South Pacific
1842 D Urville & Marescot Antique Print King Mapou-Teoa & Envoy of Mangareva Gambier
- Title : Antonio Mapoua; Koloupo (Isles Manga Reva)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31747
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of King Mapou-Teoa and his envoy who boarded D Urvilles ship the Astrolabe in August 1838, by Jacques Marescot-Duthilleul, one of the artists,draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot and published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Jacques, Marie, Eugene Marescot Duthilleul1809 - 1839 Lieutenant in the French navy and artist who accompanied Dumont D Urville on the Corvette The Astrolabe on D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas, Australia and Antarctica between 1837 and 1840. He was responsible for a number of exquisite drawings of peoples and views during the voyage that were later used for lithograph prints for publication
In 1837, a new mission of exploration in the southern Pacific Ocean was entrusted by King Louis-Philippe to Captain Dumont d Urville. This mission included improvement of scientific knowledge on the islands of the South Pacific and Indonesia, and exploration of the Antarctic continent.
The first phase of the expedition was the crossing the Sea of Weddel sea ice, on the coast of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. The second phase between May 1838 &o December 1839 consisting of visits to many South Pacific Islands: Marquesas, Polynesia, Fiji, Solomon Islands, New Guinea, Carolinas, Marianas, Moluccas and finally Sunda Islands.
At the end of this second phase, after eighteen months of difficult navigation in unhealthy climates, the sanitary condition of the crews of the two corvettes reached a critical state. During the last voyage from Sumatra (Lampang Bay) to Hobart Tasmania, eighteen patients died, including Lieutenant Marescot-Duthilleul.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mangareva is the central and largest island of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. It is surrounded by smaller islands: Taravai in the southwest, Aukena and Akamaru in the southeast, and islands in the north.
Mangareva was once heavily forested and supported a large population that traded with other islands via canoes. However, excessive logging by the islanders during the 10th to the 15th centuries resulted in deforestation of the island, with disastrous results for its environment and economy.
The first European to arrive at Mangareva was British Captain James Wilson in 1797 on the ship Duff. Wilson named the island group in honour of Admiral James Gambier, who had helped him to equip his vessel.
Mangareva along with its dependencies in the Gambier Islands were ruled by a line of kings and later regents that ruled until the French formally annexed the islands in 1881. A French protectorate was requested on 16 February 1844 by King Maputeoa but was never ratified by the French government. On 4 February 1870, Prince Regent Arone Teikatoara and the Mangarevan government formally withdrew the protectorate request and asked the French to not intervene in the kingdom\'s affairs. After Father Honoré Laval was removed to Tahiti, the native government changed its stance and an agreement between Prince Regent Arone and the French colonial authority in Tahiti was signed reaffirming the protectorate status on 30 November 1871. The Gambier Islands were finally annexed on 21 February 1881 under Prince Regent Bernardo Putairi and approved by the President of France on 30 January 1882.
1842 D Urville & Marescot Antique Print of Envoys of Mangareva Isle, Gambier Is.
- Title : Mama-Houi; Tima-Temouo (Isles Maga Reva)
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31746
Description:
This large, magnificent, original antique lithograph print of Envoys of Mangreva Island, Gambier Island visited by Dumont D Urvilles & his ship the Astrolabe in August 1838, by Jacques Marescot-Duthilleul, one of the artists,draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot and published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d UrvillesVoyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Jacques, Marie, Eugene Marescot Duthilleul1809 - 1839 Lieutenant in the French navy and artist who accompanied Dumont D Urville on the Corvette The Astrolabe on D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas, Australia and Antarctica between 1837 and 1840. He was responsible for a number of exquisite drawings of peoples and views during the voyage that were later used for lithograph prints for publication
In 1837, a new mission of exploration in the southern Pacific Ocean was entrusted by King Louis-Philippe to Captain Dumont d Urville. This mission included improvement of scientific knowledge on the islands of the South Pacific and Indonesia, and exploration of the Antarctic continent.
The first phase of the expedition was the crossing the Sea of Weddel sea ice, on the coast of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. The second phase between May 1838 &o December 1839 consisting of visits to many South Pacific Islands: Marquesas, Polynesia, Fiji, Solomon Islands, New Guinea, Carolinas, Marianas, Moluccas and finally Sunda Islands.
At the end of this second phase, after eighteen months of difficult navigation in unhealthy climates, the sanitary condition of the crews of the two corvettes reached a critical state. During the last voyage from Sumatra (Lampang Bay) to Hobart Tasmania, eighteen patients died, including Lieutenant Marescot-Duthilleul.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mangareva is the central and largest island of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. It is surrounded by smaller islands: Taravai in the southwest, Aukena and Akamaru in the southeast, and islands in the north.
Mangareva was once heavily forested and supported a large population that traded with other islands via canoes. However, excessive logging by the islanders during the 10th to the 15th centuries resulted in deforestation of the island, with disastrous results for its environment and economy.
The first European to arrive at Mangareva was British Captain James Wilson in 1797 on the ship Duff. Wilson named the island group in honour of Admiral James Gambier, who had helped him to equip his vessel.
Mangareva along with its dependencies in the Gambier Islands were ruled by a line of kings and later regents that ruled until the French formally annexed the islands in 1881. A French protectorate was requested on 16 February 1844 by King Maputeoa but was never ratified by the French government. On 4 February 1870, Prince Regent Arone Teikatoara and the Mangarevan government formally withdrew the protectorate request and asked the French to not intervene in the kingdom\'s affairs. After Father Honoré Laval was removed to Tahiti, the native government changed its stance and an agreement between Prince Regent Arone and the French colonial authority in Tahiti was signed reaffirming the protectorate status on 30 November 1871. The Gambier Islands were finally annexed on 21 February 1881 under Prince Regent Bernardo Putairi and approved by the President of France on 30 January 1882.
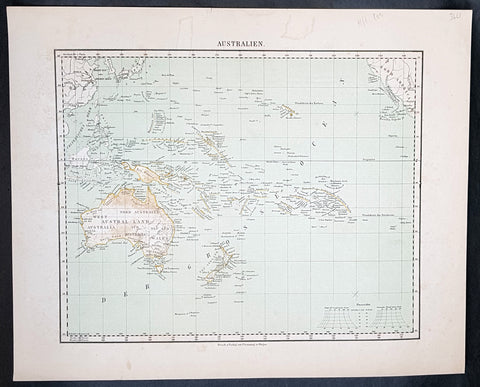
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 32163
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
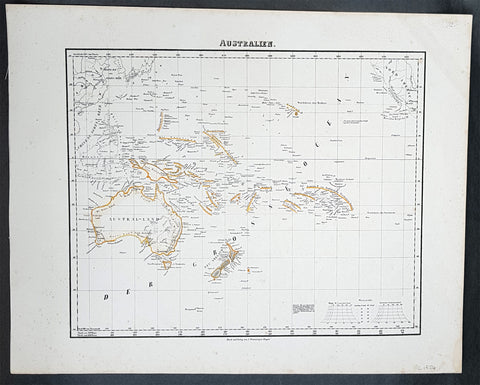
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31975
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
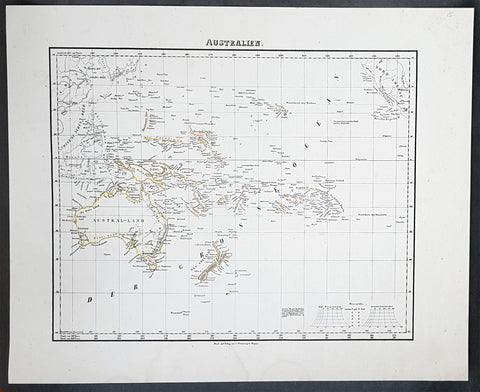
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31988
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
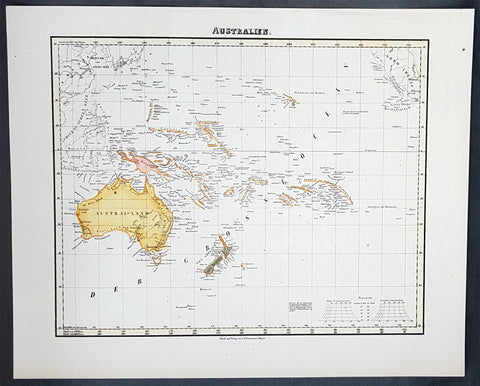
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40973
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
C1842 D Urville & Goupil Antique Print Chief Pea, Daughter & Wife of Apia, Samoa
- Title : Chef D Apia (Ise Opoulou): Jeune Fille D Apia (Ile Opoulou): Femme De Lefouga (Iles Hapai)
- Size: 22in x 14in (560mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Date : 1842
- Ref #: 31754
Description:
This magnificent, large original antique lithograph print of Pea the High Chief of the village of Apia on the Island of Upolu, Samoa along with and his daughter & wife visited in September 1838 by Dumont D Urville, by Ernest Goupil, the senior artist/draftsman aboard the Astrolabe, during D Urvilles second voyage to the South Seas between 1837 - 1840, was engraved by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayotiand was published in the 1842 1st edition of Dumont d Urvilles Voyage au Pole Sud et dans l Océanie sur les corvettes l Astrolabe et la Zélée : Exécuté par ordre du roi pendant les années 1837-1838-1839-1840.
These large magnificent lithographs from the 1st edition are extremely hard to find, most only found in museums or in private hands, and due to the artistry are a must for any collection.
Ernest Goupil was a French painter, draftsman and watercolourist He is known for the illustrations made as official painter for Dumont D Urvilles 2nd Voyage to the South Seas. In Voyage to the South Pole and in Oceania on corvettes l\'Astrobale and Zélée, executed by order of the king during the years 1837-1838-1839-1840, his drawings are transposed on stone, most notably by Emile Lassalle , Pharamond Blanchard and Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot . Dumont d\'Urville relates: On the Zélée , Mr. Goupil fills his cartons with precious paintings, and on the Astrolabe , the young surgeon Le Breton, who has a remarkable talent in this genre, also performs at my asks for charming drawings.
Some drawings were sent to the Minister of the Navy and were shown to the King, who wanted to see them transposed into painting by the marine painter Théodore Gudin , but Goupil would not have given his consent.
In August 1839 in Samarang Java , the crew is struck by a violent epidemic, and after two months of suffering, Ernest Goupil succumbs and died on January 1 , 1840 ijn Hobart-town where he was buried with full military honours.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 14in (560mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 14in (560mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Apia is the capital and the largest city of Samoa. From 1900 to 1919, it was the capital of German Samoa. The city is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa\'s second largest island. Apia is the only city in Samoa and falls within the political district (itūmālō) of Tuamasaga.
Apia was originally a small village from which the country\'s capital took its name. Apia village still exists within the larger modern capital of Apia which has grown into a sprawling urban area with many villages. Like every other settlement in the country, Apia village has its own matai chiefly leaders and fa\'alupega (genealogy and customary greetings) according to fa a Samoa.
The modern capital Apia was founded in the 1850s and has been the official capital of Samoa since 1959.
The harbor was also the site of an infamous 15 March 1889 naval standoff in which seven ships from Germany, the US, and Britain refused to leave harbor while a typhoon was clearly approaching, lest the first moved would lose face. All the ships were sunk, except the British cruiser Calliope, which barely managed to leave port at 1 mile per hour and ride out the storm. Nearly 200 American and German lives were lost, as well as six ships sunk or damaged beyond repair.
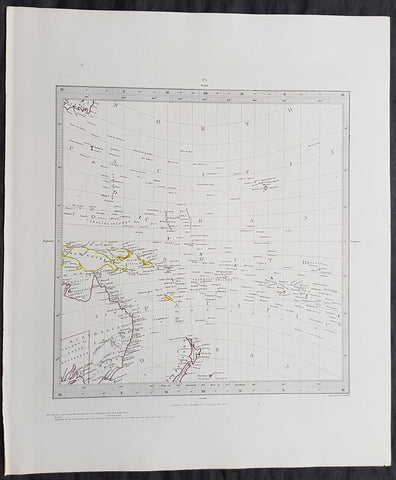
Copy of 1840 SDUK Antique Gnomonic Map East Australia, New Zealand South Pacific
- Title : Published by the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0984
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique Gnomonic Map of eastern Australia, New Zealand & The South Pacific was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 and was published in the Chapman & Hall edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
A gnomonic map projection displays all great circles as straight lines, resulting in any line segment on a gnomonic map showing a geodesic, the shortest route between the segment\'s two endpoints. This is achieved by casting surface points of the sphere onto a tangent plane, each landing where a ray from the center of the sphere passes through the point on the surface and then on to the plane. No distortion occurs at the tangent point, but distortion increases rapidly away from it. Less than half of the sphere can be projected onto a finite map. Consequently a rectilinear photographic lens cannot image more than 180 degrees.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)