Fredrick de Wit (1630-1706)
Profile : De Wit was one of the most prominent and successful map engravers and publishers in Amsterdam in the period following the decline of the Blaeu and Jansson establishments, from which he acquired many copper plates when they were dispersed at auction. His output covered most aspects of map making: sea charts, world atlases, an atlas of the Netherlands, 'town books' covering plans of towns and cities in the Netherlands and Europe, and wall maps. His work, notable for the beauty of the engraving and colouring, was very popular with Covens and Mortier issuing many editions years after his death.
Fredrick de Wit
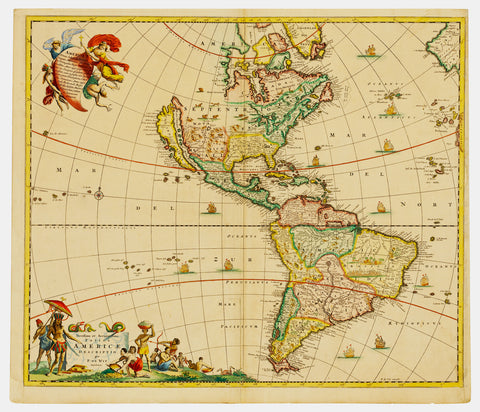
1670 Frederick De Wit Antique Map of America, California Island & 5 Great Lakes - !st Ed.
- Title : Novissima et Accuratissima totius Americae Descriptio.
- Date : 1670
- Size: 24in x 20 1/2in (605mm x 518mm)
- Ref #: 93117
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique 1st edition map of America, with California as an Island, showing one of earliest depictions of the 5 Great Lakes, was published by the Dutch cartographer Frederick De Wit in 1670.
This 17th century Dutch map is magnificent with beautiful original hand colouring, a dark strong impression, denoting an early pressing, with a dark rich uniform age toning is one of the best De Wit map I have seen for sometime.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (605mm x 518mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (586mm x 492mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L& R margins extended from the plate-mark.
Plate area: - Bottom centerfold rejoined with a small rejoin adjacent to the bottom part of the centerfold.
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background:
The first Dutch map to show five Great Lakes in North America. Based on de Wits great wall map of 1672, and with the Great Lakes considerably improved, as is the western coastline of Hudsons Bay. These two features are derived from Guillaume Sansons cartographic work published in 1669. The decorative cartouches are borrowed from the Nicolas Visschers America map of c.1658. The island of California shown with an indented northern coastline as per the Sanson model.. (Ref: Burden, Tooley, M&B)
de Wit, Frederick 1630 - 1706
Frederick de Wit (1629/1630 – 1706) was a Dutch cartographer and artist who drew, printed and sold maps. On maps his name is also written Frederic, Frederik, Frederico and Fredericus (Latinised). His surname is also written as de Witt and de Widt.
He was born in Gouda and died in Amsterdam. He was the company founder.
Frederick de Wit was born Frederick Hendricksz or Frederick son of Hendrick. He was born to a Protestant family in 1629/30, in Gouda, a small city in the province of Holland, one of the seven united provinces of the Netherlands. His father Hendrick Fredericsz (1608 – 29 July 1668) was a hechtmaecker (knife handle maker) from Amsterdam, and his mother Neeltij Joosten (d. before 1658) was the daughter of a merchant in Gouda. Frederick was married on 29 August 1661, to Maria van der Way (1632–1711), the daughter of a wealthy Catholic merchant in Amsterdam. From c. 1648 until his death at the end of July 1706, Frederick de Wit lived and worked in Amsterdam. Frederick and Maria had seven children, but only one Franciscus Xaverius (1666–1727) survived them.
By 1648, during the height of the Dutch Golden Age, De Wit had moved from Gouda to Amsterdam. As early as 1654 he had opened a printing office and shop under the name De Drie Crabben (the Three Crabs) which was also the name of his house on the Kalverstraat. In 1655, De Wit changed the name of his shop to the Witte Pascaert (the White Chart). Under this name De Wit and his firm became internationally known.
The first cartographic images that De Wit engraved were a plan of Haarlem that has been dated to 1648, and sometime before 1649 De Wit engraved the city views – city maps for the cities of Rijsel and Doornik that appeared in the richly illustrated Flandria Illustrata by the Flemish historian, Antonius Sanderus.[
The first charts engraved by De Wit were published in 1654 under the De Drie Crabben address. The first map that was both engraved and dated by De Wit was that of Denmark: REGNI DANIÆ Accuratissima delineatio Perfeckte Kaerte van t CONJNCKRYCK DENEMARCKEN in 1659. His first world maps, NOVA TOTIUS TERRARUM ORBIS TABULA AUCTORE F. DE WIT (approx. 43 × 55 cm) and Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula (a wall map approx. 140 × 190 cm) appeared around 1660.
His Atlas began to appear around 1662 and by 1671 included anywhere from 17 to 151 maps each. In the 1690s he began to use a new title page Atlas Maior but continued to use his old title page. His atlas of the Low Countries first published in 1667, was named Nieuw Kaertboeck van de XVII Nederlandse Provinciën and contained 14 to 25 maps. De Wit quickly expanded upon his first small folio atlas which contained mostly maps printed from plates that he had acquired, to an atlas with 27 maps engraved by or for him. By 1671 he was publishing a large folio atlas with as many as 100 maps. Smaller atlases of 17 or 27 or 51 maps could still be purchased and by the mid-1670s an atlas of as many as 151 maps and charts could be purchased from his shop. His atlases cost between 7 and 20 Guilders depending on the number of maps, color and the quality of binding (€47 or $70 to €160 or $240 today). In c. 1675 De Wit released a new nautical atlas. The charts in this atlas replaced the earlier charts from 1664 that are known today in only four bound examples and a few loose copies. De Wits new charts were sold in a chart book and as part of his atlases. De Wit published no fewer than 158 land maps and 43 charts on separate folio sheets.
In 1695 De Wit began to publish a town atlas of the Netherlands after he acquired a large number of city plans at the auction of the famous Blaeu publishing firms printing plates.
Dating De Wits atlases is considered difficult because usually no dates were recorded on the maps and their dates of publication extended over many years.
Through his marriage to Maria van der Way in 1661 he obtained, in 1662, the rights of Amsterdam citizenship and was able to become a member of the Guild of Saint Luke in 1664. In 1689 De Wit requested and received a fifteen-year privilege from the states of Holland and West Friesland that protected his right to publish and sell his maps. Then in 1694, he was named a good citizen of the city of Amsterdam.
After Frederick de Wits death in 1706 his wife Maria continued the business for four years printing and editing De Wits maps until 1710. However, as De Wits son Franciscus was already a prosperous stockfish merchant by this time and had little interest in his fathers business, he did not take over the publishing house. In 1710 Maria sold the firm at auction. At the auction most of the atlas plates and some of the wall map were sold to Pieter Mortier (1661–1711), a geographer, copper engraver, printer and publisher from Amsterdam. After Mortiers death, his firm eventually passed to the ownership of his son, Cornelis Mortier and Johannes Covens I who together founded Covens & Mortier on November 20, 1721. Covens & Mortier grew to become one of the largest cartography publishing houses of the 18th century. The 27 chart plates from his 1675 Sea atlas were sold at the 1710 auction, to the Amsterdam print seller Luis Renard, who published them under his own name in 1715, and then sold them to Rennier and Joshua Ottens who continued to publish them until the mid-1700s.
Most special collections libraries, rare map libraries, and private collections hold copies of De Wits atlases and maps. To date over 121 atlases and thousands of loose maps have been identified. Libraries that hold significant numbers are: The Amsterdam University Library, Utrecht University Library, Leiden University Library, Bibliothèque Royale Brussels, The Osher Map Library, Harvard Map Collection, Yale University Beinecke Library, The Library of Congress, Bayersche Staatsbibliothek, Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin, Österreichische Nationalbibliothek, Herzog August Bibliothek Wolfenbüttel, Sächsische Landesbibliothek-Staats-und Universitätsbibliothek Dresden, Hungarian National Library, and the collection bequeathed by William Dixson to the State Library of New South Wales. The museum at the Palazzo Rossi Poggi Marsili in Bologna has a map originally by Frederick de Wit (Nova totvs terrarvm orbis tabvla), engraved locally by Carlo Scotti (engraver)
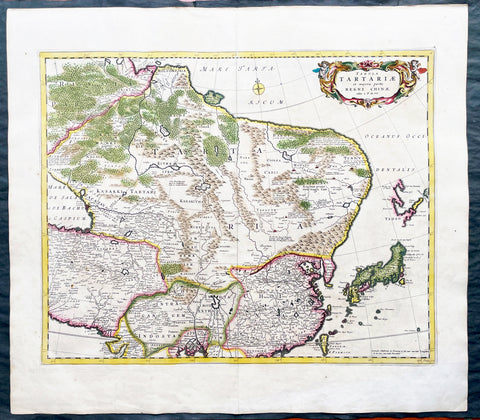
1680 Frederick de Wit Large Antiue Map of Tartary, China, Japan, Mogul, Formosa
Antique Map
- Title : Magnae Tartariae Magni Mogolis Imperii, Japoniae et Chinae...F de Wit
- Ref #: 17030
- Size: 25in x 22 1/2in (635mm x 570mm)
- Date : 1680
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large, handsome original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Tartary including China, Japan, Central Asia, parts of the Mogul Empire, Persia and Siberia - was published by Fredrick De Wit in 1680.
The map is finely engraved with detail, with fine original colour on sturdy, strong paper.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 22 1/2in (635mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Although Arabia, Persia, the Silk road to China and those parts of Northern India conquered by Alexander the Great were known to the classical world, it was not until the year AD 1375 that a map giving some idea of the real shape and size of Asia was compiled. This was the famous Catalan Map, based on reports of Franciscan missionaries and the writings of Marco Polo. A century or so later in the first Ptolemaic Atlases, there were altogether twelve maps of Asia which, of course, revealed no more or less than Ptolemy's view of the Ancient world, but in the expanded Waldseemuller editions of 1513 and 1532 there were modern regional maps including much information from Marco Polo's travels.
Later 16th century maps continue to show many of the distorted outlines copied from Ptolemy although by this time India, Ceylon and the Indies were gaining more recognizable shape. Munster was again the first publisher to print a separate map of Asia and later Ortelius issued the first separately printed map of China in 1584 and Japan in 1595. In the next century highly decorative maps were published by Van Den Keere in 1614, Speed 1627, Blaeu 1630, De Wit 1660, Visscher 1680 and others too numerous to list. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)