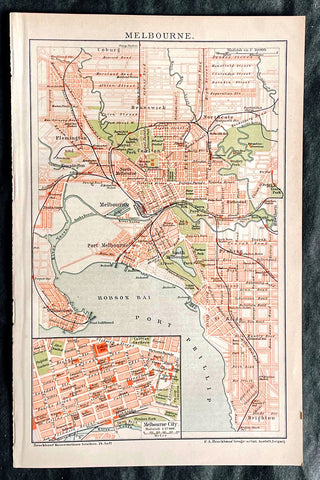
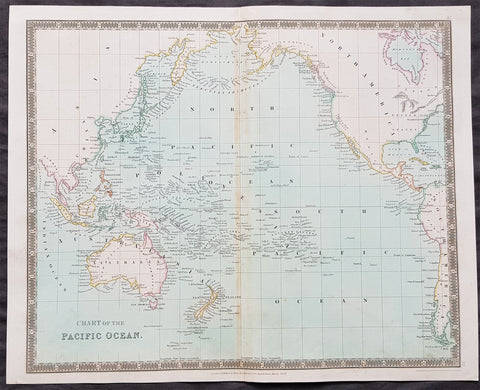
Australia/Oceania (150)
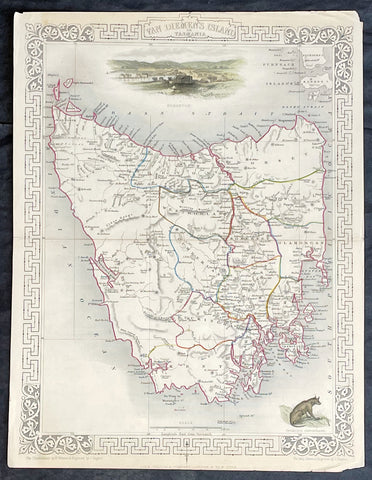
1807 Nicolas Baudin & N M Petit Antique Print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida
- Title : Terre De Diemen Arra Maida
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 93085
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print of Tasmanian Aboriginal Arra Maida, visited by the Baudin Expedition to Australia in Feb. 1802, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after Nicolas-Martin Petit (the offical artist on the ship Géographe) and was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Nicholas Martin Petit sailed with Nicolas Baudin on the expedition of the Géographe and the Naturaliste in late 1800. The scientific field of anthropology was in its infancy – the French had founded the Society of the Observers of Man in 1799. Having embarked as a fourth-class gunner’s mate, Petit, who had had some graphic arts training, became one of the expeditions two illustrators when the official artists quit. From June to November 1802, the expedition was delayed in Sydney while its two ships were repaired. During this time Petit completed portraits of people of the Cadigal, Dharawal, Gweagal, Kurringai and Darug language groups of the Sydney Harbour region. While the sitters names appear to be noted on the works, it is possible that the inscriptions merely reflect French misinterpretation of the Aborigines communications with them.
The portrait of Nourou-gal-derri is pictured advancing for battle.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1807 Baudin & Petit Antique Print Sydney Aboriginal Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan - Bennelong
- Title : Nouvelle-Hollande. Gnoung-a-gnoung-a Mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1807
- Ref #: 91239
Description:
This exquisite, rare original copper-plate engraved antique print, of the brother in law of the famous Port Jackson Aborginal leader Bennelong, Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, or Anganángan, was engraved by Barthélemy Roger, after the 1802 by Nicolas-Martin Petit, was published by Francois Peron (1775 - 1810) in the 1st edition atlas of Nicolas Thomas Baudins expedition to Australia Voyage de découvertes aux Terres Australes
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan
It is over 200 years since the death of an adventurous young Aboriginal Australian who crossed the vast Pacific Ocean to North America and returned to Sydney. From the deck of an English storeship he glimpsed many strange places, visiting Norfolk Island, Hawaii, Nootka Sound (now Vancouver, Canada) and the Spanish colonies of San Francisco, Santa Barbara and San Diego on the Californian coast.
The voyager was Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan, whose wife Warreeweer was the younger sister of the Wangal leader Woollarawarre Bennelong, at that time being feted in London society. The distance Gnung-a Gnung-a traversed was some 16,000 miles (25,750 kilometres) as the crow flies, but much further in a sailing ship driven by unpredictable winds.
On the first day he ventured into the convict settlement at Sydney Cove, in November 1790, Gnung-a Gnung-a adopted the name Collins from Acting Judge Advocate David Collins, who often mentions him in An Account of the English Colony in New South Wales, published in London in 1798.
It was the idea of Major Francis Grose, acting governor of New South Wales after the departure of Captain Arthur Phillip in 1792, to embark a native of this country on HM storeship Daedalus for the purpose of acquiring our language, wrote David Collins. The 350-ton capacity vessel was ordered to resupply provisions for the expedition to the north-west coast of North America commanded by Captain George Vancouver (1757–1798). In the navy ships HMS Discovery and HMS Chatham, Captain Vancouver was to complete the survey made by Captain James Cook.
Voyage to America
HMS Daedalus sailed from Port Jackson on 1 July 1793, passing west of the Society Islands (French Polynesia) to Owhyee (Hawaii). The commander, Lieutenant James Hanson, missed a rendezvous with Vancouvers ships at Nootka Sound on 8 October, but anchored with the two survey ships off San Francisco Bay on 21 October. The three British ships followed the coast of todays California to San Diego, leaving on 9 December 1793 and arriving at Hilo in Hawaii on 8 January 1794.
The Hawaiian King Kamehameha, who warmly welcomed Vancouver, was so impressed by the good-natured, handsome Aboriginal man on the expedition that he wanted to buy him, offering in exchange canoes, weapons and curiosities.
Gnung-a Gnung-a got on well with everyone on Daedalus and Hanson was pleased by his good nature and his willingness to do whatever was asked of him. During his month in Hawaii, he often went ashore with his shipmates. Wherever he went he readily adopted the manners of those around him, Hanson later told Collins, who remarked, with ironic humour, that...........
when at Owhyee, having discovered that favours from the females were to be procured at the easy exchange for a looking-glass, a nail, or a knife, he was not backward in presenting his little offering, and was as well received as any of the white people in the ship. It was noticed too that he always displayed some taste in selecting the object of his attentions.......
Return to Sydney
Home in Sydney Town, Gnung-a Gnung-a fought and wounded a very fine young fellow called Wyatt, who had taken up with his wife during his absence and Warreeweer became the prize of the victor.
During a ritual revenge combat in December 1795, Pemulwuy, leader of the Georges River Bidjigal near Botany Bay, launched a spear at Gnung-a Gnung-a that remained fixed in his back. The English surgeons could not extract the spear and thought he was unlikely to recover. Gnung-a Gnung-a, however, left the hospital and walked about for several weeks with the spear protruding from his back. At last, wrote Collins in a footnote..........
we heard that his wife, or one of his male friends, had fixed their teeth in the wood and drawn it out after which he recovered, and was able again to go into the field. His wife War-re-weer showed by an uncommon attention her great attachment to him.......
Before this unexpected recovery, David Collins wrote a brief appreciation of his namesake:
He was much esteemed by every white man who knew him, as well on account of his personal bravery, of which we had witnessed many distinguishing proofs, as on account of a gentleness of manners which strongly marked his disposition, and shaded off the harsher lines that his uncivilised life now and then forced into the fore-ground.
While in Sydney with a scientific expedition commanded by Nicholas Baudin in 1802, the young French artist Nicolas-Martin Petit met Gnung-a Gnung-a and sketched a striking portrait that he captioned Gnoung-a gnoung-a, mour-re-mour-ga (dit Collins)
A report in the Sydney Gazette of Sunday 15 January 1809 said that the body of Collins (Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan) had been found beside the Dry Store, site of the present Sirius Park in Bridge Street, Sydney. The newspaper said he had been known for the docility of his temper, and the high estimation in which he was universally held among the native tribes.
On the night of Thursday 12 January 1809, Gnung-a Gnung-as children, others he had adopted, and his brother Old Phillip, faced a salvo of spears in the ritual ordeal that followed death in Aboriginal society. The date of his death was not recorded, but it was customary to keep an overnight vigil over a dead body before burial and the subsequent revenge combat, so it was probably 11 January.
Gnung-a Gnung-a Murremurgan is one of many Aboriginal men and women who sailed from Sydney in English ships and played a significant role in Australias early maritime history.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning to outer margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Baudin Expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland, Australia. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of Australia until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmanias east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia, but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincents and Spencers Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by t Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast. Naturaliste took with her the Colonys staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because the quadrupeds and emus were very sick, it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Nicolas-Martin Petit 1777 – 1804
Nicholas-Martin Petit was born in Paris, the son of a fan maker, and learned graphic art in the studio of Jacques Louis David. He avoided conscription into Napoleons armies, but wanting to travel, signed up with post Captain Nicholas Baudin on a voyage to the antipodes sponsored by the French government. Petit and fellow artist Charles-Alexandre Lesueur were enlisted directly by Baudin (as 4th class gunners mates) while the two official artists were hired by the organisers of the expedition. Baudin set off in two lavishly equipped vessels, the Géographe and the Naturaliste on 19 October 1800. By the time the expedition reached Mauritius the official artists had quit. Petit and Lesueur took over their duties, but as neither was trained in scientific method or presentation, the value of their work was primarily aesthetic. The French were at this time developing a new scientific field - anthropology. The Society of the Observers of Man was founded in 1799 for this purpose. The study of Man formed part of the background for Petits sensitive drawings and paintings of the indigenous people of Van Diemens Land, Port Jackson and Western Australia. Lesueur focused on the depiction of animals. The expedition charted the coast of Western Australia and Van Diemens land but was plagued by scurvy. On 20 June 1802 the two ships limped into Port Jackson and stayed for five months to refit, during which time Petit completed a number of portraits of Sydney Indigenous people, including the two images of the Eora men, Cour-rou-bari-gal and Y-erren-gou-la-ga. Petit eventually returned to France in 1804. However, before he was well enough to complete the drawings from the expedition he was hurt in a street accident, and he died at the age of 28. Petits unfinished work was first published in 1807 in the Atlas of the Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes and as discrete prints.
Baudin, Nicolas Thomas 1754 – 1803
Baudin was a French explorer, cartographer, naturalist and hydrographer. Born a commoner in Saint-Martin-de-Ré on the Île de Ré on 17 February 1754 Baudin joined the merchant navy at the age of 15 and the French East India Company at the age of 20.
Baudin then joined the La Marine Royale (French Navy) in 1774 and served in the Caribbean as an officier bleu during the American War of Independence of 1775–1783.
In 1785 Baudin and his brother Alexandre were respectively masters of the St Remy and Caroline, taking Acadian settlers from Nantes to La Nouvelle Orléans. In New Orleans local merchants contracted him to take a cargo of wood, salted meat, cod and flour to Isle de France (now Mauritius), which he did in Josephine (also called Pepita), departing New Orleans on 14 July 1786 and arriving at Isle de France on 27 March 1787. In the course of the voyage, Josephine had called at Cap‑Français in Haiti to make a contract to transport slaves there from Madagascar; while in Haiti he also encountered the Austrian botanist Franz Josef Maerter, who apparently informed him that another Austrian botanist, Franz Boos, was at the Cape of Good Hope awaiting a ship to take him to Mauritius. Josephine called at the Cape and took Boos on board. At Mauritius, Boos chartered Baudin to transport him and the collection of plant specimens he had gathered there and at the Cape back to Europe, which Baudin did, Josephine arriving at Trieste on 18 June 1788. The Imperial government in Vienna was contemplating organizing another natural-history expedition, to which Boos would be appointed, in which two ships would be sent to the Malabar and Coromandel coasts of India, the Persian Gulf, Bengal, Ceylon, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Cochin China, Tongking, Japan and China. Baudin had been given reason to hope that he would be given command of the ships of this expedition.
Later in 1788 Baudin sailed on a commercial voyage from Trieste to Canton in Jardiniere. He apparently arrived at Canton from Mauritius under the flag of the United States of America, probably to avoid the possibility of having his ship seized by the Chinese for payment of the debts owed them by the Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste. From there, he sent Jardiniere under her second captain on a fur-trading venture to the north-west coast of America, but the ship foundered off Asuncion Island in the Marianas in late 1789.
Baudin made his way to Mauritius, where he purchased a replacement ship, Jardiniere II, but this vessel was wrecked in a cyclone that struck Port Louis on 15 December 1789. Baudin embarked on the Spanish Royal Philippines Company ship, Placeres, which sailed from Port Louis for Cadiz in August 1790. Placeres called at the Cape of Good Hope where it took on board the large number of plant and animal specimens collected in South Africa for the Imperial palace at Schönbrunn by Georg Scholl, the assistant of Franz Boos. Because of the poor condition of the ship, Placeres had to put in at the island of Trinidad in the West Indies, where Scholls collection of specimens was deposited.
Baudin proceeded to Martinique, from where he addressed an offer to the Imperial government in Vienna to conduct to Canton commissioners who would be empowered to negotiate with the Chinese merchants there a settlement of the debts incurred by the Imperial Asiatic Company, which would enable the company to renew its trade with China. On its return voyage from Canton, the proposed expedition would call at the Cape of Good Hope to pick up Scholl and the remainder of his natural-history collection for conveyance to Schönbrunn.
After returning to Vienna in September 1791, Baudin continued to press his case for an expedition under the Imperial flag to the Indian Ocean and China, and in January 1792 he was granted a commission of captain in the Imperial navy for this purpose. A ship, called Jardiniere, was acquired and the botanists Franz Bredemeyer and Joseph van der Schot appointed to the expedition. After delays caused by the outbreak of war between France and Austria (April 1792), Jardiniere departed from the Spanish port of Málaga on 1 October 1792. From the Cape of Good Hope Jardiniere sailed across the Indian Ocean to the coast of New Holland (Australia), but two consecutive cyclones prevented the expedition from doing any work there and forced Baudin to take the ship to Bombay for repairs.
From Bombay the expedition proceeded to the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea and the east coast of Africa, where it gathered botanical and zoological collections. The expedition came to an abrupt end in June 1794 when Jardiniere went aground in a storm while attempting to enter Table Bay at the Cape of Good Hope. Baudin survived the wreck and made his way to the United States, from where he went to France. He managed to send Jardinieres cargo of natural history specimens to the island of Trinidad.
In Paris, Baudin visited Antoine de Jussieu at the Museum National dHistoire Naturelle in March 1796 to suggest a botanical voyage to the Caribbean, during which he would recover the collection of specimens he had left in Trinidad. The Museum and the French government accepted the proposal, and Baudin was appointed commander of an expedition in the ship Belle Angélique, with four assigned botanists: René Maugé, André Pierre Ledru, Anselme Riedlé and Stanislas Levillain. Belle Angélique cleared Le Havre on 30 September 1796 for the Canary Islands, where the ship was condemned as unseaworthy. The expedition sailed from the Canaries in a replacement vessel, Fanny, and reached Trinidad in April 1797. The British, who had just captured the island from the Spanish in February 1797, refused to allow Baudin to recover the collection of natural-history specimens. Baudin took Fanny to St. Thomas and St. Croix, and then to Puerto Rico, specimens being collected in all three islands. At St Croix, Fanny was replaced by a newly purchased ship, renamed Belle Angelique. The expedition returned to France in June 1798 with a large collection of plants, birds and insects, which was incorporated into Napoleon Bonapartes triumphal procession celebrating his recent Italian victories.
On 24 July 1798, at the suggestion of the Ministry of Marine, Baudin presented to the Assembly of Professors and Administrators of the National Museum of Natural History a plan for a hydrographic-survey expedition to the South Seas, which would include a search for fauna and flora that could be brought back for cultivation in France. The expedition would also have the aim of promoting the economic and commercial interests of France in the regions to be visited. The expedition would require two well-equipped ships, which would carry a team of astronomers, naturalists and scientific draughtsmen over whom Baudin as commander would have absolute authority. The first part of the voyage would be devoted to a thorough exploration of the coast of Chile and the collection of animal, bird and plant specimens suitable for acclimatization in France, followed by a survey of the coasts from Peru to Mexico. The expedition would then continue into the Pacific Ocean, including a visit to Tahiti and the Society Islands, and would be completed with a survey of the yet unexplored south-west coast of New Holland (Australia). After considering this extensive proposal, the French government decided to proceed with an expedition confined to a survey of western and southern New Holland (as Australia was called at the time).
In October 1800 Baudin was selected to lead what has become known as the Baudin expedition to map the coast of Australia (New Holland). He had two ships, Géographe and Naturaliste captained by Hamelin, and a suite of nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour. He reached Australia in May 1801, and would explore and map the western coast and a part of the little-known southern coast of the continent. The scientific expedition proved a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered. The French also met Aboriginal peoples and treated them with great respect.
In April 1802 Baudin met Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, in Encounter Bay in present-day South Australia. Baudin then stopped at the British colony at Sydney for supplies. In Sydney he bought a new ship — Casuarina — named after the wood it was made from. From there he sent home Naturaliste, which had on board all of the specimens that had been discovered by Baudin and his crew. He then headed for Tasmania, before continuing north to Timor. Baudin then sailed for home, stopping at Mauritius.
According to recent researches by academics from the University of Adelaide, during Baudins expedition, François Péron, who had become the chief zoologist and intellectual leader of the mission, wrote a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.
Baudin died of tuberculosis at Mauritius on 16 September 1803, at the age of 49, apparently in the home of Madame Alexandrine Kerivel. Baudins exact resting place is not known, but the historian Auguste Toussaint believed that he was interred in the Kerivel family vault. However, the historian Edward Duyker likes to think that Baudin was buried in Le Cimetière de lOuest in the district of Port Louis just a few hundred metres from the explorers certain love: the sea.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
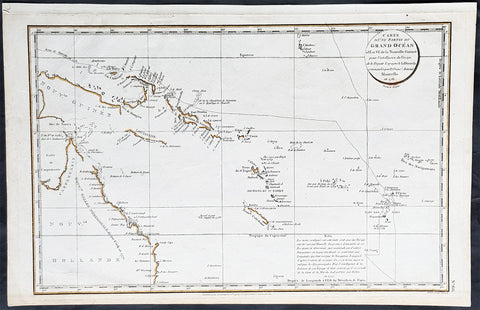
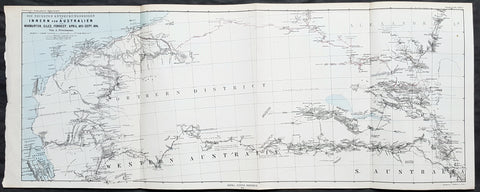
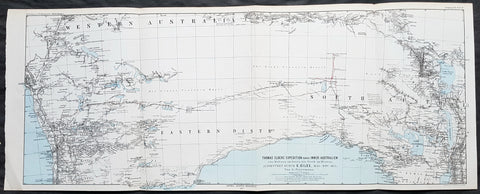
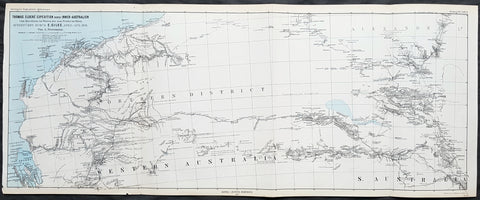
1798 Laperouse & Mourelle Antique Early Map of Queensland, PNG, Fiji etc in 1781
- Title : Carte D Une Partie Du Grand Ocean a l E. et S.E. de la Nouvelle Guinee pour l intelligence du Voyage de la Fregate Espagnole la Princesa commandee par D. Franco. Antonio Maurelle. en 1781..... Published as the (act) directs Novr. 1st 1798, by G.G. & J. Robinson
- Ref #: 31555
- Size: 16 3/4in x 11in (425mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1798
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique early map of Queensland, New Guinea, Fiji, French Polynesia & other South Pacific Islands - tracking the voyages of Francisco Antonio Mourelle in the region in 1781 was engraved in 1798 - dated - and was published in the 1st English edition of the Atlas du voyage de La Perouse G.G & J. Robinson, London in 1799.
La Perouse set sail from France in 1785 to continue the discoveries of Captain Cook. He was shipwrecked in 1788 but his narrative, maps, and views survived and were first published in 1797.
Interesting chart of Eastern Australia and part of the south-western Pacific, showing the routes taken by the Spanish explorer Don Francisco Antonio Maurelle in 1781 along the northern coast of New Guinea and across the Pacific to Fiji and Tonga, including a maunscript grid added in a contemporary hand.
Maurelle was credited with the discovery of the Hermit Islands on this voyage. The map includes the north-eastern coast of Australia, and parts of the coast of New Guinea. The map shows the 1781 route of his ship The Princesa through the Bismarck Archipelago north of New Guinea, through the Archipel de Salomos [i.e. Solomon Islands] and then east across the Pacific to the Iles de Amis [i.e. the Friendly Islands, now Tonga] where he discovered I. Vavao [ i.e. Vavau] with one of the best anchorages in the South Pacific.
The map includes the Iles de Navigateurs [i.e. Samoa], I. Fidji [i.e. Fiji], Iles de Esprit [i.e. Vanuatu or the New Hebrides Isles], and Nouvelle Caledonie [i.e. New Caledonia]. Many small islands are depicted with notes regarding their sightings by Abel Tasman, William Bligh and Maurelle.
A note on the chart states that the publisher has placed the islands according to the longitude of other navigators, rather than on Maurelles figures which were considered estimates only, and also, that Maurelles chart was based on a French chart by Jacques Nicolas Bellin published in 1742.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 3/4in x 11in (425mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Mourelle de la Rúa, Francisco Antonio 1750 – 1820
Mourelle was a Galician naval officer and explorer serving the Spanish crown. He was born in 1750 at San Adrián de Corme (Corme Aldea, Ponteceso), near La Coruña, Galicia
1775 voyage Mourelle served the Spanish navy in the Guyanas, Trinidad, and the Antilles before becoming stationed at New Spain\'s Pacific Ocean naval base at San Blas, Mexico in 1774. He joined the 1775 expedition of Bruno de Heceta and Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra, serving as Quadra\'s pilot on the schooner Sonora. On July 29, at around 49 degrees north latitude, the Sonora became separated from Heceta\'s ship Santiago. Heceta soon returned south while Quadra and Mourelle continued north, eventually reaching 58 degrees 30 minutes north latitude. They found and anchored in Bucareli Bay. Then they sailed south, arriving at Monterey, California, on October 7, and San Blas on November 20, 1775.
Mourelle\'s journal was somehow taken clandestinely to London where it was translated and published. Captain James Cook made use of the information in Mourelle\'s journal during his travels in the Pacific Northwest.
1779 voyage Mourelle again served as the pilot of Quadra, and second in command of the ship Favorita, during the 1779 expedition commanded by Ignacio de Arteaga. Leaving San Blas on February 11, 1779, the expedition reached 61 degrees north and Hinchinbrook Island at the head of the Gulf of Alaska. From there they sailed southwest along the Kenai Peninsula. The ships returned to San Blas on November 21, 1779.
Later career During his service at San Blas, Mourelle traveled extensively throughout the Pacific Ocean. From 1781 on the La Princessa, he attempted to find a southern route from the Philippines to Mexico, mapping 29 of the 50 islands in the Hermit Islands, Ninigo Islands and Tench Island in New Guinea, and Ontong Java in the Solomon Islands . He visited Tonga and travelled through the Ellice Islands (now Tuvalu). Keith S. Chambers and Doug Munro (1980) identify Niutao as the island that Mourelle named on May 5, 1781, thus solving what Europeans had called The Mystery of Gran Cocal. Due to contrary winds, he returned via Guam and took the northern route across the Pacific to Mexico. He was also familiar with the Philippines and Canton, China.
Mourelle was to command the Mexicana for a 1792 voyage to explore the Strait of Georgia but Alessandro Malaspina had one of his own officers, Cayetano Valdés, placed in command of the Mexicana. Dionisio Alcalá Galiano commanded the Sutil, the twin companion of the Mexicana.
Mourelle was transferred to Spain in 1793. He was promoted to frigate captain in the same year as the Action of 19 January 1799 where he took a leading role. He became ship\'s captain in 1806, and commodore in 1811. He commanded a squadron in 1818 that was to put down a rebellion in the Rio de la Plata, but the endeavor never got underway. Mourelle died on May 24, 1820, at the age of 64.
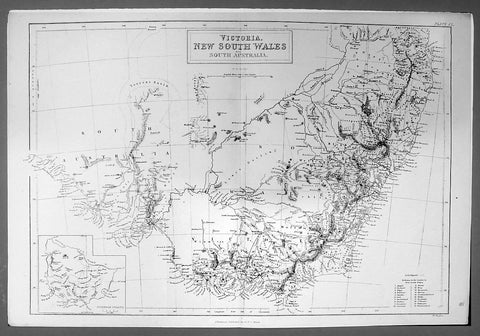
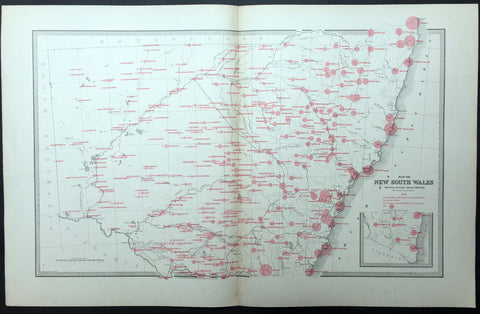
1882 Edward Stanford Large Folding Antique Map Eastern Australia, QLD, NSW, Vic
- Title : Queensland & New South Wales....London Published by Edward Stanford ...March 20th 1882
- Ref : 17064
- Size: 26 1/2in x 22in (680mm x 570mm)
- Date : 1882.
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original hand coloured folding canvas backed antique map of Vicoria, New South Wales & Queensland in Eastern Australia, illustrating Tracks of Travellers, Roads, Railways & Telegraph was published by Edward Stanford, London in 1882, dated at the foot of the map. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, red, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (680mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 22in (680mm x 570mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Stanford, Edward 1827-1904
Stanford was a prominent British mapmaker and publisher. A native of Holborn in the heart of London, Edward was apprenticed to a printer and stationer at the age of 14. After his first master died, he worked with several others, including Trelawny W. Saunders of Charing Cross. Saunders oversaw young Edward’s early career, ensuring that he became a Fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. Associations with the Society eventually brought Sanders much business and gave him a reputation as a publisher of explorers. As testament to this reputation, the Stanford Range in British Columbia was named for him by John Palliser.
Stanford briefly partnered with Saunders in 1852 before striking out on his own in 1853. He was an agent for the Ordnance Survey, the Admiralty, the Geological Survey, the Trigonometrical Survey of India, and the India Office. He also controlled the maps of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge, another lucrative source of income. In 1857, Stanford founded his namesake Geographical Establishment, with Saunders and A. K. Johnston as engravers. Thereafter, Stanford was known for his library maps, particularly those of Africa and Asia.
Although he had authored many maps, the Harrow Atlas of Modern Geography and a similar volume on classical geography, Stanford is better remembered today as the leader of a successful map business. Ever in search of more inventory, he acquired the plates and stock of John Arrowsmith, heir of the Arrowmsith family firm, in 1874. By 1881 he employed 87 people at his premises at 6 Charing Cross Road, Saunders’ old address. As he aged, he phased in his son Edward Jr. to run the business. He died in 1904. The business survived him, and the Stanford’s shop is still a prominent London landmark today.
Stanford premises were located in the Strand, London from 1853 to 1884 and then Cockspur St from 1885 to 1901 locating to its present location in Covent Garden.
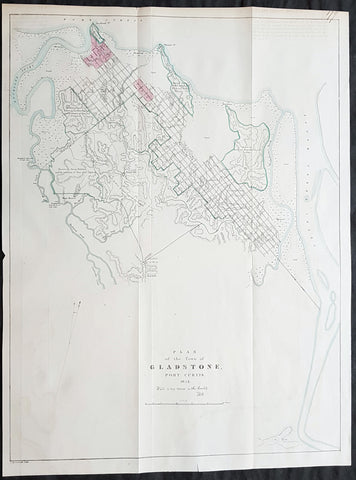
1854 John Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map, Early Town Plan of Gladstone, Queensland
- Title : Plan of the Town of Gladstone Port Curtis 1854 (Water is very scarce in this locality)
- Size: 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1854
- Ref #: 82045
Description:
This large, rare & important map, a very early plan of the Queensland town of Gladstone by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1854 - dated - and was published for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have numbered only in the 100s.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
Gladstone is a city in the Gladstone Region, Queensland, Australia. It is approximately 550 km (340 mi) by road north of Brisbane and 100 km south-east of Rockhampton. Situated between the Calliope and Boyne Rivers, Gladstone is home to Queensland\'s largest multi-commodity shipping port.
Before European settlement, the Gladstone region was home of the Toolooa (or Tulua), Meerooni and Baiali (or Byellee) Aboriginal tribes.
In May 1770, the HM Bark Endeavour, under the command of James Cook, sailed by the entrance to Gladstone Harbour under the cover of darkness. Matthew Flinders, during his 1801–1803 circumnavigation of Australia, became the first recorded European to sight the harbour in August 1802. He named the harbour Port Curtis, after Admiral Roger Curtis, a man who was of assistance to Flinders a year earlier at the Cape of Good Hope. John Oxley conducted further exploration of the harbour and surrounding countryside in November 1823. Oxley was dismissive of the region, noting the harbour was difficult to enter, the countryside was too dry, and the timber useless for construction purposes.
Nevertheless, in 1847 the British attempted to establish the new colony of North Australia at Port Curtis. Colonel George Barney was chosen to lead this experiment in colonisation and his expedition was eventful. On 25 January 1847, the Lord Auckland, carrying 87 soldiers and convicts, arrived off the southern entrance of Port Curtis and promptly ran aground on shoals off the southern tip of Facing Island. The settlers spent seven weeks on the island before being rescued by the supply ship Thomas Lowry and delivered the intended site of settlement, the region now known as Barney Point. On 30 January at a proclamation ceremony, Barney was sworn in as Lieutenant Governor of the colony of North Australia. The convict settlement lasted barely two months and cost the Imperial government ₤15,000. A change of government in Britain ordered the withdrawal of Barney and the settlers. However, interest in the region remained.
By 1853, Francis MacCabe was surveying the site of a new town on the shores of Port Curtis under the protection of several detachments of Native Police. Maurice O\'Connell was appointed government resident the following year, resulting in an influx of free settlers as land became available throughout the region. In 1863, the town became a Municipality with Richard Hetherington elected Gladstones first mayor. The fledgling town was named after the British Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone and has a 19th-century marble statue on display in its town museum.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
Plate size: - 22 1/4in x 16 3/4in (565mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
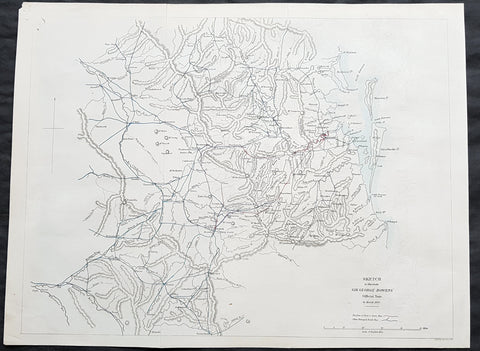
1861 Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map of Queensland, Brisbane to Toowoomba & Warwick - Bowen
- Title : Sketch to illustrate Sir George Bowens offical Tour to March 1860
- Size: 17in x 13in (430mm x 330mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1861
- Ref #: 82051
Description:
This incredibly rare & important map of the first Governor of Queensland Tour west of Queensland - from Brisbane to Toowoomba and south to Warwick in March 1860 - by John Arrowsmith was engraved in 1861 - dated at the foot of the map - a year after the granting of Statehood of Queensland in 1859 - and was published for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London. The importance & rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have numbered only in the 100s.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
Sir George Ferguson Bowen, GCMG 1821 – 1899 was a British author and colonial administrator whose appointments included postings to the Ionian Islands, Queensland, New Zealand, Victoria, Mauritius and Hong Kong.
In 1859, Bowen was appointed the first Governor of Queensland, a colony that had just been separated from New South Wales. Bowen\'s influence in Queensland was greater than that of the governors in other Australian colonies in a large part due to Robert Herbert, who accompanied Bowen from England, and later became colonial secretary and then first Premier of Queensland in 1860–66. Bowen was interested in the exploration of Queensland and in the establishment of a volunteer force, but incurred some unpopularity by refusing to sanction the issue of inconvertible paper money during the financial crisis of 1866. But overall, he was quite popular in Queensland, so that the citizens requested an extension of his five-year term as governor, resulting in his staying for further two years.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 13in (430mm x 330mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 13in (430mm x 330mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
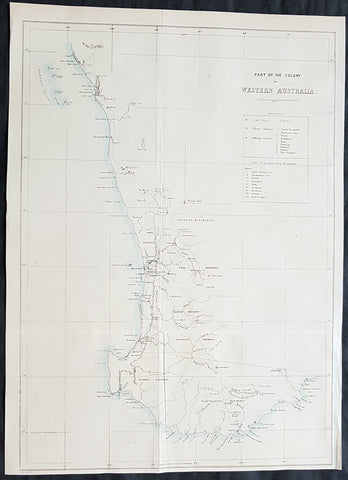
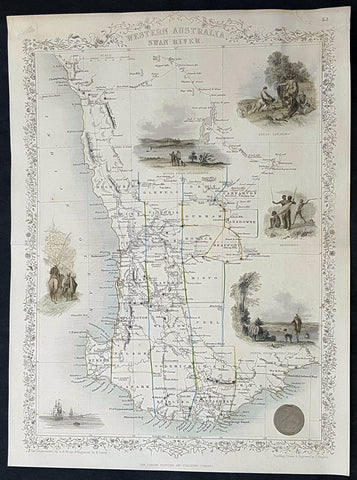
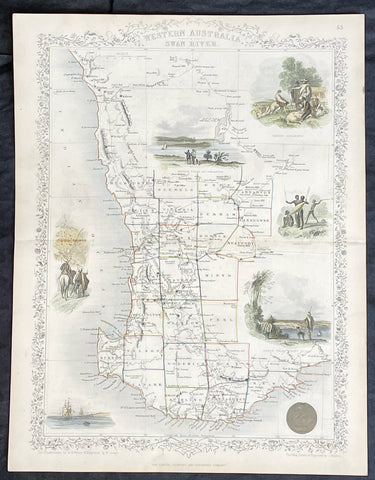
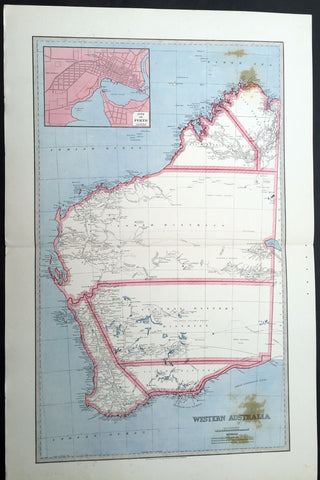
1859 John Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map of The Colony of Western Australia
- Title : Part of the Colony of Western Australia
- Size: 16 1/2in x 12in (420mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1859
- Ref #: 82049
Description:
This rare, large lithograph hand coloured early map of the southern part of the colony of Western Australia - stretching north to Hutt River, South past Bremmer Bay and east to York - by John Arrowsmith was published in 1859 for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The map details convict prisons, road stations, hiring stations, table of distances, residences, lead and copper mines, Geraldine Mine, coal seam, rivers, mountains, ranges, lakes and islands.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have had very low numbers published and are very hard, if not impossible, to be be found for sale on the open market.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 12in (420mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 12in (420mm x 305mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
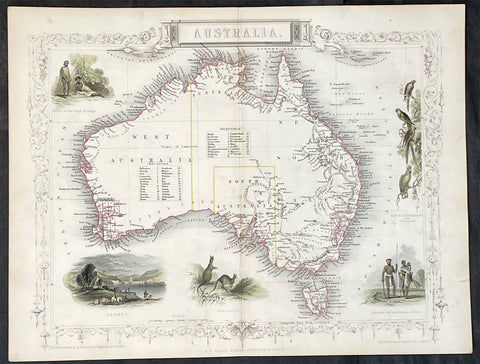
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Australia
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35511
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Australia with vignettes of Sydney Harbour, Aboriginals, Parrots and Kangaroos was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
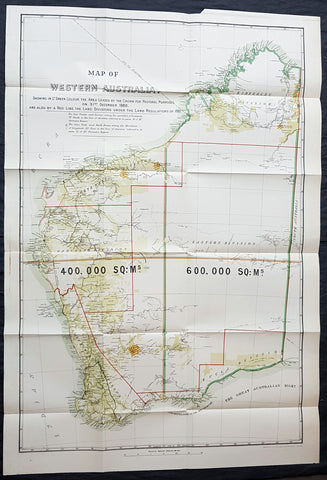
1890 John Forrest Large Antique Map Western Australia Pastoral Leases, Explorers
- Title : MAP OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA. SHOWING IN LT GREEN COLOUR THE AREA LEASED BY THE CROWN FOR PASTORAL PURPOSES ON 31ST DECEMBER 1888. AND ALSO BY A RED LINE THE LAND DIVISION UNDER THE LAND REGULATIONS OF 1887.
- Size: 39in x 27in (980mm x 685mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1890
- Ref #: 82035
Description:
This very large folding scarce original antique chromolithographic map of Western Australia for John Forrest was published by Judd & Co. London in 1890.
An extremely important map of Western Australia, issued in the year of independence for the then Surveyor General and later 1st premier of the state, John Forrest. Shown in green are the pastoral lease granted by the crown, Land Divisions drawn up for Statute in red lines and the tracks of explorers throughout WA since settlement.
This map was intended as a visual reference for the Summary of Land Regulations presented to the Houses of Parliament in 1889 in respect to the proposed introduction of Responsible Government in Western Australia. The map was drawn for the Commissioner of Lands, John Forrest. Covered in blue paper covers, detached, with advertisements.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 39in x 27in (980mm x 685mm)
Plate size: - 39in x 27in (980mm x 685mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, blue covers detached
Verso: - None
Background:
Western Australia is a state occupying the entire western third of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, and the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australias largest state, with a total land area of 2,529,875 square kilometres and the second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia\'s Sakha Republic. The state has about 2.6 million inhabitants – around 11% of the national total – of whom the vast majority (92%) live in the south-west corner, 73% of the population living in the Perth area, leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated.
The first European visitor to Western Australia was the Dutch explorer Dirk Hartog, who visited the Western Australian coast in 1616. The first European settlement of Western Australia occurred following the landing by Major Edmund Lockyer on 26 December 1826 of an expedition on behalf of the New South Wales colonial government. He established a convict-supported military garrison at King George III Sound, at present-day Albany, and on 21 January 1827 formally took possession of the western third of the continent for the British Crown. This was followed by the establishment of the Swan River Colony in 1829, including the site of the present-day capital, Perth.
York was the first inland settlement in Western Australia. Situated 97 kilometres east of Perth, it was settled on 16 September 1831.
Western Australia achieved responsible government in 1890, and federated with the other British colonies in Australia in 1901. Today its economy mainly relies on mining, agriculture and tourism. The state produces 46% of Australia\'s exports.Western Australia is the second-largest iron ore producer in the world.
Forrest, John 1847 – 1918
Forrest was an Australian explorer, the first Premier of Western Australia and a cabinet minister in Australia\\\'s first federal parliament.
As a young man, he won fame as an explorer by leading three expeditions into the interior of Western Australia, for which he was awarded the 1876 Royal Geographical Societys Patrons Medal.
He was appointed Surveyor General in 1883 and in 1890 became the first Premier of Western Australia, its only premier as a self-governing colony. Forrest\\\'s premiership gave the state ten years of stable administration during a period of rapid development and demographic change. He pursued a policy of large-scale public works and extensive land settlement, and he helped to ensure that Western Australia joined the federation of Australian states. After federation, he moved to federal politics, where he was at various times postmaster-general, Minister for Defence, Minister for Home Affairs, Treasurer and acting Prime Minister. He was affiliated with the Protectionist Party from 1901 to 1906, the Western Australian Party from 1906 to 1909, the Commonwealth Liberal Party from 1909 to 1917, then the Nationalist Party of Australia from 1917 to 1918.
Shortly before his death, Forrest was informed that the King had approved his elevation to the British peerage as Baron Forrest of Bunbury
1774 Capt. Cook, S. Parkinson & G. Stubbs - Antique Print Australian Kangaroo in 1770
- Title : Quadrupede nomme Kanguroo trouve fur la Cote de la N.Hollande
[The Kanguroo, an Animal found on the Coast of New Holland] - Ref : 35016
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a Kangaroo, first sketched by Sydney Parkinson onboard HMS Endeavour during Cooks first voyage in 1770, whilst laid up at Endeavour River in northern Queensland, was engraved by Robert Benard, after a painting by the famous English Artist George Stubbs in 1772. This original engraving was published in the 1774 French edition of Capt. James Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery to the South Seas by John Hawkesworth in An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks. Paris, 1774.
From Sydney Parkinsons Journal........soon after we arrived in the bay, we laid the ship on a steep bank, on the side of a river; set up tents on shore, unloaded her, carried all the cargo and provisions into them, and there lodged and accommodated our sick.
On the 22d, we examined the ship’s bottom, and found a large hole; through the planks into the hold, which had a piece of coral-rock, half a yard square, sticking in it: the same rock, therefore, that endangered us, yielded us the principal means of our redemption; for, had not this fragment intruded into the leak, in all probability the ship would have sunk.
We lost no time, but immediately set about repairing the ship’s bottom, and in a few days made it sound again. In the mean time, the boats were sent out, in search of another passage, which they found, and returned to the ship on the 3d of July.
On the 4th of July, the ship was carried to the other side of the river, and examined thoroughly; but, being found in good condition, she was soon placed in her former station; where she was loaded, and properly fitted to proceed on the voyage.
During the time we staid here, we picked up a great many natural curiosities from the reef we struck upon, consisting of a variety of curious shells, most of which were entirely new to Mr. Banks and Dr. Solander ...
Of quadrupeds, there are goats, wolves, a small red animal about the size of a squirrel; a spotted one of the viverra kind, and an animal of a kind nearly approaching the mus genus, about the size of a grey-hound, that had a head like a fawn’s; lips and ears, which it throws back, like a hare’s; on the upper jaw six large teeth; on the under one two only; with a short and small neck, near to which are the fore-feet, which have five toes each, and five hooked claws; the hinder legs are long, especially from the last joint, which, from the callosity below it, seems as if it lies flat on the ground when the animal descends any declivity; and each foot had four long toes, two of them behind, placed a great way back, the inner one of which has two claws; the two other toes were in the middle, and resembled a hoof, but one of them was much larger than the other. The tail, which is carried like a grey-hound’s, was almost as long as the body, and tapered gradually to the end. The chief bulk of this animal is behind; the belly being largest, and the back rising toward the posteriors. The whole body is covered with short ash-coloured hair; and the flesh of it tasted like a hare’s, but has a more agreeable flavour................
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
George Stubbs ARA 1724 – 1806 was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. His most famous work is probably Whistlejacket, a painting of a prancing horse commissioned by the 2nd Marquess of Rockingham, which is now in the National Gallery in London. This and two other paintings carried out for Rockingham break with convention in having plain backgrounds. Throughout the 1760s he produced a wide range of individual and group portraits of horses, sometimes accompanied by hounds. He often painted horses with their grooms, whom he always painted as individuals. Meanwhile, he also continued to accept commissions for portraits of people, including some group portraits. From 1761 to 1776 he exhibited at the Society of Artists of Great Britain, but in 1775 he switched his allegiance to the recently founded but already more prestigious Royal Academy of Arts.
Stubbs also painted more exotic animals including lions, tigers, giraffes, monkeys, and rhinoceroses, which he was able to observe in private menageries. His painting of a kangaroo in 1772 after Cooks 1st Voyage to Australia, was the first glimpse of this animal for many 18th-century Britons
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Western Australia or the Swan River Colony
- Title : Western Australia Swan River
- Size: 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1851
- Ref #: 93056
Description:
This original hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of Western Australia, the Swan River Colony with vignettes of Perth from Kings Park, Swan River, Aboriginals and Sheep Farming by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Very light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1851 John Tallis Beautiful Antique Map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania Australia
- Title : Van Diemens Land or Tasmania...John Tallis
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1851
- Ref #: 93054
Description:
This original steel plate engraved beautifully hand coloured antique map Van Diemens Land or Tasmania, Australia with vignettes of Hobart, Circular Head and Tasmanian Tiger, by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first reported sighting of Tasmania by a European was on 24 November 1642 by Dutch explorer Abel Tasman, who landed at todays Blackman Bay. More than a century later, in 1772, a French expedition led by Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne landed at (nearby but different) Blackmans Bay, and the following year Tobias Furneaux became the first Englishman to land in Tasmania when he arrived at Adventure Bay, which he named after his ship HMS Adventure. Captain James Cook also landed at Adventure Bay in 1777. Matthew Flinders and George Bass sailed through Bass Strait in 1798–99, determining for the first time that Tasmania was an island.
Sealers and whalers based themselves on Tasmanias islands from 1798, and in August 1803 New South Wales Governor Philip King sent Lieutenant John Bowen to establish a small military outpost on the eastern shore of the Derwent River in order to forestall any claims to the island by French explorers who had been exploring the southern Australian coastline. Bowen, who led a party of 49, including 21 male and three female convicts, named the camp Risdon. Several months later a second settlement was established by Captain David Collins, with 308 convicts, 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) to the south in Sullivans Cove on the western side of the Derwent, where fresh water was more plentiful. The latter settlement became known as Hobart Town or Hobarton, later shortened to Hobart, after the British Colonial Secretary of the time, Lord Hobart. The settlement at Risdon was later abandoned. Left on their own without further supplies, the Sullivans Cove settlement suffered severe food shortages and by 1806 its inhabitants were starving, with many resorting to scraping seaweed off rocks and scavenging washed-up whale blubber from the shore to survive.
A smaller colony was established at Port Dalrymple on the Tamar River in the islands north in October 1804 and several other convict-based settlements were established, including the particularly harsh penal colonies at Port Arthur in the southeast and Macquarie Harbour on the West Coast. Tasmania was eventually sent 75,000 convicts—four out of every ten people transported to Australia. By 1819 the Aboriginal and British population reached parity with about 5000 of each, although among the colonists men outnumbered women four to one. Wealthy middle-class free settlers began arriving in large numbers from 1820, lured by the promise of land grants and free convict labour. Settlement in the islands northwest corner was monopolised by the Van Diemens Land Company, which sent its first surveyors to the district in 1826. By 1830 one-third of Australias non-Indigenous population lived in Van Diemens Land and the island accounted for about half of all land under cultivation and exports.
Van Diemens Land—which thus far had existed as a territory within the colony of New South Wales—was proclaimed a separate colony, with its own judicial establishment and Legislative Council, on 3 December 1825. Transportation to the island ceased in 1853 and the colony was renamed Tasmania in 1856, partly to differentiate the burgeoning society of free settlers from the islands convict past.
The Legislative Council of Van Diemens Land drafted a new constitution which it passed in 1854. The following year the Privy Council approved the colony changing its name from Van Diemens Land to Tasmania, and in 1856 the newly elected bicameral parliament sat for the first time, establishing Tasmania as a self-governing colony of the British Empire.
The colony suffered from economic fluctuations, but for the most part was prosperous, experiencing steady growth. With few external threats and strong trade links with the Empire, Tasmania enjoyed many fruitful periods in the late 19th century, becoming a world-centre of shipbuilding. It raised a local defence force that eventually played a significant role in the Second Boer War in South Africa, and Tasmanian soldiers in that conflict won the first two Victoria Crosses awarded to Australians.
In 1901 the Colony of Tasmania united with the five other Australian colonies to form the Commonwealth of Australia. Tasmanians voted in favour of federation with the largest majority of all the Australian colonies.
1817 John Thomson Large Antique Map of Asia, New Holland, Australia, New Zealand
- Title : Asia
- Date : 1817
- Size: 28in x 21in (710mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92965
Description:
This large magnificent original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of Asia, Australia, New Zealand & The South Pacific by John Thomson was published in the 1817 edition of Thomsons General Atlas
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28in x 21in (710mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (560mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australias national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
The indigenous population, estimated to have been between 750,000 and 1,000,000 in 1788, declined for 150 years following settlement, mainly due to infectious disease. Thousands more died as a result of frontier conflict with settlers. A government policy of assimilation beginning with the Aboriginal Protection Act 1869 resulted in the removal of many Aboriginal children from their families and communities—often referred to as the Stolen Generations—a practice which may also have contributed to the decline in the indigenous population. As a result of the 1967 referendum, the Federal governments power to enact special laws with respect to a particular race was extended to enable the making of laws with respect to Aborigines.[68] Traditional ownership of land (native title) was not recognised in law until 1992, when the High Court of Australia held in Mabo v Queensland (No 2) that the legal doctrine that Australia had been terra nullius (land belonging to no one) did not apply to Australia at the time of British settlement.
A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s and the Eureka Rebellion against mining licence fees in 1854 was an early expression of civil disobedience. Between 1855 and 1890, the six colonies individually gained responsible government, managing most of their own affairs while remaining part of the British Empire. The Colonial Office in London retained control of some matters, notably foreign affairs, defence and international shipping.
1835 Henry Teesdale Large Antique Map of Van Diemens Land, Tasmania, Australia
- Title : Van-Diemens Land
- Ref #: 80010
- Size: 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Tasmania, Van-Diemens Land with the original 11 counties - was engraved by John Dower in 1834 and was published in the 1835 edition of Henry Teesdale's A New General Atlas of the World.
As with all the maps published by Teesdale this one is of the highest quality on strong clean & sturdy paper with beautiful original hand colouring. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first reported sighting of Tasmania by a European was on 24 November 1642 by the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman, who named the island Anthoonij van Diemenslandt, after his sponsor, the Governor of the Dutch East Indies. The name was later shortened to Van Diemen's Land by the British. In 1772, a French expedition led by Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne landed on the island. Captain James Cook also sighted the island in 1777, and numerous other European seafarers made landfalls, adding a colourful array to the names of topographical features.
The first settlement was by the British at Risdon Cove on the eastern bank of the Derwent estuary in 1803, by a small party sent from Sydney, under Lt. John Bowen. An alternative settlement was established by Capt. David Collins 5 km to the south in 1804 in Sullivans Cove on the western side of the Derwent, where fresh water was more plentiful. The latter settlement became known as Hobart Town, later shortened to Hobart, after the British Colonial Secretary of the time, Lord Hobart. The settlement at Risdon was later abandoned.
Teesdale & co., Henry fl 1828-1843
Teesdale was a prominent London publisher and founding fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. He produced large-scale maps and charts and a number of fine atlases in the early part of the nineteenth century. He employed the most skilled draftsmen and engravers and his maps are renowned for precise detail and fine coloring
1852 John Arrowsmith Rare Antique Map The First Electoral Districts of Tasmania
- Title : Van Diemens Land Divided into Electoral Districts
- Size: 18 1/2in x 13 3/4in (470mm x 350mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1852
- Ref #: 82040
Description:
This rare lithograph map of the electoral districts of Van Diemens Land (Tasmania) by John Arrowsmith was published in 1852 - 4 years prior to the first sitting of the state parliament in 1856 - for The Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers, London.
The rarity of this map cannot be overstated. Many of these maps by Arrowsmith were printed and published only for the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Papers and would have had very low numbers published and are very hard, if not impossible, to be be found for sale on the open market.
John Arrowsmith is considered one of the finest cartographers of the 19th century, famous for producing highly accurate and finely engraved maps in atlases, books & in sheet form, of all parts of the know world. Ironically he is less famous for producing many of the maps that accompanied the British Colonial Office Parliamentary Reports between 1817 to 1890, with two-thirds of the maps being produced by Arrowsmith. These maps were published solely for government review and not public sale. A few of these were subsequently published in Arrowsmiths Atlases and vice versa but a great number of them were not, making many of the maps published for the Parliamentary papers rare and rarely seen on the market. Many of them are not called for in Tooley, Clancy or other important reference material.
This is one of those maps, one of 27 we were fortunate to procure earlier this year. I have found very little historical sales data for these maps and so I have priced them based on what I feel is a fair market value for such a rare, scarce map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 13 3/4in (470mm x 350mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 13 3/4in (470mm x 350mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Bottom left margin extended
Background:
The importance of John Arrowsmiths contribution to early Australian cartography cannot be stressed enough. He was responsible for producing many of the early exploration maps of Australia for the Colonial Offices & Government publications as well as the RGS.
Maps produced after the first settlement and into the 19th century came from varied sources, first published with the First Fleet Journals by Arthur Phillip, John Hunter and Watkin Tench. Numerous European publishing houses produced atlases which included maps of Australia. Many came out in several editions and were updated as new information became available. The Australian Colonies were administered by officials responsible to the British Colonial Office and all events of importance, often illustrated by maps, were published in the British Parliamentary Papers. There a rea prime source of maps from 1830 onwards, although one or two maps may be found in Parliamentary Papers prior to this time, such as one example of a rare map of the Swan River by Captain James Stirling.
During the 19th century, as the Australian colonies were progressively granted responsible government, Parliamentary Papers for each colony became an important source of maps. These maps sources have been a hidden and untapped resource. Another good source of early maps is published journals of the explorers; the explorers earliest maps often accompanied reports in the
Journal of the Royal Geographical Society in the UK. Parallel development of Australian scientific institutions along with an interest in exploration was a strong feature of 19th century Australia. The Royal Geographical Society of Australasia was established with branches in NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Queensland. A number of important maps were published as separate sheets, increasingly by Australian printers and engravers such as Carmichael, Sands & Kenny, and Higginbotham, Robinson & Harrison.
Australian atlases were produced and repeat editions of cadastral surveys and maritime chats became increasingly available. Specialist maps were published from official sources, including geological and mineral maps. Towards the end of the century a plethora of thematic maps were published through a verity of media such as advertisements for land sales, tourists maps and street directories.
Parliamentary Papers British Parliamentary Papers were a funnel for all significant colonial events in the 19th century. They included over one hundred maps with information on topography, exploration and lad survey published between 1817 and 1890., with two-thirds of the maps being produced by John Arrowsmith. Few maps are found after the early 1860s. The maps accompanying papers relevant to gold discovery (1851-55) are a particularly good resource, documenting an important time in the history of Australia. Perhaps the most neglected source of early Australian maps are those included in the Colonial Parliamentary Papers published locally after 1836. The NSW Parliamentary Papers published between 1836 and 1900 contain over 2700 maps on 129 topics, providing a unique record of events considered important by the colonial administration. Land ownership and land use dominate, followed by maps of services relevant to land use, such as railways, roads, water supply and sewerage. Public health issues are recorded in maps as are maps of gold& mineral leases reflected the expanding diversity of the economy. The first map published in the NSW Parliamentary Papers, of the site of the new Government House, was lithographed by W.R. Baker in 1836. The total number of maps over the same period from other colonies was less than 2000 but again each colonies priorities were reflected by in the subjects covered. Tasmania reflected mainly geological and early convict disciplinary maps; South Australia, land administration and pastoral development; Victoria, maps relating to the development; Victoria, maps relating to the colonies infrastructure, especially railway and harbour development; Queensland, railway and mineral leases; Western Australia, a broad range that included two important technological innovations that shortened the time, and therefore the cost, of printing maps. Firstly , John Osborn in 1859, developed the use of a transfer paper method in photolithography which reduced printing time from days to hours. Secondly, Alfred Selwyn in 1860 used a steam-driven power press to print seven colour geological maps.
Royal Geographical Society published its first journal in 1832. This journal was to become the leading scientific medium available for explorers to publish the first news of their discoveries. However, not all explorers were published here. Between 1832 and 1880, 25 maps recorded of inland Australia, illustrating the journeys of 27 explorers. John Arrowsmith compiled 22 of the 25 maps published by the RGS again illustrating the importance of Arrowsmith to the expansion of early colonial cartography in Australia.
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of The Colony of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : New South Wales
- Size: 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1851
- Ref #: 93055
Description:
This original hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of the Colony of New South Wales with vignettes of Sydnet Cove, Murray River by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 265mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Very light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Western Australia or The Swan River Settlement
- Title : Western Australia Swan River
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35523
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Western Australia or The Swan River Settlement, Australia with vignettes of Perth, Fremantle, Aboriginals and settlers was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania, Australia
- Title : Van Diemens Land or Tasmania
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35519
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Tasmania, Australia with vignettes of Hobart and Tasmanian Tiger was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of Victoria or Port Phillip, Australia
- Title : Victoria or Port Phillip
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35503
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of Victoria, Australia with vignettes of Glenelg River, Aboriginals and Kangaroos was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1851 John Tallis Antique Map of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : New South Wales
- Date : 1851
- Size: 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 1554
Description:
This original hand coloured, steel plate engraved antique map of New South Wales, Australia with vignettes of Sydney Harbour and The Murray was engraved by John Rapkin and published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 14in x 11in (355mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The firm of Tallis & Company flourished from 1835 to 1860 with varying imprints. Their illustrated Atlas of 1850-51 was one of the last decorative atlases, all the maps being engraved on steel and all adorned with small vignettes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1785 Rigobert Bonne Antique Map of Australia, Botany Bay, Tasmania & Queensland
- Title : Nlle. Galles Merid. ou Cote Orientale de la Nouvelle Hollande Par M Bonne...Baie Botanique; Entree de la Riviere Endeavour; Esquisse de la Terre Van Diemen...
- Size: 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 285mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1785
- Ref #: 93127
Description:
This original hand coloured antique copper-plate engraved map of the discoveries of Captain James Cook and the east coast of Australia in 1770 was published in 1785 edition of Atlas des toutes les parties connues du globe terrestre by Rigobert Bonne & Guillaume Raynal.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/2in (430mm x 285mm)
Plate size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (370mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Interesting map illustrating the discoveries in Australia by Captain Cook in 1770 and all the place names along the coastline. The map also 4 inset maps of Botany Bay, the Endeavour River QLD, the SE coast of Van Diemens Land or Tasmania and the northern coastline of QLD.
1888 Picturesque Atlas of Australia Large Antique Railway Map of Queensland
- Title : Railway Postal & Telegraph Map of Queensland
- Ref #: 50329
- Size: 34in x 26in (865mm x 660mm)
- Date : 1888
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large fine original antique lithograph layered coloured map of Queensland showing the extent of Railway and postal lines, was engraved in 1888 - the date is engraved in the title - with index page - by Alex J Scally - was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
These maps were some of the best maps published at the time in the "Modern" look. The colour is bright, the engraving extremely fine and the paper heavy and stable.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 34in x 26in (865mm x 660mm)
Plate size: - 34in x 26in (865mm x 660mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1808 Wilkinson Antique Map of East Coast of Australia, New Zealand, inset Sydney
- Title : New South Wales New Zealand New Hebrides...Published Dec 12th 1808
- Ref #: 9003
- Size: 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1808
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the east coast of Australia, New Zealand and the Solomon Islands - with inset maps of Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island & Port Jackson - was published in 1808 by Robert Wilkinson - the date is included in the title - in his wideley acclaimed General Atlas of the World published between 1794 and 1816.
This is a finely engraved copper-plate map with beautiful original hand colouring on strong stable paper. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10in (320mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Pic Atlas Scally Large Antique Map of Australia
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1888
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31986
- Size: 25 1/2in x 17in (650mm x 430mm)
Description:
This large steel-plate engraved original antique lithograph map of Australia - engraved by Alex J Scally in 1888, dated at the foot of the map - was published in The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia, 1886-88. A beautiful large pre-federation antique map of Australia, highly detailed in fine condition.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 17in (650mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1845 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of Australia - Population of 213,500
- Title : Australland...1841
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40972
- Size: 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, with a population census of the entire country in 1841, by Friedrich Handtke in 1845, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1845 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of Australia - Population of 213,500
- Title : Australland...1841
- Date : 1845
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 31977
- Size: 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, with a population census of the entire country in 1841, by Friedrich Handtke in 1845, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning & spotting
Plate area: - Age toning & spotting
Verso: - Age toning & spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Large Antique Map of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
- Title : Neu Sud-Wales
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 31992
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique map of New South Wales, with an inset of a plan of Sydney Town by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
A golden age of a new kind began in New South Wales and Sydney in 1851 with the announcement of the discovery of payable gold at Ophir near Bathurst by Edward Hargraves. In that year New South Wales had about 200,000 people, a third of them within a days ride of Sydney, the rest scattered along the coast and through the pastoral districts, from the Port Phillip District in the south to Moreton Bay in the north. The gold rushes of the 1850s brought a huge influx of settlers, although initially the majority of them went to the richest gold fields at Ballarat and Bendigo, in the Port Phillip District, which in 1851 was separated to become the colony of Victoria.
Hill End, also near Bathurst N.S.W. was a locality that grew, boomed and faded with the N.S.W. Gold Rush. Called \'Bald Hills\' in 1850, \'Forbes in 1860 and finally Hill End in 1862, it was part of the Tambaroora district. At its peak, its population was 7,000. Completely reliant on mining, the town\'s decline was dramatic once the gold ran out. Hill End is famed for the unearthing of the Holtermann Specimen (correctly, the Beyers Holtermann Specimen), being the largest single mass of gold ever discovered in the world, a record that stands today. Found in 1872 at the Star Hope Mine, this single mass of quartz and gold weighed 630 lbs and when crushed produced an estimated 3,000 troy oz (205 lbs or 93 kg) of gold, thus holding more processed gold than from the largest nugget ever found, that being the Welcome Stranger from the Victorian Goldfields. Holtermann recognizing the significance of the find attempted to preserve it by buying it from the Company of which he was one of a number of directors. His efforts were in vain. It is reported that a larger mass was discovered a few days later in the same mine but was broken up underground.
Victoria soon had a larger population than New South Wales, and its upstart capital, Melbourne, outgrew Sydney. But the New South Wales gold fields also attracted a flood of prospectors, and by 1857 the colony had more than 300,000 people. Inland towns like Bathurst, Goulburn, Orange and Young flourished. Gold brought great wealth but also new social tensions. Multiethnic migrants came to New South Wales in large numbers for the first time. Young became the site of an infamous anti-Chinese miner riot in 1861 and the official Riot Act was read to the miners on 14 July – the only official reading in the history of New South Wales.[27] Despite some tension, the influx of migrants also brought fresh ideas from Europe and North America to New South Wales – Norwegians introduced Skiing in Australia to the hills above the Snowy Mountains gold rush town of Kiandra around 1861. A famous Australian son was also born to a Norwegian miner in 1867, when the bush balladeer Henry Lawson was born at the Grenfell goldfields.
In 1858, a new gold rush began in the far north, which led in 1859 to the separation of Queensland as a new colony. New South Wales thus attained its present borders, although what is now the Northern Territory remained part of the colony until 1863, when it was handed over to South Australia.
The separation and rapid growth of Victoria and Queensland mark the real beginning of New South Wales as a political and economic entity distinct from the other Australian colonies. Rivalry between New South Wales and Victoria was intense throughout the second half of the 19th century, and the two colonies developed in radically different directions. Once the easy gold ran out by about 1860, Victoria absorbed the surplus labour force from the gold fields in manufacturing, protected by high tariff walls. Victoria became the Australian stronghold of protectionism, liberalism and radicalism. New South Wales, which was less radically affected demographically by the gold rushes, remained more conservative, still dominated politically by the squatter class and its allies in the Sydney business community. New South Wales, as a trading and exporting colony, remained wedded to free trade.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia, Swan River Colony & Van Diemens Land
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 31974
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique map of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1896 F.A. Brockhaus Antique Map, Street Plan of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
- Title : Melbourne
- Ref #: 27012
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
- Date : 1896
Description:
This original antique lithograph street map of Melbourne Australia was engraved and published F.A. Brockhaus for the Brockhaus Konversations Lexikon, Germany, 1896
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Brockhaus, Friedrich Arnold (1772 - 1823)
Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus was a German encyclopedia publisher and editor, famed for publishing the Conversations-Lexikon, which is now published as the Brockhaus encyclopedia.
Brockhaus was educated at the gymnasium of his native Dortmund, and from 1788 to 1793 served an apprenticeship in a mercantile house at Düsseldorf. He then devoted two years at the University of Leipzig to the study of modern languages and literature, after which he set up in Dortmund an emporium for English goods. In 1801, he transferred this business to Arnheim, and in the following year to Amsterdam.
In 1805, having given up his first line of trade, Brockhaus began business as a publisher. Two journals projected by him were not allowed by the government to survive for any length of time, and in 1810 the complications in the affairs of Holland induced him to return homewards. In 1811 he settled at Altenburg. About three years previously he had purchased the copyright of the bankrupt Conversations-Lexikon, an encyclopedia started in 1796, and in 1810-1811 he completed the first edition of this celebrated work. It was widely imitated as a model for encyclopedias, and is still published today, known as the Brockhaus Encyclopedia.
A second edition under Brockhauss editorship was begun in 1812, and was received with universal favour. His business extended rapidly, and in 1818 Brockhaus moved to Leipzig, where he established a large printing-house. Among the more extensive of his many literary undertakings were the critical periodicals — Hermes, the Literarisches Konversationsblatt (afterwards the Blätter für literarische Unterhaltung) and the Zeilgenossen, and some large historical and bibliographical works, such as Friedrich Ludwig Georg von Raumers Geschichte der Hohenstaufen, and Friedrich Adolf Eberts Allgemeines bibliographisches Lexikon.
Brockhaus died in Leipzig. The business was carried on by his sons, Friedrich Brockhaus (1800–1865), who retired in 1850, and Heinrich Brockhaus (1804–1874), under whom it was considerably extended. Heinrich especially rendered great services to literature and science, which the University of Jena recognized by making him, in 1858, honorary Doctor of Philosophy. In the years 1842–1848, Heinrich Brockhaus was member of the Saxon second chamber, as representative for Leipzig, was made honorary citizen of that city in 1872, and died there on 15 November 1874.
His firm continues under the name F.A. Brockhaus AG in his honor. He is also the namesake of 27765 Brockhaus, a main-belt asteroid discovered in 1991.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1833 SDUK Antique Map of New South Wales w/ inset Map of Sydney Town, Australia
- Title : New South Wales...Sydney from the New South Wales Almanack...Sep 1833
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 32681
Description:
This fine original antique map of New South Wales, Australia - with an inset plan of Sydney Town - was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning, left T&B corners cropped
Plate area: - Blind Library stamp
Verso: - Re-enforced on verso along margins
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1833 SDUK Antique Map of Western Australia, Swan River Colony & Van Diemens Land
- Title : Western Australia containing the settlment of Swan River and King Georges Sound; Van-Diemens Land
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1833
- Ref #: 32682
Description:
This original antique map of Western Australia - only 4 years after the first British settlement on the Swan river & Van Diemens Land or Tasmania was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1833 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Blind Library stamp
Verso: - Re-enforced on verso along margins
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print Aboriginal Woman of Bruny Island, Tasmania in 1777
- Title : Une Femme De La Terre De Van-Diemens
- Ref : 50609
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Indigenous Woman & child of Adventure Bay, Bruny Island, Tasmania (Van Diemens Land) encountered by Captain Cook in during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery in 1777, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Adventure Bay
from Cooks Journal......on the 24th (March 1777) at 3 AM we made the Coast of Van Diemen land wrote Cook. Anderson remarked that though now the middle of summer here a spot or two of snow was seen on the highest hills… At ten we passd a point supposd to be the boundary of Stone Bay where Abel Tasman anchord, i.e. Storm Bay. According to David Samwell, surgeons first mate on the Resolution, both Ships anchored in Adventure Bay in Van Diemens Land, this Bay was so called by Captn Furneaux who had anchored here in the Adventure last Voyage.
The next day Cook and Clerke sent parties, one to cut wood and the other grass. Clerke wrote of his party from the Discovery The Guard I had sent with the Parties on shore which consisted of the following Marines, Hamlet Thompson, Geo: Moody, Ben: Harriot, Jos: Pool & Willm Broom, stole some Liquor & made themselves exceedingly drunk, for which they receivd a dozen lashes each in the Morning. The Privates were all from the Plymouth division of marines. Hamlet Thompson was from the 6th Company, George Moody from the 70th, John Herriott the 12th, James Poole the 33rd and William Broom the 36th. According to Thomas Edgar, Master, they made themselves so Beastly Drunk that they were put motionless in the Boat, and when brought on board were oblig\'d to be hoisted into the Ship.
William Bayly, astronomer on the Discovery, wrote In the morning I carried my Tent observatory & Instruments on Shore & set all up, but was not able to get any observations it being cloudy all day, in the evening Capt Cook Sent for me & told me he had Altered his mind relative to his stay, & ordered me to pack all up & carry the whole on board again, as he intend[ed] to sail for New Zealand in a day or two.
John Henry Martin, seaman on the Discovery, described the natives. They have few, or no wants, & seemed perfectly Happy, if one might judge from their behaviour, for they frequently woud burst out, into the most immoderate fits of Laughter & when one Laughed every one followed his example Emediately.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Adventure Bay is the name of both a township and a geographical feature on the eastern side of Bruny Island, Tasmania.
The first European to sight the bay was explorer Abel Tasman, who sought to anchor his vessel Heemskerck there in 1642. Instead, Heemskerck was driven back offshore by a storm, in token of which Tasman named the place Storm Bay. Captain Tobias Furneaux renamed it in March 1773, in honour of his ship HMS Adventure, which he had anchored in the bay for five days after becoming separated from Captain James Cook\'s HMS Resolution during Cook\'s second voyage to the Pacific search of Terra Australis Incognita. Furneaux\'s log made clear the bay was an excellent anchorage for resupplying vessels:....to the SW of the first watering place there is a large lagoon which I believe has plenty of fish in it for one of our Gentlemen caught upwards of 2 dozen trout, and shot a possum which was the only animal we saw. There are a great many gum trees and of a vast thickness and height, one of which measured in circumference 26 feet and the height under the branches was 20 feet.
Others among Furneaux\'s crew spotted evidence of what they believed were small deer but were more likely kangaroos. Furneaux also noted signs of an Aboriginal settlement in the form of several huts or wigwams on shore, with several bags of grass in which they carry their shellfish. - but the branches of which the huts were made were split and torn and there was not the least appearance of any people.
Reliably mapped and offering an abundance of water, fresh water and game, Adventure Bay quickly became a popular anchorage for European explorers. Cooks Resolution watered there in 1777, followed by William Bligh aboard HMS Bounty in 1788 and HMS Providence in 1792. Others who resupplied their vessels in the bay in this period included Bruni d Entrecasteaux aboard Recherché in 1792 and 1793, and Nicolas Baudin in the corvette Géographe in 1802. Matthew Flinders also tried to enter the bay with Norfolk in 1798.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773 English writer and book editor.
He is said to have been clerk to an attorney, and was certainly self-educated. In 1744, he succeeded Samuel Johnson as compiler of the parliamentary debates for the Gentleman\\\'s Magazine, and from 1746 to 1749 he contributed poems signed Greville, or H Greville, to that journal. In company with Johnson and others he started a periodical called The Adventurer, which ran to 140 issues, of which 70 were from the pen of Hawkesworth himself.
On account of what was regarded as his powerful defense of morality and religion, Hawkesworth was rewarded by the archbishop of Canterbury with the degree of LL.D, In 1754–1755 he published an edition (12 vols) of Swifts works, with a life prefixed which Johnson praised in his Lives of the Poets. A larger edition (27 vols) appeared in 1766–1779. He adapted Dryden\\\'s Amphitryon for the Drury Lane stage in 1756, and Southernes Oronooko in 1759. He wrote the libretto of an oratorio Zimri in 1760, and the next year Edgar and Emmeline: a Fairy Tale was produced at Drury Lane. His Almoran and Hamet (1761) was first drafted as a play[citation needed], and a tragedy based on it by S J Pratt, The Fair Circassian (1781), met with some success.
He was commissioned by the Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work, An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore Byrone John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook (from 1702 to 1771) drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Hawkesworth was a close imitator of Johnson both in style and thought, and was at one time on very friendly terms with him. It is said that he presumed on his success, and lost Johnsons friendship as early as 1756.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1785 Capt. Cook Antique Print Aboriginal Man of Bruny Island, Tasmania in 1777
- Title : Un Homme De La Terre De Van-Diemens
- Ref : 43195
- Size: 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of an Indigenous Man of Adventure Bay, Bruny Island, Tasmania (Van Diemens Land) encountered by Captain Cook in during his 3rd & last Voyage of Discovery in 1777, was engraved by Robert Benard - after John Webber - and published in the 1785 French edition of Capt. James Cook & Capt. James King A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northen Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S. Paris, 1785.
Adventure Bay
from Cooks Journal......on the 24th (March 1777) at 3 AM we made the Coast of Van Diemen land wrote Cook. Anderson remarked that though now the middle of summer here a spot or two of snow was seen on the highest hills… At ten we passd a point supposd to be the boundary of Stone Bay where Abel Tasman anchord, i.e. Storm Bay. According to David Samwell, surgeons first mate on the Resolution, both Ships anchored in Adventure Bay in Van Diemens Land, this Bay was so called by Captn Furneaux who had anchored here in the Adventure last Voyage.
The next day Cook and Clerke sent parties, one to cut wood and the other grass. Clerke wrote of his party from the Discovery The Guard I had sent with the Parties on shore which consisted of the following Marines, Hamlet Thompson, Geo: Moody, Ben: Harriot, Jos: Pool & Willm Broom, stole some Liquor & made themselves exceedingly drunk, for which they receivd a dozen lashes each in the Morning. The Privates were all from the Plymouth division of marines. Hamlet Thompson was from the 6th Company, George Moody from the 70th, John Herriott the 12th, James Poole the 33rd and William Broom the 36th. According to Thomas Edgar, Master, they made themselves so Beastly Drunk that they were put motionless in the Boat, and when brought on board were oblig\'d to be hoisted into the Ship.
William Bayly, astronomer on the Discovery, wrote In the morning I carried my Tent observatory & Instruments on Shore & set all up, but was not able to get any observations it being cloudy all day, in the evening Capt Cook Sent for me & told me he had Altered his mind relative to his stay, & ordered me to pack all up & carry the whole on board again, as he intend[ed] to sail for New Zealand in a day or two.
John Henry Martin, seaman on the Discovery, described the natives. They have few, or no wants, & seemed perfectly Happy, if one might judge from their behaviour, for they frequently woud burst out, into the most immoderate fits of Laughter & when one Laughed every one followed his example Emediately.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7 1/4in (240mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Adventure Bay is the name of both a township and a geographical feature on the eastern side of Bruny Island, Tasmania.
The first European to sight the bay was explorer Abel Tasman, who sought to anchor his vessel Heemskerck there in 1642. Instead, Heemskerck was driven back offshore by a storm, in token of which Tasman named the place Storm Bay. Captain Tobias Furneaux renamed it in March 1773, in honour of his ship HMS Adventure, which he had anchored in the bay for five days after becoming separated from Captain James Cook\'s HMS Resolution during Cook\'s second voyage to the Pacific search of Terra Australis Incognita. Furneaux\'s log made clear the bay was an excellent anchorage for resupplying vessels:....to the SW of the first watering place there is a large lagoon which I believe has plenty of fish in it for one of our Gentlemen caught upwards of 2 dozen trout, and shot a possum which was the only animal we saw. There are a great many gum trees and of a vast thickness and height, one of which measured in circumference 26 feet and the height under the branches was 20 feet.
Others among Furneaux\'s crew spotted evidence of what they believed were small deer but were more likely kangaroos. Furneaux also noted signs of an Aboriginal settlement in the form of several huts or wigwams on shore, with several bags of grass in which they carry their shellfish. - but the branches of which the huts were made were split and torn and there was not the least appearance of any people.
Reliably mapped and offering an abundance of water, fresh water and game, Adventure Bay quickly became a popular anchorage for European explorers. Cooks Resolution watered there in 1777, followed by William Bligh aboard HMS Bounty in 1788 and HMS Providence in 1792. Others who resupplied their vessels in the bay in this period included Bruni d Entrecasteaux aboard Recherché in 1792 and 1793, and Nicolas Baudin in the corvette Géographe in 1802. Matthew Flinders also tried to enter the bay with Norfolk in 1798.
John Hawkesworth 1715 – 1773 English writer and book editor.
He is said to have been clerk to an attorney, and was certainly self-educated. In 1744, he succeeded Samuel Johnson as compiler of the parliamentary debates for the Gentleman\\\'s Magazine, and from 1746 to 1749 he contributed poems signed Greville, or H Greville, to that journal. In company with Johnson and others he started a periodical called The Adventurer, which ran to 140 issues, of which 70 were from the pen of Hawkesworth himself.
On account of what was regarded as his powerful defense of morality and religion, Hawkesworth was rewarded by the archbishop of Canterbury with the degree of LL.D, In 1754–1755 he published an edition (12 vols) of Swifts works, with a life prefixed which Johnson praised in his Lives of the Poets. A larger edition (27 vols) appeared in 1766–1779. He adapted Dryden\\\'s Amphitryon for the Drury Lane stage in 1756, and Southernes Oronooko in 1759. He wrote the libretto of an oratorio Zimri in 1760, and the next year Edgar and Emmeline: a Fairy Tale was produced at Drury Lane. His Almoran and Hamet (1761) was first drafted as a play[citation needed], and a tragedy based on it by S J Pratt, The Fair Circassian (1781), met with some success.
He was commissioned by the Admiralty to edit Captain James Cooks papers relative to his first voyage. For this work, An Account of the Voyages undertaken ... for making discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and performed by Commodore Byrone John Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook (from 1702 to 1771) drawn up from the Journals ... (3 vols, 1773) Hawkesworth is said to have received from the publishers the sum of £6000. His descriptions of the manners and customs of the South Seas were, however, regarded by many critics as inexact and hurtful to the interests of morality, and the severity of their strictures is said to have hastened his death. He was buried in the parish church at Bromley, Kent, where he and his wife had kept a school.
Hawkesworth was a close imitator of Johnson both in style and thought, and was at one time on very friendly terms with him. It is said that he presumed on his success, and lost Johnsons friendship as early as 1756.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cook\\\'s account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus King\\\'s geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolution\\\'s consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cook\'s third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses\", which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d\'Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1865 George Frederick Sargent Antique Print View of Sydney across the Harbour
- Title : Sydney....G F Sargent....G Greatbach....William Mackenzie; London, Edinburgh & Glasgow
- Ref #: 35518
- Size: 10in x 6 1/2in (255mm x 165mm)
- Date : 1864
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique print of Sydney NSW, north across the Rocks with a view to St James Church on Kings St, across the harbour where the Harbour Bridge now sits, after the Australian artist George Frederick Sargent in 1859 was engraved by G. Greatbach and published by William Mackenzie and co. in 1865.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/4in (635mm x 540mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (590mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair to top margin, no loss
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The History of Sydney begins in prehistoric times with the occupation of the district by Australian Aborigines, whose ancestors came to Sydney in the Upper Paleolithic period. The modern history of the city began with the arrival of a First Fleet of British ships in 1788 and the foundation of a penal colony by Great Britain.
From 1788 to 1900 Sydney was the capital of the British colony of New South Wales. An elected city council was established in 1840. In 1900, Sydney became a state capital, when New South Wales voted to join the Australian Federation. Sydney today is Australias largest city and a major international capital of culture and finance.
Mackenzie, William active 1860-70
William Mackenzie, Ludgate Hill, London, Edinburgh and Glasgow, was a well-known publisher of natural history books in the 1860s & 70s. He published works by the trio of Francis Orpen Morris, Benjamin Fawcett and Alexander Francis Lydon. His best-known publication was probably County Seats of The Noblemen and Gentlemen of Great Britain and Ireland in 1870
1840 SDUK Antique Map of Australia in 1839 with Population census, Colony of SA
- Title : Australia in 1839....Published by the Society of the Diffusion of Knowledge....1840
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1840
- Ref #: 11-0924
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique map of Australia showing the boundary of the first Australian Sate - South Australia - with a Population census of all the white people residing in Australia at the time, totaling 141,000 - was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1840 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/8in (2mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1876 Petermann Antique Map Western & South Australia - Warburton, Giles, Forrest
- Title : Die Neuesten Entdeckungsreisen im Inner-Australien von Warburton, Giles, Forrest, April 1873 - Sept 1874
- Size: 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1876
- Ref #: 82055
Description:
This early folding original antique lithograph map of Western & South Australia and Alexandria land (Northern Territory) with the tracks of 3 explorers - in 1873 & 1874 - Peter Egerton-Warburton, Ernest Giles & Alexander Forrest by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1876 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Colonel Peter Egerton-Warburton CMG (1813–1889), was a British military officer, Commissioner of Police for South Australia, and an Australian explorer. In 1872 he sealed his legacy through a particularly epic expedition from Adelaide crossing the arid centre of Australia to the coast of Western Australia via Alice Springs.
William Ernest Powell Giles (1835 – 1897) best known as Ernest Giles, was an Australian explorer who led five major expeditions in central Australia.
Alexander Forrest CMG (1849 – 1901) was an explorer and surveyor of Western Australia, and later also a member of parliament.
1876 Petermann Antique Map Expedition Ernest Giles Western & South Australia, 1875
- Title : Thomas Elders Expedition durch Inner-Australien vom Beltana im Osten bis Perth im Westen, Ausgefuhrt Durch E. Giles Mai - Nov 1875
- Size: 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1876
- Ref #: 82054
Description:
This early folding original antique lithograph map of Western & South Australia - from Perth to Lake Torrens South Australia covering the 3rd & 4th expedition of the explorer Ernest Giles in 1875 by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1877 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
William Ernest Powell Giles 1835 – 1897 best known as Ernest Giles, was an Australian explorer who led five major expeditions in central Australia.
Giles did not attempt an organised expedition until 1872, when with two other men he left Chambers Pillar, South Australia (now in the Northern Territory), on 22 August and traversed much previously untrodden country to the north-west and west. Finding their way barred by Lake Amadeus and that their horses were getting very weak, a return was made to the Finke River and then to Charlotte Waters and Adelaide, where Giles arrived in January 1873. Giles looked upon his expedition as a failure, but he had done well considering the size and equipment of his party.
Giles friend Baron von Mueller raised a subscription so that a new expedition could be made. The services of William Tietkens as first assistant were obtained, and with two other men a start was made on 4 August 1873. The journey began considerably south from the previous expedition and from the Alberga River a generally western course was traversed. A month later in the Musgrave Ranges a fine running river was found and named the Ferdinand and by 3 October 1873 the party was approaching longitude 128 East. The country was extremely dry and though tested in various directions it was a constant struggle to get enough water to keep the horses going. Early in November, having passed longitude 126, a partial return was made and on 20 December 1873 the neighbourhood of Mount Scott was reached. A turn to the north and then west was made and the farthest westerly point was reached on 23 April 1874. Giles and one of the men, Alfred Gibson, had been scouting ahead when the latter\'s horse died. Giles gave him his own horse with instructions to follow their tracks back and obtain assistance. Giles made his way back to their depot on foot in eight days, almost completely exhausted, to find that Gibson had not reached the camp. A search was made for him for several days without success. The stores were almost finished, nothing further could be done, and on 21 May 1874 the return journey began. Giles named the desert Gibson Desert after his companion. On 24 June 1874 they were on a good track to the Finke River and on 13 July 1874 Charlotte Waters was reached. Giles had again failed to cross the continent, but in the circumstances all had been done that was possible.
Giles was the first European to see the rock formations of The Olgas, now known by their Aboriginal name of Kata Tjuta, and Lake Amadeus. He had wanted to name these Mt Mueller and Lake Ferdinand respectively, to honour his benefactor Baron Ferdinand von Mueller, however Mueller prevailed on him to instead honour the King Amadeus of Spain and Queen Olga of Württemberg. Giles supposedly discovered Uluru (formerly Ayers Rock), but was beaten to the claim by a competing explorer, William Gosse.
Early in 1875 Giles prepared his diaries for publication under the title Geographic Travels in Central Australia, and on 13 March 1875, with the generous help of Sir Thomas Elder, he began his third expedition. Proceeding considerably to the north from Fowler\'s Bay the country was found to be very dry. Retracing his steps Giles turned east, and eventually going round the north side of Lake Torrens reached Elder\'s station at Beltana. There the preparations for his fourth journey were made, and with Tietkens again his lieutenant, and with what Giles had always wanted, a caravan of camels, a start was made on 6 May. Port Augusta was reached on 23 May and, after taking a northerly course to clear the lakes, a generally westerly course was followed. Some water was carried, and the party was saved the continual excursions in search of water for horses that had caused so much difficulty during previous expeditions. Towards the end of September over 323 miles (520 km) had been covered in 17 days without finding water, when on 25 September the native Tommy found an abundant supply in a small hollow between sand dunes at Queen Victoria Spring, and the party was saved. After a rest of nine days the journey was resumed on 6 October the course being still west. Ten days later the expedition was attacked by a large body of aborigines and Giles was compelled to fire on them. On 4 November they met a white stockman at Tootra out-camp, east of Bindi Bindi. Their course was west to Walebing Station, then south-west and on 11 November they arrived at New Norcia where they were welcomed by Bishop Salvado. On 17 November 1875 the party arrived at Guildford and Perth the next day, where they received an enthusiastic reception.
Giles stayed for two months at Perth. Tietkens and Jess Young, another member of the expedition, went back to Adelaide by sea, and on 13 January 1876 Giles began the return journey taking a course generally about 400 miles north of the last journey. He arrived at Adelaide in September 1876 after a good journey during which the camels were found to be invaluable.
1877 Petermann Antique Map Expedition of Ernest Giles Western & South Australia in 1876
- Title : Thomas Elders Expedition durch Inner-Australien vom Murchison im Westen, bis zum Neales im Osten, Ausgefuhrt Durch E. Giles April-Aug 1876
- Size: 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1877
- Ref #: 82056
Description:
This early folding original antique lithograph map of central Western & South Australia - from Sharks Bay to border of South Australia and Alexandra Land (Northern Territory) just south of Ayers Rock, covering the 5th and final expedition of the explorer Ernest Giles in 1876 by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1877 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 11in (285mm x 280mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
William Ernest Powell Giles 1835 – 1897 best known as Ernest Giles, was an Australian explorer who led five major expeditions in central Australia.
Giles did not attempt an organised expedition until 1872, when with two other men he left Chambers Pillar, South Australia (now in the Northern Territory), on 22 August and traversed much previously untrodden country to the north-west and west. Finding their way barred by Lake Amadeus and that their horses were getting very weak, a return was made to the Finke River and then to Charlotte Waters and Adelaide, where Giles arrived in January 1873. Giles looked upon his expedition as a failure, but he had done well considering the size and equipment of his party.
Giles friend Baron von Mueller raised a subscription so that a new expedition could be made. The services of William Tietkens as first assistant were obtained, and with two other men a start was made on 4 August 1873. The journey began considerably south from the previous expedition and from the Alberga River a generally western course was traversed. A month later in the Musgrave Ranges a fine running river was found and named the Ferdinand and by 3 October 1873 the party was approaching longitude 128 East. The country was extremely dry and though tested in various directions it was a constant struggle to get enough water to keep the horses going. Early in November, having passed longitude 126, a partial return was made and on 20 December 1873 the neighbourhood of Mount Scott was reached. A turn to the north and then west was made and the farthest westerly point was reached on 23 April 1874. Giles and one of the men, Alfred Gibson, had been scouting ahead when the latter\'s horse died. Giles gave him his own horse with instructions to follow their tracks back and obtain assistance. Giles made his way back to their depot on foot in eight days, almost completely exhausted, to find that Gibson had not reached the camp. A search was made for him for several days without success. The stores were almost finished, nothing further could be done, and on 21 May 1874 the return journey began. Giles named the desert Gibson Desert after his companion. On 24 June 1874 they were on a good track to the Finke River and on 13 July 1874 Charlotte Waters was reached. Giles had again failed to cross the continent, but in the circumstances all had been done that was possible.
Giles was the first European to see the rock formations of The Olgas, now known by their Aboriginal name of Kata Tjuta, and Lake Amadeus. He had wanted to name these Mt Mueller and Lake Ferdinand respectively, to honour his benefactor Baron Ferdinand von Mueller, however Mueller prevailed on him to instead honour the King Amadeus of Spain and Queen Olga of Württemberg. Giles supposedly discovered Uluru (formerly Ayers Rock), but was beaten to the claim by a competing explorer, William Gosse.
Early in 1875 Giles prepared his diaries for publication under the title Geographic Travels in Central Australia, and on 13 March 1875, with the generous help of Sir Thomas Elder, he began his third expedition. Proceeding considerably to the north from Fowler\'s Bay the country was found to be very dry. Retracing his steps Giles turned east, and eventually going round the north side of Lake Torrens reached Elder\'s station at Beltana. There the preparations for his fourth journey were made, and with Tietkens again his lieutenant, and with what Giles had always wanted, a caravan of camels, a start was made on 6 May. Port Augusta was reached on 23 May and, after taking a northerly course to clear the lakes, a generally westerly course was followed. Some water was carried, and the party was saved the continual excursions in search of water for horses that had caused so much difficulty during previous expeditions. Towards the end of September over 323 miles (520 km) had been covered in 17 days without finding water, when on 25 September the native Tommy found an abundant supply in a small hollow between sand dunes at Queen Victoria Spring, and the party was saved. After a rest of nine days the journey was resumed on 6 October the course being still west. Ten days later the expedition was attacked by a large body of aborigines and Giles was compelled to fire on them. On 4 November they met a white stockman at Tootra out-camp, east of Bindi Bindi. Their course was west to Walebing Station, then south-west and on 11 November they arrived at New Norcia where they were welcomed by Bishop Salvado. On 17 November 1875 the party arrived at Guildford and Perth the next day, where they received an enthusiastic reception.
Giles stayed for two months at Perth. Tietkens and Jess Young, another member of the expedition, went back to Adelaide by sea, and on 13 January 1876 Giles began the return journey taking a course generally about 400 miles north of the last journey. He arrived at Adelaide in September 1876 after a good journey during which the camels were found to be invaluable.
1844 Hughes Antique Australian Map of the States of Victoria & NSW
- Title : Victoria New South Wales and South Australia
- Ref #: 91204
- Size: 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
- Date : 1844
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This finely engraved original antique map of the Australian States of NSW, Vic & part of SA was engraved by William Hughes and published by A&C Black in 1844. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 11 1/4in (430mm x 285mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1886 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Rainfall Map of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : Map of New South Wales showing Average Annual Rainfall
- Ref : 50340
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Map of Western Australia
- Title : Map of New South Wales Showing Territorial Divisions, Land Board Districts and Land Districts
- Ref : 50337
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Picturesque Atlas Large Antique Map of New South Wales, Australia
- Title : General Map of New South Wales
- Ref : 50339
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Pic Atlas Large Antique Map of NSW, Australia Political & Local Borders
- Title : Map of New South Wales Showing Territorial Divisions, Land Board Districts and Land Districts
- Ref : 50337
- Size: 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
- Date : 1886
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large fine lithograph layered coloured original map was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand Australian & New Zealand publication The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists. It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, pink, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 18in (660mm x 446mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1834 Henry Teesdale Antique Map The Pacific, Australia, New Zealand, Nth America
- Title : Chart of The Pacific Ocean.....London Published by Henry Teesdale & co. High Holborn March 1834
- Ref #: 50303
- Size: 17 1/2in x 14in (445mm x 355mm)
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Pacific Ocean, Australia, New Zealand, to North & South America by John Dower was engraved in 1834 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1835 edition of Henry Teesdales A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Teesdale & co., Henry fl 1828-1843
Teesdale was a prominent London publisher and founding fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. He produced large-scale maps and charts and a number of fine atlases in the early part of the nineteenth century. He employed the most skilled draftsmen and engravers and his maps are renowned for precise detail and fine coloring
1837 John Dower Original Antique Map of Australia - New Holland
- Title : Australia
- Date : 1837
- Size: 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 70704
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This fine steel-plate engraved original hand coloured antique map of Australia by John Dower was published by Orr & Smith, London in 1837. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9 1/2in (305mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Browning & weak along centerfold
Verso: - Strengthened along centerold
Background:
Interesting early map of Australia with only the state of South Australia delineated. The whole of the east coast is named New South Wales, the city of Melbourne was not noted, few internal details are noted. Western Australia shows significant coastal details but is still named "New Holland"
1719 Abraham Chatelain Large Antique Map Panoramic View of Alexandria, Egypt
- Title : Description de la Ville D Alexandrie des Antquites Remarquables Qu on Y Voit
- Size: 20in x 16in (515mm x 405mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1719
- Ref #: 50649
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved antique print a view of the city of Alexandria, Egypt and the surrounding ancient ruins was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20in x 16in (515mm x 405mm)
Plate size: - 19in x 15in (485mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Alexandria is the second-largest city in Egypt and a major economic centre, extending about 32 km (20 mi) along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country. Its low elevation on the Nile delta makes it highly vulnerable to rising sea levels. Alexandria is an important industrial center because of its natural gas and oil pipelines from Suez. Alexandria is also a popular tourist destination.
Alexandria was founded around a small, ancient Egyptian town c. 332 BC by Alexander the Great, king of Macedon and leader of the Greek League of Corinth, during his conquest of the Achaemenid Empire. Alexandria became an important center of Hellenistic civilization and remained the capital of Ptolemaic Egypt and Roman and Byzantine Egypt for almost 1,000 years, until the Muslim conquest of Egypt in AD 641, when a new capital was founded at Fustat (later absorbed into Cairo). Hellenistic Alexandria was best known for the Lighthouse of Alexandria (Pharos), one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World; its Great Library (the largest in the ancient world); and the Necropolis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Middle Ages. Alexandria was at one time the second most powerful city of the ancient Mediterranean region, after Rome. Ongoing maritime archaeology in the harbor of Alexandria, which began in 1994, is revealing details of Alexandria both before the arrival of Alexander, when a city named Rhacotis existed there, and during the Ptolemaic dynasty.
Alexandria figured prominently in the military operations of Napoleons expedition to Egypt in 1798. French troops stormed the city on 2 July 1798, and it remained in their hands until the arrival of a British expedition in 1801. The British won a considerable victory over the French at the Battle of Alexandria on 21 March 1801, following which they besieged the city, which fell to them on 2 September 1801. Muhammad Ali, the Ottoman governor of Egypt, began rebuilding and redevelopment around 1810, and by 1850, Alexandria had returned to something akin to its former glory.
From the late 18th century, Alexandria became a major center of the international shipping industry and one of the most important trading centers in the world, both because it profited from the easy overland connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, and the lucrative trade in Egyptian cotton.
1861 Petermann Antique Map of 4th John McDouall Stuart Expedition in Australia
- Title : Karte von J. Mac Douall Stuarts Reise durch das innere von Australien, 6 Marz bis 25 August 1860...Gotha Justus Perthes 1861
- 21 1/2in x 8 1/4in (540mm x 210mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1861
- Ref #: 82057
Description:
This long finely engraved original antique map of the expedition of John McDouall Stuart 4th expedition into the interior of Australia between March and August 1860 by Augustus Heinrich Petermann was engraved in 1861 - dated - and was published by Justus Perthes, Gotha Germany.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 8 1/4in (540mm x 210mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 8 1/4in (540mm x 210mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
John McDouall Stuart (7 September 1815 – 5 June 1866), often referred to as simply McDouall Stuart, was a Scottish explorer and one of the most accomplished of all Australia\'s inland explorers.
Stuart led the first successful expedition to traverse the Australian mainland from south to north and return, through the centre of the continent. His experience and the care he showed for his team ensured he never lost a man, despite the harshness of the country he encountered.
The explorations of Stuart eventually resulted in the 1863 annexation of a huge area of country to the Government of South Australia. This area became known as the Northern Territory. In 1911 the Commonwealth of Australia assumed responsibility for that area. In 1871-72 the Australian Overland Telegraph Line was constructed along Stuart\'s route. The principal road from Port Augusta to Darwin was also established essentially on his route and is now known as the Stuart Highway in his honour.
On 2 March 1860 the three men left Chambers Creek, aiming to find the centre of Australia. As always, Stuart travelled light, taking only as much as could be carried on a few pack horses. The secret to successful exploration, in Stuart\'s view, was to travel fast and avoid the delays and complications that always attend a large supply train.
By the time they reached Neales River (near present-day Oodnadatta) unexpected rain had ruined most of their stores and they continued on half-rations – something that Head, who had started the trip as a big man and weighed twice as much as Stuart, found difficult to adjust to. Water became more and more difficult to find and scurvy began to set in. Stuarts right eye was failing. Nevertheless, they found a major watercourse in early April which Stuart named the Finke River, and followed it north-west over the South Australian border to the MacDonnell Ranges, which he named after Sir Richard Graves MacDonnell, Governor of South Australia, on 12 April 1860.
On 22 April 1860, according to Stuarts calculations, the party reached the centre of the continent. Stuart wrote:
.......There is a high mount about two miles to the NNE which I hoped would be in the centre but on it tomorrow I will raise a cone of stones and plant the Flag there and will name it Mount Sturt after my excellent and esteemed commander of the expedition in 1844 and 45, Captain Sturt, as a mark of gratitude for the great kindness I received from him during that journey.
In fact the mountain became known as Central Mount Stuart after Stuart himself, not his mentor Sturt, and geographers no longer regard it as the true centre of Australia. Nevertheless, it retains its symbolic value......
The explorers were unable to progress much further north. Lack of water forced them back again and again. Stuart\'s scurvy was growing worse, Head was now half his original weight, and only Kekwick remained capable of heavy work. Then, on 22 May, it rained. With water now available nearly every day, they made good mileage and by mid June were able to reach a riverbed which Stuart named Tennants Creek (now the site of the township Tennant Creek). The worst of the country was now behind them and they were only about 800 km from the coast.
From here, however, progress seemed impossible. A four-day excursion to the north-west found no water at all and they had to retreat. After giving the horses a week to recover, they tried heading due north. They found another creek (later named Attack Creek) but were blocked by heavy scrub. Unlike those further south, the Warramunga Aboriginal people were hostile. On 26 June they raided the explorers camp. One stole the shoeing rasp (which Stuart was able to recover); others threw boomerangs at the horses and set fire to the grass around the camp. Like Sturt (and unlike some of the other Australian explorers) Stuart generally got on well with the Aboriginal people he encountered but he was unable to negotiate with this group and considered it unsafe to continue. That night, with even the indefatigable Kekwick complaining of weakness, the explorers abandoned their attempt to reach the north coast and reluctantly turned south.
It was 2,400 kilometres to Adelaide, all three men had scurvy, supplies were very short, the horses were in poor condition, and the country was drying out. Nevertheless, the party pressed on at Stuarts customary rapid pace. They reached the safety of Chambers Creek in August. A few days earlier, on 20 August 1860, the larger Burke and Wills expedition had finally left Melbourne.
Stuart reached Adelaide in October 1860. Although he had narrowly failed to cross the continent, his achievement in determining the centre was immense, ranked with Spekes discovery of the source of the Nile. Stuart had solved that which he attempted with Capt. Sturt 15 years earlier – the riddle of the nature of the centre of the great Australian continent. He was awarded the Royal Geographical Societys Patron\'s Medal – becoming only the second person to receive both the Patron\'s Medal and a gold watch (the other was Dr Livingstone). Belatedly, even the South Australian government started to recognise Stuart\'s abilities, and was honoured with a public breakfast at White\'s Rooms
1832 SDUK Antique Map of New York, New England & New Jersey - North America
- Title : North America Sheet VI New York, Vermont, Maine, New Hampshire,...Published Sep 1832 by Baldwin & Craddock
- Size: 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1832
- Ref #: 50273
Description:
This original steel-plate engraved antique Map of New York, New England & New Jersey was engraved by J & C Walker, in 1832 - dated at the foot of the map - and was published in the Baldwin & Craddock edition of the Society For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (410mm x 355m)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes of cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)