Rigobert Bonne (1729 - 1795)
Profile :
As Royal Hydrographer, Bonne`s principle interest lay in the production of marine charts but he issued a number of other works, often including maps by fellow cartographers. He also provided maps for a notable atlas by Guillaume Raynal and for an Historical Atlas and Encyclopedia published in association with Nicholas Desmaret (1725 – 1805)
Rigobert Bonne (3)
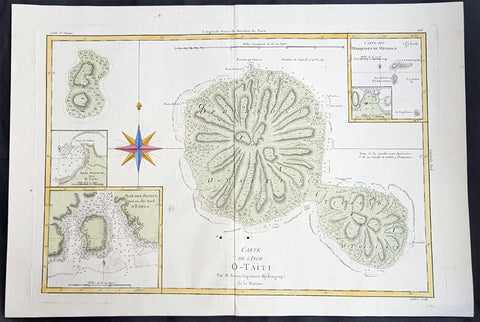
1780 Rigobert Bonne Large Antique Map of Tahiti
- Title : Carte De L 'Isle O - Taiti...Par M. Bonne...
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 40570
- Size: 15in x 11in (400mm x 275mm)
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 ½in x 11 ½in; (420mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 14 ½in x 10in; (370mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Two very small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Mai, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ships boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
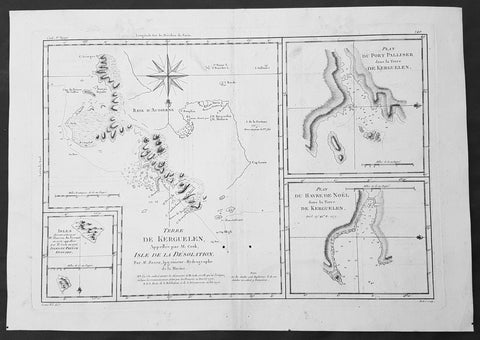
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Kerguelen, Desolation Island South Indian Ocean
- Title : Terre De Kerguelen, Appellee par M. Cook, Isle De La Desolation. Par M. Bonne; Plan Du Port Palliser dans la Terre De Kerguelen: Plan Du Havre De Noel dans la Terre De Kerguelen: Isles decouvertes par Mr. Marion Du Fresne en 1772, appellees par M.Cook en 1776, Isles Du Prince Edouard
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40585
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of parts of the Kerguelen Islands, also known as the Desolation Islands, in the southern Indian Ocean, was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
The map also includes three inset maps, the first two of Port Palliser & Noel Bay on Kerguelen Island, with the third inset map of the Prince Edward Islands - part of South Africa.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Two small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Kerguelen’s land was named for Yves de Kerguelen, a French navigator and explorer who sailed around the islands in 1772 along with Marion Du Fresne another French explorer who was in the vicinity in that same year. Capt. James Cook didn’t sight the islands until his 3rd voyage in 1776, having failed in his first attempts on earlier voyages. On Christmas Eve 1776, Cook’s ships the Resolution and the Discovery anchored in a Bay which he called Christmas Harbor, only staying long enough to replenish his water, and as the islands were so bleak and treeless, he called them Desolation Isles. Bonne’s chart was taken from original surveys by Kerguelen, Du Fresne and Capt. James Cook and was finely engraved by Gaspard Andre.
The Kerguelen Islands also known as the Desolation Islands, are a group of islands in the southern Indian Ocean constituting one of the two exposed parts of the mostly submerged Kerguelen Plateau. They are among the most isolated places on Earth, located 450 km (280 mi) northwest of the uninhabited Heard Island and McDonald Islands and more than 3,300 km (2,051 mi) from Madagascar, the nearest populated location (excluding the Alfred Faure scientific station in Ile de la Possession, about 1,340 km (830 mi) from there, and the non-permanent station located in Île Amsterdam, 1,440 km (890 mi) away). The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands, Amsterdam, and Saint Paul Islands, and France\'s Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean are part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands and are administered as a separate district.
Kerguelen Islands appear as the \"Ile de Nachtegal\" on Philippe Buache\'s map from 1754 before the island was officially discovered in 1772. The Buache map has the title Carte des Terres Australes comprises entre le Tropique du Capricorne et le Pôle Antarctique où se voyent les nouvelles découvertes faites en 1739 au Sud du Cap de Bonne Esperance (\'Map of the Southern Lands contained between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Pole, where the new discoveries made in 1739 to the south of the Cape of Good Hope may be seen\'). It is possible this early name was after Abel Tasman\'s ship \"De Zeeuwsche Nachtegaal.\" On the Buache map, \"Ile de Nachtegal\" is located at 43°S, 72°E, about 6 degrees north and 2 degrees east of the accepted location of Grande Terre.
The islands were officially discovered by the French navigator Yves-Joseph de Kerguelen-Trémarec on 12 February 1772. The next day Charles de Boisguehenneuc landed and claimed the island for the French crown. Yves de Kerguelen organised a second expedition in 1773 and arrived at the \"baie de l\'Oiseau\" by December of the same year. On 6 January 1774 he commanded his lieutenant, Henri Pascal de Rochegude, to leave a message notifying any passers-by of the two passages and of the French claim to the islands. Thereafter, a number of expeditions briefly visited the islands, including that of Captain James Cook in December 1776 during his third voyage, who verified and confirmed the passage of de Kerguelen by discovering and annotating the message left by the French navigator.
Soon after their discovery, the archipelago was regularly visited by whalers and sealers (mostly British, American and Norwegian) who hunted the resident populations of whales and seals to the point of near extinction, including fur seals in the 18th century and elephant seals in the 19th century. Since the end of the whaling and sealing era, most of the islands\' species have been able to increase their population again.
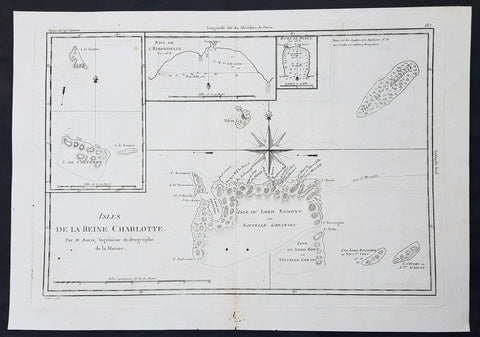
1780 Bonne Original Antique Map of Santa Cruz Isles, Solomon Islands Sth Pacific Lord Howe, Nendo
- Title : Isles De La Reine Charlotte
- Size: 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
- Ref #: 40580
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Santa Cruz Island, of the Temotu Province in the Solomon Islands, Nendo Island & Lord Howe Island was published in 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (405mm x 2805mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small worm holes in bottom margin
Plate area: - Two small worm holes adjacent to bottom centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Map of four island with compass rose. Santa Cruz Island, of Santa Cruz Island, of the Temotu Province in the Solomon Islands, based on Cook\'s discoveries, was named after Queen Charlotte, wife of King George III.
The Isle du Lord Edgemont (present day Nendo Island) and Isle du Lord Howe islands have been only partially engraved to show the explored portions.