Portraits (8)
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print of a Sydney & Port Jackson Aboriginal Warrior
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Nelle Galles Du Sud. Nourou-gal-derri & avancant pour combattre
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91240
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Aboriginal warrior of Port Jackson carrying a spear & shield, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes in 1807.
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - 2 small repair to left margin, no loss
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print of a Sydney & Port Jackson Aboriginal Warrior
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Nelle Galles Du Sud. Nourou-gal-derri & avancant pour combattre
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93087
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Aboriginal warrior of Port Jackson carrying a spear & shield, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes in 1807.
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting to left and bottom margins, not affecting the image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
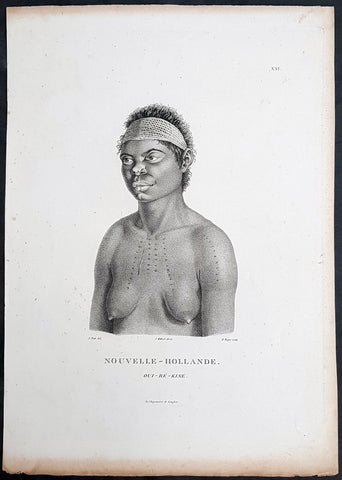
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print Sydney Aboriginal Wárrgan, Bennelong's Sister
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Oui-re-kine
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91238
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print, of the (half) sister of the famous Port Jackson Aborginal leader Bennelong, Oui-ré-kine – Wárrgan (Crow), also referred to as Worogan, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 drawing by Nicolas-Martin Petit, and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
This is a wonderful original stipple point engraving by Petit & Roger bringing to life this wonderful 1st Australian.
The sitter – identified by artist Nicolas-Martin Petit as Oui-ré-kine – Wárrgan (Crow), also referred to as Worogan. In his writings about the Eora people he knew, astronomer and collector of Sydney languages William Dawes counted Wárrgan with Bennelongs sisters, although she might have been a half-sister or other relative of Bennelongs. Her husband Yeranibe (Euranabie) was the son of Maugoran, a leader of the Burramattagal clan, making Wárrgan a sister-in-law to Bidgee Bidgee, another of Petits Sydney sitters. In 1801, Wárrgan and Yeranibe joined the Lady Nelson which, under the command of James Grant, voyaged to Jervis Bay before making a survey of Bass Strait. In The Narrative of a Voyage of Discovery performed in His Majestys vessel the Lady Nelson (1803–1804), Grant related an incident wherein Wárrgan demonstrated the use of a waddy and a woomera, and how incisions were made on the body using a shell. Both Wárrgan and Yeranibe spoke English, and acted as Grant’s interpreters.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal, Ourlaga
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Ourlaga
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93089
Description:
This exquisite, rare original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Ourlaga, visited by Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Bara-Ourou
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Bara-Ourou
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93088
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Bara-Ourou, portrait of a young man 28-30 years of age, visited by Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Grou Agara
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Grou Agara
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93086
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Grou Agara, visited by the Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida
Antique Map
- Title : Terre De Diemen Arra Maida
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93085
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida, visited by the Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print Sydney Aboriginal Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan - Bennelong
Antique Map
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Gnoung-a-gnoung-a Mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91239
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print, of the brother in law of the famous Port Jackson Aborginal leader Bennelong, Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, or Anganángan, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 by Nicolas-Martin Petit, was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan
It is over 200 years since the death of an adventurous young Aboriginal Australian who crossed the vast Pacific Ocean to North America and returned to Sydney. From the deck of an English storeship he glimpsed many strange places, visiting Norfolk Island, Hawaii, Nootka Sound (now Vancouver, Canada) and the Spanish colonies of San Francisco, Santa Barbara and San Diego on the Californian coast.
The voyager was Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, whose wife Warreeweer was the younger sister of the Wangal leader Woollarawarre Bennelong, at that time being feted in London society. The distance Gnung-a Gnung-a traversed was some 16,000 miles (25,750 kilometres) as the crow flies, but much further in a sailing ship driven by unpredictable winds.
On the first day he ventured into the convict settlement at Sydney Cove, in November 1790, Gnung-a Gnung-a adopted the name Collins from Acting Judge Advocate David Collins, who often mentions him in An Account of the English Colony in New South Wales, published in London in 1798.
It was the idea of Major Francis Grose, acting governor of New South Wales after the departure of Captain Arthur Phillip in 1792, to embark a native of this country on HM storeship Daedalus for the purpose of acquiring our language, wrote David Collins. The 350-ton capacity vessel was ordered to resupply provisions for the expedition to the north-west coast of North America commanded by Captain George Vancouver (1757–1798). In the navy ships HMS Discovery and HMS Chatham, Captain Vancouver was to complete the survey made by Captain James Cook.
Voyage to America
HMS Daedalus sailed from Port Jackson on 1 July 1793, passing west of the Society Islands (French Polynesia) to Owhyee (Hawaii). The commander, Lieutenant James Hanson, missed a rendezvous with Vancouvers ships at Nootka Sound on 8 October, but anchored with the two survey ships off San Francisco Bay on 21 October. The three British ships followed the coast of todays California to San Diego, leaving on 9 December 1793 and arriving at Hilo in Hawaii on 8 January 1794.
The Hawaiian King Kamehameha, who warmly welcomed Vancouver, was so impressed by the good-natured, handsome Aboriginal man on the expedition that he wanted to buy him, offering in exchange canoes, weapons and curiosities.
Gnung-a Gnung-a got on well with everyone on Daedalus and Hanson was pleased by his good nature and his willingness to do whatever was asked of him. During his month in Hawaii, he often went ashore with his shipmates. Wherever he went he readily adopted the manners of those around him, Hanson later told Collins, who remarked, with ironic humour, that...........
when at Owhyee, having discovered that favours from the females were to be procured at the easy exchange for a looking-glass, a nail, or a knife, he was not backward in presenting his little offering, and was as well received as any of the white people in the ship. It was noticed too that he always displayed some taste in selecting the object of his attentions.......
Return to Sydney
Home in Sydney Town, Gnung-a Gnung-a fought and wounded a very fine young fellow called Wyatt, who had taken up with his wife during his absence and Warreeweer became the prize of the victor.
During a ritual revenge combat in December 1795, Pemulwuy, leader of the Georges River Bidjigal near Botany Bay, launched a spear at Gnung-a Gnung-a that remained fixed in his back. The English surgeons could not extract the spear and thought he was unlikely to recover. Gnung-a Gnung-a, however, left the hospital and walked about for several weeks with the spear protruding from his back. At last, wrote Collins in a footnote..........
we heard that his wife, or one of his male friends, had fixed their teeth in the wood and drawn it out after which he recovered, and was able again to go into the field. His wife War-re-weer showed by an uncommon attention her great attachment to him.......
Before this unexpected recovery, David Collins wrote a brief appreciation of his namesake:
He was much esteemed by every white man who knew him, as well on account of his personal bravery, of which we had witnessed many distinguishing proofs, as on account of a gentleness of manners which strongly marked his disposition, and shaded off the harsher lines that his uncivilised life now and then forced into the fore-ground.
While in Sydney with a scientific expedition commanded by Nicholas Baudin in 1802, the young French artist Nicolas-Martin Petit met Gnung-a Gnung-a and sketched a striking portrait that he captioned Gnoung-a gnoung-a, mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
A report in the Sydney Gazette of Sunday 15 January 1809 said that the body of Collins (Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan) had been found beside the Dry Store, site of the present Sirius Park in Bridge Street, Sydney. The newspaper said he had been known for the docility of his temper, and the high estimation in which he was universally held among the native tribes.
On the night of Thursday 12 January 1809, Gnung-a Gnung-as children, others he had adopted, and his brother Old Phillip, faced a salvo of spears in the ritual ordeal that followed death in Aboriginal society. The date of his death was not recorded, but it was customary to keep an overnight vigil over a dead body before burial and the subsequent revenge combat, so it was probably 11 January.
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan is one of many Aboriginal men and women who sailed from Sydney in English ships and played a significant role in Australias early maritime history.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.