Willem Blaeu (1571 - 1638) Joan Blaeu 1596-1673
Profile :
At the beginning of the seventeenth century Amsterdam was becoming one of the wealthiest trading cities in Europe, the base of the Dutch East India Company and a center of banking and the diamond trade, its people noted for their intellectual skills and splendid craftsmanship.
At this propitious time in the history of the Northern Provinces, Willem Janszoon Blaeu, who was born at Alkmaar in 1571 and trained in astronomy and the sciences by Tycho Brahe, the celebrated Danish astronomer, founded a business in Amsterdam in 1599 as a globe and instrument maker. It was not long before the business expanded, publishing maps, topographical works and books of sea charts as well as constructing globes. His most notable early work was a map of Holland (1604), a fine World Map (1605-06) and Het Licht der Zeevaerdt (The Light of Navigation), a marine atlas, which went through many editions in different languages and under a variety of titles. At the same time Blaeu was planning a major atlas intended to include the most up-to-date maps of the whole of the known world but progress on so vast a project was slow and not until he bought between 30 and 40 plates of the Mercator Atlas from Jodocus Hondius II to add to his own collection was he able to publish, in 1630, a 60-map volume with the title Atlantis Appendix. It was another five years before the first two volumes of his planned world atlas, Atlas Novus or the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum were issued. About this time he was appointed Hydrographer to the East India Company.
In 1638 Blaeu died and the business passed into the hands of his sons, Joan and Cornelis, who continued and expanded their father's ambitious plans. After the death of Cornelis, Joan directed the work alone and the whole series of 6 volumes was eventually completed about 1655. As soon as it was finished he began the preparation of the even larger work, the Atlas Major, which reached publication in 1662 in II volumes (later editions in 9-12 volumes) and contained nearly 6oo double-page maps and 3,000 pages of text. This was, and indeed remains, the most magnificent work of its kind ever produced; perhaps its geographical content was not as up-to-date or as accurate as its author could have wished, but any deficiencies in that direction were more than compensated for by the fine engraving and colouring, the elaborate cartouches and pictorial and heraldic detail and especially the splendid calligraphy.
In 1672 a disastrous fire destroyed Blaeu's printing house in the Gravenstraat and a year afterwards Joan Blaeu died. The firm's surviving stocks of plates and maps were gradually dispersed, some of the plates being bought by F. de Wit and Schenk and Valck, before final closure in about 1695.
It ought to be mentioned here that there is often confusion between the elder Blaeu and his rival Jan J ansson (Johannes Janssonius). Up to about 1619 Blaeu often signed his works Guilielmus Janssonius or Willems Jans Zoon but after that time he seems to have decided on Guilielmus or G. Blaeu.
Willem & Joan Blaeu (1)
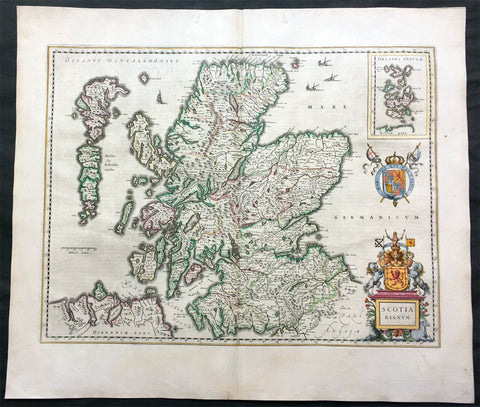
1646 Joan Blaeu Large Antique Map of Scotland - Scotia Regnum
Antique Map
- Title : Scotia Regnum
- Ref #: 61001
- Size: 22 3/4in x 19 3/4in (580mm x 500mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Scotland was published in the 1646 Dutch edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Novus.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 3/4in x 19 3/4in (580mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: When the Blaeu's published Volume V - GB & Ireland - of Atlas Novus, Scotland became one of the best-mapped countries in the world. Volume V contained forty-eight plates showing forty-nine separate maps of Scotland (plus a map of Ptolemy British Isles and six maps of Ireland). The first two plates from the atlas show the entire country ancient and modern, whilst the remaining forty-six plates cover most Scotland in forty-seven regional maps. In total the regional maps locate some 20,000 different place names. A clue as to the reason for this extraordinary explosion of geographical information is to be found on thirty-six of the regional maps, which all carry engraved credits to Timothy Pont (1524-1606)
Pont was responsible for surveying the greater part of Scotland between 1583-1600, the resulting Pont Manuscript maps were never published but were put to good use some fifty to seventy years later by Robert Gordon and Joan Blaeu. (Ref: Koeman; Tooley; M&B)