PRC Publishing
1950 Large Antique Map of the PR China - Ist Map by PRC after Revolution 1949 Rare
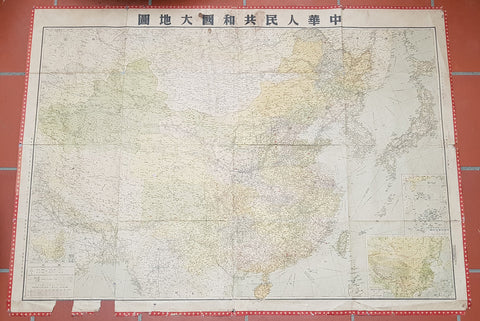
- Title : The Great Land and The People of China (Translated)
- Date : 1950
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Ref: 93112
- Size: 58 1/2in x 42 1/2in (1.485m x 1.080m)
Description:
This original extremely large very rare folding antique lithograph wall map of the Peoples Republic of China and surrounding countries was published by the Peoples Republic of China in 1950.
Considering the Chinese Communist State was established after the revolution of 1949, this map is one of the earliest, if not the earliest, available map of China released by the communist state and given the secretive nature of the PRC in the 1950s the rarity of this map cannot be overstated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 58 1/2in x 42 1/2in (1.485m x 1.080m)
Plate size: - 58 1/2in x 42 1/2in (1.485m x 1.080m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Loss to bottom sections of margins
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced on verso with archival tape
Background:
Following the Chinese Civil War and victory of Mao Zedongs Communist forces over the Kuomintang forces of Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek, who fled to Taiwan, Mao declared the founding of the Peoples Republic of China on October 1, 1949. Maos first goal was a total overhaul of the land ownership system, and extensive land reforms. Chinas old system of gentry landlord ownership of farmland and tenant peasants was replaced with a distribution system in favor of poor/landless peasants which significantly reduced economic inequality. Over a million landlords were executed. In Zhangzhuangcun, in the more thoroughly reformed north of the country, most landlords and rich peasants had lost all their land and often their lives or had fled. All formerly landless workers had received land, which eliminated this category altogether. As a result, middling peasants, who now accounted for 90 percent of the village population, owned 90.8 percent of the land. Mao laid heavy theoretical emphasis on class struggle, and in 1953 began various campaigns to persecute former landlords and merchants, including the execution of more powerful landlords. Drug trafficking in the country as well as foreign investment were largely wiped out.
Mao believed that socialism would eventually triumph over all other ideologies, and following the First Five-Year Plan based on a Soviet-style centrally controlled economy, Mao took on the ambitious project of the Great Leap Forward in 1958, beginning an unprecedented process of collectivization in rural areas. Mao urged the use of communally organized iron smelters to increase steel production, pulling workers off of agricultural labor to the point that large amounts of crops rotted unharvested. Mao decided to continue to advocate these smelters despite a visit to a factory steel mill which proved to him that high quality steel could only be produced in a factory. He thought that ending the program would dampen peasant enthusiasm for his political mobilization, the Great Leap Forward.
The implementation of Maoist thought in China may have been responsible for 40–70 million deaths including famine during peacetime, with the Great Leap Forward, Anti-Rightist Campaign of 1957–1958, and the Cultural Revolution. Millions died from both executions and forced labour. Because of Maos land reforms during the Great Leap Forward, which resulted in massive famines, thirty million perished between 1958 and 1961. By the end of 1961 the birth rate was nearly cut in half because of malnutrition. Active campaigns, including party purges and reeducation resulted in the imprisonment or execution of those deemed to hold views contrary to Maoist ideals. Maos failure with the Leap reduced his power in government, whose administrative duties fell to Liu Shaoqi and Deng Xiaoping.
To impose socialist orthodoxy and rid China of old elements, and at the same time serving certain political goals, Mao began the Cultural Revolution in May 1966. The campaign was far reaching into all aspects of Chinese life. Red Guards terrorized the streets as many ordinary citizens were deemed counter-revolutionaries. Education and public transportation came to a nearly complete halt. Daily life involved shouting slogans and reciting Mao quotations. Many prominent political leaders, including Liu and Deng, were purged and deemed capitalist-roaders. The campaign would not come to a complete end until the death of Mao in 1976.
Publishing in the Peoples Republic of China
Publishing in China dates from the invention of woodblock printing around the eighth century A.D. and was greatly expanded with the invention of movable clay type in the eleventh century. From the tenth to the twelfth century, Kaifeng, Meishan, Hangzhou, and Jianyang were major printing centers. In the nineteenth century, China acquired movable lead type and photogravure printing plates and entered the age of modern book and magazine printing. The largest of the early publishing houses were the Commercial Press (Shangwu Yinshuguan), established in 1897, and the China Publishing House (Zhonghua Shuju), established in 1912, both of which were still operating in 1987. Following the May Fourth Movement of 1919, publishers, especially those associated with various groups of intellectuals, proliferated. During the Chinese civil war, New China Booksellers (Xinhua Shudian) published a large amount of Marxist literature and educational materials in the communist-controlled areas. On the eve of the establishment of the People\\\'s Republic in 1949, there were over 700 New China Booksellers offices.
Between 1949 and 1952, the New China Booksellers offices scattered throughout the country were nationalized and given responsibility publishing, printing, and distribution. Also, several small private publishers were brought under joint stateprivate ownership, and by 1956 all private publishers had been nationalized. After a brief flourishing during the Hundred Flowers Campaign of 1956-57, the publishing industry came under strong political pressure in the Anti-Rightist Campaign of 1957. The industry had not fully recovered from this campaign when it was plunged into the Cultural Revolution, a period in which publishing was severely curtailed and limited mainly to political tracts supporting various campaigns. Following the Cultural Revolution, publishing again flourished in unprecedented ways. In 1982 the China National Publishing Administration, the umbrella organization of Chinese publishers, was placed under the Ministry of Culture, but actual management of the industry was directed through four systems of administration: direct state administration; administration by committees or organizations of the State Council or the party Central Committee; armed forces administration; and administration by provinces, autonomous regions, or special municipalities.