Antonio Zatta
Antonio Zatta (fl. 1757-1797) was a prominent Italian cartographer, engraver, and publisher in Venice during the late 18th century. He is best known for his series of maps and atlases of Italy, Europe, and the world, which were renowned for their high quality and accuracy.
Zatta was born in Venice around 1757 and initially trained as an engraver. He established his own printing and publishing company in Venice in the late 18th century and began producing maps and atlases. His first major work was the "Atlante Novissimo" in 1779, a comprehensive atlas of the world that contained 57 maps and was widely acclaimed for its accuracy and detail.
Over the next two decades, Zatta produced numerous other maps and atlases, including the "Atlante Veneto" in 1784, a comprehensive atlas of the Venetian Republic that included detailed maps of each province, and the "Atlante di Toscana" in 1792, a detailed atlas of the Tuscany region of Italy. Zatta's maps were known for their accurate depictions of geography, topography, and political boundaries, as well as their beautiful engravings and elaborate ornamentation.
Zatta's work was highly regarded by his contemporaries and he was awarded numerous honors and titles throughout his career, including being named an official geographer to the Republic of Venice. Today, his maps and atlases are highly prized by collectors and are regarded as some of the finest examples of cartography from the 18th century.
Antonio Zatta (3)
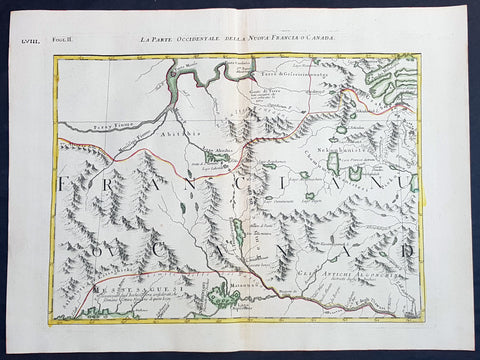
1778 Antonio Zatta & John Mitchell Antique Map of East Quebec & Western Ontario
Antique Map
- Title : La Parte Occidentale Della Nuova Francia o Canada
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93512
- Size: 21in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Description:
Description:
This wonderfully executed original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of eastern Quebec and Western Ontario - from Lake Superior in the west to Montreal in the east and Hudson Bay in the North was published as Sheet 2, of 12, of Antonio Zattas 1778 re-issue of John Mitchells famous landmark map A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America, With the Roads, Distances, Limits, and Extent of the Settlements was published in Zattas Atlas Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785)
I have included an image of the complete 12 sheet joined map by Zatta as well as an image of Mitchells map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13 1/2in (445mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Mitchell Map by John Mitchell (1711–1768) is considered the most famous map of North America both cartographically and historically, was reprinted several times during the second half of the 18th century. The Mitchell Map was used as a primary map source during the Treaty of Paris for defining the boundaries of the newly independent United States. The map remained important for resolving border disputes between the United States and Canada as recently as the 1980s dispute over the Gulf of Maine fisheries. The Mitchell Map is the most comprehensive map of eastern North America made during the colonial era. Its size is about 6.5 feet (2.0 m) wide by 4.5 feet (1.4 m) high.
John Mitchell was not a professional geographer or map-maker. Son of a wealthy Virginian family in Lancaster County, on Virginia's Northern Neck, he had been educated at Edinburgh University, Scotland; this education included the first two years of the three-year medical program. Returning to coastal Virginia, he practiced as a physician and studied the local botany. Ill health forced Mitchell and his wife to leave Virginia for London in 1746. There, he served as a consultant on exotic plants to noblemen interested in gardens. Also, it was there that Mitchell would make his famous map. Map historians have understandably been interested in why a physician and botanist who had shown no previous interest in map making should make such a large and detailed map.
Until recently, historians have argued that Mitchell was upset by the lack of interest shown by politicians in London about colonial affairs and so set out to warn them about the dangers posed to the British colonies by the French. Mitchell did so, on his own initiative, by making a first map of North America in 1750, which he then showed to the politicians he knew through his botanical and gardening activities. The map so impressed George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax, appointed president of the Board of Trade and Plantations in 1748, that Halifax opened up the official archives and solicited new maps from the colonies for Mitchell to make a new and better map. This was the map published in 1755. That is, the motive force for preparations against the French threat is understood to have come from a colonist who sought to take control of the colonies' future on behalf of the other colonists.
A re-examination of the archival evidence indicates, however, that Mitchell made his first map in 1750 at Halifax's behest. Halifax became president of the Board of Trade directly after the conclusion of the War of the Austrian Succession (1744–1748) and its North American component, King George's War. The war had ended in stalemate and a return to the Anglo-French status quo of the 1714 Treaty of Utrecht. In fact, it was a common conviction that it was only a matter of time before another global Anglo-French war would begin, and it was commonly expected that the spark of the new conflict would be the North American colonies. It was then that Halifax latched onto Mitchell as an expert informant on all things colonial; one of his requests, apparently, was for Mitchell to make a new map to show the territorial situation in North America. Certainly, it was only after 1749 that Mitchell's correspondence revealed his new interests in both geography and politics.
Mitchell compiled a first map in 1750 from the materials that he could find in London, in official archives and private hands. It proved to be inadequate. Halifax accordingly ordered the governors of the British colonies to send new maps, which most did. These became the basis, when fitted into the overall geographical frame provided by the maps of the French geographer Guillaume Delisle. Late in 1754, Halifax was using one manuscript copy of Mitchell's second map to successfully promote his political position (no compromise with the French) within the British cabinet in the build-up to the Seven Years' War aka French and Indian War. Halifax also permitted Mitchell to have the map published: it appeared in April 1755, engraved by Thomas Kitchin and published by Andrew Millar.
The published map bore the title A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America. It bore the copyright date of 13 February 1755, but the map was probably not sold to the public until April or even May. Minor corrections to the map's printing plates were made probably during the printing process.
The geographer John Green (né Braddock Mead) criticized Mitchell and his map soon after it appeared, emphasizing two failings with respect to Nova Scotia (an area of particular dispute with the French). Mitchell, Green noted, had used neither the astronomical observations for latitude and longitude made by Marquis Joseph Bernard de Chabert in the 1740s nor a 1715 chart of the Nova Scotia coast. In response, Mitchell released a new version of his map, now with two large blocks of text that described all of his data sources; the new version of the map also adjusted the coastline in line with Chabert's work but rejected the 1715 chart as deeply flawed. This version of the map, which Mitchell referred to as the "second edition," is commonly thought to have appeared sometime in 1757, but advertisements in the (London) Public Advertiser and Gazetteer and London Daily Advertiser on 23 April 1756 clearly indicate that this new map appeared at that time.
The map continued to be corrected and some boundaries updated, even after Mitchell's death in 1768.
Mitchell's map was printed in eight sheets; when assembled, it measures 136 cm by 195 cm (4 feet 6 inches by 6 feet 5 inches; height x width). The initial impressions printed in 1755 have a consistent coloring outlining British colonial claims. Mitchell extended the southern colonies across the entire continent, even over established Spanish territory west of the Mississippi. Mitchell divided up the Iroquois territories (as he understood them, reaching from Lake Champlain [Lac Irocoisia] to the Mississippi, and north of Lake Superior) between Virginia and New York, leaving only a much-reduced territory to the French.
Mitchell's map was expensive but it spawned many cheaper variants that trumpeted Halifax and Mitchell's powerful colonial vision to the British public. One of these, published in December 1755 by "a Society of Anti-Gallicans", restricted the French even further just to Quebec.
The map is liberally sprinkled with text describing and explaining various features, especially in regions that were relatively unknown or which were subject to political dispute. Many notes describe the natural resources and potential for settlement of frontier regions. Others describe Indian tribes. Many Indian settlements are shown, along with important Indian trails.
Since Mitchell's main objective was to show the French threat to the British colonies, there is a very strong pro-British bias in the map, especially with regard to the Iroquois. The map makes clear that the Iroquois were not just allies of Britain, but subjects, and that all Iroquois land was therefore British territory. Huge parts of the continent are noted as being British due to Iroquois conquest of one tribe or another. French activity within the Iroquois claimed lands is noted, explicitly or implicitly, as illegal.
In cases where the imperial claims of Britain and France were questionable, Mitchell always takes the British side. Thus many of his notes and boundaries seem like political propaganda today. Some of the claims seem to be outright falsehoods.
The map is very large and the notes are often very small, making it difficult to view online. Reduced scale copies result in unreadable notes. The following list gives a few examples of the kind of notes found on the map, with Mitchell's spelling:
- The region of today's central Tennessee and Kentucky (between the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers): A Fine Level Fertile Country of great Extent, by Accounts of the Indians and our People
- In the area between the Mississippi River and the Tennessee River: This Country of the Cherokees which extends Westward to the Mississippi and Northward to the Confines of the Six Nations was formally surrendered to the Crown of Britain at Westminster 1729
- In the Great Plains: The Nadouessoians are reckoned one of the most Populous Nations of Indians in North America, altho' the number and situation of their Villages are not known nor laid down. (Reference to the Sioux)
- Along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico, present-day Texas: Wandering Savage Indians
- Southwest of Hudson Bay: The long and Barbarous Names lately given to some of these Northern Parts of Canada and the Lakes we have not inserted, as they are of no use, and uncertain Authority.
- North of Lake Huron: MESSESAGUES—Subdued by the Iroquois and now united with them making the 8th Nation in that League. (reference to the Mississaugas)
- Missouri River: Missouri River is reckoned to run Westward to the Mountains of New Mexico, as far as the Ohio does Eastward
- Present-day Iowa: Extensive Meadows full of Buffaloes
- Sandusky, Ohio: Sandoski—Canahogue—The seat of War, the Mart of Trade, & chief Hunting Grounds of the Six Nations, on the Lakes & the Ohio.
- Central Pennsylvania, north of present-day Harrisburg: St. Anthony's Wilderness
- Illinois region: The Antient Eriez were extirpated by the Iroquois upwards of 100 years ago, ever since which time they have been in Possession of L. Erie (reference to the Erie people)
- Along Illinois River and overland to the south end of Lake Michigan: Western Bounds of the Six Nations sold and Surrendered to Great Britain
- Illinois region: The Six Nations have extended their Territories to the River Illinois, ever since the Year 1672, when they subdued, and were incorporated with, the Antient Chaouanons, the Native Proprietors of these Countries, and the River Ohio. Besides which they likewise claim a Right of Conquest over the Illinois, and all the Mississippi as far as they extend. This is confirmed by their own Claims and Possessions in 1742, which include all the Bounds here laid down, and none have ever thought fit to dispute them. (reference to the Illiniwek)
- Just below the previous note: The Ohio Indians are a mixt Tribe of the Several Indians of our Colonies, settled here under the Six Nations, who have always been in Alliance and Subjection to the English. The most numerous of them are the Delaware and Shawnoes, who are Natives of Delaware River. Those about Philadelphia were called Sauwanoos whom we now call Shawanoes, or Shawnoes. The Mohickans and Minquaas were the Antient Inhabitants of Susquehanna R. (reference to the Lenape, Shawnee, and Susquehannock Indians)
- Southeast Missouri area: Mines of Marameg, which gave rise to the famous Mississippi Scheme 1719.
- North Florida: TIMOOQUA—Destroy'd by the Carolinians in 1706 (reference to the Timucua)
- South Georgia: COUNTRY OF THE APALACHEES—Conquered & surrendered to the Carolinians, after two memorable Victories obtain'd over them & the Spaniards in 1702 & 1703 at the Places marked thus [crossed-swords] (reference to the Apalachee)
- Alabama area: The English have Factories & Settlements in all the Towns of the Creek Indians of any note, except Albamas; which was usurped by the French in 1715 but established by the English 28 years before. (reference to the Creek people)
- Yazoo River: River of the Yasous—The Indians on this River were in Alliance with the English, for which they have been destroyed by the French (reference to the Yazoo tribe)
- Many geographic features are labeled with names no longer in use or oddly spelled, including:
Des Moines River: Moingona River
Kanawha and New River together: Gr. Conhaway called Wood R. or New R.
Kentucky River: Cuttawa or Catawba R.
Clinch River: Pelisipi River (a tributary is labeled Clinch's R.)
Tennessee River: River of the Cherakees, or Hogohegee R. Upstream another label says River Hogohegee or Callamaco
French Broad River: Agiqua R.
Little Tennessee River: Tannaſsee or Satico R.
Hiwassee River: Euphasee
Ohio River: Ohio or Splawacipiki R.
Altamaha River: Alatamaha or George R.
Minnesota River: Ouadebameniſsouté or R. St. Peter (reflecting the Dakota name Watpá Mnísota and the French name Rivière de St. Pierre)
Muskegon River: Maticon R.
The map also included non-existent features, such as Isle Phelipeaux in Lake Superior, found in earlier maps by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin.
The Mitchell Map remained the most detailed map of North America available in the later eighteenth century. Various impressions (and also French copies) were used to establish the boundaries of the new United States of America by diplomats at the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the American Revolutionary War. The map's inaccuracies subsequently led to a number of border disputes, such as in Maine. Its supposition that the Mississippi River extended north to the 50th parallel (into British territory) resulted in the treaty using it as a landmark for a geographically impossible definition of the border in that region. It was not until 1842, when the Webster-Ashburton Treaty resolved these inconsistencies with fixes such as the one that created Minnesota's Northwest Angle, that the U.S.–Canada border was clearly drawn from Maine to the Oregon Country.
Similarly, during the drafting of the Northwest Ordinance, the map's inaccuracy in depicting where an east–west line drawn through the southernmost point of Lake Michigan would intersect Lake Erie led to a long dispute over the Ohio–Michigan border that culminated in the Toledo War.
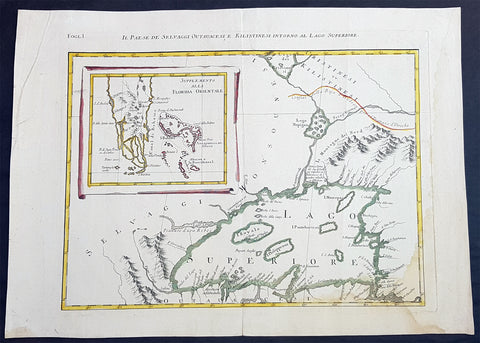
1778 Antonio Zatta & John Mitchell Antique Map of Lake Superior & Florida
Antique Map
- Title : Il Paese de Selvaggi Outauace si e Kilistinesi Intorno Al Lago Superiore; Supplemento alla Florida Orientale
- Date : 1778
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93517
- Size: 21in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Description:
This wonderfully executed original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique map of Lake Superior, with an inset map of southern Florida, was published as Sheet 1, of 12, of Antonio Zattas 1778 re-issue of John Mitchells famous landmark map A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America, With the Roads, Distances, Limits, and Extent of the Settlements was published in Zattas Atlas Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785)
I have included an image of the complete 12 sheet joined map by Zatta as well as an image of Mitchells map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13 1/2in (445mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Mitchell Map by John Mitchell (1711–1768) is considered the most famous map of North America both cartographically and historically, was reprinted several times during the second half of the 18th century. The Mitchell Map was used as a primary map source during the Treaty of Paris for defining the boundaries of the newly independent United States. The map remained important for resolving border disputes between the United States and Canada as recently as the 1980s dispute over the Gulf of Maine fisheries. The Mitchell Map is the most comprehensive map of eastern North America made during the colonial era. Its size is about 6.5 feet (2.0 m) wide by 4.5 feet (1.4 m) high.
John Mitchell was not a professional geographer or map-maker. Son of a wealthy Virginian family in Lancaster County, on Virginia's Northern Neck, he had been educated at Edinburgh University, Scotland; this education included the first two years of the three-year medical program. Returning to coastal Virginia, he practiced as a physician and studied the local botany. Ill health forced Mitchell and his wife to leave Virginia for London in 1746. There, he served as a consultant on exotic plants to noblemen interested in gardens. Also, it was there that Mitchell would make his famous map. Map historians have understandably been interested in why a physician and botanist who had shown no previous interest in map making should make such a large and detailed map.
Until recently, historians have argued that Mitchell was upset by the lack of interest shown by politicians in London about colonial affairs and so set out to warn them about the dangers posed to the British colonies by the French. Mitchell did so, on his own initiative, by making a first map of North America in 1750, which he then showed to the politicians he knew through his botanical and gardening activities. The map so impressed George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax, appointed president of the Board of Trade and Plantations in 1748, that Halifax opened up the official archives and solicited new maps from the colonies for Mitchell to make a new and better map. This was the map published in 1755. That is, the motive force for preparations against the French threat is understood to have come from a colonist who sought to take control of the colonies' future on behalf of the other colonists.
A re-examination of the archival evidence indicates, however, that Mitchell made his first map in 1750 at Halifax's behest. Halifax became president of the Board of Trade directly after the conclusion of the War of the Austrian Succession (1744–1748) and its North American component, King George's War. The war had ended in stalemate and a return to the Anglo-French status quo of the 1714 Treaty of Utrecht. In fact, it was a common conviction that it was only a matter of time before another global Anglo-French war would begin, and it was commonly expected that the spark of the new conflict would be the North American colonies. It was then that Halifax latched onto Mitchell as an expert informant on all things colonial; one of his requests, apparently, was for Mitchell to make a new map to show the territorial situation in North America. Certainly, it was only after 1749 that Mitchell's correspondence revealed his new interests in both geography and politics.
Mitchell compiled a first map in 1750 from the materials that he could find in London, in official archives and private hands. It proved to be inadequate. Halifax accordingly ordered the governors of the British colonies to send new maps, which most did. These became the basis, when fitted into the overall geographical frame provided by the maps of the French geographer Guillaume Delisle. Late in 1754, Halifax was using one manuscript copy of Mitchell's second map to successfully promote his political position (no compromise with the French) within the British cabinet in the build-up to the Seven Years' War aka French and Indian War. Halifax also permitted Mitchell to have the map published: it appeared in April 1755, engraved by Thomas Kitchin and published by Andrew Millar.
The published map bore the title A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America. It bore the copyright date of 13 February 1755, but the map was probably not sold to the public until April or even May. Minor corrections to the map's printing plates were made probably during the printing process.
The geographer John Green (né Braddock Mead) criticized Mitchell and his map soon after it appeared, emphasizing two failings with respect to Nova Scotia (an area of particular dispute with the French). Mitchell, Green noted, had used neither the astronomical observations for latitude and longitude made by Marquis Joseph Bernard de Chabert in the 1740s nor a 1715 chart of the Nova Scotia coast. In response, Mitchell released a new version of his map, now with two large blocks of text that described all of his data sources; the new version of the map also adjusted the coastline in line with Chabert's work but rejected the 1715 chart as deeply flawed. This version of the map, which Mitchell referred to as the "second edition," is commonly thought to have appeared sometime in 1757, but advertisements in the (London) Public Advertiser and Gazetteer and London Daily Advertiser on 23 April 1756 clearly indicate that this new map appeared at that time.
The map continued to be corrected and some boundaries updated, even after Mitchell's death in 1768.
Mitchell's map was printed in eight sheets; when assembled, it measures 136 cm by 195 cm (4 feet 6 inches by 6 feet 5 inches; height x width). The initial impressions printed in 1755 have a consistent coloring outlining British colonial claims. Mitchell extended the southern colonies across the entire continent, even over established Spanish territory west of the Mississippi. Mitchell divided up the Iroquois territories (as he understood them, reaching from Lake Champlain [Lac Irocoisia] to the Mississippi, and north of Lake Superior) between Virginia and New York, leaving only a much-reduced territory to the French.
Mitchell's map was expensive but it spawned many cheaper variants that trumpeted Halifax and Mitchell's powerful colonial vision to the British public. One of these, published in December 1755 by "a Society of Anti-Gallicans", restricted the French even further just to Quebec.
The map is liberally sprinkled with text describing and explaining various features, especially in regions that were relatively unknown or which were subject to political dispute. Many notes describe the natural resources and potential for settlement of frontier regions. Others describe Indian tribes. Many Indian settlements are shown, along with important Indian trails.
Since Mitchell's main objective was to show the French threat to the British colonies, there is a very strong pro-British bias in the map, especially with regard to the Iroquois. The map makes clear that the Iroquois were not just allies of Britain, but subjects, and that all Iroquois land was therefore British territory. Huge parts of the continent are noted as being British due to Iroquois conquest of one tribe or another. French activity within the Iroquois claimed lands is noted, explicitly or implicitly, as illegal.
In cases where the imperial claims of Britain and France were questionable, Mitchell always takes the British side. Thus many of his notes and boundaries seem like political propaganda today. Some of the claims seem to be outright falsehoods.
The map is very large and the notes are often very small, making it difficult to view online. Reduced scale copies result in unreadable notes. The following list gives a few examples of the kind of notes found on the map, with Mitchell's spelling:
- The region of today's central Tennessee and Kentucky (between the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers): A Fine Level Fertile Country of great Extent, by Accounts of the Indians and our People
- In the area between the Mississippi River and the Tennessee River: This Country of the Cherokees which extends Westward to the Mississippi and Northward to the Confines of the Six Nations was formally surrendered to the Crown of Britain at Westminster 1729
- In the Great Plains: The Nadouessoians are reckoned one of the most Populous Nations of Indians in North America, altho' the number and situation of their Villages are not known nor laid down. (Reference to the Sioux)
- Along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico, present-day Texas: Wandering Savage Indians
- Southwest of Hudson Bay: The long and Barbarous Names lately given to some of these Northern Parts of Canada and the Lakes we have not inserted, as they are of no use, and uncertain Authority.
- North of Lake Huron: MESSESAGUES—Subdued by the Iroquois and now united with them making the 8th Nation in that League. (reference to the Mississaugas)
- Missouri River: Missouri River is reckoned to run Westward to the Mountains of New Mexico, as far as the Ohio does Eastward
- Present-day Iowa: Extensive Meadows full of Buffaloes
- Sandusky, Ohio: Sandoski—Canahogue—The seat of War, the Mart of Trade, & chief Hunting Grounds of the Six Nations, on the Lakes & the Ohio.
- Central Pennsylvania, north of present-day Harrisburg: St. Anthony's Wilderness
- Illinois region: The Antient Eriez were extirpated by the Iroquois upwards of 100 years ago, ever since which time they have been in Possession of L. Erie (reference to the Erie people)
- Along Illinois River and overland to the south end of Lake Michigan: Western Bounds of the Six Nations sold and Surrendered to Great Britain
- Illinois region: The Six Nations have extended their Territories to the River Illinois, ever since the Year 1672, when they subdued, and were incorporated with, the Antient Chaouanons, the Native Proprietors of these Countries, and the River Ohio. Besides which they likewise claim a Right of Conquest over the Illinois, and all the Mississippi as far as they extend. This is confirmed by their own Claims and Possessions in 1742, which include all the Bounds here laid down, and none have ever thought fit to dispute them. (reference to the Illiniwek)
- Just below the previous note: The Ohio Indians are a mixt Tribe of the Several Indians of our Colonies, settled here under the Six Nations, who have always been in Alliance and Subjection to the English. The most numerous of them are the Delaware and Shawnoes, who are Natives of Delaware River. Those about Philadelphia were called Sauwanoos whom we now call Shawanoes, or Shawnoes. The Mohickans and Minquaas were the Antient Inhabitants of Susquehanna R. (reference to the Lenape, Shawnee, and Susquehannock Indians)
- Southeast Missouri area: Mines of Marameg, which gave rise to the famous Mississippi Scheme 1719.
- North Florida: TIMOOQUA—Destroy'd by the Carolinians in 1706 (reference to the Timucua)
- South Georgia: COUNTRY OF THE APALACHEES—Conquered & surrendered to the Carolinians, after two memorable Victories obtain'd over them & the Spaniards in 1702 & 1703 at the Places marked thus [crossed-swords] (reference to the Apalachee)
- Alabama area: The English have Factories & Settlements in all the Towns of the Creek Indians of any note, except Albamas; which was usurped by the French in 1715 but established by the English 28 years before. (reference to the Creek people)
- Yazoo River: River of the Yasous—The Indians on this River were in Alliance with the English, for which they have been destroyed by the French (reference to the Yazoo tribe)
- Many geographic features are labeled with names no longer in use or oddly spelled, including:
Des Moines River: Moingona River
Kanawha and New River together: Gr. Conhaway called Wood R. or New R.
Kentucky River: Cuttawa or Catawba R.
Clinch River: Pelisipi River (a tributary is labeled Clinch's R.)
Tennessee River: River of the Cherakees, or Hogohegee R. Upstream another label says River Hogohegee or Callamaco
French Broad River: Agiqua R.
Little Tennessee River: Tannaſsee or Satico R.
Hiwassee River: Euphasee
Ohio River: Ohio or Splawacipiki R.
Altamaha River: Alatamaha or George R.
Minnesota River: Ouadebameniſsouté or R. St. Peter (reflecting the Dakota name Watpá Mnísota and the French name Rivière de St. Pierre)
Muskegon River: Maticon R.
The map also included non-existent features, such as Isle Phelipeaux in Lake Superior, found in earlier maps by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin.
The Mitchell Map remained the most detailed map of North America available in the later eighteenth century. Various impressions (and also French copies) were used to establish the boundaries of the new United States of America by diplomats at the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the American Revolutionary War. The map's inaccuracies subsequently led to a number of border disputes, such as in Maine. Its supposition that the Mississippi River extended north to the 50th parallel (into British territory) resulted in the treaty using it as a landmark for a geographically impossible definition of the border in that region. It was not until 1842, when the Webster-Ashburton Treaty resolved these inconsistencies with fixes such as the one that created Minnesota's Northwest Angle, that the U.S.–Canada border was clearly drawn from Maine to the Oregon Country.
Similarly, during the drafting of the Northwest Ordinance, the map's inaccuracy in depicting where an east–west line drawn through the southernmost point of Lake Michigan would intersect Lake Erie led to a long dispute over the Ohio–Michigan border that culminated in the Toledo War.
1785 Antonio Zatta Large Antique Map of Southern United States, Texas, Mexico
Antique Map
- Title : Messico ouvero Nuova Spagna che contiene Il Nuovo Messico La Californoa Con Una Partie de Paesi Adjacenti Venezi 1785
- Ref #: 93526
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Mexico including Texas, California, and the Southern United States was engraved in 1785 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Antonio Zatta in his Atlas Atlante Novissimo. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The capture of Tenochtitlan and refounding of Mexico City in 1521 was the beginning of a 286-year-long colonial era during which Mexico was known as Nueva España (New Spain). The Kingdom of New Spain was created from the remnants of the Aztec hegemonic empire. Subsequent enlargements, such as the conquest of the Tarascan state, resulted in the creation of the Viceroyalty of New Spain in 1535. The Viceroyalty at its greatest extent included the territories of modern Mexico, Central America as far south as Costa Rica, and the western United States. The Viceregal capital Mexico City also administrated the Spanish West Indies (the Caribbean), the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines), and Spanish Florida.
The indigenous population stabilized around one to one and a half million individuals in the 17th century from the most commonly accepted five to ten million pre-contact population. The population decline was primarily the result of communicable diseases, particularly smallpox, introduced during the Columbian Exchange. During the three hundred years of the colonial era, Mexico received between 400,000 and 500,000 Europeans, between 200,000 and 250,000 Africans and between 40,000 and 120,000 Asians. The 18th century saw a great increase in the percentage of mestizos.
Colonial law with Spanish roots was introduced and attached to native customs creating a hierarchy between local jurisdiction (the Cabildos) and the Spanish Crown. Upper administrative offices were closed to native-born people, even those of pure Spanish blood (criollos). Administration was based on the racial separation, among Republics of Spaniards, Amerindians and castas, autonomous and directly dependent on the king himself.
The Council of Indies and the mendicant religious orders, which arrived in Mesoamerica as early as 1524, labored to generate capital for the crown of Spain and convert the Amerindian populations to Catholicism. The 1531 Marian apparitions to Saint Juan Diego gave impetus to the evangelization of central Mexico. The Virgin of Guadalupe became a symbol of criollo patriotism and was used by the insurgents that followed Miguel Hidalgo during the War of Independence. Some Crypto-Jewish families emigrated to Mexico to escape the Spanish Inquisition.
The rich deposits of silver, particularly in Zacatecas and Guanajuato, resulted in silver extraction dominating the economy of New Spain. Taxes on silver production became a major source of income for Spain. Other important industries were the haciendas (functioning under the encomienda and repartimiento systems) and mercantile activities in the main cities and ports. Wealth created during the colonial era spurred the development of New Spanish Baroque.
As a result of its trade links with Asia, the rest of the Americas, Africa and Europe and the profound effect of New World silver, central Mexico was one of the first regions to be incorporated into a globalized economy. Being at the crossroads of trade, people and cultures, Mexico City has been called the first world city. The Nao de China (Manila Galleons) operated for two and a half centuries and connected New Spain with Asia. Goods were taken from Veracruz to Atlantic ports in the Americas and Spain. Veracruz was also the main port of entry in mainland New Spain for European goods, immigrants, and African slaves. The Camino Real de Tierra Adentro connected Mexico City with the interior of New Spain. Mexican silver pesos became the first globally used currency and the silver mined in Mexico were used to run commerce and wage crusades in two sides of globe, at the Mediterranean were Spain fought against the Ottoman Caliphate and at Southeast Asia where the Philippines fought against the Brunei Sultanate.
Due to the importance of New Spain administrative base, Mexico was the location of the first printing shop (1539), first university (1551), first public park (1592), and first public library (1646) in the Americas, amongst other institutions. Important artists of the colonial period, include the writers Juan Ruiz de Alarcón and Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, painters Cristóbal de Villalpando and Miguel Cabrera, and architect Manuel Tolsá. The Academy of San Carlos was the first major school and museum of art in the Americas. Scientist Andrés Manuel del Río Fernández discovered the element vanadium.
Spanish forces, sometimes accompanied by native allies, led expeditions to conquer territory or quell rebellions through the colonial era. Notable Amerindian revolts in sporadically populated northern New Spain include the Chichimeca War (1576–1606), Tepehuán Revolt (1616–1620) and the Pueblo Revolt (1680). To protect Mexico from the attacks of English, French and Dutch pirates and protect the Crowns monopoly of revenue, only two ports were open to foreign trade—Veracruz on the Atlantic and Acapulco on the Pacific. Among the best-known pirate attacks are the 1663 Sack of Campeche and 1683 Attack on Veracruz.
Many Mexican cultural features including tequila, first distilled in the 16th century, charreria (17th), mariachi (18th) and Mexican cuisine, a fusion of American and European (particularly Spanish) cuisine, arose during the colonial era.
On September 16, 1810, a loyalist revolt against the ruling junta was declared by priest Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla, in the small town of Dolores, Guanajuato. This event, known as the Cry of Dolores (Spanish: Grito de Dolores) is commemorated each year, on September 16, as Mexicos independence day. The first insurgent group was formed by Hidalgo, the Spanish viceregal army captain Ignacio Allende, the militia captain Juan Aldama and La Corregidora Josefa Ortiz de Domínguez. Hidalgo and some of his soldiers were captured and executed by firing squad in Chihuahua, on July 31, 1811. Following his death, the leadership was assumed by priest José María Morelos, who occupied key southern cities.
In 1813 the Congress of Chilpancingo was convened and, on November 6, signed the Solemn Act of the Declaration of Independence of Northern America. Morelos was captured and executed on December 22, 1815.
In subsequent years, the insurgency was near collapse, but in 1820 Viceroy Juan Ruiz de Apodaca sent an army under the criollo general Agustín de Iturbide against the troops of Vicente Guerrero. Instead, Iturbide approached Guerrero to join forces, and on August 24, 1821 representatives of the Spanish Crown and Iturbide signed the Treaty of Córdoba and the Declaration of Independence of the Mexican Empire, which recognized the independence of Mexico under the terms of the Plan of Iguala.
Mexicos short recovery after the War of Independence was soon cut short again by the civil wars and institutional instability of the 1850s, which lasted until the government of Porfirio Díaz reestablished conditions that paved the way for economic growth. The conflicts that arose from the mid-1850s had a profound effect because they were widespread and made themselves perceptible in the vast rural areas of the countries, involved clashes between castes, different ethnic groups and haciendas, and entailed a deepening of the political and ideological divisions between republicans and monarchists.
Agustín de Iturbide became constitutional emperor of the First Mexican Empire in 1822. A revolt against him in 1823 established the United Mexican States. In 1824, a Republican Constitution was drafted and Guadalupe Victoria became the first president of the newly born country. Central America, including Chiapas, left the union. In 1829 president Guerrero abolished slavery. The first decades of the post-independence period were marked by economic instability, which led to the Pastry War in 1836. There was constant strife between Liberals, supporters of a federal form of government, and Conservatives, who proposed a hierarchical form of government.
During this period, the frontier borderlands to the north became quite isolated from the government in Mexico City, and its monopolistic economic policies caused suffering. With limited trade, the people had difficulty meeting tax payments and resented the central governments actions in collecting customs. Resentment built up from California to Texas. Both the mission system and the presidios had collapsed after the Spanish withdrew from the colony, causing great disruption especially in Alta California and New Mexico. The people in the borderlands had to raise local militias to protect themselves from hostile Native Americans. These areas developed in different directions from the center of the country.
Wanting to stabilize and develop the frontier, Mexico encouraged immigration into present-day Texas, as they were unable to persuade people from central Mexico to move into those areas. They allowed for religious freedom for the new settlers, who were primarily Protestant English speakers from the United States. Within several years, the Anglos far outnumbered the Tejano in the area. Itinerant traders traveled through the area, working by free market principles. The Tejano grew more separate from the government and due to its neglect, many supported the idea of independence and joined movements to that end, collaborating with the English-speaking Americans.
General Antonio López de Santa Anna, a centralist and two-time dictator, approved the Siete Leyes in 1836, a radical amendment that institutionalized the centralized form of government. When he suspended the 1824 Constitution, civil war spread across the country. Three new governments declared independence: the Republic of Texas, the Republic of the Rio Grande and the Republic of Yucatán.
The 1846 United States annexation of the Republic of Texas and subsequent American military incursion into territory that was part of Coahuila (also claimed by Texas) instigated the Mexican–American War. The war was settled in 1848 via the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Mexico was forced to give up more than one-third of its land to the U.S., including Alta California, Santa Fe de Nuevo México and the territory claimed by Texas. A much smaller transfer of territory in what is today southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico—known as the Gadsden Purchase—occurred in 1854.
The Caste War of Yucatán, the Maya uprising that began in 1847, was one of the most successful modern Native American revolts. Maya rebels, or Cruzob, maintained relatively independent enclaves in the peninsula until the 1930s.
Dissatisfaction with Santa Annas return to power led to the liberal Plan of Ayutla, initiating an era known as La Reforma. The new Constitution drafted in 1857 established a secular state, federalism as the form of government, and several freedoms. As the Conservatives refused to recognize it, the Reform War began in 1858, during which both groups had their own governments. The war ended in 1861 with victory by the Liberals, led by president Benito Juárez, who was an ethnic Zapotec.
In the 1860s Mexico was occupied by France, which established the Second Mexican Empire under the rule of the Habsburg Archduke Ferdinand Maximilian of Austria with support from the Roman Catholic clergy and the Conservatives. The latter switched sides and joined the Liberals. Maximilian surrendered, was tried on June 14, 1867, and was executed a few days later on June 19 in Querétaro.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.