Nicolas Sanson (1600-67)
Profile :
Nicolas Sanson was born in Abbeville where as a young man he studied history, particularly the ancient world, and it is said that he turned to cartography only as a means of illustrating his historical work. For this purpose he prepared a number of beautifully drawn maps, one of which came to the attention of Louis XIII. In due course the King appointed him “ Geographe Ordinaire du Roi”.
In preparation of his major atlas, “Cartes Generales de Toutes les Parties du Monde”, Sanson employed a number of engravers, one of whom, M. Tavernier engraved important maps showing the post roads, rivers and waterway system of France (1632-34) and a map of the British Isles (1640). In all Sanson produced about 300 maps of which two of North America were particularly influential: “Amerique Septentrionale” (1650) and Le Canada ou Nouvelle France (1656).
After Sansons death the business was carried on by his two surviving sons and grandson, in partnership with A.H. Jaillot. It is generally accepted that the great age of French cartography originated with the work of Nicolas Sanson but credit must go also to A. H. Jaillot (1632 – 1712) and Pierre Duval for re-engraving his maps, many still unprinted after his death, and re-publishing them in face of strong competition from the Dutch, who continued to dominate the market until the end of the 17th century.
Nicolas Sanson (3)
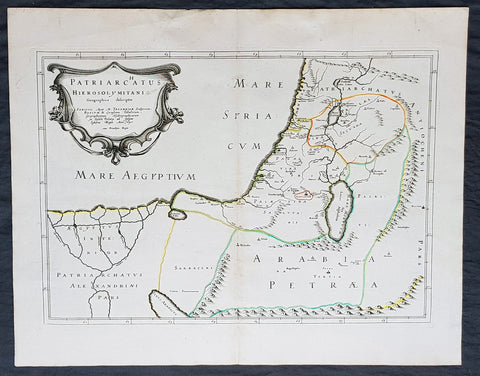
1640 Nicolas Sanson Antique Map of The Holy Land, Egypt, Saudi - Knights Templar
- Title : Patriachatus Hierosolymitani....Aput M Tavernier....1640
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 460mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1640
- Ref #: 40692
Description:
This fine original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the Holy Land, Egypt, part of Saudi Arabia and the connection to the Nights Templar (Latin: Militaris Templi Hierosolymitani) in the middle ages was engraved by Michael Tavernier in 1640 - dated in the cartouche - and was published by Nicolas Sanson in the 1653 edition of Geographia sacra, sive notitia antiqua dioecesium omnium partriarchalium, metropoliticarum, et episcopalium veteris ecclesiae. notae et animadversions Lucae Holstenii.
This is a wonderful map with original outline hand colour on strong sturdy clean paper and a heavy impression.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Templars became a favoured charity throughout Christendom and grew rapidly in membership and power. They were prominent in Christian finance. Templar knights, in their distinctive white mantles with a red cross, were among the most skilled fighting units of the Crusades. Non-combatant members of the order, who formed as much as 90% of the orders members, managed a large economic infrastructure throughout Christendom, developing innovative financial techniques that were an early form of banking, building its own network of nearly 1,000 commanderies and fortifications across Europe and the Holy Land, and arguably forming the worlds first multinational corporation.
The Templars were closely tied to the Crusades; when the Holy Land was lost, support for the order faded. Rumours about the Templars secret initiation ceremony created distrust, and King Philip IV of France – deeply in debt to the order – took advantage of this distrust to destroy them and erase his debt. In 1307, he had many of the orders members in France arrested, tortured into giving false confessions, and burned at the stake. Pope Clement V disbanded the order in 1312 under pressure from King Philip. The abrupt reduction in power of a significant group in European society gave rise to speculation, legend, and legacy through the ages.
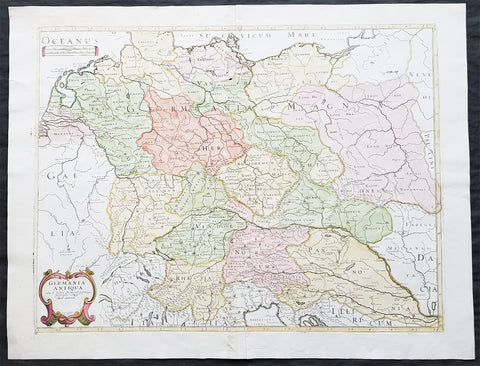
1689 Nicolas Sanson Large Antique Map of Germania & Central Europe
- Title : Germania Antiqua Aut N Sanson.....1689
- Ref #: 26191
- Size: 24in x 18 1/2in (610mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1689
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of Germania & central Europe stretching from Poland to Italy to Denmark, by Nicolas Sanson, was engraved in 1689 - dated in the cartouche - and was published by Pierre Mariette in Cartes Generales de Toutes les Parties du Monde
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 18 1/2in (610mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 16in (545mm x 405mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Germania was the Roman term for the geographical region in north-central Europe inhabited mainly by Germanic peoples.
It extended from the Danube in the south to the Baltic Sea, and from the Rhine in the west to the Vistula. The Roman portions formed two provinces of the Empire, Germania Inferior to the north (present-day southern Netherlands, Belgium, and western Germany), and Germania Superior to the south (Switzerland, southwestern Germany, and eastern France).
Germania was inhabited mostly by Germanic tribes, but also Celts, Balts, Scythians and later on Early Slavs. The population mix changed over time by assimilation, and especially by migration. The ancient Greeks were the first to mention the tribes in the area. Later, Julius Caesar wrote about warlike Germanic tribesmen and their threat to Roman Gaul, and there were military clashes between the Romans and the indigenous tribes. Tacitus wrote the most complete account of Germania that still survives.
The origin of the term Germania is uncertain, but was known by Caesars time, and may be Gaulish in origin.
Germania was inhabited by different tribes, most of them Germanic but also some Celtic, proto-Slavic, Baltic and Scythian peoples. The tribal and ethnic makeup changed over the centuries as a result of assimilation and, most importantly, migrations. The Germanic people spoke several different dialects.
Classical records show little about the people who inhabited the north of Europe before the 2nd century BC. In the 5th century BC, the Greeks were aware of a group they called Celts (Keltoi). Herodotus also mentioned the Scythians but no other tribes. At around 320 BC, Pytheas of Massalia sailed around Britain and along the northern coast of Europe, and what he found on his journeys was so strange that later writers refused to believe him. He may have been the first Mediterranean to distinguish the Germanic people from the Celts. Contact between German tribes and the Roman Empire did take place and was not always hostile. Recent excavations of the Waldgirmes Forum show signs that a civilian Roman town was established there, which has been interpreted to mean that Romans and Germanic tribesmen were living in peace, at least for a while.
Caesar described the cultural differences between the Germanic tribesmen, the Romans, and the Gauls in his book Commentarii de Bello Gallico, where he recalls his defeat of the Suebi tribes at the Battle of Vosges. He describes them at length at the beginning of Book IV and the middle of Book VI. He states that the Gauls, although warlike, had a functional society and could be civilized, but that the Germanic tribesmen were far more savage and were a threat to Roman Gaul and Rome itself. Caesar said the Germanic tribes were nomadic, with no notable settlements and a primitive culture. He used this as one of his justifications for why they had to be conquered. His accounts of barbaric northern tribes could be described as an expression of the superiority of Rome, including Roman Gaul.
Caesars accounts portray the Roman fear of the Germanic tribes and the threat they posed. The perceived menace of the Germanic tribesmen proved accurate. The most complete account of Germania that has been preserved from Roman times is Tacitus Germania.
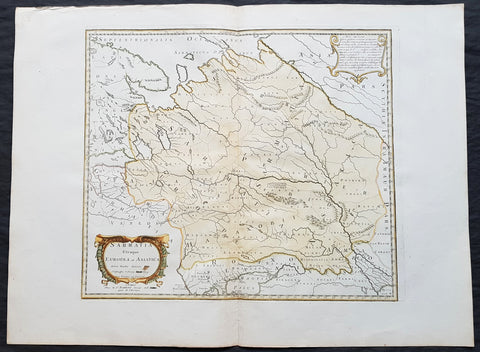
1741 Nicolas Sanson Large Antique Map of Sarmatia, Modern Day Russia & Ukraine
- Title : Sarmatia Utraque Europaea et Asiatica Autore Nicolas Sanson...1741
- Ref #: 50602
- Size: 27in x 20 1/4in (690mm x 515mm)
- Date : 1741
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the land of the Sarmatians - today stretching encompassing modern day European Russia and Ukraine and central Asia by Nicolas Sanson, was engraved in 1741 - dated in the cartouche - and was published by Robert De Vaugondy in a re-issue of Sansons atlas Cartes Generales de Toutes les Parties du Monde
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 20 1/4in (690mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 16 1/2in (485mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Sarmatians were a large Iranian confederation that existed in classical antiquity, flourishing from about the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD.
Originating in the central parts of the Eurasian Steppe, the Sarmatians started migrating westward around the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, coming to dominate the closely related Scythians by 200 BC. At their greatest reported extent, around 1st century AD, these tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black and Caspian seas as well as the Caucasus to the south. Their territory, which was known as Sarmatia to Greco-Roman ethnographers, corresponded to the western part of greater Scythia (it included todays Central Ukraine, South-Eastern Ukraine, Southern Russia, Russian Volga and South-Ural regions, also to a smaller extent north-eastern Balkans and around Moldova). In the 1st century AD, the Sarmatians began encroaching upon the Roman Empire in alliance with Germanic tribes. In the 3rd century AD, their dominance of the Pontic Steppe was broken by the Germanic Goths. With the Hunnic invasions of the 4th century, many Sarmatians joined the Goths and other Germanic tribes (Vandals) in the settlement of the Western Roman Empire. Since large parts of todays Russia, actually the land between the Ural Mountains and the Don River, were controlled in the 5th century BC by the Sarmatians, Volga–Don and Ural steppes sometimes are also called Sarmatian Motherland.
The Sarmatians were eventually decisively assimilated (e.g. Slavicisation) and absorbed by the Proto-Slavic population of Eastern Europe.