Henri Chatelain
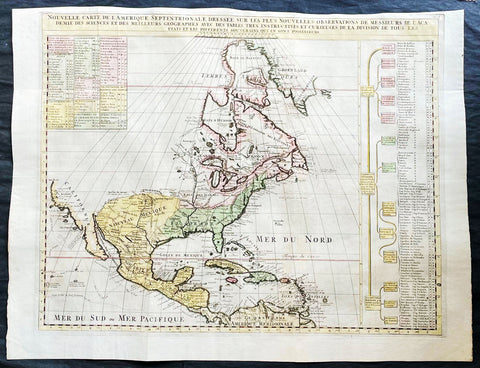
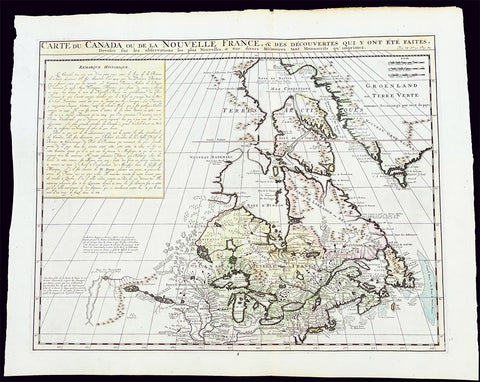
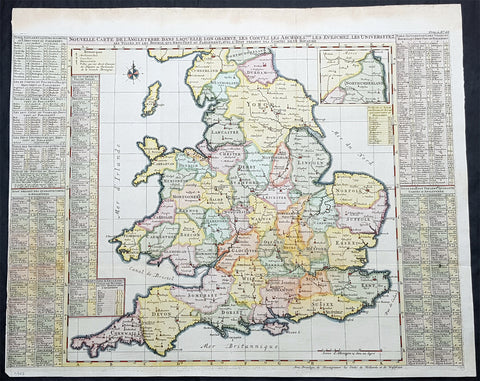
1718 Henri Chatelain & Claude Delisle Large Antique Map of North America
- Title : Nouvelle carte de l'Amerique Septentrionale dressée sur les plus nouvelles observations de messieurs de l'Academie des Sciences et des meilleurs geographes
- Ref #: 27008
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 27in x 20 1/2in (685mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1720
- Price: $1499.00US
Description:
This original large hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of North America, with a index to the territorial claims of the three Europeans powers, England, France & Spain and the indigenous peoples of those regions was published by Henri Chatelain in the 1718 edition of Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction A l'Histoire, aÌ la Chronologie & aÌ la Geìographie Ancienne & Moderne
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, red, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 20 1/2in (685mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19in (610mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped close to plate mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
An attractive map of North America, based upon Claude De L Isle's highly influential map of North America published in 1700, from Chatelain's monumental 7 volume Atlas Historique, published in Amsterdam.
California is a peninsula with a number of villages, mountains, and the Channel Islands shown. Mississippi extends far north of its true source. Large Florida and downplayed English colonies.
This fine map is a wonderful example from Chatelain's important text. By combining a wealth of information and geographical observation, with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition, this elegant map is a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
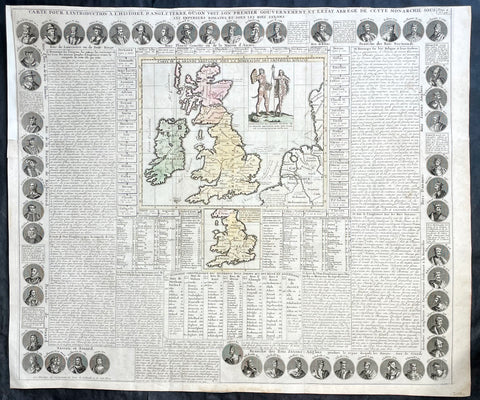
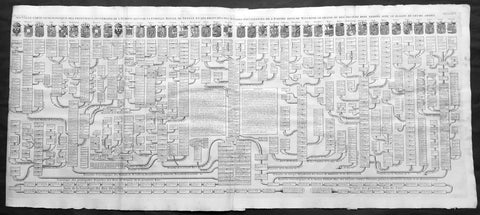
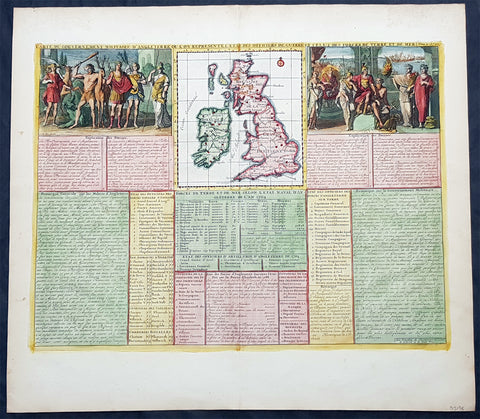
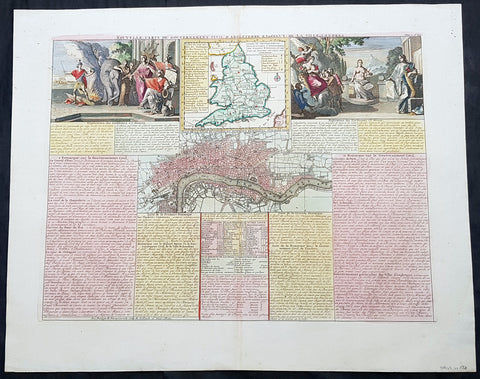
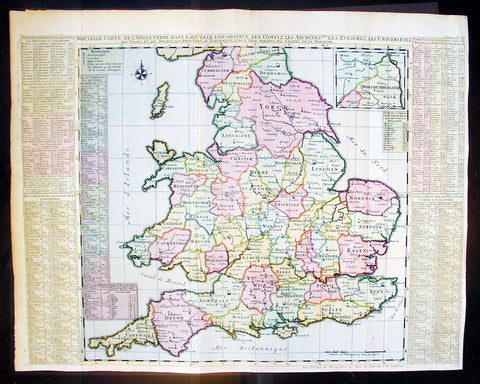
1719 Chatelain Antique Map Great Britain & Ireland Royalty Egbert to Queen Anne
- Title : Carte Pour L Introduction a L Historire S Angleteerre...
- Date : 1719
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93426
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map and illustration of Great Britain and Ireland, with text and pictorial representations of all the Kings and Queens from Egbert in 801 to Queen Anne in 1701, was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top left margin extended
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
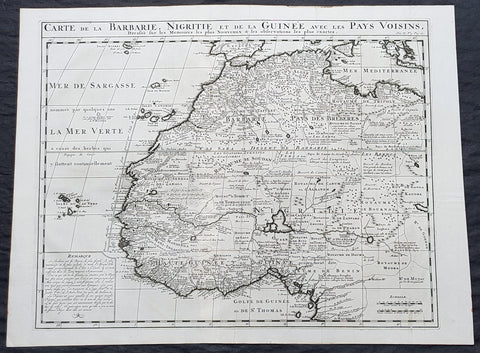
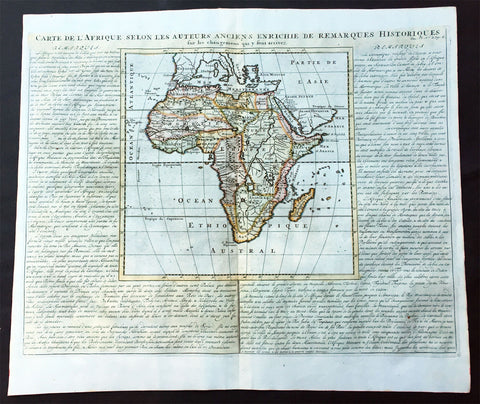
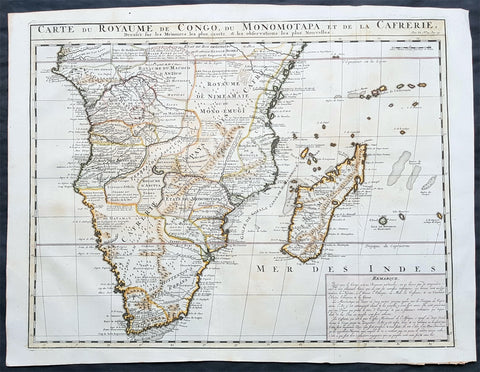
1719 Chatelain Antique Map of North & Western Africa from Barbary Coast to Benin
- Title : Carte de la Barbarie, Nigritie et de la Guinee avec les Pays Visins..
- Size: 23 1/2in x 17 1/2in (600mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50626
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map of North & Western Africa from the Barbary coast to Benin was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
These are truly some of the best early engravings of this region done at the time that were copied by the likes of Prevost, Harrison & others in the 18th century, but not with the same eye for detail.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 17 1/2in (600mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 15in (580mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\\\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\\\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (M&B; Tooley)
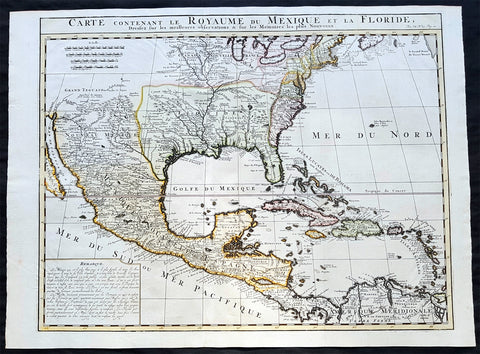
1719 Chatelain Antique Map of North America, GOM, Caribbean, United States
- Title : Carte Contenant Le Royaume Du Mexique Et La Floride
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50621
- Size: 23 1/4in x 17 1/2in (590m x 445m)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique foundation map of North America and the Caribbean - after Delisle landmark map of 1703 - was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Background:
A very attractive example of Chatelain's issue of Guillaume De L'Isle's foundation map of present-day United States, Central America and the West Indies, originally published in 1703. Guillaume De L'Isle brought a new scientific approach to mapmaking at the end of the seventeenth century and his rigorously prepared maps of all areas became the standards for much of the following century.
Amongst his most important works were those relating to the New World, especially North America, where the recent reports of French travellers into the interior were utilised. Sources for this map - the first to show the lower reaches of the Mississippi accurately - included d'Iberville, Tonty and Le Sueur, Father Gravier, and Bienville (later to become Governor of the French colony of Louisiana). Evidence of the contemporary superiority of De L'Isle's maps lies in the numerous copies, published in Paris, Amsterdam, London and Germany, and the republishing of the original plate over many years. Geographically his maps were as correct, however, this map is also remarkable for De L'Isle's political boundaries which squeeze the English Colonies, on the east coast into a narrow strip, thus allocating the greater part of North America to France. Chatelain's map has a large panel of text describing Mexico and Florida at lower left.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/4in x 17 1/2in (590m x 445m)
Plate size: - 20 3/4in x 16 1/4in (530m x 415mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections: Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Antique Map of Panama, Flora & Fauna of Australia by William Dampier
- Title : Description de l Isthme de Darien Des Proprietez du Pais et de la Ville de Panama a la quelle on a joint une description curieuse des diverses plantes, oiseaux, poissons les plus rares qui se trouvent dans la Nouvelle Hollande
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50633
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map of Panama & Central America plus plants, animals and birds from Brazil, South America and Australia, as visited by William Dampier (1651 - 1715) in 1688, was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
These are truly some of the best early engravings of this region done at the time that were copied by the likes of Prevost, Harrison & others in the 18th century, but not with the same eye for detail.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1679, William Dampier joined the crew of the buccaneer Captain Bartholomew Sharp on the Spanish Main of Central America, twice visiting the Bay of Campeche, or Campeachy as it was then known, on the north coast of Mexico. This led to his first circumnavigation, during which he accompanied a raid across the Isthmus of Darién in Panama and took part in the capture of Spanish ships on the Pacific coast of that isthmus. The pirates then raided Spanish settlements in Peru before returning to the Caribbean.
Dampier made his way to Virginia, where in 1683 he was engaged by the privateer John Cooke. Cooke entered the Pacific via Cape Horn and spent a year raiding Spanish possessions in Peru, the Galápagos Islands, and Mexico. This expedition collected buccaneers and ships as it went along, at one time having a fleet of ten vessels. Cooke died in Mexico, and a new leader, Edward Davis, was elected captain by the crew.
Dampier transferred to the privateer Charles Swans ship, Cygnet, and on 31 March 1686 they set out across the Pacific to raid the East Indies, calling at Guam and Mindanao. Spanish witnesses saw the predominantly English crew as not only pirates and heretics but also cannibals. Leaving Swan and 36 others behind on Mindanao, the rest of the privateers sailed on to Manila, Poulo Condor, China, the Spice Islands, and New Holland. Contrary to Dampiers later claim that he had not actively participated in actual piratical attacks during this voyage, he was in fact selected in 1687 to command one of the Spanish ships captured by Cygnets crew off Manila.
On 5 January 1688, Cygnet anchored two miles from shore in 29 fathoms on the northwest coast of Australia, near King Sound. Dampier and his ship remained there until March 12, and while the ship was being careened Dampier made notes on the fauna and flora and the indigenous peoples he found there. Among his fellows were a significant number of Spanish sailors, most notably Alonso Ramírez, a native of San Juan, Puerto Rico Later that year, by agreement, Dampier and two shipmates were marooned on one of the Nicobar Islands. They obtained a small canoe which they modified after first capsizing and then, after surviving a great storm at sea, called at Acheen (Aceh) in Sumatra.
Dampier returned to England in 1691 via the Cape of Good Hope, penniless but in possession of his journals. He also had as a source of income a slave known as Prince Jeoly (or Giolo), from Miangas (now Indonesia), who became famous for his tattoos (or paintings as they were known at the time). Dampier exhibited Jeoly in London, thereby also generating publicity for a book based on his diaries.
1719 Chatelain Antique Map, Views & Plans of Peru & Lima South America
- Title : Carte Particuliere du Perou, Plan de la Ville de Lima, Description de Quelques Plantes, Animaux, &....
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50632
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map & views of Peru & NW South America with a city plan of Lima was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
These are truly some of the best early engravings of this region done at the time that were copied by the likes of Prevost, Harrison & others in the 18th century, but not with the same eye for detail.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Atahualpa (also Atahuallpa), the last Sapa Inca became emperor when he defeated and executed his older half-brother Huáscar in a civil war sparked by the death of their father, Inca Huayna Capac. In December 1532, a party of conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro defeated and captured the Inca Emperor Atahualpa in the Battle of Cajamarca. The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military conflicts, it was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory and colonization of the region known as the Viceroyalty of Peru with its capital at Lima, which became known as The City of Kings. The conquest of the Inca Empire led to spin-off campaigns throughout the viceroyalty as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin as in the case of Spanish efforts to quell Amerindian resistance. The last Inca resistance was suppressed when the Spaniards annihilated the Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba in 1572.
The indigenous population dramatically collapsed due to exploitation, socioeconomic change and epidemic diseases introduced by the Spanish. Viceroy Francisco de Toledo reorganized the country in the 1570s with gold and silver mining as its main economic activity and Amerindian forced labor as its primary workforce. With the discovery of the great silver and gold lodes at Potosí (present-day Bolivia) and Huancavelica, the viceroyalty flourished as an important provider of mineral resources. Peruvian bullion provided revenue for the Spanish Crown and fueled a complex trade network that extended as far as Europe and the Philippines. Because of lack of available work force, African slaves were added to the labor population. The expansion of a colonial administrative apparatus and bureaucracy paralleled the economic reorganization. With the conquest started the spread of Christianity in South America; most people were forcefully converted to Catholicism, taking only a generation to convert the population. They built churches in every city and replaced some of the Inca temples with churches, such as the Coricancha in the city of Cusco. The church employed the Inquisition, making use of torture to ensure that newly converted Catholics did not stray to other religions or beliefs. Peruvian Catholicism follows the syncretism found in many Latin American countries, in which religious native rituals have been integrated with Christian celebrations. In this endeavor, the church came to play an important role in the acculturation of the natives, drawing them into the cultural orbit of the Spanish settlers.
By the 18th century, declining silver production and economic diversification greatly diminished royal income. In response, the Crown enacted the Bourbon Reforms, a series of edicts that increased taxes and partitioned the Viceroyalty. The new laws provoked Túpac Amaru IIs rebellion and other revolts, all of which were suppressed. As a result of these and other changes, the Spaniards and their creole successors came to monopolize control over the land, seizing many of the best lands abandoned by the massive native depopulation. However, the Spanish did not resist the Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian. The Treaty of Tordesillas was rendered meaningless between 1580 and 1640 while Spain controlled Portugal. The need to ease communication and trade with Spain led to the split of the viceroyalty and the creation of new viceroyalties of New Granada and Rio de la Plata at the expense of the territories that formed the viceroyalty of Peru; this reduced the power, prominence and importance of Lima as the viceroyal capital and shifted the lucrative Andean trade to Buenos Aires and Bogotá, while the fall of the mining and textile production accelerated the progressive decay of the Viceroyalty of Peru.
Eventually, the viceroyalty would dissolve, as with much of the Spanish empire, when challenged by national independence movements at the beginning of the nineteenth century. These movements led to the formation of the majority of modern-day countries of South America in the territories that at one point or another had constituted the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest and colony brought a mix of cultures and ethnicities that did not exist before the Spanish conquered the Peruvian territory. Even though many of the Inca traditions were lost or diluted, new customs, traditions and knowledge were added, creating a rich mixed Peruvian culture. Two of the most important indigenous rebellions against the Spanish were that of Juan Santos Atahualpa in 1742, and Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II in 1780 around the highlands near Cuzco.
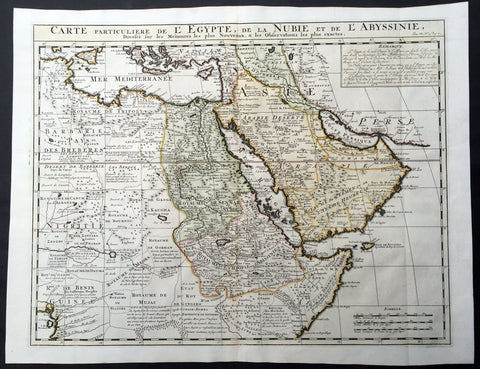
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Map of Barbary Coast, North Africa Morocco to Libya
- Title : Description Du Nil. Des Sources de son Cours Depuis Les Catactes....
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50651
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of views of the Pyramids, ruins and the Nile River, speculating on the source (not known until the mid 19th century) was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The river Nile has two major tributaries, the White Nile and Blue Nile. The White Nile is considered to be the headwaters and primary stream of the Nile itself. The Blue Nile, however, is the source of most of the water and silt. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, with the most distant source still undetermined but located in either Rwanda or Burundi. It flows north through Tanzania, Lake Victoria, Uganda and South Sudan. The Blue Nile begins at Lake Tana in Ethiopia and flows into Sudan from the southeast. The two rivers meet just north of the Sudanese capital of Khartoum.
Europeans began to learn about the origins of the Nile in the 14th century when the Pope sent monks as emissaries to Mongolia who passed India, the middle east and Africa, and described being told of the source of the Nile in Abyssinia (ancient European name for Ethiopia) Later in the 15th and 16th centuries, travelers to Ethiopia visited Lake Tana and the source of the Blue Nile in the mountains south of the lake. Although James Bruce claimed to be the first European to have visited the headwaters, modern writers give the credit to the Jesuit Pedro Páez. Páezs account of the source of the Nile is a long and vivid account of Ethiopia. It was published in full only in the early 20th century, although it was featured in works of Páezs contemporaries, including Baltazar Téllez, Athanasius Kircher and by Johann Michael Vansleb.
Europeans had been resident in Ethiopia since the late 15th century, and one of them may have visited the headwaters even earlier without leaving a written trace. The Portuguese João Bermudes published the first description of the Tis Issat Falls in his 1565 memoirs, compared them to the Nile Falls alluded to in Ciceros De Republica. Jerónimo Lobo describes the source of the Blue Nile, visiting shortly after Pedro Páez. Telles also used his account.
The White Nile was even less understood. The ancients mistakenly believed that the Niger River represented the upper reaches of the White Nile. For example, Pliny the Elder wrote that the Nile had its origins in a mountain of lower Mauretania, flowed above ground for many days distance, then went underground, reappeared as a large lake in the territories of the Masaesyli, then sank again below the desert to flow underground for a distance of 20 days journey till it reaches the nearest Ethiopians. A merchant named Diogenes reported that the Niles water attracted game such as buffalo.
Lake Victoria was first sighted by Europeans in 1858 when the British explorer John Hanning Speke reached its southern shore while traveling with Richard Francis Burton to explore central Africa and locate the great lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this vast expanse of open water for the first time, Speke named the lake after the then Queen of the United Kingdom. Burton, recovering from illness and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proved his discovery to be the true source of the Nile when Burton regarded this as still unsettled. A very public quarrel ensued, which sparked a great deal of intense debate within the scientific community and interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Spekes discovery. British explorer and missionary David Livingstone pushed too far west and entered the Congo River system instead. It was ultimately Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley who confirmed Spekes discovery, circumnavigating Lake Victoria and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the Lakes northern shore.
European involvement in Egypt goes back to the time of Napoleon. Laird Shipyard of Liverpool sent an iron steamer to the Nile in the 1830s. With the completion of the Suez Canal and the British takeover of Egypt in the 1870s, more British river steamers followed.
The Nile is the areas natural navigation channel, giving access to Khartoum and Sudan by steamer. The Siege of Khartoum was broken with purpose-built sternwheelers shipped from England and steamed up the river to retake the city. After this came regular steam navigation of the river. With British Forces in Egypt in the First World War and the inter-war years, river steamers provided both security and sightseeing to the Pyramids and Thebes. Steam navigation remained integral to the two countries as late as 1962. Sudan steamer traffic was a lifeline as few railways or roads were built in that country. Most paddle steamers have been retired to shorefront service, but modern diesel tourist boats remain on the river.
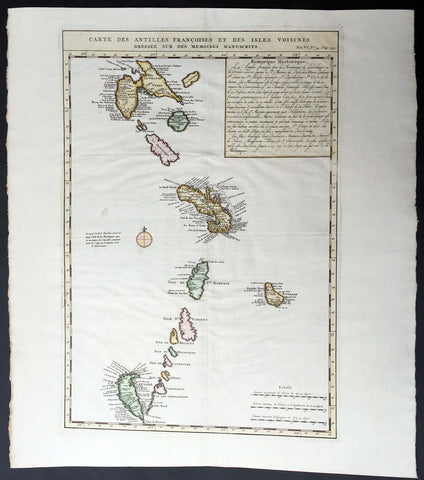
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Map of Caribbean Antilles Guadeloupe to Grenada
- Title : Carte des Antilles Francois Et Des Isles Voisines Dressee Sur Des Memoires Manuscrits
- Ref #: 50618
- Size: 21 1/2in x 19 1/4in (550m x 490m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Caribbean Antilles Islands from Guadeloupe south to the island of Grenada was published by Henri AbrahamChatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 19 1/4in (550m x 490m)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 13 1/2in (490m x 345mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Maps and Views of Mexico & Mexico City
- Title : Description, Situation & Vue De La Ville De Mexique, Des Deux Lacs
- Ref #: 50634
- Size: 20 3/4in x 17 1/2in (530m x 445m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
An exceptionally beautiful example of Abraham Chatelain's 1719 maps and views on Mexico.
This sheet combines two maps and four engraved views with extensive text describing the lands and customs of Mexico. The maps, appearing in the upper right and left quadrants detail central Mexico and Mexico City.
The first map located in the upper left, is centered on Mexico City and details from the Gulf of Mexico to the Pacific and from the Rio de Palmas to Acapulco. The second map, in the upper right, focuses more specifically on Mexico City, revealing the ancient Lake Texcoco, and the cultivated islands that once housed the great Aztec capital.
Between the two maps a large view depicts a typical Aztec temple complex. The lower views detail, from left, traditional Aztec dances with a Spanish galleon in the background, human sacrifice, and a general view of Mexico City combining European and Aztec architectural elements. The extensive surrounding text, in French, attempt to describe the customs, peoples, resources, and geography of Mexico
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 17 1/2in (530m x 445m)
Plate size: - 17in x 15in (435m x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
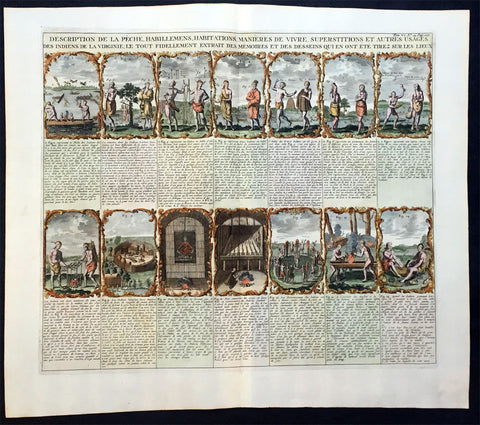
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print - 14 Views of Indians of Virginia
- Title : Description de la Peche, Habillemens, Habitations, Manieres de Vivre, Superstitions et Autres Usages des Indiens de la Virginie
- Date : 1719
- Ref # : 50636
- Size : 20in x 17 1/2in (510m x 440m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large hand coloured original antique print a decorative series of 14 views of the customs, clothing and daily lives of the Native Inhabitants of Virginia was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique. of the 16th Century.
These 14 views of native American life in Virginia - taken from Theodor de Bry's America, which are engraved from John White's drawings - includes the manner of dressing, fishing, hunting, making canoes, eating, cooking, living, worshipping, as well as burial practices and ceremonies. Each of the 14 scenes includes an explanation in French.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, orange, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510m x 450m)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 16 1/2in (440m x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print Famous Buffalo Beaver Sheet
- Title : Carte qui Contient la Maniere dont se fait la Chasse des Boeufs Sauvages
- Ref #: 50637
- Size: 20in x 17in (510m x 430m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This is the famous Beaver - Buffalo sheet from Volume Six of Chatelain's mammoth Atlas Historique. The sheet contains descriptions and illustrations of beavers and their industry, and of the canoes, dwellings, hunting, fishing, clothes, customs and writing of the Canadian Native Americans. The part of the text entitled Amors & mariages des sauvages details how the prospective groom would woo his bride, which is also illustrated. The large and pointy-toothed beaver is recognizable in later cartouches by Robert de Vaugondy, Santini and others.
This unique sheet also contains various engravings concerning Native American customs and indigenous animals in North America. Including a large engraving of an American buffalo and a grand view of Niagara Falls. At center is a table with engravings of various Indian activities, weapons and ceremonies. Most interesting are the engravings identified as the coat of arms of the Indian Nations.
Sheet contains extensive explanation in French text.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 17in (510m x 430m)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 15in (440m x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - 20cm repair to left side sheet, no loss
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print North Africa City Views Algiers, Jijel, Tripoli & Tunis
- Title : Vue de Tunis d'Alger & de Gigeri avec quelques particularitez curieuses touchant les moeurs de leur habitans & de quelques autres peuples de Barbarie
- Ref #: 50646
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print views of cities of The Barbary Coast of North Africa including Algiers and Jijel, both in Algeria, Tripoli in Libya and Tunis in Tunisia - as well as peoples & animals of the Barbary coast - was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print of 4 Various African Village Scenes
- Title : Description des Cases ou Habitations Des Negres, De Celle, Du RoiD Issiny & De ses Suites
- Ref : 50644
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique page with 4 views on showing different African village scenes with extensive text was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
These scenes were copied extensively throughout the 18th century in publications like Prevosts voyages.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print of Egypt Pyramids, & Source of the Nile River
- Title : Description Du Nil. Des Sources de son Cours Depuis Les Catactes....
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50651
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print of views of the Pyramids, ruins and the Nile River, speculating on the source (not known until the mid 19th century) was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The river Nile has two major tributaries, the White Nile and Blue Nile. The White Nile is considered to be the headwaters and primary stream of the Nile itself. The Blue Nile, however, is the source of most of the water and silt. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, with the most distant source still undetermined but located in either Rwanda or Burundi. It flows north through Tanzania, Lake Victoria, Uganda and South Sudan. The Blue Nile begins at Lake Tana in Ethiopia and flows into Sudan from the southeast. The two rivers meet just north of the Sudanese capital of Khartoum.
Europeans began to learn about the origins of the Nile in the 14th century when the Pope sent monks as emissaries to Mongolia who passed India, the middle east and Africa, and described being told of the source of the Nile in Abyssinia (ancient European name for Ethiopia) Later in the 15th and 16th centuries, travelers to Ethiopia visited Lake Tana and the source of the Blue Nile in the mountains south of the lake. Although James Bruce claimed to be the first European to have visited the headwaters, modern writers give the credit to the Jesuit Pedro Páez. Páezs account of the source of the Nile is a long and vivid account of Ethiopia. It was published in full only in the early 20th century, although it was featured in works of Páezs contemporaries, including Baltazar Téllez, Athanasius Kircher and by Johann Michael Vansleb.
Europeans had been resident in Ethiopia since the late 15th century, and one of them may have visited the headwaters even earlier without leaving a written trace. The Portuguese João Bermudes published the first description of the Tis Issat Falls in his 1565 memoirs, compared them to the Nile Falls alluded to in Ciceros De Republica. Jerónimo Lobo describes the source of the Blue Nile, visiting shortly after Pedro Páez. Telles also used his account.
The White Nile was even less understood. The ancients mistakenly believed that the Niger River represented the upper reaches of the White Nile. For example, Pliny the Elder wrote that the Nile had its origins in a mountain of lower Mauretania, flowed above ground for many days distance, then went underground, reappeared as a large lake in the territories of the Masaesyli, then sank again below the desert to flow underground for a distance of 20 days journey till it reaches the nearest Ethiopians. A merchant named Diogenes reported that the Niles water attracted game such as buffalo.
Lake Victoria was first sighted by Europeans in 1858 when the British explorer John Hanning Speke reached its southern shore while traveling with Richard Francis Burton to explore central Africa and locate the great lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this vast expanse of open water for the first time, Speke named the lake after the then Queen of the United Kingdom. Burton, recovering from illness and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proved his discovery to be the true source of the Nile when Burton regarded this as still unsettled. A very public quarrel ensued, which sparked a great deal of intense debate within the scientific community and interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Spekes discovery. British explorer and missionary David Livingstone pushed too far west and entered the Congo River system instead. It was ultimately Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley who confirmed Spekes discovery, circumnavigating Lake Victoria and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the Lakes northern shore.
European involvement in Egypt goes back to the time of Napoleon. Laird Shipyard of Liverpool sent an iron steamer to the Nile in the 1830s. With the completion of the Suez Canal and the British takeover of Egypt in the 1870s, more British river steamers followed.
The Nile is the areas natural navigation channel, giving access to Khartoum and Sudan by steamer. The Siege of Khartoum was broken with purpose-built sternwheelers shipped from England and steamed up the river to retake the city. After this came regular steam navigation of the river. With British Forces in Egypt in the First World War and the inter-war years, river steamers provided both security and sightseeing to the Pyramids and Thebes. Steam navigation remained integral to the two countries as late as 1962. Sudan steamer traffic was a lifeline as few railways or roads were built in that country. Most paddle steamers have been retired to shorefront service, but modern diesel tourist boats remain on the river.
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print of St Christopher Island, Antilles, Caribbean
- Title : Particularitez Curieuses De L'ile De St. Christopher et de la Province de Bemarin Dans Les Antilles
- Ref : 50630
- Size: 20in x 17in (510m x 430m)
- Date : 1719.
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique sheet with engraved illustrations to text on the West Indian Island of St Christopher was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
This large sheet from Volume Six of Chatelain's Atlas Historique , contains six engraved views of the Island of the main French settlement, local Indians, plantations, different types of birds, reptiles, fish and general wildlife.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17in (510m x 430m)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 15in (440m x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print of The Pyramids and Sphinx of Egypt
- Title : Description des Piramides D Egypte Tant au Dedans qu'au Dehors...
- Ref : 50648
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510m x 440m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique print including detailed French Text on the subject was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510m x 440m)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440m x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print of Various Mammals, Birds & Reptiles Elephant
- Title : Description des Quadrupeds, Oiseaux & reptiles les Plus Curieux qui se Trouvent dans la Guinee Dessinez sur les Lieux d Apres le Natural
- Ref : 50643
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique page illustrating the different mammals, birds & reptiles of Africa with extensive text was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
These scenes were copied extensively throughout the 18th century in publications like Prevosts voyages.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Repair to left side of print, no loss
Verso: - None
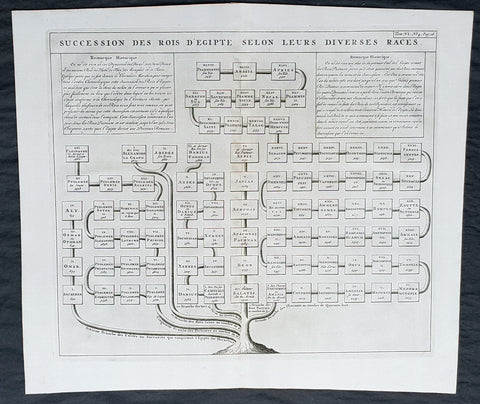
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print Succession of Egyptian Pharaohs from 1500BC
- Title : Succession Des Rois D Egipte Selon Leurs Diverses Races (Succession Of The Kings Of Egipte According To Their Various Races)
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50652-1
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print showing the known succession of Egyptian Kings going back to 1500BC was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The pharaohs were rulers of Ancient Egypt dating from the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt during the Early Dynastic Period by Narmer approximately 3100 BC. Although the specific term Pharaoh was not used by their contemporaries until the rule of Merneptah of the 19th dynasty, c. 1200 BC, the style of titulature of the rulers of Egypt remained relatively constant, initially featuring a Horus name, a Sedge and Bee (nswt-bjtj) name and a Two Ladies (nbtj) name, with the additional Golden Horus, nomen and prenomen titles being added successively during later dynasties.
Egypt remained continually governed by native pharaohs for approximately 2500 years until it was conquered by the Kingdom of Kush in 656 BC, whose rulers adopted the traditional pharaonic titulature for themselves. Following the Kushite conquest, Egypt would first see another period of independent native rule before being conquered by the Achaemenid Empire, whose rulers also adopted the title of Pharaoh. The last native Pharaoh of Egypt was Nectanebo II, who was Pharaoh before the Achaemenids conquered Egypt for a second time.
Achaemenid rule over Egypt came to an end through the conquests of Alexander the Great in 332 BC, after which it was ruled by the Hellenic Pharaohs of the Ptolemaic Dynasty. Their rule, and the independence of Egypt, came to an end when Egypt became a province of Rome in 30 BC. Augustus and subsequent Roman Emperors were styled as Pharaohs when in Egypt up until the reign of Maximinus Daia in 314 AD.
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print The Costumes of Jews & Arabs in Cairo, Egypt
- Title : Description des Piramides D Egypte Tant au Dedans qu'au Dehors...
- Ref : 50647
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510m x 440m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique print including detailed French Text on the subject was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510m x 440m)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440m x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print Views of Cairo, Egypt - Nile
- Title : Vue de la Ville Du Grand Caire et de ses Environs
- Ref #: 50650
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print of various views of Cairo and Environs was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (445mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Antique Print Views of Loango & Mbanza Loango, Congo Africa
- Title : Vue & Description de la Ville De Lovango dans la Royaume de Congo avec plu Sieurs....
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50641-1
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique print city of Mbanza Loango in the pre-colonial African Kingdom of Loango - now part of the of western part of the Republic of the Congo - with 10 vignettes of various peoples & views of Kingdom of Loango, Africa was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Kingdom of Loango was a pre-colonial African state, during approximately the 16th to 19th centuries in what is now the western part of the Republic of the Congo. Situated to the north of the more powerful Kingdom of Kongo, at its height in the 17th century Loango influence extended from Cape St Catherine in the north to almost the mouth of the Congo River.
Loango exported copper to the European market, and was a major producer and exporter of cloth.
The English traveller Andrew Battel, when he was there in about 1610, recorded that the predecessor of the unnamed king ruling at that time was named \\\"Gembe\\\" or Gymbe (modernized as Njimbe), possibly the founder of the kingdom. With the death of King Buatu in 1787, the succession of leadership is uncertain.
The kingdom is certain to have come to an end with the Conference of Berlin (1884–1885) at the latest, when European colonial powers divided most of Central Africa between them.
The origins of the kingdom are obscure. The most ancient complex society in the region was at Madingo Kayes, which was already a multi-site settlement in the first century CE. At present archaeological evidence is too scarce to say much more about developments until the late fifteenth or early sixteenth centuries.
Loango is not mentioned in early travelers\\\' accounts of the region, nor is it mentioned in the titles of King Afonso I of Kongo in 1535, though Kakongo, Vungu, and Ngoyo, its southern neighbors. It is therefore unlikely that there was a major power on the coast of Central Africa north of the Congo River.
The earliest reference to Loango in a documentary source is a mention around 1561 by Sebastião de Souto, a priest in Kongo, that King Diogo I (1545–61) sent missionaries to convert Loango to Christianity. Duarte Lopes, ambassador from Kongo to the Holy See in Rome in 1585, related that \\\"Loango is a friend of the King of Congo and it is said that he was a vassal in past times\\\" which is consistent with Loango\\\'s origins from Kakongo, a vassal of Kongo.
Dutch visitors recorded the first traditional account of the kingdom\\\'s origin in the 1630s or \\\'40s. In their account as reported by the geographer Olfert Dapper, the region where Loango would be constructed was populated by a number of small polities including Mayumba, Kilongo, Piri and Wansi, \\\"each with their own leader\\\" who \\\"made war on each other.\\\" He recorded that the founder of Loango, who boasted hailing from the district in Nzari in the small coastal kingdom of Kakongo, itself a vassal of Kongo, triumphed over all his rivals through the skillful use of alliances to defeat those who opposed him, particularly Wansa, Kilongo and Piri, the latter two of which required two wars to subdue. Once this had been effected, however, a range of more northern regions, including Docke and Sette submitted voluntarily. Having succeeded in the conquest, the new king moved northward and after having founded settlements in a variety of places, eventually built his capital in Buali in the province of Piri (from which the ethnic name \\\"Muvili\\\" eventually derived).
The English traveller Andrew Battel wrote when he was there in about 1610, that the predecessor of the unnamed king ruling at that time was named \\\"Gembe\\\" or \\\"Gymbe\\\" (modernized as \\\"Njimbe\\\"). A Dutch description published in 1625 said that a ruler who had died sometime before that date had ruled for 60 years and thus had taken the throne around 1565. The documentary chronology thus makes it very likely that Njimbe was the founder and first ruler mentioned in the traditions, and this supposition is supported by traditions recorded around 1890 by R. E. Dennett which also named Njimbe as the first ruler.
On the basis of later traditions from the nineteenth and twentieth centuries that linked the founding of Loango to that of Kongo, Phyllis Martin posited a much earlier foundation, the late fourteenth or early fifteenth centuries. She then argues that the absence of Loango from early titles of the king of Kongo is evidence that Loango was already independent at that time.
Njimbe had created a rule of succession which was in place around 1600, in which the king gave command over four provinces to members of his family, called the provinces of Kaye, Boke, Selage, and Kabango, and the king was to be chosen from a rotation between them. When the king died the ruler of Kaye took over, as he did indeed in the pre-1624 succession, and if the rule was followed then the ruler of Boke took his place; the other two provincial rulers advanced as well, and the king appointed a new ruler for Kabango.
In 1663, the king ruling then was baptized as Afonso by the Italian Capuchin priest Bernardo Ungaro, but there was considerable opposition to this from within the country, and indeed when he died, a non-Christian took over, but this one was himself overthrown by one of the Christian party in 1665. This civil war was still ongoing in the 1670s. In the aftermath of this civil war, a number of the Christian party fled to neighboring territories, one of whom, known to history as Miguel da Silva, was elected ruler of Ngoyo and was ruling there in 1682.
When Nathaniel Uring, an English merchant came to Loango to trade in 1701, he reported that the king had died and the power of the administration was in the hands of the \\\"Queen or Chief Governess of that Country,\\\" named \\\"Mucundy\\\" and with whom he had to deal as if with the ruler.[20] This title referred to a woman with a regular role in the administration as overseer of women\\\'s affairs.
Many years elapsed before we have another snapshot of Loango\\\'s government; during this time the rules of succession, whether formal or informal seem to have changed. When the French missionaries directed by Abbé Liévin-Bonaventure Proyart came to Loango in 1766, they noted that there was no clear succession to the throne, that anyone born of a person regarded as a princess (only female succession mattered) could aspire to the throne. Moreover, the death of a king was cause for a frequently long interregnum; the king ruling in 1766 had come to power only after an interregnum of seven years, during which time the affairs of the country were managed by a regent called Mani Boman. The Mani Boman was appointed by the king during his lifetime. Usually two were appointed to cover the eventuality of the death of one of the two. They, in turn received the petitions of a number of eligible candidates for the throne.
Eventually, the electors of the kingdom, who were those who held offices appointed by the late king, met to decide on the next king. In theory, as the old constitution maintained, the king named his successor as well and placed him as ruler of Kaye, to succeed him at his death, but as there was so much contention as to who should hold the position, the late king died without naming a Ma-Kaye.
Historian Phyllis Martin contends that the external trade of the country had enriched some members of the nobility ahead of others and had thus put pressure on the older constitution as wealthier upstart princes pressed their case forward. She argues that important members of the council were people who had obtained their positions through contact with external trade, particularly the slave trade, and they had come to share power with the king. She posits that this alteration in relative power allowed the council to dominate the king by forcing longer and longer interregna. In fact, after the death of King Buatu in 1787, no king was elected for over 100 years.However, to some extent royal authority remained in the hands of a person entitled the Nganga Mvumbi (priest of the corpse) who oversaw the body of the dead king awaiting burial. Several of these Nganga Mvumbi succeeded each other in the late eighteenth and through the nineteenth centuries.
1719 Chatelain Large Old, Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Carte De L Afrique Selon Les Auteurs Anciens Enrichie de Remarques Historiques
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50628
- Size: 20 3/4in x 17 1/2in (530m x 445m)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of antique map of Africa was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 17 1/2in (530m x 445m)
Plate size: - 11in x 11in (280m x 280mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Large Old, Antique Map of Saudi Arabia, Egypt, The Horn of Africa
- Title : Carte Particuliere De L Egypt De La Nubie et De Abyssinie
- Ref #: 50627
- Size: 22in x 17 1/2in (560m x 445m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Saudi Arabia, Egypt and The Horn of Africa was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famousAtlas Historique.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 17 1/2in (560m x 445m)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 16in (545m x 405mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain Original Antique Map of Southern Africa & Madagascar
- Title : Carte Du Royaume de Congo du Monomotapa et de la Cafrerie...
- Date : 1719
- Size: 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
- Ref #: 50625
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique 1719 map of central & southern Africa and the Island of Madagascar was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 17 1/2in (585mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (535mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Verso: - None
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1719 Chatelain Very Large Genealogy Chart of the Royal Families of Europe
-
Title : Nouvelle carte généalogique des principaux souverains de l'Europe issus de la famille ROYALE DE FRANCE et les branches des maisons souveraines de l'Europe issues de WITEKIND LE GRAND ou des anciens RO
(Translation...New genealogical map of the main rulers of Europe from the French Royal family and branches of sovereign houses from Europe)
- Ref #: 50688
- Size: 43 1/2in x 18 1/2in (1.09m x 470m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique genealogy chart of the Royal families of France and wider Europe was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
This very large chart illustrates the relationship between the French Royal families to also Denmark, Germany & German States, Prussia, Sweden and others.
Henri Abraham Chatelain (1684 - 1743)
was a Huguenot pastor of Parisian origins. He lived consecutively in Paris, St. Martins, London (c. 1710), the Hague (c. 1721) and Amsterdam (c. 1728).
Chatelain was a skilled artist and knew combining a wealth of historical and geographical information with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition. Groundbreaking for its time, this work included studies of geography, history, ethnology, heraldry, and cosmography. His maps with his elegant engraving are a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.The publishing firm of Chatelain, Chatelain Frères and Chatelain & Fils is recorded in Amsterdam, from around 1700-1770, with Zacharias living "op den Dam" in 1730.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, his father Zacharie Chatelain (d.1723) and Zacharie Junior (1690-1754), worked as a partnership publishing the Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction à L'Histoire under several different Chatelain imprints, depending on the Chatelain family partnerships at the time of publication. The atlas was published in seven volumes between 1705 and 1720, with a second edition appearing in 1732. The volumes I-IV with a Third edition and volume I with a final edition in 1739.
Henri Abraham Chatelain, whose "Atlas Historique" was one of the most expansive Dutch encyclopedias of the age. First published in 1705, Chatelain's Atlas Historique was part of an immense seven-volume encyclopedia. Although the main focus of the text was geography, the work also included a wealth of historical, political, and genealogical information. The text was compiled by Nicholas Gueudeville and Garillon with a supplement by H.P. de Limiers and the maps were engraved by Chatelain, primarily after charts by De L'Isle. The atlas was published in Amsterdam between 1705 and 1721 and was later reissued by Zacharie Chatelain between 1732 and 1739.
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "dernière edition, corrigée & augmentée."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the european countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celerated mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Châtelain, but Zacharie Châtelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.) (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 43 1/2in x 18 1/2in (1.09m x 470m)
Plate size: - 43in x 17in (1.07m x 435mm)
Margins: - min. 1/4in (2mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Right margin cropped to plate-mark, age toning to right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelain View of Cape Town, Table Top Mountain South Africa
- Title : Vue et Description Du Cap De Bonne Esperance
- Ref : 50640
- Size: 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (440mm x 265mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
An exceptional hand coloured original antique page of Abraham Chatelain's 1719 striking view of the Cape of Good Hope, with Dutch ships in the harbour and Table Mountain in the background.
Separating the two views is an engraved descriptive text which refers mainly to the Company’s gardens, ‘the most beautiful and curious to be seen in a country that is sterile and frightful.’
The lower engraving shows the Dutch fort at the Cape and an observatory established by the Frenchman Tachard and the Jesuit Fathers to observe the southern skies.
Background:
The first Europeans to discover the Cape were the Portuguese, with Bartholomeu Dias arriving in 1488 after journeying south along the west coast of Africa. The next recorded European sighting of the Cape was by Vasco da Gama in 1497 while he was searching for a route that would lead directly from Europe to Asia. Table Mountain was given its name in 1503 by António de Saldanha, a Portuguese admiral and explorer. He called it Taboa da caba ("table of the cape"). The name given to the mountain by the Khoi inhabitants was Hoeri 'kwaggo ("sea mountain")
The area fell out of regular contact with Europeans until 1652, when Jan van Riebeeck and other employees of the Dutch East India Company (Dutch: Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie, or simply VOC) were sent to the Cape to establish a halfway station to provide fresh water, vegetables, and meat for passing ships travelling to and from Asia. Van Riebeeck's party of three vessels landed at the cape on 6 April 1652. The group quickly erected shelters and laid out vegetable gardens and orchards, and are preserved in the Company Gardens. Water from the Fresh River, which descended from Table Mountain, was channelled into canals to provide irrigation. The settlers bartered with the native Khoisan for their sheep and cattle. Forests in Hout Bay and the southern and eastern flanks of Table Mountain provided timber for ships and houses. At this point, the VOC had a monopoly on trade and prohibited any private trade. The Dutch gave their own names to the native inhabitants that they encountered, calling the pastoralists "Hottentots," those that lived on the coast and subsisted on shellfishing," and those who were hunter-gatherers were named "Bushmen."
The first wave of Asian immigration to South Africa started in 1654. These first immigrants were banished to the Cape by the Dutch Batavian High Court. These Asians helped to form the foundation of the Cape Coloured and Cape Malay populations, as well as bringing Islam to the Cape. The first large territorial expansion occurred in 1657, when farms were granted by the VOC to a few servants in an attempt to increase food production. These farms were situated along the Liesbeeck River and the VOC still retained financial control of them. The first slaves were brought to the Cape from Java and Madagascar in the following year to work on the farms. The first of a long series of border conflicts between the inhabitants in the European-controlled area and native inhabitants began in 1658 when settlers clashed with the Khoi, who realised that they were losing territory.
Work on the Castle of Good Hope, the first permanent European fortification in the area, began in 1666. The new castle replaced the previous wooden fort that Van Riebeeck and his men built. Finally completed in 1679, the castle is the oldest building in South Africa.
Simon van der Stel, after whom the town of Stellenbosch is named, arrived in 1679 to replace Van Riebeeck as governor. Van der Stel founded the Cape wine industry by bringing grape vines with him on his ship, an industry which would quickly grow to be important for the region. He also promoted territorial expansion in the Colony.
The first non-Dutch immigrants to the Cape, the Huguenots, arrived in 1688. The Huguenots had fled from anti-Protestant persecution in Catholic France to the Netherlands, where the VOC offered them free passage to the Cape as well as farmland. The Huguenots brought important experience in wine production to the Cape, greatly bolstering the industry, as well as providing strong cultural roots.
By 1754, the population of the settlement on the Cape had reached 5,510 Europeans and 6,729 slaves. But by 1780, France and Great Britain went to war against each other. The Netherlands entered the war on the French side, and thus a small garrison of French troops were sent to the Cape to protect it against the British. These troops, however, left by 1784. By 1795, however, the Netherlands was invaded by France and the VOC was in complete financial ruin. The Prince of Orange fled to England for protection, which allowed for the establishment of the Dutch Batavian Republic. Due to the long time it took to send and receive news from Europe, the Cape Commissioner of the time knew only that the French had been taking territory in the Netherlands and that the Dutch could change sides in the war at any moment. British forces arrived at the Cape bearing a letter from the Prince of Orange asking the Commissioner to allow the British troops to protect the Cape from France until the war. The British informed the Commissioner that the Prince had fled to England. The reaction in the Cape Council was mixed, and eventually the British successfully invaded the Cape in the Battle of Muizenberg. The British immediately announced the beginning of free trade.
As elsewhere in Africa and other parts of the world, trading in slaves was a significant activity. A notable event was the mutiny, in 1766, of the slaves on the slaver ship Meermin.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (440mm x 265mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Chatelian Antique Map & Plan Lima, Peru, Colombia
- Title : Carte Particuliere Du Perou...
- Ref #: 60558
- Size: 21in x 17in (535mm x 430m)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved hand coloured original antique map, view & plan of Lima, Peru, Colombia and central South America was published as part of Henri AbrahamChatelain's 1719 edition of Atlas Historique.
As with all Chatelain's maps & views this is finely engraved with a large amount of topographical, political and historical detail.
The Atlas Historique published by Henri Chatelain was part of a major work of its time, an encyclopedia in seven volumes, including geography as one of its main subjects. The text was by Nicholas Gueudeville and the maps by Chatelain. The Atlas included one of the finest map of America (four sheets) surrounded by vignettes and decorative insets.The Atlas Historique was completed between 1705 and 1720, further issues were published up to 1739. The series was published in Amsterdam, with Chatelain’s maps based on those of G. Delisle. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (535mm x 430m)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (490mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 H. Chatelain Large Antique Map of North America Canada Great Lakes, Detroit
- Title : Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France, & des Decouvertes qui y ont ete Faites, Dressee sur les observations les plus Nouvelles, & sur divers Memoires tant Manuscrits qu' imprimez
- Ref #: 17044
- Size: 23 1/4in x 19in (590mm x 480mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique & important early map of The Great Lakes, Canada & the Upper Mid-West - with descriptive French text to the right of the map - was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/4in x 19in (590mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (525mm x 415mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Nice example of Chatelain's edition of De L'Isle's seminal map of Canada, the Great Lakes and Upper Midwest, first issued in 1703.
Chatelain's map of Canada & the Great Lakes was the first printed map to locate Detroit, first issued only 2 years after the founding of the Village by Cadillac. De L'Isle studied at the French Maritime Ministry from 1700 to 1703, during which time he took extensive notes on the work of the Jesuit Missionaries, including Franquelin, Jolliet and others. Karpinksi note that the fruits of De L'Isle's substantial efforts are born out by the great improvements in the mapping of the 5 Great Lakes and other parts of the map.
The map is one of the most important maps of Canada printed during its time, and was included in Chatelain's Atlas Historique. Numerous trading posts and missions in New France and the major towns of the adjacent British colonies are shown. The area around Hudson's Bay is inhabited by native tribes referred to as the "Christinaux or Kilistinons," while Labrador is home to the "Eskimaux."
The map features a number of notes specifically referring to the names of explorers and the dates in which they discovered certain places, such as the reference to 'Nouveau Danemarc', discovered by the Danish explorer Jan Munk in 1619. The depiction of the upper Mississippi and Ohio basins is also quite detailed, noting the French fort of 'St. Louis' or 'Crevecouer' near the present-day site of Peoria, Illinois. Perhaps the most fascinating aspect of the map is its portrayal of the "Riviere Longue," one of the most sensational and enduring cartographic misconceptions ever devised. This mythical river was reported to flow from the 'Pays des Gnacsitares' in the far west, promising the best route through the interior of the continent, supposedly placing one within close reach of the Pacific Ocean. It is a product of the imagination of the Baron Lahontan, a French adventurer, whose best-selling travel narrative Nouveaux voyages dans l'Amérique septentrionale (1703) convinced many of the world's greatest intellects of the existence of this mythical waterway. The text, 'Remarque Historique' that fills the northwestern part of the map describes the history of New France from the days of Jacques Cartier to contemporary times.
1719 Henri Chatelain Antique Map & Views of The African Island of Madagascar
- Title : Carte De L isle de Madagascar dite aujourd hui L Ile Daufine
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 50631
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map with views of the Island of Madagascar, Southern Africa - with 11 vignettes of peoples & views of the island - was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Madagascar previously known as the Malagasy Republic, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of East Africa. The nation comprises the island of Madagascar (the fourth-largest island in the world), and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from the Indian peninsula around 88 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot; over 90% of its wildlife is found nowhere else on Earth. The island\\\'s diverse ecosystems and unique wildlife are threatened by the encroachment of the rapidly growing human population and other environmental threats.
As a result of the island\\\'s long isolation from neighboring continents, Madagascar is home to an abundance of plants and animals found nowhere else on Earth. Approximately 90% of all plant and animal species found in Madagascar are endemic, including the lemurs (a type of strepsirrhine primate), the carnivorous fossa and many birds. This distinctive ecology has led some ecologists to refer to Madagascar as the \\\"eighth continent\\\",[26] and the island has been classified by Conservation International as a biodiversity hotspot.
More than 80 percent of Madagascar\\\'s 14,883 plant species are found nowhere else in the world, including five plant families. The family Didiereaceae, composed of four genera and 11 species, is limited to the spiny forests of southwestern Madagascar. Four-fifths of the world\\\'s Pachypodium species are endemic to the island. Three-fourths of Madagascar\\\'s 860 orchid species are found here alone, as are six of the world\\\'s nine baobab species. The island is home to around 170 palm species, three times as many as on all of mainland Africa; 165 of them are endemic. Many native plant species are used as herbal remedies for a variety of afflictions. The drugs vinblastine and vincristine are vinca alkaloids, used to treat Hodgkin\\\'s disease, leukemia, and other cancers, were derived from the Madagascar periwinkle. The traveler\\\'s palm, known locally as ravinala and endemic to the eastern rain forests, is highly iconic of Madagascar.
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Antique Map Great Britain & Ireland Allegorical Views
- Title : Carte Du Gouvernment Militaire D Angleterre...
- Ref #: 93425
- Size: 20 1/2in x 18 1/2in (510mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of Great Britain & Ireland, with two large allegorical views, was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 18 1/2in (510mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (470mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Antique Map of England & Wales
- Title : Nouvelle Carte de L Angleterre....
- Ref #: 93424
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of England & Wales was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21in (650mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19in (635mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Antique Map of London, England & 2 Allegorical Views
- Title : Plan de la Ville De Londres et Diversee Remarques Sur Ceite Ville
- Ref #: 93423
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 435mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of London, England with two large allegorical views, was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (470mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The 18th century was a period of rapid growth for London, reflecting an increasing national population, the early stirrings of the Industrial Revolution, and Londons role at the centre of the evolving British Empire.
In 1707, an Act of Union was passed merging the Scottish and the English Parliaments, thus establishing the Kingdom of Great Britain. A year later, in 1708 Christopher Wrens masterpiece, St Pauls Cathedral was completed on his birthday. However, the first service had been held on 2 December 1697; more than 10 years earlier. This Cathedral replaced the original St. Pauls which had been completely destroyed in the Great Fire of London. This building is considered one of the finest in Britain and a fine example of Baroque architecture.
Many tradesmen from different countries came to London to trade goods and merchandise. Also, more immigrants moved to London making the population greater. More people also moved to London for work and for business making London an altogether bigger and busier city. Britains victory in the Seven Years War increased the countrys international standing and opened large new markets to British trade, further boosting Londons prosperity.
During the Georgian period London spread beyond its traditional limits at an accelerating pace. This is shown in a series of detailed maps, particularly John Rocques 1741–45 map (see below) and his 1746 Map of London. New districts such as Mayfair were built for the rich in the West End, new bridges over the Thames encouraged an acceleration of development in South London and in the East End, the Port of London expanded downstream from the City. During this period was also the uprising of the American colonies. In 1780, the Tower of London held its only American prisoner, former President of the Continental Congress, Henry Laurens. In 1779, he was the Congresss representative of Holland, and got the countrys support for the Revolution. On his return voyage back to America, the Royal Navy captured him and charged him with treason after finding evidence of a reason of war between Great Britain and the Netherlands. He was released from the Tower on 21 December 1781 in exchange for General Lord Cornwallis.
In 1762, George III acquired Buckingham Palace (then called Buckingham House) from the Duke of Buckingham. It was enlarged over the next 75 years by architects such as John Nash.
A phenomenon of the era was the coffeehouse, which became a popular place to debate ideas. Growing literacy and the development of the printing press meant that news became widely available. Fleet Street became the centre of the embryonic national press during the century.
18th-century London was dogged by crime. The Bow Street Runners were established in 1750 as a professional police force. Penalties for crime were harsh, with the death penalty being applied for fairly minor crimes. Public hangings were common in London, and were popular public events.
In 1780, London was rocked by the Gordon Riots, an uprising by Protestants against Roman Catholic emancipation led by Lord George Gordon. Severe damage was caused to Catholic churches and homes, and 285 rioters were killed.
In the year 1787, freed slaves from London, America, and many of Britains colonies founded Freetown in modern-day Sierra Leone.
Up until 1750, London Bridge was the only crossing over the Thames, but in that year Westminster Bridge was opened and, for the first time in history, London Bridge, in a sense, had a rival. In 1798, Frankfurt banker Nathan Mayer Rothschild arrived in London and set up a banking house in the city, with a large sum of money given to him by his father, Amschel Mayer Rothschild. The Rothschilds also had banks in Paris and Vienna. The bank financed numerous large-scale projects, especially regarding railways around the world and the Suez Canal.
The 18th century saw the breakaway of the American colonies and many other unfortunate events in London, but also great change and Enlightenment. This all led into the beginning of modern times, the 19th century.
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Antique Map, a Plan of Rome, Italy
- Title : Rome Ancienne et Moderne
- Ref #: 82075
- Size: 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Rome, comparing ancient Rome against contemporary Rome in the early 18th century was published in the 1719 edition of Henri Abraham Chatelains Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13 1/2in (445mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The history of Rome spans 28 centuries. While Roman mythology dates the founding of Rome at around 753 BC, the site has been inhabited for much longer, making it one of the oldest continuously occupied sites in Europe. The cities early population originated from a mix of Latins, Etruscans, and Sabines. Eventually, the city successively became the capital of the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, and is regarded as the birthplace of Western civilization and by some as the first ever metropolis. It was first called The Eternal City by the Roman poet Tibullus in the 1st century BC, and the expression was also taken up by Ovid, Virgil, and Livy. Rome is also called the Caput Mundi (Capital of the World). After the fall of the Western Empire, which marked the beginning of the Middle Ages, Rome slowly fell under the political control of the Papacy, which had settled in the city since the 1st century AD, until in the 8th century it became the capital of the Papal States, which lasted until 1870. Beginning with the Renaissance, almost all the popes since Nicholas V (1447–1455) pursued over four hundred years a coherent architectural and urban program aimed at making the city the artistic and cultural centre of the world. In this way, Rome became first one of the major centres of the Italian Renaissance, and then the birthplace of both the Baroque style and Neoclassicism. Famous artists, painters, sculptors and architects made Rome the centre of their activity, creating masterpieces throughout the city. In 1871, Rome became the capital of the Kingdom of Italy, which, in 1946, became the Italian Republic. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1719 Henri Chatelain Large Original Antique Map of South America
- Title : Carte De La Terre Ferme, Du Perou, Du Bresil, et du Pays des Amazones..
- Ref #: 50619
- Size: 28 3/4in x 22 1/4in (730mm x 565mm)
- Date : 1719
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description: This large, scarce, highly detailed & beautifully hand coloured original antique map of South America was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in the 1719 edition of Atlas Historique.
Background: This map was engraved with Chatelain's usual eye for detail, with all the known information available at the time of publication. Old known highly detailed coastal information is included along with much speculative detail of the interior and the river systems of the Amazon and River Plate. In the southern part of the are the tracks of the exploration routes of explorers such as Magellan, Charp, Vespuce & many others. Chatelain has also included text boxes top and bottom with detailed remarks on the continent. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Atlas Historique: First published in Amsterdam from 1705 to 1720, the various volumes were updated at various times up to 1739 when the fourth edition of vol.I appeared, stated as the "derniere edition, corrigée & augmentee."
The first four volumes seem to have undergone four printings with the later printings being the most desirable as they contain the maximum number of corrections and additions. The remaining three final volumes were first issued between 1719-1720 and revised in 1732.
An ambitious and beautifully-presented work, the Atlas Historique was intended for the general public, fascinated in the early eighteenth century by the recently conquered colonies and the new discoveries. Distant countries, such as the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Mongolia, China, Japan, Indonesia, etc., take an important place in this work.
In addition to the maps, many of which are based on Guillaume De L'Isle, the plates are after the best travel accounts of the period, such as those of Dapper, Chardin, de Bruyn, Le Hay and other.
Other sections deal with the history of the European countries, and covers a wide range of subjects including genealogy, history, cosmography, topography, heraldry and chronology, costume of the world, all illustrated with numerous engraved maps, plates of local inhabitants and heraldic charts of the lineages of the ruling families of the time. The maps, prints and tables required to make up a complete set are listed in detail in each volume.
The accompanying text is in French and often is printed in two columns on the page with maps and other illustrations interspersed. Each map and table is numbered consecutively within its volume and all maps bear the privileges of the States of Holland and West-Friesland.
The encyclopaedic nature of the work as a whole is reflected in this six frontispiece. The pages are the work of the celebrated Mr. Romeijn de Hooghe. and are engraved by J.Goeree, T.Schynyoet and P.Sluyter.
New scholarship has suggested the compiler of the atlas, who is identified on the title as "Mr. C***" not to be Henri Abraham Chatelain, but Zacharie Chatelain. (See Van Waning's article in the Journal of the International Map Collectors' Society for persuasive evidence of the latter's authorship.)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - Off white
Age of map colour: - Early
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 3/4in x 22 1/4in (730mm x 565mm)
Plate size: - 28in x 21in (710mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1719 Henri Chatelain Rare Antique Map, Peoples, Animals & Views of South Africa
- Title : Coutumes Moeurs & Habillemens Des Peuples Qui Habitent Aux Environs du Cap de Bonne Esperance......
- Size: 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50639
Description:
This large original copper-plate engraved antique map with views of The Cape of Good Hope, Southern Africa - with 10 vignettes of the peoples, animals & reptiles of the area - was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
These are truly some of the best early engravings of this region done at the time that were copied by the likes of Prevost, Harrison & others in the 18th century, but not with the same eye for detail.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 440mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15in (440mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
By the early 17th century, Portugals maritime power was starting to decline, and English and Dutch merchants competed to oust Lisbon from its lucrative monopoly on the spice trade. Representatives of the British East India Company did call sporadically at the Cape in search of provisions as early as 1601, but later came to favour Ascension Island and St. Helena as alternative ports of refuge. Dutch interest was aroused after 1647, when two employees of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) were shipwrecked there for several months. The sailors were able to survive by obtaining fresh water and meat from the natives. They also sowed vegetables in the fertile soil. Upon their return to Holland, they reported favourably on the Capes potential as a warehouse and garden for provisions to stock passing ships for long voyages.
In 1652, a century and a half after the discovery of the Cape sea route, Jan van Riebeeck established a victualling station at the Cape of Good Hope, at what would become Cape Town, on behalf of the Dutch East India Company. In time, the Cape became home to a large population of vrijlieden, also known as vrijburgers (lit. free citizens), former Company employees who stayed in Dutch territories overseas after serving their contracts. Dutch traders also imported thousands of slaves to the fledgling colony from Indonesia, Madagascar, and parts of eastern Africa. Some of the earliest mixed race communities in the country were formed through unions between vrijburgers, their slaves, and various indigenous peoples. This led to the development of a new ethnic group, the Cape Coloureds, most of whom adopted the Dutch language and Christian faith.
The eastward expansion of Dutch colonists ushered in a series of wars with the southwesterly migrating Xhosa tribe, known as the Xhosa Wars, as both sides competed for the pastureland necessary to graze their cattle near the Great Fish River. Vrijburgers who became independent farmers on the frontier were known as Boers, with some adopting semi-nomadic lifestyles being denoted as trekboers. The Boers formed loose militias, which they termed commandos, and forged alliances with Khoisan groups to repel Xhosa raids. Both sides launched bloody but inconclusive offensives, and sporadic violence, often accompanied by livestock theft, remained common for several decades.
Great Britain occupied Cape Town between 1795 and 1803 to prevent it from falling under the control of the French First Republic, which had invaded the Low Countries. Despite briefly returning to Dutch rule under the Batavian Republic in 1803, the Cape was occupied again by the British in 1806. Following the end of the Napoleonic Wars, it was formally ceded to Great Britain and became an integral part of the British Empire. British emigration to South Africa began around 1818, subsequently culminating in the arrival of the 1820 Settlers. The new colonists were induced to settle for a variety of reasons, namely to increase the size of the European workforce and to bolster frontier regions against Xhosa incursions.
In the first two decades of the 19th century, the Zulu people grew in power and expanded their territory under their leader, Shaka. Shakas warfare indirectly led to the Mfecane (crushing), in which 1,000,000 to 2,000,000 people were killed and the inland plateau was devastated and depopulated in the early 1820s. An offshoot of the Zulu, the Matabele people created a larger empire that included large parts of the highveld under their king Mzilikazi.
During the early 1800s, many Dutch settlers departed from the Cape Colony, where they had been subjected to British control. They migrated to the future Natal, Orange Free State, and Transvaal regions. The Boers founded the Boer Republics: the South African Republic (now Gauteng, Limpopo, Mpumalanga and North West provinces), the Natalia Republic (KwaZulu-Natal), and the Orange Free State (Free State).
The discovery of diamonds in 1867 and gold in 1884 in the interior started the Mineral Revolution and increased economic growth and immigration. This intensified British efforts to gain control over the indigenous peoples. The struggle to control these important economic resources was a factor in relations between Europeans and the indigenous population and also between the Boers and the British.
The Anglo-Zulu War was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Following Lord Carnarvons successful introduction of federation in Canada, it was thought that similar political effort, coupled with military campaigns, might succeed with the African kingdoms, tribal areas and Boer republics in South Africa. In 1874, Sir Henry Bartle Frere was sent to South Africa as High Commissioner for the British Empire to bring such plans into being. Among the obstacles were the presence of the independent states of the Boers and the Kingdom of Zululand and its army. The Zulu nation defeated the British at the Battle of Isandlwana. Eventually, though, the war was lost, resulting in the termination of the Zulu nations independence.
The Boer Republics successfully resisted British encroachments during the First Boer War (1880–1881) using guerrilla warfare tactics, which were well suited to local conditions. The British returned with greater numbers, more experience, and new strategy in the Second Boer War (1899–1902) but suffered heavy casualties through attrition; nonetheless, they were ultimately successful.
1720 Chatelain Antique Map of England & Wales
- Title : Nouvelle Carte De L Angleterre Dans Laquelle Lon Observe Lez Comtez Les Archives
- Ref #: 16370
- Size: 25 1/2in x 20 1/2in (650m x 430m)
- Date : 1720
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of England & Wales - with side text on all the different counties - by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1720 was published in his famous Atlas Historique.
This is a magnificent map with bright hand colouring, clean strong sturdy paper and a heavy clear impression.
The Atlas Historique published by Henri Chatelain was part of a major work of its time, an encyclopedia in seven volumes, including geography as one of its main subjects. The text was by Nicholas Gueudeville and the maps by Chatelain. The Atlas included one of the finest map of America (four sheets) surrounded by vignettes and decorative insets. The Atlas Historique was completed between 1705 and 1720, further issues were published up to 1739. The series was published in Amsterdam, with Chatelain’s maps based on those of G. Delisle. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 20 1/2in (650m x 430m)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635m x 495mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None