Maps (60)
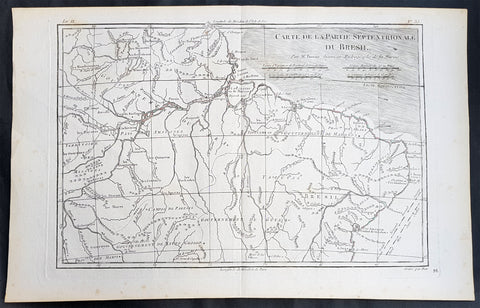
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31685
- Size: 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10in (410mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
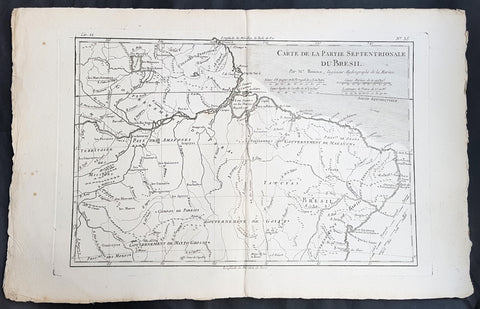
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana, Amazon River
- Title : Carte De La Partie Septentrionale Du Bresil... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40850
- Size: 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil, French Guiana & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11in (435mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Brazil is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers.
Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d état.
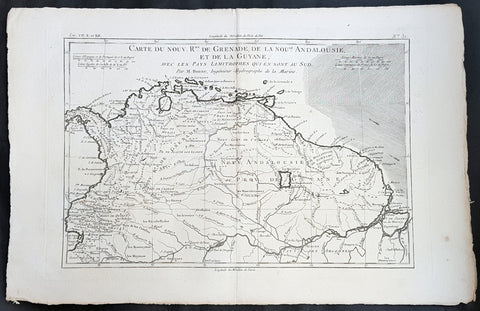
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40848
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
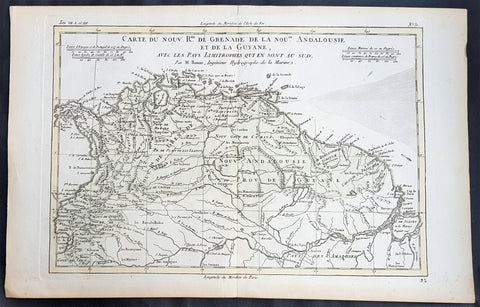
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map South America Colombia, Venezuela, Amazon River
- Title : Carte Du Nouv. Rme. De Grenade de la Noule. Andalousie et de la Guyane... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31681
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Northern South America from Colombia to Venezuela, The Guyanas, Brazil & The Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
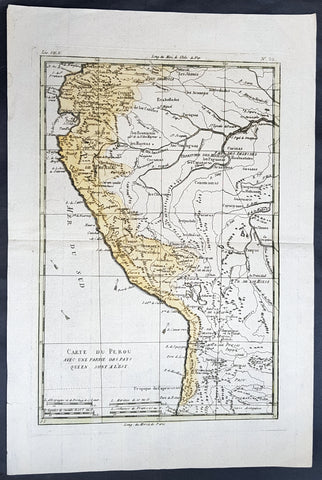
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Peru, The Amazon River, South America
- Title : Carte Du Perou avec une partie des pays quien sont al est... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 60565
- Size: 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
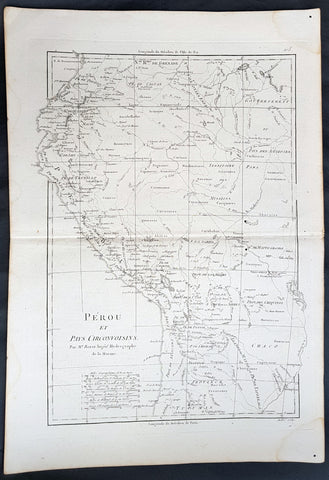
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of West South America Peru & The Amazon River
- Title : Perou et Pays Circonvoisins... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 40551
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 290mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Peru & the western Amazon River by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 11in (410mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Peru officially the Republic of Peru is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru II\'s rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
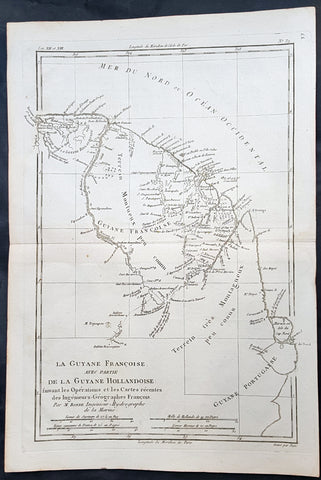
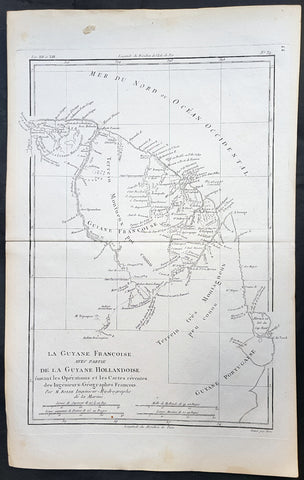
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of South America Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 16059
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
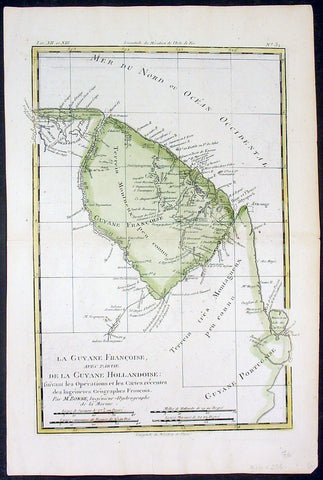
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of South America French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 16059
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
1780 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America
- Title : La Guyane Francoise avec Partie De La Guyane Hollandoise... Par M. Bonne
- Ref #: 31682
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique map of Guyana, Suriname & French Guiana, South America by Rigobert Bonne was published in the 1780 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community.
The region known as the Guianas consists of the large shield landmass north of the Amazon River and east of the Orinoco River known as the \"land of many waters. Originally inhabited by many indigenous groups, Guyana was settled by the Dutch before coming under British control in the late 18th century. It was governed as British Guiana, with a mostly plantation-style economy until the 1950s.
Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south.
Suriname was long inhabited by various indigenous people before being invaded and contested by European powers from the 16th century, eventually coming under Dutch rule in the late 17th century. During the Dutch colonial period, it was primarily a plantation economy dependent on African slaves and, following the abolition of slavery, indentured servants from Asia.
French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America in the Guyanas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west.
Before European contact, the territory was originally inhabited by Native Americans, most speaking the Arawak language, of the Arawakan language family. The people identified as Lokono. The first French establishment is recorded in 1503, but France did not establish a durable presence until colonists founded Cayenne in 1643. Guiana was developed as a slave society, where planters imported Africans as enslaved laborers on large sugar and other plantations in such number as to increase the population. Slavery was abolished in the colonies at the time of the French Revolution. Guiana was designated as a French department in 1797. But, after France gave up its territory in North America, it developed Guiana as a penal colony, establishing a network of camps and penitentiaries along the coast where prisoners from metropolitan France were sentenced to forced labor.
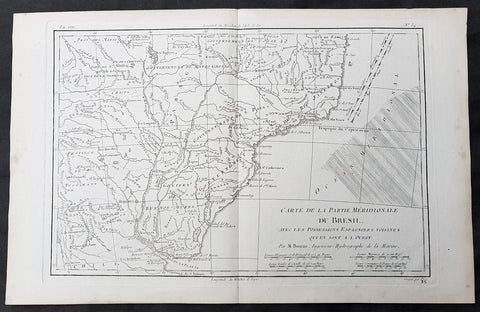
1780 Rigobert Bonne Original Antique Map of Brazil, South America
- Title : Carte de la Partie Meridionale Du Bresil....M Bonne
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31684
- Date : 1780
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved map was published in 1780 edition of Atllas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
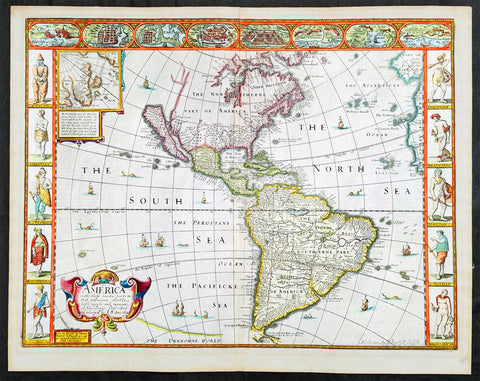
1626 (1676) John Speed Antique Map of America - Beautiful Condition
Antique Map
- Title : America with those known parts in that unknowne world both people and manner of buildings discribed and inlarged by I.S. Ano 1626.
- Date : 1626 (1676)
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35654
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of America by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World.
One of the best examples of this map I have seen. Beautiful original condition with original hand colour, clean heavy impression on sturdy clean paper with original margins, which is very rare.
This 1626 map of America is the fourth or 1676 state and is one of the most iconic maps of America, surrounded by decorative vignettes illustrating the indigenous peoples and cities of the Americas. This map is both beautiful and important. It features a number of first, including being the first atlas map to depict California as an island and to accurately depict the east coast of North America. Cartographically it follows on the earlier maps of the Dutchman Abraham Goos, the engraver, with updates to reflect the 1625 Briggs vision of an insular California
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/4in x 15 1/2in (515mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 3/4in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Old archival hinge paper top of verso, not affecting the map.
Background:
This is the first atlas map to represent California as an island. The idea of an insular California first appeared as a work of fiction in Garci Rodriguez de Montalvo's c. 1510 romance Las Sergas de Esplandian, where he writes
.....Know, that on the right hand of the Indies there is an island called California very close to the side of the Terrestrial Paradise; and it is peopled by black women, without any man among them, for they live in the manner of Amazons.....
Baja California was subsequently discovered in 1533 by Fortun Ximenez, who had been sent to the area by Hernan Cortez. When Cortez himself traveled to Baja, he must have had Montalvo's novel in mind, for he immediately claimed the 'Island of California' for the Spanish King. By the late 16th and early 17th century ample evidence had been amassed, through explorations of the region by Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarcon and others, that California was in fact a peninsula. However, by this time other factors were in play. Francis Drake had sailed north and claimed 'New Albion' (identified here on the northwest coast of California Island) near modern day Washington or Vancouver for England. The Spanish thus needed to promote Cortez's claim on the 'Island of California' to preempt English claims on the western coast of North America. Henry Briggs, an English mathematician, began promoting the idea of an insular California in 1622, citing the journals of Friar Antonio de la Ascension, who accompanied the 1602-03 Sebastian Vizcaino expedition. The significant influence of the Spanish crown on European cartographers caused a major resurgence of the Insular California theory. Just before this map was made Eusebio Kino, a Jesuit missionary, traveled overland from Mexico to California, proving conclusively the peninsularity of California. Even so, it was ultimately a 1747 royal decree from King Ferdinand VII of Spain that finally forced cartographers to give up on the alluring idea.
Other elements of interest in North America are the complete absence of the Great Lakes - which in 1626 had yet to be conceived of by any European cartographers. The Straits of Anian appear tenuously in the extreme northwest, just above California. Just east of the 'o' in 'California', on the continental mainland, there is a curious ghosted in lake called the 'Lagueo de Oro.' We have found no references or explanation for this. None of the legendary kingdoms of gold, Quivara, Teguayo, Cibola, etc. are noted. The western portions of the Hudson Bay are unmapped - suggestive of their unexplored status. The addition of Long Island and Boston, in notably darker print, are important updates over the earliest editions.
South America offers much of interest including the mythical Lake Parimia, in Guiana. The legend of Parima is associated with the English adventurer Sir Walter Raleigh's search for El Dorado. Believing El Dorado to lie in the northern part of the Amazon, Raleigh sailed down the Orinoco River just before the onset of the rainy season. Reaching a remote tribal village, Raleigh noted canoes arriving bearing gold, silver, and other treasures. Asked where the gold came from, the natives replied, 'Manoa', the term for the tribe to which the river traders belonged. Manoa, the natives claimed could be reached following a long river voyage southward to a Great Lake, called Parima. Raleigh and his associates immediately associated Manoa and Lake Parima with the golden kingdom of El Dorado, though they never visited the city or lake. Subsequent maps, including this one, mapped el Dorado and Lake Parima in this location for several hundred years. Both Raleigh and the natives were describing an actual event known to occur annually in the region. Rains would annually swell the Amazon and Orinoco river systems creating a linkage in the Rupununu flood plain, which, during heavy rains, can resemble a massive lake. The Manoa were a large and populous trading nation active in pre-colonial days whose vast empire, based in the Amazon Basin, extended form the Andes to the Orinoco. Curiously, in addition to noting the city of Manoa on Lake Parima, D'Anville also correctly maps the center of the ancient Manoan civilization between the Amazon tributaries Rio Negro and Rio Yapura. Sadly the Manoa and many of the other populous South American indigenous nations noted by the earliest explores to the region vanished, brought low by European epidemics.
Another mythical lake, Eupana, appears further south connecting the Rio de la Plata and the Paraguay River to the R. Real, thus turning eastern Brazil into an island. This is a update over many earlier maps which connected Eupana directly to the Amazon. Far in the south Speed presents us ith another anomaly, the Straits of Le Maire, which separates Tierra de Fuego from another mysterious stretch of land labeled 'States Land.' The is in fact the modern island of Isla de los Estados, the southeastern most point in South America. Jacob le Maire and his pilot Willem Schouten passed to between this island and Tierra del Fuego on their 1615 voyage around Cape Horn and into the Pacific.
In the high Arctic, near Iceland and Greenland, the supposed islands of Frisland and Brasil are noted. Frisland is little more than a double mapping of Iceland. Brasil, also known as Hy-Brasil, is a phantom island north Atlantic just west of Ireland. In Irish myths it was said to be cloaked in mist, except for one day every seven years, when it became visible but still could not be reached. Little is known of this origins of this myth, but it appears on maps in various forms from about 1325. The last known appearance was in 1865 when it appeared on a nautical chart as 'Brasil Rock.' Some speculate that it may be an early reference to Porcupine Bank, a shoal in the Atlantic Ocean about 200 kilometres (120 mi) west of Ireland.
Speed's map of America is especially noteworthy for its surrounded vignettes. To either side of the map proper there are various vignettes illustrating the indigenous peoples of the America. These includes natives of Greenland, Virginia, Florida, Mexico, New England, Peru, Brazil, and Tierra del Feugo.n Along the top of the map there are eight city views: Havanna, Santo Domingo, Cartagena, Mexico City, Cuzco, the isle of Moca, Rio de Janeiro, and Olinda.
This map was engraved for John Speed by Abraham Goos. It is the fourth state of the map issued by Thomas Bassett of Fleet Street and Richard Chiswell of St. Paul's Churchyard. Bassett, Chiswell, and others continued to republish Speed's work well after his death. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, Burden)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
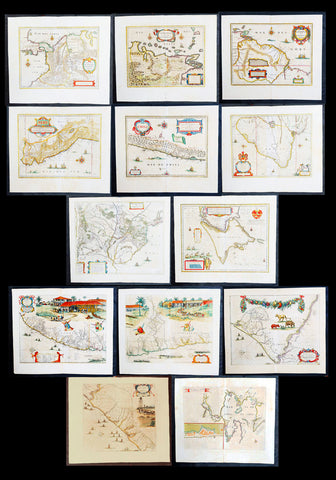
1662 Blaeu & Barlaeus Complete Set of 13 x Antique Maps of South America
Antique Map
- Titles:
1. Terra Firma
2. Venezuela
3. Guiana
4. Peru
5. Chili
6. Brasilia
7. Paraquaria
8. Tabula Magellanica
9. Preafecturae Paranambucae Prs Borealis
10. Praefecturae De Paraiba et Rio Grande
11. Praefectura De Ciriii vel Seregippe
12. Praefectura Paranambucae Pars Meridionalis
13. Sinus Omnium Sanctoru - Sizes: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)ea
- Condition: (A) Very Good to Fine Condition
- Date: 1662
- Ref #: BlaeuSA 1662
Description:
This is a unique opportunity to acquire a complete set of the 13 maps of South America, including the 4 rare uniform Blaeu-Barleus maps of the Coast of Brazil, published by Joan Blaeu in his monumental & rare 1st 1662 Atlas, Latin edition of Atlas Major.
All paper in imprinted with a large Elephant watermark donating german paper from the 1660s.
The maps cover the full geographical area from North to South, South America from Panama to Tierra Firma. Please see the background section below for details of each map. All maps have wide original margins & colour on strong sturdy paper.
Joan Blaeus 11 volumes of Atlas Major, is considered by many to be the greatest atlas set ever published. It excels in comprehensiveness, engraving, color, and overall production. The first edition was published in Latin in 1662 and was subsequently published in French, Dutch, German, and Spanish over the next 10 years.
On the 23rd of February 1672, a fire broke out in central Amsterdam, that ended the reign of one of the greatest & most prolific publishers of printed maps and atlases in publishing history. The Blaeu family had reached its zenith 10 years previously, with the publication of its greatest achievement, the Atlas Major or Great Atlas, consisting of 11 volumes, with geographical detail reflecting many of the achievements of the Golden Age of the United Netherlands. Blaeus Atlas Major were the most expensive books printed in the 17th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - Various, pls see below
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm) min
Imperfections:
Margins: - Pls see below
Plate area: - Pls see below
Verso: - Pls see below
Background:
1. Terra Firma - This regional map of the north eastern corner of South America belongs to the early group of plates printed by Willem Blaeu from 1630 onwards. It covers modern Colombia, part of Venezuela and Panama.
Plate: 19in x 14 1/2in.
Condition: Very light age toning
2. Venezuela - This map showing the area of modern Venezuela to the north of the Orinoco valley is another of the early plates of the 1630s. It extends from Lago dee Maracaibo in the west to the Island of Trinidad in the east and also shows the Dutch held Islands of Curacao, Aruba and Bonaire which served as a base of the Geotroyeerde West Indische Compaagnie (or Netherlands West Indian Company) since 1634.
Plate: 18 3/4in x 14 1/2in
Condition: Age toning, printers crease along centerfold, 8 small worm holes.
3. Guiana - This handsome map, another of the Blaeu maps of 1630, extendends from the Isla Margarita in the north-west to the coast of Northern Brazil near Sao Luis east of the Amazonas delta. The interior is dominated by a large island sea , the Parime Lacus, on whose north wesstern shores lies the fabled city of Manoa, de el Dorado, golden City of the Inca.
Plate: 19 1/4in x 14 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
4. Peru - Here willem Blaeu, this map being part of Pacific Coast of South America from Ecuador (at the left hand side) as far south as the Atacama desert in the northern reaches of Chile.
Plate: 19 1/4in x 14 3/4in
Condition: Light age toning
5. Chili - This is another of Willem Blaeus early group f maps showing the coastal region of Central Chile from Copiapo in the north as far as a point to the south of the island of Chiloe.
Plate: 16 3/4in x 14in
Condition: Light age toning
6. Brasilia - Oriented west to the top of the plate, this general map of Brazil was an early product of Joan Blaeu himself, made after he had assumed full control of the publishing house following the death of his father a few years earlier.
This plate was made to replace the De Laet derivative which Willem had acquired from the Hondius plate stock in 1629 and is considerably more detailed than its earlier name sake.
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/4in
Condition: Light age toning
7. Paraquaria - First map of Paraguay published first in this 1662 Atlas Major and so rare only published for 10 years or so.
Plate: 21 1/2in x 19 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
8. Tabula Magellanica - Beautifully engraved map of the Magellan Straits first published in 1635
Plate: 19in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
9. Preafecturae Paranambucae Prs Borealis
10. Praefecturae De Paraiba et Rio Grande
11. Praefectura De Ciriii vel Seregippe
12. Praefectura Paranambucae Pars Meridionalis
These 4 beautiful uniform maps are quite unlike any other maps found in Blaeu's Atlas Major.
Although they first appeared in the atlas for in 1662, these 4 maps first appeared in another earlier work published by Blaeu, the Rerum per octennium in Brasilia (1647) by the Remonstrant theologian Casper van Baerle (or Barlaeus) who died very soon afterwards in 1648.
Barlaeus great work, still one of the most valuable sources for Brazilian history, was published under the auspices of the Dutch governor in Brazil, Johan Maurits of Nassau Siegen, whose governorship from 1637 to 1644 Barlaeus describes in a eulogistic but nevertheless impartial account compiled from official sources.
The large pictorial vignettes of this group of maps illustrate much about local life and conditions of the time: in Preafecturae Paranambucae Prs Borealis & Praefecturae De Paraiba et Rio Grandea is shown processions of Indians from a mission, illustrated after paintings of the artist Frans Janszoon Post (1612 - 1680) who was with Johan Maurits in Brazil during the years 1637 - 1644. The buildings depicted have not been identified with any certainty but must have been in or near Pernambuco
Plates:
(9) 21in x 16 1/2in
(10) 21in x 16 1/2in
(11) 21in x 16 1/2in
(12) 17 1/2in x 16 1/2in
Conditions:
(9) Light age toning
(10) Light age toning
(11) Light age toning
(12) Light age toning
13. Sinus Omnium Sanctoru
Beautiful map of the Bahia De Todos Sanctos (All Saints Bay) in Brazil, with a large inset plan of the City of Sao Salvador.
Plate: 20in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Age toning
Caspar Barlaeus (1584 – 1648) was a Dutch polymath and Renaissance humanist, a theologian, poet, and historian.
Born Caspar (Kaspar) van Baerle in Antwerp, Barlaeus' parents fled the city when it was occupied by Spanish troops shortly after his birth. They settled in Zaltbommel, where his father eventually would become head of the Latin school. Caspar studied theology and philosophy at the University of Leiden. After his study, he preached for 1.5 years in the village of Nieuwe-Tonge, before returning to Leiden in 1612 as an under-regent of a college. From 1617 he also was professor in philosophy at the university. Because of his remonstrant sympathies, he was forced out of this job in 1619. He then studied and graduated in medicines (in Caen), but never practiced professionally.
From 1631, he was professor of philosophy and rhetoric at the Amsterdam Athenaeum, Athenaeum Illustre), which is commonly regarded as the predecessor of the University of Amsterdam; the Athenaeum had its seat in the fourteenth-century Agnietenkapel. In January 1632, Barlaeus, along with Gerard Vossius, held his inaugural speech at the Amsterdam Atheneum. Barlaeus later encouraged Martinus Hortensius to lecture –and give an inaugural speech- at the same Institution. One of his huge patrons was Amsterdam burgomaster Andries de Graeff, his neighbor at Oudezijds Achterburgwal.
Barlaeus suffered from mental illness including the delusion that he was made of glass (the Glass delusion) though Gill Speak refers to his glass delusion as ‘unsubstantiated’
Barlaeus published many volumes of poetry, particularly Latin poetry. He also wrote the eulogy that accompanies the 1622 portrait of cartographer Willem Blaeu.
Barlaeus was involved in various aspects of cartography and history. He translated Antonio de Herrera's Description of the West Indies in 1622. In 1627, Barlaeus provided the text for the atlas of Italy created by Jodocus Hondius. In 1647, he wrote an account of the Dutch colonial empire in Brazil, inspired by the leadership of John Maurice of Nassau (Johan Maurits) at Recife. The Rerum per octennium in Brasilia et alibi nuper gestarum sub praefectura, as it is called, contains numerous maps and plates of the region. The engravings of Brazilian northeastern locales, fleets, battles, and maps were for 160 years the main references to Brazilian landscapes available in Europe, and are well known by Brazilians today as the most important examples of pre-national art. Franciscus Plante wrote a similar work in the same year called Mauritias, and included the maps already published in Barlaeus' work. These were maps of Ceará, Pernambuco, Paraíba, and Pernambuco Borealá. Plante also incorporated a portrait of John Maurice that had already been included in Barlaeus' work.
In 1638, Barlaeus wrote Medicea Hospes, sive descriptio publicae gratulationis, qua ... Mariam de Medicis, excepit senatus populusque Amstelodamensis. Published by Willem Blaeu, it includes two large folding engraved views of the ceremonies on the occasion of the French queen mother Marie de Medici's triumphal entry into Amsterdam in 1638. Considered an important moment in Dutch history, Marie's visit lent de facto international recognition of the newly formed Dutch Republic. Marie de Medici actually traveled to the Netherlands as exile, but spectacular displays and water pageants took place in the city's harbor in celebration of her visit. There was a procession led by two mounted trumpeters; a large temporary structure erected on an artificial island in the Amstel River was built especially for the festival. This building was designed to display a series of dramatic tableaux in tribute to her once she set foot on the floating island and entered its pavilion.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.