America (63)
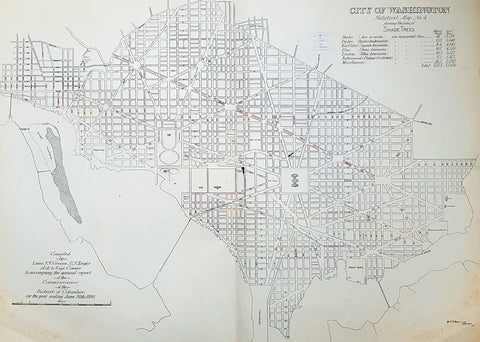
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Lines of Planted Trees in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 4 showing the lines of Shade Trees.....Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16266
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the lines of Trees planted very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
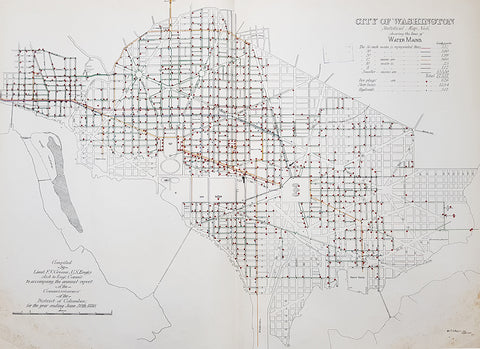
1880 F V Greene Large Antique Map Location of the Water Mains in Washington DC
- Title : City of Washington Statistical Map No 6 showing the lines of Water Mains...Compiled by Lieut. F V Greene, US Engrs. Asst to the Engr. Commr. to accompany the annual report of the Commissioners of the District of Columbia for the year ending June 30th 1880
- Size: 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1880
- Ref #: 16263
Description:
This large original lithograph map, a city plan of Washington DC, showing the location of the Water Mains very early in the cities growth, by Lieutenant Francis Vinton Greene, was published in June 1880, dated.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 30in x 23in (767mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling L&R bottom corners
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom L&R bottom corner backing canvas loose
Background:
The history of Washington, D.C. is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. Originally inhabited by an Algonquian-speaking people known as the Nacotchtank. the site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government\'s return to the capital, it had to manage reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol.
By 1870, the District\'s population had grown 75% from the previous census to nearly 132,000 residents. Despite the citys growth, Washington still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some members of Congress suggested moving the capital further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider such a proposal.
In response to the poor conditions in the capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, and created a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. The act provided for a governor appointed by the President, a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven appointed council members and a 22-member house of delegates elected by residents of the District, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city.
President Grant appointed Alexander Robey Shepherd, an influential member of the Board of Public Works, to the post of governor in 1873. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. However, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements and ultimately bankrupted the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the Districts territorial government and replaced it with a three-member Board of Commissioners appointed by the President, of which one was a representative from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. The three Commissioners would then elect one of themselves to be president of the commission.
An additional act of Congress in 1878 made the three-member Board of Commissioners the permanent government of the District of Columbia. The act also had the effect of eliminating any remaining local institutions such as the boards on schools, health, and police. The Commissioners would maintain this form of direct rule for nearly a century.
Greene, Francis Vinton 1850–1921
Greene was a United States Army officer who fought in the Spanish–American War. He came from the Greene family of Rhode Island, noted for its long line of participants in American military history.
Greene was born in Providence, Rhode Island on June 27, 1850. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point and graduated in 1870. He first served in the U.S. artillery and then transferred to the Corps of Engineers in 1872. He next served as an attaché from the War Department to the U.S. legation in St. Petersburg, Russia. While there he served in the Russian army during its war with Turkey. He was promoted to first lieutenant in 1874 and captiain in 1883. He returned to the U.S. and was a civil engineer to the city of Washington, D.C. and was a professor of artillery at West Point before resigning from the Army on December 31, 1886.
When the Spanish–American War broke out he raised the 7th New York Volunteer Infantry and was commissoned as it colonel on May 2, 1898. He was quickly promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on May 27, 1898. He commanded the second Philippine Expeditionary Force which became the 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, VIII Corps. Greene took a prominent part in the Battle of Manila in 1898. He assisted in the surrender negotiations for Manila. In August 1898 he was promoted major general of Volunteers and resigned on February 28, 1899.
After the war, he pursued a variety of occupations. He was a delegate to the Republican National Convention in 1900. He served as the New York City Police Commissioner from 1903 to 1904. He was president of the Niagara-Lockport and Ontario Power Company, along with other business ventures with Buffalo businessman John J. Albright. He died on May 13, 1921 in New York City.
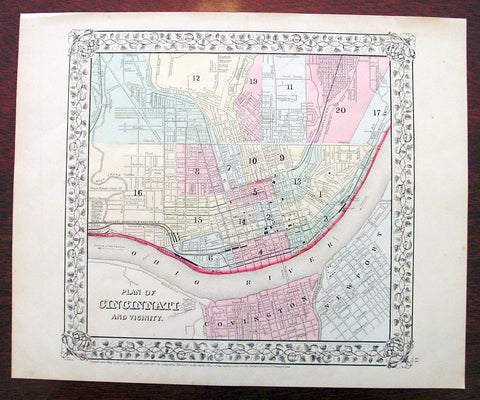
1869 Mitchell Antique Map - Plan of The City of Cincinnati
- Title : Plan of Cincinnati and Vicinity....1869 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35044
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique city plan map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
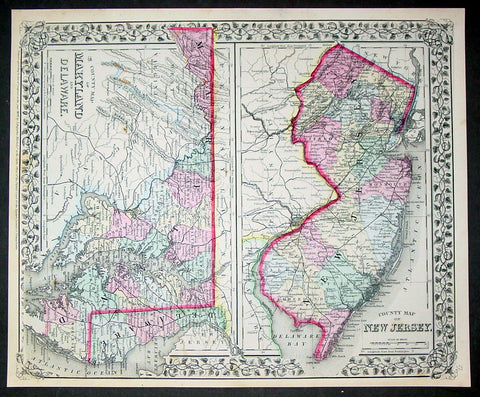
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Maps New Jersey, Maryland, Delaware
- Title : County Map of New Jersey; County Map of Maryland and Delaware....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35033
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of Virginia & West Virginia
- Title : County Map of Virginia and West Virginia....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35036
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell Antique County Map of Iowa and Missouri
- Title : County Map of the States of Iowa and Missouri....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35047
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
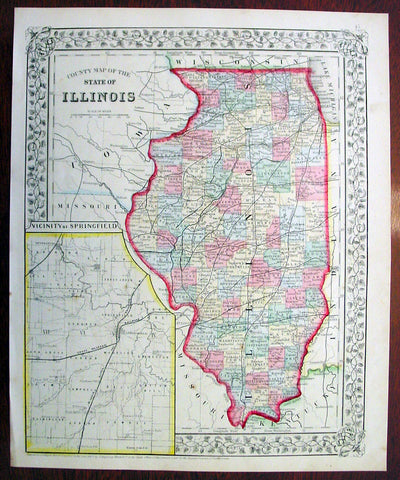
1869 Mitchell Antique Map of The State of Illinois
- Title : County Map of the State of Illinois....1869 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35045
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
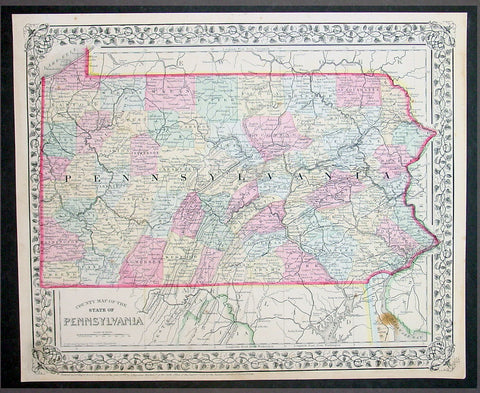
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of the State of Pennsylvania
- Title : County Map of Florida, Mobile....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35051
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
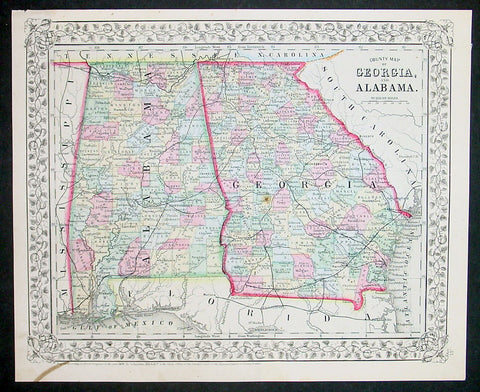
1870 Samuel Augustus Mitchell County Antique Map of Georgia and Alabama
- Title : County Map of Georgia and Alabama....1870 by S. Augustus Mitchell
- Ref #: 35038
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in the 1870 edition of his large New General Atlas - dated at the foot of the map.
These county, state, city & country maps are some of the most ornate and beautifully coloured maps published in the US in the 19th century. For over 50 years, Mitchell his son's and their successors were the most prominent cartographical publishers of maps and atlases in the United States.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 300mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
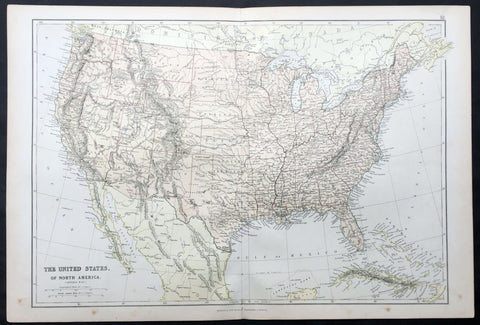
1870 Blackie & Son Large Antique Map of The United States of America
- Title : The United States of North America
- Ref #: 80558
- Size: 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large original antique lithograph map of The United States of America was engraved by Edward Weller and published by Blackie & Son of Glasgow & London in the 1870 edition of the Geographical Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 15in (560mm x 380mm)
Margins: - min 1/4in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
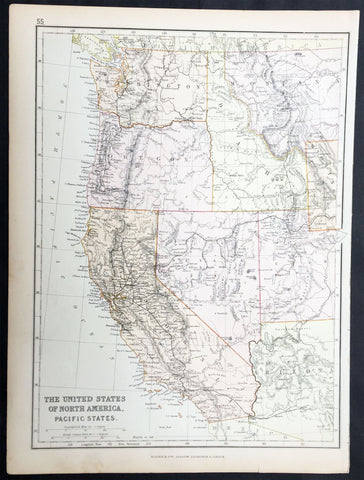
1870 Blackie & Son Antique Map The Western United States of America
- Title : The United States of North America Pacific States
- Ref #: 80560
- Size: 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1870
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique lithograph map of the Western United States of America including Washington, Oregon, California, Arizona, Nevada, Idaho, Montana, Utah & part of Wyoming was engraved by Edward Weller andpublished by Blackie & Son of Glasgow in the1870 edition of the Geographical Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper colour: - off white
Age of map colour: - Original
Colours used: - Yellow, pink, green
General colour appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
Margins: - min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
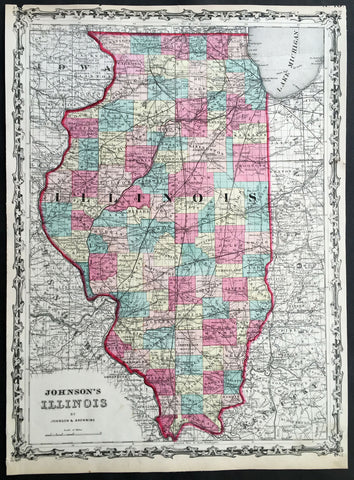
1860 A J Johnson Large Antique 1st edition Map of The State of Illinois, USA
- Title : Johnson's Illinois by Johnson & Browning
- Ref #: 50671
- Size: 17 1/2in x 13in (450mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1860
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original 1st edition map of the State of Illinois was published by A J Johnson in the 1860 edition ofJohnson's New Illustrated Family Atlas.
Background:
1st Edition, 1st issue. Most of the maps in this atlas come from Colton's 1859 edition of the General Atlas, published by Johnson and Browning, indicating the Johnson connection; some do not come from this atlas, and their sources are: the New England maps (scale 1" = 9 miles) come from Colton's map of New England and then the sub-maps of Vermont and New Hampshire, Mass/Conn/R.I.; the Ohio/Indiana is still a mystery; all the 1" = 24 miles maps (Iowa, Kentucky, etc.) come from Colton's Map of the United States and the Canadas, originally published by J. Calvin Smith in 1843 (see W. Heckrotte's copies and his list of editions); and the Colton General Atlas maps used by Johnson come from Colton's Travellers Series of maps - see our copies of Penn., Indiana. Colton mentions "The National Atlas of the United States, constructed from the Public Surveys..large Folio" as in preparation in his 1855 catalogue; this may be the embryonic Johnson Atlas. Colton used his wall maps "cut up" for pocket maps and Atlases. Johnson's maps of S. America, Europe, Africa, and (in the first edition, first issue, only) China, East Indies etc., all come from D. Griffing Johnson's Map of the World, 1847. These atlas maps are updated (esp. Africa). Colton took over the publication of the World Map in 1849, issued editions to 1868 (Ristow p318). Also, Johnson's N. America map is the inset N. America in Smith's Map of the U.S., the Canadas, etc. This first issue of Johnson's Family Atlas differs from the later 1860 edition in a small N.Y. (from the Colton U.S. map), small Texas, and many of the maps have fewer views or no views or different configurations. Clearly, this was a first attempt that was refined later in the year. Another issue of this same edition was published in Richmond, Virginia, the home town of Browning (I.L.). The California map originates with Johnson's New Illustrated and Embellished County
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink green yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 13in (450mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 13in (450mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in 312mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning, light chipping to margin edges
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Uniform age toning
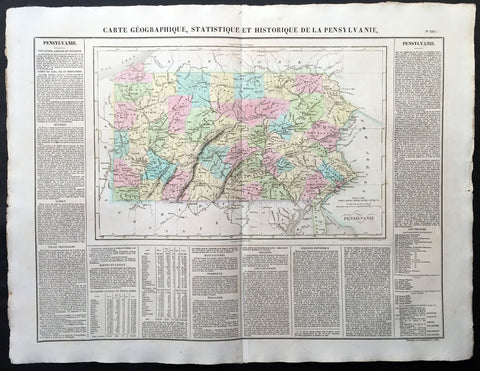
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of Pennsylvania, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique De la Pensylvanie
- Ref #: 70012
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
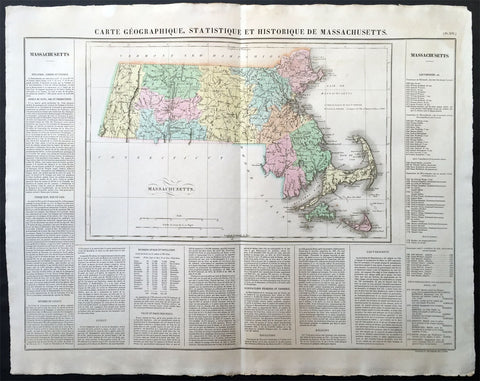
1825 Carey & Lea, Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of Massachusetts, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique Du Massachusetts
- Ref #: 70007
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None
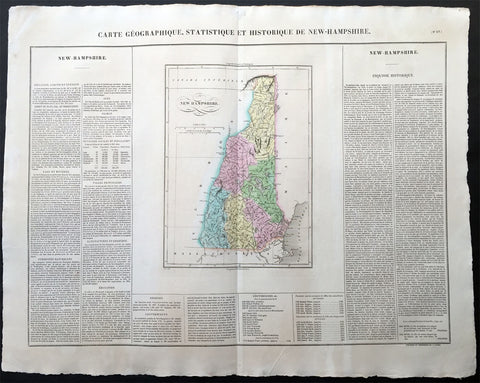
1825 Carey & Lea Buchon Large Antique Map of the State of New Hampshire, USA
-
Title : Carte Geographique, Statistique et Historique De New-Hampshire
- Ref #: 70006
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1825
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map was published in the 1825 French edition of Carey & Lea's American Atlas by Jean Alexandre Buchon.
This map is in exceptionally fine condition, on clean, sturdy and stable heavy paper, heavy engraving and beautiful original hand colour.
In 1822, Henry Charles Carey and Isaac Lea published their American Atlas. This volume was based on Emmanuel Las Cases' Atlas Historique of 1803, with updated maps and text modified by Carey, a political economist.
He considered himself an American foil to John Stuart Mill and the London economists who were proclaimers of "the gloomy science" influenced by Ricardo and Malthus. Instead of preaching overpopulation and degeneration of the human species, Carey illustrated the nations of the western hemisphere through maps that showed an expanding region with ample promise of developing into lands of great new opportunity and growth. The sheets from this atlas, which cover North America, Central America, South America and the West Indies, are comprised of an engraved map surrounded by text documenting the history, climate, population and so forth of the area depicted. The atlas is particularly known for its excellent early maps of the states and territories of the United States. Many of these maps were drawn by Fielding Lucas, Jr., an important Baltimore cartographer. All of the maps show excellent and very up-to-date detail, providing fine verbal and graphic pictures of states and territories in the early 19th century (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: None
Verso: - None