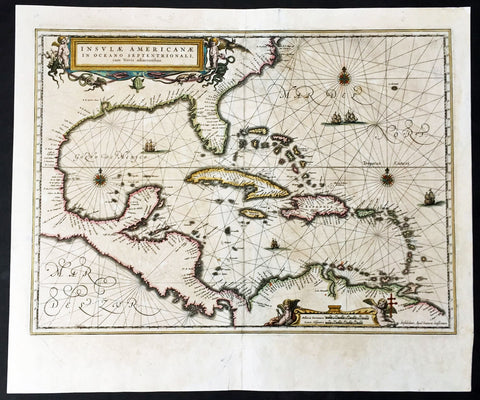
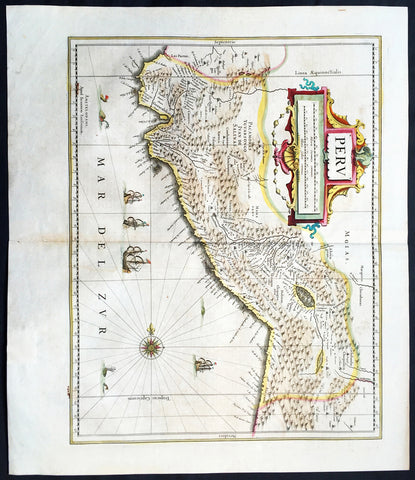
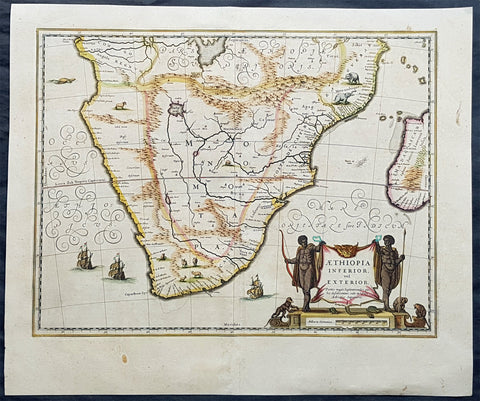
Products
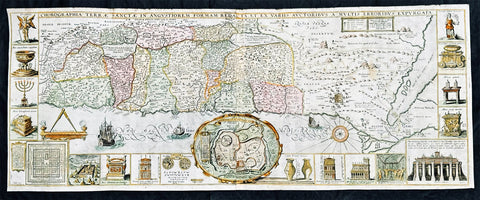
1632 Jacob Tirinus Large Early Antique 1st Edition Map of The Holy Land, Palestine, Israel
- Title : Chorographia Terrae Sanctae in angustiorem Formam Redacta, et ex variis auctoribus a multis errorbus expurgata
- Ref #: 35659
- Size: 33 1/2in x 13 1/2in (850mm x 345mm)
- Date : 1632
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent, hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique 1st edition map of the Holy Land by Johann Belling & Augustus Vindel was published in the 1632 edition of Commentarius in Sacram Scripturam (Commentary on the New and Old Testament) by the Belgian Jesuit monk Jacobus Tirinus.
This is without doubt one of the most visually stunning maps of the Holy land ever published and there have been many elaborated & beautiful maps of this important region published since the dark ages, when the Holy Land was considered the geographical center of the world.
This map was originally prepared in 1632 for Tirinuss study of the Holy Land and was originally engraved by Cornelius Galle and printed in Antwerp by Martinus Nutius. Tirinuss work went through many editions and printings
Background: Oriented to the East the map is surrounded with panels of vignettes displaying sacred objects including a menorah, the arc of the covenant, the altar of sacrifices, the Tabernacle, and a plan and elevations of the Temple. At center is an inset bird's-eye plan of ancient Jerusalem based on the Spanish biblical geographer, Juan Bautista Vilalpando. Oriented with east at top, the map includes the territories of the twelve tribes on both sides of the Jordan River and the route of the Exodus and Wandering. The map depicts from Syria and Tyre southward as far as the Sinai, Egypt and Thebes. At the southern most point, in Egypt, is located the city of Thebes and, slightly to the north, near Memphis, the wildly misshapen Pyramids of Egypt. Slightly further north is the city of Tanis, possible resting place for the Ark of the Covenant. In this spirit, slightly to the south of Tanis, the city of Ramesse is indicated as the starting point of the Biblical Exodus and the wandering of the Hebrews. Following their path into the desert and across the Red Sea – where Pharaoh is shown being inundated by the returning waters following Moses’ parting of the Red Sea. Now in the Sinai, we can follow the footsteps of the Hebrews to Mount Sinai (Sinai Mons), where Moses is drawn throwing down the tablets of God. Slightly to the northwest of this location a cleft in the mountains reveals the location of the ancient Nabatean city of Petra. With regard to Petra, the location and gorge detail is surprisingly accurate considering that it was only “discovered” by the Swiss adventurer Johannes L. Burckhardt, in 1812, 200 years after this map was drawn. Heading northward the lands claimed by the various tribes of Israel are beautifully detailed along with major cities, camps, roads, and trade routes. The Mediterranean is decorated with sailing ships and, in the lower left quadrant, a surveying tool between two censors. Surrounding the map proper on the left, right, and bottom margins, there are 19 maps and images of Biblical objects. The largest and most central of these is a stunning inset of Jerusalem, which notes the various temples and important buildings located there. Other images include the Arc of the Covenant, Israelite coins, Roman antiquities, views of a Menorah, various angels, and a plan of the Temple. All in all an extraordinary piece, one of the most attractive maps of the Holy Land ever made.
Jacobus Tirinus (1580 - 1636) or Jacobi Tirini was a Jesuit monk, theologian, historian, and Biblical scholar. His major work is the Commentarius in Sacram Scripturam a two volume Bible commentary. Tirini was born in Antwerp, Belgium in 1580. Following his admission into the Jesuit Order, Tirini became a respected Biblical scholar and a prominent member of the Order. He was assigned First Superior to the Antwerp Jesuit House as well as "Directior of the Holland Mission". Tirini's Biblial commentaries are still referenced today.(Ref: Laor; M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow, red, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 33 3/4in x 13 3/4in (855mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 33in x 13in (840mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
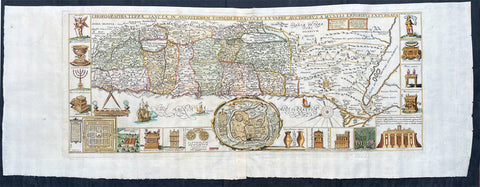
1632 Jacobus Tirinus Large Antique Map of The Holy Land, Palestine, XII Tribes
- Title : Chorographia Terrae Sanctae in angustiorem Formam Redacta, et ex variis auctoribus a multis errorbus expurgata
- Ref #: 17009
- Size: 40in x 19in (1060m x 395mm)
- Date : 1632
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent, hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of the Holy Land by Johann Belling & Augustus Vindel was published in Commentarius in Sacram Scripturam (Commentary on the New and Old Testament) by the Belgian Jesuit monk Jacobus Tirinus.
This is without doubt one of the most visually stunning maps of the Holy land ever published and there have been many elaborated & beautiful maps of this important region published since the dark ages, when the Holy Land was considered the geographical center of the world.
This map was originally prepared in 1632 for Tirinus study of the Holy Land and was originally engraved by Cornelius Galle and printed in Antwerp by Martinus Nutius. Tirinuss work went through many editions and printings up until the mid 18th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 40in x 19in (1060m x 395mm)
Plate size: - 32 1/2in x 13in (825mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Oriented to the East the map is surrounded with panels of vignettes displaying sacred objects including a menorah, the arc of the covenant, the altar of sacrifices, the Tabernacle, and a plan and elevations of the Temple. At center is an inset bird\\\'s-eye plan of ancient Jerusalem based on the Spanish biblical geographer, Juan Bautista Vilalpando. Oriented with east at top, the map includes the territories of the twelve tribes on both sides of the Jordan River and the route of the Exodus and Wandering. The map depicts from Syria and Tyre southward as far as the Sinai, Egypt and Thebes. At the southern most point, in Egypt, is located the city of Thebes and, slightly to the north, near Memphis, the wildly misshapen Pyramids of Egypt. Slightly further north is the city of Tanis, possible resting place for the Ark of the Covenant. In this spirit, slightly to the south of Tanis, the city of Ramesse is indicated as the starting point of the Biblical Exodus and the wandering of the Hebrews. Following their path into the desert and across the Red Sea – where Pharaoh is shown being inundated by the returning waters following Moses’ parting of the Red Sea. Now in the Sinai, we can follow the footsteps of the Hebrews to Mount Sinai (Sinai Mons), where Moses is drawn throwing down the tablets of God. Slightly to the northwest of this location a cleft in the mountains reveals the location of the ancient Nabatean city of Petra. With regard to Petra, the location and gorge detail is surprisingly accurate considering that it was only “discovered” by the Swiss adventurer Johannes L. Burckhardt, in 1812, 200 years after this map was drawn. Heading northward the lands claimed by the various tribes of Israel are beautifully detailed along with major cities, camps, roads, and trade routes. The Mediterranean is decorated with sailing ships and, in the lower left quadrant, a surveying tool between two censors. Surrounding the map proper on the left, right, and bottom margins, there are 19 maps and images of Biblical objects. The largest and most central of these is a stunning inset of Jerusalem, which notes the various temples and important buildings located there. Other images include the Arc of the Covenant, Israelite coins, Roman antiquities, views of a Menorah, various angels, and a plan of the Temple. All in all an extraordinary piece, one of the most attractive maps of the Holy Land ever made.
Tirinus, Jacobus 1580 - 1636
Or Jacobi Tirini was a Jesuit monk, theologian, historian, and Biblical scholar. His major work is the Commentarius in Sacram Scripturam a two volume Bible commentary. Tirini was born in Antwerp, Belgium in 1580. Following his admission into the Jesuit Order, Tirini became a respected Biblical scholar and a prominent member of the Order. He was assigned First Superior to the Antwerp Jesuit House as well as Directior of the Holland Mission. Tirinis Biblial commentaries are still referenced today.(Ref: Laor; M&B; Tooley)
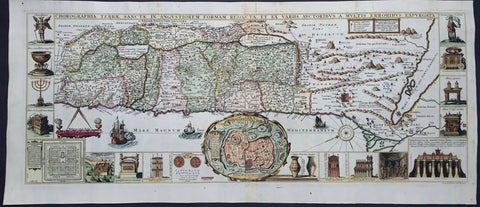
1632 Jacobus Tirinus Large Antique Map of The Holy Land, Palestine, XII Tribes
- Title : Chorographia Terrae Sanctae in angustiorem Formam Redacta, et ex variis auctoribus a multis errorbus expurgata
- Ref #: 93379
- Size: 34in x 15in (865mm x 380mm)
- Date : 1632
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large magnificent, hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of the Holy Land by Johann Belling & Augustus Vindel was published in Commentarius in Sacram Scripturam (Commentary on the New and Old Testament) by the Belgian Jesuit monk Jacobus Tirinus.
This is without doubt one of the most visually stunning maps of the Holy land ever published and there have been many elaborated & beautiful maps of this important region published since the dark ages, when the Holy Land was considered the geographical center of the world.
This map was originally prepared in 1632 for Tirinus study of the Holy Land and was originally engraved by Cornelius Galle and printed in Antwerp by Martinus Nutius. Tirinuss work went through many editions and printings up until the mid 18th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 34in x 15in (865mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 32 1/2in x 12 1/2in (825mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Oriented to the East the map is surrounded with panels of vignettes displaying sacred objects including a menorah, the arc of the covenant, the altar of sacrifices, the Tabernacle, and a plan and elevations of the Temple. At center is an inset bird\\\'s-eye plan of ancient Jerusalem based on the Spanish biblical geographer, Juan Bautista Vilalpando. Oriented with east at top, the map includes the territories of the twelve tribes on both sides of the Jordan River and the route of the Exodus and Wandering. The map depicts from Syria and Tyre southward as far as the Sinai, Egypt and Thebes. At the southern most point, in Egypt, is located the city of Thebes and, slightly to the north, near Memphis, the wildly misshapen Pyramids of Egypt. Slightly further north is the city of Tanis, possible resting place for the Ark of the Covenant. In this spirit, slightly to the south of Tanis, the city of Ramesse is indicated as the starting point of the Biblical Exodus and the wandering of the Hebrews. Following their path into the desert and across the Red Sea – where Pharaoh is shown being inundated by the returning waters following Moses’ parting of the Red Sea. Now in the Sinai, we can follow the footsteps of the Hebrews to Mount Sinai (Sinai Mons), where Moses is drawn throwing down the tablets of God. Slightly to the northwest of this location a cleft in the mountains reveals the location of the ancient Nabatean city of Petra. With regard to Petra, the location and gorge detail is surprisingly accurate considering that it was only “discovered” by the Swiss adventurer Johannes L. Burckhardt, in 1812, 200 years after this map was drawn. Heading northward the lands claimed by the various tribes of Israel are beautifully detailed along with major cities, camps, roads, and trade routes. The Mediterranean is decorated with sailing ships and, in the lower left quadrant, a surveying tool between two censors. Surrounding the map proper on the left, right, and bottom margins, there are 19 maps and images of Biblical objects. The largest and most central of these is a stunning inset of Jerusalem, which notes the various temples and important buildings located there. Other images include the Arc of the Covenant, Israelite coins, Roman antiquities, views of a Menorah, various angels, and a plan of the Temple. All in all an extraordinary piece, one of the most attractive maps of the Holy Land ever made.
Tirinus, Jacobus 1580 - 1636
Or Jacobi Tirini was a Jesuit monk, theologian, historian, and Biblical scholar. His major work is the Commentarius in Sacram Scripturam a two volume Bible commentary. Tirini was born in Antwerp, Belgium in 1580. Following his admission into the Jesuit Order, Tirini became a respected Biblical scholar and a prominent member of the Order. He was assigned First Superior to the Antwerp Jesuit House as well as Directior of the Holland Mission. Tirinis Biblial commentaries are still referenced today.(Ref: Laor; M&B; Tooley)
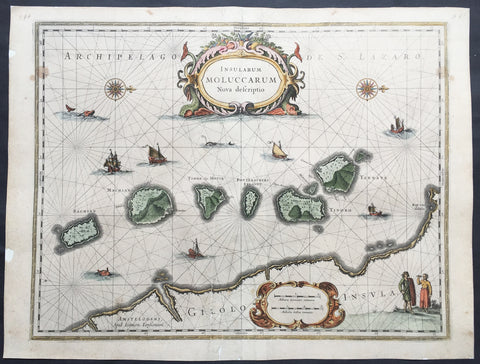
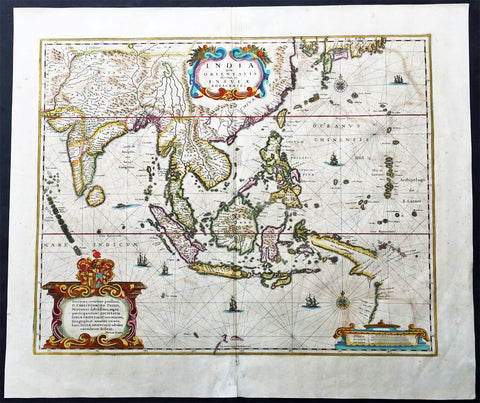
1633 Jan Jansson Old, Antique Map of The Maluku or Spice Islands, Indonesia
- Title : Insularum Moluccarum Nova descriptio
- Ref #: 42018
- Size: 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
- Date : 1633
- Condition: (B+) Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Maluku or Spice Islands of Indonesia was published by Jan Jansson in the 1633 edition of Atlas Novus.
Background: The Maluku Islands (also known as the Moluccas, Moluccan Islands, the Spice Islands) are an archipelago in Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Geographically they are located east of Sulawesi (Celebes), west of New Guinea, and north of Timor. The islands were also historically known as the Spice Islands by the Chinese and Europeans, but this term has also been applied to other islands. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to top and bottom margin, slight separation into border
Plate area: - Repairs adjacent to bottom centrefold, slight separation
Verso: - Map professionally backed onto archival paper
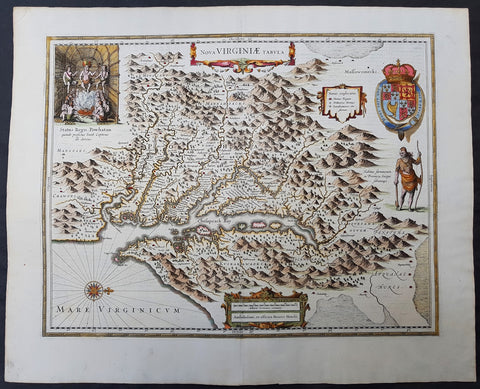
1633 John Smith & Hondius Original Antique Map of Virginia, Chesapeake Bay - Pocahontas
- Title : Nova Virginiae Tabula
- Date : 1633
- Size: 23in x 18 3/4in (585mm x 475mm)
- Ref #: 70818
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This superb original antique hand coloured map of Chesapeake Bay, Virginia was published in the 1633 edition of Mercators Atlas.
Although this map bears the name of Henricus Hondius, the plate originated from his brother Joducus II in 1618, after Captain John Smith\'s famous map of 1612, and was published in many editions of Mercators Atlas after 1630. Willem Blaeu also purchased this copper-plate from the Hondius plate stock in 1629 and was published in many future Blaeu atlases.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 18 3/4in (585mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15 1/2in (500mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - 4 very small worm holes
Verso: - None
Background:
This is one of the most important seventeenth century maps of the Chesapeake Bay region. The early settlement of Jamestown Iamestowne is noted along with a number of other place names, both in English and Native American. The map was derived from Capt. John Smith's map of 1612 and was the first to depict the bay and its tributaries with any accuracy.
Capt John Smith's fine survey work, as well as reports from indigenous American Indian tribes, and fanciful wishful thinking, combine to make this one of the most interesting maps of America to emerge in the 17th century. Philip D. Burden, the author of The Mapping of America, considers this map, Nova Virginiae Tabula, to be 'one of the most important maps of America ever produced and certainly one of the greatest influence.' Oriented to the west, this map covers from Cape Henry to the Susquehanna River and inland as far as the Appellation Mountains. The Chesapeake Bay is shown in full as are many of its river estuaries, though topographically this map places a number of mountain ranges where there are in fact none.
To fully understand this map one must first realize that most Europeans believed the Pacific, or at least some great bay that led to the Pacific, lay just a few days travel inland. In the minds of most Europeans of the period, the trade potential for the Virginia colony was entirely dependent upon it being a practical access point to the riches of Asia. Thus the significance of large and mysterious body of water appearing in the land of the Massawomecks, in the upper right quadrant, becomes apparent. Of course, much of this land was entirely unexplored by the European settlers in Jamestown, shown here on the Powhatan River (James River), who relied heavily upon American Indian reports for much of their cartographic knowledge of the Virginia hinterlands. The Massawomecks themselves were a rival of the Powhatan and made their home near the headwaters of the Potomac. These, like many other indigenous groups of the region made only a brief and frequently violent appearance during the 17th century before entirely disappearing, mostly from disease and war, in the early 18th century.
In the upper left quadrant there is an image of the American Indian chief of the Powhatan sitting enthroned before a great fire in his long house. One of the more popular legends regarding John Smith was his capture and trial before the chief of the Powahatan. Smith was convinced that his liberation had something to do with the youthful daughter of Chief Powahatan, Pocahontas, taking a liking to him. Although this grew into a fictitious legend of its own, the truth is more likely that Powhatan saw Smith and his Englishmen as potential allies against the rival American Indian groups, such as the Massawomecks, that were pressing hard against his borders.
There are a number of different editions of this map and its publication by various map houses in various states made it the first widely distributed map of the Virginia colony and of John Smith's important map. There was, however, a scandal relating to its publication. The map was originally drawn and engraved in 1618 by Jodocus Hondius based upon the first edition of John Smith's 1612 map. When Jodocus died in 1629, he and his brother, Henricus Hondius, while collaborating on the Hondius Atlas Major, had established and maintained separate business for some 10 years. Jodocus' death enabled the competing cartographer, Willem Blaeu to acquire a large number of Jodocus' map plates, which he promptly published in 1630 as the Atlantis Appendix. Henricus, in the meantime, had been counting on Jodocus' new plates to enhance his own, by then outdated, Hondius Atlas Major. A surviving contract dated March 2, 1630 reveals that Henricus Hondius and his partner Joannes Janssonius hired engravers to produce a number of new map plates copying the work of Jodocus – now in the hands of the Blaeu firm. This map was among the most important of that group and accounts for variants of this map being issued by competing Blaeu and Hondius firms.
The History of Virginia begins with documentation by the first Spanish explorers to reach the area in the 1500s, when it was occupied chiefly by Algonquian, Iroquoian, and Siouan peoples. After a failed English attempt to settle Virginia in the 1580s by Walter Raleigh permanent English settlement began in Virginia with Jamestown, Virginia, in 1607. The Virginia Company colony was looking for gold but failed and the colonists could barely feed themselves. The famine during the harsh winter of 1609 forced the colonists to eat leather from their clothes and boots and resort to cannibalism.[1] The colony nearly failed until tobacco emerged as a profitable export. It was grown on plantations, using primarily indentured servants for the intensive hand labor involved. After 1662, the colony turned black slavery into a hereditary racial caste. By 1750, the primary cultivators of the cash crop were West African slaves. While the plantations thrived because of the high demand for tobacco, most white settlers raised their families on subsistence farms. Warfare with the Virginia Indian nations had been a factor in the 17th century; after 1700 there was continued conflict with natives east of the Alleghenies, especially in the French and Indian War (1754-1763), when the tribes were allied with the French. The westernmost counties including Wise and Washington only became safe with the death of Bob Benge in 1794.
The Virginia Colony became the wealthiest and most populated British colony in North America, with an elected General Assembly. The colony was dominated by rich planters who were also in control of the established Anglican Church. Baptistand Methodist preachers brought the Great Awakening, welcoming black members and leading to many evangelical and racially integrated churches. Virginia planters had a major role in gaining independence and in the development of democratic-republican ideals of the United States. They were important in the Declaration of Independence, writing the Constitutional Convention (and preserving protection for the slave trade), and establishing the Bill of Rights. The state of Kentuckyseparated from Virginia in 1792. Four of the first five presidents were Virginians: George Washington, the "Father of his country"; and after 1800, "The Virginia Dynasty" of presidents for 24 years: Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and James Monroe.
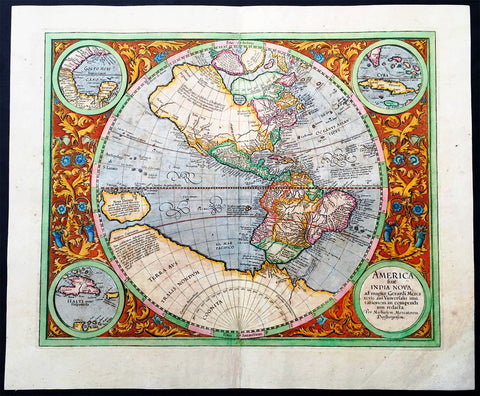
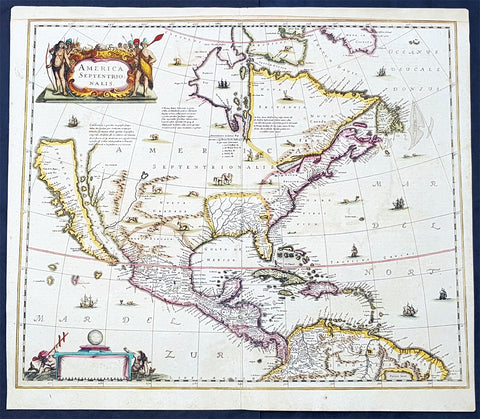
1633 Mercator Antique Map of America & The Great Southern Land - Terra Australis
- Title : America sive India Nova. ad magna Gerardi Mercatoris aui Universalis imitationem in compendium redacta. Per Michaelem Mercatorem Duysburgensem
- Ref #: 61017
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 3/4in (545mm x 450mm)
- Date : 1633
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique early map of America and the Great Southern Continent (Terra Australis) that was envisaged in the southern Hemisphere, prior to the discovery of Australia by Captain Cook in 1769 - the only map attributed to Gerard Mercator's Grandson Michael - was published in the 1633 French edition of Mercator's Atlas.
This map is magnificent with beautiful original hand colouring, wide margins and stable paper. Backed with transparent archival Japanese paper. Original colouring such as this is scarce and hard to find.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 3/4in (545mm x 450mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14 3/4in (470mm x 376mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning, light creasing & uplift along center-fold
Verso: - Backed with transparent archival Japanese paper
Background: Largely based on Rumold Mercator's world map of 1587, this map aptly reflects 16th-century knowledge, theories and suppositions regarding the New World. Naturally, most of this new knowledge was coastal, and configurations of any large areas were greatly hampered by the lack of a sound means of determining longitude. Nevertheless, the collective accomplishment of explorers and mapmakers represented in this map is astounding, showing in a generally correct way the vast extent of the New World. "A few of the most famous theories are still present: a large inland lake in Canada, two of the four islands of the North Pole, a bulge to the west coast of South America and the large southern continent" (Burden).
The map appeared in 1595 and 1606 editions of the Atlantis Pars Altera , after which the plate was sold to Jodocus Hondius, who reissued the maps in varying editions through 1639. The present example includes French text on verso, confirming it to be a Hondius issue.
Several of the more fascinating theories are present, including the multiple islands of the North Polar Sea, bulging South America and vast unknown southern continent. The St. Lawrence crosses half the continent. No sign of the English in Virginia. The search for a water course across North America is interupted only by some mid-continental mountains. Evidence of the Spanish explorations in the Southwest is present and the Colorado and Gila Rivers already reflect a good knowledge of this area, as does the peninsular Baja California, based upon Uloa's work.
The depiction of the NW Passage and Western North America are also of great interest. Annotations reference the voyages of Columbus and Magellan.(Ref: Burden; Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
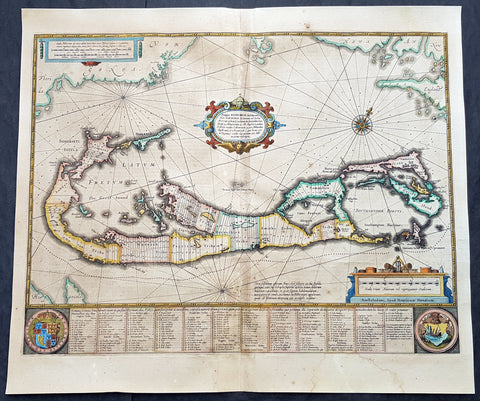
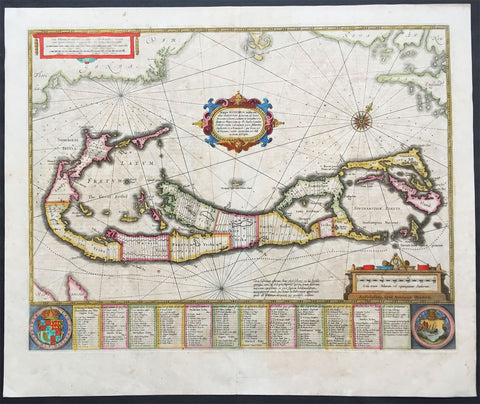
1634 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of The Island of Bermuda
- Title : Mappa Aestivarum Insularum, alias Barmudas Dictarum ... Accurate Descripta
- Ref #: 93407
- Size: 21 1/2in x 18 1/2in (545mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1634
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Island of Bermuda was published in the 1634 Dutch edition of Atlas Nouvs by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
A much sought after map of Bermuda, with decorative cartouche, compass rose with the Island divided into lots and tribes, listed at the base of the map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 18 1/2in (545mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15 3/4in (490mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, light soiling
Plate area: - Soiling, small restoration along centerfold above cartouche and bottom rose
Verso: - Centerfold re-enforced, small repair to left side of text
Background:
Like all 17th century maps of Bermuda this map is based ultimately on the survey made by John Norwood of the Bermuda Company in 1618 in the form as published by the English map-maker John Speed in 1627.
Although discovered in 1515 by Spaniard Juan de Bermudez, after whom the island is supposedly named, it was the shipwreck of a party of Virginia colonists in 1610 led by Sir George Somers that gave Bermuda its first known inhabitants. The Latin title reflects this fact, for Aestivarum Insularum means summers (or Somers) Islands. The experience of Somers and his men inspired William Shakespeare, who dispatched Ariel to \"fetch dew from the still-vext Bermoothes\" and populated the islands with the cast of The Tempest.
The place names and the list of Proprietors given below the map itself all recall the original members of the Bermuda Company, the latter being listed as eight tribes (or parishes).
In 1610, the Virginia Company, in a True Declaration of the Estate of the Colonie of Virginia, said of Bermuda: These Islands of Bermudos, have evere beene accounted as an inchaunted pile of rocks, and a desert inhabitation for Divels; but all the Faities of the rockes were but flocks of Birds, and all the Divels that haunted the woods, were but heards of Swine.
In the upper left-hand and right-hand corners of the map appear the adjacent coasts of the North American colonies of Virginia and New England with, just below the cartouche a tiny outline of Bermuda itself, intended to show its correct proportion and position against the mainland.(Ref Tooley M&B)
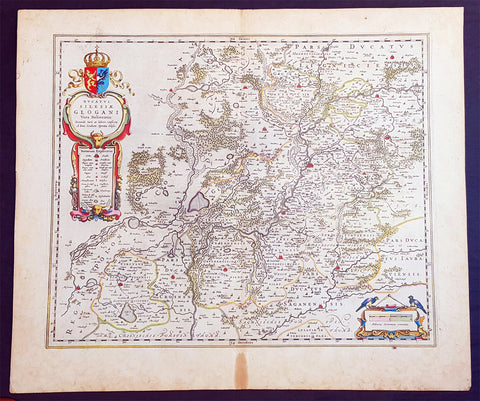
1634 Joan Blaeu Large Antique Map of Glogow, Lower Silesia, Poland
- Title : Ducatus Silesiae Glogani Vera Delineatio.
- Ref #: 93486
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1634
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique, rare map of the Duchy of Glogow, in the ancient region of Silesia, Poland - centering on the city of Glogow - was published by Joan Blaeu in the 1634 French edition of Atlas Nouvs,.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20 1/2in (600mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16 1/2in (510mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Duchy of Głogów was one of the Duchies of Silesia ruled by the Silesian Piasts. Its capital was Głogów in Lower Silesia.
In 1177, under the rule of Konrad Spindleshanks, the youngest son of High Duke Władysław II the Exile of Poland, the town of Głogów had already become the capital of a duchy in its own right. However, when Konrad died between 1180 and 1190, his duchy was again inherited by his elder brother Bolesław I the Tall, Duke of Wrocław. After the death of Bolesławs grandson Duke Henry II the Pious at the 1241 Battle of Legnica his sons in 1248 divided the Lower Silesian Duchy of Wrocław among themselves. Konrad I, a child when his father died, claimed his rights too and in 1251 and received the northern Głogów territory from his elder brother Bolesław II the Bald, then Duke of Legnica.
Under the rule of Konrads son Henry III the principality became smaller, as fragmentation and division continued, and other, smaller duchies were split from it like Ścinawa (Steinau, Stínava) and Żagań (Sagan, Zaháň) in 1273 as well as the duchies of Oleśnica (Oels, Olešnice) and Wołów (Wohlau, Volov) in 1312. After Henrys son Przemko II had died without heirs in 1331, King John the Blind was able to seize the duchy as a fiefdom of the Kingdom of Bohemia and granted it to the Piast Duke Henry I of Jawor six years later. As Henry I left no issue, King Johns son, Charles IV incorporated one half of Głogów into Crown of Bohemia, granting the remaining half to Duke Henry V of Iron of Żagań in 1349.
When in 1476 the Głogów line of the Piast dynasty became extinct with the death of Henry XI, fights over his succession broke out between his cousin Duke Jan II the Mad of Żagań and Elector Albert III Achilles of Brandenburg, the father of Henrys widow Barbara of Brandenburg. In consequence the duchys northern part of Krosno Odrzańskie (Crossen an der Oder) was incorporated by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1482. The truce however was broken by Duke Jan II, who continued his attacks on the neighbouring territories and in 1480 even invaded the royal Bohemian half of the Głogów duchy. This action finally brought the Bohemian antiking Matthias Corvinus to the scene, who in 1488 conquered Głogów, deposed Jan II and made his son János the duke.
Upon Matthias death in 1490 his territories were reacquired by Bohemian king Vladislaus II Jagiellon, who granted the fief of Głogów to his brothers John I Albert in 1491 and later Sigismund I the Old in 1499, both future kings of Poland. In 1506 the duchy finally became an immediate dominion of the Bohemian Crown, which, after Vladislaus son Louis II Jagiellon had died in 1526, were inherited by Archduke Ferdinand I of Austria and became part of the Habsburg Monarchy.
Głogów remained part of the Crown of Bohemia within the province of Silesia until the end of the First Silesian War in 1742 when, like the majority of Silesia, it became part of Frederick the Greats Kingdom of Prussia (which was definitively confirmed by the Treaty of Aachen in 1748). Even the Seven Years War did not change this status. In 1815 the Duchy (along with other Silesian duchies) ceased to exist due to radical administrative reform. All of Silesia was unified into a single administrative unit, Province of Silesia (Provinz Schlesien).
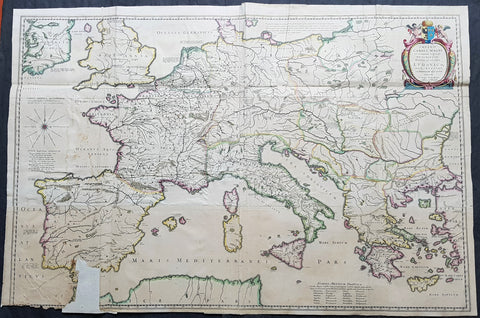
1634 Joan Blaeu Large Rare Antique Map of Europe under Charlemagne I, 8th Century
- Title : Imperii Caroli Magni et vicinarum regionum Descriptio Dedieata et inferipta Ludovico... Petro Bertio.
- Size: 39 1/2in x 26 1/2in (1.00mm x 670mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1634
- Ref #: 70607
Description:
This large superbly hand coloured original copper plate engraved, 4 x sheet, antique map of Europe, as it was under Charlemagne I, was originally published by the 16th century cartographer Petrus Bertius and later re-engraved and published in the 1634 German edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus.
The map has been damaged at the bottom left sheet, with image missing. As this is a large folding map, the folds, sometime in the past, have been re-enforced and refolded.
This map is rare and hard to find and in fine condition can sell over $1500US.
A large four sheet historical map showing the empire of Charlemagne, aka Carolus Magnus, aka Charles the Great. Charlemagne ruled in the 8th century and is regarded as the founding father of both France and Germany. Blaeu credits Petrus Bertius for the cartography. Bertius (1565-1629) was a professor of mathematics and librarian at Leyden University. He was also cartographer and a prolific writer on historical and theological subjects. The map shows the majority of Europe, from southeastern Ireland south to Gibraltar and westward to Germany and Greece.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39 1/2in x 26 1/2in (1.00m x 670mm)
Plate size: - 39in x 26in (980mm x 660mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left corner margins lost
Plate area: - Folds as issued, bottom 4in x 2in section missing. Light soiling
Verso: - Folds re-enforced on verso
Background:
Charlemagne 742 - 814, numbered Charles I, was king of the Franks from 768, king of the Lombards from 774, and emperor of the Romans from 800. He united much of western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. He was the first recognised emperor to rule from western Europe since the fall of the Western Roman Empire three centuries earlier. The expanded Frankish state that Charlemagne founded is called the Carolingian Empire. He was later canonized by Antipope Paschal III.
Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon, born before their canonical marriage. He became king in 768 following his fathers death, initially as co-ruler with his brother Carloman I. Carlomans sudden death in December 771 under unexplained circumstances left Charlemagne as the sole ruler of the Frankish Kingdom. He continued his fathers policy towards the papacy and became its protector, removing the Lombards from power in northern Italy and leading an incursion into Muslim Spain. He campaigned against the Saxons to his east, Christianizing them upon penalty of death and leading to events such as the Massacre of Verden. He reached the height of his power in 800 when he was crowned Emperor of the Romans by Pope Leo III on Christmas Day at Romes Old St. Peters Basilica.
Charlemagne has been called the Father of Europe (Pater Europae), as he united most of Western Europe for the first time since the classical era of the Roman Empire and united parts of Europe that had never been under Frankish or Roman rule. His rule spurred the Carolingian Renaissance, a period of energetic cultural and intellectual activity within the Western Church. Emperors of the Holy Roman Empire considered themselves successors of Charlemagne, as did the French and German monarchs. However, the Eastern Orthodox Church views Charlemagne more controversially, labelling as heterodox his support of the filioque and the Popes recognition of him as legitimate Roman Emperor rather than Irene of Athens of the Byzantine Empire. These and other machinations led to the eventual split of Rome and Constantinople in the Great Schism of 1054.
Charlemagne died in 814, having ruled as emperor for almost 14 years and as king for almost 46 years. He was laid to rest in his imperial capital city of Aachen. He married at least four times and had three legitimate sons, but only his son Louis the Pious survived to succeed him.
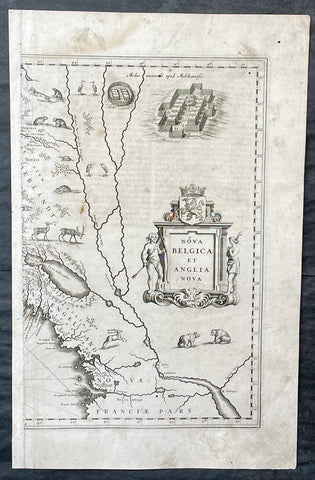
1635 Joan Blaeu Antique Half Page Map of New England, Nova Belgica et Anglia
- Title : Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova
- Date : 1635
- Size: 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Ref: 16385
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique half right hand page map of New England & NE America by Joan Blaeu was published in the 1635 German edition of Atlas Novus.
This is the right hand, cartouche title section of this important map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling, small worm hole top right margin
Plate area: - Light soiling, 4 small worm holes
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas published at the time. It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map is the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Niev Nederland.
It has been noted that the time difference between 1614, the date of the manuscript, and Blaeus map whose first appearance is in 1635, appears long for such an important advance. It would seem highly feasible that Blaeu, who published many separately issued maps, would have wanted to produce one like this sooner. However, evidence points to the fact that it could not have been made before 1630. The Stokes Collection in New York possesses an example of the map on thicker paper without text on the reverse which could well be a proof issue of some kind.
There are features on Blaeus map that differ from the Block chart. Some of these could be accounted for by the fact that the surviving figurative map is not the original, and that the copyist omitted some place names that are referred to in the text of de Laets work. Block drew on Champlains map of 1612 for the depiction of the lake named after him, but it is here called Lacus Irocoisiensis. … The lack of interrelation between the Dutch or English colonies and the French, led for some time to the eastward displacement of this lake when its true position would be north of the Hudson River.
Some nomenclature has its origins in Blaeus second Paskaert of c.1630, and others, such as Manatthans, in de Laet. The colony of Nieu Pleimonth is identified. This and other English names along that part of the coast are largely derived from Smith\\\'s New England, 1616. Cape Cod is here improved over the Block manuscript by being reconnected to the mainland, the narrow strait having been removed. The coastline between here and Narragansett Bay, which can be clearly recognized, is not so accurate. Adriaen Blocx Eylandt leads us to the Versche Rivier, or Connecticut River, which Block ascended as far as was possible. t Lange Eyland is named; however, it is incorrectly too far east, being applied to what is possibly Fishers Island. De Groote bay marks Long Island Sound. The Hudson River is still not named as such, but is littered with Dutch settlements, and the failed Fort Nassau is here depicted renamed as Fort Orange. He does, however, improve on the direction of its flow. Blaeu separates the sources of the Hudson and Delaware Rivers which had been causing some confusion. Nieu Amsterdam is correctly marked as a fort at the tip of an island separated on the east side by Hellegat, or the East River. The coastline south of Sandy Hook also shows signs of improvement.
The whole map is adorned by deer, foxes, bears, egrets, rabbits, cranes and turkeys. Beavers, polecats and otters appear on a printed map for the first time. The Mohawk Indian village top right is derived from the de Bry-White engravings.
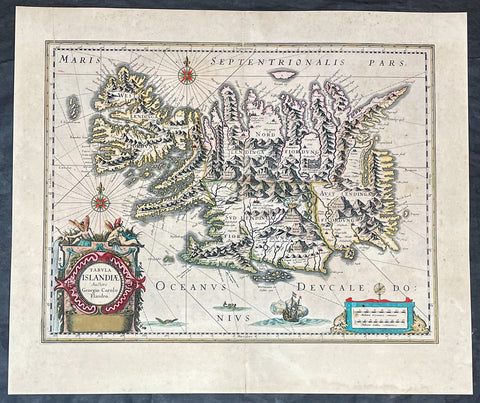
1635 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of Iceland - Joris Carolus
- Title :Tabula Islandia Auctore Georgio Carolo Flandro
- Ref #: 27017
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1647
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique map of Iceland, by Willem Blaeu, was engraved by Jodocus Hondius after Joris Carolus, and was published by Willem Blaeus son, Joan, in the 1635 French edition of Atlas Nouvs
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Original printers crease top left margin into border, uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background:
This map of Iceland is perhaps the most familiar of all the outlines of the island ever published. The author is stated to be one Joris Carolus, a Dutch navigator from Enkhuizen, whose map was first engraved and prepared by Jodocus Hondius the younger in 1628, whose plates were bought by Willem Blaeu in 1629. Iceland bears the imprint of Willem Blaeu who issued it in his Appendix of 1630.
The Carolus map was copied by virtually all mapmakers throughout the rest of the 17th century and well into the 18th. Some of the information is derived from a map made famous by the Flemish cartographer Abraham Ortelius, the Islandia of Gudhbrandur Thorlaksson (1541 - 1627) Bishop of Holar, who had studied mathematics and astronomy as well as theology, while other information, such as place names, is derived from Gerard Mercator's map of 1595.
Willem Blaeu reprinted the map without change in his subsequent atlas editions, as did Joan after him, including the great atlas of 1662. In the southern southern part is shown the lively impression of Hekla in full eruption, described as mons perpetuo ardens while immediately to the west, the Bishopric of Skalholt is marked. To the south a note by Eiapialla hokel (Eyjafjallajokull) states that here may be found falcones albi or white falcons, presumably referring to the gyr falcon.
1635 Willem Hondius & Anthony van Dyck Portait of Willem Hondius son of Jodocus
- Title : Guilielmus Hondius, Calcographus Hagae Comitis. Ant. van Dyck pinxit, Guil. Hondius sculp
- Date : 1630-40
- Size: 9 3/4in x 7in (250mm x 180mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 91420
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique print of Guillaume Hondius, was engraved by himself (Guillaume Hondius) after the famous Flemish painter Anthony van Dyck 1599 - 1641 as part of his Iconographie series of engraved portraits of famous people at the time, between 1630-40.
A wonderfully detailed and charismatic portrait, this exquisite work illustrates the technical mastery and artistic vision of Van Dyck. Guillaume Hondius' stately yet approachable expression reflects Van Dyck's refined ability to comfort and relax his subjects, resulting in a realistic and acute portrait. This piece is intriguing because the subject and the engraver are one and the same, yet the image essentially is still Van Dyck's. Guillaumine Hondius engraves himself through the eyes of Van Dyck, depicted with kind eyes, a broad nose, and a pointy chin. Hondius stands with a calm demeanor, holding up his elaborately draped garment with his left hand and gazing straight out at us.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 9 3/4in x 7in (250mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 9 3/4in x 7in (250mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Dark age toning
Background:
Anthony van Dyck (also spelled van Dyke) was a renowned Flemish Baroque painter born on March 22, 1599, in Antwerp, Belgium, and died on December 9, 1641, in London, England. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential portrait painters of his time, known for his elegant and refined style.
Van Dyck showed great artistic talent from a young age and began his artistic training under the guidance of Hendrick van Balen, a local painter in Antwerp. Recognizing his potential, his parents enrolled him as an apprentice with Peter Paul Rubens, the leading Flemish painter of the time. Van Dyck spent six years in Rubens' studio, absorbing the master's techniques and developing his own skills.
By the age of 19, van Dyck had already established himself as an accomplished artist and was admitted as a master to the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke. He primarily focused on religious and mythological subjects during his early years, reflecting the influence of Rubens' style. However, van Dyck soon turned his attention to portraiture, a genre that would bring him great success and recognition.
In the early 1620s, van Dyck traveled to Italy, where he spent several years studying the works of Italian Renaissance masters such as Titian and Tintoretto. This period of Italian sojourn greatly influenced his artistic style, leading to a refinement and sophistication in his portraiture. He became particularly renowned for his ability to capture the personality and character of his sitters, employing a sensitive and flattering approach.
Upon his return to Antwerp in 1627, van Dyck's reputation as a portraitist had grown significantly, attracting commissions from aristocrats, nobles, and prominent figures of the time. His portraits exuded a sense of grandeur and elegance, often featuring his subjects in elaborate costumes and settings. Van Dyck's remarkable talent for capturing the likeness and personality of his sitters earned him patrons and clients across Europe.
In 1632, van Dyck was invited to England by King Charles I, who had heard of his remarkable skill as a portrait painter. He was appointed as the court artist and granted a knighthood, becoming Sir Anthony van Dyck. During his time in England, van Dyck produced numerous portraits of the royal family, aristocracy, and influential figures of the British court. His ability to convey grace, poise, and nobility in his subjects revolutionized the art of portraiture in England.
Van Dyck's impact on English art was profound, and he played a crucial role in elevating the status of portrait painting within the art world. His influence extended beyond his lifetime, as many English portraitists were inspired by his style and approach. Van Dyck's legacy can be seen in the works of later artists such as Thomas Gainsborough, Joshua Reynolds, and Thomas Lawrence.
Despite his success, van Dyck's life was plagued by financial troubles and personal difficulties. He led a lavish lifestyle and accumulated significant debts, which he struggled to repay. Moreover, his health deteriorated in his later years, possibly due to the strain of his extensive work. Van Dyck passed away in London at the age of 42, leaving behind a rich artistic legacy.
Anthony van Dyck's mastery of portraiture, characterized by his skillful rendering of his subjects' individuality and his elegant style, has made him one of the most celebrated painters in art history. His works continue to be admired and studied, serving as a testament to his enduring influence and artistic brilliance.
Hondius, Guillaume or Willem (1598/9 - 1658/60)
Willem Hondius was one of seven children of Hendrik Hondius the Elder (1573 – c. 1649) and Sara Jansdochter. His father was one of the most important Dutch reproductive printmakers and publishers in the early 17th century. A connection with the Hondius family of cartographers in Amsterdam is possible but has not been established.
In 1636 Willem visited Danzig in Poland. In 1641 he moved there from The Hague for good. Hondius was supported at the royal court of King Władysław IV Waza. The King awarded him the title of Chalcographus privilegialus (privileged engraver) and Chalcographus Regius (Royal engraver).
He was married twice, first in 1632 in The Hague to Kornelia van den Enden, secondly in 1646 in Danzig to Anna Mackensen, daughter of the Royal Goldsmith.
In August 1651, in the wake of the Khmelnytsky Uprising, Hondius joined the army of Janusz Radziwiłł conquering Kiev. The first ever portrait of the famous Cossack leader Bohdan Khmelnytsky was engraved during this campaign.
Nothing is known of Hondius after 1652, though he may have lived until 1658.
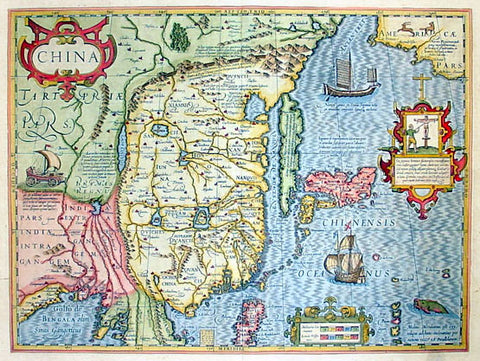
1636 Jan Jansson Antique Map of China, with Korea, Japan & Part of America
- Title : China
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 480mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1636
- Ref #: 75010
Description:
This map of China, Japan with Korea and parts of the west coast of America was the first Chinese map published by Mercator first released in 1606. This map was published in the 1636 edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius & Jan Jansson.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic and beautiful
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (470mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair to top margin centerfold, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: This boldly engraved and hand coloured map combines elements of the maps complied by the two Portuguese Jesuits priests, on Japan by Luis Teixeira (1595) and on China by Luis Jorge de Barbuda (1584). Amoungst the decorative features including sea monsters, ships both European and Chinese and a wind powered land cart is also a vignette depicting the torture of Christians in Japan if caught.
Although Mercator has faithfully followed the Ortelius/Teixeira type of map he has added an explanation for Korea saying it was not yet certain whether it was an island or part of the mainland.
In contrast to the relatively late mapping of the major continents by the Europeans the mapping of China stretches back as far back as 1100BC. Almost 100years after Ptolemy produced "Geographia" and around the same time paper was invented in China an 18-sheet map of China was produced by Pei Hsui (AD 224-71). In the following years contact was re-established between the Chinese and Europeans - contact was known between the two cultures from before Ptolemy - through Marco Polo, Carpini (1245), Rubruquis (1252) and other Franciscan missionaries and it was through the accounts of their travels that scholars began to reshape their ideas of Cathay. In the 16th & 17th centuries the Jesuits exerted a considerable influence on Chinese mapmaking. Matteo Ricci complied the first European map of the world printed and circulated in China (1584 - 1602) Ludovico Georgio who's map of China was used by Ortelius (1584) and subsequently by other Dutch publishers; Father Martino Martini an Italian Jesuit who compiled the first European Atlas of China Atlas Sinensis which was used by Blaeu, Jansson and others. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
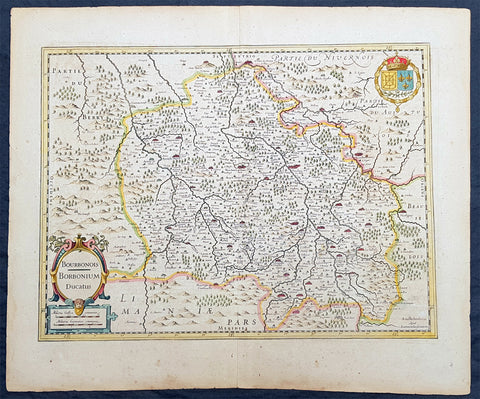
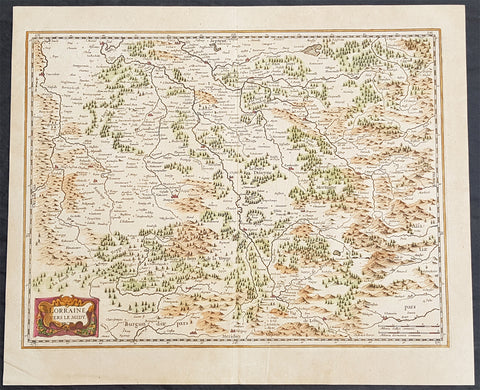
1636 Jan Jansson Antique Map of The Bourbon or Bourbonnais Region Central France
- Title : Boubonoius; Borbonium Ducatus
- Ref #: 41641
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (490mm x 340mm)
- Date : 1636
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Bourbon or Bourbonnais Region of central France was published in the rare 1636 English edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
There was only one English edition of Mercators Atlas published in 1636 by Jansson & Hondius. These maps - with English text on the verso - are now understandably scarce.
The text running for two pages on the back of the map generally describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (490mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background:
Bourbonnais was a historic province in the centre of France that corresponded to the modern département of Allier, along with part of the département of Cher. Its capital was Moulins.
The title of the ruler of Bourbonnais between 913 and 1327, was Sire de Bourbon (or Seigneur de Bourbon). The first lord of Bourbonnais known by name was Adhémar (or Aymon I of Bourbon). Aymon\'s father was Aymar (894-953), sire of Souvigny, his only son with Ermengarde.Aymar lived during the reign of Charles the Simple who, in 913, gave him fiefs on the Allier River in which would become Bourbonnais. He acquired the castle of Bourbon (today Bourbon-l\'Archambault). Almost all early lords took the name d\'Archambaud, after the palace, but later the family became known as the \"House of Bourbon\".
The first House of Bourbon ended in 1196, with the death of Archambault VII, who had only one heir, Mathilde of Bourbon. She married Guy II of Dampierre, who added Montlucon to the possessions of the lords of Bourbon. The second house of Bourbon started in 1218, with Archambault VIII, son of Guy II and Mahaut, and brother of William II of Dampierre. He was followed by his son Archambaut IX, who died in Cyprus in 1249, during a crusade. The House of Burgundy then acquired Bourbonnais.
In 1272, Beatrice of Burgundy (1258-1310), Lady of Bourbon, married Robert de France (1256-1318), Count of Clermont, son of king Louis IX (Saint-Louis). Thus began the long-lasting House of Bourbon, which would provide the kings of France from Henry IV to Louis-Phillipe in 1848, when France abolished its monarchy.
The Bourbons had concluded an alliance with the royal power. They put their forces at the service of the king, thus benefitting from the geographic position of Bourbonnais, located between the royal fidemesne and the duchies of Aquitaine and Auvergne. This alliance, as well as the marriage of Béatrix de Bourgogne and Robert de France, aided the rise and prosperity of the province. In 1327, King Charles (le Bel) elevated Boubonnais to the status of a duchy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
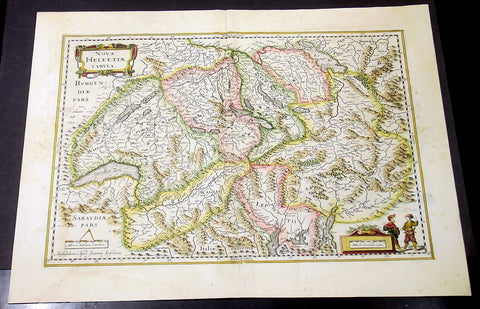
1636 Jansson Large Original Antique Map of Switzerland
- Title : Nova Helvetiae Tabula
- Date : 1636
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 41664
- Size: 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Switzerland was published in the rare 1636 English edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
As there were so few of these atlases published in English that maps from them are now understandably scarce.
The text running for two pages on the back of the map generally describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures.
The text running for two pages on the back of the map generally describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 14 1/2in (485mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss
Verso: - None
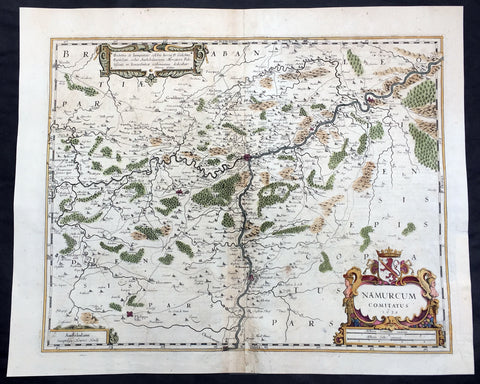
1636 Mercator Hondius Large Antique Map of Namur Region of Belgium, Huy & Meuse
- Title : Namurcum Comitatus 1632
- Date : 1636
- Size: 22in x 18in (570mm x 470mm)
- Ref #: 41622
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Belgium region of Namur - centering on the cities of Namur, Huy, Dinant and the Meuse River - was engraved in 1632 by Henricus Hondius - dated - and was published in the rare 1636 English edition of Mercator's Atlas, by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
As there were so few of these atlases published with English text on the verso that maps from them are now understandably scarce.
Background: Namur is a province of Wallonia, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders (clockwise from the West) on the Walloon provinces of Hainaut, Walloon Brabant, Liège and Luxembourg in Belgium, and on France. Its capital is the city of Namur.
The text running for two pages on the verso of this map describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (570mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin repaired
Plate area: - Centrefold re-joined with small loss to bottom border
Verso: - Centerfold re-joined, colour bleed through.
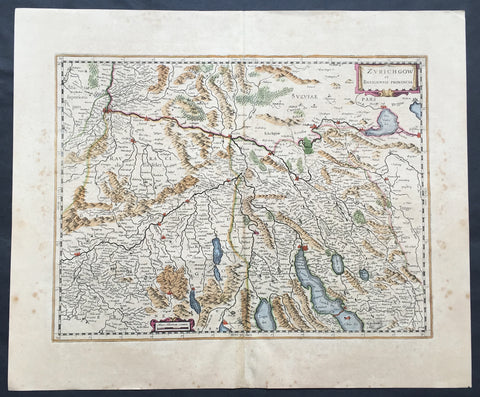
1636 Mercator Hondius Large Old, Antique Map Zurich & Basel Cantons, Switzerland
- Title : Zurichgow et Basiliensis Provincia
- Ref #: 41665
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1636
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the northern Cantons of Zurich & Basel, Switzerland was published in the rare 1636 English edition of Mercator's Atlas, by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
The map encompasses an area along the Rhine River north from Basel, south to Zurich & Lake Zurich, east into western Austria and as far west to the city of Solothurn.
As there were so few of these atlases published with English text on the verso, maps from them are now understandably scarce.
The text running for two pages on the verso of this map describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures.
Jodocus Hondius (1563 - 1612), one of the most notable engravers of his time, is known for his work in association with many of the cartographers and publishers prominent at the end of the sixteenth and the beginning of the seventeenth century.
In 1604 Hondius bought the plates of Mercator's Atlas which, in spite of its excellence, had not competed successfully with the continuing demand of Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
To meet this competition Hondius added about 40 maps to Mercator's original number and from 1606 published enlarged editions in many languages, still under Mercator's name but with his own name as publisher. These atlases have become known as the Mercator/Hondius series. The following year the maps were re-engraved in miniature form and issued as a pocket Atlas Minor.
After the death of Jodocus Hondius the Elder in 1612, work on the two atlases, folio and miniature, was carried on by his widow and sons, Jodocus II and Henricus, and eventually in conjunction with Jan Jansson in Amsterdam. In all, from 1606 onwards, nearly 50 editions with increasing numbers of maps with texts in the main European languages were printed. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (470mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning, light uplift along centerfold
Verso: - Bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss
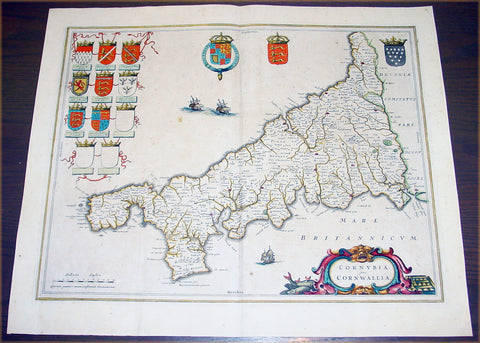
1637 Joan Blaeu Antique Map The English County of Cornwall
- Title : Cornubia sive Cornwallia
- Date : 1637
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 50606
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of English county of Cornwall was published in the 1637 German edition of Joan Blaeu's Atlas Novus.
Background: Blaeu is one of the most revered map makers of all time and it is easy to see why in this beautiful original map.
The high level of the topographical detail, the quality of the paper, the artistic professionalism of the engraving and the beauty of the original hand colouring combine to produce a work of art that is both functional and of exceptional beauty. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, red, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15 3/4in (500mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting & browning
Verso: - Light spotting & browning
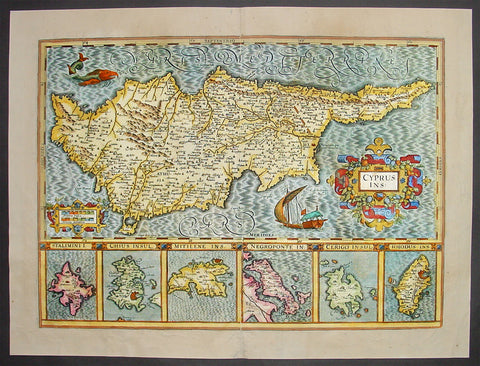
1638 Antique Map of Cyprus and 6 Greek Islands By Mercator-Hondius
- Title: Cyprus Ins
- Date: 1638
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Ref: 50675
- Size: 22in x 16 3/4in (560mm x 425mm)
This beautifully hand coloured original antique Map of Cyprus with below six inset maps of Greek islands: Stalimini, Chios, Mitilene, Negroponte, Cerigo, Rhodes, was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. Decorative cartouche, sailing ship and sea monster. The map is borrowed from Ortelius' map of Cyprus and is one of the most sought after of all early maps of Cyprus.
These original maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 16 3/4in (560mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14in (495mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing in margins
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Various weak creases on verso re-enforced with archival transparent tape
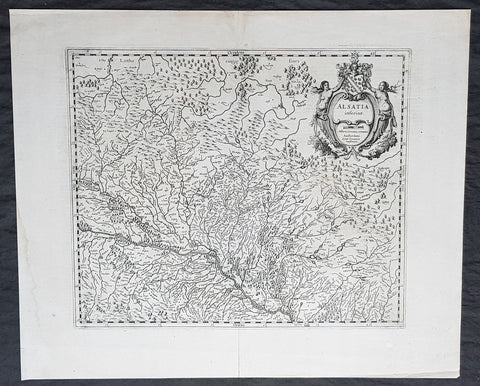
1638 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Alsace Region, France
- Title : Alsatia inferior..Per Gerardam Mercatorem Cum privilegio
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1638
- Ref #: 92839
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the French region of Alsace by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1638 German edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Alsace is a cultural and historical region in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland.
As in much of Europe, the prosperity of Alsace came to an end in the 14th century by a series of harsh winters, bad harvests, and the Black Death. These hardships were blamed on Jews, leading to the pogroms of 1336 and 1339. In 1349, Jews of Alsace were accused of poisoning the wells with plague, leading to the massacre of thousands of Jews during the Strasbourg pogrom. Jews were subsequently forbidden to settle in the town. An additional natural disaster was the Rhine rift earthquake of 1356, one of Europes worst which made ruins of Basel. Prosperity returned to Alsace under Habsburg administration during the Renaissance.
Holy Roman Empire central power had begun to decline following years of imperial adventures in Italian lands, often ceding hegemony in Western Europe to France, which had long since centralized power. France began an aggressive policy of expanding eastward, first to the rivers Rhône and Meuse, and when those borders were reached, aiming for the Rhine. In 1299, the French proposed a marriage alliance between Philip IV of Frances sister Blanche and Albert I of Germanys son Rudolf, with Alsace to be the dowry; however, the deal never came off. In 1307, the town of Belfort was first chartered by the Counts of Montbéliard. During the next century, France was to be militarily shattered by the Hundred Years War, which prevented for a time any further tendencies in this direction. After the conclusion of the war, France was again free to pursue its desire to reach the Rhine and in 1444 a French army appeared in Lorraine and Alsace. It took up winter quarters, demanded the submission of Metz and Strasbourg and launched an attack on Basel.
In 1469, following the Treaty of St. Omer [fr], Upper Alsace was sold by Archduke Sigismund of Austria to Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy. Although Charles was the nominal landlord, taxes were paid to Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor. The latter was able to use this tax and a dynastic marriage to his advantage to gain back full control of Upper Alsace (apart from the free towns, but including Belfort) in 1477 when it became part of the demesne of the Habsburg family, who were also rulers of the empire. The town of Mulhouse joined the Swiss Confederation in 1515, where it was to remain until 1798.
By the time of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century, Strasbourg was a prosperous community, and its inhabitants accepted Protestantism in 1523. Martin Bucer was a prominent Protestant reformer in the region. His efforts were countered by the Roman Catholic Habsburgs who tried to eradicate heresy in Upper Alsace. As a result, Alsace was transformed into a mosaic of Catholic and Protestant territories. On the other hand, Mömpelgard (Montbéliard) to the southwest of Alsace, belonging to the Counts of Württemberg since 1397, remained a Protestant enclave in France until 1793.
This situation prevailed until 1639, when most of Alsace was conquered by France to keep it out of the hands of the Spanish Habsburgs, who by secret treaty in 1617 had gained a clear road to their valuable and rebellious possessions in the Spanish Netherlands, the Spanish Road. Beset by enemies and seeking to gain a free hand in Hungary, the Habsburgs sold their Sundgau territory (mostly in Upper Alsace) to France in 1646, which had occupied it, for the sum of 1.2 million Thalers. When hostilities were concluded in 1648 with the Treaty of Westphalia, most of Alsace was recognized as part of France, although some towns remained independent. The treaty stipulations regarding Alsace were complex. Although the French king gained sovereignty, existing rights and customs of the inhabitants were largely preserved. France continued to maintain its customs border along the Vosges mountains where it had been, leaving Alsace more economically oriented to neighbouring German-speaking lands. The German language remained in use in local administration, in schools, and at the (Lutheran) University of Strasbourg, which continued to draw students from other German-speaking lands. The 1685 Edict of Fontainebleau, by which the French king ordered the suppression of French Protestantism, was not applied in Alsace. France did endeavour to promote Catholicism. Strasbourg Cathedral, for example, which had been Lutheran from 1524 to 1681, was returned to the Catholic Church. However, compared to the rest of France, Alsace enjoyed a climate of religious tolerance.
France consolidated its hold with the 1679 Treaties of Nijmegen, which brought most remaining towns under its control. France seized Strasbourg in 1681 in an unprovoked action. These territorial changes were recognised in the 1697 Treaty of Ryswick that ended the War of the Grand Alliance.
The year 1789 brought the French Revolution and with it the first division of Alsace into the départements of Haut- and Bas-Rhin. Alsatians played an active role in the French Revolution. On 21 July 1789, after receiving news of the Storming of the Bastille in Paris, a crowd of people stormed the Strasbourg city hall, forcing the city administrators to flee and putting symbolically an end to the feudal system in Alsace. In 1792, Rouget de Lisle composed in Strasbourg the Revolutionary marching song La Marseillaise (as Marching song for the Army of the Rhine), which later became the anthem of France. La Marseillaise was played for the first time in April of that year in front of the mayor of Strasbourg Philippe-Frédéric de Dietrich. Some of the most famous generals of the French Revolution also came from Alsace, notably Kellermann, the victor of Valmy, Kléber, who led the armies of the French Republic in Vendée and Westermann, who also fought in the Vendée.
At the same time, some Alsatians were in opposition to the Jacobins and sympathetic to the restoration of the monarchy pursued by the invading forces of Austria and Prussia who sought to crush the nascent revolutionary republic. Many of the residents of the Sundgau made pilgrimages to places like Mariastein Abbey, near Basel, in Switzerland, for baptisms and weddings. When the French Revolutionary Army of the Rhine was victorious, tens of thousands fled east before it. When they were later permitted to return (in some cases not until 1799), it was often to find that their lands and homes had been confiscated. These conditions led to emigration by hundreds of families to newly vacant lands in the Russian Empire in 1803–4 and again in 1808. A poignant retelling of this event based on what Goethe had personally witnessed can be found in his long poem Hermann and Dorothea.
In response to the hundred day restoration of Napoleon I of France in 1815, Alsace along with other frontier provinces of France was occupied by foreign forces from 1815 to 1818, including over 280,000 soldiers and 90,000 horses in Bas-Rhin alone. This had grave effects on trade and the economy of the region since former overland trade routes were switched to newly opened Mediterranean and Atlantic seaports.
The population grew rapidly, from 800,000 in 1814 to 914,000 in 1830 and 1,067,000 in 1846. The combination of economic and demographic factors led to hunger, housing shortages and a lack of work for young people. Thus, it is not surprising that people left Alsace, not only for Paris – where the Alsatian community grew in numbers, with famous members such as Baron Haussmann – but also for more distant places like Russia and the Austrian Empire, to take advantage of the new opportunities offered there: Austria had conquered lands in Eastern Europe from the Ottoman Empire and offered generous terms to colonists as a way of consolidating its hold on the new territories. Many Alsatians also began to sail to the United States, settling in many areas from 1820 to 1850. In 1843 and 1844, sailing ships bringing immigrant families from Alsace arrived at the port of New York. Some settled in Texas and Illinois, many to farm or to seek success in commercial ventures: for example, the sailing ships Sully (in May 1843) and Iowa (in June 1844) brought families who set up homes in northern Illinois and northern Indiana. Some Alsatian immigrants were noted for their roles in 19th-century American economic development. Others ventured to Canada to settle in southwestern Ontario, notably Waterloo County.
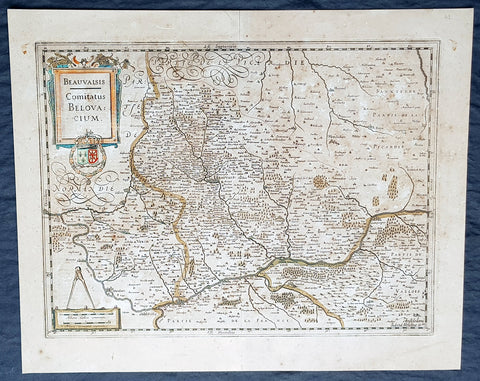
1638 Gerard Mercator & Henricus Hondius Antique Map of Beauvais Region, France
- Title : Beauvaisis Comitatus Belovacium
- Size: 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1638
- Ref #: 50178
Description:
This original copper plate engraved antique map of the Beauvais region of Northern France - centering on the city of Beauvais & the Oise River running through the cities of Noyon, Compiègne, Creil by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the early 1638 Latin edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604, and continued to be published until the end of the 1630s by Henricus Hondius, when some of the plates were re-engraved and updated with the help of Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 17in (530mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (475mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
Beauvais is a city and commune in northern France. It serves as the capital of the Oise département, in the Hauts-de-France region. Beauvais is located approximately 75 kilometres from Paris.
Beauvais was known to the Romans by the Gallo-Roman name of Caesaromagus (magos is Common Celtic for field). The post-Renaissance Latin rendering is Bellovacum from the Belgic tribe the Bellovaci, whose capital it was. In the ninth century it became a countship, which about 1013 passed to the bishops of Beauvais, who became peers of France from the twelfth century. At the coronations of kings the Bishop of Beauvais wore the royal mantle and went, with the Bishop of Langres, to raise the king from his throne to present him to the people.
De Bello Gallico II 13 reports that as Julius Caesar was approaching a fortified town called Bratuspantium in the land of the Bellovaci, its inhabitants surrendered to him when he was about 5 Roman miles away. Its name is Gaulish for place where judgements are made, from *bratu-spantion. Some say that Bratuspantium is Beauvais. Others theorize that it is Vendeuil-Caply or Bailleul sur Thérain.
From 1004 to 1037, the Count of Beauvais was Odo II, Count of Blois.
In a charter dated 1056/1060, Eudo of Brittany granted land in pago Belvacensi (Beauvais, Picardy) to the Abbey of Angers Saint-Aubin
In 1346 the town had to defend itself against the English, who again besieged it in 1433. The siege which it endured in 1472 at the hands of the Duke of Burgundy, was rendered famous by the heroism of the towns women, under the leadership of Jeanne Hachette, whose memory is still celebrated by a procession on 27 June (the feast of Sainte Angadrême), during which women take precedence over men.
An interesting hoard of coins from the High Middle Ages became known as the Beauvais Hoard, because some of the British and European coins found with the lot were from the French abbey located in Beauvais. The hoard, which contained a variety of rare and extremely rare Anglo-Norman pennies, English and foreign coins, was reputed to have been found in or near Paris.
1638 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of the Principality of Dombes, Ain, SE France
- Title : La Principaute De Dombes
- Ref #: 50239
- Size: 22in x 19in (560mm x 480mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Principality of Dombes of south-eastern France - now a part of the Ain Dept. centering on the cities of Mascon & Lyon on the Saone and Rhone Rivers - was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas published by Henricus Hondius.& Jan Jansson.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (460mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
The Dombes is an area in south-eastern France, once an independent municipality, formerly part of the province of Burgundy, and now a district comprised in the department of Ain, and bounded on the west by the Saône River, by the Rhône, on the east by the Ain and on the north by the district of Bresse.
The Dombes once formed part of the kingdom of Arles. In the 11th century, when the kingdom began to break up, the northern part of the Dombes came under the power of the lords of Bâgé, and in 1218, by the marriage of Marguerite de Baugé with Humbert IV of Beaujeu, passed to the lords of Beaujeu. The southern portion was held in succession by the lords of Villars and of Thoire. Its lords took advantage of the excommunication of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor to assert their complete independence of the Holy Roman Empire.
In 1400, Louis II, Duke of Bourbon, acquired the northern part of the Dombes, together with the lordship of Beaujeu, and two years later bought the southern part from the sires de Thoire, forming the whole into a new sovereign principality of the Dombes, with Trévoux as its capital.
The principality was confiscated by King Francis I of France in 1523, along with the other possessions of the Constable de Bourbon, was granted in 1527 to the queen-mother, Louise of Savoy, and after her death was held successively by kings Francis I, Henry II and Francis II, and by Catherine de\' Medici. In 1561 it was granted to Louis, duc de Montpensier, by whose descendants it was held till, in 1682, Anne Marie Louise of Orléans, the duchess of Montpensier, gave it to Louis XIV\'s bastard, the Duke of Maine, as part of the price for the release of her lover Lauzun.
The eldest son of the duke of Maine, Louis-Auguste de Bourbon (1700–1755), prince of Dombes, served in the army of Prince Eugene of Savoy against the Turks (1717), took part in the War of the Polish Succession (1733–1734), and in that of the Austrian Succession (1742-1747). He was made colonel-general of the Swiss regiment, governor of Languedoc and master of the hounds of France. He was succeeded, as prince of Dombes, by his brother the count of Eu, who in 1762 surrendered the principality to the crown. The little principality of Dombes showed in some respects signs of a vigorous life; the princes mint and printing works at Trévoux were long famous, and the college at Thoissey was well endowed and influential.
1638 Jan Jansson Antique Map of The Picardy Region of Northern France - Calais
- Title : Picardia Vera Et Inferior
- Ref #: 50241
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Picardy Region of Northern France - centering on the city of Cambray, NW to Calais, South to Soissons and east to Charleville - was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15 3/4in (545mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Picardy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of Northern France and now part of the new region Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie.
From the 5th century the area was part of the Frankish Empire, and in the feudal period it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois,Vermandois, and Laonnois. According to the 843 Treaty of Verdun the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France.
The name Picardy (which may have referred to a Frankish tribe of picards or pike-bearers) was not used until the 12th or 13th century. During this time, the name applied to all lands where the Picard language was spoken, which included all the territories from Paris to the Netherlands. In the Latin Quarter of Paris, people identified a Picard Nation (Nation Picarde) of students at Sorbonne University, most of whom actually came from Flanders. During the Hundred Years\' War, Picardy was the centre of the Jacquerie peasant revolt in 1358.
From 1419 onwards, the Picardy counties (Boulogne, Ponthieu, Amiens, Vermandois) were gradually acquired by the Burgundian duke Philip the Good, confirmed by King Charles VII of France at the 1435 Congress of Arras. In 1477, King Louis XI of France led an army and occupied key towns in Picardy. By the end of 1477, Louis would control all of Picardy and most of Artois.
In the 16th century, the government (military region) of Picardy was created. This became a new administrative region of France, separate from what was historically defined as Picardy. The new Picardy included the Somme département, the northern half of the Aisne département, and a small fringe in the north of the Oise département.
In 1557, Picardy was invaded by Hapbsburg forces under the command of Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy. After a seventeen-day siege, St. Quentin would be ransacked while Noyon would be burned by the Habsburg army.
In the 17th century, an infectious disease similar to English sweat originated from the region and spread across France. It was called Suette des picards or Picardy sweat.
Sugar beet was introduced by Napoleon I during the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century, in order to counter the United Kingdom, which had seized the sugar islands possessed by France in the Caribbean. The sugar industry has continued to play a prominent role in the economy of the region.
One of the most significant historical events to occur in Picardy was the series of battles fought along the Somme during World War I. From September 1914 to August 1918, four major battles, including the Battle of the Somme, were fought by British, French, and German forces in the fields of Northern Picardy. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
1638 Jan Jansson Large, Old Antique Map of Africa Morocco, Gibraltar & NW Africa
- Title : Fezzae et Marocchi Regna Africae Celeberrima
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92950
- Size: 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
Description:
This fine large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Morocco & the Straits of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean was published by Jan Jansson in the 1638 Latin edition of Atlas Novus.
Background: Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 19 1/2in (600mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in left margin, reapir to top and bottom margin not affecting the image
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1638 Jansson Large Antique Map of The Netherlands & Belgium
- Title : Belgii Veteris Typus...Abrahami Ortelii...Petrus Karius
- Ref #: 61036
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of The Netherlands & Belgium was engraved by Peter Karius and was published in the 1638 Latin edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (480mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing in bottom margin
Plate area: - Centerfold Re-joined
Verso: - Soiling
1638 Jansson Old, Antique Map of the Dauphine Region of France, Grenoble
- Title : Nova et acurrata Descriptio Delphinatus vulgo Dauphine
- Ref #: 50244
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Dauphine region of southern France - centering on the city of Grenoble - with the Rhone River to the west and north with Savoy & Piedmont to the east was published by Jan Jansson in the 1638 edition ofAtlas Novus. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/4in (520mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1638 Jansson Old, Antique Map of the Turkish Empire, Saudi Arabia, Middle East
- Title : Turcicum Imperium
- Ref #: 61009
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautiful, old original antique map* of The Turkish Empire in Europe, Africa & Asia centering on Saudi Arabia by Jan Jansson was published in the 1638 Latin edition for Mercator's Atlas by both Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
Background: This is the standard 17th century view of the Turkish Empire, including the Balkans in south-eastern Europe, the North African littoral, the Levant and the Arabian Peninsula in addition to the area of Modern Turkey & Persia.
Much of the place name information on this map is derived from the maps published in 1561 by the Italian mapmaker, Giacomo Gastaldi, whose maps exercised great influence over later European mapmakers, throughout the 17th century.
Formidable though the barrier presented by the Turkish Empire in the Near East was, by the early years of the 17th century it was beginning to show signs of decadence and weakness, especially after the defeat of the Turkish navy at the hands of the combined Christian forces of Western Europe at the battle of Lepanto in 1571, from which Turkish naval power never fully recovered.
Centered on the palace of the Sultans at Constantinople, the administration of the empire was passed down through local rulers, the Beys, Deys and Pashas, who never lost an opportunity to enrich themselves and to develop often considerable powers of their own.
Further defeats of the Turks occurred in 1669 when Candia (Crete) was taken by the Venetians, and in 1683 when they suffered a humiliating defeat outside Wien (Vienna) at the north-western extremity of European Turkey. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early & Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Several small repairs to margins, no loss
Plate area: - Centerfold re-joined light uplift along centerfold, light age toning
Verso: - Repairs as noted
1638 Joan Blaeu & Abraham Ortelius Antiue Map of France
- Title : Gallia Vetus...Abrah Ortelii
- Date : 1638
- Size: 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70606
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of France, after Abraham Ortelius, was published by Joan Blaeu in the 1638 French edition of Atlas Nouvs,.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1638 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of America - Americae nova Tabula
- Title : Americae nova Tabula Auct: Guiljesino Blaeuw
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 50685
- Size : 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 450mm)
Description:
This magnificent, classic hand coloured original antique map of America 2nd State - the quintessential image of 17th America - was published in the 1638 French edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus. This map is in wonderful condition with a few minor repairs as mentioned below.
General Condition:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original color
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic & beautiful
Paper size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 450mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 16 1/2in (555mm x 415mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repair to centerfold, no loss.
Plate area: - Small professional repair to below Atlantic monster. Center-fold creases & re-joined at bottom, slight separation
Verso: - Creasing and restoration to center-fold, top & left margin, no loss
Background:
Originally issued by Joan Blaeus father, Willem, as early as 1617, this general map of the Americas was one of the longest lived plates in the atlas, having been used as an atlas map since 1630.
Here is the general seventeenth century European view of the Western Hemisphere: the delineation of the coasts and the nomenclature of the Pacific as well as the Atlantic coasts are basically Spanish in origin and follow the maps of the Fleming Abraham Ortelius and his countryman Cornelis Wytfliet. To these, Willem Blaeu inserted, on the east coast, the English names given by the Roanoke colonists in Virginia, and by Martin Frobisher, John Davis and Henry Hudson in the far north. In Florida and along the St Lawrence, Blaeu added the names given by the French settlers, almost the only memorials to their ill-fated venture in Florida during the latter part of the sixteenth century.
When Blaeu first made his map in the early years of the seventeenth century, Europeans still had no real knowledge of the nature of the Mississippi system. From the expedition journals of Hernando de Soto (1539 - 1543) they had inferred an extensive range of mountains trending eastwards to the north of the Gulf of Mexico in la Florida apparently precluding a great river system. The Great Lakes were as yet unknown although by the time Blaeu issued this map in its atlas form in the Huron region together with the hearsay accounts from Coral Indians were becoming well known through his 1632 map of the region. Evidently, this appears to have been unknown to Blaeu at the time, but surprisingly, he never incorporated the information on later printings of the map. The same applies to Manhattan and Long Island as well, despite the fact that only a short distance from Amsterdam, the Leiden academic Johannes D Late had published the first edition of his monumental work on the Americas which provided source material for any number of maps of the Americas throughout the remainder of the century and beyond.
In common with the other general continental maps in Blaeus atlas's, he has provided perspective plans or views of settlements in the Americas, including Havana, St Domingo, Cartagena, Mexico, Cusco, Potisi, I.la Moca in Chile, Rio Janeiro and Olianda in Pharnambucco, as well as the vignette illustrations of native figures taken from the accounts of John White (Virginia) or Hans Staden (Brazil) and others. (Ref: Burden; RGS; Koeman; Tooley)
1638 Joducus Hondius Antique Map of the Lorraine Region of NE France - Grand Est
- Title : Lorraine Vers Le Midy
- Ref #: 50250
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the ancient Lorraine region of France - centering on the Moselle River with the city of Nancy to the north Faucogney-et-la-Mer to the south & the Meuse River to the west - by Gerard Mercator was published by Jodocus Hondius in the 1638 edition of Mercators Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 1/2in (545mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (500mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Lorraine is a cultural and historical region in north-eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Lorraines name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia, which in turn was named for either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. It later was ruled as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766.
1638 Joducus Hondius Antique Map Poitou Region, France, Huguenots Fled to Acadia
- Title : Poictou Pictaviensis Comitatus...Jodocus Hondius
- Ref #: 41644
- Size: 22 1/4in x 18 1/2in (570mm x 470mm)
- Date : 1636
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Poitou region of SW France centering on the cities of Nantes and Rochelle was published in the rare 1636 English edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas, published later by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
As there were so few of these atlases published with English text on the verso that maps from them are now understandably scarce.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/4in x 18 1/2in (570mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Centrefold re-joined with light uplift
Plate area: - Centrefold re-joined with light uplift, light creasing
Verso: - Light creasing, small repair bottom left not affecting the image
Background:
Poitou was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. The main historical cities are Poitiers Châtellerault (France\'s kings establishment in Poitou), Niort, La Roche-sur-Yon, Thouars, and Parthenay.
The region of Poitou was called Thifalia (or Theiphalia) in the sixth century.
There is a marshland called the Poitevin Marsh (French Marais Poitevin) on the Gulf of Poitou, on the west coast of France, just north of La Rochelle and west of Niort.
By the Treaty of Paris of 1259, King Henry III of England recognized his loss of continental Plantaganet territory to France (including Normandy, Maine, Anjou, and Poitou).
During the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries Poitou was a hotbed of Huguenot (French Calvinist) activity among the nobility and bourgeoisie and was severely affected by the French Wars of Religion (1562–1598).
Many of the Acadians who settled in what is now Nova Scotia beginning in 1604, and later in New Brunswick, came from the region of Poitou. After the Acadians were deported by the British beginning in 1755, some of them eventually took refuge in Québec. A large portion of these refugees were also deported to Louisiana in 1785 and eventually became known as Cajuns (from Acadians).
After the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685, a strong Counter-Reformation effort was made by the French Roman Catholic Church; in 1793, this was partially responsible for the three-year-long open revolt against the French Revolutionary Government in the Bas-Poitou (Département of Vendée). Indeed, during Napoleon’s Hundred Days in 1815, the Vendée stayed loyal to the Restoration Monarchy of King Louis XVIII and Napoleon dispatched 10,000 troops under General Lamarque to pacify the region.
As noted by Lampert, The persistent Huguenots of 17th Century Poitou and the fiercely Catholic rebellious Royalists of what came be the Vendée of the late 18th Century had ideologies very different, indeed diametrically opposed to each other. The common thread connecting both phenomena is a continuing assertion of a local identity and opposition to the central government in Paris, whatever its composition and identity. (...) In the region where Louis XIII and Louis XIV had encountered stiff resistance, the House of Bourbon gained loyal and militant supporters exactly when it had been overthrown and when a Bourbon loyalty came to imply a local loyalty in opposition to the new central government, that of Robespierre
1638 Willem Blaeu Antique Map of Mansfeld Land, in SW Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
- Title : Mansfelda Comitatus
- Ref #: 70078
- Size: 22 1/2in x 17in (570mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the ancient region of Mansfeld Land located in the in southwestern region of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany - centering on the city of Mansfeld - by was published in the 1638 Latin edition edition of Willem Blaeus Atlas Novus.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 17in (570mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 16 1/4in (495mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mansfeld Land is a region in the southwestern corner of the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. The region derives its name from the counts of Mansfeld, who ruled this region for about 1,000 years.
The House of Mansfeld, whose members belonged to the Saxon nobility and served as counts in the Hassegau, was first documented in a 973 deed. The counts built Mansfeld Castle, whose foundations date back to the late 11th century, when one Hoyer of Mansfeld served as field marshal to Emperor Henry V. The first reference of the fortress coincides with the extinction of the elder line in 1229. The estates were inherited by the Lords of Querfurt, who also adopted the comital title, calling themselves Counts of Mansfeld from that time on.
The settlement of Mansfeld received town privileges in 1400, and grew through the development of copper and silver mining, an activity in which Hans Luder from Möhra, father to Martin Luther and Mansfeld citizen from 1484, was employed as a master smelter. Luthers family had arrived into a modest prosperity, he himself attended the local school between 1488 and 1496. The building known as Luther\'s School had to be torn down and rebuilt in 2000 due to structural problems. His parents house is preserved and today a museum. Luther also acted as an altar server at the St George parish church.
The Counts of Mansfeld had already lost Imperial immediacy in 1580. When the comital line finally became extinct in 1780, the estates around Mansfeld were incorporated into the Prussian Duchy of Magdeburg. The town retained the status of an independent city (Immediatstadt), it was temporarily part of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Westphalia and after the 1815 Congress of Vienna belonged to the Prussian Province of Saxony.
1639 Henricus Hondius Antique 1st Edition Map of North America California Island
- Title : America Septentrionalis
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43161-1
- Size: 23in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique rare 1st state map of North America, with California as an Island, by Henricus Hondius was published in the 1639 French edition.
There were only 3 publications of this map by Hondius in the 1630s & 40s with Jan Jansson replacing the map with his signature in 1641.
The now seldom seen first state of an important, early Dutch map of North America. It one of the first Dutch atlas maps to show California as an island, preceded only by the Hondius Hondius world map of 1633. A note on the map recounting the story of the origin of the California-as-an-island refers to a Dutch captain who obtained a map of California depicted as an island from a captured Spanish ship. The note even provides the dimensions of the island. The Hondius map was an important conduit for bringing the island myth into the cartographic mainstream. Further, Tooley noted the map was also first attempt in Holland to add lakes connected to the St. Lawrence. One of these lakes on the map is in the approximate shape and position of Lake Ontario.
This was also one of a very few, early Dutch maps specifically of North America (as opposed to the entire Western Hemisphere). Aside from the rare De Jode map of 1593, this is the only folio-sized map of North America produced during the entire Dutch Golden Age.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (500mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin extended from plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Henricus Hondius beautifully engraved map of North America had significant influence in perpetuating the theory of California as an island. This was of the influence of his powerful Dutch publishing house with no earlier maps representing California as an island maps having such a wide audience. The 1630s were a decade of constant development in the houses of Blaeu, Hondius & Jansson. It is interesting to note that Blaeu never produced a single sheet map of North America; producing a map of just the whole American continent, first produced in 1617. Also during this decade Joannes Janssonius became an active partner of Hondius, and although this map does not bear his mark, it is believe it was his creation, based on the very similar South American, at the same time, displaying his name.
Cartographically this map is a careful composition of many different sources. The depiction and nomenclature of the west, along with that of California, derive directly from the Henry Briggs The North Part of America, 1625. A legend placed strategically over the north-west coastline offers the opportunity to discontinue a coastline least understood. An unnamed lake still feeds a Rio del Norto flowing incorrectly south-west into what should be the headwaters of the Gulf of California. On the east bank of this river is Real de Nueua Mexico, or Santa Fe. The Gulf of Mexico and the Florida peninsula originate from the Hessel Gerritsz chart of c.1631.
The east coast, however, is harder to define; the south-east appears to be quite generic in form. It is the area north of here that does not appear to be from a particular source. The Chesapeake Bay area is defined in about as much detail as the scale and style of the map will allow, Iames Towne being clearly identified. NOVUM BELGIUM is unlike any other before it, the area between the Zuitt Reuier (Delaware River) and the Noort R (Hudson River) being greatly elongated on a north-east to south-west axis. New Amsterdam is curiously not designated although Fort Orange is present. For New England just a select few names have been chosen from John Smiths map of the area, 1616. The Gulf of St. Lawrence appears to follow de Laet more than Champlain. The latter is used to depict a single great Lake; however, its name, Lac des Iroquois, is borrowed from one nearby. Interestingly the author chose not use Champlains more recent 1632 map but the earlier 1612 Carte Geographique De La Nouvelle France; To avoid unknown territory he does not venture the river system further west, unlike Champlain. Along the Atlantic coast of Labrador we find for the first time much Dutch Nomenclature, reflecting their increased whaling activities in these waters. Hudson Bay is clearly derived from Briggs, 1625, except for the west coast where he introduces the cartography of Thomas James, 1633. The addition of a fox here could be seen as a veiled reference to Luke Foxe, whose own map of the previous year bears just such an animal.
1639 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of France
- Title : Galliae supera omnes in hac...auctore Henrico Hondio
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 17039
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of France was published by Henricus Hondius & Jan Jansson in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/2in (500mm x 375mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1639 Henricus Hondius Large Antique Map of South America - Beautiful
- Title : Americae Pars Meridionalis Henrici Hony...
- Ref #: 43162
-
Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1639
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique copper plate engraved antique map of South America by Henricus Hondius was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Beautiful large map, the second by Hondius, with original hand colouring and strong sturdy paper.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 18 1/4in (545mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin extended from plate-mark, small repair to bottom margin
Plate area: - Offsetting
Verso: - Bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss
Background:
Between 1452 and 1493, a series of papal bulls (Dum Diversas, Romanus Pontifex, and Inter caetera) paved the way for the European colonization and Catholic missions in the New World. These authorized the European Christian nations to \"take possession\" of non-Christian lands and encouraged subduing and converting the non-Christian people of Africa and the Americas.
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime powers of that time, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas in the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west. Through the treaty they agreed that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries. The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (which is now known to include most of the South American soil), would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. Because accurate measurements of longitude were not possible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas, Christopher Columbus sailed near the Orinoco Delta and then landed in the Gulf of Paria (Actual Venezuela). Amazed by the great offshore current of freshwater which deflected his course eastward, Columbus expressed in his moving letter to Isabella I and Ferdinand II that he must have reached heaven on Earth (terrestrial paradise):
Great signs are these of the Terrestrial Paradise, for the site conforms to the opinion of the holy and wise theologians whom I have mentioned. And likewise, the [other] signs conform very well, for I have never read or heard of such a large quantity of fresh water being inside and in such close proximity to salt water; the very mild temperateness also corroborates this; and if the water of which I speak does not proceed from Paradise then it is an even greater marvel, because I do not believe such a large and deep river has ever been known to exist in this world.
Beginning in 1499, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it into colonies.
European diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles and typhus) to which the native populations had no resistance were the overwhelming cause of the depopulation of the Native American population. Cruel systems of forced labor (such as encomiendas and mining industry\'s mita) under Spanish control also contributed to depopulation. Lower bound estimates speak of a decline in the population of around 20–50 per cent, whereas high estimates arrive at 90 per cent.[42] Following this, African slaves, who had developed immunity to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their American subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end. However, most initial attempts at this were only partially successful; American groups simply blended Catholicism with their traditional beliefs. The Spaniards did not impose their language to the degree they did their religion. In fact, the missionary work of the Roman Catholic Church in Quechua, Nahuatl, and Guarani actually contributed to the expansion of these American languages, equipping them with writing systems.
Eventually the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a Mestizo class. Mestizos and the Native Americans were often forced to pay unfair taxes to the Spanish government (although all subjects paid taxes) and were punished harshly for disobeying their laws. Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers. This included a great number of gold and silver sculptures, which were melted down before transport to Europe.
In 1616, the Dutch, attracted by the legend of El Dorado, founded a fort in Guayana and established three colonies: Demerara, Berbice, and Essequibo.
In 1624 France attempted to settle in the area of modern-day French Guiana, but was forced to abandon it in the face of hostility from the Portuguese, who viewed it as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas. However French settlers returned in 1630 and in 1643 managed to establish a settlement at Cayenne along with some small-scale plantations.
Since the sixteenth century there were some movements of discontent to Spanish and Portuguese colonial system. Among these movements, the most famous being that of the Maroons, slaves who escaped their masters and in the shelter of the forest communities organized free communities. Attempts to subject them by the royal army was unsuccessful, because the Maroons had learned to master the South American jungles. In a royal decree of 1713, the king gave legality to the first free population of the continent: Palenque de San Basilio in Colombia today, led by Benkos Bioho. Brazil saw the formation of a genuine African kingdom on their soil, with the Quilombo of Palmares.
Between 1721 and 1735, the Revolt of the Comuneros of Paraguay arose, because of clashes between the Paraguayan settlers and the Jesuits, who ran the large and prosperous Jesuit Reductions and controlled a large number of Christianized Indians.
Between 1742 and 1756, was the insurrection of Juan Santos Atahualpa in the central jungle of Peru. In 1780, the Viceroyalty of Peru was met with the insurrection of curaca Condorcanqui or Tupac Amaru II, which would be continued by Tupac Catari in Upper Peru.
In 1763, the African Cuffy led a revolt in Guyana which was bloodily suppressed by the Dutch. In 1781, the Revolt of the Comuneros (New Granada), an insurrection of the villagers in the Viceroyalty of New Granada, was a popular revolution that united indigenous people and mestizos. The villagers tried to be the colonial power and despite the capitulation were signed, the Viceroy Manuel Antonio Flores did not comply, and instead ran to the main leaders José Antonio Galán. In 1796, Essequibo (colony) of the Dutch was taken by the British, who had previously begun a massive introduction of slaves.
During the eighteenth century, the figure of the priest, mathematician and botanist José Celestino Mutis (1732–1808), was delegated by the Viceroy Antonio Caballero y Gongora to conduct an inventory of the nature of the Nueva Granada, which became known as the Botanical Expedition, which classified plants, wildlife and founded the first astronomical observatory in the city of Santa Fé de Bogotá.
On August 15, 1801, the Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt reached Fontibón where Mutis, and began his expedition to New Granada, Quito. The meeting between the two scholars are considered the brightest spot of the botanical expedition. Humboldt also visited Venezuela, Mexico, United States, Chile, and Peru. Through his observations of temperature differences between the Pacific Ocean between Chile and Peru in different periods of the year, he discovered cold currents moving from south to north up the coast of Peru, which was named the Humboldt Current in his honour.
Between 1806 and 1807, British military forces tried to invade the area of the Rio de la Plata, at the command of Home Riggs Popham and William Carr Beresford, and John Whitelocke. The invasions were repelled, but powerfully affected the Spanish authority
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1639 Henricus Hondius Original Antique Map of the German State of Thuringia
- Title : Thuringia Lantgraviatus
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 23434
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of the German State of Thuringia or Thüringen in central Germany was published by Henricus Hondius in the 1639 edition of Mercators Atlas.
The map centers on the city of Erfurt and alos includes major cities of Gotha, Weimar, Schwartzburg, Halle, Jena, Mulhausen and others
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (520mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold,
Verso: - Small repair to bottom left margin
Background:
Named after the Thuringii tribe who occupied it around AD 300, Thuringia came under Frankish domination in the 6th century.
Thuringia became a landgraviate in 1130 AD. After the extinction of the reigning Ludowingian line of counts and landgraves in 1247 and the War of the Thuringian Succession (1247–1264), the western half became independent under the name of \"Hesse\", never to become a part of Thuringia again. Most of the remaining Thuringia came under the rule of the Wettin dynasty of the nearby Margraviate of Meissen, the nucleus of the later Electorate and Kingdom of Saxony. With the division of the house of Wettin in 1485, Thuringia went to the senior Ernestine branch of the family, which subsequently subdivided the area into a number of smaller states, according to the Saxon tradition of dividing inheritance amongst male heirs. These were the \"Saxon duchies\", consisting, among others, of the states of Saxe-Weimar, Saxe-Eisenach, Saxe-Jena, Saxe-Meiningen, Saxe-Altenburg, Saxe-Coburg, and Saxe-Gotha; Thuringia became merely a geographical concept.
Thuringia generally accepted the Protestant Reformation, and Roman Catholicism was suppressed as early as 1520; priests who remained loyal to it were driven away and churches and monasteries were largely destroyed, especially during the German Peasants\' War of 1525. In Mühlhausen and elsewhere, the Anabaptists found many adherents. Thomas Müntzer, a leader of some non-peaceful groups of this sect, was active in this city. Within the borders of modern Thuringia the Roman Catholic faith only survived in the Eichsfeld district, which was ruled by the Archbishop of Mainz, and to a small degree in Erfurt and its immediate vicinity.
1639 Hondius & Mercator Antique Map Mughal Empire Northern India, Tibet, Nepal
- Title : Magni Mogolis Imperium
- Date : 1639
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 43148
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique and very important map of Mughal Empire of Northern India, Tibet, Nepal and central Asia by Henricus Hondius was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerardi Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas.
Background: This map centers on the Mughal capital of Agra, with the map covering, roughly, from Kabul to Orissa and Deccan, and from Persia to Bengal. It depicts the empire prior to the conquest of Orissa and Deccan, most likely during the reign of Shah Jahan, of Taj Mahal fame. Relief is shown pictorially. An elaborate title cartouche appears in the upper left quadrant. The map is embellished with images of tigers, elephants, caravans, and galleons.
There is much of interest. In particular, is the map detailed breakdown of the caravan network between Gujarat and Agra, between Agra and the desert outpost of Jaisalmer, and between Agra and the Silk Road center of Kabul. While the map does not show roads, for surely none as such existed at the time, it does show the network of towns, waystations and caravanserai built to support the bustling trade system.
The apocryphal Lake of Chiamay appears just north of the Bay of Bengal as the source of four important Southeast Asian river systems including the Irrawaddy, the Dharla, the Chao Phraya, and the Brahmaputra. The curious Lake of Chiamay (also called Chiam-may or Chian-may), roughly located in the area of Assam but sometimes as far north as Tibet and China, began to appear in maps of this region as early as the 16th century and persisted well into the mid 18th century. Its origins are unknown but may originate in a lost 16th century geography prepared by the Portuguese scholar Jao de Barros. It was speculated to be the source of five important Southeast Asian River systems and was mentioned in the journals of Sven Hedin. There are even records that the King of Siam led an invasionary force to take control of the lake in the 16th century. Nonetheless, the theory of Lake Chiamay was ultimately disproved and it disappeared from maps entirely by the 1760s.
There are two states of this map, the present example being the first state, first issued in 1638 by Henricus Hondius, and the second state a few years later in 1641 by Jan Jannson. With the exception of the signature imprint, the plates are identical. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 14 1/2in (500mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom centerfold re-joined.
Plate area: - Light colour offset
Verso: - Bottom centerfold re-joined
1639 Hondius & Mercator Antique Map of Morea The Greek Peloponnese
- Title : Morea olim Peloponnesus
- Date : 1639
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 480mm)
- Ref #: 43164
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Greek Peloponnese was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerardi Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Background: The Peloponnese Peninsula had played a central role in both history and culture since Homeric times. The large peninsula is connected to mainland Greece only by the narrow Isthmus of Corinth, and jutting deeply southwards, it lay along the crossroads of shipping in the Mediterranean and Aegean seas. Many places still familiar today are labelled on the map, including 'Coryato' (Corinth), 'Napoli' (Nafplio), Patras and 'Cithera' (Cythera), while Athens appears in Attica, to the northeast.
Prominenty featured in the upper part of the map is the Gulf of Lepanto in 1571, the site of an epic naval battle between the forces of the Ottoman Empire and the combined forces of various European states. The outcome was a historical turning point, as it ensured Western maritime supremacy over the Ottomans for decades to come. Even in 1619, almost half a century later, when the present map was printed, the Battle of Lepanto was still top of mind. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss
1639 Hondius Antique Map of Australia, East Indies, India to China - Duyfken
- Title : India quae Orientalis dicitur et Insulae Adiacentes
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43140
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19 1/4in (570mm x 485mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique and very important map of the East Indies, India, SE Asia, China, Japan Philippines and Australia - the first to map the west coast of Cape York Peninsular northern Queensland as well as parts of the SW coast of Western Australia, with place names, was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
An important Dutch map of South East Asia, noteworthy for including the discoveries made in New Guinea and northern Queensland, Australia by the Dutch vessel Duyfken in 1605-06. Under the command of Willem Janzoon, the Duyfken explored the eastern shore of the Gulf of Carpentaria, just below the Cape York Peninsula, a venture which was famously the first recorded European contact with Australia.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/4in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light offsetting, light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
This map of the East Indies extending from India to Japan and south to Australia, shows some of the Dutch discoveries along the West Australian coastline like the Swan River, Nassau River, Coen River and the Batavia River borrows heavily from the exact map by Joan Blaeu. On the eastern part lower right of the map is a small section of Cape York Peninsular. This map is one of the first printed maps to show any part of the Australian coastline. It continued to be an issued unchanged from 1635 up until the 1660's, long after some of the information it contained had been superseded. This was despite the fact that Joan Blaeu as cartographer to the Dutch East India Company from 1638 to 1673 had access to the latest information concerning the extension of the Dutch maritime power in the East Indies, publishing the results of such discoveries (especially of Australia) on large World maps, such as that of 1648. In other words, atlas map's of the East Indies and part of Australia ignores the results of Abel Tasman's discoveries made during the voyage of 1642-44. In 1642, Tasman was appointed commander of an expedition to the South Seas, during which he discovered the Island later named after him as well as part of the coast of New Zealand. His voyage 1644 coasted along the shore of the Gulf of Carpentaria and along the northern coast of Australia as far as the Tropic of Capricorn.
Tasman's discoveries were published very soon afterwards on Blaeu's large World Maps, rendering it all the more curious that the atlas map was never revised. In affect, this map remained an historical map of the archipelago, showing discoveries made. albeit in a rather haphazard and fortuitous manner by the Dutch, between 1606 and 1623.. The design of the map emphasises the importance of the commercial interests in the East Indies, centred as it is on the heart of what was to become The Netherlands East Indies and later Indonesia. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
1639 Hondius Antique Map of Bermuda
- Title : Mappa Aestivarum Insularum, alias Barmudas Dictarum ... Accurate Descripta
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 43135
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19 1/4in (570mm x 485mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Island of Bermuda was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Henricus Hondius. A much sought after map of Bermuda, with decorative cartouche, compass rose with the Island divided into lots and tribes, listed at the base of the map.
Background:
Like all 17th century maps of Bermuda this map is based ultimately on the survey made by John Norwood of the Bermuda Company in 1618 in the form as published by the English map-maker John Speed in 1627. Although discovered in 1515 by Spaniard Juan de Bermudez, after whom the island is supposedly named, it was the shipwreck of a party of Virginia colonists in 1610 led by Sir George Somers that gave Bermuda its first known inhabitants. The Latin title reflects this fact, for Aestivarum Insularum means summers (or Somers) Islands. The experience of Somers and his men inspired William Shakespeare, who dispatched Ariel to "fetch dew from the still-vext Bermoothes" and populated the islands with the cast of The Tempest.
The place names and the list of Proprietors given below the map itself all recall the original members of the Bermuda Company, the latter being listed as eight tribes (or parishes). In 1610, the Virginia Company, in a True Declaration of the Estate of the Colonie of Virginia, said of Bermuda: These Islands of Bermudos, have evere beene accounted as an inchaunted pile of rocks, and a desert inhabitation for Divels; but all the Faities of the rockes were but flocks of Birds, and all the Divels that haunted the woods, were but heards of Swine. In the upper left-hand and right-hand corners of the map appear the adjacent coasts of the North American colonies of Virginia and New England with, just below the cartouche a tiny outline of Bermuda itself, intended to show its correct proportion and position against the mainland.(Ref Tooley M&B)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/4in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 3/4in (520mm x 400mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
1639 Hondius Antique Map of Magellan Straits, South America
- Title : Freti Magellanici ac novi Freti vulgo Le Maire exactissima delinatio..
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43137
- Size: 22in x 18in (560mm x 470mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Straits of Magellan, Le Maire Strait, Fire Lands and the southern tip of Patagonia was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 andcontinued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Early impression of this fine map of Tierra del Fuego. With a Dutch translation of the explanatory text of the passage by Barent Jansz. Potgieter who accompanied captain Sebald de Weert to the Straits in 1599/1600, being the first Dutch vessels to sail through the Strait of Magellan.
After various English voyages, the Dutch appeared in the Strait of Magellan in 1599. One of the Dutch pioneering voyages to the Southwest was the one by Jacques Mahu and Simon de Cordes, who were sent out by Rotterdam merchants.
The five ships of this fleet were the first Dutch vessels to sail through the Strait of Magellan. One of them, the De Liefde, completed the crossing of the Pacific, reached Japan and laid the foundations for Dutch trade. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Bottom centerfold re-joined, no loss
1639 Hondius Old, Antique Map of Henneberg, Thuringia Region Germany - Meiningen
- Title : Principatus Hennenbergensis
- Ref #: 23433
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Henneberg county in the Thuringia region of Southern Germany - centering on the cities of Henneberg andMeiningen was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson. (Ref: Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of East Indies, Australia - Voyage of Dufken, Spice Islands
- Title : Indiae Orientalis Nova Descriptio
- Ref #: 43144
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This beautiful, very significant original antique map of SE Asia, the East Indies PNG and significantly a small portion of the west coast of Australia's Cape York Peninsular was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercator's Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning, bottom centerfold restored
Plate area: - Uniform age toning, centerfold re-joined
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background: This landmark map is the first published record of the discoveries made by the Dutch ship Dufken on route to Cape York in Australia. New Guinea ("Landt vande Papuos") is marked the (Is)land next to it is called ÔNieu ZeelandtÕ and the island Duyfkens is named after the ship Duyfken.
With the first publication of this map 27 years had passed since the voyage of the Dufken and its discoveries of PNG and NW Australia had been completed. The Dutch East India Company had suppressed the discoveries until it was sure how profitable or not Australia would be.
Jansson & Hondius were the first to published this map in 1630 and it is believed the information was leaked from the Blaeu firm - the official cartographers to the Dutch East India Company. Surprisingly Blaeu did not publish a similar map for another two years. It must have been incredibly galling for Blaeu to have known of the discoveries for nearly thirty years and then to have been beaten to publication by his fiercest rival Jansson & Hondius.
Given this information this is an incredibly significant map of this imporatant region being the first map published with concrete first hand knowledge of the area which prior had been mapped based mainly on speculation or second hand knowledge.
The text running for two pages on the back of the map generally describes the region or country name, history (as it was), temperature, seasons, soil and agricultural productivity. Also described is the topography, wildlife, local inhabitants their culture and religion, as well as a description of major European and local towns and cities. This text makes extremely enjoyable reading and a very good insight not only into the area described but the general European attitudes towards alien countries and cultures. (Ref: Suraz; Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 93508
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper plate engraved antique landmark 1st edition map of the NE region of North America, the original colonial states from Virginia to New England, was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas
A magnificent early map of NE North America published only 19 years after the landing of the Pilgrims at Plymouth Rock, Massachusetts.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 384mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
This influential map is derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. Enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, it carries de Laets narrative on the reverse. De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the names Manbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam. The nomenclature is virtually identical, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630s the families of Blaeu and Hondius - Jansson of ten produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, the latter relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, this one first published in 1636, the second edition was published in 1647 renamed Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova within a new square cartouche. State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Ref: 43134
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured, important original antique map of the north east regions of the United States from Virginia, Chesapeake Bay, to New York & New England by Jan Jansson was published in the 1639 French edition of the Jansson, Hondius Atlas.
A beautiful map with sturdy, clean paper original wide margins and beautiful original hand colouring.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Very light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
A beautiful original 17th map of Virginia, New York and New England which was derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. This version is enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, with de Laets narrative on the verso (De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the namesManbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam)
The nomenclature on this map is virtually identical to the De Laet map, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630's the families of Blaeu and Jansson produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, the first one published in 1636 - entitled Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia.
The second edition in which the title of the map was changed to Nova Belgium et Anglia Nova (to give more weight to Dutch claims in North America) within a new square cartouche was first published in 1647.
State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden; AMPR)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America, Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean
- Title : Insulae Americanae in Oceano Septentrionali cum terris adiacentibus
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 43142
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Gulf of Mexico, The Caribbean, Virginia to Florida to Texas and Central America, Venezuela was published in the 1639 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Nouvs.
This map has been re-joined along the centerold and has some uplift along the centerfold and has been priced accordingly.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595.
After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 andcontinued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18 3/4in (570mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/4in (525mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Light uniform age toning, centerfold re-joined with light uplift
Verso: - Light age toning
Background: Cartographically this map draws on the extremely rare chart by Hessel Gerritsz, c.1631. The area of coverage is exactly the same with the exception of the addition of the west coast of Central America. The nomenclature of the North American part is virtually identical, the only notable addition being the naming of Virginia. It reflects the firsthand knowledge of Gerritsz during his voyage to South America and the West Indies undertaken in 1628. The distance between Chesapeake Bay and Albemarle Sound is accurately portrayed at 1°; even in Gerritsz's acclaimed NOVA ANGLIA ..., for de Laet, 1630, this distance is over 2°. It seems likely that a Spanish chart was used as the nomenclature along the south-east coast lacks any of the French influences often seen at the time.(Ref: Burden; Tooley, Koeman)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of Peru, South America
- Title : Peru
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43147
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the ancient South American country of Peru was published in the 1639 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Nouvs.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Jansson in this map shows the Pacific coast of South America from Ecuador - at the left hand side - as far south as the Atacama desert in the northern reaches of Chile.
Although the interior terrain is not mapped with any particular degree of accuracy, this map nevertheless conveys a vivid impression of the difficult terrain of the Andes in Peru.
As early as 1520, Spanish settlers in Panama had heard tales of a powerful civilisation rich in gold that lay to the south, and in 1522 an expedition was organised to find this land and the people called Biru or Piru in the south. In 1524 Francisco Pizarro led the first of his expeditions that led ultimately to the discovery & conquest of the Inca Empire which extended over wide areas of modern Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and part of Chile. Pizarro obtained from Atahuallpa, the head of the Inca Empire, a huge ransom of silver and gold that made Spain rich almost beyond the most inventive dreams of the Spanish conquerors, and once the mountain city of Cuzco was captured in 1533, the Spanish hold over much of South America was virtually complete.
A beautiful map with a fine impression on clean heavy paper with beautiful hand colouring. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
1639 Jan Jansson Large Original, Antique Map of South Africa
- Title : Aethiopia Inferior vel Exterior...
- Date : 1639
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 43145
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the southern & central parts of Africa, with the south-west coast of Madagascar, was published by Jan Jansson in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Gerardi Mercators Atlantis Novi.
Background: This handsome map formed the standard for the depiction of South Africa throughout the 17th century, covering the region from Congo-Zanzibar to the Cape. Both Blaeu & Jansson based this map on Portuguese exploration, most detail is confined to the coastlines. There are two large lakes in the interior, one unnamed and the other called Zachef, which is the lake out of which the Zambere (Zambesi River) flows, probably based on reports of Lake Ngami, which was not conclusively discovered until the mid 19th century. The interior shows the mythical Mountains of the Moon or Lunae Montes. Indigenous animals including elephants and monkeys are illustrated, while large galleons sail the sea. The dramatic title cartouche is drawn on an ox hide held up by natives, with monkeys and turtles at their feet.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Norwich; Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, red, orange, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom margin centerfold re-joined, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None