Prints (7)
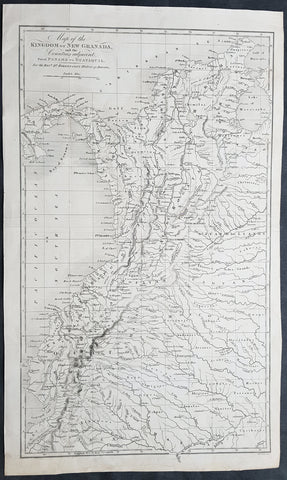
1824 William Robertson Large Antique Map of NW South America - Panama to Peru
- Title : Map of the Kingdom of New Granada and the Countries adjacent from Panama to Guayquil
- Date : 1824
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 01-9624
- Size: 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (445mm x 270mm)
Description:
This large highly detailed original copper-plate engraved antique map of north west South America - from Panama to Peru - was engraved by Sydney Hall and published in the 1824 edition of the Rev. Dr Robertsons The History of America. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (445mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 10 1/2in (445mm x 270mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime European powers of that time, on the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas, by which they agreed, with the support of the Pope, that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries.
The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\\\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (known to comprise most of the South American soil) would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. As accurate measurements of longitude were impossible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
Beginning in the 1530s, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it in colonies.
European infectious diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles, and typhus) – to which the native populations had no immune resistance – caused large-scale depopulation of the native population under Spanish control. Systems of forced labor, such as the haciendas and mining industry\\\'s mita also contributed to the depopulation. After this, African slaves, who had developed immunities to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their native subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end; however, many initial attempts at this were only partially successful, as native groups simply blended Catholicism with their established beliefs and practices. Furthermore, the Spaniards brought their language to the degree they did with their religion, although the Roman Catholic Churchs evangelization in Quechua, Aymara, and Guaraní actually contributed to the continuous use of these native languages albeit only in the oral form.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a mestizo class. At the beginning, many mestizos of the Andean region were offspring of Amerindian mothers and Spanish fathers. After independence, most mestizos had native fathers and European or mestizo mothers.
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal. Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered. They also significantly increased economic and trade relations, not just between the old and new world but between the different South American regions and peoples. Finally, with the expansion of the Portuguese and Spanish languages, many cultures that were previously separated became united through that of Latin American.
Guyana was first a Dutch, and then a British colony, though there was a brief period during the Napoleonic Wars when it was colonized by the French. The country was once partitioned into three parts, each being controlled by one of the colonial powers until the country was finally taken over fully by the British.
The European Peninsular War (1807–1814), a theater of the Napoleonic Wars, changed the political situation of both the Spanish and Portuguese colonies. First, Napoleon invaded Portugal, but the House of Braganza avoided capture by escaping to Brazil. Napoleon also captured King Ferdinand VII of Spain, and appointed his own brother instead. This appointment provoked severe popular resistance, which created Juntas to rule in the name of the captured king.
Many cities in the Spanish colonies, however, considered themselves equally authorized to appoint local Juntas like those of Spain. This began the Spanish American wars of independence between the patriots, who promoted such autonomy, and the royalists, who supported Spanish authority over the Americas. The Juntas, in both Spain and the Americas, promoted the ideas of the Enlightenment. Five years after the beginning of the war, Ferdinand VII returned to the throne and began the Absolutist Restoration as the royalists got the upper hand in the conflict.
The independence of South America was secured by Simón Bolívar (Venezuela) and José de San Martín (Argentina), the two most important Libertadores. Bolívar led a great uprising in the north, then led his army southward towards Lima, the capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Meanwhile, San Martín led an army across the Andes Mountains, along with Chilean expatriates, and liberated Chile. He organized a fleet to reach Peru by sea, and sought the military support of various rebels from the Vice-royalty of Peru. The two armies finally met in Guayaquil, Ecuador, where they cornered the Royal Army of the Spanish Crown and forced its surrender.
In the Portuguese Kingdom of Brazil, Dom Pedro I (also Pedro IV of Portugal), son of the Portuguese King Dom João VI, proclaimed the independent Kingdom of Brazil in 1822, which later became the Empire of Brazil. Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by the crown in Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediatized by the United Kingdom.
Robertson , William 1721 - 1793
Rev Robertson was a Scottish historian, minister in the Church of Scotland, and Principal of the University of Edinburgh. The thirty years during which he presided over the University perhaps represent the highest point in its history. He made significant contributions to the writing of Scottish history and the history of Spain and Spanish America.
Robertson was born at the manse of Borthwick, Midlothian, the son of Robertson the local minister.
He was educated at Borthwick Parish School and Dalkeith Grammar School. He was the son of William Robertson and his wife Eleanor Pitcairn. He married his cousin Mary Nesbit in 1751. The family moved to Edinburgh when his father became appointed minister of Old Greyfriars Kirk.
He studied divinity at Edinburgh University (1733–41), and was licensed to preach in 1741. He was granted a Doctor of Divinity in 1759. He became minister at Gladsmuir (East Lothian) in 1743 and in 1759 at Lady Yester\\\'s Kirk and Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh. A staunch Presbyterian and Whig, he volunteered to defend the city against the Jacobites led by Prince Charles Edward Stuart in 1745.
In 1754 he was an original member of The Select Society, also referred to as the Edinburgh Select Society.
Robertson became royal chaplain to George III (1761), principal of the University of Edinburgh (1762), Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland in 1763, and Historiographer Royal in 1764, reviving a role within the Royal household in Scotland that had been in abeyance from 1709 until 1763. He was also a member of The Poker Club.
One of his most notable works is his History of Scotland 1542–1603, begun in 1753 and first published in 1759. Robertson also contributed to the history of Spain and Spanish America in his History of America (1777), the first sustained attempt to describe the discovery, conquest and settlement of Spanish America since Herreras Décadas and his biography of Charles V. In that work he had provided a masterly survey of the progress of European society, in which he traced the erosion of the feudal system caused by the rise of free towns, the revival of learning and Roman law, and by the emergence of royal authority and the balance of power between states. It was the development of commerce, assisted by law and private property, which was held to be chiefly responsible for the advance in civilisation.
He was a significant figure in the Scottish Enlightenment and also of the moderates in the Church of Scotland.
In 1783 he was a founding member of the Royal Society of Edinburgh.
He died of jaundice on 11 June 1793, at Grange House in south Edinburgh (the huge now-demolished mansion which gave its name to the Grange district. Robertson is buried at Greyfriars Kirkyard, Edinburgh. The grave is within a very large stone mausoleum. second only to William Adam\\\'s mausoleum immediately to the south. Both stand to the south-west of the church, near the entrance to the Covenanters Prison.
Publications
- The Situation of the World at the Time of Christ\\\'s Appearance (sermon) (1755)
The History of Scotland 1542-1603 (1759) (3 vols.)
- History of the Reign of the Emperor Charles V (1769) (4 vols.)
- The History of America (1777, 1796) (3 vols.)
- An Historical Disquisition Concerning the Knowledge Which the Ancients Had of India (1791)
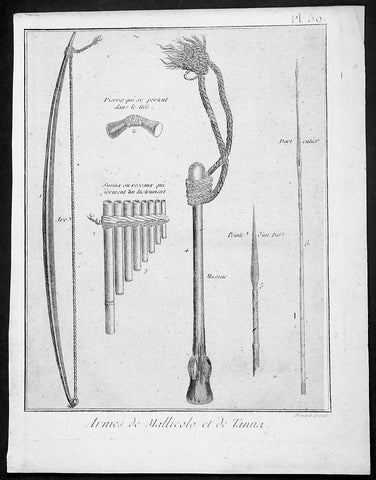
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print Weapons & Musical Instruments Vanuatu Islands, 1774
- Title : Armes de Mallicolo et de Tanna
- Ref : 91211
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of 6 different types of arms and musical instruments, from the Islands of Malakula (Mallicolo) & Tanna in the Vanuatu group of Islands in the South Pacific, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery in the South Seas in September 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
The six objects engraved are;
1. Arc - Bow
2. Pierres qui seportent dans le nes - Stone used as a support
3. Syrinx ou roseaux quiserment un instrument - Multi tune flute
4. Massue - Club with rope attachment
5. peinte d un parl - Arrow head
6. Dart enier - Spear
Cook Journal July, 1774
Arrival at The New Hebrides
On 17th Cook saw land bearing SW and later on decided this was the Australia Del Espiritu Santo of Quiros or what M. D. Bougainville calls the Great Cyclades. The island was Maewo. The next day its northern end was rounded in a gale and the ship sailed south between it and the island called by Bougainville the Isle of Lepers - Omba.
On 20th they crossed Patteson Passage with a view of geting to the South to explore the lands which lies there, and sailed down the west coast of Pentecost Isle (Raga). To the south they saw the island of Ambrin and behind it Paama and Epi. On 22nd, approaching Mallicollo (Malekula) we perceived a creek which had the appearence of a good harbour. Cook sent Lieutt [Richard] Pickersgill and the Master [Joseph Gilbert] in two Armd boats to Sound and look for Anchorage. The following day a good many [natives] came round us, some came in Canoes and others swam off\\\'... four I took into the Cabbin and made them various presents. Later, after some misunder-standing some natives began to Shoot Arrows... a Musquet discharged in the air and a four pounder over their heads sent them all off in the utmost confusion; those in the Cabbin leaped out of the Windows... About 9 o\\\'Clock we landed in the face of about 4 or 500 Men who were assembled on the Shore, armd with Bows and Arrows, clubs and Spears, but they made not the least opposission, on the contrary one Man gave his Arms to a nother and Met us in the water with a green branch in his hand, which [he] exchanged for the one I held in my hand. Just before departing Cook remarked they have not so much as a name for a Dog, consequently can have none, for which reason we left them a Dog and a Bitch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Malakula Island also spelled Malekula, is the second-largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, in the Pacific Ocean region of Melanesia.
Discovered by the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós in 1606 and visited by Captain Cook in 1774.
Vanuatu officially the Republic of Vanuatu is a Pacific island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 kilometres east of northern Australia, 540 kilometres northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island in 1606. Since the Portuguese and Spanish monarchies had been unified under the king of Spain in 1580 (following the vacancy of the Portuguese throne, which lasted for sixty years, until 1640, when the Portuguese monarchy was restored), Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo.
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queiros, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit, believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands on 22 May, naming them the Great Cyclades. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Man of Terra del Fuego, Chile in 1774
- Title : Homme du Canal de Noel Dans La Terre De Feu
- Ref : 31813
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, portrait of a Man of Christmas Sound on the S.W. Coast of Terra del Fuego Chile, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in December 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Journal
.......followed the coast of Tierra del Fuego (Chile) at the end of December 1774 making for Cape Horn. The coast comprised of hundreds of small islands, some of which were charted and named but many were not. The Resolution was kept at a safe distance from the shore and soon passed the Grafton Islands, Noir Island, Tower Rocks and the Gilbert Islands (named after the Master). On the 19th they passed a large inlet, which is now called Cook Bay. Cook needed provisions and to check the state of the Resolution,so he found an inlet suitable for this purpose on the 20th. They stayed there for eight days over Christmas, which earned the inlet the name Christmas Sound..........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tierra del Fuego Spanish for Land of Fire is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, with an area of 48,100 km2 and a group of many islands, including Cape Horn and Diego Ramírez Islands. Tierra del Fuego is divided between Chile and Argentina, with the latter controlling the eastern half of the main island and the former the western half plus the islands south of Beagle Channel.
The name Tierra del Fuego derives from the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan sailing for the Spanish Crown, in 1520 he was the first European to visit these lands. He believed he was seeing the many fires (fuego in Spanish) of the Yaghan, which were visible from the sea, and that the Indians were waiting in the forests to ambush his armada.
In 1525 Francisco de Hoces was the first to speculate that Tierra del Fuego was one or more islands rather than part of what was then called Terra Australis. Francis Drake in 1578 and a Dutch VOC expedition in 1616 learned more about the geography. The latter expedition named Cape Horn.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1778 Capt Cook Antique Print Portrait of a Man of Terra del Fuego, Chile in 1774
- Title : Homme du Canal de Noel Dans La Terre De Feu
- Ref : 16354
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print, portrait of a Man of Christmas Sound on the S.W. Coast of Terra del Fuego Chile, visited by Captain James Cook during his 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas in December 1774, was engraved by Robert Benard - after William Hodges - and was published in the 1778 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 2nd Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas A voyage towards the South Pole, and round the World. Performed in His Majestys ships the Resolution and Adventure, in the years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775..... Paris : Hotel de Thou ......1778
Cook Journal
.......followed the coast of Tierra del Fuego (Chile) at the end of December 1774 making for Cape Horn. The coast comprised of hundreds of small islands, some of which were charted and named but many were not. The Resolution was kept at a safe distance from the shore and soon passed the Grafton Islands, Noir Island, Tower Rocks and the Gilbert Islands (named after the Master). On the 19th they passed a large inlet, which is now called Cook Bay. Cook needed provisions and to check the state of the Resolution,so he found an inlet suitable for this purpose on the 20th. They stayed there for eight days over Christmas, which earned the inlet the name Christmas Sound..........
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tierra del Fuego Spanish for Land of Fire is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, with an area of 48,100 km2 and a group of many islands, including Cape Horn and Diego Ramírez Islands. Tierra del Fuego is divided between Chile and Argentina, with the latter controlling the eastern half of the main island and the former the western half plus the islands south of Beagle Channel.
The name Tierra del Fuego derives from the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan sailing for the Spanish Crown, in 1520 he was the first European to visit these lands. He believed he was seeing the many fires (fuego in Spanish) of the Yaghan, which were visible from the sea, and that the Indians were waiting in the forests to ambush his armada.
In 1525 Francisco de Hoces was the first to speculate that Tierra del Fuego was one or more islands rather than part of what was then called Terra Australis. Francis Drake in 1578 and a Dutch VOC expedition in 1616 learned more about the geography. The latter expedition named Cape Horn.
William Hodges RA 1744 – 1797 was an English painter. He was a member of James Cooks second voyage to the Pacific Ocean, and is best known for the sketches and paintings of locations he visited on that voyage, including Table Bay, Tahiti, Easter Island, and the Antarctic.
Between 1772 and 1775 Hodges accompanied James Cook to the Pacific as the expeditions artist. Many of his sketches and wash paintings were adapted as engravings in the original published edition of Cooks journals from the voyage.
Most of the large-scale landscape oil paintings from his Pacific travels for which Hodges is best known were finished after his return to London; he received a salary from the Admiralty for the purposes of completing them. These paintings depicted a stronger light and shadow than had been usual in European landscape tradition. Contemporary art critics complained that his use of light and colour contrasts gave his paintings a rough and unfinished appearance.
Hodges also produced many valuable portrait sketches of Pacific islanders and scenes from the voyage involving members of the expedition..
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1750 Prevost Antique View of Juan Fernandez Island Chile, Alex. Selkirk & R. Crusoe
- Title: Vue de la Place de Juan Fernandez ou le Chef d Escadre avont sa Tente
- Date: 1750
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 34129
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print was engraved by Jakob van Schley and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Alexander Selkirk (1676 - 1721) was a Scottish sailor who spent four years as a castaway when he was marooned on an uninhabited island, Juan Fernández Island off the coast of Chile. It is his travels that provided the inspiration for Daniel Defoe\'s novel Robinson Crusoe.
At an early period he was engaged in buccaneer expeditions to the South Seas and in 1703 joined in with the expedition of famed privateer and explorer William Dampier. While Dampier was captain of the St. George, Selkirk served on the galley Cinque Ports, the St. George\'s companion, as a sailing master serving under Thomas Stradling.
In October 1704, after the ships had parted ways because of a dispute between Stradling and Dampier, the Cinque Ports was brought by Stradling to the uninhabited archipelago of Juan Fernández off the coast of Chile for a mid-expedition restocking of supplies and fresh water. Selkirk had grave concerns by this time about the seaworthiness of this vessel (indeed, the Cinque Ports later foundered, losing most of its hands). He tried to convince some of his crewmates to desert with him, remaining on the island; he was counting on an impending visit by another ship. No one else agreed to come along with him. Stradling declared that he would grant him his wish and leave him alone on Juan Fernández. Selkirk promptly regretted his decision. He chased and called after the boat, to no avail. Selkirk lived the next four years and four months without any human company. All he had brought with him was a musket, gunpowder, carpenter\'s tools, a knife, a Bible, some clothing and rope.
His long-anticipated rescue occurred on 1 February 1709 by way of the Duke, a privateering ship piloted by the above-mentioned William Dampier. Selkirk was discovered by the Duke\'s captain, Woodes Rogers, who referred to him as Governor of the island. Now rescued, he was almost incoherent in his joy. The agile Selkirk, catching two or three goats a day, helped restore the health of Rogers\' men. Rogers eventually made Selkirk his mate, giving him independent command of one of his ships. Rogers\' A cruising voyage round the world: first to the South-Sea, thence to the East-Indies, and homewards by the Cape of Good Hope was published in 1712 and included an account of Selkirk\'s ordeal. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 250mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \"La Vie de Marianne\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévost\'s Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1750 Prevost Antique View of Juan Fernandez Island Chile, Alex. Selkirk & R. Crusoe
- Title: Vue de la Place de Juan Fernandez ou le Chef d Escadre avont sa Tente
- Date: 1750
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25754
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print was engraved by Jakob van Schley and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Alexander Selkirk (1676 - 1721) was a Scottish sailor who spent four years as a castaway when he was marooned on an uninhabited island, Juan Fernández Island off the coast of Chile. It is his travels that provided the inspiration for Daniel Defoe\'s novel Robinson Crusoe.
At an early period he was engaged in buccaneer expeditions to the South Seas and in 1703 joined in with the expedition of famed privateer and explorer William Dampier. While Dampier was captain of the St. George, Selkirk served on the galley Cinque Ports, the St. George\'s companion, as a sailing master serving under Thomas Stradling.
In October 1704, after the ships had parted ways because of a dispute between Stradling and Dampier, the Cinque Ports was brought by Stradling to the uninhabited archipelago of Juan Fernández off the coast of Chile for a mid-expedition restocking of supplies and fresh water. Selkirk had grave concerns by this time about the seaworthiness of this vessel (indeed, the Cinque Ports later foundered, losing most of its hands). He tried to convince some of his crewmates to desert with him, remaining on the island; he was counting on an impending visit by another ship. No one else agreed to come along with him. Stradling declared that he would grant him his wish and leave him alone on Juan Fernández. Selkirk promptly regretted his decision. He chased and called after the boat, to no avail. Selkirk lived the next four years and four months without any human company. All he had brought with him was a musket, gunpowder, carpenter\'s tools, a knife, a Bible, some clothing and rope.
His long-anticipated rescue occurred on 1 February 1709 by way of the Duke, a privateering ship piloted by the above-mentioned William Dampier. Selkirk was discovered by the Duke\'s captain, Woodes Rogers, who referred to him as Governor of the island. Now rescued, he was almost incoherent in his joy. The agile Selkirk, catching two or three goats a day, helped restore the health of Rogers\' men. Rogers eventually made Selkirk his mate, giving him independent command of one of his ships. Rogers\' A cruising voyage round the world: first to the South-Sea, thence to the East-Indies, and homewards by the Cape of Good Hope was published in 1712 and included an account of Selkirk\'s ordeal. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 250mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \"La Vie de Marianne\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévost\'s Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
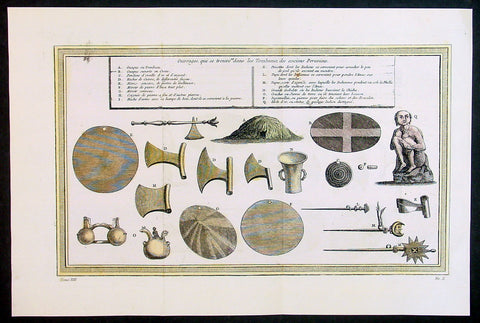
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Print of Artifacts Recovered from Inca Burial Tomb
- Title: Puvrages qui se trouvent dans les Tombeaux des anciens Peruviens
- Date: 1755
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 34132
- Size: 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique print of artifacts found in an Inca Tomb in Peru by Jakob van Schley in 1755 - after De Bry - was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The Inca Empire also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire, was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America, and possibly the largest empire in the world in the early 16th century. Its political and administrative structure \"was the most sophisticated found among native peoples\" in the Americas.The administrative, political and military center of the empire was located in Cusco in modern-day Peru. The Inca civilization arose from the highlands of Peru sometime in the early 13th century. Its last stronghold was conquered by the Spanish in 1572.
From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined Peru, large parts of modern Ecuador, western and south central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, north and central Chile and a small part of southwest Colombia into a state comparable to the historical empires of Eurasia. Its official language was Quechua.Many local forms of worship persisted in the empire, most of them concerning local sacred Huacas, but the Inca leadership encouraged the worship of Inti – their sun god – and imposed its sovereignty above other cults such as that of Pachamama. The Incas considered their king, the Sapa Inca, to be the \"son of the sun.\"
The Inca Empire was unique in that it lacked many features associated with civilization in the Old World. In the words of one scholar, \"The Incas lacked the use of wheeled vehicles. They lacked animals to ride and draft animals that could pull wagons and plows... [They] lacked the knowledge of iron and steel... Above all, they lacked a system of writing... Despite these supposed handicaps, the Incas were still able to construct one of the greatest imperial states in human history\". Notable features of the Inca Empire include its monumental architecture, especially stonework, extensive road network reaching all corners of the empire, finely-woven textiles, use of knotted strings (quipu) for record keeping and communication, agricultural innovations in a difficult environment, and the organization and management fostered or imposed on its people and their labor.
The Incan economy has been described in contradictory ways by scholars: as \"feudal, slave, socialist (here one may choose between socialist paradise or socialist tyranny)\". The Inca empire functioned largely without money and without markets. Instead, exchange of goods and services was based on reciprocity between individuals and among individuals, groups, and Inca rulers. \"Taxes\" consisted of a labor obligation of a person to the Empire. The Inca rulers (who theoretically owned all the means of production) reciprocated by granting access to land and goods and providing food and drink in celebratory feasts for their subjects.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (385mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 8 1/2in (355mm x 220mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)