Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg
Profile :
Braun and Hogenberg were two cartographers who are known for creating the famous Civitates Orbis Terrarum, which is considered one of the most important works of the 16th century. The Civitates Orbis Terrarum is a collection of city maps and views of European & New World cities, along with illustrations of important buildings, monuments, and notable people.
Georg Braun was born in Cologne, Germany, in 1541, and was a Catholic cleric who became the canon of the Cologne Cathedral. He was interested in geography and history and was a member of the Cologne Society of Antiquarians. Franz Hogenberg was a Flemish engraver born in Mechelen, Belgium, in 1535. He was trained as an artist and engraver and moved to Cologne in the 1560s, where he worked with Braun.
Braun and Hogenberg collaborated on the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, which was first published in 1572. The work was intended to be a comprehensive description of all the cities of the world, but only the cities of Europe were covered. The first edition of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum contained 546 views of cities, including maps and views of the most important cities of Europe. The work was an enormous undertaking and required the skills of many artists and engravers. The illustrations were based on contemporary maps and views, but the artists added their own interpretations and artistic touches to the images.
Braun and Hogenberg's work was highly influential and helped to shape the way that Europeans saw their cities and their world. The Civitates Orbis Terrarum was an important source of information about the cities of Europe, and it helped to stimulate interest in urban development and planning. The work was also an important contribution to the history of cartography and printing.
After the publication of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, Braun and Hogenberg continued to work together on other projects, including an atlas of the world, which was published in 1575. Hogenberg died in 1590, but Braun continued to work on the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, publishing new editions until his death in 1622. The work continued to be popular and influential in the 17th and 18th centuries, and it remains an important historical and artistic achievement.
Georg Braun (1541 – 1622) was a topo-geographer. From 1572 to 1617 he edited the Civitates orbis terrarum, which contains 546 prospects, bird's-eye views and maps of cities from all around the world. He was the principal editor of the work, he acquired the tables, hired the artists, and wrote the texts. He died as an octogenarian in 1622, as the only survivor of the original team to witness the publication of volume VI in 1617. Braun was born and died in Cologne. His principal profession was as a Catholic cleric, however, he spent thirty-seven years as canon and dean at the church, St. Maria ad Gradus, in Cologne. His six-volume work was inspired by Sebastian Münster's Cosmographia. In form and layout it resembles the 1570 Theatrum orbis terrarum by Abraham Ortelius, as Ortelius was interested in a complementary companion for the Theatrum.
The Braun publication set new standards in cartography for over 100 years. Frans Hogenberg (1535–1590, from Mechelen) created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel created those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were Joris Hoefnagel, Jacob Hoefnagel, cartographer Daniel Freese, and Heinrich Rantzau. Also, works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were used. Mainly, European cities are depicted in the publication, however, Casablanca and Mexico City/Cuzco on one sheet are also included in volume I.
Frans Hogenberg (1535 – 1590) was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. Hogenberg was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg. In 1568 he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He is known for portraits and topographical views as well as historical allegories. He also produced scenes of contemporary historical events. Hogenberg died in Cologne.
Braun & Hogenberg (2)
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map View of Gorlitz-Zgorzelec, Germany & Poland
Antique Map
- Title : Gorlitz
- Ref #: 93432
- Size: 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1574
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map, a birds eye view of the city of Gorlitz-Zgorzelec, in the state of Saxony, in the region of Lusatia, in far eastern Germany, on the border with Poland, was published in the 1574 edition of Braun & Hogenbergs atlas Civitates Orbis Terrarum
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 12 1/2in (510mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
As a small Sorbian village named Gorelic in the Margraviate of Meissen, a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, Gorlitz was temporarily conquered and held by the Kingdom of Poland during Bolesław I Chrobrys invasion of Lusatia between 1002 and 1031, after which the region fell back to the Margraviate of Meissen. In 1075, the village was assigned to the Duchy of Bohemia. The date of the towns foundation is unknown. However, Goreliz was first mentioned in a document from the King of Germany, and later Holy Roman Emperor, Henry IV in 1071. This document granted Gorlitz to the Diocese of Meissen, then under Bishop Benno of Meissen. Currently, this document can be found in the Saxony State Archives in Dresden.[3] The origin of the name Gorlitz is derived from the Slavic word for burned land,[4] referring to the technique used to clear land for settlement. Zgorzelec and Czech Zhořelec have the same derivation. In the 13th century the village gradually became a town. Due to its location on the Via Regia, an ancient and medieval trade route, the settlement prospered.
In the following centuries Gorlitz was a wealthy member of the Lusatian League, which consisted of Bautzen, Gorlitz, Kamenz, Lauban, Löbau and Zittau. In 1352 during the reign of Casimir the Great, Lusatian German colonists from Gorlitz founded the town of Gorlice in southern Poland near Kraków.
The Protestant Reformation came to Gorlitz in the early 1520s and by the last half of the 16th century, it and the surrounding vicinity, became almost completely Lutheran.
After suffering for years in the Thirty Years War, the region of Upper Lusatia (including Gorlitz) was ceded to the Electorate of Saxony in 1635. After the Napoleonic Wars, the 1815 Congress of Vienna transferred the town from the Kingdom of Saxony to the Kingdom of Prussia. Gorlitz was subsequently administered within the Province of Silesia, and, after World War I, the Province of Lower Silesia, until 1945.
From 1815 until 1918, Gorlitz belonged to the Province of Silesia in the Kingdom of Prussia, and later to the Province of Lower Silesia in the Free State of Prussia. It is the largest town of the former Province of Lower Silesia that lies west of the Oder-Neisse line and hence remained in Germany after World War II. Today, Gorlitz lies opposite the Polish town of Zgorzelec, which was part of Gorlitz until 1945. Together they form the German-Polish Euro City of Gorlitz-Zgorzelec.
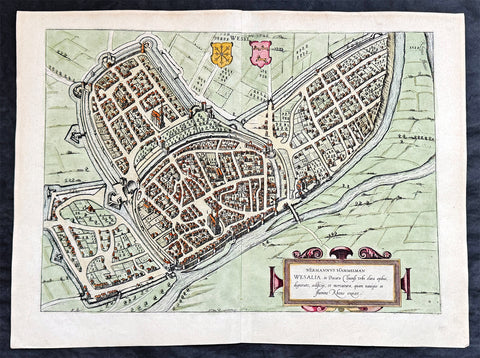
1574 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map View of Wesel North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany
- Title : Hermannus Hammelman Wesalia in Ducatu Cliuensi
- Size: 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1574
- Ref #: 81068-1
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved hnd coloured antique map, plan, a birds eye view of city of Wesel in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1574 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, pink, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (545mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 13 1/2in (480mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Wesel is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel district.
The city originated from a Franconian manor that was first recorded in the 8th century. In the 12th century, the Duke of Clèves took possession of Wesel. The city became a member of the Hanseatic League during the 15th century. Wesel was second only to Cologne in the lower Rhine region as an entrepôt. It was an important commercial centre: a clearing station for the trans-shipment and trading of goods.
In 1590 the Spanish captured Wesel after a four-year siege. The city changed hands between the Dutch and Spanish several times during the Eighty Years War. In 1672 a French force under Louis II de Bourbon, Prince de Condé captured the city. Wesel was inherited by the Hohenzollerns of the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1609 but they were unable to take control of Wesel until the Treaty of Nijmegen in 1678. Although the city had been heavily fortified the Prussians evacuated the city during the Seven Years War and it was occupied by the French. It was returned to Prussia at the end of the war. Friedrich Wilhelm von Dossow was the Prussian Governor of Wesel during the 18th century. Wesel was ceded to the French in 1805 under the treaty of Schönbrunn. The French heavily fortified the city constructing a rectangular fort called the Citadelle Napoleon at Büderich and the Citadelle Bonaparte on an island in the Rhine off Wesel. Though blockaded by the Allies in 1813 the city remained in French hands until after the Battle of Waterloo. After the Napoleonic Wars of the early 19th century, the city became part of the Prussian Rhine Province and the Citadelle Napoleon was renamed Fort Blücher.