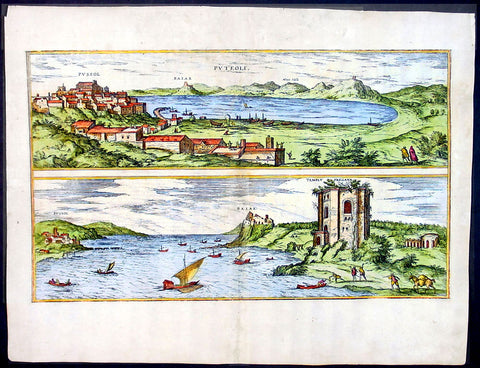
City & Views (2)
1575 Braun & Hogenberg Map of Pozzuoli Bay Naples Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Puteoli et Baiae
- Date : 1575
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92687
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique 2 x birds-eye view of the Bay of Pozzuoli -in the Gulf of Naples - with The city of Pozzuoli & the Port Of Baia visible was published by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg for the 1575 atlas of town plans Civiates Orbis Terrarum Vol II intended as a companion to Abraham Ortelius's master Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published in 1570.
The Gulf of Naples is a 10-mile wide gulf located in the south western coast of Italy, (province of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean Sea & is bordered on the north by the cities of Naples and Pozzuoli. To the east is Mount Vesuvius, and on the south by the Sorrentine Peninsula and its main town Sorrento; the Peninsula separates it from the Gulf of Salerno.
Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of Dicaearchia. The Roman colony was established in 194 BC, and took the Latin name Puteoli 'little wells', referring to the many hot springs in the area, most notably Solfatara. This is because Pozzuoli lies in the center of the Campi Flegrei, a caldera.
Puteoli was the great emporium for the Alexandrian grain ships, and other ships from all over the Roman world. It also was the main hub for goods exported from Campania, including blown glass, mosaics, wrought iron, and marble. The Roman naval base at nearby Misenum housed the largest naval fleet in the ancient world. It was also the site of the Roman Dictator Sulla's country villa and the place where he died in 78 BC.
The local volcanic sand, pozzolana formed the basis for the first effective concrete, as it reacted chemically with water. Instead of just evaporating slowly off, the water would turn this sand/lime mix into a mortar strong enough to bind lumps of aggregate into a load-bearing unit. This made possible the cupola of the Pantheon, the first real dome.
Background of Civitates Orbis Terrarum
The first volume of the Civitates Orbis Terrarum was published in Cologne in 1572. The sixth and the final volume appeared in 1617.
This great city atlas, edited by Georg Braun and largely engraved by Franz Hogenberg, eventually contained 546 prospects, bird-eye views and map views of cities from all over the world. Braun (1541-1622), a cleric of Cologne, was the principal editor of the work, and was greatly assisted in his project by the close, and continued interest of Abraham Ortelius, whose Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of 1570 was, as a systematic and comprehensive collection of maps of uniform style, the first true atlas.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 410mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 12in (485mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repair to top centre margin
Plate area: - Small professional repairs & light age toning to centrefold
Verso: - None
1685 G B Falda & Sandrart Antique Print Villa Gardens Doria Pamphili, Rome Italy
Antique Map
- Title : Prospecto Del Palazzo & Giardino Pamphilio Detto Del Bel Respiro...Architettura del Caualier Alessandro Algardi...Simon Felice delin....Norimburga appresso Gioni. Gac. de Sandart
- Ref #: 93463
- Size: 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
- Date : 1685
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper plate engraved antique print of the Villa & Gardens of Doria Pamphili, Rome was engraved by Simone Felice for the 1685 edition of Giovanni Battista Faldas Li giardini di Roma, disegnati da Giovanni Battista Falda nuovamente dati alle stampe con direttione di Giov. Giacomo de Sandrart (The gardens of Rome, designed by Giovanni Battista Falda again printed with the direction of Giov. Giacomo de Sandrart) published in Nuremberg by Johann von Sandrart.
The work is based on the original series edited by Gian Giacomo de Rossi a few years earlier (the first edition was certainly published after 1677 but before 1683) which included 19 tables of plants and perspective views of the most famous Roman gardens, 14 of which were engraved by GB Falda and 5 by Simon Felice.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 19in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 9 1/2in (400mm x 250mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Villa Doria Pamphili is a seventeenth-century villa with what is today the largest landscaped public park in Rome, Italy. It is located in the quarter of Monteverde, on the Gianicolo (or the Roman Janiculum), just outside the Porta San Pancrazio in the ancient walls of Rome where the ancient road of the Via Aurelia commences.
It began as a villa for the Pamphili family and when the line died out in the eighteenth century, it passed to Prince Giovanni Andrea IV Doria, and has been known as the Villa Doria Pamphili since.
The nucleus of the villa property, the Villa Vecchia or old villa, already existed before 1630, when it was bought by Pamfilio Pamfili, who had married the heiress Olimpia Maidalchini, to enjoy as a suburban villa. Thereafter he set about buying up neighbouring vineyards to accumulate a much larger holding, which was often known as the Bel Respiro or beautiful breath as it stood on high ground, above the malarial areas of Rome, and offered spectacular views which were a desirable feature of Baroque villa settings.
In 1644 Cardinal Giambattista Pamphili became elected to the papacy and took the name of Innocent X. In accordance with this change in status, the Pamphili aspired to a grander and more expansively sited new villa. Early designs were made, possibly by Virgilio Spada rather than the traditional attribution to Borromini, but these were rejected. Instead the project was placed in the hands of the Bolognese sculptor Alessandro Algardi in 1644, assisted by Giovanni Francesco Grimaldi.
The initial design had a central casino (not the modern usage as a gambling establishment) with wings, but only the central block was built. There is uncertainty as to who the architect was; Algardi was not an architect, and it may be that he had help from Carlo Rainaldi and that the construction was supervised by Grimaldi. The layout has a central circular room around which the other rooms were arranged. Construction began in 1645 and was complete by 1647 although embellishments and the garden layouts were not finished until 1653. The casino, sometimes known as the Casino del Bel Respiro, was designed as a complement to the Pamphili collection of sculptures both ancient and modern, and other Roman antiquities such as vases, sarcophagi and inscriptions; it was only ever intended for display of the collection and the family and guests resided in the older Vecchia Vigna.
As a show case for sculpture, the somewhat crowded Casino facades have rhythmically alternating windows with niches which were elaborately adorned with sculptures, both antique and modern, with busts in hollowed roundels, with panels of bas-reliefs, and reliefs.
The exterior containing statues gives a rich allure that was architecturally somewhat conservative for its date, looking back towards the Villa Medici or the Casina Pio IV, and rather more Mannerist than Baroque. It offered a foretaste of the richly stuccoed and frescoed interiors, where the iconographic program set out to establish the antiquity of the Pamphili, a family then somewhat parvenu in Rome, with origins in Gubbio. Inside, Algardi provided further bas-reliefs and stucco framing for the heroic frescoes drawn from Roman history painted by Grimaldi.
The casino is set into the hill slope such that the main entrance on the north side is at a level above the giardino segreto or secret garden enclosure on its south side, a parterre garden with low clipped hedges. The gardens on the sloping site were laid out from around 1650 by Innocents nephew, Camillo Pamphili, formalizing the slope as a sequence from the parterres that flank the Casino, to a lower level below, framed by the boschi or formalized woodlands that rose above clipped hedges, and eventually arriving at a rusticated grotto in the form of an exedra, from which sculptured figures emerge from the rockwork. The exedra, now grassed, formerly enframed a Fountain of Venus by Algardi, which is preserved in the Villa Vecchia, together with Algardis bas-reliefs of putti representing Love and the Arts that were formerly here. The fountain spilled into a small cascade that let into a short length of formal canal, which was intended to remind the viewer of the similar Canopus at Hadrians Villa— another programmatic connection of the Pamphili with Antiquity.
When Girolamo Pamphili died in 1760 without male heirs, the disputes which broke out among the possible heirs were settled in 1763 when Pope Clement XIII Rezzonico granted to Prince Giovanni Andrea IV Doria the right to take the surname, the arms and the vast properties of the Pamphili; the Princes claim was based on the marriage between Giovanni Andrea III Doria and Anna Pamphili. Since then, the villa has been known as the Villa Doria Pamphili.
Throughout the 18th century, features were regularly added such as fountains and gateways by Gabriele Valvassori and other architects retained by the Pamphili and their heirs. After the Napoleonic era, more sweeping changes were made. The parterres that were formal extensions of the casino were retained but replanted with the patterned planting of colourful carpet bedding supplied from greenhouses by the old villa. (Today the parterres have been replanted in 16th-century style, with panels of scrolling designs in close-clipped greens set in wide gravel walks.) In the sloping outer gardens the changes were more extensive, recasting them in the naturalistic manner of English landscape gardens. The grounds, filled with many surprise features and picturesque incidents, swept down to a small lake at the bottom, which already had an air of atmospheric maturity when it was painted in the 1830s by Alexandre-Gabriel Decamps. In the wooded, natural-appearing landscapes with clumps of characteristic umbrella-like stone pines along horizons stand statues and vases, which evoke a nostalgic antiquity. The 18th-century English landscape gardens such as Stowe and Stourhead that were the inspiration for this style aimed to bring to life the Italian landscapes with Roman ruins painted by Claude and Poussin. A notable difference is that at the Villa Doria Pamphilis giardino inglese the Roman remains are likely to be genuine. The site of the villa contained several Roman tombs that yielded vases, sarcophagi and inscriptions that were added to the Pamphili collection.
Falda, Giovanni Battista 1643 – 1678
Falda was an Italian architect, engraver and artist. He is known for his engravings of both contemporary and antique structures of Rome.
Falda was sent as a boy to Rome, to work in the studio of Bernini, and his draughtsmanship caught the eye of the publisher Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi. He engraved for Le fontane di Roma (Fountains in Rome) and for Palazzi di Roma (Palaces of Rome). The former books was expanded after Faldas death with engravings by Francesco Venturini. The latter was published in 1655 in collaboration with Pietro Ferrerio. He is sometimes known as Falda da Valduggia because of his birthplace.
His works became particularly popular with the first waves of Grand Tour participants during the latter parts of the 17th century and Falda became a commercial success as a result. His works appealed to tourists keen to retain a detailed and accurate representation of those parts of Rome they had visited.