Products
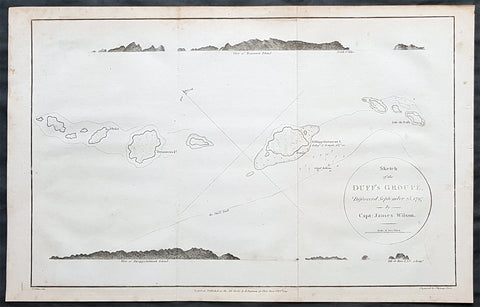
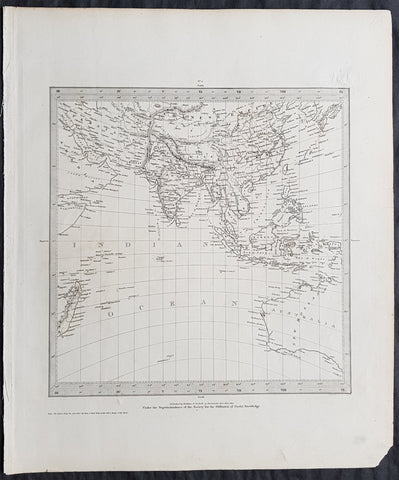
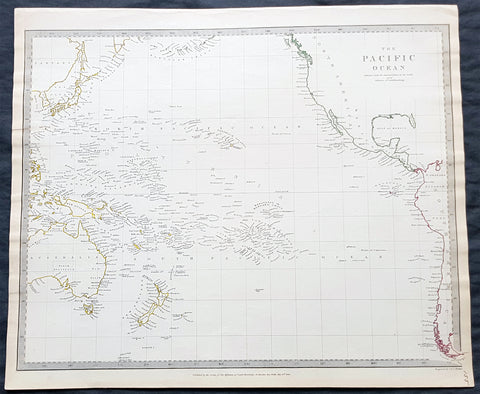
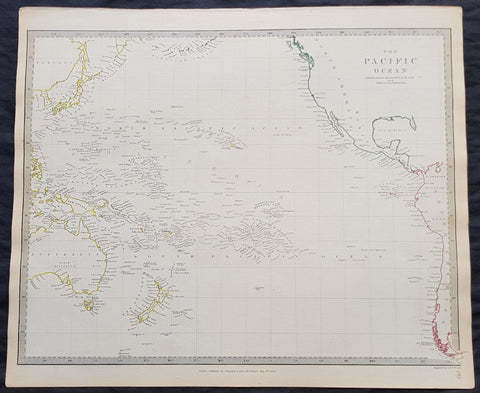
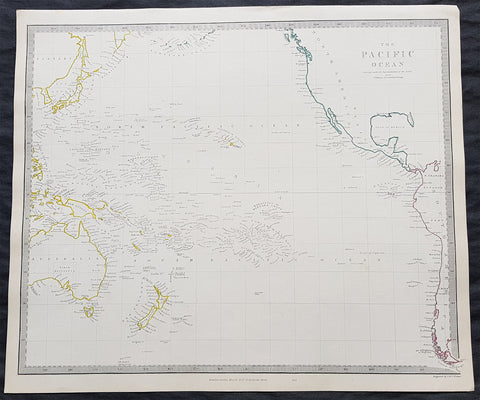
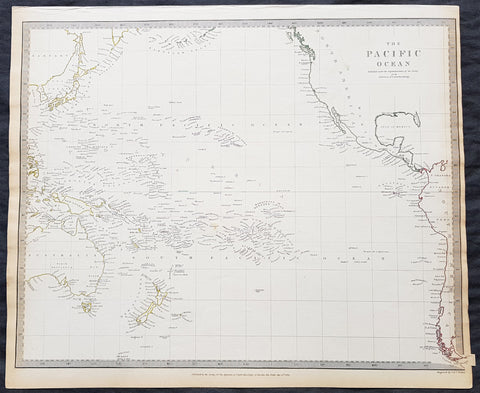
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Map 3 x Cook Islands & 1 x Society Island - Cook in 1777
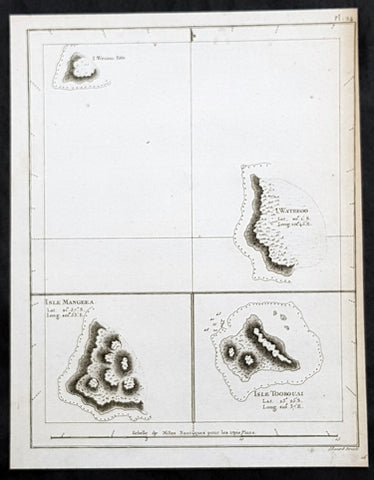
- Title : I. Wenooa Ette; I. Wateeoo; Isle Mangeea; Isle Toobouai
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 32164
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of three of the Cook Islands, Takutea (Wanooaette) Atiu (Wateeoo) and Mangaia (Mangeea) and a 4th map of the Island of Tubuai (Toobouai) in French Polynesia near Tahiti, visited by Captain Cook in HMS Resolution & Discovery in September 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\\\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom margin cropped into title
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Cook Islands is a self-governing island country in the South Pacific Ocean in free association with New Zealand. It comprises 15 islands whose total land area is 240 square kilometres.
Spanish ships visited the islands in the 16th century; the first written record of contact with the islands came in 1595 with the sighting of Pukapuka by Spanish sailor Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, who called it San Bernardo (Saint Bernard). Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, a Portuguese captain working for the Spanish crown, made the first recorded European landing in the islands when he set foot on Rakahanga in 1606, calling it Gente Hermosa.
British navigator Captain James Cook arrived in 1773 and 1777 and named the island of Manuae Hervey Island. Later, the name Hervey Islands came to be applied to the entire southern group; the name Cook Islands, in honour of Cook, first appeared on a Russian naval chart published in the 1820s
Takutea, in the Cook Islands, is a small uninhabited island 21 kilometres northwest of Atiu in the southern Cook Islands.
Takutea is the only island in the Cook Islands that never had a permanent population. When Captain James Cook sighted the island on 4 April 1777, and some crew members went ashore, they found some huts, but no evidence of a permanent settlement.
Atiu, also known as Enuamanu (meaning land of the birds), is an island 187 km northeast of Rarotonga, in the Southern Islands group of the Cook Islands Archipelago.
The first recorded European to arrive at Atiu was Captain Cook. He sighted the island on March 31, 1777 and made tentative contact with some of the people over the next few days.
Mangaia (traditionally known as A ua u Enua, which means terraced) is the most southerly of the Cook Islands and the second largest, after Rarotonga.
The first recorded European to arrive at Mangaia was Captain James Cook on 29 March 1777.
Tubuai part of the Society Islands is located 640 km south of Tahiti. Tubuai was first viewed by Europeans when it was mapped by Captain James Cook in 1777, although his party did not disembark. Cook discovered the islands name, Toobouai, from the natives who surrounded his ship in their canoes (a Tahitian named Omai, who was part of Cooks group, translated)
The next Europeans to arrive were the mutineers of the HMS Bounty in 1789. Mutineer Fletcher Christian, in looking for an island on which to permanently hide, had scoured Blighs maps and nautical charts and decided on Tubuai.
Upon arrival at Tubuai, a conflict arose while the mutineers were still on their ship and several islanders were killed in their canoes. The site of this event in the lagoon on the north side of the island is called Baie Sanglant (Bloody Bay)
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Thomas Bowen (1767-1790) was an engraver and son of Emanuel Bowen, map and print seller, engraver to George II and to Louis XV of France who worked in London from 1714 producing some the best and most attractive maps of the 18th century. He had plans for completing a major County Atlas but, finding the task beyond his means, joined with Thomas Kitchin to publish “The Large English Atlas”. Many of the maps were issued individually from 1749 onwards and the whole atlas was not finally completed until 1760. With one or two exceptions they were the largest maps of the counties to appear up to that time (27” x 20”) and were unusual in that blank areas around each map are filled with historical and topographical detail which makes fascinating and amusing reading. The atlas was reissued later in reduced size. Apart from his county maps and atlases of different parts of the world he also issued (with John Owen) a book of road maps based, as was usual at that time, on Ogilby but again incorporating his own style of historical and heraldic detail. Thomas helped his father during his lifetime and produced many fine maps in his own right after his fathers death.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Map of Kerguelen Island, South Indian Ocean Cook in 1776
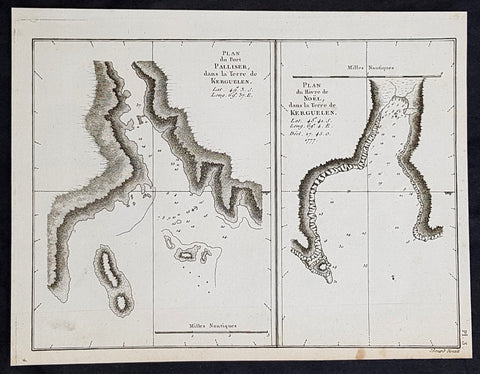
- Title : Plan du Port Palliser dans la Terre de Kerguelen; Plan du du Havre de Noel dans la Terre de Kerguelen....1777
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 32194
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of two maps on one sheet, the first of Port Palliser on the Island of Kerguelen and the second of Christmas Bay also located on the Island of Kerguelen in the very Southern Indian Ocean - midway between Africa, Antarctica and Australia - visited by Captain Cook in HMS Resolution & Discovery in December 25-30th 1776, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Thomas Bowen - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\\\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (245mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Kerguelen Islands, sometimes called the Desolation Islands, are located in the southern Indian Ocean and were discovered by the French navigator Yves de Kerguelen-Trémarec in 1772. On Christmas Day, 1776 Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored in Oiseau Bay, which he named Christmas Harbour. Cooks men discovered a bottle containing a message in Latin left by Kerguelens men. Cook wrote in his log: I could have very properly called the island Desolation Island to signalise its sterility, but in order not to deprive M. de Kerguelen of the glory of having discovered it, I have called it Kerguelen Land.
The Kerguelen Islands or the Kerguelen Archipelago are located in the southern Indian Ocean. The main island, Grande Terre, is 6,675 km² and it is surrounded by another 300 smaller islands and islets, forming an archipelago of 7,215 km². The climate is cold and very windy and the seas are usually rough. The islands are part of a submarine large igneous province called the Kerguelen Plateau.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Thomas Bowen (1767-1790) was an engraver and son of Emanuel Bowen, map and print seller, engraver to George II and to Louis XV of France who worked in London from 1714 producing some the best and most attractive maps of the 18th century. He had plans for completing a major County Atlas but, finding the task beyond his means, joined with Thomas Kitchin to publish “The Large English Atlas”. Many of the maps were issued individually from 1749 onwards and the whole atlas was not finally completed until 1760. With one or two exceptions they were the largest maps of the counties to appear up to that time (27” x 20”) and were unusual in that blank areas around each map are filled with historical and topographical detail which makes fascinating and amusing reading. The atlas was reissued later in reduced size. Apart from his county maps and atlases of different parts of the world he also issued (with John Owen) a book of road maps based, as was usual at that time, on Ogilby but again incorporating his own style of historical and heraldic detail. Thomas helped his father during his lifetime and produced many fine maps in his own right after his fathers death.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print of Chief Otago of Tongatapu, Tonga Islands in 1777
- Title : Otago, Chef de L Isle d Amersterdam
- Ref : 16358
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Otago, Chief of the Island of Tongatapu (Amsterdam) the largest island in the Tonga Island, drawn during a visit by Captain Cook in 1777, during his 3rd and last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Cooks on-board artist, John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tonga officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 169 islands, of which 36 are inhabited. The total surface area is about 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) scattered over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the southern Pacific Ocean. It has a population of 107,122 people, of whom 70% reside on the main island of Tongatapu.
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616 when the Dutch vessel Eendracht, captained by Willem Schouten, made a short visit to trade. Later came other Dutch explorers, including Jacob Le Maire (who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu); and in 1643 Abel Tasman (who visited Tongatapu and Haapai).
Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook (Royal Navy) in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Alessandro Malaspina (Spanish Navy) in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and the Wesleyan Methodist Reverend Walter Lawry in 1822.
Tonga became known in the West as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the inasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tui Tonga (the islands paramount chief) and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Visit to Tahiti in 1777 - Antique Print of Gifts for Cook & Men
- Title : Jeune Femme De O-Tahiti Apportant un Present
- Ref : 21348
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a young Tahitian woman giving the ritual presentation of gifts of tapa cloth and two breast plates, along with food to Captain Cook and his crew, during a visit by Cook in 1777 during his 3rd and last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after Cooks on-board artist, John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
............Webber remarked on the ritual presentation of gifts of tapa cloth and two breast plates, along with food to Cook and his crew by two girls. The design of the girl’s attire recalls the wide panniers of eighteenth-century fashion, suggesting that the artist may have taken significant artistic license. However, the depiction is in concordance with Cook’s account. He describes seeing the girls dressed prior to their presentation, remarking on the “rather curious” manner in which one end of the cloth “was held up over the girls heads while the remainder was wraped round them under the armpits, then the upper ends were let fall and hung down in foulds to the ground over the other and looked something like a circular hooped petticoat. After ward round the out side of all were, were wraped several pieces of different Coloured cloth, which considerably increased the Size so that the whole was not less than five or six yards in circuit and was as much as the girls could support..............
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Cook Antique Print HMS Resolution & Discovery, Prince William Sound, Alaska
- Title : Vue de Lanse Fermee de l entree Du Prince Guillaume (Entrance & view of the Prince William)
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 31839
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Cooks ships HMS Resolution and Discovery anchored in Snug Corner Cove, Prince William Sound, Alaska, visited by Captain Cook in 1778, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and was published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King publication A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majestys Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
May 1778.........On the 12th at nine in the morning, wrote Ledyard, we entered an inlet… at six in the evening perceiving bad weather approaching… both ships anchored… The pinnace of the Resolution with the first lieutenant, some other gentlemen and myself went to the opposite shore to shoot some wild fowl. The first lieutenant was John Gore. The inlet was named Sandwich Sound by Cook, after the Earl of Sandwich, First Lord of the Admiralty, but in the published version of his journal the name appeared as Prince Williams Sound, after George IIIs third son, Duke of Clarence, later William IV. The ships had anchored off Cape Hinchinbrook, named after the country seat of the Earl of Sandwich.
Some local inhabitants appeared and came aboard the ships. Clerke gave them a Glass Bowl, with which they seem\'d much delighted, and toss\'d me, in spight of all my motions to the contrary, one of their Frocks, which was made of Water fowl Skins, and exceedingly well calculated, to keep out both Wet & Cold; then, both Boats put off and made for the Shore, paddling & singing with all the Jollity imaginable. We either found these good folks on of their Jubilee Days, or they are a very happy Race.
They sailed on until Cook found a fine bay or rather harbour which he later called a very snug place and named Snug Corner Bay. Samwell on 14th wrote we secured the Ship with the small Anchor; in carrying this out in the Launch one of the Sailors was so unfortunate as to get his Leg entangled in the Buoy rope which carried him down with the Anchor, however he disengaged himself when he got to the bottom & came up again & saved his Life tho\' he had his Leg broke in a very dangerous Manner.
We heeled the ship to port wrote Gilbert, to examine the leak on the starboard buttock… it being close below the wale and occasioned by some of the seems being very open and the oakum quite rotten and great part of it got out. In two days we repaired this defect being obliged to put two and half inch rope along the seams which were too wide for caulking.
On 18th King noted two boats, one with Mr Gore & the other with the Master, were sent away, the first to explore the Inlet to the Noward: the other to the N end of the Island near us to make observations on the tides. William Bligh was master on the Resolution. They returned by Dusk, Mr Gore had proceeded up the Inlet & perceivd that it took a direction to the NE, & he thought that it bid fair for opening a communication to some other Sea; but the mate that was with him form\'d a very contrary opinion… the Captn judg\'d it the Wisest way to lose no more time, being certain that if we were amongst Islands, we shoud soon come to more Passages. Henry Roberts was the masters mate referred to here. Cook had sent him and others to sketch out the parts they examined
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins cropped close to borders
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Prince William Sound is located on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula, its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. Other settlements on the sound contain numerous small islands, including Cordova and Whittier plus the Alaska native villages of Chenega and Tatitlek.
James Cook entered Prince William Sound in 1778 and named it Sandwich Sound, after his patron the Earl of Sandwich. The name was changed to honour King George III third son, Prince William Henry, then aged 13 and serving as a midshipman in the Royal Navy.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1786 Bowen Antique Map 3 x Cook Islands & 1 x Society Island - Cooks Voyage 1777
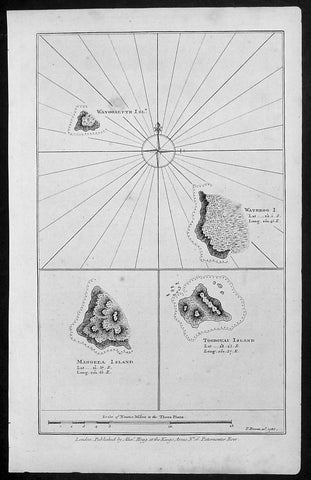
- Title : Wanooaette Isl; Wateeoo I; Mangeea Island Toobouai Island
- Size: 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 21697
- Date : 1786
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of three of the Cook Islands, Takutea (Wanooaette) Atiu (Wateeoo) and Mangaia (Mangeea) and a 4th map of the Island of Tubuai (Toobouai) in French Polynesia near Tahiti, visited by Captain Cook in HMS Resolution & Discovery in September 1777, during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery, was published in George Andersons A New, Authentic, and Complete Account of Voyages Round the World, Undertaken and Performed by Royal Authority. Containing a New, Authentic, Entertaining, Instructive, Full and Complete History of Captain Cooks First, Second, Third and Last Voyages.. ... published by Alexander Hogg, London 1786.
These maps of three Cook Islands :
1.Wanooaette, (Takutea)
2. Wateeoo (Atiu)
3. Mangeea ( Mangaia)
4. inset map of Toobouai (Tubuai) in the Society Islands in French Polynesia
All maps were charted by James Cook in 1777 while sailing for the Society Islands (French Polynesia) with livestock he carried aboard the Discovery and the Resolution. As he sailed toward Tahiti he discovered Toobouai (Tubuai) Island on 13 August 1777 where they stayed for 6 weeks. Relief shown by hachures and soundings.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9 1/2in (345mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
George William Anderson
A Collection of voyages round the world : performed by royal authority : containing a complete historical account of Captain Cooks first, second, third and last voyages, undertaken for making new discoveries, &c. ... : to which are added genuine narratives of other voyages of discovery round the world, &c. viz. those of Lord Byron, Capt. Wallis, Capt. Carteret, Lord Mulgrave, Lord Anson, Mr. Parkinson, Capt. Lutwidge, Mess. Ives, Middleton, Smith, &c published by Alex. Hogg, 1786.
Spanish ships visited the islands in the 16th century; the first written record of contact with the islands came in 1595 with the sighting of Pukapuka by Spanish sailor Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, who called it San Bernardo (Saint Bernard). Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, a Portuguese captain working for the Spanish crown, made the first recorded European landing in the islands when he set foot on Rakahanga in 1606, calling it Gente Hermosa.
British navigator Captain James Cook arrived in 1773 and 1777 and named the island of Manuae Hervey Island. Later, the name Hervey Islands came to be applied to the entire southern group; the name Cook Islands, in honour of Cook, first appeared on a Russian naval chart published in the 1820s
Takutea, in the Cook Islands, is a small uninhabited island 21 kilometres northwest of Atiu in the southern Cook Islands.
Takutea is the only island in the Cook Islands that never had a permanent population. When Captain James Cook sighted the island on 4 April 1777, and some crew members went ashore, they found some huts, but no evidence of a permanent settlement.
Atiu, also known as Enuamanu (meaning land of the birds), is an island 187 km northeast of Rarotonga, in the Southern Islands group of the Cook Islands Archipelago.
The first recorded European to arrive at Atiu was Captain Cook. He sighted the island on March 31, 1777 and made tentative contact with some of the people over the next few days.
Mangaia (traditionally known as A ua u Enua, which means terraced) is the most southerly of the Cook Islands and the second largest, after Rarotonga.
The first recorded European to arrive at Mangaia was Captain James Cook on 29 March 1777.
Tubuai part of the Society Islands is located 640 km south of Tahiti. Tubuai was first viewed by Europeans when it was mapped by Captain James Cook in 1777, although his party did not disembark. Cook discovered the islands name, Toobouai, from the natives who surrounded his ship in their canoes (a Tahitian named Omai, who was part of Cooks group, translated)
The next Europeans to arrive were the mutineers of the HMS Bounty in 1789. Mutineer Fletcher Christian, in looking for an island on which to permanently hide, had scoured Blighs maps and nautical charts and decided on Tubuai.
Upon arrival at Tubuai, a conflict arose while the mutineers were still on their ship and several islanders were killed in their canoes. The site of this event in the lagoon on the north side of the island is called Baie Sanglant (Bloody Bay)
1787 Bankes Antique Print Capt. Wallis making peace with Queen Purea of Tahiti in 1767
- Title : The Interview bewteen Capt Wallis and Oberea after Peace being established with the Natives
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21662
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis negotiating Peace Terms with Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti in 1767 (please read more below) was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Capt. Wallis making peace with Queen Purea of Tahiti in 1767
- Title : The Interview bewteen Capt Wallis and Oberea after Peace being established with the Natives
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21553-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis negotiating Peace Terms with Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti in 1767 (please read more below) was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Capt. Wallis making peace with Queen Purea of Tahiti in 1767
- Title : The Interview bewteen Capt Wallis and Oberea after Peace being established with the Natives
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21524
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis negotiating Peace Terms with Queen Purea (Oberea) of Tahiti in 1767 (please read more below) was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Human Sacrifice at Māori Tahiti - Cooks 3rd Voyage 1777
- Title : A Human Sacrifice in a Morai in Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21624-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a Human Sacrifice at the Utu-ai-mahurau Marae on Tahiti witnessed by Captain Cooks during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Island of Raiatea, French Polynesia Cooks Voyages 1769
- Title : View of the new discoverd island of Ulietea, with some of its inhabitants, a double canoe, and other small craft, a boat house with the model of a double canoe, & c.
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21479
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Raiatea (Ulietea) during Captain Cooks 1st Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1769 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
A traditional name for the island is Havaii, homeland of the Māori people.
The first European to record sighting Ra\'iātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Ra\'iātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, traveled with the European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
King Tamatoa VI was the last monarch, reigning from 1884-1888.
Cooks First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cooks command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on the Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earth\'s distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research.
Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Island of Raiatea, French Polynesia Cooks Voyages 1769
- Title : View of the new discoverd island of Ulietea, with some of its inhabitants, a double canoe, and other small craft, a boat house with the model of a double canoe, & c.
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21703
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Raiatea (Ulietea) during Captain Cooks 1st Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1769 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
A traditional name for the island is Havaii, homeland of the Māori people.
The first European to record sighting Ra\'iātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Ra\'iātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, traveled with the European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
King Tamatoa VI was the last monarch, reigning from 1884-1888.
Cooks First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cooks command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on the Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earth\'s distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research.
Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Island of Raiatea, French Polynesia Cooks Voyages 1769
- Title : View of the new discoverd island of Ulietea, with some of its inhabitants, a double canoe, and other small craft, a boat house with the model of a double canoe, & c.
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 40221
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Raiatea (Ulietea) during Captain Cooks 1st Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1769 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Raiatea, is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the centre of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the organised migrations to Hawaii, Aotearoa and other parts of East Polynesia started at Raiātea.
A traditional name for the island is Havaii, homeland of the Māori people.
The first European to record sighting Ra\'iātea was Pedro Fernandes de Queirós in 1606; it was charted as La Fugitiva The Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who sailed with explorer James Cook, was born in Ra\'iātea around 1725.
Cook visited Raiatea in 1769 and again in 1773-1774. Omai (c.1751-1780), another young man from Raiātea, traveled with the European explorers to London in 1774 and also served as an interpreter to Captain Cook on his second and third journey.
King Tamatoa VI was the last monarch, reigning from 1884-1888.
Cooks First Voyage (1768-1771)
The first voyage under Captain James Cooks command was primarily of a scientific nature. The expedition on the Endeavour initially sailed to Tahiti to observe the transit of the planet Venus in order to calculate the earth\'s distance from the sun. Cook landed on the South Pacific island in April of 1769 and in June of that year the astronomical observations were successfully completed. In addition to these labors, very good relations with the Tahitians were maintained and the naturalists Joseph Banks and Daniel C. Solander conducted extensive ethnological and botanical research.
Another purpose of the voyage was to explore the South Seas to determine if an inhabitable continent existed in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Upon leaving Tahiti, Cook named and charted the Society Islands and then continued southwest to New Zealand. His circumnavigation and exploration of that country also resulted in a detailed survey. Cook proceeded to Australia, where he charted the eastern coast for 2,000 miles, naming the area New South Wales. As a result of these surveys, both Australia and New Zealand were annexed by Great Britain. In addition to these explorations, the Endeavour returned to England without a single death from scurvy among its men, an historic feat at the time. The combination of these accomplishments brought Cook prominence, promotion, and the opportunity to lead further expeditions.
1787 Bankes Antique Print of Dancing Girls & Gifts in Tahiti During Cooks 3rd Voyage, 1777
- Title : Habit of a Young Woman of Otaheite Dancing; Habit of a Young Woman of Otaheite bringing a Present
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 40216
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Nomuka, a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai islands, in the Kingdom of Tonga, during Captain Cooks 3rd Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nomuka is a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai group of islands in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is part of the Nomuka Group of islands, also called the Otu Muomua.
Nomuka, is 7 square kilometres in area and contains a large, brackish lake (Ano Lahi) in the middle, and also three other smaller lakes—Ano Haamea, Ano Fungalei, and Molou. There are approximately 400-500 inhabitants who subsist on fishing, farming, and remittances from family members abroad. The island has a secondary school, two primary schools, and a kindergarten. It also has seven churches.
The island is accessible by boat only. Boats leave weekly from Nukualofa and Lifuka, Haapai. There is one guesthouse on the island, and three or four small fale koloa, or convenience stores.
Notable historic visitors include Abel Tasman, Captain Cook, Captain Bligh, and William Mariner. The Dutch Abel Tasman made the first European discovery of the island on 24 January 1643. A party went ashore to get water, and the description of the huge lake they brought back afterwards leaves little doubt about the identification. Tasman called it Rotterdam island, after the city of Rotterdam, a major port in the Netherlands, and noted in his maps the indigenous name of Amamocka, a misspelling of ʻa Nomuka, ʻa being a subject indicating article. We also find the name of Amorkakij for Nomuka iki. Captain Bligh in the Bounty spent 3 days wooding and watering at Nomuka in April 1789. The Mutiny on the Bounty occurred the day after they left.
Cooks Diary.........as it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was \"welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands\".
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this \"proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam \", the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, \"as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.\"
Cook\'s Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as \"whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
Cook\'s Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
1787 Bankes Antique Print of Dancing Girls & Gifts in Tahiti During Cooks 3rd Voyage, 1777
- Title : Habit of a Young Woman of Otaheite Dancing; Habit of a Young Woman of Otaheite bringing a Present
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21526
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Nomuka, a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai islands, in the Kingdom of Tonga, during Captain Cooks 3rd Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nomuka is a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai group of islands in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is part of the Nomuka Group of islands, also called the Otu Muomua.
Nomuka, is 7 square kilometres in area and contains a large, brackish lake (Ano Lahi) in the middle, and also three other smaller lakes—Ano Haamea, Ano Fungalei, and Molou. There are approximately 400-500 inhabitants who subsist on fishing, farming, and remittances from family members abroad. The island has a secondary school, two primary schools, and a kindergarten. It also has seven churches.
The island is accessible by boat only. Boats leave weekly from Nukualofa and Lifuka, Haapai. There is one guesthouse on the island, and three or four small fale koloa, or convenience stores.
Notable historic visitors include Abel Tasman, Captain Cook, Captain Bligh, and William Mariner. The Dutch Abel Tasman made the first European discovery of the island on 24 January 1643. A party went ashore to get water, and the description of the huge lake they brought back afterwards leaves little doubt about the identification. Tasman called it Rotterdam island, after the city of Rotterdam, a major port in the Netherlands, and noted in his maps the indigenous name of Amamocka, a misspelling of ʻa Nomuka, ʻa being a subject indicating article. We also find the name of Amorkakij for Nomuka iki. Captain Bligh in the Bounty spent 3 days wooding and watering at Nomuka in April 1789. The Mutiny on the Bounty occurred the day after they left.
Cooks Diary.........as it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was \"welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands\".
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this \"proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam \", the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, \"as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.\"
Cook\'s Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as \"whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
Cook\'s Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
1787 Bankes Antique Print of Mummified Chief Tu of Tahiti During Cooks 3rd Voyage 1777
- Title : The Body of Tee a Chief as preserved after Death in Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21624
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of the mummified remains of the Tahitian Chief Tu visited by Captain James Cook during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print of The Tahitian Fleet - Capt Cooks 3rd Voyage in 1777
- Title : View of the Fleet of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21525-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print of The Tahitian Fleet - Capt Cooks 3rd Voyage in 1777
- Title : View of the Fleet of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 40220-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print of The Tahitian Fleet - Capt Cooks 3rd Voyage in 1777
- Title : View of the Fleet of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 31793-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print of The Tahitian Fleet - Capt Cooks 3rd Voyage in 1777
- Title : View of the Fleet of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21658-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print of The Tahitian Fleet - Capt Cooks 3rd Voyage in 1777
- Title : View of the Fleet of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21397-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Tahitian Tools, Instruments & Flute - Capt Cook 1769
- Title : Various Instruments used by the Natives of Ohaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21670-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of various Instruments and tools of Tahiti and surrounding Islands visited by Captain James Cook in 1769, during his First Voyage of Discovery was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
The tools & instruments listed are;
The tools & instruments listed are;
1. Instrument for beating Breadfruit into paste
2. Thatching Needle
3. 3. Different Gouges or Chisels
4. An Adze of the smaller kind used for carving
5. The Nasal Flute blown by the Natives thro the nose
6. An instrument for beating the cloth
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Cooks Voyages 1768–1779
First voyage (1768–71)
In 1766, the Admiralty engaged Cook to command a scientific voyage to the Pacific Ocean. The purpose of the voyage was to observe and record the transit of Venus across the Sun for the benefit of a Royal Society inquiry into a means of determining longitude. Cook, at the age of 39, was promoted to lieutenant to grant him sufficient status to take the command. For its part the Royal Society agreed that Cook would receive a one hundred guinea gratuity in addition to his Naval pay.
The expedition sailed aboard HMS Endeavour, departing England on 26 August 1768. Cook and his crew rounded Cape Horn and continued westward across the Pacific to arrive at Tahiti on 13 April 1769, where the observations of the Venus Transit were made. However, the result of the observations was not as conclusive or accurate as had been hoped. Once the observations were completed, Cook opened the sealed orders which were additional instructions from the Admiralty for the second part of his voyage: to search the south Pacific for signs of the postulated rich southern continent of Terra Australis. Cook then sailed to New Zealand and mapped the complete coastline, making only some minor errors. He then voyaged west, reaching the south-eastern coast of Australia on 19 April 1770, and in doing so his expedition became the first recorded Europeans to have encountered its eastern coastline.
On 23 April he made his first recorded direct observation of indigenous Australians at Brush Island near Bawley Point, noting in his journal: “...and were so near the Shore as to distinguish several people upon the Sea beach they appear\'d to be of a very dark or black Colour but whether this was the real colour of their skins or the Clothes they might have on I know not. On 29 April Cook and crew made their first landfall on the mainland of the continent at a place now known as the Kurnell Peninsula. Cook originally christened the area as \"Stingray Bay\", but later he crossed this out and named it Botany Bay after the unique specimens retrieved by the botanists Joseph Banks and Daniel Solander. It is here that James Cook made first contact with an aboriginal tribe known as the Gweagal.
After his departure from Botany Bay he continued northwards. He stopped at Bustard Bay (now known as Seventeen Seventy or 1770) at 8 o’clock on 23 May 1770. On 24 May Cook and Banks and others went ashore. Continuing north, on 11 June a mishap occurred when HMS Endeavour ran aground on a shoal of the Great Barrier Reef, and then nursed into a river mouth on 18 June 1770. The ship was badly damaged and his voyage was delayed almost seven weeks while repairs were carried out on the beach (near the docks of modern Cooktown, Queensland, at the mouth of the Endeavour River). The voyage then continued, sailing through Torres Strait and on 22 August Cook landed on Possession Island, where he claimed the entire coastline that he had just explored as British territory. He returned to England via Batavia (modern Jakarta, Indonesia), where many in his crew succumbed to malaria, and then the Cape of Good Hope, arriving at the island of Saint Helena on 12 July 1771.
Cook\'s journals were published upon his return, and he became something of a hero among the scientific community. Among the general public, however, the aristocratic botanist Joseph Banks was a greater hero. Banks even attempted to take command of Cook\'s second voyage, but removed himself from the voyage before it began, and Johann Reinhold Forster and his son Georg Forster were taken on as scientists for the voyage. Cook\'s son George was born five days before he left for his second voyage.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print Tahitians Attacking Capt. Wallis, Matavai Bay Tahiti in 1767
- Title : The Natives of Ohaheite attacking Capt. Wallis the first Discoverer of that Hospitable Island
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21524-1
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Captain Samuel Wallis being attacked in Matavai Bay, Tahiti on 24th and 26th of June 1767 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of Nomuka Island, Tonga - Cooks Voyages in 1777
- Title : View in Anamooka and the Inhabitants
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21527
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Nomuka, a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai islands, in the Kingdom of Tonga, during Captain Cooks 3rd Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nomuka is a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai group of islands in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is part of the Nomuka Group of islands, also called the Otu Muomua.
Nomuka, is 7 square kilometres in area and contains a large, brackish lake (Ano Lahi) in the middle, and also three other smaller lakes—Ano Haamea, Ano Fungalei, and Molou. There are approximately 400-500 inhabitants who subsist on fishing, farming, and remittances from family members abroad. The island has a secondary school, two primary schools, and a kindergarten. It also has seven churches.
The island is accessible by boat only. Boats leave weekly from Nukualofa and Lifuka, Haapai. There is one guesthouse on the island, and three or four small fale koloa, or convenience stores.
Notable historic visitors include Abel Tasman, Captain Cook, Captain Bligh, and William Mariner. The Dutch Abel Tasman made the first European discovery of the island on 24 January 1643. A party went ashore to get water, and the description of the huge lake they brought back afterwards leaves little doubt about the identification. Tasman called it Rotterdam island, after the city of Rotterdam, a major port in the Netherlands, and noted in his maps the indigenous name of Amamocka, a misspelling of ʻa Nomuka, ʻa being a subject indicating article. We also find the name of Amorkakij for Nomuka iki. Captain Bligh in the Bounty spent 3 days wooding and watering at Nomuka in April 1789. The Mutiny on the Bounty occurred the day after they left.
Cooks Diary.........as it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was \"welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands\".
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this \"proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam \", the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, \"as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.\"
Cook\'s Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as \"whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
Cook\'s Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of Nomuka Island, Tonga - Cooks Voyages in 1777
- Title : View in Anamooka and the Inhabitants
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21643
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Nomuka, a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai islands, in the Kingdom of Tonga, during Captain Cooks 3rd Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nomuka is a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai group of islands in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is part of the Nomuka Group of islands, also called the Otu Muomua.
Nomuka, is 7 square kilometres in area and contains a large, brackish lake (Ano Lahi) in the middle, and also three other smaller lakes—Ano Haamea, Ano Fungalei, and Molou. There are approximately 400-500 inhabitants who subsist on fishing, farming, and remittances from family members abroad. The island has a secondary school, two primary schools, and a kindergarten. It also has seven churches.
The island is accessible by boat only. Boats leave weekly from Nukualofa and Lifuka, Haapai. There is one guesthouse on the island, and three or four small fale koloa, or convenience stores.
Notable historic visitors include Abel Tasman, Captain Cook, Captain Bligh, and William Mariner. The Dutch Abel Tasman made the first European discovery of the island on 24 January 1643. A party went ashore to get water, and the description of the huge lake they brought back afterwards leaves little doubt about the identification. Tasman called it Rotterdam island, after the city of Rotterdam, a major port in the Netherlands, and noted in his maps the indigenous name of Amamocka, a misspelling of ʻa Nomuka, ʻa being a subject indicating article. We also find the name of Amorkakij for Nomuka iki. Captain Bligh in the Bounty spent 3 days wooding and watering at Nomuka in April 1789. The Mutiny on the Bounty occurred the day after they left.
Cooks Diary.........as it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was \"welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands\".
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this \"proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam \", the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, \"as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.\"
Cook\'s Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as \"whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
Cook\'s Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of Nomuka Island, Tonga - Cooks Voyages in 1777
- Title : View in Anamooka and the Inhabitants
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 40224
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Nomuka, a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai islands, in the Kingdom of Tonga, during Captain Cooks 3rd Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nomuka is a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai group of islands in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is part of the Nomuka Group of islands, also called the Otu Muomua.
Nomuka, is 7 square kilometres in area and contains a large, brackish lake (Ano Lahi) in the middle, and also three other smaller lakes—Ano Haamea, Ano Fungalei, and Molou. There are approximately 400-500 inhabitants who subsist on fishing, farming, and remittances from family members abroad. The island has a secondary school, two primary schools, and a kindergarten. It also has seven churches.
The island is accessible by boat only. Boats leave weekly from Nukualofa and Lifuka, Haapai. There is one guesthouse on the island, and three or four small fale koloa, or convenience stores.
Notable historic visitors include Abel Tasman, Captain Cook, Captain Bligh, and William Mariner. The Dutch Abel Tasman made the first European discovery of the island on 24 January 1643. A party went ashore to get water, and the description of the huge lake they brought back afterwards leaves little doubt about the identification. Tasman called it Rotterdam island, after the city of Rotterdam, a major port in the Netherlands, and noted in his maps the indigenous name of Amamocka, a misspelling of ʻa Nomuka, ʻa being a subject indicating article. We also find the name of Amorkakij for Nomuka iki. Captain Bligh in the Bounty spent 3 days wooding and watering at Nomuka in April 1789. The Mutiny on the Bounty occurred the day after they left.
Cooks Diary.........as it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was \"welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands\".
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this \"proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam \", the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, \"as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.\"
Cook\'s Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as \"whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
Cook\'s Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of Nomuka Island, Tonga - Cooks Voyages in 1777
- Title : View in Anamooka and the Inhabitants
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21459
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Nomuka, a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai islands, in the Kingdom of Tonga, during Captain Cooks 3rd Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nomuka is a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai group of islands in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is part of the Nomuka Group of islands, also called the Otu Muomua.
Nomuka, is 7 square kilometres in area and contains a large, brackish lake (Ano Lahi) in the middle, and also three other smaller lakes—Ano Haamea, Ano Fungalei, and Molou. There are approximately 400-500 inhabitants who subsist on fishing, farming, and remittances from family members abroad. The island has a secondary school, two primary schools, and a kindergarten. It also has seven churches.
The island is accessible by boat only. Boats leave weekly from Nukualofa and Lifuka, Haapai. There is one guesthouse on the island, and three or four small fale koloa, or convenience stores.
Notable historic visitors include Abel Tasman, Captain Cook, Captain Bligh, and William Mariner. The Dutch Abel Tasman made the first European discovery of the island on 24 January 1643. A party went ashore to get water, and the description of the huge lake they brought back afterwards leaves little doubt about the identification. Tasman called it Rotterdam island, after the city of Rotterdam, a major port in the Netherlands, and noted in his maps the indigenous name of Amamocka, a misspelling of ʻa Nomuka, ʻa being a subject indicating article. We also find the name of Amorkakij for Nomuka iki. Captain Bligh in the Bounty spent 3 days wooding and watering at Nomuka in April 1789. The Mutiny on the Bounty occurred the day after they left.
Cooks Diary.........as it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was \"welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands\".
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this \"proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam \", the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, \"as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.\"
Cook\'s Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as \"whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
Cook\'s Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of Nomuka Island, Tonga - Cooks Voyages in 1777
- Title : View in Anamooka and the Inhabitants
- Size: 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
- Ref #: 21455
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of a view of the Island of Nomuka, a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai islands, in the Kingdom of Tonga, during Captain Cooks 3rd Voyage of discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 7 1/2in (305mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nomuka is a small island in the southern part of the Ha apai group of islands in the Kingdom of Tonga. It is part of the Nomuka Group of islands, also called the Otu Muomua.
Nomuka, is 7 square kilometres in area and contains a large, brackish lake (Ano Lahi) in the middle, and also three other smaller lakes—Ano Haamea, Ano Fungalei, and Molou. There are approximately 400-500 inhabitants who subsist on fishing, farming, and remittances from family members abroad. The island has a secondary school, two primary schools, and a kindergarten. It also has seven churches.
The island is accessible by boat only. Boats leave weekly from Nukualofa and Lifuka, Haapai. There is one guesthouse on the island, and three or four small fale koloa, or convenience stores.
Notable historic visitors include Abel Tasman, Captain Cook, Captain Bligh, and William Mariner. The Dutch Abel Tasman made the first European discovery of the island on 24 January 1643. A party went ashore to get water, and the description of the huge lake they brought back afterwards leaves little doubt about the identification. Tasman called it Rotterdam island, after the city of Rotterdam, a major port in the Netherlands, and noted in his maps the indigenous name of Amamocka, a misspelling of ʻa Nomuka, ʻa being a subject indicating article. We also find the name of Amorkakij for Nomuka iki. Captain Bligh in the Bounty spent 3 days wooding and watering at Nomuka in April 1789. The Mutiny on the Bounty occurred the day after they left.
Cooks Diary.........as it was, Cook did not encounter the Tongan islands until his Second Voyage, when he stopped at both \'Eua and Tongatapu (or, by Tasman\'s nomenclature, Middleburg and Amsterdam respectively) in October of 1773. Here he was \"welcomed a shore by acclamations from an immence [sic] crowd of Men and Women not one of which had so much as a stick in their hands\".
Indeed, Cook found the islanders to be so accommodating that he returned to the archipelago in 1774 on his way back from New Zealand. Stopping at the island of Nomuka, Cook was sought out by name, and with this \"proof that these people have a communication with Amsterdam \", the cultural unity of the islands was established.
It was at this time that he famously named the island group the Friendly Archipelago, \"as a lasting friendship seems to subsist among the Inhabitants and their Courtesy to Strangers intitles [sic] them to that Name.\"
Cook\'s Third Voyage also included a visit to Tonga, this time for a stay of several months. Cook first dropped anchor at Nomuka in May, and then, at the invitation of the great chief Finau, travelled to another island, Lifuka. Here, Cook and his men were treated to such entertainments as \"whould [sic] have met with universal applause on a European Theatre.
Cook\'s Third Voyage (1776-1779)
In the course of his first two voyages, Cook circumnavigated the globe twice, sailed extensively into the Antarctic, and charted coastlines from Newfoundland to New Zealand. Following these achievements, Cook\'s third voyage was organized to seek an efficient route from England to southern and eastern Asia that would not entail rounding the Cape of Good Hope. The search for such a Northwest (or Northeast) Passage had been on the agenda of northern European mariners and merchants since the beginning of European expansion in the late fifteenth century. England\'s growing economic and colonial interests in India in the later eighteenth century provided the stimulus for the latest exploration for this route.
Cook, again in command of the Resolution, was to approach the Northwest Passage from the Pacific accompanied by a second ship, the Discovery, captained by Charles Clerke. The ships left England separately, regrouped at Cape Town, and continued on to Tasmania, New Zealand, and Tahiti. The expedition then sailed north and made landfall at Christmas Island and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook continued northward and charted the west coast of North America from Northern California as far as the Bering Strait. He returned to Hawaii for the winter and was killed in a skirmish with natives on February 14, 1779. Upon Cook\'s death, Clerke took command of the expedition but died six months later. The ships returned to England in 1780 under John Gore, who had commanded the Discovery after Cook\'s death. From start to finish, the voyage had lasted more than four years. (Ref Tooley; M&B; Clancy)
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of the Islands of Tahiti - Cooks 3rd Voyage, 1777
- Title : View of the Islands of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 40220
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of the Islands of Tahiti - Cooks 3rd Voyage, 1777
- Title : View of the Islands of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21525
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of the Islands of Tahiti - Cooks 3rd Voyage, 1777
- Title : View of the Islands of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 21658
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1787 Bankes Antique Print View of the Islands of Tahiti - Cooks 3rd Voyage, 1777
- Title : View of the Islands of Otaheite
- Size: 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
- Ref #: 31793
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original cooper-plate engraved antique print of Matavai Bay and the Island of Tahiti during Captain Cooks visit to the Island during his 3rd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in 1777 was published in Thomas Bankes 1787 edition of A New, Royal and Authentic System of Universal Geography, Antient and Modern..... printed by Charles Cook, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/2in (240mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
CooksThird Voyage (1776–79)
On his last voyage, Cook again commanded HMS Resolution, while Captain Charles Clerke commanded HMS Discovery. The voyage was ostensibly planned to return the Pacific Islander, Omai to Tahiti, or so the public were led to believe. The trip\\\'s principal goal was to locate a Northwest Passage around the American continent. After dropping Omai at Tahiti, Cook travelled north and in 1778 became the first European to begin formal contact with the Hawaiian Islands. After his initial landfall in January 1778 at Waimea harbour, Kauai, Cook named the archipelago the \\\"Sandwich Islands\\\" after the fourth Earl of Sandwich—the acting First Lord of the Admiralty.
From the Sandwich Islands Cook sailed north and then north-east to explore the west coast of North America north of the Spanish settlements in Alta California. He made landfall on the Oregon coast at approximately 44°30′ north latitude, naming his landing point Cape Foulweather. Bad weather forced his ships south to about 43° north before they could begin their exploration of the coast northward. He unknowingly sailed past the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and soon after entered Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. He anchored near the First Nations village of Yuquot. Cook\\\'s two ships remained in Nootka Sound from 29 March to 26 April 1778, in what Cook called Ship Cove, now Resolution Cove, at the south end of Bligh Island, about 5 miles (8 km) east across Nootka Sound from Yuquot, lay a Nuu-chah-nulth village (whose chief Cook did not identify but may have been Maquinna). Relations between Cook\\\'s crew and the people of Yuquot were cordial if sometimes strained. In trading, the people of Yuquot demanded much more valuable items than the usual trinkets that had worked in Hawaii. Metal objects were much desired, but the lead, pewter, and tin traded at first soon fell into disrepute. The most valuable items which the British received in trade were sea otter pelts. During the stay, the Yuquot \\\"hosts\\\" essentially controlled the trade with the British vessels; the natives usually visited the British vessels at Resolution Cove instead of the British visiting the village of Yuquot at Friendly Cove.
After leaving Nootka Sound, Cook explored and mapped the coast all the way to the Bering Strait, on the way identifying what came to be known as Cook Inlet in Alaska. In a single visit, Cook charted the majority of the North American north-west coastline on world maps for the first time, determined the extent of Alaska, and closed the gaps in Russian (from the West) and Spanish (from the South) exploratory probes of the Northern limits of the Pacific.
By the second week of August 1778 Cook was through the Bering Strait, sailing into the Chukchi Sea. He headed north-east up the coast of Alaska until he was blocked by sea ice. His furthest north was 70 degrees 44 minutes. Cook then sailed west to the Siberian coast, and then south-east down the Siberian coast back to the Bering Strait. By early September 1778 he was back in the Bering Sea to begin the trip to the Sandwich (Hawaiian) Islands. He became increasingly frustrated on this voyage, and perhaps began to suffer from a stomach ailment; it has been speculated that this led to irrational behaviour towards his crew, such as forcing them to eat walrus meat, which they had pronounced inedible.
Cook returned to Hawaii in 1779. After sailing around the archipelago for some eight weeks, he made landfall at Kealakekua Bay, on \\\'Hawaii Island\\\', largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Cook\\\'s arrival coincided with the Makahiki, a Hawaiian harvest festival of worship for the Polynesian god Lono. Coincidentally the form of Cook\\\'s ship, HMS Resolution, or more particularly the mast formation, sails and rigging, resembled certain significant artefacts that formed part of the season of worship. Similarly, Cook\\\'s clockwise route around the island of Hawaii before making landfall resembled the processions that took place in a clockwise direction around the island during the Lono festivals. It has been argued (most extensively by Marshall Sahlins) that such coincidences were the reasons for Cook\\\'s (and to a limited extent, his crew\\\'s) initial deification by some Hawaiians who treated Cook as an incarnation of Lono. Though this view was first suggested by members of Cook\\\'s expedition, the idea that any Hawaiians understood Cook to be Lono, and the evidence presented in support of it, were challenged in 1992.
After a month\\\'s stay, Cook attempted to resume his exploration of the Northern Pacific. Shortly after leaving Hawaii Island, however, the Resolution\\\'s foremast broke, so the ships returned to Kealakekua Bay for repairs.
Tensions rose, and a number of quarrels broke out between the Europeans and Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay. An unknown group of Hawaiians took one of Cook\\\'s small boats. The evening when the cutter was taken, the people had become \\\"insolent\\\" even with threats to fire upon them. Cook was forced into a wild goose chase that ended with his return to the ship frustrated.[53] He attempted to kidnap and ransom the King of Hawaiʻi, Kalaniʻōpuʻu.
That following day, 14 February 1779, Cook marched through the village to retrieve the King. Cook took the King (aliʻi nui) by his own hand and led him willingly away. One of Kalaniʻōpuʻu\\\'s favorite wives, Kanekapolei and two chiefs approached the group as they were heading to boats. They pleaded with the king not to go until he stopped and sat where he stood. An old kahuna (priest), chanting rapidly while holding out a coconut, attempted to distract Cook and his men as a large crowd began to form at the shore. The king began to understand that Cook was his enemy. As Cook turned his back to help launch the boats, he was struck on the head by the villagers and then stabbed to death as he fell on his face in the surf. He was first struck on the head with a club by a chief named Kalaimanokahoʻowaha or Kanaʻina (namesake of Charles Kana\\\'ina) and then stabbed by one of the king\\\'s attendants, Nuaa. The Hawaiians carried his body away towards the back of the town, still visible to the ship through their spyglass. Four marines, Corporal James Thomas, Private Theophilus Hinks, Private Thomas Fatchett and Private John Allen, were also killed and two others were wounded in the confrontation.
The esteem which the islanders nevertheless held for Cook caused them to retain his body. Following their practice of the time, they prepared his body with funerary rituals usually reserved for the chiefs and highest elders of the society. The body was disembowelled, baked to facilitate removal of the flesh, and the bones were carefully cleaned for preservation as religious icons in a fashion somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of European saints in the Middle Ages. Some of Cook\\\'s remains, thus preserved, were eventually returned to his crew for a formal burial at sea.
Clerke assumed leadership of the expedition, and made a final attempt to pass through the Bering Strait. He died from tuberculosis on 22 August 1779 and John Gore, a veteran of Cook\\\'s first voyage, took command of Resolution and of the expedition. James King replaced Gore in command of Discovery. The expedition returned home, reaching England in October 1780. After their arrival in England, King completed Cook\\\'s account of the voyage.
David Samwell, who sailed with Cook on Resolution, wrote of him: \\\"He was a modest man, and rather bashful; of an agreeable lively conversation, sensible and intelligent. In temper he was somewhat hasty, but of a disposition the most friendly, benevolent and humane. His person was above six feet high: and, though a good looking man, he was plain both in dress and appearance. His face was full of expression: his nose extremely well shaped: his eyes which were small and of a brown cast, were quick and piercing; his eyebrows prominent, which gave his countenance altogether an air of austerity.
Tahiti previously also known as Otaheite is the largest island in the Windward group of French Polynesia. The island is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands in the central Southern Pacific Ocean.
The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in HMS Dolphin, sighting the island on 18 June 1767, and eventually harboring in Matavai Bay. This bay was situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare-Arue, governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-a\\\\\\\'a-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha, and the chiefdom of Ha apape, governed by Amo and his wife Oberea (Purea). Wallis named the island King Georges Island. The first contacts were difficult, since on the 24 and 26 June 1767, Tahitian warriors in canoes showed aggression towards the British, hurling stones from their slings. In retaliation, the British sailors opened fire on the warriors in the canoes and on the hills. In reaction to this powerful counter-attack, the Tahitians laid down peace offerings for the British. Following this episode, Samuel Wallis was able to establish cordial relations with the female chieftain “Oberea “ (Purea) and remained on the island until 27 July 1767.
In July 1768, Captain James Cook was commissioned by the Royal Society and on orders from the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty to observe the transit of Venus across the sun, a phenomenon that would be visible from Tahiti on 3 June 1769. He arrived in Tahitis Matavai Bay, commanding the HMS Endeavour on 12 April 1769. On 14 April, Cook met with Tutaha and Tepau. On 15 April, Cook picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus along with Banks, Parkinson, Daniel Solander, to protect Charles Greens observatory. The length of stay enabled them to undertake for the first time real ethnographic and scientific observations of the island. Assisted by the botanist Joseph Banks, and by the artist Sydney Parkinson, Cook gathered valuable information on the fauna and flora, as well as the native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island, Otaheite. On 28 April, Cook met Purea and Tupaia, and Tupaia befriended Banks following the transit. On 21 June, Amo visited Cook, and then on 25 June, Pohuetea visited, signifying another chief seeking to ally himself with the British.
Cook and Banks circumnavigated the island from 26 June to 1 July. On the exploration, they met Ahio, chief of Ha apaiano o or Papenoo, Rita, chief of Hitia a, Pahairro, chief of Pueu, Vehiatua, chief of Tautra, Matahiapo, chief of Teahupo o, Tutea, chief of Vaira o, and Moe, chief of Afa\\\\\\\'Ahiti. In Papara, guided by Tupaia, they investigated the ruins of Mahaiatea marae, an impressive structure containing a stone pyramid or ahu, measuring 44 feet high, 267 feet long and 87 feet wide. Cook and the Endeavour departed Tahiti on 13 July 1769, taking Raiatean navigator Tupaia along for his geographic knowledge of the islands.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773, greeted by the chiefs Tai and Puhi, besides the youg ari i Vehiatua II and his stepfather Ti itorea. Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus where he met Tu, the paramount chief. Cook picked up two passengers from Tahiti during this trip, Porea and Ma\\\\\\\'i, with Hitihiti later replacing Porea when Cook stopped at Raiatea. Cook took Hitihiti to Tahiti on 22 April, during his return leg. Then, Cook departed Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
During his final visit, Cook returned Mai to Tahiti on 12 Aug. 1777, after Mais long visit in England. Cook also brought two Maori from Queen Charlotte Sound, Te Weherua and Koa. Cook first harbored in Vaitepiha Bay, where he visited Vehiatua II s funeral bier and the prefabricated Spanish mission house. Cook also met Vehiatua III, and inscribed on the back of the Spanish cross, Georgius tertius Rex Annis 1767, 69, 73, 74 & 77, as a counterpoint to Christus Vincit Carolus III imperat 1774 on the front. On 23 Aug., Cook sailed for Matavai Bay, where he met Tu, his father Teu, his mother Tetupaia, his brothers Ari ipaea and Vaetua, and his sisters Ari ipaea-vahine, Tetua-te-ahamai, and Auo. Cook also observed a human sacrifice, taata tapu, at the Utu-ai-mahurau marae, and 49 skulls from previous victims.
On 29 Sept. 1777, Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea. Cook met Mahine in an act of friendship on 3 Oct., though he was an enemy of Tu. When a goat kid was stolen on 6 Oct., Cook in a rampage, ordered the burning of houses and canoes until it was returned. Cook sailed for Huahine on 11 Oct., Raiatea on 2 Nov., and Borabora on 7 Dec.
On 26 October 1788, HMS Bounty, under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit trees (Tahitian: uru) to the Caribbean. Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist from James Cooks first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the Bounty offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
1797 Wilson Large Antique Map of the Duff Isles, Solomon Islands, South Pacific
- Title : 1799 James Wilson Antique Map of Duff or Wilson Islands, Santa Cruz Solomons Is.
- Date : 1799
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90613
- Size: 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 255mm)
Description:
This copper-plate engraved original antique map of Duff or Wilson Islands located northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands in the Solomon Islands province of Temotu, in the South Pacific was engraved in by Thomas foot and was published in the 1799 edition Captain James Wilsons A missionary voyage to the Southern Pacific Ocean, performed in the years 1796, 1797, 1798, in the ship Duff commanded by Captain James Wilson.Compiled from journals of the officers and the missionaries. With a preliminary discourse on the geography and history of the South Sea Islands; and an appendix, including details never before published of the natural and civil state of Otaheite.
Captain James Wilson (1760–1814), commanded the British ship Duff, which the London Missionary Society contracted in 1797 to convey a team of missionaries (consisting of thirty men, six women, and three children) to their postings in Tahiti, Tonga, and the Marquesas Islands. During the voyage, Wilson also surveyed (or confirmed the locations of) numerous islands in the Pacific, including Vanua Balavu, Fulaga and Ogea Levu in Fiji, Mangareva in the Gambier Islands, Pukarua in the Tuamotus, and Satawal, Elato, and Lamotrek, in the Caroline Islands.
Three years after the establishment of the British mission in Tahiti, the directors of the Society appointed a committee to consider a suitable memorial for presentation to Wilson for his services in helping to establish the first mission in the South Seas.
He published an account of his voyage: A Missionary Voyage to the Southern Pacific Ocean in 1799. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 10 1/2in (405mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soling
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Light soling
Background:
The Duff Islands are a small island group lying to the northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands in the Solomon Islands province of Temotu. They are also sometimes known as the Wilson Islands.
The first recorded sighting by Europeans of the Duff Islands was by the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós where it anchored on 8 April 1606. Its inhabitants named the islands as Taumako. They were charted by Quirós as Nuestra Señora del Socorro (Our Lady of Succour in Spanish).
The Duff Islands were named after missionary ship Duff, captained by James Wilson, which reached them in 1797.
1798 Laperouse & Mourelle Antique Early Map of Queensland, PNG, Fiji etc in 1781
Antique Map
- Title : Carte D Une Partie Du Grand Ocean a l E. et S.E. de la Nouvelle Guinee pour l intelligence du Voyage de la Fregate Espagnole la Princesa commandee par D. Franco. Antonio Maurelle. en 1781..... Published as the (act) directs Novr. 1st 1798, by G.G. & J. Robinson
- Ref #: 31555
- Size: 16 3/4in x 11in (425mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1798
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique early map of Queensland, New Guinea, Fiji, French Polynesia & other South Pacific Islands - tracking the voyages of Francisco Antonio Mourelle in the region in 1781 was engraved in 1798 - dated - and was published in the 1st English edition of the Atlas du voyage de La Perouse G.G & J. Robinson, London in 1799.
La Perouse set sail from France in 1785 to continue the discoveries of Captain Cook. He was shipwrecked in 1788 but his narrative, maps, and views survived and were first published in 1797.
Interesting chart of Eastern Australia and part of the south-western Pacific, showing the routes taken by the Spanish explorer Don Francisco Antonio Maurelle in 1781 along the northern coast of New Guinea and across the Pacific to Fiji and Tonga, including a maunscript grid added in a contemporary hand.
Maurelle was credited with the discovery of the Hermit Islands on this voyage. The map includes the north-eastern coast of Australia, and parts of the coast of New Guinea. The map shows the 1781 route of his ship The Princesa through the Bismarck Archipelago north of New Guinea, through the Archipel de Salomos [i.e. Solomon Islands] and then east across the Pacific to the Iles de Amis [i.e. the Friendly Islands, now Tonga] where he discovered I. Vavao [ i.e. Vavau] with one of the best anchorages in the South Pacific.
The map includes the Iles de Navigateurs [i.e. Samoa], I. Fidji [i.e. Fiji], Iles de Esprit [i.e. Vanuatu or the New Hebrides Isles], and Nouvelle Caledonie [i.e. New Caledonia]. Many small islands are depicted with notes regarding their sightings by Abel Tasman, William Bligh and Maurelle.
A note on the chart states that the publisher has placed the islands according to the longitude of other navigators, rather than on Maurelles figures which were considered estimates only, and also, that Maurelles chart was based on a French chart by Jacques Nicolas Bellin published in 1742.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 3/4in x 11in (425mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mourelle de la Rúa, Francisco Antonio 1750 – 1820
Mourelle was a Galician naval officer and explorer serving the Spanish crown. He was born in 1750 at San Adrián de Corme (Corme Aldea, Ponteceso), near La Coruña, Galicia
1775 voyage Mourelle served the Spanish navy in the Guyanas, Trinidad, and the Antilles before becoming stationed at New Spain\'s Pacific Ocean naval base at San Blas, Mexico in 1774. He joined the 1775 expedition of Bruno de Heceta and Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra, serving as Quadra\'s pilot on the schooner Sonora. On July 29, at around 49 degrees north latitude, the Sonora became separated from Heceta\'s ship Santiago. Heceta soon returned south while Quadra and Mourelle continued north, eventually reaching 58 degrees 30 minutes north latitude. They found and anchored in Bucareli Bay. Then they sailed south, arriving at Monterey, California, on October 7, and San Blas on November 20, 1775.
Mourelle\'s journal was somehow taken clandestinely to London where it was translated and published. Captain James Cook made use of the information in Mourelle\'s journal during his travels in the Pacific Northwest.
1779 voyage Mourelle again served as the pilot of Quadra, and second in command of the ship Favorita, during the 1779 expedition commanded by Ignacio de Arteaga. Leaving San Blas on February 11, 1779, the expedition reached 61 degrees north and Hinchinbrook Island at the head of the Gulf of Alaska. From there they sailed southwest along the Kenai Peninsula. The ships returned to San Blas on November 21, 1779.
Later career During his service at San Blas, Mourelle traveled extensively throughout the Pacific Ocean. From 1781 on the La Princessa, he attempted to find a southern route from the Philippines to Mexico, mapping 29 of the 50 islands in the Hermit Islands, Ninigo Islands and Tench Island in New Guinea, and Ontong Java in the Solomon Islands . He visited Tonga and travelled through the Ellice Islands (now Tuvalu). Keith S. Chambers and Doug Munro (1980) identify Niutao as the island that Mourelle named on May 5, 1781, thus solving what Europeans had called The Mystery of Gran Cocal. Due to contrary winds, he returned via Guam and took the northern route across the Pacific to Mexico. He was also familiar with the Philippines and Canton, China.
Mourelle was to command the Mexicana for a 1792 voyage to explore the Strait of Georgia but Alessandro Malaspina had one of his own officers, Cayetano Valdés, placed in command of the Mexicana. Dionisio Alcalá Galiano commanded the Sutil, the twin companion of the Mexicana.
Mourelle was transferred to Spain in 1793. He was promoted to frigate captain in the same year as the Action of 19 January 1799 where he took a leading role. He became ship\'s captain in 1806, and commodore in 1811. He commanded a squadron in 1818 that was to put down a rebellion in the Rio de la Plata, but the endeavor never got underway. Mourelle died on May 24, 1820, at the age of 64.
1827 Dumont D Urville Large Antique Early Map of New Zealand
Antique Map
- Title : Carte Generale de la Partie De La Nouvelle Zelande Reconnue par le Capitaine de Fregate Dumont D Urville Dressee par Mr Loottin Enseigue de v au Expedition de la Corvette de S M L Astrolobe Janvier, Fevrier, Mars, 1827
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1827
- Ref #: 42011
Description:
This magnificent large original & scarce copper-plate engraved antique map of the North Island & part of the South Island of New Zealand by Dumont D Urville and Lieutenant Victor Lottin, aboard the ship The Astrolabe during the first D Urville voyage to the South Seas 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Alphonse Chassant, 1808-1907 and published in the 1836 edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Fantastic & rare map by D Urville & Lottin with surveys made of the north, south east coasts of New Zealands North Island & the north west part of the South Island, between January and March 1827.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
On 25 April 1826, Dumont d Urville, with the rank of commander, sailed from Toulon as chief of the ship formerly named the Coquille, renamed Astrolabe, on a voyage of exploration and scientific inquiry which lasted till 24 March 1829. On 10 January 1827 the Astrolabe came in sight of the north-west coast of the South Island of New Zealand. On 14 January the ship passed the entrance to the modern Golden Bay, which had been visited by Abel Tasman. The ship anchored off the west side of Tasman Bay. This bay had not been investigated at close quarters previously. In the following days d Urville established that it was a great deal bigger than Cooks mapping indicated, and his officers surveyed and charted it. Adele Island, Pepin Island, and Croisilles Harbour are modern names derived from those given by d Urville. On 23 January d Urville made for a channel which he had noticed at a distance some time before, and which seemed to him to communicate between Tasman Bay and Cooks Admiralty Bay. This was the channel culminating in French Pass and dividing D Urville Island from the mainland. Victor Lottin and Gressien, two of d Urville\'s officers, on the same day saw the pass at close quarters from two of the ships boats. On 25 January d Urville went through the pass into Admiralty Bay in a ship\'s boat. On 28 January the Astrolabe made the hazardous passage into Admiralty Bay. The investigation of Tasman Bay and the discovery of French Pass and the insularity of D Urville Island were significant contributions by d Urville to the discovery of New Zealands coastline.
From Cook Strait d Urville went north along the coast to Whangarei Harbour, which was surveyed and charted on 21–23 February 1827. The Astrolabe then doubled back to Hauraki Gulf, passing between the main coastal islands on the west side of the gulf on 25–27 February. The Astrolabe had been preceded in this passage by the Prince Regent in 1820, but the surveys and charts made under d Urville\'s command were notable contributions to the cartography of New Zealands coast. Lottin crossed the isthmus on 26 February and made a survey of Manukau Harbour, discovered in 1820 by Samuel Marsden. From Hauraki Gulf d Urville proceeded to North Cape and then to the Bay of Islands, leaving New Zealand in March 1827.
Lottin, Victor Charles 1795 - 1858. Lottin was a French frigate captain and geographer who took part in the voyage made around the world by the Astrolabe, under the command of Dumont-d Urville. He served as a lieutenant on the research expedition to Iceland and Greenland. During these two excursions, Lottin drew several maps and gathered a large quantity of objects of natural history, and made mention of the aurora borealis, inserted in the Annales Maritimes (1839). He was a member of the Academy of Sciences, Section of Geography and Navigation (elected in 1852) and a Knight of the Legion of Honour.
He died at Versailles on 18 February 1858.
1827 Dumont D Urville Large Antique Map The Island of Tongatapu Tonga, Astrolabe
- Title : Plan de L Isle Tonga-Tabou Leve et dresse par M.E. Paris, Enseigne de Vaisseau Expedition de la Corvette de S M L Astrolobe Avril et Mai, 1827
- Size: 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (675mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1827
- Ref #: 32157
Description:
This magnificent large original & scarce lithograph antique map of the largest island in the Tonga Isalnd group, Tongatapu, by Dumont D Urville and Lieutenant Victor Lottin, aboard the ship The Astrolabe during the first D Urville voyage to the South Seas 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Alphonse Chassant, 1808-1907 and published in the 1836 edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (675mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (675mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Centerfold re-joined, left side of image re-joined, no loss
Verso: - Repairs as noted above
Background:
This map illustrates the route taken by the ship The Astrolabe and Dumont D Urville & crew after leaving New Zealand in March 1827. D Urville extensively surveyed Tongatapu and nearby island between April & May 1827.
1831 SDUK Antique Gnomonic Map of Western Australia & The Indian Ocean, SE Asia
- Title : Published by Baldwin & Craddock...June 1831
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1831
- Ref #: 32534
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique Gnomonic Map of Western Australia & The Indian Ocean was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1831 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
A gnomonic map projection displays all great circles as straight lines, resulting in any line segment on a gnomonic map showing a geodesic, the shortest route between the segment\'s two endpoints. This is achieved by casting surface points of the sphere onto a tangent plane, each landing where a ray from the center of the sphere passes through the point on the surface and then on to the plane. No distortion occurs at the tangent point, but distortion increases rapidly away from it. Less than half of the sphere can be projected onto a finite map. Consequently a rectilinear photographic lens cannot image more than 180 degrees.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Blind Library stamp
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1836 D Urville & Sainson Antique Print Men & Women of Vanikoro Isle, Solomon Is.
- Title : Vanikoro. Coiffures des habitans des deux sexes
- Size: 20 1/2in x 13 1/2in (520mm x 345mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1836
- Ref #: 31751
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of hair styles of the men & woman of the island of Vanikoro, part of the Solomon Islands in the south Pacific (and last resting place of the ill fated La Perouse expedition), by Louis Auguste de Sainson, artist on the Astrolabe, during the first of Dumont D Urvilles voyages to the South Seas, between 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Antoine Maurin 1793 - 1860 and published in the 1836 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Louis Auguste de Sainson, (1800-1848). Sainson was a French draftsman & artist who specialized in natural history and geography. He accompanied the expedition of the corvette L Astrolabe as a naturalist directed by Jules Dumont d\'Urville between 1826-1829.
He began his naval career in a secretarial position at the French Atlantic port of Rochefort, working there from 1825 till 1826. He then volunteered to join the Astrolabe as a draughtsman, after being recommended to the expedition by Quoy, one of the naturalists on the expedition, joining the ship at Toulon on 7 February 1826.
He was responsible for the bulk of the drawings produced during the expedition, with over 500 in three years. Many of his drawings paintings and prints now reside in Australian, New Zealand & French museums.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 13 1/2in (520mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 13 1/2in (520mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Vanikoro (sometimes wrongly named Vanikolo) is an island in the Santa Cruz group, located 118 kilometres to the Southeast of the main Santa Cruz group. It is part of the Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands.
The first sighting of Vanikoro by Europeans was in September 1595, by the second Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mendaña. It was sighted by Lorenzo Barreto, while in command of one of the smaller vessels on a voyage around the then Santa Cruz, which is today\'s Nendo Island.
The French explorer Jean-François de La Pérouse was stranded on Vanikoro after both his vessels, La Boussole and the Astrolabe, struck the then unknown reefs of the island in 1788. It is reported that some of the men were killed by the local inhabitants, while the surviving sailors built a smaller vessel and left the island, but were never seen again. Those that remained on the island died before search parties of Dumont D Urville arrived in 1826.
1836 D Urville & Sainson Antique Print of Vanikoro & Tikopia Islands, Solomon Isands
- Title : Tikopia et Vanikoro: Costumes des habitans de Vanikoro: Costumes des habitans de Tikopia
- Size: 19 1/2in x 13in (495mm x 330mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1836
- Ref #: 31735
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of the peoples of the island of Vanikoro & Tikopia, part of the Solomon Islands in the south Pacific (and last resting place of the ill fated La Perouse expedition), by Louis Auguste de Sainson, artist on the Astrolabe, during the first of Dumont D Urvilles voyages to the South Seas, between 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Antoine Maurin 1793 - 1860 and published in the 1836 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Louis Auguste de Sainson, (1800-1848). Sainson was a French draftsman & artist who specialized in natural history and geography. He accompanied the expedition of the corvette L Astrolabe as a naturalist directed by Jules Dumont d\'Urville between 1826-1829.
He began his naval career in a secretarial position at the French Atlantic port of Rochefort, working there from 1825 till 1826. He then volunteered to join the Astrolabe as a draughtsman, after being recommended to the expedition by Quoy, one of the naturalists on the expedition, joining the ship at Toulon on 7 February 1826.
He was responsible for the bulk of the drawings produced during the expedition, with over 500 in three years. Many of his drawings paintings and prints now reside in Australian, New Zealand & French museums.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 13in (495mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 13in (495mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Vanikoro (sometimes wrongly named Vanikolo) is an island in the Santa Cruz group, located 118 kilometres to the Southeast of the main Santa Cruz group. It is part of the Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands.
The first sighting of Vanikoro by Europeans was in September 1595, by the second Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mendaña. It was sighted by Lorenzo Barreto, while in command of one of the smaller vessels on a voyage around the then Santa Cruz, which is today\'s Nendo Island.
The French explorer Jean-François de La Pérouse was stranded on Vanikoro after both his vessels, La Boussole and the Astrolabe, struck the then unknown reefs of the island in 1788. It is reported that some of the men were killed by the local inhabitants, while the surviving sailors built a smaller vessel and left the island, but were never seen again. Those that remained on the island died before search parties of Dumont D Urville arrived in 1826.
Tikopia is a small high island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Solomon Islands of Melanesia, but is culturally Polynesian. The first Europeans arrived on 22 April 1606 as part of the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernandes de Queirós.
In 1964, explorers found artefacts from the shipwreck of the expedition of Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse.
1836 Dumont D Urville Large Antique Print Monument to La Perouse Solomon Islands
- Title : Inauguration du Monument
- Size: 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1836
- Ref #: 31734-1
Description:
This large original antique lithograph print of Dumont D Urville Inauguration of a monument to Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse on the island of Vanikoro, part of the Solomon Islands in the south Pacific (the last resting place of La Perouse & his crew), by Louis Auguste de Sainson, the artist on the Astrolabe, during the first of Dumont D Urvilles first voyage to the South Seas between 1826 - 1829, was engraved by Antoine Maurin 1793 - 1860 and published in the 1836 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage de la corvette L Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829......
Louis Auguste de Sainson, (1800-1848). Sainson was a French draftsman & artist who specialized in natural history and geography. He accompanied the expedition of the corvette L Astrolabe as a naturalist directed by Jules Dumont d\\\'Urville between 1826-1829.
He began his naval career in a secretarial position at the French Atlantic port of Rochefort, working there from 1825 till 1826. He then volunteered to join the Astrolabe as a draughtsman, after being recommended to the expedition by Quoy, one of the naturalists on the expedition, joining the ship at Toulon on 7 February 1826.
He was responsible for the bulk of the drawings produced during the expedition, with over 500 in three years. Many of his drawings paintings and prints now reside in Australian, New Zealand & French museums.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (495mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Re-join to bottom margin
Plate area: - 9in & 2in re-join to bottom to centre of image
Verso: - Repair as noted, light spotting
Background:
Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse (1741 – 1788) was a French Naval officer and explorer whose expedition vanished in Oceania.
Lapérouse was appointed in 1785 by Louis XVI and by the Secretary of State of the Navy, the Marquis de Castries, to lead an expedition around the world. Many countries were initiating voyages of scientific explorations at that time.
The expeditions aims were to complete the Pacific discoveries of James Cook (whom Lapérouse greatly admired), correct and complete maps of the area, establish trade contacts, open new maritime routes and enrich French science and scientific collections. His ships were LAstrolabe (under Fleuriot de Langle) and La Boussole, both 500 tons. They were storeships reclassified as frigates for the occasion. Their objectives were geographic, scientific, ethnological, economic (looking for opportunities for whaling or fur trading), and political (the eventual establishment of French bases or colonial cooperation with their Spanish allies in the Philippines). They were to explore both the north and south Pacific, including the coasts of the Far East and of Australia, and send back reports through existing European outposts in the Pacific.
La Perouse visited Australia, arriving off Botany Bay on 24 January 1788. There Lapérouse encountered a British convoy (known later as the First Fleet) led by Captain Arthur Phillip RN, who was to establish the penal colony of New South Wales. While it had been intended that the colony would be located at Botany Bay, Phillip had quickly decided that the site was unsuitable and the colony would instead be established at Sydney Cove in Port Jackson. High winds – which had hindered Lapérouses ships in entering Botany Bay – delayed the relocation until 26 January (later commemorated as Australia Day).
The French were received courteously and spent six weeks at the British colony (their last recorded landfall). While Lapérouse and Phillip did not meet, French and British officers visited each other formally on at least 11 occasions, and offered each other assistance and supplies. During their stay, the French established an observatory and a garden, held masses, and made geological observations. Lapérouse also took the opportunity to send journals, charts and letters back to Europe, with the British merchant ship Alexander. The chaplain from L Astrolabe, Father Louis Receveur, never recovered from injuries he had sustained in a clash with indigenous people in the Samoan Islands and died at Botany Bay on 17 February; Receveur was buried on shore at Frenchmans Cove.
On 10 March, after taking on sufficient wood and fresh water, the French expedition left New South Wales – bound for New Caledonia, Santa Cruz, the Solomons, the Louisiades, and the western and southern coasts of Australia. While Lapérouse had reported in a letter from Port Jackson that he expected to be back in France by June 1789, neither he nor any members of his expedition were seen again by Europeans.
1840 SDUK Antique Gnomonic Map East Australia, New Zealand South Pacific
- Title : Published by the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 24676-1
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique Gnomonic Map of eastern Australia, New Zealand & The South Pacific was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
A gnomonic map projection displays all great circles as straight lines, resulting in any line segment on a gnomonic map showing a geodesic, the shortest route between the segment\'s two endpoints. This is achieved by casting surface points of the sphere onto a tangent plane, each landing where a ray from the center of the sphere passes through the point on the surface and then on to the plane. No distortion occurs at the tangent point, but distortion increases rapidly away from it. Less than half of the sphere can be projected onto a finite map. Consequently a rectilinear photographic lens cannot image more than 180 degrees.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Gnomonic Map East Australia, New Zealand South Pacific
- Title : Published by the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0974
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique Gnomonic Map of eastern Australia, New Zealand & The South Pacific was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
A gnomonic map projection displays all great circles as straight lines, resulting in any line segment on a gnomonic map showing a geodesic, the shortest route between the segment\'s two endpoints. This is achieved by casting surface points of the sphere onto a tangent plane, each landing where a ray from the center of the sphere passes through the point on the surface and then on to the plane. No distortion occurs at the tangent point, but distortion increases rapidly away from it. Less than half of the sphere can be projected onto a finite map. Consequently a rectilinear photographic lens cannot image more than 180 degrees.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 24668
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0954-1
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0964
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 91362
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1840 SDUK Antique Map of The Pacific Ocean, North America, Japan, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : The Pacific Ocean.....Published by Chapman & Hall...May 15th 1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 31980
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of The Pacific Ocean from North America, Japan, Australia & New Zealand was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1842 D Urville & Goupil Antique Print of Men of Santa Isabel Isle, Solomon Isle.
- Title : Naturels D Isabelle (Isle Solomon)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31745
Description:
This magnificent, large original antique lithograph print of profiles of 4 different men of the island of Santa Isabel of the Solomon Islands, visited in November & December 1838 by Dumont D Urville, drawn by Ernest Goupil, artist/draftsman aboard the Astrolabe during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayoti and was published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Ernest Goupil was a French painter, draftsman and watercolourist He is known for the illustrations made as official painter for Dumont D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas. In Voyage to the South Pole and in Oceania on corvettes l\'Astrobale and Zélée, executed by order of the king during the years 1837-1838-1839-1840, his drawings are transposed on stone, most notably by Emile Lassalle , Pharamond Blanchard and Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot . Dumont d\'Urville relates: On the Zélée , Mr. Goupil fills his cartons with precious paintings, and on the Astrolabe , the young surgeon Le Breton, who has a remarkable talent in this genre, also performs at my asks for charming drawings.
Some drawings were sent to the Minister of the Navy and were shown to the King, who wanted to see them transposed into painting by the marine painter Théodore Gudin , but Goupil would not have given his consent.
In August 1839 in Samarang Java , the crew is struck by a violent epidemic, and after two months of suffering, Ernest Goupil succumbs and died on January 1 , 1840 ijn Hobart-town where he was buried with full military honours.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (530mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (530mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Santa Isabel Island (also known as Isabel, Ysabel and Mahaga) is the longest in the Solomon Islands, the third largest in terms of surface area, and the largest in the group of islands in Isabel Province.
The first European contact to the Solomon Islands was made at Santa Isabel Island, by the Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña on 7 February 1568. It was charted as Santa Isabel de la Estrella (St. Elizabeth of the Star of Bethlehem in Spanish). A settlement was established by the Spaniards, and a small boat (known in the accounts as the brigantine) was built to survey and chart the surrounding sea and islands. These local explorations led by Maestre de Campo Pedro Ortega Valencia and Alférez Hernando Enríquez resulted in the discoveries of the islands of Malaita, Guadalcanal, Savo, Vangunu, Choiseul, Makira, Ulawa, Malaupaina, Malaulalo, Ali\'ite, and Ugi Island. The Spanish immediately came into contact with Solomon Islanders and at first the relationship was cordial. However, the Spanish expedition\'s need for fresh food and water quickly led to tension and conflict, the Solomon Islanders’ subsistence economy being unable to provide continuous supplies to the Spanish.
Having found no gold and little food, and beset by attacks and sickness, the Spanish colonists shifted their colony to the site of today\'s Honiara on Guadalcanal, and the settlement on Santa Isabel was abandoned.
Santa Isabel islanders suffered attacks from blackbirding in the nineteenth century (the often brutal recruitment or kidnapping of labourers for the sugar plantations in Queensland and Fiji).
In April 1885 a German Protectorate was declared over the North Solomon Islands, including Santa Isabel Island. In 1900, under the terms of Treaty of Berlin (14 November 1899), Germany transferred the North Solomon Islands (except for Bougainville and its surrounding islands) to the British Solomon Islands Protectorate in exchange for the British giving up all claims to Samoa. Missionaries settled on Santa Isabel Island under both protectorates, converting most of the population to Christianity. In the early 20th century several British and Australian firms began large-scale coconut planting.