John Bartholomew
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Australia
- Title : Australia...Gold Areas marked thus....
- Date : 1855
- Size: 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50227
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of Australia by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
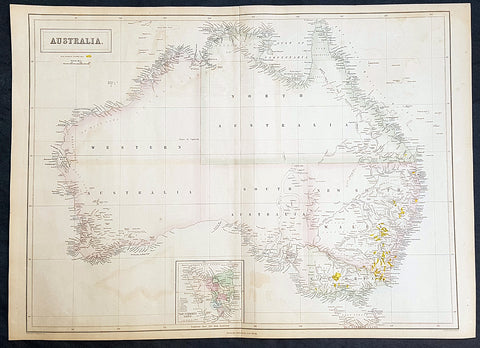
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Australia - 1st Gold Rush
- Title : Australia
- Size: 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1855
- Ref #: 93000
Description:
This large original steel-plate engraved rare antique map of Australia, with early Goldfields marked in yellow, by the famous Scottish cartographer John Bartholomew was published by A&C Black in 1855.
Rare large, highly detailed, antique Goldfields map of Australia, published prior to Queensland statehood in 1859 and during the first Australian gold rush of the 1850s.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 17in (595mm x 435mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.Jacques Nicholas Bellin
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of South Eastern Australia
- Title : Victoria. New South Wales and South Australia...Gold Deposits..
- Date : 1855
- Size: 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27097
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of South Eastern Australia by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Victoria, Australia
- Title : Victoria The Gold Districts are coloured (sic yellow)
- Date : 1855
- Size: 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27096
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of Victoria, Australia (with an inset map of the Mt Alexander & Castlemaine regions) by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
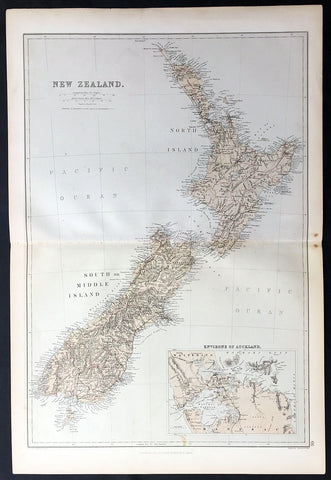
1870 Blackie & Son Large Antique Map of New Zealand w/ inset plan of Auckland
- Title : New Zealand
- Ref: 80571
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original antique map of New Zealand with an inset map of Auckland and its environs by John Bartholomew was published by Blackie & Son of Glasgow & London in the 1870 edition of the Geographical Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None