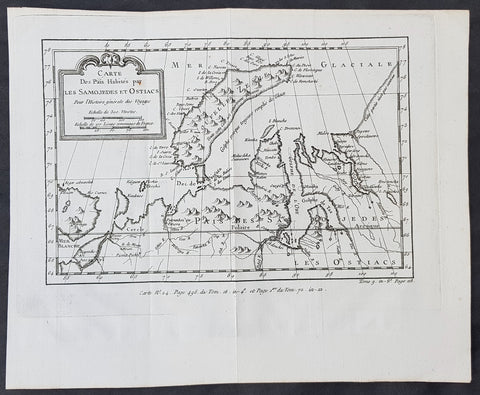
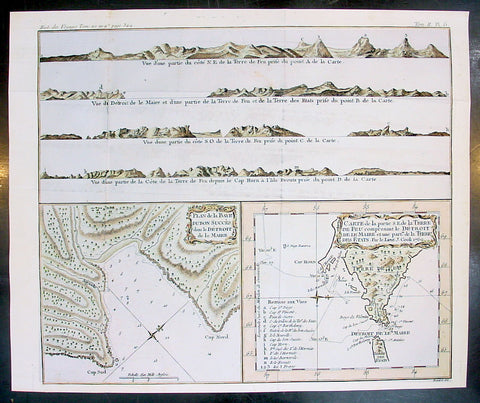
Jacques Nicholas Bellin (1703 - 1772)
Profile :
A French hydrographer, geographer, and member of the French intellectual group called the philosophes.
Bellin was born in Paris. He was hydrographer of France's hydrographic office, member of the Académie de Marine and of the Royal Society of London. Over a 50-year career, he produced a large number of maps of particular interest to the Ministère de la Marine. His maps of Canada and of French territories in North America (New France, Acadia, Louisiana) are particularly valuable. He died at Versailles.
In 1721, at age 18, he was appointed hydrographer (chief cartographer) to the French Navy. In August 1741, he became the first Ingénieur de la Marine of the Depot des cartes et plans de la Marine (the French Hydrographical Office) and was named Official Hydrographer of the French King.
During his reign the Depot came out with prodigious amount of charts and maps among which was a large folio format sea-charts of France, the Neptune Francois. He also produced a number of sea-atlases of the world, e.g., the Atlas Maritime and the Hydrographie Francaise. These gained fame, distinction and respect all over Europe and were republished throughout the 18th and even in the succeeding century.
Bellin also came out with smaller format maps such as the 1764 Petit Atlas Maritime (5 vols.) containing 580 finely detailed charts.
Bellin set a very high standard of workmanship and accuracy thus gaining for France a leading role in European cartography and geography. Many of his maps were copied by other mapmakers of Europe
He was one of the Encyclopédistes, a group of 18th century intellectuals in France who compiled the 35-volume Encyclopédie which was edited by Denis Diderot and Jean le Rond d'Alembert. Bellin contributed 994 articles.
The Encyclopédistes, were part of the group called philosophes among whose members were the great minds of the Age of Enlightenment, e.g., Montesquieu, Voltaire, Rousseau, Baron d'Holbach.
Bellin contributed a number of maps to 15-vol. Histoire Generale des Voyages of Antoine François Prévost or simply known l'Abbe Prevost. One of these maps led to a geographical blunder whose impact reverberates to this day. This was the map of the Philippines which Bellin copied from a world-famous chart produced in 1734 by the Spanish missionary to the Philippines, Fr. Pedro Murillo Velarde.
Unlike many other European mapmakers of the time who outright appropriated Murillo's map, Bellin had the intellectual integrity to fully credit Murillo as his source, an open acknowledgement shown in the title cartouche of Bellin's map which came out the same year as the original work by Murillo.
Shown in Bellin's map was an island named "Limasava", a word invented in 1667 by Spanish friar, Fr. Francisco Combés, S.J., to refer to the way station of the Armada de Molucca under the command of the Portuguese captain-general Fernao de Magalhaes during its navigation in Philippine waters. Combés, who had not read a single eyewitness account of the Magellan expedition relied on two sources, the hopelessly garbled Italian translation of the Antonio Pigafetta account by Giovanni Battista Ramusio and the secondhand account by Antonio de Herrera y Tordesillas. Ramusio wrote the fleet anchored in March–April 1521 in Butuan in Mindanao, and from there sailed for Cebu with a brief stopover at "Messana". In the authentic Pigafetta account, the port was an isle named Mazzaua while the stopover isle was named Gatighan. Antonio de Herrera y Tordesillas gave a faithful narration of the Mazzaua anchorage.
Combés disregarded de Herrera's version and adopted Ramusio's. He wrote that Magellan's fleet had anchored at Butuan and from their sailed for Cebu making a stop at a way station he named Limasaua.
Five years earlier than Combés, Fr. Francisco Colín wrote the Armada moored at Butuan from March–April 1521 where Magellan and his men together with the natives celebrated an Easter Sunday mass on 31 March 1521. From Butuan the fleet sailed for Cebu making a brief stop at a way station he called "Dimasaua", an invented word meaning "this is not the Mazagua of Antonio de Herrera where supposedly an Easter Sunday mass was held which I already said happened in Butuan."
This episode was projected in the 1734 map made by Murillo who used Combés name, "Limassava" not "Dimasaua" which map Bellin copied
In 1789, Augustinian Carlo Amoretti, Italian Encyclopedist and librarian of Biblioteca Ambrosiana in Milan, discovered the authentic Italian manuscript of Antonio Pigafetta among the scattered holdings of the library. Here it came out that the port of March–April 1521 was not Butuan but Mazaua. Amoretti, who himself had not read any of five eyewitness reports of the incident including two French versions of Pigafetta's account, asserted in a footnote that Mazaua was probably the isle named Limasava in Bellin's map, thus interchanging the real port of Mazaua with the way station Gatighan.
Largely with the appearance of the eyewitness account of Ginés de Mafra, the only seaman in Magellan's fleet to return to Mazaua, whose testimony reveals a concrete, measurable description of Mazaua, the skein starting from the garbled version of Pigafetta by Ramusio to the mishandling by Combés to Bellin and finally to Amoretti has been unraveled: Pigafetta's Gatighan is Bellin's Limasava.
Published Works:
- Hydrographie française (1753)
- Carte de l'Amérique septentrionale (Map of Northern America) (1755)
- Le petit Atlas François. Recueil de Cartes et Plans des quatre parties du Monde (1758)
- Petit Atlas Maritime (1764)
- Nouvelle méthode pour apprendre la géographie (1769)
Jacques Nicholas Bellin (135)
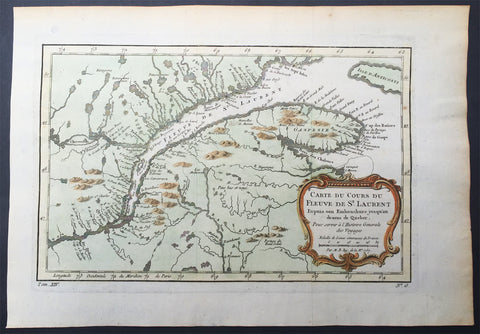
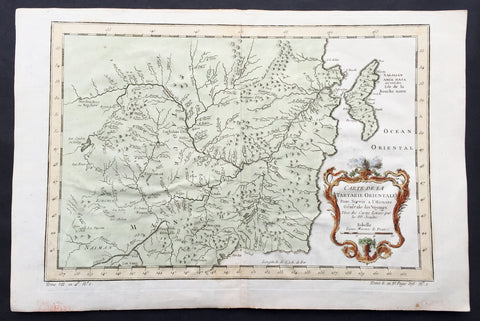
1757 Nicolas Bellin Large Antique Map Mouth of St Lawrence River Quebec, Canada
- Title : Carte Du Cours Du Fleuve De St Laurent...1757
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 61087
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved beautifully hand colored antique mapof the mouth of the St Lawrence River to the city of Quebec, Canada by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - dated - and was published in the French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Norse explored the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in the 11th century and were followed by fifteenth and early sixteenth century European mariners, such as John Cabot, and the brothers Gaspar and Miguel Corte-Real. The first European explorer known to have sailed up the Saint Lawrence River itself was Jacques Cartier. At that time, the land along the river was inhabited by the St. Lawrence Iroquoians; at the time of Cartiers second voyage in 1535. Because Cartier arrived in the estuary on Saint Lawrences feast day, he named it the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The Saint Lawrence River is partly within the U.S. and as such is that countrys sixth oldest surviving European place-name.
The earliest regular Europeans in the area were the Basques, who came to the St Lawrence Gulf and River in pursuit of whales from the early 16th century. The Basque whalers and fishermen traded with indigenous Americans and set up settlements, leaving vestiges all over the coast of eastern Canada and deep into the Saint Lawrence River. Basque commercial and fishing activity reached its peak before the Armada Invencibles disaster (1588), when the Spanish Basque whaling fleet was confiscated by King Philip II of Spain and largely destroyed. Initially, the whaling galleons from Labourd were not affected by the Spanish defeat.
Until the early 17th century, the French used the name Rivière du Canada to designate the Saint Lawrence upstream to Montreal and the Ottawa River after Montreal. The Saint Lawrence River served as the main route for European exploration of the North American interior, first pioneered by French explorer Samuel de Champlain.
Control of the river was crucial to British strategy to capture New France in the Seven Years War. Having captured Louisbourg in 1758, the British sailed up to Quebec the following year thanks to charts drawn up by James Cook. British troops were ferried via the Saint Lawrence to attack the city from the west, which they successfully did at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. The river was used again by the British to defeat the French siege of Quebec under the Chevalier de Lévis in 1760.
In 1809, the first steamboat to ply its trade on the St. Lawrence was built and operated by John Molson and associates, a scant two years after Fultons steam-powered navigation of the Hudson River. The Accommodation with ten passengers made her maiden voyage from Montreal to Quebec City in 66 hours, for 30 of which she was at anchor. She had a keel of 75 feet, and length overall of 85 feet. The cost of a ticket as eight dollars upstream, and nine dollars down. She had berths that year for twenty passengers.
Within a decade, daily service was available in the hotly-contested Montreal-Quebec route.
Because of the virtually impassable Lachine Rapids, the Saint Lawrence was once continuously navigable only as far as Montreal. Opened in 1825, the Lachine Canal was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids. An extensive system of canals and locks, known as the Saint Lawrence Seaway, was officially opened on 26 June 1959 by Elizabeth II (representing Canada) and President Dwight D. Eisenhower (representing the United States). The Seaway (including the Welland Canal) now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to Lake Superior.
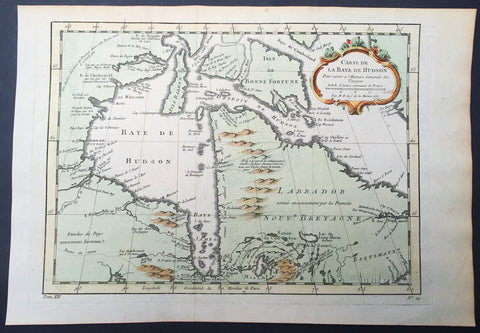
1757 Nicolas Bellin Large Antique Map of Hudsons Bay & Provinces, Canada
- Title : Carte De La Baye De Hudson...1757
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 61092
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved beautifully hand colored antique map of Hudson Bay and surrounding provinces and Islands, Canada by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - dated - and was published in the French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Norse explored the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in the 11th century and were followed by fifteenth and early sixteenth century European mariners, such as John Cabot, and the brothers Gaspar and Miguel Corte-Real. The first European explorer known to have sailed up the Saint Lawrence River itself was Jacques Cartier. At that time, the land along the river was inhabited by the St. Lawrence Iroquoians; at the time of Cartiers second voyage in 1535. Because Cartier arrived in the estuary on Saint Lawrences feast day, he named it the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The Saint Lawrence River is partly within the U.S. and as such is that countrys sixth oldest surviving European place-name.
The earliest regular Europeans in the area were the Basques, who came to the St Lawrence Gulf and River in pursuit of whales from the early 16th century. The Basque whalers and fishermen traded with indigenous Americans and set up settlements, leaving vestiges all over the coast of eastern Canada and deep into the Saint Lawrence River. Basque commercial and fishing activity reached its peak before the Armada Invencibles disaster (1588), when the Spanish Basque whaling fleet was confiscated by King Philip II of Spain and largely destroyed. Initially, the whaling galleons from Labourd were not affected by the Spanish defeat.
Until the early 17th century, the French used the name Rivière du Canada to designate the Saint Lawrence upstream to Montreal and the Ottawa River after Montreal. The Saint Lawrence River served as the main route for European exploration of the North American interior, first pioneered by French explorer Samuel de Champlain.
Control of the river was crucial to British strategy to capture New France in the Seven Years War. Having captured Louisbourg in 1758, the British sailed up to Quebec the following year thanks to charts drawn up by James Cook. British troops were ferried via the Saint Lawrence to attack the city from the west, which they successfully did at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. The river was used again by the British to defeat the French siege of Quebec under the Chevalier de Lévis in 1760.
In 1809, the first steamboat to ply its trade on the St. Lawrence was built and operated by John Molson and associates, a scant two years after Fultons steam-powered navigation of the Hudson River. The Accommodation with ten passengers made her maiden voyage from Montreal to Quebec City in 66 hours, for 30 of which she was at anchor. She had a keel of 75 feet, and length overall of 85 feet. The cost of a ticket as eight dollars upstream, and nine dollars down. She had berths that year for twenty passengers.
Within a decade, daily service was available in the hotly-contested Montreal-Quebec route.
Because of the virtually impassable Lachine Rapids, the Saint Lawrence was once continuously navigable only as far as Montreal. Opened in 1825, the Lachine Canal was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids. An extensive system of canals and locks, known as the Saint Lawrence Seaway, was officially opened on 26 June 1959 by Elizabeth II (representing Canada) and President Dwight D. Eisenhower (representing the United States). The Seaway (including the Welland Canal) now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to Lake Superior.
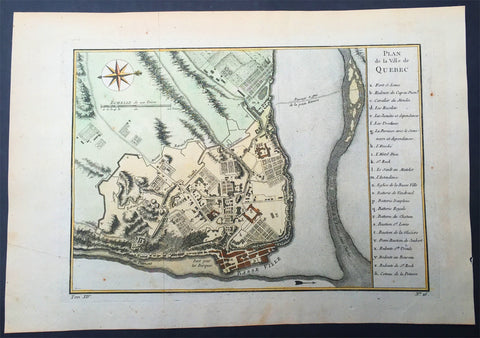
1757 Nicolas Bellin Large Antique Map of the City of Quebec, Canada
- Title : Plan de la Ville Quebec
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 61091
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved beautifully hand colored antique map, a plan of the City of Quebec, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin were engraved in 1757 and were published in the French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Quebec City is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec.
Quebec City is one of the oldest European settlements in North America. While many of the major cities in Latin America date from the sixteenth century, among cities in Canada and the U.S., few were created earlier than Quebec City (St. John\\\\\\\'s, Harbour Grace, Port Royal, St. Augustine, Santa Fe, Jamestown, and Tadoussac). Also, Quebec\\\\\\\'s Old Town (Vieux-Québec) is the only North American fortified city north of Mexico whose walls still exist.
French explorer Jacques Cartier built a fort at the site in 1535, where he stayed for the winter before going back to France in spring 1536. He came back in 1541 with the goal of building a permanent settlement. This first settlement was abandoned less than one year after its foundation, in the summer 1542, due in large part to the hostility of the natives combined with the harsh living conditions during winter.
Quebec was founded by Samuel de Champlain, a French explorer and diplomat, on 3 July 1608, and at the site of a long abandoned St. Lawrence Iroquoian settlement called Stadacona. Champlain, also called The Father of New France, served as its administrator for the rest of his life.
The name Canada refers to this settlement. Although the Acadian settlement at Port-Royal was established three years earlier, Quebec came to be known as the cradle of the Francophone population of North America. The place seemed favourable to the establishment of a permanent colony.
The population of the settlement remained small for decades. In 1629 it was captured by English privateers, led by David Kirke, during the Anglo-French War. However, Samuel de Champlain argued that the English seizing of the lands was illegal as the war had already ended; he worked to have the lands returned to France. As part of the ongoing negotiations of their exit from the Anglo-French War, in 1632 the English king Charles agreed to return the lands in exchange for Louis XIII paying his wife\\\\\\\'s dowry. These terms were signed into law with the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye. The lands in Quebec and Acadia were returned to the French Company of One Hundred Associates.
In 1665, there were 550 people in 70 houses living in the city. One-quarter of the people were members of religious orders: secular priests, Jesuits, Ursulines nuns and the order running the local hospital, Hotel-Dieu.
Quebec City was the headquarters of many raids against New England during the four French and Indian Wars. In the last war, the French and Indian War (Seven Years\\\\\\\' War), Quebec City was captured by the British in 1759 and held until the end of the war in 1763. It was the site of three battles during Seven Years\\\\\\\' War - the Battle of Beauport, a French victory (31 July 1759); the Battle of the Plains of Abraham, in which British troops under General James Wolfe defeated the French General Louis-Joseph de Montcalm on 13 September 1759 and shortly thereafter took the city; and the final Battle of Sainte-Foy, a French victory (28 April 1760). France ceded New France, including the city, to Britain in 1763.
At the end of French rule in 1763, forests, villages, fields and pastures surrounded the town of 8,000 inhabitants. The town distinguished itself by its monumental architecture, fortifications, affluent homes of masonry and shacks in the suburbs of Saint-Jean and Saint-Roch. Despite its urbanity and its status as capital, Quebec City remained a small colonial city with close ties to its rural surroundings. Nearby inhabitants traded their farm surpluses and firewood for imported goods from France at the two city markets.
During the American Revolution, revolutionary troops from the southern colonies assaulted the British garrison in an attempt to liberate Quebec City, in a conflict now known as the Battle of Quebec. The defeat of the revolutionaries from the south put an end to the hopes that the peoples of Quebec would rise and join the American Revolution so that Canada would join the Continental Congress and become part of the original United States of America along with the other British colonies of continental North America. In effect, the outcome of the battle would be the effective split of British North America into two distinct political entities. The city itself was not attacked during the War of 1812, when the United States again attempted to annex Canadian lands. Fearing another American attack on Quebec City in the future, construction of the Citadelle of Quebec began in 1820. The Americans never did attack Canada after the War of 1812, but the Citadelle continued to house a large British garrison until 1871. The Citadelle is still in use by the military and is also a tourist attraction.
From the 1840s to 1867, the capital of the Province of Canada rotated between Kingston, Montreal, Toronto, Ottawa and Quebec City (from 1852 to 1856 and from 1859 to 1866).
Long before the Royal Military College of Canada was established in 1876, there were proposals for military colleges in Canada. Staffed by British Regulars, adult male students underwent a 3 month long military course in Quebec City in 1864 at the School of Military Instruction in Quebec City. Established by Militia General Order in 1864, the school enabled Officers of Militia or Candidates for Commission or promotion in the Militia to learn Military duties, drill and discipline, to command a Company at Battalion Drill, to Drill a Company at Company Drill, the internal economy of a Company and the duties of a Company\\\\\\\'s Officer. The school was retained at Confederation, in 1867. In 1868, The School of Artillery was formed in Montreal.
In 1867, Ottawa (which was chosen to be the permanent capital of the Province of Canada) was chosen by Queen Victoria to be the capital of the Dominion of Canada. The Quebec Conference on Canadian Confederation was held in the city in 1864. Throughout its over 400 years of existence, Quebec City has served as the capital for Quebec, and Canada. From 1608 to 1627 and 1632 to 1763, it was the capital of French Canada and all of New France; from 1763 to 1791, it was the capital of the Province of Quebec; from 1791 to 1841, it was the capital of Lower Canada; from 1852 to 1856 and from 1859 to 1866, it was capital of the Province of Canada; and since 1867, it has been capital of the Province of Quebec. The administrative region in which Quebec City is situated is officially referred to as Capitale-Nationale, and the term national capital is used to refer to Quebec City itself at provincial level
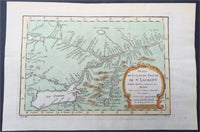
1757 Nicolas Bellin Large Antique Map St Lawrence River to Lake Ontario, Canada
- Title : Suite Du Cours De St Laurent...1757
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 61090
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved beautifully hand colored antique map of the St Lawrence River to Lake Ontario, Canada by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - dated - and was published in the French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The Norse explored the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in the 11th century and were followed by fifteenth and early sixteenth century European mariners, such as John Cabot, and the brothers Gaspar and Miguel Corte-Real. The first European explorer known to have sailed up the Saint Lawrence River itself was Jacques Cartier. At that time, the land along the river was inhabited by the St. Lawrence Iroquoians; at the time of Cartiers second voyage in 1535. Because Cartier arrived in the estuary on Saint Lawrences feast day, he named it the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The Saint Lawrence River is partly within the U.S. and as such is that countrys sixth oldest surviving European place-name.
The earliest regular Europeans in the area were the Basques, who came to the St Lawrence Gulf and River in pursuit of whales from the early 16th century. The Basque whalers and fishermen traded with indigenous Americans and set up settlements, leaving vestiges all over the coast of eastern Canada and deep into the Saint Lawrence River. Basque commercial and fishing activity reached its peak before the Armada Invencibles disaster (1588), when the Spanish Basque whaling fleet was confiscated by King Philip II of Spain and largely destroyed. Initially, the whaling galleons from Labourd were not affected by the Spanish defeat.
Until the early 17th century, the French used the name Rivière du Canada to designate the Saint Lawrence upstream to Montreal and the Ottawa River after Montreal. The Saint Lawrence River served as the main route for European exploration of the North American interior, first pioneered by French explorer Samuel de Champlain.
Control of the river was crucial to British strategy to capture New France in the Seven Years War. Having captured Louisbourg in 1758, the British sailed up to Quebec the following year thanks to charts drawn up by James Cook. British troops were ferried via the Saint Lawrence to attack the city from the west, which they successfully did at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. The river was used again by the British to defeat the French siege of Quebec under the Chevalier de Lévis in 1760.
In 1809, the first steamboat to ply its trade on the St. Lawrence was built and operated by John Molson and associates, a scant two years after Fultons steam-powered navigation of the Hudson River. The Accommodation with ten passengers made her maiden voyage from Montreal to Quebec City in 66 hours, for 30 of which she was at anchor. She had a keel of 75 feet, and length overall of 85 feet. The cost of a ticket as eight dollars upstream, and nine dollars down. She had berths that year for twenty passengers.
Within a decade, daily service was available in the hotly-contested Montreal-Quebec route.
Because of the virtually impassable Lachine Rapids, the Saint Lawrence was once continuously navigable only as far as Montreal. Opened in 1825, the Lachine Canal was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids. An extensive system of canals and locks, known as the Saint Lawrence Seaway, was officially opened on 26 June 1959 by Elizabeth II (representing Canada) and President Dwight D. Eisenhower (representing the United States). The Seaway (including the Welland Canal) now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to Lake Superior.
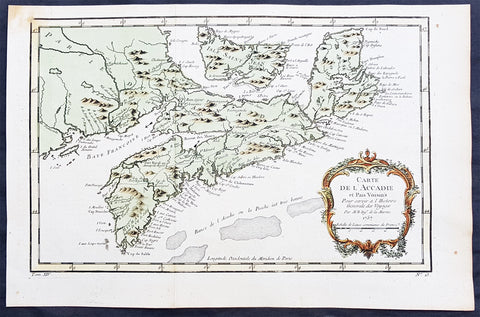
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Arcadia in Nova Scotia, Canada
- Title : Carte De L' Accadie...Par M B. 1757
- Ref #: 61093
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)ea
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured originalantique map* of Arcadia, Nova Scotia, Canada by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Background : Acadia was a colony of New France in north-eastern North America that included parts of eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces, and modern-day Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and early 18th centuries, Norridgewock on the Kennebec River and Castine at the end of the Penobscot River were the southernmost settlements of Acadia. The actual specification by the French government for the territory refers to lands bordering the Atlantic coast, roughly between the 40th and 46th parallels. Later, the territory was divided into the British colonies which became Canadian provinces and American states. The population of Acadia included members of the Wabanaki Confederacy and descendants of emigrants from France (i.e., Acadians). The two communities intermarried, which resulted in a significant portion of the population of Acadia being Métis.
The first capital of Acadia, established in 1605, was Port-Royal. A British force from Virginia attacked and burned down the town in 1613 but it was later rebuilt nearby, where it remained the longest serving capital of French Acadia until the British Siege of Port Royal in 1710. Over seventy-four years there were six colonial wars, in which English and later British interests tried to capture Acadia starting with King William's War in 1689. During these wars, along with some French troops from Quebec, some Acadians, the Wabanaki Confederacy, and French priests continuously raided New England settlements along the border in Maine. While Acadia was officially conquered in 1710 during Queen Anne's War, present-day New Brunswick and much of Maine remained contested territory. Present-day Prince Edward Island (Île Saint-Jean) and Cape Breton (Île Royale) as agreed under Article XIII of the Treaty of Utrecht remained under French control. By militarily defeating the Wabanaki Confederacy and the French priests, present-day Maine fell during Father Rale's War. During King George's War, France and New France made significant attempts to regain mainland Nova Scotia. After Father Le Loutre's War, present-day New Brunswick fell to the British. Finally, during the French and Indian War (the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War), both Île Royale and Île Saint-Jean fell to the British in 1758.
Today, the term Acadia is used to refer to regions of North America that are historically associated with the lands, descendants, and/or culture of the former French region. It particularly refers to regions of The Maritimes with French roots, language, and culture, primarily in New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, the Magdalen Islands and Prince Edward Island, as well as in Maine It can also be used to refer to the Acadian diasporain southern Louisiana, a region also referred to as Acadiana. In the abstract, Acadia refers to the existence of a French culture in any of these regions.
People living in Acadia, and sometimes former residents and their descendants, are called Acadians, also later known as Cajuns after resettlement in Louisiana.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
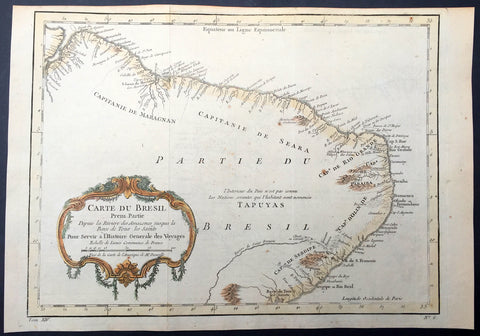
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, South America
- Title : Carte Du Bresil.....
- Ref #: 61101
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Brazil, South America by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar.
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
ackground:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
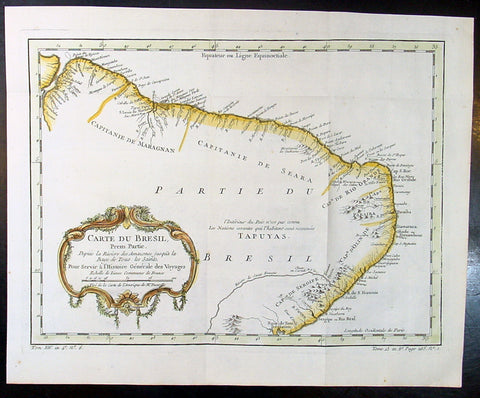
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, South America
- Title : Carte Du Bresil.....
- Ref #: 60941
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Brazil, South America by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar.
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
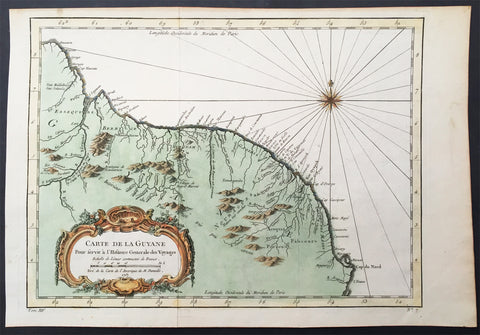
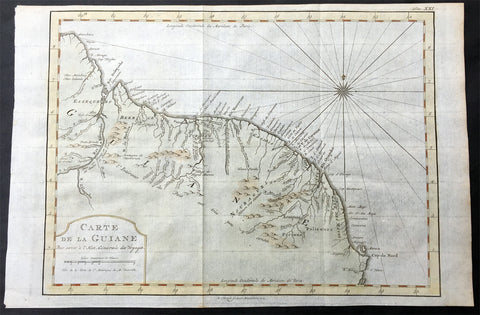
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Guyana, South America
- Title : Carte De La Guyane...Par M B. 1757
- Ref #: 61099
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Country of Guyana South America by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12 mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
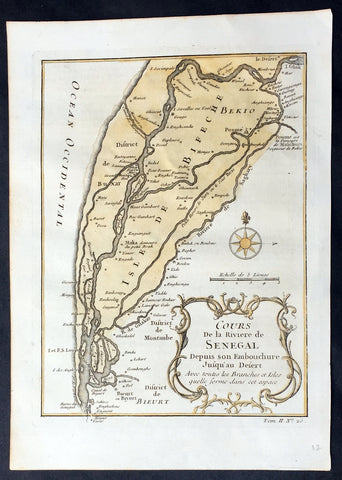
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map Saloum River Delta, Senegal West Africa
- Title : Cours de la Riviere de Senegal...
- Ref #: 92505
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Saloum Delta in the Fatck Region of South Senegal, West Africa by Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The Saloum River rises about 105 kilometers east of Kaolack, Senegal, and flows into the Atlantic Ocean. The significant Saloum Delta is located at its mouth, which is protected as Saloum Delta National Park. The river basin lies within the Serer pre-colonial Kingdom of Saloum. Mangrove forests occupy a 5-kilometer belt on either side of the river almost 70 kilometers upstream.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
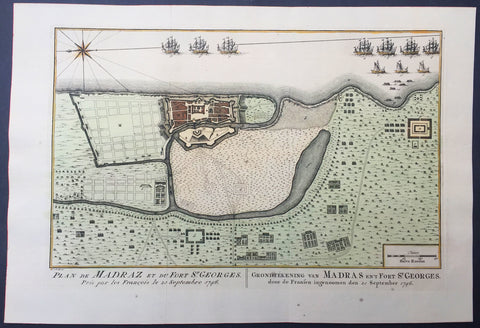
1757 Prevost & Schley Antique Map Ft St George Madras, Chennai, Tamil Nadu India
- Title : Plan de Madraz et du Fort St Georges. Pris par les Francois le 23 Septembre 1746
- Ref #: 61073
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the city of Chennai (Madras) the capital of Tamil Nadu, India and the old British Fort of St George (during the brief French occupation in 1746) - with separate Index of all the buildings and important places by Jakob van Schley in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Fort St George (or historically, White Town) is the name of the first English (later British) fortress in India, founded in 1644 at the coastal city of Madras, the modern city of Chennai. The construction of the fort provided the impetus for further settlements and trading activity, in what was originally an uninhabited land. Thus, it is a feasible contention to say that the city evolved around the fortress. The fort currently houses the Tamil Nadu legislative assembly and other official buildings.
The East India Company (EIC), which had entered India around 1600 for trading activities, had begun licensed trading at Surat, which was its initial bastion. However, to secure its trade lines and commercial interests in the spice trade, it felt the necessity of a port closer to the Malaccan Straits, and succeeded in purchasing a piece of coastal land, originally called Chennirayarpattinam or Channapatnam, from aVijayanagar chieftain named Damerla Chennappa Nayaka based in Chandragiri, where the Company began the construction of a harbour and a fort. The fort was completed on 23 April 1644 at a cost of £3000, coinciding with St George's Day, celebrated in honour of the patron saint of England. The fort, hence christened Fort St George, faced the sea and some fishing villages, and it soon became the hub of merchant activity. It gave birth to a new settlement area called George Town (historically referred to as Black Town), which grew to envelop the villages and led to the formation of the city of Madras. It also helped to establishEnglish influence over the Carnatic and to keep the kings of Arcot and Srirangapatna, as well as the French forces based at Pondichéry, at bay. In 1665, after the EIC received word of the formation of the newFrench East India Company, the fort was strengthened and enlarged while its garrison was increased. According to the 17th century traveller Thomas Bowrey, Fort St. George was:
"without all dispute a beneficiall place to the Honourable English India Company, and with all the Residence of theire Honourable Agent and Governour all of their Affaires Upon this Coast and the Coast of Gingalee, the Kingdoms also of Orixa, (Orissa) Bengala (Bengal), and Pattana (Patna), the said Governour and his Councell here resideigne, for the Honour of our English Nation keepinge and maintainneinge the place in great Splendour, Civil and good Government, Entertaineinge nobly all Foraign Embassadors, and provideinge great quantities of Muzlinge (Muslin) Callicoes (Calico) &c. to be yearly transported to England."
The Fort is a stronghold with 6 metres (20 ft) high walls that withstood a number of assaults in the 18th century. It briefly passed into the possession of the French from 1746 to 1749, but was restored to Great Britain under the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, which ended the War of the Austrian Succession.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12 mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
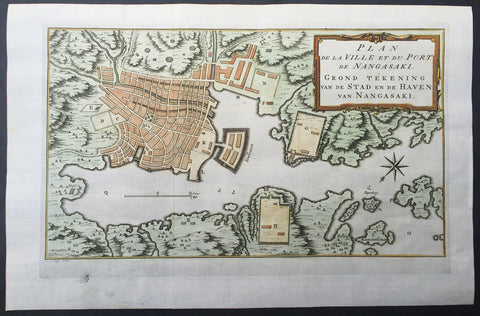
1757 Prevost & Schley Antique Map of The Port of Nagasaki, Japan - VOC, Deshima
- Title : Plan De La Ville et du Port du Nangasaki - Grond Tekening van de Stad en de Haven van Nangasaki
- Ref #: 61059
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the Japanese City & Port of Nagasaki by Jakob van Schley in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Oriented to the southeast, the map highlights principal points of interest and major buildings with the Deshima central to the map. The Deshima was an artificial island in the bay of Nagasaki where the Dutch East India Company (VOC) were allowed to trade with the representatives of the Shogun in Edo.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 8 1/2in (345mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
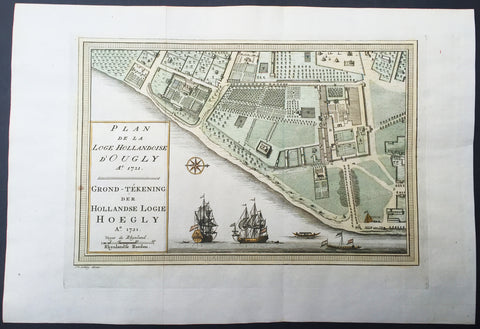
1757 Prevost & Schley Antique Map VOC Fort Hoogly & Chuchura, West Bengal, India
- Title : Plan de la Loge Hollandoise d Ougly A. 1721
- Ref #: 61069
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the Dutch East Indies Fort of Hoogly in West Bengal, India and the Dutch Fort town Chuchura south of Hooghly - with separate Index of all the buildings and important places by Jakob van Schley in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Hooghly district is one of the districts of the state of West Bengal in India. It can alternatively be spelt Hoogli or Hugli. The district is named after the Hooghly River.
The district of Hooghly derived its name from the town of Hooghly on the west bank of the Hooghly River about 40 km north of Kolkata. This town was a river port in the fifteenth century.
The district has thousands of years of rich heritage in the form of the great Bengali kingdom of Bhurshut. The first European to reach this area was the Portuguese sailor Vasco-Da-Gama. In 1536 Portuguese traders obtained a permit from Sultan Mahmud Shah to trade in this area. In those days the Hooghly River was the main route for transportation and Hooghly served as an excellent trading port.
Within a few decades the town of Hooghly turned into a major commercial center and the largest port in Bengal. Later in 1579-80 Emperor Akbar gave permission to a Portuguese captain Pedro Tavares to establish a city anywhere in the Bengal province. They chose Hooghly, and it became the first European settlement in Bengal. In 1599 the Portuguese traders built a convent and a church in Bandel. This is the first Christian church in Bengal known as ‘Bandel Church’ today.
The Portuguese traders started misusing their powers. They started slave trading, robbery and converting natives into Christians by pressure. At one of point they even stopped paying taxes to the Mughal Empire. As a result, Emperor Shah Jahan ordered the then-ruler of Bengal province, Qasim Khan Juvayni, to block the city of Hooghly. This eventually led to a war in which the Portuguese were defeated comprehensively.
Among other European powers that came to Hooghly were the Dutch, the Danish, the British, the French, the Belgians and the Germans. Dutch traders centered their activities in the town Chuchura which is south of Hooghly. Chandannagar became the base of the French and the city remained under their control from 1816 to 1950. Similarly, the Danish establishment in settlement in Serampore (1755). All these towns are on the west bank of the Hooghly River and served as ports. Among these European countries, the British ultimately became most powerful.
Initially the British were based in and around the city of Hooghly like traders from other countries. In 1690 Job Charnock decided to shift the British trading center from Hooghly-Chinsura to Calcutta. The reason behind this decision was the strategically safe location of Calcutta and its proximity to the Bay of Bengal. As a result, the center of gravity of trade and commerce in the Bengal province shifted from the town of Hooghly to Calcutta. Hooghly lost its importance as Calcutta prospered.
After the Battle of Buxar this region was brought under direct British rule until India’s independence in 1947. After independence this district merged into the state of West Bengal.
Though the city of Hooghly is more than 500 years old, the district of Hooghly was formed in 1795 with the city of Hooghly as its headquarters. Later the headquarters shifted to the town of Chuchura. In 1843 the Howrah district was created from the southern portion of this district. And in 1872, the south-west portion of this district was merged into the Medinipur district. The last change in area occurred in 1966.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12 mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
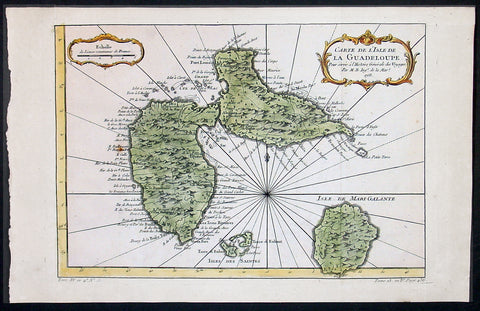
1758 Bellin Antique Map of Guadeloupe Islands, Caribbean, West Indies
- Title : Carte De L'Isle De La Guadeloupe...1758
- Ref #: 60955
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of the Caribbean Island of Guadeloupe was engraved in 1758 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published for Antoine-François Prevost's monumental 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague between 1747 & 1780. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
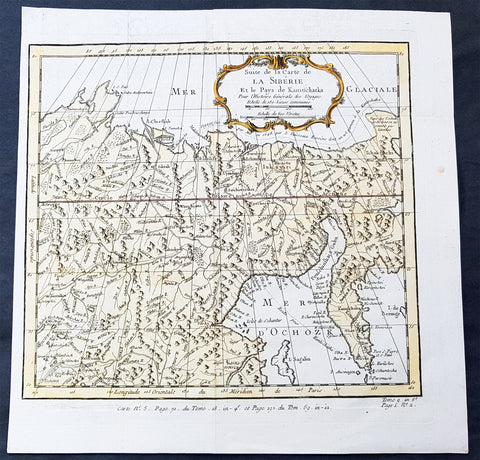
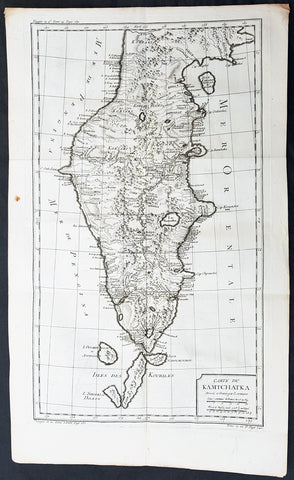
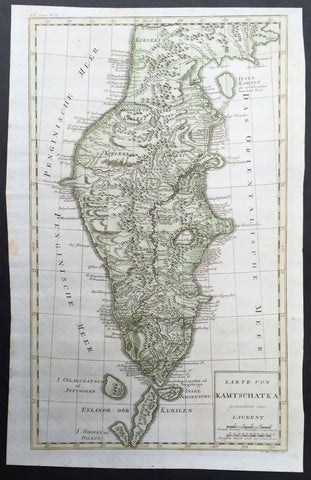
1758 Bellin Old, Antique Map of Eastern Siberia and the Kamchatka Peninsula Russia
- Title : Suite de la Carte de La Siberie et le Pays Kamtschatka
- Ref #: 60929
- Size: 11 3/4in x 11 3/4in (300mm x 300mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Eastern Russia & Siberia including the Kamchatka Peninsular and south to northern China by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 12in (305mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 9 1/2in (285mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
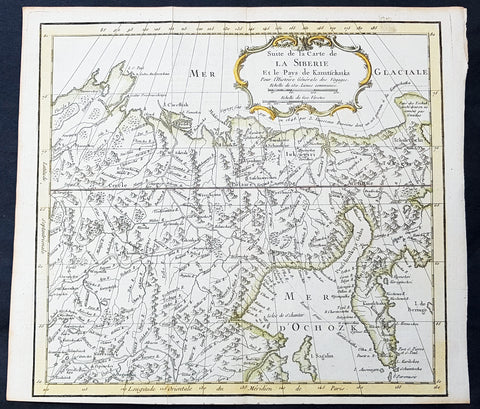
1758 Bellin Old, Antique Map of Eastern Siberia and the Kamchatka Peninsula Russia
- Title : Suite de la Carte de La Siberie et le Pays Kamtschatka
- Ref #: 15934
- Size: 12in x 12in (305mm x 305mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Eastern Russia & Siberia including the Kamchatka Peninsular and south to northern China by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 12in (305mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 9 1/2in (285mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
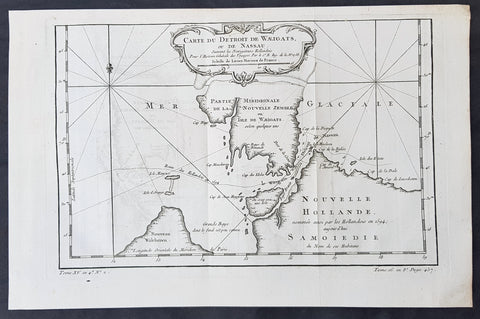
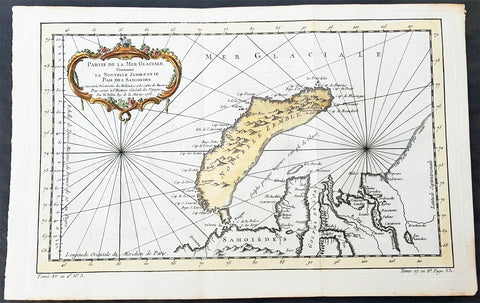
1758 Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya Nenets, Russia Willem Barentsz
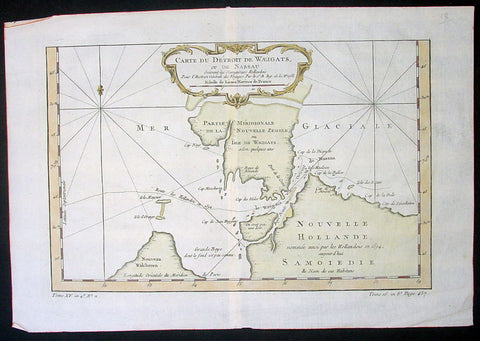
- Title : Carte Du Détroit De Weigats ou De Nassau, suivant les Navigateurs Hollandois Pour l Histoire Générale des Voyages.1758
- Size: 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 60965
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, with the Kara Straits and parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets - here named New Holland by the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1758 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The map depicts the Détroit de Waeigats - currently the Kara Straits - that divides the island of Novaya Zemlya from the northern Russian mainland. Novaya Zemlya was also called \"Isle De Waeigats\" & the northern Russian coast was called \"Nouvelle Hollande\", by Willem Barentsz during the Dutch in a 1594 Arctic exploration.
Willem Barentsz 1550 – 1597 was a Dutch navigator, cartographer, and Arctic explorer. He went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northeast passage. During his third expedition, the crew was stranded on Novaya Zemlya for almost a year. Barentsz died on the return voyage in 1597. In the 19th century, the Barents Sea was named after him.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 9 1/2in (370mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
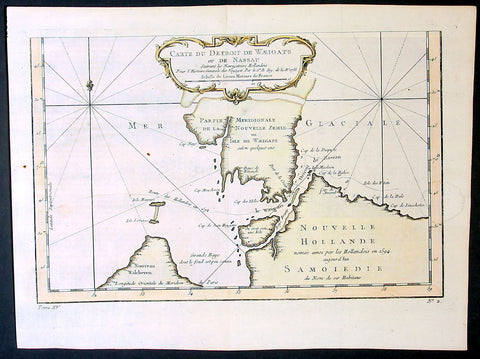
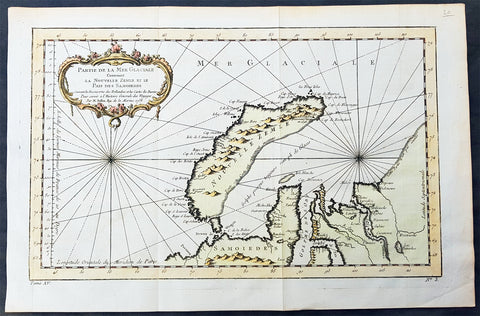
1758 Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya Nenets, Russia Willem Barentsz
- Title : Carte Du Détroit De Weigats ou De Nassau, suivant les Navigateurs Hollandois Pour l Histoire Générale des Voyages.1758
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 23311
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, with the Kara Straits and parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets - here named New Holland by the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1758 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The map depicts the Détroit de Waeigats - currently the Kara Straits - that divides the island of Novaya Zemlya from the northern Russian mainland. Novaya Zemlya was also called \"Isle De Waeigats\" & the northern Russian coast was called \"Nouvelle Hollande\", by Willem Barentsz during the Dutch in a 1594 Arctic exploration.
Willem Barentsz 1550 – 1597 was a Dutch navigator, cartographer, and Arctic explorer. He went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northeast passage. During his third expedition, the crew was stranded on Novaya Zemlya for almost a year. Barentsz died on the return voyage in 1597. In the 19th century, the Barents Sea was named after him.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
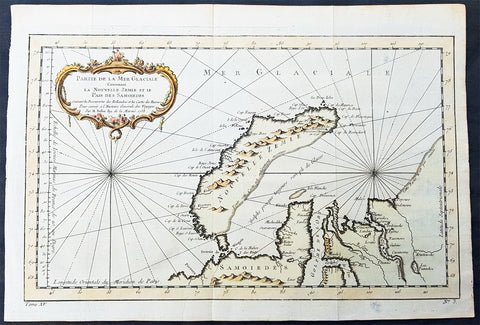
1758 Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya Nenets, Russia Willem Barentsz
- Title : Carte Du Détroit De Weigats ou De Nassau, suivant les Navigateurs Hollandois Pour l Histoire Générale des Voyages.1758
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 25639
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, with the Kara Straits and parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets - here named New Holland by the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1758 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The map depicts the Détroit de Waeigats - currently the Kara Straits - that divides the island of Novaya Zemlya from the northern Russian mainland. Novaya Zemlya was also called \"Isle De Waeigats\" & the northern Russian coast was called \"Nouvelle Hollande\", by Willem Barentsz during the Dutch in a 1594 Arctic exploration.
Willem Barentsz 1550 – 1597 was a Dutch navigator, cartographer, and Arctic explorer. He went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northeast passage. During his third expedition, the crew was stranded on Novaya Zemlya for almost a year. Barentsz died on the return voyage in 1597. In the 19th century, the Barents Sea was named after him.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
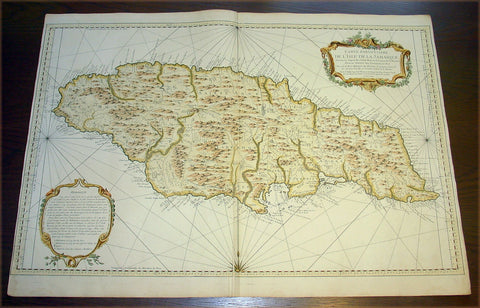
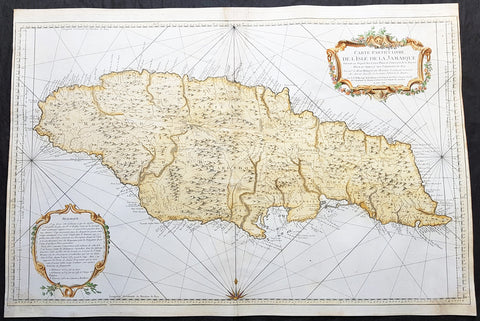
1758 Bellin Very Large Antique Map Sea Chart of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica
- Title : Carte Particuliere De L'Isle De La Jamaique ...MDCCLVIII
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50655
- Size: 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
Description:
This very large finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map, sea chart, of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica was engraved and published by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 - dated in the title cartouche.
A very attractive, large and detailed chart of this strategically and economically important island, by the leading French hydrographer of the period. With a lengthy text panel of observations in the lower left corner and decorative title cartouche in the upper right corner. The island is divided into its provinces with towns and villages named. Reference is also made to the cultivation of coffee and sugar. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Blue
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 36in x 23 1/2in (910mm x 600mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (55mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Printers crease adjacent to bottom & top centerfold
Verso: - None
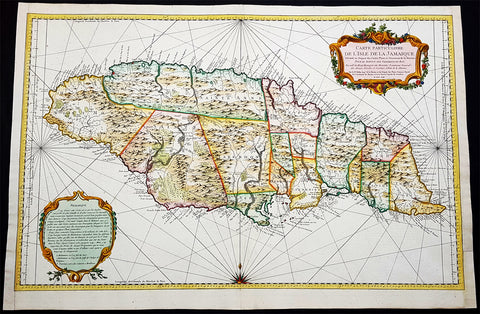
1758 J N Bellin Large Antique Map of The Caribbean Island of Jamaica
- Title : Carte Particuliere De L Isle De La Jamaique Dressee au Depost des Cartes Plans et Journaux de la Marine . . . M. DCC LVIII
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93355
- Size: 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, a sea chart, of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 - dated in the title cartouche - was published by the Depot De La Marine, Paris.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 36in x 23 1/2in (915mm x 600mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins extended from border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
At the time of publishing the Island of Jamaica was under the British, after 150 years of Spanish rule. The focus of the British was trade and specifically that of Sugar, which required a large labor force. This labor, as in all of the Americas, was supplied from the abhorrent African slave trade.
Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Previously inhabited by the indigenous Arawak and Taíno peoples, the island came under Spanish rule following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people died of disease, and the Spanish transplanted African slaves to Jamaica as labourers. The island remained a possession of Spain until 1655, when England conquered it and renamed it Jamaica. Under British colonial rule Jamaica became a leading sugar exporter, with its plantation economy highly dependent on African slaves. The British fully emancipated all slaves in 1838, and many freedmen chose to have subsistence farms rather than to work on plantations. Beginning in the 1840s, the British utilized Chinese and Indian indentured labour to work on plantations.
Spanish Town has the oldest cathedral of the British colonies in the Caribbean. The Spanish were forcibly evicted by the English at Ocho Rios in St. Ann. In the 1655 Invasion of Jamaica, the English, led by Sir William Penn and General Robert Venables, took over the last Spanish fort on the island. The name of Montego Bay, the capital of the parish of St. James, was derived from the Spanish name manteca bahía (or Bay of Lard), alluding to the lard-making industry based on processing the numerous boars in the area.
In 1660, the population of Jamaica was about 4,500 white and 1,500 black. By the early 1670s, as the English developed sugar cane plantations and imported more slaves, black people formed a majority of the population. The colony was shaken and almost destroyed by the 1692 Jamaica earthquake.
The Irish in Jamaica also formed a large part of the islands early population, making up two-thirds of the white population on the island in the late 17th century, twice that of the English population. They were brought in as indentured labourers and soldiers after the conquest of Jamaica by Cromwells forces in 1655. The majority of Irish were transported by force as political prisoners of war from Ireland as a result of the ongoing Wars of the Three Kingdoms at the time. Migration of large numbers of Irish to the island continued into the 18th century.
Jews were expelled from Spain in 1492 and then forcibly converted to Christianity in Portugal, during a period of persecution by the Inquisition. Some Spanish and Portuguese Jewish refugees went to the Netherlands and England, and from there to Jamaica. Others were part of the Iberian colonisation of the New World, after overtly converting to Catholicism, as only Catholics were allowed in the Spanish colonies. By 1660, Jamaica had become a refuge for Jews in the New World, also attracting those who had been expelled from Spain and Portugal.
An early group of Jews arrived in 1510, soon after the son of Christopher Columbus settled on the island. Primarily working as merchants and traders, the Jewish community was forced to live a clandestine life, calling themselves Portugals. After the British took over rule of Jamaica, the Jews decided the best defense against Spains regaining control was to encourage making the colony a base for Caribbean pirates. With the pirates installed in Port Royal, which became the largest city in the Caribbean, the Spanish would be deterred from attacking. The British leaders agreed with the viability of this strategy to forestall outside aggression.
When the English captured Jamaica in 1655, the Spanish colonists fled after freeing their slaves. The slaves dispersed into the mountains, joining the maroons, those who had previously escaped to live with the Taíno native people. During the centuries of slavery, Maroons established free communities in the mountainous interior of Jamaica, where they maintained their freedom and independence for generations. The Jamaican Maroons fought the British during the 18th century. Under treaties of 1738 and 1739, the British agreed to stop trying to round them up in exchange for their leaving the colonial settlements alone, but serving if needed for military actions. Some of the communities were broken up and the British deported Maroons to Nova Scotia and, later, Sierra Leone. The name is still used today by modern Maroon descendants, who have certain rights and autonomy at the community of Accompong.
During its first 200 years of British rule, Jamaica became one of the worlds leading sugar-exporting, slave-dependent colonies, producing more than 77,000 tons of sugar annually between 1820 and 1824. After the abolition of the international slave trade in 1807, the British began to import indentured servants to supplement the labour pool, as many freedmen resisted working on the plantations. Workers recruited from India began arriving in 1845, Chinese workers in 1854.
1758 J N Bellin Large Antique Map of The Caribbean Island of Jamaica
- Title : Carte Particuliere De L Isle De La Jamaique Dressee au Depost des Cartes Plans et Journaux de la Marine . . . M. DCC LVIII
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 82084
- Size: 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, a sea chart, of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 - dated in the title cartouche - was published by the Depot De La Marine, Paris.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 36in x 23 1/2in (915mm x 600mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margin cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - Professional restoration to top centerfold, 2 names penned in to top of map & bottom right corner
Verso: - Professional restoration along centerfold
Background:
At the time of publishing the Island of Jamaica was under the British, after 150 years of Spanish rule. The focus of the British was trade and specifically that of Sugar, which required a large labor force. This labor, as in all of the Americas, was supplied from the abhorrent African slave trade.
Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Previously inhabited by the indigenous Arawak and Taíno peoples, the island came under Spanish rule following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people died of disease, and the Spanish transplanted African slaves to Jamaica as labourers. The island remained a possession of Spain until 1655, when England conquered it and renamed it Jamaica. Under British colonial rule Jamaica became a leading sugar exporter, with its plantation economy highly dependent on African slaves. The British fully emancipated all slaves in 1838, and many freedmen chose to have subsistence farms rather than to work on plantations. Beginning in the 1840s, the British utilized Chinese and Indian indentured labour to work on plantations.
Spanish Town has the oldest cathedral of the British colonies in the Caribbean. The Spanish were forcibly evicted by the English at Ocho Rios in St. Ann. In the 1655 Invasion of Jamaica, the English, led by Sir William Penn and General Robert Venables, took over the last Spanish fort on the island. The name of Montego Bay, the capital of the parish of St. James, was derived from the Spanish name manteca bahía (or Bay of Lard), alluding to the lard-making industry based on processing the numerous boars in the area.
In 1660, the population of Jamaica was about 4,500 white and 1,500 black. By the early 1670s, as the English developed sugar cane plantations and imported more slaves, black people formed a majority of the population. The colony was shaken and almost destroyed by the 1692 Jamaica earthquake.
The Irish in Jamaica also formed a large part of the islands early population, making up two-thirds of the white population on the island in the late 17th century, twice that of the English population. They were brought in as indentured labourers and soldiers after the conquest of Jamaica by Cromwells forces in 1655. The majority of Irish were transported by force as political prisoners of war from Ireland as a result of the ongoing Wars of the Three Kingdoms at the time. Migration of large numbers of Irish to the island continued into the 18th century.
Jews were expelled from Spain in 1492 and then forcibly converted to Christianity in Portugal, during a period of persecution by the Inquisition. Some Spanish and Portuguese Jewish refugees went to the Netherlands and England, and from there to Jamaica. Others were part of the Iberian colonisation of the New World, after overtly converting to Catholicism, as only Catholics were allowed in the Spanish colonies. By 1660, Jamaica had become a refuge for Jews in the New World, also attracting those who had been expelled from Spain and Portugal.
An early group of Jews arrived in 1510, soon after the son of Christopher Columbus settled on the island. Primarily working as merchants and traders, the Jewish community was forced to live a clandestine life, calling themselves Portugals. After the British took over rule of Jamaica, the Jews decided the best defense against Spains regaining control was to encourage making the colony a base for Caribbean pirates. With the pirates installed in Port Royal, which became the largest city in the Caribbean, the Spanish would be deterred from attacking. The British leaders agreed with the viability of this strategy to forestall outside aggression.
When the English captured Jamaica in 1655, the Spanish colonists fled after freeing their slaves. The slaves dispersed into the mountains, joining the maroons, those who had previously escaped to live with the Taíno native people. During the centuries of slavery, Maroons established free communities in the mountainous interior of Jamaica, where they maintained their freedom and independence for generations. The Jamaican Maroons fought the British during the 18th century. Under treaties of 1738 and 1739, the British agreed to stop trying to round them up in exchange for their leaving the colonial settlements alone, but serving if needed for military actions. Some of the communities were broken up and the British deported Maroons to Nova Scotia and, later, Sierra Leone. The name is still used today by modern Maroon descendants, who have certain rights and autonomy at the community of Accompong.
During its first 200 years of British rule, Jamaica became one of the worlds leading sugar-exporting, slave-dependent colonies, producing more than 77,000 tons of sugar annually between 1820 and 1824. After the abolition of the international slave trade in 1807, the British began to import indentured servants to supplement the labour pool, as many freedmen resisted working on the plantations. Workers recruited from India began arriving in 1845, Chinese workers in 1854.
1758 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Russia The Island of Novaya Zemlya
- Title : Partie De La Mer Glaciale Contenant La Nouvelle Zemle...M. Bellin...1758
- Ref #: 60968
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (380mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Novaya Zemlya also known as Nova Zembla (especially in Dutch), is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in northern Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the Northern island. Novaya Zemlya is composed of two islands, the northern Severny Island and the southern Yuzhny Island, which are separated by Matochkin Strait.
The Russians knew of Novaya Zemlya from the 11th century, when hunters from Novgorod visited the area. For western Europeans, the search for the Northern Sea Route in the 16th century led to its exploration. The first visit from a west European was by Hugh Willoughby in 1553, and he met Russian ships from the already established hunting trade. Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya in 1594, and in a subsequent expedition of 1596 rounded the Northern point and wintered on the Northeast coast. (Barentsz died during the expedition, and may have been buried on the Northern island.) During a later voyage by Fyodor Litke in 1821–1824, the west coast was mapped. Henry Hudson was another explorer who passed through Novaya Zemlya while searching for the Northeast Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1758 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Russia The Island of Novaya Zemlya
- Title : Partie De La Mer Glaciale Contenant La Nouvelle Zemle...M. Bellin...1758
- Ref #: 25638
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (380mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Novaya Zemlya also known as Nova Zembla (especially in Dutch), is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in northern Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the Northern island. Novaya Zemlya is composed of two islands, the northern Severny Island and the southern Yuzhny Island, which are separated by Matochkin Strait.
The Russians knew of Novaya Zemlya from the 11th century, when hunters from Novgorod visited the area. For western Europeans, the search for the Northern Sea Route in the 16th century led to its exploration. The first visit from a west European was by Hugh Willoughby in 1553, and he met Russian ships from the already established hunting trade. Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya in 1594, and in a subsequent expedition of 1596 rounded the Northern point and wintered on the Northeast coast. (Barentsz died during the expedition, and may have been buried on the Northern island.) During a later voyage by Fyodor Litke in 1821–1824, the west coast was mapped. Henry Hudson was another explorer who passed through Novaya Zemlya while searching for the Northeast Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1758 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Russia The Island of Novaya Zemlya
- Title : Partie De La Mer Glaciale Contenant La Nouvelle Zemle...M. Bellin...1758
- Ref #: 25638
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (380mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Novaya Zemlya also known as Nova Zembla (especially in Dutch), is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in northern Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the Northern island. Novaya Zemlya is composed of two islands, the northern Severny Island and the southern Yuzhny Island, which are separated by Matochkin Strait.
The Russians knew of Novaya Zemlya from the 11th century, when hunters from Novgorod visited the area. For western Europeans, the search for the Northern Sea Route in the 16th century led to its exploration. The first visit from a west European was by Hugh Willoughby in 1553, and he met Russian ships from the already established hunting trade. Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya in 1594, and in a subsequent expedition of 1596 rounded the Northern point and wintered on the Northeast coast. (Barentsz died during the expedition, and may have been buried on the Northern island.) During a later voyage by Fyodor Litke in 1821–1824, the west coast was mapped. Henry Hudson was another explorer who passed through Novaya Zemlya while searching for the Northeast Passage.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 9in (355mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1760 Bellin Antique Map of Manchurian Empire, Mongolia, China, Sakhalin Islands
- Title: Carte De la Tartarie Orientale...P.P Jesuits
- Date: 17560
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 60927
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of old Manchurian Empire - now NE China, Mongolia & Russia stretching from Beijing to the Sakhalin Islands by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1760 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1760 Bellin Antique Map The Entrance to the Sierra Leone River, Africa
- Title: Carte De L Entrée De La Riviere De Sierra Leona...
- Date: 1760
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25836
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Sierra Leone River estuary by J N Bellin in 1760 was published in Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague between 1747 & 1785.
The Sierra Leone River is a river estuary on the Atlantic Ocean in Western Sierra Leone. It is formed by the Port Loko Creek and Rokel River and is between 4 and 10 miles wide (6–16 km) and 25 miles (40 km) long. It is the largest natural harbour in the African continent. Several islands, including Tasso Island (the largest), Tombo Island, and the historically important Bunce Island, are located in the estuary. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description: Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 7in (230mm x 180mm)
Margins: - min. 1/4in (10mm)
Imperfections: Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
1760 Bellin Large Original Antique Map of Kamchatka Peninsula, in Eastern Russia
- Title : Carte Du Kamtschatka Dressee et Gravee par Laurent.
- Ref #: 60969
- Size: 23in x 14 1/2in (585mm x 370mm)
- Date : 1747
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Kamchatka Peninsula, in Eastern Russia by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1760 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 23in x 14 1/2in (585mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 12 1/2in (520mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1760 Nicolas Bellin Antique Map of The Falkland Islands, South America
- Title : Carte des Îles Malouines
- Ref #: 93383
- Size: 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 235mm)
- Date : 1760
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the Falkland Islands by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1760 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titled Histoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 235mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 8in (330mm x 195mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Although Fuegians from Patagonia may have visited the Falkland Islands in prehistoric times, the islands were uninhabited when Europeans first discovered them. Claims of discovery date back to the 16th century, but no consensus exists on whether early explorers discovered the Falklands or other islands in the South Atlantic. The first recorded landing on the islands is attributed to English captain John Strong, who, en route to Perus and Chiles littoral in 1690, discovered the Falkland Sound and noted the islands water and game.
The Falklands remained uninhabited until the 1764 establishment of Port Louis on East Falkland by French captain Louis Antoine de Bougainville, and the 1766 foundation of Port Egmont on Saunders Island by British captain John MacBride. Whether or not the settlements were aware of each others existence is debated by historians. In 1766, France surrendered its claim on the Falklands to Spain, which renamed the French colony Puerto Soledad the following year. Problems began when Spain discovered and captured Port Egmont in 1770. War was narrowly avoided by its restitution to Britain in 1771.
Both the British and Spanish settlements coexisted in the archipelago until 1774, when Britains new economic and strategic considerations led it to voluntarily withdraw from the islands, leaving a plaque claiming the Falklands for King George III. Spains Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata became the only governmental presence in the territory. West Falkland was left abandoned, and Puerto Soledad became mostly a prison camp. Amid the British invasions of the Río de la Plata during the Napoleonic Wars in Europe, the islands governor evacuated the archipelago in 1806; Spains remaining colonial garrison followed suit in 1811, except for gauchos and fishermen who remained voluntarily.
Thereafter, the archipelago was visited only by fishing ships; its political status was undisputed until 1820, when Colonel David Jewett, an American privateer working for the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, informed anchored ships about Buenos Aires 1816 claim to Spains territories in the South Atlantic. Since the islands had no permanent inhabitants, in 1823 Buenos Aires granted German-born merchant Luis Vernet permission to conduct fishing activities and exploit feral cattle in the archipelago. Vernet settled at the ruins of Puerto Soledad in 1826, and accumulated resources on the islands until the venture was secure enough to bring settlers and form a permanent colony. Buenos Aires named Vernet military and civil commander of the islands in 1829, and he attempted to regulate sealing to stop the activities of foreign whalers and sealers. Vernets venture lasted until a dispute over fishing and hunting rights led to a raid by the American warship USS Lexington in 1831, when United States Navy commander Silas Duncan declared the dissolution of the islands government.
Buenos Aires attempted to retain influence over the settlement by installing a garrison, but a mutiny in 1832 was followed the next year by the arrival of British forces who reasserted Britains rule. The Argentine Confederation (headed by Buenos Aires Governor Juan Manuel de Rosas) protested against Britains actions and Argentine governments have continued since then to register official protests against Britain. The British troops departed after completing their mission, leaving the area without formal government. Vernets deputy, the Scotsman Matthew Brisbane, returned to the islands that year to restore the business, but his efforts ended after, amid unrest at Port Louis, gaucho Antonio Rivero led a group of dissatisfied individuals to murder Brisbane and the settlements senior leaders; survivors hid in a cave on a nearby island until the British returned and restored order. In 1840, the Falklands became a Crown colony, and Scottish settlers subsequently established an official pastoral community. Four years later, nearly everyone relocated to Port Jackson, considered a better location for government, and merchant Samuel Lafone began a venture to encourage British colonisation.
Stanley, as Port Jackson was soon renamed, officially became the seat of government in 1845. Early in its history, Stanley had a negative reputation due to cargo-shipping losses; only in emergencies would ships rounding Cape Horn stop at the port. Nevertheless, the Falklands geographic location proved ideal for ship repairs and the Wrecking Trade, the business of selling and buying shipwrecks and their cargoes. Aside from this trade, commercial interest in the archipelago was minimal due to the low-value hides of the feral cattle roaming the pastures. Economic growth began only after the Falkland Islands Company, which bought out Lafones failing enterprise in 1851, successfully introduced Cheviot sheep for wool farming, spurring other farms to follow suit. The high cost of importing materials, combined with the shortage of labour and consequent high wages, meant the ship repair trade became uncompetitive. After 1870, it declined as the replacement of sail ships by steamships was accelerated by the low cost of coal in South America; by 1914, with the opening of the Panama Canal, the trade effectively ended. In 1881, the Falkland Islands became financially independent of Britain. For more than a century, the Falkland Islands Company dominated the trade and employment of the archipelago; in addition, it owned most housing in Stanley, which greatly benefited from the wool trade with the UK.
1760 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Novaya Zemlya & Barent Arctic Russia
- Title : Carte des Pais Habites par Les Samojedes et Ostiacs...
- Size: 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
- Ref #: 60930
- Date : 1760
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique map of Russian Island of Novaya Zemlya, parts of the Russian northern mainland region of Nenets and the environs of the Arctic Barents & Kara Sea by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in the 1760 edition of Antoine François Prevosts Histoire Generale des Voyages
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 12in x 10in (305mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1764 Bellin Antique Map - Plan of The City of New Orleans, Louisiana, North America
- Title : Plan de la Nouvelle Orleans
- Ref #: 17041
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1764
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured rare antique map, an early plan of the city of New Orleans, Louisiana by Jacques Nicolas Bellin, in 1764 was published in Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8in (280mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background: This scarce 1764 map by Bellin is one of the earliest obtainable maps of New Orleans. Oriented to the east, Bellin's map covers the original settlement of New Orleans along the Mississippi River and inland as far theFosse plein d'eau (roughly translated: 'Pit full of Water') near modern day Dauphine Street, and from modern day Iberville Street (shown but not named) to modern day Barracks Street (shown but not named). The map shows some 100 buildings with some 18 specifically identified via an alphabetically coded table set just above the map.
Among the locations noted in the key is one that provides an eerie echo of the slave trade. Item Q is identified as Cabanes des Negroes qui prennent soin Moulin or 'Cabins of Negros that care for mill.' Note how these cabins, as well as the adjacent mill, are both well outside the ordered structure of the city as well as conveniently located near the Corps de Garde des Bourgeois
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1765 Bellin Large Antique World Map of Global Winds & Magnetic Variations
- Title : Carte des Variations de la Boussole et des Vents Generaux que l'on Trouve dans les Mers les Plus Frequentees
- Date : 1765
- Size: 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35665
Description:
This original very large hand coloured copper plate engraved antique world map, illustrating global magnetic and ocean wind variations, was engraved in 1765 - dated- and published by Jacques Nicholas Bellin, Paris.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 23in (875mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
An elegantly designed and precisely drafted sea chart of the oceans sailed by French navigators in the 18th century. Drawn by J. N. Bellin, who during his over fifty years of work in the French Hydrographic Service was appointed the first Ingenieur hydrographe de la Marine. This chart extends from California to Japan and focuses on the Atlantic and Indian oceans. The French sphere of influence in the West Indies, Africa, and India, would have generated this interest in compass and wind variations applied to a Mercator projection covering most of the world.
By 1765, France had lost most of its overseas empire in America following the Seven Years War (French and Indian War in America), so knowledge of the sea routes was important to holding what was left. Besides a wealth of hydrographic information, including little wind heads throughout, this beautiful map features an exquisite title cartouche featuring the French crown surmounting the globe. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, Burden)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1765 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, San Salvador to Sao Paulo
- Title : Suite du Bresil
- Ref #: 61077
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil from San Salvador to Sao Paulo in the south by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1765 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 7in (230mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1770 Bellin Antique Map & Views Tierra del Fuego Magellan Straits, South America
- Title : Plan de Baye Dubon Succes dans le Detriot de le Maire: Carte de la Partie de la Terre De Feu comprenant le Detroit de le Marie et une Part de la Terre des Stats Par le Lieut J Cook 1769
- Ref #: 25587
- Size: 15 1/2in x 13in (395m x 330mm)
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map & views of Tierra del Fuego opposite the Magellan Straits as surveyed by Capt James Cook during his 2nd voyage of Discovery in 1769, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1770 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Tierra del Fuego Spanish for \"Land of Fire\" is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
The name Tierra del Fuego derives from the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan sailing for the Spanish Crown, in 1520 he was the first European to visit these lands. He believed he was seeing the many fires (fuego in Spanish) of the Yaghan, which were visible from the sea, and that the \"Indians\" were waiting in the forests to ambush his armada.
In 1525 Francisco de Hoces was the first to speculate that Tierra del Fuego was one or more islands rather than part of what was then called Terra Australis. Francis Drake in 1578 and a Dutch VOC expedition in 1616 learned more about the geography. The latter expedition named Cape Horn.
On his first voyage with the HMS Beagle in 1830, Robert FitzRoy picked up four native Fuegians, including \"Jemmy Button\" (Orundellico) and brought them to England. The surviving three were taken to London to meet the King and Queen and were, for a time, celebrities. They returned to Tierra del Fuego in the Beagle with FitzRoy and Charles Darwin, who made extensive notes about his visit to the islands.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 13in (395m x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 12 /12in (380mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1770 JN Bellin Very Large Original Antique World Map on Mercators Projection
- Title : Essay d' une Carte Reduite Contenant les parties connuees Du Globe Terrestre
- Date : 1770
- Size: 32in x 23in (815mm x 585mm)
- Ref #: 61143
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original antique World Map on Mercator's Projection was first engraved in 1748 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin, dated in the title, and was updated to 1770 showing the discoveries by Captain James Cook in Australia & New Zealand in 1769-1770.
Background: The map presents the entire world on Mercator Projection based on a Paris (L’Isle de Fer) meridian, exhibiting post-Cook geography throughout, but most specifically in the Pacific and along the northwest coast of America.
North America to the west of the Mississippi is vaguely rendered according to 16th century expeditions into the region by Coronado, La Salle, De Soto, and others.
Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de l’Ouest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the “Archipel de Nord”.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labeled “Nouvelle Holland”, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state.
It is of interest that there is a common misconception regarding this map that suggests the first edition was dated 1748. There are editions with a printed date of 1748, but these are actually later editions. The 1748 date is a printing error in which “8” and “4” are transposed, the actual date of publication being 1784. The first edition of this map is the 1778 example shown here. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 32in x 23in (815mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2n x 20 1/2in (725mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small worm hole restoration adjacent to SW Africa
Verso: - Folds as issued
1771 Bellin Large Original Antique Map of The Kamchatka Peninsula Eastern Russia
- Title : Karte Von Kamtschatka gezeichnet von Laurent...P. Mol Sculs..... 1771
- Ref #: 32212
- Size: 21in x 13 1/2in (530mm x 340mm)
- Date : 1771
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Kamchatka Peninsula, in Eastern Russia by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1773 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 13 1/2in (530mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 12 1/2in (520mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1773 Bellin Antique Map The Course of the Orinoco River South America - Rare
- Title : Cours De L Orenoque...1773
- Ref #: 92803
- Size: 18 1/2in x 11 1/2in (460mm x 295mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Orinoco River, South America, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1750 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The mouth of the Orinoco River at the Atlantic Ocean was documented by Columbus on 1 August 1498, during his third voyage. Its source at the Cerro Delgado–Chalbaud, in the Parima range, was not explored until 1951, 453 years later. The source, near the Venezuelan–Brazilian border, at 1,047 metres (3,435 ft) above sea level (02°19′05″N 63°21′42″W), was explored in 1951 by a joint Venezuelan–French team.
The Orinoco Delta, and tributaries in the eastern llanos such as the Apure and Meta, were explored in the 16th century by German expeditions under Ambrosius Ehinger and his successors. In 1531 Diego de Ordaz, starting at the principal outlet in the delta, the Boca de Navios, sailed up the river to the Meta. Antonio de Berrio sailed down the Casanare to the Meta, and then down the Orinoco River and back to Coro. In 1595, after capturing de Berrio to obtain information while conducting an expedition to find the fabled city of El Dorado, the Englishman Sir Walter Raleigh sailed down the river, reaching the savannah country.
Alexander von Humboldt explored the basin in 1800, reporting on the pink river dolphins. He published extensively on the river\'s flora and fauna
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 11 1/2in (460mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 10in (455mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1773 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Guyana, South America
- Title: Carte De La Guiane.....
- Date: 1773
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92804
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Guyana, South America by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1773 - dated - and was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Guyana officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a sovereign state on the northern mainland of South America. It is, however, often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Suriname to the east and Venezuela to the west.
There are nine indigenous tribes residing in Guyana: the Wai Wai, Macushi, Patamona, Lokono, Kalina, Wapishana, Pemon, Akawaio and Warao. Historically the Lokono and Kalina tribes dominated Guyana. Although Christopher Columbus sighted Guyana during his third voyage (in 1498), and Sir Walter Raleigh wrote an account of its discovery in 1596, the Dutch were the first to establish colonies: Essequibo (1616), Berbice (1627), and Demerara (1752). After the British assumed control in 1796, the Dutch formally ceded the area in 1814. In 1831 the three separate colonies became a single British colony known as British Guiana.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 245mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Copy of 1753 Bellin Antique Map Plan of the City of Cayenne French Guyana, South America
- Title: La Ville De Cayenne...1753
- Date: 1753
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25648
- Size: 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved original antique map a plan of the city of Cayenne capital of French Guyana, South America was engraved by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1753 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Jacques Nicolas Bellin for Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague in 1747. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (390mm x 275mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 9 1/2in (290mm x 245mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
Copy of 1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Map of Xi an & Guanzhong in Shaanxi Province China
- Title: Villes De La Province De Chensi (Si-ngan-fu Capitale / Tchouang Lan ou Chwang lan)
- Date: 1755
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 25726
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a birds-eye view of the walled city of Xi an & the historical region of the Guanzhong Plain in the Shaanxi Province of Northern China by Jakob van Schley in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Shaanxi is a province of the People\'s Republic of China. Officially part of the Northwest China region.
Shaanxi is considered one of the cradles of Chinese civilization. Thirteen feudal dynasties established their capitals in the province during a span of more than 1,100 years, from the Zhou Dynasty to the Tang Dynasty.
The province\'s principal city and current capital, Xi\'an, is one of the four great ancient capitals of China and is the eastern terminus of the Silk Road, which leads to Europe, the Arabian Peninsula and Africa.
Under the Han Dynasty, the Northern Silk Road was expanded to advance exploration and military purposes to the west. This Northern Silk Road is the northernmost of the Silk Roads and is about 2,600 kilometres (1,600 mi) in length. It connected the ancient Chinese capital of Xi an to the west over the Wushao Ling Pass to Wuwei and emerging in Kashgar before linking to ancient Parthia.
Under the Ming dynasty, Shaanxi was incorporated into Gansu but was again separated in the Qing dynasty.
One of the most devastating earthquakes in history occurred near Hua Shan, in south-eastern part of Shaanxi Province on January 23, 1556, killing an estimated 830,000 people (see 1556 Shaanxi earthquake).
Xi an is the capital of Shaanxi province in China. It is a sub-provincial city located in the center of the Guanzhong Plain in Northwestern China. One of the oldest cities in China, Xi\'an is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals, having held the position under several of the most important dynasties in Chinese history, including Western Zhou, Qin, Western Han, Sui, and Tang. Xi\'an is the starting point of the Silk Road and home to the Terracotta Army of Emperor Qin Shi Huang.
Guanzhong Plain, is a historical region of China corresponding to the lower valley of the Wei River. It is called Guanzhong or \'within the passes\', as opposed to \'Guandong\' or \'east of the pass\', i.e., the North China Plain. The North China Plain is bordered on the west by mountains. The Yellow River cuts through the mountains at the Hangu Pass or Tongguan separating Guanzhong from Guandong.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 9in (280mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)