Products
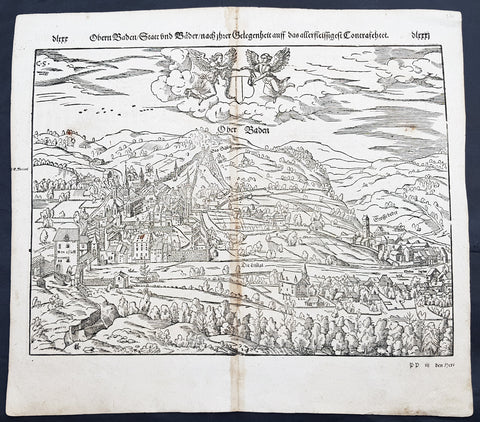
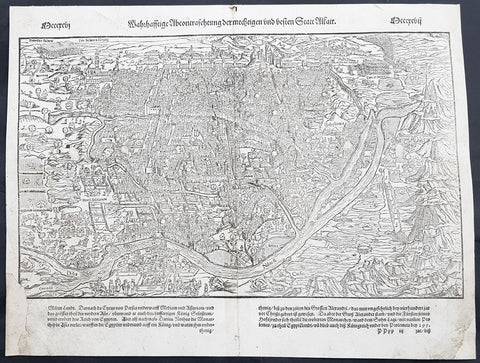
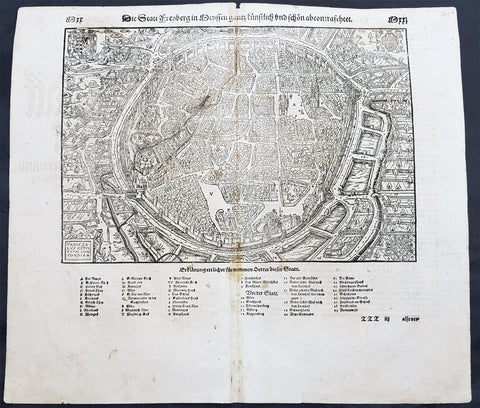
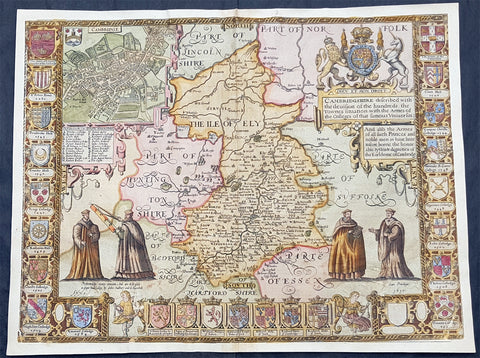
1575 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Cairo, Egypt
- Title : Warhaffte abcontrafehtung der machtigen und vesten Statt Alkair
- Size: 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1575
- Ref #: 91302
Description:
This original wood-block engraved antique double page view of Cairo, as it looked in the mid 16th century under Ottoman rule, was published in the early 1575 edition of Sebastian Munsters Cosmographia by Sebastian Petri, Basle.
Sebastian Petris re-release of Cosomgraphia in 1588 produced some fine woodcut maps in the copperplate style. The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R bottom margin restored
Plate area: - 4 small tears repaired in center of image
Verso: - Restoration as noted, light age toning
Background:
Cairo is the capital of Egypt. The city\'s metropolitan area is one of the largest in Africa, the largest in the Middle East and the Arab world, and the 15th-largest in the world, and is associated with ancient Egypt, as the famous Giza pyramid complex and the ancient city of Memphis are located in its geographical area. Located near the Nile Delta, modern Cairo was founded in 969 CE by the Fatimid dynasty, but the land composing the present-day city was the site of ancient national capitals whose remnants remain visible in parts of Old Cairo. Cairo has long been a center of the region\'s political and cultural life, and is titled the city of a thousand minarets for its preponderance of Islamic architecture.
Although Cairo avoided Europes stagnation during the Late Middle Ages, it could not escape the Black Death, which struck the city more than fifty times between 1348 and 1517. During its initial, and most deadly waves, approximately 200,000 people were killed by the plague, and by the 15th century, Cairos population had been reduced to between 150,000 and 300,000. The citys status was further diminished after Vasco da Gama discovered a sea route around the Cape of Good Hope between 1497 and 1499, thereby allowing spice traders to avoid Cairo. Cairo\'s political influence diminished significantly after the Ottomans supplanted Mamluk power over Egypt in 1517. Ruling from Constantinople, Sultan Selim I relegated Egypt to a province, with Cairo as its capital. For this reason, the history of Cairo during Ottoman times is often described as inconsequential, especially in comparison to other time periods. However, during the 16th and 17th centuries, Cairo remained an important economic and cultural centre. Although no longer on the spice route, the city facilitated the transportation of Yemeni coffee and Indian textiles, primarily to Anatolia, North Africa, and the Balkans. Cairene merchants were instrumental in bringing goods to the barren Hejaz, especially during the annual hajj to Mecca. It was during this same period that al-Azhar University reached the predominance among Islamic schools that it continues to hold today; pilgrims on their way to hajj often attested to the superiority of the institution, which had become associated with Egypt\'s body of Islamic scholars. By the 16th century, Cairo also had high-rise apartment buildings where the two lower floors were for commercial and storage purposes and the multiple stories above them were rented out to tenants.
Under the Ottomans, Cairo expanded south and west from its nucleus around the Citadel. The city was the second-largest in the empire, behind Constantinople, and, although migration was not the primary source of Cairo\'s growth, twenty percent of its population at the end of the 18th century consisted of religious minorities and foreigners from around the Mediterranean. Still, when Napoleon arrived in Cairo in 1798, the city\'s population was less than 300,000, forty percent lower than it was at the height of Mamluk—and Cairene—influence in the mid-14th century.
The French occupation was short-lived as British and Ottoman forces, including a sizeable Albanian contingent, recaptured the country in 1801. Cairo itself was besieged by a British and Ottoman force culminating with the French surrender on 22 June 1801. The British vacated Egypt two years later, leaving the Ottomans, the Albanians, and the long-weakened Mamluks jostling for control of the country. Continued civil war allowed an Albanian named Muhammad Ali Pasha to ascend to the role of commander and eventually, with the approval of the religious establishment, viceroy of Egypt in 1805.
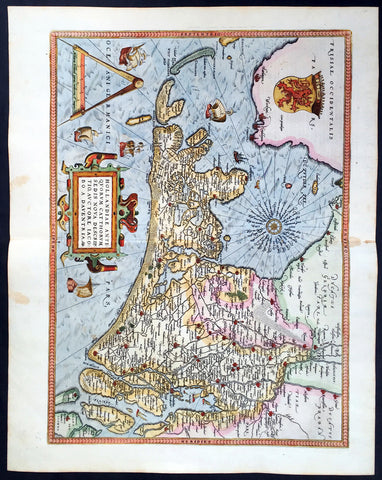
1579 Abraham Ortelius Antique Map of Holland - Hollandia Antiquorum Catthorum
- Title : Hollandia Antiquorum Catthorum Sedis Nova Descriptio, Avctore Iacobo A Daventria
- Ref #: 50664
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (550mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1579
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Holland, 1st edition - based on the cartographic works of Jacob van Deventer - was published by Abraham Ortelius in the 1579 Latin edition of Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
Ortelius published a total of 7300 of this map between 1570 to 1641 from 3 States:
1570-1584 state 1
1587-1595 State 2
1598-1641 State3.
According to Marcel Van dem Broecke there are estimated to be only 140 loose copies in circulation.
Background: It would be hard to imagine a more inauspicious period for a nation's cultural development than the years between 1520 and 1600 in the Low Countries. Under the harsh domination of the Spanish Emperors, facing fanatical religious persecution and the threat of the Inquisition, the constant presence of foreign troops and even the destruction of some of their cities, the Dutch, nevertheless, in 1581 contrived to break their subservience to Spain and form their own federation. Belgium, being mainly Catholic, remained within the orbit of the Empire though henceforward was recognized as a separate state. In such circumstances there would seem to have been little chance for growth of a national entity in the small Northern Provinces but, on the contrary, under the leadership of Amsterdam, their banking and commercial enterprise soon dominated Europe. The attempt by Philip II to eliminate their control of European coastal trade by the use of Portuguese craft inspired the Dutch, first, to seek a North East passage to India and Asia and then, failing that, to challenge Spanish and Portuguese power directly, not only in European waters but also in the East, and eventually to eclipse it. English attempts to gain a foothold in the Indies were bitterly opposed and the English turned their attention to India where only a handful of Dutch settlements existed.
In spite of the turmoil arising out of these events, first Antwerp and then Amsterdam became centres of the arts and their cartographers, engravers and printers produced magnificent maps and charts of every kind which many claim have never been surpassed. Later in this chapter an account is given of Gerard Mercator, who studied at Louvain under Gemma Frisius, the Dutch astronomer and mathematician, and later moved to Duisburg in the Rhineland where most of his major work was carried Out. There he produced globes, maps of Europe, the British Isles and the famous World Map using his newly invented method of projection, all of which were widely copied by most of the cartographers of the day. The first part of his Atlas - the word chosen by Mercator to describe a collection of maps - was published in 1585, the second in 1589, and the third in 1595, a year after his death.
Other great names of the time were Abraham Ortelius, native of Antwerp, famous for his world atlas, Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, issued in 1570; Waghenaer, noted for his sea atlases of 1584 and 1592, Gerard de Jode and Jodocus and Henricus Hondius, followed in the next century by W. J. Blaeu and his sons and Jan Jansson. The Blaeu and Jansson establishments were noted mainly for land atlases but their sea atlases and pilot books were also published in numerous editions which went some way to meeting the rising demand for aids to navigation in European and Mediterranean waters. Their productions were challenged by other, smaller publishers specializing in such works, Jacob Colom, Anthonie Jacobsz, Pieter Goos, Hendrick Doncker, to mention a few, and, later, the charts issued by the van Keulen family and their descendants covered practically all the seas of the known world. As we reach the second half of the seventeenth century the details of publication of these sea atlases and pilot books become more and more interwoven and complicated. Not infrequently the same charts were issued under the imprint of different publishers; at death the engraved plates were sold or passed to their successors and were re-issued, with minor alterations and often without acknowledgement to the originator, all of which adds to problems of identification. Although, in this period, charts of every kind must have been issued in great quantity, good copies are now hard to find.
By about the year 1700 Dutch sea power and influence was waning and although their pilot books and charts remained much in demand for many years to come, leadership in the production of land atlases passed into the hands of the more scientific French cartographers who, in their turn, dominated the map trade for most of the following century.
Atlas Background: For the first time, in 1570, all the elements of the modern Atlas were brought to publication in Abraham Ortelius' Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. This substantial undertaking assembled fifty-three of the best available maps of the world by the most renowned and up to date geographers.
Unlike earlier compositions, such as the Italian composite or "Lafreri" Atlases, each of Ortelius' maps was engraved specifically for his Atlas according to uniform format. Through its launching, pre-eminence in map publishing was transferred from Italy to the Netherlands, leading to over a hundred years of Dutch supremacy in all facts of cartographical production.
There were a total of 7300 copies of Theatrum published between 1570 - 1612 from 31 editions. (Ref: Van Den Broecke; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early color
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (550mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14in (495mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light browning in top and bottom margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1587 Abraham Ortelius Antique Title Page from the Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum
- Title : Theatre de l univers : contenant les cartes de tout le monde, avec une brieve declaration d icelles par Abraham Ortelius...MDLXXXVII (1587)
- Size: 15 3/4in x 10 3/4in (400mm x 270mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1587
- Ref #: 32035
Description:
These original copper-plate engraved antique Title Page, with a quote by Cicero on the verso, was published in the 1587 French edition of Abraham Ortelius Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 3/4in x 10 3/4in (400mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 15 3/4in x 10 3/4in (400mm x 270mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling, old ink text in left margin
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
This is the French version of Abraham OrteliusTheatrum orbis terrarum, considered to be the first modern atlas. Ortelius was one of the leading humanists of the Low Countries and was acquainted with many European intellectuals. Theatrum orbis terrarum was incredibly successful, despite being the most expensive book produced in the second half of the sixteenth century. Interest in it was extended by the continued issue of updated versions. Produced during the European Age of Discovery, new editions reflected the latest geographic knowledge, and each version contained new maps and information.
Theatrum orbis terrarum translates as Theatre of the lands of the world. The idea of the world as a theatre is echoed by William Shakespeare in his naming of the Globe theatre, and in Jaquess famous speech in As You Like It, beginning All the worlds a stage, and all the men and women merely players. The influence of Elizabethan exploration and the ideas of new and strange lands and peoples are reflected in many of Shakespeares plays.
The opening double-page spread of the world in this book, engraved by Francis Hogenberg, is among the most widely reproduced early-modern maps. It reflects contemporary theories about what remained undiscovered: Ortelius believed there to be a large southern continent which he named Terra Australis Nondum Cognita, or Southern Land Not Yet Known.
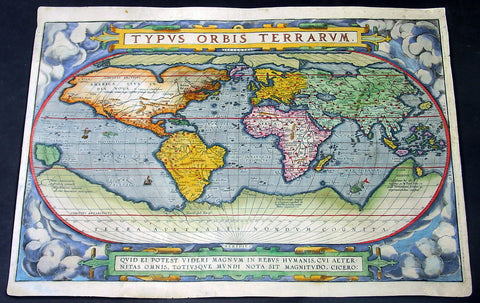
1588 Abraham Ortelius Antique Oval World Map - Rarest Edition, Ort 2:3
- Title : Typus Orbis Terrarum
- Date : 1588
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: Ort1
- Size: 20in x 14 ½in (510mm x 370mm)
This magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved rare antique Oval World map (Ort 2:3) was engraved by Franciscus (Frans) Hogenberg and was published in the 1588 edition of Abraham Ortelius Atlas <i>Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. </i>
To emphasis how rare this map is consider the following. Ortelius published a total of 6950 of these world maps in 3 states (3250 1st state, 500 2nd state & 3200 3rd state) between 1570 and 1612. Today only 411 are known to have survived. Of these surviving 411 only 14 are of the 2nd state (Ort 2) and of these 14 only 4 are Ort 2:3 state, making this one of the rarest Ortelius maps available on the market at any time. Blank verso.
This map is part of my personal collection and has been framed to Museum quality. I will sell the map with the frame, with additional cost TBN if required.
The map was acquired from Marcel P R van den Broecke - author of Ortelius Atlas Maps - in Holland, collector and dealer and is accompanied by Certificate of Authenticity from Marcel van den Broecke.
Ortelius published 3 World maps over the life of his atlas <i>Theatrum Orbis Terrarum</i>, between 1570 & 1612. These 3 maps are referred to as Ort 1, Ort 2 & Ort 3. Over the life of these maps, necessary changes, repairs & updates were made to the plates, these changes are referred to as states. The first map or Ort 1 required 5 changes, Ort 2 required 3 changes and Ort 3 was changed twice.
This map was published in 1588 and is the last state of Ort 2, identified by the changes to the western South American coastline, whilst still retaining the decorative cloud surround as in Ort1. Ort 3 was changed by removing the cloud surrounds replacing them with medallions and strap-work This is a beautiful map with original hand colouring, on sturdy clean paper with original margins.
Below is a concise list of the states of the map <i>Typus Orbis Terrarum</i>
- 1st edition (Ort 1) – States 1.1 through to 1.5.
A total of 3250 maps from this plate were published between 1570 & 1584. Today it is estimated that there are 236 loose copies in circulation of all 5 states.
- 2nd edition (Ort 2) - States 2.1 through to 2.3.
A total of only 500 maps from this plate were published between 1586 & 1588. Today it is estimated that there are 14 loose copies in circulation of all 3 states.
- 3rd edition (Ort 3) – States 3.1 through to 3.2.
A total of 3200 maps from this plate were published between 1589 & 1612. Today it is estimated that there are 161 loose copies in circulation of both states. (Ref: Van Den Broecke; Tooley; Shirley; Rosenthal)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 14 ½in (510mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 19 ½in x 13 1/4in (495mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min ½in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional 11cm restoration to bottom margin, 1cm into image. Light soiling
Plate area: - Small 2cm sq professional restoration below the ST of Australis
Verso: - Map backed on fine archival Japanese paper
Background:
The Ortelius world map is a simplified one-sheet reduction of Mercators large world map which had appeared the year before. Nearly all the legends, textual panels and decorative features of Mercators map have been omitted; between the oval circumference of the map and the outer frame are now clouds and below, a quotation from Cicero. From surviving correspondence, it is known that Mercator generously encouraged Ortelius to make use of his published research; he also provided him with coordinates of places in America and other newly discovered regions of the world. In the first edition South America retains the unusual bulged south-west coast as drawn by Mercator. There is also a prudent comment adjacent to New Guinea querying whether this large island is part of the southern continent or not.
The original plate, like a number of others in the Atlas, were signed by the engraver Franciscus (Frans) Hogenberg and was used for the first sixteen editions of the Theatrum.
In nearly all places there is text on the reverse of the map in the language indicated but a few copies are known which lack reverse text. Between 1575 and 1579 the plate became cracked along the lower left hand corner. The crack was roughly mended and the whole border of the clouds substantially reworked; editions from 1579 to 1584 contain this revised state 2 of plate 1. Ortelius subsequently produced two further world maps, each slightly improved geographically.
Several of these states co-existed; for instance although plate 3 carries the date 1587, it does not seem to have been issued until 1592. Only one example has been sighted of the first state plate 2 of 1586. State 3 of plate 2 is also uncommon but it re-appears in the British Librarys copy of the Dutch 1598 edition of the Theatrum which, as noted by Koeman, was often made up of earlier stock sheets.
Ortelius map was copied widely, and derivatives were later used to illustrate works by Voisin, Broughton, Maffei, Bell-Forest, Petri, Hakluyt and others.
Cartographical sources were Gerard Mercator 1569 & Gastaldi 1561 world maps and Diego Gutierrez portolan map of the Atlantic.
Next to the list at the bottom of the text, Ortelius mentions in his Catalogues Auctorum the world maps by Peter ab Aggere from Mechelen, Sebastian Cabotus from Venice, Laurentius Fries from Antwerp, Jacobus Gastaldi, Gemma Frisius from Antwerp, Guicciardinus from Antwerp, Doco ab Hemminga Frisius, and Orontius Finæus from Paris.
Background of the Atlas <i>Theatrum Orbis Terrarum</i>
For the first time, in 1570, all the elements of the modern Atlas were brought to publication in Abraham Ortelius Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. This substantial undertaking assembled fifty-three of the best available maps of the world by the most renowned and up to date geographers.
Unlike earlier compositions, such as the Italian composite or Lafreri Atlases, each of Ortelius maps was engraved specifically for his Atlas according to uniform format. Through its launching, pre-eminence in map publishing was transferred from Italy to the Netherlands, leading to over a hundred years of Dutch supremacy in all facts of cartographical production.
There were a total of 7300 copies of Theatrum published between 1570 - 1612 from 31 editions.
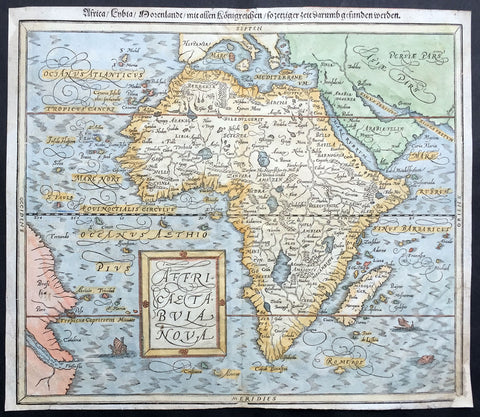
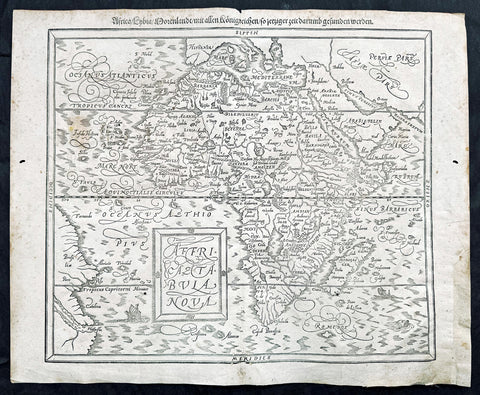
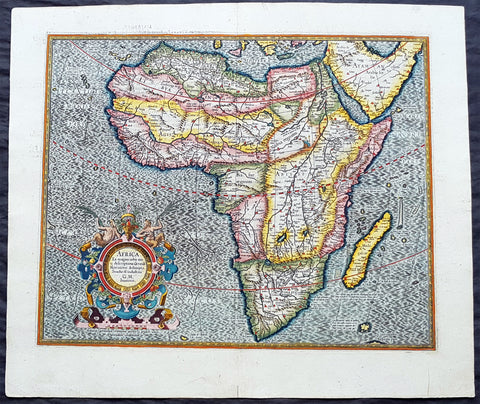
1588 Munster Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africae Tabula Nova
- Ref #: 43175
- Size: 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1588
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Africa was published in the 1588 edition of Sebastian MunstersCosmographia published by Sebastian Petri, Basle.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
Sebastian Petri re-release of Cosomgraphia in 1588 produced some fine woodcut maps in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Margins: - 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair to bottom right & top left corner margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Re-enforced along centerfold
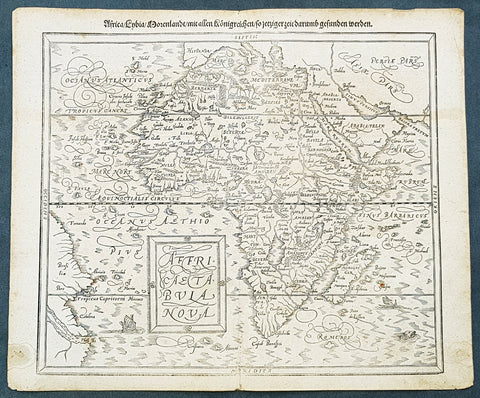
1588 Sebastian Munster Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africae tabula nova / Africa, Lybia, Morenlandt, mit allen Königreichen so jetziger zeit darumb gefunden werden
- Date : 1588
- Size: 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 340mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35664
Description:
A great example of the original wood-block engraved antique map of the whole continent of Africa published by Sebastian Munster in the 1588 edition of Cosmographia.
This is Munsters 2nd map of Africa, after the Abraham Ortelius continental map of 1574. The woodblock map is elegantly engraved in the style of copper engravings. It depicts the continent with a jagged coastline with several prominent bays. In the interior there are several large lakes, including the twin lakes source of the Nile. The coast of Brazil appears in the lower left corner. Two small ships, a sea monster and a block-style title cartouche decorate the map. German text and illustration on verso.
The Cosmographia or Cosmography was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world.
It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century and passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Die Newe Welt oder Inseln, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically unique.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia, with numerous illustrations.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 13 1/2in (420mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small extension to bottom right corner margin, repair to bottom centerfold, not affecting image.
Plate area: - 2 very small worm holes
Verso: - Repairs as noted
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle(c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
Sebastian Petri re-release of Cosomgraphia in 1588 produced some fine woodcut maps in the copperplate style. The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1588 Sebastian Munster Antique Map of Africa, Source of Nile & Cannibals
- Title : Africa Mit Seinen Besondern Lanendern, Thieren und Wunderbarlichen Dingen (Africa with its special countries, animals, and wonderful things)
- Size: 13 1/2in x 8 1/2in (345mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1588
- Ref #: 17058
Description:
This original wood-block engraved antique map of Africa, to text, by Sebastian Munster was published by Sebastian Petri in the 1588 edition of Cosmographia.
Most editions of Munster Cosmographia contained a small woodcut map of Africa as a text illustration. It excludes the Horn of Africa and the Cape of Good Hope, but Mons Lunae origina of the Nile appears, with many kingdoms Central and North Africa. Additional text and woodcuts appear on the verso of a battle and cannibal.
The Cosmographia or Cosmography was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world.
It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century and passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Die Newe Welt oder Inseln, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically unique.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemy\\\'s Geographia, with numerous illustrations.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 8 1/2in (345mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 6in x 5in (150mm x 130mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munsters Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. dAnville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century, (Ref: Norwich; Tooley)
1588 Sebastian Munster Antique Map of Africa, Source of Nile & Cannibals
- Title : Africa Mit Seinen Besondern Lanendern, Thieren und Wunderbarlichen Dingen (Africa with its special countries, animals, and wonderful things)
- Size: 13 1/2in x 8 1/2in (345mm x 230mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1588
- Ref #: 93337
Description:
This original wood-block engraved antique map of Africa, to text, by Sebastian Munster was published by Sebastian Petri in the 1588 edition of Cosmographia.
Most editions of Munster Cosmographia contained a small woodcut map of Africa as a text illustration. It excludes the Horn of Africa and the Cape of Good Hope, but Mons Lunae origina of the Nile appears, with many kingdoms Central and North Africa. Additional text and woodcuts appear on the verso of a battle and cannibal.
The Cosmographia or Cosmography was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world.
It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century and passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Die Newe Welt oder Inseln, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically unique.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemy\\\'s Geographia, with numerous illustrations.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 8 1/2in (345mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 6in x 5in (150mm x 130mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munsters Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. dAnville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century, (Ref: Norwich; Tooley)
1588 Sebastian Munster Antique Map of Continental Africa
- Title : Africae tabula nova / Africa, Lybia, Morenlandt, mit allen Königreichen so jetziger zeit darumb gefunden werden
- Size: 16 1/4in x 13 1/4in (415mm x 335mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1588
- Ref #: 93336
Description:
A great example of the original wood-block engraved antique map of the whole continent of Africa published by Sebastian Munster in the 1588 edition of Cosmographia.
Great map with original margins, on stable age toned paper with a nice impression.
This is Munsters 2nd map of Africa, after the Ortelius continental map of 1574. The woodblock map is elegantly engraved in the style of copper engravings. It depicts the continent with a jagged coastline with several prominent bays. In the interior there are several large lakes, including the twin lakes source of the Nile. The coast of Brazil appears in the lower left corner. Two small ships, a sea monster and a block-style title cartouche decorate the map. German text and illustration on verso.
The Cosmographia or Cosmography was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world.
It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century and passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Die Newe Welt oder Inseln, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically unique.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia, with numerous illustrations.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/4in (415mm x 335mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/4in (415mm x 335mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning, 2 very small repairs to margins not affecting image
Background:
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle(c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
Sebastian Petri re-release of Cosomgraphia in 1588 produced some fine woodcut maps in the \"copperplate style\". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
1588 Sebastian Munster Antique Print View of Comar, in Alsace region of France
- Title : Die Statt Colmar
- Date : 1588
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 30354
- Size : 18in x 14in (460mm x 360mm)
Description:
This original antique double page view of the city of Colmar, in the Alsace region in north-eastern France, was published in the 1588 release of Sebastian Munsters Cosmographia by Sebastian Petri, Basle. Sebastian Petri re-release of Cosomgraphia in 1588 produced some fine woodcut maps & plans in the \"copperplate style\". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18in x 14in (460mm x 360mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (460mm x 360mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling
Plate area: - Soiling
Verso: - Soiling
Background:
Colmar is the third-largest commune of the Alsace region in north-eastern France. It is the seat of the prefecture of the Haut-Rhin department and the arrondissement of Colmar-Ribeauvillé.
The town is situated on the Alsatian Wine Route and considers itself to be the capital of Alsatian wine (capitale des vins d Alsace). The city is renowned for its well-preserved old town, its numerous architectural landmarks, and its museums, among which is the Unterlinden Museum, with the Isenheim Altarpiece.
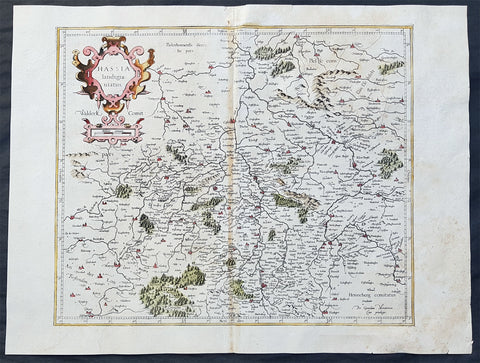
1589 Gerard Mercator Original 1st Ed. Antique Map of German State of Hesse
- Title : Hassia landtgrauiatus
- Date : 1589
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 50254
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original and extremely scarce 1st edition antique map of the German State of Hesse or Hessia in central Germany was published by Gerard Mercator.
These original maps by Gerard Mercator from his original 16th century atlas are rare and hard to find. These original map are identifiable by the design on the verso of the map without the long description, scroll design and were engraved prior to the sale of Mercators plates to Hondius in the first decade of the 17th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/4in x 13 1/2in (415mm x 345mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light browning along centerfold, light age toning
Verso: - Small repair to top centerfold
Background:
As early as the Paleolithic period, the Central Hessian region was inhabited. Due to the favorable climate of the location, people lived there about 50,000 years ago during the last glacial period, as burial sites show from this era. Finds of paleolitical tools in southern Hesse in Rüsselsheim suggest Pleistocene hunters about 13,000 years ago. The Züschen tomb (German: Steinkammergrab von Züschen, sometimes also Lohne-Züschen) is a prehistoric burial monument, located between Lohne and Züschen, near Fritzlar, Hesse, Germany. Classified as a gallery grave or a Hessian-Westphalian stone cist (hessisch-westfälische Steinkiste), it is one of the most important megalithic monuments in Central Europe. Dating to the late fourth millennium BC (and possibly remaining in use until the early third), it belongs to the Late Neolithic Wartberg culture.
An early Celtic presence in what is now Hesse is indicated by a mid-fifth-century BC La Tène-style burial uncovered at Glauberg. The region was later settled by the Germanic Chatti tribe around the first century BC, and the name Hesse is a continuation of that tribal name.
The ancient Romans had a military camp in Dorlar, and in Waldgirmes directly on the eastern outskirts of Wetzlar was a civil settlement under construction. Presumably, the provincial government for the occupied territories of the right bank of Germania was planned at this location. The governor of Germania, at least temporarily, likely had resided here. The settlement appears to have been abandoned by the Romans after the devastating Battle of the Teutoburg Forest failed in the year 9 AD. The Chatti were also involved in the Revolt of the Batavi in 69 AD.
Hessia, from the early seventh century on, served as a buffer between areas dominated by the Saxons (to the north) and the Franks, who brought the area to the south under their control in the early sixth century and occupied Thuringia (to the east) in 531. Hessia occupies the northwestern part of the modern German state of Hesse; its borders were not clearly delineated. Its geographic center is Fritzlar; it extends in the southeast to Hersfeld on the Fulda River, in the north to past Kassel and up to the rivers Diemel and Weser. To the west, it occupies the valleys of the Rivers Eder and Lahn (the latter until it turns south). It measured roughly 90 kilometers north-south, and 80 north-west.
The area around Fritzlar shows evidence of significant pagan belief from the first century on. Geismar was a particular focus of such activity; it was continuously occupied from the Roman period on, with a settlement from the Roman period, which itself had a predecessor from the fifth century BC. Excavations have produced a horse burial and bronze artifacts. A possible religious cult may have centered on a natural spring in Geismar, called Heilgenbron; the name \"Geismar\" (possibly \"energetic pool\") itself may be derived from that spring. The village of Maden, Gudensberg (de), now a part of Gudensberg near Fritzlar and less than ten miles from Geismar, was likely an ancient religious center; the basalt outcrop of Gudensberg is named for Wodan, and a two-meter tall quartz megalith called the Wotanstein is in the center of the village.
By 650, the Franks were establishing themselves as overlords, which is suggested by archeological evidence of burials, and were building fortifications in various places, including Christenberg. By 690, they were taking direct control over Hessia, apparently to counteract expansion by the Saxons, who built fortifications in Gaulskopf and Eresburg across the River Diemel, the northern boundary of Hessia. The Büraburg (which already had a Frankish settlement in the sixth century) was one of the places the Franks fortified to resist the Saxon pressure, and according to John-Henry Clay, the Büraburg was \"probably the largest man-made construction seen in Hessia for at least seven hundred years\". Walls and trenches totaling one kilometer in length were made, and they enclosed \"8 hectares of a spur that offered a commanding view over Fritzlar and the densely populated heart of Hessia\".
Following Saxon incursions into Chattish territory in the seventh century, two gaue had been established—a Frankish one, comprising an area around Fritzlar and Kassel, and a Saxon one. In the 9th century, the Saxon Hessengau also came under the rule of the Franconians. In the 12th, century it was passed to Thuringia.
In the War of the Thuringian Succession (1247–1264), Hesse gained its independence and became a Landgraviate within the Holy Roman Empire. It shortly rose to primary importance under Landgrave Philip the Magnanimous, who was one of the leaders of German Protestantism. After Philip\'s death in 1567, the territory was divided among his four sons from his first marriage (Philip was a bigamist) into four lines: Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel), Hesse-Darmstadt, Hesse-Rheinfels, and the also previously existing Hesse-Marburg. As the latter two lines died out quite soon (1583 and 1605, respectively), Hesse-Kassel and Hesse-Darmstadt were the two core states within the Hessian lands. Several collateral lines split off during the centuries, such as in 1622, when Hesse-Homburg split off from Hesse-Darmstadt. In the late 16th century, Kassel adopted Calvinism, while Darmstadt remained Lutheran and subsequently the two lines often found themselves on different sides of a conflict, most notably in the disputes over Hesse-Marburg and in the Thirty Years\' War, when Darmstadt fought on the side of the Emperor, while Kassel sided with Sweden and France.
The Landgrave Frederick II (1720–1785) ruled as a benevolent despot, 1760–1785. He combined Enlightenment ideas with Christian values, cameralist plans for central control of the economy, and a militaristic approach toward diplomacy. He funded the depleted treasury of the poor nation by renting out 19,000 soldiers in complete military formations to Great Britain to fight in North America during the American Revolutionary War, 1776–1783. These soldiers, commonly known as Hessians, fought under the British flag. The British used the Hessians in several conflicts, including in the Irish Rebellion of 1798. For further revenue, the soldiers were rented out elsewhere, as well. Most were conscripted, with their pay going to the Landgrave.
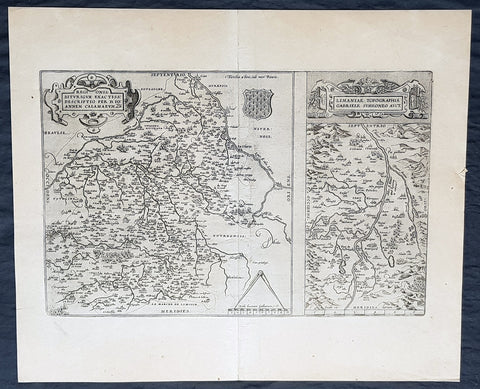
1589 Mercator Antique Atlas Title Page from Italy, Yugoslavia & Greece
-
Title : Italiae Sclavoniae, et Graeciae tabule geographice, per Gerardum Mercatorem....
- Date : 1589
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 16281
- Size: 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique Title page from Gerard Mercator's Italy & SW Europe section was published in the 1589 edition of the Geographiaatlas.
After the sale of Mercator's plates to in 1605, Hondius continued to publish the original plates with little alteration until 1630 when along with Jansson many of the original plates were altered or re-engraved either decoratively or topographically or both. This map is from one of the last unaltered editions of Mercator's atlas. (Ref: Koeman, Tooley)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 7 1/2in (290mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to bottom right corner
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning
1595 Abraham Ortelius Antique Epitome Atlas with 106 Maps - Rare, Unique & Beautiful
-
Title: Epitome theatri Orteliani...Philippo Gallaeo Arnoldus Cocinx MDXCV
- Ref: 3090
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
-
Size: 8vo
- Date: 1595
Description:
This stunning, original antique pocket Epitome Atlas, Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theatre of the Orb of the World) - with 106 beautifully hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique maps of the entire 16th century world, by Abraham Ortelius, was published in 1595 - dated on the title page, Latin edition - by Philip Galle.
The atlas has been lovingly and professionally restored with fine vellum binding, end papers. Each page has been lovingly cleaned and faithfully re-coloured and tabbed back into the atlas as originally published. Along with the new end papers, the atlas contains the original dated title page, frontispiece, 6 text pages 109 maps, descriptive text and finally three index pages shown to the left.
A unique opportunity to acquire one of the best, if not the best Epitome Atlas, on the market.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later & early coloring
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, pink, blue, black
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Atlas size: - 8vo
Map sizes: - 5 3/4in x 4in (145mm x 100mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: None
Plate area: - Very light ink notations on title and Psalm pages, light age toning on a few pages
Verso: - None
Background: The pocket versions, or Epitome, of Abraham Ortelius folio Atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum was published by Philip Galle with text by Pieter Heyns. Between 1577 & 1598 Galle issued 11 editions, of which 10 editions were printed by Christopher Platin , with this lone edition printed by Arnoldus Coninx in 1595,making it an extremely rare & unique item. .
The Dutch edition published by Heyn's son Zacharias in 1596, was a re-issue of of the 1583 edition. In addition to the Dutch, French, Latin & Italian editions an English one was produced. The maps for the English edition, the last from Galles map plates, were printed in Antwerp and shipped to London for publication by John Norton in 1602.
The first two editions, of Epitome, contained sixty-six miniatures and six small folding maps including one of the world dated 1574. They were all rather crudely drawn and engraved by Galle, with narrow decorated borders. From 1583 he gradually introduced a new set of maps, adding quality and quantity replacing the originals until they had grown to 123 by 1598.
Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theatre of the Orb of the World) is considered to be the first true modern atlas. Written by Abraham Ortelius, strongly encouraged by Gillis Hooftman and originally printed on 20 May 1570 in Antwerp, it consisted of a collection of uniform map sheets and supporting text bound to form a book for which copper printing plates were specifically engraved. The Ortelius atlas is sometimes referred to as the summary of sixteenth-century cartography. The publication of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570) is often considered as the official beginning of the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography (approximately 1570s–1670s) (Ref: King; Van Den Broecke; Tooley)
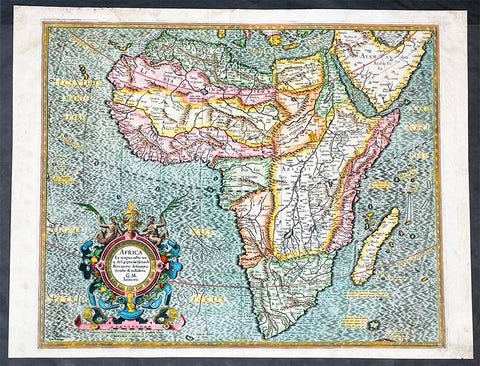
1595 Gerard Mercator Original True Rare 1st Edition Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africa Ex Magna orbis terra descriptione Gerardi Mercatoris desumpta. Studio & industria GM Iunioris
- Size: 21in x 16 1/4in (535mm x 415mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1595
- Ref #: 27016
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original, true rare 1st edition* antique map, of Africa by Gerard Mercator was published in the 1595 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas, Atlas Sive Cosmographicae Meditationes Illustrissimi Ducis.
* True 1st edition identified on the verso of the map, according to Koemans Atlantes Neerlandica, illustrating the letter "C" under the title "Africa".
As indicated in the title Cartouche, this map this is a reduction by Gerard Mercator Junior of Africa, compiled from Gerard Mercators world map of 1569. This rendition was drawn by Mercators grandson (also named Gerard) in 1595.
The map is typical of 16th century cartography of Africa containing some fantastical detail especially in regards to the interior. The depiction of the Nile is based on Ptolemys geography with some complex modifications from various sources, including Abyssinian monks. The source of the Nile is shown as a series of lakes located in the Lune Montes just north of the Tropic of Capricorn. Another branch of the Nile flows from the west, with this system rambling through what is the Sahara Desert. Mercator adds a lake named Sac. Haf lac, from the 1507 Waldseemuller world map. This lake feeds both the Zambere River and the Nile. In Abissini, the legendary Christian King Prester John sits on his throne. The boldly engraved oceans, beautiful calligraphy, and strapwork cartouche (surmounted by two satyrs) make this a decorative masterpiece.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/4in (535mm x 415mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, small rejoin in bottom right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning, left & top margin re-enforced
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
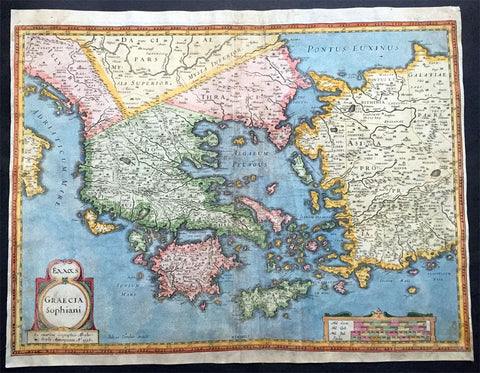
1596 Hondius Large Antique Map of Greece - Ist Edition
- Title : Exxas; Graecia Sophiani. Ex Contibus Geographicis Abraham Ortelli Antierpiensis Ao. 1596
- Ref #: 35084
- Size: 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 390mm)
- Date : 1596
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique scarce map of Greece, Greek Islands & Western Turkey was engraved by Joducus Hondius in 1596 - dated in the title - and was published in P Bertius Atlas Historical Atlas in 1618. Blank verso.
This is a rare 1st edition of this map. It has undergone some professional restoration and is priced accordingly.
There were only 2 editions of this map engraved by Hondius in 1596, one with and one without dots in the sea. This one has the dots. In later editions the Hondius signature was removed as was the date from the title. (Ref: Koeman; M&B)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (510mm x 390mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 14 1/4in (510mm x 365mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (7mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling, bottom left corner professionally restored
Plate area: - Profession repairs to centerfold, light soiling
Verso: - Soiling on verso
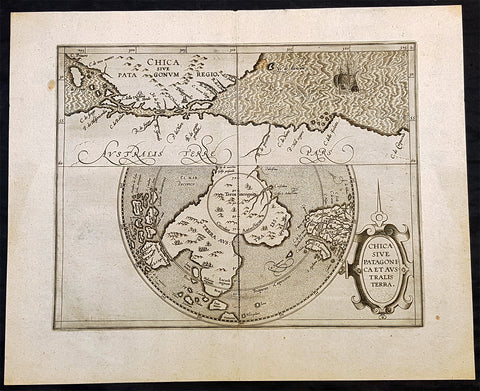
1597 Cornelis Wytfliet Antique Map Early Important Map of Australia, South America Terra Australis
- Title : Chica Sive Patagonica et Australis Terra
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1597
- Ref #: 41718
Description:
A fine original antique, and incredibly important map of Patagonia & the Magellan Straits but more importantly one of the first maps to depict a distinctive outline of Australia - depicted here as part of Terra Australis the Great Southern Land - and was published by Cornelis van Wytfliet in the 1597 edition of Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum.
Wytfliets famous map of the southern continent from the first atlas of the Americas, Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum, sive Occidentis Notitia in 1597.
In the top part of the map, Patagonia is separated by a strait from a large southern continent named Australis Terrae Pars. The naming of C. Della Victoria and the illustration of Magellans ship, Victoria, indicates, although not names on the map, as the Strait of Magellan. The lower portion of the map is a polar projection, showing Terra Australis as the large landmass made up of four peninsulas, one reaching towards New Guinea which is shown as an island. This and the other peninsula to the west is one of the earliest and clearest indications of cartographical knowledge of Northern Australia, specifically Northern Queensland, the Gulf of Carpentaria & parts of the Northern Territory.
Gunter Schilder discusses this map at length and points to its significance to Major Collingridge and others as proof that Australia had already been discovered in the sixteenth century....
Wytfliet notes The Australis Terra is the most southern of all lands; it is separated from New Guinea by a narrow strait; its shores are hitherto but little known, since, after one voyage and another, that route has been deserted, and seldom is the country visited unless when sailors are driven there by storms. The Australis Terra begins at two or three degrees from the equator, and is maintained by some to be of so great an extent that if it were thoroughly explored it would be regarded as a fifth part of the world.
Wyfliets depiction of a narrow strait separating Australis Terra from New Guinea, predates that of Torress discovery in 1606. Torress passage was not known to the world until the end of the 18th century, when Dalrymple discovered Torress journal of the voyage amongst archives in Manila.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/4in x 9 1/4in (285mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1597 Cornelis van Wytfliet published his Augmentum to Ptolemys Geography. Dedicated to Philip III of Spain it is a history of the New World to date, recording its discovery, natural history etc. For the book Wytfliet had engraved nineteen maps, by whom we do not know, one of the world and eighteen regional maps of the Americas. As such this book can be truly called the first atlas of the New World, America.
Wytfliet, Cornelis van d. 1597
Cornelius Wytfliet or Cornelis van Wytfliet was a geographer from Leuven in the Habsburg Netherlands, best known for producing the first atlas of the Americas.
Cornelius was the son of Catherine Huybrechts and her husband, Gregorius Wytfliet, who was advocate fiscal of Leuven University from 1557 to 1594. After graduating Licentiate in Laws from the University of Leuven, Wytfliet moved to Brussels and became secretary to the Council of Brabant. He died in or shortly after 1597, when his Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum (a work adding new discoveries to Ptolemy\\\'s description of the world) was published
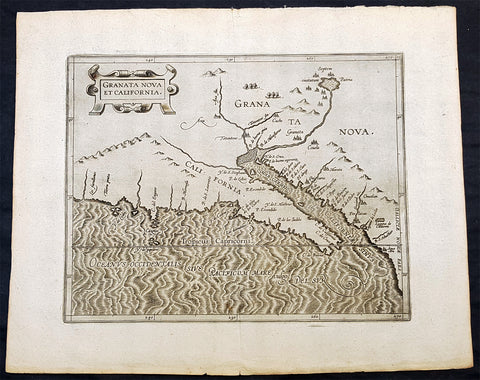
1597 Cornelis Wytfliet Antique Map Early Important Map of California & SW America
- Title : Granata Nova et California
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1597
- Ref #: 41716
Description:
A fine original antique, and incredibly important map the first to focus on California & the SW was published by Cornelis van Wytfliet in the 1597 edition of Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum.
The first printed map devoted to California and the south-west of the present day United States. One of the most interesting features is the depiction of so many fabled places largely from Spanish sources. Most notable amongst these are the seven cities of Cibola. The seven cities originated from the narrative of Fray Marcos de Niza in 1539. Some of the other nomenclature originates from Coronados epic exploration. The outline map is fairly accurate and is derived largely from Petrus Plancius large world map of 1592. The main coastal irregularity is the westward slant of the Californian coastline. Bearing in mind that it would be shown as part of an island in twenty five years, this is quite forgivable. No other states of the map are known and all issues are without text on the back (Burden 106).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/4in x 9 1/4in (285mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1597 Cornelis van Wytfliet published his Augmentum to Ptolemys Geography. Dedicated to Philip III of Spain it is a history of the New World to date, recording its discovery, natural history etc. For the book Wytfliet had engraved nineteen maps, by whom we do not know, one of the world and eighteen regional maps of the Americas. As such this book can be truly called the first atlas of the New World, America.
Wytfliet, Cornelis van d. 1597
Cornelius Wytfliet or Cornelis van Wytfliet was a geographer from Leuven in the Habsburg Netherlands, best known for producing the first atlas of the Americas.
Cornelius was the son of Catherine Huybrechts and her husband, Gregorius Wytfliet, who was advocate fiscal of Leuven University from 1557 to 1594. After graduating Licentiate in Laws from the University of Leuven, Wytfliet moved to Brussels and became secretary to the Council of Brabant. He died in or shortly after 1597, when his Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum (a work adding new discoveries to Ptolemys description of the world) was published
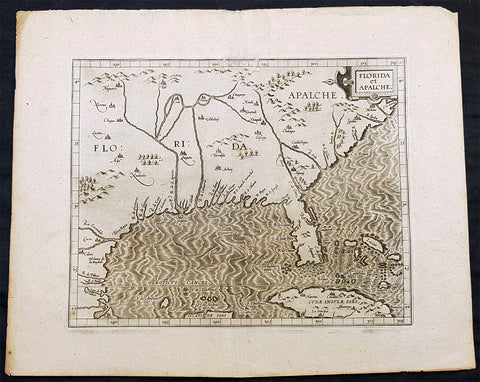
1597 Cornelis Wytfliet Early Antique Map of Florida, Louisiana, North America
- Title : Florida et Apalche
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1597
- Ref #: 41717
Description:
A fine original antique, and incredibly important map of the southern United States, one of only 3 maps printed prior to 1600, to depict this area with any accuracy, was published by Cornelis van Wytfliet in the 1597 edition of Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum. Wytfliet copied information from the Abraham Ortelius 1584 map Geronimo de Chaves map entitled La Florida, augmented with written accounts of Hernando de Soto inland expedition of 1539-42. Wytfliet also expands the area covered south to include parts of Cuba and north to C. de Arenas or the area of the Outer Banks of Carolina. It also enabled him to include the territory called Apalache. As such it is one of the few maps of the sixteenth century to record inland information largely from first hand European sources. Along with the Ortelius map of 1584, and the Johannes Metellus of 1598, these are the only printed maps of the present day southern United States published in the sixteenth century. The Florida peninsula is altered in shape from the Ortelius in that it is more rectangular and has a pronounced neck. The source for this delineation appears to be unknown. The Rio del Spirito Santo shown here is the Mississippi River. As noted by Burden:
The Florida Peninsula is altered in shape from Ortelius, in that it is more rectangular and has a pronounced neck. The source of this delineation appears to be unknown. The Rio del Spirito Santo shown here is the Mississippi River.
The map is known in only one state, but was also copied by Metellus in 1598.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/4in x 9 1/4in (285mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small professional repair to top border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1597 Cornelis van Wytfliet published his Augmentum to Ptolemys Geography. Dedicated to Philip III of Spain it is a history of the New World to date, recording its discovery, natural history etc. For the book Wytfliet had engraved nineteen maps, by whom we do not know, one of the world and eighteen regional maps of the Americas. As such this book can be truly called the first atlas of the New World, America.
Wytfliet, Cornelis van d. 1597
Cornelius Wytfliet or Cornelis van Wytfliet was a geographer from Leuven in the Habsburg Netherlands, best known for producing the first atlas of the Americas.
Cornelius was the son of Catherine Huybrechts and her husband, Gregorius Wytfliet, who was advocate fiscal of Leuven University from 1557 to 1594. After graduating Licentiate in Laws from the University of Leuven, Wytfliet moved to Brussels and became secretary to the Council of Brabant. He died in or shortly after 1597, when his Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum (a work adding new discoveries to Ptolemy\\\'s description of the world) was published
1598 Braun & Hogenberg Antique Map View Old Town of Gallipoli Apulia South Italy
- Title : Gallipolis
- Ref #: 82085
- Size: 20 3/4in x 16in (520mm x 405mm)
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautiful original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map a birds eye view of the Old Town of Gallipoli located on the Salentine Peninsula, in Apulia, Southern Italy & the Angevine-Aragonese Castle, was engraved by the Italian Natale Bonifacio di Girolamo, was published in the 1598 edition of Braun & Hogenbergs atlas on Civitates Orbis Terrarum
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 3/4in x 16in (520mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16in (520mm x 405mm)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top of right margin cropped to border
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Gallipoli is a southern Italian town and comune in the province of Lecce, in Apulia.
The town is located by the Ionian Sea, on the west coast of the Salentina Peninsula. The town of Gallipoli is divided into two parts, the modern and the old city. The new town includes all the newest buildings including a skyscraper. The old town is located on a limestone island, linked to the mainland by a bridge built in the 16th century.
According to a legend, the city was founded in ancient times by Idomeneus of Crete. Pliny the Elder attributes the foundation to the Senones Gauls, while more likely it was a Messapic settlement. Historically, what is known is that Gallipoli was a city of the Greater Greece, ruling over a large territory including today\'s Porto Cesareo. In 265 BC it sided with Pyrrhus and Taranto against ancient Rome, suffering a defeat which relegated it to a Roman colony (later a municipium).
In the early Middle Ages, it was most likely sacked by the Vandals and the Goths. Rebuilt by the Byzantines, Gallipoli lived an economically and socially flourishing period due to its geographical position. Later it was owned by the Roman Popes, and was a centre of fighting against the Greek monastic orders.
In the 11th century Gallipoli was conquered by the Normans and, in 1268, it was besieged by Charles I of Anjou, causing numerous inhabitants to flee to the nearby Alezio. The city was repopulated around 1300, under the feudal rule of the principality of Taranto. In 1484 the Venetians tried to occupy it, but without results. King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies started the construction of the port, which in the 18th century became the largest olive oil market in the Mediterranean.
After the unification of Italy (1861), Gallipoli was capital of a circondario, together with Lecce and Taranto.
1598 J Moretus & A Ortelius 1st Edition of The Peutinger Tables, Ancient Roman Empire Maps x 4
- Title : Tabula Peutingeriana. Tabula itineraria ex illustri Peutingerorum Bibliotheca quae Augusta Vindel. est. Beneficio Marco Velseri septemviri Augustani in lucem edita.
- Size: 22in x 20in (560mm x 510mm) each
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1598
- Ref #: 50519, 50520, 50521, 50522
Description:
For three decades, locating rare & unusual and maps has been one our main goals and I believe with the following maps we have reach a milestone. The following maps originate from the oldest direct linage of any maps we have offered, going back to the height of the Roman Empire. These are some of the rarest and most fascinating maps it has been my pleasure to offer.
In 1265 a Monk, in the German city of Colmar produced a hand written map, on parchment, of the imperial highways and cities of the ancient Roman world. When joined, the result was a scroll measuring 6.75m long & 34cm wide, covering an area from southeast England to present day Sri-Lanka. That map of 1265 was copied from an earlier 4th or 5th century map, itself copied from a 2nd century map that originated from a 1st century BC map from Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, a Roman General & architect. When Agrippa died in 12BC his map was engraved in marble and displayed in the Porticus Vipsania in the Campus Agrippae area in Rome.
In 1494 the German Scholar, Conrad Celtes, discovered the Colmar scroll in a library, in the city of Worms. After his death in 1508, Celtes bequeathed the scroll to Konrad Peutinger, after whom the map is named. The scroll was kept in the Peutinger family until it was purchased by Prince Eugene of Savoy in 1714 and finally purchased for the Habsburg Imperial Court Library in Vienna, where it resides today.
As early as 1577 Abraham Ortelius, the Flemish cartographer, was aware of the existence of the Peutinger Tables, at that stage owned by Mark Welser. In 1591 Welser had two sections of the scroll printed by Aldus Manutius in Venice. Ortelius thought these inadequate and so commissioned the scroll engraved onto 8 separate plates . Ortelius supervised the engraving of the plates but did not live to see the results. In December 1598 the first edition of the 8 plates were printed individually, in limited numbers, by Johannes Moretus in Antwerp and are today amongst some of the rarest sets of maps available. To save space for printing in the first & second atlases in 1619 & 1624, two plates were printed per page, thus saving space. At that point a change was made to each plate, the engraving of a descriptive title at the bottom of each plate.
These maps we are offering are unique, being printed two per page but without the addition of the titles. So the conclusion we have come to is that these were prototypes printed to see if the printing of two plates per page were possible prior to the changes to the plates, making them unique.
We know that there were a total of 300 sets of these tables published in 1619 & 1624 atlases Theatrum Geographiae Veteris & Parergon , of which very few have survived. As for the 1598 edition, we do not know the number published or how many have survived but there is no doubt the number is very low in the single digits. Also I can find no record of sale for this original 1598 1st Moretus edition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 20in (560mm x 510mm) each
Plate size: - 20 1/4in x 7 1/2in (505mm x 195mm) each
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Tabula Peutingerian also referred to as Peutingers Tabul or The Peutinger Table, is an illustrated itinerarium (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the cursus publicus, the road network of the Roman Empire. The map covers Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia, including the Middle East, Persia, and India.
The map was found as a 13th-century parchment copy based on a document from the 4th or 5th century, that contained a copy of the world map, originally prepared by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa a Roman general & architect active during the reign of the emperor Augustus (27 BC – AD 14). After Agrippas death in 12 BC, that map was engraved in marble and put on display in the Porticus Vipsania in the Campus Agrippae area in Rome, close to the Ara Pacis building.
The original Roman map, of which the 13th century parchment copy may be the only surviving copy, was last revised in the 4th or early 5th century. This is illustrated by the inclusion of the city of Constantinople, founded in 328, and the prominence of Ravenna, seat of the Western Roman Empire from 402 to 476, which suggests a fifth-century revision. The presence of certain cities of Germania Inferior that were destroyed in the mid-fifth century also provides proof or 4th or 5th century revision.
The surviving 13th century map itself was created by a monk in Colmar in modern-day eastern France in 1265. It is a parchment scroll, 0.34 metres (1 foot 1 inch) high and 6.75 metres (22.1 feet) long, assembled from eleven sections, a medieval reproduction of the original scroll.
The 13th century parchment map is very schematic, designed to give a practical overview of the road network, as opposed to an accurate representation of geographic features: the land masses shown are distorted, especially in the east–west direction. The map shows many Roman settlements and the roads connecting them, as well as other features such as rivers, mountains, forests and seas. The distances between settlements are also given. In total no fewer than 555 cities and 3,500 other place names are shown on the map. The three most important cities of the Roman Empire at the time – Rome, Constantinople and Antioch – are represented with special iconic decoration.
Besides the totality of the empire, the map also shows areas in the Near East, India and the Ganges, Sri Lanka (Insula Taprobane), and even an indication of China. It even shows a Temple to Augustus at Muziris (present day Kodungallur) on the modern-day Malabar Coast, one of the main ports for trade with the Roman Empire on the southwest coast of India. On the western end of the scroll, the absence of Morocco, the Iberian Peninsula, and the British Isles indicates that a twelfth original section has been lost in the surviving copy; the missing section was reconstructed in 1898 by Konrad Miller.
The map appears to be based on itineraries, lists of destinations along Roman roads, as the distances between points along the routes are indicated. Travellers would not have possessed anything so sophisticated as a modern map, but they needed to know what lay ahead of them on the road and how far. The Peutinger Table represents these roads as a series of stepped lines along which destinations have been marked in order of travel. The shape of the parchment pages accounts for the conventional rectangular layout. However, a rough similarity to the coordinates of Ptolemys earth-mapping gives some writers hope that some terrestrial representation was intended by the unknown original compilers.
The stages and cities are represented by hundreds of functional place symbols, used with discrimination from the simplest icon of a building with two towers to the elaborate individualized portraits of the three great cities. Some conclud that the semi-schematic, semi-pictorial symbols reproduce Roman cartographic conventions of the itineraria picta described by 4th-century writer Vegetius, of which this is the sole known testimony.
The 13th century copy map was discovered in a library in the city of Worms by German scholar Conrad Celtes in 1494, who was unable to publish his find before his death and bequeathed the map in 1508 to Konrad Peutinger, a German humanist and antiquarian in Augsburg, after whom the map is named. The Peutinger family kept possession of the map for more than two hundred years until it was sold in 1714. It then bounced between several royal and elite families until it was purchased by Prince Eugene of Savoy for 100 ducats; upon his death in 1737, it was purchased for the Habsburg Imperial Court Library in Vienna (Hofbibliothek). It is today conserved at the Austrian National Library at the Hofburg palace in Vienna.
The map was copied for Dutch cartographer Abraham Ortelius by Johannes Moretus and published separetly, shortly after his death, in 1598. The maps were not published in an atlas until 1619 by Petrus Bertius and again in the Ortelius Parageon in 1624.
A partial first edition was printed at Antwerp in 1591 (titled Fragmenta tabulæ antiquæ) , Johannes Moretus, printed the full Tabula in December 1598, in Antwerp. Johannes Janssonius published another version in Amsterdam, c. 1652.
In 1753 Franz Christoph von Scheyb published a copy, and in 1872 Konrad Miller, a German professor, was allowed to copy the map. Several publishing houses in Europe then made copies. In 1892 publishers Williams and Norgate published a copy in London, and in 1911 a sheet was added showing the reconstructed sections of the British Isles and the Iberian peninsula missing in the original.
1598 Munster Antique Map a View of the German City of Landau, Munich, Bavaria
- Title : Die Statt Landaw
- Ref #: 33576
- Size: 17in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
- Date : 1628
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the German City of Landau in the state of Bavaria NE of Munich was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1628 edition of Cosmographia.
Landau or Landau in der Pfalz (pop. 41,821) is an autonomous (kreisfrei) city surrounded by the Südliche Weinstraße ("Southern Wine Route") district of southern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a university town (since 1990), a long-standing cultural centre, and a market and shopping town, surrounded by vineyards and wine-growing villages of the Palatinate wine region. Landau lies east of the Palatinate forest, Europe's largest contiguous forest, direct on the German Wine Route.
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographia appeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications of Cosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 14 1/2in (435mm x 370mm)
Margins: - 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: -Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
1598 Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Baden bei Zürich, Aargau, Switzerland
- Title : Die Statt Baden
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 30357
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the Swiss city of Baden bei Zürich on the Limmat River in the Canton of Aargau was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Baden sometimes unofficially, to distinguish it from other Badens, called Baden bei Zürich (Baden near Zürich) or Baden im Aargau (Baden in Aargau) is a municipality in Switzerland. It is the seat of the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau. Located 25 km northwest of Zürich in the Limmat Valley (Limmattal) mainly on the western side of the Limmat, its mineral hot springs have been famed since at least the Roman era.
Baden is first attested in Roman sources as Aquae Helveticae (Waters of the Helvetii). Hippocrates had counseled against the use of water from mineral springs, but by the time of Vitruvius, Pliny, and Galen they were being selectively employed for certain ailments. In addition to their medical use, the Romans also revered natural springs for recreational and religious use. Tacitus mentions the town obliquely, describing it as a place built up into a semblance of a town... much used for its healthful waters. This Roman vicus was to the north of the Baden gorge on the Haselfeld, founded to support the legionary camp at Vindonissa. There was a pool complex on the left bank of the Limmat fed by a system of springs with 47 °C water. The main axis of the vicus was the Vindonissa road, which ran parallel to the slope. It was flanked by porticos, beyond which lay commercial and residential buildings. The center of the settlement had some wealthy villa-like structures. The resort, residential, and commercial districts all grew to a respectable size over the first half of the 1st century. In ad 69, however, the 21st Legion burned the town amid the conflicts of the Year of the Four Emperors. Its wooden buildings destroyed, the town was rebuilt in stone. The town shrank some after the closing of the Vinonissa camp in ad 101 but survived on trade. Reginus\'s pottery workshop and Gemellianus\'s bronze works flourished during the second half of the 2nd century Around the middle of the 3rd century, however, the settlement was threatened by multiple Alemanni invasions and the Huns. The pools were fortified and a large number of coins stamped with references to the hot springs show it continued to be settled and frequented into late antiquity, but expansion of the settlement of Haselfeld came to an end.
The baths were frequented again by the time of Charlemagne. A medieval necropolis in Kappelerhof has been dated as far back as the 7th century and a local lord fortifying the Stein by the 10th. The modern name Baden is first attested in 1040. Around that time, its land was held by the Lenzburgs, some of whom styled themselves as the Counts of Baden in the 12th century and erected a castle. Upon their extinction around 1172, their domains were divided among the Hohenstaufens, Zähringens, and Kyburgs, with the Kyburgs gaining control of Baden through the marriage of Harmanns III with its heiress Richenza. Around 1230, they founded the medieval city of Baden, holding markets and erecting a bridge across the river in 1242. Upon the death of the childless Hartman IV in 1264, his lands were seized by Rudolf von Habsburg by right of his wife Gertrude\'s claim. Stein Castle was held by Habsburg bailiffs and maintained the administration and archives for their surrounding territory. The Confederation besieged and destroyed the castle and its records in 1415 during its conquest of Aargau. Thus, the County of Baden was established.
Under the Confederation, their bailiff held a castle on the right bank of the Limmat, controlling access to the bridge. The Swiss Diet met at Baden repeatedly from 1426 to about 1712, making Baden a kind of capital for Switzerland. The Town Hall (Rathaus) where it met is beautifully carved and can still be visited. Over the course of the 15th century, the town regained its popularity as a Spa Resort (Kurort). The town was the site of a famous debate on transubstantiation from May 21 to June 18, 1526. Although Zwingli refused to attend in person, he printed broadsheets throughout its duration and sent his assistant Johann Oecolampadius to debate Johann Eck and Thomas Murner. In the end, a majority decided against the reformers but a substantial bloc emerged on their behalf as well. Johann Pistorius held a disputation in the city in 1589. Stein was refortified sometime between 1658 and 1670 but the fortress was abandoned in 1712. In 1714, the treaties of Rastatt and Baden ended hostilities between France and the Habsburgs, the last theater of the War of the Spanish Succession. Another Treaty of Baden ended the Toggenburg War among the Protestant and Catholic Swiss cantons in 1718. Baden was the capital of the canton of Baden from 1798 until 1803, when the canton of Aargau was created.
In the 19th century, the waters were considered efficacious for gout and rheumatism. They were frequented by Goethe, Nietzsche, Thomas Mann, and particularly often by Hermann Hesse, who visited the town annually over almost thirty years. The SNB connecting Zürich to Baden was Switzerland\'s first railway, opening in 1847. Prior to the First World War, foreign visitors were few in number, but the summer tourist season was thought to swell the town. Around the same time, an industrial quarter opened up NW of the baths
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning along centerfold, light soiling
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of the city of Poitiers in Poitou France
- Title : Die Statt Puttiers
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 30381
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the French city of Poitiers on the Clain River in the Vienne Dept of central western France, was published in the French Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Poitiers is a city on the Clain river in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and also of the Poitou.
The type of political organisation existing in Poitiers during the late medieval or early modern period can be glimpsed through a speech given on 14 July 1595 by Maurice Roatin, the town\'s mayor. He compared it to the Roman state, which combined three types of government: monarchy (rule by one person), aristocracy (rule by a few), and democracy (rule by the many). He said the Roman consulate corresponded to Poitiers\' mayor, the Roman senate to the town\'s peers and échevins, and the democratic element in Rome corresponded to the fact that most important matters can not be decided except by the advice of the Mois et Cent (broad council).1 The mayor appears to have been an advocate of a mixed constitution; not all Frenchmen in 1595 would have agreed with him, at least in public; many spoke in favour of absolute monarchy. The democratic element was not as strong as the mayor\'s words may seem to imply: in fact, Poitiers was similar to other French cities, Paris, Nantes, Marseille, Limoges, La Rochelle, Dijon, in that the town\'s governing body (corps de ville) was highly exclusive and oligarchical: a small number of professional and family groups controlled most of the city offices. In Poitiers many of these positions were granted for the lifetime of the office holder.
The city government in Poitiers based its claims to legitimacy on the theory of government where the mayor and échevins held jurisdiction of the citys affairs in fief from the king: that is, they swore allegiance and promised support for him, and in return he granted them local authority. This gave them the advantage of being able to claim that any townsperson who challenged their authority was being disloyal to the king. Every year the mayor and the 24 échevins would swear an oath of allegiance between the hands of the king or his representative, usually the lieutenant général or the sénéchaussée. For example, in 1567, when Maixent Poitevin was mayor, king Henry III came for a visit, and, although some townspeople grumbled about the licentious behaviour of his entourage, Henry smoothed things over with a warm speech acknowledging their allegiance and thanking them for it.
In this era, the mayor of Poitiers was preceded by sergeants wherever he went, consulted deliberative bodies, carried out their decisions, heard civil and criminal suits in first instance, tried to ensure that the food supply would be adequate, visited markets.
In the 16th century, Poitiers impressed visitors because of its large size, and important features, including royal courts, university, prolific printing shops, wealthy religious institutions, cathedral, numerous parishes, markets, impressive domestic architecture, extensive fortifications, and castle.
16th-century Poitiers is closely associated with the life of François Rabelais and with the community of Bitards.
The town saw less activity during the Renaissance. Few changes were made in the urban landscape, except for laying way for the rue de la Tranchée. Bridges were built where the inhabitants had used gués. A few hôtels particuliers were built at that time, such as the hôtels Jean Baucé, Fumé and Berthelot. Poets Joachim du Bellay and Pierre Ronsard met at the University of Poitiers, before leaving for Paris.
During the 17th century, many people emigrated from Poitiers and the Poitou to the French settlements in the new world and thus many Acadians or Cajuns living in North America today can trace ancestry back to this region.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13 1/4in (380mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins cropped into border
Plate area: - Light toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light toning along centerfold
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Munster Large Antique Print View of Worms Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Wormbs
- Ref #: 30347
- Size: 15 1/2in x 13in (420mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the Germany city of Wormbs was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1598 edition ofCosmographia.
Worms is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, situated on the Upper Rhine about 60 kilometres (40 miles) south-southwest of Frankfurt-am-Main. It had some 80,000 inhabitants as of 2013.
A pre-Roman foundation, Worms was the capital of the kingdom of the Burgundians in the early 5th century and hence the scene of the medieval legends referring to this period, notably the first part of the Nibelungenlied. Worms has been a Roman Catholic bishopric since at least 614, and was an important palatinate of Charlemagne. Worms Cathedral is one of the Imperial Cathedrals and among the finest examples of Romanesque architecture in Germany. Worms prospered in the High Middle Ages as an Imperial Free City. Among more than a hundred Imperial Diets held at Worms, the Diet of 1521 (commonly known as the Diet of Worms) ended with the Edict of Worms in which Martin Luther was declared a heretic. Today, the city is an industrial centre and is famed as the origin of Liebfraumilch wine. Other industries include chemicals and metal goods.
Background: For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle hisCosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
Sebastian Münster (1488-1552) was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and Hebrew scholar whose work Cosmographia (1544; "Cosmography") was the earliest German description of the world and a major work in the revival of geographic thought in 16th-century Europe. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French, Italian, English, and even Czech. Altogether, about 40 editions of the Cosmographiaappeared between 1544 and 1628 and was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. Münster was a major influence in popular thinking in Europe for the next 200 years.
This success was due not only to the level of descriptive detail but also to the fascinating full page maps & views as well as smaller woodcuts that were included in the text. Many of the woodcuts were executed by famous engravers of the time including Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel.
Aside from the well-known maps present in the Cosmographia, the text is thickly sprinkled with vigorous views: portraits of kings and princes, costumes and occupations, habits and customs, flora and fauna, monsters, wonders, and horrors about the known -- and unknown -- world, and was undoubtedly one of the most widely read books of its time.
Münster acquired the material for his book in three ways. Firstly he researched all available literary sources across Germany, Switzerland and other parts of Europe. Secondly he obtained original manuscript material from locals all over Europe for description of the countryside, cities, villages, towns, rivers and local history. Finally, he obtained further material first hand on his travels (primarily in south-west Germany, Switzerland, and Alsace).
In 1588 Sebastian Petri re-released Cosomgraphia and re-issued many of Munsters maps and views in the "copperplate style". The maps in this release were more sophisticated than with earlier publications ofCosomgraphia and were based on the 1570 release of Abraham Ortelius monumental work Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 13in (420mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 13in (420mm x 330mm)
Margins: - 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margins cropped to image
Plate area: -Age toning along center-fold
Verso: - Light soiling
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Luneburg Hamburg, Germany
- Title : Die Statt Leunenburg
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 30328
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Lüneburg (Lunenburg) incorporated into the city of Hamburg in Lower Saxony was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Lüneburg also called Lunenburg in English, is a town in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is located about 50 km southeast of Hamburg, and belongs to that citys wider metropolitan region.
With the demise of the Hanseatic League – and the absence of herrings around 1560 around Falsterbo in Scania – the biggest customers of Lüneburg\'s salt broke away and the town rapidly became impoverished. Hardly any new houses were built in central Lüneburg after this time, which is why the historical appearance of the town centre has remained almost unchanged until the present day.
The town became part of the Electorate of Hanover in 1708, the Kingdom of Westphalia in 1807, the First French Empire in 1810, the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814, and the Prussian Province of Hanover in 1866.
In the centuries after the collapse of the League, it was as if Lüneburg had fallen into a Sleeping Beauty slumber. Heinrich Heine, whose parents lived in Lüneburg from 1822 to 1826, called it his residence of boredom (Residenz der Langeweile). Near the end of the 19th century Lüneburg evolved into a garrison town, and it remained so until the 1990s.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (3mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Age toning along centerfold, light soiling
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map Birds Eye View of Weissenburg Bavaria Germany
- Title : Die Statt Wyssenburg
- Date : 1598
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref # : 30351
- Size : 15in x 13in (380mm x 340mm)
Description:
This fine original wood block engraved antique map a birds eye view of the German city of Weißenburg (Weissenburg) in Bavaria in Middle Franconia - identified by the cities Coate of Arms with double headed eagle atop of a castle - was published in the German Section of Sebastian Munsters 1598 edition of Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung (Cosmographia, that is: description of the whole world, in it all monarchies Keyser thumben, kingdoms, prince thumben, graff and herrschafften, countries, places and municipalities.)
Weißenburg in Bayern (formerly also Weißenburg im Nordgau) is a town in Middle Franconia, Germany. It is the capital of the district Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen. Weissenburg is located in central Bavaria, in the south of the administrative region Mittelfranken.
The history of Weißenburg is generally traced back to the Roman fort that was built in the area towards the end of the first century. The settlement, which included Thermae, lay on the border of the Roman Empire and on the Tabula Peutingeriana from the 4th century it had the name Biriciana. Germanic tribes destroyed the fort and settled in what is still the city centre. The first mention of the name Weißenburg is in a deed dating from 867. The city became the seat of a royal residence during the reign of the Franks and according to legend, Charlemagne stayed there to supervise the construction of Fossa Carolina.
The city became a Free Imperial City in 1296 and continued to grow until the Reformation. Following the example of Nuremberg the city joined the Protestant side but it suffered heavily in the ensuing wars. However, the rights of the city as a Free Imperial City and an Imperial Estate were restored in the final peace treaty and some growth resumed. Despite its insignificant size and economic importance, the city, like the other 50-odd free imperial cities, was virtually independent.
Weissenburg lost its independence in 1802 and became part of the Bavarian kingdom in 1806. It was however saved from insignificance with the construction of a railway between Nuremberg and Augsburg which goes through the city and which supported industrialisation. Following World War II over 6,000 refugees and people expelled from the territories which Germany lost settled in the city and have since played an important role in its industry and culture.
The many stages in the history of Weissenburg can still be seen today. There are many ruins from the Roman times. One of the finest is the remains of a Roman bath which was excavated in 1977 and has been turned into a museum. The city wall from the Middle Ages has survived almost intact with its towers and in the Gothic Town Hall the city\'s elected members have held their meetings from 1476.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 13in (410mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Repair to bottom margin, no loss
Plate area: - Age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Cosmographia, Das ist: Beschreibung der gantzen Welt, Darinnen Aller Monarchien Keyserthumben, Königreichen, Fürstenthumben, Graff- und Herrschafften, Länderen, Stätten und Gemeinden.Ursprung, Regiment, Reichthumb, Gewalt und.Beschaffenheit. Dessgleichen Aller deren, beyder Ständen, Regenten: Keysern, Königen, Bäpsten, Bischoffen.Genealogien und Stammbäumen.zusammen getragen. by Sebastian Münster was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world. It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628, long after Munsters death. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century. It passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Tabula novarum insularum, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically discrete.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemys Geographia with illustrations.
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map View of Freiberg, Saxony Southern Germany
- Title : Die Statt Freyberg
- Date : 1598
- Size: 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
- Ref #: 30329
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the German City of Freiberg, Saxony was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1598 edition of Cosmographia.
Freiberg (German for "free for mining activities") is a university and mining town in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is a so-called Große Kreisstadt (large county town) and the administrative centre of Mittelsachsendistrict.
Background:
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold
Verso: - Light age toning along centerfold
1598 Sebastian Munster Antique Map, Birds Eye View, The City of Tours, France
- Title : Die Statt Tours
- Date : 1598
- Size: 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
- Ref #: 30380
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique print a view of the French city of Tours was published by Sebastian Munster in the 1598 edition of Cosmographia.
Tours is a city located in the centre-west of France. It is the administrative centre of the Indre-et-Loire department and the largest city in the Centre-Val de Loire region of France (although it is not the capital, which is the region's second-largest city, Orléans). Tours stands on the lower reaches of the River Loire, between Orléans and the Atlantic coast. The surrounding district, the traditional province of Touraine, is known for its wines, for the alleged perfection (as perceived by some speakers) of its local spoken French, and for the Battle of Tours (732).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
For a variety of reasons town plans were comparatively latecomers in the long history of cartography. Few cities in Europe in the middle ages had more than 20,00 inhabitants and even London in the late Elizabethan period had only 100-150,000 people which in itself was probably 10 times that of any other English city. The Nuremberg Chronicle in 1493 included one of the first town views of Jerusalem, thereafter, for most of the sixteenth century, German cartographers led the way in producing town plans in a modern sense. In 1544 Sebastian Munster issued in Basle his Cosmographia containing roughly sixty-six plans and views, some in the plan form, but many in the old panorama or birds eye view..
1601 Abraham Ortelius Antique Title Page from The Theatrum Orbis Terrarum Atlas
- Title : Theatrum Orbis Terrarum Abrahami Orteli Quod ante...Apud Joannem Moretum...Anno CICICCI (MDCI) (1601)
- Size: 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 270mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Date : 1601
- Ref #: 32026
Description:
This hand coloured original copper plate engraved title page was published in the 1601 Latin edition of the first concise Atlas of the World Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. by Abraham Ortelius.
There were a total of 7300 copies of Theatrum published between 1570 - 1612 of which 200 were published in 1601. (Ref: Van Den Broecke; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 10 1/2in (430mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13 3/4in x 9in (350mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning & light creasing
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Old tape residue neutralised
Background:
Theatrum Orbis Terrarum is considered to be the first true modern atlas. Written by Abraham Ortelius, strongly encouraged by Gillis Hooftman and originally printed on May 20, 1570, in Antwerp, it consisted of a collection of uniform map sheets and sustaining text bound to form a book for which copper printing plates were specifically engraved. The Ortelius atlas is sometimes referred to as the summary of sixteenth-century cartography. The publication of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570) is often considered as the official beginning of the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography (approximately 1570s–1670s)
The atlas contained virtually no maps from the hand of Ortelius, but 53 bundled maps of other masters, with the source as indicated. Previously, only the pooling of disparate maps were released as custom on order. The Ortelius atlas, however, dropped the maps for this all in the same style and on the same size on copper plates, logically arranged by continent, region and State. He provided the maps in addition to a descriptive comment and referrals on the reverse. As such, this was the first time that the entirety of Western European knowledge of the world was brought together in one book.
In the bibliography, the section Catalogue Auctorum, not only were the 33 cartographers mentioned, whose work in the Theatrum was recorded (at that time not yet the habit), but also the total of 87 cartographers of the 16th century that Ortelius knew. This list grew in every Latin Edition, and included no less than 183 names in 1601. Among the sources are mentioned among other things the following: for the world map the World Map (1561) by Giacomo Gastaldi, the porto Avenue of the Atlantic coast (1562) by Diego Gutierrez, the world map (1569) of Gerardus Mercator, which have 8 maps derived from the Theatrum.
For the map of Europe, wall map (1554). of the Mercator map of Scandinavia (1539) by Olaus Magnus, map of Asia was derived from his own Asia-map from 1567, which in turn was inspired by that of Gastaldi (1559). Also for the Africa map he referred to Gastaldi.
This work by Ortelius, consisted of a collection of the best maps, refined by himself, combined into one map or split across multiple, and on the same size (folios of approximately 35 x 50 cm). The naming and location coordinates were not normalized.
After the initial publication of Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, Ortelius regularly revised and expanded the atlas, reissuing it in various formats until his death in 1598. From its original seventy maps and eighty-seven bibliographic references in the first edition (1570), the atlas grew through its thirty-one editions to encompass 183 references and 167 maps in 1612.
The online copy of the 1573 volume held by the State Library of New South Wales contains 70 numbered double-page sheets, tipped onto stubs at the centerfold, with 6 maps combined with descriptive letterpress on the recto of each first leaf. The legends of most maps name the author whose map Ortelius adapted. In the preface Ortelius credits Franciscus Hogenberg with engraving nearly all the maps.
The 1573 Additamentum to the atlas is notable for containing Humphrey Llwyds Cambriae Typus, the first map to show Wales on its own.
From the 1630s, the Blaeu family issued their work under a similar title, Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive, Atlas Novus.
All those editions had the same structure. They started with an allegorical title page, on which the five known continents, were presented by allegorical women, with Europe as the Queen. Then a command to Philip II, King of Spain and the low countries, and a poem by Adolphus Mekerchus (Adolf of Meetkercke). From 1579, the editions contain a portrait of Ortelius by Philip Galle, an introduction by Ortelius, in the Latin editions followed by a recommendation by Mercator. This is followed by the bibliography (Auctorum Catalog), an index (Index Tabularum), the cards with text on the back, starting from 1579 in the Latin editions followed by a register of place names in ancient times (Nomenclator), the treatise, the Mona Druidum insula of the Welsh scientist Humphrey Lhuyd (Humphrey Llwyd) over the Anglesey coat of arms, and finally the privilege and a colophon.
The moneyed middle class, which had much interest in knowledge and science, turned out to be very much interested in the convenient size and the pooling of knowledge. For buyers who were not strong in Latin, published at the end of 1572, in addition to three Latin, there were a Dutch, German and French 2nd Edition. This rapid success prompted the Ortelius Theatrum constantly continued to expand and improve. In 1573, he released 17 more additional maps under the title Additamentum Theatri Orbis Terrarum, which in these master works were published, bringing the total at 70 maps. By Ortelius death in 1598, there were twenty-five editions that appeared in seven different languages.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1606 Gerard Mercator Antique Map British Islands Anglesey, Wight Guernsey Jersey
- Title : Anglesey; Wight Vectis, olim; Garnesay: Jarsay
- Ref #: 17014
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (550mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1606
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper plate engraved antique map of the 4 British Islands of Anglesey, Wight Guernsey Jersey by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the 1606 edition of Mercators Atlas, Atlas Sive Cosmographicae Meditationes Illustrissimi Ducis.
This map is beautiful with early original hand colour, heavy dark impression, on heavy paper and original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (550mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/4in x 12 1/2in (440mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age Toning
Anglesey is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. The English name of the island may be derived from the Old Norse; either Ǫngullsey Hook Island or Ǫnglisey Ǫngli's Island. No record of such an Ǫngli survives, but the place name was used by Viking raiders as early as the 10th century and later adopted by the Normans during their invasions of Gwynedd. The traditional folk etymology reading the name as the Island of the Angles (English)] may account for its Norman use but has no merit, as the Angles name itself is probably cognate with the shape of the Angeln peninsula. All of them ultimately derive from the proposed Proto-Indo-European root *ank- (to flex, bend, angle). Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries and into the 20th, it was usually spelt Anglesea in documents.
The oldest records that give a name for the Isle of Wight are from the Roman Empire: it was then called Vectis or Vecta in Latin, Iktis or Ouiktis in Greek. From the Anglo-Saxon period Latin Vecta, Old English Wiht and Old Welsh forms Gueid and Guith are recorded. In Domesday Book it is Wit; the modern Welsh name is Ynys Wyth (ynys = island). These are all variant forms of the same name, possibly Celtic in origin. It may mean "place of the division", because the island divides the two arms of the Solent.
The Channel Islands are an archipelago of British Crown Dependencies in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two separate bailiwicks: the Bailiwick of Jersey and the Bailiwick of Guernsey. They are considered the remnants of the Duchy of Normandy, and are not part of the United Kingdom. They have a total population of about 168,000 and their respective capitals, Saint Helier and Saint Peter Port, have populations of 33,500 and 16,488, respectively. The total area of the islands is 194 km.
Both Bailiwicks have been administered separately since the late 13th century; each has its own independent laws, elections, and representative bodies (although in modern times, politicians from the islands' legislatures are in regular contact). Any institution common to both is the exception rather than the rule.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1606 Mercator Old, Antique Atlas Title Page of Geographia Atlas on France
- Title : Galliae tabule Geograpicae per Gerardum Mercatorem Fllustrissimi Ducis...
- Ref #: 92698
- Size: 18in x 10 1/2in (460mm x 270mm)
- Date : 1606
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique Title Page* was published as the Front Piece of Gerard Mercator's edition of the Geographia Atlas of France, published in 1606.
After the sale of Mercator's plates to Henricus Hondius in 1605, Hondius continued to publish the original plates with little alteration until 1630 when, along with Jan Jansson, many of the original plates were altered and published in new editions of Mercator's atlas. (Ref: Koeman, Tooley)
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18in x 10 1/2in (460mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning
1607 Mercator Antique Map of Spain & Portugal
- Title : Hispania Nova Descriptio de Integro...Petrus Kaerius
- Date : 1607
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 42002
- Size: 20in x 18in (510mm x 430mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Spain & Portugal by Gerard Mercator was published by Rumold Mercator &Jodocus Hondius in the very early 1607 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas.
This map is magnificent with beautiful original hand colouring. Original colouring such as this is scarce and hard to find.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Background:
Many of the original charts and maps drawn by the first Portuguese and Spanish navigators have survived for the very good reason that, on completion of their voyages, pilots were obliged to hand over their manuscript notes to the Casa da India (founded 1504) in Lisbon or to the equivalent Casa de Contrataci6n de las Indias (founded 1504) in Seville. The clear intention was to maintain secrecy over new discoveries and control over the distribution of cartographic material, not always successfully, as it happened; pilots and navigators seem to have changed allegiance with impunity and, in consequence, many of the earliest and most informative charts were compiled as far away as Genoa, Venice, Florence and Ancona, presumably from sources outside the Portuguese and Spanish 'Casas'.It is apparent that few manuscripts reached the printing stage and, indeed, are so rare that any study of them must be regarded as a specialist subject. (Ref Tooley M&B)(Ref: Koeman; Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red, green, purple, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 18in (510mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 16in (420mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left margin cropped into border
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Light re-enforcing along centerfold
1607 Mercator Hondius Original Antique Map of Ireland - Rare and beautiful
- Title : Irlandiae regnum
- Date : 1607
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 42003
- Size: 20in x 18in (560mm x 430mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Ireland by Gerald Mercator was published by Rumold Mercator & Jodocus Hondius in the very early 1607 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas.
This map is magnificent with beautiful original hand colouring. Original colouring such as this is scarce and hard to find.
These maps, published in the early editions of Mercators atlas, are the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his sons Rumold & Henricus as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
The earliest maps of Ireland up to the year 1500 or so share the shortcomings of those of the rest of the British Isles especially as represented on world maps. It was not to be expected that lands literally on the very edge of the known world could be depicted with any accuracy; very often one feels that the cartographers or engravers placed the islands in the nearest available space consistent with their imagined position. Even in the first printed Ptolemaic map there is still much distortion in Ireland's shape and geographical position but, on the other hand, a quite surprising number of place names and other details are shown, as many, in fact, as in the rest of Britain put together. This detailed knowledge is not as puzzling as it might appear, for the Ptolemy maps, at least the later editions from 1513 onwards, were based on Italian portulan charts and these, in turn, reflected knowledge gained during the long commercial relationship which had existed between Italy and Ireland ever since the thirteenth century. The distortions on land-surveyed maps remained uncorrected until late in the seventeenth century but a quite accurate coastal outline was given in the marine atlases of Waghenaer, Dudley, Blaeu and later Dutch chart makers.
Apart from a few manuscript maps and very rare maps printed in Rome and Venice (George Lily, 1546, and others in the period 1560-66) Ireland is shown on Mercator's large map of the British Isles (1564), and in his Atlas (1595) and as a separate sheet in the Ortelius atlases (from 1 573). The most important map, however, was compiled by an Italian, Baptista Boazio, probably in the 1 5 8os. This has survived in manuscript form and may have been used by Pieter van der Keere for a map published by Jodocus Hondius in 1591. Boazio's map was subsequently published by John Sudbury, who later sold Speed's maps, and this version was included in editions of the Ortelius atlases from 6oz onwards. The Boazio map is a quite splendid map, very decorative, some copies even showing an Eskimo complete with kayak and hunting spear. Thereafter the trend is familiar: Camden, Speed, Blaeu, Jansson, Sanson and others of the Dutch and French schools all included a general map or maps of the Irish provinces in their atlases. Speed's map of the whole of Ireland was based at least partly on surveys by Robert Lythe (c.1570) and Francis Jobson(c.1590) and included figures in national costume; it was for long regarded as the best map available and was much copied by publishers in other countries.
In 1685 the first atlas of Ireland to match Saxton's At/as of Eng/andand Wales was published by Sir William Petty as Hiberniae Detineaho, the result of a highly organized and detailed survey (the 'Down' survey) carried out in the years following 1655. Re-issued in miniature form soon afterwards by Francis Lamb, Petty's Atlas was widely used as the basis for practically all maps of Ireland produced by English, French, Dutch and German publishers in the following century. Apart from re-issues of Petty's Atlas and its many copyists there were maps by George Grierson, a Dublin publisher, John Rocque, the Huguenot surveyor and engraver who spent some years in Dublin, and Bernard Scale, Rocque's brother-in-law.
Towards the end of the century many large-scale maps were published but, as in England, private mapping was gradually overtaken and eventually replaced by the Ordnance Survey maps produced between the years 1824 and 1846.(Ref: Koeman, Tooley)
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red, green, purple, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 18in (560mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 14in (420mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to margins
Plate area: - Old professional repair to 45mm sq to left side
Verso: - Old professional repair to text "H"
1609 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of India, China & SE Asia
- Title : India Orientalis
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1609
- Ref #: 75001
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original map of India, SE Asia & the East Indies was published in Gerard Mercator's French edition of Atlas sive Cosmographicae published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson in 1609..
Background: One of the finest of the early Dutch maps of the region published. It was first published in 1606 as one of the 37 new maps engraved by Jodocus Hondius' for Mercators Atlas.
The map extends from India to the coasts of Southern China including the Pearl Jodocus HondiusRiver Estuary, Canton and Formosa. It also includes all of the Malay peninsula and Indochina, northern Borneo and the Philippines.
Hondius shared the classic view of the SE Asian River Systems, mapping five rivers from the Mekong westward, as originating in a lake in the Himalayas. The kingdom of Lan Na is shown originating in what is today northern Thailand and a depiction of the Mergui Archipelago off the Burmese portion of the Malay Peninsula as an island studded sea. The old capital of Siam, Ayuthaya, is shown on an island in the Gulf of Siam.
The decorative detail includes a large sea monster and an oriental junk in the Bay of Bengal as well as fine scrollwork title & scale cartouches. One of the most interesting & unusual features of the Southern Malay peninsula is its dissection in two, the southern part becoming an island just south of Malacca where it is separated from the rest of the peninsula by a large north-easterly channel. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 14in (490mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1609 Mercator & Hondius Large Antique Map of Austria
- Title : Austria Archiducatus
- Ref #: 60052
- Size: 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1609
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of Austria was published in the 1609 French edition of Mercators Atlas published by Henricus Hondius and Jan Jansson.
These maps, published in the later editions of Mercators atlas, are derived from the original maps drawn and engraved by Gerald Mercator in the mid to late 16th century, published by his son Rumold as an atlas, after his death, in 1595. After two editions the plates were purchased by Jodocus Hondius in 1604 and continued to be published until the mid 1630's when the plates were re-engraved and updated by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18in (560mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 13in (485mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1609 Mercator Hondius Antique Map of Siberia, China, Central Asia, North America
- Title : Tartaria
- Date : 1609
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50661
- Size: 23in x 19in (580mm x 480mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Central Asia, China & Eastern Russia with a very early view of the NW coast of America - one of the first maps to depict this region - by Gerard Mercator was published by Joducus Hondius in the 1609 French edition of Mercators Atlas.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy, stained & weak in places
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (580mm x 480mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 13 1/2in (490mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background:
A beautifully ornate map in a style highly popular in the 16th and early 17th centuries. To the left of the map is the image of a man of Central Asia and another of an Arctic Hunter, possibly an Eskimo. The rest of the map is full of detail both real and myth, some of which is no doubt borrowed from the writings of Marco Polo considered at the time one of the foremost expert on China and Central Asia. Overlooked by some experts is the inclusion of the NW Coastline of America important as it would be 150 years before this region was thoroughly mapped by Capt. James Cook in the 1770's.
The newly discovered northern coastline of Nova Zembla is shown with a notation concerning the Dutch expedition led by Willem Barents in 1594-96. Interesting notations in Siberia, Ung quae Gog and Sumongul quae Mogog, refer to the mythological lands of Gog and Magog. These lands, noted in the Bible as being situated in the remotest parts of the earth, were originally depicted on maps just north of Israel. Also shown is the Great Wall of China, Korea is depicted as an Island, a very early example of the the Northwest Coast of America, naming Cape de Fortuna and the Straits of Anian. The map extends west to include the Black Sea and Russia, but the primary focus of the map is Tartaria, Central Asia China and Asiatic Russia. Decorative vignettes in include a nomadic tribe, tents and livestock. An early map of the region and certainly one of the most decorative of the genre.
Jodocus Hondius (1563 - 1612), one of the most notable engravers of his time, is known for his work in association with many of the cartographers and publishers prominent at the end of the sixteenth and the beginning of the seventeenth century.
In 1604 Hondius bought the plates of Mercator's Atlas which, in spite of its excellence, had not competed successfully with the continuing demand of Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
To meet this competition Hondius added about 40 maps to Mercator's original number and from 1606 published enlarged editions in many languages, still under Mercator's name but with his own name as publisher. These atlases have become known as the Mercator/Hondius series. The following year the maps were re-engraved in miniature form and issued as a pocket Atlas Minor.
After the death of Jodocus Hondius the Elder in 1612, work on the two atlases, folio and miniature, was carried on by his widow and sons, Jodocus II and Henricus, and eventually in conjunction with Jan Jansson in Amsterdam. In all, from 1606 onwards, nearly 50 editions with increasing numbers of maps with texts in the main European languages were printed. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley)
1610 Johannes Kip Antique Map of the County of Flintshire, Wales, Great Britain
- Title : Flint Comitatus quem Ordovices olim Incolucrunt
- Ref #: 01-3604
- Size: 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1610
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
A very attractive early original hand coloured antique map of Flintshire (Welsh: Sir y Fflint) Wales, based on the first survey of the county by Christopher Saxton, was engraved by William Kip for William Camden's Britannia* (London: 1607-1637).
As well as still being the earliest printed map of Flintshire at an 'affordable' price it is also the first detailed one dedicted solely to the county.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, green, brown
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 13in (380mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling to margin edges
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Britannia', was one of the most popular and influential books of the period. The work of the Elizabethan antiquarian, William Camden (1551-1623), it was a detailed historical and topographical description of Great Britain. Its patriotic sentiments, in particular, both appealed to and generated the growing sense of nationalism that was coursing through late Tudor / early Stuart society. Between 1607 and 1637, county maps engraved by William Kip and William Hole, and based largely on Saxton's surveys, were added. These maps have the distinction of being the first set to show each county individually as opposed to several being grouped together on one page. Camden's Britannia continued to be published well into the 19th century; from 1695 to 1772, county maps by Robert Morden were used, and from 1789 to c.1815, those by the renowned John Cary.
1610 John Speed Antique Map of The English County of Cambridgeshire
- Title : Cambridgeshire described with the deuision of the hundreds, the Townes situation with the Armes of the Colleges of that famous Vniuersiti...And also the Armes of all such Princes and noble men as have heertofore borne the Honorable tytles & dignities of the Earldome of Cambridge....Performed by John Speede and are to be sold in popes alley by John Sudbury and G Humbell...Cum Privilego 1610.
- Size: 20 1/2in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1610
- Ref #: 80002
Description:
This original hand coloured antique 1st edition map of the English county of Cambridgeshire was engraved in 1610 - dated -and was published by John Sudbury & George Humble in the 1612 1st edition of John Speeds famous atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine.
The map has some loss mainly along the borders and a few small areas below both sets of figures. Map has been mounted onto an original index page fro m Speeds atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15in (510mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Map cropped to and into borders
Plate area: - Small loss below both sets of figures at the bottom of the map
Verso: - Backed onto original Speed index double page
Background:
Strong reference is made to Cambridges famous and renowned university with the (twenty five) armourials of the colleges and four scholarly figures. The birds eye view plan of Cambridge city is based on the one done by John Hammond in 1592.
1611 John Speed 1st Edition Map of Great Britain & Ireland - London & Edinbugh
- Title : The Kingdome of Great Britaine and Ireland....Graven by J Hondius and are to be solde by J Sudbury and George Humble in Pope Heads Alley in London cum privilage Regis 1610
- Ref #: 93433
- Size: 21in x 15 3/4in (535mm x 400mm)
- Date : 1611
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This magnificent, beautifully hand coloured, original copper-plate engraved antique map (a true rare 1st edition - Shirley 316, catch word wee on verso) by John Speed, was engraved by the famous cartographer Jodocus Hondius and published by Sudbury & Humble in Speeds 1611-12 edition of his atlas Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine.
A beautiful example of the first state of one the most visually striking maps ever produced of the British Isles, embellished with finely detailed views of both London and Edinburgh. The strong printing impression of this example highlights the exquisite engraving of this map, particularly the delicate detail of the two inset views.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14in (470mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - All margins professionally restored from printed borders
Plate area: - Small repair to bottom centerfold
Verso: - Centerfold re-enforced.
Background:
John Speed spent 15 years gathering materials for his atlas of the British Isles, in which this map was the first to appear. Moreover, Speed went to considerable lengths to secure a top engraving talent—a fascinating story in itself--to produce this and many of the other maps in this atlas. Speed sent the visual, raw materials for his maps—drafts of the map themselves and design sketches--to Amsterdam to be engraved by Jodocus Hondius, who at the time was one of the most prominent and successful map publishers in all of Europe. Hondius, however, was well known to English map publishers, as he had worked as an engraver for hire in London in the 1580’s, where he had fled due to religious persecution in his homeland. Still, it is surprising that Speed was able to secure the services of Hondius at the height of his career, and, in fact, Hondius died shortly after completing this project. Hondius’ distinctive style can be seen in this map in its stippled seas and in its decorative detail that is rich without being disorganized or distracting.
The map itself of England was based on that of Saxton, who produced some years earlier the very first atlas of Great Britain. Ireland and Scotland were based on maps by Hondius and Mercator, respectively. The view of London was modeled after a c. 1600 drawing by C. J. Visscher, which was not published until 1616. The Edinburgh view is an adaptation of an earlier manuscript showing the city under siege in 1544.
1611 Philipp Cluver Antique Map The Netherlands, Belgium, parts France & Germany
- Title : Germaniae Cisrhenanae ut interl. caesaris et Traiani suit imperii Scaldis item Mosae ac Rheni ostiorum antiqua Descriptio
- Size: 11 1/2in x 11 1/2in (295mm x 295mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1611
- Ref #: 23967
Description:
This fine original wood-block engraved antique map of The Netherlands, Belgium, Northern France and parts of Western Germany was published in the 1611 edition of Philip Cluvers first publication Commentarius de tribus Rheni alveis, et ostiis; item. De Quinque populis quondam accolis; scilicet de Toxandris, Batavis, Caninefatibus, Frisiis, ac Marsacis. (Ref: King; Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 11 1/2in (295mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 10in (255mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to left & right margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Clüver was an antiquary, who was given a special appointment at Leiden as geographer and put in charge of the university\'s library, but his lifes project, it developed, was a general study of the geography of Antiquity, based not only on classical literary sources, but — and this was his contribution — supplemented by wide travels and local inspections. He became virtually the founder of historical geography.
Clüvers first work, in 1611, concerning the lower reaches of the Rhine and its tribal inhabitants in Roman times (Commentarius de tribus Rheni alveis, et ostiis; item. De Quinque populis quondam accolis; scilicet de Toxandris, Batavis, Caninefatibus, Frisiis, ac Marsacis) touched a source of national pride among the Seventeen Provinces, for the Dutch were enjoying a twelve years truce in their Eighty Years War of liberation.
Cluver, Philipp 1580 – 1622
Clüver - also Klüwer, Cluwer, or Cluvier, Latinized as Philippus Cluverius and Philippi Cluverii) - was an Early Modern German geographer and historian.
Clüver was born in Danzig (Gdańsk), in Royal Prussia, a province of the Kingdom of Poland. After spending some time at the Polish court of Sigismund III Vasa, he began the study of law at the University of Leiden (Dutch Republic), but soon he turned his attention to history and geography, which were then taught there by Joseph Scaliger.
Clüver received science education from his father, who was Münzmeister at Danzig (coin master), but when Clüver went into different studies, his father stopped supporting his studies. He therefore travelled from Leiden across Hungary to Bohemia, where he did military service for a few years. While in Bohemia, he translated into Latin a defense by Baron Popel Lobkowitz, who was imprisoned. Upon his return to Leiden, he faced sanctions by the imperial (Habsburg) authorities for this, which however he could avoid with the help of his Leiden friends.
Clüver also travelled in England, Scotland, and France. He did all travel on foot, finally returning to Leiden, where (after 1616) he received a regular pension from the university. He died in Leiden.
Clüver was an antiquary, who was given a special appointment at Leiden as geographer and put in charge of the university\\\'s library, but his lifes project, it developed, was a general study of the geography of Antiquity, based not only on classical literary sources, but — and this was his contribution — supplemented by wide travels and local inspections. He became virtually the founder of historical geography.
Clüver\\\'s first work, in 1611, concerning the lower reaches of the Rhine and its tribal inhabitants in Roman times (Commentarius de tribus Rheni alveis, et ostiis; item. De Quinque populis quondam accolis; scilicet de Toxandris, Batavis, Caninefatibus, Frisiis, ac Marsacis) touched a source of national pride among the Seventeen Provinces, for the Dutch were enjoying a twelve years\\\' truce in their Eighty Years War of liberation.
Clüvers Germaniae antiquae libri tres (Leiden, 1616) depends on Tacitus and other Latin authors. A volume on the antiquities of Sicily, with notes on Sardinia and Corsica (Sicilia Antiqua cum minoribus insulis ei adjacentibus item Sardinia et Corsica), published at Leiden by Louis Elsevier in 1619, is a useful source, with many reference from writers of Antiquity and maps that are often detached and sold to map collectors. His Introductio in universam geographiam, totally 6 parts, (published posthumously from 1624) was the first comprehensive modern geography, and became a standard geographical textbook.
Clüver was also a prolific a writer on mathematical and theological subjects. He is remembered by collectors and historians of cartography for his edition of Ptolemys Geographia (based on Mercators edition of 1578) and for miniature atlases that were reprinted for most of the 17th century. Many of his maps were etched for him by Petrus Bertius.
1611 Speed Antique Map of the British Islands of Holy, Farne, Jersey & Guernsey
- Title : Holy Iland; Garnsay; Farne; Jarsey
- Date : 1611
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 92499
- Size: 21in x 16in (535mm x 405mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map by John Speed of the English Islands of Holy & Farne Island's; Guernsey & Jersey was published by John Sudbury & George Humbell in the 1611 1st edition of John Speeds famous atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine, first published in 1611.
The verso contains text in English describing the 4 Islands and their history. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later color
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, red, pink
General color appearance: - Beautiful
Paper size: - 21in x 16in (535mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 15 1/2in (520mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Restoration to top, left & bottom margins
Plate area: - Light creasing, repair to bottom publishers cartouche, no lo0ss
Verso: - Colour show through, restoration to bottom centrefold and margins as noted
1612 Abraham Ortelius Antique Maps of Loire Valley, River & Alliers River France
- Title : Regionis Biturigum Exactiss Descriptio per D. Ioannem Calamaeum. Limaniae Topographia Gabriele Symeoneo Auct. [The region of Berry exactly described by Jean Chameau. The topography around of Lyons by Gabriel Symeon]
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1612
- Ref #: 50228-1
Description:
These original copper-plate engraved antique maps, the first of the Loire River & Valley and the second of the Alliers River, was published by Abraham Ortelius in the 1612 Latin edition of Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
These are two rare regional Abraham Ortelius maps on a single folio sheet. The Left Map, centered on Bourges, depicts the Loire Valley region from Gian to St. Sebastian in the south and from Le Blanc east as far as Nevers. Several important cities are noted, including Argenton, Neuers (Nevers), Bourges, Le Blang en Berry, Romarantin, Vierzon, Chasteau Neuf, and others. The right map follows the flow of the Alliers River from Randan to Gondole. Important cities, including Beauregard, Cleremont, among several others are noted. Each map features a decorative cartouche and details their respective regions in wonderful detail with attention to forests, cities, rivers and villages.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 12 1/2in (490mm x 310mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Loire Valley spanning 280 kilometres , is located in the middle stretch of the Loire River in central France, in both the administrative regions Pays de la Loire and Centre-Val de Loire. The area of the Loire Valley comprises about 800 square kilometres. It is referred to as the Cradle of the French and the Garden of France due to the abundance of vineyards, fruit orchards (such as cherries), and artichoke, and asparagus fields, which line the banks of the river. Notable for its historic towns, architecture, and wines, the valley has been inhabited since the Middle Palaeolithic period.
The Allier is a river in central France. It is a left tributary of the Loire. Its source is in the Massif Central, in the Lozère department, east of Mende. It flows generally north. It joins the Loire west of the city of Nevers.
1612 Antique Frontispiece Portrait of Antonio Albizzi - Principum Christianoru
- Title : Principum Christianorum Stemmata
- Ref #: 80765
- Size: 17 1/4in x 11in (440mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1612
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique frontispiece and portrait of Antonio Albizzi was published by him in the 1612 edition of Principum Christianorum Stemmata.
Antonio Albizzi (latin : Antonius Albicius) was an Italian jurist and genealogist, born in Florence in 1547. In 1576 he was in the service of Cardinal-Archduke Andreas of Austria. In 1585 he converted to Lutheranism and spent the rest of his life in the Protestant Imperial City of Kempten, where he died in 1626. His most famous work wasPrincipum Christianorum Stemmata [Augsburg 1612], an unusual collection of engravings showing the family trees of the leading royal and noble houses of Europe of that time (and unusually also including the genealogy of the Turkish Emperors). The fine decorative engravings include family trees, portraits and coats of arms and are set against the backdrop of City views and panoramas closely copied from the Civitates Orbis Terrarum of Georg Braun & Franz Hogenberg [1572-1618]. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/4in x 11in (440mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Very light age toning
Verso: - Very light age toning
1613 Gerard Mercator Large Antique Map of Africa - Africa Ex Magna
- Title : Africa Ex Magna orbis terra descriptione Gerardi Mercatoris desumpta. Studio & industria GM Iunioris
- Size: 22in x 18 3/4in (560mm x 475mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1613
- Ref #: 34173
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Africa by Gerard Mercator was published by Henricus Hondius in the 1613 French edition of Mercators Atlas, Atlas Sive Cosmographicae Meditationes Illustrissimi Ducis.
This map is exceptional with original hand colour, heavy dark impression, clean heavy paper and original margins.
As indicated in the title Cartouche, this map this is a reduction by Gerard Mercator Junior of Africa, compiled from Gerard Mercator\'s world map of 1569. This rendition was drawn by Mercator\'s grandson (also named Gerard) in 1595.
The map is typical of 16th century cartography of Africa containing some fantastical detail especially in regards to the interior. The depiction of the Nile is based on Ptolemys geography with some complex modifications from various sources, including Abyssinian monks. The source of the Nile is shown as a series of lakes located in the Lune Montes just north of the Tropic of Capricorn. Another branch of the Nile flows from the west, with this system rambling through what is the Sahara Desert. Mercator adds a lake named Sac. Haf lac, from the 1507 Waldseemuller world map. This lake feeds both the Zambere River and the Nile. In Abissini, the legendary Christian King Prester John sits on his throne. The boldly engraved oceans, beautiful calligraphy, and strapwork cartouche (surmounted by two satyrs) make this a decorative masterpiece.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18 3/4in (560mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
1613 Gerard Mercator Large Antique Map of Europe - Europa ad Magnae
- Title : Europa ad magnae Europae Gerardi Mercatoris P. imitationem Rumoldi Mercatoris . . ..
- Date : 1613
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 93357
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 435mm)
Description:
The beautiful original hand colouring on this map is incredibly striking, on this original antique map of Europe published in the 1613 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas Sive Cosmographia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 435mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15 1/4in (470mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling, age toning, old neutralised tape mark bottom right
Plate area: - Neutralised tape mark bottom right
Verso: - Soiling, age toning, old neutralised tape mark
Background:
The detail for the map is taken from Mercators large 1569 world wall map and includes much detail, both real and fictitious. The original colouring denotes the political country boundaries of the 15th & 16th centuries. To the north are shown the islands of the Northern Arctic, Terra Polaris Pars, Greenland and the eastern extremity of America. To the south of Iceland is the fictitious island of Frisland where the Venetian brothers Nicolo and Antonio Zeno claimed where they were stranded after discovering America before Columbus. The younger Zeno produced a map describing these false discoveries. Mercator accepted these falsehoods and copied them into this map. Other cartographers at this time were fooled by Mercator and also copied his mistake. Frisland appears more dominate than the real island of Iceland.
The map is beautifully engraved, with Mercators recognisable flair and beautiful, rare original hand colouring. A beautiful map
1613 Mercator Antique Map of America & The Great Southern Land - Terra Australis
- Title : America sive India Nova. ad magna Gerardi Mercatoris aui Universalis imitationem in compendium redacta. Per Michaelem Mercatorem Duysburgensem
- Ref #: 61033
- Size: 20 1/2in x 17 1/2in (510mm x 445mm)
- Date : 1613
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique early map of America and the Great Southern Continent (Terra Australis) that was envisaged in the southern Hemisphere, prior to the discovery of Australia by Captain Cook in 1769 - the only map attributed to Gerard Mercator's Grandson Michael - was published in the 1633 French edition of Mercator's Atlas.
This map is magnificent with beautiful original hand colouring, wide margins and stable paper. Backed with transparent archival Japanese paper. Original colouring such as this is scarce and hard to find.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 3/4in (545mm x 450mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14 3/4in (470mm x 376mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: Largely based on Rumold Mercator's world map of 1587, this map aptly reflects 16th-century knowledge, theories and suppositions regarding the New World. Naturally, most of this new knowledge was coastal, and configurations of any large areas were greatly hampered by the lack of a sound means of determining longitude. Nevertheless, the collective accomplishment of explorers and mapmakers represented in this map is astounding, showing in a generally correct way the vast extent of the New World. "A few of the most famous theories are still present: a large inland lake in Canada, two of the four islands of the North Pole, a bulge to the west coast of South America and the large southern continent" (Burden).
The map appeared in 1595 and 1606 editions of the Atlantis Pars Altera , after which the plate was sold to Jodocus Hondius, who reissued the maps in varying editions through 1639. The present example includes French text on verso, confirming it to be a Hondius issue.
Several of the more fascinating theories are present, including the multiple islands of the North Polar Sea, bulging South America and vast unknown southern continent. The St. Lawrence crosses half the continent. No sign of the English in Virginia. The search for a water course across North America is interupted only by some mid-continental mountains. Evidence of the Spanish explorations in the Southwest is present and the Colorado and Gila Rivers already reflect a good knowledge of this area, as does the peninsular Baja California, based upon Uloa's work.
The depiction of the NW Passage and Western North America are also of great interest. Annotations reference the voyages of Columbus and Magellan.(Ref: Burden; Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
1614 Sebastian Munster Antique Map of America - Americae sive Novi Orbis Nova
- Title : Americae sive Novi Orbis Nova Descriptio / Die Newe Welt oder Inseln so hinder Hispania gegen Orient/ ben dem Landt Indie gelegen
- Date : 1614
- Ref: 82003
- Size: 17in x 14 1/2in (430mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of America - the second published by Munster since his 1540 map and geographically based on the same 1570 Abraham Ortelius map - was published by Sebastian Petri in the 1514 edition of Cosmographia.
This map in this condition is rare. It is clean with a heavy impression, original margins in the original B&W as published. One of the best examples of this map I have seen for sometime.
The Cosmographia or Cosmography was first published in 1544 and is the earliest German-language description of the world.
It had numerous editions in different languages including Latin, French (translated by François de Belleforest), Italian, English, and Czech. The last German edition was published in 1628. The Cosmographia was one of the most successful and popular books of the 16th century and passed through 24 editions in 100 years. This success was due to the notable woodcuts (some by Hans Holbein the Younger, Urs Graf, Hans Rudolph Manuel Deutsch, and David Kandel). It was most important in reviving geography in 16th-century Europe. Among the notable maps within Cosmographia is the map Die Newe Welt oder Inseln, which is credited as the first map to show the American continents as geographically unique.
Munsters earlier geographic works were Germania descriptio (1530) and Mappa Europae (1536). In 1540, he published a Latin edition of Ptolemy\\\'s Geographia, with numerous illustrations.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 14 1/2in (430mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 14 1/2in (430mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map covers all of North and South America from a mysterious inland lake (Conibas?) to Tierra del Fuego, and from New Guiana to beyond the easternmost coast of Brazil. This map is Petris major revision of Sebastian Munster\\\'s original 1540 map of America and is based almost entirely on Ortelius 1570 map of the same region. The map features many of the cartographic anomalies and false suppositions common to the period. Teirra de Fuego remains connected to the mysterious southern continent - suggesting that information from Drake\\\'s voyages had not yet filtered into central Europe. The large bulge on the western coast of South America, near Chile, also remains. A collection of islands in the pacific, situated suspiciously close to the western coast of the Pacific is identified as the Archipeago di San Lazao, a term that Magellan gave the Ladrones, which are in fact located much further west. New Guinea is oversized and apparently connected to the unknown southern continent. IN North America a great bay in inland lake or bay extends into the heart of the continent from the map\\\'s border. This is most likely a remnant of Verazanno\\\'s Sea and the precursor of the legendary Lake Conibas. On the west coast of North America Quivara, Anian, and Tolm, possibly terms derived from Marco Polo, appear prominently. This map was engraved in woodcut c. 1588 and published in Basel by Sebastian Petri. After 1588, this map was only issued in posthumous German editions of Sebastian Munsters Cosmographia issued in 1592, 1598, 1614, and 1628, and is thus rare.
1619 Jan Jansson Antique Map Loire & Rhone Rivers, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France
- Title : Lionnois, Forest et Beaviolois
- Ref #: 50247
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1619
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of The Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of France - centering on the Loire & Rhone Rivers and the cities of Lyon, Vienne & Macon - by Jan Jansson - was published in the 1619 edition of Mercators Atlas by Jan Jansson and Henricus Hondius.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15in (535mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Lyon is the third-largest city and second-largest urban area of France. It is located in the country\'s east-central part at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône.
Fernand Braudel remarked, Historians of Lyon are not sufficiently aware of the bi-polarity between Paris and Lyon, which is a constant structure in French development...from the late Middle Ages to the Industrial Revolution. In the late 15th century, the fairs introduced by Italian merchants made Lyon the economic counting house of France. Even the Bourse (treasury), built in 1749, resembled a public bazaar where accounts were settled in the open air. When international banking moved to Genoa, then Amsterdam, Lyon remained the banking centre of France.
During the Renaissance, the cities development was driven by the silk trade, which strengthened its ties to Italy. Italian influence on Lyons architecture is still visible among historic buildings. In the later 1400s and 1500s Lyon was also a key centre of literary activity and book publishing, both of French writers (such as Maurice Scève, Antoine Heroet, and Louise Labé) and of Italians in exile (such as Luigi Alamanni and Gian Giorgio Trissino).
In 1572, Lyon was a scene of mass violence by Catholics against Protestant Huguenots in the St. Bartholomew\'s Day Massacre. Two centuries later, Lyon was again convulsed by violence when, during the French Revolution, the citizenry rose up against the National Convention and supported the Girondins. The city was besieged by Revolutionary armies for over two months before surrendering in October 1793. Many buildings were destroyed, especially around the Place Bellecour, while Jean-Marie Collot d\'Herbois and Joseph Fouché administered the execution of more than 2,000 people. The Convention ordered that its name be changed to Liberated City and a plaque was erected that proclaimed Lyons made war on Liberty; Lyons no longer exists. A decade later, Napoleon ordered the reconstruction of all the buildings demolished during this period.
The Convention was not the only target within Lyon during the 1789-1799 French Revolution. After the National Convention faded into history, the French Directory appeared and days after the September 4, 1797, Coup of 18 Fructidor, a Directory\'s commissioner was assassinated in Lyon.
The city became an important industrial town during the 19th century. In 1831 and 1834, the canuts (silk workers) of Lyon staged two major uprisings for better working conditions and pay. In 1862, the first of Lyon\'s extensive network of funicular railways began operation.