Willem Blaeu (1571 - 1638) Joan Blaeu 1596-1673
Profile :
At the beginning of the seventeenth century Amsterdam was becoming one of the wealthiest trading cities in Europe, the base of the Dutch East India Company and a center of banking and the diamond trade, its people noted for their intellectual skills and splendid craftsmanship.
At this propitious time in the history of the Northern Provinces, Willem Janszoon Blaeu, who was born at Alkmaar in 1571 and trained in astronomy and the sciences by Tycho Brahe, the celebrated Danish astronomer, founded a business in Amsterdam in 1599 as a globe and instrument maker. It was not long before the business expanded, publishing maps, topographical works and books of sea charts as well as constructing globes. His most notable early work was a map of Holland (1604), a fine World Map (1605-06) and Het Licht der Zeevaerdt (The Light of Navigation), a marine atlas, which went through many editions in different languages and under a variety of titles. At the same time Blaeu was planning a major atlas intended to include the most up-to-date maps of the whole of the known world but progress on so vast a project was slow and not until he bought between 30 and 40 plates of the Mercator Atlas from Jodocus Hondius II to add to his own collection was he able to publish, in 1630, a 60-map volume with the title Atlantis Appendix. It was another five years before the first two volumes of his planned world atlas, Atlas Novus or the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum were issued. About this time he was appointed Hydrographer to the East India Company.
In 1638 Blaeu died and the business passed into the hands of his sons, Joan and Cornelis, who continued and expanded their father's ambitious plans. After the death of Cornelis, Joan directed the work alone and the whole series of 6 volumes was eventually completed about 1655. As soon as it was finished he began the preparation of the even larger work, the Atlas Major, which reached publication in 1662 in II volumes (later editions in 9-12 volumes) and contained nearly 6oo double-page maps and 3,000 pages of text. This was, and indeed remains, the most magnificent work of its kind ever produced; perhaps its geographical content was not as up-to-date or as accurate as its author could have wished, but any deficiencies in that direction were more than compensated for by the fine engraving and colouring, the elaborate cartouches and pictorial and heraldic detail and especially the splendid calligraphy.
In 1672 a disastrous fire destroyed Blaeu's printing house in the Gravenstraat and a year afterwards Joan Blaeu died. The firm's surviving stocks of plates and maps were gradually dispersed, some of the plates being bought by F. de Wit and Schenk and Valck, before final closure in about 1695.
It ought to be mentioned here that there is often confusion between the elder Blaeu and his rival Jan J ansson (Johannes Janssonius). Up to about 1619 Blaeu often signed his works Guilielmus Janssonius or Willems Jans Zoon but after that time he seems to have decided on Guilielmus or G. Blaeu.
Willem & Joan Blaeu (5)
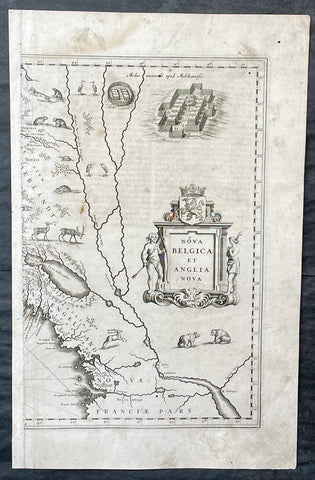
1635 Joan Blaeu Antique Half Page Map of New England, Nova Belgica et Anglia
Antique Map
- Title : Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova
- Date : 1635
- Size: 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Ref: 16385
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique half right hand page map of New England & NE America by Joan Blaeu was published in the 1635 German edition of Atlas Novus.
This is the right hand, cartouche title section of this important map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling, small worm hole top right margin
Plate area: - Light soiling, 4 small worm holes
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas published at the time. It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map is the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Niev Nederland.
It has been noted that the time difference between 1614, the date of the manuscript, and Blaeus map whose first appearance is in 1635, appears long for such an important advance. It would seem highly feasible that Blaeu, who published many separately issued maps, would have wanted to produce one like this sooner. However, evidence points to the fact that it could not have been made before 1630. The Stokes Collection in New York possesses an example of the map on thicker paper without text on the reverse which could well be a proof issue of some kind.
There are features on Blaeus map that differ from the Block chart. Some of these could be accounted for by the fact that the surviving figurative map is not the original, and that the copyist omitted some place names that are referred to in the text of de Laets work. Block drew on Champlains map of 1612 for the depiction of the lake named after him, but it is here called Lacus Irocoisiensis. … The lack of interrelation between the Dutch or English colonies and the French, led for some time to the eastward displacement of this lake when its true position would be north of the Hudson River.
Some nomenclature has its origins in Blaeus second Paskaert of c.1630, and others, such as Manatthans, in de Laet. The colony of Nieu Pleimonth is identified. This and other English names along that part of the coast are largely derived from Smith\\\'s New England, 1616. Cape Cod is here improved over the Block manuscript by being reconnected to the mainland, the narrow strait having been removed. The coastline between here and Narragansett Bay, which can be clearly recognized, is not so accurate. Adriaen Blocx Eylandt leads us to the Versche Rivier, or Connecticut River, which Block ascended as far as was possible. t Lange Eyland is named; however, it is incorrectly too far east, being applied to what is possibly Fishers Island. De Groote bay marks Long Island Sound. The Hudson River is still not named as such, but is littered with Dutch settlements, and the failed Fort Nassau is here depicted renamed as Fort Orange. He does, however, improve on the direction of its flow. Blaeu separates the sources of the Hudson and Delaware Rivers which had been causing some confusion. Nieu Amsterdam is correctly marked as a fort at the tip of an island separated on the east side by Hellegat, or the East River. The coastline south of Sandy Hook also shows signs of improvement.
The whole map is adorned by deer, foxes, bears, egrets, rabbits, cranes and turkeys. Beavers, polecats and otters appear on a printed map for the first time. The Mohawk Indian village top right is derived from the de Bry-White engravings.
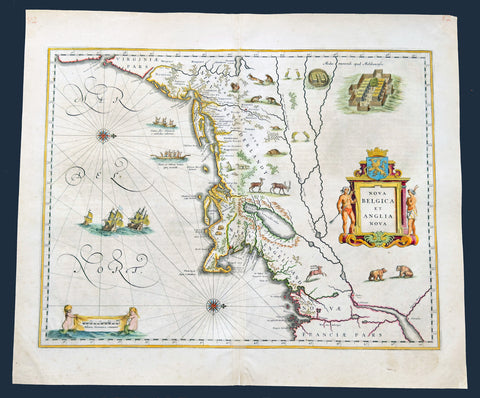
1641 Joan Blaeu Antique Landmark Map New England & New Netherlands
Antique Map
- Title : Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 480mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1641
- Ref #: 61201
Description:
This beautiful, original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique landmark map of the Dutch & British colonies of New England & NE America, centering on New York and Manhattan stretching from Virginia to Maine, by Joan Blaeu was published in the 1641 German edition of Atlas Novus.
This important landmark map of the American Northeast, presenting the regions settled by the Dutch (New Netherlands) and the English (New England). Oriented to the west, Blaeu's map covers the American coast from Virginia, past New York and Long Island to Cape Cod, New England, and Quebec. The map is the first of the region to depict the fur-bearing and food animals of the region accurately, and it does so in profusion. Between this imagery and the fleet of trade ships heading towards the coast, the decorative elements vividly emphasize the region's resource wealth.
This map is cartographically derived from data accumulated by Adriaen Block and other Dutch fur traders active in the early 17th century. Burden writes of the Block:
......This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas at the time...... It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript map of Adriaen Block, 1614. Indeed, it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map was the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Nieu Nederland.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Old soiling bottom left of verso not affecting the image. Top, bottom of centerfold re-enforced on verso. Top left corner of margin re-enforced
Background:
This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas published at the time. It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map is the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Niev Nederland.
It has been noted that the time difference between 1614, the date of the manuscript, and Blaeus map whose first appearance is in 1635, appears long for such an important advance. It would seem highly feasible that Blaeu, who published many separately issued maps, would have wanted to produce one like this sooner. However, evidence points to the fact that it could not have been made before 1630. The Stokes Collection in New York possesses an example of the map on thicker paper without text on the reverse which could well be a proof issue of some kind.
There are features on Blaeus map that differ from the Block chart. Some of these could be accounted for by the fact that the surviving figurative map is not the original, and that the copyist omitted some place names that are referred to in the text of de Laets work. Block drew on Champlains map of 1612 for the depiction of the lake named after him, but it is here called Lacus Irocoisiensis. … The lack of interrelation between the Dutch or English colonies and the French, led for some time to the eastward displacement of this lake when its true position would be north of the Hudson River.
Some nomenclature has its origins in Blaeus second Paskaert of c.1630, and others, such as Manatthans, in de Laet. The colony of Nieu Pleimonth is identified. This and other English names along that part of the coast are largely derived from Smiths New England, 1616. Cape Cod is here improved over the Block manuscript by being reconnected to the mainland, the narrow strait having been removed. The coastline between here and Narragansett Bay, which can be clearly recognized, is not so accurate. Adriaen Blocx Eylandt leads us to the Versche Rivier, or Connecticut River, which Block ascended as far as was possible. t Lange Eyland is named; however, it is incorrectly too far east, being applied to what is possibly Fishers Island. De Groote bay marks Long Island Sound. The Hudson River is still not named as such, but is littered with Dutch settlements, and the failed Fort Nassau is here depicted renamed as Fort Orange. He does, however, improve on the direction of its flow. Blaeu separates the sources of the Hudson and Delaware Rivers which had been causing some confusion. Nieu Amsterdam is correctly marked as a fort at the tip of an island separated on the east side by Hellegat, or the East River. The coastline south of Sandy Hook also shows signs of improvement.
The whole map is adorned by deer, foxes, bears, egrets, rabbits, cranes and turkeys. Beavers, polecats and otters appear on a printed map for the first time. The Mohawk Indian village top right is derived from the de Bry-White engravings.
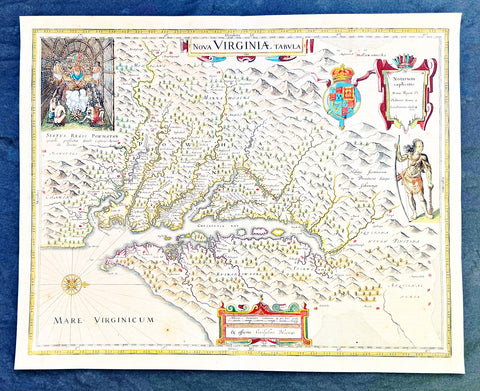
1642 Blaeu, Hondius & John Smith Antique Map of Virginia, America - Pocahontas
- Title : Nova Virginiae Tabula
- Date : 1642
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35667
- Size: 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Description:
This superb original antique hand coloured map of Chesapeake Bay, Virginia was published in the 1642 Dutch edition of Mercators Atlas.
This map by Blaeu comes directly from John Smiths map of Virginia. Blaeu bought this plate from Joducus Hondius who had engraved it directly from John Smith map. It is the only map on the market that is unchanged from Smiths map.
Although this map bears the name of Willem Blaeu, it comes from the plate stock of the Amsterdam publisher Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1629. Blaeu then issued the map in his Atlantis Appendix and in most editions of the firms atlases thereafter.
The map is a version of the map by the Englishman Captain John Smith in 1612. His map was the first to depict with reasonable accuracy Chesapeake Bay with its tributaries and became the accepted prototype map for most subsequent maps of the colony published either in Britain or Europe during the remainder of the 17th century.
Captain Smiths maps acted as a promotional piece for the vast area of North America called Virginia and it exerted a great influence of the history of English colonisation in America.
John Smith (1579-1631) was the foremost English settler in Virginia. His many adventures included being captured several times, defeating an Indian chief in hand to hand combat as well as the celebrated incident in which Pocahontas saved him from Powhatan who is himself the subject of the portrait at the upper left hand corner of Blaeus map.
While the geographical detail of the map shows information accurate at the time of Smiths travels, earlier descriptions of Virginia are recalled. When Smiths map appeared in 1612, the engraver turned to an engraving by the German Theodor de Bry based on the drawings made by John White in the 1580s for the portrait of Powhatan, and the figure of an Indian in war paint at the right to represent the Susquehanna chief. All of these elements were combined by the Amsterdam engraver Dirk Grijp for the Dutch version of Smiths map as issued by the Hondius firm in 1618. Thus, when Blaeu purchased the plate it was already a decade old and it was issued unchanged except for his imprint and a few very small retouches until the 1660s. The Blaeu derivative was the most popular version of Captain Smith Map published during the seventeenth century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (510mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning, light crease along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
This is one of the most important seventeenth century maps of the Chesapeake Bay region. The early settlement of Jamestown Iamestowne is noted along with a number of other place names, both in English and Native American. The map was derived from Capt. John Smith\'s map of 1612 and was the first to depict the bay and its tributaries with any accuracy.
Capt John Smith's fine survey work, as well as reports from indigenous American Indian tribes, and fanciful wishful thinking, combine to make this one of the most interesting maps of America to emerge in the 17th century. Philip D. Burden, the author of The Mapping of America, considers this map, Nova Virginiae Tabula, to be \'one of the most important maps of America ever produced and certainly one of the greatest influence.\' Oriented to the west, this map covers from Cape Henry to the Susquehanna River and inland as far as the Appellation Mountains. The Chesapeake Bay is shown in full as are many of its river estuaries, though topographically this map places a number of mountain ranges where there are in fact none.
To fully understand this map one must first realize that most Europeans believed the Pacific, or at least some great bay that led to the Pacific, lay just a few days travel inland. In the minds of most Europeans of the period, the trade potential for the Virginia colony was entirely dependent upon it being a practical access point to the riches of Asia. Thus the significance of large and mysterious body of water appearing in the land of the Massawomecks, in the upper right quadrant, becomes apparent. Of course, much of this land was entirely unexplored by the European settlers in Jamestown, shown here on the Powhatan River (James River), who relied heavily upon American Indian reports for much of their cartographic knowledge of the Virginia hinterlands. The Massawomecks themselves were a rival of the Powhatan and made their home near the headwaters of the Potomac. These, like many other indigenous groups of the region made only a brief and frequently violent appearance during the 17th century before entirely disappearing, mostly from disease and war, in the early 18th century.
In the upper left quadrant there is an image of the American Indian chief of the Powhatan sitting enthroned before a great fire in his long house. One of the more popular legends regarding John Smith was his capture and trial before the chief of the Powahatan. Smith was convinced that his liberation had something to do with the youthful daughter of Chief Powahatan, Pocahontas, taking a liking to him. Although this grew into a fictitious legend of its own, the truth is more likely that Powhatan saw Smith and his Englishmen as potential allies against the rival American Indian groups, such as the Massawomecks, that were pressing hard against his borders.
There are a number of different editions of this map and its publication by various map houses in various states made it the first widely distributed map of the Virginia colony and of John Smith\'s important map. There was, however, a scandal relating to its publication. The map was originally drawn and engraved in 1618 by Jodocus Hondius based upon the first edition of John Smith\'s 1612 map. When Jodocus died in 1629, he and his brother, Henricus Hondius, while collaborating on the Hondius Atlas Major, had established and maintained separate business for some 10 years. Jodocus\' death enabled the competing cartographer, Willem Blaeu to acquire a large number of Jodocus\' map plates, which he promptly published in 1630 as the Atlantis Appendix. Henricus, in the meantime, had been counting on Jodocus\' new plates to enhance his own, by then outdated, Hondius Atlas Major. A surviving contract dated March 2, 1630 reveals that Henricus Hondius and his partner Joannes Janssonius hired engravers to produce a number of new map plates copying the work of Jodocus – now in the hands of the Blaeu firm. This map was among the most important of that group and accounts for variants of this map being issued by competing Blaeu and Hondius firms.
The History of Virginia begins with documentation by the first Spanish explorers to reach the area in the 1500s, when it was occupied chiefly by Algonquian, Iroquoian, and Siouan peoples. After a failed English attempt to settle Virginia in the 1580s by Walter Raleigh permanent English settlement began in Virginia with Jamestown, Virginia, in 1607. The Virginia Company colony was looking for gold but failed and the colonists could barely feed themselves. The famine during the harsh winter of 1609 forced the colonists to eat leather from their clothes and boots and resort to cannibalism.[1] The colony nearly failed until tobacco emerged as a profitable export. It was grown on plantations, using primarily indentured servants for the intensive hand labor involved. After 1662, the colony turned black slavery into a hereditary racial caste. By 1750, the primary cultivators of the cash crop were West African slaves. While the plantations thrived because of the high demand for tobacco, most white settlers raised their families on subsistence farms. Warfare with the Virginia Indian nations had been a factor in the 17th century; after 1700 there was continued conflict with natives east of the Alleghenies, especially in the French and Indian War (1754-1763), when the tribes were allied with the French. The westernmost counties including Wise and Washington only became safe with the death of Bob Benge in 1794.
The Virginia Colony became the wealthiest and most populated British colony in North America, with an elected General Assembly. The colony was dominated by rich planters who were also in control of the established Anglican Church. Baptistand Methodist preachers brought the Great Awakening, welcoming black members and leading to many evangelical and racially integrated churches. Virginia planters had a major role in gaining independence and in the development of democratic-republican ideals of the United States. They were important in the Declaration of Independence, writing the Constitutional Convention (and preserving protection for the slave trade), and establishing the Bill of Rights. The state of Kentucky separated from Virginia in 1792. Four of the first five presidents were Virginians: George Washington, the "Father of his country"; and after 1800, "The Virginia Dynasty" of presidents for 24 years: Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and James Monroe.
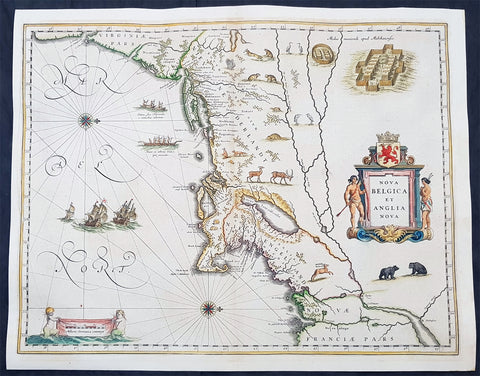
1642 Joan Blaeu Antique Map New England & NE America, Virginia New York to Maine
- Title : Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova
- Size: 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1642
- Ref #: 93080
Description:
This beautiful, original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of New England & NE America, centering on New York and Manhattan stretching from Virginia to Maine, by Joan Blaeu was published in the 1642 edition of Atlas Novus
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning, printers crease in left margin into border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas published at the time. It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map is the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Niev Nederland.
It has been noted that the time difference between 1614, the date of the manuscript, and Blaeus map whose first appearance is in 1635, appears long for such an important advance. It would seem highly feasible that Blaeu, who published many separately issued maps, would have wanted to produce one like this sooner. However, evidence points to the fact that it could not have been made before 1630. The Stokes Collection in New York possesses an example of the map on thicker paper without text on the reverse which could well be a proof issue of some kind.
There are features on Blaeus map that differ from the Block chart. Some of these could be accounted for by the fact that the surviving figurative map is not the original, and that the copyist omitted some place names that are referred to in the text of de Laets work. Block drew on Champlains map of 1612 for the depiction of the lake named after him, but it is here called Lacus Irocoisiensis. … The lack of interrelation between the Dutch or English colonies and the French, led for some time to the eastward displacement of this lake when its true position would be north of the Hudson River.
Some nomenclature has its origins in Blaeus second Paskaert of c.1630, and others, such as Manatthans, in de Laet. The colony of Nieu Pleimonth is identified. This and other English names along that part of the coast are largely derived from Smith\\\'s New England, 1616. Cape Cod is here improved over the Block manuscript by being reconnected to the mainland, the narrow strait having been removed. The coastline between here and Narragansett Bay, which can be clearly recognized, is not so accurate. Adriaen Blocx Eylandt leads us to the Versche Rivier, or Connecticut River, which Block ascended as far as was possible. t Lange Eyland is named; however, it is incorrectly too far east, being applied to what is possibly Fishers Island. De Groote bay marks Long Island Sound. The Hudson River is still not named as such, but is littered with Dutch settlements, and the failed Fort Nassau is here depicted renamed as Fort Orange. He does, however, improve on the direction of its flow. Blaeu separates the sources of the Hudson and Delaware Rivers which had been causing some confusion. Nieu Amsterdam is correctly marked as a fort at the tip of an island separated on the east side by Hellegat, or the East River. The coastline south of Sandy Hook also shows signs of improvement.
The whole map is adorned by deer, foxes, bears, egrets, rabbits, cranes and turkeys. Beavers, polecats and otters appear on a printed map for the first time. The Mohawk Indian village top right is derived from the de Bry-White engravings.
1662 Joan Blaeu Complete Set of 9 Antique Maps of North America from Atlas Major, 1st Edition
Antique Map
- Titles:
1. Extrema Americae....Terra Nova Francia;
2. Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova;
3. Nova Virginiae Tabula;
4. Virginiae partis australis, et Floridae;
5. Nova Hispania;
6. Yucatan...Guatimala;
7. Insulae Americanae;
8. Canibales Insulae;
9. Mappa Aestivarum Insularum Alias Barmudas - Sizes: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)ea
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date: 1662
- Ref #: BlaeuNA 1662
Description:
This is a unique opportunity to acquire a complete set of 9 maps of North America published by Joan Blaeus in the monumental & rare 1st 1662 Latin edition of Atlas Major. The maps cover the geographical detail of Canada, North America, Mexico, The Caribbean & Central America. Please see the background section below for details of each map. All maps have wide original margins & colour on strong sturdy paper.
Joan Blaeus 11 volumes of Atlas Major, is considered by many to be the greatest atlas set ever published. It excels in comprehensiveness, engraving, color, and overall production. The first edition was published in Latin in 1662 and was subsequently published in French, Dutch, German, and Spanish over the next 10 years.
On the 23rd of February 1672, a fire broke out in central Amsterdam, that ended the reign of one of the greatest & most prolific publishers of printed maps and atlases in publishing history. The Blaeu family had reached its zenith 10 years previously, with the publication of its greatest achievement, the Atlas Major or Great Atlas, consisting of 11 volumes, with geographical detail reflecting many of the achievements of the Golden Age of the United Netherlands. Blaeus Atlas Major were the most expensive books printed in the 17th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - Various, pls see below
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm) min
Imperfections:
Margins: - Pls see below
Plate area: - Pls see below
Verso: - Pls see below
Background:
1. Extrema Americae ( Eastern Canada) - Rare only published in Atlas Major. Derived mainly from the Samuel de Champlain Nouvelle France map of 1632, this map reflects the growing financial importance of the waters of New France to Europe.
Plate: 22 1/2in x 17 3/4in.
Condition: Age toning, text show-through & browning to image.
2. Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova (New England) - NE America, centering on New York and Manhattan from Virginia to the St Lawrence River. This map is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way.
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Age toning, text show-through & browning to image.
3. Nova Virginiae Tabula (John Smiths Virginia & Chesapeake Bay) This map was printed from a plate engraved by Dirk Grijp from a previous plates by Henricus Hondius.
Plate: 19in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
4. Virginiae partis australis, et Floridae Virginia, the Carolinas & Georgia.
Plate: 20in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
5. Nova Hispania et Nova Galicia Western Mexico
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
6. Yucatan...Guatimala (Yucatan, Central America) Rare only published in Atlas Major.
Plate: 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
7. Insulae Americana (GOM, Caribbean)
Plate: 20 1/2in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
8. Canibales Insulae (Lesser Antilles Islands) Rare, printed only in Atlas Major
Plate: 21in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Age toning
9. Mappa Aestivarum Insularum Alias Barmudas Dictarum Bermuda. Like all 17th century maps of Bermuda this map is based ultimately on the survey made by John Norwood, of the Bermuda Company, in 1618 in the form as published by the English map-maker John Speed in 1627.
Plate: 21in x 16in
Condition: Light age toning