Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg
Profile :
Braun and Hogenberg were two cartographers who are known for creating the famous Civitates Orbis Terrarum, which is considered one of the most important works of the 16th century. The Civitates Orbis Terrarum is a collection of city maps and views of European & New World cities, along with illustrations of important buildings, monuments, and notable people.
Georg Braun was born in Cologne, Germany, in 1541, and was a Catholic cleric who became the canon of the Cologne Cathedral. He was interested in geography and history and was a member of the Cologne Society of Antiquarians. Franz Hogenberg was a Flemish engraver born in Mechelen, Belgium, in 1535. He was trained as an artist and engraver and moved to Cologne in the 1560s, where he worked with Braun.
Braun and Hogenberg collaborated on the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, which was first published in 1572. The work was intended to be a comprehensive description of all the cities of the world, but only the cities of Europe were covered. The first edition of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum contained 546 views of cities, including maps and views of the most important cities of Europe. The work was an enormous undertaking and required the skills of many artists and engravers. The illustrations were based on contemporary maps and views, but the artists added their own interpretations and artistic touches to the images.
Braun and Hogenberg's work was highly influential and helped to shape the way that Europeans saw their cities and their world. The Civitates Orbis Terrarum was an important source of information about the cities of Europe, and it helped to stimulate interest in urban development and planning. The work was also an important contribution to the history of cartography and printing.
After the publication of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, Braun and Hogenberg continued to work together on other projects, including an atlas of the world, which was published in 1575. Hogenberg died in 1590, but Braun continued to work on the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, publishing new editions until his death in 1622. The work continued to be popular and influential in the 17th and 18th centuries, and it remains an important historical and artistic achievement.
Georg Braun (1541 – 1622) was a topo-geographer. From 1572 to 1617 he edited the Civitates orbis terrarum, which contains 546 prospects, bird's-eye views and maps of cities from all around the world. He was the principal editor of the work, he acquired the tables, hired the artists, and wrote the texts. He died as an octogenarian in 1622, as the only survivor of the original team to witness the publication of volume VI in 1617. Braun was born and died in Cologne. His principal profession was as a Catholic cleric, however, he spent thirty-seven years as canon and dean at the church, St. Maria ad Gradus, in Cologne. His six-volume work was inspired by Sebastian Münster's Cosmographia. In form and layout it resembles the 1570 Theatrum orbis terrarum by Abraham Ortelius, as Ortelius was interested in a complementary companion for the Theatrum.
The Braun publication set new standards in cartography for over 100 years. Frans Hogenberg (1535–1590, from Mechelen) created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel created those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were Joris Hoefnagel, Jacob Hoefnagel, cartographer Daniel Freese, and Heinrich Rantzau. Also, works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were used. Mainly, European cities are depicted in the publication, however, Casablanca and Mexico City/Cuzco on one sheet are also included in volume I.
Frans Hogenberg (1535 – 1590) was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. Hogenberg was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg. In 1568 he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He is known for portraits and topographical views as well as historical allegories. He also produced scenes of contemporary historical events. Hogenberg died in Cologne.
Braun & Hogenberg (3)
1572 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Print View Lake Agnano Cave of Dogs Naples, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Antri Sibillae, Lacus Agnianus
- Ref #: 35013
- Size: 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1572
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique print, a birds eye view of the Italian Volcanic Lake Agnano and the Grotta del cane or Fontana - Cave of the Dogs - located in Pozzuoli, north of Naples, Italy was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The top view of Lake Agnano shows friends Abraham Ortelius & Georg Hoffnagel meeting at the Lake in a way to impress upon the reader the real importance of Nature. These are beautifully engraved with wonderful hand colouring on strong, sturdy paper.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Colour show-through
The Cave of Dogs is a small cave on the eastern side of the Phlegraean Fields near Pozzuoli, Naples. Inside the cave is a fumarole that releases carbon dioxide of volcanic origin. It was a famous if gruesome tourist attraction for travellers on the Grand Tour. The CO2 gas, being denser than air, tends to accumulate in the deeper parts of the cave. Local guides, for a fee, would suspend small animals inside it—usually dogs—until they became unconscious. Because humans inhaled air from a higher level they were not affected. The dogs might be revived by submerging them in the cold waters of the nearby Lake Agnano. Famous tourists who came to see this attraction included Goethe, Alexandre Dumas père, and Mark Twain. The lake became polluted and it was drained in 1870; the spectacle fell into desuetude and the cave was closed. However the area is now being restored by volunteers.
Lago di Agnano or Lake Agnano was a circular lake, some 6½ km in circumference, which occupied the crater of the extinct volcano of Agnano 8 km west of Naples, Italy. It was apparently not formed until the Middle Ages, as it is not mentioned by ancient writers; it was drained in 1870.
On the south bank are the Stufe di San Germano, natural sulphureous vapour baths, and close by is the Grotta del Cane. From the floor of this cave warm carbonic acid gas constantly rises to a height of 18 inches (46 cm): the fumes render a dog insensible in a few seconds. It is mentioned by Pliny the Elder. Remains of an extensive Roman building and some statues have been discovered close by.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1572 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Print View Lake Agnano Cave of Dogs Naples, Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Antri Sibillae, Lacus Agnianus
- Ref #: 35013
- Size: 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1572
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique print, a birds eye view of the Italian Volcanic Lake Agnano and the Grotta del cane or Fontana - Cave of the Dogs - located in Pozzuoli, north of Naples, Italy was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1572 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The top view of Lake Agnano shows friends Abraham Ortelius & Georg Hoffnagel meeting at the Lake in a way to impress upon the reader the real importance of Nature. These are beautifully engraved with wonderful hand colouring on strong, sturdy paper.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 16in (525mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13in (470mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Colour show-through
The Cave of Dogs is a small cave on the eastern side of the Phlegraean Fields near Pozzuoli, Naples. Inside the cave is a fumarole that releases carbon dioxide of volcanic origin. It was a famous if gruesome tourist attraction for travellers on the Grand Tour. The CO2 gas, being denser than air, tends to accumulate in the deeper parts of the cave. Local guides, for a fee, would suspend small animals inside it—usually dogs—until they became unconscious. Because humans inhaled air from a higher level they were not affected. The dogs might be revived by submerging them in the cold waters of the nearby Lake Agnano. Famous tourists who came to see this attraction included Goethe, Alexandre Dumas père, and Mark Twain. The lake became polluted and it was drained in 1870; the spectacle fell into desuetude and the cave was closed. However the area is now being restored by volunteers.
Lago di Agnano or Lake Agnano was a circular lake, some 6½ km in circumference, which occupied the crater of the extinct volcano of Agnano 8 km west of Naples, Italy. It was apparently not formed until the Middle Ages, as it is not mentioned by ancient writers; it was drained in 1870.
On the south bank are the Stufe di San Germano, natural sulphureous vapour baths, and close by is the Grotta del Cane. From the floor of this cave warm carbonic acid gas constantly rises to a height of 18 inches (46 cm): the fumes render a dog insensible in a few seconds. It is mentioned by Pliny the Elder. Remains of an extensive Roman building and some statues have been discovered close by.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
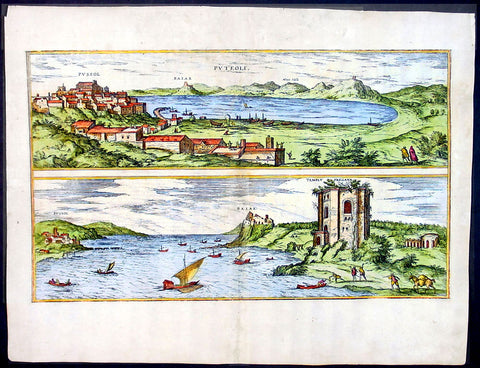
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Map of Pozzuoli Bay Naples Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Puteoli et Baiae
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92687
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique 2 x birds-eye view of the Bay of Pozzuoli -in the Gulf of Naples - with The city of Pozzuoli & the Port Of Baia visible was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The Gulf of Naples is a 10-mile wide gulf located in the south western coast of Italy, (province of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean Sea & is bordered on the north by the cities of Naples and Pozzuoli. To the east is Mount Vesuvius, and on the south by the Sorrentine Peninsula and its main town Sorrento; the Peninsula separates it from the Gulf of Salerno.
Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of Dicaearchia. The Roman colony was established in 194 BC, and took the Latin name Puteoli 'little wells', referring to the many hot springs in the area, most notably Solfatara. This is because Pozzuoli lies in the center of the Campi Flegrei, a caldera.
Puteoli was the great emporium for the Alexandrian grain ships, and other ships from all over the Roman world. It also was the main hub for goods exported from Campania, including blown glass, mosaics, wrought iron, and marble. The Roman naval base at nearby Misenum housed the largest naval fleet in the ancient world. It was also the site of the Roman Dictator Sulla's country villa and the place where he died in 78 BC.
The local volcanic sand, pozzolana formed the basis for the first effective concrete, as it reacted chemically with water. Instead of just evaporating slowly off, the water would turn this sand/lime mix into a mortar strong enough to bind lumps of aggregate into a load-bearing unit. This made possible the cupola of the Pantheon, the first real dome.
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 12in (485mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repair to top centre margin
Plate area: - Small professional repairs & light age toning to centrefold
Verso: - None