Maps (72)
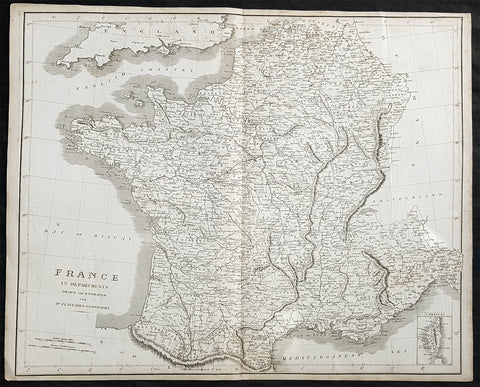
1814 Dr Playfairs Large Antique Map of France in Departments
Antique Map
- Title : France in Departments Drawn and Engraved for Dr Playfairs Geography.
- Size: 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1814
- Ref #: 31154
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved map of France was published in the 1814 edition of A System of Geography Ancient and Modern (1810–14) (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
Playfair, Rev James Octavius 1738 - 1819
Rev Playfair was a Scottish minister and author and an eminent figure in the Scottish Enlightenment. He was born at West Bendochy in Perthshire the son of George Playfair (d. 1786), a farmer, and his wife, Jean Roger (d. 1804).[1]
He studied at St Andrews University and then became minister of Newtyle (1770–77) and Meigle (1777–1800). He was then appointed Principal of St Andrews University in 1800. During this period he was also minister of St Leonard\\\'s Church in St Andrews.
In 1779 St Andrews awarded him an honorary doctorate (DD). In 1787 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposers were John Playfair (a distant cousin) and Alexander Fraser Tytler.[2]
He was the official histiographer of the then Prince of Wales.
He died at Dalmarnock near Glasgow. He is buried in Glasgow but is also memorialised on the grave of his wife in the churchyard of St Andrews Cathedral.
Publications:
1. A System of Chronology (1782)
2. A System of Geography Ancient and Modern (1810–14)
3. General Atlas Ancient and Modern (1814)
4. A Geographical and Statistical Description of Scotland (1819)
1856 Capt. Richard Delafield Antique Map City & Naval Defenses of Toulon, France
Antique Map
- Title : Defenses of the Harbor and Naval Depot at Toulon
- Ref #: 90127
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original lithograph map of the city and naval defenses of Toulon, France was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Llight age toning along folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
In the beginning of 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
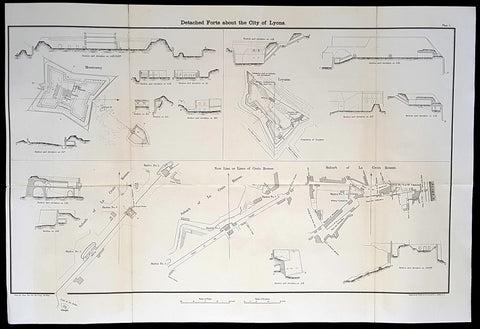
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics Forts City of Lyons, France
Antique Map
- Title : Detached Forts about the City of Lyons
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90193
- Size: 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
This large original lithograph print, schematics of the forts or Belts of Lyon, France - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 29in x 20in (735mm x 515mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The ceintures de Lyon (Belts of Lyon) were a series of fortifications built between 1830 and 1890 around the city of Lyon, France to protect the city from foreign invasion.
The belts comprised two defensive barriers that included forts, lunettes, ramparts, batteries, and other defensive structures. Many of these structures proved to be ineffective in war due to advancement in weapon technology and the evolution of attack strategies at the time. Some of the fortifications of the ceintures de Lyon have been destroyed, though many remain today.
In 1830 the maréchal de camp, Hubert Rohault de Fleury, commenced a project designed by military engineer Baron Haxo. With a budget of 10,000,000 francs (approximately €67,000,000 as of 2015) allocated for Lyon between 1831 and 1839, this first project included the restoration of the fortifications between Croix Rousse and Fourvière; the construction of two forts on the plateau of Caluire (Fort de Montessuy and Fort de Caluire, connected by the Enceinte de Caluire), facing the Dombes; closing access to the Presquîle by the construction of a south-facing building; building two forts – Fort de la Duchère and Fort de Grange Blanche – to protect access routes towards Paris and Auvergne.
The fortification of the city is divided into three sectors: The north was protected by the wall of Croix-Rousse and the structures between the Rhône and the Saône. The command was situated at fort de Montessuy. The west was covered by the hillfort of Fourvière and the associated forts of Vaise at Sainte-Foy. The command was situated at fort Saint-Irénée. The east was defended by the Redoute du Haut-Rhône and Fort de la Vitriolerie on the left bank of the Rhône. The command was situated at Fort Lamothe.
The work required almost 20,000 workers, which were locally sourced in an attempt to avoid insurrection such as the ongoing unrest of the Lyon silk workers (Canuts) over increased capitalism. Work began in 1831 to build seven structures, each structure requiring between 400 and 500 workers. The scope of this project included the construction of Fort de Montessuy and Fort de Caluire to the north; Fort des Brotteaux, Fort Montluc and Fort du Colombier to the east; the Redoute de la Part-Dieu to the west; and Fort Saint-Irénée, to protect the entire area.
In January 1831, an uprising began at a work site in Charpennes, however it was quickly stopped by the army. Other insurrections took place the same year, a series of Canut revolts, which succeeded in rallying soldiers on the side of the Canuts, resulting in the death of captain Viquesnel, aide-de-camp of Fleury, and the temporary withdrawal of the 20,000 soldiers who eventually retook the city in December 1831.
In 1832, three other structures were built to reinforce the defenses to the east: The Redoute de la Tête dor, Fort La Motte, and the Redoute des Hirondelles. A treaty was signed between the city of Lyon and the War Department, which stipulated that the city had to cede the land necessary for the construction of military buildings to the War Department, while the forts themselves would still belong to the city if the military decided to abandon them. It is thanks to this treaty that the forts of Croix Rousse, Fourvière, Loyasse, Vaise, and Saint-Jean would later be returned to the city.
Construction resumed in 1840. First the Fort de la Vitriolerie in 1840, then Fort de Sainte-Foy-lès-Lyon and the Lunette des Charpennes in 1842, Fort de la Duchère in 1844, the Redoute du Petit Sainte-Foy-lès-Lyon in 1852, and finally the Redoute du haut-Rhône in 1854.
A law was voted in on 10 July 1851, which defined the methods of destruction of these buildings or construction on their land. By 1854, 19 structures including 10 forts had been built around Lyon, creating a nearly 14-kilometre (8.7 mi) fortified perimeter.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
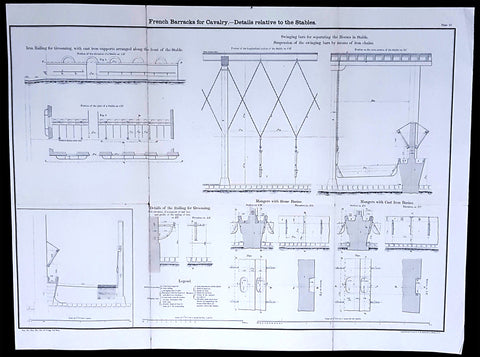
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics of French Calvary Barracks, Stables
Antique Map
- Title : French Barracks for Cavalry - Details relative to the Stables
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90125
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, internal schematics of the French Cavalry Barracks & Stables - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The arrival of explosive shells in the 19th century led to yet another stage in the evolution of fortification. Star forts did not fare well against the effects of high explosive and the intricate arrangements of bastions, flanking batteries and the carefully constructed lines of fire for the defending cannon could be rapidly disrupted by explosive shells.
Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the counter scarp. The ditch was extremely vulnerable to bombardment with explosive shells.
In response, military engineers evolved the polygonal style of fortification. The ditch became deep and vertically sided, cut directly into the native rock or soil, laid out as a series of straight lines creating the central fortified area that gives this style of fortification its name.
Wide enough to be an impassable barrier for attacking troops, but narrow enough to be a difficult target for enemy shellfire, the ditch was swept by fire from defensive blockhouses set in the ditch as well as firing positions cut into the outer face of the ditch itself.
The profile of the fort became very low indeed, surrounded outside the ditch covered by caponiers by a gently sloping open area so as to eliminate possible cover for enemy forces, while the fort itself provided a minimal target for enemy fire. The entrypoint became a sunken gatehouse in the inner face of the ditch, reached by a curving ramp that gave access to the gate via a rolling bridge that could be withdrawn into the gatehouse.
Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the blockhouses and firing points in the ditch to the fort proper, with magazines and machine rooms deep under the surface. The guns, however, were often mounted in open emplacements and protected only by a parapet; both in order to keep a lower profile and also because experience with guns in closed casemates had seen them put out of action by rubble as their own casemates were collapsed around them.
Gone were citadels surrounding towns: forts were to be moved to the outside of the cities some 12 km to keep the enemy at a distance so their artillery could not bombard the city center. From now on a ring of forts were to be built at a spacing that would allow them to effectively cover the intervals between them.
The new forts abandoned the principle of the bastion, which had also been made obsolete by advances in arms. The outline was a much simplified polygon, surrounded by a ditch. These forts, built in masonry and shaped stone, were designed to shelter their garrison against bombardment. One organizing feature of the new system involved the construction of two defensive curtains: an outer line of forts, backed by an inner ring or line at critical points of terrain or junctions (see, for example, Séré de Rivières system in France).
Traditional fortification however continued to be applied by European armies engaged in warfare in colonies established in Africa against lightly armed attackers from amongst the indigenous population. A relatively small number of defenders in a fort impervious to primitive weaponry could hold out against high odds, the only constraint being the supply of ammunition.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
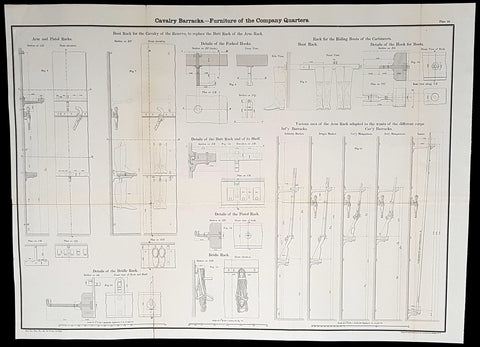
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics of Calvary Barracks Rifles, Pistols
Antique Map
- Title : Cavalry Barracks - Furniture of the Company Quarters...
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90133
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of the internals of cavalry barracks and quarters (guns, boots, pistols etc) - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The arrival of explosive shells in the 19th century led to yet another stage in the evolution of fortification. Star forts did not fare well against the effects of high explosive and the intricate arrangements of bastions, flanking batteries and the carefully constructed lines of fire for the defending cannon could be rapidly disrupted by explosive shells.
Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the counter scarp. The ditch was extremely vulnerable to bombardment with explosive shells.
In response, military engineers evolved the polygonal style of fortification. The ditch became deep and vertically sided, cut directly into the native rock or soil, laid out as a series of straight lines creating the central fortified area that gives this style of fortification its name.
Wide enough to be an impassable barrier for attacking troops, but narrow enough to be a difficult target for enemy shellfire, the ditch was swept by fire from defensive blockhouses set in the ditch as well as firing positions cut into the outer face of the ditch itself.
The profile of the fort became very low indeed, surrounded outside the ditch covered by caponiers by a gently sloping open area so as to eliminate possible cover for enemy forces, while the fort itself provided a minimal target for enemy fire. The entrypoint became a sunken gatehouse in the inner face of the ditch, reached by a curving ramp that gave access to the gate via a rolling bridge that could be withdrawn into the gatehouse.
Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the blockhouses and firing points in the ditch to the fort proper, with magazines and machine rooms deep under the surface. The guns, however, were often mounted in open emplacements and protected only by a parapet; both in order to keep a lower profile and also because experience with guns in closed casemates had seen them put out of action by rubble as their own casemates were collapsed around them.
Gone were citadels surrounding towns: forts were to be moved to the outside of the cities some 12 km to keep the enemy at a distance so their artillery could not bombard the city center. From now on a ring of forts were to be built at a spacing that would allow them to effectively cover the intervals between them.
The new forts abandoned the principle of the bastion, which had also been made obsolete by advances in arms. The outline was a much simplified polygon, surrounded by a ditch. These forts, built in masonry and shaped stone, were designed to shelter their garrison against bombardment. One organizing feature of the new system involved the construction of two defensive curtains: an outer line of forts, backed by an inner ring or line at critical points of terrain or junctions (see, for example, Séré de Rivières system in France).
Traditional fortification however continued to be applied by European armies engaged in warfare in colonies established in Africa against lightly armed attackers from amongst the indigenous population. A relatively small number of defenders in a fort impervious to primitive weaponry could hold out against high odds, the only constraint being the supply of ammunition.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
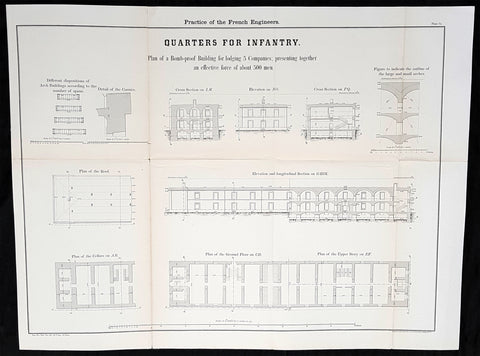
1856 Capt Delafield Large Antique Schematics French Infantry Barracks & Quarters
Antique Map
- Title : Theory and Practice of the French Engineers....Quaters for Infantry..Plan of the Bob Proof Building for lodging 5 Companies presenting together an effective force of about 500 men.
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90126
- Size: 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Description:
This large original lithograph print, schematics of barracks and quarters for infantry in France - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 20in (660mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The arrival of explosive shells in the 19th century led to yet another stage in the evolution of fortification. Star forts did not fare well against the effects of high explosive and the intricate arrangements of bastions, flanking batteries and the carefully constructed lines of fire for the defending cannon could be rapidly disrupted by explosive shells.
Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the counter scarp. The ditch was extremely vulnerable to bombardment with explosive shells.
In response, military engineers evolved the polygonal style of fortification. The ditch became deep and vertically sided, cut directly into the native rock or soil, laid out as a series of straight lines creating the central fortified area that gives this style of fortification its name.
Wide enough to be an impassable barrier for attacking troops, but narrow enough to be a difficult target for enemy shellfire, the ditch was swept by fire from defensive blockhouses set in the ditch as well as firing positions cut into the outer face of the ditch itself.
The profile of the fort became very low indeed, surrounded outside the ditch covered by caponiers by a gently sloping open area so as to eliminate possible cover for enemy forces, while the fort itself provided a minimal target for enemy fire. The entrypoint became a sunken gatehouse in the inner face of the ditch, reached by a curving ramp that gave access to the gate via a rolling bridge that could be withdrawn into the gatehouse.
Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the blockhouses and firing points in the ditch to the fort proper, with magazines and machine rooms deep under the surface. The guns, however, were often mounted in open emplacements and protected only by a parapet; both in order to keep a lower profile and also because experience with guns in closed casemates had seen them put out of action by rubble as their own casemates were collapsed around them.
Gone were citadels surrounding towns: forts were to be moved to the outside of the cities some 12 km to keep the enemy at a distance so their artillery could not bombard the city center. From now on a ring of forts were to be built at a spacing that would allow them to effectively cover the intervals between them.
The new forts abandoned the principle of the bastion, which had also been made obsolete by advances in arms. The outline was a much simplified polygon, surrounded by a ditch. These forts, built in masonry and shaped stone, were designed to shelter their garrison against bombardment. One organizing feature of the new system involved the construction of two defensive curtains: an outer line of forts, backed by an inner ring or line at critical points of terrain or junctions (see, for example, Séré de Rivières system in France).
Traditional fortification however continued to be applied by European armies engaged in warfare in colonies established in Africa against lightly armed attackers from amongst the indigenous population. A relatively small number of defenders in a fort impervious to primitive weaponry could hold out against high odds, the only constraint being the supply of ammunition.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873 - Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
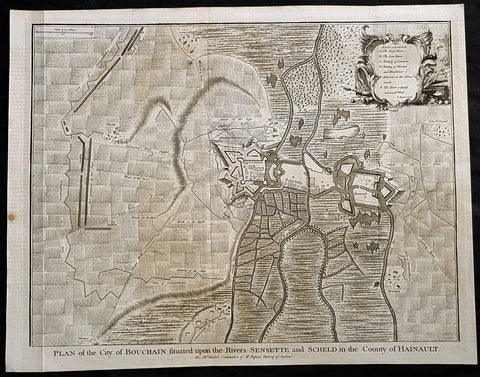
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22156-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
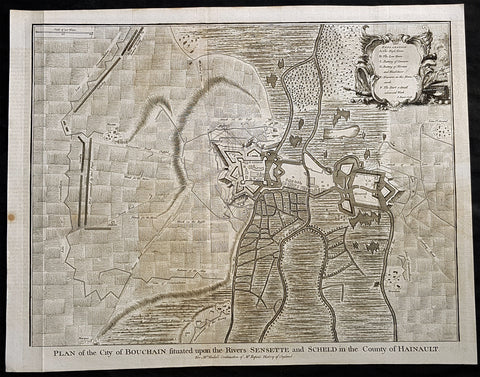
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22156-1
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
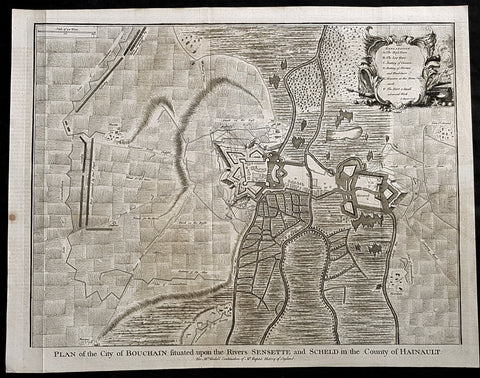
1745 Tindal Antique Map Battle Plan of Siege of Bouchain, Calais, France in 1711
Antique Map
- Title : Plan of the City of Bouchain Situated upon the Rivers Sensette and Scheld in the County of Hainault
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 22198
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, battle plan & birds eye view of the French city of Bouchain on the Schedlt River, in the Pas-de-Calais dept. in northern France - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engraved by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Siege of Bouchain (9 August – 12 September 1711), following the Passage of the Lines of Ne Plus Ultra (5 August 1711), was a siege of the War of the Spanish Succession, and the last major victory of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. Marlborough broke through the French defensive lines and took Bouchain after a siege of 34 days. Its capture left Cambrai the only French-held fortress between the allied army and Paris.
Throughout the early summer of 1711 Marlborough\'s army, having taken the important fortress of Douai the previous year, manoeuvred indecisively in northern France, blocked by the French Lines of Ne Plus Ultra – a massive series of fieldworks stretching from the Channel coast to the Ardennes at Namur. The allied army had been weakened by the withdrawal of Prince Eugene\'s army to cover the upper Rhine, as the deposed Elector of Bavaria attempted to take advantage of the disruption caused by the death of the Emperor Joseph. On 6 July, Marlborough captured the small fortress of Arleux, just to the north of the Lines, west of Bouchain, both to deny its use to the French as a sally-port, and to secure the water supply to Douai, which could be cut off by damming the canal that supplied the town. The Duke was then wrong-footed by Villars as the French army crossed the Lines on 22/23 July and retook Arleux, with the allied army too far to the west to intervene in time, and the defences were levelled before the French retreated back across the Lines. Marlborough, initially furious, soon retook the initiative by marching his army as if to assault the Lines near Arras, and carrying out a detailed personal reconnaissance there on 4 August in full view of Villars\' covering army. That night the army struck camp, leaving their campfires burning to deceive the French, and marched eastwards to Arleux. At midnight a force from Douai under Cadogan crossed the unguarded French lines, and by 8 am the advance guard of the main army was also crossing over. Villars, arriving on the scene with a few hundred cavalry, realised he had been outmanoeuvred, and though he attempted to offer battle in front of Bourlon Wood, Marlborough declined to attack, the Marshal\'s position being even stronger than the one in which he had given Marlborough\'s army such a mauling two years earlier at Malplaquet. He thus drew off and attempted to hinder Marlborough\'s siege of Bouchain which followed.
To defend the town Bouchain\'s governor, de Ravignau, had some 5,000 men against Marlborough\'s besieging army of 30,000, and the advantage of one of the strongest fortresses left to France, surrounded by the marshy land of the confluence of the rivers Scheldt and Sensée. In addition, Villars\' strong army had taken up position to the west of the allied camp, and had managed to open a tenuous link to the besieged garrison. Marlborough responded by using earthwork gun batteries to counter Villars, used a crack assault force managed by 18 August to once more cut the Marshal\'s communication with Bouchain, and established a fieldwork-protected corridor from the siege camp to his main supply port at Marchiennes on the Scarpe. Frequent raids by Villars on both the supply convoys on the Scarpe, and towards Douai, failed to interrupt the siege, and the garrison marched out to become prisoners of war on 13 September 1711.
Bouchain was Marlborough\'s last campaign. On the last day of the year he was stripped of his position as Captain-General, and of all his other offices. Command of the army on the continent for the campaign of 1712 was given to the Duke of Ormonde, and strict limitations were placed on his freedom of movement. Particularly he was prohibited from engaging the French in battle, as Anglo-French peace talks were well advanced, and the opportunity of seizing Cambrai and marching on Paris, opened by Marlborough\'s gains the year before, was abandoned. Before the year was out, the British army would withdraw from the alliance, leaving the remaining allies, under Eugene of Savoy to be defeated at Denain.
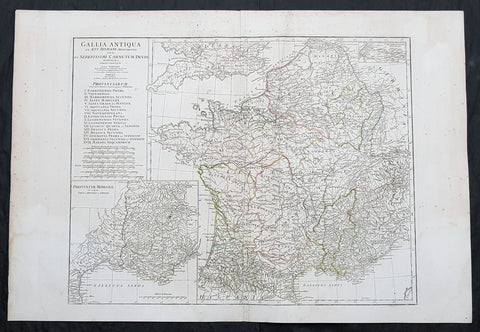
1760 J B D Anville Large Antique Map of Roman France
Antique Map
- Title : Gallia Antiqua ex Aevi Romani......D Anville...MDCCLX
- Size: 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1760 (dated)
- Ref #: 92296
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique map of Roman France was engraved in 1760 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anvilles large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21in (760mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 23 1/2in x 18 1/4in (595mm x 465mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing, light age toning
Plate area: - Creasing
Verso: - Creasing, light age toning
Background:
In 600 BC, Ionian Greeks, originating from Phocaea, founded the colony of Massalia (present-day Marseille), on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. This makes it Frances oldest city. At the same time, some Gallic Celtic tribes penetrated parts of the current territory of France, and this occupation spread to the rest of France between the 5th and 3rd century BC.
The concept of Gaul emerged at that time; it corresponds to the territories of Celtic settlement ranging between the Rhine, the Atlantic Ocean, the Pyrenees and the Mediterranean. The borders of modern France are roughly the same as those of ancient Gaul, which was inhabited by Celtic Gauls. Gaul was then a prosperous country, of which the southernmost part was heavily subject to Greek and Roman cultural and economic influences.
Around 390 BC the Gallic chieftain Brennus and his troops made their way to Italy through the Alps, defeated the Romans in the Battle of the Allia, and besieged and ransomed Rome. The Gallic invasion left Rome weakened, and the Gauls continued to harass the region until 345 BC when they entered into a formal peace treaty with Rome. But the Romans and the Gauls would remain adversaries for the next centuries, and the Gauls would continue to be a threat in Italy.
Around 125 BC, the south of Gaul was conquered by the Romans, who called this region Provincia Nostra (Our Province), which over time evolved into the name Provence in French. Julius Caesar conquered the remainder of Gaul and overcame a revolt carried out by the Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix in 52 BC. According to Plutarch and the writings of scholar Brendan Woods, the Gallic Wars resulted in 800 conquered cities, 300 subdued tribes, one million men sold into slavery, and another three million dead in battle.
Gaul was divided by Augustus into Roman provinces. Many cities were founded during the Gallo-Roman period, including Lugdunum (present-day Lyon), which is considered the capital of the Gauls. These cities were built in traditional Roman style, with a forum, a theatre, a circus, an amphitheatre and thermal baths. The Gauls mixed with Roman settlers and eventually adopted Roman culture and Roman speech (Latin, from which the French language evolved). The Roman polytheism merged with the Gallic paganism into the same syncretism.
From the 250s to the 280s AD, Roman Gaul suffered a serious crisis with its fortified borders being attacked on several occasions by barbarians. Nevertheless, the situation improved in the first half of the 4th century, which was a period of revival and prosperity for Roman Gaul. In 312, Emperor Constantin I converted to Christianity. Subsequently, Christians, who had been persecuted until then, increased rapidly across the entire Roman Empire. But, from the beginning of the 5th century, the Barbarian Invasions resumed. Teutonic tribes invaded the region from present-day Germany, the Visigoths settling in the southwest, the Burgundians along the Rhine River Valley, and the Franks (from whom the French take their name) in the north.
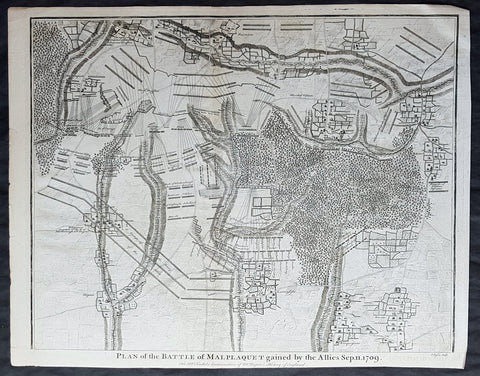
1745 Nicolas Tindal Original Antique Map Battle of Malplaquet, Northern France in 1709
- Title : Plan of the Battle of Malplaquet gained by the Allies Sep. 11 1709.
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Ref #: 15659
- Date : 1745
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique map, plan of the Battle of Malplaquet, northern France in 1709 - during the Spanish War of Succession (1701-13) - was engrvaed by John Basire and was published in the 1745 edition of Nicholas Tindals Continuation of Mr. Rapin\'s History of England.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession. Led by the Duke of Marlborough, the army of the Grand Alliance attacked and defeated the French army near Malplaquet under the command of Marshal Villars. The heavy losses suffered by the Allies caused the battle to be considered a Pyrrhic victory.
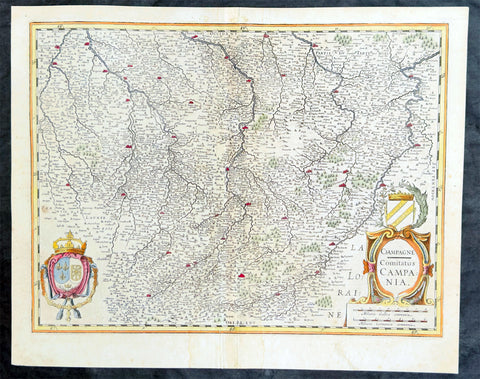
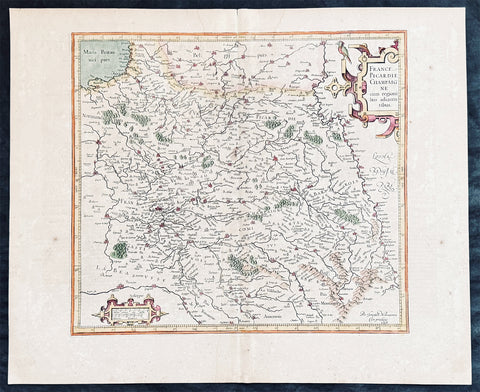
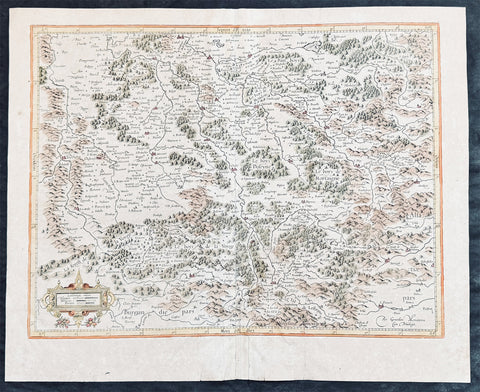
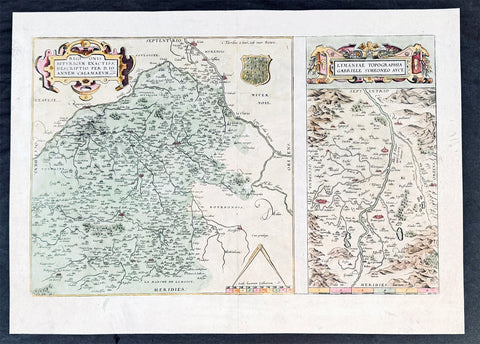
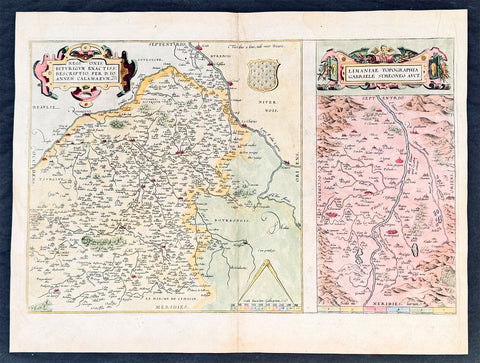
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map, Champagne Region of France
- Title : Champagne...Comitatus Campania
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26134
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Champagne by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, blue, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map, Champagne Region of France
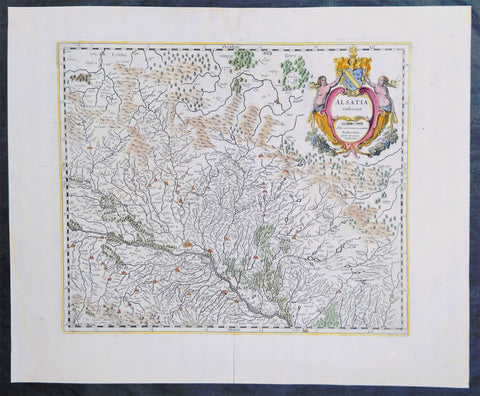
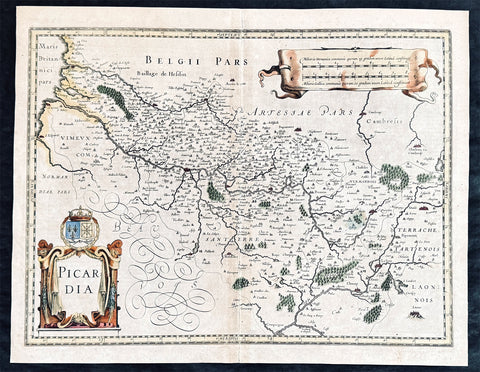
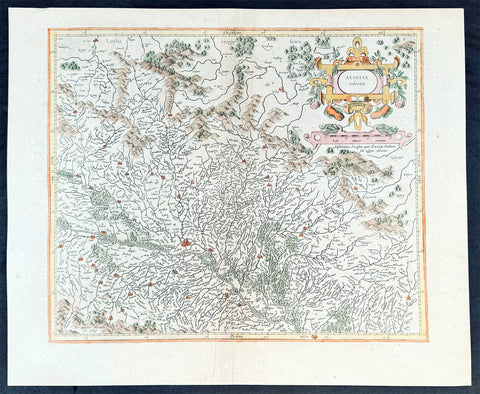
1638 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Alsace Region, France
- Title : Alsatia inferior..Per Gerardam Mercatorem Cum privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1638
- Ref #: 92839
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Alsace by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1638 German edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Alsace is a cultural and historical region in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland.
As in much of Europe, the prosperity of Alsace came to an end in the 14th century by a series of harsh winters, bad harvests, and the Black Death. These hardships were blamed on Jews, leading to the pogroms of 1336 and 1339. In 1349, Jews of Alsace were accused of poisoning the wells with plague, leading to the massacre of thousands of Jews during the Strasbourg pogrom. Jews were subsequently forbidden to settle in the town. An additional natural disaster was the Rhine rift earthquake of 1356, one of Europes worst which made ruins of Basel. Prosperity returned to Alsace under Habsburg administration during the Renaissance.
Holy Roman Empire central power had begun to decline following years of imperial adventures in Italian lands, often ceding hegemony in Western Europe to France, which had long since centralized power. France began an aggressive policy of expanding eastward, first to the rivers Rhône and Meuse, and when those borders were reached, aiming for the Rhine. In 1299, the French proposed a marriage alliance between Philip IV of Frances sister Blanche and Albert I of Germanys son Rudolf, with Alsace to be the dowry; however, the deal never came off. In 1307, the town of Belfort was first chartered by the Counts of Montbéliard. During the next century, France was to be militarily shattered by the Hundred Years War, which prevented for a time any further tendencies in this direction. After the conclusion of the war, France was again free to pursue its desire to reach the Rhine and in 1444 a French army appeared in Lorraine and Alsace. It took up winter quarters, demanded the submission of Metz and Strasbourg and launched an attack on Basel.
In 1469, following the Treaty of St. Omer [fr], Upper Alsace was sold by Archduke Sigismund of Austria to Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy. Although Charles was the nominal landlord, taxes were paid to Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor. The latter was able to use this tax and a dynastic marriage to his advantage to gain back full control of Upper Alsace (apart from the free towns, but including Belfort) in 1477 when it became part of the demesne of the Habsburg family, who were also rulers of the empire. The town of Mulhouse joined the Swiss Confederation in 1515, where it was to remain until 1798.
By the time of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century, Strasbourg was a prosperous community, and its inhabitants accepted Protestantism in 1523. Martin Bucer was a prominent Protestant reformer in the region. His efforts were countered by the Roman Catholic Habsburgs who tried to eradicate heresy in Upper Alsace. As a result, Alsace was transformed into a mosaic of Catholic and Protestant territories. On the other hand, Mömpelgard (Montbéliard) to the southwest of Alsace, belonging to the Counts of Württemberg since 1397, remained a Protestant enclave in France until 1793.
This situation prevailed until 1639, when most of Alsace was conquered by France to keep it out of the hands of the Spanish Habsburgs, who by secret treaty in 1617 had gained a clear road to their valuable and rebellious possessions in the Spanish Netherlands, the Spanish Road. Beset by enemies and seeking to gain a free hand in Hungary, the Habsburgs sold their Sundgau territory (mostly in Upper Alsace) to France in 1646, which had occupied it, for the sum of 1.2 million Thalers. When hostilities were concluded in 1648 with the Treaty of Westphalia, most of Alsace was recognized as part of France, although some towns remained independent. The treaty stipulations regarding Alsace were complex. Although the French king gained sovereignty, existing rights and customs of the inhabitants were largely preserved. France continued to maintain its customs border along the Vosges mountains where it had been, leaving Alsace more economically oriented to neighbouring German-speaking lands. The German language remained in use in local administration, in schools, and at the (Lutheran) University of Strasbourg, which continued to draw students from other German-speaking lands. The 1685 Edict of Fontainebleau, by which the French king ordered the suppression of French Protestantism, was not applied in Alsace. France did endeavour to promote Catholicism. Strasbourg Cathedral, for example, which had been Lutheran from 1524 to 1681, was returned to the Catholic Church. However, compared to the rest of France, Alsace enjoyed a climate of religious tolerance.
France consolidated its hold with the 1679 Treaties of Nijmegen, which brought most remaining towns under its control. France seized Strasbourg in 1681 in an unprovoked action. These territorial changes were recognised in the 1697 Treaty of Ryswick that ended the War of the Grand Alliance.
The year 1789 brought the French Revolution and with it the first division of Alsace into the départements of Haut- and Bas-Rhin. Alsatians played an active role in the French Revolution. On 21 July 1789, after receiving news of the Storming of the Bastille in Paris, a crowd of people stormed the Strasbourg city hall, forcing the city administrators to flee and putting symbolically an end to the feudal system in Alsace. In 1792, Rouget de Lisle composed in Strasbourg the Revolutionary marching song La Marseillaise (as Marching song for the Army of the Rhine), which later became the anthem of France. La Marseillaise was played for the first time in April of that year in front of the mayor of Strasbourg Philippe-Frédéric de Dietrich. Some of the most famous generals of the French Revolution also came from Alsace, notably Kellermann, the victor of Valmy, Kléber, who led the armies of the French Republic in Vendée and Westermann, who also fought in the Vendée.
At the same time, some Alsatians were in opposition to the Jacobins and sympathetic to the restoration of the monarchy pursued by the invading forces of Austria and Prussia who sought to crush the nascent revolutionary republic. Many of the residents of the Sundgau made pilgrimages to places like Mariastein Abbey, near Basel, in Switzerland, for baptisms and weddings. When the French Revolutionary Army of the Rhine was victorious, tens of thousands fled east before it. When they were later permitted to return (in some cases not until 1799), it was often to find that their lands and homes had been confiscated. These conditions led to emigration by hundreds of families to newly vacant lands in the Russian Empire in 1803–4 and again in 1808. A poignant retelling of this event based on what Goethe had personally witnessed can be found in his long poem Hermann and Dorothea.
In response to the hundred day restoration of Napoleon I of France in 1815, Alsace along with other frontier provinces of France was occupied by foreign forces from 1815 to 1818, including over 280,000 soldiers and 90,000 horses in Bas-Rhin alone. This had grave effects on trade and the economy of the region since former overland trade routes were switched to newly opened Mediterranean and Atlantic seaports.
The population grew rapidly, from 800,000 in 1814 to 914,000 in 1830 and 1,067,000 in 1846. The combination of economic and demographic factors led to hunger, housing shortages and a lack of work for young people. Thus, it is not surprising that people left Alsace, not only for Paris – where the Alsatian community grew in numbers, with famous members such as Baron Haussmann – but also for more distant places like Russia and the Austrian Empire, to take advantage of the new opportunities offered there: Austria had conquered lands in Eastern Europe from the Ottoman Empire and offered generous terms to colonists as a way of consolidating its hold on the new territories. Many Alsatians also began to sail to the United States, settling in many areas from 1820 to 1850. In 1843 and 1844, sailing ships bringing immigrant families from Alsace arrived at the port of New York. Some settled in Texas and Illinois, many to farm or to seek success in commercial ventures: for example, the sailing ships Sully (in May 1843) and Iowa (in June 1844) brought families who set up homes in northern Illinois and northern Indiana. Some Alsatian immigrants were noted for their roles in 19th-century American economic development. Others ventured to Canada to settle in southwestern Ontario, notably Waterloo County.
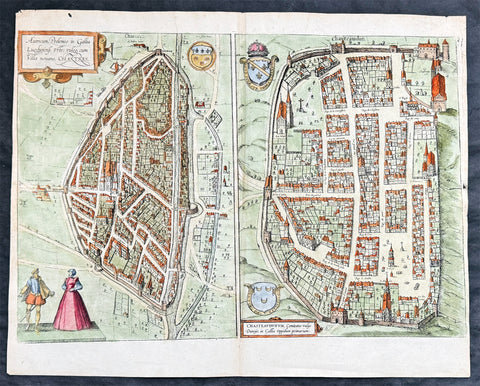
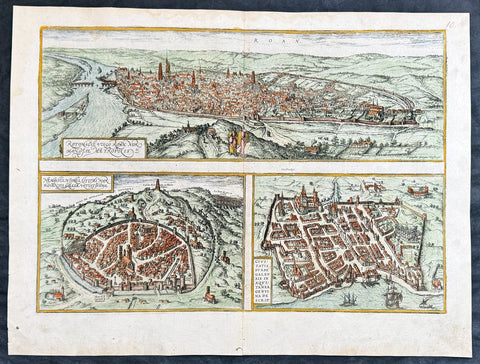
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Birds Eye Views Chartres & Chateaudu Loire France
- Title : Autricum, Prolemeo in Gallia Lugdunensis Urbs; vulgo, cum Villa nouano, Chartres / Chasteaudunum, Comitatus vulgo Dunoys in Gallia Oppidum primorium
- Size: 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 30267
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique print, a birds eye view of cities of Chartres and Chateaudu , in Loire, France was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarumintended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius\'s master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Chartres is a commune and capital of the Eure-et-Loir department in France. It is located about 90 km (56 mi) southwest of Paris.
Chartres was in Gaul one of the principal towns of the Carnutes, a Celtic tribe. In the Gallo-Roman period, it was called Autricum, name derived from the river Autura (Eure), and afterwards civitas Carnutum, city of the Carnutes, from which Chartres got its name. The city was burned by the Normans in 858, and unsuccessfully besieged by them in 911.
During the Middle Ages, it was the most important town of the Beauce. It gave its name to a county which was held by the counts of Blois, and the counts of Champagne, and afterwards by the House of Châtillon, a member of which sold it to the Crown in 1286.
In 1417, during the Hundred Years War, Chartres fell into the hands of the English, from whom it was recovered in 1432.
In 1528, it was raised to the rank of a duchy by Francis I.
In 1568, during the Wars of Religion, Chartres was unsuccessfully besieged by the Huguenot leader, the Prince of Condé. It was finally taken by the royal troops of Henry IV on 19 April 1591. On Sunday, 27 February 1594, the cathedral of Chartres was the site of the coronation of Henry IV after he converted to the Catholic faith, the only king of France whose coronation ceremony was not performed in Reims.
In 1674, Louis XIV raised Chartres from a duchy to a duchy peerage in favor of his nephew, Duke Philippe II of Orléans. The title of Duke of Chartres was hereditary in the House of Orléans, and given to the eldest son of the Duke of Orléans.
In the 1870-1871 Franco-Prussian War, Chartres was seized by the Germans on 2 October 1870, and continued during the rest of the war to be an important centre of operations.
Chateaudun is located about 45 km northwest of Orléans, and about 50 km south-southwest of Chartres. It lies on the river Loir, a tributary of the Sarthe.
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map City Views of Rouen, Nimes & Bordeaux France
- Title : Rotomagus Vulgo Roan Normandie Metropolis / Nemausus, Nismes, Civitas Narbonensis . . . / Civitatis Burdengalensis in Aquitanea, Genuina Descrip (Rouen, Nimes & Bordeaux)
- Size: 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 40168
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique of 3 x maps, birds eye city views of Rouen, Nime, and Bordeaux, France was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius Master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (480mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Rouen: The cities favourable position between the Seine to the south and the hills in the north is clearly illustrated in this view; which is seen from the east from an ideal hill and which also shows the intact city walls from the Roman era. The staffage emphasizes the course taken by the road from Paris leading into the city.
Nimes was a flourishing settlement even in Celtic times and due to its favourable location on the Via Domitia, a major transportation route linking Italy and Spain, was developed into the capital of Narbonensis province. Amongst other things, it was given a 7-km-long city wall and the dominant Tour Magne watchtower (top centre). Also stemming from Roman times is the imposing amphitheatre which could seat some 23,000 spectators and is used for performances even today. Its facade, comprising two storeys, each with 60 arches, is clearly recognizable, even in foreshortening. Above the cathedral and clock tower lies the Maison Carrée, a Roman temple built by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa around 19 B.C. The 49-m-high Pont du Gard aqueduct, mentioned by Braun and visible top right, is an important work of Roman civil engineering.
Bordeaux: The fortifications were built by Charles VII of France only following the reconquest of Bordeaux in 1452. Shown on a smaller scale to the right of the château is the Gothic cathedral of Saint-André with its free-standing clock tower, the Tour Pey-Berland. Outside the city walls lie the ruins of the Roman amphitheatre.
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map the Picardy Region of France
- Title : France Picardie Champagne cum regionibus adiacentibus
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26131
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
1628 Jan Jansson Antique Map of the Picardy or Picardie Region of France
- Title : Picardia
- Size: 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26133
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Jan Jansson was published in the early 1628 French edition of Janssons Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, brown, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\\\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map the Southern Lorraine Region of France
Antique Map
- Title : La Partie Meridionale de Lorraine...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26142
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map ancient region of southern Lorraine, France by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630\\\'s when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, creasing
Plate area: - Age toning, creasing
Verso: - Age toning, creasing
Background:
Lorraine is a cultural and historical region in north-eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Lorraines name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia, which in turn was named for either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. It later was ruled as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766.
1628 Gerard Mercator Antique Map Lotharingia Region - Netherlands Germany France
Antique Map
- Title : Lotharingia Ducatus...Per Geradum Mercatorem Cum Privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26141
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the historical region of Lotharingia region of present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany), Saarland (Germany), and Lorraine (France) by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630\\\'s when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink, brown
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning, light creasing
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Lotharingia was a medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire, comprising the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany), Saarland (Germany), and Lorraine (France). It was named after King Lothair II who received this territory after the kingdom of Middle Francia of his father Lothair I was divided among his sons in 855.
Lotharingia was born out of the tripartite division in 855 of the kingdom of Middle Francia, which itself was formed after the threefold division of the Carolingian Empire by the Treaty of Verdun of 843. Conflict between East and West Francia over Lotharingia was based on the fact that these were the old Frankish homelands of Austrasia, so possession of them was of great prestige.
1628 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map the Alsace Region of France
- Title : Alsatia inferior..Per Gerardam Mercatorem Cum privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 26113
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Alsace by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1628 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Alsace is a cultural and historical region in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland.
As in much of Europe, the prosperity of Alsace came to an end in the 14th century by a series of harsh winters, bad harvests, and the Black Death. These hardships were blamed on Jews, leading to the pogroms of 1336 and 1339. In 1349, Jews of Alsace were accused of poisoning the wells with plague, leading to the massacre of thousands of Jews during the Strasbourg pogrom. Jews were subsequently forbidden to settle in the town. An additional natural disaster was the Rhine rift earthquake of 1356, one of Europes worst which made ruins of Basel. Prosperity returned to Alsace under Habsburg administration during the Renaissance.
Holy Roman Empire central power had begun to decline following years of imperial adventures in Italian lands, often ceding hegemony in Western Europe to France, which had long since centralized power. France began an aggressive policy of expanding eastward, first to the rivers Rhône and Meuse, and when those borders were reached, aiming for the Rhine. In 1299, the French proposed a marriage alliance between Philip IV of Frances sister Blanche and Albert I of Germanys son Rudolf, with Alsace to be the dowry; however, the deal never came off. In 1307, the town of Belfort was first chartered by the Counts of Montbéliard. During the next century, France was to be militarily shattered by the Hundred Years War, which prevented for a time any further tendencies in this direction. After the conclusion of the war, France was again free to pursue its desire to reach the Rhine and in 1444 a French army appeared in Lorraine and Alsace. It took up winter quarters, demanded the submission of Metz and Strasbourg and launched an attack on Basel.
In 1469, following the Treaty of St. Omer [fr], Upper Alsace was sold by Archduke Sigismund of Austria to Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy. Although Charles was the nominal landlord, taxes were paid to Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor. The latter was able to use this tax and a dynastic marriage to his advantage to gain back full control of Upper Alsace (apart from the free towns, but including Belfort) in 1477 when it became part of the demesne of the Habsburg family, who were also rulers of the empire. The town of Mulhouse joined the Swiss Confederation in 1515, where it was to remain until 1798.
By the time of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century, Strasbourg was a prosperous community, and its inhabitants accepted Protestantism in 1523. Martin Bucer was a prominent Protestant reformer in the region. His efforts were countered by the Roman Catholic Habsburgs who tried to eradicate heresy in Upper Alsace. As a result, Alsace was transformed into a mosaic of Catholic and Protestant territories. On the other hand, Mömpelgard (Montbéliard) to the southwest of Alsace, belonging to the Counts of Württemberg since 1397, remained a Protestant enclave in France until 1793.
This situation prevailed until 1639, when most of Alsace was conquered by France to keep it out of the hands of the Spanish Habsburgs, who by secret treaty in 1617 had gained a clear road to their valuable and rebellious possessions in the Spanish Netherlands, the Spanish Road. Beset by enemies and seeking to gain a free hand in Hungary, the Habsburgs sold their Sundgau territory (mostly in Upper Alsace) to France in 1646, which had occupied it, for the sum of 1.2 million Thalers. When hostilities were concluded in 1648 with the Treaty of Westphalia, most of Alsace was recognized as part of France, although some towns remained independent. The treaty stipulations regarding Alsace were complex. Although the French king gained sovereignty, existing rights and customs of the inhabitants were largely preserved. France continued to maintain its customs border along the Vosges mountains where it had been, leaving Alsace more economically oriented to neighbouring German-speaking lands. The German language remained in use in local administration, in schools, and at the (Lutheran) University of Strasbourg, which continued to draw students from other German-speaking lands. The 1685 Edict of Fontainebleau, by which the French king ordered the suppression of French Protestantism, was not applied in Alsace. France did endeavour to promote Catholicism. Strasbourg Cathedral, for example, which had been Lutheran from 1524 to 1681, was returned to the Catholic Church. However, compared to the rest of France, Alsace enjoyed a climate of religious tolerance.
France consolidated its hold with the 1679 Treaties of Nijmegen, which brought most remaining towns under its control. France seized Strasbourg in 1681 in an unprovoked action. These territorial changes were recognised in the 1697 Treaty of Ryswick that ended the War of the Grand Alliance.
The year 1789 brought the French Revolution and with it the first division of Alsace into the départements of Haut- and Bas-Rhin. Alsatians played an active role in the French Revolution. On 21 July 1789, after receiving news of the Storming of the Bastille in Paris, a crowd of people stormed the Strasbourg city hall, forcing the city administrators to flee and putting symbolically an end to the feudal system in Alsace. In 1792, Rouget de Lisle composed in Strasbourg the Revolutionary marching song La Marseillaise (as Marching song for the Army of the Rhine), which later became the anthem of France. La Marseillaise was played for the first time in April of that year in front of the mayor of Strasbourg Philippe-Frédéric de Dietrich. Some of the most famous generals of the French Revolution also came from Alsace, notably Kellermann, the victor of Valmy, Kléber, who led the armies of the French Republic in Vendée and Westermann, who also fought in the Vendée.
At the same time, some Alsatians were in opposition to the Jacobins and sympathetic to the restoration of the monarchy pursued by the invading forces of Austria and Prussia who sought to crush the nascent revolutionary republic. Many of the residents of the Sundgau made pilgrimages to places like Mariastein Abbey, near Basel, in Switzerland, for baptisms and weddings. When the French Revolutionary Army of the Rhine was victorious, tens of thousands fled east before it. When they were later permitted to return (in some cases not until 1799), it was often to find that their lands and homes had been confiscated. These conditions led to emigration by hundreds of families to newly vacant lands in the Russian Empire in 1803–4 and again in 1808. A poignant retelling of this event based on what Goethe had personally witnessed can be found in his long poem Hermann and Dorothea.
In response to the hundred day restoration of Napoleon I of France in 1815, Alsace along with other frontier provinces of France was occupied by foreign forces from 1815 to 1818, including over 280,000 soldiers and 90,000 horses in Bas-Rhin alone. This had grave effects on trade and the economy of the region since former overland trade routes were switched to newly opened Mediterranean and Atlantic seaports.
The population grew rapidly, from 800,000 in 1814 to 914,000 in 1830 and 1,067,000 in 1846. The combination of economic and demographic factors led to hunger, housing shortages and a lack of work for young people. Thus, it is not surprising that people left Alsace, not only for Paris – where the Alsatian community grew in numbers, with famous members such as Baron Haussmann – but also for more distant places like Russia and the Austrian Empire, to take advantage of the new opportunities offered there: Austria had conquered lands in Eastern Europe from the Ottoman Empire and offered generous terms to colonists as a way of consolidating its hold on the new territories. Many Alsatians also began to sail to the United States, settling in many areas from 1820 to 1850. In 1843 and 1844, sailing ships bringing immigrant families from Alsace arrived at the port of New York. Some settled in Texas and Illinois, many to farm or to seek success in commercial ventures: for example, the sailing ships Sully (in May 1843) and Iowa (in June 1844) brought families who set up homes in northern Illinois and northern Indiana. Some Alsatian immigrants were noted for their roles in 19th-century American economic development. Others ventured to Canada to settle in southwestern Ontario, notably Waterloo County.
1628 Jan Jansson Antique Map of the Picardy Region of France
- Title : Picardia
- Size: 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1628
- Ref #: 50241
Description:
This original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of the French region of Picardy or Picardie by Jan Jansson was published in the early 1628 Latin edition of Janssons Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - later
Colors used: - Green, blue, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 17in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\\\\\\\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
1612 Abraham Ortelius Antique Maps of Loire Valley, River & Alliers River France
- Title : Regionis Biturigum Exactiss Descriptio per D. Ioannem Calamaeum. Limaniae Topographia Gabriele Symeoneo Auct. [The region of Berry exactly described by Jean Chameau. The topography around of Lyons by Gabriel Symeon]
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1612
- Ref #: 50228
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique map, the first of the Loire River & Valley and the second of the Alliers River, was published by Abraham Ortelius in the 1612 Latin edition of Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
These are two rare regional Abraham Ortelius maps on a single folio sheet. The Left Map, centered on Bourges, depicts the Loire Valley region from Gian to St. Sebastian in the south and from Le Blanc east as far as Nevers. Several important cities are noted, including Argenton, Neuers (Nevers), Bourges, Le Blang en Berry, Romarantin, Vierzon, Chasteau Neuf, and others. The right map follows the flow of the Alliers River from Randan to Gondole. Important cities, including Beauregard, Cleremont, among several others are noted. Each map features a decorative cartouche and details their respective regions in wonderful detail with attention to forests, cities, rivers and villages.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Loire Valley spanning 280 kilometres , is located in the middle stretch of the Loire River in central France, in both the administrative regions Pays de la Loire and Centre-Val de Loire. The area of the Loire Valley comprises about 800 square kilometres. It is referred to as the Cradle of the French and the Garden of France due to the abundance of vineyards, fruit orchards (such as cherries), and artichoke, and asparagus fields, which line the banks of the river. Notable for its historic towns, architecture, and wines, the valley has been inhabited since the Middle Palaeolithic period.
The Allier is a river in central France. It is a left tributary of the Loire. Its source is in the Massif Central, in the Lozère department, east of Mende. It flows generally north. It joins the Loire west of the city of Nevers.
1575 Abraham Ortelius Antique Maps of Loire Valley, River & Alliers River France
- Title : Regionis Biturigum Exactiss Descriptio per D. Ioannem Calamaeum. Limaniae Topographia Gabriele Symeoneo Auct. [The region of Berry exactly described by Jean Chameau. The topography around of Lyons by Gabriel Symeon]
- Size: 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1575
- Ref #: 50228-1
Description:
These original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique maps, the first of the Loire River & Valley and the second of the Alliers River, was published by Abraham Ortelius in the 1575 French edition of Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
These are two rare regional Abraham Ortelius maps on a single folio sheet. The Left Map, centered on Bourges, depicts the Loire Valley region from Gian to St. Sebastian in the south and from Le Blanc east as far as Nevers. Several important cities are noted, including Argenton, Neuers (Nevers), Bourges, Le Blang en Berry, Romarantin, Vierzon, Chasteau Neuf, and others. The right map follows the flow of the Alliers River from Randan to Gondole. Important cities, including Beauregard, Cleremont, among several others are noted. Each map features a decorative cartouche and details their respective regions in wonderful detail with attention to forests, cities, rivers and villages.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 19 1/2in (535mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (2mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Loire Valley spanning 280 kilometres , is located in the middle stretch of the Loire River in central France, in both the administrative regions Pays de la Loire and Centre-Val de Loire. The area of the Loire Valley comprises about 800 square kilometres. It is referred to as the Cradle of the French and the Garden of France due to the abundance of vineyards, fruit orchards (such as cherries), and artichoke, and asparagus fields, which line the banks of the river. Notable for its historic towns, architecture, and wines, the valley has been inhabited since the Middle Palaeolithic period.
The Allier is a river in central France. It is a left tributary of the Loire. Its source is in the Massif Central, in the Lozère department, east of Mende. It flows generally north. It joins the Loire west of the city of Nevers.
1575 Abraham Ortelius Antique Maps of Loire Valley, River & Alliers River France
- Title : Regionis Biturigum Exactiss Descriptio per D. Ioannem Calamaeum. Limaniae Topographia Gabriele Symeoneo Auct. [The region of Berry exactly described by Jean Chameau. The topography around of Lyons by Gabriel Symeon]
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1575
- Ref #: 30021
Description:
These original copper-plate engraved hand coloured antique maps, the first of the Loire River & Valley and the second of the Alliers River, was published by Abraham Ortelius in the 1575 French edition of Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
These are two rare regional Abraham Ortelius maps on a single folio sheet. The Left Map, centered on Bourges, depicts the Loire Valley region from Gian to St. Sebastian in the south and from Le Blanc east as far as Nevers. Several important cities are noted, including Argenton, Neuers (Nevers), Bourges, Le Blang en Berry, Romarantin, Vierzon, Chasteau Neuf, and others. The right map follows the flow of the Alliers River from Randan to Gondole. Important cities, including Beauregard, Cleremont, among several others are noted. Each map features a decorative cartouche and details their respective regions in wonderful detail with attention to forests, cities, rivers and villages.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, blue, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Soiling
Background:
The Loire Valley spanning 280 kilometres , is located in the middle stretch of the Loire River in central France, in both the administrative regions Pays de la Loire and Centre-Val de Loire. The area of the Loire Valley comprises about 800 square kilometres. It is referred to as the Cradle of the French and the Garden of France due to the abundance of vineyards, fruit orchards (such as cherries), and artichoke, and asparagus fields, which line the banks of the river. Notable for its historic towns, architecture, and wines, the valley has been inhabited since the Middle Palaeolithic period.
The Allier is a river in central France. It is a left tributary of the Loire. Its source is in the Massif Central, in the Lozère department, east of Mende. It flows generally north. It joins the Loire west of the city of Nevers.