style map of western Canada, covering 3.9 million square kilometres.
Lewis and Clark were the first Americans to venture into the newly acquired territory of the Louisiana Purchase, at the order of President Thomas Jefferson. They discovered many new geographical features, Indian tribes, and animal and plant species. John Colter was a member of the expedition who subsequently became a guide for others in the Old West, and did some explorations of his own.
John C. Frémont led many important explorations in the Great Plains, Great Basin, Oregon territory, and Mexican Alta California.
Joseph Reddeford Walker was one of the most prominent of the explorers, and charted many new paths through the West, which often were then utilized by emigrants crossing to settle in Western towns and communities. In 1833, his exploring party discovered a route along the Humboldt River across present-day Nevada, ascending the Sierra Nevada following the Carson River and descending via Stanislaus River drainages to Monterey. His return route across the southern Sierra was via Walker Pass, named after Walker by John Charles Fremont. The approach of the Sierra via the Carson River route later became known as the California Trail, the primary route for the emigrants to the gold fields during the California gold rush.
As the American population of the West increased, the US government launched ongoing official explorations mainly through the US Army Corps of Topographical Engineers. One of the main officers and explorers in this unit was George Wheeler. In 1872, the US Congress authorized an ambitious plan to map the portion of the United States west of the 100th meridian at a scale of 8 miles to the inch. This plan necessitated what became known as the Wheeler Survey, along with the Clarence King and John Wesley Powell Surveys, and expeditions by Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden. In 1879, all such efforts were reorganized as the United States Geological Survey.
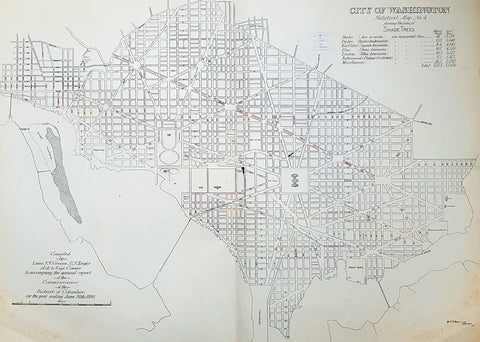
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Lines of Planted Trees in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 4 showing the lines of Shade Trees.....Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16266
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the lines of Trees planted very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
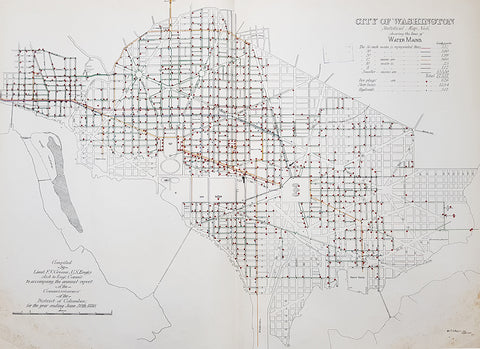
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Location of the Water Mains in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 6 showing the lines of Water Mains...Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16263
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the location of the Water Mains very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
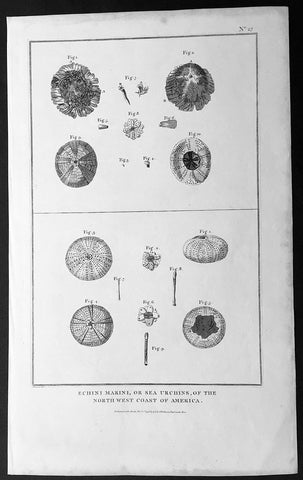
1798 Laperouse Large Antique Print of Sea Urchins of NW America, California
- Title : Echini Marini, or Sea Urchins, of the North West Coast of America. Published as the (act) directs Novr. 1st 1798, by G.G. & J. Robinson
- Size: 16 1/2in x 10 1/2in (420mm x 265mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1798
- Ref #: 31738
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique print of various Sea Urchins found off the NW coast of America, collected during the voyages of Jean-François de Galaup, Comte de la Pérouse between 1785 to 1788 was engraved in 1798 - dated - and was published in the 1st English edition of the Atlas du voyage de La Perouse G.G & J. Robinson, London in 1799.
La Perouse set sail from France in 1785 to continue the discoveries of Captain Cook. He was shipwrecked in 1788 but his narrative, maps, and views survived and were first published in 1797.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 10 1/2in (420mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 10 1/2in (420mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1783 the French government resolved to send an expedition to the Pacific to complete Captain James Cook\'s unfinished work, and in particular to explore the passages in the Bering Sea, which had been a mystery to Europeans since the sixteenth century. King Louis XVI himself took a hand in drafting the plan and itinerary, a copy of which is in the Municipal Library at Rouen, France, and when La Pérouse was selected to lead the fleet gave him an audience before he sailed. In command of two ships, La Boussole and L Astrolabe (Commandant de Langle), he left Brest on 1 August 1785 making for Brazil. Doubling Cape Horn he refitted in Chile, then sailed to the Sandwich Islands and thence to Alaska, where he turned south exploring and surveying the coast as far as California. After a short refit at Monterey, he sailed across the Pacific, discovered uncharted islands, and visited Macao and Manila. After six weeks reprovisioning and refreshing he left on 10 April 1787 to survey the coasts and territories north of Korea, which had been described and commented on by Christian missionaries. He sailed up the Gulf of Tartary, naming several points on both its shores and learned that Sakhalin was an island. In September he put in to Kamchatka to replenish his supplies. From there he dispatched an officer, Lesseps, overland to Paris with accounts of his discoveries, while he turned south making for New Holland. In December, at Tutuila, Samoa, which Bougainville had called the Navigator Islands when he explored them in 1768, natives suddenly attacked a party from L\'Astrolabe seeking water and killed de Langle and eleven others. La Pérouse left without taking reprisals and sailed through the Pacific Islands to Norfolk Island and to Botany Bay. He was sighted off the coast there on 24 January 1788 but bad weather prevented his entering the bay for two days. By then Governor Arthur Phillip had sailed to Port Jackson, but John Hunter had remained with the Sirius and the transports, and assisted La Pérouse to anchor. He established a camp on the northern shore, now called after him, and maintained good relations with the English during his six-week stay. He sailed on 10 March and was not heard of again. His disappearance led the French government in 1791 to equip another expedition under Bruny d Entrecasteaux to look for him, but the search was fruitless.
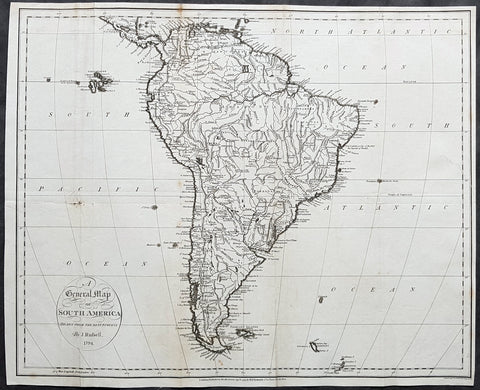
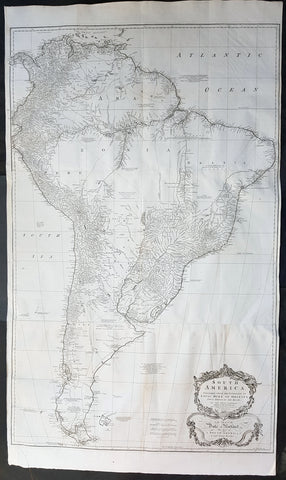
1794 John Russell Large Antique Map of South America
- Title : A General Map of South America Drawn fro the Best Surveys by J Russell 1794
- Ref #: 92579
- Size: 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1794
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map of South America by John Russell was published by H D Symonds in 1794 - dated. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, small repair to left fold & right side of image no loss
Verso: - Folds as issued, soiling along folds
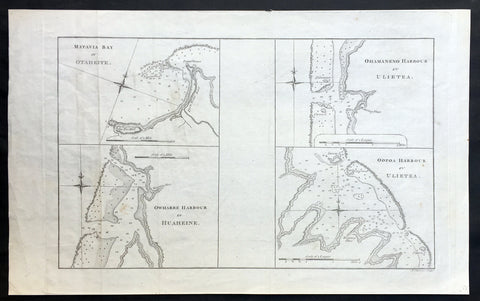
1773 Cook Antique Maps Tahiti, Raiatea & Huaheine Isles French Polynesia in 1769
- Title : Matavia Bay in Otaheite ; Owharre Harbour in Huaheine ; Ohamaneno Harbour in Ulietea ; Oopoa Harbour in Ulietea
- Size: 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 31216
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map, four maps on the one sheet;
1. Matavia Bay, Tahiti (Otaheite) - Windward Islands
2. Ohamaneno (Vaiaau) Harbour Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
3. Owharre (Bourayne Bay) Harbour in Huaheine - Leeward Islands
4. Oopoa (Opoa) Harbour, Raiatea (Ulietea) - Leeward Islands
all located in French Polynesia, South Pacific were complied by Capt James Cook during his first voyage of discovery in 1769, was published in the 1773 edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1773
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (365mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - None
Background:
Matavai Bay is located on the north coast of Tahiti, the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia.
The first European known to have visited Tahiti was Lieutenant Samuel Wallis, in Dolphin, who landed on 17 June 1767 in Matavai Bay.
Captain James Cook anchored in the bay on 13 April 1769, on a sandy spit on the northeast end of Matavai Bay - named Point Venus by Cook.
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
Captain Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774.
Huahine is an island located among the Society Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Leeward Islands group (Iles sous le Vent).
Captain Cook arrived Fare Harbour on 16 July 1769, with Tupaia navigating the HMS Endeavour. They met with leading chief Ori (Mato). Cook returned on 3 Sept. 1773 and met with Oris son Teri itaria, the new ari i rahi of the island.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
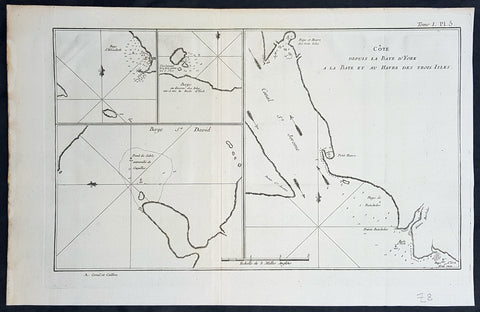
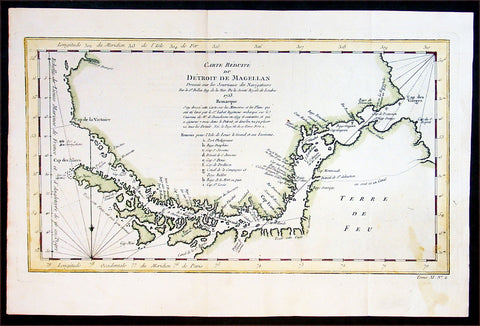
1774 Hawkesworth Antique Map of Magellan Straits, Bachelor River, Punta Arenas, Chile, Byron 1766
- Title : Baye d Elizabeth; Baye au dessons des Isles vis a vis la Rade d York; Côte depuis la Baye d York a la Baye et au Havre des Trois Isles; Baye St. David
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 16027
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map, four maps on the one sheet, of;
1. Elizabeth Bay.
2. York Bay.
3. York Bay-Three Island Bay
4.St. Davids Bay.
all located north of Carlos III island, on Punta Arenas in the Chilean Arctic - from Bachelor River north to York Bay - in the Straits of Magellan, Chile. This chart was compiled by Commodore John Byron, who visited the region in HMS Dolphin on his circumnavigation of the globe, between 1764-66, and was published in the 1774 French edition of John Hawkesworths An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. Paris 1774
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
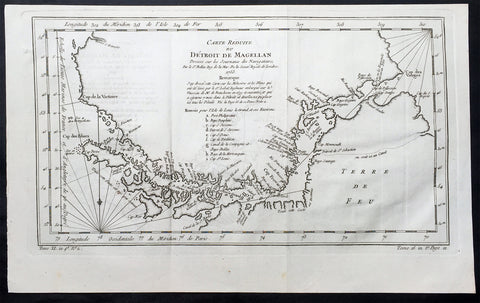
The Strait of Magellan
(Estrecho de Magallanes) is a navigable sea route separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Ferdinand Magellan a Portuguese explorer and navigator in the service of Charles I of Spain, became the first European to navigate the strait in 1520 during his circumnavigation of the globe.
Other early explorers included Francis Drake (1578). In February 1696 the first French expedition, under the command of M. de Gennes reached the Strait of Magellan. The expedition is described by the young French explorer, engineer and hydrographer François Froger in his A Relation of a Voyage (1699).
The strait was first carefully explored and thoroughly charted by Phillip Parker King, who commanded the British survey vessel HMS Adventure, and in consort with HMS Beagle spent five years surveying the complex coasts around the strait (1826–1830). A report on the survey was presented at two meetings of the Geographical Society of London in 1831.
Vice-Admiral The Hon. John Byron was a British Royal Navy officer and politician. He was known as Foul-weather Jack because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sailed in the squadron under George Anson on his voyage around the world, though Byron made it to southern Chile, and returned to England with the captain of HMS Wager. He was governor of Newfoundland following Hugh Palliser, who left in 1768. He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764-1766. He fought in battles in The Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral of the White before his death in 1786.
In early 1764 the British Admiralty determined that it would require a permanent naval settlement off the South American coast, in order to resupply naval vessels seeking to enter the Pacific via Cape Horn. Captain Byron was selected to explore the South Atlantic for a suitable island upon which to establish such a settlement. The South American mainland was controlled by Spain, which was hostile to local expansion of British interests; to disguise Byrons mission it was announced that he had been appointed the new commander of the Navys East Indies Station. Byron set sail in June 1764, ostensibly to take up the East Indies post. For the voyage he was granted command of the 24-gun frigate HMS Dolphin and the 20-gun sloop HMS Tamar.
Byron\'s two-vessel flotilla crossed the Atlantic over the winter of 1764 and made its way slowly down the South American coast. The Admiralty had ordered Byron to first seek Pepys Island, reputedly discovered off the Patagonian coast by the corsair Ambrose Cowley in 1683. Byron reached the co-ordinates given by Cowley in January 1765, but there was no sign of the island and the search was swiftly abandoned. On 5 February Byron reached the Patagonian settlement of Port Desire where he resupplied his vessels from the storeship HMS Florida.
Between June 1764 and May 1766, Byron completed his own circumnavigation of the globe as captain of HMS Dolphin. This was the first such circumnavigation that was accomplished in less than 2 years. His actions nearly caused a war between Great Britain and Spain, as both countries had armed fleets ready to contest the sovereignty of the Falkland Islands. Later Byron encountered islands and extant residents of the Tuamotus and Tokelau Islands, and Nikunau in the southern Gilbert Islands; he also visited Tinian in the Northern Marianas Islands.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print of a Man of Kamchatka Peninsula East Russia, 1779
- Title : Homme Du Kamtchatka
- Ref : 31798
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a man of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Eastern Russia, drawn during a visit by Captain Clerke in 1779 (after Cooks death) during Captain Cooks 3rd and last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Cooks on-board artist, John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a 1,250-kilometre-long peninsula in the Russian Far East.
After the death of James Cook in early 1779, Captain Charles Clerke took control of Cooks 3rd Voyage of Discovery. Clerke, who was dying of tuberculosis, sailed north of Hawaii, landing on the Kamchatka peninsula where the Russians helped him with supplies and to make repairs to the ships. He made a final attempt to pass beyond the Bering Strait and died on his return at Petropavlovsk on 22 August 1779. From here the ships\' reports were sent overland, reaching London five months later. Following the death of Clerke, Resolution and Discovery turned for home commanded by John Gore, a veteran of Cook\'s first voyage (and now in command of the expedition), and James King. After passing down the coast of Japan they reached Macao, in China in the first week of December and from there followed the East India trade route via Sunda Strait to Cape Town
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print Woman of Nootka Sound, Vancouver Isle Canada, 1778
- Title : Une Femme De L Entreee De Nootka
- Ref : 31768
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a woman of Nootka Sound, on the West Coast of Vancouver Island, Canada, drawn during a visit by Captain Cook in 1778, during his 3rd and last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Cooks on-board artist, John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nootka Sound is a sound of the Pacific Ocean, on the rugged west coast of Vancouver Island, in the Canadian province of British Columbia, historically known as King George\'s Sound. It separates Vancouver Island and Nootka Island.
On August 8, 1774, the Spanish Navy ship Santiago, under Juan Pérez, entered and anchored in the inlet. Although the Spanish did not land, natives paddled to the ship to trade furs for abalone shells from California. Pérez named the entrance to Nootka Sound Surgidero de San Lorenzo. The word surgidero means source. When Esteban José Martinez arrived in 1789 he gave Nootka Sound the name Puerto de San Lorenzo de Nuca. The Spanish establishment established at Friendly Cove he gave the name Santa Cruz de Nuca.
In March 1778, Captain James Cook of the Royal Navy landed on Bligh Island and named the inlet\"King George\'s Sound. He recorded that the native name was Nutka or Nootka, apparently misunderstanding his conversations at Friendly Cove/Yuquot; his informant may have been explaining that he was on an island (itchme nutka, a place you can go around). There may also have been confusion with Nuu-chah-nulth, the natives\' autonym (name for themselves). It may also have simply been based on Cook’s mis-pronunciation of Yuquot, the native name of the place. The earlier Spanish and British names for the Sound swiftly went out of use.
At the time, the Spanish monopolized the trade between Asia and North America, and had granted limited licenses to the Portuguese. The Russians had established a growing fur trading system in Alaska. The Spanish began to challenge the Russians, with Pérez\'s voyage being the first of many to the Pacific Northwest. The British also became increasingly active in the region.
The next European to visit Nootka Sound after James Cook was the British trader James Hanna in August 1785. Hanna traded iron bars for furs. He sold the furs in China for a handsome profit, beginning an era of the Maritime Fur Trade.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1787 Bankes Antique Print English or Nanwalek Bay Alaska, Cooks 3rd Voyage 1778
- Title : View of Oonalashka and the Inhabitants
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 40213
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print a view of English or Nanwalek Bay, Alaska visited by Captain James Cook in June/July 1778, during his third voyage of discovery - after John Webber - was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
Cooks Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nanwalek, formerly Alexandrovsk and English Bay, Alaska is census-designated place (CDP) in the Kenai Peninsula Borough, Alaska, United States that contains a traditional Alutiiq village.
Cooks Diary.......English Bay, Unalaska......the next day, the 27th, wrote Cook the fog partly despersed. At 7 AM wieghed and steered to the North… the wind faild and obliged us to Anchor. They sailed on and anchored in a bay for a few days on 28th. According to Samwell the next day We hoisted out our launch sent her ashore to fill the empty Water Casks both Ships completed their water. On 30th Many Canoes trading about the Ship… We find many Notes written in the Russian Language among these People dated in the Year 1776. The weather was, wrote Samwell moderate & hazy
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Print of an Inca Marriage Ceremony - Peru
- Title : Ceremonie du Mariage des Incas
- Ref #: 26001
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Inca Marriage Ceremony, Peru by Jakob van Schley - after De Bry - in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Women and men had paralleled roles, but were separate in Inca society. They were equally valued for the part they played in their society despite their differing roles.Marriage was no different.
Incan women were typically married at the age of sixteen, while men married at the age of twenty. Age, however, was not as important as keeping track of the stage of life that a person was at, such as whether or not they were able to work or be married. Ranks played a role in a person\'s marriage status as well. Men of lower rank could only have one wife; people of ranks higher than the kuraka were allowed more. If a man had more than one wife, one served as the principal wife while the other(s) were considered secondary. Having more wives showed that the man had more labour showing that the household was wealthy. The death of the principal wife was sometimes met with suspicion that the husband played a role in her death. The man had to find a new principal wife before he was able to recover from the previous wife\'s death. To prevent such suspicion and to increase the likelihood of a successful marriage, there were situations in which the couple could test how well the marriage would work out.
Trial marriages were typical of Inca culture. In this type of marriage, the man and woman would agree to try out being married to one another for a few years. At the end of this time, the woman could go home to her parents if she wished, and her husband could also send her home if he did not think it would work out. However, once the marriage was made final, they could only divorce if the woman was childless. To make the marriage final, the provincial governor had to approve the union.
In the Inca society, a wedding was a simple event. Instead, it was looked at more as a business-like agreement. Therefore, marriage was an economic agreement between two families. Parents on either side had to come to an agreement before the marriage took place and the couple could not be directly related to one another. Women would almost always marry men in the same social class as themselves. However, while it was very rare for them to marry a man with a higher social ranking, it was still possible for some young women. The only way for a young woman to alter her social ranking would be if a man of higher ranking took notice of her.
Once a woman was married, she was expected to collect food and cook, watch over the animals and the children, and to supply cloth to the government. Women of higher ranking also weaved, like those of lower ranks, but their work was used in special clothing for the higher ranks. A man\'s role sometimes resembled those of a woman, but acted in conjunction with one another. A woman’s household obligations would not change after she became pregnant. When she did find out she was pregnant she prayed and made offerings to an Inca god, Kanopa.Using marriage as an alliance strategy was also common among the Inca. Even before the Spaniards\' arrival, the Inca used marriage as a way to claim themselves to power. After the Spaniards arrival the Inca allowed marriages between the Inca and Spaniards in order to gain power during a time of civil war
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Print of an Inca Marriage Ceremony - Peru
- Title : Ceremonie du Mariage des Incas
- Ref #: 34095
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Inca Marriage Ceremony, Peru by Jakob van Schley - after De Bry - in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Women and men had paralleled roles, but were separate in Inca society. They were equally valued for the part they played in their society despite their differing roles.Marriage was no different.
Incan women were typically married at the age of sixteen, while men married at the age of twenty. Age, however, was not as important as keeping track of the stage of life that a person was at, such as whether or not they were able to work or be married. Ranks played a role in a person\'s marriage status as well. Men of lower rank could only have one wife; people of ranks higher than the kuraka were allowed more. If a man had more than one wife, one served as the principal wife while the other(s) were considered secondary. Having more wives showed that the man had more labour showing that the household was wealthy. The death of the principal wife was sometimes met with suspicion that the husband played a role in her death. The man had to find a new principal wife before he was able to recover from the previous wife\'s death. To prevent such suspicion and to increase the likelihood of a successful marriage, there were situations in which the couple could test how well the marriage would work out.
Trial marriages were typical of Inca culture. In this type of marriage, the man and woman would agree to try out being married to one another for a few years. At the end of this time, the woman could go home to her parents if she wished, and her husband could also send her home if he did not think it would work out. However, once the marriage was made final, they could only divorce if the woman was childless. To make the marriage final, the provincial governor had to approve the union.
In the Inca society, a wedding was a simple event. Instead, it was looked at more as a business-like agreement. Therefore, marriage was an economic agreement between two families. Parents on either side had to come to an agreement before the marriage took place and the couple could not be directly related to one another. Women would almost always marry men in the same social class as themselves. However, while it was very rare for them to marry a man with a higher social ranking, it was still possible for some young women. The only way for a young woman to alter her social ranking would be if a man of higher ranking took notice of her.
Once a woman was married, she was expected to collect food and cook, watch over the animals and the children, and to supply cloth to the government. Women of higher ranking also weaved, like those of lower ranks, but their work was used in special clothing for the higher ranks. A man\'s role sometimes resembled those of a woman, but acted in conjunction with one another. A woman’s household obligations would not change after she became pregnant. When she did find out she was pregnant she prayed and made offerings to an Inca god, Kanopa.Using marriage as an alliance strategy was also common among the Inca. Even before the Spaniards\' arrival, the Inca used marriage as a way to claim themselves to power. After the Spaniards arrival the Inca allowed marriages between the Inca and Spaniards in order to gain power during a time of civil war
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Print of Aztec Dancers & Musicians Mexico - after De Bry
- Title : Amusemens De L Empereur Apres Son Diner
- Ref #: 25962
- Size: 10in x 10in (255mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique print of Aztec dancers and musicians performing for the Aztec Emperor, in modern day Mexico, by Jakob van Schley - after De Bry - in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 10in (255mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 8in x 6in (205mm x 155mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1755 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, Camarin to Cape St Marie
- Title : Suite du Bresil.
- Ref #: 61078
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Southern Brazil from from Camarin to Cape St Marie by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7in (240mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Copy of 1753 Bellin Antique Map Plan of the City of Cayenne French Guyana, South America
- Title: La Ville De Cayenne...1753
- Date: 1753
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25648
- Size: 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved original antique map a plan of the city of Cayenne capital of French Guyana, South America was engraved by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1753 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Jacques Nicolas Bellin for Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague in 1747. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
1753 Bellin Original Antique Map of Magellan Straits, Argentine Tierra Del Fuego
- Title : Carte Reduite du Detroit De Magellan...1753
- Ref #: 60961
- Size: 15in x 9 1/2in (380m x 240mm)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Magellan Straits between the South American mainland and Tierra Del Fuego map - with major points of discovery and remarks in a 9 legend points by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1753 - dated - and was published in Antoine-François Prevosts L Histoire Generale des VoyagesPierre de Hondt, The Hague.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380m x 240mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 8in (370mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Antoine François Prevost d Exiles 1697 – 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist.He was born at Hesdin, Artois, and first appears with the full name of Prevost d Exiles, in a letter to the booksellers of Amsterdam in 1731. His father, Lievin Prévost, was a lawyer, and several members of the family had embraced the ecclesiastical estate. Prevost was educated at the Jesuit school of Hesdin, and in 1713 became a novice of the order in Paris, pursuing his studies at the same time at the college in La Flèche.
At the end of 1716 he left the Jesuits to join the army, but soon tired of military life, and returned to Paris in 1719, apparently with the idea of resuming his novitiate. He is said to have travelled in the Netherlands about this time; in any case he returned to the army, this time with a commission. Some biographers have assumed that he suffered some of the misfortunes assigned to his hero Des Grieux. Whatever the truth, he joined the learned community of the Benedictines of St Maur, with whom he found refuge, he himself says, after the unlucky termination of a love affair. He took his vows at Jumièges in 1721 after a year\'s novitiate, and in 1726 took priests orders at St Germer de Flaix. He spent seven years in various houses of the order, teaching, preaching and studying. In 1728 he was sent to the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Pres, Paris, where he contributed to the Gallia Christiana, a work of historiographic documentation undertaken communally by the monks in continuation of the works of Denys de Sainte-Marthe, who had been a member of their order. His restless spirit made him seek from the Pope a transfer to the easier rule of Cluny; but he left the abbey without leave (1728), and, learning that his superiors had obtained a lettre de cachet against him, fled to England.
In London he acquired a wide knowledge of English history and literature, as can be seen in his writings. Before leaving the Benedictines Prévost had begun perhaps his most famous novel, Mémoires et aventures d’un homme de qualité qui s’est retiré du monde, the first four volumes of which were published in Paris in 1728, and two years later at Amsterdam. In 1729 he left England for the Netherlands, where he began to publish (Utrecht, 1731) a novel, the material of which, at least, had been gathered in London Le Philosophe anglais, ou Histoire de Monsieur Cleveland, fils naturel de Cromwell, ecrite par lui-même, et traduite de l anglais (Paris 1731-1739, 8 vols., but most of the existing sets are partly Paris and partly Utrecht). A spurious fifth volume (Utrecht, 1734) contained attacks on the Jesuits, and an English translation of the whole appeared in 1734.
Meanwhile, during his residence at the Hague, he engaged on a translation of De Thou\'s Historia, and, relying on the popularity of his first book, published at Amsterdam a Suite in three volumes, forming volumes v, vi, and vii of the original Mémoires et aventures d’un homme de qualite. The seventh volume contained the famous Manon Lescaut, separately published in Paris in 1731 as Histoire du Chevalier des Grieux et de Manon Lescaut. The book was eagerly read, chiefly in pirated copies, being forbidden in France. In 1733 he left the Hague for London in company of a lady whose character, according to Prevosts enemies, was doubtful. In London he edited a weekly gazette on the model of Joseph Addisons Spectator, Le Pour et contre, which he continued to produce in collaboration with the playwright Charles-Hugues Le Febvre de Saint-Marc, with short intervals, until 1740.
In the autumn of 1734 Prevost was reconciled with the Benedictines, and, returning to France, was received in the Benedictine monastery of La Croix-Saint-Leufroy in the diocese of Evreux to pass through a new, though brief, novitiate. In 1735 he was dispensed from residence in a monastery by becoming almoner to the Prince de Conti, and in 1754 obtained the priory of St Georges de Gesnes. He continued to produce novels and translations from the English, and, with the exception of a brief exile (1741–1742) spent in Brussels and Frankfurt, he resided for the most part at Chantilly until his death, which took place suddenly while he was walking in the neighbouring woods. The cause of his death, the rupture of an aneurysm, is all that is definitely known. Stories of crime and disaster were related of Prevost by his enemies, and diligently repeated, but appear to be apocryphal.
Prevosts other works include:
- Le Doyen de Killerine, Killerine, histoire morale composee sur les memoires d une illustre famille d Irlande (Paris, 1735; 2nd part, the Hague, 1739, 3rd, 4th and 5th parts, 1740)
- Tout pour l\'amour (1735), a translation of Drydens tragedy
- Histoire d une Grecque moderne (Amsterdam [Paris] 2 vols., 1740)
- l Histoire de Marguerite d Anjou (Amsterdam [Paris] 2 vols., 1740)
Memoires pour servir a l histoire de Malte (Amsterdam, 1741)
- Campagnes philosophiques, ou memoires ... contenant l histoire de la guerre d Irlande (Amsterdam, 1741)
- Histoire de Guillaume le Conquerant (Paris, 1742)
- Histoire generale des voyages (15 vols., Paris, 1746-1759), continued by other writers
- Manuel Lexique (Paris, 1750), continued by other writers
- Translations from Samuel Richardson:
Lettres anglaises ou Histoire de Miss Clarisse Harlovie (1751), from Richardson\'s Clarissa, and Nouvelles lettres anglaises, ou Histoire du chevalier Grandisson (Sir Charles Grandison, 1755).
- Mémoires pour servir a l\'histoire de la vertu (1762), from Mrs Sheridan\'s
Memoires of Miss Sidney Bidulph
- Histoire de la maison de Stuart (3 vols., 1740) from Hume\'s History of England to 1688
- Le Monde moral, ou Mémoires pour servir a l\'histoire du coeur humain (2 vols., Geneva, 1760)
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of West South America Peru & The Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Perou... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40843
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
1780 Bonne Antique Map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40849
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
In 1498 French Guiana was first visited by Europeans when Christopher Columbus sailed to the region on his third voyage and named it the \"Land of pariahs\".[citation needed] In 1608 the Grand Duchy of Tuscany did an expedition to the area in order to create an Italian colony for the commerce of Amazonian products to Renaissance Italy, but the sudden death of Ferdinando I de\' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany stopped it.
In 1624 France attempted to settle in the area, but was forced to abandon it in the face of hostility from the Portuguese, who viewed it as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas. However French settlers returned in 1630 and in 1643 managed to establish a settlement at Cayenne along with some small-scale plantations. This second attempt would again be abandoned following Amerindian attacks. In 1658 the Dutch West Indies Company seized French territory to establish the Dutch colony of Cayenne. The French returned once more in 1664, and founded a second settlement at Sinnamary (this was attacked by the Dutch in 1665).
In 1667 the English seized the area. Following the Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667 the area was given back to France. The Dutch briefly occupied it for a period in 1676.
After the Treaty of Paris in 1763, which deprived France of almost all her possessions in the Americas other than Guiana and a few islands, Louis XV sent thousands of settlers to Guiana who were lured there with stories of plentiful gold and easy fortunes to be made. Instead they found a land filled with hostile natives and tropical diseases. One and a half years later only a few hundred survived. These fled to three small islands which could be seen off shore and named them the Iles de Salut (or \"Islands of Salvation\"). The largest was called Royal Island, another St. Joseph (after the patron saint of the expedition), and the smallest of the islands, surrounded by strong currents, Île du Diable (the infamous \"Devil\'s Island\"). When the survivors of this ill-fated expedition returned home, the terrible stories they told of the colony left a lasting impression in France.
In 1794, after the death of Robespierre, 193 of his followers were sent to French Guiana. In 1797 the republican general Pichegru and many deputies and journalists were also sent to the colony. When they arrived they found that only 54 of the 193 deportées sent out three years earlier were left; 11 had escaped, and the rest had died of tropical fevers and other diseases. Pichegru managed to escape to the United States and then returned to France where he was eventually executed for plotting against Napoleon.
Later on, slaves were brought out from Africa and plantations were established along the more disease-free rivers. Exports of sugar, hardwood, Cayenne pepper and other spices brought a certain prosperity to the colony for the first time. Cayenne, the capital, was surrounded by plantations, some of which had several thousand slaves.
1755 Kitchin & Boulton Large Original Antique Map of South America
- Title : South America. Performed Under the Patronage of Louis Duke of Orleans First Prince of the Blood...Tho. Kitchin sculp. 1755
- Size: 53in x 30 1/2in (1.35m x 780mm)
- Ref #: 41163
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large finely engraved original antique map of South America was engraved by the famous English cartographer Thomas Kitchin in 1755 - dated and signed at the foot of the map - after JB D Anville, was published in Malachy Postlethweyts Dictionary of Trade & Commerce
These large maps are hard to find in such good condition and make fantastic historical reference tools due to the high level of detail.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 53in x 30 1/2in (1.35m x 780mm)
Plate size: - 48in x 30 1/2in (1.22m x 780mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Background:
A curious and uncommon joined three panel 1755 wall map of South America by Thomas Kitchin and published by the English publisher Malachy Postlethwayte. A derivative of D\'Anville\'s earlier map, Postlethwayte\'s map covers the entire continent from the Lesser Antilles and Panama to Cape Horn. Published in three separate panels, this map can be either joined as a single massive map as assembled, as above, in separate sections. D\'Anville\'s map, and by extension this revision of that map by Bolton and Postlethwayte, represents a serious attempt to compile all of the accurate scientific knowledge of the South American continent available at the time. While cartographically very similar to D\'Anville\'s map, Postlethwayte\'s work is a full re-engraving in which all text has been translated to english, a new cartouche of a rococo ethic incorporated, and Postlethwayte\'s own fascinating Anglo-centric commentary added. This primary cartographic development on this, the Postlethwayte variant of D\'Anville\'s map is the incorporation of data associated with the expedition of Charles Marie de La Condamine - which being published in 1748 Postlethawyte postulates was not available to D\'Anville.
Our survey of this map beings with the coast which Spanish and Portuguese navigators had mapped with considerable accuracy as early as the late 16th century. This, like most early maps of the area, contrasts a detailed mapping of the coast with a speculative discussion of the interior, particularly Patagonia and the Amazon Basin. The map offers a fairly accurate discussion of both the east and west coasts with exceptional detail in the populated Andean regions of Venezuela, Columbia, ecuador (Labeled Quito), and Peru. Cuzco, Lima, Quito, Valladolid, Arequipa, Trujillo and other important trading centers of the region are noted. In Portuguese controlled Brazil, Rio de Janeiro, San Salvador and San Sebastian are identified.
Much of South America\'s interior, particularly the inland river basins, dominated by the Paraguay River in the south, the Amazon River in the center, and the Orinoco in the north, were largely unexplored. Nonetheless, several corrections and updates appear. D\'Anville (also Bolton and Postlethwayte) have done away with the myth of Lake Parima (supposedly in southern Guyana), the site of the legendary city of Manoa or el Dorado, and instead correctly identify the vast flood plain located in this same region. The cities and tribes identified along the Amazon river mostly date to the journals of the harrowing 16th century Francisco Orellana voyage - a clear indication of how little information actually emerged from the Amazon Basin.
Further south, the cartographers have retained the mythical Laguna de Xarayes as the northern terminus of the Paraguay River. The Xarayes, a corruption of \'Xaraies\' meaning \'Masters of the River,\' were an indigenous people occupying what are today parts of Brazil\'s Matte Grosso and the Pantanal. When Spanish and Portuguese explorers first navigated up the Paraguay River, as always in search of el Dorado, they encountered the vast Pantanal flood plain at the height of its annual inundation. Understandably misinterpreting the flood plain as a gigantic inland sea, they named it after the local inhabitants, the Xaraies. The Laguna de los Xarayes almost immediately began to appear on early maps of the region and, at the same time, almost immediately took on a legendary aspect. Later missionaries and chroniclers, particularly Díaz de Guzmán, imagined an island in this lake and curiously identified it as an \'Island of Paradise,\'
...an island [of the Paraguay River] more than ten leagues [56 km] long, two or three [11-16 km] wide. A very mild land rich in a thousand types of wild fruit, among them grapes, pears and olives: the Indians created plantations throughout, and throughout the year sow and reap with no difference in winter or summer, ... the Indians of that island are of good will and are friends to the Spaniards; Orejón they call them, and they have their ears pierced with wheels of wood ... which occupy the entire hole. They live in round houses, not as a village, but each apart though keep up with each other in much peace and friendship. They called of old this island Land of Paradise for its abundance and wonderful qualities.
D\'Anville, to his credit, shows the \'Laguna\' and its island in a much reduced form compared to earlier cartographers acknowledges that its existence is dubious. Our map, clearly referring to the work of Díaz de Guzmán, identifies the island as the \'I. de Orejones.\'
Far to the south Patagonia is crisscrossed with a number of speculative rivers based upon assumptions from earlier cartographers. Postlethwayte includes annotations referencing the failure to discover one such pass between Julian Bay (Chile) and the Campana River. earlier in the century speculation on such a pass fueled the famous South Sea Company, one of the modern world\'s first stock bubbles, but when no such pass was discovered, the bubble burst. Another element that bears attention in this region is a curious note about an island on the Sauces River (Rio Negro, Argentina) that is supposedly inhabited by white people - possibly the survivors of a shipwreck?
Malachy Postlethwayt (c. 1707 - 1767) was a British economist and commercial expert famous for his publication of the commercial dictionary titled The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce in 1751. The dictionary was a translation and adaptation of the Dictionnaire économique of the French Inspector General of the Manufactures for the King, Jacques Savary des Brûlons. Malachy claims to have spent nearly 20 years adapting and researching his important dictionary, which attained a popular following. The second edition of the Dictionary issued in 1752, was updated with a series of fine maps based upon D\'Anville\'s work, but updated by Postlethwayt to reflect his political and social views. Politically Postlethwayt was extremely conservative and highly patriotic though his views more often than not took the form of rants against the social and political enemies of the British Empire. In the mid-1740s Postlethwayt lobbied for the Royal Africa Company and was known for his pro-slavery advocacy. His belief that the slave trade had a place in the larger \"political arithmetic\" of empire, promoted through his many popular books and other publications, in time became the party line for the ruling class. Despite his misguided feelings about the Africa slave trade, Postlethwayt was an influential and thoughtful economist whose ideas influenced Adam Smith, Samuel von Pufendorf, Alexander Hamilton, and others. Postlethwayt also commonly spelled his name as Postlethawyte and Postlethwait.
Samuel Boulton (fl. 1775 - 1800) was a historian and cartographer active in the late 18th century. In general Boulton is an extremely elusive figure of which little is known. His most important work is his magnificent map of Africa published in conjunction with Robert Sayer and, later, Laurie and Whittle.
1772 Tobias Lotter Large Antique Map of South America, Magellan, Drake, Le Maire
- Title : America Meridionalis ...Tobiam Conr. Lotter...1772
- Date : 1772
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
- Ref #: 61139
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of South America was engraved by Gustav Conrad Lotter in 1772 - dated at the foot of the map - and published by his father Tobias Conrad Lotter.
The map shows the routes of the voyages by various famous explorers to South America including: Magellan (1520), Drake (1577), le Maire & Schouten (1616), Sarmineto (1570) and others. The map also illustrates various river systems and other speculative information about the unexplored interior of the Continent. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (595mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
1797 John Russell Old, Antique Map of South America
- Title : South America from the best Authorities
- Ref : 70198
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1797
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique map of South America was engraved in 1797 by John Russell and published by Charles Dilly & John Robinson. London.(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (260mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (260mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Peru, South America
- Title : Perou et Pays Circonvoisins... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40551
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10 1/2in (370mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31682
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
1980 R V Tooley The Mapping of America 1st Edition, Signed
- Title : The Mapping of America
- Ref #: 91439
- Size: 4to
- Date : 1980
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
Signed first edition of R V Tooley's The Mapping of America by RV Tooley, London: Holland Press, 1980, hardcover. Copy #49 from an edition of 300 specially bound copies, Cartographica 2.
Includes numerous black and white maps and an index by Douglas Matthews. A close to near fine copy in three quarter leather binding with marbled paper covered boards and all page edges gilt but with a tiny rub to the spine and some light rubbing to bottom of boards, else fine.
Signed under frontispiece photograph of Tooley.
Ronald Vere Tooley (1898 - 1986) was an English map dealer, an authority on early maps and cartographers, a noted compiler of catalogues on maps, cartography and antiquarian books, author of Maps and Map-makers, and founder of the Map Collectors' Circle which published a series of monographs on historical cartography in the period 1963-1975. He is considered the founder of the antiquarian map trade.
Tooley was born on Michaelmas and adopted the nickname "Mick"
Tooley was born and raised in Islington, London, and educated at the City of London School. Towards the end of World War I he enlisted in the Queen’s Westminster Rifles. After his basic training he left for France and took part in the Battle of Cambrai, where he was one of 120 survivors from an initial force of 400 men. On being demobilised in 1919 and having no definite career plans, he came across an illustrated catalogue of antiquarian books, published by James Tregaskis of Great Russell Street. The idea of working in the bookselling field appealed to him, and armed with a letter of introduction he made the acquaintance of Francis Edwards Ltd., and was summarily employed.
After World War I the book trade enjoyed a time of relative prosperity, but with the Wall Street collapse in 1929, economic depression hit the commercial sector in many countries, the secondhand book trade being no exception. In the 1930s Tooley left Francis Edwards Ltd and opened The Atlas Bookshop, just off Charing Cross Road, and started dealing almost exclusively in antiquarian maps. Between 1932 and 1934 he collaborated with a Mr M. Sinelnikoff of Orion Booksellers Ltd. Sinelnikoff’s passion was old maps, charts and globes, and with Tooley's interest, a fertile conjunction of scholarly minds was created. Tooley had always been interested in Colour Plate books, and in 1935 Batsford published his first book on the subject Some English Books with Coloured Plates. When The Atlas Bookshop closed in 1936 Tooley started work at the Parker Gallery in Albemarle Street - the firm specialising in military and sporting prints as well as old maps. With the outbreak of World War II in 1939 Tooley found work as a telephone operator, but still worked with old books and maps in his spare time.
In 1946 the management of Francis Edwards Ltd, keenly aware of Tooley's considerable business expertise and knowledge of old maps, invited him to rejoin the firm. Here he continued his research, spending long hours in the Map Room of the British Museum. His talents soon led to his being appointed a director of the firm. In 1949 his second book Maps & Map-makers was published, praised as a sound introduction and guide to a complex field, and running to many editions.[3] Tooley retired from Francis Edwards Ltd in 1975 and in 1979 joined Peter Scott and Peter Kalms in setting up a new company R.V.Tooley Ltd, he was joined by his stepson Douglas Adams and in October 1979 his stepson Stephen Luck joined them, first trading at Tring, Hertfordshire and then in the Spring of 1980 33 Museum Street, this company closed in 1982 and became Tooley Adams & Co. Together they developed the firm into one of the leading antique map dealers, supplying maps to dealers, museums and libraries all over the world.
"The Map Collector’s Series" is widely regarded as the greatest of Tooley's achievements. The idea of producing a series of monographs on maps was first discussed in 1960 with Robert Stockwell. The interest generated by this idea was widespread and led to The Map Collector’s Circle being formed in April 1963 under Tooley and David Schrire. The series was acclaimed throughout the world, and seen as an important contribution to cartography. It also led to the founding of the Carta Press, aimed at publishing authoritative works on cartography. The first publication, in 1968, was Maps of the African Continent and Southern Africa, and was followed in 1970 by County Atlases of the British Isles by R.A. Skelton of the Map Room of the British Museum. The Map Collector magazine was started by Tooley in 1977 when the Map Collector’s Circle ceased publishing. Each issue of The Map Collector consisted of articles and information provided by respected authorities, collectors and dealers. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1802 Poirson Large Antique Map of French & Dutch Guyana
- Title : Carte De La Guiane Francaise et Hollandaise...J B Poirson...1802
- Ref #: 92520
- Size: 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1802
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of French & Dutch Guyana, South America, was engraved by Jean Baptiste Poirson in 1802 - the date is engraved in the Title.
J.B. Poirson (1760-1831) was a French geographer & engineer who published a number of Atlases - including the Malte-Brun Atlas - between 1790 & 1830. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18in (585mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (500mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1753 Bellin Antique Map of the Magellan Straits, South America
- Title : Carte Reduite du Detroit De Magellan...1753
- Ref #: 91218
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique map of the Magellan Straits between the South American mainland and Tierra Del Fuego - with major points discovered and remarked in a 9 point legend - was engraved by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1753 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in Antoine-François Prevost's monumental 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague between 1747 & 1780. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 8in (355mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light stain bottom right corner
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1773 Bellin Antique Map The Course of the Orinoco River South America - Rare
- Title : Cours De L Orenoque...1773
- Ref #: 92803
- Size: 18 1/2in x 11 1/2in (460mm x 295mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Orinoco River, South America, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The mouth of the Orinoco River at the Atlantic Ocean was documented by Columbus on 1 August 1498, during his third voyage. Its source at the Cerro Delgado–Chalbaud, in the Parima range, was not explored until 1951, 453 years later. The source, near the Venezuelan–Brazilian border, at 1,047 metres (3,435 ft) above sea level (02°19′05″N 63°21′42″W), was explored in 1951 by a joint Venezuelan–French team.
The Orinoco Delta, and tributaries in the eastern llanos such as the Apure and Meta, were explored in the 16th century by German expeditions under Ambrosius Ehinger and his successors. In 1531 Diego de Ordaz, starting at the principal outlet in the delta, the Boca de Navios, sailed up the river to the Meta. Antonio de Berrio sailed down the Casanare to the Meta, and then down the Orinoco River and back to Coro. In 1595, after capturing de Berrio to obtain information while conducting an expedition to find the fabled city of El Dorado, the Englishman Sir Walter Raleigh sailed down the river, reaching the savannah country.
Alexander von Humboldt explored the basin in 1800, reporting on the pink river dolphins. He published extensively on the river\'s flora and fauna
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 11 1/2in (460mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 10in (455mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1753 Bellin & Henry Ellis Antique Map of Hudsons Bay, Search for the NW Passage
- Title : Carte Des parties Du Nord-Ouest De L Amerique..Par M.B....1753
- Ref #: 91259
- Size: 12 1/2in x 10in (320m x 255mm)
- Date : 1753
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Hudsons Bay, Canada and Henry Ellis voyage to discover the North West passage by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Henry Ellis 1721 – 1806 was an explorer, author, and a colonial governor of U.S. state of Georgia and Nova Scotia.
Ellis was born in County Monaghan, Ireland. He was educated in law at the Temple Church in London. In May 1746, he went out as agent of a company for the discovery of the Northwest Passage. After extinguishing with difficulty a fire in his ship, he sailed to Greenland, where he exchanged commodities with the Inuit peoples on 8 July. He then proceeded to Fort Nelson, and wintered in Hayes River. He renewed his efforts in June 1747, without success, and returned to England; where he arrived on 14 October. He published an accounts of his explorations in 1748, entitled \"Voyage made to Hudson\'s Bay in 1746, by the Dobbs Galley and The California, to discover a Northwest Passage\" and in 1750 published \"Considerations on the Great Advantages which would Arise from the Discovery of the North West Passage\". After publishing these accounts, Ellis was inducted into the Royal Society.
From 1750 to 1755, Ellis worked as a slave trader, purchasing slaves from Africa and shipping them to Jamaica.
Lord Halifax, President of the Board of Trade named Ellis lieutenant governor of Georgia, 15 August 1756. Ellis arrived at Savannah, Georgia on 16 February 1757, and on 17 May 1758, was made royal governor. His administration of the colony was highly esteemed. Recognizing the danger posed to the colony by hostile neighbors, he established a treaty with the Creeks. He published \"Heat of the Weather in Georgia\" in Philosophical trans of the Royal Society in 1758. The subtropical climate took its toll on his health, and he had to be removed from governor then left Georgia on 2 November 1760, and stopping in New York to request military assistance to the southern colonies.
After his return to England his knowledge of American affairs were called into requisition for developing the plan for taxing the colonies, and in return for this service he was rewarded with sinecure offices. From 1761 to 1763 he held the commission of governor of Nova Scotia, though he did not enter on the duties of his office. He afterward resided in Italy, principally occupied in scientific researches.Before he died he had a friendship with the creek leader.
He died on January 21, 1806 (aged 84–85) in Naples, Italy.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12 1/2in x 10in (320m x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8in (280mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1744 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Hudsons Bay & Surrounds, Canada
- Title : Karte Von Der Hudsons Bay Durch N Bellin..1744
- Ref #: 41156
- Size: 14in x 9 1/2in (355mm x 240mm)
- Date : 1744
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Hudsons Bay, Canada by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1744 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Hudson Bay is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of 1,230,000 km2 (470,000 sq mi). It drains a very large area, about 3,861,400 km2 (1,490,900 sq mi), that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, Ontario, Quebec and parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay\'s southern arm is called James Bay.
English explorers and colonists named Hudson Bay after Sir Henry Hudson who explored the bay beginning August 2, 1610 on his ship Discovery.:170 On his fourth voyage to North America, Hudson worked his way around Greenland\'s west coast and into the bay, mapping much of its eastern coast. Discovery became trapped in the ice over the winter, and the crew survived onshore at the southern tip of James Bay. When the ice cleared in the spring, Hudson wanted to explore the rest of the area, but the crew mutinied on June 22, 1611. They left Hudson and others adrift in a small boat. No one knows the fate of Hudson or the crew members stranded with him, but historians see no evidence that they survived for long afterwards.
In 1668, Nonsuch reached the bay and traded for beaver pelts, leading to the creation of the Hudson\'s Bay Company (HBC) which still bears the historic name. The HBC negotiated a trading monopoly from the English crown for the Hudson Bay watershed, called Rupert\'s Land. France contested this grant by sending several military expeditions to the region, but abandoned its claim in the Treaty of Utrecht (April 1713).
During this period, the Hudson\'s Bay Company built several factories (forts and trading posts) along the coast at the mouth of the major rivers (such as Fort Severn, Ontario; York Factory and Churchill, Manitoba). The strategic locations were bases for inland exploration. More importantly, they were trading posts with the indigenous peoples who came to them with furs from their trapping season. The HBC shipped the furs to Europe and continued to use some of these posts well into the 20th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9 1/2in (355mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1757 Bellin Antique Map of Rio de la Plata, River Plate, Buenos Aires, Argentina
- Title : Carte de la Riviere de la Plata...
- Ref #: 61103
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Río de la Plata of Argentina, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The Río de la Plata River Plate in British English and La Plata River (occasionally Plata River) in other English-speaking countries — is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and the Paraná rivers. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf or a marginal sea. For those who consider it a river—as is the case mostly in Argentina—it would be the widest river in the world, with a maximum width of about 220 kilometres.
The Río de la Plata was first explored by the Portuguese in 1512–13. The Spanish first explored it in 1516, when the navigator Juan Díaz de Solís traversed it during his search for a passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans, calling it the Mar Dulce, or \"freshwater sea.\" The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan briefly explored the estuary in 1520 before his expedition continued its circumnavigation, and in 1521 Cristóvão Jacques also explored the Plate River estuary and ascended the Parana River for the first time, entering it for about 23 leagues (around 140 km) to near the present city of Rosario.[12] The area was also visited by Francis Drake\'s fleet in early 1578, in the early stages of his circumnavigation.
Explorer Sebastian Cabot made a detailed study of the river and its tributaries and gave it its modern name. He explored the Paraná and Uruguay rivers between 1526 and 1529, ascending the Paraná as far as the present-day city of Asunción, and also explored up the Paraguay River. Cabot acquired silver trinkets trading with the Guaraní near today\'s Asunción, and these objects (together with legends of a \"Sierra de la Plata\" in the South American interior brought back by earlier explorers) inspired him to rename the river \"Río de la Plata\" (\"River of Silver\").
The first European colony was the city of Buenos Aires, founded by Pedro de Mendoza on 2 February 1536. This settlement, however, was quickly abandoned; the failure to establish a settlement on the estuary led to explorations upriver and the founding of Asunción in 1537. Buenos Aires was subsequently refounded by Juan de Garay on 11 June 1580.
The city of Buenos Aires sits along the southern coast of the Río de la Plata.
During the colonial era the Río de la Plata was made the center of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata, but the region\'s development was largely neglected by the Spanish Empire until the 1760s, when Portugal and Britain threatened to expand into the estuary. The governorate was elevated to form the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. In 1806 and 1807 the river was the scene of an important British invasion that aimed to occupy the area.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, South America
- Title : Carte Du Bresil.....
- Ref #: 61101
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Brazil, South America by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar.
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
ackground:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1757 Nicolas Bellin Antique Map, Plan of the City of Buenos Aires, Argentina
- Title : Plan De La Ville de Buenos - Ayres
- Ref #: 61102
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* a plan of the Capital City of Argentina Buenos Aires by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in the 1757 French & Dutch edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Background: Seaman Juan Díaz de Solís, navigating in the name of Spain, was the first European to reach the Río de la Plata in 1516. His expedition was cut short when he was killed during an attack by the native Charrúa tribe in what is now Uruguay.
The city of Buenos Aires was first established as Ciudad de Nuestra Señora Santa María del Buen Ayre (literally "City of Our Lady Saint Mary of the Fair Winds") after Our Lady of Bonaria (Patroness Saint of Sardinia) on 2 February 1536 by a Spanish expedition led by Pedro de Mendoza. The settlement founded by Mendoza was located in what is today the San Telmo district of Buenos Aires, south of the city center.
More attacks by the indigenous people forced the settlers away, and in 1542 the site was abandoned. A second (and permanent) settlement was established in 11 June 1580 by Juan de Garay, who arrived by sailing down the Paraná River from Asunción (now the capital of Paraguay). He dubbed the settlement "Santísima Trinidad" and its port became "Puerto de Santa María de los Buenos Aires.
From its earliest days, Buenos Aires depended primarily on trade. During most of the 17th and 18th centuries, Spanish ships were menaced by pirates, so they developed a complex system where ships with military protection were dispatched to Central America, cross the land, from there to Lima, Peru and from it to the inner cities of the viceroyalty. Because of this, products took a very long time to arrive in Buenos Aires, and the taxes generated by the transport made them prohibitive. This scheme frustrated the traders of Buenos Aires, and a thriving contraband industry developed. This also instilled a deep resentment in porteños towards the Spanish authorities.
Sensing these feelings, Charles III of Spain progressively eased the trade restrictions and finally declared Buenos Aires an open port in the late 18th century. The capture of Porto Bello by British forces also fueled the need to foster commerce via the Atlantic route, to the detriment of Lima-based trade. One of his rulings was to split a region from the Viceroyalty of Perú and create instead the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, with Buenos Aires as the capital. However, Charles's placating actions did not have the desired effect, and the porteños, some of them versed in the ideology of the French Revolution, became even more convinced of the need for independence from Spain. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 7 1/2in (290mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1869 Mitchell Antique Map - Plan of The City of Cincinnati
- Title : Plan of Cincinnati and Vicinity....1869 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35044
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique city plan map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Maps New Jersey, Maryland, Delaware
- Title : County Map of New Jersey; County Map of Maryland and Delaware....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35033
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of Virginia & West Virginia
- Title : County Map of Virginia and West Virginia....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35036
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell Antique County Map of Iowa and Missouri
- Title : County Map of the States of Iowa and Missouri....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35047
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1869 Mitchell Antique Map of The State of Illinois
- Title : County Map of the State of Illinois....1869 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35045
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of the State of Pennsylvania
- Title : County Map of Florida, Mobile....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35051
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None