Joducus Hondius (1563 - 1612) Henricus Hondius, (1587 - 1638)
Joducus Hondius - son (1594 - 1629)
Jodocus Hondius, one of the most notable engravers of his time, is known for his work in association with many of the cartographers and publishers prominent at the end of the sixteenth and the beginning of the seventeenth century.
A native of Flanders, he grew up in Ghent, apprenticed as an instrument and globe maker and map engraver. In 1584, to escape the religious troubles sweeping the Low Countries at that time, he fled to London where he spent some years before finally settling in Amsterdam about 1593. In the London period he came into contact with the leading scientists and geographers of the day and engraved maps in The Mariner's Mirrour, the English edition of Waghenaer's Sea Atlas, as well as others with Pieter van den Keere, his brother-in-law. No doubt his temporary exile in London stood him in good stead, earning him an international reputation, for it could have been no accident that Speed chose Hondius to engrave the plates for the maps in The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine in the years between 1605 and 1610.
In 1604 Hondius bought the plates of Mercator's Atlas which, in spite of its excellence, had not competed successfully with the continuing demand for the Ortelius Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. To meet this competition Hondius added about 40 maps to Mercator's original number and from 16o6 published enlarged editions in many languages, still under Mercator's name but with his own name as publisher. These atlases have become known as the Mercator/Hondius series. The following year the maps were re-engraved in miniature form and issued as a pocket Atlas Minor. After the death of Jodocus Hondius the Elder in 1611, work on the two atlases, folio and miniature, was carried on by his widow and sons, Jodocus II and Henricus, and eventually in conjunction with Jan Jansson in Amsterdam. In all, from 1606 onwards, nearly 50 editions with increasing numbers of maps with texts in the main European languages were printed.
Joducus & Henricus Hondius (1)
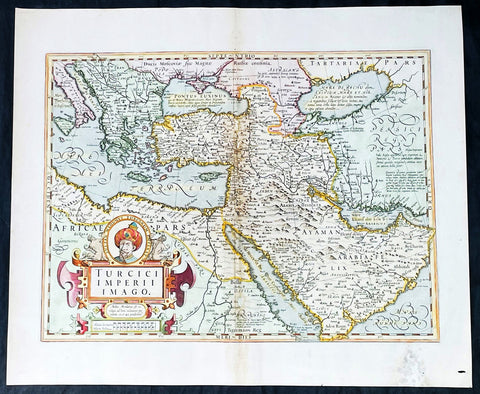
1628 Henricus Hondius Antique Map Ottoman Empire Saudi Arabia to Southern Europe
Antique Map
- Title : Turcici Imperii Imago
- Date : 1628
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18 1/2in (570mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A-) Good Condition
- Ref: 35642
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of The Ottoman Empire in the mid 17th century from Saudi Arabia to southern Europe was published in the 1628 French edition of Mercator's atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 3/4in x 19 3/4in (580mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 13 3/4in (500mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling, small wormhole, light creasing
Plate area: - Small loss and creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling and creasing
Background:
The Ottoman Empire also historically known in Western Europe as the Turkish Empire or simply Turkey, was a state that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia and North Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Oghuz Turkish tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe, and with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the 1453 conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, at the height of its power under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was a multinational, multilingual empire controlling most of Southeast Europe, parts of Central Europe, Western Asia, parts of Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, North Africa and the Horn of Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states. Some of these were later absorbed into the Ottoman Empire, while others were granted various types of autonomy during the course of centuries.
With Constantinople as its capital and control of lands around the Mediterranean basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds for six centuries. While the empire was once thought to have entered a period of decline following the death of Suleiman the Magnificent, this view is no longer supported by the majority of academic historians. The empire continued to maintain a flexible and strong economy, society and military throughout the 17th and much of the 18th century. However, during a long period of peace from 1740 to 1768, the Ottoman military system fell behind that of their European rivals, the Habsburg and Russian empires. The Ottomans consequently suffered severe military defeats in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, which prompted them to initiate a comprehensive process of reform and modernisation known as the Tanzimat. Thus, over the course of the 19th century, the Ottoman state became vastly more powerful and organised, despite suffering further territorial losses, especially in the Balkans, where a number of new states emerged. The empire allied with Germany in the early 20th century, hoping to escape from the diplomatic isolation which had contributed to its recent territorial losses, and thus joined World War I on the side of the Central Powers. While the Empire was able to largely hold its own during the conflict, it was struggling with internal dissent, especially with the Arab Revolt in its Arabian holdings. During this time, atrocities were committed by the Ottoman government against the Armenians, Assyrians and Pontic Greeks.
The Empire\'s defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories, which were divided between the United Kingdom and France. The successful Turkish War of Independence against the occupying Allies led to the emergence of the Republic of Turkey in the Anatolian heartland and the abolition of the Ottoman monarchy.